Page 1

IBM System z10™
Enterprise Class
Hardware Overview
CMG – April 15, 2008
Tom Russell – IBM Canada
Thanks to Harv Emery, John Hughes, WSC
IBM Systems
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Page 2

IBM System z
Trademarks
The following are trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
AIX*
APPN*
Cell Broadband Engine
DB2*
DB2 Connect
DirMaint
DRDA*
Distributed Relational Database Architecture
e-business logo*
ECKD
Enterprise Storage Server*
ESCON*
FICON*
GDPS*
* Registered trademarks of IBM Corporation
The following are trademarks or registered trademarks of other companies.
InfiniBand® is a registered trademark of the InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA).
Intel is a trademark of Intel Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
Java and all Java-related trademarks and logos are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc., in the United States and other countries
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
Microsoft, Windows and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Red Hat, the Red Hat "Shadow Man" logo, and all Red Hat-based trademarks and logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., in the United States and other countries.
SET and Secure Electronic Transaction are trademarks owned by SET Secure Electronic Transaction LLC.
* All other products may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Notes:
Performance is in Internal Throughput Rate (ITR) ratio based on measurements and projections using standard IBM benchmarks in a controlled environment. The actual throughput that
any user will experience will vary depending upon considerations such as the amount of multiprogramming in the user's job stream, the I/O configuration, the storage configuration, and
the workload processed. Therefore, no assurance can be given that an individual user will achieve throughput improvements equivalent to the performance ratios stated here.
IBM hardware products are manufactured from new parts, or new and serviceable used parts. Regardless, our warranty terms apply.
All customer examples cited or described in this presentation are presented as illustrations of the manner in which some customers have used IBM products and the results they may
have achieved. Actual environmental costs and performance characteristics will vary depending on individual customer configurations and conditions.
This publication was produced in the United States. IBM may not offer the products, services or features discussed in this document in other countries, and the information may be
subject to change without notice. Consult your local IBM business contact for information on the product or services available in your area.
All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
Information about non-IBM products is obtained from the manufacturers of those products or their published announcements. IBM has not tested those products and cannot confirm the
performance, compatibility, or any other claims related to non-IBM products. Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the suppliers of those products.
Prices subject to change without notice. Contact your IBM representative or Business Partner for the most current pricing in your geography.
Geographically Dispersed Parallel Sysplex
HiperSockets
HyperSwap
IBM*
eServer
IBM logo*
IMS
InfoPrint*
Language Environment*
MQSeries*
Multiprise*
NetView*
On demand business logo
OS/390*
Parallel Sysplex*
POWER6
PR/SM
Processor Resource/Systems Manager
RACF*
Resource Link
RMF
S/390*
Sysplex Timer*
System z
System z9
System z10
TotalStorage*
Virtualization Engine
VSE/ESA
VTAM*
WebSphere*
z/Architecture
z/OS*
z/VM*
z/VSE
zSeries*
2
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 3

IBM System z
System z10 EC New Functions and Features
Five hardware models
Faster Processor Unit (PU)
Up to 64 customer PUs
36 CP Subcapacity Settings
Star Book Interconnect
Up to 1,520 GB memory
Fixed HSA as standard
Large Page (1 MB)
HiperDispatch
Enhanced CPACF SHA 512,
AES 192 and 256-bit keys
Hardware Decimal Floating Point
New Capacity on Demand
architecture and enhancements
SOD: PSIFB for z9 EC & BC for
non-dedicated CF Models*
6.0 GBps InfiniBand HCA to I/O
interconnect
FICON Enhancements
SCSI IPL included in Base LIC
OSA-Express3 10 GbE (2Q08)*
HiperSockets enhancements
InfiniBand Coupling Links (2Q08)*
STP using InfiniBand (2Q08)*
Standard ETR Attachment
FICON LX Fiber Quick Connect
Power Monitoring support
Scheduled Outage Reduction
72 New Instructions
Capacity Provisioning
No support for Japanese Compatibility Mode (JCM)
No support for MVS Assist instructions
3
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Improved RAS
* All statements regarding IBM's plans, directions, and intent are subject to change
or withdrawal without notice. Any reliance on these Statements of General Direction
is at the relying party's sole risk and will not create liability or obligation for IBM.
IBM Systems
Page 4
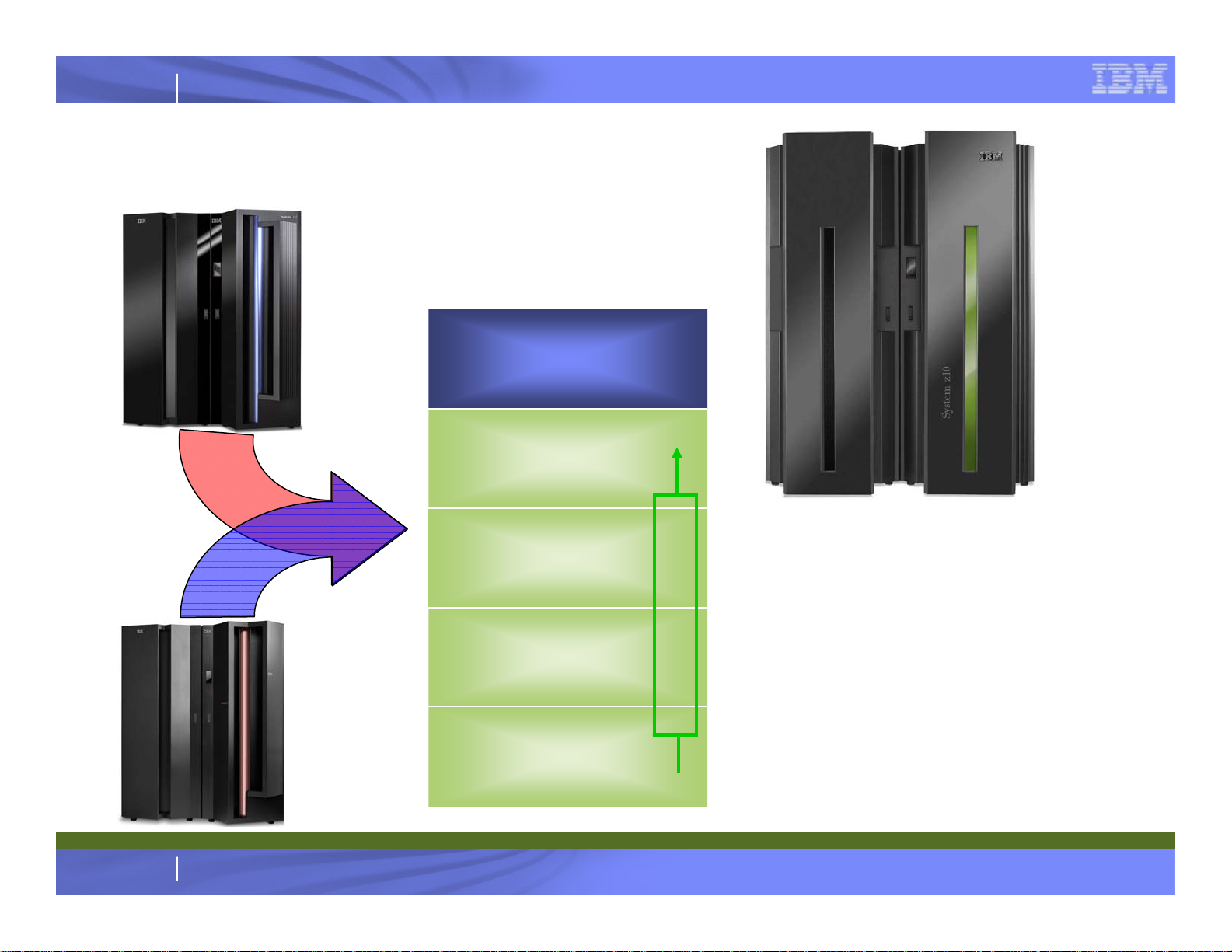
IBM System z
z10 EC System Upgrades
E64
z9 EC
E56
z10 EC to higher z10 EC model
E40
E26
Concurrent Upgrade
z990
4
© 2008 IBM Corporation
E12
► Concurrent upgrade of z10 EC
Models E26, E40 and E56.
Upgrade to E64 is disruptive
► When upgrading to z10 EC E64,
unlike the z9 EC, the first Book is
retained
Any z9 EC to any z10 EC
Any z990 to any z10 EC
IBM Systems
Page 5

