Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
General Description Features
ICS9176-01
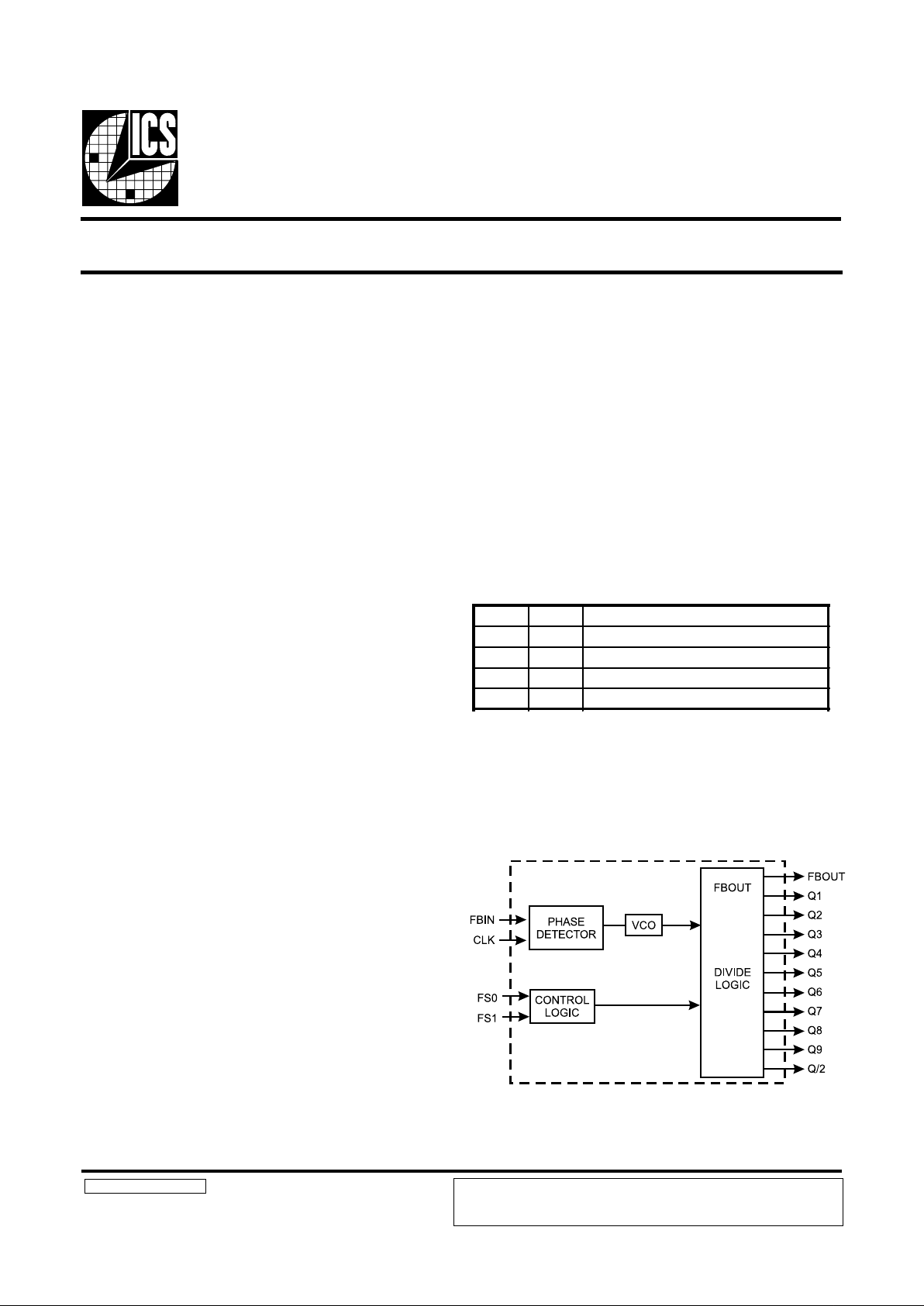
Block Diagram
ICS9176-01-01RevB061297P
Low Skew Output Buffer
Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
the ICS9176-01 is designed specifically to support the tight
timing requirements of high-performance microprocessors
and chip sets. Because the jitter of the device is limited to
±250ps, the ICS9176-01 is ideal for clocking Pentium™
systems. The 10 high drive (40mA), low-skew (±250ps)
outputs make the ICS9176-01 a perfect fit for PCI clocking
requirements.
