Page 1
查询ICS342供应商
Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock Synthesizer
ICS342
Description
The ICS342 is a low cost, dual-output, field
programmable clock synthesizer. The ICS342 can
generate two output frequencies from 250 kHz to 200
MHz, using up to two independently configurable PLLs.
The outputs may employ Spread Spectrum techniques
to reduce system electro-magnetic interference (EMI).
Using ICS’ VersaClock
PLL and output, the ICS342 contains a One-Time
Programmable (OTP) ROM to allow field
programmability. Programming features include 2
selectable configuration registers. Using Phase-Locked
Loop (PLL) techniques, the device runs from a
standard fundamental mode, inexpensive crystal, or
clock. It can replace multiple crystals and oscillators,
saving board space and cost.
The device also has a power down feature that
tri-states the clock outputs and turns off the PLLs when
the PDTS
The ICS342 is also available in factory programmed
custom versions for high-volume applications.
pin is taken low.
TM
software to configure the
Features
• 8-pin SOIC package
• Highly accurate frequency generation
• M/N Multiplier PLL: M = 1...2048, N = 1...1024
• Output clock frequencies up to 200 MHz
• Two ROM locations for frequency and spread
selection
• Spread spectrum capability for lower system EMI
• Center or Down Spread up to 4% total
• Selectable 32 kHz or 120 kHz modulation
• Input crystal frequency from 5 to 27 MHz
• Input clock frequency from 2 to 50 MHz
• Operating voltage of 3.3 V
• Advanced, low power CMOS process
• For one output clock, use the ICS341. For three
output clocks, see the ICS343. For more than three
outputs, see the ICS345 or ICS348.
• Available in Pb (lead) free packaging
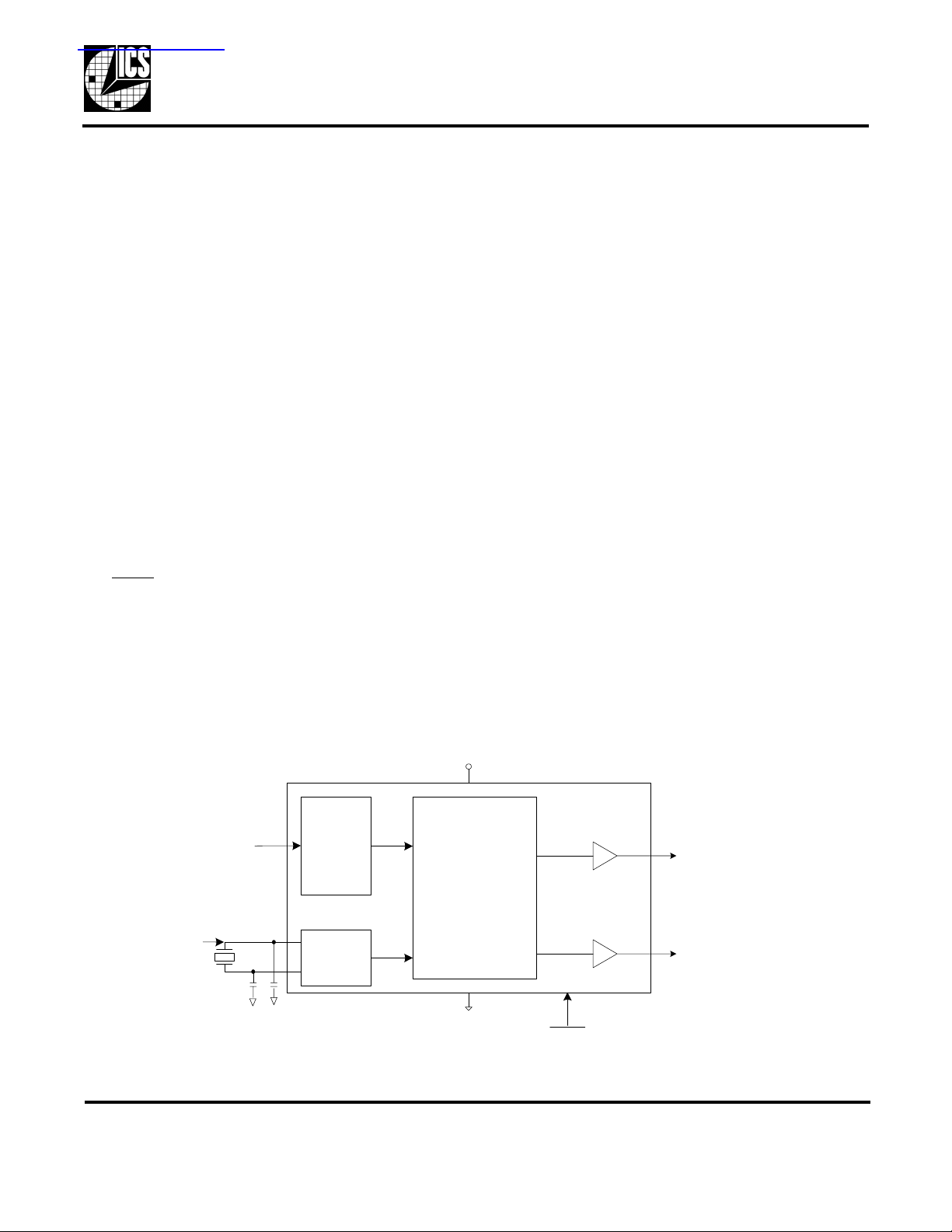
Block Diagram
VDD
OTP ROM
SEL
Crystal or
clock input
X1/ICLK
X2
External capacitors are
required with a crystal input.
