ICST AV9169CM-271, AV9169CJ-271, ICS9169CM-271 Datasheet
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
General Description Features
ICS9169C-271
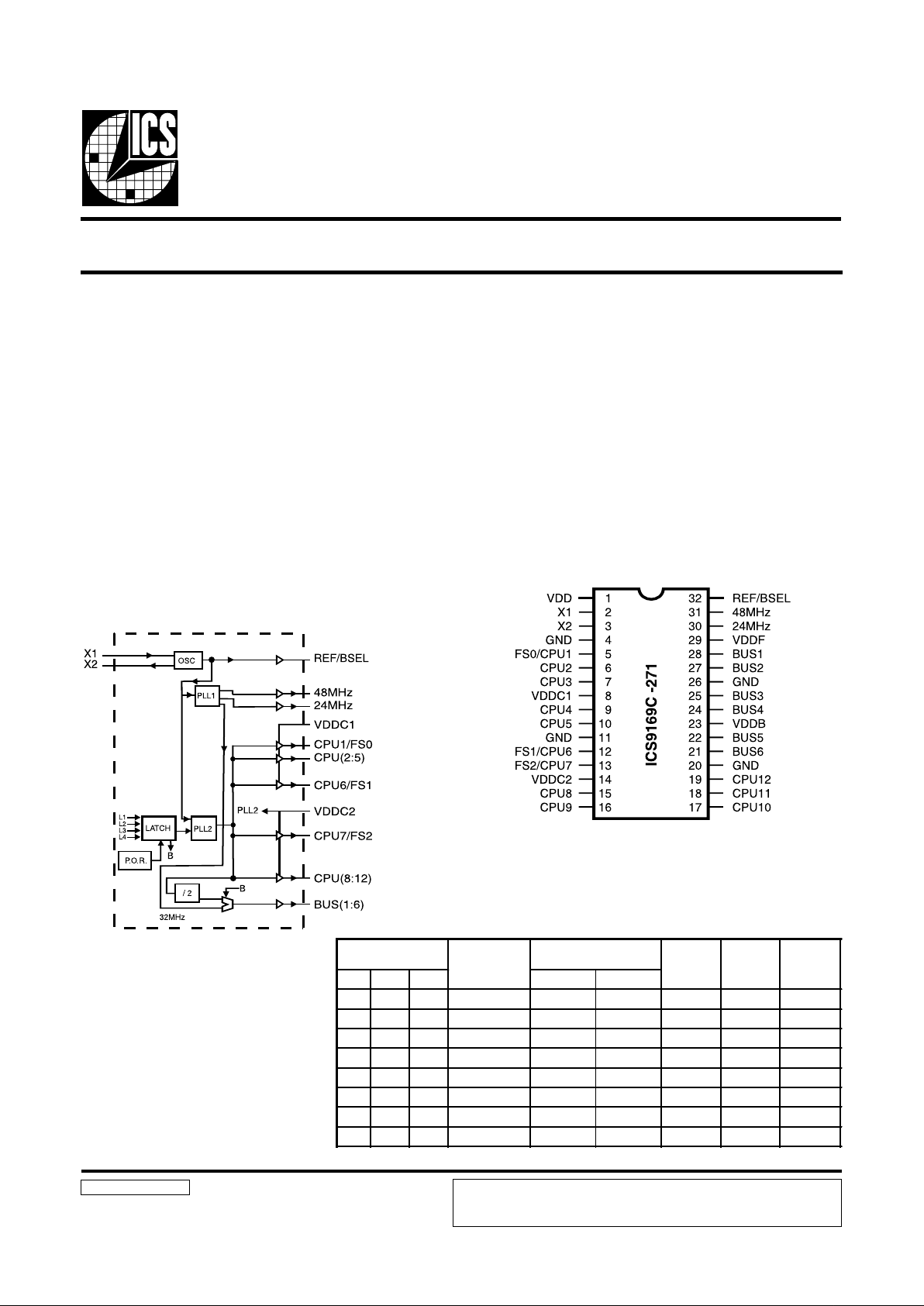
Block Diagram
Frequency Generator for Pentium™ Based Systems
9169C-271RevC060297P
Pin Configuration
The ICS9169C-271 is a low-cost frequency generator
designed specifically for Pentium based chip set systems.
