Page 1

IBM® SPSS® Amos™ 21
User’s Guide
James L. Arbuckle
Page 2

Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in the “Notices” section
on page 631.
This edition applies to IBM® SPSS® Amos™ 21 and to all subsequent releases and modifications until
otherwise indicated in new editions.
Microsoft product screenshots reproduced with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
Licensed Materials - Property of IBM
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1983, 2012. U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights - Use, duplication or
disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp.
© Copyright 2012 Amos Development Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
AMOS is a trademark of Amos Development Corporation.
Page 3

Contents
Part I: Getting Started
1 Introduction 1
Featured Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
About the Tutorial . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
About the Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
About the Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Other Sources of Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Acknowledgements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Tutorial: Getting Started with
Amos Graphics 7
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Launching Amos Graphics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Creating a New Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Specifying the Data File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Specifying the Model and Drawing Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Naming the Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Drawing Arrows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Constraining a Parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Altering the Appearance of a Path Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
To Move an Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
To Reshape an Object or Double-Headed Arrow . . . . . . . . . . . 15
To Delete an Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
To Undo an Action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
To Redo an Action . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
iii
Page 4

Setting Up Optional Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Performing the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Viewing Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
To View Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
To View Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Printing the Path Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Copying the Path Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Copying Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Part II: Examples
1 Estimating Variances and Covariances 23
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Bringing In the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Analyzing the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Specifying the Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Naming the Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Changing the Font . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Establishing Covariances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Performing the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Viewing Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Viewing Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Optional Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Calculating Standardized Estimates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Rerunning the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Viewing Correlation Estimates as Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Distribution Assumptions for Amos Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Generating Additional Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Modeling in C# . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Other Program Development Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
iv
Page 5

2 Testing Hypotheses 41
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Parameters Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Constraining Variances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Specifying Equal Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Constraining Covariances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Moving and Formatting Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Data Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Performing the Analysis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Viewing Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Optional Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Covariance Matrix Estimates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Displaying Covariance and Variance Estimates
on the Path Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Labeling Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Hypothesis Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Displaying Chi-Square Statistics on the Path Diagram . . . . . . . . . . .53
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Timing Is Everything . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
3 More Hypothesis Testing 59
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Bringing In the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Testing a Hypothesis That Two Variables Are Uncorrelated . . . . . . .60
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Viewing Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Viewing Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
v
Page 6

4 Conventional Linear Regression 67
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Analysis of the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Fixing Regression Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Viewing the Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Viewing Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Viewing Additional Text Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Assumptions about Correlations among Exogenous Variables . . . 77
Equation Format for the AStructure Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
5 Unobserved Variables 81
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Measurement Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Structural Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Changing the Orientation of the Drawing Area . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Creating the Path Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Rotating Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Duplicating Measurement Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Entering Variable Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Completing the Structural Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Viewing the Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
vi
Page 7

Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Testing Model B against Model A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
6 Exploratory Analysis 101
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Model A for the Wheaton Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Results of the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Dealing with Rejection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Modification Indices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Model B for the Wheaton Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Graphics Output for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Misuse of Modification Indices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Improving a Model by Adding New Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Model C for the Wheaton Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Results for Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Testing Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Parameter Estimates for Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Multiple Models in a Single Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Output from Multiple Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Viewing Graphics Output for Individual Models . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Viewing Fit Statistics for All Four Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Obtaining Optional Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Obtaining Tables of Indirect, Direct, and Total Effects . . . . . . . 122
vii
Page 8

Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Fitting Multiple Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
7 A Nonrecursive Model 129
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Felson and Bohrnstedt’s Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Model Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Results of the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Obtaining Standardized Estimates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Obtaining Squared Multiple Correlations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Stability Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
8 Factor Analysis 137
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
A Common Factor Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Drawing the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Results of the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Obtaining Standardized Estimates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Viewing Standardized Estimates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
viii
Page 9

9 An Alternative to Analysis of Covariance 145
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Analysis of Covariance and Its Alternative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Analysis of Covariance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Model A for the Olsson Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Identification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Specifying Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Searching for a Better Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Requesting Modification Indices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Model B for the Olsson Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Model C for the Olsson Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Drawing a Path Diagram for Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Results for Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Fitting All Models At Once . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Fitting Multiple Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
10 Simultaneous Analysis of Several Groups 159
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Analysis of Several Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Conventions for Specifying Group Differences . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Specifying Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
ix
Page 10

Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Multiple Model Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
11 Felson and Bohrnstedt’s Girls and Boys 175
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Felson and Bohrnstedt’s Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Specifying Model A for Girls and Boys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Specifying a Figure Caption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Text Output for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Graphics Output for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Obtaining Critical Ratios for Parameter Differences . . . . . . . . 182
Model B for Girls and Boys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Fitting Models A and B in a Single Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Model C for Girls and Boys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Results for Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Fitting Multiple Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
x
Page 11

12 Simultaneous Factor Analysis for
Several Groups 195
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Model A for the Holzinger and Swineford Boys and Girls . . . . . . . . 196
Naming the Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Specifying the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Model B for the Holzinger and Swineford Boys and Girls . . . . . . . . 200
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
13 Estimating and Testing Hypotheses
about Means 209
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Means and Intercept Modeling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Model A for Young and Old Subjects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Mean Structure Modeling in Amos Graphics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Model B for Young and Old Subjects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Comparison of Model B with Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
xi
Page 12

Multiple Model Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Mean Structure Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Fitting Multiple Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
14 Regression with an Explicit Intercept 221
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
Assumptions Made by Amos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Results of the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
15 Factor Analysis with Structured Means 229
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Factor Means . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Model A for Boys and Girls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Specifying the Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Understanding the Cross-Group Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Model B for Boys and Girls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Comparing Models A and B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
xii
Page 13

Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Fitting Multiple Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
16 Sörbom’s Alternative to
Analysis of Covariance 241
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Assumptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Changing the Default Behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Results for Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Model C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Results for Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
Model D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
Results for Model D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Model E. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Results for Model E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Fitting Models A Through E in a Single Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Comparison of Sörbom’s Method with the Method of Example 9 . . . . 256
Model X. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
Modeling in Amos Graphics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
Results for Model X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
Model Y. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
Results for Model Y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
Model Z. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
xiii
Page 14

Results for Model Z . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
Model D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
Model E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
Fitting Multiple Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
Models X, Y, and Z . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
17 Missing Data 269
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
Incomplete Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Saturated and Independence Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
Results of the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Graphics Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 275
Fitting the Factor Model (Model A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 276
Fitting the Saturated Model (Model B) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 277
Computing the Likelihood Ratio Chi-Square Statistic and P . . . . 281
Performing All Steps with One Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
18 More about Missing Data 283
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Missing Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Results for Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
xiv
Page 15

Graphics Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
Text Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 290
Output from Models A and B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
Model A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
Model B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
19 Bootstrapping 295
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
The Bootstrap Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
A Factor Analysis Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
Monitoring the Progress of the Bootstrap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
Results of the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
20 Bootstrapping for Model Comparison 303
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
Bootstrap Approach to Model Comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
Five Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 308
Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
Modeling in VB.NET. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
21 Bootstrapping to Compare
Estimation Methods 311
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
Estimation Methods. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
xv
Page 16

About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
About the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
Modeling in VB.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
22 Specification Search 319
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
About the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
Specification Search with Few Optional Arrows. . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Specifying the Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Selecting Program Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
Performing the Specification Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323
Viewing Generated Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324
Viewing Parameter Estimates for a Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
Using BCC to Compare Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Viewing the Akaike Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
Using BIC to Compare Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 328
Using Bayes Factors to Compare Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
Rescaling the Bayes Factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
Examining the Short List of Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
Viewing a Scatterplot of Fit and Complexity. . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Adjusting the Line Representing Constant Fit . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Viewing the Line Representing Constant C – df. . . . . . . . . . . 336
Adjusting the Line Representing Constant C – df . . . . . . . . . . 337
Viewing Other Lines Representing Constant Fit. . . . . . . . . . . 338
Viewing the Best-Fit Graph for C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
Viewing the Best-Fit Graph for Other Fit Measures . . . . . . . . 339
Viewing the Scree Plot for C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
Viewing the Scree Plot for Other Fit Measures . . . . . . . . . . . 342
Specification Search with Many Optional Arrows . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
Specifying the Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
Making Some Arrows Optional . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
Setting Options to Their Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
xvi
Page 17

Performing the Specification Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
Using BIC to Compare Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
Viewing the Scree Plot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
23 Exploratory Factor Analysis by
Specification Search 349
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
About the Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
Opening the Specification Search Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
Making All Regression Weights Optional . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
Setting Options to Their Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
Performing the Specification Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 353
Using BCC to Compare Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Viewing the Scree Plot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Viewing the Short List of Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Heuristic Specification Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
Performing a Stepwise Search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
Viewing the Scree Plot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
Limitations of Heuristic Specification Searches . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
24 Multiple-Group Factor Analysis 363
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
Model 24a: Modeling Without Means and Intercepts . . . . . . . . . . 363
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
Opening the Multiple-Group Analysis Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . 364
Viewing the Parameter Subsets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
Viewing the Generated Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
Fitting All the Models and Viewing the Output . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
xvii
Page 18

Customizing the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
Model 24b: Comparing Factor Means . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
Specifying the Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
Removing Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
Generating the Cross-Group Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
Fitting the Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
Viewing the Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
25 Multiple-Group Analysis 377
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
About the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
Constraining the Latent Variable Means and Intercepts . . . . . . . . 378
Generating Cross-Group Constraints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
Fitting the Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
Viewing the Text Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
Examining the Modification Indices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
Modifying the Model and Repeating the Analysis . . . . . . . . . 383
26 Bayesian Estimation 385
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
Bayesian Estimation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
Selecting Priors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
Performing Bayesian Estimation Using Amos Graphics . . . . . . 388
Estimating the Covariance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 388
Results of Maximum Likelihood Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
Bayesian Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
Replicating Bayesian Analysis and Data Imputation Results . . . . . . 392
Examining the Current Seed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
Changing the Current Seed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
Changing the Refresh Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
xviii
Page 19