MDS 342 F 1 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
with PLL
Divider
Values
Crystal
Oscillator
CLK1
PLL Clock Synthesis,
Spred Spectrum and
Control Circuitry
CLK2
GND
PDTS (both outputs and PLL)
Page 2
ICS342
Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock
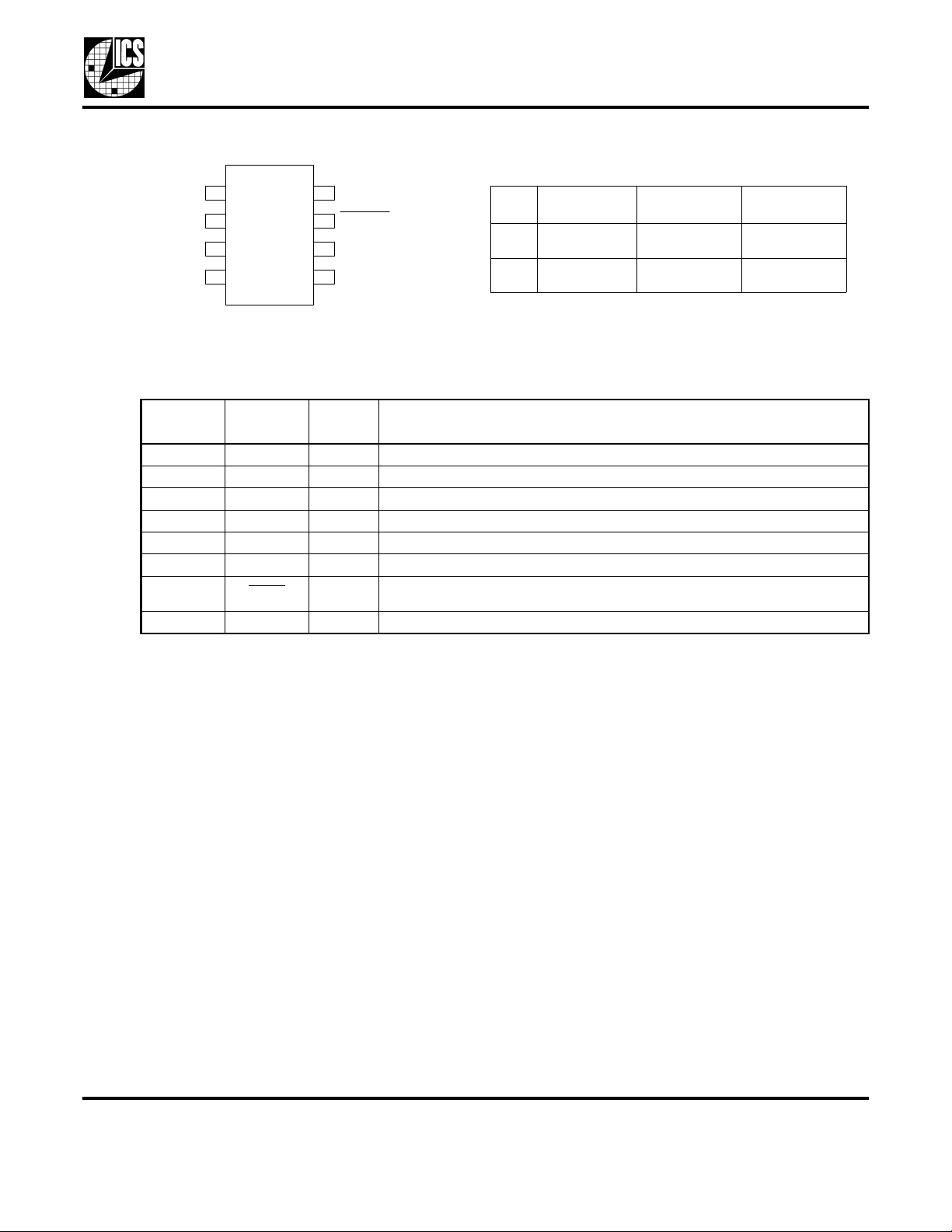
Pin Assignment
X1/I CLK
VDD
GND
CLK1
2
3
4
8-pin (150 mil) SOIC
Pin Description
Pin
Number
1 X1/ICLK XI Connect this pin to a crystal or external clock input.
2 VDD Power Connect to +3.3 V.
3 GND Power Connect to ground.
4 CLK1 Output Clock output. Weak internal pull-down when tri-state.
5 CLK2 Output Clock output. Weak internal pull-down when tri-state.
6 SEL Input Select for frequency selection on CLK1 and CLK2. Internal pull-up resistor.
7PDTS
8 X2 XO Connect this pin to a crystal, or float for clock input.
Pin
Name
Output Clock Selection Table
8
X21
PDTS
7
SEL
6
5
CLK2
Pin
Type
Input
Powers down entire chip. Tri-states CLK outputs when low. Internal pull-up
resistor.
SEL CLK1 (MHz) CLK2 (MHz) Spread
Percentage
0User
Configurable
1User
Configurable
User
Configurable
User
Configurable
User
Configurable
User
Configurable
Pin Description
External Components
Series Termination Resistor
Clock output traces over one inch should use series
termination. To series terminate a 50Ω trace (a
commonly used trace impedance), place a 33Ω resistor
in series with the clock line, as close to the clock output
pin as possible. The nominal impedance of the clock
output is 20Ω.
Decoupling Capacitor
As with any high-performance mixed-signal IC, the
ICS342 must be isolated from system power supply
noise to perform optimally.
A decoupling capacitor of 0.01µF must be connected
between VDD and the PCB ground plane.
Crystal Load Capacitors
The device crystal connections should include pads for
small capacitors from X1 to ground and from X2 to
ground. These capacitors are used to adjust the stray