The integrated buffer minimizes skew and provides all the
clocks required. A 14.318 MHz XTAL oscillator provides
the reference clock to generate standard Pentium frequencies.
The CPU clock makes gradual frequency transitions without
violating the PLL timing of internal microprocessor clock
multipliers. A raised frequency setting of 68.5MHz is av ailable
for Turbo-mode of the 66.8MHz CPU. The ICS9169C-271
contains 12 CPU clocks, 4 PCI clocks, 1 REF at 48MHz and 1 at
24MHz.
The twelve CPU clock outputs provide sufficient clocks for
the CPU, chip set, memory and up to two DIMM connectors
(with four clocks to each DIMM). Either synchronous(CPU/
2) or asynchronous (32 MHz) PCI bus operation can be selected
by latching data on the BSEL input.
32-Pin SOIC/SOJ
Functionality
3.3V±10%, 0-70°C
Crystal (X1, X2) = 14.31818 MHz
Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
• Twelve selectable CPU clocks operate up to 83.3MHz
• Maximum CPU jitter of ± 200ps
• Six BUS clocks support sync or async bus operation
• ±250ps skew for all synchronous clock edges
• CPU clocks BUS clocks skew 1-4ns (CPU early)
• Integrated buffer outputs drive up to 30pF loads
• 3.0V - 3.7V supply range, CPU(1:12) outputs
2.5V(2.375-2.62V) VDD option
• 32-pin SOIC/SOJ package
• Logic inputs latched at Power-On for frequency
selection saving pins as Input/Output
• 48 MHz clock for USB support and 24 MHz clock
for FD.
ADDRESS
SELECT
CPU(1:12)
(MHz)
BUS (1:6)M Hz
48MHz 24MHz REF
FS2 FS1 FS0 BSEL=1 BSEL=0
00 0 50 25 32 48 24 REF
00 1 60 30 32 48 24 REF
0 1 0 66.8 33.4 32 48 24 REF
0 1 1 75.9 32 32 48 24 REF
1 0 0 55 27.5 32 48 24 REF
1 0 1 75.9 37.5 32 48 24 REF
1 1 0 83.3 41.7 32 48 24 REF
1 1 1 68.5 34.25 32 48 24 REF
VDD Groups:
VDD = X1, X2, REF/BSEL
VDDC1 = CPU1-6
VDDC2 = CPU7-12 & PLL Core
VDDB = BUS1-6
VDDF = 48/24 MHz
Latched Inputs:
L1 = BSEL
L2 = FS0
L3 = FS1
L4 = FS2
ICS reserves the right to make changes in the device data identified in this publication
without further notice. ICS advises its customers to obtain the latest version of all
device data to verify that any information being relied upon by the customer is current
and accurate.
2
ICS9169C-271
Pin Descriptions
* The internal pull up will vary from 350K to 500K based on temperature
PIN NUMBER PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
1 VDD PWR
Power for device logic and crystal oscillator circuit and
14.318 MHz output.
2X1 IN
XTAL or external reference frequency input. This input
includes XTAL load capacitance and feedback bias for a
12-16MHz crystal, nominally 14.31818MHz External crystal
load of 30pF to GND recommended for VDD power on faster
than 2.0ms.
3 X2 OUT
XTAL output which includes XTAL load capacitance.
External crystal load of 10pF to GND recommended for VDD
power on faster than 2.0ms.
4,11,20,26 GND PWR Ground for device logic.
5
CPU(1) OUT
Processor clock output which is a multiple of the input
reference frequency.
