ICST AV9170-05CS08, AV9170-05CN08, AV9170-04CS08, AV9170-04CN08, AV9170-02CS08 Datasheet
...
Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
General Description Features
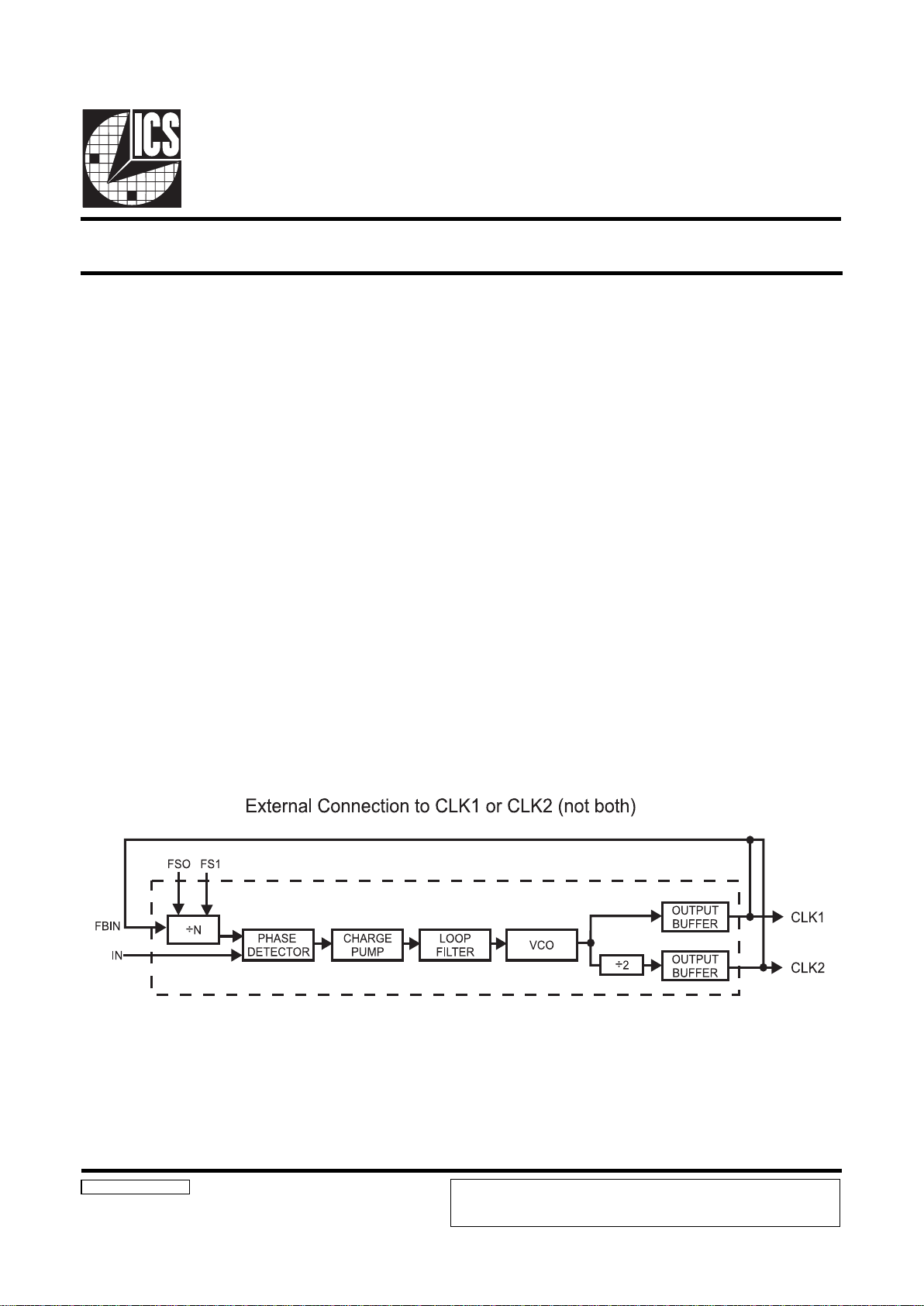
AV9170
Block Diagram
Clock Synchronizer and Multiplier
AV 9170 Rev E 9/24/99
On-chip Phase-Locked Loop for clocks synchronization
Synchronizes frequencies up to 107 MHz
(output) @ 5.0V
±1ns skew (max) between input & output clocks @ 5.0V
Can recover poor duty cycle clocks
CLK1 to CLK2 skew controlled to within ±1ns @ 5.0V
3.0 - 5.5V supply range
Low power CMOS technology
Small 8-pin DIP or SOIC package
On chip loop filter
AV9170-01, -04 for output clocks 20-107 MHz @ 5.0V,
20 - 66.7 MHz @ 3.3V
AV9170-02, -05 for output clocks 5-26.75 MHz @ 5.0V,
5 - 16.7 MHz @ 3.3V
The AV9170 generates an output clock which is synchronized
to a given continuous input clock with zero delay (±1ns at 5V
VDD). Using ICSs proprietary phase-locked loop (PLL) analog CMOS technology, the AV9170 is useful for regenerating
clocks in high speed systems where skew is a major concern.
