Page 1

Front cover
IBM Power Systems S822LC
for High Performance Computing
Technical Overview and Introduction
Alexandre Caldeira
Volker Haug
Scott Vetter
Redpaper
Page 2

Page 3

International Technical Support Organization
IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance
Computing
September 2016
REDP-5405-00
Page 4

Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page v.
First Edition (September 2016)
This edition applies to the IBM Power Systems S822LC model 8335-GTB.
© Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2016. All rights reserved.
Note to U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule
Contract with IBM Corp.
Page 5

Contents
Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .v
Trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vi
IBM Redbooks promotions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Authors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .x
Now you can become a published author, too! . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .x
Comments welcome. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .x
Stay connected to IBM Redbooks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 Server features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.1.1 Minimum features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1.2 System cooling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2 The NVIDIA Tesla P100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.3 Operating system support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3.1 Ubuntu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3.2 Additional information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.4 Operating environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.5 Physical package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.6 System architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.7 The POWER8 processor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.7.1 POWER8 processor overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.7.2 POWER8 processor core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.7.3 Simultaneous multithreading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.7.4 Memory access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.7.5 On-chip L3 cache innovation and Intelligent Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.7.6 L4 cache and memory buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.7.7 Hardware transactional memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1.7.8 Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1.7.9 NVLink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.8 Memory subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.8.1 Memory riser cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.8.2 Memory placement rules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.8.3 Memory bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.9 System bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.10 Internal I/O subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.11 Slot configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.12 System ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.13 PCI adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.13.1 PCI Express . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.13.2 LAN adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.13.3 Compute Intensive Accelerator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.13.4 Fibre Channel adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.13.5 CAPI enabled Infiniband adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.14 Internal storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.14.1 Disk and media features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.15 External I/O subsystems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. iii
Page 6

1.16 IBM System Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.17 Java. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.1 Main management components overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.2 Service processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.2.1 Open Power Abstraction Layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.2.2 Intelligent Platform Management Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.3 Reliability, availability, and serviceability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.3.2 IBM terminology versus x86 terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2.3.3 Error handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2.3.4 Serviceability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2.3.5 Manageability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
IBM server racks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Water cooling option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
IBM 7014 Model S25 rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
IBM 7014 Model T00 rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
IBM 7014 Model T42 rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
IBM 42U SlimRack 7965-94Y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
The AC power distribution unit and rack content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Rack-mounting rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Useful rack additions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
OEM racks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Energy management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
IBM EnergyScale technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
On Chip Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Energy consumption estimation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
IBM Redbooks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Other publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Online resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Help from IBM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
iv IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 7

Notices
This information was developed for products and services offered in the U.S.A.
IBM may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in other countries. Consult
your local IBM representative for information on the products and services currently available in your area. Any
reference to an IBM product, program, or service is not intended to state or imply that only that IBM product,
program, or service may be used. Any functionally equivalent product, program, or service that does not
infringe any IBM intellectual property right may be used instead. However, it is the user's responsibility to
evaluate and verify the operation of any non-IBM product, program, or service.
IBM may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter described in this document. The
furnishing of this document does not grant you any license to these patents. You can send license inquiries, in
writing, to:
IBM Director of Licensing, IBM Corporation, North Castle Drive, Armonk, NY 10504-1785 U.S.A.
The following paragraph does not apply to the United Kingdom or any other country where such
provisions are inconsistent with local law: INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION
PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT,
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer of
express or implied warranties in certain transactions, therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This information could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made
to the information herein; these changes will be incorporated in new editions of the publication. IBM may make
improvements and/or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this publication at any time
without notice.
Any references in this information to non-IBM websites are provided for convenience only and do not in any
manner serve as an endorsement of those websites. The materials at those websites are not part of the
materials for this IBM product and use of those websites is at your own risk.
IBM may use or distribute any of the information you supply in any way it believes appropriate without incurring
any obligation to you.
Any performance data contained herein was determined in a controlled environment. Therefore, the results
obtained in other operating environments may vary significantly. Some measurements may have been made
on development-level systems and there is no guarantee that these measurements will be the same on
generally available systems. Furthermore, some measurements may have been estimated through
extrapolation. Actual results may vary. Users of this document should verify the applicable data for their
specific environment.
Information concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the suppliers of those products, their published
announcements or other publicly available sources. IBM has not tested those products and cannot confirm the
accuracy of performance, compatibility or any other claims related to non-IBM products. Questions on the
capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the suppliers of those products.
This information contains examples of data and reports used in daily business operations. To illustrate them
as completely as possible, the examples include the names of individuals, companies, brands, and products.
All of these names are fictitious and any similarity to the names and addresses used by an actual business
enterprise is entirely coincidental.
COPYRIGHT LICENSE:
This information contains sample application programs in source language, which illustrate programming
techniques on various operating platforms. You may copy, modify, and distribute these sample programs in
any form without payment to IBM, for the purposes of developing, using, marketing or distributing application
programs conforming to the application programming interface for the operating platform for which the sample
programs are written. These examples have not been thoroughly tested under all conditions. IBM, therefore,
cannot guarantee or imply reliability, serviceability, or function of these programs.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. v
Page 8

Trademarks
IBM, the IBM logo, and ibm.com are trademarks or registered trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. These and other IBM trademarked terms are
marked on their first occurrence in this information with the appropriate symbol (® or ™), indicating US
registered or common law trademarks owned by IBM at the time this information was published. Such
trademarks may also be registered or common law trademarks in other countries. A current list of IBM
trademarks is available on the Web at http://www.ibm.com/legal/copytrade.shtml
The following terms are trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation in the United States,
other countries, or both:
AIX®
DS8000®
Easy Tier®
EnergyScale™
IBM®
IBM FlashSystem®
IBM z™
POWER®
POWER Hypervisor™
Power Systems™
POWER8®
PowerHA®
PowerLinux™
PowerPC®
PowerVM®
Real-time Compression™
Redbooks®
Redpaper™
Redbooks (logo) ®
Storwize®
System Storage®
XIV®
The following terms are trademarks of other companies:
Linux is a trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other countries, or both.
Java, and all Java-based trademarks and logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its
affiliates.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
vi IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 9

IBM REDBOOKS PROMOTIONS
Find and read thousands of
IBM Redbooks publications
Search, bookmark, save and organize favorites
Get up-to-the-minute Redbooks news and announcements
Link to the latest Redbooks blogs and videos
Download
Now
Get the latest version of the Redbooks Mobile App
iOS
Android
Place a Sponsorship Promotion in an IBM
Redbooks publication, featuring your business
or solution with a link to your web site.
Qualified IBM Business Partners may place a full page
promotion in the most popular Redbooks publications.
Imagine the power of being seen by users who download
millions of Redbooks publications each year!
®
®
Promote your business
in an IBM Redbooks
publication
ibm.com/Redbooks
About Redbooks Business Partner Programs
IBM Redbooks promotions
Page 10

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
Page 11

Preface
This IBM® Redpaper™ publication is a comprehensive guide that covers the IBM Power
Systems™ S822LC 8335-GTB server designed for impressive High Performance Computing
applications that support the Linux operating system (OS) as well as High Performance Data
Analytics, the enterprise datacenter, and accelerated cloud deployments.
The objective of this paper is to introduce the major innovative Power S822LC features and
their relevant functions:
Powerful POWER8® processors that offer 16 cores at 3.259 GHz or 3.857 GHz turbo
A 19-inch rack-mount 2U configuration
NVIDIA NVLink technology for exceptional processor to accelerator intercommunication
Four SXM2 form factor connectors for the NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPU
This publication is for professionals who want to acquire a better understanding of IBM Power
Systems products. The intended audience includes the following roles:
Clients
Sales and marketing professionals
Technical support professionals
performance or 20 cores at 2.860 GHz or 3.492 GHz turbo
IBM Business Partners
Independent software vendors
This paper expands the set of IBM Power Systems documentation by providing a desktop
reference that offers a detailed technical description of the Power S822LC server.
This paper does not replace the latest marketing materials and configuration tools. It is
intended as an additional source of information that, together with existing sources, can be
used to enhance your knowledge of IBM server solutions.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. ix
Page 12
Authors
This paper was produced by a team of specialists from around the world working at the
International Technical Support Organization, Austin Center.
Alexandre Caldeira is a Certified IT Specialist and is the Product Manager for Power
Systems Latin America. He holds a degree in Computer Science from the Universidade
Estadual Paulista (UNESP) and an MBA in Marketing. His major areas of focus are
competition, sales, marketing and technical sales support. Alexandre has more than 16 years
of experience working on IBM Systems Solutions and has worked also as an IBM Business
Partner on Power Systems hardware, AIX, and IBM PowerVM® virtualization products.
Volker Haug is an Executive IT Specialist & Open Group Distinguished IT Specialist within
IBM Systems in Germany supporting Power Systems clients and Business Partners. He
holds a Diploma degree in Business Management from the University of Applied Studies in
Stuttgart. His career includes more than 29 years of experience with Power Systems, AIX,
and PowerVM virtualization. He has written several IBM Redbooks® publications about
Power Systems and PowerVM. Volker is an IBM POWER8® Champion and a member of the
German Technical Expert Council, which is an affiliate of the IBM Academy of Technology.
The project that produced this publication was managed by:
Scott Vetter
Executive Project Manager, PMP
Thanks to the following people for their contributions to this project:
George Ahrens, Nick Bofferding, Charlie Burns, Sertac Cakici, Dan Crowell,
Daniel Henderson, Yesenia Jimenez, Ann Lund, Benjamin Mashak, Chris Mann,
Michael J Mueller, Kanisha Patel, Matt Spinler, Jeff Stuecheli, Uma Yadlapati, and
Maury Zipse.
Now you can become a published author, too!
Here’s an opportunity to spotlight your skills, grow your career, and become a published
author—all at the same time! Join an ITSO residency project and help write a book in your
area of expertise, while honing your experience using leading-edge technologies. Your efforts
will help to increase product acceptance and customer satisfaction, as you expand your
network of technical contacts and relationships. Residencies run from two to six weeks in
length, and you can participate either in person or as a remote resident working from your
home base.
Find out more about the residency program, browse the residency index, and apply online at:
ibm.com/redbooks/residencies.html
Comments welcome
Your comments are important to us!
x IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 13

