Page 1

VHF TRANSCEIVER
i2200H
SERVICE
MANUAL
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 2

MODEL VERSION SYMBOL
EUR
TPE
KOR
EXP
EXP-1
INTRODUCTION
This service manual describes the latest service information
for the IC-2200H VHF TRANSCEIVER at the time of publication.
DANGER
NEVER connect the transceiver to an AC outlet or to a DC
power supply that uses more than 16 V. This will ruin the
transceiver.
DO NOT expose the transceiver to rain, snow or any liquids.
DO NOTreverse the polarities of the power supply when con-
necting the transceiver.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm (100 mW)
to the antenna connector. This could damage the transceiver’s front end.
ORDERING PARTS
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component par t number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
1130008350 S.IC LV2105V IC-2200H MAIN UNIT 5 pieces
8810009610 Screw
FH M2.6×6 ZK
IC-2200H Cover 10 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
REPAIR NOTES
1. Make sure a problem is internal before disassembling the
transceiver.
2. DO NOT open the transceiver until the transceiver is
disconnected from its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn
them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An insu-
lated tuning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the trans-
ceiver is defective.
6. DO NOT transmit power into a signal generator or a
sweep generator.
7.
ALWAYS connect a 40 dB to 50 dB attenuator between
the transceiver and a deviation meter or spectrum analyzer when using such test equipment.
8.
READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly
before connecting equipment to the transceiver.
To upgrade quality, any electrical or mechanical par ts and
internal circuits are subject to change without notice or
obligation.
Europe
EUR-1
USA
Taiwan
U.S.A.
Korea
Export
Europe-1
Export-1
IC-2200H
Icom, Icom Inc. and are registered trademarks of Icom Incorporated (Japan) in the United States, the United Kingdom,
Germany, France, Spain, Russia and/or other countries.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
2 - 1 IC-2200H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 - 1
2 - 2 HM-133V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 - 2
SECTION 3 OPTIONAL UNIT INSTALLATION
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISSASEMBLY
7 - 1 IC-2200H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 - 1
7 - 2 HM-133V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 - 1
SECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
9 - 1 LOGIC UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 - 1
9 - 2 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 - 3
9 - 3 HM-133V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 - 5
9 - 4 HM-118TN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 - 7
SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAMS
10 - 1 IC-2200H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 - 1
10 - 2 HM-133V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 - 2
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAMS
11 - 1 LOGIC UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 - 1
11 - 2 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 - 2
11 - 3 HM-133V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11 - 3
SECTION 12 HM-118/N (OPTIONAL UNIT)
12 - 1 INSIDE VIEW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12 - 1
12 - 2 BOARD LAYOUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12 - 1
12 - 3 MECHANICAL PARTS LIST AND DISSASEMBLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12 - 2
SECTION 13 UT-108 (OPTIONAL UNIT)
13 - 1 BOARD LAYOUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13 - 1
SECTION 14 UT-115 (OPTIONAL UNIT)
14 - 1 BOARD LAYOUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14 - 1
14 - 2 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14 - 2
14 - 3 BLOCK DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14 - 2
14 - 4 VOLTAGE DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14 - 3
Page 4
1 - 1
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
M GENERAL
• Frequency range :
*1Specifications guaranteed 144.000 – 146.000 MHz only
*
2
Specifications guaranteed 144.000 – 148.000 MHz only
• Mode : FM, AM (Receive only)
• Number of memory channel : 206 (include in 6 band edges memory and 1 call channel)
• Usable temperature range : –10˚C to +60˚C; +14˚F to +140˚F
• Scan type : Full, Program, Priority, Memory channel, Bank, Skip and Tone scans
• Frequency resolution : 5, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, 25, 30 and 50 kHz
• Frequency stability : ±10 ppm (–10˚C to +60˚C; +14˚F to +140˚F)
• Power supply requirement : 13.8 V DC ±15 % (negative ground)
• Current drain (at 13.8 V DC) : Receive Standby (squelched) 0.8 A
Max. audio 1.0 A
Transmit at 65 W or 50 W 15.0 A (except [TPE])
at 25 W 9.0 A
at 24 W 10.0 A ([TPE] only)
at 10 W 6 A (except [TPE])
at 5 W 5 A
• Antenna connector : SO-239 (50 Ω)
• Dimensions : 140(W)×40(H)×146(D) mm;
(projections not included) 5
1
⁄2(W)×19⁄16(H)×53⁄4(D) inch
• Weight : Approx. 1.25 kg; 2 lb 12 oz
M TRANSMITTER
• Output power :
• Modulation system : Variable reactance frequency
• Maximum frequency deviation : ±5.0/±2.5* kHz *except [EXP-1]
• Spurious emissions : Less than –60 dBc
• Microphone connector : 8-pin modular (600 Ω)
M RECEIVER
• Receive system : Double-conversion superheterodyne
• Intermediate frequency : 1st 21.7 MHz
2nd 450 kHz
• Sensitivity (at 12 dB SINAD) : Less than 0.18 µV
• Squelch sensitivity (threshold) : Less than 0.13 µV
• Selectivity : (Wide) More than ±6 kHz at 6 dB, More than ±14 kHz at 60 dB
(Narrow)* More than ±3 kHz at 6 dB, More than ±9 kHz at 55 dB
*except [EXP-1]
• Spurious and image rejection : More than 60 dB
• Audio output power
(at 13.8 V) : More than 2.4 W at 10% distortion with an 8Ω load
• External speaker connector : 2-conductor 3.5(d) mm (
1
⁄8")/8Ω
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
High Middle-high Middle-low Low
65 W 25 W 10 W 5 W
50 W 25 W 10 W 5 W
24 W 10 W – 5 W
Version
except
[TPE], [KOR
]
[KOR]
[TPE]
Receive (MHz) Transmit (MHz)
118.000 – 174.000*
1
144.000 – 146.000
118.000 – 174.000*
2
144.000 – 148.000
118.000 – 174.000*
2
136.000 – 174.000*
2
144.000 – 146.000 144.000 – 146.000
Version
[EUR]
[USA]
[EXP], [EXP-1]
[EUR-1], [TPE],
[KOR]
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 5

