ICP N2A460GKA200, N2A460GKA100, N2A460AKA200, N2A448GKA200, N2A448GKA100 Owner’s Manual
...Page 1

Theseinstructionsmustbereadand understoodcompletelybeforeattemptinginstallation.
Safety Labeling and Signal Words
DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION, and
NOTE
The signal words DANGER, WARNING,
CAUTION, and NOTE are used to identify levels of
hazard seriousness. The signal word DANGER is
only used on product labels to signify an immediate
hazard. The signal words WARNING, CAUTION,
and NOTE will be used on product labels and
throughout this manual and other manuals that may
apply to the product.
DANGER - Immediate hazards which will result in
severe personal injury or death.
WARNING - Hazards or unsafe practices which
could result in severe personal injury or death.
CAUTION - Hazards or unsafe practices which
may result in minor personal injury or product or
property damage.
NOTE - Used to highlight suggestions which will
result in enhanced installation, reliability, or operation.
Signal Words in Manuals
The signal word WARNING is used throughout this
manual in the following manner:
The signal word CAUTION is used throughout this
manual in the following manner:
Signal Words on Product Labeling
Signal words are used in combination with colors
and/or pictures on product labels.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Inspect New Unit ............................... 2
Safety Considerations ........................... 2
Location ....................................... 2
Clearances ................................. 2 - 3
Unit Support ................................... 4
Refrigeration System ........................ 4 - 8
Electrical Wiring ............................ 9 - 10
Start-up Procedure ............................ 11
Refrigerant Charge ........................ 11- 12
Sequence of Operation ......................... 13
Troubleshooting ............................... 13
Maintenance .................................. 13
Comfort Alert TM Diagnostics Codes .............. 14
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, AND/OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to carefully read and follow this warning
could result in equipment malfunction, property
damage, personal injury and/or death.
Installation or repairs made by unqualified per-
sons could result in equipment malfunction, prop-
erty damage, personal injury and/or death.
The information contained in this manual is in-
tended for use by a qualified service technician fa-
miliar with safety procedures and equipped with
the proper tools and test instruments.
Installation must conform with local building
codes and with the National Electrical Code
NFPA70 current edition or Canadian Electrical
Code Part 1 CSA C.22.1.
421 01 5002 01 May 2009
Page 2

INSPECT NEW UNIT
After uncrating unit, inspect thoroughly for hidden company immediately and file a concealed damage
damage. If damage is found, notify the transportation claim.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Consult a qualified installer, service agency, or the
dealer/distributor for information and assistance. The
qualified installer must use factory authorized kits and
accessories when modifying this product. Refer to the
individual instructions packaged with the kit or accessory
when installing.
The weight of the product requires careful and proper
handling procedures when lifting or moving to avoid
personal injury. Use care to avoid contact with sharp or
pointed edges.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses, protective
clothing, and work gloves. Use a heat sinking material -
such as a wet rag - during brazing operations. Keep a fire
extinguisher available. Consult local codes and the
National Electric Code (NEC) for special requirements.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or
maintenance can void the warranty.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to turn off the main (remote) electrical dis-
connect device could result in personal injury or
death.
Before installing, modifying or servicing system,
turn OFF the main (remote) electrical disconnect
device. There may be more than one disconnect
device. Lock out and tag switch with a suitable
warning label.
LOCATION
Check local codes for regulations concerning zoning,
noise, platforms, and other issues.
Locate unit away from fresh air intakes, vents, or
bedroom windows. Noise may carry into the openings
and disturb people inside.
Locate unit in a well drained area, or support unit high
enough so that water runoff will not enter the unit.
Locate unit away from areas where heat, lint, or exhaust
fumes will be discharged onto unit (as from dryer vents).
CLEARANCES
Nominal minimum clearances are 48 inches (1.2m)
above unit for discharge air and 18 inches (457mm) on
each side of the coil for intake air. Clearance on any one
side of the coil (normally between unit and structure) may
be reduced to 6 inches (152mm). Nominal minimum
clearances are based on a solid parallel object such as a
wall or roof overhang.
The clearance may be reduced for a single object with
small surface area, such as the end of a wall, outside
corner of a wall, fence section, post, etc. As a general
rule, the minimum clearance from the unit should equal
the width of the object. For example, a 6 inch (152mm)
fence post should be a minimum of 6 inches (152mm)
from the unit.
Locate unit away from recessed or confined areas where
recirculation of discharge air may occur (refer to
CLEARANCES section of this document).
Roof-top installation is acceptable providing the roof will
support the unit and provisions are made for water
drainage and noise/vibration dampening.
NOTE: Roof mounted units exposed to wind may require
wind baffles. Consult the manufacturer for additional
information.
Do not install unit under roof overhangs unless gutters are
present. A minimum vertical clearance of 48 inches
(1.2m) is required to the overhang.
