
1
M-7084
User Manual
Warranty
All products manufactured by ICP DAS are under
warranty regarding defective materials for a period of one
year from the date of delivery to the original purchaser.
Warning
ICP DAS assumes no liability for damages resulting
from the use of this product. ICP DAS reserves the right to
change this manual at any time without notification. The
information furnished by ICP DAS is believed to be accurate
and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by ICP
DAS for its use, or for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties resulting from its use.
Copyright
Copyright 1999 - 2012 ICP DAS. All rights reserved.
Trademark
The names used for identification only may be registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
Date: 2019/3/4
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

2
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ...................................................................................... 5
1.1 More Information ..................................................................... 6
1.2 Terminal Assignment ............................................................... 7
1.3 Specifications ........................................................................... 8
1.3.1 I/O Specifications ............................................................ 8
1.3.2 System Specifications ..................................................... 9
1.4 Block Diagram ....................................................................... 10
1.4.1 Block Diagram for the M-7084 ..................................... 10
1.5 Dimensions ............................................................................. 11
1.6 Wiring ..................................................................................... 12
1.6.1 M-7084 Wiring .............................................................. 12
1.6.2 Wiring Recommendations ............................................. 12
1.7 Quick Start .............................................................................. 13
1.8 Default Settings ...................................................................... 15
1.9 Configuration Tables .............................................................. 16
1.10 M-7000 Notes ....................................................................... 20
1.10.1 Protocol Switching ...................................................... 20
1.10.2 INIT Mode ................................................................... 21
1.11 Mounting .............................................................................. 22
1.11.1 Din-Rail Mounting ...................................................... 22
1.11.2 Piggyback Mounting ................................................... 24
1.11.3 Wall Mounting ............................................................ 25
1.12 Technical Support ................................................................ 26
2. DCON Protocol .............................................................................. 27
2.1 %AANNTTCCFF .................................................................. 31
2.2 #AA ........................................................................................ 34
2.3 #AAN ..................................................................................... 35
2.4 $AA0N ................................................................................... 37
2.5 $AA0N(Data) ......................................................................... 39
2.6 $AA2 ...................................................................................... 41
2.7 $AA3N ................................................................................... 43
2.8 $AA3N(Data) ......................................................................... 45
2.9 $AA4 ...................................................................................... 47
2.10 $AA4VV .............................................................................. 49
2.11 $AA5 .................................................................................... 51
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

3
2.12 $AA5VV .............................................................................. 53
2.13 $AA6 .................................................................................... 55
2.14 $AA6N ................................................................................. 57
2.15 $AA7 .................................................................................... 59
2.16 $AA7VV .............................................................................. 61
2.17 $AA7CNRVV ...................................................................... 63
2.18 $AA8CN ............................................................................... 65
2.19 $AAF .................................................................................... 67
2.20 $AAI ..................................................................................... 68
2.21 $AAM ................................................................................... 70
2.22 $AAP .................................................................................... 71
2.23 $AAPN ................................................................................. 73
2.24 @AABB ............................................................................... 75
2.25 @AABBVV ......................................................................... 77
2.26 @AAFA ............................................................................... 79
2.27 @AAFAVV .......................................................................... 81
2.28 @AAFH ............................................................................... 83
2.29 @AAFHVV .......................................................................... 85
2.30 @AAFT ................................................................................ 87
2.31 @AAFTVV .......................................................................... 89
2.32 @AAGN ............................................................................... 91
2.33 @AAPN(Data) ..................................................................... 93
2.34 @AASC ................................................................................ 95
2.35 @AASCVV .......................................................................... 97
2.36 ~** ........................................................................................ 99
2.37 ~AA0 .................................................................................. 100
2.38 ~AA1 .................................................................................. 102
2.39 ~AA2 .................................................................................. 104
2.40 ~AA3EVV .......................................................................... 106
2.41 ~AAI ................................................................................... 108
2.42 ~AAO(Name) ..................................................................... 110
2.43 ~AARD ............................................................................... 112
2.44 ~AARDVV ......................................................................... 114
2.45 ~AATnn .............................................................................. 116
3. Modbus RTU Protocol ................................................................. 119
3.1 M-7084 Modbus Address Mapping ..................................... 120
4. Troubleshooting ............................................................................ 122
4.1 Communicating with the module ......................................... 123
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

4
A. Appendix ..................................................................................... 124
A.1 INIT Mode ........................................................................... 124
A.2 Dual Watchdog Operation ................................................... 126
A.3 Frame Ground ...................................................................... 127
A.4 Node Information Area ....................................................... 129
A.5 Reset Status ......................................................................... 130
A.6 Frequency Measurement ..................................................... 131
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
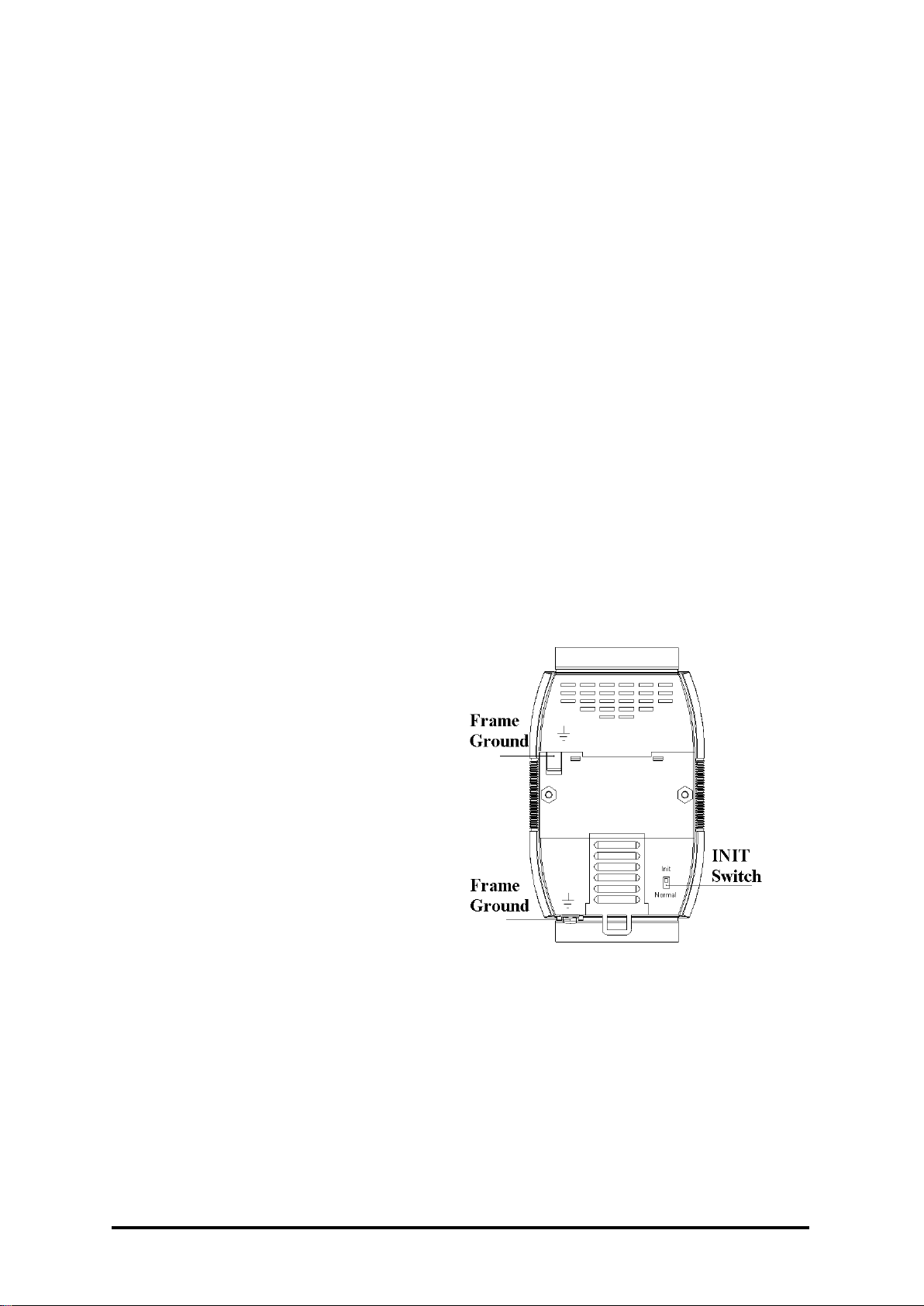
5
Some M-7000 modules feature
a new design for the frame
ground and INIT switch as
shown in the figure (rear
view). The frame ground
provides enhanced static
protection (ESD) abilities and
ensures the module is more
reliable. The INIT switch
allows easier access to INIT
mode. Please refer to Sections
A.1 and A.3 for more details.
1. Introduction
The I-7000 series is a family of network data acquisition and
control modules, providing analog-to-digital, digital-to-analog,
digital input/output, timer/counter and other functions. The
modules can be remotely controlled using a set of commands,
which we call the DCON protocol. Communication between
the module and the host is in ASCII format via an RS-485 bidirectional serial bus standard. Baud Rates are software
programmable and transmission speeds of up to 115.2 Kbps
can be selected.
The functionality of the M-7000 series is the same as the I7000 series, with the exception that the M-7000 series offers
extended support for the Modbus RTU protocol.
The M-7084 supports up counting, up-down counting, pulse
direction counting, quadrature counting and frequency
measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