By the use of the two select pins, multiples or divisions of the
input clock can be generated with zero delay (see Tables 2 and
3). The standard versions produce two outputs, where CLK2
is always a divide by two version of CLK1.
The AV9170 is also useful to recover poor duty cycle clocks.
A 50 MHz signal with a 20/80% duty cycle, for example, can
be regenerated to the 48/52% typical of the part.
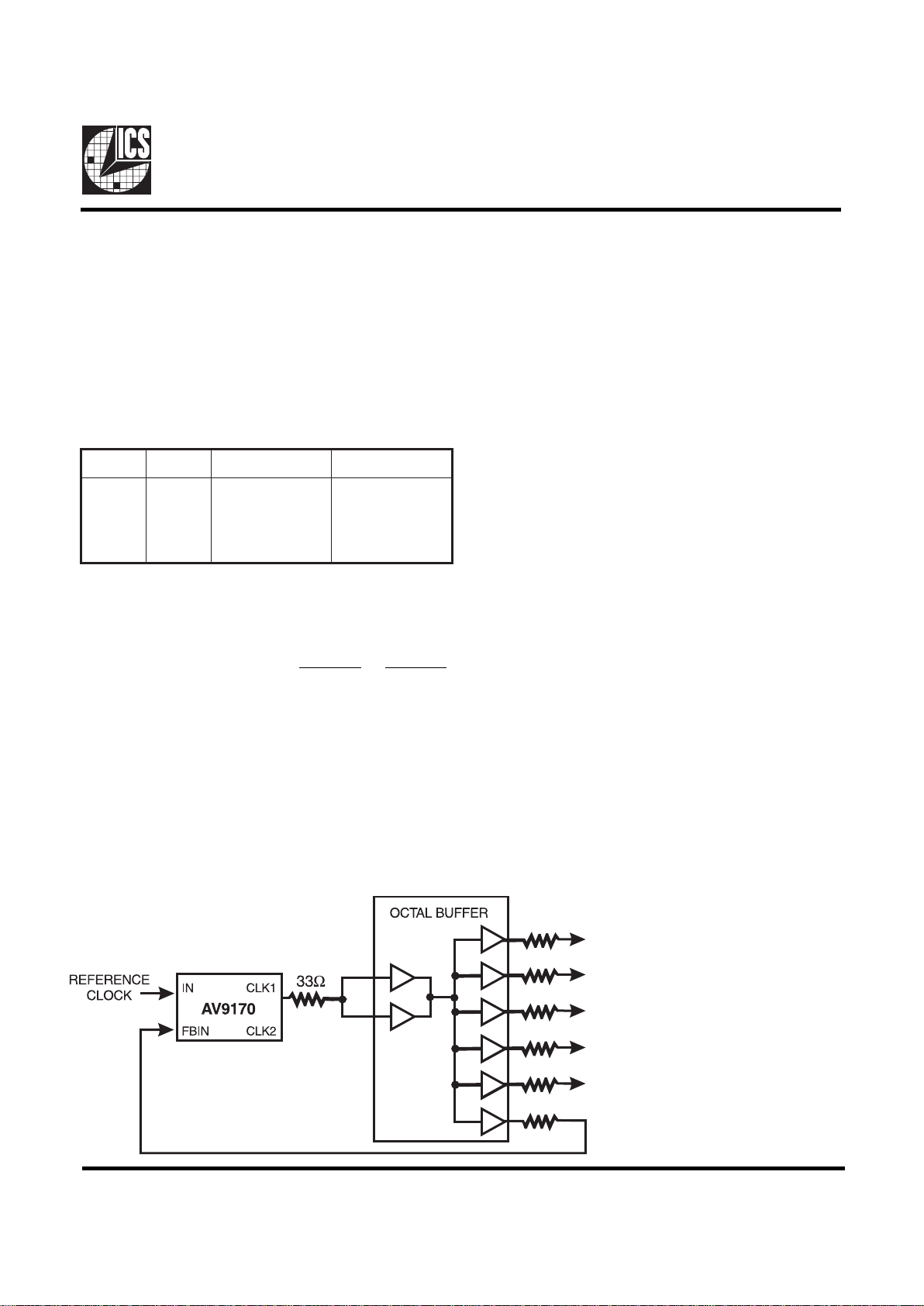
The AV9170 allows the user to control the PLL feedback,
making it possible, with an additional 74F240 octal buffer (or
other such device that offers controlled skew outputs), to
synchronize up to 8 output clocks with zero delay compared to
the input (see Figure 1). Application notes for the AV9170 are
available. Please consult ICS.