Inside corner locations on single story structures require
evaluation. Large overhanging soffits may cause air
recirculation in a corner area even though recommended
minimum clearances are maintained. As a guide, locate
the unit far enough out so that half of the discharge grille is
out from under the soffit.
When placing two or more units side-by-side, provide a
minimum of 18 inches (457mm) between units.
Provide minimum service clearance of 24 inches
(610mm) from control box corner and side service panel.
Refer to Figure 1.
2 421 01 5002 01
Page 3
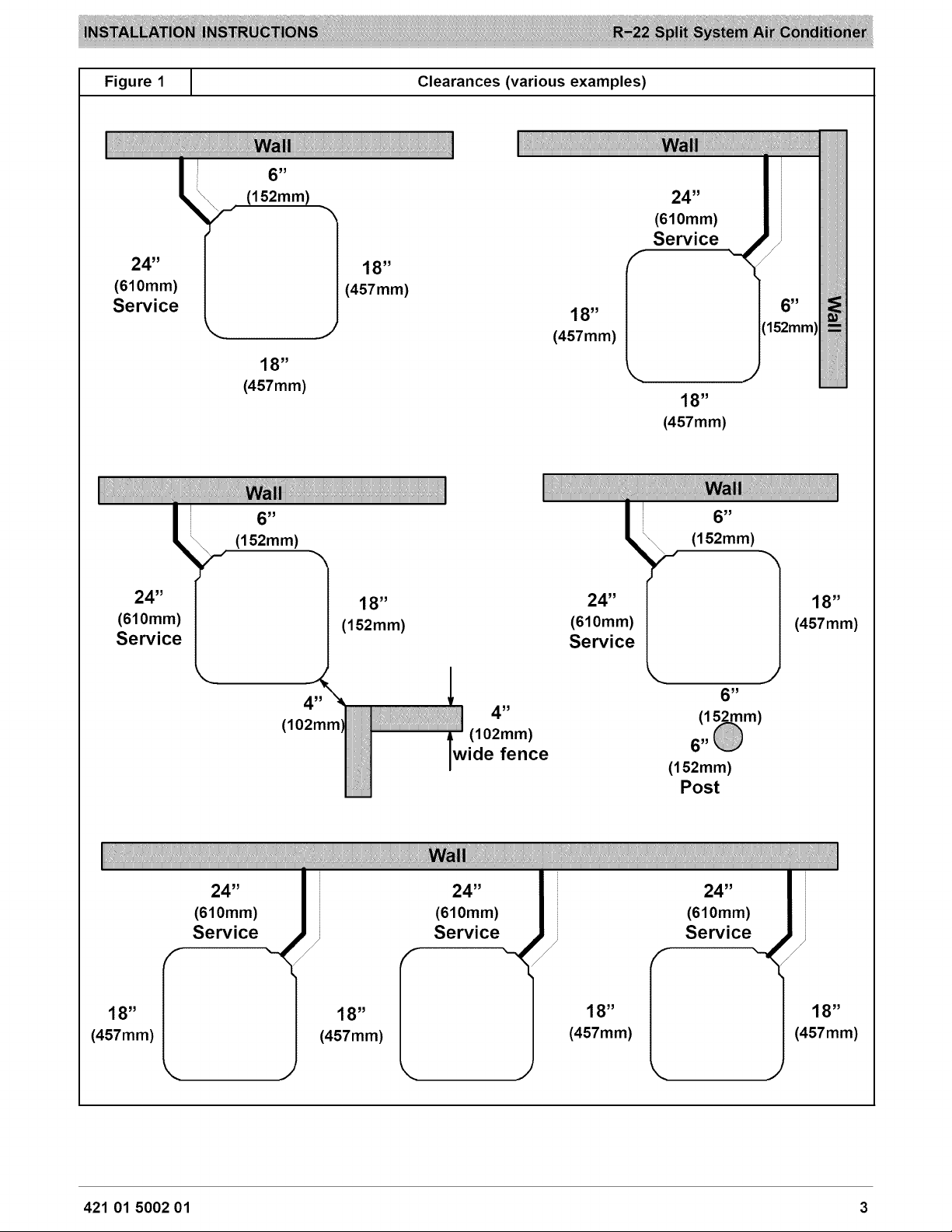
Figure1 _ Clearances (various examples)
,,
(152mm)
24"
(610mm)
Service
18"
(457mm)
18"
(457mm)
18"
(457mm)
24"
(610mm)
Service
18"
(457mm)
24"
(610mm) I
Service !\"
(610mm)
Service
24"
,,
(152mm)
4"
(102mm}
18"
(152mm)
(102mm)
wide fence
(610mm)
Service
24" Jr
,,
(152mm)
24"
(610mm)
18"
(457mm)
Service
\
,,
(610mm)
Service
f
24" J
18"
(457mm)
421 01 5002 01 3
I
18"
(457mm)
18"
(457mm)
(457mm)
18"
Page 4

UNIT SUPPORT
NOTE: Unit must be level + 2 degrees {% inch rise or fall
per foot of run (10mm rise or fall per 305 mm of run) } or
compressor may not function properly.