We want our papers to be as helpful as possible. Send us your comments about this paper or
other IBM Redbooks publications in one of the following ways:
Use the online Contact us review Redbooks form found at:
ibm.com/redbooks
Send your comments in an email to:
redbooks@us.ibm.com
Mail your comments to:
IBM Corporation, International Technical Support Organization
Dept. HYTD Mail Station P099
2455 South Road
Poughkeepsie, NY 12601-5400
Stay connected to IBM Redbooks
Find us on Facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/IBMRedbooks
Follow us on Twitter:
http://twitter.com/ibmredbooks
Look for us on LinkedIn:
http://www.linkedin.com/groups?home=&gid=2130806
Explore new Redbooks publications, residencies, and workshops with the IBM Redbooks
weekly newsletter:
https://www.redbooks.ibm.com/Redbooks.nsf/subscribe?OpenForm
Stay current on recent Redbooks publications with RSS Feeds:
http://www.redbooks.ibm.com/rss.html
Preface xi
Page 14

xii IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 15

Chapter 1. Architecture and technical
1
description
The IBM Power System S822LC for High Performance Computing (8335-GTB) server, the
first Power System offering with NVIDIA NVLink Technology, removes GPU computing
bottlenecks by employing the high-bandwith and low-latency NVLink interface from CPU to
GPU and GPU to GPU. This unlocks new performance and new applications for accelerated
computing.
Power System LC servers are a product of a co-design with OpenPOWER Foundation
ecosystem members. Power S822LC for High Performance Computing innovation partners
include IBM, NVIDIA, Mellanox, Canonical, Wistron, and more.
The Power S822LC server offers a modular design to scale from single racks to hundreds,
simplicity of ordering, and a strong innovation roadmap for GPUs.
The IBM Power System S822LC for High Performance Computing (8335-GTB) server, the
first Power System offering with NVIDIA NVLink Technology, removes GPU computing
bottlenecks by employing the high-bandwith and low-latency NVLink interface from CPU to
GPU and GPU to GPU. This unlocks new performance and new applications for accelerated
computing
The IBM Power S822LC for High Performance Computing (8335-GTB) server offers two
processor sockets for a total of 16 cores at 3.259 GHz (3.857 GHz turbo) or 20 cores at 2.860
GHz (3.492 GHz turbo) in a 19-inch rack-mount, 2U (EIA units) drawer configuration. All the
cores are activated.
The server provides eight memory daughter cards with 16 GB (4x4 GB), 32 GB (4x8 GB),
64 GB (4x16 GB), and 128 GB (4x32 GB), allowing for a maximum system memory of
1024 GB.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. 1
Page 16

Figure 1-1 shows the front view of a Power S822LC server.
POWER8 Processor (2x)
Operator Interface
•1 USB 3.0
• Green, Amber, Blue LED’s
Cooling Fans (x4)
• Coun ter- Rotat ing
• Hot s wap
PCIe slot (1x)
• PCIe Gen3 x8 (CAPI)
PCIe slot (2x)
• PCIe Gen3 x16 (CAPI)
• PCIe Gen3 x8
NIVIDIA P100 GPU (4x)
• PCIe Gen3 (CAPI)
• 300W Capable
• PCIe riser cards
Power Supplies (2x)
• 1,300 W
• Hot Swap
Memory riser cards (8x)
• 1 Buffer Chip per Riser
• 4 DIMMs per Riser
• 32 DIMMs total
Front Bezel removed
Internal Storage
• 2 SFF-4 bays
• HHD or SSD
Figure 1-1 Front view of the Power S822LC server
1.1 Server features
The server chassis of the Power S822LC server contains two processor modules attached
directly to the board. Each POWER8 processor module is either 8-core or 10-core and has a
64-bit architecture, up to 512 KB of L2 cache per core, and up to 8 MB of L3 cache per core.
The clock speed of each processor available varies based on the model of the server that is
used.
The Power S822LC computing server provides eight DIMM memory slots. Memory features
that are supported are 16 GB (#EM55), 32 GB (#EM56), 64 GB (#EM57), and 128 GB
(#EM58), allowing for a maximum of 1024 GB DDR4 system memory.
The physical locations of the main server components are shown in Figure 1-2.
Figure 1-2 Location of server main components
The servers support four SXM2 form factor connectors for NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPU (#EC4C,
#EC4D, or #EC4F) only. Optional water cooling is available.
This summary describes the standard features of the Power S822LC model 8355-GTA
server:
19” rack-mount (2U) chassis
2 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 17

Two POWER8 processor modules:
– 8-core 3.3259 GHz processor module
– 10-core 2.860 GHz processor module
Up to 1024 GB of 1333 MHz DDR4 ECC memory
Two SFF bays for two HDDs or two SSDs that supports:
– Two 1 TB 7200 RPM NL SATA disk drives (#ELD0)
– Two 2 TB 7200 RPM NL SATA disk drives (#ES6A)
– Two 480 GB SATA SSDs (#ELS5)
– Two 960 GB SATA SSDs (#ELS6)
– Two 1.92 TB SATA SSDs (#ELSZ)
– Two 3.84 TB SATA SSDs (#ELU0)
Integrated SATA controller
Three PCIe Gen 3 slots:
– One PCIe x8 Gen3 Low Profile slot, CAPI enabled
– Two PCIe x16 Gen3 Low Profile slot, CAPI enabled
Four SXM2 form factor connectors for NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPU (#EC4C, #EC4D, or
#EC4F) only
Integrated features:
– EnergyScale™ technology
– Hot-swap and redundant cooling
– One front USB 2.0 port for general usage
– One rear USB 3.0 port for general usage
– One system port with RJ45 connector
Two power supplies
1.1.1 Minimum features
The minimum Power S822LC model 8355-GTB server initial order must include:
Two processor modules with at least 16 CPUs
128 GB of memory (eight 16 GB memory DIMMs)
Two #EC4C Compute Intensive Accelerator - NVIDIA GP100
Two power supplies and power cords
An OS indicator
A rack integration indicator
A Language Group Specify
Linux is the supported OS. The Integrated 1Gb Ethernet port can be used as the base LAN
port.
1.1.2 System cooling
Air or water cooling depends on the GPU that is installed. See 1.13.3, “Compute Intensive
Accelerator” on page 26 for a list of GPUs available.
Feature code #ER2D is the water cooling indicator for the 8335-GTB.
Note: If #ER2D is ordered, you must order #EJTX fixed rail kit. Ordering #ER2D with
#EJTY slide rails is not supported.
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 3
Page 18

1.2 The NVIDIA Tesla P100
NVIDIA’s new NVIDIA Tesla P100 accelerator (see Figure 1-3) takes GPU computing to the
next level. This section discusses the Tesla P100 accelerator.
Figure 1-3 NVIDIA Tesla P100 accelerator
With a 15.3 billion transistor GPU, a new high performance interconnect that greatly
accelerates GPU peer-to-peer and GPU-to-CPU communications, new technologies to
simplify GPU programming, and exceptional power efficiency, Tesla P100 is not only the most
powerful, but also the most architecturally complex GPU accelerator architecture ever built.
Key features of Tesla P100 include:
Extreme performance
Powering HPC, Deep Learning, and many more GPU Computing areas
NVLink
NVIDIA’s new high speed, high bandwidth interconnect for maximum application
scalability
HBM2
Fast, high capacity, extremely efficient CoWoS (Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate) stacked
memory architecture
Unified Memory, Compute Preemption, and New AI Algorithms
Significantly improved programming model and advanced AI software optimized for the
Pascal architecture;
16nm FinFET
Enables more features, higher performance, and improved power efficiency
4 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 19