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC Key Dates
IBM System z10 Announce – February 26, 2008
► First Day Orders
► Resource Link
► Capacity Planning Tools (zPCR, zTPM, zCP3000)
► SAPR Guide (SA06-016-00) and SA Confirmation Checklist available
Availability – February 26, 2008
► z10 EC all Models
► Upgrades from z990, z9 EC to z10 EC
Availability – May 26, 2008
► Model upgrades within z10 EC
► Feature Upgrades within the z10 EC – May 26, 2008
™
support available
Planned Availability* – 2Q 2008
► OSA Express3 10 GbE LR – the first of a new OSA generation
► InfiniBand Coupling Links for any z10 EC and ICF-only z9 EC and BC machines
New ITSO Redbooks (Draft versions)
● z10 EC Technical Introduction, SG24-7515 - February 26, 2008
● z10 EC Technical Guide, SG24-7516 - February 26, 2008
● z10 EC Capacity on Demand, SG24-7504 - March, 2008
● Getting Started with InfiniBand on z10 EC and System z9, SG24-7539 – May, 2008
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subj ect to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
5
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 6

IBM System z
z10 EC Multi-Chip Module (MCM)
96mm x 96mm MCM
► 103 Glass Ceramic layers
► 7 chip sites
► 7356 LGA connections
► 17 and 20 way MCMs
PU 1
S 2
PU 4 PU 3
S 3
CMOS 11s chip Technology
► PU, SC, S chips, 65 nm
► 5 PU chips/MCM – Each up to 4 cores
● One memory control (MC) per PU chip
● 21.97 mm x 21.17 mm
● 994 million transistors/chip
● L1 cache/PU
– 64 KB I-cache
– 128 KB D-cache
● L1.5 cache/PU
– 3 MB
PU 0PU 2
● 4.4 GHz
● Approx 0.23 ns Cycle Time
● 6 Km of wire
► 2 Storage Control (SC) chip
● 21.11 mm x 21.71 mm
SC 0SC 1
● 1.6 billion transistors/chip
● L2 Cache 24 MB per SC chip (48 MB/Book)
● L2 access to/from other MCMs
● 3 Km of wire
S 0
► 4 SEEPROM (S) chips
● 2 x active and 2 x redundant
S 1
● Product data for MCM, chips and other engineering
information
► Clock Functions – distributed across PU and SC chips
● Master Time-of-Day (TOD) and 9037 (ETR)
functions are on the SC
6
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 7

IBM System z
z10 EC Chip Relationship to POWER6™
Siblings, not identical twins
Share lots of DNA
► IBM 65nm Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) technology
► Design building blocks:
● Latches, SRAMs, regfiles, dataflow elements
► Large portions of Fixed Point Unit (FXU), Binary Floating-
point Unit. (BFU), Hardware Decimal Floating-point Unit
(HDFU), Memory Controller (MC), I/O Bus Controller (GX)
► Core pipeline design style
Enterprise Quad Core
z10 Processor Chip
● High-frequency, low-latency, mostly-in-order
► Many designers and engineers
Different personalities
► Very different Instruction Set Architectures (ISAs)
● very different cores
► Cache hierarchy and coherency model
► SMP topology and protocol
► Chip organization
► IBM z Chip optimized for Enterprise Data Serving Hub
7
© 2008 IBM Corporation
POWER6 Dual Core Chip
IBM Systems
Page 8