The ICS9176-01 has 10 outputs synchronized in phase and
fre-quency to an input clock. The internal phase locked loop
(PLL) acts either as a 1X clock multiplier or a 1/2X clock
multiplier depending on the state of the input control pins T0
and T1. With metal mask options, any type of ratio between
the input clock and output clock can be achieved, including
2X.
The PLL maintains the phase and frequency relationship between the input clock and the outputs by externally feeding
back FBOUT to FBIN. Any change in the input will be tracked
by all 10 outputs. However, the change at the outputs will
happen smoothly so no glitches will be present on any driven
input. The PLL circuitry matches rising edges of the input
clock and the output clock. Since the input to FBIN skew is
guaran-teed to ±500ps, the part acts as a “zero delay” buffer.
The ICS9176-01 has a total of eleven outputs. Of these,
FBOUT is dedicated as the feedback into the PLL and another,
Q/2, has an output frequency half that of the remaining nine.
These nine outputs can either be running at the same speed as
the input, or at half the frequency of the input. With Q/2 as the
feedback to FBIN, the nine ‘Q’ outputs will be running at twice
the input frequency in the normal divide-by-1 mode. In this
case, the output can go to 120 MHz with a 60 MHz input clock.
The maximum rise and fall time of an output is 1ns and each is
TTL-compatible with a 40mA symmetric drive.
The ICS9176-01 is fabricated using CMOS technology which
results in much lower power consumption and cost compared
with the gallium arsenide based 1086E. The typical operating
current for the ICS9176-01 is 60mA versus 115mA for the
GA1086E.
Functionality
• ICS9176-01-01 is pin compatible with Triquint GA1086
• ±500ps skew (max) between input and outputs
• ±250ps skew (max) between outputs
• 10 symmetric, TLL-compatible outputs
• 28-pin PLCC or 28-pin wide SOIC surface mount
package
• High drive, 40mA outputs
• Power-down option
• Output frequency range 20 MHz to 120 MHz
• Input frequency range 20 MHz to 100 MHz
• Ideal for PCI bus applications
FS1 FS0 DESCRIPTION
0 0 Power-down
0 1 Test Mode (PLL Off CLK=outputs)
1 0 Normal (PLL On)
1 1 Divide by 2 Mode
ICS reserves the right to make changes in the device data identified in this publication
without further notice. ICS advises its customers to obtain the latest version of all
device data to verify that any information being relied upon by the customer is current
and accurate.