A. GROUND LEVEL INSTALLATION
The unit must be level and supported above grade by
beams, platform, or a pad. Platform or pad can be of open
or solid construction but should be of permanent
materials such as concrete, bricks, blocks, steel, or
pressure- treated timbers approved for ground contact.
Soil conditions must be considered so that the platform or
pad does not shift or settle and leave the unit partially
supported. Minimum pad dimensions are shown in Figure
2.
If beams or an open platform are used for support, it is
recommended that the soil be treated or area be graveled
to reduce the growth of grasses and weeds.
To minimize vibration or noise transmission, it is
recommended that supports not be in contact with the
building structure. However, slabs on grade constructions
with an extended pad are normally acceptable.
B. ROOF TOP INSTALLATION
This type of installation is not recommended on wood
frame structures where low noise levels are required.
Supporting structure or platform for the unit must be level.
If installation is on a fiat roof, locate unit minimum 6 inches
(152mm) above roof level.
Place the unit over one or more load bearing walls. If there
are several units, mount them on platforms that are
self-supporting and span several load bearing walls.
These suggestions are to minimize noise and vibration
transmission through the structure. If the structure is a
home or apartment, avoid locating the unit over
bedrooms or study.
NOTE: When unit is to be installed on a bonded
guaranteed roof, a release must be obtained from the
building owner to free the installer from all liabilities.
C. FASTENING UNIT DOWN
If conditions or local codes require the unit be attached in
place, remove the knockouts in the base pan and install
tie down bolts through the holes (refer to Figure 2).
Contact local distributor for hurricane hold-down details
and the P.E. (Professional Engineer) certification, when
required.
PROPERTY DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in proper-
ty damage.
Inadequate unit support may cause excessive
vibration, noise, and/or stress on the refrigerant
lines, leading to refrigerant line failure.
Figure 2 J Tie Down Knockouts
3/8"(10mm) dia. Tie Down Knockouts
In Base Pan (2 places)
A
Base Pan Width
View From Top I
Base
Pan
Depth
oO
Inches (mm)
Base Pan
Width x Depth
23 x 23
(584 x 584)
251¼6 x 251¼6
(652 x 652)
31Y8 x 31Y8
(791 x 791)
3415A6x 3415A6
(887 x 887)
Tie Down
Knockouts
A B C
73A 47A6 18
(197) (113) (457)
91A6 47A6 21¼
(230) (113) (540)
91A6 6Y2 245/8
(230) (165) (625)
91A6 6Y2 287A6
(230) (165) (722)
Minimum
MountingPad
Dimensions
23 x 23
(584 x 584)
26 x 26
(660 x 660)
31Y2x 31Y2
(800 x 800)
35 x 35
(889 x 889)
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
A. COMPONENT MATCHES
Check to see that the proper system components are in
place, especially the indoor coil.
R-22 outdoor units can only be used with R-22 specific
indoor coils. If there is a refrigerant mis-match, consult
the indoor coil manufacturer to determine if a refrigerant
conversion kit is available for the indoor coil.
This outdoor unit is designed for use only with indoor coils
that utilize a TXV refrigerant metering device. If any other
type of metering device is installed on the indoor coil,
consult the indoor coil manufacturer to determine ifa TXV
conversion kit is available.
4 421 01 5002 01
PRODUCT DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in product
damage.
Indoor coil and outdoor unit must be listed as a
certified combination (match) in the ARI Unitary
Directory of Certified Products.
When installing a TXV on an indoor coil, follow the
instructions provided with the new TXV.