IBM System z
Orderable Processor Features
Books
/PUs
1/17
2/34
3/51
4/68
4/77
CPsModel
IFLs
uIFLs
0 - 12
0 - 12E12
0 - 11
0 - 26
0 - 26E26
0 - 25
0 - 40
0 - 40E40
0 - 39
0 - 56
0 - 56E56
0 - 55
0 - 64
0 - 64E64
0 - 63
zAAPs
ICFs
zIIPs
0 - 6
0-12
0 - 6
0 - 13
0-16
0 - 13
0 - 20
0-16
0 - 20
0 - 28
0-16
0 - 28
0 - 32
0-16
0 - 32
Opt
Saps
0-3
0-7
0-11
0-18
0-21
Std
Saps
3
6
9
10
11
Std
Spares
2
2
2
2
2
Note: A minimum of one CP, IFL, or ICF must be
purchased on every model.
Note: One zAAP and one zIIP may be purchased for
each CP purchased.
8
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Note: System z10 EC is designed not to require
Optional SAPs for production workloads except
sometimes for TPF or z/TPF workloads.
IBM Systems
Page 9
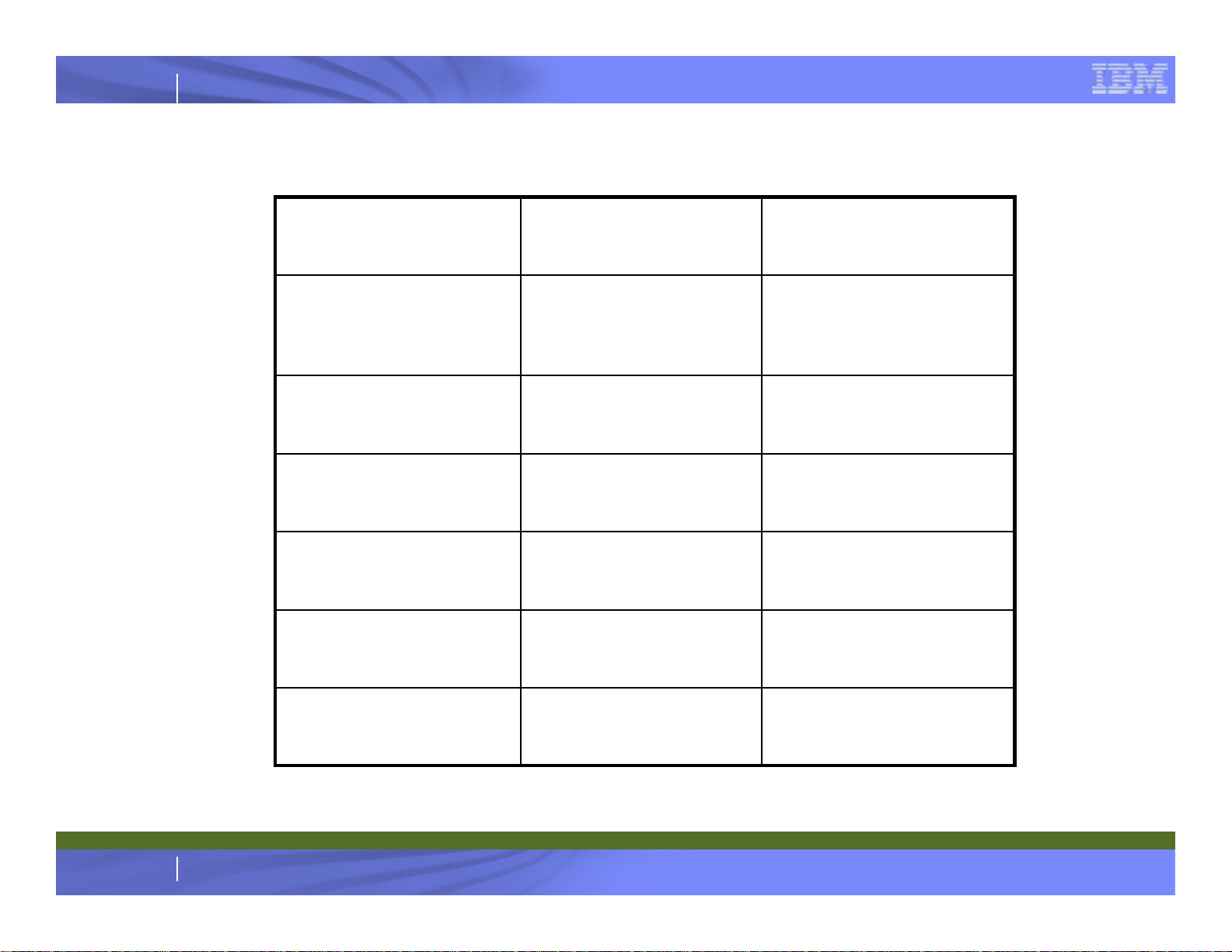
IBM System z
z9 vs z10 EC CEC Structure
z10 ECz9 EC
SMP Configuration
Topology
Max Memory
Cache Levels
S54
4 books, 64 PUs
Dual Ring
One or Two Hops
Up to 512GB
-HSA?
L1 per PU
L2 per Book
E64
4 books, 77 PUs
Fully Connected
NoYesJumper Books
Up to 1,520 GB
+ 16 GB HSA
L1 and L1.5 per PU
L2 per Book
4 KB and 1 MB4 KBPage Sizes
9
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 10

