
PCI-1002 Series Card
User Manual
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board Version 3.0, Jun. 2018
SUPPORTS
Board includes PCI-1002L, PCI-1002H, PCI-1002LU, PCI-1002HU, PEX-1002L and
PEX-1002H.
WARRANTY
All products manufactured by ICP DAS are warranted against defective materials
for a period of one year from the date of delivery to the original purchaser.
WARNING
ICP DAS assumes no liability for damages consequent to the use of this product.
ICP DAS reserves the right to change this manual at any time without notice. The
information furnished by ICP DAS is believed to be accurate and reliable. However,
no responsibility is assumed by ICP DAS for its use, nor for any infringements of
patents or other rights of third parties resulting from its use.
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2018 by ICP DAS. All rights are reserved.
TRADEMARK
Names are used for identification only and may be registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
CONTACT US
If you have any question, please feel to contact us at:
service@icpdas.com; service.icpdas@gmail.com
We will give you quick response within 2 workdays.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PACKING LIST ....................................................................................................................................................................... 3
1. INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................................ 4
1.1 FEAT UR ES ............................................................................................................................................................ 5
1.2 SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.2.1 PCI-1002L/1002H/1002LU/1002HU ............................................................................................................ 6
1.2.2 PEX-1002L/1002H ......................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2.3 Analog Input Range ........................................................................................................................................ 8
1.2.4 AD Trigger Methods ....................................................................................................................................... 8
1.2.5 Interrupt Channel ........................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2.6 Programmable Timer/Counter ...................................................................................................................... 9
1.3 THE BLOCK DIAGRAMS ........................................................................................................................................ 10
2. HARDWARE CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................................................ 11
2.1 BOARD LAYOU T .................................................................................................................................................. 11
2.2 JP1: AD INPUT TYPE SELECTION ......................................................................................................................... 13
2.3 VR1/VR2/VR3: AD CALIBRATION ..................................................................................................................... 13
2.4 CARD ID SWITCH ................................................................................................................................................ 14
2.5 JP2: DI PORT SETTINGS (PULL-HIGH/LOW) ........................................................................................................ 15
2.6 SYSTEM BLOCK ................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.7 AD INPUT SIGNAL CONNECTION ........................................................................................................................... 16
2.8 PIN ASSIGNMENTS .............................................................................................................................................. 21
3. HARDWARE INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................................ 23
4. SOFTWARE INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................................. 27
4.1 OBTAINING/INSTALLING THE DRIVER INSTALLER PACKAGE .................................................................................... 27
4.2 PNP DRIVER INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................................. 30
4.3 VERIFYING THE INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................................. 32
4.3.1 Accessing Windows Device Manager ............................................................................................................ 32
4.3.2 Check that the Installation ............................................................................................................................ 35
5. BOARD TESTING .............................................................................................................................................. 36
5.1 SELF-TEST WIRING ............................................................................................................................................ 36
5.1.1 Digital Input/Output Test Wiring ................................................................................................................... 36
5.1.2 Analog Input Test Wiring ............................................................................................................................... 37
5.2 LAUNCH THE TEST PROGRAM............................................................................................................................... 38

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 2
6. I/O REGISTER ADDRESS .................................................................................................................................. 41
6.1 HOW TO FIND THE I/O ADDRESS ......................................................................................................................... 41
6.2 THE I/O ADDRESS MAP ...................................................................................................................................... 45
6.2.1 Section1 ......................................................................................................................................................... 46
6.2.2 Section2 ......................................................................................................................................................... 47
7. FUNCTION OPERATIONS ................................................................................................................................. 52
7.1 DIGITAL I/O ....................................................................................................................................................... 52
7.2 THE 8254 TIMER ............................................................................................................................................... 53
7.3 THE AD TIMER ..................................................................................................................................................... 54
7.4 AD CONVERSION ................................................................................................................................................ 56
7.4.1 AD Conversion Trigger Modes ....................................................................................................................... 58
7.4.2 AD Transfer Modes ........................................................................................................................................ 58
7.4.3 Software Triggers and Polling Techniques ..................................................................................................... 59
8. DEMO PROGRAMS ........................................................................................................................................... 62
8.1 DEMO PROGRAM FOR WINDOWS .......................................................................................................................... 62
8.2 DEMO PROGRAM FOR DOS .................................................................................................................................. 64
8.3 DIAGNOSTIC PROGRAM ........................................................................................................................................ 65
8.3.1 Power-on Plug & Play Test ............................................................................................................................ 65
8.3.2 Driver Plug & Play Test .................................................................................................................................. 65
8.3.3 DI O Te s t ......................................................................................................................................................... 66
8.3.4 AD Test .......................................................................................................................................................... 66
APPENDIX: DAUGHTER BOARD ............................................................................................................................... 67
A1. DB-37 and DN-37 ............................................................................................................................................... 67
A2. DB-1825 .............................................................................................................................................................. 67
A3. DB-8225 .............................................................................................................................................................. 68
A3. DB-16P Isolated Input Board ............................................................................................................................. 68
A4. DB-16R Relay Board ........................................................................................................................................... 69

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 3
Packing List
The shipping package includes the following items:
One PEX/PCI-1002 series card hardware
One printed Quick Start Guide
One Software Utility CD
One CA-4002 D-Sub Connect
Note:
If any of these items is missing or damaged, contact the dealer from whom you purchased the product. Save
the shipping materials and carton in case you need to ship or store the product in the future.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 4
1. Introduction
The PCI-1002LU/HU and PEX-1002LU/HU cards are the new generation product that ICP DAS
provides to meet RoHS compliance requirement and is designed as completely compatible with the
PCI-1002L/H. Users can replace the PCI-1002L/H by the PCI-1002LU/HU and PEX-1002LU/HU directly
without software/driver modification.
The PCI-1002L/H supports 5 V PCI bus and PCI-1002LU/HU supports 3.3 V/5 V PCI bus, while the
PEX-1002L/H supports PCI Express bus. The PCI-1002 series is a family of AD board and features
low-gain 110 kS/s or high-gain 44 kS/s analog input. It provides 12-bit 32 single-ended analog input
channels or 16 differential analog input channels, 16 digital input channel and 16 digital output
channel.
The PCI-1002LU/HU and PEX-1002L/U provide pull-high/low jumpers allow user to predefine the DI
status instead of floating when the DI channels are unconnected or broken. The PEX-1002L/H adds a
Card ID switch for users to recognize the board by the ID via software when using two or more
PEX-1002L/H cards in one computer.
PCI-1002LU/HU (Universal PCI version) and PEX-1002L/H (PCI Express) is fully compatible with the
PCI-1002L/H (PCI version). PCI-1002LU/HU and PEX-1002L/H (new version) sell now; PCI-1002L/H
(old version) will be phase out.
These cards support various OS such as Linux, DOS, 32/64-bit Windows 10/8/7/2008/2003/XP. DLL
and Active X control together with various language sample program base on Turbo C++, Borland
c++, Microsoft C++, Visual C++, Borland Delphi, Borland C++ Builder, Visual Basic, C#.NET, Visual
Basic.NET and LabVIEW are provided in order to help users to quickly and easily develop their own
applications.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 5
1.1 Features
• Bus: 5 V PCI (Peripherals Component Interface) bus for PCI-1002L/H
• Universal PCI card, supports both 5 V and 3.3 V PCI bus for PCI-1002LU/HU
• PCI Express card, supports PCI Express x1 for PEX-1002L/H
• Card ID function for PEX-1002L/H
AD:
• The sampling rate of single channel or multiple channels is 110 kS/s. for low gain model and 44
kS/s. for high gain model.
• 32 single-ended / 16 differential programmable inputs.
• Provides three different AD trigger methods.
• Provides three different external trigger methods.
• Programmable gain control, programmable offset control.
DIO:
• 16 digital inputs and 16 digital outputs (TTL compatible).
• High speed data transfer rate: 2.7 M word/sec (non-burst mode).
• Digital input port can be set to pull-high or pull-low (PCI-1002 LU/HU and PEX-1002L/H only).
Timer:
• One 16-bit machine independent timer for software (Timer 2).
• Two 16-bit pacer timers for AD converter and interrupt (Timer0, Timer1).