1 - 2
• UT-115 SPECIFICATIONS
M GENERAL
• Usable temperature range : –10˚C to +60˚C; +14˚F to +140˚F
• Power supply requirement : 5.0 V DC
(4.5 V–8.5 V for AMBE IC VCC line)
• AF input level : 1 V
p-p typical
• Modulation output level : 350 mV
p-p typical
• Demodulation input level : 500 mV
p-p typical
• AF output level : 750 mV
p-p typical
• CODEC type : AMBE
• Transfer speed : 4.8 kbps
• Control signal input voltage : 3.0 V–5.0 V for High
0 V for Low
• Control signal output voltage : Open collector for High
0 V for Low
• Current drain (at 5.0 V DC) : 55 mA typical
• Dimentions : 30(W)×38(D) mm;
(projections not included) 1
3
⁄16(W)×11⁄2(D) inch
• Weight : Approx. 6 g;
7
⁄32 oz
(accessoreis not included)
• Connector : AXN430C330
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 6
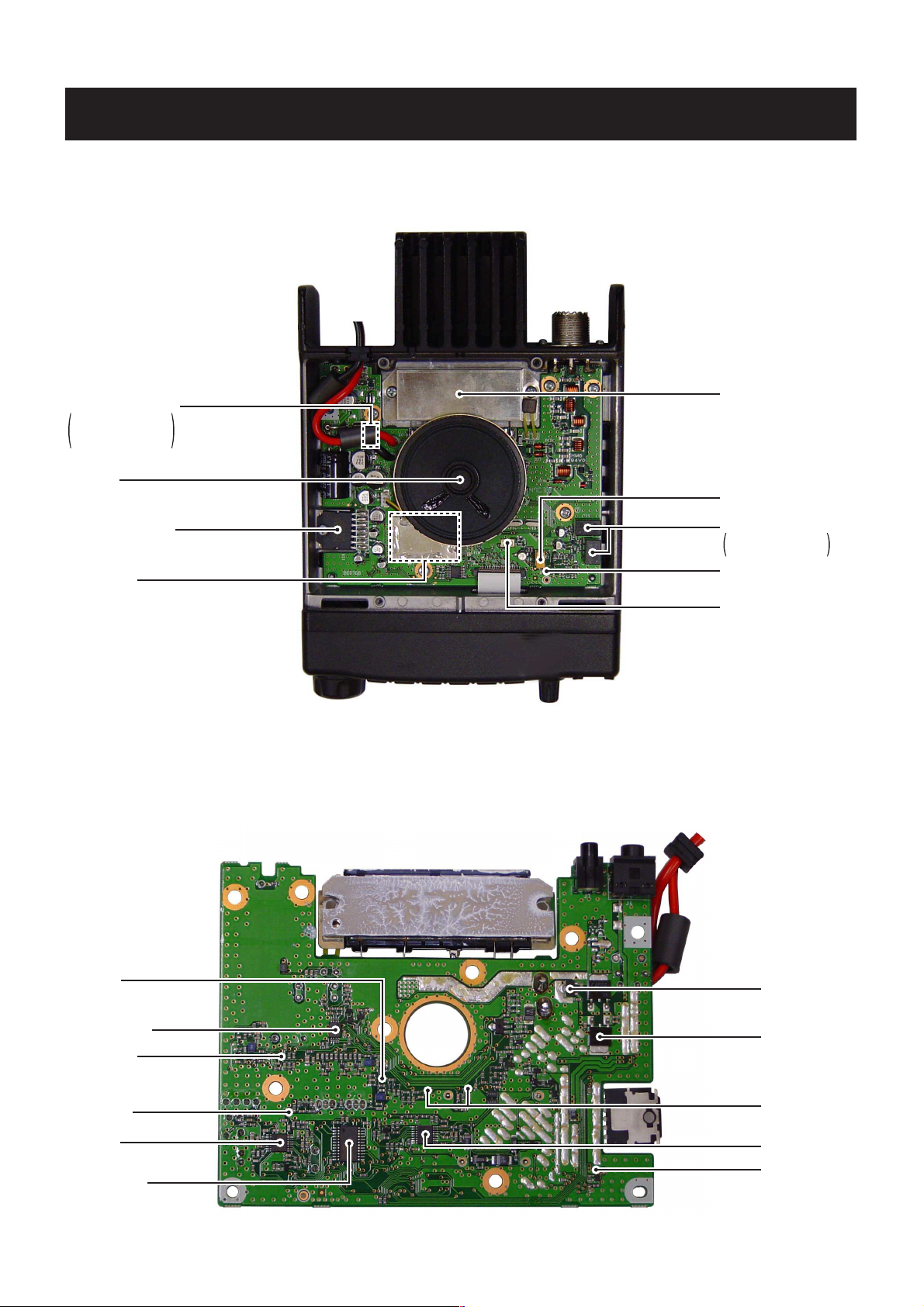
2 - 1
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEWS
2-1 IC-2200H
• MAIN UNIT (TOP VIEW)
Power module
(IC10: S-AV36)
Discriminator
(X2: CDB450C24)
AGC
(Q38: XP6501)
Reference oscillator
(X1: CR-779 21.25MHz)
Power switch circuit
Q28*: 2SC4684
Q30: DTA143TUA
Q31: DTC143ZU
Speaker
AF power amplifier
(IC9: TA7252AP)
VCO circuit
*Located under side of the point
IF filter
FI1: CFWS450F
FI2: CFWS450HT
Power module
(IC10: S-AV36)
Discriminator
(X2: CDB450C24)
AGC
(Q38: XP6501)
Reference oscillator
(X1: CR-779 21.25MHz)
Power switch circuit
Q28*: 2SC4684
Q30: DTA143TUA
Q31: DTC143ZU
Speaker
AF power amplifier
(IC9: TA7252AP)
VCO circuit
*Located under side of the point
2nd IF filter
FI1: CFWS450F
FI2: CFWS450HT
• MAIN UNIT (BOTTOM VIEW)
APC controller
(IC6: NJM3404AV)
C5V regulator
(IC8: TA78L05F)
+8V regulator
(IC7: TA7808F)
TX/RX switch
(D6, D7: MA77)
PLL IC
(IC1: LV2105V)
Enphasis switch
(Q41: 2SC4617)
RF amplifier
(Q27: 3SK299)
Mixer
(Q19: 3SK299)
IF amplifier
(Q16: 2SC4406)
IF detector
(IC4: TA31136FN)
D/A converter
(IC5: M62363FP)
APC controller
(IC6: NJM3404AV)
C5V regulator
(IC8: TA78L05F)
+8V regulator
(IC7: TA7808F)
TX/RX switch
(D6, D7: MA77)
PLL IC
(IC1: LV2105V)
Enphasis switch
(Q41: 2SC4617)
RF amplifier
(Q27: 3SK299)
1st Mixer
(Q19: 3SK299)
IF amplifier
(Q16: 2SC4406)
FM IF IC
(IC4: TA31136FN)
D/A converter
(IC5: M62363FP)
Page 7
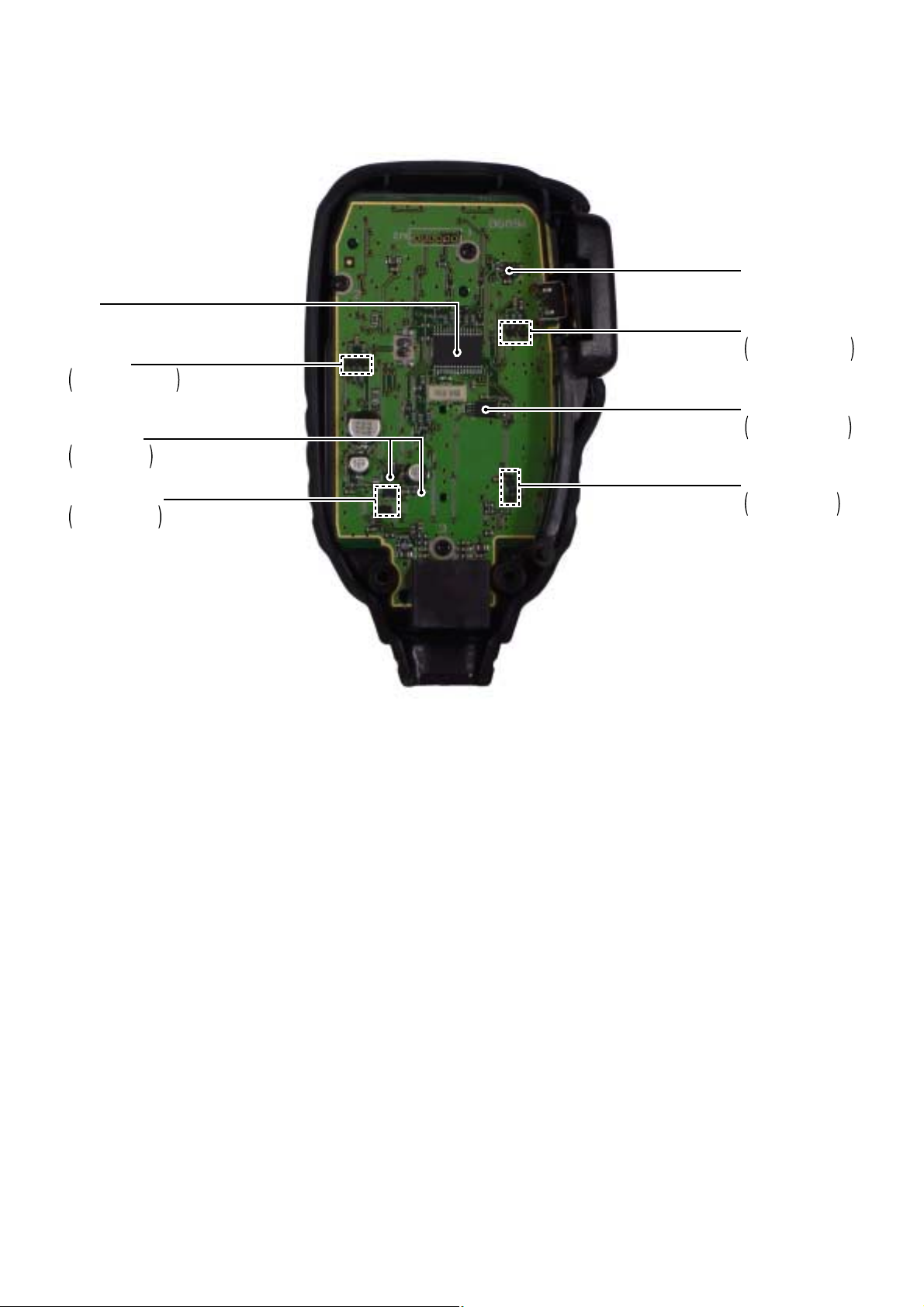
2-2 HM-133V
2 - 2
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
CPU
CPU
(IC1: µPD789071)
(IC1: µPD789071)
LED driver
LED driver
Q6, Q7: 2SA1586
Q6, Q7: 2SA1586
DS10*: LT1EP53A
DS10*: LT1EP53A
5V regulator
5V regulator
Q1: 2SC2712
Q1: 2SC2712
D1: MA8056
D1: MA8056
Regulator switch
Regulator switch
Q8: 2SC2712
Q8: 2SC2712
Q9: DTB113ZK
Q9: DTB113ZK
Reset IC
Reset IC
(IC3: BD5245G)
(IC3: BD5245G)
LED driver
LED driver
Q4, Q5: 2SA1586
Q4, Q5: 2SA1586
DS11*: LT1EP53A
DS11*: LT1EP53A
EE-PROM
EE-PROM
(IC6: BR24L02FV)
IC6: BR24L02FV
[MAIN-A] unit only
Data buffer circuit
Data buffer circuit
Q2: DTC114EU
Q2: DTC114EU
Q3: DTA114EU
Q3: DTA114EU
*Located under side of the point
Page 8
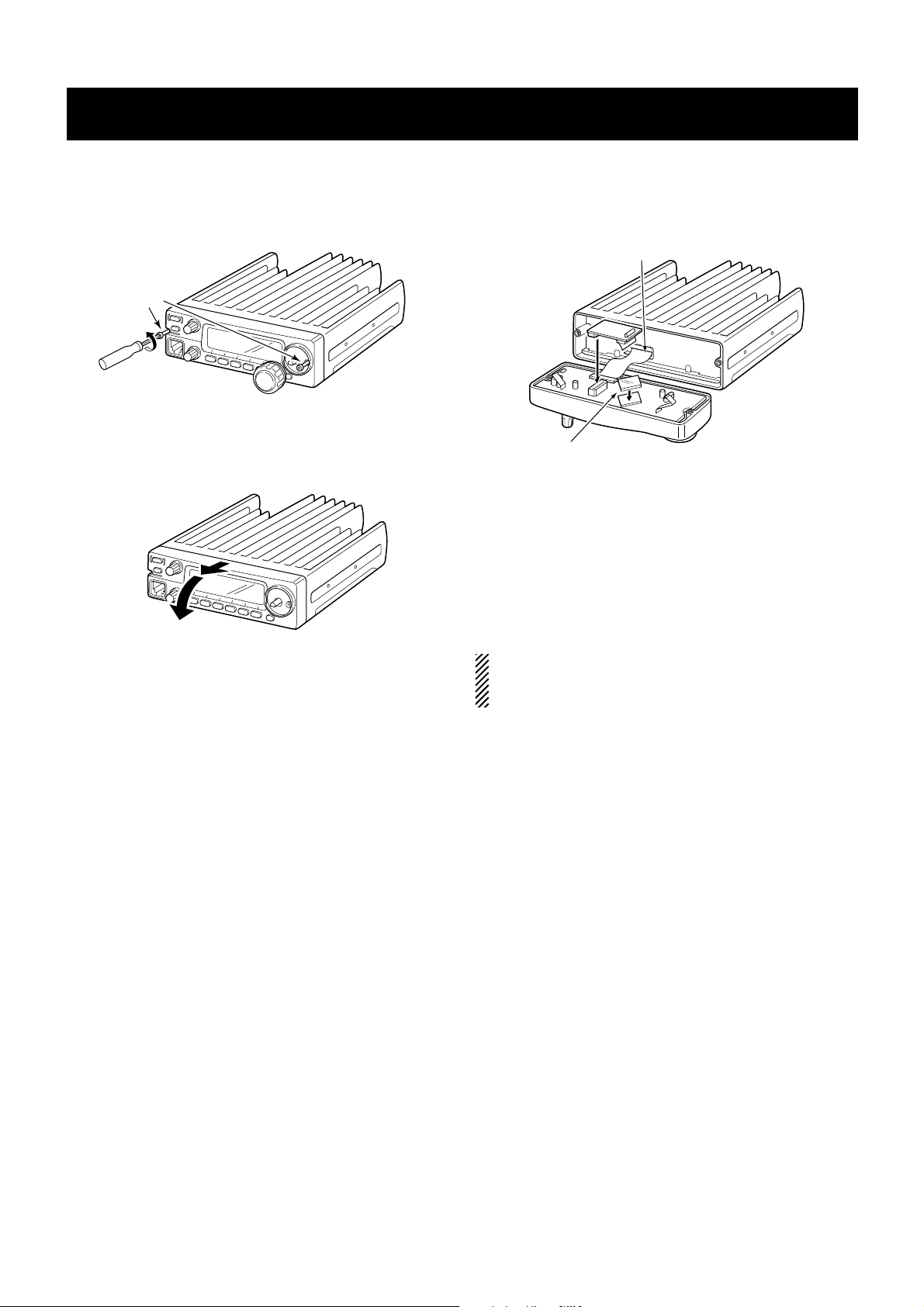
SECTION 3 OPTIONAL UNIT INSTALLATION
3 - 1
➀ Remove [DIAL] and unscrew the 2 allen-socket bolts from
the front panel using with an allen wrench (2.5 mm;
1
⁄10″).
NOTE: When attaching the front panel to the main unit,
make sure the flat cable are running in the groove to prevent catching between front panel and main unit.
➅ Return the front panel and the allen-socket bolts to their
original position.
➂ Attach the insulation sheet (supplied as accessory) to IC
on the Front unit.
➃ Remove the protective paper attached to the bottom of
the optional unit to expose the adhesive strip.
➁ Detach the front panel from the main unit.
➄ Intall the unit as illustrated below. Insert tightly to avoid
bad contact.
Allen-socket
bolts
Flat cable
Insulation sheet
Page 9
4 - 1
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
4-1-1 ANTENNA SWITCHING CIRCUIT
(MAIN UNIT)
The antenna switching circuit functions as a low-pass filter
while receiving and a resonator circuit while transmitting.
The circuit does not allow transmit signals to enter receiver
circuits.
Received signals enter the antenna connector and pass
through the low-pass filter (L47, L48, C208, C210, C217).
The filtered signals are passed through the λ/4 type antenna switching circuit (D16, D19, L45, L46) and limiter circuits
(D15). The signals are then applied to the squelch attenuator circuit.
4-1-2 SQUELCH ATTENUATOR CIRCUIT
(MAIN UNIT)
The attenuator circuit attenuates the signal strength to a
maximum of 10 dB to protect the RF amplifier from distortion
when excessively strong signals are received.
The current flow of the antenna switching circuit (D16, D19)
is controlled by the [SQL] control via the attenuator controller (IC6a, D18). When the [SQL] control is rotated clockwise deeper than 12 o’clock, the current of D16 and D19 is
increased. In this case, D16 and D19 act as an attenuator.
4-1-3 RF CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The RF circuit amplifies signals within the range of frequency coverage and filters out-of-band signals.
The signals from the squelch attenuator circuit pass through
the tunable bandpass filter (D13). The filtered signals are
amplified at the RF amplifier (Q27) and then enter another
three-stage bandpass filters (D9–D11) to suppress unwanted signals. The filtered signals are applied to the 1st mixer
circuit (Q19).
The tunable bandpass filters (D13–D16) employ varactor
diodes to tune the center frequency of the RF passband for
wide bandwidth receiving and good image response rejection. These diodes are controlled by the CPU (LOGIC unit;
IC1) via the D/A convertor (IC5).
4-1-4 1ST MIXER AND 1ST IF CIRCUITS
(MAIN UNIT)
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signals to a fixed
frequency of the 1st IF signal with the PLL output frequency.
By changing the PLL frequency, only the desired frequency
will pass through a pair of crystal filters at the next stage of
the 1st mixer.
The RF signals from the bandpass filter are applied to the
1st mixer circuit (Q19). The applied signals are mixed with
the 1st LO signal coming from the RX-VCO circuit (Q7, D5,
D38) to produce a 21.7 MHz 1st IF signal. The 1st IF signal
passes through a pair of crystal filters (FI3, FI4) to suppress
out-of-band signals. The filtered signal is amplified at the 1st
IF amplifier (Q16), and applied to the 2nd IF circuit via the
limiter circuit (D29).
4-1-5 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
(MAIN unit)
The 2nd mixer circuit converts the 1st IF signal to a 2nd IF
signal. A double-conversion superheterodyne system
improves the image rejection ratio and obtains stable receiver gain.
The 1st IF signal from the IF amplifier (Q16) is applied to the
2nd mixer section of the FM IF IC (IC4, pin 16) and is then
mixed with the 2nd LO signal for conversion to a 450 kHz
2nd IF signal.
IC4 contains the 2nd mixer, limiter amplifier, quadrature
detector, S-meter detector, active filter and noise amplifier
circuits, etc. A frequency from the PLL reference oscillator is
used for the 2nd LO signal (21.25 MHz).
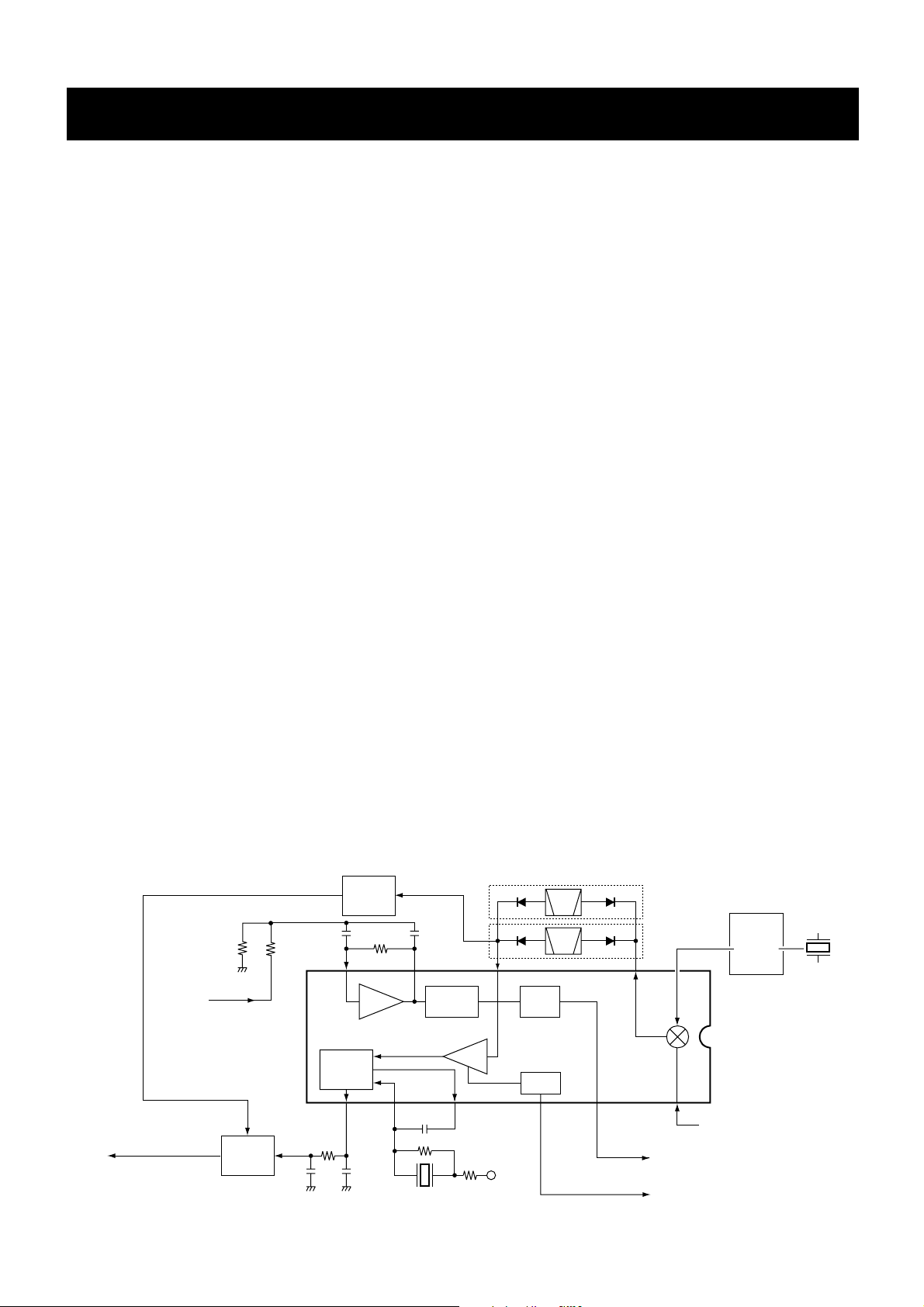
Mixer
16
Limiter
amp.
2nd IF filter
450 kHz
(for wide)
(for narrow)
X1
21.25 MHz
IC4 TA31136FN
12
1st IF from the
IF amplifier (Q16)
"SD" signal to the CPU
(FRONT unit; IC1, pin 4)
11109
8
Q37, Q38
7
AF signal "DETO"
R5V
X2
2
Active
filter
Noise
detector
FM
detector
13
"NOIS" signal to the CPU
(FRONT unit; IC1, pin 26)
RSSI
Noise
comp.
PLL IC
IC1
116
"SQLIN" signal from
the D/A converter IC
(IC5, pin 11)
AM
detector
IC12
AM/FM
selector
FI2
3
FI1
• 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUIT
Page 10
4 - 2
The 2nd IF signal from the 2nd mixer (IC4, pin 3) passes
through the ceramic filter (FI1) (during wide channel spacing
selection or passes through FI2 during narrow channel
spacing selection; [W/N] only).
4-1-6 AM/FM SELECTOR CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
IC-2200H can receive AM and FM signal. The 2nd IF signal
is detected AM or FM detector circuits respectively.
(1) AM DETECTOR CIRCUIT
The filtered signal is applied to the AM detector circuit (Q37,
Q38) to demodulate 2nd IF signal into AM AF signals. The
AM AF signals are applied to the AF circuit via the AM/FM
selector switch (IC12, pin 6).
(2) FM DETECTOR CIRCUIT
The filtered signal is amplified at the limiter amplifier section
(IC4, pin 5), and is then applied to the quadrature detector
section (IC4, pins 10, 11 and X2) to demodulate the 2nd IF
signal into FM AF signals. The FM AF signals are output
from pin 9 (IC4) and are then applied to the AF circuit via the
AM/FM selector switch (IC12, pin 7).
4-1-7 AF CIRCUITS (LOGIC UNIT)
The AF circuits are composed of digital and analog AF circuits. The AF signals are amplifies the demodulated AF signals to drive a speaker.
(1) IN CASE OF DIGITAL AF SIGNALS
The digital AF signals are applied to the optional digital unit
(UT-115*) via the J4 (pin 23) by the “DETO” line. The audio
signals that are converted to analog signals at the UT-115
are applied to the analog selector circuit (IC525, pin 8) from
the optional digital voice unit passed through the J4 (pin 22)
via the “AFOUT” line. The signals pass through the highpass filter (IC3c, pins 8, 9) from the analog selector (IC525,
pin 9), and are then applied to the analog switch (IC6, pin 1).
*Refer to “4-6 UT-115 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION” (page 4-7 )
in detail.
(2) IN CASE OF ANALOG AF SIGNALS
The analog AF signals are applied to the analog selector
(IC525, pin 11), and pass through the high-pass filter (IC3c,
pins 8, 9). The filtered signals are applied to the analog
switch (IC6, pin 1).
The audio signals are applied to the AF mute switch (MAIN
unit; Q29) via the VOL adjust pot (R61). The signals are
amplified at the AF amplifier (MAIN unit; IC9, pin 1) to obtain
2.4 W audio output power after being passed through the
emphasis switch (MAIN unit; Q41). The amplified AF signals
are applied to the speaker via the J4 (MAIN unit) and J6
(MAIN unit).
4-1-8 SQUELCH CIRCUITS
(MAIN AND LOGIC UNITS)
•
NOISE SQUELCH
The noise squelch circuit cuts out AF signals when no RF
signals are received. By detecting noise components in the
AF signals, the squelch circuit switches the AF mute switch.
A portion of detected audio signals from the FM IF IC (IC4,
pin 9) are applied to the active filter section of the IC (IC4,
pin 8) as “SQLIN” signal, after passing through the D/A converter (IC5, pin 12). The active filter section of the IC amplifies and filters noise components. The filtered signals are
applied to the noise detector section in the IC and output
from pin 13 as the “NOIS” signal.
The “NOIS” signal from IC4 (pin 13) is applied to the CPU
(LOGIC unit; IC1, pin 26). The CPU analyzes the noise condition and outputs “AFMUTE” and “FILC” signals via the I/O
expander IC (LOGIC unit; IC2) to toggle the AF mute (Q29)
and emphasis (Q41) switches.
Even when the squelch is closed, the AF mute switch (Q29)
opens at the moment of emitting beep tones.
• TONE SQUELCH
The tone squelch circuit detects AF signals and opens the
squelch only when receiving a signal containing a matching
subaudible tone (CTCSS). When tone squelch is in use, and
a signal with a mismatched or no subaudible tone is
received, the tone squelch circuit mutes the AF signals even
when noise squelch is open.
AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC4, pin 9) are applied to the
AM/FM selector (IC12, pin 6 or 7), and then pass through
the analog selector (LOGIC unit; IC525, pins 10, 11). The
signals pass through the low-pass filter (LOGIC unit; Q3) to
remove AF (voice) signals, and is applied to the CTCSS
decoder inside the CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1, pin 1) via the
“CTCIN” line to control the AF mute switch.
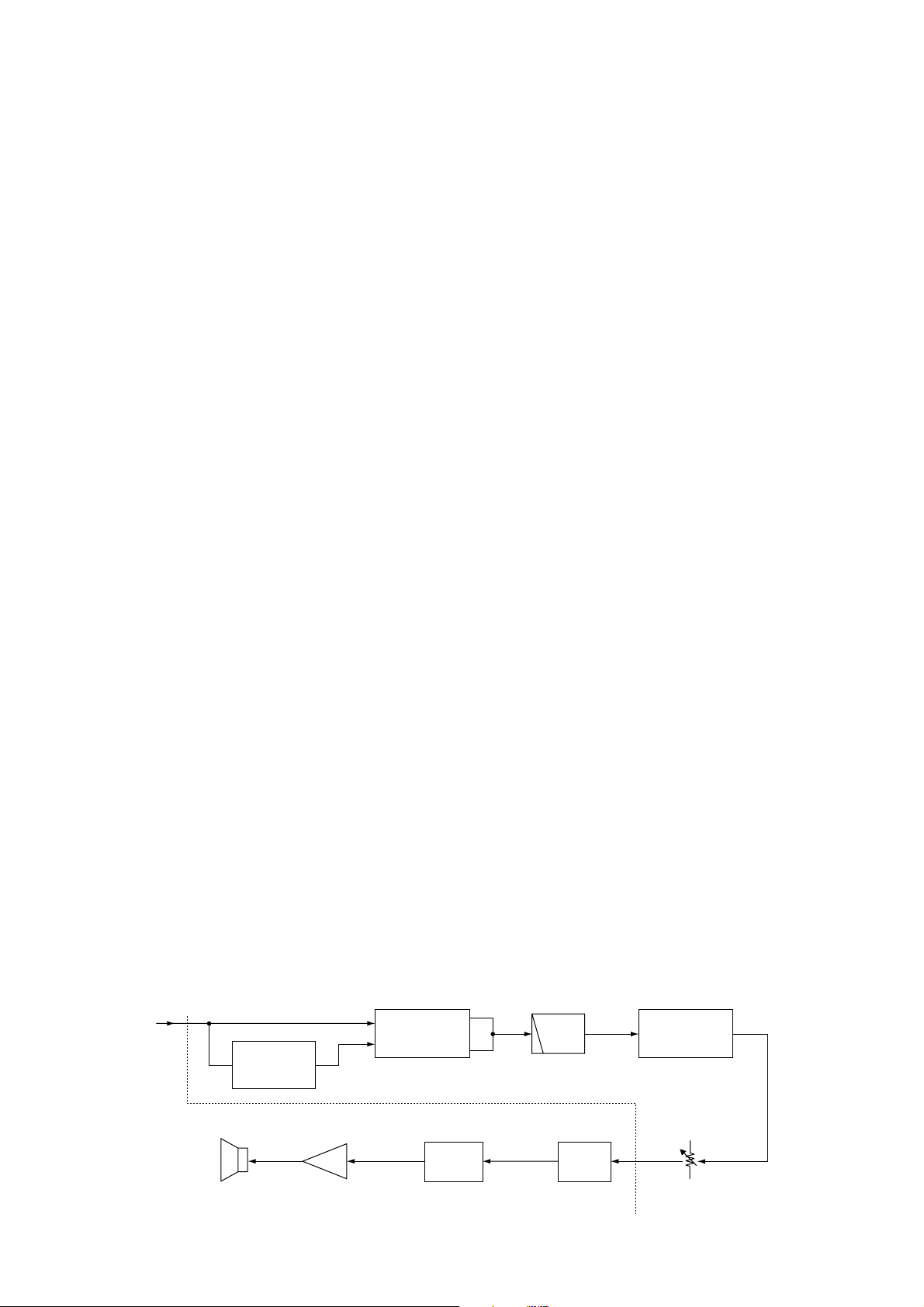
Analog selector
(IC525)
Analog switch
(IC6)
Optional unit
(UT-115)
"DETO" AF signal from the AM/FM
selector (MAIN unit; IC12, pin 1)
11
1
R61
11
IC3
Q29
Q41
8
15
9
9
10
8
AF
IC9
Speaker
(SP1)
HPF
LOGIC unit
MAIN unit
AF
mute
Emphasis
switch
AF
volume
• AF CIRCUIT
Page 11
4 - 3
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
4-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
(LOGIC unit)
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies audio signals with
+6 dB/octave pre-emphasis characteristics from the microphone to a level needed for the modulation circuit.
The AF signals from the microphone pass through the
microphone switch (IC2, D4), and are then amplified at the
microphone amplifier (IC3a ,pin 2). The amplified signals
pass through (or bypass) the ALC circuit.
4-2-2 ALC CIRCUIT (LOGIC UNIT)
The ALC (Automatic Level Control) circuit reduces the gain
of IF amplifiers in order for the transceiver to output a constant RF power set by the RF power setting even when the
supplied voltage shifts, etc.
• IN CASE OF PASSING THROUGH THE ALC CIRCUIT
The amplified signals are applied to the ALC switch (IC520,
pin 3), and are then output from pin 4. The signals are
applied to the ALC amplifier (IC514, pin 3), and are then
reapplied to the ALC switch (IC520, pin 8). The signals pass
through the high-pass filter (IC3d, pins 12, 14), and are then
applied to the analog switch (IC6, pin 4).
• IN CASE OF BYPASSING THE ALC CIRCUIT
The amplified signals are applied to the ALC switch (IC520,
pin 2), and are then output from pin 1. The signals are
applied to the ALC switch (IC520, pin 9) again, and then
pass through the high-pass filter (IC3d, pins 12, 14) via the
IC520, pin 10. The signals are applied to the analog switch
(IC6, pin 4).
4-2-3 DIGITAL SWITCH CIRCUIT (LOGIC UNIT)
The signals from the analog switch (IC6, pin 3) pass through
the high-pass filter (IC3, pins 6, 7), and are then reapplied to
the analog switch (IC6, pin 9). The signals are applied to the
DI/AN switch via the “MOD_I” line.
• IN CASE OF DIGITAL AF SIGNALS
The AF signals are applied to the DI/AN switch (IC522, pin
10), and are then applied to the optional digital voice unit
after being passed through the J4 (pin 4) via the “ANALOGUE_MOD_IN” line. The A/D converted AF signals are
applied to the DI/AN switch (IC522, pin 1) from the J4 (pin 3)
via the “DIGITAL_MOD_OUT” line. The digital AF signals
from DI/AN switch (IC522, pin 2) are applied to the modulation circuit after being passed through the J3 via the
“MODIN” line.
• IN CASE OF ANALOG AF SIGNALS
The AF signals are applied to the DI/AN switch (IC522, pin
9), and are then reapplied to the switch (pin 4) from pin
8.The signals output from the switch (pin 3) as analog AF
signals , and are then applied to the modulation circuit after
being passed through the J3 via the “MODIN” line.
4-2-4 MODULATION CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The modulation circuit modulates the VCO oscillating signal
(RF signal) using the microphone audio signals.
The digital or analog audio signals (MODIN) change the
reactance of D2 and D4 to modulate the oscillated signal at
the TX-VCO circuit (Q6). The modulated signal is amplified
at the LO amplifier (Q9) and buffer amplifier (Q11), then
applied to the drive amplifiers.
4-2-5 DRIVE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The drive amplifier circuit amplifies the VCO oscillating signal to the level needed at the power amplifier.
The RF signal from the buffer amplifier (Q11) passes
through the T/R switch (D6) and is amplified at the pre-drive
(Q17) and drive (Q35) amplifiers. The amplified signal is
applied to the power amplifier circuit.
4-2-6 POWER AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The power amplifier circuit amplifies the driver signal to an
output power level.
The RF signal from the drive amplifier (Q35) is applied to the
power module (IC10) to obtain 65 W (50 W for Korea version, 25 W for Taiwan version) of RF power.
The amplified signals is passed through the antenna switching circuit (D12), APC detector circuit (D14, D17, L39), and
low-pass filter (L47, L48, C208, C210, C217) and is then
applied to the antenna connector.
Control voltage for the power amplifier (IC10, pin 2) are controlled by the APC circuit to protect the power module from
a mismatched condition as well as to stabilize the output
power.
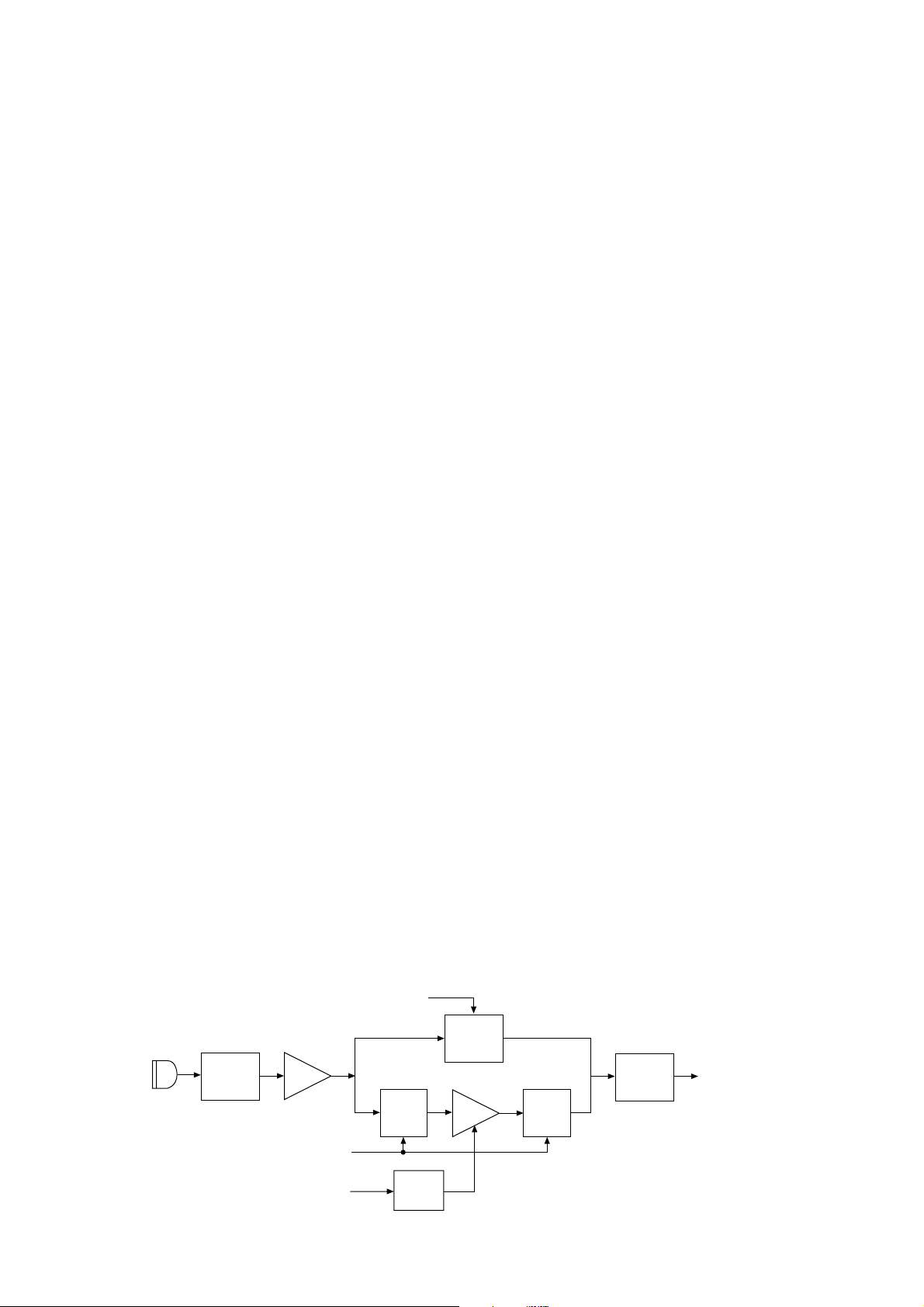
Microphone
MIC
switch
"THROUGH" from the CPU
(MAIN unit; IC1, pin 80)
"ALC" from the CPU
(MAIN unit; IC1, pin 81)
"THROUGH" from the CPU
(MAIN unit; IC1, pin 80)
IC3A
IC2, D4
Through
switch
Switch
ALC
switch
ALC
switch
MIC
IC514
IC520 IC520
IC520
Q524
IC525
to the modulator circuit
ALC
Power
supply
• ALC CIRCUIT
Page 12
4 - 4
4-2-7 APC CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The APC circuit protects the power amplifier from a mismatched output load and stabilizes the output power.
The APC detector circuit (D14, D17, L39) detects forward
signals and reflection signals at D14 and D17 respectively.
The combined voltage is at minimum level when the antenna impedance is matched at 50 Ω and is increased when it
is mismatched.
The detected voltage is applied to the differential amplifier
(IC6, pin 2), and the power setting voltage is applied to the
other input (pin 1) for the reference.
When antenna impedance is mismatched, the detected voltage exceeds the power setting voltage. The output voltage
of the differential amplifier (IC6, pin 1) controls the input current of the power module (IC10) to reduce the output power.
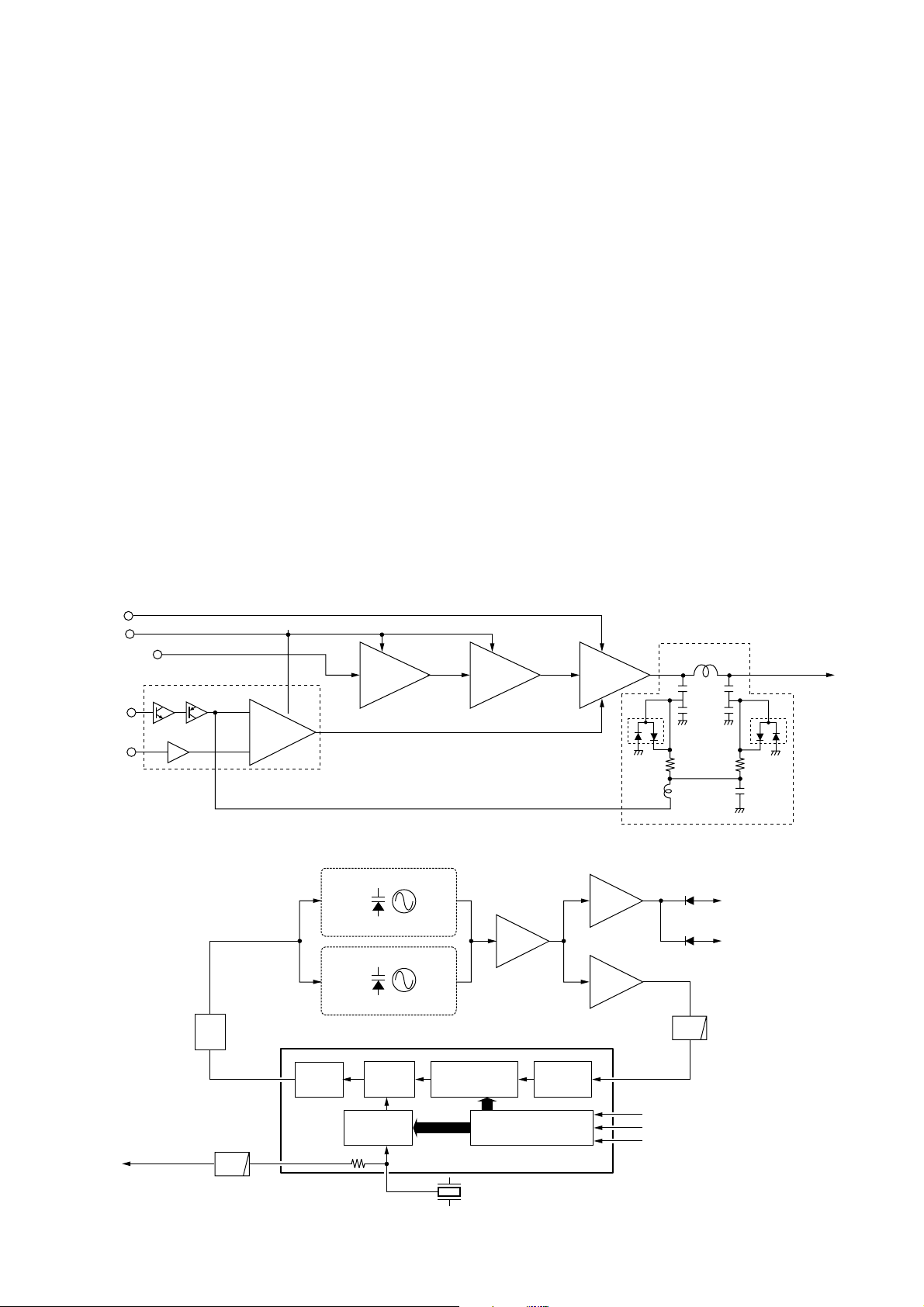
4-3 PLL CIRCUITS
4-3-1 PLL CIRCUIT
A PLL circuit provides stable oscillation of the transmit frequency and the receive 1st LO frequency. The PLL circuit
compares the phase of the divided VCO frequency to the
reference frequency. The PLL output frequency is controlled
by the divided ratio (N-data) of a programmable divider.
An oscillated signal from the VCO passes thorough the LO
and buffer amplifiers (Q9, Q12) is applied to the PLL IC (IC1,
pin 6) and is prescaled in the PLL IC based on the divided
ratio (N-data). The reference signal is generated at the reference oscillator (X1) and is also applied to the PLL IC. The
PLL IC detects the out-of-step phase using the reference
frequency and outputs it from pin 15. The output signal is
passed through the loop filter (Q2, R6, R11–R15, C11, C12)
and is then applied to the VCO circuit as the lock voltage via
the “LV” line.
4-3-2 VCO CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The VCO circuit contains a separate TX-VCO (Q6, D2, D4)
and RX-VCO (Q7, D5, D38). The oscillated signal is amplified at the LO (Q9) and buffer (Q11) amplifiers, and is then
applied to the T/R switching circuit (D6, D7). Then the Tx
and Rx signals are applied to the pre-driver (Q17) and 1st
mixer (Q19) respectively.
A portion of the signal from Q4 is amplified at the buffer
amplifier (Q6) and is then fed back to the PLL IC (IC1 pin 2)
as the comparison signal.
Power
amp.
IC6
APC
amp.
Driver
amp.
+
—
Pre
drive
HV
to the antenna
T1
TXC
IC11
Q26, Q39, Q40
RF signal
T8
APC control circuit
Q17
Q35
IC10
Power detector circuit
L39
D14 D17
• APC CIRCUIT
Shift register
Prescaler
Phase
detector
Charge
pump
Loop
filter
Programmable
divider
Reference
divider
X1
21.25 MHz
1
LO
Buffer
Buffer
2
3
4
PLLCK
PLLDATA
PLLSTB
to transmitter circuit
to 1st mixer circuit
D6
D7
Q11
Q12
Q9
9
6
Q6, D2, D4
TX VCO
Q7, D5
RX VCO
IC1 LV2105V
21.25 MHz 2nd LO signal
to the FM IF IC (IC4, pin 2)
16
LPF
LPF
• PLL CIRCUIT
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 13
4 - 5
4-3-3 REFERENCE OSCILLATOR CONTROL
CIRCUIT (LOGIC AND MAIN UNITS)
The reference oscillator control circuit changes the reference frequency when using digital voice function.
When digital voice signals output from the optional digital
voice unit, the “REFMOD” signal outputs from it via the J4
(pin 4) at the same time. The “REFMOD” signal is applied to
the amplifier (IC521, pin 3), and passes through the CTCSS
switch (IC524, pins 6 and 1). The signal is applied to the D/A
convertor (MAIN unit; IC5, pin 13) via the “CTCSS” line. The
output signal from the D/A convertor (MAIN unit; IC5, pin 14)
is applied to the reference oscillator (MAIN unit; X1) to control the reference frequency while transmitting digital signals
as “DTC” line.
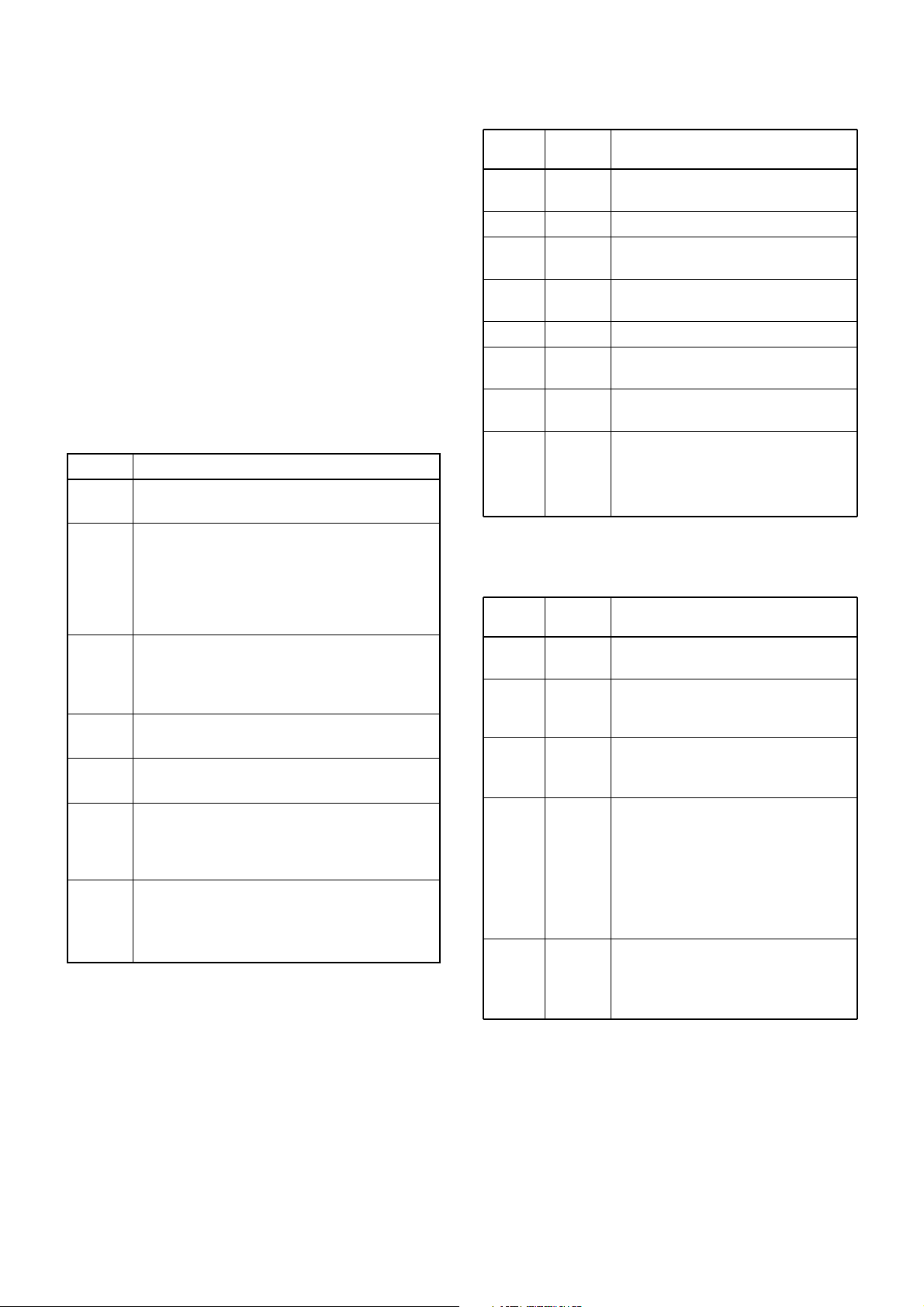
4-4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
VOLTAGE LINES
Description
The 13.8 V voltage from the connected DC
power supply.
The same voltage as the HV line which is controlled by the HVSW circuit (Q28, Q30, Q31).
When the [POWER] switch (LOGIC unit; S1) is
pushed, the CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1, pin 40) outputs the “PWRON” control signal to the power
switching circuit to turn the circuit ON.
Common 5 V for the CPU (LOGIC unit; IC1)
converted from the HV line by the C5V regulator
circuit (IC8). The circuit outputs the voltage
regardless of the power ON/OFF condition.
Common 8 V converted from the SWHV line by
the +8V regulator circuit (IC7).
Common 5 V converted from the +8V line by the
+5V regulator circuit (Q21, Q22).
Transmit 8 V controlled by the T8 regulator circuit (Q14, Q15) using the “TXC” signal from the
I/O expander IC (IC2, pin 6). The voltage is converted from the +8V line at the regulator circuit.
Receive 5 V controlled by the R5 regulator circuit (Q25) using the “RXC” signal from the I/O
expander IC (IC2, pin 5). The voltage is converted from the +5 V line at the regulator circuit.
Line
HV
SWHV
C5V
+8V
+5V
T8
R5V
Pin
number
2
3
10
11
14
15
22
23
Port
name
T3
SQLATT
FC
SQLIN
DTC
MOD
T2
T1
Description
Outputs RF tracking voltage while
receiving.
Outputs attenuator control signal.
Outputs reference frequency control
voltage.
Outputs squelch control signal to
adjust threshold level.
Outputs DTCS slope correction signal.
Outputs transmitting deviation control
signal.
Outputs RF tracking voltage while
receiving.
• Outputs RF tracking voltage while
receiving.
• Outputs transmitting power control
signal while transmitting.
4-5 PORT ALLOCATIONS
4-5-1 D/A CONVERTER IC (MAIN UNIT; IC5)
Pin
number
4
5
6
11
14
Port
name
AFMUTE
RXC
TXC
W/N
SHIFT
Description
Outputs AF mute control signal.
High: While muting.
Outputs R5 regulator (Q25) control
signal.
Low: While receiving.
Outputs T8 regulator (Q14 and Q15)
control signal.
High: While transmitting.
Outputs 2nd IF filter select signal
([W/N] version ONLY).
High: While wide passband width
(±5.0 kHz) is selected (FI1 is
selected).
Low: While narrow passband width
(±2.5 kHz) is selected (FI2 is
selected).
Outputs VCO regualtor (Q1, Q3, Q5,
Q8, D1) control signal.
Low: While transmitting.
High: While receiving.
4-5-2 EXPANDER IC (MAIN UNIT; IC2)
Page 14
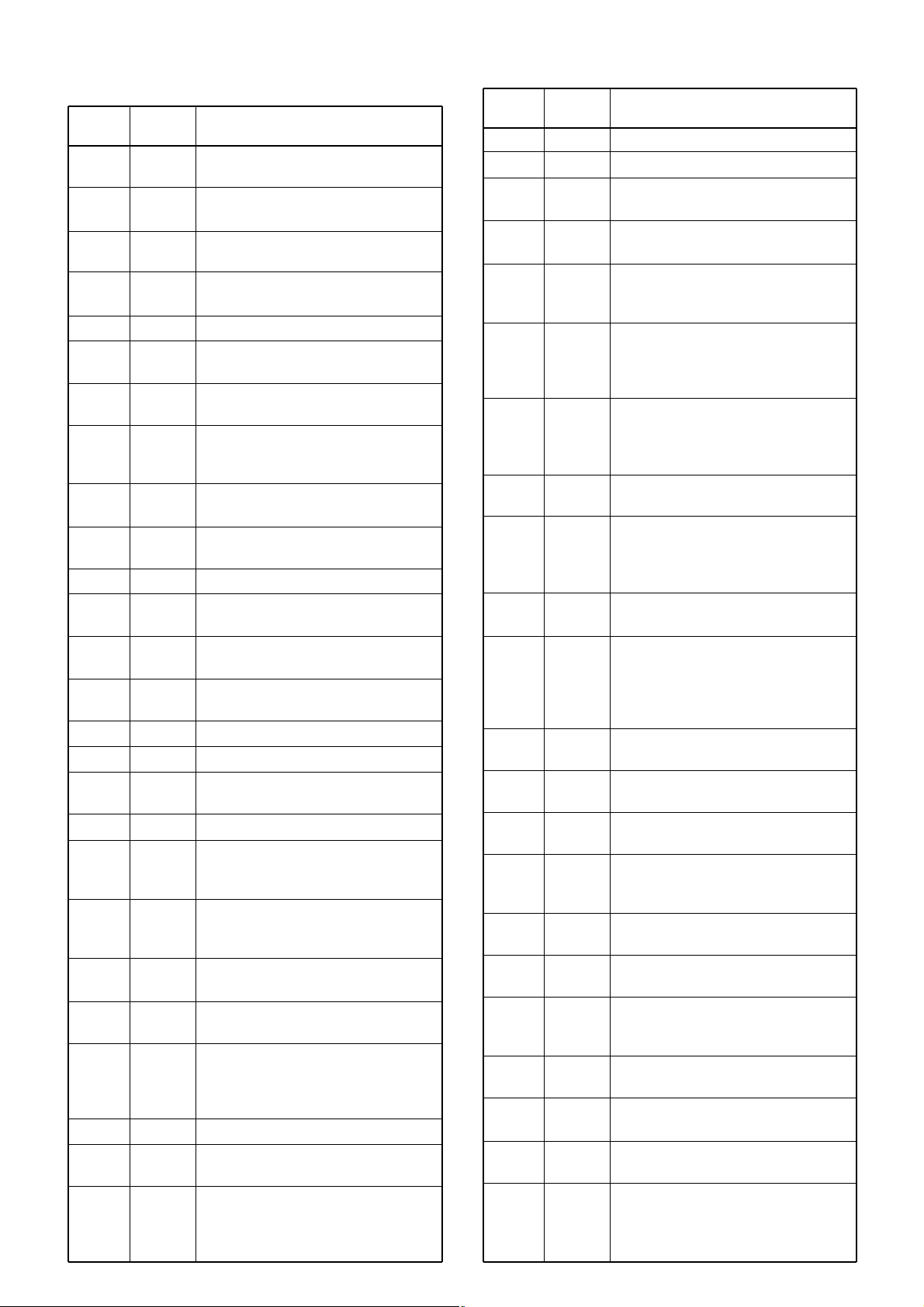
Port
name
IS0–IS2
KS1, KS2
KR3–KR0
PTT
DI_SEC
TX_DIGI
SO
OPSCK
OPV1
DASTB
OPV2
EXTMIC
DUSE
ESCK
ESDA
OP_PS
THROUGH
ALC
OPT3
OPT2
OPT1
SEG1–
SEG36
COM4–
COM1
VL3–
VL1
IDET
4-5-3 CPU (LOGIC UNIT; IC1)
Pin
number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
14
19
25
26
28
29
30
31
34
35
40
42
43
44
45
46
47
49
51
Port
name
CTCIN
SQLV
MICUD
SD
LVIN
TEMP
DET0
COLOR
DIM0
DIM1
CSHIFT
RESET
PWRSW
NOIS
DICK
DIUD
CLIN
CLOUT
SCK
BUSY
PWRON
BSHIFT
PLLSTB
PLLCK
EXSTB
OPV3
UNLK
REMO
MICS
AFON
Description
Input port for the CTCSS/DTCS signals.
Input port for squelch volume detecting signal.
Input port for the [∫] and [√] switches
from the external microphone.
Input port for the S-meter voltage
detecting signal.
Input port for the PLL lock voltage.
Input port for the transceiver’s internal
temperature detecting signal.
Input port for the weather channel
alert detecting sinal.
Outputs LCD backlight color select
signal.
Low: Umber color is selected.
Output LCD backlight brightness controls signals
Outputs the CPU clock shift control
signal.
Input port for the reset signal.
Input port for [POWER] switch.
Low: [POWER] switch is pushed.
Input port for the noise pulse signal for
squelch and CPU.
Input ports for encoder signals.
Input port for the cloning signal.
Output port for the cloning signal.
Outputs serial clock signal to the D/A
convertor (MAIN unit; IC5, pin 7).
Outputs “BUSY” signal to the UT-115.
Outputs [POWER] switch control signal.
High: [POWER] is ON.
Outputs band shift signal.
Low : While receiving Air band
(118–136 MHz).
Outputs strobe signal to the PLL IC
(MAIN unit; IC1, pin 4).
Outputs clock signal to the PLL IC
(MAIN unit; IC1, pin 2).
• Outputs strobe signal to the
expander IC (MAIN unit; IC2, pin 1).
• Input port for the optional unit detecting signal.
Input port for the PLL unlock signal.
Input port for the HM-133V remote
microphone signals.
Output transmitting/receiving AF filter
select signal to the analog swtich (IC6,
pin 6 [“AFON” is applied to the
pin 12]).
Pin
number
53–55
56, 57
58–61
62
64
65
66
67
68
69
73
74
75
76
77
80
81
84
85
86
90,
92–127
128–131
134–136
144
Description
Output initial matrix strobe signals.
Output key scan signals
Input ports for the keyboard matrix
signals.
Input port for the [PTT] switch signal.
High: While transmitting.
Outputs digital/analog select signal
while the UT-115 is installed.
High : Digital is selected.
Outputs filter characteristic control signal while the UT-115 is installed.
Low : While transmitting digital sig-
nal.
• Outputs serial data to D/A convertor
(MAIN unit; IC5, pin 8).
• Outputs DTMF clock signal to the
expander IC (MAIN unit; IC2, pin 2).
Outputs clock signal to the optional
unit.
• Input port for the optional unit detecting signal.
• Outputs strobe signal to the D/A converter (MAIN unit; IC5, pin 6).
Input port for the optional unit detecting signal.
Input port for detecting signal whether
the multifunction microphone is connected or not.
Low: The multifuntion microphone is
connected.
Outputs low-pass filter cut-off frequency control signal when using DTCS.
Outputs clock signal to the EEPROM
(IC5, pin 6).
I/O port for data signals from/to the
EEPROM (IC5, pin 5).
Outputs the optional unit power supply
controll signal.
High : Power is ON.
Outputs the ALC circuit control signal.
High : The ALC circuit is OFF.
Outputs the ALC circuit control signal.
High : The ALC circuit is ON.
I/O ports for the optional unit control
signals.
Output LCD segment signals.
Output LCD common signals.
Output LCD device signals.
Input port for the current drain detecting signal while transmitting.
4 - 6
Page 15
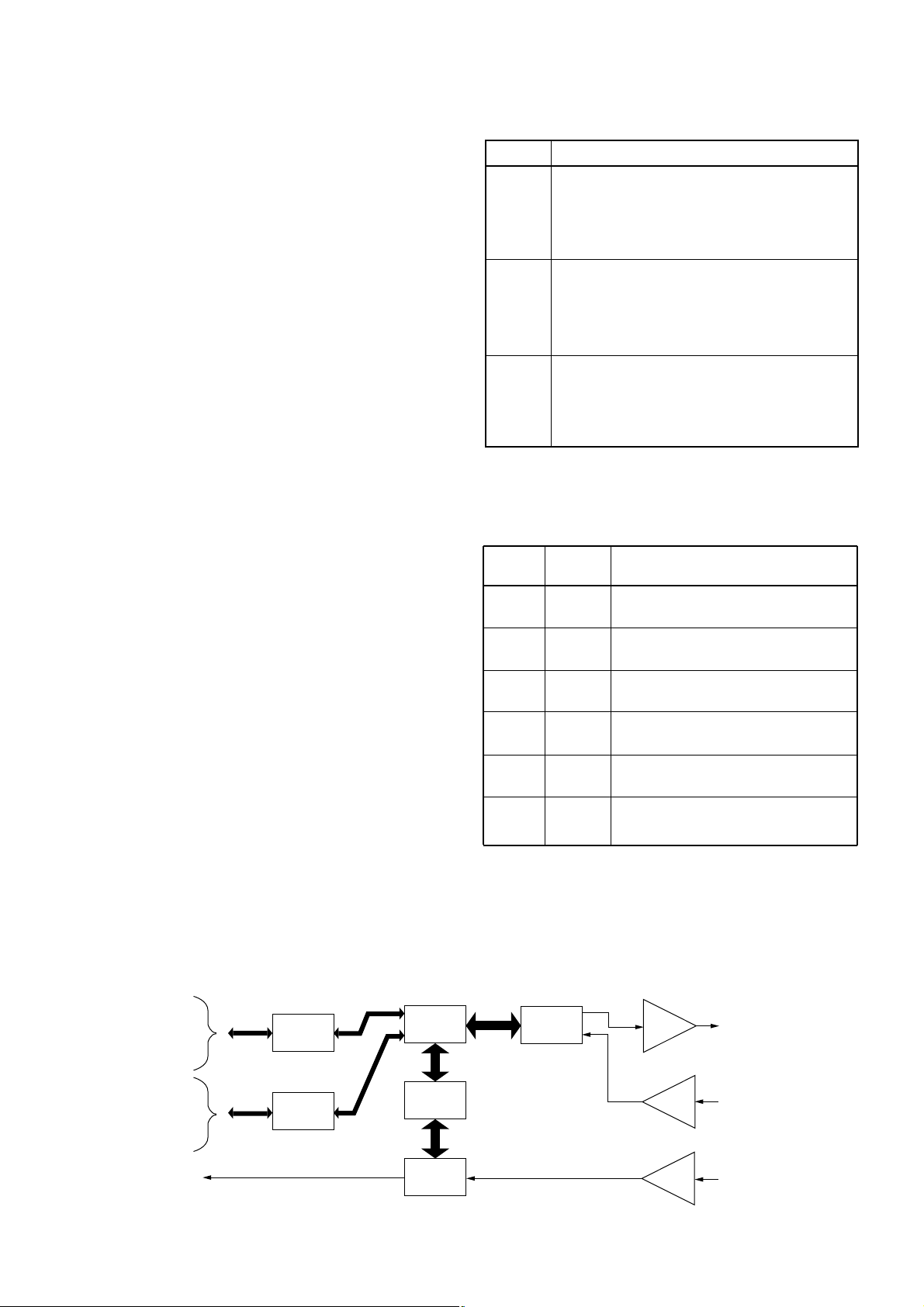
4-6 UT-115 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4-6-1 RECEIVER CIRCUIT
The detected digital signals “FMDET” from the connected
transceiver via the J301 (pin 22) are amplified at the buffer
amplifier (IC251, pin 2). The amplified signals are applied to
the GMSK modem circuit (IC252, pin 11), and are then
applied to the CPU (IC204) as clock synchronizer digital signal. The digital signals from the CPU are applied to the
AMBE voice CODEC IC (IC151) to precess code extention,
and are then applied to the linear CODEC IC (IC50) as 32
bits digital voice data. The applied digital signals are converted to the analog AF signals at the D/A converter section
(IC50), and are then applied to the connected transceiver
via the J301 (pin 21) as “DAFOUT” signal.
4-6-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUIT
The analog AF signals “AMODIN” from the connected transceiver via the J301 (pin 4) are amplified at the buffer amplifier (IC251, pin 6). The amplified signals are applied to the
linear CODEC IC (IC50, pin 5) to convert 32 bits digital voice
data at the A/D converter section via the “ADIN” line. The
digital signals are applied to the AMBE voice CODEC IC
(IC151) to process code compression, and are then applied
to the CPU (IC204). The digital signals from the CPU convert to the GMSK base band signal at the GMSK modem
(IC252), and are then amplified at the buffer amplifier
(IC253, pin 5). The amplified signals are applied to the connected transceiver via the J301 (pin 3).
4-6-3 RESET CIRCUIT
The UT-115 has the reset IC (IC203). The IC outputs reset
signal to the CPU (IC204, pin 7) when “VDD” port (pin 2)
becomes more than 2.8 V.
4-6-4 RS-232C CIRCUIT
IC351 is a RS-232C compatible serial interface IC which
converts data between the CPU and the external equipment
(EX: Personal Computer).
4-6-5 LEVEL CONVERTER CIRCUIT
The level converter circuit (Q305 and Q306) converts communication data level between the CPU (IC204) and the
connected transceiver’s CPU.
Q301, Q302 and Q303 convert control signals level between
the UT-115 and the connected transceiver.
4-7 UT-115 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
VOLTAGE LINES
4-8 UT-115 PORT ALLOCATIONS
4-8-1 MODEM IC (IC252)
4 - 7
Description
The 5 V voltage from the connected transceiver
via the J301 (pin 29). The 5V line is controlled by
the +5V control circuit (Q50 and Q51). The circuit is controlled by the “PSAVE” signal from the
CPU (IC204, pin 58 and 59).
Common 3.3 V converted from the 5V line by the
3.3V regulator circuit (IC1). One of the 3.3 V line
is controlled by the +3V control circuit (Q400 and
Q401). The circuit is controlled by the “PSAVE”
signal from the CPU (IC204, pin 58 and 59).
Common 3.2 V converted from the 4.5–8 V line
by the 3.2V regulator circuit (IC2). The circuit is
controlled by the “APWR” signal from the CPU
(IC204, pin 16).
Line
5V
3.3V
3.2V
Pin
number
2
7
19
20
21
22
Port
name
MCLK
ACQ
TXDT
RXDT
RXCK
TXCK
Description
Outputs 2.4576 MHz clock signal to
the CPU (IC151, pin 39).
Outputs the PLL band width control
signal while receiving.
Outputs transmitting data signal to the
CPU (IC204, pin 54).
Input port for receiving data signal
from the CPU (IC204, pin 53).
Input port for receive clock signal from
the CPU (IC204, pin 52).
Outputs transmit clock signal to the
CPU (IC204, pin 51).
Linear
CODEC
Buffer
IC253B
Buffer
IC251A
Buffer
IC251B
IC50
IC151
Q305, Q306
IC351
-"232C_RX" signal
to the J301, pin 25
-"232C_TX" signal
to the J301, pin 26
-"TXD_2" signal to
the J301, pin 16
-"RXD_2" signal to
the J301, pin 17
"DAFOUT" signal to
the J301, pin 22
"DMOD" signal
to the J301, pin 3
"FMDET" signal
from the J301, pin 23
"AMODIN" signal
from the J301, pin 4
IC204 IC252
DSP
CODEC
CPU
CODEC
Modem
RS-232C
Level
converter
• UT-115 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Page 16
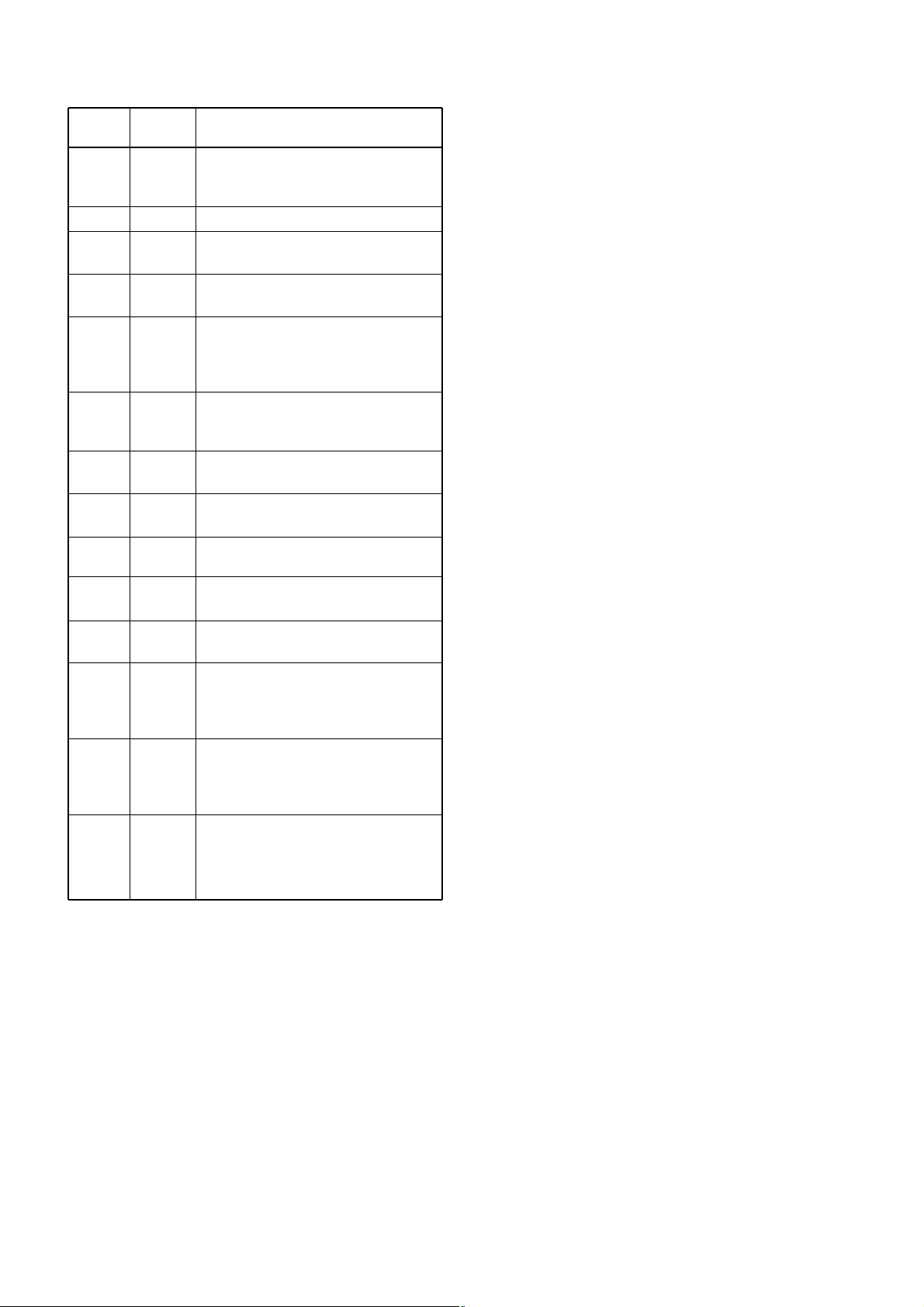
4 - 8
Pin
number
7
10
11
16
29
31
33
34
36
37
38
58
59
61
62
Port
name
RES
OSC2
OSC1
APWR
RMUTE_C
PTTOUT_C
ATXD
ACLK
ASTB
ARXD
ARES
PSAVE
BUSY
PTTIN
Description
Input port for the reset signal from the
reset IC (IC203, pin 1).
Low :The CPU is reset.
Outputs 9.8304 MHz reference signal.
Input port for 9.8304 MHz reference
signal.
Outputs 3.2V regulator circuit (IC2,
pin 3) control signal.
Outputs receive AF mute control signal
to the connected transceiver via the
J301 (pin 24).
High :While muting.
Outputs PTT signal to the connected
transceiver via the J301 (pin 2).
High :While transmitting.
Outputs transmit data signal to the
CPU (IC151, pin 32).
Outputs clock signal to the CPU
(IC151, pins 28 and 34).
Outputs strobe signal to the CPU
(IC151, pins 30 and 38).
Input port for receive data signal from
the CPU (IC151, pin 42).
Outputs reset signal to the linear
CODEC IC (IC50, pin 13).
Output power save control signal to
the +3V controller circuit (Q400 and
Q401).
Low :Power save is ON.
Input port for the BUSY signal from the
connected transceiver via the J301
(pin 6).
High :While receiving signals.
Input port for the PTT signal from the
connected transceiver via the J301
(pin 1).
High :While transmitting.
4-8-2 CPU (IC2)
Page 17
5 - 1
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
5-1 PREPARATION
Enter the adjustment mode when adjusting the IC-2200H Then the JIG cable as shown the page 5-2 is required .
■ REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
DC power supply
RF power meter
(terminated type)
Frequency counter
Standard signal
generator (SSG)
FM deviation meter
Oscilloscope
Audio generator
Attenuator
EQUIPMENT GREDE AND RANGE EQUIPMENT GREDE AND RENGE
Output voltage : 13.8 V DC
Current capacity : 20 A or more
Measuring range : 0.1–100 W
Frequency range : 50–400 MHz
Impedance : 50 Ω
SWR : Less than 1.2 : 1
Frequency range : 0.1–400 MHz
Frequency accuracy : ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Frequency range : 0.1–400 MHz
Output level : 0.1 µV–32 mV
(–127 to –17 dBm)
Frequency range : 0–400 MHz
Measuring range : 0 to ±5 kHz
Frequency range : DC–400 MHz
Measuring range : 0.01–10 V
Frequency range : 300–3000 Hz
Measuring range : 1–500 mV
Power attenuation : 50 or 60 dB
Capacity : 150 W or more
■ ENTERING THE ADJUSTMENT MODE
q Turn the transceiver’s power OFF.
w Connect the JIG cable to the [MIC] jack.
e Push and hold the [SET] and [MONI] keys, and then turn power ON.
NOTE: Exiting from the adjustment mode when the transciever’s power is OFF.
■ OPERATING ON THE ADJUSTMENT MODE
• Change the adjustment value : [DIAL]
• Verifying the adjustment value : [M/CALL] key
• Forward the adjustment item : [BANK] key
• Go back the adjustment item : [V/MHz] key
• Store the adjustment value in the memory : [S.MW] key
CAUTION: Need to push the [S.MW] key when storing the adjustment value in the memory. Otherwise, the transceiver is not
adjusted properly.
IMPORTANT!: The transceiver need to be cancelled adjustment mode (as following method) to use normal mode when
adjustments are finished, otherwise the transceiver does not work properly.
q: Turn the power OFF.
w: Push and hold [S.MW] and [SET] keys, and then turn the power ON.
Page 18