IBM System z
z10 EC HiperDispatch
HiperDispatch – z10 EC unique function
► Dispatcher Affinity (DA) - New z/OS Dispatcher
► Vertical CPU Management (VCM) - New PR/SM Support
Hardware cache optimization occurs when a given unit of work is consistently
dispatched on the same physical CPU
► Up till now software, hardware, and firmware have had pride in the fact of how
independent they were from each other
► Non-Uniform-Memory-Access has forced a paradigm change
● CPUs have different distance-to-memory attributes
● Memory accesses can take a number of cycles depending upon cache level /
local or remote repository accessed
The entire z10 EC hardware/firmware/OS stack now tightly collaborates to
obtain the hardware’s full potential
All supported z/OS releases (z/OS 1.7 requires the zIIP web deliverable)
10
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 11
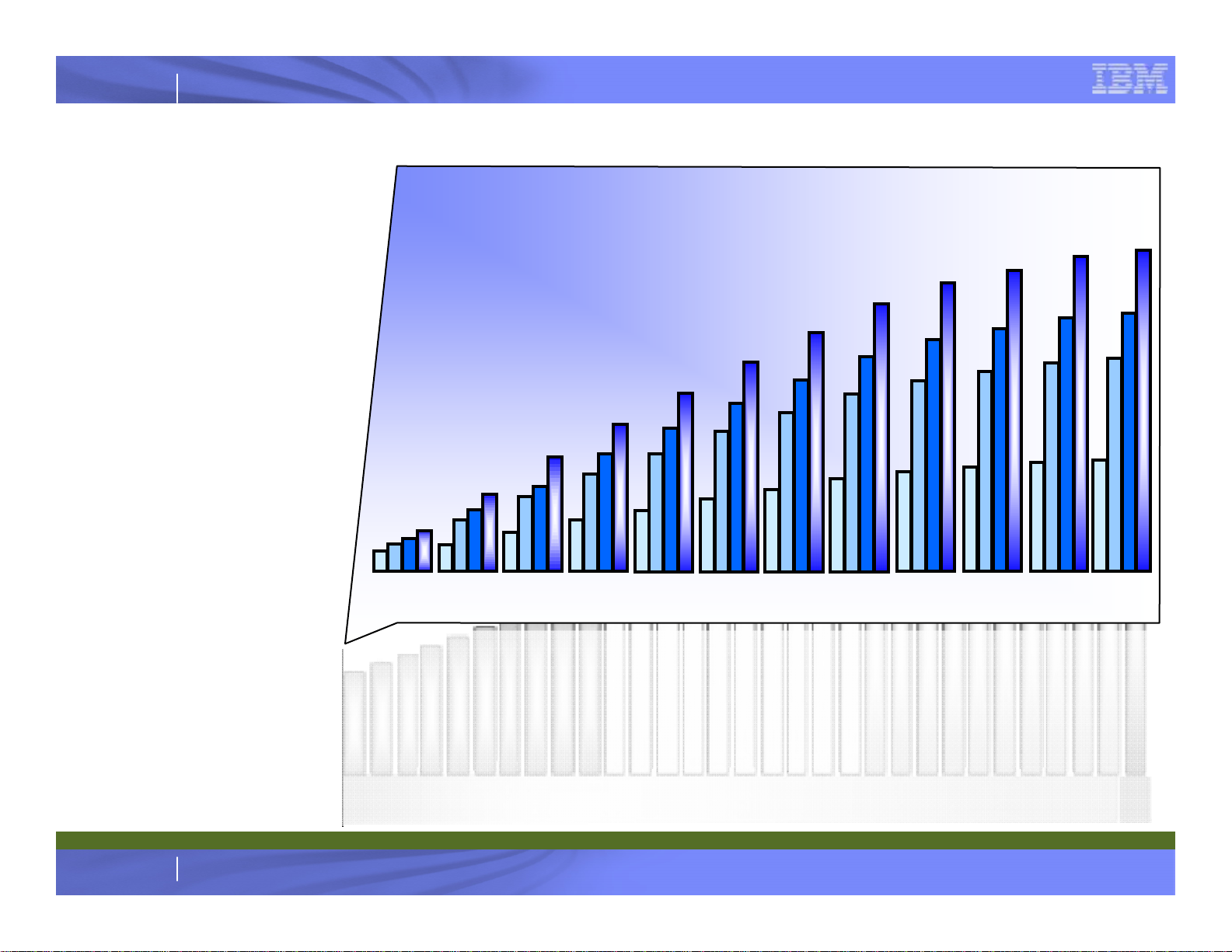
IBM System z
System z9 EC CP Subcapacity (12 or Fewer CPs)
CP Capacity
Relative to Full Speed
Subcapacity CP settings
7nn = 100%
6nn
5nn
4nn
¡
¡
¡
aa%
bb%
cc%
nn = 01 Through 12
1-CP through 12-CP only
Available on any hardware model
409
509
609
709
410
510
610
710
411
511
611
401
501
601
701
402
502
602
702
403
503
603
703
404
504
604
704
405
505
605
705
406
506
606
706
407
507
607
707
408
508
608
708
1-way 2-way 3-way 4-way 5-way 6-way
7-way 8-way
9-way
10-way
The System z10 EC will offer 36 CP subcapacity settings with the first twelve or fewer
CPs (general purpose) engines.
► All CPs must be the same capacity within one z10 EC
► On machines with 13 or more CPs, all CPs must run at full speed
711
11-way
412
512
612
12-way
712
11
The entry point is approximately xx% of the capacity of the full speed CP
All specialty engines run at full speed. The one for one entitlement to purchase one
zAAP and one zIIP for each CP purchased is the same for CPs of any speed.
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 12
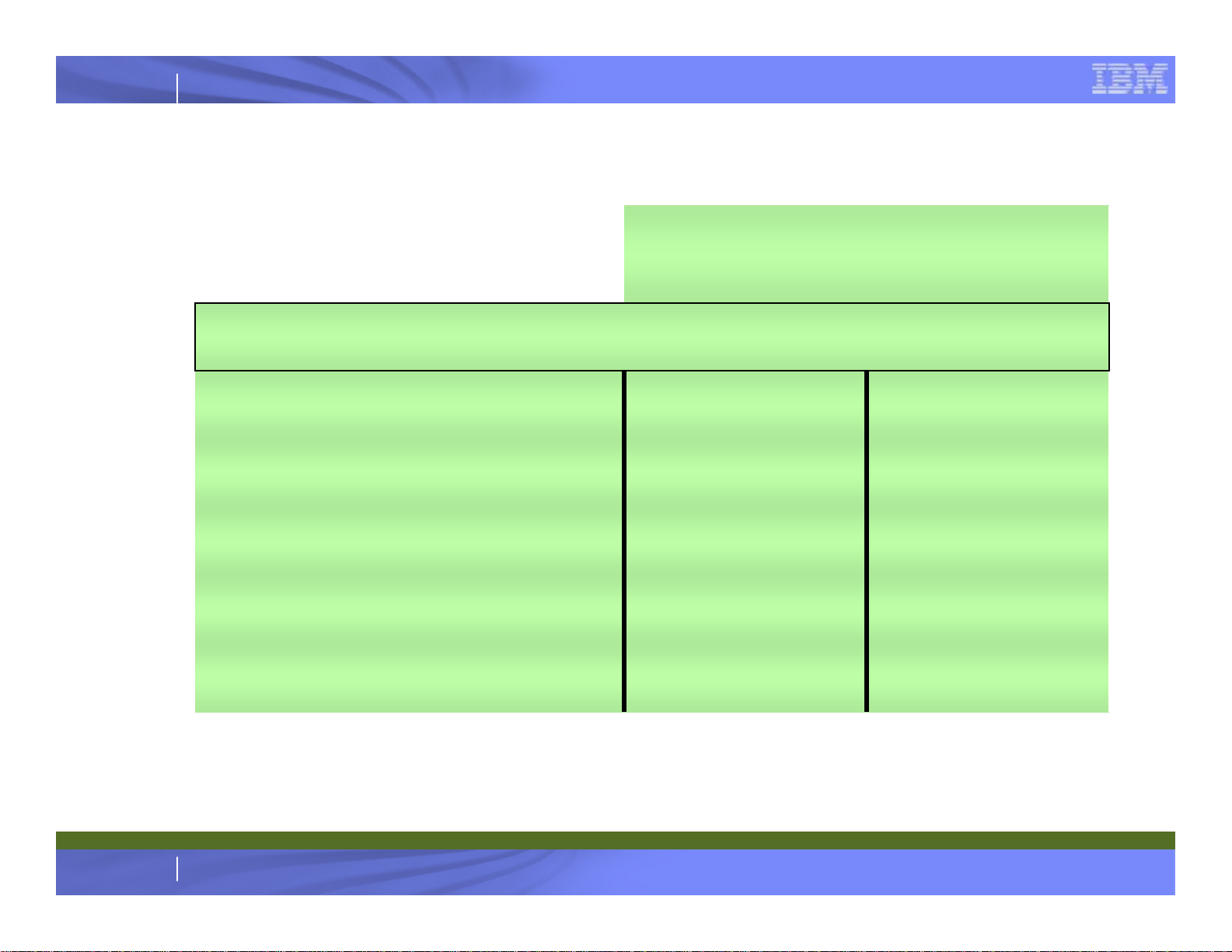
IBM System z
LSPR Ratios and MSU Values for System z10 EC
z10 EC to z9 EC
Ratios
z10 EC MSU
Values*
LSPR mixed workload average, multi-image for z/OS 1.8 with HiperDispatch
active on z10 EC!
Uni-processor
16-way z10 EC to 16-way z9 EC
32-way z10 EC to 32-way z9 EC
56-way z10 EC to 54-way z9 EC
64-way z10 EC to 54-way z9 EC
1.62
1.49
1.49
1.54
1.70
115 for 701
1,264 for 716
2,200 for 732
3,395 for 756
3,739 for 764
12
* Reflects Mainframe Charter Technology Dividend.
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 13
IBM System z
z10 EC Capacity Planning in a nutshell
GHz
MIPs
MSUs
tables
13
?
HiperDispatch
Don’t use “one number” capacity comparisons!
Work with IBM technical support for capacity planning!
Customers can now use zPCR
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 14