The Tesla P100 was built to deliver exceptional performance for the most demanding
compute applications, delivering:
5.3 TFLOPS of double precision floating point (FP64) performance
10.6 TFLOPS of single precision (FP32) performance
21.2 TFLOPS of half-precision (FP16) performance
In addition to the numerous areas of high performance computing that NVIDIA GPUs have
accelerated for a number of years, most recently Deep Learning has become a very important
area of focus for GPU acceleration. NVIDIA GPUs are now at the forefront of deep neural
networks (DNNs) and artificial intelligence (AI). They are accelerating DNNs in various
applications by a factor of 10x to 20x compared to CPUs, and reducing training times from
weeks to days. In the past three years, NVIDIA GPU-based computing platforms have helped
speed up Deep Learning network training times by a factor of fifty. In the past two years, the
number of companies NVIDIA collaborates with on Deep Learning has jumped nearly 35x to
over 3,400 companies.
New innovations in the Pascal architecture, including native 16-bit floating point (FP)
precision, allow GP100 to deliver great speedups for many Deep Learning algorithms. These
algorithms do not require high levels of floating-point precision, but they gain large benefits
from the additional computational power FP16 affords, and the reduced storage requirements
for 16-bit datatypes.
For more detailed information on the NVIDA Tesla P100, see:
https://devblogs.nvidia.com/parallelforall/inside-pascal/
1.3 Operating system support
The Power S822LC (8335-GTB) server supports Linux, which provides a UNIX like
implementation across many computer architectures.
For more information about the software that is available on Power Systems, see the Linux on
Power Systems website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/software/linux/index.html
The Linux operating system is an open source, cross-platform OS. It is supported on every
Power Systems server IBM sells. Linux on Power Systems is the only Linux infrastructure that
offers both scale-out and scale-up choices.
1.3.1 Ubuntu
Ubuntu Server 16.04, at the time of writing, is the supported OS for the S822LC.
For more information about Ubuntu Server for Ubuntu for POWER8, see the following
website:
http://www.ubuntu.com/download/server/power8
1.3.2 Additional information
For more information about the IBM PowerLinux™ Community, see the following website:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/group/tpl
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 5
Page 20

For more information about the features and external devices that are supported by Linux,
see the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/software/linux/index.html
1.4 Operating environment
Table 1-1 provides the operating environment specifications for the Power S822LC servers.
Table 1-1 Operating environment for Power S822LC servers
Power S822LC server operating environment
Description Operating Non-operating
Temperature Allowable: 5 - 40 degrees Ca
(41 - 104 degrees F)
Recommended: 18 - 27
degrees C
(64 - 80 degrees F)
Relative humidity 8 - 80% 8 - 80%
Maximum dew point 24 degrees C (75 degrees F) 27 degrees C (80 degrees F)
Operating voltage 200 - 240 V AC N/A
Operating frequency 50 - 60 Hz +/- 3 Hz N/A
Power consumption 2550 watts maximum N/A
Power source loading 2.6 kVA maximum N/A
Thermal output 8703 BTU/hr maximum N/A
Maximum altitude 3,050 m
(10,000 ft)
Noise level and sound power 7.6/6.7 bels operating/ idling N/A
a. Heavy workloads might see some performance degradation above 35 degrees C if internal
temperatures trigger a CPU clock reduction.
1 - 60 degrees C
(34 - 140 degrees F)
N/A
Tip: The maximum measured value is expected from a fully populated server under an
intensive workload. The maximum measured value also accounts for component tolerance
and operating conditions that are not ideal. Power consumption and heat load vary greatly
by server configuration and usage. Use the IBM Systems Energy Estimator to obtain a
heat output estimate that is based on a specific configuration, which is available at the
following website:
http://www-912.ibm.com/see/EnergyEstimator
1.5 Physical package
Table 1-2 on page 7 shows the physical dimensions of the Power S822LC chassis. The
servers are available only in a rack-mounted form factor and take 2U (2 EIA units) of rack
space.
6 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 21

Table 1-2 Physical dimensions for the Power S822LC servers
Dimension Power S822LC (8335-GTB) server
Width 441.5 mm (17.4 in.)
Depth 822 mm (32.4 in.)
Height 86 mm (3.4 in.)
Weight (maximum configuration) 30 kg (65 lbs.)
1.6 System architecture
This section describes the overall system architecture for the Power S822LC computing
servers. The bandwidths that are provided throughout the section are theoretical maximums
that are used for reference.
The speeds that are shown are at an individual component level. Multiple components and
application implementation are key to achieving the preferred performance. Always do the
performance sizing at the application workload environment level and evaluate performance
by using real-world performance measurements and production workloads.
The Power S822LC server is a two single chip module (SCM) system. Each SCM is attached
to four memory riser cards that have buffer chips for the L4 Cache and four memory RDIMM
slots. The server has a maximum capacity of 32 memory DIMMs when all the memory riser
cards are populated, which allows for up to 1024 GB of memory.
The servers have a total of three PCIe Gen3 slots with all of these slots being CAPI-capable.
The system has sockets for four GPUs each 300 W capable.
An integrated SATA controller is fed through a dedicated PCI bug on the main system board
and allows for up to two SATA HDDs or SSDs to be installed. This bus also drives the
integrated Ethernet and USB port.
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 7
Page 22

B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
B
u
f
f
e
r
C
a
c
h
e
L
4
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
R
D
I
M
M
P
H
B
0
P
H
B
1
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
P
H
B
0
P
H
B
1
P
C
I
e
G
e
n
3
x
8
C
A
P
I
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
P
C
I
e
G
e
n
3
x
1
6
C
A
P
I
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
P
C
I
e
G
e
n
3
x
1
6
C
A
P
I
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
SATA
Controller
SFF-4
HDD/
SSD
USB 3.0
Front
USB 3.0
Rear
VGA
Management
1 Gbps
Ethernet
System Planar
12.8 GBps
28.8 GBps
x
8
x
1
6
x
8
x
1
6
POWER8
SCM0
POWER8
SCM1
SFF-4
HDD/
SSD
PLX
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
Figure 1-4 shows the logical system diagram for the Power S822LC servers.
Figure 1-4 Power S822LC server logical system diagram
8 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 23

1.7 The POWER8 processor
This section introduces the latest processor in the Power Systems product family and
describes its main characteristics and features in general.
The POWER8 processor in the S822LC for High Performance Computing is unique to the
8335-GTB. Engineers removed the A-Bus interface along with SMP over PCI support to make
room for the NVLink interface. The resulting chip grows slightly from 649 mm
1.7.1 POWER8 processor overview
2
to 659 mm2.
The POWER8 processor is manufactured by using the IBM 22 nm Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI)
technology. Each chip is 649 mm
the chip contains up to 12 cores, two memory controllers, Peripheral Component Interconnect
Express (PCIe) Gen3 I/O controllers, and an interconnection system that connects all
components within the chip. Each core has 512 KB of L2 cache, and all cores share 96 MB of
L3 embedded DRAM (eDRAM). The interconnect also extends through module and system
board technology to other POWER8 processors in addition to DDR4 memory and various I/O
devices.
POWER8 processor-based systems use memory buffer chips to interface between the
POWER8 processor and DDR4 memory. Each buffer chip also includes an L4 cache to
reduce the latency of local memory accesses.
2
and contains 4.2 billion transistors. As shown in Figure 1-5,
Figure 1-5 The POWER8 processor chip
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 9
Page 24

Here are additional features that can augment the performance of the POWER8 processor:
Support for DDR4 memory through memory buffer chips that offload the memory support
from the POWER8 memory controller.
An L4 cache within the memory buffer chip that reduces the memory latency for local
access to memory behind the buffer chip; the operation of the L4 cache is not apparent to
applications running on the POWER8 processor. Up to 128 MB of L4 cache can be
available for each POWER8 processor.
Hardware transactional memory.
On-chip accelerators, including on-chip encryption, compression, and random number
generation accelerators.
CAPI, which allows accelerators that are plugged into a PCIe slot to access the processor
bus by using a low latency, high-speed protocol interface.
Adaptive power management.
Table 1-3 summarizes the technology characteristics of the POWER8 processor.
Table 1-3 Summary of POWER8 processor technology
Technology 8335-GTB POWER8 processor
Die size 659 mm
Fabrication technology 22 nm lithography
Copper interconnect
SOI
eDRAM
2
Maximum processor cores 12
Maximum execution threads core/chip 8/96
Maximum L2 cache core/chip 512 KB/6 MB
Maximum On-chip L3 cache core/chip 8 MB/96 MB
Maximum L4 cache per chip 128 MB
Maximum memory controllers 2
SMP design-point 16 sockets with POWER8 processors
Compatibility Specific to the 8335-GTB
10 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 25