Page 5
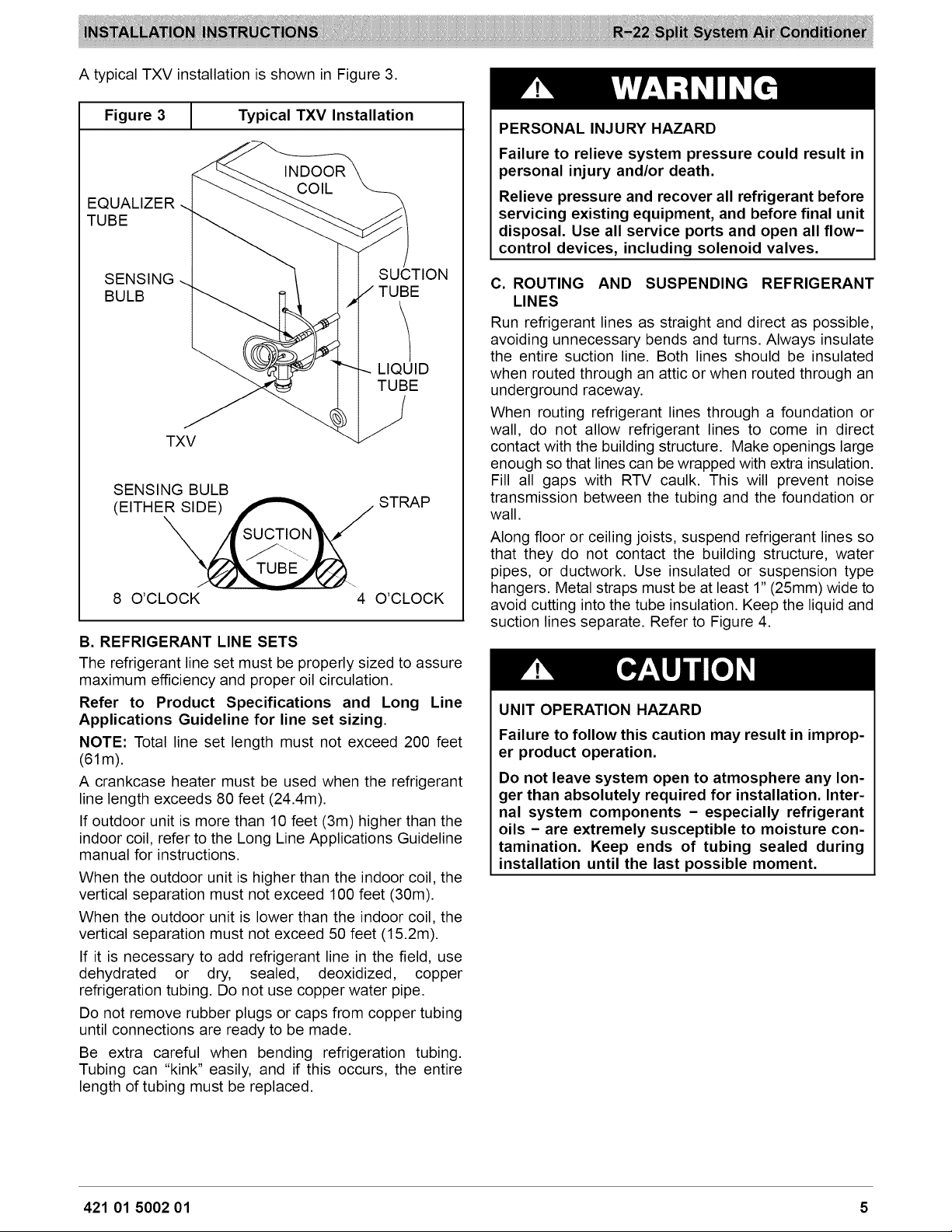
A typical TXV installation is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 | Typical TXV Installation
.L
EQUALIZER
TUBE
SENSING
SUCTION
BULB
LIQUID
TUBE
TXV
SENSING BULB
STRAP
(EITHE_
8 O'CLOCK
4 O'CLOCK
B. REFRIGERANT LINE SETS
The refrigerant line set must be properly sized to assure
maximum efficiency and proper oil circulation.
Refer to Product Specifications and Long Line
Applications Guideline for line set sizing.
NOTE: Total line set length must not exceed 200 feet
(61m).
A crankcase heater must be used when the refrigerant
line length exceeds 80 feet (24.4m).
If outdoor unit is more than 10 feet (3m) higher than the
indoor coil, refer to the Long Line Applications Guideline
manual for instructions.
When the outdoor unit is higher than the indoor coil, the
vertical separation must not exceed 100 feet (30m).
When the outdoor unit is lower than the indoor coil, the
vertical separation must not exceed 50 feet (15.2m).
If it is necessary to add refrigerant line in the field, use
dehydrated or dry, sealed, deoxidized, copper
refrigeration tubing. Do not use copper water pipe.
Do not remove rubber plugs or caps from copper tubing
until connections are ready to be made.
Be extra careful when bending refrigeration tubing.
Tubing can "kink" easily, and if this occurs, the entire
length of tubing must be replaced.
PERSONALINJURY HAZARD
Failure to relieve system pressure could result in
personal injury and/or death.
Relieve pressure and recover all refrigerant before
servicing existing equipment, and before final unit
disposal. Use all service ports and open all flow-
control devices, including solenoid valves.
C. ROUTING AND SUSPENDING REFRIGERANT
LINES
Run refrigerant lines as straight and direct as possible,
avoiding unnecessary bends and turns. Always insulate
the entire suction line. Both lines should be insulated
when routed through an attic or when routed through an
underground raceway.
When routing refrigerant lines through a foundation or
wall, do not allow refrigerant lines to come in direct
contact with the building structure. Make openings large
enough so that lines can be wrapped with extra insulation.
Fill all gaps with RTV caulk. This will prevent noise
transmission between the tubing and the foundation or
wall.