6
1.1 The 7000 Series Overview
1.2 Related Documentation for the 7000 Series
1.3 Common Features of the 7000 Series
1.4 The 7000 Series System Network Configuration
1.5 7000 Dimensions
1.1 More Information
For more information regarding the I-7000/M-7000 series,
please refer to chapter 1 of the “I-7000 Bus Converter User‟s
Manual” as shown below or visit the ICP DAS website
http://www.icpdas.com.
For details of INIT mode operation, please refer to
Section A.1 INIT Mode.
For details of module watchdog and host watchdog,
please refer to Section A.2 Dual Watchdog Operation.
For details of ESD protection and grounding, please
refer to Section A.3 Frame Ground.
The node information area can be written with some
information, please refer to Section A.4 Node Information
Area for details.
There is a way to check whether the module is reset,
please refer to Section A.5 Reset Status for details.
For details of frequency measurement, please refer to
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

7
1.2 Terminal Assignment
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
8
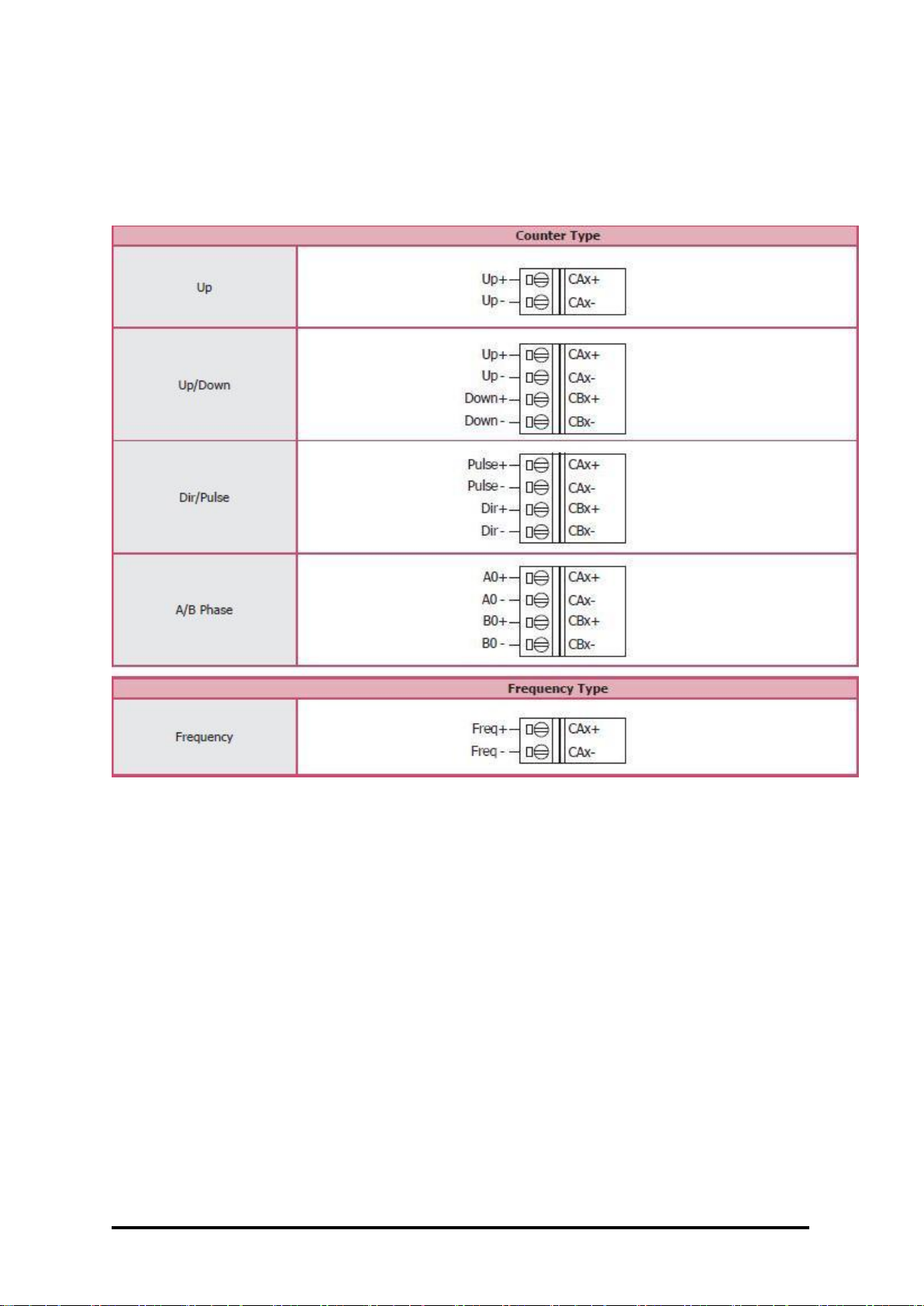
Counter/Frequency/Encoder Input
Channels
4-channel Up/Down Counter (CW/CCW)
4-channel Direction/Pulse Counter (Bidirection)
4-channel A/B Phase (Quadrature Counting)
8-channel Up Counter
8-channel Frequency
Contact
Wet
Sink/Source (NPN/PNP)
Sink
Types
Counter, Frequency, Encoder
Counter/Encoder Bits
32-bit (4,294,967,295)
On Voltage Level
+3.5 VDC ~ +30 VDC
Off Voltage Level
+1 VDC Max.
Programmable Digital Filter
1 ~ 32767 μs
Individual Channel Configuration
Yes
Counter Mode
Up, Up/Down
Encoder Mode
CW/CCW, Direction/Pulse, AB Phase
Frequency Mode
Yes
Max. Speed
3.5 VDC ~ 10 VDC: 200 kHz
10 VDC ~ 30 VDC: 150 kHz
Frequency Accuracy
±0.4% of Input Frequency
Virtual Battery Backup to Preserve
Counter Values
Yes
1.3 Specifications
1.3.1 I/O Specifications
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
9
Communication
Interface
RS-485
Format
N81, N82, E81, O81
Baud Rate
1200 ~ 115200 bps
Protocol
Modbus RTU, DCON
Dual Watchdog
Yes, Module (1.6 Seconds),
Communication (Programmable)
LED Indicator
Power
1 LED, Red
Isolation
Intra-module Isolation, Field-to-Logic
3000 VDC
EMS Protection
ESD (IEC 61000-4-2)
+/-4 kV Contact for Each Terminal
EFT (IEC 61000-4-4)
+/-4 kV for Power
Surge (IEC 61000-4-5)
+/-3 kV for Power Line
Power
Reverse Polarity Protection
Yes
Input Range
10 ~ 30 VDC
Consumption
1.32 W Max.
Mechanical
Dimensions (W x L x H)
72 mm x 123 mm x 35 mm
Installation
DIN-Rail, Wall Mounting
Environment
Operating Temperature
-25 ~ +75°C
Storage Temperature
-30 ~ +80°C
Humidity
10 ~ 90% RH, Non-condensing
1.3.2 System Specifications
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
10
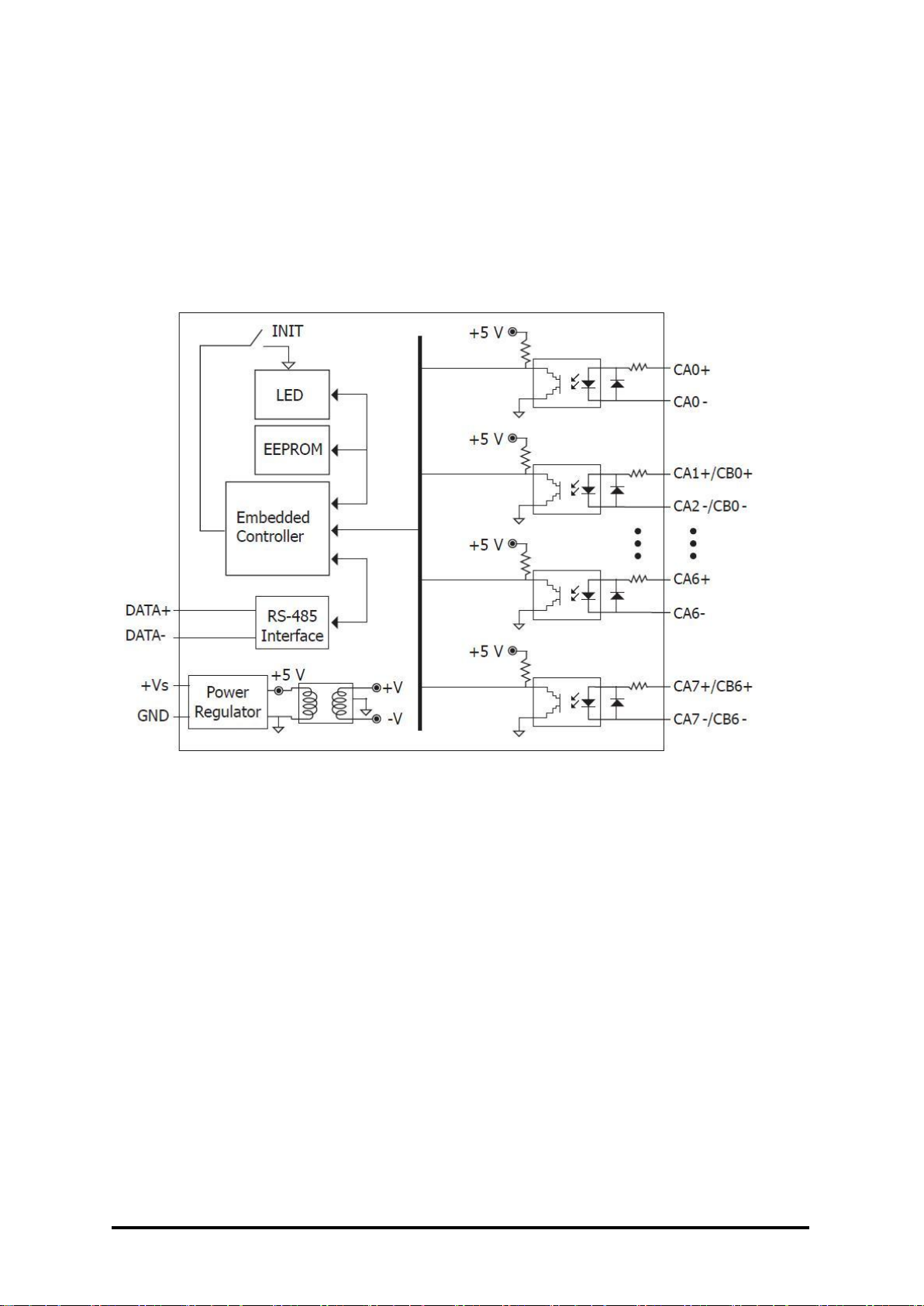
1.4 Block Diagram
1.4.1 Block Diagram for the M-7084
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
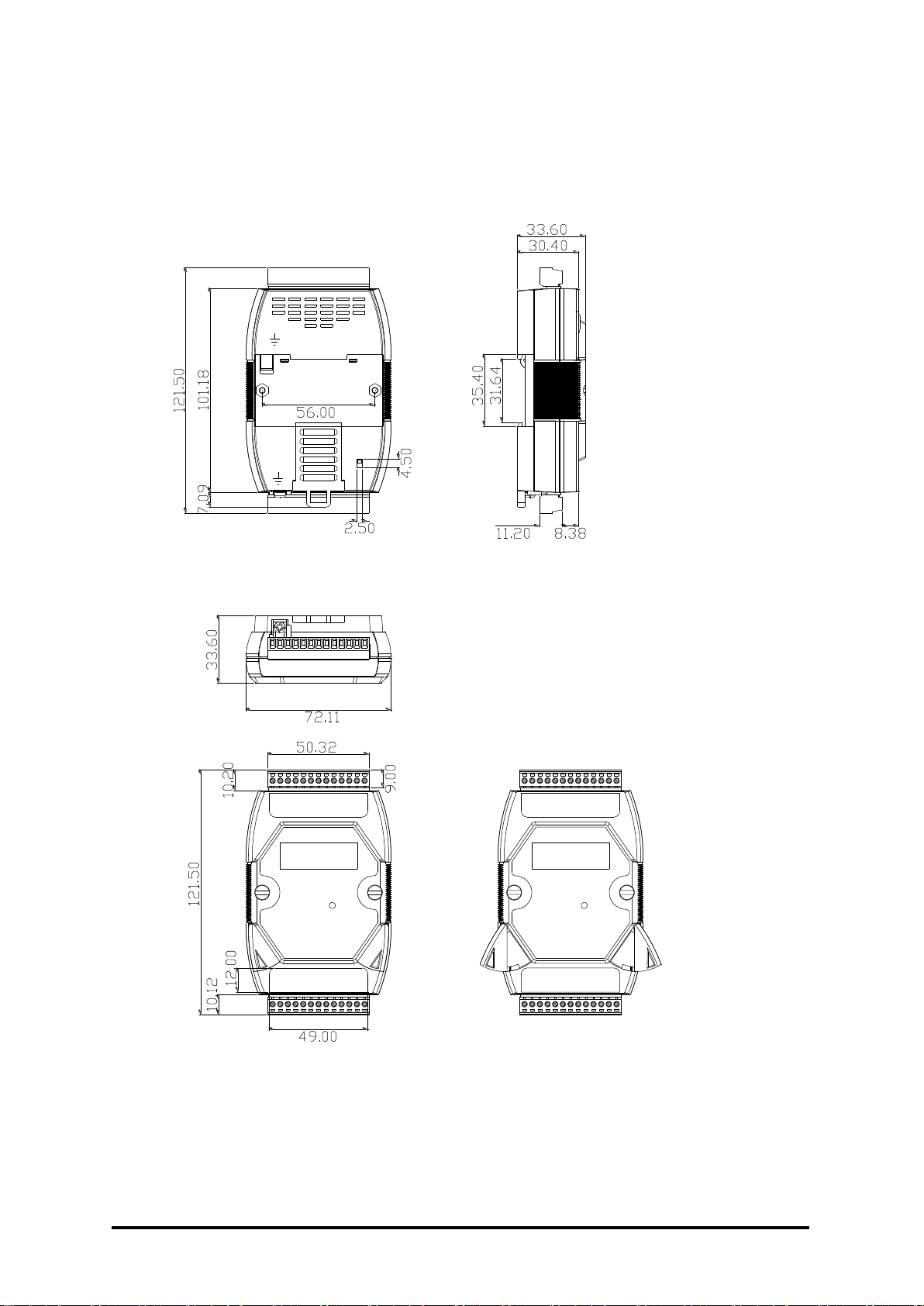
11
Back View
Top View
Front View
Side View
Unit : mm
lnit
Normal
1.5 Dimensions
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
12
1.6 Wiring
1.6.1 M-7084 Wiring
1.6.2 Wiring Recommendations
Use 26-12 AWG wire for signal connections.
Strip the wire to a length of 7±0.5mm.
Use a crimp terminal for wiring.
Avoid high-voltage cables and power equipment as
much as possible.
For RS-485 communication, use insulated and twisted
pair 24 AWG wire, e.g. Belden 9841.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