Figure 1-6 on page 11 shows the areas of the processor that were modified to include the
2 C4 rows
added
x8 I OP
x8 P HB
NVLink support added in extended ESA-bus removed, NVLink added
Chip height:
2
nd
CAPP unit added, X2 r emoved
NVLink and additional CAPI interface.
Figure 1-6 Areas modified on the POWER8 processor core
1.7.2 POWER8 processor core
The POWER8 processor core is a 64-bit implementation of the IBM Power Instruction Set
Architecture (ISA) Version 2.07 and has the following features:
Multi-threaded design, which is capable of up to eight-way simultaneous multithreading
(SMT)
32 KB, eight-way set-associative L1 instruction cache
64 KB, eight-way set-associative L1 data cache
Enhanced prefetch, with instruction speculation awareness and data prefetch depth
awareness
Enhanced branch prediction, which uses both local and global prediction tables with a
selector table to choose the preferred predictor
Improved out-of-order execution
Two symmetric fixed-point execution units
Two symmetric load/store units and two load units, all four of which can also run simple
fixed-point instructions
An integrated, multi-pipeline vector-scalar floating point unit for running both scalar and
SIMD-type instructions, including the Vector Multimedia eXtension (VMX) instruction set
and the improved Vector Scalar eXtension (VSX) instruction set, and capable of up to
eight floating point operations per cycle (four double precision or eight single precision)
In-core Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption capability
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 11
Page 26

Hardware data prefetching with 16 independent data streams and software control
Hardware decimal floating point (DFP) capability.
More information about Power ISA Version 2.07 can be found at the following website:
https://www.power.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/PowerISA_V2.07_PUBLIC.pdf
Figure 1-7 shows a picture of the POWER8 core, with some of the functional units
highlighted.
Figure 1-7 POWER8 processor core
1.7.3 Simultaneous multithreading
Simultaneous multithreading (SMT) allows a single physical processor core to dispatch
simultaneously instructions from more than one hardware thread context. With SMT, each
POWER8 core can present eight hardware threads. Because there are multiple hardware
threads per physical processor core, additional instructions can run at the same time. SMT is
primarily beneficial in commercial environments where the speed of an individual transaction
is not as critical as the total number of transactions that are performed. SMT typically
increases the throughput of workloads with large or frequently changing working sets, such
as database servers and web servers.
Table 1-4 shows a comparison between the different POWER processors options for a
Power S822LC server and the number of threads that are supported by each SMT mode.
Table 1-4 SMT levels that are supported by a Power S822LC server
Cores per system SMT mode Hardware threads per system
16 Single Thread (ST) 16
16 SMT2 32
16 SMT4 64
16 SMT8 128
20 Single Thread (ST) 20
20 SMT2 40
20 SMT4 80
12 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 27

20 SMT8 160
POWER8
SCM
Memory
Controller
Memory
Controller
Buffer
Chip
Buffer
Chip
Buffer
Chip
16 MB
L4
Cache
Memory
Riser Card
4 x RDIMMs
28.8 GBps
The architecture of the POWER8 processor, with its larger caches, larger cache bandwidth,
and faster memory, allows threads to have faster access to memory resources, which
translates into a more efficient usage of threads. Therefore, POWER8 allows more threads
per core to run concurrently, increasing the total throughput of the processor and of the
system.
1.7.4 Memory access
On the Power S822LC server, each POWER8 module has two memory controllers, each
connected to two memory channels. Each memory channel operates at 1600 MHz and
connects to a memory riser card. Each memory riser card has a memory buffer that is
responsible for many functions that were previously on the memory controller, such as
scheduling logic and energy management. The memory buffer also has 16 MB of L4 cache.
Also, the memory riser card houses four industry-standard RDIMMs.
Each memory channel can address up to 64 GB. Therefore, the Power S822LC server can
address up to 1 TB (1024 GB) of total memory.
Figure 1-8 shows a POWER8 processor that is connected to four memory riser cards and its
components.
Figure 1-8 Logical diagram of the POWER8 processor connected to four memory riser cards
1.7.5 On-chip L3 cache innovation and Intelligent Cache
The POWER8 processor uses a breakthrough in material engineering and microprocessor
fabrication to implement the L3 cache in eDRAM and place it on the processor die. L3 cache
is critical to a balanced design, as is the ability to provide good signaling between the L3
cache and other elements of the hierarchy, such as the L2 cache or SMP interconnect.
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 13
Page 28

The on-chip L3 cache is organized into separate areas with differing latency characteristics.
Each processor core is associated with a fast 8 MB local region of L3 cache (FLR-L3), but
also has access to other L3 cache regions as shared L3 cache. Additionally, each core can
negotiate to use the FLR-L3 cache that is associated with another core, depending on
reference patterns. Data can also be cloned to be stored in more than one core’s FLR-L3
cache, again depending on reference patterns. This
the POWER8 processor to optimize the access to L3 cache lines and minimize overall cache
latencies.
Figure 1-5 on page 9 show the on-chip L3 cache, and highlights the fast 8 MB L3 region that
is closest to a processor core.
The innovation of using eDRAM on the POWER8 processor die is significant for several
reasons:
Latency improvement
A six-to-one latency improvement occurs by moving the L3 cache on-chip compared to L3
accesses on an external (on-ceramic) Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC).
Bandwidth improvement
A 2x bandwidth improvement occurs with on-chip interconnect. Frequency and bus sizes
are increased to and from each core.
No off-chip driver or receivers
Removing drivers or receivers from the L3 access path lowers interface requirements,
conserves energy, and lowers latency.
Intelligent Cache management enables
Small physical footprint
The performance of eDRAM when implemented on-chip is similar to conventional SRAM
but requires far less physical space. IBM on-chip eDRAM uses only a third of the
components that conventional SRAM uses, which has a minimum of six transistors to
implement a 1-bit memory cell.
Low energy consumption
The on-chip eDRAM uses only 20% of the standby power of SRAM.
1.7.6 L4 cache and memory buffer
POWER8 processor-based systems introduce an additional level in memory hierarchy. The
L4 cache is implemented together with the memory buffer in the memory riser cards. Each
memory buffer contains 16 MB of L4 cache. On a Power S822LC server, you can have up to
128 MB of L4 cache by using all the eight memory riser cards.
14 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 29

Figure 1-9 shows a picture of the memory buffer, where you can see the 16 MB L4 cache and
processor links and memory interfaces.
Figure 1-9 Memory buffer chip
1.7.7 Hardware transactional memory
Transactional memory is an alternative to lock-based synchronization. It attempts to simplify
parallel programming by grouping read and write operations and running them as a single
operation. Transactional memory is like database transactions, where all shared memory
accesses and their effects are either committed all together or discarded as a group. All
threads can enter the critical region simultaneously. If there are conflicts in accessing the
shared memory data, threads try accessing the shared memory data again or are stopped
without updating the shared memory data. Therefore, transactional memory is also called a
lock-free synchronization. Transactional memory can be a competitive alternative to
lock-based synchronization.
Transactional memory provides a programming model that makes parallel programming
easier. A programmer delimits regions of code that access shared data and the hardware
runs these regions atomically and in isolation, buffering the results of individual instructions,
and trying execution again if isolation is violated. Generally, transactional memory allows
programs to use a programming style that is close to coarse-grained locking to achieve
performance that is close to fine-grained locking.
Most implementations of transactional memory are based on software. The POWER8
processor-based systems provide a hardware-based implementation of transactional memory
that is more efficient than the software implementations and requires no interaction with the
processor core, therefore allowing the system to operate in maximum performance.
1.7.8 Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface
Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface (CAPI) defines a coherent accelerator interface
structure for attaching special processing devices to the POWER8 processor bus.
The CAPI can attach accelerators that have coherent shared memory access with the
processors in the server and share full virtual address translation with these processors,
which use a standard PCIe Gen3 bus.
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 15
Page 30

