Integrated
Circuit
Systems, Inc.
General Description Features
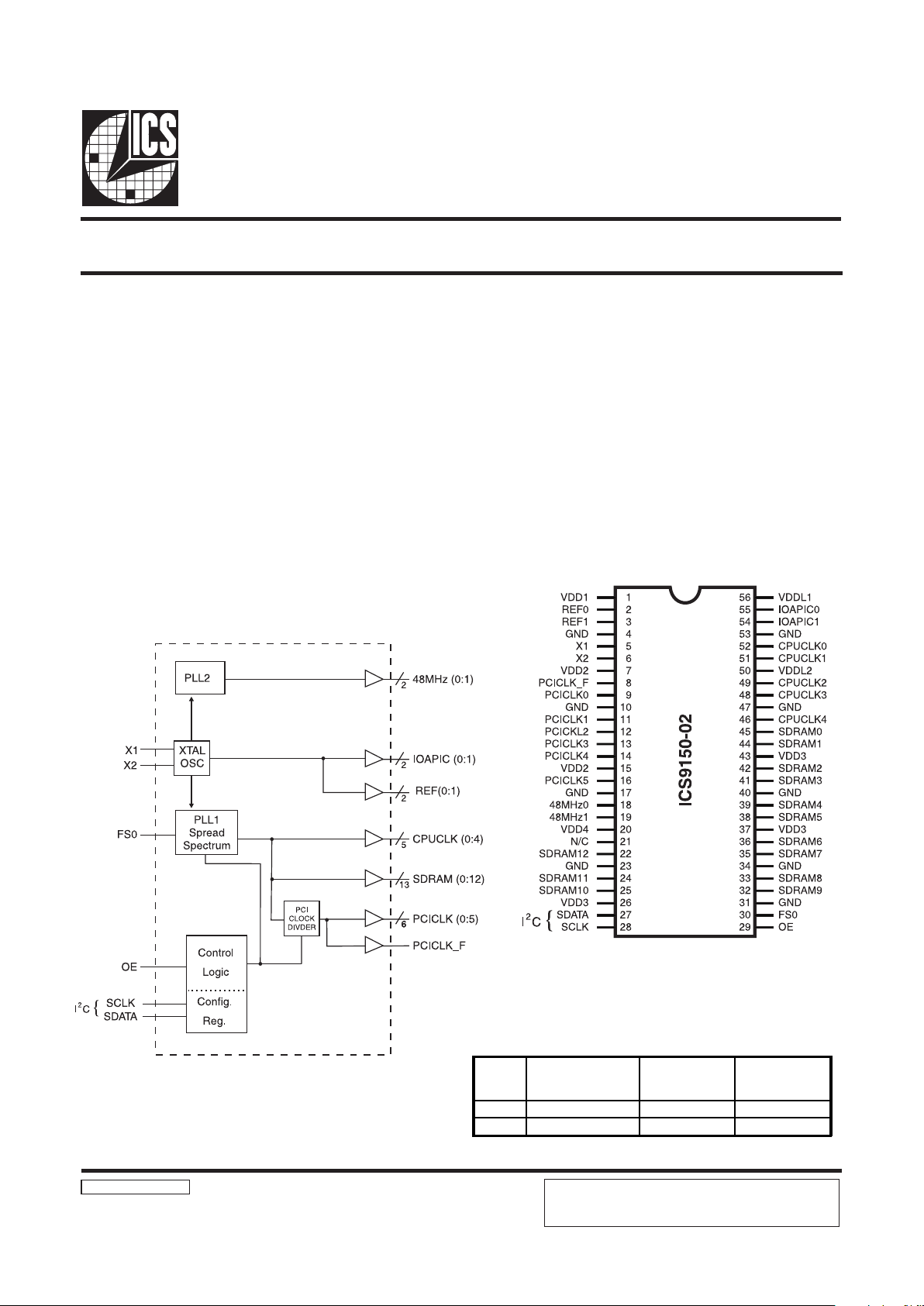
ICS9150-02
Block Diagram
Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corporation
Pentium Pro and SDRAM Frequency Generator
9150-02 Rev D 09/18/97
Pin Configuration
The ICS9150-02 generates all clocks required for high speed RISC
or CISC microprocessor systems such as Intel Pentium Pro. Two
different reference frequency multiplying factors are externally selectable
with smooth frequency transitions. An output enable is provided for
testability.
High drive PCICLK & SDRAM outputs typically provide greater
than 1 V/ns slew rate into 30pF loads. CPUCLK outputs typically
provide better than 1V/ns slew rate into 20 pF loads while maintaining
50
±
5% duty cycle. The REF clock outputs typically provide better
than 0.5V/ns slew rates.
Generates five processor, six bus, two 14.31818M Hz and 13
SDRAM clocks.
Synchronous clocks skew matched to 250 ps window on
PCLKs and 500ps window on BCLKs
Test clock mode eases system design
Spread Spectrum available
I
2
C interface for programming
Skew from CPU (earlier) to PCI clock -1 to 4ns, center
2.6ns
3.0V 3.7V supply range
56-pin SSOP package
56-Pin SSOP
FS0
CPUCLK,
SDRAM
(MH z)
X1, REF
(M Hz)
PCICLK
(M Hz)
0 60.0 14.318 30
1 66.6 14.318 33.3
Functionality
PRODUCT PREVIEW documents contain information on new
products in the sampling or preproduction phase of development.
Characteristic data and other specifications are subject to change
without notice.