2
ICS9176-01
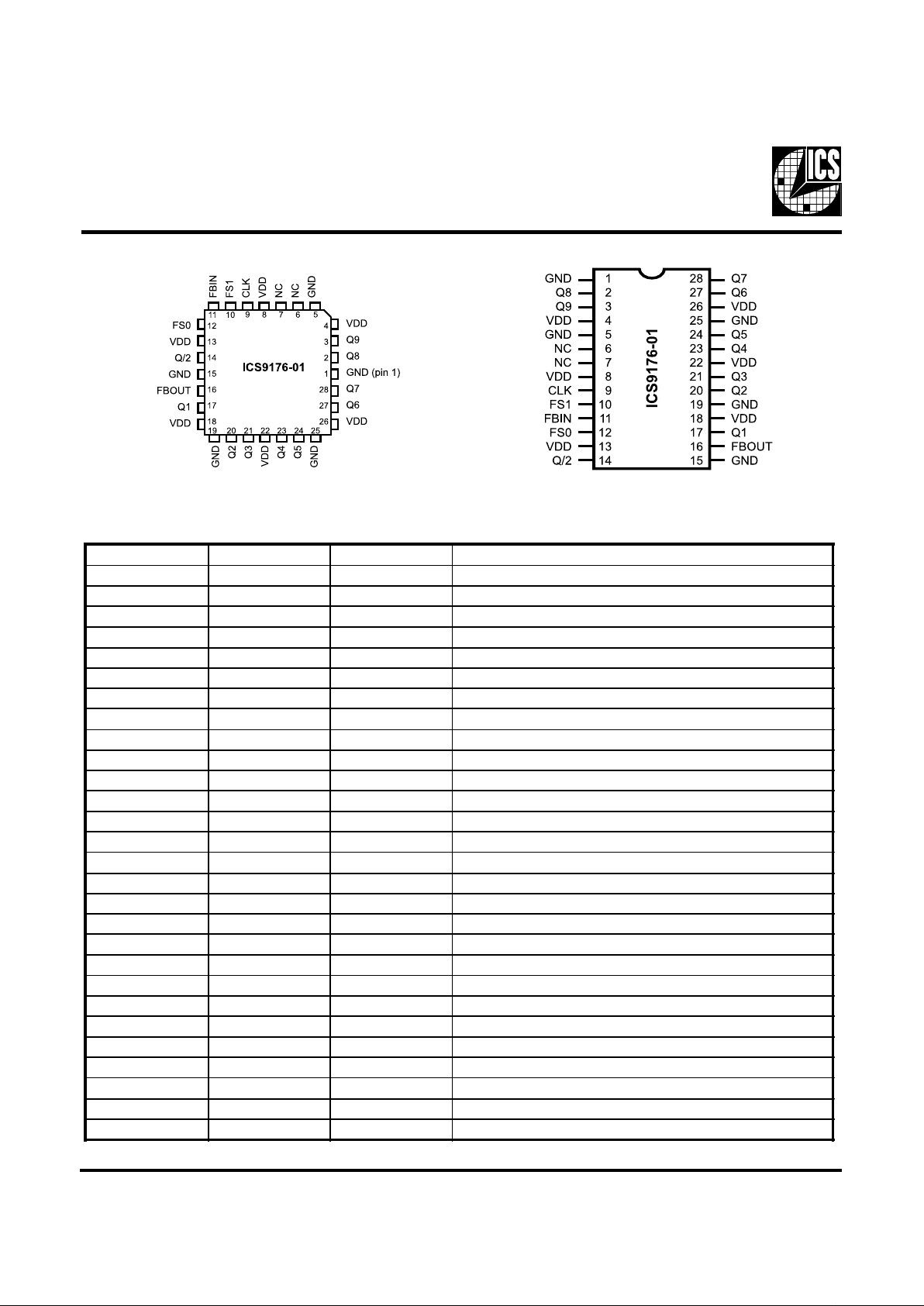
Pin Configuration
Pin Description
28-Pin PLCC
28-Pin SOIC
PIN NUMBER PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
1 GND - GROUND.
2 Q8 Output Output clock 8
3 Q9 Output Output clock 9.
4 VDD - Power supply (+5V).
5 GND - GROUND.
6 NC - No Connect.
7 NC - No Connect.
8 VDD - Power supply (+5V).
9 CLK Input Input for reference clock.
10 FS1 Input FS1 selects normal operation, power-down, or test mode.
11 FBIN Input FEEDBACK INPUT from output FBOUT.
12 FS0 Input FS0 selects normal operation, power-down, or test mode.
13 VDD - Power Supply (+5V).
14 Q/2 Output Half-clock output.
15 GND - GROUND.
16 FBOUT Output FEEDBACK OUTPUT to Input FBIN.