capacitance of the board to match the nominally
required crystal load capacitance. Because load
capacitance can only be increased in this trimming
process, it is important to keep stray capacitance to a
minimum by using very short PCB traces (and no vias)
been the crystal and device. Crystal capacitors must be
connected from each of the pins X1 and X2 to ground.
The value (in pF) of these crystal caps should equal
(C
-6 pF)*2. In this equation, CL= crystal load
L
capacitance in pF. Example: For a crystal with a 16 pF
load capacitance, each crystal capacitor would be 20
pF [(16-6) x 2] = 20.
PCB Layout Recommendations
For optimum device performance and lowest output
phase noise, the following guidelines should be
observed.
1) The 0.01µF decoupling capacitor should be mounted
on the component side of the board as close to the
MDS 342 F 2 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
Page 3

Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock
ICS342
VDD pin as possible. No vias should be used between
the decoupling capacitor and VDD pin. The PCB trace
to VDD pin should be kept as short as possible, as
should the PCB trace to the ground via. Distance of the
ferrite bead and bulk decoupling from the device is less
critical.
2) The external crystal should be mounted just next to
the device with short traces. The X1 and X2 traces
should not be routed next to each other with minimum
spaces, instead they should be separated and away
from other traces.
3) To minimize EMI, the 33Ω series termination resistor
(if needed) should be placed close to the clock output.
4) An optimum layout is one with all components on the
same side of the board, minimizing vias through other
signal layers. Other signal traces should be routed
away from the ICS342. This includes signal traces just
underneath the device, or on layers adjacent to the
ground plane layer used by the device.