Assessing Convergence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
Diagnostic Plots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
Bivariate Marginal Posterior Plots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
Credible Intervals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
Changing the Confidence Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
Learning More about Bayesian Estimation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
27 Bayesian Estimation Using a
Non-Diffuse Prior Distribution 409
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
About the Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
More about Bayesian Estimation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
Bayesian Analysis and Improper Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
Fitting a Model by Maximum Likelihood . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
Bayesian Estimation with a Non-Informative (Diffuse) Prior. . . . . . . 412
Changing the Number of Burn-In Observations . . . . . . . . . . . 412
28 Bayesian Estimation of Values
Other Than Model Parameters 423
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
About the Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
The Wheaton Data Revisited . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
Indirect Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 424
Estimating Indirect Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
Bayesian Analysis of Model C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
Additional Estimands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
Inferences about Indirect Effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431
xix
Page 20

29 Estimating a User-Defined Quantity
in Bayesian SEM 437
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437
About the Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437
The Stability of Alienation Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437
Numeric Custom Estimands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 443
Dragging and Dropping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
Dichotomous Custom Estimands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
Defining a Dichotomous Estimand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
30 Data Imputation 461
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
About the Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
Multiple Imputation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
Model-Based Imputation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
Performing Multiple Data Imputation Using Amos Graphics . . . . . . 462
31 Analyzing Multiply Imputed Datasets 469
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
Analyzing the Imputed Data Files Using SPSS Statistics . . . . . . . . 469
Step 2: Ten Separate Analyses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
Step 3: Combining Results of Multiply Imputed Data Files . . . . . . . 471
Further Reading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 473
32 Censored Data 475
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 475
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 475
Recoding the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
Analyzing the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
Performing a Regression Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 478
xx
Page 21

Posterior Predictive Distributions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 481
Imputation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 484
General Inequality Constraints on Data Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 488
33 Ordered-Categorical Data 489
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
Specifying the Data File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
Recoding the Data within Amos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 492
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
Fitting the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 501
MCMC Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 504
Posterior Predictive Distributions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
Posterior Predictive Distributions for Latent Variables. . . . . . . . . . 511
Imputation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 516
34 Mixture Modeling with Training Data 521
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
Performing the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 524
Specifying the Data File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 526
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 530
Fitting the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 532
Classifying Individual Cases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 535
Latent Structure Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
35 Mixture Modeling without Training Data 539
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 539
About the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 539
Performing the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
xxi
Page 22

Specifying the Data File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 542
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
Constraining the Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 546
Fitting the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 548
Classifying Individual Cases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
Latent Structure Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
Label Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 554
36 Mixture Regression Modeling 557
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
First Dataset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
Second Dataset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
The Group Variable in the Dataset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 560
Performing the Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 561
Specifying the Data File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 563
Specifying the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 566
Fitting the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 567
Classifying Individual Cases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 572
Improving Parameter Estimates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 573
Prior Distribution of Group Proportions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 575
Label Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 576
37 Using Amos Graphics
without Drawing a Path Diagram 577
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 577
About the Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
A Common Factor Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
Creating a Plugin to Specify the Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 578
Controlling Undo Capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 583
Compiling and Saving the Plugin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 585
Using the Plugin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 586
xxii
Page 23

Other Aspects of the Analysis in Addition to Model Specification . . . 588
Defining Program Variables that Correspond to
Model Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 588
Part III: Appendices
A Notation 591
B Discrepancy Functions 593
C Measures of Fit 597
Measures of Parsimony . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 598
NPAR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 598
DF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 598
PRATIO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 599
Minimum Sample Discrepancy Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 599
CMIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 599
P . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 599
CMIN/DF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 601
FMIN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 602
Measures Based On the Population Discrepancy . . . . . . . . . . . . 602
NCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 602
F0. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 603
RMSEA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 603
PCLOSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
Information-Theoretic Measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
AIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 605
BCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 606
BIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 606
CAIC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 607
ECVI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 607
MECVI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 608
xxiii
Page 24

Comparisons to a Baseline Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 608
NFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 609
RFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 610
IFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 611
TLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 611
CFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 612
Parsimony Adjusted Measures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 612
PNFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
PCFI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
GFI and Related Measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
GFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 613
AGFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 614
PGFI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 615
Miscellaneous Measures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 615
HI 90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 615
HOELTER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 615
LO 90 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 616
RMR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 616
Selected List of Fit Measures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 617
D Numeric Diagnosis of Non-Identifiability 619
E Using Fit Measures to Rank Models 621
F Baseline Models for
Descriptive Fit Measures 625
G Rescaling of AIC, BCC, and BIC 627
Zero-Based Rescaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 627
Akaike Weights and Bayes Factors (Sum = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 628
Akaike Weights and Bayes Factors (Max = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 629
xxiv
Page 25

Notices 631
Bibliography 635
Index 647
xxv
Page 26

Page 27
spatial
visperc
cubes
lozenges
wordmean
paragraph
sentence
e1
e2
e3
e4
e5
e6
verbal
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Input:
spatial
visperc
cubes
.43
lozenges
.54
wordmean
.71
paragraph
.77
sentence
.68
e1
e2
e3
e4
e5
e6
verbal
.70
.65
.74
.88
.83
.84
.49
Chi-square = 7.853 (8 df)
p = .448
Output:
Introduction
IBM SPSS Amos implements the general approach to data analysis known as
structural equation modeling (SEM), also known as analysis of covariance
structures, or causal modeling. This approach includes, as special cases, many well-
known conventional techniques, including the general linear model and common
factor analysis.
Chapter
1
IBM SPSS Amos (Analysis of Moment Structures) is an easy-to-use program for
visual SEM. With Amos, you can quickly specify, view, and modify your model
graphically using simple drawing tools. Then you can assess your model’s fit, make
any modifications, and print out a publication-quality graphic of your final model.
Simply specify the model graphically (left). Amos quickly performs the
computations and displays the results (right).
1
Page 28

2
Chapter 1
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is sometimes thought of as esoteric and difficult
to learn and use. This is incorrect. Indeed, the growing importance of SEM in data
analysis is largely due to its ease of use. SEM opens the door for nonstatisticians to
solve estimation and hypothesis testing problems that once would have required the
services of a specialist.
IBM SPSS Amos was originally designed as a tool for teaching this powerful and
fundamentally simple method. For this reason, every effort was made to see that it is
easy to use. Amos integrates an easy-to-use graphical interface with an advanced
computing engine for SEM. The publication-quality path diagrams of Amos provide a
clear representation of models for students and fellow researchers. The numeric
methods implemented in Amos are among the most effective and reliable available.
Featured Methods
Amos provides the following methods for estimating structural equation models:
Maximum likelihood
Unweighted least squares
Generalized least squares
Browne’s asymptotically distribution-free criterion
Scale-free least squares
Bayesian estimation
IBM SPSS Amos goes well beyond the usual capabilities found in other structural
equation modeling programs. When confronted with missing data, Amos performs
state-of-the-art estimation by full information maximum likelihood instead of relying
on ad-hoc methods like listwise or pairwise deletion, or mean imputation. The program
can analyze data from several populations at once. It can also estimate means for
exogenous variables and intercepts in regression equations.
The program makes bootstrapped standard errors and confidence intervals available
for all parameter estimates, effect estimates, sample means, variances, covariances,
and correlations. It also implements percentile intervals and bias-corrected percentile
intervals (Stine, 1989), as well as Bollen and Stine’s (1992) bootstrap approach to
model testing.
Multiple models can be fitted in a single analysis. Amos examines every pair of
models in which one model can be obtained by placing restrictions on the parameters
of the other. The program reports several statistics appropriate for comparing such
Page 29

models. It provides a test of univariate normality for each observed variable as well as
a test of multivariate normality and attempts to detect outliers.
IBM SPSS Amos accepts a path diagram as a model specification and displays
parameter estimates graphically on a path diagram. Path diagrams used for model
specification and those that display parameter estimates are of presentation quality.
They can be printed directly or imported into other applications such as word
processors, desktop publishing programs, and general-purpose graphics programs.
About the Tutorial
The tutorial is designed to get you up and running with Amos Graphics. It covers some
of the basic functions and features and guides you through your first Amos analysis.
Once you have worked through the tutorial, you can learn about more advanced
functions using the online Help, or you can continue working through the examples to
get a more extended introduction to structural modeling with IBM SPSS Amos.
3
Introduction
About the Examples
Many people like to learn by doing. Knowing this, we have developed many examples
that quickly demonstrate practical ways to use IBM SPSS Amos. The initial examples
introduce the basic capabilities of Amos as applied to simple problems. You learn
which buttons to click, how to access the several supported data formats, and how to
maneuver through the output. Later examples tackle more advanced modeling
problems and are less concerned with program interface issues.
Examples 1 through 4 show how you can use Amos to do some conventional
analyses—analyses that could be done using a standard statistics package. These
examples show a new approach to some familiar problems while also demonstrating
all of the basic features of Amos. There are sometimes good reasons for using Amos
to do something simple, like estimating a mean or correlation or testing the hypothesis
that two means are equal. For one thing, you might want to take advantage of the ability
of Amos to handle missing data. Or maybe you want to use the bootstrapping capability
of Amos, particularly to obtain confidence intervals.
Examples 5 through 8 illustrate the basic techniques that are commonly used
nowadays in structural modeling.
Page 30

4
Chapter 1
Example 9 and those that follow demonstrate advanced techniques that have so far not
been used as much as they deserve. These techniques include:
Simultaneous analysis of data from several different populations.
Estimation of means and intercepts in regression equations.
Maximum likelihood estimation in the presence of missing data.
Bootstrapping to obtain estimated standard errors and confidence intervals. Amos
makes these techniques especially easy to use, and we hope that they will become
more commonplace.
Specification searches.
Bayesian estimation.
Imputation of missing values.
Analysis of censored data.
Analysis of ordered-categorical data.
Mixture modeling.
Tip: If you have questions about a particular Amos feature, you can always refer to the
extensive online Help provided by the program.
About the Documentation
IBM SPSS Amos 21 comes with extensive documentation, including an online Help
system, this user’s guide, and advanced reference material for Amos Basic and the
Amos API (Application Programming Interface). If you performed a typical
installation, you can find the IBM SPSS Amos 21 Programming Reference Guide in
the following location: C:\Program
Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Documentation\Programming Reference.pdf.
Other Sources of Information
Although this user’s guide contains a good bit of expository material, it is not by any
means a complete guide to the correct and effective use of structural modeling. Many
excellent SEM textbooks are available.
Page 31

Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal contains
methodological articles as well as applications of structural modeling. It is
published by Taylor and Francis (http://www.tandf.co.uk).
Carl Ferguson and Edward Rigdon established an electronic mailing list called
Semnet to provide a forum for discussions related to structural modeling. You can
find information about subscribing to Semnet at
www.gsu.edu/~mkteer/semnet.html.
Acknowledgements
Many users of previous versions of Amos provided valuable feedback, as did many
users who tested the present version. Torsten B. Neilands wrote Examples 26 through
31 in this User’s Guide with contributions by Joseph L. Schafer. Eric Loken reviewed
Examples 32 and 33. He also provided valuable insights into mixture modeling as well
as important suggestions for future developments in Amos.
A last word of warning: While Amos Development Corporation has engaged in
extensive program testing to ensure that Amos operates correctly, all complicated
software, Amos included, is bound to contain some undetected bugs. We are
committed to correcting any program errors. If you believe you have encountered one,
please report it to technical support.
5
Introduction
James L. Arbuckle
Page 32

Page 33

Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
Introduction
Remember your first statistics class when you sweated through memorizing formulas
and laboriously calculating answers with pencil and paper? The professor had you do
this so that you would understand some basic statistical concepts. Later, you
discovered that a calculator or software program could do all of these calculations in
a split second.
This tutorial is a little like that early statistics class. There are many shortcuts to
drawing and labeling path diagrams in Amos Graphics that you will discover as you
work through the examples in this user’s guide or as you refer to the online help. The
intent of this tutorial is to simply get you started using Amos Graphics. It will cover
some of the basic functions and features of IBM SPSS Amos and guide you through
your first Amos analysis.
Once you have worked through the tutorial, you can learn about more advanced
functions from the online help, or you can continue to learn incrementally by working
your way through the examples.
If you performed a typical installation, you can find the path diagram constructed
in this tutorial in this location:
C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Tutorial\<language>. The file Startsps.amw
uses a data file in SPSS Statistics format. Getstart.amw is the same path diagram but
uses data from a Microsoft Excel file.
Chapter
2
Tip: IBM SPSS Amos 21 provides more than one way to accomplish most tasks. For
all menu commands except Tools > Macro, there is a toolbar button that performs the
same task. For many tasks, Amos also provides keyboard shortcuts. The user’s guide
7
Page 34

8
Chapter 2
demonstrates the menu path. For information about the toolbar buttons and keyboard
shortcuts, see the online help.
About the Data
Hamilton (1990) provided several measurements on each of 21 states. Three of the
measurements will be used in this tutorial:
Average SAT score
Per capita income expressed in $1,000 units
Median education for residents 25 years of age or older
You can find the data in the Tutorial directory within the Excel 8.0 workbook
Hamilton.xls in the worksheet named Hamilton. The data are as follows:
SAT Income Education
899 14.345 12.7
896 16.37 12.6
897 13.537 12.5
889 12.552 12.5
823 11.441 12.2
857 12.757 12.7
860 11.799 12.4
890 10.683 12.5
889 14.112 12.5
888 14.573 12.6
925 13.144 12.6
869 15.281 12.5
896 14.121 12.5
827 10.758 12.2
908 11.583 12.7
885 12.343 12.4
887 12.729 12.3
790 10.075 12.1
868 12.636 12.4
904 10.689 12.6
888 13.065 12.4
Page 35

Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
The following path diagram shows a model for these data:
This is a simple regression model where one observed variable, SAT, is predicted as a
linear combination of the other two observed variables, Education and Income. As with
nearly all empirical data, the prediction will not be perfect. The variable Other
represents variables other than Education and Income that affect SAT.
Each single-headed arrow represents a regression weight. The number
1 in the
figure specifies that Other must have a weight of 1 in the prediction of SAT. Some such
constraint must be imposed in order to make the model identified, and it is one of the
features of the model that must be communicated to Amos.
9
Launching Amos Graphics
You can launch Amos Graphics in any of the following ways:
Click Start on the Windows task bar, and choose All Programs > IBM SPSS
Statistics
Double-click any path diagram (*.amw).
Drag a path diagram (*.amw) file from Windows Explorer to the Amos Graphics
window.
Click Start on the Windows task bar, and choose All Programs > IBM SPSS
Statistics
diagram in the View Path Diagrams window.
From within SPSS Statistics, choose Analyze > IBM SPSS Amos from the menus.
> IBM SPSS Amos 21 > Amos Graphics.
> IBM SPSS Amos 21 > View Path Diagrams. Then double-click a path
Page 36

10
Chapter 2
Creating a New Model
E From the menus, choose File > New.
Your work area appears. The large area on the right is where you draw path diagrams.
The toolbar on the left provides one-click access to the most frequently used buttons.
You can use either the toolbar or menu commands for most operations.
Page 37

Specifying the Data File
The next step is to specify the file that contains the Hamilton data. This tutorial uses a
Microsoft Excel 8.0 (*.xls) file, but Amos supports several common database formats,
including SPSS Statistics *.sav files. If you launch Amos from the Add-ons menu in
SPSS Statistics, Amos automatically uses the file that is open in SPSS Statistics.
E From the menus, choose File > Data Files.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click File Name.
E Browse to the Tutorial folder. If you performed a typical installation, the path is
C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Tutorial\<language>.
E In the Files of type list, select Excel 8.0 (*.xls).
E Select Hamilton.xls, and then click Open.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click OK.
11
Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
Specifying the Model and Drawing Variables
The next step is to draw the variables in your model. First, you’ll draw three rectangles
to represent the observed variables, and then you’ll draw an ellipse to represent the
unobserved variable.
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Observed.
E In the drawing area, move your mouse pointer to where you want the Education
rectangle to appear. Click and drag to draw the rectangle. Don’t worry about the exact
size or placement of the rectangle because you can change it later.
E Use the same method to draw two more rectangles for Income and SAT.
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Unobserved.
Page 38

12
Chapter 2
E In the drawing area, move your mouse pointer to the right of the three rectangles and
click and drag to draw the ellipse.
The model in your drawing area should now look similar to the following:
Naming the Variables
E In the drawing area, right-click the top left rectangle and choose Object Properties from
the pop-up menu.
E Click the Text tab.
E In the Variable name text box, type Education.
E Use the same method to name the remaining variables. Then close the Object
Properties dialog box.
Page 39

Your path diagram should now look like this:
Drawing Arrows
Now you will add arrows to the path diagram, using the following model as your guide:
13
Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Path.
E Click and drag to draw an arrow between Education and SAT.
E Use this method to add each of the remaining single-headed arrows.
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Covariances.
E Click and drag to draw a double-headed arrow between Income and Education. Don’t
worry about the curve of the arrow because you can adjust it later.
Page 40

14
Chapter 2
Constraining a Parameter
To identify the regression model, you must define the scale of the latent variable Other.
You can do this by fixing either the variance of Other or the path coefficient from Other
to SAT at some positive value. The following shows you how to fix the path coefficient
at unity (1).
E In the drawing area, right-click the arrow between Other and SAT and choose Object
Properties
E Click the Parameters tab.
E In the Regression weight text box, type 1.
from the pop-up menu.
E Close the Object Properties dialog box.
There is now a
1 above the arrow between Other and SAT. Your path diagram is now
complete, other than any changes you may wish to make to its appearance. It should
look something like this:
Page 41

Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
Altering the Appearance of a Path Diagram
You can change the appearance of your path diagram by moving and resizing objects.
These changes are visual only; they do not affect the model specification.
To Move an Object
E From the menus, choose Edit > Move.
15
E In the drawing area, click and drag the object to its new location.
To Reshape an Object or Double-Headed Arrow
E From the menus, choose Edit > Shape of Object.
E In the drawing area, click and drag the object until you are satisfied with its size and
shape.
To Delete an Object
E From the menus, choose Edit > Erase.
E In the drawing area, click the object you wish to delete.
Page 42

16
Chapter 2
To Undo an Action
E From the menus, choose Edit > Undo.
To Redo an Action
E From the menus, choose Edit > Redo.
Setting Up Optional Output
Some of the output in Amos is optional. In this step, you will choose which portions of
the optional output you want Amos to display after the analysis.
E From the menus, choose View > Analysis Properties.
E Click the Output tab.
E Select the Minimization history, Standardized estimates, and Squared multiple correlations
check boxes.
Page 43

Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
17
E
Close the Analysis Properties dialog box.
Page 44

18
Chapter 2
Performing the Analysis
The only thing left to do is perform the calculations for fitting the model. Note that in
order to keep the parameter estimates up to date, you must do this every time you
change the model, the data, or the options in the Analysis Properties dialog box.
E From the menus, click Analyze > Calculate Estimates.
E Because you have not yet saved the file, the Save As dialog box appears. Type a name
for the file and click Save.
Amos calculates the model estimates. The panel to the left of the path diagram displays
a summary of the calculations.
Viewing Output
When Amos has completed the calculations, you have two options for viewing the
output: text and graphics.
To View Text Output
E From the menus, choose View > Text Output.
The tree diagram in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window allows you to
choose a portion of the text output for viewing.
E Click Estimates to view the parameter estimates.
Page 45

Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
19
To View Graphics Output
E Click the Show the output path diagram button .
E In the Parameter Formats pane to the left of the drawing area, click Standardized
estimates.
Page 46

20
Chapter 2
Your path diagram now looks like this:
The value 0.49 is the correlation between Education and Income. The values 0.72 and
0.11 are standardized regression weights. The value 0.60 is the squared multiple
correlation of SAT with Education and Income.
E In the Parameter Formats pane to the left of the drawing area, click Unstandardized
estimates
.
Your path diagram should now look like this:
Printing the Path Diagram
E From the menus, choose File > Print.
The Print dialog box appears.
Page 47

E Click Print.
Copying the Path Diagram
21
Tutorial: Getting Started with Amos Graphics
Amos Graphics lets you easily export your path diagram to other applications such as
Microsoft Word.
E From the menus, choose Edit > Copy (to Clipboard).
E Switch to the other application and use the Paste function to insert the path diagram.
Amos Graphics exports only the diagram; it does not export the background.
Copying Text Output
E In the Amos Output window, select the text you want to copy.
E Right-click the selected text, and choose Copy from the pop-up menu.
E Switch to the other application and use the Paste function to insert the text.
Page 48