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 6
1.2 Specifications
1.2.1 PCI-1002L/1002H/1002LU/1002HU
Model Name
PCI-1002L
(Phased-out)
PCI-1002H
(Phased-out)
PCI-1002LU
PCI-1002HU
Analog Input
Channels
32 single-ended/16 differential
AD Converter
12-bit, 8 μs Conversion time
Sampling Rate
110 kS/s.
44 kS/s.
110 kS/s.
44 kS/s.
FIFO Size
N/A
Over voltage Protection
Continuous +/-35 Vp-p
Input Impedance
10 MΩ/6 pF
Trigger Modes
Software, Internal programmable pacer, External (5 V/TTL compatible)
Data Transfer
Polling, Interrupt
Accuracy
0.01 % of FSR ±1 LSB @ 25 °C, ± 10 V
Zero Drift
+/- 4 ppm/°C of FSR
Digital Input
Channels
16
Compatibility
5 V/TTL
Input Voltage
Logic 0: 0.8 V max.; Logic 1: 2.0 V min.
Response Speed
1.0 MHz
Digital Output
Channels
16
Compatibility
5 V/TTL
Output Voltage
Logic 0: 0.4 V max.; Logic 1: 2.4 V min.
Output Capability
Sink: 2.4 mA @ 0.8 V; Source: 0.8 mA @ 2.0 V
Response Speed
1.0 MHz
Timer/Counter
Channels
3(Independent x 1/Internal pacer x 1/External pacer x 1)
Resolution
16-bit
Compatibility
5 V/TTL
Input Frequency
10 MHz max.
Reference Clock
Internal: 4 MHz
General
Bus Type
5 V PCI, 32-bit, 33 MHz
3.3 V/5 V Universal PCI, 32-bit, 33 MHz
Data Bus
16-bit
Card ID
No
I/O Connector Female DB37 x 1, 20-pin box header x 2
Dimensions (L x W x D)
175 mm x 105 mm x 22mm
188 mm x 105 mm x 22 mm
Power Consumption
960 mA @ +5 V
Operating Temperature
0 ~ 60 °C
Storage Temperature
-20 ~ 70 °C
Humidity
5 ~ 85% RH, non-condensing

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 7
1.2.2 PEX-1002L/1002H
Model Name
PEX-1002L
PEX-1002H
Analog Input
Channels
32 single-ended/16 differential
AD Converter
12-bit, 8 μs Conversion time
Sampling Rate
110 kS/s.
44 kS/s.
FIFO Size
N/A
Over voltage Protection
Continuous +/-35 Vp-p
Input Impedance
10 MΩ/6 pF
Trigger Modes
Software, Internal programmable pacer, External (5 V/TTL compatible)
Data Transfer
Polling, Interrupt
Accuracy
0.01 % of FSR ±1 LSB @ 25 °C, ± 10 V
Zero Drift
+/- 4 ppm/°C of FSR
Digital Input
Channels
16
Compatibility
5 V/TTL
Input Voltage
Logic 0: 0.8 V max.; Logic 1: 2.0 V min.
Response Speed
500 kHz
Digital Output
Channels
16
Compatibility
5 V/TTL
Output Voltage
Logic 0: 0.4 V max.; Logic 1: 2.4 V min.
Output Capability
Sink: 2.4 mA @ 0.8 V; Source: 0.8 mA @ 2.0 V
Response Speed
500 kHz
Timer/Counter
Channels
3(Independent x 1/Internal pacer x 1/External pacer x 1)
Resolution
16-bit
Compatibility
5 V/TTL
Input Frequency
10 MHz max.
Reference Clock
Internal: 4 MHz
General
Bus Type
PCI Express x 1
Data Bus
16-bit
Card ID
Yes (4-bit)
I/O Connector Female DB37 x 1, 20-pin box header x 2
Dimensions (L x W x D)
188 mm x 105 mm x 22 mm
Power Consumption 900 mA @ +3.3 V
350 mA @ +12 V
Operating Temperature
0 ~ 60 °C
Storage Temperature
-20 ~ 70 °C
Humidity
5 ~ 85% RH, non-condensing

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 8
1.2.3 Analog Input Range
Model
PCI-1002L/LU and PEX-1002L (Low-Gain)
Gain 1 2 4 8
Bipolar
±10 V
±5 V
±2.5 V
±1.25 V
Sampling Rate Max. 100 kS/s.
Model
PCI-1002H/HU and PEX-1002H (High-Gain)
Gain 1 10 100 1000
Bipolar
±10 V
±1 V
±0.1 V
±0.01 V
Sampling Rate Max. 44 kS/s. 36 kS/s. 7 kS/s. 0.8 kS/s.
1.2.4 AD Trigger Methods
Trigger methods:
Software trigger.
Pacer trigger: 16-bit programmable timer/counter.
External trigger: Pre-trigger, Post-trigger, external Pacer trigger.
Figure 1-1: Trigger methods of PCI-1002 series.
External trigger
t
Start
End
Post-trigger mode
CHn
External trigger
Start
End
CHn
Pre-trigger mode
t
t
Start End
Normal trigger mode
CHn
Pacer or software trigger
CHn
External trigger
End Start
External pacer trigger mode
t

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 9
1.2.5 Interrupt Channel
Interrupt: INTA (Automatically assigned by PCI-initiator).
Enable/Disable: Via PCI control register and add-on control register.
Interrupt source: (Selected by on-board control register)
1. AD conversion interrupt.
2. Pacer 0 interrupt (Timer 0).
3. Pacer 1 interrupt (Timer 1).
4. External interrupt.
Figure 1-2: Programmable interrupt source.
1.2.6 Programmable Timer/Counter
Type: 82C54 – 8 programmable timer/counter.
Timers:
• Timer 0 for Pacer triggers and interrupts.
• Timer 1 for External trigger and interrupt.
• Timer 2 for software machine independent timer.
AD busy
IRQ
1.
Pacer 0
IRQ
2.
Pacer 1
IRQ
3.
External
IRQ
Falling edge of
4.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 10
1.3 The Block Diagrams
Here’s the block diagram of PCI-1002 series:
Figure 1-3: The PCI-1002 series block diagram.
X86 System
PCI BUS
PCI Interface System
EPROM
Local System Controller
Status
Control
16 bits DI
16 bits DO
Pacer
Generator
A/D
Data
Buffer
Analog Inputs
Digital Outputs
Digital Inputs
A/D control logic
12-bit A/D
Converter
MuxGain
4MHz
Interrupt

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 11
2. Hardware Configuration
2.1 Board Layout
Figure 2.1 and Figure 2.2 shows the layout of the PEX-1002L/H and PCI-1002LU/HU boards and the
locations of the configuration jumper and connector for signal wiring.
PEX-1002L/H
PEX-1002
H
CON2
CON2
SW1
1 2 3 4
CON
1
JP1
VR3VR2VR1
PEX-1002L
JP2
CON1
16-channel Digital Output
Refer to Section 2.8 “Pin Assignments” for
more details.
CON2
16-channel Digital Input
CON3
The terminal for the AD and DA converters for
voltage input/output
SW1 Card ID function
Refer to Section 2.4 “Card ID Switch” for more
details.
JP1 Analog input type selection
Refer to Section 2.2 “JP1: A D Inp ut Type
Selection” for more details.
VR1/VR2/VR3 AD Calibration
Refer to Section 2.3 “VR1/VR2/VR3: AD
Calibration” for more details.
JP2 Pull-high/pull-low jumper for DI
Refer to Section 2.5 “JP2: DI Port Settings
(Pull-High/Low)” for more details.
Figure 2-1

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 12
PCI-1002LU/HU.
PCI
-
1002
LU
/
HU REV
:
B
CON
3
CON2
CON1
JP
1
VR3
VR2
VR1
CON1
16-channel Digital Output
Refer to Section 2.8 “Pin Assignments”
for
more details.
CON2
16-channel Digital Input
CON3
The terminal for the AD and DA converters for
voltage input/output
JP1 AD input type selection
Refer to Section 2.2 “JP1: AD Input Type
Selection” for more details.
VR1/VR2/VR3 AD Calibration
Refer to
Section 2.3 “VR1/VR2/VR3: AD
Calibration” for more details.
Figure 2-2
PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 13
VR1, VR2, VR3
2.2 JP1: AD Input Type Selection
This jumper is used to select the analog input type. For single-ended inputs, connect pin1, 3 and
pin2, 4. For differential inputs, pin3, 5 and pin4, 6 should be connected. The configuration is
illustrated in the figure below.
JP4
1
5
2
6
JP4
1
5
2
6
3 4 3 4
Single-Ended Differential
Inputs (Default)
For detailed information about the single-ended and differential input w i ring, refer to Section 2.7 “AD
Input Signal Connection”.
2.3 VR1/VR2/VR3: AD Calibration
AD Calibration for PCI-1002 series card:
Step 1: Apply +10 V to channel 0.
Step 2: Apply +0 V to channel 1.
Step 3: Apply -10 V to channel 2.
Step 4: Run DEMO6.EXE of DOS.
Step 5: Adjust VR1 until channel 0 = fff or ffe
Step 6: Adjust VR2 until channel 1 = 800 or 801
Step 7: Adjust VR3 until channel 2 = 000 or 001
Step 8: Repeat Step 4, Step 5 and Step 6 until all are OK.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 14
2.4 Card ID Switch
The PEX-1002L/H has a Card ID switch (SW1) with which users can recognize the board by the ID via
software when using two or more PEX-1002L/H cards in one computer. The default Card ID is 0x0.
For detail SW1 Card ID settings, refer to Table 2-1. Note that the Card ID function is only supported by
the PEX-1002L/H.
Table 2-1 (*) Default Settings; OFF 1; ON 0
Card ID (Hex)
1
ID0
2
ID1 3 ID2 4 ID3
(*) 0x0
ON
ON
ON
ON
0x1
OFF
ON
ON
ON
0x2
ON
OFF
ON
ON
0x3
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
0x4
ON
ON
OFF
ON
0x5
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
0x6
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
0x7
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
0x8
ON
ON
ON
OFF
0x9
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
0xA
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
0xB
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
0xC
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
0xD
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
0xE
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
0xF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
(Default Settings)