ICS reserves the right to make changes in the device data identified in this publication
without further notice. ICS advises its customers to obtain the latest version of all
device data to verify that any information being relied upon by the customer is current
and accurate.
2
AV9170
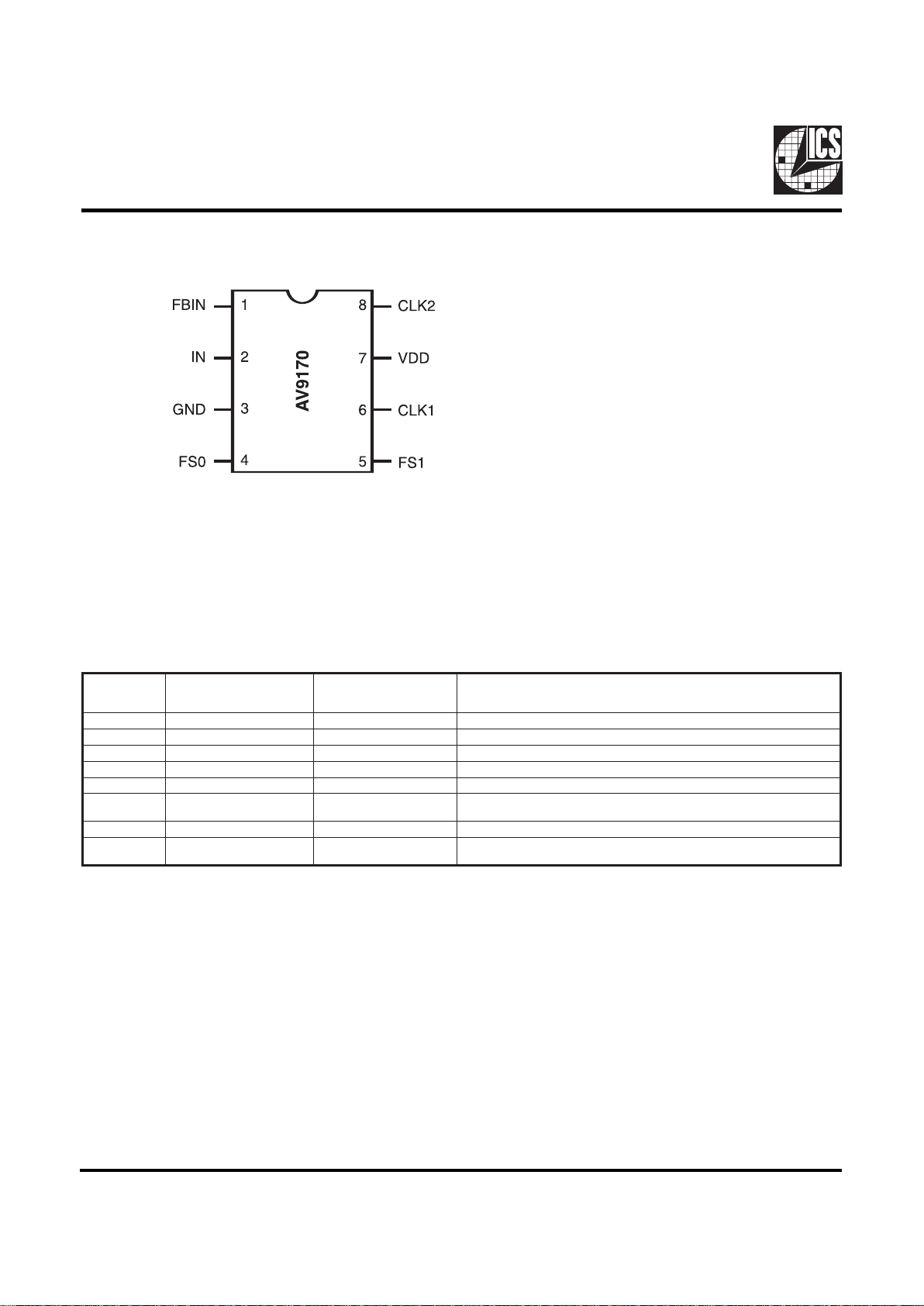
Pin Descriptions
Pin Configuration
8-Pin DIP or SOIC
NIP
-EBMUN
R
EMANNIPEPYTNOITPIRCSED
1NIBFtupnITUPNIKCABDEEF
2NItupnIkcolcecnereferrofTUPNI
3DNG—DNUORG
40SFtupnI0TCELESYCNEUQERF
51SFtupnI1TCELESYCNEUQERF
61KLCtuptuO
rof5,4,3,2,1selbaTeeS(1tuptuoKCOLC
)seulav
7DDV — ylppuSrewoP
8KLC
tuptuOrof5,4,3,2,1selbaTeeS(2tuptuoKCOLC
)seulav
3
AV9170
The AV9170 has the following characteristics:
1. Rising edges at IN and FBIN are lined up. Falling
edges are not synchronized.