Page 49

Estimating Variances and Covariances
Introduction
This example shows you how to estimate population variances and covariances. It also
discusses the general format of Amos input and output.
Example
1
About the Data
Attig (1983) showed 40 subjects a booklet containing several pages of advertisements.
Then each subject was given three memory performance tests.
Test Explanation
recall
cued
place
Attig repeated the study with the same 40 subjects after a training exercise intended
to improve memory performance. There were thus three performance measures
before training and three performance measures after training. In addition, she
recorded scores on a vocabulary test, as well as age, sex, and level of education.
Attig’s data files are included in the Examples folder provided by Amos.
The subject was asked to recall as many of the advertisements as possible.
The subject’s score on this test was the number of advertisements recalled
correctly.
The subject was given some cues and asked again to recall as many of the
advertisements as possible. The subject’s score was the number of
advertisements recalled correctly.
The subject was given a list of the advertisements that appeared in the
booklet and was asked to recall the page location of each one. The subject’s
score on this test was the number of advertisements whose location was
recalled correctly.
23
Page 50

24
Example 1
Bringing In the Data
E From the menus, choose File > New.
E From the menus, choose File > Data Files.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click File Name.
E Browse to the Examples folder. If you performed a typical installation, the path is
C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Examples\<language>.
E In the Files of type list, select Excel 8.0 (*.xls), select UserGuide.xls, and then click
Open.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click OK.
Amos displays a list of worksheets in the UserGuide workbook. The worksheet
Attg_yng contains the data for this example.
E In the Select a Data Table dialog box, select Attg_yng, then click View Data.
The Excel worksheet for the Attg_yng data file opens.
Page 51
Estimating Variances and Covariances
As you scroll across the worksheet, you will see all of the test variables from the Attig
study. This example uses only the following variables: recall1 (recall pretest), recall2
(recall posttest), place1 (place recall pretest), and place2 (place recall posttest).
E After you review the data, close the data window.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click OK.
25
Analyzing the Data
In this example, the analysis consists of estimating the variances and covariances of the
recall and place variables before and after training.
Specifying the Model
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Observed.
E In the drawing area, move your mouse pointer to where you want the first rectangle to
appear. Click and drag to draw the rectangle.
E From the menus, choose Edit > Duplicate.
E Click and drag a duplicate from the first rectangle. Release the mouse button to
position the duplicate.
Page 52

26
Example 1
E Create two more duplicate rectangles until you have four rectangles side by side.
Tip: If you want to reposition a rectangle, choose Edit > Move from the menus and drag
the rectangle to its new position.
Naming the Variables
E From the menus, choose View > Variables in Dataset.
The Variables in Dataset dialog box appears.
E Click and drag the variable recall1 from the list to the first rectangle in the drawing
area.
E Use the same method to name the variables recall2, place1, and place2.
E Close the Variables in Dataset dialog box.
Page 53

Changing the Font
E Right-click a variable and choose Object Properties from the pop-up menu.
The Object Properties dialog box appears.
E Click the Text tab and adjust the font attributes as desired.
27
Estimating Variances and Covariances
Establishing Covariances
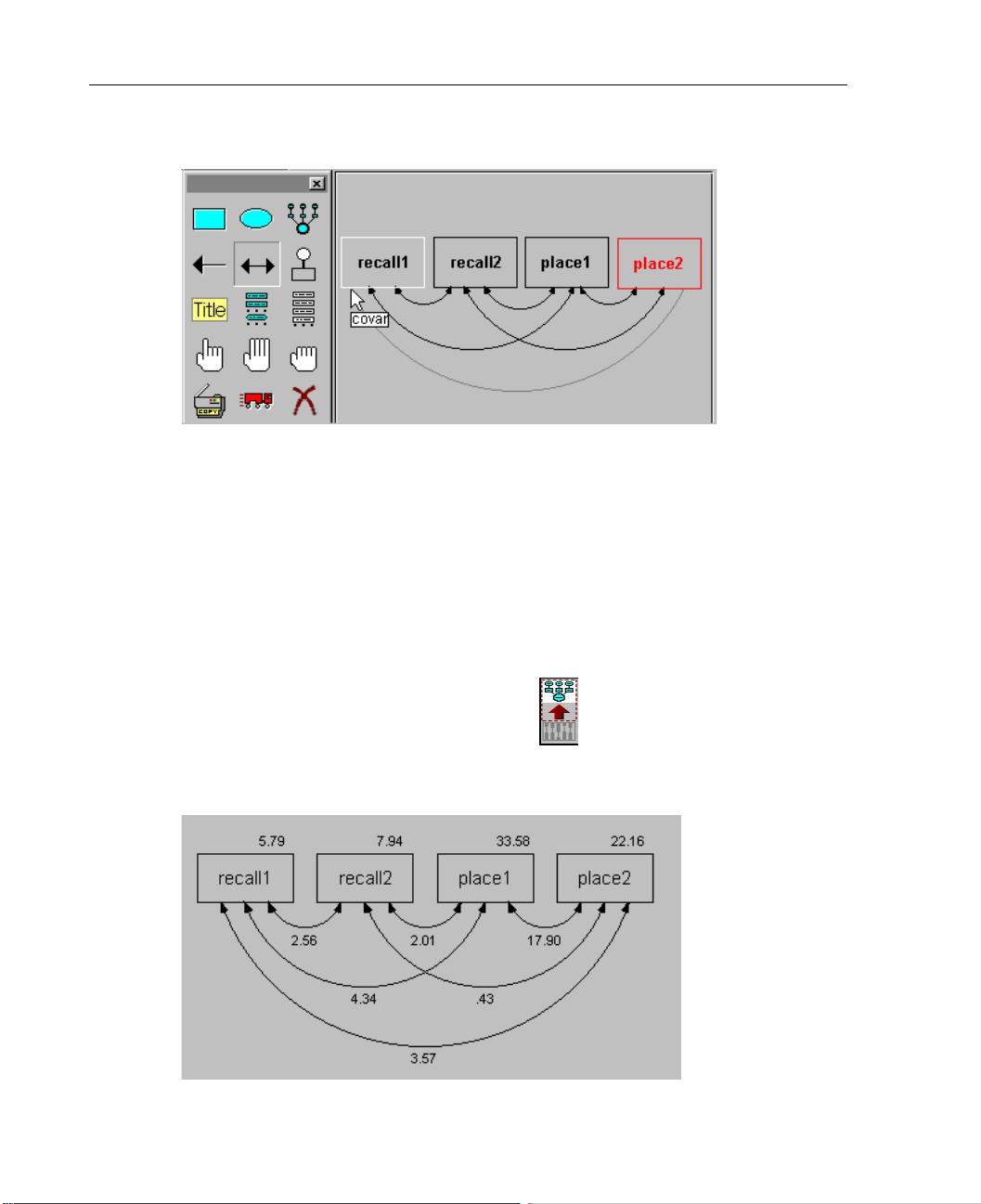
If you leave the path diagram as it is, Amos Graphics will estimate the variances of the
four variables, but it will not estimate the covariances between them. In Amos
Graphics, the rule is to assume a correlation or covariance of 0 for any two variables
that are not connected by arrows. To estimate the covariances between the observed
variables, we must first connect all pairs with double-headed arrows.
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Covariances.
E Click and drag to draw arrows that connect each variable to every other variable.
Your path diagram should have six double-headed arrows.
Page 54
28
Example 1
Performing the Analysis
E From the menus, choose Analyze > Calculate Estimates.
Because you have not yet saved the file, the Save As dialog box appears.
E Enter a name for the file and click Save.
Viewing Graphics Output
E Click the Show the output path diagram button .
Amos displays the output path diagram with parameter estimates.
Page 55

In the output path diagram, the numbers displayed next to the boxes are estimated
variances, and the numbers displayed next to the double-headed arrows are estimated
covariances. For example, the variance of recall1 is estimated at 5.79, and that of
place1 at 33.58. The estimated covariance between these two variables is 4.34.
Viewing Text Output
E From the menus, choose View > Text Output.
E In the tree diagram in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window, click Estimates.
29
Estimating Variances and Covariances
The first estimate displayed is of the covariance between recall1 and recall2. The
covariance is estimated to be 2.56. Right next to that estimate, in the S.E
. column, is an
estimate of the standard error of the covariance, 1.16. The estimate 2.56 is an
Page 56

30
2.56 1.96 1.160 2.56 2.27±=×±
2.20 2.56 1.16⁄=()
p 0.03=
Example 1
observation on an approximately normally distributed random variable centered
around the population covariance with a standard deviation of about 1.16, that is, if the
assumptions in the section “Distribution Assumptions for Amos Models” on p. 35 are
met. For example, you can use these figures to construct a 95% confidence interval on
the population covariance by computing . Later, you
will see that you can use Amos to estimate many kinds of population parameters
besides covariances and can follow the same procedure to set a confidence interval on
any one of them.
Next to the standard error, in the
C.R. column, is the critical ratio obtained by
dividing the covariance estimate by its standard error . This ratio
is relevant to the null hypothesis that, in the population from which Attig’s 40 subjects
came, the covariance between recall1 and recall2 is 0. If this hypothesis is true, and
still under the assumptions in the section “Distribution Assumptions for Amos
Models” on p. 35, the critical ratio is an observation on a random variable that has an
approximate standard normal distribution. Thus, using a significance level of 0.05, any
critical ratio that exceeds 1.96 in magnitude would be called significant. In this
example, since 2.20 is greater than 1.96, you would say that the covariance between
recall1 and recall2 is significantly different from 0 at the 0.05 level.
The P column, to the right of C.R., gives an approximate two-tailed p value for
testing the null hypothesis that the parameter value is 0 in the population. The table
shows that the covariance between recall1 and recall2 is significantly different from 0
with . The calculation of P assumes that parameter estimates are normally
distributed, and it is correct only in large samples. See Appendix A for more
information.
The assertion that the parameter estimates are normally distributed is only an
approximation. Moreover, the standard errors reported in the S.E. column are only
approximations and may not be the best available. Consequently, the confidence
interval and the hypothesis test just discussed are also only approximate. This is
because the theory on which these results are based is asymptotic. Asymptotic means
that it can be made to apply with any desired degree of accuracy, but only by using a
sufficiently large sample. We will not discuss whether the approximation is
satisfactory with the present sample size because there would be no way to generalize
the conclusions to the many other kinds of analyses that you can do with Amos.
However, you may want to re-examine the null hypothesis that recall1 and recall2 are
uncorrelated, just to see what is meant by an approximate test. We previously
concluded that the covariance is significantly different from 0 because 2.20 exceeds
1.96. The p value associated with a standard normal deviate of 2.20 is 0.028 (twotailed), which, of course, is less than 0.05. By contrast, the conventional t statistic (for
Page 57