IBM System z
Evolution of System z Specialty Engines
Building on a strong track record of
technology innovation with specialty
engines – DB Compression, SORT,
Encryption, Vector Facility
Cell Broadband Engine™
IBM System z9
Integrated
Information
Processor (IBM
zIIP) 2006
System z Application
Eligible for zIIP:
Assist Processor
DB2 remote
(zAAP) 2004
access and
BI/DW
Integrated Facility
for Linux (IFL)
2000
Internal Coupling
Facility (ICF) 1997
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
14
© 2008 IBM Corporation
*SOD: IBM plans to enhance z/VM in a future release to support the new
System z10 EC capability to allow any combination of CP, zIIP, zAAP, IFL,
and ICF processor-types to reside in the same z/VM LPAR
Eligible for zAAP:
Java
™
execution
environment
z/OS XML
ISVs
New! IPSec
encryption
z/OS XML
z/OS Global
Mirror*
IBM Systems
Page 15

IBM System z
Large Page Support
Issue: Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) Coverage shrinking as % of
memory size
► Over the past few years application memory sizes have dramatically increased due to
support for 64-bit addressing in both physical and virtual memory
► TLB sizes have remained relatively small due to low access time requirements and
hardware space limitations
► TLB coverage today represents a much smaller fraction of an applications working
set size leading to a larger number of TLB misses
► Applications can suffer a significant performance penalty resulting from an increased
number of TLB misses as well as the increased cost of each TLB miss
Solution: Increase TLB coverage without proportionally enlarging the TLB
size by using large pages
► Large Pages allow for a single TLB entry to fulfill many more address translations
► Large Pages will provide exploiters with better TLB coverage
Benefit:
► Designed for better performance by decreasing the number of TLB misses that an
application incurs
15
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 16

IBM System z
New Instructions
A large variety of facilities added in the System z10 EC
► General-Instructions Extension Facility (72 new)
► Execute-Extension Facility (1 new)
► Parsing-Enhancement Facility (2 new)
► Compare-and-Swap-and-Store Facility 2 (new function)
► Message-Security-Assist Extensions (new functions)
► Enhanced-DAT Facility (1 new, 3 changed)
► Configuration-Topology Facility (1 new, 1 changed)
Potential for:
► Significant performance improvement
► Enhanced capabilities
► Simpler code
16
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 17

IBM System z
Examples – New Instructions
Compare and Branch
► Replaces Compare, followed by Branch on Condition
Compare and Trap
► Program Check (Data Exception) if Compare is True
New Immediate instructions
► Saves having storage references
Primary motivation: Performance
► ARCH(8) TUNE(8) options in compilers
► I expect Java to get the most benefit
17
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 18

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC Capacity on Demand
(CoD)
18
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 19

IBM System z
Removing Road Blocks
A permanent upgrade cannot occur while CBU or On/Off CoD is active.
Only one solution can be active at a time
Limited to the permanent capacity
► After a permanent capacity upgrade, the old temporary contract may become useless.
Cannot add temporary capacity while a Concurrent Book Add is in progress.
No CBU-like replacement capacity offering where a disaster is not involved.
When On/Off CoD or CBU records are activated/deactivated, all
processors
defined in those records must be activated/deactivated.
The HMC requires connectivity to the IBM Support System to obtain temporary
records or verify passwords at the time of activation.
► HMC connectivity or response time is a potential inhibitor.
► The process to activate capacity can take too long.
No way to determine which capacity is billable versus replacement
Drastic system slow down occurs if CBU or CBU test expires
Automation provides only limited control
19
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 20

IBM System z
The Basics – Temporary Upgrades
Capacity Backup (CBU)
► Predefined capacity for disasters on a other “lost” server(s)
► Concurrently add CPs, IFLs, ICFs, zAAPs, zIIPs, SAPs
► Pre-paid
Capacity for Planned Events (CPE)
► CBU-like offering, when a disaster is not declared
► Example: System migration (push/pull) or relocation ( d ata center move)
► Predefined capacity for a fixed period of time (3 days)
► Pre-paid
On/Off Capacity on Demand (On/Off CoD)
► Satisfy periods of peek demand for computing resources
► Concurrent 24 hour rental of CPs, IFLs, ICFs, zAAPs, zIIPs, SAPs
► Supported through a new software offering – Capacity Provisioning Manager (CPM)
► Post-paid
20
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 21

IBM System z
System z10 EC Capacity on Demand Reinvented!
Permanent and temporary offerings – with you in charge
► Permanent offerings – Capacity Upgrade on Demand (CUoD), Customer
Initiated Upgrade (CIU)
► Temporary offerings
● Additional capacity - On/Off Capacity on Demand (On/Off CoD)
● Replacement capacity - Backup Upgrade (CBU)
and a new one – Capacity for Planned Event (CPE)
No customer interaction with IBM at time of activation
► Broader customer ability to order temporary capacity
Multiple offerings can be in use simultaneously
► All offerings on Resource Link
► Each offering independently managed and priced
Flexible offerings may be used to solve multiple situations
► Configurations based on real time circumstances
► Ability to dynamically move to any other entitled configuration
Offerings can be reconfigured or replenished dynamically
► Modification possible even if offering is currently active
► Some permanent upgrades permitted while temporary offerings are active
Policy based automation capabilities
► Using Capacity Provisioning Manager with z/OS 1.9
► Using scheduled operations via HMC
21
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 22

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC Memory
22
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 23

IBM System z
z10 EC – HSA considerations
HSA of 16GB provided as standard outside of purchased memory
The HSA has been designed to eliminate planning for HSA. Preplanning
for HSA expansion for configurations is eliminated because HCD/IOCP
will, via the IOCDS process, always reserves HSA space for:
►4 CSSs
►15 LPs in each CSS (total of 60 LPs)
►Subchannel set-0 with 63.75k devices in each CSS
23
►Subchannel set-1 with 64k devices in each CSS
►All the above are designed to be activated and used with dynamic I/O
changes
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 24