2. The relationship between the frequencies at FBIN and IN
with CLK1 feedback is shown in Table 1 below.
3. The frequency of CLK2 is half the CLK1 frequency.
4. The CLK1 frequency ranges are:
The AV9170 will only operate correctly within these
frequency ranges.
Using the AV9170
Eliminate High Speed
Clock Routing Problems
The AV9170 makes it possible to route lower speed clocks
over long distances on the PC board and to place an AV9170
next to the device requiring a higher speed clock. The
multiplied output can then be used to produce a phase locked,
higher speed output clock.
Compensate for Propagation Delays
Including an AV9170 in a timing loop allows the use of PALs,
gate arrays, etc., with loose timing specifications. The
AV9170 compensates for the delay through the PAL and
synchronizes the output to the input reference clock.
Operating Frequency Range
The AV9170 is offered in versions optimized for operation
in two frequency ranges. The -01 and -04 cover high
frequencies, 20 to 100 MHz.* The -02 and -05 operate from
5 to 25 MHz.* The AV 9 17 0 can be supplied with custom
multiplication factors and operating ranges. Consult ICS for
details.
3.3V VDD Operation
The AV9170 does operate at both 5.0V and 3.3V system
conditions. Please note the Electrical Characteristic specifications at 3.3V include a limited output frequency (66.6 MHz
max.) and a wider skew of FBIN to CLK1. For 3.3V±5%
(3.15V min.), this skew is -5.0 to 0 ns. At 3.3V±10% (3.0V
min.), the skew is widened to -8 ns to 0 ns and should be
accounted for in system design.
*At 3.3V, the maximum CLK1 frequency is 66.7 MHz for -01,