Applications can have customized functions in FPGAs and enqueue work requests directly in
Custom
Hardware
Application
CAPP
Coherence Bus
PSL
FPGA or ASIC
POWER8
PCIe Gen3
Transport for encapsulated messages
shared memory queues to the FPGA, and by using the same effective addresses (pointers) it
uses for any of its threads running on a host processor. From a practical perspective, CAPI
allows a specialized hardware accelerator to be seen as an additional processor in the
system, with access to the main system memory, and coherent communication with other
processors in the system.
The benefits of using CAPI include the ability to access shared memory blocks directly from
the accelerator, perform memory transfers directly between the accelerator and processor
cache, and reduce the code path length between the adapter and the processors. This is
possibly because the adapter is not operating as a traditional I/O device, and there is no
device driver layer to perform processing. It also presents a simpler programming model.
Figure 1-10 shows a high-level view of how an accelerator communicates with the POWER8
processor through CAPI. The POWER8 processor provides a Coherent Attached Processor
Proxy (CAPP), which is responsible for extending the coherence in the processor
communications to an external device. The coherency protocol is tunneled over standard
PCIe Gen3, effectively making the accelerator part of the coherency domain.
Figure 1-10 CAPI accelerator that is attached to the POWER8 processor
The accelerator adapter implements the Power Service Layer (PSL), which provides address
translation and system memory cache for the accelerator functions. The custom processors
on the system board, consisting of an FPGA or an ASIC, use this layer to access shared
memory regions, and cache areas as though they were a processor in the system. This ability
enhances the performance of the data access for the device and simplifies the programming
effort to use the device. Instead of treating the hardware accelerator as an I/O device, it is
treated as a processor, which eliminates the requirement of a device driver to perform
communication, and the need for Direct Memory Access that requires system calls to the
operating system (OS) kernel. By removing these layers, the data transfer operation requires
much fewer clock cycles in the processor, improving the I/O performance.
The implementation of CAPI on the POWER8 processor allows hardware companies to
develop solutions for specific application demands and use the performance of the POWER8
processor for general applications and the custom acceleration of specific functions by using
a hardware accelerator, with a simplified programming model and efficient communication
with the processor and memory resources.
16 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 31

For a list of supported CAPI adapters, see 1.13.5, “CAPI enabled Infiniband adapters” on
page 27.
1.7.9 NVLink
NVLink is NVIDIA’s new high-speed interconnect technology for GPU-accelerated computing.
Supported on SXM2 based Tesla P100 accelerator boards, NVLink significantly increases
performance for both GPU-to-GPU communications, and for GPU access to system memory.
Today, multiple GPUs are common in workstations as well as the nodes of HPC computing
clusters and deep learning training systems. A powerful interconnect is extremely valuable in
multiprocessing systems. Our vision for NVLink was to create an interconnect for GPUs that
would offer much higher bandwidth than PCI Express Gen3 (PCIe), and be compatible with
the GPU ISA to support shared memory multiprocessing workloads.
Support for the GPU ISA means that programs running on NVLink-connected GPUs can
execute directly on data in the memory of another GPU as well as on local memory. GPUs
can also perform atomic memory operations on remote GPU memory addresses, enabling
much tighter data sharing and improved application scaling.
NVLink uses NVIDIA’s new High-Speed Signaling interconnect (NVHS). NVHS transmits data
over a differential pair running at up to 20 Gb/sec. Eight of these differential connections form
a
Link that connects two processors (GPU-to-GPU or GPU-to-CPU). A single Link supports up
to 40 GB/sec of bidirectional bandwidth between the endpoints. Multiple Links can be
combined to form
NVLink implementation in Tesla P100 supports up to four Links, allowing for a gang with an
aggregate maximum theoretical bandwidth of 160 GB/sec bidirectional bandwidth.
Sub-Link that sends data in one direction, and two sub-links - one for each direction - form a
Gangs for even higher-bandwidth connectivity between processors. The
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 17
Page 32
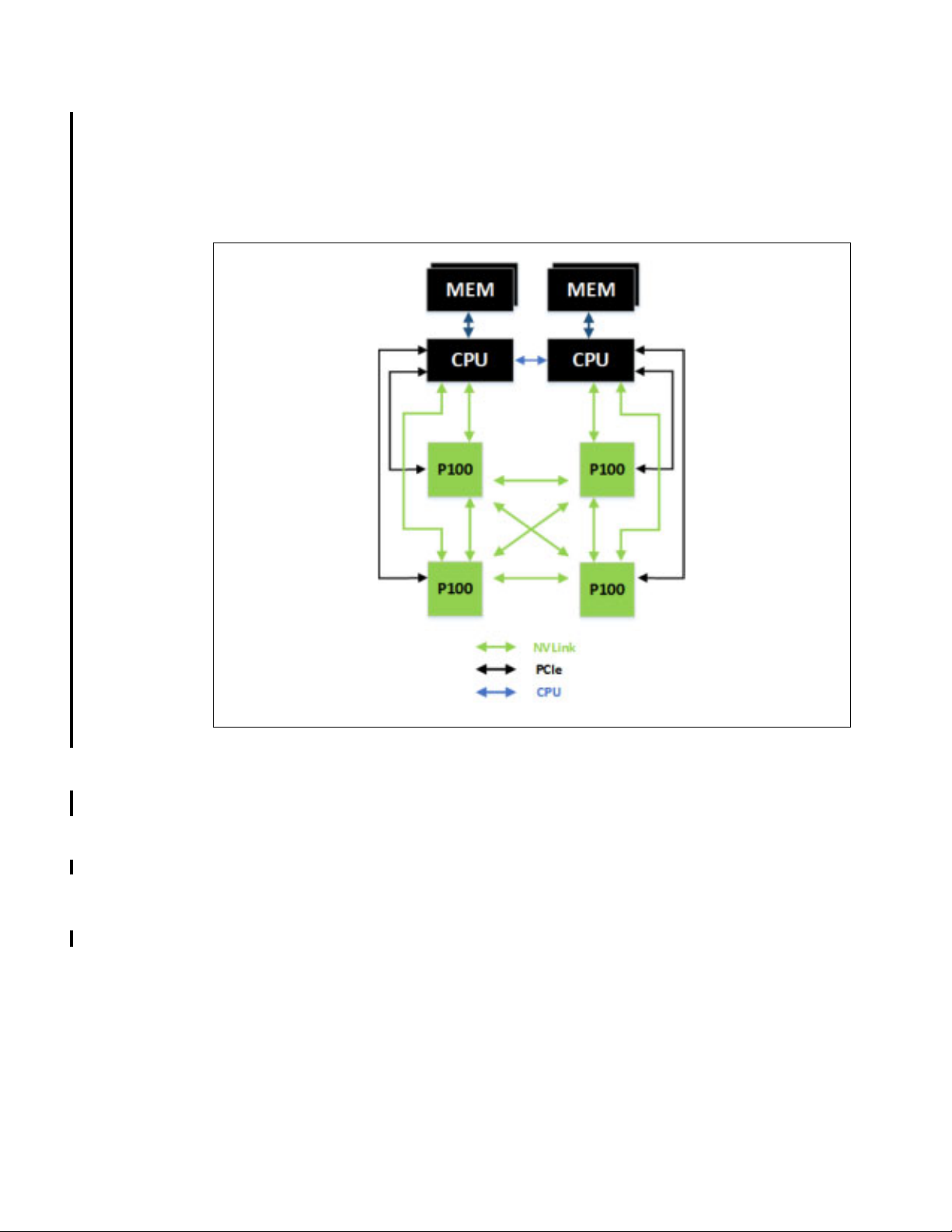
While NVLink primarily focuses on connecting multiple NVIDIA Tesla P100s together it can
also connect Tesla P100 GPUs with IBM Power CPUs with NVLink support. Figure 1-11 on
page 18 highlights an example of a four-GPU system with dual NVLink-capable CPUs
connected with NVLink. In this configuration, each GPU has 120 combined GB/s bidirectional
bandwidth to the other three GPUs in the system, and 40 GB/s bidirectional bandwidth to a
CPU.
Figure 1-11 CPU to GPU and GPU to GPU interconnect using NVLink
1.8 Memory subsystem
The Power S822LC server is a two-socket system that supports two POWER8 SCM
processor modules. The server supports a maximum of 32 DDR4 RDIMMs slots housed in
eight memory riser cards.
Memory features equate to a riser card with four memory DIMMs. Memory feature codes that
are supported are 16 GB, 32 GB, 64 GB, and 128 GB, and run at speeds of 1600 MHz,
allowing for a maximum system memory of 1024 GB.
1.8.1 Memory riser cards
Memory riser cards are designed to house up to four industry-standard DRAM memory
DIMMs and include a set of components that allow for higher bandwidth and lower latency
communications:
Memory Scheduler
Memory Management (RAS Decisions & Energy Management)
18 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 33