IBM System z
z10 EC Memory Offering and Assignment
Customer Memory Granularity for ordering:
►16 GB: Std - 16 to 256; Flex - 32 to 256
Model
Standard
Memory
GB
Flexible
Memory
GB
NA16 - 352E12
32 - 35216 - 752E26
32 - 75216 - 1136E40
32 - 113616 - 1520E56
32 - 113616 - 1520E64
►32 GB: Std - 288 to 512; Flex - 288 to 512
►48 GB: Std - 560 to 944; Flex - 560 to 944
►64 GB: Std - 1008 to 1520; Flex - 1008 to 1136
LIC CC controls purchased memory
Maximum Physical Memory:
384 GB per book, 1.5 TB per system
►Up to 48 DIMMs per book
►64 GB minimum physical memory in each book
►Physical Memory Increments:
● 32 GB – Eight 4GB DIMMs (FC #1604)
Preferred if can fulfill purchase memory
● 64 GB – Eight 8 GB DIMMs (FC #1608)
Used where necessary
For Flexible, if required, 16 GB “Pre-planned
24
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Memory” features (FC # 1996) are added to
the configuration.
IBM Systems
Page 25

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC Cryptography
25
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 26

IBM System z
z10 EC CP Assist for Cryptographic Functions
(CPACF)
z9
DES
TDES
AES-128
SHA-1, 224, 256
PRNG
Integrated Cryptographic Service Facility (ICSF)
PU PU PU PU PU PU PU PU
CP Assist for Cryptograph ic Function
Crypto Express2
z10 EC
DES
TDES
AES-128, 192, 256
SHA-1, SHA2:
(224, 256, 384, 512)
PRNG
26
High performance clear key symmetric encryption/decryption
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 27

IBM System z
z10 EC Cryptographic Support
CP Assist for Cryptographic Function (CPACF)
► Standard on every CP and IFL
► Supports DES, TDES, AES and SHA
► Pseudo Random Number Generation (PRNG)
► New to z10 EC
● Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) – 192 and 256
● Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) – 384 and 512
Crypto Express2
► Two configuration modes
● Coprocessor (default)
– Federal Information Processing Standard
(FIPS) 140-2 Level 4 certified
● Accelerator (configured from the HMC)
► Three configuration options
● Default set to Coprocessor
Coprocessor
1
Coprocessor
Coprocessor
2
Accelerator
► Concurrent Patch
Dynamic Add Crypto to LPAR
► No recycling of LPAR
► No POR required
TKE 5.0 workstation with TKE 5.2 LIC
► Diskette drive support – read only
27
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Accelerator
3
Accelerator
IBM Systems
Page 28

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC Availability
28
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 29

IBM System z
System z10 EC continues to focus on RAS
Keeping your system available is key to our total design
Sources of Outages - Pre z9
-Hrs/Year/Syst-
Scheduled (CIE+Disruptive Patches + ECs)
Planned - ( M ES + Dr iver Up g rad es)
Unscheduled (UIRA)
Impact of Outage
Unscheduled
Outages
Scheduled
Outages
Planned
Outages
Preplanning
requirements
Prior
Servers
9
9
z
1
0
E
C
z10 ECz9 EC
9
9
I
n
c
r
e
9
a
s
e
d
F
o
c
u
s
9
9
9
9
29
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 30

IBM System z
z10 EC Enhancements designed to avoid Outages
Continued Focus on Firmware Quality
Reduced Chip Count on MCM
Memory Subsystem Improvements
DIMM FRU indicators
Single Processor Core Checkstop
Single Processor Core Sparing
Point to Point SMP Fabric (not a ring)
Rebalance PSIFB and I/O Fanouts
Redundant 100Mb Ethernet service
network w/ VLAN
CoD – Flexible Acitvation/Deactivation
Elimination of unnecessary CBU passwords
Enhanced Driver Maintenance (EDM) Upgrades
► Multiple “from” sync point support
► Improved control of channel LIC levels
Reduce Pre-planning to Avoid POR
► 16 GB for HSA
► Dynamic I/O Enabled by Default
► Add Logical Channel Subsystem (LCSS)
► Change LCSS Subchannel Sets
► Add/Delete Logical Partitions
Reduce Pre-Planning to Avoid LPAR Deactivate
► Change Partition Logical Processor Config
► Change Partition Crypto Coprocessor Config
30
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 31

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC I/O Structure
31
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 32

IBM System z
z10 EC Book Layout – Under the covers
Fanouts
MCM
Memory
DCA Power
Supplies
HCA2-O (InfiniBand)
HCA2-C (I/O cages)
MBA (ICB-4)
MRU
32
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Connections
IBM Systems
Page 33

IBM System z
z10 EC – Under the covers (Model E56 or E64)
Internal
Batteries
(optional)
Processor Books,
Memory, MBA and
Power
Supplies
3x I/O
cages
Fiber Quick Connect
(FQC) Feature
(optional)
HCA cards
InfiniBand I/O
Interconnects
Cooling
Units
2 x Support
Elements
FQC
33
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 34

IBM System z
z10 EC Channel Type and Crypto Overview
FICON/FCP
► FICON Express4
► FICON Express2 (carry forward only)
► FICON Express (carry forward only)
Networking
► OSA-Express3 (2Q2008)
● 10 Gigabit Ethernet LR
► OSA-Express2
● 1000BASE-T Ethernet
● Gigabit Ethernet LX and SX
● 10 Gigabit Ethernet LR
► HiperSockets (Define only)
● Layer 2 support
Coupling Links
► InfiniBand (PSIFB) – 2Q2008
► ISC-3 (Peer mode only)
► ICB-4 (Not available on Model E64)
► IC (Define only)
Time Features
► STP - Optional
► ETR Attach – Standard
Crypto
► Crypto Express2
● Configurable Coprocessor or Accelerator
Channel types not supported:
ESCON
Note: ICB-4 cables are available as features.
All other cables are sourced separately
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
34
© 2008 IBM Corporation
► OSA-Express
► ICB-3
► Features not supported on System z9
IBM Systems
Page 35

IBM System z
Connectivity for Coupling and I/O
Up to 8 fanout cards per book
► Up to 16 ports per book
– 48 Port System Maximum
Fanout cards - InfiniBand pairs dedicated to
function
IFB
HCA2-C
IFB
HCA2-C fanout – I/O Interconnect
► Supports all I/O, ISC-3 and Crypto Express2
cards in I/O cage domains
Up to 16 CHPIDs – across 2 ports
HCA2-O fanout – InfiniBand Coupling*
IFB
HCA2-O
IFB
► New CHPID type – CIB for Coupling
– Fiber optic external coupling link
2 CHPIDs – 1 per port
MBA fanout (Not available on Model E64)
ICB-4
MBA
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
35
© 2008 IBM Corporation
ICB-4
► ICB-4
► New connector and cables
IBM Systems
Page 36