Estimating Variances and Covariances
p 0.016=()
example, Runyon and Haber, 1980, p. 226) is 2.509 with 38 degrees of freedom
. In this example, both p values are less than 0.05, so both tests agree in
rejecting the null hypothesis at the 0.05 level. However, in other situations, the two
p values might lie on opposite sides of 0.05. You might or might not regard this as
especially serious—at any rate, the two tests can give different results. There should be
no doubt about which test is better. The t test is exact under the assumptions of
normality and independence of observations, no matter what the sample size. In Amos,
the test based on critical ratio depends on the same assumptions; however, with a finite
sample, the test is only approximate.
Note: For many interesting applications of Amos, there is no exact test or exact standard
error or exact confidence interval available.
On the bright side, when fitting a model for which conventional estimates exist,
maximum likelihood point estimates (for example, the numbers in the Estimate
column) are generally identical to the conventional estimates.
E Now click Notes for Model in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window.
31
The following table plays an important role in every Amos analysis:
Number of distinct sample moments: 10
Number of distinct parameters to be estimated: 10
Degrees of freedom (10 – 10): 0
Page 58

32
Example 1
The Number of distinct sample moments referred to are sample means, variances, and
covariances. In most analyses, including the present one, Amos ignores means, so that
the sample moments are the sample variances of the four variables, recall1, recall2,
place1, and place2, and their sample covariances. There are four sample variances and
six sample covariances, for a total of 10 sample moments.
The Number of distinct parameters to be estimated are the corresponding
population variances and covariances. There are, of course, four population variances
and six population covariances, which makes 10 parameters to be estimated.
The Degrees of freedom is the amount by which the number of sample moments
exceeds the number of parameters to be estimated. In this example, there is a one-toone correspondence between the sample moments and the parameters to be estimated,
so it is no accident that there are zero degrees of freedom.
As we will see beginning with Example 2, any nontrivial null hypothesis about the
parameters reduces the number of parameters that have to be estimated. The result will
be positive degrees of freedom. For now, there is no null hypothesis being tested.
Without a null hypothesis to test, the following table is not very interesting:
Chi-square = 0.00
Degrees of freedom = 0
Probability level cannot be computed
If there had been a hypothesis under test in this example, the chi-square value would have
been a measure of the extent to which the data were incompatible with the hypothesis. A
chi-square value of 0 would ordinarily indicate no departure from the null hypothesis.
But in the present example, the 0 value for degrees of freedom and the 0 chi-square value
merely reflect the fact that there was no null hypothesis in the first place.
Minimum was achieved
This line indicates that Amos successfully estimated the variances and covariances.
Sometimes structural modeling programs like Amos fail to find estimates. Usually,
when Amos fails, it is because you have posed a problem that has no solution, or no
unique solution. For example, if you attempt maximum likelihood estimation with
observed variables that are linearly dependent, Amos will fail because such an analysis
cannot be done in principle. Problems that have no unique solution are discussed
elsewhere in this user’s guide under the subject of identifiability. Less commonly,
Amos can fail because an estimation problem is just too difficult. The possibility of
such failures is generic to programs for analysis of moment structures. Although the
computational method used by Amos is highly effective, no computer program that
does the kind of analysis that Amos does can promise success in every case.
Page 59

Optional Output
So far, we have discussed output that Amos generates by default. You can also request
additional output.
Calculating Standardized Estimates
You may be surprised to learn that Amos displays estimates of covariances rather than
correlations. When the scale of measurement is arbitrary or of no substantive interest,
correlations have more descriptive meaning than covariances. Nevertheless, Amos and
similar programs insist on estimating covariances. Also, as will soon be seen, Amos
provides a simple method for testing hypotheses about covariances but not about
correlations. This is mainly because it is easier to write programs that way. On the other
hand, it is not hard to derive correlation estimates after the relevant variances and
covariances have been estimated. To calculate standardized estimates:
E From the menus, choose View > Analysis Properties.
33
Estimating Variances and Covariances
E In the Analysis Properties dialog box, click the Output tab.
E Select the Standardized estimates check box.
E Close the Analysis Properties dialog box.
Page 60

34
Example 1
Rerunning the Analysis
Because you have changed the options in the Analysis Properties dialog box, you must
rerun the analysis.
E From the menus, choose Analyze > Calculate Estimates.
E Click the Show the output path diagram button.
E In the Parameter Formats pane to the left of the drawing area, click Standardized
estimates
.
Viewing Correlation Estimates as Text Output
E From the menus, choose View > Text Output.
Page 61
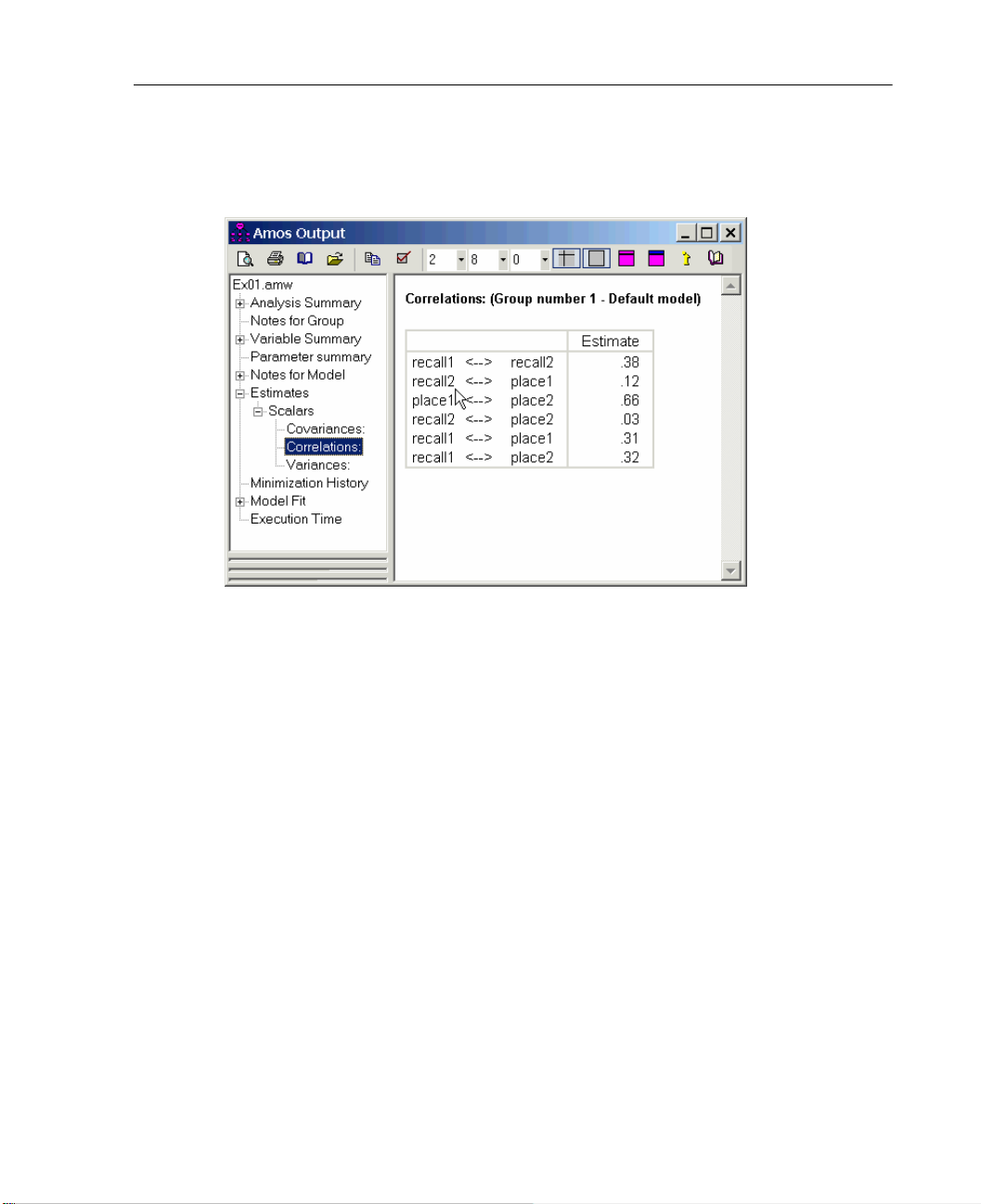
Estimating Variances and Covariances
E
In the tree diagram in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window, expand
Estimates, Scalars, and then click Correlations.
35
Distribution Assumptions for Amos Models
Hypothesis testing procedures, confidence intervals, and claims for efficiency in
maximum likelihood or generalized least-squares estimation depend on certain
assumptions. First, observations must be independent. For example, the 40 young
people in the Attig study have to be picked independently from the population of young
people. Second, the observed variables must meet some distributional requirements. If
the observed variables have a multivariate normal distribution, that will suffice.
Multivariate normality of all observed variables is a standard distribution assumption
in many structural equation modeling and factor analysis applications.
There is another, more general, situation under which maximum likelihood
estimation can be carried out. If some exogenous variables are fixed (that is, they are
either known beforehand or measured without error), their distributions may have any
shape, provided that:
For any value pattern of the fixed variables, the remaining (random) variables have
a (conditional) normal distribution.
The (conditional) variance-covariance matrix of the random variables is the same
for every pattern of the fixed variables.
Page 62