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 15
2.5 JP2: DI Port Settings (Pull-High/Low)
This DI ports can be pull-high or pull-low that is selected by JP2. The pull-high/low jumpers of the
card allow user to predefine the DI status instead of floating when the DI channels are unconnected
or broken. The configuration is illustrated in the figure below. Note: This function only supports
PEX-1002L/H.
JP2
+5V GND
JP2
+5V GND
Pull-High Pull-Low (Default)
2.6 System Block
PCI-1002 series card system function block.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 16
2.7 AD Input Signal Connection
The PCI-1002 series card can measure either single-ended or differential-type analog input signals.
The user must decide which mode is most suitable for measurement purposes. Please refer to the
Section 2.2 “JP1: AD Input Type Selection”to see how to configure the JP1 jumper based on your
analog input type.
In general, there are four different analog signal connection methods, as shown in Figure 2-3 to
Figure 2-7. The connection shown in Figure 2-3 is suitable for grounded analog input signals. The
connection shown in Figure 2-4 is used to measure more channels than that shown in Figure 2-3,
but is only suitable for large analog input signals. The connection shown in Figure 2-5 is suitable for
thermocouple connections and the connection shown in Figure 2-6 is suitable for floating analog
input signals.
Note: In Figure 2-5, the maximum common mode voltage between the analog input source and the
AGND is 70 V
p-p
, so the user must ensure that the input signals is within this specification. If the
common mode voltage is above 70 V
p-p
, the input multiplexer will be permanently damaged!
The simplest way to select your input signal connection configuration is listed b elow.
1. Grounding source input signal see Figure 2-3
2. Thermocouple input signal see Figure 2-5
3. Floating source input signal see Figure 2-6
4. If Vin > 0.1 V, gain<=10 and more channels are needed see Figure 2-4
5. Current source input signal see Figure 2-7
If you are unsure of the characteristics of your input signal, follow these test steps:
Step1: Try and record the measurement results when using Figure 2-3.
Step2: Try and record the measurement results when using Figure 2-6.
Step3: Try and record the measurement results when using Figure 2-4.
Step4: Compare the three results and select the best one.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 17
Figure 2-3: Differential input with grounded source (Right way)
A/D CH0 HI
A/D CH n HI
A/D CHn LO
A.GND n
A/D CH 0 LO
Es 1
Es n
S
S
A.GND 1
Figure 2-3: Wrong way
A/D CH0 HI
A/D CH0 LO
AGND
GND1
Es1
A/D CHn HI
A/D CHn LO
AGND
GNDn
Esn

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 18
Figure 2-4: Single-ended input with floating signal source
A
/
D CH0
A
/D CH
1
A/D CH n
AGND
Es
Figure 2-5: Differential input with floating thermocouple signal
A/D CH 0 HI
A. GND
A/D CH n LO
A/D CH n HI
A/D CH 0 LO
Do not join LO to A.GND at the computer
CAUTION: In Figure 2-5, the maximum common mode voltage between the analog input source
and the AGND is 70 V
p-p
. Make sure that the input signal is under specification first! If the common
mode voltage is over 70 V
p-p
, the input multiplexer will be permanently damaged.
Note: If the input signal is not
thermocouple, the user should
use an oscilloscope to
measure common mode
voltage of Vin before
connecting to PCI-1002 series
card. Don’t use a voltage
meter or multi-meter.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 19
Figure 2-6: Differential input with floating signal source
A
/D CH
0 HI
A/
D CH
0 LO
A/
D CH n HI
A.GND
A/
D CH n LO
A.GND
Es
1
Es n
Figure 2-7: Connecting to a 4 ~ 20 mA Source
AI CHn
AGND
R
+
-
(Shunt Resistor)
Example: A 20 mA source current through a 125 Ω resistor (e.g. 125 Ω, 0.1% DIP Resistors) between
+ and – terminals and the board will read a 2.5 VDC voltage. You can use the I = V/R (Ohm’s law) to
calculate what value the source current should have.
Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
= 2.5 V / 125 Ω
= 0.02 A
= 20 m

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 20
Figure 2-8: Signal Shielding
Signal shielding connections in Figure 2-3 to Figure 2-7 are all the same, as show in the below figure.
Use a single-point connection to frame ground (not A.GND or D.GND)
Vin
PCI
-
1002
Series card
A.GND
D.GND
Frame Ground

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 21
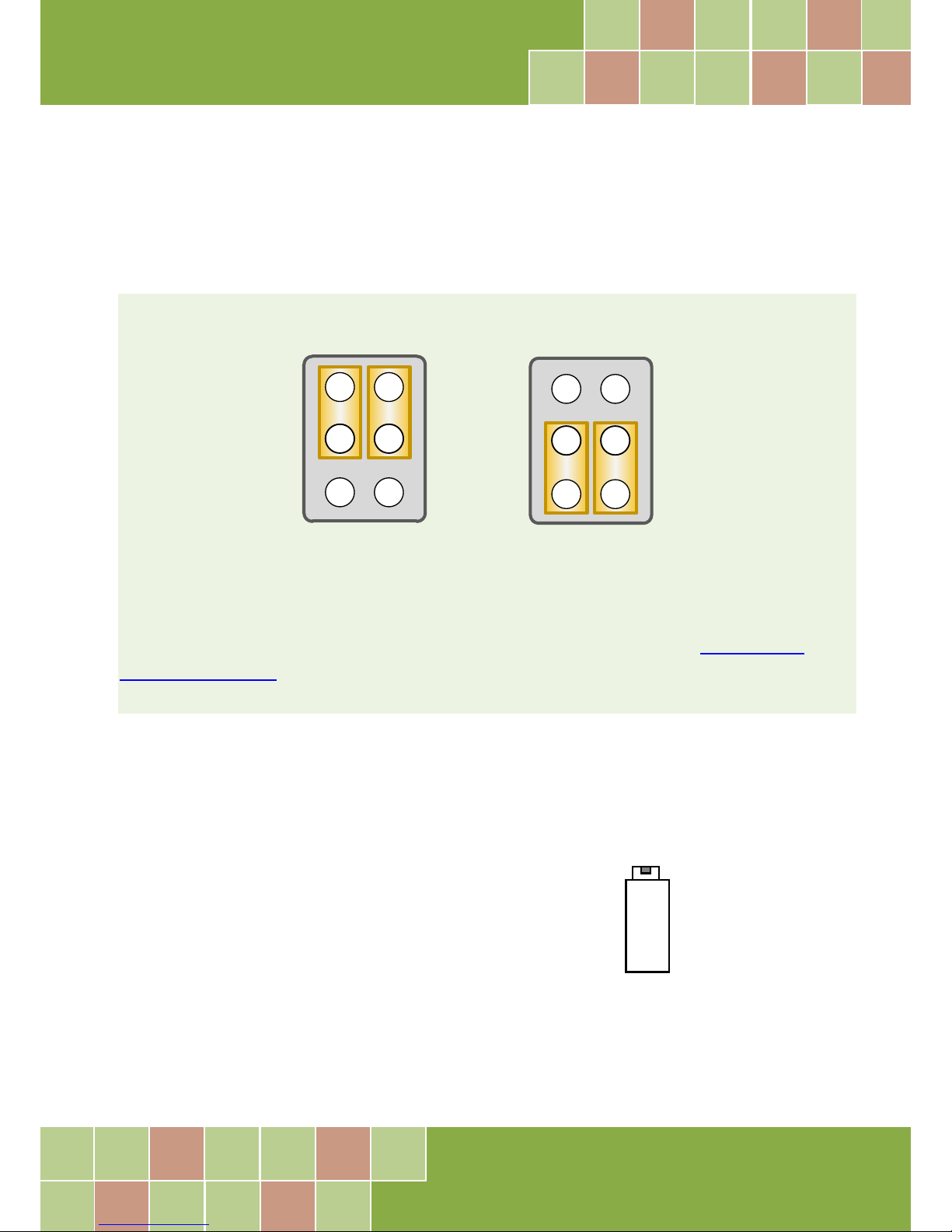
2.8 Pin Assignments
CON1 and CON2: Digital Output and Digital Input connector