Buffer Cache
Connection to system backplane
DDR3 DIMM (4x)
Memory Buffer
By adopting this architecture, several decisions and processes regarding memory
optimizations are run outside the processor, saving bandwidth and allowing for faster
processor to memory communications. It also allows for more robust reliability, availability,
and serviceability (RAS). For more information about RAS, see 2.3, “Reliability, availability,
and serviceability” on page 33.
A detailed diagram of the memory riser card that is available for the Power S822LC server
and its location on the server are shown in Figure 1-12.
Figure 1-12 Memory riser card components and server location
The buffer cache is a L4 cache and is built on eDRAM technology (same as the L3 cache),
which has lower latency than regular SRAM. Each memory riser card has a buffer chip with
16 MB of L4 cache, and a fully populated Power S822LC server (two processors and eight
memory riser cards) has 128 MB of L4 cache. The L4 cache performs several functions that
have a direct impact on performance and brings a series of benefits for the Power S822LC
server:
Reduces energy consumption by reducing the number of memory requests.
Increases memory write performance by acting as a cache and by grouping several
random writes into larger transactions.
Partial write operations that target the same cache block are “gathered” within the L4
cache before written to memory, becoming a single write operation.
Reduces latency on memory access. Memory access for cached blocks has up to 55%
lower latency than non-cached blocks.
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 19
Page 34
1.8.2 Memory placement rules
Each feature code equates to a riser card with four memory DIMMs.
The following memory feature codes are orderable:
16 GB DDR4: A riser card with four 4 GB 1600 MHz DDR4 DRAMs (#EM55)
32 GB DDR4: A riser card with four 8 GB 1600 MHz DDR4 DRAMs (#EM56)
64 GB DDR4: A riser card with four 16 GB 1600 MHz DDR4 DRAMs (#EM57)
128 GB DDR4: A riser card with four 32 GB 1600 MHz DDR4 DRAMs (#EM58)
The supported maximum memory is 1024 GB by installing a quantity of eight #EM58
components.
For the Power S822LC model 8335-GTB server:
It is required that all the memory modules be populated.
Memory features cannot be mixed.
The base memory is 128 GB with eight 16 GB, 1600 MHz DDR3 memory modules
(#EM55).
Memory upgrades are not supported.
Table 1-5 shows the supported quantities for each memory feature code.
Table 1-5 Supported quantity of feature codes for model 8335-GTB
Memory features 128 GB 256 GB 512 GB 1024 GB
16 GB (#EM55) 8
32 GB (#EM56) 8
64 GB (#EM57) 8
128 GB (#EM58) 8
1.8.3 Memory bandwidth
The POWER8 processor has exceptional cache, memory, and interconnect bandwidths.
Table 1-6 shows the maximum bandwidth estimates for a single core on the Power S822LC
server.
Table 1-6 Power S822LC single-core bandwidth estimates
Single core 8335-GTB
L1 (data) cache 137.28 GBps 156.43 GBps
L2 cache 137.28 GBps 156.43 GBps
Total installed memory
2.860 GHz 3.259 GHz
L3 cache 183.04 GBps 208.57 GBps
20 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 35
The bandwidth figures for the caches are calculated as follows:
L1 cache: In one clock cycle, two 16-byte load operations and one 16-byte store operation
can be accomplished. The value varies depending on the clock of the core, and the
formulas are as follows:
– 2.860 GHz Core: (2 * 16 B + 1 * 16 B) * 2.860 GHz = 137.28 GBps
– 3.259 GHz Core: (2 * 16 B + 1 * 16 B) * 3.259 GHz = 156.43 GBps
L2 cache: In one clock cycle, one 32-byte load operation and one 16-byte store operation
can be accomplished. The value varies depending on the clock of the core, and the
formula is as follows:
– 2.860 GHz Core: (1 * 32 B + 1 * 16 B) * 2.860 GHz = 137.28 GBps
– 3.259 GHz Core: (1 * 32 B + 1 * 16 B) * 3.259 GHz = 156.43 GBps
L3 cache: One 32-byte load operation and one 32-byte store operation can be
accomplished at half-clock speed, and the formula is as follows:
– 2.860 GHz Core: (1 * 32 B + 1 * 32 B) * 2.860 GHz = 183.04 GBps
– 3.259 GHz Core: (1 * 32 B + 1 * 32 B) * 3.259 GHz = 208.57 GBps
For the entire Power S822LC server populated with the two processor modules, the overall
bandwidths are shown in Table 1-7.
Table 1-7 Power S822LC server - total bandwidth estimates
Total bandwidths 8335-GCB
20 cores @ 2.860 GHz 16 cores @ 3.259 GHz
L1 (data) cache 2,746 GBps 2,503 GBps
L2 cache 2,746 GBps 2,503 GBps
L3 cache 3,661 GBps 3,337 GBps
Total memory 230 GBps 230 GBps
PCIe Interconnect 128 GBps 128 GBps
Where:
Total memory bandwidth: Each POWER8 processor has four memory channels running at
9.6 GBps capable of writing 2 bytes and reading 1 byte at a time. The bandwidth formula is
calculated as follows:
Four channels * 9.6 GBps * 3 bytes = 192 GBps per processor module
SMP interconnect: The POWER8 processor has two 2-byte 3-lane A buses working at
6.4 GHz. Each A bus has three active lanes. The bandwidth formula is calculated as
follows:
3 A buses * 2 bytes * 6.4 GHz = 38.4 GBps
PCIe Interconnect: Each POWER8 processor has 32 PCIe lanes running at 8 Gbps
full-duplex. The bandwidth formula is calculated as follows:
Thirty-two lanes * 2 processors * 8 Gbps * 2 = 128 GBps
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 21
Page 36

1.9 System bus
This section provides more information about the internal buses.
The Power S822LC servers have internal I/O connectivity through Peripheral Component
Interconnect Express Gen3 (PCI Express Gen3 or PCIe Gen3) slots.
The internal I/O subsystem on the systems is connected to the PCIe controllers on a
POWER8 processor in the system. Each POWER8 processor has a bus that has 32 PCIe
lanes running at 9.6 Gbps full-duplex and provides 64 GBps of I/O connectivity to the PCIe
slots, SAS internal adapters, and USB ports.
Some PCIe devices are connected directly to the PCIe Gen3 buses on the processors, and
other devices are connected to these buses through PCIe Gen3 Switches. The PCIe Gen3
switches are high-speed devices (512 GBps - 768 GBps each) that allow for the optimal
usage of the processors PCIe Gen3 x16 buses by grouping slower x8 or x4 devices that might
plug into a x8 slot and not use its full bandwidth. For more information about which slots are
connected directly to the processor and which ones are attached to PCIe Gen3 switches
(referred as PLX), see 1.7, “The POWER8 processor” on page 9.
22 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 37

A diagram showing the Power S822LC server buses and logical architecture is shown in
P
H
B
0
P
H
B
1
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
P
H
B
0
P
H
B
1
P
C
I
e
G
e
n
3
x
8
C
A
P
I
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
P
C
I
e
G
e
n
3
x
1
6
C
A
P
I
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
P
C
I
e
G
e
n
3
x
1
6
C
A
P
I
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
SATA
Controller
SFF-4
HDD/
SSD
USB 3.0
Front
USB 3.0
Rear
VGA
Management
1 Gbps
Ethernet
12.8 GBps
x
8
x
1
6
x
8
x
1
6
POWER8
SCM0
POWER8
SCM1
SFF-4
HDD/
SSD
PLX
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
M
e
m
o
r
y
C
o
n
t
r
o
l
l
e
r
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
L
i
n
k
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
N
V
I
D
I
A
P
1
0
0
S
X
M
2
.
0
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
S
M
P
A
B
u
s
Figure 1-13.
Figure 1-13 Power S822LC server buses and logical architecture
Each processor has 32 PCIs lanes split into three channels: two channels are PCIe Gen3 x8
and one channel is PCIe Gen 3 x16.
The PCIe channels are connected to the PCIe slots, which can support GPUs and other
high-performance adapters, such as InfiniBand.
Table 1-8 lists the total I/O bandwidth of a Power S822LC server.
Table 1-8 I/O bandwidth
I/O I/O bandwidth (maximum theoretical)
Total I/O bandwidth 64 GBps simplex
128 GBps duplex
For the PCIe Interconnect, each POWER8 processor has 32 PCIe lanes running at 9.6 Gbps
full-duplex. The bandwidth formula is calculated as follows:
Thirty-two lanes * 2 processors * 9.6 Gbps * 2 = 128 GBps
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 23
Page 38

1.10 Internal I/O subsystem
IBM Confidential
PCIe Slot 1
• Gen 3 x 16 Interfac e
• CAPI enabled
• Full height, full length slot
PCIe Slot 2
• Gen 3 x 8 Interf ace
• Half height, half length slot
• PLX switch base
PCIe Slot 3
• Gen 3 x 16 Interfac e
• Half height, half length slot
• CAPI Enabled
USB 3.0
1Gb EN IPMI VGA
The internal I/O subsystem is on the system board, which supports PCIe slots. PCIe adapters
on the Power S822LC server are not hot-pluggable.
1.11 Slot configuration
The Power S822LC server has three PCIe Gen3 slots.
Figure 1-14 is a rear view diagram of the PCIe slots for the Power S822LC server.
Figure 1-14 Power S822LC server rear view PCIe slots and connectors
Table 1-9 shows the PCIe Gen3 slot configuration for the Power S822LC server.
Table 1-9 Power S822LC server PCIe slot properties
Slot Description Card size CAPI
Slot 1
PCIe Gen3 x16 Half height,
half length
Slot 2 PCIe Gen3 x8 Half height,
half length
Slot 3 PCIe Gen3 x16 Full height,
half length
24 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Power limit
capable
Ye s 7 5 W
Ye s 5 0 W
Ye s 7 5 W
Page 39