36
Example 1
The (conditional) expected values of the random variables depend linearly on the
values of the fixed variables.
A typical example of a fixed variable would be an experimental treatment, classifying
respondents into a study group and a control group, respectively. It is all right that
treatment is non-normally distributed, as long as the other exogenous variables are
normally distributed for study and control cases alike, and with the same conditional
variance-covariance matrix. Predictor variables in regression analysis (see Example 4)
are often regarded as fixed variables.
Many people are accustomed to the requirements for normality and independent
observations, since these are the usual requirements for many conventional procedures.
However, with Amos, you have to remember that meeting these requirements leads
only to asymptotic conclusions (that is, conclusions that are approximately true for
large samples).
Modeling in VB.NET
It is possible to specify and fit a model by writing a program in VB.NET or in C#. Writing
programs is an alternative to using Amos Graphics to specify a model by drawing its path
diagram. This section shows how to write a VB.NET program to perform the analysis of
Example 1. A later section explains how to do the same thing in C#.
Amos comes with its own built-in editor for VB.NET and C# programs. It is
accessible from the Windows Start menu. To begin Example 1 using the built-in editor:
E From the Windows Start menu, choose All Programs > IBM SPSS Statistics >
IBM SPSS Amos 21 > Program Editor.
E In the Program Editor window, choose File > New VB Program.
Page 63

37
Estimating Variances and Covariances
E Enter the VB.NET code for specifying and fitting the model in place of the ‘Your code
goes here
comment. The following figure shows the program editor after the complete
program has been entered.
Note: The Examples directory contains all of the pre-written examples.
Page 64

38
Example 1
E From the Program Editor menus, choose File > Open.
E Select the file Ex01.vb in the \Amos\21\Examples\<language> directory.
To open the VB.NET file for the present example:
The following table gives a line-by-line explanation of the program.
Program Statement Explanation
Declares Sem as an object of type
Dim Sem As New AmosEngine
Sem.TextOutput
Sem.BeginGroup …
Sem.AStructure("recall1")
Sem.AStructure("recall2")
Sem.AStructure("place1")
Sem.AStructure("place2")
Sem.FitModel()
Sem.Dispose()
Try/Finally/End Try
AmosEngine. The methods and properties of
the Sem object are used to specify and fit the
model.
Creates an output file containing the results of
the analysis. At the end of the analysis, the
contents of the output file are displayed in a
separate window.
Begins the model specification for a single
group (that is, a single population). This line
also specifies that the Attg_yng worksheet in the
Excel workbook UserGuide.xls contains the
input data.
Sem.AmosDir() is the location of the
Amos program directory.
Specifies the model. The four AStructure
statements declare the variances of recall1,
recall2, place1, and place2 to be free
parameters. The other eight variables in the
Attg_yng data file are left out of this analysis. In
an Amos program (but not in Amos Graphics),
observed exogenous variables are assumed by
default to be correlated, so that Amos will
estimate the six covariances among the four
variables.
Fits the model.
Releases resources used by the Sem object. It is
particularly important for your program to use
an AmosEngine object’s
Dispose method before
creating another AmosEngine object. A process
is allowed only one instance of an AmosEngine
object at a time.
The Try block guarantees that the Dispose
method will be called even if an error occurs
during program execution.
E To perform the analysis, from the menus, choose File > Run.
Page 65

Generating Additional Output
Some AmosEngine methods generate additional output. For example, the Standardized
method displays standardized estimates. The following figure shows the use of the
Standardized method:
39
Estimating Variances and Covariances
Modeling in C#
Writing an Amos program in C# is similar to writing one in VB.NET. To start a new
C# program, in the built-in program editor of Amos:
E Choose File > New C# Program (rather than File > New VB Program).
E Choose File > Open to open Ex01.cs, which is a C# version of the VB.NET program
Ex01.vb.
Page 66

40
Example 1
Other Program Development Tools
The built-in program editor in Amos is used throughout this user’s guide for writing
and executing Amos programs. However, you can use the development tool of your
choice. The Examples folder contains a VisualStudio subfolder where you can find
Visual Studio VB.NET and C# solutions for Example 1.
Page 67

Testing Hypotheses
Introduction
This example demonstrates how you can use Amos to test simple hypotheses about
variances and covariances. It also introduces the chi-square test for goodness of fit and
elaborates on the concept of degrees of freedom.
Example
2
About the Data
We will use Attig’s (1983) spatial memory data, which were described in Example 1.
We will also begin with the same path diagram as in Example 1. To demonstrate the
ability of Amos to use different data formats, this example uses a data file in SPSS
Statistics format instead of an Excel file.
Parameters Constraints
The following is the path diagram from Example 1. We can think of the variable
objects as having small boxes nearby (representing the variances) that are filled in
once Amos has estimated the parameters.
41
Page 68

42
Example 2
You can fill these boxes yourself instead of letting Amos fill them.
Constraining Variances
Suppose you want to set the variance of recall1 to 6 and the variance of recall2 to 8.
E In the drawing area, right-click recall1 and choose Object Properties from the pop-up
menu.
E Click the Parameters tab.
E In the Variance text box, type 6.
E With the Object Properties dialog box still open, click recall2 and set its variance to 8.
Page 69

E
Close the dialog box.
The path diagram displays the parameter values you just specified.
This is not a very realistic example because the numbers 6 and 8 were just picked out
of the air. Meaningful parameter constraints must have some underlying rationale,
perhaps being based on theory or on previous analyses of similar data.
Specifying Equal Parameters
43
Testing Hypotheses
Sometimes you will be interested in testing whether two parameters are equal in the
population. You might, for example, think that the variances of recall1 and recall2
might be equal without having a particular value for the variances in mind. To
investigate this possibility, do the following:
E In the drawing area, right-click recall1 and choose Object Properties from the pop-up
menu.
E Click the Parameters tab.
E In the Variance text box, type v_recall.
E Click recall2 and label its variance as v_recall.
E Use the same method to label the place1 and place2 variances as v_place.
It doesn’t matter what label you use. The important thing is to enter the same label for
each variance you want to force to be equal. The effect of using the same label is to
Page 70

44
Example 2
require both of the variances to have the same value without specifying ahead of time
what that value is.
Benefits of Specifying Equal Parameters
Before adding any further constraints on the model parameters, let’s examine why we
might want to specify that two parameters, like the variances of recall1 and recall2 or
place1 and place2, are equal. Here are two benefits:
If you specify that two parameters are equal in the population and if you are correct
in this specification, then you will get more accurate estimates, not only of the
parameters that are equal but usually of the others as well. This is the only benefit
if you happen to know that the parameters are equal.
If the equality of two parameters is a mere hypothesis, requiring their estimates to
be equal will result in a test of that hypothesis.
Constraining Covariances
Your model may also include restrictions on parameters other than variances. For
example, you may hypothesize that the covariance between recall1 and place1 is equal
to the covariance between recall2 and place2. To impose this constraint:
E In the drawing area, right-click the double-headed arrow that connects recall1 and
place1, and choose
E Click the Parameters tab.
E In the Covariance text box, type a non-numeric string such as cov_rp.
E Use the same method to set the covariance between recall2 and place2 to cov_rp.
Object Properties from the pop-up menu.
Page 71

Testing Hypotheses
45
Moving and Formatting Objects
While a horizontal layout is fine for small examples, it is not practical for analyses that
are more complex. The following is a different layout of the path diagram on which
we’ve been working:
Page 72

46
Example 2
You can use the following tools to rearrange your path diagram until it looks like the
one above:
To move objects, choose Edit > Move from the menus, and then drag the object to
To copy formatting from one object to another, choose Edit > Drag Properties from
For more information about the Drag Properties feature, refer to online help.
Data Input
This example uses a data file in SPSS Statistics format. If you have SPSS Statistics
installed, you can view the data as you load it. Even if you don’t have SPSS Statistics
installed, Amos will still read the data.
E From the menus, choose File > Data Files.
its new location. You can also use the
Move button to drag the endpoints of arrows.
the menus, select the properties you wish to apply, and then drag from one object
to another.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click File Name.
E Browse to the Examples folder. If you performed a typical installation, the path is
C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Examples\<language>.
E In the Files of type list, select SPSS Statistics (*.sav), click Attg_yng, and then click
Open.
E If you have SPSS Statistics installed, click the View Data button in the Data Files dialog
box. An SPSS Statistics window opens and displays the data.
Page 73

E
Review the data and close the data view.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click OK.
Performing the Analysis
E From the menus, choose Analyze > Calculate Estimates.
E In the Save As dialog box, enter a name for the file and click Save.
Amos calculates the model estimates.
Viewing Text Output
E From the menus, choose View > Text Output.
E To view the parameter estimates, click Estimates in the tree diagram in the upper left
pane of the Amos Output window.
47
Testing Hypotheses
Page 74

48
10 7 3=–
Example 2
E Now click Notes for Model in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window.
You can see that the parameters that were specified to be equal do have equal
estimates. The standard errors here are generally smaller than the standard errors
obtained in Example 1. Also, because of the constraints on the parameters, there are
now positive degrees of freedom.
While there are still 10 sample variances and covariances, the number of parameters to
be estimated is only seven. Here is how the number seven is arrived at: The variances
of recall1 and recall2, labeled v_recall, are constrained to be equal, and thus count as
a single parameter. The variances of place1 and place2 (labeled v_place) count as
another single parameter. A third parameter corresponds to the equal covariances
recall1 <> place1 and recall2 <> place2 (labeled cov_rp). These three parameters,
plus the four unlabeled, unrestricted covariances, add up to seven parameters that have
to be estimated.
The degrees of freedom ( ) may also be thought of as the number of
constraints placed on the original 10 variances and covariances.
Optional Output
The output we just discussed is all generated by default. You can also request additional
output:
E From the menus, choose View > Analysis Properties.
E Click the Output tab.
E Ensure that the following check boxes are selected: Minimization history, Standardized
estimates
, Sample moments, Implied moments, and Residual moments.
Page 75

Testing Hypotheses
49
E From the menus, choose Analyze > Calculate Estimates.
Amos recalculates the model estimates.
Covariance Matrix Estimates
E To see the sample variances and covariances collected into a matrix, choose View > Text
from the menus.
Output
E Click Sample Moments in the tree diagram in the upper left corner of the Amos Output
window.
Page 76