IBM System z
SAPs, I/O Buses, Links, and I/O Connectivity
Model
E12
E26
E40
E56
E64
Books/
PUs
1/17
2/34
3/51
4/68
4/77
Std
SAPS
Opt
SAPs
0-3
0-7
0-11
0-18
0-21
Maximum
HCAs/
Buses
8/163
16/326
20/409
24/4810
24/4811
Maximum
PSIFB+ICB4
Links + I/O
cards
16 + 0 Cards
32 + 0 Cards
ICB-4 limit 16
32 + 32 Cards
ICB-4 limit 16
32 + 64 Cards
ICB-4 limit 16
32 + 64 Cards
No ICB-4
Maximum I/O
Cards +
PSIFB/ICB4
Links
64 + 0
PSIFB + ICB4
84 + 8
PSIFB + ICB4
84 + 16
PSIFB + ICB4
84 + 24
PSIFB + ICB4
84 + 24 PSIFB
Max
FICON/
ESCON
CHPIDs
256/
960
336/
1024
336/
1024
336/
1024
336/
1024
Note: Only TPF may need Opt SAPs for normal workload
Note: PSIFB and ICB4 do not reside in I/O cages
Note: Plan Ahead for up to 2 additional I/O cages
This assumes no PSC24V power sequence cards
a. 0 to 24 I/O cards – 1 cage
b. 25 to 48 I/O cards – 2 cages
c. 49 to 84 I/O cards – 3 cages
36
© 2008 IBM Corporation
Note: Include Crypto Express2 cards in I/O card count
Limits:
a. 4 LCSSs maximum
b. 15 partitions maximum per LCSS, 60 maximum
c. 256 CHPIDs maximum per LCSS, 1024 maximum
IBM Systems
Page 37

IBM System z
InfiniBand glossary
DescriptionTerm
Gbps
1x
12x
SDR
DDR
12x IB-SDR
12x IB-DDR
1x IB-DDR LR*
Gigabits per second
GigaBytes per secondGBps
One “lane”, one pair of fibers
12 “lanes”, 12 pairs of fiber
Single Data Rate – 2.5 Gbps per “lane” (0.3 GBps)
Double Data Rate – 5 Gbps per “lane” (0.5 GBps)
12 “lanes” (pairs) for a total link data rate of 3 GBps, 150 meters point-to-point
Used with OM3, 2000 MHz-k 50 micron multimode fiber optic cabling with MPO
connectors
12 “lanes” (pairs) for a total link data rate of 6 GBps, 150 meters point-to-point
Used with OM3, 2000 MHz-k 50 micron multimode fiber optic cabling with MPO
connectors
One “lane” (one pair), 5 Gbps link data rate, unrepeated distance of 10 km
Used with 9 micron single mode fiber optic cabling with LC Duplex connectors
InfiniBand® is a registered trademark of the InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA)
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
37
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 38

IBM System z
z9 EC and z10 EC System Structure for I/O
Processor
MBA Fanout
STI-MP
I/O Domain*
z9 EC
Memory
Up to16 x 2.7 GBps
Passive
Connection
Redundant I/O Interconnect
Processor
MBA Fanout
STIs
for
I/O Domain*
Memory
STI-MP
Processor
HCA2-C Fanout
IFB-MP
I/O Domain*
z10 EC
Memory
Up to16 x 6 GBps
I/O Interconnect
Passive
Connection
Redundant I/O Interconnect
Processor
HCA2-C Fanout
for
I/O Domain*
Memory
IFB-MP
38
Crypto
FICON/FCP
Crypto
ISC-3
Networking
ESCON
I/O Cage
FICON/FCP
*Note: Each I/O domain supports up to 4 features only
© 2008 IBM Corporation
ISC -3
Networking
ESCON
Crypto
FICON/FCP
ISC-3
Networking
ESCON
I/O Cage
Crypto
FICON/FCP
ISC -3
Networking
ESCON
IBM Systems
Page 39

IBM System z
System z10 EC FICON Enhancements
Extended Distance FICON (CHPID type FC) performance enhancements
► Enhancement to the industry standard FICON architecture (FC-SB-3)
● Implements a new protocol for ‘persistent’ Information Unit (IU) pacing that can help
to optimize link utilization
● Requires supporting Control Unit(s) (e.g. DS8000 at new level)
► Designed to improve performance at extended distance
● May benefit z/OS Global Mirror (previously called XRC)
● May simplify requirements for channel extension equipment
► Transparent to operating systems
► Applies to FICON Express4 and Express2 channels
Enhancements for Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) performance
► Designed to support up to 80% more I/O operations per second compared to System z9
for small block (4 kB) I/O operations on a FICON Express4 channel
► Transparent to operating systems
► Applies to FICON Express4 and Express2 channels (CHPID type FCP) communicating
to SCSI devices. (Improvement on FICON Express2 is expected to be less than on
FICON Express4)
39
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 40

IBM System z
OSA-Express3 – 10 GbE (2Q2008)
Double the port density compared to
10 GbE OSA-Express3
Designed to Improve Performance for
standard and jumbo frames
10 Gigabit Ethernet LR (Long Reach)
► Two ports per feature
► Small form factor connector (LC
Duplex) single mode
► CHPID type OSD (QDIO)
40
© 2008 IBM Corporation
PCI-E
LC Duplex SM
PCI-E
LC Duplex SM
IBM Systems
Page 41

IBM System z
z10 EC InfiniBand PSIFB* Coupling Connectivity (2Q2008)
Up to 16 CHPIDs – across 2 ports
12x IB-DDR
6 GBps
Minimum – 0
Maximum – 32 ports
Order increment – 2 ports
Distance – 150 meters
OM3 fiber optic cables
IFB
HCA2-O
Point-to-point up to 150 m (492 ft)
Maximum of 16 HCA2-O fanouts
► 2 ports per HCA2-O fanout
► Up to 16 CHPIDs per HCA1-O fanout
● Distribute across 2 ports as desired
12x IB-DDR (6 GBps)
► z10 EC to z10 EC
12x IB-SDR (3 GBps)
► z10 EC to System z9 Dedicated Coupling Facility
OS Support::
► z/OS 1.7 + zIIP Web Deliverable
► z/VM 5.3 – Dynamic I/O Suppoort
IFB
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
41
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 42