The two x16 slots that are provided by the internal PCIe riser (Slot 1 and Slot 3) can be
populated with GPU adapters (NVIDIA) or can be used for any high-profile (not LP) adapters.
Mixing of GPU and other high-profile adapters on the internal PCIe riser is supported.
Only LP adapters can be placed in LP slots. An x8 adapter can be placed in an x16 slot, but
an x16 adapter cannot be placed in an x8 slot. One LP slot must be used for a required
Ethernet adapter (#5260, #EL3Z, or #EN0T).
1.12 System ports
The system board has one 1 Gbps Ethernet port, one Intelligent Platform Management
Interface (IPMI) port and a VGA port, as shown in Figure 1-14 on page 24.
The integrated system ports are supported for modem and asynchronous terminal
connections with Linux. Any other application that uses serial ports requires a serial port
adapter to be installed in a PCI slot. The integrated system ports do not support IBM
PowerHA® configurations. The VGA port does not support cable lengths that exceed
3 meters.
1.13 PCI adapters
This section covers the various types and functions of the PCI adapters that are supported by
the Power S822LC servers.
1.13.1 PCI Express
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) uses a serial interface and allows for
point-to-point interconnections between devices (by using a directly wired interface between
these connection points). A single PCIe serial link is a dual-simplex connection that uses two
pairs of wires, one pair for transmit and one pair for receive, and can transmit only one bit per
cycle. These two pairs of wires are called a
these configurations, the connection is labeled as x1, x2, x8, x12, x16, or x32, where the
number is effectively the number of lanes.
The PCIe interfaces that are supported on this server are PCIe Gen3, which are capable of
16 GBps simplex (32 GBps duplex) on a single x16 interface. PCIe Gen3 slots also support
previous generation (Gen2 and Gen1) adapters, which operate at lower speeds, according to
the following rules:
Place x1, x4, x8, and x16 speed adapters in the same size connector slots first, before
mixing adapter speed with connector slot size.
Adapters with lower speeds are allowed in larger sized PCIe connectors, but larger speed
adapters are not compatible in smaller connector sizes (that is, a x16 adapter cannot go in
an x8 PCIe slot connector).
PCIe adapters use a different type of slot than PCI adapters. If you attempt to force an
adapter into the wrong type of slot, you might damage the adapter or the slot.
lane. A PCIe link can consist of multiple lanes. In
POWER8 based servers can support two different form factors of PCIe adapters:
PCIe low profile (LP) cards, which are used with the Power S822L server.
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 25
Page 40
PCIe full height and full high cards are designed for the 4 EIA scale-out servers, such as
the Power S824L server.
Before adding or rearranging adapters, use the System Planning Tool to validate the new
adapter configuration. For more information, see the System Planning Tool website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/support/tools/systemplanningtool/
If you are installing a new feature, ensure that you have the software that is required to
support the new feature and determine whether there are any existing update prerequisites to
install. To obtain this information, use the IBM prerequisite website:
https://www-912.ibm.com/e_dir/eServerPreReq.nsf
The following sections describe the supported adapters and provide tables of orderable
feature code numbers.
1.13.2 LAN adapters
To connect the Power S822LC servers to a local area network (LAN), you can use the LAN
adapters that are supported in the PCIe slots of the system unit. Table 1-10 lists the
supported local area network (LAN) adapters for the Power S822LC servers.
Table 1-10 Supported LAN adapters)
Feature
code
Description Max OS
support
EC3A PCIe3 LP 2-Port 40 GbE NIC RoCE QSFP+ Adapter 2 Linux
EL3Z PCIe2 LP 2-port 10/1 GbE BaseT RJ45 Adapter 3 Linux
EL4M PCIe2 x4 LP 4-port (UTP) 1GbE Adapter 3 Linux
EN0T PCIe2 LP 4-Port (10Gb+1 GbE) SR+RJ45 Adapter 3 Linux
EN0v PCIe2 LP 4-port (10Gb+1GbE) Copper SFP+RJ45 Adapter 3 Linux
1.13.3 Compute Intensive Accelerator
Compute Intensive Accelerators are GPUs that are developed by NVIDIA. With NVIDIA
GPUs, the Power S822LC server can offload processor-intensive operations to a GPU
accelerator and boost performance. The Power S822LC server aims to deliver a new class of
technology that maximizes performance and efficiency for all types of scientific, engineering,
Java, big data analytics, and other technical computing workloads.
Table 1-11 on page 26 lists the available Compute Intensive Accelerators.
Table 1-11 Graphics processing units adapters that are supported
Feature
code
EC4C Two Air-Cooled NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs (for First Pair) 2 Linux
Description Max OS
support
EC4D Two Air-Cooled NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs (for Second Pair) 2 Linux
EC4F Four Water-Cooled NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs 4 Linux
26 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 41

1.13.4 Fibre Channel adapters
The Power S822LC server support direct or SAN connection to devices that use Fibre
Channel adapters. Table 1-12 summarizes the available Fibre Channel adapters, which all
have LC connectors.
If you are attaching a device or switch with an SC type fiber connector, then an LC-SC 50
Micron Fibre Converter Cable (#2456) or an LC-SC 62.5 Micron Fibre Converter Cable
(#2459) is required.
Table 1-12 Fibre Channel adapters supported
Feature
code
EL43 PCIe3 LP 16Gb 2-port Fibre Channel Adapter 2 Linux
Description Max OS
1.13.5 CAPI enabled Infiniband adapters
The available CAPI adapters are shown in Table 1-13.
Table 1-13 Available CAPI adapters
Feature
code
Description Max OS support
support
EC3E PCIe3 LP 2-port 100Gb EDR InfiniBand Adapter x16 2 Linux
EC3T PCIe3 LP 1-port 100Gb EDR InfiniBand Adapter x16 2 Linux
1.14 Internal storage
The internal storage on the Power S822LC server contains the following features:
A storage backplane for two 2.5-inch SFF Gen4 SATA HDDs or SDDs.
Limitation: The disks use an SFF-4 carrier. Disks that are used in other Power
Systems usually have SFF-3 or SFF-2 carrier and are not compatible with this system.
One integrated SATA disk controller without RAID capability.
The storage split backplane feature is not supported.
Table 1-14 on page 27 presents a summarized view of these features.
Table 1-14 Summary of features for the integrated SATA disk controller
Option Integrated SATA disk controller
Supported RAID types JBOD
Disk bays Two SFF Gen4 (HDDs/SDDs)
SATA controllers Single
IBM Easy Tier® capable controllers No
External SAS ports No
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 27
Page 42

Option Integrated SATA disk controller
SFF-4 Carrier
SATA HDD or SSD
SFF-4 Carrier
SATA HDD or SSD
Front bezel is removed in this illustration
Integrated
SATA controller
Internal SATA Cable
SATA
SATA
System Planar
Split backplane No
The 2.5-inch or small form factor (SFF) SAS bays can contain SATA drives (HDD or SSD) that
are mounted on a Gen4 tray or carrier (also knows as SFF-4). SFF-2 or SFF-3 drives do not
fit in an SFF-4 bay. All SFF-4 bays support concurrent maintenance or hot-plug capability.
Figure 1-15 shows the server front view with the standard backplane.
Figure 1-15 Server front view with SFF-4 locations
Figure 1-16 shows the logical connections of the integrated SATA disk controller.
Figure 1-16 Logical diagram for integrated SATA disk controller
1.14.1 Disk and media features
The servers support the attachment of up to two SATA storage devices that are listed on
Ta bl e 1 -1 5.
28 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Table 1-15 Supported storage devices
Feature
code
ELD0 1 TB 7.2k RPM SATA SFF-4 disk drive 2 Linux
Description Max OS
support
Page 43
Feature
code
ES6A 2 TB 7.2k RPM 5xx SATA SFF-4 Disk Drive 2 Linux
The Power S822LC server is designed for network installation or USB media installation. It
does not support an internal DVD drive.
Description Max OS
1.15 External I/O subsystems
The Power S822LC server does not support external PCIe Gen3 I/O expansion drawers and
EXP24S SFF Gen2-bay drawers.
1.16 IBM System Storage
The IBM System Storage® disk systems products and offerings provide compelling storage
solutions with superior value for all levels of business, from entry-level to high-end storage
systems. For more information about the various offerings, see the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/disk
The following section highlights a few of the offerings.
support
IBM Network Attached Storage
IBM Network Attached Storage (NAS) products provide a wide-range of network attachment
capabilities to a broad range of host and client systems, such as IBM Scale Out Network
Attached Storage and the IBM System Storage N series. For more information about the
hardware and software, see the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/network
IBM Storwize family
The IBM Storwize® family is the ideal solution to optimize the data architecture for business
flexibility and data storage efficiency. Different models, such as the IBM Storwize V3700,
IBM Storwize V5000, and IBM Storwize V7000, offer storage virtualization, IBM Real-time
Compression™, Easy Tier, and many more functions. For more information, see the following
website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/storwize
IBM FlashSystem family
The IBM FlashSystem® family delivers extreme performance to derive measurable economic
value across the data architecture (servers, software, applications, and storage). IBM offers a
comprehensive flash portfolio with the IBM FlashSystem family. For more information, see the
following website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/flash
IBM XIV Storage System
The IBM XIV® Storage System is a high-end disk storage system, helping thousands of
enterprises meet the challenge of data growth with hotspot-free performance and ease of
use. Simple scaling, high service levels for dynamic, heterogeneous workloads, and tight
Chapter 1. Architecture and technical description 29
Page 44