5 - 2
‘‘
CONNECTIONS
pin 6 (MIC)
pin 4 (PTT)
pin 7 (GND)
pin 5 (MICE)
to the antenna connector
STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR
0.1 300 MHz
127 to 17 dBm (0.1 V to 32 mV)
RF POWER METER
50 , 1 80 W
FM DEVIATION
METER
ATTENUATOR
50 dB or 60 dB
POWER SUPPLY
13.8 V, 20 A or more
CAUTION!
DO NOT transmit
while an SSG is
connected to the
antenna connector.
JIG CABLE INFORMATION
to the microphone connector
AUDIO GENERATOR
300 Hz to 3 kHz
ADJUSTMENT ITEM EXPLANATION
Fr
dt+[DIGITAL]trtrtrtrSqSr
rE
*dF*Et
*F9
*F2 *F3 *F4 *F5 *F6 *F7
*F8*dE *F9*FA
*F0 *F1
*CS*dt
*F2
*F1
*F3 *F5 *F7*F4 *F6 *F8
PO
Starting item
PO+[MID] PO+[MID]+[LOW] PO+[LOW] PU dE *dP dE+[DIGITAL] dt
*bP
*dE*dE
*53 *54 *55 *56 *57 *51+[.] *52+[.] *55+[.]*53+[.] *54+[.]*52
*56+[.]*57+[.]
Sr+[.]*C6
*dd*dd*db *dd*db*db *db*dE+[DIGITAL]
*dE+[DIGITAL] *dE+[DIGITAL] *dd+[DIGITAL] *dd+[DIGITAL] *dd+[DIGITAL] *dd+[DIGITAL]
*dd+[DIGITAL]
*dd
*FN*FN*dU *FN *FN
*db+[DIGITAL] *db+[DIGITAL] *db+[DIGITAL] *db+[DIGITAL] *db+[DIGITAL]
*PN *PP *51
NOTE: DO NOT adjust items
with "*" mark at below
explanation. Those items are
adjusted automatically when
other adjustment items are
adjusted.
*Not adjust items
Page 19