Along floor or ceiling joists, suspend refrigerant lines so
that they do not contact the building structure, water
pipes, or ductwork. Use insulated or suspension type
hangers. Metal straps must be at least 1" (25mm) wide to
avoid cutting into the tube insulation. Keep the liquid and
suction lines separate. Refer to Figure 4.
UNIT OPERATION HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in improp-
er product operation.
Do not leave system open to atmosphere any lon-
ger than absolutely required for installation. Inter-
nal system components - especially refrigerant
oils - are extremely susceptible to moisture con-
tamination. Keep ends of tubing sealed during
installation until the last possible moment.
421 01 5002 01 5
Page 6

Figure4
Routing and Suspending Refrigerant Lines
O TOC w
I_"_ __r LIQUID TUBE
S CTO,
THROUGH THE WALL
UNIT OPERATION HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in improp-
er product operation.
Do not bury more than 36" (lm) of line set under-
ground. Refrigerant may migrate to cooler buried
section during extended periods of unit shut-
down, causing refrigerant slugging and possible
compressor damage at start-up.
If ANY section of the line set is buried under-
ground, provide a minimum 6"(152mm) vertical
rise at the service valve.
HANGER STRAP
(AROUND SUCTION X.. --
TUBE ONLY) _.J
r JOIST
S;'cTA:'oO2T
h
1" (25mm) MIN -_D,-I I_
SUSPENSION
Liquid Line Filter-Drier
Figure 5 Installed at Indoor Coil
LIQUID TUBE
D. OUTDOOR UNIT HIGHER THAN INDOOR UNIT
Proper oil return to the compressor should be maintained
with suction gas velocity. If velocities drop below 1500
fpm (feet per minute), oil return will be decreased. To
maintain suction gas velocity, do not upsize vertical
suction risers.
E. LIQUID LINE FILTER-DRIER
Outdoor units are shipped with an appropriate filter-drier
for installation in the liquid line. Leave the plugs in the tube
ends until the filter-drier is installed. The optimal location
for the filter-drier is close to the indoor coil. Install the
filter-drier with the arrow pointing towards the indoor coil.
Refer to Figure 5.
Filter-Drier
(arrow points towards indoor coil)
38-11-84
6 421 01 5002 01
Page 7

F, SERVICEVALVES
Service valves are closed and tube stubs are plugged
from the factory. Outdoor units are shipped with a
refrigerant charge sealed in the unit. Leave the service
valves closed until all other refrigerant system work is
complete or the charge will be lost. Leave the plugs in
place until line set tubing is ready to be inserted.
Service valve bodies are brass and tube stubs are copper.
Figure 6 | Service Valve
,,L
H. EVACUATING LINE SET AND INDOOR COIL
The unit is shipped with a factory refrigerant charge. The
liquid line and suction line service valves have been
closed after final testing at the factory. Do not disturb
these valves until the line set and indoor coil have been
evacuated and leak checked, or the charge in the unit
may be lost.
NOTE: Do not use any portion of the factory charge for
purging or leak testing. The factory charge is for filling the
system only after a complete evacuation and leak check
has been performed.
VALVE CORE X
G. BRAZING CONNECTIONS
NOTE: Remove valve core from schrader port on both
Service Valves BEFORE brazing. This helps prevent
overheating and damage to valve seals (refer to Figure 6).
Replace valve core when brazing is completed.
FIRE HAZARD
Failure to remove refrigerant and oil charge before
brazing could result in personal injury, death, and/
or property damage.
Refrigerant and oil mixture could ignite and burn
as it escapes and contacts brazing torch. Make
sure the refrigerant charge is properly removed
from both the high and low sides of the system be-
fore brazing any component or lines.
Clean line set tube ends with emery cloth or steel brush.
Remove any grit or debris.
Insert line set tube ends into service valve tube stubs.
Apply heat absorbing paste or heat sink product between
service valve and joint. Wrap service valves with a heat
sinking material such as a wet cloth.
Braze joints using a SiI-Fos or Phos-copper alloy.
PRODUCT DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in product
damage.
Braze with SiI-Fos or Phos-copper alloy on cop-
per-to-copper joints and wrap a wet cloth around
rear of fitting to prevent damage to TXV.
PRODUCT DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in product
damage.
Never use the outdoor unit compressor as a vacu-
um pump. Doing so may damage the compressor.
Line set and indoor coil should be evacuated using the
recommended deep vacuum method of 500 microns. If
deep vacuum equipment is not available, the alternate
triple evacuation method may be used by following the
specified procedure.
If vacuum must be interrupted during the evacuation
procedure, always break vacuum with dry nitrogen.
Deep Vacuum Method
The deep vacuum method requires a vacuum pump
capable of pulling a vacuum to 500 microns and a vacuum
gauge capable of accurately measuring this vacuum
level. The deep vacuum method is the most positive way
of assuring a system is free of air and water.
Watch the vacuum gauge as the system is pulling down.