17 Q1 Output Output clock 1.
18 VDD - Power Supply (+5V).
19 GND - GROUND.
20 Q2 Output Output clock 2.
21 Q3 Output Output clock 3.
22 VDD - Power supply (+5V).
23 Q4 Output Output clock 4.
24 Q5 Output Output clock 5.
25 GND - GROUND.
26 VDD - Power Supply (+5V).
27 Q6 Output Output clock 6.
28 Q7 Output Output clock 7.
3
ICS9176-01
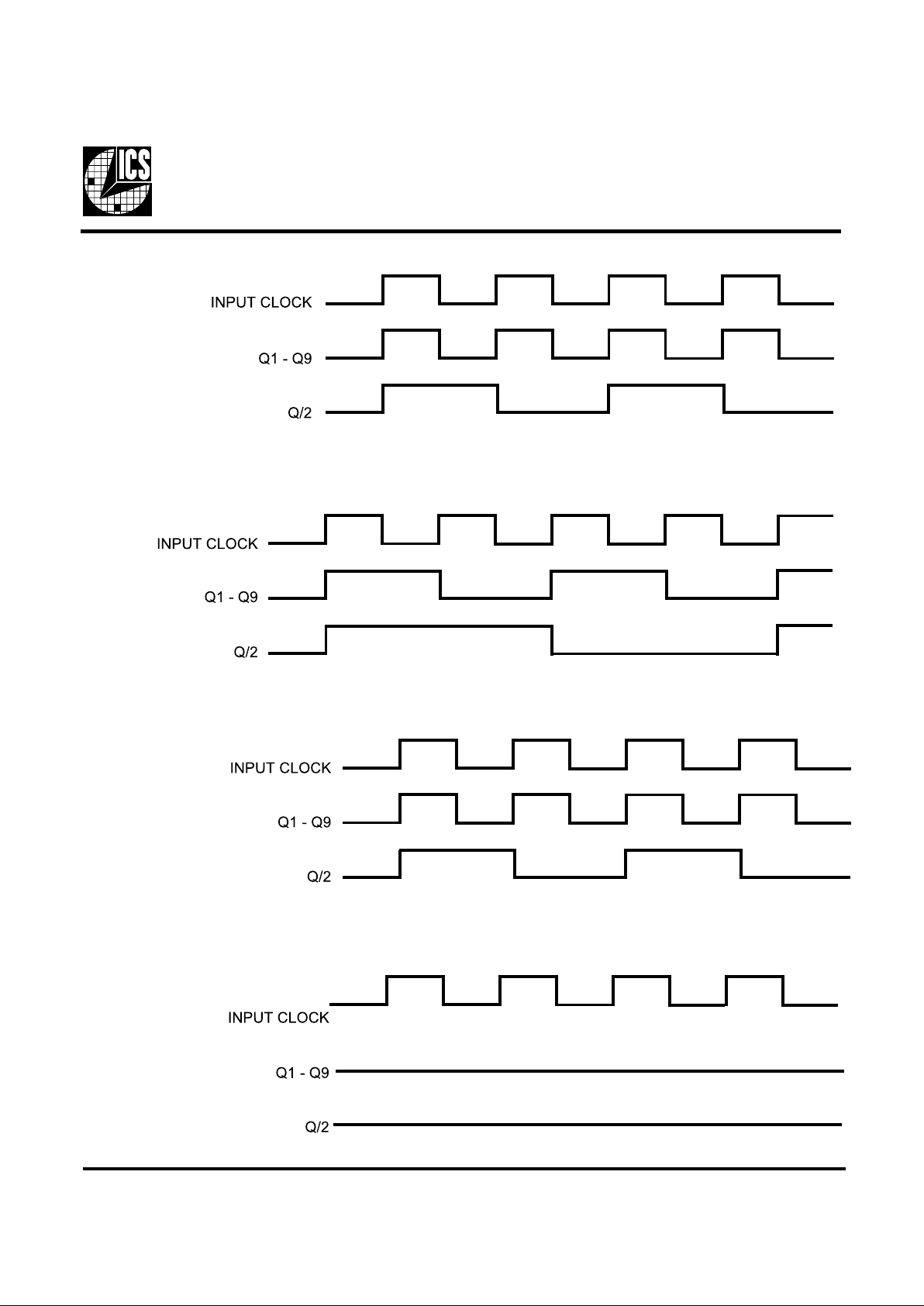
Timing Diagrams
Note: In test mode, the VCOs are bypassed. The test clock input is simply buffered, then output. The part is transparent. Damage
to the device may occur if an output is shorted or forced to ground or VDD.
Timing in Power-down Mode
Timing in Eliminate by Test Mode
Timing in Divide by 2 Mode
Timing in Divide by 1 Mode
 Loading...
Loading...