FS0 IN Frequency multiplier select pins. 350K internal pull up.
6,7,9,10,15,16,17,18,19
CPU
(2:5) (8:12)
OUT
Processor clock outputs which are a multiple of the input
reference frequency.
8
VDDC1 PWR
Power for CPU(1:6) output buffers only. Can be reduced VDD
for 2.5V (2.375-2.62V) next generation processor clocks.
12
CPU(6) OUT
Processor clock output which is a multiple of the input
reference frequency internal pull up devices.
FS1 IN
Frequency multiplier select pin. See shared pin description.
350K internal pull up.
13
CPU(7) OUT
Processor clock output which is a multiple of the input
reference frequency internal pull up devices.
FS2 IN
Frequency multiplier select pin. See shared pin description.
350K internal pull up.
14 VDDC2 PWR
Power for CPU PLL, logic and CPU(7:12)output buffers. Must
be nominal 3.3V (3.0 to 3.7V)
21,22,24,25,27,28 BUS (1:6) OUT
BUS clock outputs which are a multiple of the input
reference clock.
23 VDDB PWR Power for BUS clock buffers BUS(1:6).
29 VDDF PWR Power for fixed clock buffer (48 MHz, 24 Mhz).
30 24MHz OUT
Fixed 24MHz clock (assuming a 14.31818MHz REF
frequency).
31 48MHz OUT
Fixed 48MHz clock (assuming a 14.31818MHz
REF frequency).
32
REF OUT
Fixed 14.31818MHz clock (assuming a 14.31818MHz
REF frequency).
BSEL IN
Selection for synchronous or asynchronous bus clock
operation. See shared pin programming description late in this
data sheet for further explanation. 350K internal pull up.
3
ICS9169C-271
The ICS9169C-271 includes a production test verification
mode of operation. This requires that the FS0 and FS1 pins
be programmed to a logic high and the FS2 pin be
programmed to a logic low(see Shared Pin Operation section).
In this mode the device will output the following
frequencies.
Note: REF is the frequency of either the crystal connected
between the devices X1and X2 or, in the case of a device
being driven by an external reference clock, the frequency
of the reference (or test) clock on the device’s X1 pin.