The response of the gauge is an indicator of the condition
of the system (refer to Figure 7).
With no leaks in the system, allow the vacuum pump to
run for 30 minutes minimum at the deep vacuum level.
Figure 7 Deep Vacuum Gauge Response
5000
4500
4000
3500
3000
2500
o
2000
1500
1000
500
and System Conditions
LEAKIN
SYSTEM
VACUUM TIGHT
TOO WET
TIGHT
DRY SYSTEM
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
MINUTES
421 01 5002 01 7
Page 8

TripleEvacuationMethod
The triple evacuation method should only be used when
system does not contain any water in liquid form and
vacuum pump is only capable of pulling down to 28 inches
of mercury (711mm Hg). Refer to Fig.8 and proceed as
follows:
1. Pull system down to 28 inches of mercury
(711mm Hg) and allow pump to continue operating
for an additional 15 minutes.
,
Close manifold valves or valve at vacuum pump
and shut off vacuum pump.
3.
Connect a nitrogen cylinder and regulator to
system and fill with nitrogen until system pressure
is 2 psig.
,
Close nitrogen valve and allow system to stand for
1 hour. During this time, dry nitrogen will diffuse
throughout the system absorbing moisture.
,
Repeat this procedure as indicated in Figure 8.
6.
After the final evacuate sequence, confirm there
are no leaks in the system. If a leak is found, repeat
the entire process after repair is made.
Figure 8 _ Triple Evacuation Sequence
NOTE: Open the Suction service valve first. If the Liquid
service valve is opened first, oil from the compressor may
be drawn into the indoor coil TXV, restricting refrigerant
flow and affecting operation of the system.
Remove Suction service valve cap and insert a hex
wrench into the valve stem. Hold the valve body steady
with an end-wrench and back out the stem by turning the
hex wrench counterclockwise. Turn the stem until it just
contacts the rolled lip of the valve body.
After the refrigerant charge has bled into the system,
open the Liquid service valve.
NOTE: These are not back-seating valves. It is not
necessary to force the stem tightly against the rolled lip.
The service valve cap is a primary seal for the valve and
must be properly tightened to prevent leaks. Make sure
cap is clean and apply refrigerant oil to threads and
sealing surface on inside of cap.
Tighten cap finger tight and then tighten additional Y6of a
turn (1 wrench fiat) to properly seat the sealing surfaces.
J. GAUGE PORTS
Check for leaks at the schrader ports and tighten valve
cores if necessary. Install plastic caps finger tight.
IEvAcuATE I
[BREAKVACUUM WITH DRY NITROGEN ]
IEVAc UATE I
[BREAKWOUUMWITHDRYN,TROGEN1
IEVAc UATE I
CHECK FOR TIGHT, DRY SYSTEM l
(IF IT HOLDS DEEPVACUUM)
CHARGE SYSTEM ]
I. OPENING SERVICE VALVES
Outdoor units are shipped with a refrigerant charge
sealed in the unit. Opening the service valves releases
this charge into the system.
1
8 421 01 5002 01
Page 9

ELECTRICAL WIRING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to turn off the main (remote) electrical dis-
connect device could result in personal injury or
death.
Before installing, modifying or servicing system,
turn OFF the main (remote) electrical disconnect
device. There may be more than one disconnect
device.
The supply voltage must be 208/230 volts (197 volt
minimum to 253 volts maximum) 60 Hz single phase.
Outdoor units are approved for use with copper
conductors only. Do not use aluminum wire.
Refer to unit rating plate for minimum circuit ampacity and
circuit protection requirements.
Grounding
Permanently ground unit in accordance with the National
Electrical Code and local codes or ordinances. Use a
copper conductor of the correct size from the grounding
lug in control box to a grounded connection in the service
panel or a properly driven and electrically grounded
ground rod.
Wiring Connections
Make all outdoor electrical supply (Line Voltage)
connections with raintight conduit and fittings. Most
codes require a disconnect switch outdoors within sight of
the unit. Consult local codes for special requirements.
Route electrical supply (Line Voltage) wiring through
knockout hole in bottom of Control Box. Connect wires to
Contactor and Ground Lug according to Wiring Diagram
on unit. Also refer to Figure 9.
Route thermostat wiring through rubber grommet in
bottom of Control Box. Low voltage lead wires are
provided in the control box for connection to thermostat
wires (use wire nuts). Refer to Wiring Diagram on unit and
Figure 10 for low voltage wiring examples.
NOTE: Use No. 18 AWG (American Wire Gage)
color-coded, insulated (35 °C minimum) wire. If
thermostat is located more than 100 feet (31 m) from unit
as measured along the control voltage wires, use No. 16
AWG color-coded wires to avoid excessive voltage drop.
NOTE: Some models are factory equipped with Comfort
Alert TM Diagnostics device. If Comfort Alert is used as a
field installed option, then a hot bundle must be run for
proper connection.