ICS342 Configuration Capabilities
The architecture of the ICS342 allows the user to easily
configure the device to a wide range of output
frequencies, for a given input reference frequency.
The frequency multiplier PLL provides a high degree of
precision. The M/N values (the multiplier/divide values
available to generate the target VCO frequency) can be
set within the range of M = 1 to 2048 and N = 1 to 1024.
The ICS342 also provides separate output divide
values, from 2 through 20, to allow the two output clock
banks to support widely differing frequency values from
the same PLL.
Each output frequency can be represented as:
OutputFreq
REFFreq
-------------------------------------OutputDivide
M
-----
⋅=
N
ICS VersaClock Software
ICS applies years of PLL optimization experience into a
user friendly software that accepts the user’s target
reference clock and output frequencies and generates
the lowest jitter, lowest power configuration, with only a
press of a button. The user does not need to have prior
PLL experience or determine the optimal VCO
frequency to support multiple output frequencies.
VersaClock software quickly evaluates accessible VCO
frequencies with available output divide values and
provides an easy to understand, bar code rating for the
target output frequencies. The user may evaluate
output accuracy, performance trade-off scenarios in
seconds.
Spread Spectrum Modulation
The ICS342 utilizes frequency modulation (FM) to
distribute energy over a range of frequencies. By
modulating the output clock frequencies, the device
effectively lowers energy across a broader range of
frequencies; thus, lowering a system’s electromagnetic
interference (EMI). The modulation rate is the time from
transitioning from a minimum frequency to a maximum
frequency and then back to the minimum.
Spread Spectrum Modulation can be applied as either
“center spread” or “down spread”. During center spread
modulation, the deviation from the target frequency is
equal in the positive and negative directions. The
effective average frequency is equal to the target
frequency. In applications where the clock is driving a
component with a maximum frequency rating, down
spread should be applied. In this case, the maximum
frequency, including modulation, is the target
frequency. The effective average frequency is less than
the target frequency.
The ICS342 operates in both center spread and down
spread modes. For center spread, the frequency can
be modulated between +/- 0.125% to +/-2.0%. For
down spread, the frequency can be modulated
between -0.25% to -4.0%.
Both output frequency banks will utilize identical spread
spectrum percentage deviations and modulation rates,
if a common VCO frequency can be identified.
Spread Spectrum Modulation Rate
The spread spectrum modulation frequency applied to
the output clock frequency may occur at a variety of
rates. For applications requiring the driving of
“down-circuit” PLLs, Zero Delay Buffers, or those
adhering to PCI standards, the spread spectrum
modulation rate should be set to 30-33 kHz. For other
applications, a 120 kHz modulation option is available.
MDS 342 F 3 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
Page 4

Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses above the ratings listed below can cause permanent damage to the ICS342. These ratings, which
are standard values for ICS commercially rated parts, are stress ratings only. Functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of the
specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods can
affect product reliability. Electrical parameters are guaranteed only over the recommended operating
temperature range.
Parameter Condition Min. Typ. Max. Units
Supply Voltage, VDD Referenced to GND 7 V
Inputs Referenced to GND -0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
Clock Outputs Referenced to GND -0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
Storage Temperature -65 150 °C
Soldering Temperature Max 10 seconds 260 °C
Junction Temperature 125 °C
Recommended Operation Conditions
ICS342
Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units
Ambient Operating Temperature (ICS342M) 0 +70 °C
Ambient Operating Temperature (ICS342MI) -40 +85 °C
Power Supply Voltage (measured in respect to GND) +3.15 +3.3 +3.45 V
Power Supply Ramp Time 4 ms
DC Electrical Characteristics
Unless stated otherwise, VDD = 3.3V ±5%, Ambient Temperature -40 to +85°C
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Operating Voltage VDD 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
Operating Supply Current
Input High Voltage
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
Input High Voltage, PDTS
Input Low Voltage, PDTS V
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage V
IDD
IH
IL
V
IH
IL
IH
IL
Configuration
Dependent - See
Versa Clock
TM
Estimates
Two 33.3333 MHz
outputs, PDTS
= 1, no
13 mA
mA
load, Note 1
PDTS
= 0 20 µA
SEL pin 2 V
SEL pin 0.4 V
VDD-0.5 V
0.4 V
ICLK VDD/2+1 V
ICLK VDD/2-1 V
MDS 342 F 4 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
Page 5

Parameter Symbol Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Output High Voltage
(CMOS High)
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage V
Short Circuit Current I
Nominal Output
Impedance
Internal pull-up resistor R
Internal pull-down
resistor
Input Capacitance C
V
R
OH
OH
OL
OS
Z
O
PUP
PD
IN
ICS342
Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock
I
= -4 mA VDD-0.4 V
OH
I
= -12 mA 2.4 V
OH
IOL = 12mA 0.4 V
±70 mA
20 Ω
SEL, PDTS pins 250 kΩ
CLK output 525 kΩ
Inputs 4 pF
Note 1: Example with 25 MHz crystal input with two outputs of 33.3
AC Electrical Characteristics
Unless stated otherwise, VDD = 3.3V ±5%, Ambient Temperature -40 to +85° C
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Input Frequency F
Output Frequency 0.25 200 MHz
Output Rise Time t
Output Fall Time t
Duty Cycle Note 2 40 49-51 60 %
Power-up time PLL lock time from
One Sigma Clock Period Jitter Configuration Dependent 50 ps
Maximum Absolute Jitter t
IN
OR
OF
ja
MHz, no load, and VDD = 3.3 V.