13
1.7 Quick Start
To install the module, follow the steps below:
1. Refer to Section 1.2 for the terminal assignment and
Section 1.6 for the wiring diagram.
2. Connect the module to the RS-485 network using the
DATA+ and DATA- terminals. See Section 1.2 for the
terminal assignment. If the host is only equipped with an
RS-232 interface, then an RS-232 to RS-485 converter
will be required. Refer to the “I-7000 Bus Converter
User’s Manual” for more information.
3. Connect the module to the power supply using the +Vs
and GND terminals. See Section 1.2 for the terminal
assignment. Note that the voltage supplied to the module
should be in the range of +10 to +30 VDC.
4. Configure the module by sending the %AANNTTCCFF
command and the $AA7CNRVV command. See Section
2.1 and 2.17 for details. For M-7000 modules using the
Modbus RTU protocol, configure the module using the
following registers: 40257 ~ 40264, 40485, and 40486.
The default settings for the module can be found in
Section 1.8.
5. To read data from the input channels, send the #AAN
command to the module. See Sections 2.3 for details. For
M-7000 modules using the Modbus RTU protocol, use
Function 03h to read the data from the input channels.
6. If the host is a PC with a Windows operating system
installed, the DCON Utility can be used to allow easy
configuration and reading of data. The DCON Utility can
be downloaded from the ICP DAS website
(http://www.icpdas.com). The documentation for the
DCON Utility can be found in the ”Getting Started For
I-7000 Series Modules” manual.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

14
Please refer to the “I-7000 Bus Converter User’s Manual”
and ”Getting Started For I-7000 Series Modules” manuals
for more details. The “Getting Started For I-7000 Series
Modules” manual can be downloaded from the ICP DAS
website (http://www.icpdas.com).
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