IBM System z
System z9 InfiniBand PSIFB* Coupling Connectivity
(2Q2008 – Dedicated CF only; SOD – Any z9)
Up to 16 CHPIDs – across 2 ports
12x IB-SDR
3 GBps
Minimum – 0
Maximum – 16 ports
Order increment – 2 ports
Distance – 150 meters
OM3 fiber optic cables
IFB
HCA1-O
IFB
Point-to-point up to 150 m (492 ft)
Maximum of 8 HCA1-O fanouts
► 2 ports per HCA1-O fanout
► Up to 16 CHPIDs per HCA1-O fanout
● Distribute across 2 ports as desired
12x IB-SDR (3 GBps)
► z10 EC to System z9 Dedicated Coupling Facility
OS Support for non-dedicated CFs
► Support: z/OS 1.7 + zIIP Web Deliverable
► Dynamic I/O configuration to define, modify and
query a CHPID when z/VM 5.3 is the controlling
LPAR for I/O
* All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
42
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 43

IBM System z
System z – Supported Coupling Links
PSIFB**
(2Q2008)
16*
z10 EC
z9 Dedicated CF
Any z9
z990
z890
* Maximum of 32 PSIFB + ICB4 links on System z10 EC. ICB-4 not supported on Model E64.
** All statements regarding IBM's future direction and intent are subject to change or
withdrawal without notice and represent goals and objectives only.
32*
16
N/A
Except E64
IC
32
32
32
32
32
Max # LinksISC-3ICB-3ICB-4System
6448N/A
64481616
64481616SOD**
64481616N/A
6448168
43
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 44

IBM System z
z10 Parallel Sysplex Coexistence and Coupling Connectivity
2094
z9 EC
ISC-3, ICB-4
2094
2066
z800, z900
None!
2096
STI
z9 BC
ISC-3, ICB-4
z9 EC
Dedicated CF
PSIFB, ISC-3, ICB-4
z9 BC Dedicated CF
PSIFB, ISC-3, ICB-4
2094
IFB
STI
STI
12x IB-SDR
3 GBps
2096
STI
IFB
12x IB-SDR
3 GBps
z10 EC
E64 no ICB-4
STI
IFB
STI
IFB
STI
STI
12x IB-DDR
6 GBps
IFB
2064
STI
IB
IB
M
M
2084
STI
z990
ISC-3, ICB-4
IBM
2086
STI
z890
ISC-3, ICB-4
z10 EC
PSIFB, ISC-3, and
ICB-4 (Except E64)
44
Machine Types and Coupling Technologies Planned to be Supported by z10 EC Servers
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 45

IBM System z
z10 EC Physical Planning
Top of machine must be clear
to allow backup cooling airflow.
z9 ECz10 ECDimension
Change
z9 EC to z10
Z Frame A Frame A Frame Z Frame
Front Back
(Cool Aisle) (Warm Aisle)
Check the latest IMPP!
Height
Full/Red
Width
Depth w/o
Covers
Depth with
Covers
Electrical Service Requirements:
79.3/72.1 in
2015/1832 mm
61.7 in
1568 mm
50 in
1270 mm
71 in
1803 mm
!
W
E
N
76.4/72.1 in
1941/1832 mm
61.6 in
1565 mm
46.1 in
1171 mm
62.1 in
1577 mm
1
I/O cage
I/O cage
+2.9/+0 in
+74/+0 mm
+.1 in
+3 mm
+3.9 in
+99 mm
+8.9 in
+226 mm
2
3
I/O cage
2x60A2x60A2x60A1 book
4x60A4x60A2x60A2 book
4x60A4x60A4x60A3 book
4x60A4x60A4x60A4 book
Same power plugs/service as z990 and
z9 EC, but large configurations need 4.
15% better performance/kWh than z9 EC
45
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 46

IBM System z
System z10 EC Exploitation: z/OS Support Summary
Release
z/OS 1.7
z/OS 1.7 w/zIIP
z/OS 1.8
InfiniBand Coupling
z10 GA1 Support
65535 MP Factors
Crypto Toleration
Links
P
P
P
PP
W
P
P
P
PPP
P
Decimal Floating Point **
Crypto Exploitation
HiperDispatch
W
N
P
Greater than 54 CPs (64)
Large Page Support
> 128GB (1TB)
Large Memory
N
N
N
N
N
Capacity Provisioning
Enhancements
RMF FICON
N
N
NNNPPWW
NNNNBPPWW
46
B
z/OS 1.9
Legend
B – FMID in Base product (assumes service identified in z9 EC PSP Bucket is installed)
W – FMIDs shipped in a Web Deliverable
P – PTFs required
N – Not Supported
** Level of decimal floating-point exploitation will vary by z/OS release and PTF level.
© 2008 IBM Corporation
P
P
BB
P
WW
P
P
BBB
B
P
P
BB
IBM Systems
Page 47

IBM System z
z/VSE & z/VM Support Summary
z990z890
z9 EC
z9 BC
(WdfM)
x
x
Note: z/VM requires Compatibility Support which allows z/VM to IPL and operate on the z10 providing z9 functionality for the base OS and Guests
*z/VSE V3 can execute in 31-bit mode only. It does not implement z/Architecture, and specifically does not implement 64-bit mode capabilities.
z/VSE V3 is designed to exploit select features of IBM System z9 and zSeries hardware.
Note: z/VSE V4 is designed to exploit 64 bit real memory addressing, but will not support 64-bit virtual memory addressing
x
x
z10
x
x
x
x
End of
Market
End of
Service
Ship
Date
3/05TBD5/08xxxx3.1z/VSE*
3/07TBDTBDxx4.1
12/054/09**6/07xxxx5.2 z/VM
6/079/10**TBDxx5.3
47
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 48

IBM System z
Linux on System z – Plans for z10 EC
Program Support
IBM Systems Director Active Energy Manager (AEM) for Linux on System z
Compatibility
Existing Linux on System z distributions* (most recent service levels):
► Novell SUSE SLES9
► Novell SUSE SLES10
► Red Hat RHEL4
► Red Hat RHEL5
Exploitation*
IBM is working with its Linux distribution partners to include support in future
Linux on System z distribution releases or versions for:
► Capacity Provisioning
► Large Page Support
► CPACF Enhancements
► Dynamic Change of Partition Cryptographic Coprocessors
► HiperSockets Layer 2 Support
*For latest information and details contact your Linux distributor.
48
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 49

IBM System z
IBM System z10 EC - TPF and z/TPF Support
z990z890
z9 EC
z9 BC
z10
End of
Service
c
4.1TPF
x
c
c
x
x
c
x
x
c
x
x
z/TPF Migration Portal
► http://www.ibm.com/tpf/ztpfmigration
A PRPQ for HLASM running on Linux on z is available
► z/TPF uses the GNU Cross Compiler (GCC) running under Linux for System z
c
x
– Supports up to 30 LPARs with PJ29309
Ship
Date
2/01TBDx
9/05TBDxx1.1z/TPF
49
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
Page 50

IBM System z
Any Questions?
Tom_Russell@ca.ibm.com
50
© 2008 IBM Corporation
IBM Systems
 Loading...
Loading...