Fundamental Crystal 5 27 MHz
Input Clock 2 50 MHz
20% to 80%, Note 1 1 ns
80% to 20%, Note 1 1 ns
410ms
power-up, Note 3
PDTS
goes high until
0.2 2 ms
stable CLK output, Spread
Spectrum Off, Note 3
goes high until
PDTS
47ms
stable CLK output, Spread
Spectrum On, Note 3
Deviation from Mean.
+200 ps
Configuration Dependent
Note 1: Measured with 15 pF load.
Note 2: Duty Cycle is configuration dependent. Most configurations are minimum 45% and maximum 55%.
Note 3: ICS test mode output occurs for first 170 clock cycles on CLK2 for each PLL powered up. PDTS
transition high on select address change.
MDS 342 F 5 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
Page 6

Thermal Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Thermal Resistance Junction to
Ambient
Thermal Resistance Junction to Case θ
ICS342
Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock
θ
θ
θ
Still air 150 °C/W
JA
1 m/s air flow 140 °C/W
JA
3 m/s air flow 120 °C/W
JA
JC
40 °C/W
MDS 342 F 6 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
Page 7

Field Programmable Dual Output SS VersaClock
Package Outline and Package Dimensions (8-pin SOIC, 150 Mil. Body)
Package dimensions are kept current with JEDEC Publication No. 95
ICS342
INDEX
AREA
8
Symbol Min Max Min Max
Millimeters Inches
A 1.35 1.75 .0532 .0688
A1 0.10 0.25 .0040 .0098
E
H
B 0.330.51.013.020
C 0.19 0.25 .0075 .0098
D 4.80 5.00 .1890 .1968
E 3.80 4.00 .1497 .1574
e 1.27 BASIC 0.050 BASIC
1 2
H 5.80 6.20 .2284 .2440
h 0.250.50.010.020
D
L 0.401.27.016.050
α 0° 8° 0° 8°
A
A1
- C -
e
B
SEATING
.10 (.004)
PLANE
C
h x 45
C
L
Ordering Information
Part / Order Number Marking Shipping
packaging
ICS342MP 342MP (top line) Tubes 8-pin SOIC 0 to +70° C
ICS342MIP 342MIP (top line) Tubes 8-pin SOIC -40 to +85° C
ICS342MLF 342MLF (top line) Tubes 8-pin SOIC 0 to +70° C
“LF” denotes Pb (lead) free package.
While the information presented herein has been checked for both accuracy and reliability, Integrated Circuit Systems (ICS)
assumes no responsibility for either its use or for the infringement of any patents or other rights of third parties, which would
result from its use. No other circuits, patents, or licenses are implied. This product is intended for use in normal commercial
applications. Any other applications such as those requiring extended temperature range, high reliability, or other extraordinary
environmental requirements are not recommended without additional processing by ICS. ICS reserves the right to change any
circuitry or specifications without notice. ICS does not authorize or warrant any ICS product for use in life support devices or
critical medical instruments.
MDS 342 F 7 Revision 090704
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ● 525 Race Street, San Jose, CA 95126 ● tel (408) 297-1201 ● www.icst.com
Package Temperature
 Loading...
Loading...