15
1.8 Default Settings
Default settings for the M-7084 modules are as follows:
。 Protocol: Modbus RTU
。 Module Address: 01
。 Type: Type 50, up counter
。 Baud Rate: 9600 bps
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
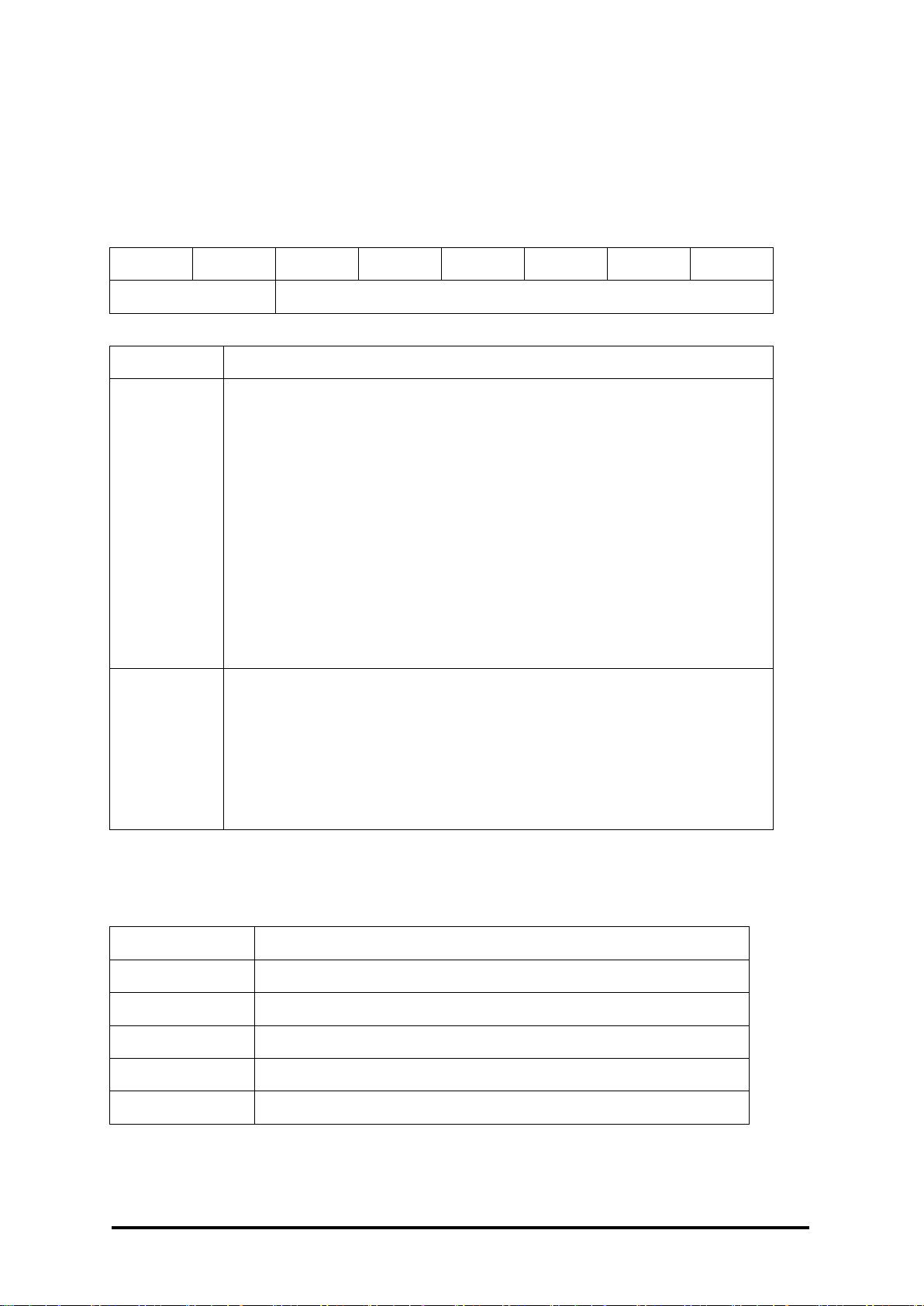
16
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Data
Baud
Key
Description
Baud
Baud Rate
03: 1200
04: 2400
05: 4800
06: 9600
07: 19200
08: 38400
09: 57600
0A: 115200
Data
Data Format
0: eight data bits, no parity, and one stop bit
1: eight data bits, no parity, and two stop bit
2: eight data bits, even parity, and one stop bit
3: eight data bits, odd parity, and one stop bit
Type Code
Input Type
50
Up counter
51
Frequency
54
Up/down counter
55
Pulse/direction counter
56
Quadrature counter
1.9 Configuration Tables
Baud Rate Setting (CC)
Type Setting (TT)
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
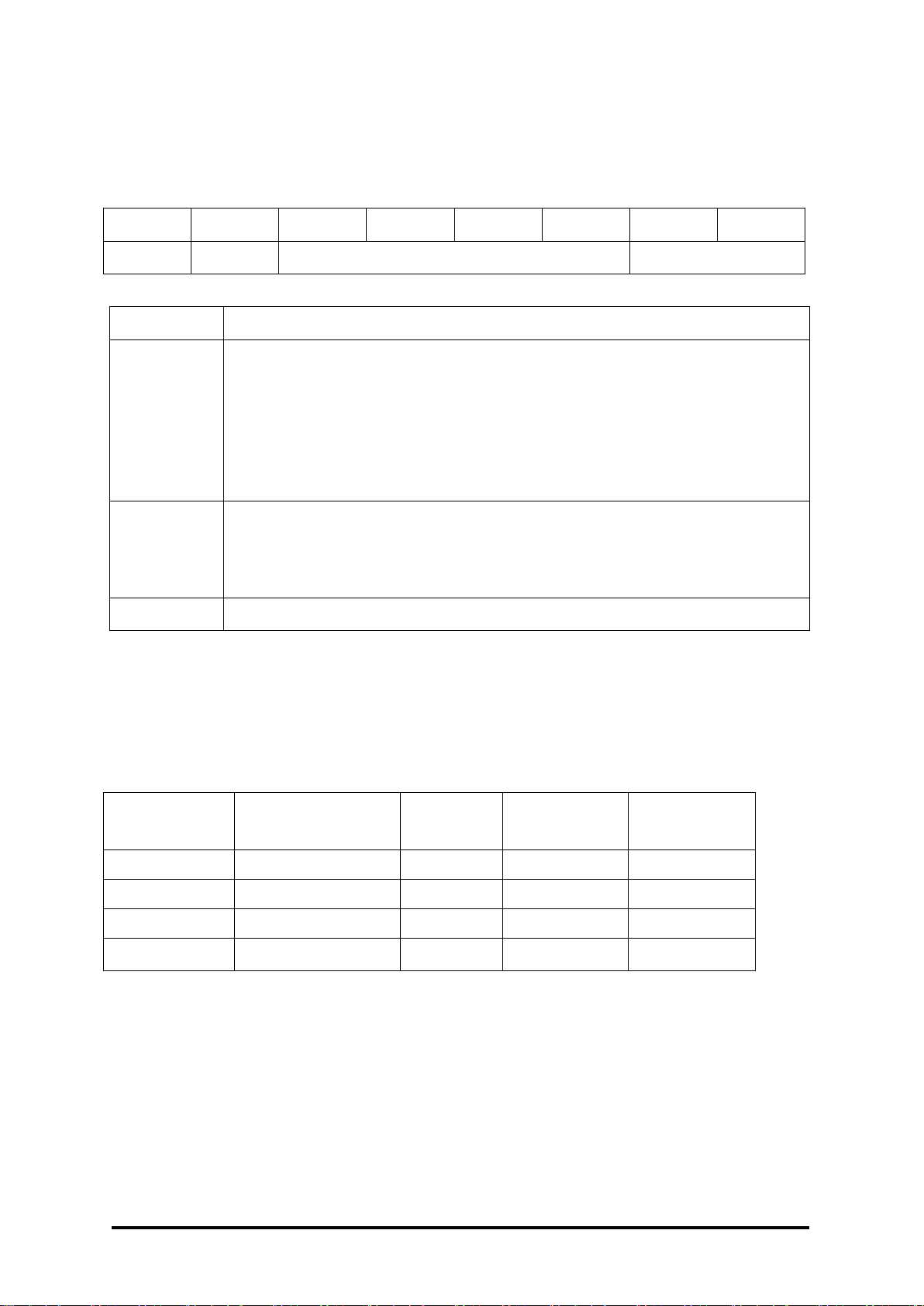
17
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
RD
CS
RD
DF
Key
Description
DF
Data format
00: Engineering unit. The data consist of „+‟, 6
digits and one decimal point. This data format
is only for the frequency type.
10: Hexadecimal
CS
Checksum setting
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
RD
Reserved
Type Code
Counter type
Data
Format
Min
Max
50
Up
Hex
00000000
FFFFFFFF
54
Up/down
Hex
80000000
7FFFFFFF
55
Pulse/direction
Hex
80000000
7FFFFFFF
56
Quadrature
Hex
80000000
7FFFFFFF
Data Format Setting (FF)
Note: The reserved bits should be zero.
Counter Type and Data Format Table
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
18
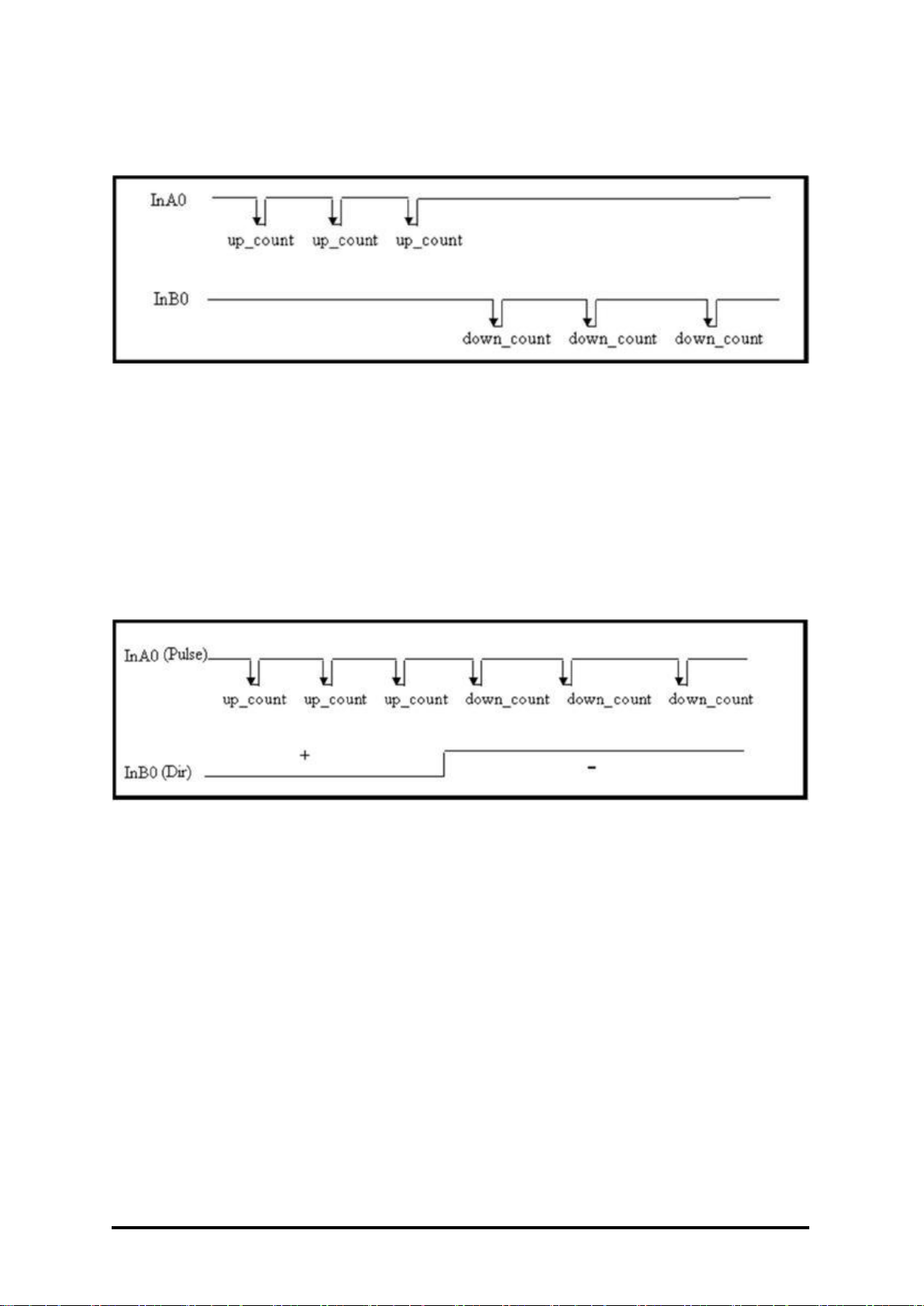
Up/down Counting
When InA0 is used as an up counting clock and InB0 is used
as a down counting clock, the counter will be increased by
one for every falling edge of InA0 and decreased by one for
every falling edge of InB0.
Pulse/direction Counting
The InB0 is used for direction counting. When InB0 is high,
the counter will be increased by one for every falling edge of
InA0. When InB0 is low, the counter will be decreased by
one for every falling edge of InA0.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