Preliminary Product Preview
2
ICS9150-02
Preliminary Product Preview
Pin Descriptions
Power Groups
VDD1 = REF (0:1), X1, X2
VDD2 = PCICLK_F, PCICLK (0:5)
VDD3 = SDRAM (0:12), Supply for PLL core
VDD4 = 48 MHz
VDDL1 = IOAPIC (0:1)
VDDL2 = CPUCLK (0:4)
PIN NUMBER PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
2, 3 REF (0:1) OUT 14.318 MHz reference clock outputs.
4, 10, 17, 23, 31,
34, 40, 47, 53
GND PWR Ground.
5X1 IN
14.318MHz input. Has internal load cap, (33pF).
6 X2 OUT
Crystal output. Has internal load cap (33pF) and feedback
resistor to X1
8 PCICLK_F OUT Free running BUS clock.
9, 11, 12, 13
14, 16
PCICLK (0:5) OUT BUS clock outputs.
18, 19 48MHz OUT 48MHz clock outputs
21 N/C - Pins are not internally connected.
27 SDATA IN Serial data in for serial config port.
28 SCLK IN Clock input for serial config port.
29
OE IN Logic input for output enable, tristates all outputs when low.
30 SEL 66/60# IN Selects 60MHz or 66MHz for SDRAM and CPU.
1, 7, 15, 20, 26,
37, 43
VDD2, VDD1,
VDD3, VDD4
PWR Nominal 3.3V power supply. See power groups for function.
50, 56 VDDL2, VDDL1 PWR CPU and IOAPIC clock bu ffer power s upply (2.5 - VDD)
22, 24, 25, 32, 33,
35, 36, 38, 39, 41,
42, 44, 45
SDRAM (0:12) OUT SDRAM clocks (60/66.6MHz)
54, 55 IOAP IC (1: 0) OU T IOAPIC cloc k output. (14 .31818 MHz) Po wered by VDDL1
46, 48, 49, 51, 52 CPUCL K (0: 4) OUT CPU Output clocks. Powe red by VDDL2 (60 or 66.6MHz)

3
ICS9150-02
Preliminary Product Preview
VDD(1,2,3,4)
This is the power supply to the internal core logic of the device as well
as the clock output buffers for REF(0:1), PCICLK, 48MHz (0:1)
and SDRAM(0:7).
This pin operates at 3.3V volts. Clocks from the listed buffers that it
supplies will have a voltage swing from Ground to this level. For the
actual guaranteed high and low voltage levels for the Clocks, please
consult the DC parameter table in this data sheet.
VDDL1,2
This is the power supplies for the CPUCLK and IOAPCI output
buffers. The voltage level for these outputs may be 2.5 or 3.3volts.
Clocks from the buffers that each supplies will have a voltage swing
from Ground to this level. For the actual Guaranteed high and low
voltage levels of these Clocks, please consult the DC parameter
table in this Data Sheet.
GND
This is the power supply ground (common or negative) return pin for
the internal core logic and all the output buffers.
X1
This input pin serves one of two functions. When the device is used
with a Crystal, X1 acts as the input pin for the reference signal that
comes from the discrete crystal. When the device is driven by an
external clock signal, X1 is the device input pin for that reference
clock. This pin also implements an internal Crystal loading capacitor
that is connected to ground. With a nominal value of 33pF no
external load cap is needed for a C
L
=17 to 18pF crystal.
X2
This Output pin is used only when the device uses a Crystal as the
reference frequency source. In this mode of operation, X2 is an
output signal that drives (or excites) the discrete Crystal. The X2 pin
will also implement an internal Crystal loading capacitor nominally
33pF.
CPUCLK (0:4)
These Output pins are the Clock Outputs that drive processor and
other CPU related circuitry that requires clocks which are in tight
skew tolerance with the CPU clock. The voltage swing of these
Clocks are controlled by the Voltage level applied to the VDDL2 pin
of the device. See the Functionality Table for a list of the specific
frequencies that are available for these Clocks and the selection
codes to produce them.
SDRAM(0:12)
These Output Clocks are use to drive Dynamic RAMs and are low
skew copies of the CPU Clocks. The voltage swing of the
SDRAMs output is controlled by the supply voltage that is applied
to VDD3 of the device, operates at 3.3 volts.
Technical Pin Function Descriptions
IOAPIC (0:1)
These Outputs are fixed frequency Output Clocks that run at the
Reference Input (typically 14.31818MHz) . Its voltage level swing
is controlled by VDDL1 and may operate at 2.5 or 3.3volts.
REF (0:1)
The REF Output is a fixed frequency Clock that runs at the same
frequency as the Input Reference Clock X1 or the Crystal (typically
14.31818MHz) attached across X1 and X2.
PCICLK_F
This Output is equal to PCICLK(0:5).
PCICLK (0:5)
These Output Clocks generate all the PCI timing requirements for a
Pentium/Pro based system. They conform to the current PCI
specification. They run at 1/2 CPU frequency.
FS0
This Input pin controls the frequency of the Clocks at the CPU,
PCICLK and SDRAM output pins. If a logic 1 value is present on
this pin, the 66.6 MHz Clock will be selected. If a logic 0 is used,
the 60MHz frequency will be selected.
I
2
C
The SDATA and SCLOCK Inputs are use to program the device.
The clock generator is a slave-receiver device in the I
2
C protocol.
It will allow read-back of the registers. See configuration map for
register functions. The I
2
C specification in Philips I2C Peripherals
Data Handbook (1996) should be followed.
48MHz
This is a fixed frequency clock that is typically used to drive Super
I/O peripheral device needs and USB.
OE
Output Enable tristates the outputs when held low. This pin will
override the I
2
C Byte 0 function, so that the outputs will be tristated
when the OE is low regardless of the I
2
C defined function. When OE
is high, the I
2
C function is in active control.
 Loading...
Loading...