5 - 3
5-2 SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENTS (TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING)
REFERENCE
FREQUENCY
[Fr]
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
[rE]
VHF
OUTPUT
POWER
(High)
[PO]
(Middle)
[PO+MID]
(Middle-Low)
[PO+MID+LOW]
(Low)
[PO+LOW]
PROTECT
VOLTAGE
[PU]
FREQUENCY
DEVIATION
(Analog)
[dE]
DIGITAL VCO
DEVIATION
[dE+DIGITAL]
DTCS WAVE
FORM
[dt]
1
1
1
2
3
4
1
1
1
1
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• Loosely couple a frequency counter to the antenna
connector on the rear panel.
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• Connect an RF power meter to the antenna connector.
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• [High]/[Low] switch : High
• Connect an RF power meter to the antenna connector.
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• Connect an audio generator to the [MIC] jack and set
as : 1 kHz/80 mV rms
• Connect an FM deviation meter to the antenna connector and set as :
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis : OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• No audio signal is applied to the [MIC] jack.
• Connect an FM deviation meter to the antenna con-
nector and set as :
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis : OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• No audio signal is applied to the [MIC] jack.
• DTCS code : 023
• Set an FM deviation meter as:
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis : OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• Transmitting
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to 146.0000 MHz.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set the VHF high power to 67 W.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
•
Turn the [DIAL] to set the VHF middle power to 25 W.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set the VHF low power to 10 W.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set the VHF low power to 5 W.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key while transmitting.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to ±4.6 kHz.
• Push the [S.MW] key after finish adjustment.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to ±1.25 kHz.
• Push the [S.MW] key after finish adjustment.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to flat wave form as shown
below.
• Push the [S.MW] key after finish adjustment.
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION OPERATION
Set to flat wave
form
Page 20

5 - 4
SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENTS (TRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING)–Continued
DIGITAL
REFERENCE
DEVIATION
[dt+DIGITAL]
RECEIVER
SENSITIVITY
[tr]
SQUELCH
LEVEL
(Wide)
[Sq]
S-METER
(FM mode)
[Sr]
(AM mode)
[Sr+.]
1
1
2
3
4
1
1
2
• Operating frequency : 146.0 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• No audio signal is applied to the [MIC] jack.
• Connect an FM deviation meter to the antenna con-
nector and set as :
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis : OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• Transmitting
• Operating frequency : 118.020 MHz
• Connect an SSG to the antenna connector and set as
Level : 0.5 µV* (–113 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ± 3.5 kHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 136.020 MHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 147.980 MHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 173.980 MHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 145.020 MHz
• Connect an SSG to the antenna connector and set as
Level : 0.1 µV* (–127 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ± 3.5 kHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 145.020 MHz
• Connect an SSG to the antenna connector and set as
Level : 1.3 µV* (–105 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ± 3.5 kHz
• Receiving
• Operating frequency : 127.020 MHz
• Connect an SSG to the antenna connector and set as
Level : 1.0 µV* (–107 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : 30 %
• Receiving
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to ±0.85 kHz.
• Push the [S.MW] key after finish adjustment.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to squelch tight point.
• Turn the [DIAL] to set to squelch threshold point.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
• Push the [S.MW] key.
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION OPERATION
*This output level of a standard signal generator (SSG) is indicated as SSG’s open circuit.
Page 21

5 - 5
5-3 UT-115 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
• PREPARATION
Enter the adjustment mode when adjusting the UT-115.
■ REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
DC power supply 1
DC power supply 2
Frequency counter
Oscilloscope
EQUIPMENT GREDE AND RANGE EQUIPMENT GREDE AND RENGE
Output voltage : 5.0 V DC
Current capacity : 1 A or more
Output voltage : 8.0 V DC
Current capacity : 1 A or more
Frequency range : 0.1–100 MHz
Frequency accuracy : ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Frequency range : DC–400 MHz
Measuring range : 0.01–10 V
■ ENTERING THE ADJUSTMENT MODE
Connect J301, pin 14 to GND, then the UT-115 enters adjustment mode.
NOTE: Exit from the adjustment mode to disconnect J310, pin 14 from GND before the UT-115 adjustment is fihished
■ CONNECTION
Power supply
8 V DC / 1 A
Power supply
5 V DC / 1 A
J301, Pin 14
Entering adjustment mode
• UT-115 BOTTOM VIEW
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 22

5 - 6
5-4 TRIMMER ADJUSTMENTS
CODEC
FREQUENCY
SET
MODEM
FREQUENCY
SET
MODURATION
OUTPUT
LEVEL
ADJUSTMENT
ADJUSTMENT
MEASUREMENT MEASUREMENT
VALUE
POINT
UNIT LOCATION
UNIT ADJUST
1
1
1
2
3
MAIN
MAIN
MAIN
Connect the frequency counter to
the check point CP101.
Connect the frequency counter to
the check point CP216.
• Transmit the UT-115 to connect
J301, pin 1 to GND.
• Connect the oscilloscope to the
J301, pin 21.
Disconnect J301, pin 1 from GND.
16.38400 MHz ±10 Hz
2.457600 MHz ±3 Hz
350 mV
p-p ±10 mV
MAIN
MAIN
MAIN
C102
C207
R264
J301, Pin 21
Modulation output level
check point
J301, Pin 1
Transmit the UT-115
CP101
CODEC frequency set check point
CP216
MODEM frequency set check point
C207
MODEM frequency set adjustment
C102
CODEC frequency set adjustment
• UT-115 TOP VIEW
• UT-115 BOTTOM VIEW
Page 23

[LOGIC UNIT]
[LOGIC UNIT]
IC1 1140011860 S.IC M30220FCRP (FX-2698A) [EXP] B
1140011861 S.IC M30220FCRP (FX-2698A-1) [USA] B
1140011910 S.IC M30220MA-132RP (FX-2698A-1)
except [EXP] and [USA] B
IC2 1130004200 S.IC TC4S66F (TE85R) B
IC3 1110005340 S.IC NJM12902V-TE1 B
IC4 1110006210 S.IC BD5242FVE-TR B
IC5 1140008650 S.IC HN58X2464TI B
IC6 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR T
IC24 1110002860 S.IC TA75S393F (TE85R) T
IC514 1110005310 S.IC AN6123MS B
IC520 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR T
IC521 1130008560 S.IC TC75S51F (TE85L) B
IC522 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR B
IC524 1130011780 S.IC SN74AHC2G53HDCTR B
IC525 1130011770 S.IC CD4066BPWR T
Q1 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R) T
Q2 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q3 1590001650 S.TRANSISTOR XP4601 (TX) B
Q5 1590000660 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144TU T106 B
Q6 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R B
Q7 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R) B
Q8 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R) B
Q12 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R) B
Q513 1520000200 S.TRANSISTOR 2SB798-T2 DK B
Q514 1530002690 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-GR (TE85R) B
Q515 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R B
Q524 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R T
Q525 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q527 1590002230 S.TRANSISTOR UMG2N TL B
Q528 1590002430 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EE TL T
D1 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) T
D2 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) T
D3 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
D4 1750000520 S.DIODE DAN222TL B
D6 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL B
D7 1750000520 S.DIODE DAN222TL T
D8 1750000520 S.DIODE DAN222TL T
D9 1750000520 S.DIODE DAN222TL T
D11 1710000611 DIODE 1SS133 T77 (26M/M)
[TPE], [KOR], [EUR-1] only B
D13 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61
except [EXP], [EXP-1] B
D15 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 [EXP], [EXP-1] only B
D16 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61
[EUR], [EUR-1], [EXP], [EXP-1] only B
D17 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61
[TPE], [KOR], [EXP], [EXP-1] only B
D21 1750000520 S.DIODE DAN222TL T
D22 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61
[TPE], [EXP], [EXP-1] only B
D23 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 [TPE], [KOR] only B
D25 1790001260 S.DIODE MA2S077-(TX) B
D27 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 except [EXP-1] B
D28 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 [EXP], [EXP-1] only B
D526 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) B
X1 6050011500 S.XTAL CR-739 (9.8304 MHz) B
R1 7030008010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 kΩ) T
R2 7030005310 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 kΩ) T
R3 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) T
R4 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R5 7030005230 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 334 X (330 kΩ) T
R6 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) T
R7 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R8 7030007290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 222 X (2.2 kΩ) T
R9 7030005220 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 kΩ) T
R10 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) T
R11 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R12 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) T
R13 7030008010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 kΩ) B
R14 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R15 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
S.=Surface mount
R16 7030005070 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 kΩ) B
R17 7030005070 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 kΩ) B
R18 7030005720 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 563 X (56 kΩ) B
R19 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R20 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R21 7030005070 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 kΩ) B
R22 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R23 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R24 7030007340 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 kΩ) B
R25 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R26 7030005220 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 kΩ) B
R27 7030003630 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ)
[EXP] only B
7030007350 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 kΩ) [other] B
R28 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R29 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R30 7030007340 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 kΩ) B
R31 7030005720 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 563 X (56 kΩ) B
R32 7030007570 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 122X (1.2 kΩ) B
R34 7030005070 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 kΩ) B
R35 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R36 7030008010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 kΩ) B
R37 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R38 7030008400 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 182 X (1.8 kΩ) B
R39 7030005100 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 154 X (150 kΩ) B
R40 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R41 7030008010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 kΩ) B
R42 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R43 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R44 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R45 7030008410 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 392 X (3.9 kΩ) B
R46 7410000770 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 102JV (1 kΩ) T
R47 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) T
R48 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R49 7030005600 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 kΩ) B
R50 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R51 7030005530 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 100 X (10 Ω) B
R52 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) T
R53 7030007310 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 155 X (1.5 MΩ) B
R55 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ)
[EUR], [EXP], [EXP-1] only B
R56 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω) B
R57 7030007340 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 kΩ) B
R58 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R59 7030007340 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 153 X (15 kΩ) B
R60 7030005720 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 563 X (56 kΩ) B
R61 7210001870 VARIABLE EVU-F2AF20 A14 (10KA) T
R62 7210001860 VARIABLE EVU-F2AF20 B14 (10KB) T
R64 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R67 7030008290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 kΩ) B
R69 7030005100 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 154 X (150 kΩ) B
R70 7030007350 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 kΩ) B
R71 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R72 7030005110 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 224 X (220 kΩ) B
R73 7030008300 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 184 X (180 kΩ) B
R74 7030005100 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 154 X (150 kΩ) B
R75 7030005070 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 683 X (68 kΩ) B
R76 7030008290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 kΩ) B
R77 7030009290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 562 X (5.6 kΩ) B
R78 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R79 7030005040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 kΩ) B
R80 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R81 7030005310 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 kΩ) B
R82 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R83 7030005590 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 680 X (68 Ω) B
R84 7030005030 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 152 X (1.5 kΩ) B
R85 7030005210 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 822 X (8.2 kΩ) B
R86 7030009160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 181 X (180 Ω) B
R87 7410000950 S.ARRAY EXB-V8V 102JV T
R89 7030009280 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GE B
R91 7030005310 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 124 X (120 kΩ) B
R92 7030008290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 kΩ) B
R93 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R94 7030005570 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 820 X (82 Ω) B
R96 7030007350 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 393 X (39 kΩ) B
R97 7030007270 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 151 X (150 Ω) B
R100 7030007280 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 331 X (330 Ω) B
R101 7030005040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 kΩ) B
R103 7030005100 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 154 X (150 kΩ) B
6 - 1
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6-1 IC-2200H
Page 24

[LOGIC UNIT]
R104 7030005080 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 823 X (82 kΩ)
[USA] only B
7030008290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 183 X (18 kΩ) [other] B
R105 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R106 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R107 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R108 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R109 7030005600 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 273 X (27 kΩ)
[USA] only B
R112 7030008010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 kΩ) B
R114 7030008010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 123 X (12 kΩ) B
R128 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R129 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R133 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R134 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R135 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R136 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R137 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R515 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R516 7030010040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GE-JPW T
R517 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R519 7030005010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680 Ω) B
R520 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R521 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R522 7030005100 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 154 X (150 kΩ) B
R523 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R524 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R525 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R526 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R527 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
R530 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R531 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R532 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R533 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R534 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R536 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) T
R537 7030005010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680 Ω) T
R538 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R539 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R541 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R542 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R543 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R545 7410000770 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 102JV (1 kΩ) T
R546 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) T
R548 7030000240 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 68 Ω (680) T
R549 7030000240 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 68 Ω (680) B
R550 7030010040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GE-JPW B
R551 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) B
C1 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C4 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K T
C5 4030017420 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H470J T
C7 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C8 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K T
C9 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C10 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C11 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C13 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C14 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C15 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C16 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C19 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C20 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C23 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K T
C28 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C30 4030017420 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H470J B
C31 4030017420 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H470J T
C32 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR B
C33 4030013960 S.CERAMIC C1005 JB 1C 473K-T-N B
C34 4030017790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E682K B
C35 4030017040 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A333K B
C36 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C37 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C38 4030018080 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1H182K B
C39 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C40 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C41 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C42 4030016950 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A473K B
C43 4030016950 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A473K B
C44 4030018240 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E562K B
C45 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C46 4030016970 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C223K B
C47 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C48 4030017760 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1H222K B
C49 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C51 4030017030 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A273K B
C52 4030017420 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H470J T
S.=Surface mount
6 - 2
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[LOGIC UNIT]
C53 4030017500 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H560J B
C54 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C55 4030017600 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H080C B
C56 4030017760 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1H222K B
C57 4030018110 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1H272K B
C59 4030017640 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H150J B
C62 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C64 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C65 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C66 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K T
C67 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR B
C68 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C69 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C70 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K T
C71 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C72 4030017040 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A333K B
C73 4510005860
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA2R2SR B
C74 4030018240 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E562K B
C75 4030017450 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E271K B
C76 4030017040 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A333K B
C77 4510005860
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA2R2SR B
C78 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C79 4030017440 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H221J B
C80 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C81 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C82 4030017730 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E471K B
C583 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C584 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C585 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C586 4510005600
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CS100SR B
C587 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L B
C588 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B
C591 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K T
C592 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C593 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C594 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C595 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K T
C596 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C597 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C599 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C600 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K T
C601 4550006210 S.TANTALUM ECST1CX106R T
C602 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L B
J1 6450002210 CONNECTOR 3017-8821 <KIN> T
J3 6510024230 S.CONNECTOR 08-6210-0363-40-800 B
J4 6510021970 S.CONNECTOR AXN330C130P B
DS1 5030002660 LCD IS08264E00V2 T
DS2 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS3 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS4 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS5 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS6 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS7 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS8 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS9 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS10 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS11 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS12 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
DS13 5040001760 S.LED SEC 2422C T
S1 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S2 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S3 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S4 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S5 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S6 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S7 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S8 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
S9 2250000460 ENCODER EVQ-VENF0224B T
S10 2260001890 S.SWITCH SKQDPA T
EP1 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT T
EP2 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP3 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP4 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP5 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT T
EP6 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP7 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP8 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP9 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP10 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP11 8930062251 LCD CONTACT SRCN-2698-SP-N-W-1 T
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
Page 25