19
Quadrature Counting
When InA0 is used as the A signal and InB0 is used as the B
signal, the counter will be increased by one when the InA0
phase leads by 90 degrees to InB0 and the counter will be
decreased by one when the InA0 phase lags by 90 degrees to
InB0.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

20
1.10 M-7000 Notes
The main difference between the I-7000 and M-7000 series is
that the M-7000 series has additional support for the Modbus
RTU communication protocol, which is the default protocol
of the M-7000 series. The communication Baud Rates for the
Modbus RTU protocol can be in the range of 1200 bps to
115200 bps.
Modbus functions supported by the module are described in
Chapter 3.
1.10.1 Protocol Switching
To switch to the DCON protocol:
1. Set Modbus register 00257 to 0. See Section 3.1 for
details.
2. After a power-on reset, the communication protocol will
be changed to DCON.
To switch to the Modbus RTU protocol:
1. Sends the $AAPN command and set N to a value of 1.
Note that for the modules without frame ground, the
INIT* terminal should be connected to the GND terminal,
and for the modules with frame ground, the slide switch
on the rear side of the module should be set to the INIT
position, see the figure on the next page. See Section 2.23
for details.
2. After a power-on reset, the communication protocol will
be changed to the Modbus RTU protocol.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

21
1.10.2 INIT Mode
When the module is powered on, with the rear slide switch set
to the INIT position as shown in the figure below for modules
with frame ground, or with the INIT* pin connected to the
GND pin for modules without frame ground, the module is in
INIT mode, (see Section A.1 for details), and the
communication settings are as follows:
1. Address: 00
2. Baud Rate: 9600 bps
3. No checksum
4. Protocol: DCON
If communication with the module is not possible, set the
module to the INIT mode and use the above settings to
communicate with the module. To read the current settings,
send the commands $AA2, (see Section 2.6), and $AAP, (see
Section 2.22). To set new settings, send the commands
%AANNTTCCFF, (see Section 2.1) and $AAPN, (see
Section 2.23). The new communication settings will be
effective after the next power-on reset.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
22
Part number
Max. number of modules
Dimensions
DRS-360
5
360mm x 35mm
1.11 Mounting
1.11.1 Din-Rail Mounting
There are three new DIN rail models available. Each is made
of stainless steel, which is stronger than those made of
aluminum. There is a screw at one end and a ring terminal is
included so that it can be easily connected to the earth ground.
The three new DIN rail models are as follows.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
23
Part number
Max. number of modules
Dimensions
DRS-240
3
240mm x 35mm
Part number
Max. number of modules
Dimensions
DRS-125
2
125mm x 35mm
Note: It is recommended that a 16 – 14 AWG wire is used to
connect the DIN rail to the earth ground.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
24
1.11.2 Piggyback Mounting
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
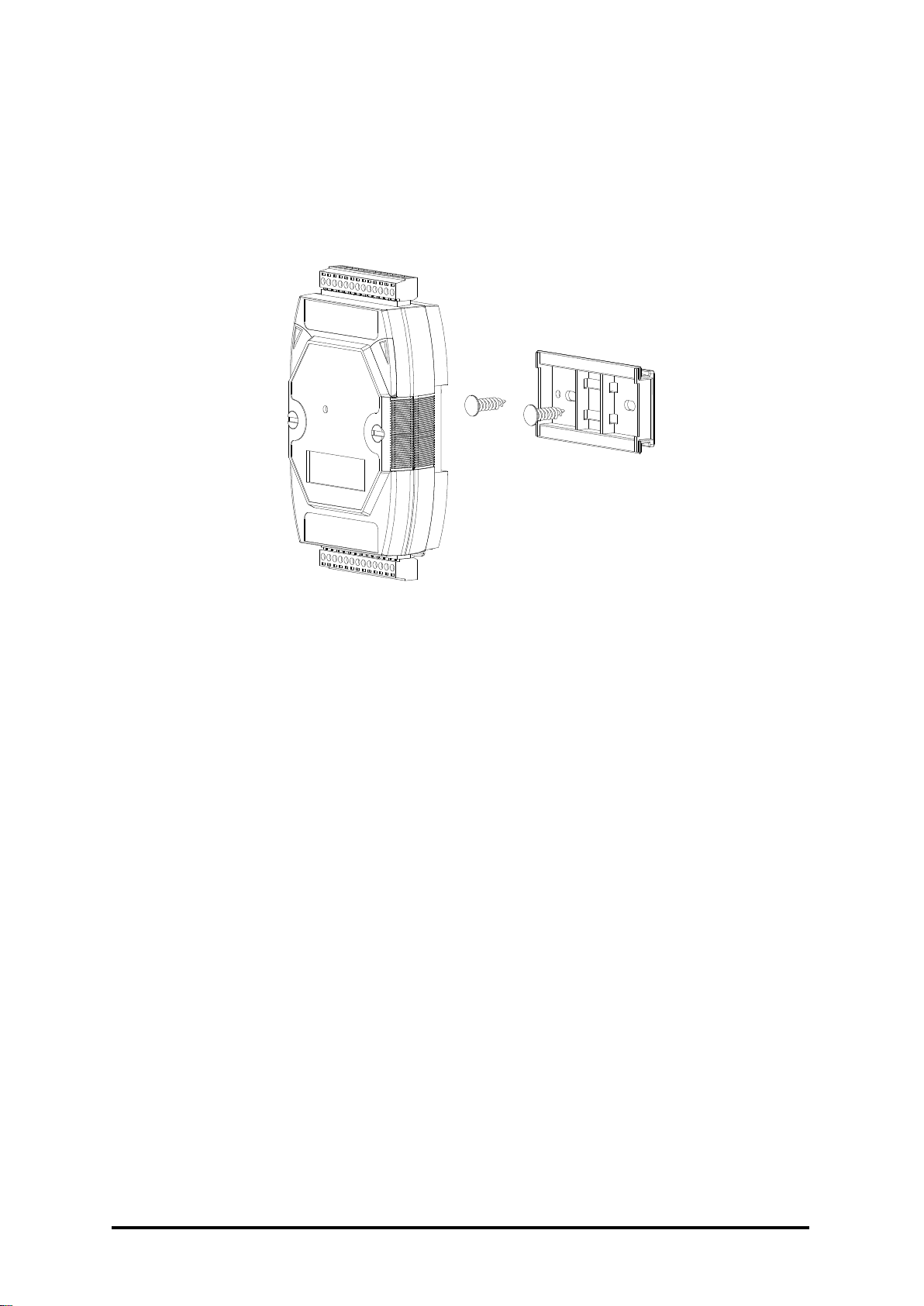
25
1.11.3 Wall Mounting
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

26
1.12 Technical Support
Should you encounter any problems while using the
I-7000 and M-7000 module, and are unable to find the help
you need in this manual or on our website, please contact ICP
DAS Product Support.
Email: service@icpdas.com
Website:
http://www.icpdas.com.tw/contact_us/contact_us.html
When requesting technical support, be prepared to provide the
following information about your system:
1. Module name and serial number: The serial number can be
found printed on the barcode label attached to the cover of
the module.
2. Firmware version: See Sections 2.19 and 3.1 for
information regarding the command used to identify the
firmware version.
3. Host configuration (type and operating system)
4. If the problem is reproducible, please give full details
describing the procedure used to reproduce the problem.
5. Any specific error messages displayed. If a dialog box
with an error message is displayed, please include the full
text of the dialog box, including the text in the title bar.
6. If the problem involves other programs or hardware
devices, please describe the details of the problem in full.
7. Any comments and suggestions related to the problem are
welcome.
ICP DAS will reply to your request by email within three
business days.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
27
Leading
Character
Module
Address
Command
[CHKSUM]
CR
Leading
Character
Module
Address
Data
[CHKSUM]
CR
2. DCON Protocol
All communication with I-7000 modules consists of
commands generated by the host and responses transmitted by
the I-7000 modules. Each module has a unique ID number
that is used for addressing purposes and is stored in nonvolatile memory. The ID is 01 by default and can be changed
using a user command. All commands to the modules contain
the ID address, meaning that only the addressed module will
respond. The only exception to this is command ~** (Section
2.36), which is sent to all modules, but the modules do not
reply to the command.
Command Format:
Response Format:
CHKSUM A 2-character checksum which is present when
the checksum setting is enabled. See Sections
1.9 (Data Format Setting) and 2.1 for details.
CR End of command character, carriage return
(0x0D)
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