Shared Pin Operation - Input/Output Pins 5, 12, 13 and 32
on the ICS9169C-271 serve as dual signal functions to the
device. During initial power-up, they act as input pins. The
logic level (voltage) that is present on these pins at this time
is read and stored into a 4-bit internal data latch. At the end
of Power-On reset, (see AC characteristics for timing v alues),
the device changes the mode of operation for these pins to
an output function. In this mode the pins produce the
specified buffered clocks to external loads.
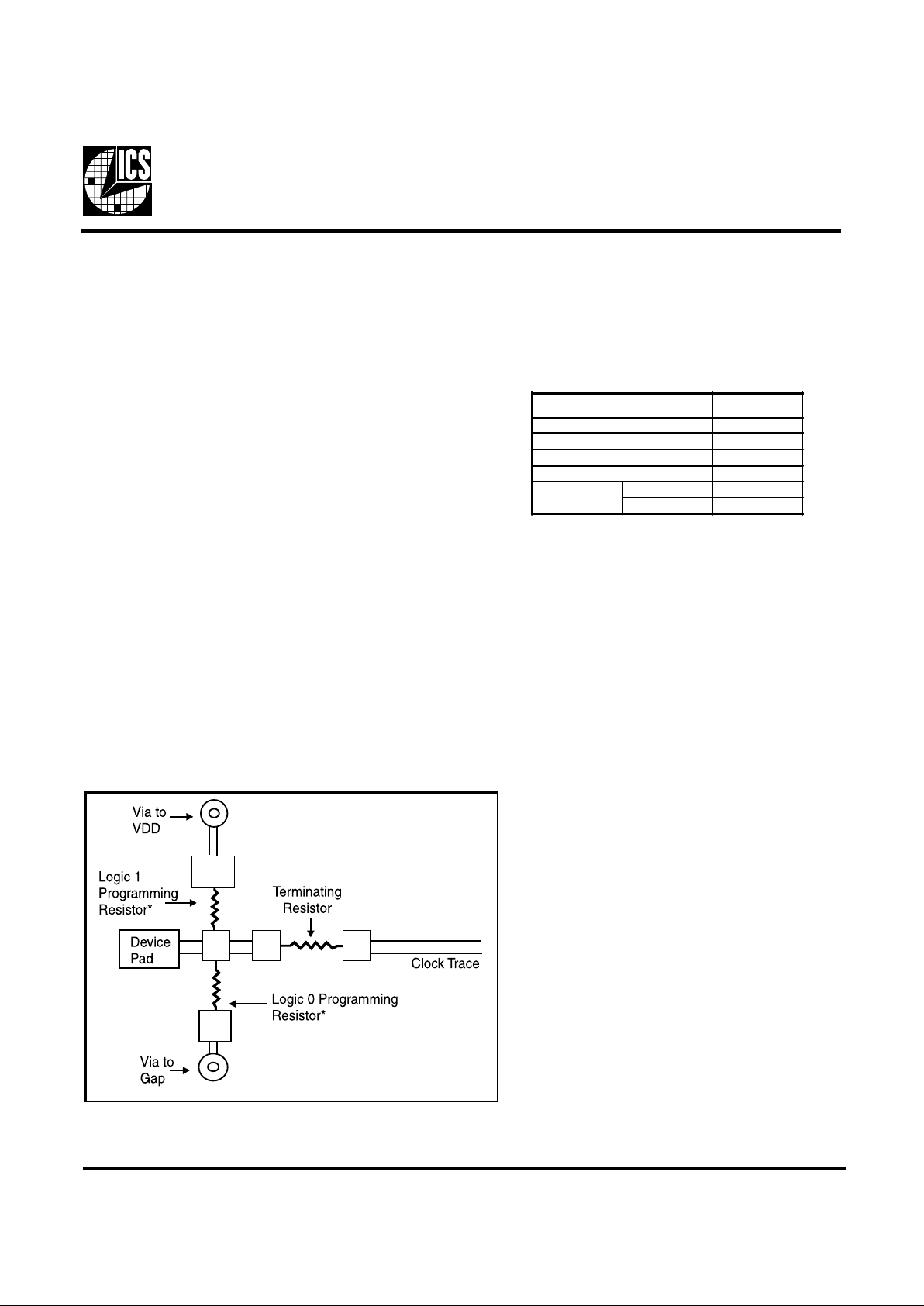
To program (load) the internal configuration register for
these pins, a resistor is connected to either the VDD (logic 1)
power supply or the GND (logic 0) voltage potential. A 10
Kilohm(10K) resistor is used to provide both the solid CMOS
programming voltage needed during the power-up
programming period and to provide an insignificant load on
the output clock during the subsequent operating period.
Figs. 1 and 2 show the recommended means of implementing
this function. In Fig. 1 either one of the resistors is loaded
onto the board (selective stuff ing) to configure the device’s
internal logic. Figs. 2a and b provide a single resistor loading
option where either solder spot tabs or a physical jumper
header may be used.
These figures illustrate the optimal PCB physical layout
options. These configuration resistors are of such a large
ohmic value that they do not effect the low impedance clock
signals. The layouts have been optimized to provide as little
impedance transition to the clock signal as possible, as it
passes through the programming resistor pad(s).
Shared Pin Operation Input/Output Pins
Test Mode Operation
Pin Frequency
REF REF
48MHz REF/2
24MHz REF/4
CPU (1:12) REF2
BUS (1:6)
BSEL=1 REF/4
BSEL = 0 REF/3
Fig. 1
(Resistors are surface mount devices
shown schematically between 5.m. pads)
*use only one programming resistor
 Loading...
Loading...