Figure 9
1
Electrical Supply (Line Voltage) Connections
DISCONNECT
PER NEC AND/OR
LOCAL CODES
1
L1
FIELD POWER
WIRING L2
FIELD GROUND
CONTACTOR
Ij2_or 13 <_)
-®
WIRING j
GROUND
LUG
421 01 5002 01 9
Page 10

Figure10
1
Typical Thermostat Connections
THERMOSTAT FURNACE AIR CONDITIONER
24 VAC HOT
24 VAC COM
HEAT STAGE 1
COOL STAGE 1
INDOOR FAN
THERMOSTAT
24 VAC HOT D
24 VAC COM D
HEAT STAGE 1
COOL STAGE 1
INDOOR FAN D
THERMOSTAT
D _ _
E_- --
--I-q
- -D -
-D
-D
FAN COIL
--F-I
- -D -
--[_-
-D
FAN COIL
...... i
..... J
AIR CONDITIONER
...... i
..... 4
i
A
(c)
v
i
i
v
I
AC with Comfort Alert
24 VAC HOT D
24 VAC COM D
HEAT STAGE 1
COOL STAGE 1
INDOOR FAN D "
.... D
.... D _
..... D
.... D
.... D
10 421 01 5002 01
Page 11

START-UP PROCEDURE
1. Set indoor thermostat selector switch to OFF.
2. Turn ON all electrical disconnect devices.
3. If unit has a crankcase heater, energize the heater
and wait 24 hours before proceeding.
REFRIGERANT CHARGE
Outdoor units are shipped with a refrigerant charge to
match a specific indoor coil and 15 feet (4.6m) of
refrigerant line. If shorter or longer refrigerant lines or a
different indoor coil are used, the charge will have to be
adjusted.
For different line lengths, add or remove charge based on
0.6 ounces (17g) charge per foot (305mm) of difference.
For example, a 25 foot (7.6m) line set is 10 feet (3m)
longer than the specified 15feet (4.6m). Add 0.6 ounces
(17g) charge for each of the extra 10 feet (3m):
10 x 0.6 = 6.0 ounces additional charge
(3m x 17g = 51g additional charge)
This outdoor unit is designed for use only with indoor coils
that utilize a TXV refrigerant metering device. With an
indoor TXV, use the subcooling method to make final
charge adjustments:
NOTE: Only use subcooling charging method when
• outdoor ambient temperature is between 70°F and 100°F
(21°C and 38°C)
• indoor temperature is between 70 ° and 80°F
(21°C and 27°C)
• line set is less that 80 feet (24.4m).
1. Operate unit a minimum of 15 minutes before
checking charge.
NOTE: If outdoor unit has a 2-speed fan motor,
motor will operate in low speed when outdoor
ambient temperature is below 82°F (28°C). Pull
one of the yellow low voltage wires off the fan
control and the unit will default to high speed fan for
servicing. Reconnect wire after servicing.
2. Measure liquid service valve pressure by attaching
an accurate gauge to service port.
3. Measure liquid line temperature by attaching an
accurate thermistor type sensor or electronic
thermometer to liquid line near outdoor coil.
4. Refer to unit rating plate for required subcooling
temperature.
5. Refer to Figure 11. Find the required liquid line
temperature where the rating plate subcooling
temperature intersects measured liquid service
valve pressure.
6. If the measured liquid line temperature is higher
than the chart number, add refrigerant to lower the
measured temperature.
4. Set indoor thermostat at desired temperature. Be
sure setpoint is below indoor ambient temperature
or thermostat will not call for cooling.
5. Set indoor thermostat selector switch to COOL.
Operate unit for minimum 15 minutes, then check
system refrigerant charge.
NOTE: When adding refrigerant, charge in liquid
form, using a flow restricting device, into the
suction port.
If the measured liquid line temperature is lower
than the chart number, reclaim refrigerant to raise
the measured temperature.
Tolerance is + 3°F (+1.7°C).
421 01 5002 01 11
Page 12

Figure11
Measured Liquid
Pressure (psig)
163
171
179
187
196
205
214
223
233
243
253
264
274
285
297
309
Rating Plate (required) Subcooling Temperature °F (oC)
oF oF oF oF
5 10 15 20
R-22 Required Liquid Line Temperature °F (°C)
83
86
89
92
95
98
101
104
107
110
113
116
119
122
125
128
iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii_;_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_i_ii_i_!i!i!