28
Checksum Calculation:
1. Calculate the ASCII code sum of all the characters in the
command/response string except for the carriage return
character (CR).
2. The checksum is equal to the sum masked by 0FFh.
Example:
Command string: $012(CR)
1. Sum of the string = “$”+”0”+”1”+”2” =
24h+30h+31h+32h = B7h
2. Therefore the checksum is B7h, and so
CHKSUM = “B7”
3. The command string with the checksum = $012B7(CR)
Response string: !01200600(CR)
1. Sum of the string =
“!”+”0”+”1”+”2”+”0”+”0”+”6”+”0”+”0” =
21h+30h+31h+32h+30h+30h+36h+30h+30h = 1AAh
2. Therefore the checksum is AAh, and so
CHKSUM = “AA”
3. The response string with the checksum
= !01200600AA(CR)
Note:
All characters should be in upper case.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
29
General Command Sets
Command
Response
Description
Section
%AANNTTCCFF
!AA
Sets the Module Configuration
2.1
$AA2
!AANNTTCCFF
Reads the Module Configuration
2.6
$AA5
!AAS
Reads the Reset Status
2.11
$AAF
!AA(Data)
Reads the firmware Version
2.19
$AAI
!AAS
Reads the INIT Status
2.20
$AAM
!AA(Data)
Reads the Module Name
2.21
$AAP
!AASC
Reads the communication protocol
2.22
$AAPN
!AA
Sets the communication protocol
2.23
~AAI
!AA
Software INIT
2.41
~AAO(Name)
!AA
Sets the Module Name
2.42
~AARD
!AAVV
Reads the Response Delay Time
2.43
~AARDVV
!AA
Sets the Response Delay Time
2.44
~AATnn
!AA
Sets the Software INIT Timeout
2.45
Counter/Frequency Command Sets
Command
Response
Description
Section
#AA
>(Data)
Reads the Input Data of All
Channels
2.2
#AAN
>(Data)
Reads the Input Data of the
Specified Channel
2.3
$AA0N
!AA(Data)
Reads the Low Pass Filter Time of
the Specified Channel
2.4
$AA0N(Data)
!AA
Sets the Low Pass Filter Time of the
Specified Channel
2.5
$AA3N
!AA(Data)
Reads the Maximum Counter Value
of the Specified Channel
2.7
$AA3N(Data)
!AA
Sets the Maximum Counter Value of
the Specified Channel
2.8
$AA4
!AAVV
Reads the Low Pass Filter Channel
Mask
2.9
$AA4VV
!AA
Sets the Low Pass Filter Channel
Mask
2.10
$AA5VV
!AA
Starts/Stop Counting
2.12
$AA6
!AAVV
Reads the Start/Stop Counting
Status
2.13
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
30
Command
Response
Description
Section
$AA6N
!AA
Clears the Counter Value of the
Specified Channel
2.14
$AA7
!AAVV
Shows the Overflow Status of All
Channels
2.15
$AA7VV
!AA
Clears the Overflow Status
2.16
$AA7CNRVV
!AA
Sets the Single Channel Type
2.17
$AA8CN
!AACNRVV
Reads the Channel Type of the
Specified Channel
2.18
@AABB
!AAVV
Reads the Battery Backup Status
2.24
@AABBVV
!AA
Sets the Battery Backup Status
2.25
@AAFA
!AAVV
Reads the Auto Frequency Mode
Status
2.26
@AAFAVV
!AA
Sets the Auto Frequency Mode
Status
2.27
@AAFH
!AAVV
Reads the High Frequency Mode
Status
2.28
@AAFHVV
!AA
Sets the High Frequency Mode
Status
2.29
@AAFT
!AAVV
Reads the Frequency Measurement
Timeout
2.30
@AAFTVV
!AA
Sets the Frequency Measurement
Timeout
2.31
@AAGN
!AA(Data)
Reads the Preset Counter Value of
the Specified Channel
2.32
@AAPN(Data)
!AA
Sets the Preset Counter Value of the
Specified Channel e
2.33
@AASC
!AAVV
Reads the Stop Counting on
Overflow Status
2.34
@AASCVV
!AA
Sets the Stop Counting on Overflow
Status
2.35
Host Watchdog Command Sets
Command
Response
Description
Section
~**
No Response
Host OK
2.36
~AA0
!AASS
Reads the Status
2.37
~AA1
!AA
Resets the Status
2.38
~AA2
!AAVV
Reads the Timeout Settings
2.39
~AA3EVV
!AA
Sets the Timeout Settings
2.40
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

31
2.1 %AANNTTCCFF
Description:
Sets the configuration of a module.
Syntax:
%AANNTTCCFF[CHKSUM](CR)
% Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be configured in
hexadecimal format (00 to FF)
NN New address of the module in hexadecimal format (00
to FF)
TT New type code. Not used by the M-7084. It should
be set to 00 for the M-7084
CC New Baud Rate code, see Section 1.9 for details. The
INIT* pin must be connected to ground in order to
change Baud Rates. For the module with frame
ground, this is achieved by moving the rear slide
switch to the INIT position. See Section A.1 for
details.
FF Used to set the data format and checksum (Section
1.9). The INIT* pin must be connected to ground in
order to change the checksum setting. For the module
with frame ground, this is achieved by moving the rear
slide switch to the INIT position. See Section A.1 for
details.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

32
Response:
Valid Command: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter for a valid command
? Delimiter for an invalid command. If the Baud Rate
or checksum settings are changed without connecting
the INIT* pin to ground or switching the rear slide
switch to the INIT position, the module will return an
invalid command.
AA Address of the module in hexadecimal format (00 to
FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
Examples:
Command: %0102000600 Response: !02
Changes the address of module 01 to 02. The module
returns a valid response.
Command: %0101000A00 Response: ?01
Changes the Baud Rate of module 01 to 115200bps. The
module returns an invalid command, because it is not in
INIT* mode.
Command: %0101000A00 Response: !01
Changes the Baud Rate of module 01 to 115200bps and
the module is in INIT* mode. The module returns a
valid response.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

33
Related Commands:
Section 2.6 $AA2, Section 2.41 ~AAI, Section 2.45 ~AATnn
Related Topics:
Section 1.9 Configuration Tables, Section A.1 INIT* pin
Operation
Notes:
1. Changes to the address and data format settings take effect
immediately after a valid command is received. Changes
to the Baud Rate and checksum settings take effect on the
next power-on reset.
2. For the M-7084, changing the Baud Rate and checksum
settings can be achieved using software only and is
performed using the following commands:
I. Send a ~AATnn command. See Section 2.45 for
details.
II. Send a ~AAI command. See Section 2.41 for details.
III. Send a %AANNTTCCFF command.
If the command is valid, the Baud Rate and checksum
settings will be changed after the module responds
with !AA.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

34
2.2 #AA
Description:
Reads the data from every input channels.
Syntax:
#AA[CHKSUM](CR)
# Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
Response:
Valid Response: >(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
> Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response
(Data) Data from every input channels, see Section 1.9 for
the details of data format.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
Examples:
Command: #01 Response:
>000012340000567800009ABC0000DEF000001111000022
220000333300004444
Reads module 01 and receives the data.
Related Commands:
Section 2.1 %AANNTTCCFF, Section 2.6 $AA2
Related Topics:
Section 1.9 Configuration Tables
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

35
2.3 #AAN
Description:
Reads the input of channel N.
Syntax:
#AAN[CHKSUM](CR)
# Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
N The channel to be read, zero based.
Response:
Valid Response: >(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
> Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response. An
invalid command is returned if the specified
channel is incorrect.
(Data) Input data of the specified channel, see Section 1.9
for details of the data format.
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

36
Examples:
Command: #032 Response: >00001234
Reads data from channel 2 of module 03.
Command: #029 Response: ?02
Reads data from channel 9 of module 02. An error is
returned because channel 9 is invalid.
Related Commands:
Section 2.1 %AANNTTCCFF, Section 2.6 $AA2
Related Topics:
Section 1.9 Configuration Tables
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

37
2.4 $AA0N
Description:
Reads the low pass filter time of channel N.
Syntax:
$AA0N[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
0 Command to read the low pass filter time of a
channel
N Specifies the channel to be read (0 ~ 7)
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
(Data) Low pass filter time is micro seconds, consisting of
5 decimal digits in the range 00001 ~ 32767.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

38
Examples:
Command: $0103 Response: !0100010
Reads the channel 3 low pass filter time of module 01
and the module responds with 00010 which means 10
micro seconds.
Related Commands:
Section 2.5 $AA0N(data), Section 2.9 $AA4, Section 2.10
$AA4vv
Notes:
1. The low pass filter time should be the same for channel 0
and 1. When it is set to either one of the channel 0 or 1,
both channels will be set to the same value.
2. The low pass filter time should be the same for channel 2
and 3. When it is set to either one of the channel 2 or 3,
both channels will be set to the same value.
3. The low pass filter time should be the same for channel 4,
5, 6 and 7. When it is set to either one of the channel 4, 5,
6 or 7, all of the 4 channels will be set to the same value.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

39
2.5 $AA0N(Data)
Description:
Sets the low pass filter time of a channel.
Syntax:
$AA0N(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
0 Command to read the low pass filter time of a
channel
N Specifies the channel to be read (0 ~ 7)
(Data) Low pass filter time is micro seconds, consisting of
5 decimal digits in the range 00001 ~ 32767.
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

40
Examples:
Command: $010300010 Response: !01
Sets the channel 3 low pass filter time of module 01 to
10 micro seconds and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.4 $AA0N, Section 2.9 $AA4, Section 2.10 $AA4vv
Notes:
1. The low pass filter time should be the same for channel 0
and 1. When it is set to either one of the channel 0 or 1,
both channels will be set to the same value.
2. The low pass filter time should be the same for channel 2
and 3. When it is set to either one of the channel 2 or 3,
both channels will be set to the same value.
3. The low pass filter time should be the same for channel 4,
5, 6 and 7. When it is set to either one of the channel 4, 5,
6 or 7, all of the 4 channels will be set to the same value.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