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 22
CON3: Sin gle -ended input and Differential input for Analog Input connector
Single-Ended Input
Differential Input

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 23
3. Hardware Installation
Note:
It is recommended that the driver is installed before installing the hardware as the computer may need to be
restarted once the driver is installed in certain operating systems, such as Windows 2000 or Windows XP, etc.
Installing the driver first helps reduce the time required for installation and restarting the computer.
To install the PCI-1002 series card, follow the procedure described below:
Step 1: Install the driver for your board on Host computer.
For detailed information about
the driver installation, please
refer to Chapter 4 “Software
Installation”.
Step 2: Configure the Card ID using the DIP Switch (SW1).
For detailed information about the card ID (SW1), please refer to
Section 2.4 “Card ID Switch” .
Note
The Card ID function is only supported by the PEX-1002L/H.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 24
Step 3: Shut down and switch off
the power to the computer, and
then disconnect the power
supply.
Step 4: Remove all covers from the
computer.
Step 5: Select a vacant PCI/PCI Express slot.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 25
Step 6: Unscrew and remove the PCI
slot cover from the computer case.
Step 7: Remove the connector cover form your
card.
Step 8: Carefully insert your board into the PCI/PCI Express slot by gently pushing down on
both sides of the board until it slides into the PCI connector.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 26
Step 9: Confirm that the board is correctly inserted in the
motherboard, and then secure your board in place using
the retaining screw that was removed in Step 6.
Step 10: Replace the covers on the
computer.
Step 11: Re-attach any cables, insert the power cord and then switch on the power to the
computer.
Once the computer reboots, follow any
message prompts that may be
displayed to complete the Plug and Play
installation procedure. Refer to Chapter
4 “Software Installation” for more
information.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 27
4. Software Installation
This chapter provides a detailed description of the process for installing the PCI-1002 series driver
and how to verify whether the PCI-1002 series was properly installed. PCI-1002 series card can be
used on DOS, Linux and 32-/64-bit XP/2003/2008/7/8/10 based systems, and the drivers are fully
Plug and Play (PnP) compliant for easy installation.
4.1 Obtaining/Installing the Driver Installer
Package
The driver installation package for PCI-1002 series board can be found on the companion CD-ROM,
or can be obtained from the ICP DAS FTP web site. Install the appropriate driver for your operating
system. The location and website addresses for the installation package are indicated below.
UniDAQ Driver/SDK (It is recommended to install this driver for new user.)
Operating
System
Windows 2000, 32/64-bit Windows XP, 32/64-bit Windows 2003,
32/64-bit Windows 2008, 32/64-bit Windows Vista, 32/64-bit Windows 7, 32/64-bit
Windows 8, 32/64-bit Windows 10
Driver Name
UniDAQ Driver/SDK (unidaq_win_setup_xxxx.exe)
CD-ROM CD:\\ NAPDOS\PCI\UniDAQ\DLL\Driver\
Web site http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/unidaq/dll/driver/
Installation
Procedure
Please follow the following steps to setup software:
Step 1: Double click the UniDAQ_Win_Steupxxx.exe to setup it.
Step 2: When the Setup Wizard screen is displayed, click the Next> button.
Step 3: When the Information screen is displayed, click the Next> button.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 28
Installation
Procedure
Step 4: Select the folder where the drivers are to install. The default path is
C:\ICPDAS\UniDAQ. But if you wish to install the drivers to a different location , click the
“Browse…” button and select the relevant folder and then click the Next> button.
Step 5: When the Select Components screen is displayed, check PCI-1002 series board
on the list, then click the Next> button.
Step 6: When the Select Additional Tasks screen is displayed, click the Next> button.
Step 7: When the Download Information screen is displayed, click the Next> button.
Step 8: Select the item “Yes, resta r t the computer now”, press the Finish button.
System will reboot.
For more detailed information about how to install the UniDAQ driver, refer to “Section 2.2
Install UniDAQ Driver DLL” of the UniDAQ Software Manual, which can be found in the
\NAPDOS\PCI\UniDAQ\Manual\ folder on the companion CD, or can be downloaded from:
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/unidaq/manual/

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 29
PCI-1002 Series Classic Driver (Recommended to install this driver for have been used
PCI-1002 series boards of regular user)
OS
Windows 95/98/ME、Windows NT、Windows 2000、32-bit Windows XP、
32-bit Windows 2003、32-bit Windows Vista、32-bit Windows 7, 32-bit
Windows 8, 32-bit Windows 10
CD-ROM CD:\\ NAPDOS\PCI\PCI-1002\DLL_OCX\
Web Site
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/pci-1002/dll_ocx/
Driver Name
PCI-1002 Series Classic Driver
Win2K_XP_7 Folder
pci_1002_win2K.exe
For Windows 2000, 32-bit Windows
XP/2003/Vista/7
Win98 Folder
pci_1002_win98.exe For Windows 95/98/ME
WinNT Folder
Pci_1002_winnt.exe For Windows NT 4.0
Installing Procedure
Please follow the following steps to setup software:
Step 1: Double click the PCI-1002 series classic driver to setup it.
Step 2: When the Setup Wizard screen is displayed, click the Next> button.
Step 3: Select the folder where the drivers are to install. The default path is
C:\DAQPro\PCI-1002_xxxx. But if you wish to install the drivers to a different
location , click the “Change…” button and select the relevant folder and then click
the Next> button.
Step 4: Select the item “No, I will restart my computer later”, pr es s the Finish
button.
For detailed information about how to install the PCI-1002 Classic Driver, refer to
the PCI-1002 Series Software manual , which can be found in the
\NAPDOS\PCI\PCI-1002\Manual\ folder on the companion CD, or can be
downloaded from:
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/pci-1002/manual/

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 30
4.2 PnP Driver Installation
Step 1: Correctly shut down and power off your computer and disconnect the power supply, and
then install your board into the computer. For detailed information about the hardware installation
of PCI-1002 series board, refer to Chapter 3 “Hardware Installation”.
Step 2: Power on the computer and complete the Plug and Play installation.
Note:
recent operating systems , such as Windows 7/8/10 will automatically detect the new hardware and install the
necessary drivers etc., so Steps 3 to 5 can be skipped.
Step 3: Select “Install the software automatically [Recommended]” and click the “Next>” button.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 31
Step 4: Click the “Finish” button.
Step 5: Windows pops up “Found New Hardware” dialog box again.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 32
4.3 Verifying the Installation
To verify that the driver was correctly installed, use the Windows Device Manager to view and
update the device drivers installed on the computer, and to ensure that the hardware is operating
correctly. The following is a description of how access the Device Manager in each of the major
versions of Windows. Refer to the appropriate description for the specific operating system to verify
the installation.
4.3.1 Accessing Windows Device Manager
Windows 95/98/ME
Step 1: Either right-click the “My Computer” icon on the desktop and then click “Properties”, or
open the “Control Panel” and double-click the “System” icon to open the System Properties dialog
box.
Step 2: In the System Properties dialog box, click the “Device Manager” tab.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 33
Windows 2000/XP
Step 1: Click the “Start” button and then point to “Settings” and click “Control Panel”.
Double-click the “System” icon to open the “System Properties” dialog box.
Step 2: Click the “Hardware” tab and then click the “Device Manager” button.
Windows Server 2003
Step 1: Click the “Start” button and point to “Administrative Tools”, and then click the “Computer
Management” option.
Step 2: Expand the “System Tools” item in the console tree, and then click “Device Manager”.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 34
Windows 7/10
Step 1: Click the “Start” button, and then click “Control Panel”.
Step 2: Click “System and Maintenance”, and then click “Device Manager”.
Alternatively,
Step 1: Click the “Start” button.
Step 2: In the Search field, type
Device Manager and then press
Enter.
Note:
Administrator privil eg es are r equi r ed for this operation. If you are prompted for an administrator password or
confirmation, enter the password or provide confirmation by clicking the “Yes” button in the User Account
Control message.
Windows 8
Step 1: To display the Start screen icon from
the desktop view, hover the mouse cursor
over the bottom-left corner of screen.
Step 2: Right-click the Start screen icon and
then click “Device Manager”.
Alternatively, press [Windows Key] +[X] to
open the Start Menu, and then select Device
Manager from the options list.
Right-click