50
Example 2
E In the tree diagram, expand Estimates and then click Matrices.
The following is the sample covariance matrix:
The following is the matrix of implied covariances:
Note the differences between the sample and implied covariance matrices. Because the
model imposes three constraints on the covariance structure, the implied variances and
covariances are different from the sample values. For example, the sample variance of
place1 is 33.58, but the implied variance is 27.53. To obtain a matrix of residual
covariances (sample covariances minus implied covariances), put a check mark next to
Residual moments on the Output tab and repeat the analysis.
The following is the matrix of residual covariances:
Page 77

Testing Hypotheses
Displaying Covariance and Variance Estimates on the Path Diagram
As in Example 1, you can display the covariance and variance estimates on the path
diagram.
E Click the Show the output path diagram button.
E In the Parameter Formats pane to the left of the drawing area, click Unstandardized
estimates
clicking Standardized estimates.
The following is the path diagram showing correlations:
. Alternatively, you can request correlation estimates in the path diagram by
51
Labeling Output
It may be difficult to remember whether the displayed values are covariances or
correlations. To avoid this problem, you can use Amos to label the output.
E Open the file Ex02.amw.
E Right-click the caption at the bottom of the path diagram, and choose Object Properties
from the pop-up menu.
E Click the Text tab.
Page 78

52
Example 2
Notice the word \format in the bottom line of the figure caption. Words that begin with
a backward slash, like
information about the currently displayed model. The text macro \format will be
replaced by the heading Model Specification, Unstandardized estimates, or
Standardized estimates, depending on which version of the path diagram is displayed.
\format, are called text macros. Amos replaces text macros with
Hypothesis Testing
The implied covariances are the best estimates of the population variances and
covariances under the null hypothesis. (The null hypothesis is that the parameters
required to have equal estimates are truly equal in the population.) As we know from
Example 1, the sample covariances are the best estimates obtained without making any
assumptions about the population values. A comparison of these two matrices is
relevant to the question of whether the null hypothesis is correct. If the null hypothesis
is correct, both the implied and sample covariances are maximum likelihood estimates
of the corresponding population values (although the implied covariances are better
estimates). Consequently, you would expect the two matrices to resemble each other.
On the other hand, if the null hypothesis is wrong, only the sample covariances are
Page 79

53
Testing Hypotheses
maximum likelihood estimates, and there is no reason to expect them to resemble the
implied covariances.
The chi-square statistic is an overall measure of how much the implied covariances
differ from the sample covariances.
Chi-square = 6.276
Degrees of freedom = 3
Probability level = 0.099
In general, the more the implied covariances differ from the sample covariances, the
bigger the chi-square statistic will be. If the implied covariances had been identical to
the sample covariances, as they were in Example 1, the chi-square statistic would have
been 0. You can use the chi-square statistic to test the null hypothesis that the
parameters required to have equal estimates are really equal in the population.
However, it is not simply a matter of checking to see if the chi-square statistic is 0.
Since the implied covariances and the sample covariances are merely estimates, you
can’t expect them to be identical (even if they are both estimates of the same population
covariances). Actually, you would expect them to differ enough to produce a chi-square
in the neighborhood of the degrees of freedom, even if the null hypothesis is true. In
other words, a chi-square value of 3 would not be out of the ordinary here, even with a
true null hypothesis. You can say more than that: If the null hypothesis is true, the chisquare value (6.276) is a single observation on a random variable that has an
approximate chi-square distribution with three degrees of freedom. The probability is
about 0.099 that such an observation would be as large as 6.276. Consequently, the
evidence against the null hypothesis is not significant at the 0.05 level.
Displaying Chi-Square Statistics on the Path Diagram
You can get the chi-square statistic and its degrees of freedom to appear in a figure
caption on the path diagram using the text macros
text macros with the numeric values of the chi-square statistic and its degrees of
freedom. You can use the text macro
\p to display the corresponding right-tail
probability under the chi-square distribution.
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Figure Caption.
E Click the location on the path diagram where you want the figure caption to appear.
The Figure Caption dialog box appears.
\cmin and \df. Amos replaces these
Page 80

54
Example 2
E In the Figure Caption dialog box, enter a caption that includes the \cmin, \df, and \p text
macros, as follows:
When Amos displays the path diagram containing this caption, it appears as follows:
Page 81

Modeling in VB.NET
The following program fits the constrained model of Example 2:
55
Testing Hypotheses
Page 82

56
Example 2
This table gives a line-by-line explanation of the program:
Program Statement Explanation
Declares Sem as an object of type
Dim Sem As New AmosEngine
Sem.TextOutput
Sem.Standardized()
Sem.ImpliedMoments()
Sem.SampleMoments()
Sem.ResidualMoments()
Sem.BeginGroup …
Sem.AStructure("recall1 (v_recall)")
Sem.AStructure("recall2 (v_recall)")
Sem.AStructure("place1 (v_place)")
Sem.AStructure("place2 (v_place)")
Sem.AStructure("recall1 <> place1 (cov_rp)")
Sem.AStructure("recall2 <> place2 (cov_rp)")
Sem.FitModel()
Sem.Dispose()
Try/Finally/End Try
AmosEngine. The methods and
properties of the Sem object are used to
specify and fit the model.
Creates an output file containing the
results of the analysis. At the end of the
analysis, the contents of the output file
are displayed in a separate window.
Displays standardized estimates, implied
covariances, sample covariances, and
residual covariances.
Begins the model specification for a
single group (that is, a single
population). This line also specifies that
the SPSS Statistics file Attg_yng.sav
contains the input data.
is the location of the Amos program
directory.
Specifies the model. The first four
AStructure statements constrain the
variances of the observed variables
through the use of parameter names in
parentheses. Recall1 and recall2 are
required to have the same variance
because both variances are labeled
v_recall. The variances of place1 and
place2 are similarly constrained to be
equal. Each of the last two
lines represents a covariance. The two
covariances are both named cov_rp.
Consequently, those covariances are
constrained to be equal.
Fits the model.
Releases resources used by the Sem
object. It is particularly important for
your program to use an AmosEngine
object’s
Dispose method before creating
another AmosEngine object. A process is
allowed to have only one instance of an
AmosEngine object at a time.
This Try block guarantees that the
Dispose method will be called even if an
error occurs during program execution.
Sem.AmosDir()
AStructure
Page 83

E
To perform the analysis, from the menus, choose File > Run.
Timing Is Everything
The AStructure lines must appear after BeginGroup; otherwise, Amos will not recognize
that the variables named in the
attg_yng.sav dataset.
In general, the order of statements matters in an Amos program. In organizing an
Amos program, AmosEngine methods can be divided into three general groups
Group 1 — Declarative Methods
This group contains methods that tell Amos what results to compute and display.
TextOutput is a Group 1 method, as are Standardized, ImpliedMoments, SampleMoments,
and ResidualMoments. Many other Group 1 methods that are not used in this example
are documented in the Amos 21 Programming Reference Guide.
Group 2 — Data and Model Specification Methods
Testing Hypotheses
AStructure lines are observed variables in the
57
1
.
This group consists of data description and model specification commands.
BeginGroup and AStructure are Group 2 methods. Others are documented in the Amos
21 Programming Reference Guide.
Group 3 — Methods for Retrieving Results
These are commands to…well, retrieve results. So far, we have not used any Group 3
methods. Examples using Group 3 methods are given in the Amos 21 Programming
Reference Guide.
Tip: When you write an Amos program, it is important to pay close attention to the
order in which you call the Amos engine methods. The rule is that groups must appear
in order: Group 1, then Group 2, and finally Group 3.
For more detailed information about timing rules and a complete listing of methods and
their group membership, see the Amos 21 Programming Reference Guide.
1 There is also a fourth special group, consisting of only the Initialize Method. If the optional Initialize Method
is used, it must come before the Group 1 methods.
Page 84

Page 85

More Hypothesis Testing
Introduction
This example demonstrates how to test the null hypothesis that two variables are
uncorrelated, reinforces the concept of degrees of freedom, and demonstrates, in a
concrete way, what is meant by an asymptotically correct test.
Example
3
About the Data
For this example, we use the group of older subjects from Attig’s (1983) spatial
memory study and the two variables age and vocabulary. We will use data formatted
as a tab-delimited text file.
Bringing In the Data
E From the menus, choose File > New.
E From the menus, choose File > Data Files.
E In the Data Files dialog box, select File Name.
E Browse to the Examples folder. If you performed a typical installation, the path is
C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Examples\<language>.
59
Page 86

60
Example 3
E In the Files of type list, select Text (*.txt), select Attg_old.txt, and then click Open.
E In the Data Files dialog box, click OK.
Testing a Hypothesis That Two Variables Are Uncorrelated
Among Attig’s 40 old subjects, the sample correlation between age and vocabulary is
–0.09 (not very far from 0). Is this correlation nevertheless significant? To find out, we
will test the null hypothesis that, in the population from which these 40 subjects came,
the correlation between age and vocabulary is 0. We will do this by estimating the
variance-covariance matrix under the constraint that age and vocabulary are
uncorrelated.
Specifying the Model
Begin by drawing and naming the two observed variables, age and vocabulary, in the
path diagram, using the methods you learned in Example 1.
Amos provides two ways to specify that the covariance between age and vocabulary
is 0. The most obvious way is simply to not draw a double-headed arrow connecting
the two variables. The absence of a double-headed arrow connecting two exogenous
variables implies that they are uncorrelated. So, without drawing anything more, the
Page 87

More Hypothesis Testing
model specified by the simple path diagram above specifies that the covariance (and
thus the correlation) between age and vocabulary is 0.
The second method of constraining a covariance parameter is the more general
procedure introduced in Example 1 and Example 2.
E From the menus, choose Diagram > Draw Covariances.
E Click and drag to draw an arrow that connects vocabulary and age.
E Right-click the arrow and choose Object Properties from the pop-up menu.
E Click the Parameters tab.
E Type 0 in the Covariance text box.
E Close the Object Properties dialog box.
Your path diagram now looks like this:
61
Page 88