41
2.6 $AA2
Description:
Reads the module configuration.
Syntax:
$AA2[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
2 Command to read the module configuration
Response:
Valid Command: !AATTCCFF[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
TT Type code of the module, should be 00 for M-7084.
CC Baud Rate code of the module, see Section 1.9 for
details.
FF Checksum and counter update direction settings of
the module, see Section 1.9 for details.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

42
Examples:
Command: $012 Response: !01000600
Reads the configuration of module 01.
Related Commands:
Section 2.1 %AANNTTCCFF
Related Topics:
Section 1.9 Configuration Tables
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

43
2.7 $AA3N
Description:
Reads the maximum counter value of channel N.
Syntax:
$AA3N[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
3 Command to read the maximum counter value of a
channel
N Specifies the channel to be read (0 ~ 7)
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
(Data) The maximum counter value in eight hexadecimal
digits
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

44
Examples:
Command: $0132 Response: !01FFFFFFFF
Reads the channel 2 maximum counter value of module
01 and the module responds with FFFFFFFF.
Related Commands:
Section 2.8 $AA3N(Data)
Note:
The maximum counter value is only available to the channels
that are set to up counter type (type code 50).
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

45
2.8 $AA3N(Data)
Description:
Sets the maximum counter value of a channel.
Syntax:
$AA3N(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
3 Command to set the maximum counter value of a
channel
N Specifies the channel to be read (0 ~ 7)
(Data) The maximum counter value in eight hexadecimal
digits
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

46
Examples:
Command: $0132F0000000 Response: !01
Sets the channel 2 maximum counter value of module 01
to 0xF0000000 and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.7 $AA3N
Note:
The maximum counter value is only available to the channels
that are set to up counter type (type code 50).
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

47
2.9 $AA4
Description:
Reads the enabled/disabled low pass filter status of each
channel.
Syntax:
$AA4[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
4 Command to read the low pass filter status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
low pass filter is enable for the channel and 0 means
that the low pass filter is disabled for the channel.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

48
Examples:
Command: $014 Response: !013A
Reads the low pass filter enabled/disabled status for
module 01 and returns a response of 3A, meaning that
low pass filter for channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are enabled
and disabled for all other channels.
Related Commands:
Section 2.10 $AA4VV
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

49
2.10 $AA4VV
Description:
Specifies the channel(s) which low pass filter should be
enabled.
Syntax:
$AA4VV[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
4 Command to enable/disable the low pass filter
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
low pass filter is enable for the channel and 0 means
that the low pass filter is disabled for the channel.
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

50
Examples:
Command: $0143A Response: !01
Enables the low pass filter of channels 1, 3, 4, and 5
and disables all other channels of module 01. The
module returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.9 $AA4
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

51
2.11 $AA5
Description:
Reads the reset status of a module.
Syntax:
$AA5[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
5 Command to read the module reset status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAS[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
S Reset status of the module
1: This is the first time the command has been sent
since the module was powered on.
0: This is not the first time the command has been
sent since the module was powered on, which
denotes that there has been no module reset since
the last $AA5 command was sent.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

52
Examples:
Command: $015 Response: !011
Reads the reset status of module 01. The response
shows that it is the first time the $AA5 command has
been sent since the module was powered-on.
Command: $015 Response: !010
Reads the reset status of module 01. The response
shows that there has been no module reset since the
last $AA5 command was sent.
Related Topics:
Section A.5 Reset Status
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

53
2.12 $AA5VV
Description:
Specifies the channel(s) to count.
Syntax:
$AA5VV(VV)[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
5 Command to start counting
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
channel is counting and 0 means that the channel is
not counting.
Response:
Valid Response: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response. An
invalid command is returned if an attempt is made
to enable a channel that is not present.
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

54
Examples:
Command: $0153A Response: !01
Sets channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 to count and all other
channels not counting for module 01. The module
returns a valid response.
Command: $016 Response: !013A
Reads the counting status of module 01 and returns a
response of 3A, meaning that channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are
counting and all other channels are not counting.
Related Commands:
Section 2.13 $AA6
Note:
The command is not available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

55
2.13 $AA6
Description:
Reads the start/stop counting status of each channel.
Syntax:
$AA6[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
6 Command to read the channel counting status
Response:
Valid Response: !AAVV(VV)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
channel is counting and 0 means that the channel is
not counting.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

56
Examples:
Command: $0153A Response: !01
Sets channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 to count and all other
channels not counting for module 01. The module
returns a valid response.
Command: $016 Response: !013A
Reads the counting status of module 01 and returns a
response of 3A, meaning that channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are
counting and all other channels are not counting.
Related Commands:
Section 2.12 $AA5VV
Note:
The command is not available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

57
2.14 $AA6N
Description:
Sets the counter value of a channel to preset value.
Syntax:
$AA6N[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
6 Command to clear the counter value
N Specifies the channel to be cleared (0 ~ 7)
Response:
Valid command: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

58
Examples:
Command: $0161 Response: !01
Clears the counter value of channel 1 of module 01 and
the module returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.15 $AA7
Notes:
1. The overflow status is cleared by the command, too.
2. The command is not available to the channels that are set
to type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

59
00: no over/underflow
01: overflow
10: underflow
11: not applicable
2.15 $AA7
Description:
Reads the counter overflow status of each channel.
Syntax:
$AA7[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
7 Command to read the counter overflow status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. For type code 50, when the bit is 1 it
means that the counter of the channel is overflowed
and 0 means that the counter of the channel is not
overflowed. For type code 54 ~ 56, the overflow
status is represented by two bits.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

60
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
Examples:
Command: $017 Response: !013A
Reads the counter overflow status for module 01 and
returns a response of 3A, meaning that counters of
channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are overflowed.
Related Commands:
Section 2.16 $AA7VV
Note:
The command is not available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

61
2.16 $AA7VV
Description:
Specifies the channels which counter overflow status are to be
cleared.
Syntax:
$AA7VV[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
7 Command to clear the counter overflow status
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
counter overflow status of the channel should be
cleared.
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

62
Examples:
Command: $0173A Response: !01
Clears the counter overflow status of channels 1, 3, 4,
and 5 for module 01 and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.15 $AA7
Note:
The command is not available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

63
2.17 $AA7CNRVV
Description:
Sets the type code of a channel.
Syntax:
$AA7CNRVV[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
7 Command to set the channel range code
CN N specifies the input channel to be set (0-7)
RVV VV represents the type code of the channel to be set.
Refer to the Analog Input Type Setting table in
Section 1.9 for details.
Response:
Valid Response: !AA [CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response or
invalid type code
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

64
Examples:
Command: $017C0R50 Response: !01
Sets the type code for channel 0 of module 01 to be 50
(up counting) and the module returns a valid response.
Command: $037C1R30 Response: ?03
Sets the type code for channel 1 of module 03 to be 30.
The module returns an invalid response because the type
code is invalid.
Related Commands:
Section 2.18 $AA8CN
Related Topics:
Section 1.9 Configuration Tables
Note:
If the type code of a channel is set to one of 54 ~ 56, then the
adjacent channel in the same pair will be set to the same type
code.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

65
2.18 $AA8CN
Description:
Reads the type code information of a channel.
Syntax:
$AA8CN[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
8 Command to read the type code of a channel
CN N specifies which channel to access for the type
code information (N=0-7).
Response:
Valid Response: !AACNRVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response or
invalid channel
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
CN N specifies which input channel to access to
retrieve the type code information.
RVV VV represents the type code of the specified input
channel. Refer to the Analog Input Type Setting
table in Section 1.9 for details.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

66
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
Examples:
Command: $018C0 Response: !01C0R50
Reads the channel 0 input range of module 01 and returns
50 (up counting).
Related Commands:
Section 2.17 $AA7CNRVV
Related Topics:
Section 1.9 Configuration Tables
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

67
2.19 $AAF
Description:
Reads the firmware version of a module.
Syntax:
$AAF[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
F Command to read the firmware version
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
(Data) Firmware version string of the module
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
Examples:
Command: $01F Response: !01A2.0
Reads the firmware version of module 01, and shows
that it is version A2.0.
Command: $02F Response: !02B1.1
Reads the firmware version of module 02, and shows
that it is version B1.1.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

68
2.20 $AAI
Description:
Reads the INIT status.
Syntax:
$AAI[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
I Command to read the INIT status
Response:
Valid Response: !AAS[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
S INIT status:
0= the INIT pin is shorted to GND.
1= the INIT pin is not shorted to GND.
2= Update CJC temperature once only.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

69
Examples:
Command: $01I Response: !010
Reads the INIT status of module 01 and the module
responds with 0, meaning that the INIT pin is shorted to
GND.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

70
2.21 $AAM
Description:
Reads the name of a module.
Syntax:
$AAM[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
M Command to read the module name
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
(Name) Name string of the module
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
Examples:
Command: $01M Response: !017084
Reads the module name of module 01 and returns the
name “7084”.
Related Commands:
Section 2.23 ~AAO(Name)
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

71
2.22 $AAP
Description:
Reads the communication protocol information.
Syntax:
$AAP[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
P Command to read the communication protocol
Response:
Valid Response: !AASC[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
S The protocols supported by the module
0: only DCON protocol is supported
1: both the DCON and Modbus RTU protocols are
supported
C The current protocol that is saved in the EEPROM
that will be used at the next power-on reset
0: the protocol set in the EEPROM is DCON
1: the protocol set in the EEPROM is Modbus RTU
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

72
Examples:
Command: $01P Response: !0110
Reads the communication protocol of module 01 and
returns a response of 10 meaning that it supports both
the DCON and Modbus RTU protocols and the
protocol that will be used at the next power-on reset is
DCON.
Related Commands:
Section 2.23 $AAPN
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