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 35
4.3.2 Check that the Installation
Check the PCI-1002 series card which listed correctly or not, as illustrated below.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 36
5. Board Testing
This chapter provides detailed information about the “Self-Test” process, which is used to confirm
that the PCI-1002 series board is operating correctly. Before beginning the “Self-Test” process,
ensure that both the hardware and driver installation procedures are fully completed. For detailed
information about the hardware and driver installation, refer to Chapter 3 “Hardware Installation”
and Chapter 4 “Software Installation”.
5.1 Self-Test Wiring
5.1.1 Digital Input/Output Test Wiring
Before beginning the “Self-Test ” procedure, ensure that the following items are available:
A CA-2002 Cable
(Optional, Website: http://www.icpdas.com/products/Accessories/cable/cable_selection.htm)
Step 1: Use the CA-2002 cable to connect the CON1 with CON2 on your board.
CA-2002

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 37
5.1.2 Analog Input Test Wiring
Before beginning the “Self-Test ” procedure, ensure that the following items are available:
A CA-3710 Cable
(Optional, Website: http://www.icpdas.com/products/Accessories/cable/cable_selection.htm)
A DN-37 Terminal Board
(Optional, Website:
http://www.icpdas.com/root/product/solutions/pc_based_io_board/daughter_boards/dn-37.html)
Provide a stable signal source. (For example, dry battery)
Step 1: Connect the DN-37 to the CON3 connector on your board using the CA-3710 cable.
Step 2: Wire the signal source to AD channel0, and then keep set the JP1 jumper to Single-Ended
(default settings, refer to Section 2.2 “JP1: AD Input Type Selection” for more detailed), and
wire the signals as follows:
Step 3: Connect the AI 0 (Pin01) to signal positive (+) and then A.GND (Pin17) to signal negative (-).

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 38
5.2 Launch the Test Program
The following example use UniDAQ driver to perform self-test. If you install the PCI-1002 series
classic driver, please refer to Quick Start Guide of the PCI-1002
(http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/pci-1002/manual/quickstart/classic/) to
execute the self-test.
Step 1: Double-click the UniDAQ Utility software. The UniDAQ Utility will be placed in the default
path “C:\ICPDAS\UniDAQ\Driver” after completing installation.
Step 2: Confirm that your board has been successfully
installed in the Host system. Note that the device
number starts from 0.
Step 3: Click the “TEST” button to start the test.
Note:
The PEX-1002L/H and PCI-1002LU/HU software is fully
compatible with the PCI-1002L/H series software.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 39
Step 4: Check the results of the Digital Input and Digital Output functions test.
1. Click the “Digital Output” tab.
2. Select “Port 0” from the “Port Number” drop-down menu.
3. Check the checkboxes for channels 0, 2, 4 and 6.
4. Click the “Digital Input” tab.
5. Select “Port 0” from the “Port Number” drop-down menu.
6. The DI indicators will turn red when the corresponding DO channels 0, 2, 4 and 6 are ON.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 40
Step 5: Check the results of the Analog Input function test.
1. Click the “Analog Input” tab.
2. Confirm the configuration settings for the card type, input range and sample rate items.
3. Click “Start” button to start test.
4. Check Analog Input on Channel 0 textbox. The other channels value for floating number.
10
Note:
When reading analog-input, the
non-wired channel gets floating
value. User can wire these
unused channels to GND for
getting stable state if need.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 41
6. I/O Register Address
6.1 How to Find the I/O Address
During the power-on stage, the Plug and Play BIOS will assign an appropriate I/O address to each
PCI-1002 Series board installed in the system. Each board includes four fixed ID numbers that are
used to identify the board, and are indicated below:
Table 6-1:
PCI-1002L/H, PCI-1002LU/HU and PEX-1002L/H
Vendor ID
0x1234
Device ID
0x1002
We provide the following necessary functions:
1. P1002_DriverInit(&wBoard)
This function can detect how many PCI-1002 series cards are in the system. The function is
implemented based on the PCI Plug & Play mechanism-1. It will find all PCI-1002 series cards
installed in this system & save all their resources in the library.
wBoard=1 only one PCI-1002 in this PC system.
wBoard=2 there are two PCI-1002 in this PC system.
2. P1002_GetConfigAddressSpace(wBoardNo, *wBase, *wIrq, *wPLX)
Use this function to save resources of all PCI-1002 installed in this system.
Then the application program can control all functions of PCI-1002 directly.
wBoardNo=0 to N totally N+1 cards of PCI-1002
wBase base address of the board control word
wIrq allocated IRQ channel number of this board
wPLX base address of PCI-interface-IC
The PIO_PISO.EXE utility will detect and show all PIO/PISO cards installed in this PC. Refer to
“PIO_PISO.EXE Utility” for more information.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 42
Here’s the sample program source code:
/* Step1: Detect all PCI-1002 cards first */
wRetVal=P1002_DriverInit(&wBoards);
printf("Threr are %d PCI-1002 Cards in this PC\n",wBoards);
/* Step2: Save resources of all PCI-1002 cards installed in this PC */
for (i=0; i<wBoards; i++)
{
P1002_GetConfigAddressSpace(i,&wBase,&wIrq,&wPLX);
printf("\nCard_%d: wBase=%x, wIrq=%x, wPLX=%x", i,wBase,wIrq,wPLX);
wConfigSpace[i][0]=wBaseAddress; /* save all resource of this card */
wConfigSpace[i][1]=wIrq; /* save all resource of this card */
wConfigSpace[i][2]=wPLX; /* save all resource of this card */
}
/* Step3: Control the PCI-1002 directly */
wBase=wConfigSpace[0][0]; /* get base address the card_0 */
outpw(wBase+0x20,wDoValue); /* control the DO states of card_0 */
wDiValue=inpw(wBase+0x20); /* read the DI states of card_0 */
wBase=wConfigSpace[1][0]; /* get base address of card_1 */
outpw(wBase+0x20,wDoValue); /* control the DO states of card_1 */
wDiValue=inpw(wBase+0x20); /* read the DI states of card_1 */
wPLX=wConfigSpace[2][2]; /* get PCI-interface base address of card-2 */
_outpd(wPLX+0x4c,0x41); /* channel_1, interrupt active_Low */
…
…
_outpd(wPLX+0x4c,0); /* disable all interrupt */

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 43
PIO_PISO.EXE Utility
The PIO_PISO.EXE utility is valid for all PIO/PISO cards. This program shows all PCI hardware ID
regarding the PIO and PISO series DAQ cards. It is useful to test if the card Plug & Play successfully
when the computer bootup. If the PIO or PISO series card does not shown in the screen correctly,
please try to use another PCI slot and try again.
The user can execute the PIO_PISO.EXE to get the following information:
List all PIO/PISO cards installed in this PC
List all resources allocated to every PIO/PISO cards
List the wSlotBus and wSlotDevice for specified PIO/PISO card identification.
For Windows OS
The PIO_PISO.EXE utility is located on the CD as below and is useful for all PISO/PIO series boards.
(CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\Utility\Win32\PIO_PISO\)
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/utility/win32/pio_piso/

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 44
For DOS
The PIO_PISO.EXE for DOS is contained in:
CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\Utility\DOS\
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/utility/dos/
The PIO_PISO program source is given as follows:
/* -------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Find all PIO_PISO series cards in this PC system */
/* step 1 : plug all PIO_PISO cards into PC */
/* step 2 : run PIO_PISO.EXE */
/* ------------------------------------------------------------- */
#include "PIO.H"
WORD wBase,wIrq;
WORD wBase2,wIrq2;
int main()
{
int i,j,j1,j2,j3,j4,k,jj,dd,j11,j22,j33,j44;
WORD wBoards,wRetVal;
WORD wSubVendor,wSubDevice,wSubAux,wSlotBus,wSlotDevice;
char c;
float ok,err;
clrscr();
wRetVal=PIO_DriverInit(&wBoards,0xff,0xff,0xff); /*for PIO-PISO */
printf("\nThrer are %d PIO_PISO Cards in this PC",wBoards);
if (wBoards==0 ) exit(0);
printf("\n-----------------------------------------------------");
for(i=0; i<wBoards; i++)
{
PIO_GetConfigAddressSpace(i,&wBase,&wIrq,&wSubVendor,
&wSubDevice,&wSubAux,&wSlotBus,&wSlotDevice);
printf("\nCard_%d:wBase=%x,wIrq=%x,subID=[%x,%x,%x],
SlotID=[%x,%x]",i,wBase,wIrq,wSubVendor,wSubDevice,
wSubAux,wSlotBus,wSlotDevice);
printf(" --> ");
ShowPioPiso(wSubVendor,wSubDevice,wSubAux);
}
PIO_DriverClose();
}