62
Example 3
E From the menus, choose Analyze > Calculate Estimates.
The Save As dialog box appears.
E Enter a name for the file and click Save.
Amos calculates the model estimates.
Viewing Text Output
E From the menus, choose View > Text Output.
E In the tree diagram in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window, click Estimates.
Although the parameter estimates are not of primary interest in this analysis, they are
as follows:
In this analysis, there is one degree of freedom, corresponding to the single constraint
that age and vocabulary be uncorrelated. The degrees of freedom can also be arrived
at by the computation shown in the following text. To display this computation:
E Click Notes for Model in the upper left pane of the Amos Output window.
Page 89

The three sample moments are the variances of age and vocabulary and their
covariance. The two distinct parameters to be estimated are the two population
variances. The covariance is fixed at 0 in the model, not estimated from the sample
information.
Viewing Graphics Output
E Click the Show the output path diagram button.
E In the Parameter Formats pane to the left of the drawing area, click Unstandardized
estimates.
63
More Hypothesis Testing
The following is the path diagram output of the unstandardized estimates, along with
the test of the null hypothesis that age and vocabulary are uncorrelated:
The probability of accidentally getting a departure this large from the null hypothesis
is 0.555. The null hypothesis would not be rejected at any conventional significance
level.
Page 90

64
df 38=
p 0.56=
Example 3
The usual t statistic for testing this null hypothesis is 0.59 ( ,
two-sided). The probability level associated with the t statistic is exact. The probability
level of 0.555 of the chi-square statistic is off, owing to the fact that it does not have an
exact chi-square distribution in finite samples. Even so, the probability level of 0.555
is not bad.
Here is an interesting question: If you use the probability level displayed by Amos
to test the null hypothesis at either the 0.05 or 0.01 level, then what is the actual
probability of rejecting a true null hypothesis? In the case of the present null
hypothesis, this question has an answer, although the answer depends on the sample
size. The second column in the next table shows, for several sample sizes, the real
probability of a Type I error when using Amos to test the null hypothesis of zero
correlation at the 0.05 level. The third column shows the real probability of a Type I
error if you use a significance level of 0.01. The table shows that the bigger the sample
size, the closer the true significance level is to what it is supposed to be. It’s too bad
that such a table cannot be constructed for every hypothesis that Amos can be used to
test. However, this much can be said about any such table: Moving from top to bottom,
the numbers in the 0.05 column would approach 0.05, and the numbers in the 0.01
column would approach 0.01. This is what is meant when it is said that hypothesis tests
based on maximum likelihood theory are asymptotically correct.
The following table shows the actual probability of a Type I error when using Amos
to test the hypothesis that two variables are uncorrelated:
Sample Size
Nominal Significance Level
0.05 0.01
3 0.250 0.122
4 0.150 0.056
5 0.115 0.038
10 0.073 0.018
20 0.060 0.013
30 0.056 0.012
40 0.055 0.012
50 0.054 0.011
100 0.052 0.011
150 0.051 0.010
200 0.051 0.010
500 0.050 0.010
>
Page 91

Modeling in VB.NET
Here is a program for performing the analysis of this example:
65
More Hypothesis Testing
The
AStructure method constrains the covariance, fixing it at a constant 0. The program
does not refer explicitly to the variances of age and vocabulary. The default behavior
of Amos is to estimate those variances without constraints. Amos treats the variance of
every exogenous variable as a free parameter except for variances that are explicitly
constrained by the program.
Page 92

Page 93

Conventional Linear Regression
Introduction
This example demonstrates a conventional regression analysis, predicting a single
observed variable as a linear combination of three other observed variables. It also
introduces the concept of identifiability.
Example
4
About the Data
Warren, White, and Fuller (1974) studied 98 managers of farm cooperatives. We will
use the following four measurements:
Test Explanation
performance
knowledge
value
satisfaction
A fifth measure, past training, was also reported, but we will not use it.
In this example, you will use the Excel worksheet Warren5v in the file
UserGuide.xls, which is located in the Examples folder. If you performed a typical
installation, the path is C:\Program Files\IBM\SPSS\Amos\21\Examples\
<language>.
A 24-item test of performance related to “planning, organization,
controlling, coordinating, and directing”
A 26-item test of knowledge of “economic phases of
management directed toward profit-making...and product
knowledge”
A 30-item test of “tendency to rationally evaluate means to an
economic end”
An 11-item test of “gratification obtained...from performing the
managerial role”
67
Page 94

68
Example 4
Here are the sample variances and covariances:
Warren5v also contains the sample means. Raw data are not available, but they are not
needed by Amos for most analyses, as long as the sample moments (that is, means,
variances, and covariances) are provided. In fact, only sample variances and
covariances are required in this example. We will not need the sample means in
Warren5v for the time being, and Amos will ignore them.
Analysis of the Data
Suppose you want to use scores on knowledge, value, and satisfaction to predict
performance. More specifically, suppose you think that performance scores can be
approximated by a linear combination of knowledge, value, and satisfaction. The
prediction will not be perfect, however, and the model should thus include an error
variable.
Here is the initial path diagram for this relationship:
Page 95

69
Conventional Linear Regression
The single-headed arrows represent linear dependencies. For example, the arrow
leading from knowledge to performance indicates that performance scores depend, in
part, on knowledge. The variable error is enclosed in a circle because it is not directly
observed. Error represents much more than random fluctuations in performance scores
due to measurement error. Error also represents a composite of age, socioeconomic
status, verbal ability, and anything else on which performance may depend but which
was not measured in this study. This variable is essential because the path diagram is
supposed to show all variables that affect performance scores. Without the circle, the
path diagram would make the implausible claim that performance is an exact linear
combination of knowledge, value, and satisfaction.
The double-headed arrows in the path diagram connect variables that may be
correlated with each other. The absence of a double-headed arrow connecting error
with any other variable indicates that error is assumed to be uncorrelated with every
other predictor variable—a fundamental assumption in linear regression. Performance
is also not connected to any other variable by a double-headed arrow, but this is for a
different reason. Since performance depends on the other variables, it goes without
saying that it might be correlated with them.
Specifying the Model
Using what you learned in the first three examples, do the following:
E Start a new path diagram.
E Specify that the dataset to be analyzed is in the Excel worksheet Warren5v in the file
UserGuide.xls.
E Draw four rectangles and label them knowledge, value, satisfaction, and performance.
E Draw an ellipse for the error variable.
E Draw single-headed arrows that point from the exogenous, or predictor, variables
(knowledge, value, satisfaction, and error) to the endogenous, or response, variable
(performance).
Note: Endogenous variables have at least one single-headed path pointing toward them.
Exogenous variables, in contrast, send out only single-headed paths but do not receive any.
Page 96

70
Example 4
E Draw three double-headed arrows that connect the observed exogenous variables
(knowledge, satisfaction, and value).
Your path diagram should look like this:
Identification
In this example, it is impossible to estimate the regression weight for the regression of
performance on error, and, at the same time, estimate the variance of error. It is like
having someone tell you, “I bought $5 worth of widgets,” and attempting to infer both
the price of each widget and the number of widgets purchased. There is just not enough
information.
You can solve this identification problem by fixing either the regression weight
applied to error in predicting performance, or the variance of the error variable itself,
at an arbitrary, nonzero value. Let’s fix the regression weight at 1. This will yield the
same estimates as conventional linear regression.
Fixing Regression Weights
E Right-click the arrow that points from error to performance and choose Object Properties
from the pop-up menu.
E Click the Parameters tab.
E Type 1 in the Regression weight box.
Page 97

Conventional Linear Regression
71
Setting a regression weight equal to 1 for every error variable can be tedious.
Fortunately, Amos Graphics provides a default solution that works well in most cases.
E Click the Add a unique variable to an existing variable button.
E Click an endogenous variable.
Amos automatically attaches an error variable to it, complete with a fixed regression
weight of 1. Clicking the endogenous variable repeatedly changes the position of the
error variable.
Page 98

72
Example 4
Viewing the Text Output
Here are the maximum likelihood estimates:
Amos does not display the path performance <— error because its value is fixed at the
default value of 1. You may wonder how much the other estimates would be affected
if a different constant had been chosen. It turns out that only the variance estimate for
error is affected by such a change.
The following table shows the variance estimate that results from various choices for
the performance <— error regression weight.
Fixed regression weight Estimated variance of error
0.5 0.050
0.707 0.025
1.0 0.0125
1.414 0.00625
2.0 0.00313
Suppose you fixed the path coefficient at 2 instead of 1. Then the variance estimate
would be divided by a factor of 4. You can extrapolate the rule that multiplying the path
coefficient by a fixed factor goes along with dividing the error variance by the square
Page 99

73
Conventional Linear Regression
of the same factor. Extending this, the product of the squared regression weight and the
error variance is always a constant. This is what we mean when we say the regression
weight (together with the error variance) is unidentified. If you assign a value to one
of them, the other can be estimated, but they cannot both be estimated at the same time.
The identifiability problem just discussed arises from the fact that the variance of a
variable, and any regression weights associated with it, depends on the units in which
the variable is measured. Since error is an unobserved variable, there is no natural way
to specify a measurement unit for it. Assigning an arbitrary value to a regression weight
associated with error can be thought of as a way of indirectly choosing a unit of
measurement for error. Every unobserved variable presents this identifiability
problem, which must be resolved by imposing some constraint that determines its unit
of measurement.
Changing the scale unit of the unobserved error variable does not change the overall
model fit. In all the analyses, you get:
Chi-square = 0.00
Degrees of freedom = 0
Probability level cannot be computed
There are four sample variances and six sample covariances, for a total of 10 sample
moments. There are three regression paths, four model variances, and three model
covariances, for a total of 10 parameters that must be estimated. Hence, the model has
zero degrees of freedom. Such a model is often called saturated or just-identified.
The standardized coefficient estimates are as follows:
Page 100

74
Example 4
The standardized regression weights and the correlations are independent of the units
in which all variables are measured; therefore, they are not affected by the choice of
identification constraints.
Squared multiple correlations are also independent of units of measurement. Amos
displays a squared multiple correlation for each endogenous variable.
Note: The squared multiple correlation of a variable is the proportion of its variance that
is accounted for by its predictors. In the present example, knowledge, value, and
satisfaction account for 40% of the variance of performance.
Viewing Graphics Output
The following path diagram output shows unstandardized values:
 Loading...
Loading...