73
2.23 $AAPN
Description:
Sets the communication protocol.
Syntax:
$AAPN[CHKSUM](CR)
$ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
P Command to set the communication protocol
N 0: DCON protocol
1: Modbus RTU protocols
Before using this command, the rear slide switch
must be in the INIT position. The new protocol is
saved in the EEPROM and will be effective after
the next power-on reset.
Response:
Valid Response: !AASC[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Response: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid response
? Delimiter character for an invalid response
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

74
Examples:
Command: $01P1 Response: ?01
Sets the communication protocol of module 01 to
Modbus RTU and returns an invalid response because
the module is not in INIT mode.
Command: $01P1 Response: !01
Sets the communication protocol of module 01 to
Modbus RTU and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.22 $AAP
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

75
2.24 @AABB
Description:
Reads the battery backup counter status of each channel.
Syntax:
@AABB[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
BB Command to read the battery backup counter status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
battery backup counter is enabled for the channel
and 0 means that the battery backup counter is
disabled for the channel.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

76
Examples:
Command: @01BB Response: !013A
Reads the battery backup counter status for module 01
and returns a response of 3A, meaning that battery
backup counter for channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are enabled
and disabled for all other channels.
Related Commands:
Section 2.25 @AABBVV
Note:
The command is not available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

77
2.25 @AABBVV
Description:
Specifies the channels which battery backup counter function
should be enabled.
Syntax:
@AABBVV[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
BB Command to enable the battery backup counter
function
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
battery backup counter is enabled for the channel
and 0 means that the battery backup counter is
disabled for the channel.
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

78
Examples:
Command: @01BB 3A Response: !01
Sets the battery backup counter function of channels 1,
3, 4, and 5 for module 01 to be enabled and returns a
valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.24 @AABB
Note:
The command is not available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

79
2.26 @AAFA
Description:
Reads the automatic frequency mode status of each channel.
Syntax:
@AAFA[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
FA Command to read the automatic frequency mode
status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
automatic frequency mode is enabled for the
channel and 0 means that the automatic frequency
mode is disabled for the channel.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

80
Examples:
Command: @01FA Response: !013A
Reads the automatic frequency mode status for module
01 and returns a response of 3A, meaning that
automatic frequency mode for channels 1, 3, 4, and 5
are enabled and disabled for all other channels.
Related Commands:
Section 2.27 @AAFAVV
Related Topics:
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement
Note:
The command is only available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

81
2.27 @AAFAVV
Description:
Specifies the channels which automatic frequency mode is to
be enabled.
Syntax:
@AAFAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
FA Command to enable the automatic frequency mode
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
automatic frequency mode is enabled for the
channel and 0 means that the automatic frequency
mode is disabled for the channel.
Response:
Valid Command: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

82
Examples:
Command: @01FA3A Response: !01
Enables the automatic frequency mode of channels 1,
3, 4, and 5 for module 01 and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.26 @AAFA
Related Topics:
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement
Note:
The command is only available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

83
2.28 @AAFH
Description:
Reads the high frequency mode status of each channel.
Syntax:
@AAFH[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
FH Command to read the high frequency mode status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
high frequency mode is enabled for the channel and
0 means that the high frequency mode is disabled
for the channel.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

84
Examples:
Command: @01FH Response: !013A
Reads the high frequency mode status for module 01
and returns a response of 3A, meaning that battery
backup counter for channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are enabled
and disabled for all other channels.
Related Commands:
Section 2.29 @AAFHVV
Related Topics:
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement
Note:
The command is only available to the channels that are set to
type code 51, frequency measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

85
2.29 @AAFHVV
Description:
Specifies the channels which high frequency mode is enabled.
Syntax:
@AAFH[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
FH Command to enable the high frequency mode
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
high frequency mode is enabled for the channel and
0 means that the high frequency mode is disabled
for the channel.
Response:
Valid Command: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

86
Examples:
Command: @01FH3A Response: !01
Enables the high frequency mode of channels 1, 3, 4,
and 5 for module 01 and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.28 @AAFH
Related Topics:
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement
Note:
1. The command is only available to the channels that are set
to type code 51, frequency measurement.
2. It is recommended to set to high frequency mode for
frequency larger than 10 KHz.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

87
2.30 @AAFT
Description:
Reads the frequency measurement timeout setting.
Syntax:
@AAFT[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
FT Command to read the frequency measurement
timeout setting
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV Two hexadecimal digits to represent the timeout
value in tenths of a second, for example, 01 denotes
0.1 seconds and FF denotes 25.5 seconds.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

88
Examples:
Command: @01FT Response: !010A
Reads the frequency measurement timeout for module
01 and returns a response of 0A, meaning that
frequency measurement timeout value is 1 second.
Related Commands:
Section 2.31 @AAFTVV
Related Topics:
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement
Note:
1. The command is only available to the channels that are set
to type code 51, frequency measurement.
2. If there is no input pulse detected during the frequency
measurement time out, then the frequency of the channel is
set to 0 Hz.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

89
2.31 @AAFTVV
Description:
Sets the frequency measurement time out value of a module.
Syntax:
@AAFTVV[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
FT Command to set the frequency measurement time
out
VV Two hexadecimal digits to represent the timeout
value in tenths of a second, for example, 01 denotes
0.1 seconds and FF denotes 25.5 seconds.
Response:
Valid Command: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

90
Examples:
Command: @01FT0A Response: !01
Sets the frequency measurement timeout for module
01 to 1 second and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.30 @AAFT
Related Topics:
Section A.6 Frequency Measurement
Note:
1. The command is only available to the channels that are set
to type code 51, frequency measurement.
2. If there is no input pulse detected during the frequency
measurement time out, then the frequency of the channel is
set to 0 Hz.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

91
2.32 @AAGN
Description:
Reads the preset counter value of channel N.
Syntax:
@AAGN[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
G Command to read the preset counter value of a
channel
N Specifies the channel to be read (0 ~ 7)
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
(Data) The preset counter value in eight hexadecimal digits
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

92
Examples:
Command: @01G2 Response: !0100000000
Reads the channel 2 maximum counter value of module
01 and the module responds with 00000000.
Related Commands:
Section 2.33 @AAPN(Data)
Note:
The preset counter value is only available to the channels that
are set to up counter type (type code 50).
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

93
2.33 @AAPN(Data)
Description:
Sets the preset counter value of a channel.
Syntax:
@AAPN(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be set (00 to FF)
P Command to set the preset counter value of a
channel
N Specifies the channel to be read (0 ~ 7)
(Data) The preset counter value in eight hexadecimal digits
Response:
Valid command: !AA(Data)[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

94
Examples:
Command: @01P2F0000000 Response: !01
Sets the channel 2 preset counter value of module 01 to
0xF0000000 and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.32 @AAGN
Note:
The preset counter value is only available to the channels that
are set to up counter type (type code 50).
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

95
2.34 @AASC
Description:
Reads the stop counting on overflow status of each channel.
Syntax:
@AASC[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
SC Command to read the stop counting on overflow
status
Response:
Valid Command: !AAVV[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
stop counting on overflow is enabled for the
channel and 0 means that the stop counting on
overflow is disabled for the channel.
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

96
Examples:
Command: @01SC Response: !013A
Reads the stop counting on overflow status for module
01 and returns a response of 3A, meaning that stop
counting on overflow for channels 1, 3, 4, and 5 are
enabled and disabled for all other channels.
Related Commands:
Section 2.35 @AASCVV
Note:
The command is only available to the channels that are set to
type code 50, up counter measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

97
2.35 @AASCVV
Description:
Specifies the channels which stop counting on overflow are
enabled.
Syntax:
@AASCVV[CHKSUM](CR)
@ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
SC Command to enable the stop counting on overflow
VV A two-digit hexadecimal value, where bit 0
corresponds to channel 0, bit 1 corresponds to
channel 1, etc. When the bit is 1 it means that the
stop counting on overflow is enabled for the
channel and 0 means that the stop counting on
overflow is disabled for the channel.
Response:
Valid Command: !AA[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid Command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
There will be no response if the command syntax is incorrect,
there is a communication error, or there is no module with the
specified address.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

98
Examples:
Command: @01SC3A Response: !01
Enables the stop counting on overflow of channels 1, 3,
4, and 5 for module 01 and returns a valid response.
Related Commands:
Section 2.34 @AASC
Note:
The command is only available to the channels that are set to
type code 50, up counter measurement.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

99
2.36 ~**
Description:
Informs all modules that the host is OK.
Syntax:
~**[CHKSUM](CR)
~ Delimiter character
** Host OK command
Response:
No response.
Examples:
Command: ~** No response
Sends a “Host OK” command to all modules.
Related Commands:
Section 2.37 ~AA0, Section 2.38 ~AA1, Section 2.39 ~AA2,
Section 2.40 ~AA3EVV
Related Topics:
Section A.2 Dual Watchdog Operation
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13

100
2.37 ~AA0
Description:
Reads the host watchdog status of a module.
Syntax:
~AA0[CHKSUM](CR)
~ Delimiter character
AA Address of the module to be read (00 to FF)
0 Command to read the module status
Response:
Valid command: !AASS[CHKSUM](CR)
Invalid command: ?AA[CHKSUM](CR)
! Delimiter character for a valid command
? Delimiter character for an invalid command
AA Address of the responding module (00 to FF)
SS Two hexadecimal digits that represent the host
watchdog status, where:
Bit 7: 0 indicates that the host watchdog is disabled,
and 1 indicates that the host watchdog is enabled,
Bit 2: 1 indicates that a host watchdog timeout has
occurred, and 0 indicates that no host watchdog
timeout has occurred.
The host watchdog status is stored in EEPROM and
can only be reset by using the ~AA1 command.
M-7084 User Manual, Rev. A1.3 7PH-013-A13
 Loading...
Loading...