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 45
6.2 The I/O Address Map
The list of PCI-1002 registers is given below. The address of each register is found by simply adding
the offset to the base address of the corresponding section. More detailed descriptions of each
register will be shown in the following text and the software manual.
Section
offset
Name
Access
Length
1
4ch
PCI interrupt control register
R/W
8/16/32 bits
2
00h 8254 timer1 R/W 8/16/32 bits
04h
8254 timer2
R/W
8/16/32 bits
08h
8254 timer3
R/W
8/16/32 bits
0Ch
8254 control register
W
8/16/32 bits
10h
Analog input channel control register
W
8/16/32 bits
10h
Status register
R
8/16/32 bits
14h
Analog input gain control register
W
8/16/32 bits
18h
General control register
W
8/16/32 bits
1Ch
AD software trigger
W
8/16/32 bits
1Ch
Clear Interrupt
R
8/16/32 bits
20h
Digital output register
W
16/32 bits
20h
Digital input register
R
16/32 bits
30h
AD data register
R
16/32 bits

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 46
6.2.1 Section1
Although there are 128 I/O ports used by the on-board PCI interface controller, only one register is
used in real applications!! Users should keep the other registers from being modified! The PCI
interrupt control register (4Ch) controls the interrupt sent to your system. The register is set to
“disable interrupt” after power-on or a hardware reset signal. Thus, no interrupt will be generated
before this register is activated even if user enables the add-on interrupt! In order to enable the
PCI-interrupt, always write 43h to this register. Write 03h to this register if you want to disable the
PCI interrupt.
Here’s the format of the PCI interrupt control register:
Bit 31 - Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5 -Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1 - Bit 0
Not used
Interrupt Enable
Not used
Interrupt Flag
Interrupt Select
Bit 6: Write a ‘1’ to enable the PCI-interrupt and a ‘0’ to disable PCI interrupt.
Bit 2: This bit is readable but can’t be written. A ‘1’ indicates that Add-on has generated interrupt,
‘0’ means that add-on hasn’t generated interrupt.
Bit 1-0: Always write 1 to these two bits.
Notes:
1. Because PCI-1002 series supports “Plug&Play”, the interrupt number will be automatically assigned by your
system. Use the standard PCI mechanism or the software in our library to find out the interrupt number.
2. If your system supports “Shared IRQ”, several peripherals will share the same IRQ at the same time. You
must use Bit-2 to find out if this IRQ was generated from your PCI-1002 series.
3. For more information about the PCI interrupt control, refers to the PLX-9050 user reference manual.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 47
6.2.2 Section2
This section is used by the add-on control logic. 64 bytes of I/O locations are used. Detailed
descriptions are shown below.
6.2.2.1 The 8254 Registers
The 8254, programmable timer/counter is used to generate periodic AD trigger signals, periodic
interrupt signals and the machine- independent timer for PCI-1002. Addresses 00h, 04h, 08h and
0Ch are used to control the 8254.
Timer 0 is used as Pacer 0. Timer 1 is used as Pacer 1. Timer 2 is used as a machine-independent
timer, P1002_Dealy(). For more details about the programming information, please refer to Intel’s
“Microsystem Components Handbook”.
6.2.2.2 The DI/DO Registers
Address 20h is used for DI / DO ports. Writing to this port will write data to DO register. Reading
from this port will read the data from DI.
6.2.2.3 The AD Buffer
Address 30h is used for AD buffer. Only read operations are available at this address. Reading from
this port will read the data from AD buffer. The format of AD buffer is:
Bit 15 - Bit 12 Bit 11 - Bit 0
Analog Input Channel AD Data
Bit 15-12: The channel number of analog input. Only the lower 4 bits of the channel number are
shown in this register.
Bit 11-0: The AD data.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 48
6.2.2.4 The Status Register
Address 10h is used by the status register. Reading from this address will get the data from the
status register. The format of status register is:
Bit 7 - Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Gain Control 8254
Timer 1
8254
Timer 0
8254
Timer 2
Reserved
Analog Input
Type
AD Ready
Bit 7-6 : Current AD gain control.
Bit 5 : Output of 8254 timer 1.
Bit 4 : Output of 8254 timer 0.
Bit 3 : Output of 8254 timer 2.
Bit 2 : Reserved. Used for hardware testing.
Bit 1 : Analog input type, ‘1’ indicates that analog input type is single-ended and ‘0’
indicates analog input is differential.
Bit 0 : AD ready signal. ‘0’ indicates not ready, AD is under conversion. ‘1’ indicates ready, AD is
completely converted and is idle now.
6.2.2.5 The AD Software Trigger Register
Writing to this port (1Ch) will generate an AD trigger pulse signal.
Note: Although a very fast trigger can be performed (more than the speed of AD controller, 110 K) via this method, a
reasonable delay time should be left between the two triggers.
Figure 6-1: Software trigger delay time.
AD
Busy
Software
trigger
8 µs
Delay time
Conversion Time

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 49
6.2.2.6 Clear Interrupt
Reading from 1Ch will clear the add-on interrupt.
6.2.2.7 The Analog Input Selection Register
Address 10h is used by the analog input channel selection register and address 14h is used by the
analog gain control selection register. Write 0-31 to port 10h to select the channel number (for
differential input, write 0-15). Write 0-3 to port 14h to select the gain control.
Figure 6-2: Analog input control.
Notes:
1. For Single-ended Inputs, channels 0-31 are available. For Differential Inputs, channels 0-15
are available. Input numbers which are more than the available channel will be discarded.
Thus, for single-ended inputs, only the last 5 bits are taken as the channel number. And for
differential inputs, only the last 4 bits are taken as the channel number.
2. Only the last two digits are taken as the gain control code. The gain control code and the
corresponding gain is:
For PCI-1002L/LU and PEX-1002L:
[Bit1, Bit0]
[0 0]
[0 1]
[1 0]
[1 1]
Gain 1 2 4 8
For PCI-1002H/HU and PEX-1002H:
[Bit1, Bit0]
[0 0]
[0 1]
[1 0]
[1 1]
Gain
1
10
100
1000
3. These registers are set to 0 after powered-on or hardware reset signals.
…
Analog inputs
…
Channel select
Analog
Mux.
Select
Gain control
ADC
AMP

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 50
6.2.2.8 The General Control Register
A general control register (18h) is used to control the add-on interrupt signal source and the AD
trigger method. The format of this register is:
Bit 4 - Bit2
Bit 1 – Bit 0
Interrupt source selection register
AD trigger method selection register
Interrupt Source Selecti on Re gister
There are four interrupts selectable for PCI-1002 series card (refer to Section 1.2.5 “Interrupt
Channel”).
[Bit 4, Bit 3, Bit 2]
Descriptions
[0, 0, 0]
No interrupt source, disable all interrupts.
[0, 0, 1] Interrupt after AD completes conversion.
[0, 1, 0]
Interrupt after 8254 timer 0 falls.
[0, 1, 1]
Interrupt after external trigger falls.
[1, 0, 0]
Interrupt after 8254 timer 1 falls.
Others No interrupt source, Disable all interrupts.
Note: Bit 2-4 of general control register is set to 0 after hardware reset.
AD Trigger Method Selection Regi ster
Here’s a list of our trigger options (refer to Section 1.2.4 “AD Trigger Methods”):
[Bit 1, Bit 0] Descriptions
[0, 0]
General trigger mode.
8254 timer 0 trigger (internal pacer trigger) or software trigger.
[0, 1]
External clock trigger mode.
[1, 0]
Pre-trigger mode.
[1, 1] Post-trigger mode.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 51
Notes:
1. In general trigger mode, both 8254 timer 0 and software triggers are treated as AD trigger signals. In this
mode, 8254 timer 0 and software trigger should not work at the same time!! This means users should not
generate the software trigger while 8254 timer 0 is activated.
2. In external clock trigger mode, external trigger input is taken as the AD trigger signal. An event of the external
trigger input fall (falling edge) will generate one AD trigger.
3. The pre-trigger mode is used for pre-trigger method. The mode is incorporated with the 8254 timer 1. First,
setup 8254 timer 1 properly. Then set the trigger mode to pre-trigger. Once pre-trigger mode has been activated,
the 8254 timer 1 will automatical l y turn on and start to perform A D t ri gger s . It wi ll continue until the AD trigger
logic receives a falling external trigger signal. Any change to the trigger mode selection will turn off the
pre-trigger mode.
4. The post-trigger mode is used for post-trigger method. The mode working incorporated with the 8254 timer 1.
First, setup 8254 timer 1 properly. Then set the trigger mode to post-tr i gge r. Once post-trigger mode has been
activated, the 8254 timer 1 will automatically turn off until it receives a falling external trigger signal. Any change
to the trigger mode selection will turn off the post-trigger mode.
5. The AD trigg er is set to 0 aft er eit her pow er -on or hardware reset.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 52
7. Function Operations
7.1 Digital I/O
The PCI-1002 series provide 16 Digital Input channels and 16 Digital Output channels. All levels are
TTL compatible. The connection diagram and block diagram are given below:
Figure 7-1: DIO function diagram.
CN2
BaseAddr+20h
write signal
BaseAddr+20h
read signal.
DI port
DO port
CN1
Local Data Bus
D0 ... D15