[LOGIC UNIT]
EP12 0910057732 PCB B 6048B
IC1 1130008350 S.IC LV2105V-TLM B
IC2 1130011760 S.IC CD4094BPWR T
IC4 1110003490 S.IC TA31136FN (D,EL) B
IC5 1190000350 S.IC M62363FP-650C B
IC6 1110004050 S.IC NJM3404AV-TE1 B
IC7 1180001250 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L) B
IC8 1180000970 S.IC AN78L05M-(E1) B
IC9 1110002550 IC TA7252AP T
IC10 1150002180 S.IC S-AV36 (I) T
IC11 1110004050 S.IC NJM3404AV-TE1 T
IC12 1130011780 S.IC SN74AHC2G53HDCTR T
Q1 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) B
Q2 1590001650 S.TRANSISTOR XP4601 (TX) B
Q3 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) B
Q4 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) B
Q5 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) B
Q6 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T
Q7 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T
Q8 1590001040 S.TRANSISTOR DTA113ZU T106 B
Q9 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T
Q10 1560000810 S.FET 2SK1069-4-TL T
Q11 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T
Q12 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25 T
Q13 1590000720 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA T106 except [EXP-1] T
Q14 1510000590 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1362-Y (TE85L) T
Q15 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) T
Q16 1530003220 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4406-4-TL B
Q17 1530000370 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC3356-T1B B
Q19 1580000760 S.FET 3SK299-T1 U73 B
Q21 1590001010 S.TRANSISTOR DTB113ZK T146 T
Q22 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 T
Q25 1590001010 S.TRANSISTOR DTB113ZK T146 T
Q26 1590000720 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA T106 B
Q27 1580000760 S.FET 3SK299-T1 U73 B
Q28 1530002970 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4684 (TE16R) B
Q29 1530003090 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4213-B (TE85R) B
Q30 1510000890 S.TRANSISTOR DTA143TU T106 T
Q31 1590001320 S.TRANSISTOR DTC143ZUA T106 T
Q34 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R) B
Q35 1530002340 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2954-T1 B
Q36 1590001040 S.TRANSISTOR DTA113ZU T106 T
Q37 1590001190 S.TRANSISTOR XP6501-(TX) .AB T
Q38 1590001190 S.TRANSISTOR XP6501-(TX) .AB T
Q39 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q40 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q41 1530003630 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TLS B
D1 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) B
D2 1750000720 S.VARICAP HVC375BTRF T
D3 1750000770 S.VARICAP HVC376BTRF T
D4 1720000730 S.VARICAP MA2S30400L T
D5 1720000730 S.VARICAP MA2S30400L T
D6 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX) B
D7 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX) B
D9 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF B
D10 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF B
D11 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF B
D12 1710001060 DIODE XB15A407 T
D13 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF B
D14 1790000980 S.DIODE MA742 (TX) T
D15 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 T
D16 1710000870 S.DIODE HVU131TRF T
D17 1790000980 S.DIODE MA742 (TX) T
D18 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) B
D19 1710001080 DIODE XB15A308 T
D20 1730000520 ZENER RD20E B2 T
D21 1790000700 DIODE DSA3A1 T
D23 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) except [EXP-1] B
D24 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) except [EXP-1] T
D25 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) except [EXP-1] T
D26 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) except [EXP-1] B
D27 1710001060 DIODE XB15A407 T
D29 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL B
S.=Surface mount
6 - 3
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[MAIN UNIT]
D30 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D31 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) B
D38 1720000730 S.VARICAP MA2S30400L T
FI1 2020001520 CERAMIC CFWLA450KFFA-B0 (CFWS450F) T
FI2 2020001460 CERAMIC
CFWLA450KHFA-B0 (CFWS450HT)
except [EXP-1] T
FI3 2030000270 MONOLITH FL-363 (21.7 MHz) T
FI4 2030000270 MONOLITH FL-363 (21.7 MHz) T
X1 6050011870 S.XTAL CR-779 (21.250 MHz) T
X2 6070000200 DISCRIMINATOR
CDBLA450KCAY24-B0 (CDB450C24)
T
L1 6200009350 S.COIL ELJRE R22G-F3 T
L2 6200003640 S.COIL MLF1608E 100K-T T
L3 6200001620 S.COIL ELJFC 1R0K-F B
L6 6200009920 S.COIL C2012C-R10G T
L7 6200010570 S.COIL C6342A-R11J-A T
L8 6200004870 S.COIL ELJFC 2R7K-F T
L9 6200004880 S.COIL ELJFC 3R3K-F T
L10 6200001620 S.COIL ELJFC 1R0K-F B
L11 6200009350 S.COIL ELJRE R22G-F3 T
L12 6200009350 S.COIL ELJRE R22G-F3 T
L13 6200006980 S.COIL ELJRE R10G-F T
L14 6200006990 S.COIL ELJRE 56NG-F B
L15 6200007000 S.COIL ELJRE 82NG-F T
L18 6200005730 S.COIL ELJRE 39NG-F B
L19 6200004920 S.COIL MLF1608A 2R2K-T B
L20 6200005740 S.COIL ELJRE 47NG-F B
L21 6200006670 S.COIL ELJRE 68NG-F B
L22 6200006670 S.COIL ELJRE 68NG-F B
L25 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J B
L26 6200003280 S.COIL NL 252018T-2R2J B
L31 6200009890 S.COIL C2012C-82NG T
L32 6200009890 S.COIL C2012C-82NG T
L37 6200010050 S.COIL AS080547-47N T
L38 6200009930 S.COIL C2012C-68NG T
L39 6200010050 S.COIL AS080547-47N T
L40 6200010420 S.COIL FHW1210HC 1R0JGT T
L42 6200007370 S.COIL ELJFC R82K-F B
L43 6200009460 S.COIL 0.25-1.9-7TL 67N T
L45 6200008150 S.COIL 0.35-1.6-7TL 44N T
L46 6200010060 S.COIL AS080647-56N T
L47 6200010060 S.COIL AS080647-56N T
L48 6200010060 S.COIL AS080647-56N T
L52 6200002650 S.COIL NL 252018T-R18J B
L56 6200006670 S.COIL ELJRE 68NG-F B
L57 6190001520 S.COIL ZBFS5101-PT T
L58 6190001520 S.COIL ZBFS5101-PT T
L59 6190001520 S.COIL ZBFS5101-PT T
L60 6190001520 S.COIL ZBFS5101-PT T
L61 6200003640 S.COIL MLF1608E 100K-T T
L62 6200003640 S.COIL MLF1608E 100K-T T
R1 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ) T
R2 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T
R3 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) T
R4 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω) [EXP] T
7030003310 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 820 V (82 Ω) [other] T
R5 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R6 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R7 7510001660 S.THRMISTOR NTCG16 4LH 473KT T
R8 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R9 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R10 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T
R11 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R12 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R13 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ) B
R14 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ) B
R15 7030003730 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ) B
R16 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) B
R17 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R18 7030003390 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω) B
R19 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ) T
R20 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ) T
R21 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R22 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R23 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) T
R24 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B
R25 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T
R26 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R27 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ) T
R28 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T
R29 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
Page 26

[MAIN UNIT]
R30 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ) T
R31 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T
R32 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) T
R33 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) T
R34 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R35 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω) T
R36 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T
R37 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T
R39 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R40 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R41 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) T
R42 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) T
R43 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ) B
R44 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R45 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R46 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R47 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) T
R48 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) T
R49 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R50 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R51 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R52 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B
R54 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω) B
R55 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R56 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R57 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B
R58 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R59 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B
R60 7030003260 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 330 V (33 Ω) B
R62 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R63 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω) B
R64 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R66 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R71 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R72 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B
R73 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) B
R76 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R78 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R79 7030003360 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 221 V (220 Ω) B
R81 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R88 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R90 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R92 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω) T
R93 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R95 7030000230 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 56 Ω (560) T
R96 7030000410 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.8 kΩ T
R101 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R103 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) B
R104 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R106 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R107 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R108 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B
R109 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ) B
R110 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R111 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R112 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) T
R113 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R114 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R117 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R118 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R119 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R120 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) T
R121 7030000260 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 100 Ω (101) T
R122 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R123 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ) B
R124 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ) T
R125 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω) T
R126 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ) T
R127 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ) B
R128 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R129 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R130 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ) B
R131 7030003670 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 823 V (82 kΩ) B
R135 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] T
R136 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] T
R137 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] B
R138 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] B
R139 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] B
R140 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] T
R150 7030006070 S.RESISTOR ERJ12YJ101U (100 Ω) T
R152 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω) B
R153 7030003330 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 121 V (120 Ω) B
S.=Surface mount
6 - 4
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[MAIN UNIT]
R154 7030003330 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 121 V (120 Ω) B
R155 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ) B
R156 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R157 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R168 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω) B
R169 7030003230 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 180 V (18 Ω) B
R170 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω) B
R171 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] B
R172 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
except [EXP-1] T
R173 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R174 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R175 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T
R176 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T
R177 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω) B
R178 7030003270 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 390 V (39 Ω) B
R179 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω) B
R180 7030003220 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 150 V (15 Ω) B
R181 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω) B
R182 7030003240 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 220 V (22 Ω) B
R183 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R184 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R185 7030003220 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 150 V (15 Ω) B
R186 7030005501 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 124V (120 kΩ) T
R187 7030005501 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 124V (120 kΩ) T
R188 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R189 7030005981 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 333V T
R190 7030005981 S.RESISTOR ERA3YED 333V T
R191 7030003730 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ) T
R192 7030003730 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ) T
R193 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ) T
R194 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R195 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R201 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) T
R202 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) T
R203 7030003710 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) T
R204 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R205 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ) T
R207 7030003710 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ) T
R208 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ) T
R209 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) T
R212 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ) T
R213 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω) T
R214 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R220 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ) T
R221 7030003770 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 564 V (560 kΩ) T
R223 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T
R224 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V [EXP-1] only B
R225 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V [EXP-1] only T
R226 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V B
R228 7520000120 POSISTOR PTFM04BC222Q2N34B0 T
R229 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V B
R230 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R231 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V T
R232 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) T
R233 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V B
R234 7030011140 RESISTOR ERJ8GEYJ JPW T
R236 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V B
R237 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T
R238 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) T
C1 4550006160 S.TANTALUM ECST1CY155R B
C2 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C4 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T
C5 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T
C7 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C8 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C9 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T T
C10 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP T
C11 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L B
C12 4550007060 S.TANTALUM ECSTIAX336R B
C13 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T T
C14 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C15 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C16 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T
C17 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C20 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T T
C21 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T
C22 4030007060 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 270J-T B
C23 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T B
C24 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L B
C25 4030009920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050B-T T
C26 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T T
C28 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C29 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T T
C30 4030006950 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 040C-T B
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
Page 27

[MAIN UNIT]
C31 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C32 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T
C34 4030009500 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5B-T T
C36 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C37 4030009500 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5B-T T
C38 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C39 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C40 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C41 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C42 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C44 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C45 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C47 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C48 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C49 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T T
C50 4030006940 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 030C-T T
C51 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C52 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C53 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C54 4030007000 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 090D-T T
C55 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T
C56 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C57 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C58 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C59 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C60 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C61 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C62 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T
C63 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C64 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T
C65 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C66 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C67 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C68 4030007000 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 090D-T T
C69 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR T
C70 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C71 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B
C72 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C73 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C74 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C75 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C76 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T B
C77 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C78 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C79 4030007080 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 390J-T B
C80 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C81 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C82 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR T
C83 4030012600 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1A 105M-T B
C84 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T B
C85 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T B
C86 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C87 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T B
C88 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T B
C89 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C90 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T B
C91 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C93 4030006910 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5C-T B
C94 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C95 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C97 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T B
C98 4030008900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 333K-T B
C100 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T B
C101 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C105 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C108 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C111 4030009990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 200J-T B
C113 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C117 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C118 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP T
C120 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C122 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C123 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C124 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T B
C125 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR T
C127 4030006920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010C-T B
C128 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C131 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T B
C133 4030006920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010C-T B
C134 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C136 4030009560 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H R75B-T B
C137 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C138 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C139 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T B
C140 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C141 4030006930 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 020C-T B
C145 4030006920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010C-T B
C146 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
S.=Surface mount
6 - 5
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[MAIN UNIT]
C148 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T B
C149 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C152 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T B
C153 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C154 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C157 4510006250
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA331UP T
C158 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C160 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C161 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C162 4030009550 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 2R5B-T B
C163 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C164 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C166 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP T
C168 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C169 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C170 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C172 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C173 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C174 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C175 4510006250
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA331UP T
C176 4030011040 S.CERAMIC GRM31M4C2H2R0CY21L T
C177 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR T
C178 4030006950 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 040C-T B
C179 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C180 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C181 4510004440
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA010SR T
C182 4030007150 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 151J-T B
C184 4030006960 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050C-T B
C185 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C187 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C188 4510004440
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA010SR T
C189 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C190 4030011020 S.CERAMIC GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L T
C191 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T
C192 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C193 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C194 4510006220
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA101UP T
C195 4510004640
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA470SP T
C196 4030011020 S.CERAMIC GRM31M4C2H1R0CY21L T
C197 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T T
C198 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C200 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C201 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T T
C204 4510006260
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1AA471UP T
C205 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C206 4030011110 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H9R0DV01L T
C207 4510006020 ELECTROLYTIC 16 MV 2200 HC T
C208 4030011210 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H330JV01L T
C209 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C210 4030011160 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H150JV01 T
C211 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C212 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C215 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T
C216 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T
C217 4030011230 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H390JV01L T
C218 4030011190 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H270JV01L T
C221 4030010780 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 1R5C-T T
C222 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C224 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C225 4030017200 S.CERAMIC GRM31BR32J102KY01L T
C227 4030011210 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H330JV01L T
C228 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T
C230 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR except [EXP-1] T
C232 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C233 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C240 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C241 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C242 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C243 4030017810 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 102J-T B
C244 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C245 4030008680 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1C 105Z-T B
C246 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C247 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C250 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T B
C251 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C252 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C253 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T B
C254 4550006080 S.TANTALUM TEESVB2 1C 106M8L B
C255 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C256 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C257 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C258 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C259 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C265 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C266 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C267 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C268 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T
C269 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T T
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
Page 28

[MAIN UNIT]
IC1 1140005870 S.IC µPD7564AG-555-E1 B
IC2 1130008630 S.IC MC14028BF-EL B
IC3 1110006010 S.IC S-80845CLUA-B66-T2 B
Q1 1530001940 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-BL (TE85R) B
Q2 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106 B
Q3 1590001330 S.TRANSISTOR DTA114EUA T106 B
Q4 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q5 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q6 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q7 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q8 1530001940 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-BL (TE85R) B
Q9 1590001010 S.TRANSISTOR DTB113ZK T146 B
D1 1790000950 S.ZENER MA8056-M (TX) B
D3 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D4 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D5 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D6 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D7 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D8 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D9 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D10 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D11 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D12 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D13 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D14 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D15 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
D16 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
D17 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
D18 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
D19 1750000550 S.DIODE 1SS355 TE-17 B
X1 6060000530 CERAMIC
CSBLB600KJ28T-B0 (CSB600J200T)
B
L1 6200001520 S.COIL MLF2012D R82K-T B
L2 6200001520 S.COIL MLF2012D R82K-T B
R2 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R3 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R4 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R5 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R6 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B
R7 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B
R8 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B
R9 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R10 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R11 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R12 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R13 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R14 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R15 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R16 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R18 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) B
R19 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) B
R20 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) B
R21 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ) B
R22 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R23 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R24 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R25 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R26 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R27 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ) B
R29 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω) B
R30 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ) B
R31 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R32 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R33 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R34 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R35 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R36 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R37 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B
R38 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R39 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B
R40 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B
R41 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
C1 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T B
C2 4510006220 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA101UP B
C3 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T B
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
C271 4550006140 S.TANTALUM ECST1EY474R T
C272 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T
C273 4550006480 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1C 475M8L T
C278 4510004540
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV0JA470SR T
C279 4510004440
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA010SR T
C280 4550006130 S.TANTALUM ECST1VY224R B
C281 4510005830
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HAN010R T
C282 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C283 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C284 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T B
C285 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
except [EXP-1] T
C286 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C287 4030017810 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 102J-T B
C288 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T B
C289 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C290 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C291 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C292 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C293 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C294 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C295 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T T
C296 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C297 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C299 4030012600 S.CERAMIC C2012 JB 1A 105M-T T
C300 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C301 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
C302 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T T
J4 6450002220 CONNECTOR PJ-0008P-5 <KUO> B
J6 6510014960 S.CONNECTOR B2B-ZR-SM3-TF T
J7 6450001430 CONNECTOR HSJ1462-01-010 B
J11 6510024240 S.CONNECTOR 04-6274-036-000-800 T
W1 8900011880 CABLE OPC-1210 (P=0.5 N=36 L=70)
W5 7120000470 JUMPER ERDS2T0
W6 8900010980 CABLE OPC-1131 <CMI>
EP1 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP2 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP3 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT T
EP4 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT T
EP5 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP6 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP7 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT T
EP8 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP9 9040901901 TUBE IRRAX 0.7 (d) L=12 mm
EP10 0910057743 PCB B 6076C
EP11 6910000640 BEAD FSRH090160RN000B
[USA], [EUR], [EUR-1] only
EP12 6910000640 BEAD FSRH090160RN000B
[USA], [EUR], [EUR-1] only
S.=Surface mount
6 - 6
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
6-2 HM-133V
Page 29

S.=Surface mount
6 - 7
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[MAIN UNIT]
C4 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T B
C5 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C9 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C10 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C11 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C12 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C13 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C14 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T B
C15 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C16 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C17 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C18 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C19 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C21 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C22 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C23 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C24 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C25 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C26 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C27 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C29 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR B
C30 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C31 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR B
J1 6510023110 CONNECTOR 3008L-8P8C <KIN> B
DS1 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS2 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS3 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS4 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS5 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS6 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS7 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS8 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS10 5010000150 S.LED LT1EP53A T
DS11 5010000150 S.LED LT1EP53A T
MC1 7700002310 MICROPHONE EM-140 T
S1 2260000980 SWITCH SKHHLP014A B
EP1 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP2 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP3 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP4 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP5 0910055172 PCB B 5811B
IC1 1140011490 S.IC µPD789071MC-041-5A4-E1 B
IC3 1110006310 S.IC BD5245G-TR B
IC6 1130012030 S.IC BR24L02FV-WE2 B
Q1 1530001940 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-BL (TE85R) B
Q2 1590000680 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114EUA T106 B
Q3 1590001330 S.TRANSISTOR DTA114EUA T106 B
Q4 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q5 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q6 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q7 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q8 1530001940 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC2712-BL (TE85R) B
Q9 1590001010 S.TRANSISTOR DTB113ZK T146 B
D1 1790000950 S.ZENER MA8056-M (TX) B
D3 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D4 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D5 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D6 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D7 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D9 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D10 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D11 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
D12 1750000940 S.DIODE ISS400 TE61 B
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
[MAIN-A BOARD]
[MAIN-A UNIT]
D16 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
D17 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
D18 1730002280 S.ZENER MA8091-M (TX) B
X1 6060000610 S.CERAMIC EFOS4914E3 B
L1 6200001520 S.COIL MLF2012D R82K-T B
L2 6200001520 S.COIL MLF2012D R82K-T B
R2 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R3 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R4 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R5 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R6 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B
R7 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ) B
R8 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ) B
R9 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R10 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R11 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R12 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R13 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R14 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω) B
R15 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω) B
R16 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R18 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R19 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ) B
R22 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R23 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R24 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R25 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ) B
R27 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R35 7030000400 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 1.5 kΩ B
R36 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R37 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ) B
R38 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ) B
R39 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B
R40 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ) B
R41 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ) B
R42 7030003860 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GE JPW V B
R43 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R44 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R45 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R46 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R47 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R48 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R49 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R50 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R51 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
C1 4030006850 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 471K-T B
C2 4510006220 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA101UP B
C5 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C9 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C10 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C11 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T B
C12 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C13 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C14 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T B
C15 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C16 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C17 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C18 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C19 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C21 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C22 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C23 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C24 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C25 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C26 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C27 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C29 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR B
C30 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C31 4510004630 S.ELECTROLYTIC ECEV1CA100SR B
J1 6510023110 CONNECTOR 3008L-8P8C <KIN> B
DS1 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS2 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS3 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS4 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS5 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS6 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
Page 30

[MAIN-A UNIT]
DS7 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS8 5010000120 S.LED LN1371G-(TR) T
DS10 5010000150 S.LED LT1EP53A T
DS11 5010000150 S.LED LT1EP53A T
MC1 7700002310 MICROPHONE EM-140 T
S1 2260000980 SWITCH SKHHLP014A B
EP1 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP2 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP3 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP4 6910012350 S.BEAD MMZ1608Y 102BT B
EP5 0910057281 PCB B 6094A
S.=Surface mount
6 - 8
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[MAIN UNIT]
IC1 1130007560 S.IC LC73881M-TLM B
IC2 1130007300 S.IC TC4W66FU (TE12L) B
X1 6050005090 XTAL CR-245 (4.194304 MHz) T
L1 6200001260 S.COIL MLF2012A 1R8M-T B
R1 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R2 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R3 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R4 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R5 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R6 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ) B
R7 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R8 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ) B
R9 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ) B
R10 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ) B
C1 4550006300 S.TANTALUM ECST1AY475R B
C2 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T B
C3 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T B
C4 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C5 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C6 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
C7 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T B
J1 6510018440 S.CONNECTOR AXN430C330P B
EP1 0910050481 PCB B 5191A
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
6-3 UT-108 (OPTIONAL UNIT)
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 31

S.=Surface mount
6 - 9
M.=Mounted side (T: Mounted on the Top side, B: Mounted on the Bottom side)
[MAIN UNIT]
IC1 1180002390 S.REG S-812C33AMC-C2N-T2 T
IC2 1180002370 S.REG R1111N321B-TR T
IC50 1130011630 S.IC AD73311ARS T
IC101 1130008360 S.IC TC7SHU04FU (TE85L) B
IC103 1130006890 S.IC TC7S04FU (TE85R) T
IC151 1130010920 S.IC AMBE-2020 T
IC202 1130010460 S.IC TC7SH08FU (TE85L) B
IC203 1110005730 S.IC S-80928CNMC-G8Y-T2 B
IC204 1140010770 S.IC HD64F3687FP B
IC251 1110005290 S.IC NJM2115V-TE1 B
IC252 1110005430 S.IC CMX589AD5 B
IC253 1110006200 S.IC NJM13404V-TE1 B
IC254 1130004200 S.IC TC4S66F (TE85R) B
IC351 1120002980 S.IC MAX3226EAE-T T
Q50 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) T
Q51 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q201 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q202 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q251 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q252 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q301 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q302 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q303 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
Q305 1590001660 S.TRANSISTOR XP4312 (TX) B
Q306 1590001660 S.TRANSISTOR XP4312 (TX) B
Q400 1510000770 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1586-GR (TE85R) B
Q401 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106 B
D151 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX) T
D152 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX) B
X101 6050011240 S.XTAL CR-708 (16.384 MHz) T
X201 6050011700 S.XTAL CR-760 (9.8304 MHz) T
L50 6200003960 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T
L151 6200003960 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R0K-T B
L201 6200003960 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R0K-T B
L351 6200003960 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R0K-T T
R1 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R2 7030000180 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 22 Ω (220) T
R50 7030005010 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 681 X (680 Ω) T
R51 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) T
R52 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R53 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R54 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R55 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R56 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R57 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R58 7030010040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GE-JPW B
R59 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) T
R60 7030005050 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 103 X (10 kΩ) T
R100 7030010040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GE-JPW T
R101 7030005160 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 105 X (1 MΩ) B
R102 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R103 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) T
R151 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) T
R152 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) T
R201 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R202 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R203 7030005040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 kΩ) B
R204 7030005040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 kΩ) B
R205 7030005040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 472 X (4.7 kΩ) B
R206 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R209 7030005120 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 102 X (1 kΩ) B
R211 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R212 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R216 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R217 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R218 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R219 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R221 7030010040 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GE-JPW B
R251 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R252 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R253 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R254 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R255 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R256 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R257 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R258 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
6-4 UT-115 (OPTIONAL UNIT)
[MAIN UNIT]
R260 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R261 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R262 7030005220 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 223 X (22 kΩ) T
R264 7310004610 S.TRIMMER EVM-2WSX80 B15 (104) T
R267 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R268 7030006610 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 394 X (390 kΩ) B
R269 7030005060 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 333 X (33 kΩ) B
R270 7030005240 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 473 X (47 kΩ) B
R308 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) T
R309 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) T
R315 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) T
R316 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) T
R317 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) B
R318 7030004980 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 101 X (100 Ω) T
R400 7030005090 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 104 X (100 kΩ) B
R401 7030009290 S.RESISTOR ERJ2GEJ 562 X (5.6 kΩ) B
C1 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L T
C2 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L T
C5 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K B
C7 4550005980 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 475M8L T
C8 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C9 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L T
C10 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C11 4550006480 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1C 475M8L T
C50 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C51 4030016970 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C223K T
C53 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C54 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L T
C55 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C56 4030016950 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A473K B
C57 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C58 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C102 4540000070 S.TRIMMER TZY2Z100A001 T
C103 4030017590 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H070C T
C104 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C106 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C150 4550000460 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1C 105M8L T
C151 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C152 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C153 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C154 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C155 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C156 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C157 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C159 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K T
C201 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C202 4030017590 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H070C B
C203 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C204 4030017390 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H180J T
C205 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C206 4030016790 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1C103K B
C207 4540000080 S.TRIMMER TZY2R200A001 T
C250 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C252 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B
C253 4030017400 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EC1H220J B
C255 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B
C256 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C257 4030017030 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A273K B
C258 4030017030 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A273K B
C259 4030017760 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1H222K T
C260 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B
C261 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C262 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T B
C263 4030016930 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1A104K B
C333 4030017460 S.CERAMIC ECJ0EB1E102K T
C351 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T
C352 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T
C353 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T
C354 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T T
C355 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T T
C401 4550006250 S.TANTALUM TEESVA 1A 106M8L B
J301 6510018440 S.CONNECTOR AXN430C330P B
EP1 0910057812 PCB B 6071B
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION M.
NO. NO.
Page 32

SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS AND DISSASEMBLY
7 - 1
7-1 IC-2200H
J1 6450002210 Connector 3017-8821 1
R61 7210001870 Variable resistor EVU-F2AF20 A14 1
R62 7210001860 Variable resistor EVU-F2AF20 B14 1
S9 2250000460 Switch EVQ-VENF0224B 1
DS1 5030002660 LCD IS08264E00V2 1
EP11 8930062251 LCD contact SRCN-2698-SP-N-W-1 1
MP1 8210020350 2698 front panel 1
MP2 8210020340 2698 reflector 1
MP3 8930061130 2698 2-button 1
MP4 8930061140 2698 7-button 1
MP5 8930045610 2088 LCD filter 1
MP6 8810008990 Screw PH BT M2 × 10 ZK 4
MP7 8510015700 2698 front plate 1
MP8 8610011620 Knob N316 1
MP9 8610011610 Knob N317 2
MP11 8930062710 Sponge (HR) 1
MP12 8930062700 Himelon sheet (CM) 1
[LOGIC UNIT]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
7-2 HM-133V
W1 8900011270 Cable OPC-1153 1
MP1 8210018830 2539 front panel [HM-133] 1
8210018890 2539 front panel (A) [HM-133S] 1
8210018910 2539 front panel (B) [HM-133V] 1
MP2 8210018840 2539 rear panel 1
MP3 8930057380 2539 PTT button 1
MP4 8930057390 2539 LED lens 2
MP5 8930057570 2539 SW rubber 1
MP6 8930057520 2539 keyboard [HM-133] 1
8930057710 2539 keyboard (A) [HM-133S] 1
8930057700 2539 keyboard (B) [HM-133V] 1
MP8 8810009370 Screw PH BT M3 × 12 ZK 2
MP9 8810009560 Screw PH BT M2 × 6 ZK 3
[CHASSIS PARTS]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
Screw abbreviations BT, A: Self-tapping
PH: Pan head FH: Flat head
ZK: Black BS: Brass
NI: Nickel NI-ZU: Nickel-Zinc
J4 6450002220 Connector PJ-0008P-5 1
J7 6450001430 Connector HSJ1462-01-010 1
W6 8900010980 DC power cable OPC-1131 1
MP1 8510014470 2509 VCO case 1
MP2 8510014460 2509 VCO cover 1
MP3 8930005320 Filter spacer 2
MP4 8930062610 2698 M-holder 1
[MAIN UNIT]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
J1 6510004880 Connector MR-DS-E 01 1
SP1 2510001030 Speaker VS-57-0837A 1
MP1 8010019380 2698 chassis 1
MP2 8110008040 2698 cover 1
MP3 8930045600 2088 SP rubber 1
MP4 8930062130 Thermally sheet (AP) 1
MP6 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3 × 8 NI-ZU 12
MP7 8810009610 Screw FH M2.6 × 6 ZK 4
MP8 8810005160 Cap bolt M3 × 20 ZK 2
[CHASSIS PARTS]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
F1 5210000080 Fuse FGB 20A 1
W1 8900010990 DC power cable OPC-1132 1
MC1 0880001490 Microphone HM-133V 1
MP1 8010019260 2633 mobile bracket 1
MP2 8820000530 Flange bolt M4 × 8 NI 4
MP3 8810000470 Screw PH M5 × 12 (+
-
)4
MP4 8810000950 Screw PH A M5 × 12 4
MP5 8850000150 Flat washer M5 NI BS 4
MP6 8850000390 Spring washer M5 4
MP7 8830000120 Nut M5 4
MP8 8930007300 Mic hanger [USA] only 1
MP9 8930062650 Insulation sheet (HS) 1
[ACCESSORIES]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
J1 6510023110 Connector 3008L-8P8C 1
S1 2260000980 Switch SKHHLP014A 1
MC1 7700002310 Microphone EM-140 1
[MAIN/MAIN-A UNIT]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
MC1
W1
MP2
MP3
MP4
MP5
MP6
MP7
MP1 F1 MP8 MP9
Page 33

HM-133V
7 - 2
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Unit abbreviations
(C):CHASSIS PARTS
(M): MAIN/MAIN-A UNIT
MAIN/MAIN-A UNIT
MP6 (C)
S1 (M)
MP9 (C)
MC1 (M)
MP3 (C)
MP2 (C)
MP8 (C)
(2
61.0
(2
54.3
1
/8)
13
/32)
J1 (C)
MP6 (C)
104.0
(4
3
/32)
Unit: mm (inch)
(1
31.5
1
/4)
MP5 (C)
MP1 (C)
IC-2200H
Unit abbreviations
(C):CHASSIS PARTS
(L): LOGIC UNIT
(M): MAIN UNIT
MP4 (C)
MP8 (C)
MP1 (L)
MP3 (L)
MP12 (L)
J1 (M)
W1 (C)
J1 (L)
R61 (L)
DS1 (L)
R62 (L)
EP11 (L)
MP7 (L)
A
MP5 (L)
MP6 (L)
MP2 (L)
S9 (L)
MAIN UNIT
LOGIC UNIT
A
MP1 (M)
MP2 (M)
MP1 (C)
MP4 (C)
J7 (M)
J4 (M)
W6 (M)
MP6 (C)
B
MP4 (M)
MP9 (L)
MP8 (L)
MP4 (L)
MP11 (L)
/16)
1
27.3
(1
/32)
31
50.0
(1
/4)
3
146.0
(5
/16)
9
40.0
(1
Unit: mm (inch)
140.0
1
(5
141.0
(5 9/16)
MP3 (C)
SP1 (C)
/32)
5
207.5
(8
/2)
B
MP6 (C)
MP2 (C)
MP7 (C)
Page 34

8 - 1
SECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
• TRANSISTORS AND FET’S • DIODES
2SA1362 Y 2SA1576A T106 R 2SA1586 GR 2SB798 T2 DK 2SC2712 BL
2SC2954 T1 2SC3356 2SC4116 BL 2SC4116 GR
2SC4213 B
2SC4226 T1 R25 2SC4406 2SC4617 TLS 2SC4684
2SK1069 4 TL
3SK299 T1 U73 DTA113 ZU T106 DTA114EUA T106 DTA143TUA
DTA144 EE TL
DTA144EUA T106 DTB113ZK DTC114EUA T106 DTC143ZUA
DTC144EUA T106
DTC144TU T106
UMG2N
XP4601
XP6501 AB
(Symbol: AEY) (Symbol: FR) (Symbol: SG) (Symbol: DK) (Symbol: BL)
(Symbol: QK) (Symbol: R25) (Symbol: LL) (Symbol: LG)
(Symbol: AB)
(Symbol: R25) (Symbol: JT) (Symbol: BS) (Symbol: C4684)
(Symbol: FJ)
(Symbol: U73) (Symbol: 111) (Symbol: 14) (Symbol: 93)
(Symbol: 16)
(Symbol: 16) (Symbol: G11) (Symbol: 24) (Symbol: E23)
(Symbol: 26_)
(Symbol: 06)
(Symbol: G2) (Symbol: 5C)
(Symbol: 5N)
1SS133 1SS355 1SS400 DA221 TL DAN222TL
DSA3A1 HVC350B HVC375B HVC376B
HVU131TRF
MA2S077 MA2S111 MA2S30400 L MA77
MA742
MA8056 M MA8091 M RD20E B2 XB15A308
XB15A407
(Symbol: A) (Symbol: A) (Symbol: K) (Symbol: N)
(Color: Green) (Symbol: B0) (Symbol: B8) (Symbol: B9)
(Symbol: P1)
(Symbol: S) (Symbol: A) (Symbol: K) (Symbol: 4B)
(Symbol: M1U)
(Symbol: 5-6) (Symbol: 9-1) (Symbol: 20 B2) (Symbol: T8)
B
E
B
C
E
B
E
C
C
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
B
E
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
B
C
E
S
G
D
Yellow
green
AC
A
AC
AC
C
AC
AC
AC
AC
A
C
A1
C
A2
AC
D
S
B
E
B
E
G2
G1
C
C
B
C
E
B
C
E
B1
E1
B2
C1
C2
B
C
E
B
C
E
E1
B1
C2
C1
B2
E2
B
C
E
B
E
E1
E2
B2
C
C1
B1
C2
B
C
E
B
C
E
AC
AC
A
C
Page 35

SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
9-1 LOGIC UNIT
• TOP VIEW
PWR
S.MW/MW
MICROPHONE
VOL
SQL
SET/LOCK MONI/ANM
LOW/DUP
TONE/T-SCAN M/CALL/PRIO V/MHz/SCAN BANK/OPT
DIAL
814
14 8
17
71
814
71
1
to the microphone
2
7
8
J1
8V
EXTMIC
MICE
GND
MICUD
PTT
MIC
MICIN
9 - 1
Page 36

• BOTTOM VIEW (LOGIC UNIT)
1
36 37
109 108
144
72
8
5
1
8
14
7
1
1
4
8
71
814
5
4
73
OPV115
1
16
to the optional unit
30
J4
OPV2
OPV3
GND
OPT3
OPT2
OPT1
SIG_OUT
NC
BUSY
NC
MIC_IN
MIC_OUT
PTTO
PTTI
OPSCK
SI
OPSO
NC
CCS
REFMOD
AFOUT
DETO
RX_MUTE
232RX
232TX
NC
+8V
+5V
GND
1 36
to the MAIN unit J11
J3
232TX
232RX
GND
CLONE
POWON
LVIN
VOLOUT
C5V
+8V
+8V
+8V
EXSTB
GND
GND
SO
PLLCK
PLLSTB
OE
BSHIFT
DIGI_W
REF_V
UNLK
MODIN
TEMP
SCK
OPV1
MICGND
MICGND
+5V
+5V
+5V
IDET
DETO
CTCSS
SD
NOIS
9 - 2
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 37

ANT
CHASSIS
unit J1
DC power
black
EP12
EP11
red
1
8
16
9
1
4
8
5
14
85
36
to the LOGIC unit J3
35
2
1
J11
232TX
GND
PWRON
VOLOUT
+8V
+8V
GND
SO
PLLSTB
BSHIFT
REF_V
MODIN
SCK
GND
+5V
+5V
DETO
SD
232RX
CLONE
LVIN
C5V
+8V
EXSTB
GND
PLLCK
OE
DEGI_W
UNLK
TEMP
OPV1
GND
+5V
IDET
CTCSS
NOIS
9-2 MAIN UNIT
• TOP VIEW
9 - 3
Page 38

85
14
1
8
16
1
12
24
13
9
16
9
1
8
DATA SP
• BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN UNIT)
9 - 4
Page 39

9-3 HM-133V
• TOP VIEW (MAIN UNIT) • TOP VIEW (MAIN-A UNIT)
9 - 5
NOTE:
HM-133V’s main unit has 2 versions (MAIN or MAIN-A).
MAIN unit employs old type CPU, MAIN-A unit employs new type one.
Make sure to be used whether MAIN unit or MAIN-A unit before servicing.
VFO/LOCK MR/CALL BANK/OPTION
F-1
DTMF-S
1 2 3 A
F-2
FUNC
VFO/LOCK MR/CALL BANK/OPTION
F-1
DTMF-S
1 2 3 A
F-2
FUNC
4 5 6 B
7 8 9 C
*
0 # D
4 5 6 B
7 8 9 C
*
0 # D
Page 40

• BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN-A UNIT) • BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN UNIT)
9 - 6
PTT
1
5
8
4
1
15
30 16
71
82
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J1
J1
E
MICE
M8VSW
M8V
MDATA
MIC
PTT
MU/D
PTT
10
1
11
20
1
8
16
9
71
82
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J1
J1
E
MICE
M8VSW
M8V
MDATA
MIC
PTT
MU/D
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 41

UP
UP DOWN
LOCK
PTT
DN
1
11
20
10
1
7
14 8
71
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J1
82
J1
U/D
PTT
MIC
HANG
8V
NC
MICE
GND
9-4 HM-118TN
• TOP VIEW • BOTTOM VIEW (HM-118TN)
9 - 7
Page 42

Explanatory notes
VOLTAGE LINE
ANTENNA
LPF
LPF
LPF
LPF
BPF BPF
LPF
ANT
SW
TX/RX
SW
AF
AMP
RF
AMP
PWR
AMP
DRIVE
PRE
BUFF
BUFF
LO
AMP
IF
AMP
APC
CTRL
FIL
LOOP
PLL
IC
LCD
HPF
ATT
BPF
CERAMIC
BPF
CERAMIC
HPF
X1
CR-779
BPF
XTAL
X2 CDB450C24
D/A
AF
MUTE
+5
REG
+8
REG
J4
EXT SP-JACK
SP1
W6
T8
REG
MATRIX
X1
CR-739
RS-232C TX/RX/GND
J7
DRIVE
AMP
ALC
AMP
AMP
LPF
CTCIN
LIMIT
PWR
DET
D12 XB15A407
D19 XB15A308
D16 HVU131TRF
D14 MA742
D17 MA742
IC6a NJM3404AV
Q26 DTA144EU
HV
IC10
S-AV36
D6 MA77
D7 MA77
Q11 2SC4226Q9 2SC4226
Q12 2SC4226
Q6 2SC4226
Q7 2SC4226
D15 1SS355D18 MA2S111
IC6a NJM3404AV
D13 HVC350B
D11 HVC350B
FI4 FL-363
D9 HVC350B
D10 HVC350B
Q27 3SK299
FI3 FL-363
Q16
2SC4406
D29 DA221
D2 HVC375B
D4 MA2S304
D5,D38 MA2S304
REF
OSC
Q4 2SC4116
D3 HVC376B
Q2 XP4601
IC1 LV2105V
CP
OUT
(LOOP-SW)
HVSW
C5V
REG
C5V+8V+5V SWHV
Q28 2SC4684
Q30 DTA143TUA
Q31 DTC143ZU
IC8 IC7 Q21
DTB113ZK
Q22
DTC144EU
TA7808F TA78L05F
PWRON
SWHV
IC1 M30220
CPU
T8
TXC
R5V
R5
REG
RXC
+8V
SHIFT
T8
VCO
REG
Q1 2SC4116
Q3 2SC4116
Q5 2SC4116
Q8 DTA113ZU
IF DET-IC
(2nd-MIX,IF-AMP,
NOISE-AMP,FMDET,
IC4 TA31136FN
FI1
CFWS450F CFWS450HT
FI2
W/N SW
RSSI,SQLSW)
Q13 DTA144EU
Q34 2SC4116
D23-D26 MA2S111
DC AMP
Q10 2SK1069
PORT
EXP
IC2 CD4094BPWR
IC3b NJM12902V
ANALOG SW
IC3c NJM12902V
IC3d NJM12902V
MIC
SW
IC6 CD4066BPWR
DIMMER
EEPROM
RESET
IC5 HN58X2464TI
DS1
IS08264E
Q6 2SA1576
Q7,Q8,Q12 2SC4116
DS2-DS13 SEC2422C
INT/KEY
D7-D9,D21 DAN222
D11 1SS133
D12-D17,D22,D23,
D6 DA221
Q5 DTC144TU
CLONE
BUFF
IC4 BD5242FVE
Q3 XP4601
CLOCK
SHIFT
D25 MA2S077
AF OUT
SP
CLONE
T3
T2
T3 SQLATT
IC2
MIC
JACK
MICDATA
BUFF
PTTSW
IC24 TA75S393F
D1 MA8091
D2 MA2S111
Q1 2SC4116
D4
VOL SQL
DIAL
Q29
2SC4213
IC9
TA7252AP
MAIN
LOGIC
MOD
LVIN
DTC/FC
T/R
VOLIN
VOLOUT
DETO
SQLIN
SD/NOIS
CTCSS/
Q19
3SK299
EXT MIC
R5VR5V
R5V
Q17 2SC3356
T1
*ONLY W/N Ver.
C5V
HV
Q14 2SA1362
Q15 2SC4116
Q25
TX
RX
COMMON
DATA/CONTROL/BUS,ets
AM DET
AGC
AM/FM
SELECT
AGC
AGC AGC
OPTION
CONNECT
Q35 2SC2954
T8
50
-
100mW
Tx* 136.000
-
174.000MHz
Rx* 118.000
-
174.000MHz
*Depended on versions
Rx 96.300-152.300MHz
Tx 136.000-174.000MHz
SW
ANALOG
SEL
THROUGH
ALC
SW SW
ALC
SW
AMP
MIC
SECRET
IC3A
NJM12902V
IC520
IC520
CD4066BPWR
IC520
IC525
IC514
AN6123MS
CUTOFF
SHIFT
DI/AN
SW
DI/AN
SW
AFOUT
TONE
CUTOFF
SHIFT
MOD_I
DIGITAL MOD OUT
ANALOGUE MOD IN/MIC_IN
AFOUT(DIGI_AFOUT)
DETOUT(DIGI_AFI)
IC522 CD4066BPWR
REFMOD
AMP
REG
OPTION
REG
MODIN
CTCSS
Q513 2SB798
Q514 2SC4116
D526 MA2S111
IC521 TC75S51F
Q515 2SA1576
Q525 DTC144EU
Q527
IC525 CD4066BPER
AM MODE
REG
Q36 DTA113ZU
IC12 SN74AHC2G53HDCT
Q37,Q38
XP6501
IC11 NJM3404V
CURRENT
DET
IC11 NJM3404V
for CPU
BSHIFT
ALC
SECRET DIGI,AN
DIGI,AN
TX_DIGI
AN
OP_PS
SW
SECRET
SW
CTCSS
DETO
AN
UMG2N
TXAF
DETO
RXAF
MIC_OUT
DIGI
IC524
SN74AHC2G53HDCT
Q2
DTC144EU
DTB113ZK
IC5
M62363FP
IC525
SECRET
SIG_OUT
TC4S66F
DAN222
THROUGH
DI_SEC
ALC
PS
Q524
2SA1576
THROUGH
D1 MA2S111
D30 1SS355
Q39,Q40 DTC144EU
D31 MA2S111
LIMIT
CD4066BPWR
CD4066BPWR
Q528 DTA144EE
CD4066BPWR
CD4066BPWR
IC522 CD4066BPWR
EMPHASIS
SW
Q41
2SC4617
PROTECT
REVERSE
& OVER
VOLTAGE
D21 DSA3A1
D20 RD20E
21.7MHz
(21.25MHz)
D27,28 1SS400
SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAMS
10-1 IC-2200H
10 - 1
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
Page 43

10-2 HM-133V
10 - 2
M8V
MIC
GND
MDATA
Q8 2SC2712
Q9 DTB113ZK
REG CTRL
Q1 2SC2712
D1 MA8056
5V REG
DS1-DS8 LN1371G
BACK
LIGHT
Q2 DTC114EU
Q3 DTA114EU
DATA
BUFF
5V
(MAIN)
IC3 S-80845CLUA
D13 1SS355
(MAIN-A)
IC3 BD5245G
RESET
D16,D17 MA8091
PROTECTO
MIC
PROTECTO
D18 MA8091
IC2
MC14028BF
(MAIN only)
MATRIX
DRIVER
KEY MATRIX
D3-D7,D9-D12
1SS355 (MAIN)
1SS400 (MAIN-A)
CPU
IC1
µPD7564AG (MAIN)
µPD789071 (MAIN-A)
EE-PROM
DATA
RESET
IC6
BR24L02FV
(MAIN -A only)
LED/
DRIVER
DRIVER
Q4,Q5 2SA1586
DS11 LT1EP53A
LED/
Q6,Q7 2SA1586
DS10 LT1EP53A
D14,D15 1SS355 (MAIN only)
Explanatory notes
DATA BAS
COMMON
TX
VOLTAGE LINE
Page 44

SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAMS
11-1 LOGIC UNIT
11 - 1
to the
microphone
to the
optional
unit
to the MAIN
unit J11
LOGIC UNIT
J1
EP1
MICIN
EP2
GND
EP3
MIC
EP4
MICE
EP5
PTT
EP6
EXTMIC
EP7
MICUD
EP8
8V
J4
16 15
OPV1
R4 10k
OPSCK
OPV2
R128 10k
SI
OPV3
R106 10k
OPSO
OPT3
CCS
OPT2
REFMOD
OPT1
AFOUT
SIG_OUT
DETO
RX_MUTE
BUSY
232RX
EP9
232TX
EP10
MIC_IN
MIC_OUT
+8V
PTTO
+5V
PTTI
GND
30 1
J3
NOIS
SD
CTCSS
DETO
IDET
+5V
+5V
+5V
MICGND
MICGND
OPV1
SCK
TEMP
MODIN
UNLK
REF_V
DIGI_W
BSHIFT
OE
PLLSTB
PLLCK
SO
GND
GND
EXSTB
+8V
+8V
+8V
C5V
VOLOUT
LVIN
POWON
CLONE
GND
232RX
232TX
TX: 0V
RX: 4.5V
C11 0.001
D3 MA8091
DETO/DIGI_AFI
MIC_IN/ANALOGUE_MOD_IN
MIC_OUT/DIGI_MOD_OUT
C602
C19
0.01
+5V
+8V
C5V
C1 0.001
C4 0.001
R2
120k
R1 12k
C16 0.001
R5500R549
10
Q513
2SB798
C593
C5 47p
R5
R3 10k
D1 MA8091
R9
D2 MA2S111
R10
7.5V
C20 0.001
C23 0.001
R11 100k
R107 100k
68
C601
Q514
2SC4116
D526
MA2S111
0.1
C7 0.001
C9 0.001
330k
1
5
3
2
IC24
TA75S393F
22k
Q1
2SC4116
10k
C28 0.001
R129 100k
R548
68
10
C10 0.001
+8V
+5V
R6
100k
4
R8
2.2k
C31 47p
R543 47k
C13 0.001
R12
+8V
+5V
R541 47k
R526
C14
0.001
C15 0.001
100k
R20 1k
R101 4.7k
R542 47k
R527
10k
1k
C30 47p
TX: 5.0V
RX: 0V
D4
DAN222
RX_MUTE
+5V
C8
0.01
REMO
PTT
EXTM1
MICUD
OPV1
OPSCK
OPV2
EXSTB
OPSO
OPT3
CCS
OPT2
OPT1
AFOUTR7 100
SIG_OUT
DETO
BUSY
232RX
232TX
PTTO
PTTI
+5V
+8V
OP_PS
NOIS
IDET
OPV1
SCK
TEMP
UNLK
REF_V
DIGI_W
BSHIFT
PLLSTB
PLLCK
EXSTB
+8V
C5V
LVIN
232RX
232TX
+8V
+5V
C5V
R13
R15
1k
12k
IC2
R14
10k
C32
+8V
+5V
C5V
MIC
+5V +5V
+5V
+8V
C5V
ALC
C584
DETO
SI
SD
OE
SO
+5V +5V
+8V
+5V
C5V
+5V
AF OUT
MIC_OUT/DIGI_MOD_OUT
MIC_IN/ANALOGUE_MOD_IN
+8V
+5V
C5V
REFMOD
R62
+8V
+8V
EVU-F2AF20B14
+5V
C5V
MODIN
+5V
C5V
C5V
VOLOUT
TC4S66F
10
1
2
3
C33
0.047
IC520
CD4066BPWR
1
I/O1
2
O/I1
3
O/I2
4
I/O2
5
CONT2
6
CONT3
78
VSS
MIC_IN/ANALOGUE_MOD_IN
MIC_OUT/DIGI_MOD_OUT
DETO
AF OUT AFOUT
at ALC ON: 0.95V
IC514
C585
AN6123MS
0.1
3
INPUT
4
GND
51
OUTPUT VCC
C599
0.1
at ALC ON: 1.3V
R531
47k
C596
0.001
R520
47k
3
5
-
4
1
+
2
IC521
TC75S51F
R22 1k
R61
EVU-F2AF20A14
VOLOUT
R24
15k
C37
0.01
1.3V
C35
0.033
R21
R17
68k
68k
C38
0.0018
IC5
HN58X2464TI
1
A0
2
A1
3
A2
45
VSS
0.1
R537
R521
+5V
C5V
680
47k
R522
150k
R16
C34
C591
0.001
R516
0
R536
10k
+5V
DIGITAL: 5.0V
+5V
68k
0.0068
C36
0.1
+8V
5
R23
100k
4
VDD
CONT1
CONT4
I/O4
O/I4
O/I3
I/O3
DET
Q524
R515
2SA1576
100
R532
47k
+5V +5V
Q515
2SA1576
R524
10k
R523
1M
SQLV
C40
5.0V
R25
10k
R28
100k
Q3
XP4601
4
5
6
0.2V
R29
10k
8
VCC
7
WP
6
SCL
SDA
IC3
NJM12902V
3
+
2
-
CP1
R105
R109
14
13
12
11
10
9
2
R530
0.001
3
2
1
R32
100k
47k
R103
R104
150k
82k
27k
[USA]
18k
C79
[OTHER]
220p
BIAS BIAS BIAS
Q528
DTA144EE
R546
100k
C583
0.1
C592
0.001
R5171MC587
C586
10
at ALC ON: 4.95V
C594
0.001
R534
47k
CTCSS
VOLIN
0.7V
R34
68k
R37
100k
1.2k
C46
0.022
C48
0.0022
C5V
C5V
R58
R40
100k
R57
C52
15k
C62
0.001
POWON
CLONE
4
C78
0.01
V+
IC3
NJM12902V
GND
11
1
1.9V
R519
680
R38
C47
0.1
C42
C44
0.047
0.0056
R30
15k
THROUGH
DI_SEC
C595
0.001
R533
47k
C600
0.001
10
MODIN
C49
0.1
47k
47p
S1
PWR
C588
R35
100k
IC525
CD4066BPWR
1
I/O1
2
O/I1
3
O/I2
4
I/O2
5
CONT2
6
CONT3
78
VSS
R26 22k
DETO
R525
100
IC522
CD4066BPWR
1
I/O1
2
O/I1
3
O/I2
4
I/O2
5
CONT2
6
CONT3
78
VSS
IC524
SN74AHC2G53HDCT
1
COM
2
INH
3
GND
45
GND
C5V
C51
0.027
3
C5V
IC4
BD5242FVE-TR
4
+5V
D6
DA221
+8V
+5V
C5V C5V
8
EXTM1
470p
X1
CR-739
R48
1M
15p
R137
47k
0.1
MMUT
R51
10
MICS
R47
100k
R52
1k
DETO
C5V
C5V
1.9V
R136
100k
1.9V
IC3
NJM12902V
12
+
14
13
-
R39 150k
1.8k
Q527
UMG2N
1
4
3
2
51
SECRET
14
VDD
13
CONT1
12
CONT4
11
I/O4
10
O/I4
9
O/I3
I/O3
14
VDD
13
CONT1
12
CONT4
11
I/O4
10
O/I4
9
O/I3
I/O3
THROUGH
8
VCC
7
Y0
6
Y1
A
DIGI
DIGI
MOD_I
C597
DIGI
AN
AN
0.001
VOLIN
C56
0.0022
C41
C54
0.1
0.01
C57
0.0027
R49
27k
R45
3.9k
R19 1k
R27
R36
39k
12k
C45
0.01
R114
12k
D25
MA2S077
C80
0.01
Explanatory notes
R53
1.5M
R50
C43
0.047
R41 12k
C53 56p
1M
C81
R112
R56
1
IC3
NJM12902V
9
-
10
+
Q2
DTC144EU
0.01
C82
12k
C558pC59
C6710C68
VOLTAGE LINE
TX LINE
SQLV
RX LINE
COMMON LINE
DIGITAL LINE
[TPE], [KOR], [EUR-1]
D11
1SS133
except [EXP/-1]
D13
1SS400
[EXP/-1]
D15
CTCIN
R108
10k
2
CT
SUB
VOUT
GND
VDD
51
Q5
DTC144TU
R93 1k
RESET
ESCK
ESDA
PWRSW
CLIN
R59
15k
C64
0.01
CLOUT
PWRON
1SS400
[EUR/-1], [EXP/-1]
1SS400
D16
[TPE], [KOR], [EXP/-1]
D17
1SS400
[TPE], [EXP/-1]
D22
1SS400
[TPE], [KOR]
D23
1SS400
except [EXP-1]
D27
1SS400
[EXP/-1]
D28
1SS400
V-MHz/SCAN
D7
DAN222
KS2
KS1
IS2
IS1
IS0
D8
DAN222
KS2
S2
SKQDPA
M-CALL/PRIO
S3
SKQDPA
TONE/T-SCAN
S4
SKQDPA
LOW/DUP
S5
SKQDPA
KS1
C66
0.01
IC6
CD4066BPWR
1
I/O1
VDD
2
O/I1
CONT1
3
O/I2
CONT4
4
I/O4
I/O2
5
CONT2
O/I4
6
CONT3
O/I3
78
VSS
I/O3
R134
10k
EXTMIC
REF_V
C5V
IDET
DUSE
CTCIN
SQLV
C5V
+5V
MICUD
SD
LVIN
TEMP
DETO
COLOR
DIM0
DIM1
DIM2
OE
CSHIFT
RESET
XIN
C5V
PWRSW
DICK
DIUD
CLIN
CLOUT
BUSY
OPSO
SI
C5V
+5V
SCK
NOIS
KR0
KS1
KS1
D9
DAN222
D21
DAN222
MONI/ANM
SET/LOCK
KR1
KR2
S-MW/MW
BANK/OPT
KR3
SIG_OUT
+8V
+5V +5V
R72
220k
R75 68k
R74 150k
R73 180k
S34
S35
S36
S37
S38
S39
SEG34
SEG35
SEG36
COM4
COM3
COM4
COM3
SEG34
SEG35
SEG36
125
126
127
128
129
SEG2
SEG1
SEG0
COM3
COM2
COM1
IC1
M30220MA-132RP
P44/TA2OUT
P43/TA1IN
P42/TA1OUT
P41/TA0IN
P40/TA0OUT
P35
RMUT
IS0
IS1
IS2
KS1
KR0
KR1
KR2
KR3
R81
120k
R76
18k
C74
S33
SEG32
SEG33
SEG32
SEG33
123
124
SEG3
P34
KS2
KR3
0.0056
S32
SEG4
P33/KI19
14
13
12
11
10
9
C70
0.01
C39
0.001
S6
SKQDPA
S7
SKQDPA
S8
SKQDPA
S10
SKQDPA
+5V
C5V
R18
56k
R545
1k
R46
1k
AFON
RMUT
R135 10k
R133 47k
MOD_I
R60
56k
VOLIN
C69
R64
IS2
0.1
+5V
1M
R31
56k
1
P96/AN6
2
P95/AN5
3
P94/AN4
4
P93/AN3
5
P92/AN2
6
P91/AN1
7
P90/AN0
8
P87/TA7IN
9
P86/TA7OUT
10
P85/TA6IN
11
P84/TA6OUT
12
P83/TA5IN
13
P82/TA5OUT
14
P81/TA4IN/INT5
15
P80/TA4OUT/INT5
16
CNVSS
17
XCIN
18
XCOUT
19
RESET
20
XOUT
21
VSS
22
XIN
23
VCC
24
P77/NMI
25
P76/INT2
26
P75/INT1
27
P74/INT0
28
P73/CTS2/RTS2
29
P72/CLK2
30
P71/RXD2/SCL
31
P70/TXD2/SDA
32
P67/TXD1
33
P66/RXD1
34
P65/CLK1
35
P64/CTS1/RTS1/C
36
P63/TXD0
C5V
+5V
COMEXP
D11
IS2
D13
TXFREF
IS2
D15
SCRAM
C72 0.033
C73 2.2
C71 0.01
C5V
R67 18k
R71 10k
C5V
IDET
REF_V
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
VREF
AVSS
AVCC
P97/AN7
P131/DA1
P130/ADTRG/DAO
P62/RXD0
P61/CLK0
P60/CTS0/RTS0
P57/CKOUT
P56/INT3
P55/TB5IN
3738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071
PWRON
DIGI_W
BSHIFT
PLLSTB
BAND1
D22
IS1
D23
BAND2
IS1
BAND3
D16
IS1
D17
BAND4
Q525
DTC144EU
R70 39k
R69 150k
TX_DIGI
DS1
IS08264E
132
133
134
135
136
137
C2
C1
VL3
VL2
VL1
VSS
P132/DA2
P54/TB4IN
P53/TB3IN
P52/TB2IN
P51/TB1IN
P50/TB0IN
P47/TA3IN/INT4
P46/TA3OUT/INT4
PLLCK
EXSTB
UNLK
REMO
CCS
MICS
KR0
W/N
D27
IS0
D28
ANI
IS0
DIMMER DIM0 DIM1 DIM2
DIM-1
DIM-2
DIM-3
DIM-4
S40
COM2
COM1
COM2
COM1
130
131
COM0
P45/TA2IN
MMUT
AFON
0V 0V 5.0V
0V 5.0V 5.0V
5.0V 0V 5.0V
5.0V 5.0V 5.0V
R78 100k
S30
S31
SEG30
SEG31
SEG30
SEG31
121
122
SEG6
SEG5
P32/KI18
P31/KI17
KR2
KR1
C75
S29
SEG28
SEG29
SEG28
SEG29
119
120
SEG7
P30/KI16
KR0
PTT
IC3
NJM12902V
270p
6
-
5
S27
S28
SEG26
SEG27
SEG26
SEG27
117
118
SEG9
SEG8
P27/KI15
P26/KI14
SECRET
DI_SEC
R87
1k
+8V
C5V
1.9V
7
+
R84
C76
S24
S25
S26
SEG24
SEG25
SEG24
SEG25
115
116
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
P25/KI13
P24/KI12
P23/KI11
TX_DIGISOOPSCK
1.5k
0.033
S23
SEG22
SEG23
SEG22
SEG23
113
114
SEG13
P22/KI10
OPV1
S21
S22
SEG21
SEG21
112
SEG15
SEG14
P21/KI9
P20/KI8
OPV2
DIM0
DIM1
DIM2
COLOR
R91
120k
R92
18k
S18
S19
S20
SEG18
SEG19
SEG20
SEG18
SEG19
SEG20
109
110
111
SEG18/P102
SEG17/P101
SEG16/P100
P17/KI7
P16/KI6
P15/KI5
72
PTTI
PTTO
RX_MUTE
R80
1k
R821kR85
R551
10k
R96
39k
C77
2.2
1.9V
S15
S16
S17
SEG15
SEG16
SEG17
SEG19/P103
SEG20/P104
SEG21/P105
SEG22/P106
SEG23/P107
SEG24/P110
SEG25/P111
SEG26/P112
SEG27/P113
SEG28/P114
SEG29/P115
SEG30/P116
SEG31/P117
SEG32/P120
SEG33/P121
SEG34/P122
SEG35/P123
SEG36/P124
SEG37/P125
SEG38/P126
SEG39/P127
SEG40/P00
SEG41/P01
SEG42/P02
SEG43/P03
SEG44/P04
SEG45/P05
SEG46/P06
SEG47/P07
P10/KI0
P11/KI1
P12/KI2
P13/KI3
P14/KI4
DS3
SEC2422C
R
G
DS5
SEC2422C
R
G
DS7
SEC2422C
R
G
R79
4.7k
8.2k
S14
SEG14
VSS
VCC
S13
SEG13
DICK
S12
SEG11
SEG12
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
C5V
+5V
DS2
SEC2422C
DS4
SEC2422C
DS6
SEC2422C
R538
S10
S11
10111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940
SEG9
SEG10
R55
1k[EXP/-1]
R
G
R
G
R
G
Q7
2SC4116
Q8
2SC4116
Q12
2SC4116
+8V+8V+8V
DIAL
S9
DIUD
SEG8
R539
SEG7
R42 1M
47k
SEG6
SEG4
SEG5
R43 1M
DS9
SEC2422C
DS11
SEC2422C
DS13
SEC2422C
R89 390
R86 180
R97 150
R100 330
R77 5.6k
EVQ-VENF02
1
2
3
4
SEG2
SEG3
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
C5V
SEG1
R44 1M
R
G
R
G
R
G
R83 68
R94 82
A
B
NC
COM
123456789
SEG1
+8V
S1S2S3S4S5S6S7S8S9
THROUGH
DS8
SEC2422C
DS10
SEC2422C
DS12
SEC2422C
OPT1
OPT2
OPT3
ALC
DIGI
OP_PS
ESDA
ESCK
DUSE
EXTMIC
C65
0.01
R
G
R
G
R
G
Q6
2SA1576
AN
+8V
47k
only
Page 45

11-2 MAIN UNIT
VOLTAGE LINE
Explanatory notes
TX LINE
RX LINE
COMMON LINE
J11
SD
DETO
+5V +5V
+5V
GND
SCK
MODIN
REF_V
BSHIFT
PLLSTB
SO
GND
+8V
+8V
VOLOUT
PWRON
GND
232TX
NOIS
CTCSS
IDET
+5V
GND
OPV1
TEMP
UNLK
DEGI_W
OE
PLLCK
GND
EXSTB
+8V
C5V
LVIN
CLONE
232RX
C228 0.01
C42 0.001
C290 0.001
C41 0.001
C40 0.001
C292 0.001
EP5
EP6
J7
EP4
EP3
+8V
C2
0.001
R5
4.7k
D1
MA2S111
Q1
2SC4116
C10
47
C14
0.001
IC2
CD4094BPWR
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
STR
D
CLK
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
GND QS
Q'S
Q8
Q7
Q6
Q5
OE
V+
SHIFT
SHIFT
C17
0.001
R16
22k
Q5
2SC4116
Q8
DTA113ZU
R1
68k
R4
82
C7
0.001
D2
HVC375BD4MA2S304
L2
10µ
L6
C2012C-
R10G
C20
47p
R22
1k
Q3
2SC4116
R19
8.2k
C25
5p
R23
22k
C29
7p
Q6
2SC4226
L8
2.7µ
R28
1k
C34
0.5p
R32
10
C28
0.001
C36
0.001
R27
1.8k
R20
5.6k
D5
MA2S304
C21
22p
C26
10p
R25
10k
C32
12p
Q7
2SC4226
L9
3.3µ
R31
1k
C37
0.5p
R33
10
C38
0.001
R30
2.7k
C31
0.001
L7
110n
D38
MA2S304
C9
27p
C5
0.01
L1
0.22µ
R34
100k
L11
0.22µ
C48
0.001
C44
0.001
R35
330
Q9
2SC4226
C49
10p
R39
100k
C56
0.001
L12
0.22µ
R41
470
Q11
2SC4226
C50
3p
R40
100k
C57
0.001
L13
0.1µ
Q12
2SC4226
R42
470
C58
0.001
TXC
TXC
C59
0.001
R45
100k
C64
0.1
C63
0.001
R47
2.2k
R48
2.2k
Q14
2SA1362
Q15
2SC4116
C69
10
T8
C61
22p
L14
56n
C65
22p
C67
0.001
R49
4.7k
D6
MA77
R50
4.7k
C72
0.001
C242
0.001
R153
120
R152
47
R154
120
C74
0.001
C76
7p
L18
39n
R54
22
Q17
2SC3356
C91
0.001
R57
33k
L21
68n
R60
33
C90
33p
C253
12p
R185
15
D30
1SS355
R184
1k
C251
0.001
R183
4.7k
Q35
2SC2954
L56
68n
C252
0.001
C254
10
C250
56p
R180
15
R179
150
R178
39
R177
150
IN
VGG
VDD
OUT
IC10
S-AV36
123
4
C247
0.001
R95
56
R96
1.8k
C137
0.001
R92 270
C123
0.001
R231
0
C125
10
C246
0.001
C118
47
C122
0.001
-
+
-
+
IC11
NJM3404AV
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
C257
0.001
C255
0.001
R193
330k
L61
10µ
R189
33k
C300
0.001
L57
ZBFS5101-PT
L59
ZBFS5101-PT
L58
ZBFS5101-PT
L60
ZBFS5101-PT
C302
0.001
C215
0.1
R150
100
C174
0.001
L40
1µ
D27
XB15A407
D12
XB15A407
C225
0.001
C218
27p
L37
47n
C227
33p
C190
1p
C191
12p
D14
MA742
D17
MA742
C196
1p
C197
12p
R126
8.2k
R124
8.2k
L42
0.82µ
C198
0.001
C217
39p
L47
56n
L48
56n
C208
33p
C210
15p
R131
82k
R188
100k
C258
0.001
C256
0.001
R190
33k
R191
270k
R220
330k
R221
560k
R192
270k
R194
100k
C259
0.001
R187
120k
C301
0.001
L62
10µ
J1
J3
CHASSIS
UNIT
+8V
C169
0.001
Q39
DTC144EU
R233
0
R230
47k
Q40
DTC144EU
Q26
DTA144EU
R109
3.9k
+
2
3
1
IC6
NJM3404AV
C294
0.001
C293
0.001
C288
0.22
R104
1k
C283
0.001
R228
PTH9M04
R106
10k
C297
0.001
TXC
IDET
IDET
REF_V
C77
0.01
L19
2.2µ
C80
22p
R56
470
R226
0
Q16
2SC4406
R214
10k
R58
100k
C244
0.1
D29
DA221
C93
0.5p
FI3
FL-363
C97
5p
FI4
FL-363
C243
0.001
R72
1.5k
C108
0.001
C111
20p
R78
1k
L25
2.2µ
Q19
3SK299
R79
220
C113
0.001
R51
4.7k
C240
0.001
R168
270
R169
18
R170
270
C79
39p
L20
47n
C87
56p
C88
56p
L22
68n
D7
MA77
R81
10k
L26
2.2µ
C124
5p
C127
1p
L31
82n
D9
HVC350B
C131
82p
C128
0.001
D10
HVC350B
C139
82p
R93
220k
C138
0.001
C136
0.75p
C133
1p
R234
0
C141
2p
L32
82n
C145
1p
D11
HVC350B
R101
220k
C146
0.001
C152
1p
C148
150p
C158
0.001
R174
100
R1101kC162
2.5p
L38
68n
C160
0.001
C245
1
R195
100k
R113
1k
Q27
3SK299
C222
0.01
R111
100
C164
0.001
C286
0.001
C170
0.001
R114
47k
R117
10k
C1784pL52
0.18µ
D13
HVC350B
R119
220k
C180
0.001
C182
150p
L43
67n
C184
5p
R123
6.8k
C221
1.5p
D15
1SS355
D16
HVU131TRF
D19
XB15A308
L45
44n
C201
22p
C206
9p
L46
56n
C187
0.001
C193
0.001
D18
MA2S111
+
7
6
5
R127
120k
R129
100k
C209
0.1
R128
100k
R130
27k
C211
0.001
T1
SQLATT
T2
T3
T3
LVIN
LVIN
C1
1.5
R6
470
R12
100
C11
10
C1233C24
10
R18
390
R29
10k
R229
0
Q10
2SK1069
R36
1k
R21
100
R37
47k
C52
0.001
C51
0.001
TEMP
Q2
XP4601
R13 2.7k
1234
5
6
R14
1M
R15
270k
L3 1µ
C15
0.001
L10
1µ
DTC
FC
TEMP
R7
47k
C4
0.1
R8
100k
C2811R2
1k
R3
470k
C8
0.001
R10
47k
D3
HVC376B
C13
15p
C16
12p
X1
CR-779
C22
27p
C23
33p
R24
2.2k
C30
4p
Q4
2SC4116
C241
0.1
R17
220k
R26
10k
IC1
LV2105V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
XIN
CL
DI
CE
VCCR
PI
GNDR
TEST
XOUT
OUT
PE
VCCD
GNDD
PDN
PDP
CP
PLLCK
PLLDATA
PLLSTB
C289
0.001
EP8
EP7
C39
0.1
C291
0.001
PLLCK
PLLDATA
PLLSTB
C55
22p
R44
100
C62
12p
C68
9p
C60
0.001
L15
82n
UNLK
UNLK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
OSCIN
OSCOUT
MIXOUT
VCC
IFIN
DEC
FILOUT
FILIN
MIXIN
GND
N-REC
N-DET
RSSI
IFOUT
QUAD
AFOUT
IC4
TA31136FN
C81
0.01
C83
1
C78
0.1
R52
1.5k
C75
0.001
C73
22p
EP2
C71
47p
EP1
C66
22p
R46
680
R43
8.2k
C53
0.001
C84
220p
C85
220p
R55
47k
R59
2.2k
C224
0.1
C216 0.1
R224 0
(only W
version)
D23
MA2S111
R137
12k
OI
R138
12k
R225 0
(only W
version)
D24
MA2S111
FI1
CFWS450F
D26
MA2S111
OI
D25
MA2S111
FI2
CFWS450HT
R139
15k
R135
12k
R136
12k
R172
100k
C285
0.047
C230
10
Q13
DTA144EU
C82
10
C86
0.001
C94
0.001
R71
470
C101
0.001
C105
0.001
R64
100k
R157
47k
C233
0.1
R156
47k
Q34
2SC4116
C232
0.1
R155
3.3k
C95
0.001
R66
100k
X2
CDB450C24
R73
3.3k
C100
82p
C161
0.001
IC12
SN74AHC2G53HDCT
COM
INH
GND
GND
VCC
Y0
Y1
A
123
4
876
5
R213
10
C265
0.001
Q36
DTA113ZU
DETO
DETO
C268
0.01
Q38
XP6501
R212
22k
R208
680k
R207
180k
C267
0.001
R204
100k
R205
330k
C273
4.7
Q37
XP6501
C269
0.01
R203
180k
R202
1k
R201
470
C271
0.47
R209
100
C272
0.1
W/N
W/N
BSHIFT
BSHIFT
SD
NOIS
DEGI_W
SD
NOIS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
IC5
M62363FP-650C
VIN1
VOUT1
VOUT2
VIN2
VDD
LD
CLK
DI
VIN3
VOUT3
VOUT4
VIN4 VIN5
VOUT5
VOUT6
VIN6
DO
VDAREF
RESET
GND
VIN7
VOUT7
VOUT8
VIN8
RXC
RXC
R88
470
Q25
DTB113ZK
T3
SQLATT
OPV1
OPV1
SCK
SCK
R173 10k
SO
SO
FC
SQLIN
C134 0.001
R90
220k
T2
C140
0.01
C117
0.01
C120
0.01
T2
T1
CTCCS
CTCSS
DTC
MOD
MOD
MODIN
MODIN
IC9
TA7252AP
1234567
INNFDC
GND
OUT
BOOT
VCCC195
47
C280
0.22
C204
470
C194
100
C279 1
R125
22
C278
47
C192
0.001
C287
0.001
R238
47k
C299
1
Q41
2SC4617
R237
47k
Q29
2SC4213
R118
10k
C181
1
R112
33k
R122
47k
C185
0.001
VOLOUT
VOLOUT
FILC
J4
R176
1k
CLONE
CLONE
J6
DEGI_W
Q21
DTB113ZK
Q22
DTC144EU
FILC
SQLIN
R63 220
4
8
GND
V+
IC6
NJM3404AV
C154
0.001
C157
330
IO
IC7
TA7808F
231
G
C166
100
C168
0.001
C172
0.001
Q28
2SC4684
C175
330
C179
0.001
R120
10k
R121
100
Q30
DTA143TUA
Q31
DTC143ZU
PWRON
PWRON
C295
470p
C205
0.001
C207
2200
D21
DSA3A1
C173
0.001
C177
10
2
IO
IC8
AN78L05M
3
1
G
D20
RD20E
C189
0.001
CP3
C212
0.001
CP4
R223
47k
OE
OE
R11
10k
TXC
W6
+8V
+8V
+8V
+8V
+8V+8V+8V
+5V+5V
+8V
C5V
+5V
+8V
C5V
+5V
+8V
C5V
SCK
EXSTB
SCKSCK
EXSTB
+5V
+8V
C5V
+5V
+8V
C5V
+8V
+5V
C5V C5V
+8V
+5V
+5V
+8V +8V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+8V
+8V+8V
+8V
+8V
+8V
+5V
+5V
T8 T8
HV HV
HVHVHV
HV
CP1
only W/N version
C5V
C5V
MAIN UNIT
R9
10k
LV
LVLVLV
C54
9p
C70
0.001
R5V
R18122R182
22
R232
100k
R103
470k
C153
0.1
R108 12k
C163 0.001
R107
4.7k
C282
0.001
C296
0.001
C149
0.1
C176
2p
L39
47n W5
R186
120k
IC6
NJM3404AV
TXC
TXC
REF_V
C47
0.1
C45
0.001
R236
0
AFMUTE
SO
R140
15k
C266
0.001
R171
1k
C98
0.033
1234
5
6
1234
5
6
AFMUTE
R175
47k
C200
0.001
C284
0.022
C188
1
D31 MA2S111
R5VR5VR5V
R5V
R5V R5V R5V R5V
R5VR5V
R5V
R5V
R5V R5V
R5V
AGC1AGC1
AGC1
AGC1 AGC1
AGC1AGC1
AGC1
AGC1
1
2
35
36
232TX
232RX
DATA
HV
HV
HV
POWER
SP
TI
TI
R76
100
C89
0.01
R62
1k
TI
HV
ANT
to the LOGIC
unit J3
MOD
SCK
EXSTB
+8V
C5V
AGC1
R5V
TX: 0V
RX: 7.0V
TX: 6.6V
RX: 0V
TX: 4.2V
RX: 0V
TX: 0V
RX: 3.5V
TX: 0V
RX: 1.1V
TX: 7.8V
RX: 0V
5.4V
4.9V
4.9V
TX: 6.9V
RX: 0V
TX: 6.7V
RX: 0V
TX: 0.3V
RX: 7.8V
TX: 0V
RX: 3.9V
TX: 0V
RX: 4.6V
1.4V
RX FM-Wide: 4.6V
RX FM-Narrow: 0V
TX: 0V
RX: 5.0V
13.8V
7.9V
13.0V
5.1V
RX FM[W/N]: 0V
RX AM: 1.75V
RX FM[W/N]: 5.1V
RX AM: 0.2V
11 - 2
Page 46