78
81
84
87
9O
93
96
99
102
105
108
111
114
117
120
123
73
76
79
82
85
88
91
94
97
IO0
103
106
109
112
115
118
68
71
74
77
8O
83
86
89
92
95
98
101
104
107
110
iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!_!;!i
113
12 421 01 5002 01
Page 13

SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
With power supplied to indoor and outdoor units, When thermostat is satisfied, its contacts open,
transformer is energized, de-energizing contactor and blower relay. Compressor
On a call for cooling, the thermostat makes circuits R-Y
and motors stop.
and R-G. Circuit R-Y energizes contactor, starting NOTE: If indoor unit is equipped with a time-delay relay
outdoor fan motor and compressor. Circuit R-G circuit, the blower runs an additional length of time to
energizes indoor unit blower relay, starting indoor blower increase system efficiency.
motor.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Some models are factory equipped with the Comfort
Alert TM Diagnostics device in the control box (refer to
Figure 12). Comfort Alert provides around-the-clock
monitoring for common electrical problems, compressor
defects, and broad system faults. If trouble is detected, an
alert code is displayed with a flashing LED indicator. Alert
codes are listed in Figure 13.
The device is factory wired and requires no
modification. Low voltage lead wires are provided in the
control box for connection to thermostat wires (use wire
nuts).
The Comfort Alert device operates by monitoring the
compressor power leads and the thermostat demand
signal (Y terminal).
MAINTENANCE
Condensate Drain
During the cooling season, check monthly for free flow of
drainage and clean if necessary.
Cleanliness
These tips will help keep the air conditioner looking better
and working more efficiently:
,
Free flow of air is essential. Keep fences, shrubs,
trash cans, and other obstructions at least 18
inches (457mm) from all coil inlets.
,
Keep the coil free of grass clippings, leaves,
weeds, and other debris.
NOTE: Coil may occasionally require cleaning with
a liquid solution. The coil must be cold when
cleaning. Use an alkaline based cleaner only.
Cleaning a hot coil or using an acid based cleaner
will remove the paint from the fins and may clog the
coil.
,
Never use a weather cover over the outdoor unit
unless it is a ventilated type or made of breathable
fabric that will allow moisture to evaporate rapidly.
A cover that holds moisture in the unit will cause
more rust build-up and damage than normal
exposure to weather.
Figure 12
Comfort Alert TM Diagnostics
(some models)
Compressor Wires
Through Holes (3)
421 01 5002 01 13
Page 14

Figure13
StatusLED
Green"POWER"
Red "TRIP"
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 1
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 2
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 3
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 4
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 5
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 6
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 7
Yellow "ALERT"
Flash Code 9
• Flash Code number corresponds to a number of LED flashes, followed by a pause and then repeated•
• TRIP and ALERT LEDs flashing at same time means control circuit voltage is too low for operation•
Status LED Description
Module has power
Thermostat demand signal
Y1 is present, but the
compressor is not running 3.
Long Run Time 1
Compressor is running 2.
extremely long run cycles 3.
System Pressure Trip 1
Discharge or suction 2.
pressure out of limits or 3.
compressor overloaded 4.
Short Cycling 1
Compressor is running 2.
only briefly 3.
Locked Rotor 1
Open Circuit 1
Open Start Circuit 1
Current only in run circuit 2.
Open Run Circuit 1
Current only in start circuit 2.
Low Voltage 1. Control circuit transformer is overloaded
Control circuit < 17VAC 2. Low line voltage (contact utility if voltage at disconnect is low)
Comfort Alert
Supply voltage is present at module terminals
1. Compressor protector is open
2. Outdoor unit power disconnect is open
Compressor circuit breaker or fuse(s) is open
4.
Broken wire or connector is not making contact
5.
Low pressure switch open if present in system
6.
Compressor contactor has failed open
•Low refrigerant charge
Evaporator blower is not running
Evaporator coil is frozen
4.
Faulty metering device
5.
Condenser coil is dirty
6.
Liquid line restriction (filter drier blocked if present in system)
7.
Thermostat is malfunctioning
•High head pressure
Condenser coil poor air circulation (dirty, blocked, damaged)
Condenser fan is not running
Return air duct has substantial leakage
• If high pressure switch open, go to Flash Code 2 information
If low pressure switch open, go to Flash Code 1 information
Thermostat demand signal is intermittent
4.
Loose wiring at contactor coil
•Run capacitor has failed
2.
Low line voltage (contact utility if voltage at disconnect is low)
3.
Excessive liquid refrigerant in compressor
4.
Compressor bearings are seized
•Outdoor unit power disconnect is open
2.
Compressor circuit breaker or fuse(s) is open
3.
Compressor contactor has failed open
4.
High pressure switch is open and requires manual reset
5.
Open circuit in compressor supply wiring or connections
6.
Unusually long compressor protector reset time due to
extreme ambient temperature
7.
Compressor windings are damaged
•Run capacitor has failed
Open circuit in compressor start wiring or connections
3.
Compressor start winding is damaged
•Open circuit in compressor run wiring or connections
Compressor run winding is damaged
Diagnostics (some models)
Status LED Troubleshooting Information
International Comfort Products, LLC
14 Lewisburg, TN 37091 USA 421 01 5002 01
 Loading...
Loading...