-04 and 16.7 MHz for -02, -05.
Figure 1:
Application of
AV9170 for Multiple Outputs
VDD=5V VDD=3.3V
AV9170-01, -04 20 < f
CLK1
< 107 MHz* < 66.7
AV9170-02, -05 5 < f
CLK1
< 26.75 MHz* < 16.7
1SF0SFf
NIBF
)20-,10-(f
NIBF
)50-,40-(
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
•2f
NI
•4f
NI
f
NI
8 • f
NI
•3f
NI
•5f
NI
•6f
NI
01 • f
NI
Functionality (Table 1:)
4
AV9170
1SF0SF1KLC2KLC
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
4xNI
8xNI
2xNI
61xNI
2xNI
4xNI
NI
8xNI
1SF0SF1KLC2KLC
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
2xNI
4xNI
NI
8xNI
NI
2xNI
2÷NI
4xNI
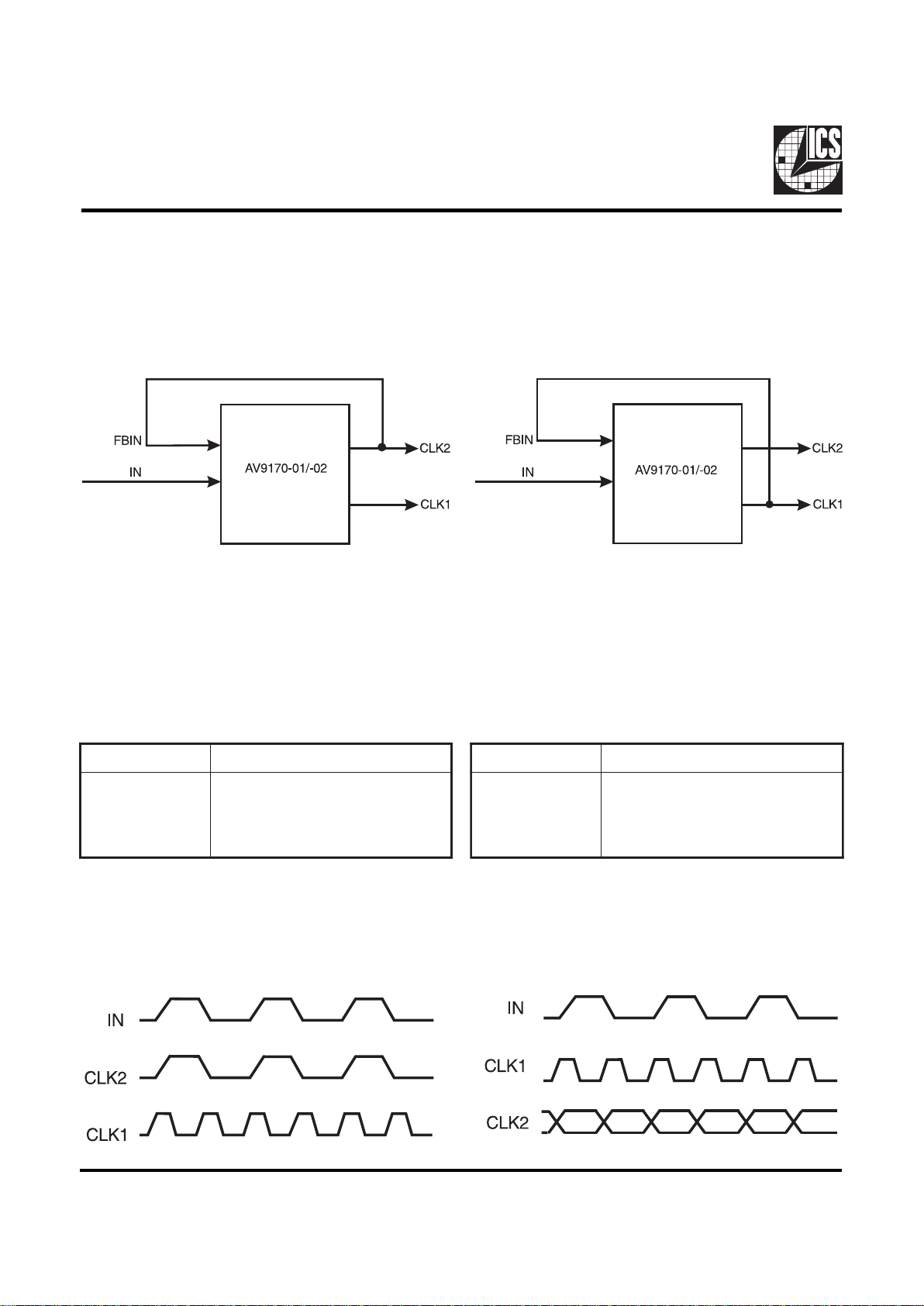
Figure 4:
Input and Output Clock Waveforms
with CLK2 Connected to FBIN
Using CLK2 Feedback
Connecting CLK2 to FBIN as shown in Figure 2 will cause all
of the rising edges to be aligned (Figure 4).
Figure 5:
Input and Output Clock Waveforms
with CLK1 Connected to FBIN
T able 2:
Functionality T able for A V9170-01, -02
with CLK2 Feedback
T able 3:
Functionality T able for A V9170-01, -02
with CLK1 Feedback
Using CLK1 Feedback
With CLK1 connected to FBIN as shown in Figure 3, the input
and CLK1 output will be aligned on the rising edge, but CLK2
can be either rising or falling (Figure 5). Consult ICS if the
CLK1 frequency is desired to be higher than 107 MHz.
For CLK2 frequencies 10 - 53.5 MHz* (-01)
For CLK2 frequencies 2.5 - 13.37 MHz (-02)
*Maximum 33.3 MHz @ 3.3V (-01), 8.33 MHz@ 3.3V (-02)
Figure 2:
For CLK1 frequencies 20 - 107 MHz (-01)
For CLK1 frequencies 5 - 26.75 MHz (-02)
Maximum 66.7 MHz @ 3.3V (-01), 16.7 MHz@ 3.3V (-02)
Figure 3:
 Loading...
Loading...