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 53
7.2 The 8254 Timer
The PCI-1002 series provide 3 independent, 16-bit timer/counters. Each timer has different
functions. Timer 0 is uses Pacer 0. Timer 1 is uses Pacer 1. Timer 2 is uses a machine independent
timer. The block diagram is given as follows:
Figure 7-2: 8254 control diagram.
Timer0
Timer1
Timer2
Local Data
Bus
EN
EN
EN
User
CLK
CLK
CLK
4 M Hz
OUT0
OUT1
OUT2
VCC
Pacer 0
Pacer 1
8254
Status

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 54
7.3 The AD Timer
The AD trigger is controlled by on-board AD trigger controller. The function diagram of AD trigger is
shown below:
Figure 7-3: AD trigger controller.
AD trigger logic receives the external trigger and then performs the correct AD trigger function. In
order to be recognized by the AD trigger controller, the external trigger signal must be a TTL
compatible signal, with the minimum duration of pulse width to avoid noise. This signal must satisfy
the following specifications:
Symbol
Name
Minimum
Maximun
Tdu
Duration time
40 ns
∞
Tre
Recover time
100 ns
∞
Mux
8254
Timer 1
EN
CLK
4 MHz
Q
D
External Trigger
Software Trigger
8254
Timer 0
External
Trigger.
0
1
Trigger Select
To AD
Select
PR
RS
External trigger
tdu
tre

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 55
Note:
The PCI-1002 series is designed only as a time sensitive trigger (trigger depends only on receiving a falling
edge external trigger signal). For a level sensitive external trigger (trigger depends only on the level of the input
signals), make the following circuit outside the PCI-1002 series:
DAC
PCI-1002
DO
Input
Comparator
TTL buffer
External

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 56
7.4 AD Conversion
An AD conversion can be initiated in one of three ways: software command, internal programmable
interval timer, or by external trigger to the AD. At the end of the AD conversion, it is possible to
transfer the data in two ways: by polling a status register and reading data when ready, or by
generating a hardware interrupt signal to call service routine. All operating modes are selected by a
control register on the PCI-1002 series.
Before using the AD conversion function, please follow this checklist:
AD data register (BASE+30h) store the AD conversion data.
AD data conversion ready register (BASE +10h)
Check AD conversion ready.
AD gain control register (BASE+14h) Select gain.
AD multiplex control register (BASE+10h) Select analog input channel.
AD mode control register (BASE+18h) Select trigger mode and interrupt source.
AD software trigger control register (BASE+1Ch).
JP1 to select single-ended or differential input.
3 Trigger logic: Software, Pacer or External trigger.
2 Transfer logic: Polling or Interrupt.
Here’s the block diagram:
CN3
16/8 to 1
Multi-
plexer
Gain
Control
12 bits
AD
Buffer
Memory
BASE+30h
CPU
Trigger
Logic
BASE+14h
BASE+10hHgh
BASE+1Ch
Software Trigger

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 57
AD conversion flow:
Before using the AD converter, please select either single-ended or differential input (JP1).
The software driver supports two different modes: polling and interrupt. The user can control the
AD conversion by polling mode very easy. Using the software driver is recommended if using
interrupt.
The multiplexer can select 32 single-ended or 16 differential signals into the gain control module.
The settling time of multiplexer depends on the impedance of the signal source. Because the
software doesn’t control the settling time, please make sure to leave enough settling time if
switching from one channel to the next channel.
The gain control module also needs settling time if gain control code changed. Again, because the
software doesn’t control settling time, please delay enough settling time if the gain control code is
changed.
Remember to delay the extra setting time when gain of channel is changed.
The software driver provides a machine independent timer, P1002_Delay(), for settling time delays.
This subroutine assumes a machine independent timer will be implemented. However, if using call
P1002_Delay(), the counter 0 will be reserved and can’t be used as a user programmable
timer/counter.
The gain control module’s output feeds into the AD converter. The AD converter needs a trigger
signal to start an AD conversion cycle. The PCI-1002 series supports three trigger modes: software,
pacer, and external trigger.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 58
7.4.1 AD Conversion Trigger Modes
The PCI-1002 series supports three trigger modes.
1 : Software Trigger :
Write any value to the AD software trigger control register, BASE+1Ch, and it will initiate an AD
conversion cycle. This mode is very simple but controlling the sampling rate very difficult.
2 : Pacer Trigger Mode :
See section 4.2 for a block diagram for this pacer timer. The sample rate of pacer is very precise.
3 : External Trigger Mode :
When a rising edge of external trigger signal is applied, an AD conversion will be performed. The
external trigger source comes from Pin-19 of CON3.
7.4.2 AD Transfer Modes
PCI-1002 series supports two transfer modes.
1: Polling transfer:
This mode can be used with all trigger modes. You have to disable timer 0 before polling. The
software reads the AD data register from [BASE+30h] when READY bit of Register [BASE +10h] =1.
2: Interrupt transfer:
This mode can be used with either a pacer trigger or external. A hardware interrupt signal is sent to
the PC when an AD conversion is completed.
If using interrupt transfer, it is recommended to use PCI-1002 software driver.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 59
7.4.3 Software Triggers and Polling Techniques
The easiest way to control is by following these steps:
1. Send 00h to AD mode control register (Software Trigger + Polling Transfer)
2. Send channel number to multiplexer control register.
3. Send the gain control code value to gain control register.
4. Send any value to software trigger control register to generate a software trigger signal.
5. Scan the READY bit until READY bit =1
6. Read the 12-bit AD data.
7. Convert this 12-bit binary data to the floating point value.
For example:
/* -------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* DEMO 3: AdPolling */
/* Compiler: Borland C++ 3.1, Mode Large */
/* Output Code: HEX code */
/* -------------------------------------------------------------- */
#include "P1002.H"
WORD wBaseAddr,wIrq;
//-------------------------------------------------------
WORD P1002_Delay(WORD wDownCount)
{
WORD h,l;
int count;
wDownCount &= 0x7fff;
if (wDownCount<1) wDownCount=1;
/* Clock in=4M --> count 4000 = 1 ms, count 1 = 0.25 us */
l=wDownCount&0xff;
wDownCount=wDownCount / 256;
h=wDownCount&0xff;
outp(wBaseAddr+3*4,0xB0); /* mode_0, counter_2 */
outp(wBaseAddr+2*4,l); /* counter_2 low byte first */
outp(wBaseAddr+2*4,h); /* counter_2 high byte ,0x07D0=2000 */

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 60
outp(wBaseAddr+3*4,0x80); /* latch counter_2 */
l=inp(wBaseAddr+2*4); /* delay starting two CLKs */
h=inp(wBaseAddr+2*4);
for (count=32767;count>0;count--)
{
outp(wBaseAddr+12,0x80); /* latch counter_2 */
l=inp(wBaseAddr+8);
h=inp(wBaseAddr+8);
if (h>=0x80) return NoError;
}
return TimeOut;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------
void AdPolling(UCHAR channel, UCHAR gain, WORD delay)
{
outp(wBaseAddr+0x18,0); // Select Mode 0
outp(wBaseAddr+0x10,channel);
outp(wBaseAddr+0x14,gain);
P1002_Delay(delay);
outp(wBaseAddr+0x1c,01); // AD software trigger
}
void SetupTimer(WORD wChannel, WORD wCoef)
{
WORD cmd;
wChannel=wChannel&0x03;
cmd=0x34+(wChannel<<6);
outpw(wBaseAddr+3*4, cmd);
outp(wBaseAddr+wChannel*4, (UCHAR)(wCoef&0xff));
outp(wBaseAddr+wChannel*4, (UCHAR)(wCoef>>8));
}
//===================================================
void main()
{
int i,j;
WORD wBoards,wRetVal,wPLX;
WORD Drdy,wAdData=0;
char c;