11-3 HM-133V
• MAIN UNIT
• MAIN-A UNIT
11 - 3
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J1
MC1
C:5.0V
MAIN UNIT
C23
R5 470
0.001
C:7.7V
J1
M8V M8V
MU/D
M8VSW
PTT
MICE MICE
MIC MIC
E
MDATA MDATA
C21 0.001
C22 0.001
EP1
C19 0.001
D18 MA8091
C18 0.001
L2 0.82µ
EP2
C17 0.001
L1 0.82µ
EP3
EP4
C16 0.001
C11 22p
D1
C10 22p
MA8056
C9 22p
Q1
2SC2712
C29
10
M8V
C5 22p
5V 5V 5V
C2
100
R:7.7V
T:7.6V
Q9
DTB113ZK
Q8
2SC2712
R38 220k
MICE
C30 0.1
PTT
F-1
F-2
VFO
MR
BAND
UP
DN
S1
SKHHLP014A
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
D17
MA8091
C1
470p
D16
MA8091
R:7.1V
T:7.0V
NOTE
F: FUNC acting
D: DTMF acting
P: PTT-M acting
C: COMMON
R: RX
T: TX
R40
2.2k
R39 2.2k
C31
10
Explanatory notes
MICEMICE
VOLTAGE LINE
TX LINE
R15
Q7
2SA1586
R16
10k
F:1.9V D:1.9V
D3 1SS355
D4 1SS355
D5 1SS355
D6 1SS355
D7 1SS355
D8 1SS355
D9 1SS355
D10 1SS355
D11 1SS355
D12 1SS355
ABCD
S9 S10 S11 S12
3
S13 S14
2
S17
1
S21
69
5
8
S18
4
7
S22
#
S15 S16
0
S19
S23
R22 100k
R24 100k
DTMF
S20
S25
R23 100k
R25 100k
R30
5.6k
FUNC
X1
CSB600J200T
S24
S26
D19
1SS355
R34 47k
R33 47k
R32 47k
R31 47k
C3
100p
C4
100p
C24
0.001
5V
470
R
DS10
LT1EP53A
5V
5V
C13
0.001
R35
DS7
LN1371G
DS8
LN1371G
R37 1.5k
R14
680
Q6
2SA1586
R13
10k
F:1.9V
G
D15
IC1 µPD7564AG-555
1
P00/INTO0
2
P01/SCK
3
P02/SO
4
P03/SI
5
P80
6
P81
7
P82
8
CL2
9
CL1
10
VDD
IC3
S-80845CLUA-B66-T2
C15
0.001
1.5k
C:3.8V C:3.8V C:3.8V
R4
1.5k
R36
10k
DS3
LN1371G
DS4
LN1371G
Q2
DTC114EU
DS5
LN1371G
DS6
LN1371G
R8 12k
R41 10k
R11
D14
R12
10k
1SS355
VDD
Q5
2SA1586
Q3
Q1
B
C
D
A
680
R
DS11
LT1EP53A
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
C26
0.001
1SS355
IC2
MC14028BF
1
Q4
2
Q2
3
Q0
4
Q7
5
Q9
6
Q5
7
Q6
8
VSS9Q8
T:1.9V
R18 470k
R19 470k
R20 470k
R21 470k
20
VSS
19
P113
18
P112
17
P111
16
P110
15
P103
14
P102
13
P101
12
P100
11
RESET
C:5.0V
O
I
R29
G
100
R10
680
Q4
2SA1586
G
C14
0.047
R3
1.5k
R27 1M
R7 33k
C27
R9
10k
0.001
P:1.9V
D13
DS1
LN1371G
DS2
LN1371G
Q3
DTA114EU
1SS355
R2
1.5k
R26 47k
R6 33k
C12
0.001
C25
0.001
C:3.8V
R:7.5V
T:7.5V
Q9
DTB113ZK
MKEY-I0
MKEY-I1
MKEY-I2
MKEY-I3
C:5.0V
R38 220k
F:1.9V
Q8
2SC2712
R16
Q7
2SA1586
10k
MASK
FLASH
R37
1.5k
R15 470
R
DS10
LT1EP53A
0
10k
C24 0.001
R36
R41 10k
5V
R14 680
Q6
2SA1586
R42 0
DS7
LN1371G
DS8
LN1371G
10k
R13
10k
G
5V
5V
5V
5V
R35
1.5k
C:3.8V
DS5
LN1371G
DS6
LN1371G
R8 12k
Q2
DTC114EU
Q5
C26 0.001
2SA1586
F:1.9V
R12
D:1.9V
R27 10k
C:5.0V
10k
T:1.9V
IC1
µPD789071MC-041-5A4
P102P31/BZO903VPP4RESET5X26X17VSS8VDD9P30/TO9010P27/TI80/TO80
1
IC3 BD5245G
1
OUT
2
VDD
3
VSS
R4
1.5k
C:3.8V C:3.8V
DS3
LN1371G
DS4
LN1371G
C12 0.001
R10 680
R11 680
Q4
2SA1586
R
DS11
LT1EP53A
11
5V
C13
0.001
X1
EFOS4914E3
5
CD
4
NC
R3
1.5k
DS1
LN1371G
DS2
LN1371G
R6 33kR7 33k
Q3
DTA114EU
C27
0.001
R9
10k
G
P:1.9V
LED-S2
SEND
LED-M2
LED-M1
16
17
18
P0719P0620P0521P0422P0323P0224P0125P0026P1527P1428P1329P1230P11
P21/SO20/TXD20
P20/SCK20/ASCK20
P26/INTP2/CPT90
P25/INTP113P24/INTP014P23/SS2015P22/SI120/RXD20
12
R18 10k
R19 47k
5V
7WP8
VCC
C15 0.001
IC6
BR24L02FV-W
1A02A13A24
C14 0.01
C25 0.001
R2
1.5k
C:3.8V
MODE-G(LEDM2)
MODE-R(LED-M1)
5
6
SCL
SDA
VSS
5V
5V
5V
5V
MAIN-A UNIT
EP4
C31
10
L1 0.82µ
R39 2.2kR40 2.2k
R5 470
C11 22p
C10 22p
C23 0.001
C:7.6V
J1
M8V M8V
MU/D
5V
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J1
5V
M8VSW
PTT
MICE MICE
MIC MIC
E
MDATA MDATA
C22 0.001
D17
MA8091
EP1
C21 0.001
C1
470p
L2 0.82µ
MC1
C19 0.001
D16
MA8091
EP2
C18 0.001
D18 MA8091
R:6.8V
T:6.8V
EP3
C16 0.001
C17 0.001
C30 0.1
D1
MA8056
C9 22p
C29
10
M8V
C5 22p
Q1
2SC2712
5V 5V 5V
C2 100
MICE
MICEMICE
Explanatory notes
VOLTAGE LINE
TX LINE
MKEY-08
MKEY-07
MKEY-06
MKEY-05
5V
R44 1k
R45 1k
R46 1k
R47 1k
R48 1k
R49 1k
5V
R51 1k
D5
1SS400D31SS400
5V5V
PTT
S1
SKHHLP014A
R50 1k
D10
D4
1SS400
D7
1SS400
ABCD
S9
BANDUP DN
F-2
MR
S3
F-1
VFO
S2
NOTE
F: FUNC acting
D: DTMF acting
P: PTT-M acting
C: COMMON
R: RX
T: TX
3
S6S7 S8
S13 S14 S15 S16
2
S5
S17
1
S4
S21
1SS400
S11
S10
69
5
8
S18
4
7
S22
D11
1SS400
1SS400
D6
1SS400
S12
#
0
DTMF
S20
FUNC
S24
D9
S19
S23
MKEY-04
MKEY-03
MKEY-02
MKEY-01
MKEY-00
R43 1k
D12
1SS400
R22 4.7k
R23 4.7k
S25
S26
R24 4.7k
R25 4.7k
Page 47

12 - 1
SECTION 12 HM-118/N (OPTIONAL UNIT)
12-1 INSIDE VIEW (HM-118/N)
12-2 BOARD LAYOUTS
• TOP VIEW (MAIN UNIT)
• TOP VIEW (MAIN-A UNIT)
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
UP swtich
UP swtich
(S3: SKHHLM)
(S3: SKHHLM)
UP DOWN LOCK switch
UP DOWN LOCK switch
(S2: SSSS81560A)
(S2: SSSS81560A)
Microphone
Microphone
(MC1: KUC2123-030245)
(MC1: KUC2123-030245)
DOWN switch
DOWN switch
(S4: SKHHLM)
(S4: SKHHLM)
PTT switch
PTT switch
(S1: JPM1990-2013R)
(S1: JPM1990-2013R)
Page 48

12 - 2
• BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN UNIT)
• BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN-A UNIT)
12-3 MECHANICAL PARTS LIST AND DISSASEMBLY
MP1 8210015430 2129 front panel [HM-118] 1
8210015431 2129 front panel-1 [HM-118N] 1
MP2 8210015330 1743 REAR PANEL [HM-118] 1
8210015331 1743 REAR PANEL-1 [HM-118N] 1
MP4 8930046350 1743 hook plate 1
MP5 8930046530 1743 PTT button [HM-118] 1
8930052400 2129 PTT button [HM-118N] 1
MP12 8930046930 1135 U/D button (B) [HM-118] 1
8930025191 1135 U/D button-1 [HM-118N] 1
MP13 8610010640 Knob K-226 1
MP15 8810009760 Screw PH BT M3
× 12 ZK 2
MP16 8810009260 Screw PH BT 2
× 6 NI 3
MP18 8810008890 Screw FH M3
× 6 NI 1
MP19 8830001060 Nut M3 NI 1
MP25 8810009810 Screw PH BT M3
× 14 ZK 1
MP27 8930052390 1743 SW rubber [HM-118N] 1
[CHASSIS PARTS]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
MC1 7700002120 Microphone KUC2123-030245 1
W1 8900008000 Cable OPC-784 [HM-118] 1
8900008001 Cable OPC-784A [HM-118N]
S1 2230001020 Switch JPM1990-2013R 1
S2 2220000620 Switch SSSS81560A 1
S3 2260002500 Switch SKHHLM 1
S4 2260002500 Switch SKHHLM 1
[MAIN/MAIN-A UNIT]
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
Screw abbreviations BT: Self-tapping PH: Pan head
FH: Flat head ZK: Black
NI: Nickel
UP DOWN
LOCK
UP
DN
PTT
MP4 (C)
MP25 (C)MP2 (C)
MP18 (C)
UP DOWN
LOCK
UP
DN
PTT
MC1 (M)
MAIN/MAIN-A UNIT
S1 (M)
MP13 (C)
MP1 (C)
S4 (M)
MP12 (C)
S3 (M)
S2 (M)
MP5 (C)
MP16 (C)
MP19 (C)
W1 (M)
MP15 (C)
HM-118/N
Unit abbreviations
(C):CHASSIS PARTS
(M): MAIN/MAIN-A UNIT
Page 49

SECTION 13 UT-108 (OPTIONAL UNIT)
• BOTTOM VIEW
1
41
58
5
10
6
PTTIN_C1
15
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J4
30
16
J1
PTTOUT
DMOD
AMODIN
F_RXD
BUSY_C
RES
NC
NC
NC
NC
GND
GND
P01
NC
AGND
5V
VCC_8V
TXD
232_TX
232_RX
RMUTE
FMDET
DAFOUT
REFMOD
NC
FLASH
RXD_2_C
TXD_2_C
NC
13 - 1
13-1 BOARD LAYOUT
• TOP VIEW
Page 50

SECTION 14 UT-115 (OPTIONAL UNIT)
14-1 BOARD LAYOUT
• TOP VIEW
14 - 1
125
26
1
10
1
8
16
9
20
11
50
51 75
76
100
• BOTTOM VIEW
1
1
12
24
13
1
116
17
32
33 48
49
64
4
8
5
4
8
5
PTTIN_C1
15
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit J4
30
16
J301
PTTOUT
DMOD
AMODIN
F_RXD
BUSY_C
RES
NC
NC
NC
NC
GND
GND
P01
NC
AGND
5V
VCC_8V
TXD
232_TX
232_RX
RMUTE
FMDET
DAFOUT
REFMOD
NC
FLASH
RXD_2_C
TXD_2_C
NC
Page 51

14-3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
FOR FM_TRANCEVER
OPTION CONNECTOR
BUFF
F_RXD
RES
TXD
TXD_2
RXD_2
232_RX
232_TX
REFMOD
DMOD
FMDET
DAFOUT
AMODIN
5V
APWR
3.2V
REG
3.3V
REG
+5V
CTRL
BUFF
IC251B
NJM2115
IC251A
NJM2115
BUFF
BUFF
IC253B
NJM13404
IC253A
NJM13404
RS-232C_DATA
FOR FM_TRANCEVER CPU
FLASH WRITER
LEVEL
CONVERT
Q305 XP4312
Q306 XP4312
IC351
MAX3226
RS-232C
RESET
MODEM
2.4576MHz
CPU
IC151
AMBE-2020
DSP
CODEC
LINEAR
CODEC
IC50
AD73311
Q400 2SA1586
Q401 DTC144
PSAVE
+3V
CTRL
3.3V
3.3V
5V
X101
CR-708
INV
IC101
TC7SHU04
16.384MHz
9.8304MHz
X201
CR-760
3.2V
IC204
HD64F3687
IC203
S-80928CNMC
IC252
CMX589AD5
Q50 2SA1586
Q51 DTC144
3.3V
PSAVE
IC2
R1111N321B
IC1
S-812C33AMC
VCC: 4.5
-
8.5V
J301
LINE
DATA BUS LINE
TX LINE
RX LINE
VOLTAGE LINE
Explanatory notes
14 - 2
14-2 SEMICONDUCTOR INFORMATION
• TRANSISTORS AND FET’S
• DIODES
2SA1586 GR DTC144EUA T106 XP4312
(Symbol: SG) (Symbol: 26_) (Symbol: 7T)
MA2S111 MA2S728
(Symbol: A) (Symbol: B)
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
B
E
C
B
C
E
AC AC
E1
B1
C2
C1
B2
E2
Page 52

14-4 VOLGTAGE DIAGRAM
VOLTAGE LINE
Explanatory notes
TX LINE
RX LINE
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
IC151
AMBE-2020
GND
CODEC_RX_CLK
CHAN_RX_CLK
CODEC_RX_STRB
CHAN_RX_STRB
CODEC_RX_DATA
CHAN_RX_DATA
CODEC_TX_CLK
CHAN_TX_CLK
GND
VDD
CODEC_TX_STRB
CHAN_TX_STRB
VDD
GND
CODEC_TX_DATA
CHAN_TX_DATA
NC
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
GND
CLOCK_MODE
GND
GND
VDDNCGND
VDDNCNCNCNCNCGND
VDD
GNDNCX1
X2/CLKIN
RESETN
RATE_SEL0
RATE_SEL1
RATE_SEL2
RATE_SEL3
RATE_SEL4
CHANN_SEL0
VDD
CHANN_SEL1
NC
SOFT_EN
BAUD_SEL0
BAUD_SEL1
SLIP_EN
SLEEP_EN
CODEC_SLE0
CODEC_SEL1
VAD_EN
VDD
GND
GND
VDD
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
GND
NCNCNCNCNC
NC
VDD
GND
GND
VDD
VDD
NCNCNCNCNCNCNC
EPR
NC
NC
VDD
ENCODER_EN
GND
IC204
HD64F3687
123456789101112131415
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
333435363738394041424344454647
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
P36
P37
P52/WKP2
P53/WKP3
P54/WKP4
P55/WKP5/ADTRG
P10/TMOW
P11/PWM
P12
P56/SDA
P57/SCL
P74/TMRIV
P75/TMCIV
P76/TMOV
P24
P63/FTIOD0
P62/FTIOC0
P61/FTIOB0
NMI
P60/FTIOA0
P64/FTIOA1
P65/FTIOB1
P66/FTIOC1
P67/FTIOD1
P85
P86
P20/SCK3
P21/RXD
P22/TXD
P23
P70/SCK3_2
P87
P71/RXD_2
P72/TXD_2
P14/IRQ0
P15/IRQ1/TMIB1
P16/IRQ2
P17/IRQ3/TRGV
P33
P32
P31
P30
PB3/AN3
PB2/AN2
PB1/AN1
PB0/AN0
PB4/AN4
PB5/AN5
PB6/AN6
PB7/AN7
AVCC
X2
X1
VCL
RES
TEST
VSS
OSC2
OSC1
VCC
P50/WKP0
P51/WKP1
P34
P35
IC50
AD73311ARS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
VOUTP
VOUTN
AVDD1
AGND1
VINP
VINN
REFOUT
REFCAP
AVDD2
AGND2 DGND
DVDD
RESET
SCLK
MCLK
SDO
SDOFS
SDIFS
SDI
SE
IC252
CMX589AD5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
XTAL
XTAL/CLK_RX
CLKDIVA
CLKDIVB
RX_HOLD
RXDCACQ
PLLACQ
RX_PSAVE
VBIAS
RXFB
RX_SIG_IN
VSS DOC2
DOC1
BT
TXO
TXE
TXP
TXD
RXD
RXC
TXC
S/N
VDD
IC351
MAX3226EAE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
READY
C1+
V+
C1
C2+
C2
V
-
R1IN R1OUT
INVALID
T1IN
FORCEON
T1OUT
GND
VCC
FORCEOFF
J301
to the IC-2200H
LOGIC unit JJ4
PTTIN_C
PTTOUT
DMOD
AMODIN
F_RXD
BUSY_C
RES
GND
GND
P01
AGND
5V
TXD
232_TX
232_RX
RMUTE
FMDET
DAFOUT
REFMOD
CCS
FLASH
RXD_2_C
TXD_2_C
VCC_8V
3
2
1
4
5
IC1
S-812C33AMC-C2N-T2
VOUT
VIN
GND
NC
NC
4
IC2
R1111N321B
5
3
2
1
VDD
GND
CE
VOUT
NC
C2
10
C5
0.001
R400
100k
R401
5.6k
Q401
DTC144EU
C401
10
3.3V
3.3V
C8
0.1
C7
4.7
R2
22
C11
4.7
R1
47k
Q51
DTC144EU
R60
10k
R59
100k
Q50
2SA1586
L50
1µ
C5410C55
0.1
C333
0.001
C57
0.1
R51
1k
C51
0.022
R50
680
C50
0.1
DAFOUT
AGND
CP50
R52
100
C56
0.047
R58
0
ADIN
ADREF
C58
0.1
C150
1
C102
TZY2Z100A001
X101
CR-708
C103
7p
R101
1M
IC101
TC7SHU04FU
1
2
34
5
C104
0.1
R102
100
R103
1k
5
IC103
TC7S04FU
1
2
34
C106
0.1
R57
47k
-
+
+
567
8
432
1
IC251
NJM2115V
ADREF
R53
47k
R54
47k
C53
0.1
AMODIN
R55
100k
ADIN
C250
0.1
R56
100
R252
100k
R251
47k
C252
1
MCLK
MCLK
R261
47k
R255
47k
R254
47k
R253
47k
R257
47k
R100
0
C255
1
R256 100k
C253 22p
R260
100k
R258
100k
C256
0.1
PSAVE
TXCK
RXCK
RXDT
TXDT
TXCK
RXCK
RXDT
TXDT
TXCK
RXCK
RXDT
TXDT
Q251
DTC144EU
ACQ
CP256
CP255
CP254
C257
0.027
C258
0.027
C259
0.0022
R262
22k
R264
100k
+
-
+
567
8
432
1
IC253
NJM13404V
R269
33k
R267
100k
C261
0.1
C260
1
C262
1
CP252
CP251
1
2
3
5
4
IC254
TC4S66F
R268
390k
R270
47k
C263
0.1
DMOD
REFMOD
C351 0.22
C352 0.22
C353 0.22
C354 0.22
232_RX
R308
100
R309
100
232_TX
C355
0.1
C9
10
C10
0.1
C153
0.1
C154
0.1
ATXD
ACLK
ASTB
ARXD
AEPR
ARES
SCLK
SO
SEN
SI
C155
0.1
C156
0.1
D151
MA2S728
ARES
R1511kR152
47k
C152
0.1
C151
0.1
C157
0.1
C159
0.1
Q252
DTC144EU
DCEL
AEPR
RMUTE
Q202
DTC144EU
IC202
TC7SH08FU
51
2
34RXD
C201
0.1
F_RXD
FLASH
Q201
DTC144EU
NMI
P85
R206
1k
R201
1k
R2021kR203
4.7k
R204
4.7k
R205
4.7k
P86
P87
TXD
RES
1
2
6
5
43
Q306
XP4312
RXD_2
Q305
XP4312
1
2
6
5
43
Q301
DTC144EU
PTTIN
Q303
DTC144EU
Q302
DTC144EU
BUSY
PTTIN
AGND
DMOD
AMODIN
TXD
F_RXD
232_TX
232_RX
RES
RMUTE
FMDET
FMDET
DAFOUT
REFMOD
FLASH
RXD_2_C
RXD_2
TXD_2
TXD_2
L351
1µ
MCLK
ATXD
ACLK
NMI
ASTB
ARXD
ARES
MCLK
P85
P86
P87
RXD
TXD
R219
47k
R218
47k
RXD_2
TXD_2
P01
D152
MA2S111
TXCK
RXCK
RXDT
TXDT
PSAVE
BUSY
PTTIN
P01
CP216
R220 0
R221 0
R211
47k
C205
0.1
X201
CR-760
(9.8304 MHz)
C202
7p
C207
TZY2R200A001
C204
18p
4
IC203
S-80928CNMC
5
3
2
1
VDD
OUT
VSS
CD
NC
R209
1k
C206
0.01
R212
47k
R217
47k
R216
47k
C203
0.1
L201
1µ
C1
10
Q400
2SA1586
L151
1µ
CP101
ACQ
ACQ
APWR
TXD_2_C
PTTOUT_C
R318 100
R317 100
R315 100
R316 100
3.3V 3.3V
3.3V3.3V3.3V
3.3V 3.3V
APWR
APWRAPWR
APWR
PSAVE PSAVE
PSAVE
DCEL
DCEL DCEL
DCEL
PTTOUT_C
PTTOUT_C
VCC_8V
5V
VCC_8V
5V
VCC_8V
5V5V
VCC_8VVCC_8V
5V
VCC_8V
5V
5V
VCC_8V VCC_8V
5V
VCC_8V
5V 5V
VCC_8V
VCC_8V
AEPR
RMUTE_C
ACQ
RES
3.3V
PSAVE ON: L(0.0V)
PSAVE OFF: H(3.3V)
PSAVE OFF: L(0.0V)
PSAVE ON: H(3.3V)
3.2V
4.0-8.5V
PSAVE OFF: L(0.0V)
PSAVE ON: H(5.0V)
5.0V
3.2V
3.2V
4.7V
3.25V
TX: 350mVp-p
3.25V
3.25V
TX: 350mVp-p
PSAVE ON: L(0.0V)
PSAVE OFF: H(3.3V)
3.3V
3.3V
BUSY: H(3.3V)
RX: L(0.0V)
TX: H(3.3V)
RX: L(0.0V)
TX: H(3.3V)
3.3V
4.5-8.5V 5.0V
3.2V
14 - 3
Page 53

Page 54

1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
S-14017HZ-C1
C 2004 Icom Inc.
Downloaded by
RadioAmateur.EU
 Loading...
Loading...