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 61
clrscr();
P1002_DriverInit(&wBoards);
printf("\n(1) Threr are %d PCI-1002 Cards in this PC",wBoards);
if ( wBoards==0 )
{
putch(0x07); putch(0x07); putch(0x07);
printf("(1) There are no PCI-1002 card in this PC !!!\n"); exit(0);
}
printf("\n(2) Show the Configuration Space of all PCI-1002:");
for(i=0; i<wBoards; i++)
{
P1002_GetConfigAddressSpace(i,&wBaseAddr,&wIrq,&wPLX);
printf("\n Card_%d: wBaseAddr=%x, wIrq=%x, wPLX=%x",i,wBaseAddr,wIrq,wPLX);
}
P1002_GetConfigAddressSpace(0,&wBaseAddr,&wIrq,&wPLX); /* select card_0 */
printf("\n(3) *** Card_0, wBaseAddr=%x ***\n",wBaseAddr);
SetupTimer(0,1); // AdPolling have to disable timer 0
AdPolling(0,0,23); // channel=0, gain=+/-10, delay=23us
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
outp(wBaseAddr+0x1c,01); // AD software trigger
while(1)
{
if( ((inpw(wBaseAddr+0x10))&0x01)==1) // check if AD ready?
break;
}
wAdData=((inpw(wBaseAddr+0x30))&0x0fff);
printf("\nRang:+/-10V, Counter %d ,ADC channel 0 value: 0x%xH",i,wAdData);
}
P1002_DriverClose();
}

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 62
BCB4 for Borland C
++
Builder 4
P100x.H Header files
P100xbc.LIB Linkage library for BCB only
Delphi4 for Delphi 4
PIO100x.PAS Declaration files
VC6 for Visual C
++
6
P100x.H Header files
P100.LIB Linkage library for VC only
VB6 for Visual Basic 6
P100x.BAS Declaration files
VB.NET2005 for VB.NET2005
P100x.vb Visual Basic Source files
CSharp2005 for C#.NET2005
P100.cs Visual C# Source files
For detailed information about the DLL function of the PCI-1002 series, please refer to DLL
Software Manual (CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\PCI-1002\Manual\)
8. Demo Programs
8.1 Demo Program for Windows
Please note that none of the demo programs will work normally if the DLL driver has not been
installed correctly. During the DLL driver installation process, the install shield will register the
correct kernel driver to the operating system and copy the DLL driver and demo programs to the
correct location depending on the driver software package you have selected (Win98/Me/NT/2000
and 32/64-bit Win XP/2003/2008/7/8/10). After installing the driver, the related demo programs,
development library and declaration header files for the different development environments will
be available in the following folders.
Demo Program for PCI-1002 Series Classic Driver
The demo program is contained in:
CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\PCI-1002\DLL_OCX\Demo\
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/pci-1002/dll_ocx/demo/

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 63
Demo Program for UniDAQ SDK Driver
The demo program is contained in:
CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\UniDAQ\DLL\Demo\
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/unidaq/dll/demo/
There are about demo program given as follows:
Analog Input Pacer
Analog Input Pacer Continue
Analog Input Pacer Scan
Analog Input Pacer Scan Continue
Analog Input Pacer Scan EXT
Analog Input Polling
Analog Output
Analog Output Current
Digital I/O
Digital I/O by Card ID
For detailed information about the DLL function and demo program of the UniDAQ, please refer to
UniDAQ DLL Software Manual (CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\UniDAQ\Manual\)

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 64
…\1002\BC\LARGE\DEMO> demo program
…\1002\BC\LARGE\LIB> library and driver
A list of available demo programs is as follows:
DEMO1: Digital Output
DEMO2: Digital output and Digital Input test by itself.
DEMO3: ADC Polling for channel 0.
DEMO4: ADC Polling for channel 0, 1, 2, 3 using different gains -1, 2, 4 or 8.
DEMO5: ADC Pacer trigger.
DEMO6: AD Calibration.
Note that the demo6 only used when the AD value is inaccurate, it can adjust the reference value of
AD permanently. Each PCI-1002 Series card is already fully calibrated when shipped from the factory,
so it is usually unnecessary to calibrate the board again unless the accuracy is lost.
DEMO7: Find card number.
8.2 Demo Program for DOS
The demo program is contained in:
CD:\NAPDOS\PCI\PCI-1002\dos\
http://ftp.icpdas.com/pub/cd/iocard/pci/napdos/pci/pci-1002/dos/

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 65
8.3 Diagnostic Program
8.3.1 Power-on Plug & Play Test
The operation steps for a power-on Plug & Play test are as follows:
Step 1: Power-off PC
Step 2: Install PCI-1002 without any extra external connector
Step 3: Power-on PC and check the PC screen very carefully
Step 4: The PC will perform a self-test first
Step 5: Detect the non-PCI physical devices installed in the system
Step 6: Show the information of these device in screen
Step 7: Detect the PCI Plug & Play devices installed in the system
Show all PCI-device information check here carefully
There will be a PCI device with vendor_ID=1234, device_ID=1002 (PCI-1002 series)
If the Plug & Play ROM-BIOS detects the PCI-1002 series card during the power-on time, the
software driver of DOS, and Windows 95/NT/2000/XP will function well later. If the Plug & Play
ROM-BIOS can’t find the PCI-1002 series, all software drivers will not function. Therefore the user
must make sure that the power-on procedure is correct.
8.3.2 Driver Plug & Play Test
Step 1: Power-off PC.
Step 2: Install PCI-1002 without any extra external connectors.
Step 3: Power-on PC. Run DEMO7.EXE of DOS.
Step 4: The I/O base address of all PCI-1002 installed in the system will be shown in screen.
Step 5: Is the total number of boards correct?
Step 6: Install a 20-pin flat cable into one of these PCI-1002 cards.
Step 7: One card’s DO=DI This is the physical card number. Remember this number.
Step 8: Repeat the previous two steps to find the physical card number for each board.

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 66
8.3.3 DIO Test
Step 1: Power-off PC.
Step 2: Install one PCI-1002 card with a 20-pin flat cable between CON1 and CON2.
Step 3: Power-on PC, Then run DEMO2.EXE of DOS.
Step 4: The DO and DI will show either TEST OK or TEST ERROR.
8.3.4 AD Test
Step 1: Power-off PC.
Step 2: Install one PCI-1002 card.
Step 3: Power-on PC, run DEMO6.EXE of DOS
Step 4: Apply +10V to channel 0.
Step 5: Apply +0V to channel 1.
Step 6: Apply -10V to channel 2.
Step 7: Run DEMO6.EXE.
Step 8: Check channel 0 = fff or ffe?
Step 9: Check channel 1 = 800 or 801?
Step 10: Check channel 2 = 000 or 001?

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 67
Appendix: Daughter Board
A1. DB-37 and DN-37
DB-37: The DB-37 is a general purpose daughter board for D-sub 37
pins. It is designed for easy wire connection.
DN-37: The DN-37 is a general purpose daughter board for DIN Rail
Mounting. It is designed for easy wire connection. It is Din-Rail
mounted.
A2. DB-1825
The DB-1825 is a daughter board designed for 32 channels AD cards
such as ISO-AD32 and PCI-1002 series that can easy signal connection
and measurement. Refer to Appendix A for “DB-1825 User Manual”.
DB-37
DB-1825
DN-37

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 68
A3. DB-8225
The DB-8225 provides an on-board CJC (Cold Junction Compensation)
circuit for thermocouple measurement and a terminal block for easy
signal connection and measurement. The CJC is connected to AD
channel_0. The PCI-1002 series can connect CON3 directly to DB-8225
through a 37-pin D-sub connector. Refer to “DB-8225 User Manual” for
details.
A3. DB-16P Isolated Input Board
The DB-16P is a 16-channel isolated digital input daughter board. The
optically isolated input of the DB-16P consists of a bi-directional
optocoupler with a resistor for current sensing. You can use the
DB-16P to sense DC signal from TTL levels up to 24 V, or use the
DB-16P to sense a wide range of AC signals. You can use this board to
isolate the computer from large common-mode voltage, ground loops and transient voltage spikes
that often occur in industrial environments.
DB-16P
V+
V-
20-Pin
DI
PIO
-821 series card
DI
AC or DC Signal 0 V~24 V
Opto
-Isolate
DB-16P
R
PCI-1002 series card
DB-8225

PCI-1002 Series Card
12-bit, 110 kS/s or 44 kS/s Multi-function Board
User Manual, Ver. 3.0, Jun. 2018, PMH-015-30, Page: 69
A4. DB-16R Relay Board
The DB-16R, a 16-channel relay output board, consists of 16 Form C
relays for efficient load switching via programmable controls. It is
connected and functionally compatible with 785 series board but
feature an industrial-type terminal block. Relays are energized by
applying 5-volt signal to the appropriate relay channel on the 20-pin flat
connector. There are 16 enunciator LEDs for each relay, light when their associated relay is activated.
To avoid overloading your PC’s power supply, this board provides a screw terminal for an external
power supply.
Note:
Channel: 16 Form C Relay
Relay: Switching up to 0.5 A at 110 VAC/ 1 A at 24 VDC
DB-16R
PCI
-1002 series card
20
-Pin
DO
DB-16R
Normally Open
Normally Closed
Com
Form C Relay
 Loading...
Loading...