1.17 Java
integration with hypervisors and the OpenStack platform enable optimal storage agility for
cloud environments.
XIV Storage Systems extend ease of use with integrated management for large and multi-site
XIV deployments, reducing operational complexity and enhancing capacity planning. For
more information, see the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/disk/xiv/index.html
IBM System Storage DS8000
The IBM System Storage DS8800 storage system is a high-performance, high-capacity, and
secure storage system that delivers the highest levels of performance, flexibility, scalability,
resiliency, and total overall value for the most demanding, heterogeneous storage
environments. The storage system can manage a broad scope of storage workloads that
exist in today’s complex data center, doing it effectively and efficiently.
Additionally, the IBM System Storage DS8000® storage system includes a range of features
that automate performance optimization and application quality of service, and also provide
the highest levels of reliability and system uptime. For more information, see the following
website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/disk/ds8000/index.html
When running Java applications on the POWER8 processor, the pre-packaged Java that is
part of a Linux distribution is designed to meet the most common requirements.
If you require a different level of Java, there are several resources available.
Current information about IBM Java and tested Linux distributions are available here:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/java/jdk/linux/tested.html
Additional information about the OpenJDK port for Linux on PPC64 LE, as well as some
pre-generated builds can be found here:
http://cr.openjdk.java.net/~simonis/ppc-aix-port/
Launchpad.net has resources for Ubuntu builds. You can find out about them here:
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/openjdk-9
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/openjdk-8
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/openjdk-7
30 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 45

Chapter 2. Management, Reliability,
2
Availability, and Serviceability
The IBM Power Systems S822LC (8335-GTB) server uses the Open Power Abstraction Layer
(OPAL) baremetal firmware for a non-virtualized configuration.
This chapter attempts to identify and clarify the tools that are available for managing the
S822LC server.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. 31
Page 46

2.1 Main management components overview
!"#$%!&
&'
"
()
()
$%
$%
'
*
+
()
$%
Figure 2-1 shows the logical management flow of a Linux on Power Systems server.
Figure 2-1 Logical diagram of a Linux on Power Systems server
The service processor, or baseboard management controller (BMC), provides a hypervisor
and operating system-independent layer that uses the robust error detection and self-healing
functions that are built into the IBM POWER8 processor and memory buffer modules. OPAL is
the system firmware in the stack of POWER8 processor-based Linux on Power Systems
servers.
2.2 Service processor
The service processor, or BMC, is the primary control for autonomous sensor monitoring and
event logging features on the Power S822LC server.
BMC supports the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI V2.0) and Data Center
Management Interface (DCMI V1.5) for system monitoring and management.
BMC monitors the operation of the firmware during the boot process and also monitors the
hypervisor for termination. The firmware code update is supported through the BMC and IPMI
2.2.1 Open Power Abstraction Layer
interfaces.
For the 8335-GTB, only the OPAL Bare Metal (ECXX) is available.
For more information about OPAL skiboot, go to the following website:
https://github.com/open-power/skiboot
32 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 47

2.2.2 Intelligent Platform Management Interface
The IPMI is an open standard for monitoring, logging, recovery, inventory, and control of
hardware that is implemented independent of the main CPU, BIOS, and OS. The Power
S822LC server provides one 10Mb/100Mb baseT IPMI port.
The
ipmitool is a utility for managing and configuring devices that support IPMI. It provides a
simple command-line interface (CLI) to the service processor. You can install the ipmitool
from the Linux distribution packages in your workstation or another server (preferably on the
same network as the installed server). For example, in Ubuntu, run the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install ipmitool
To connect to your system with IPMI, you must know the IP address of the server and have a
valid password. To power on the server with ipmitool, complete the following steps:
1. Open a terminal program.
2. Power on your server by running the following command:
ipmitool -I lanplus -H fsp_ip_address -P ipmi_password power on
3. Activate your IPMI console by running the following command:
ipmitool -I lanplus -H fsp_ip_address -P ipmi_password sol activate
2.3 Reliability, availability, and serviceability
This chapter provides information about IBM Power Systems reliability, availability, and
serviceability (RAS) design and features.
The elements of RAS can be described as follows:
Reliability Indicates how infrequently a defect or fault in a server occurs
Availability Indicates how infrequently the functioning of a system or application is
Serviceability Indicates how well faults and their effects are communicated to system
2.3.1 Introduction
The IBM Power Systems S822LC servers are bringing POWER8 processor and memory
RAS functions into a highly competitive cloud data center with open source Linux technology
as an operating system and virtualization.
The Open Power Abstraction Layer (OPAL) firmware provides a hypervisor and operating
system independent layer that uses the robust error-detection and self-healing functions built
into the POWER8 processor and memory buffer modules.
The processor address-paths and data-paths are protected with parity or error-correcting
codes (ECCs); the control logic, state machines, and computational units have sophisticated
error detection. The processor core soft errors or intermittent errors are recovered with
processor instruction retry. Unrecoverable errors are reported as machine check (MC) errors.
Errors that affect the integrity of data lead to system checkstop.
impacted by a fault or defect
managers and how efficiently and nondisruptively the faults are
repaired
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 33
Page 48

RAS enhancements of POWER8 processor-based scale-out servers
The Power S822LC servers, in addition to being built on advanced RAS characteristics of the
POWER8 processor, offer reliability and availability features that often are not seen in such
scale-out servers.
Here is a brief summary of these features:
Processor enhancements integration
POWER8 processor chips are implemented by using 22 nm technology, and are
integrated on SOI modules.
The processor design supports a spare data lane on each fabric bus, which is used to
communicate between processor modules. A spare data lane can be substituted for a
failing one dynamically during system operation.
A POWER8 processor module has improved performance, including support of a
maximum of 12 cores because doing more work with less hardware in a system supports
greater reliability. The Power S822LC servers offer two processor socket offerings with
8-core and 10-core processor configurations. So, there are 16-core and 20-core
configurations that are available.
The On Chip Controller (OCC) monitors various temperature sensors in the processor
module, memory modules, and environmental temperature sensors, and steers the
throttling of processor cores and memory channels if the temperature rises over
thresholds that are defined by the design. The power supplies have their own independent
thermal sensors and monitoring.
Power supplies and voltage regulator modules monitor Over-Voltage, Under-Voltage, and
Over-Current conditions. They report to a “power good” tree that is monitored by the
service processor.
I/O subsystem
The PCIe controllers are integrated into the POWER8 processor. All the PCIe slots are
directly driven by the PCIe controllers.
34 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 49

Memory subsystem
The memory subsystem has proactive memory scrubbing to prevent accumulation of
multiple single-bit errors. The ECC scheme can correct the complete failure of any one
memory module within an ECC word. After marking the module as unusable, the ECC
logic can still correct single-symbol (two adjacent bit) errors. An uncorrectable error of data
of any layer of cache up to the main memory is marked to prevent usage of fault data. The
processor’s memory controller and the memory buffer have retry capabilities for certain
fetch and store faults.
2.3.2 IBM terminology versus x86 terminology
The different components and descriptions in the boot process have similar functions, but
have different terms for POWER8 processor-based and x86-based scale-out servers.
Table 2-1 shows a quick overview of the terminology.
Table 2-1 Terminology
IBM x86 Description
SBE Undisclosed Self-Boot Engine: Starts the boot process.
Host Boot BIOS Core, Powerbus (SMP), and memory initialization.
OPAL BIOS/ VT-d / UEFI KVM hardware abstraction, PCIe RC, IODA2 (VT-d),
and open firmware.
OCC PCU, off chip
HBRT N/A Correctable error monitoring and OCC monitoring.
2.3.3 Error handling
This section describes how the Power S822LC server handles different errors and recovery
functions. It provides some general information and helps you understand some techniques.
Processor core/cache correctable error handling
The OPAL firmware provides a hypervisor and operating system-independent layer that uses
the robust error-detection and self-healing functions that are built into the POWER8 processor
and memory buffer modules.
The processor address-paths and data-paths are protected with parity or error-correction
codes (ECC). The control logic, state machines, and computational units have sophisticated
error detection. The processor core soft errors or intermittent errors are recovered with
processor instruction retry. Unrecoverable errors are reported as an MC. Errors that affect the
integrity of data lead to system checkstop.
The Level 1 (L1) data and instruction caches in each processor core are parity-protected, and
data is stored through to L2 immediately. L1 caches have a retry capability for intermittent
errors and a cache set delete mechanism for handling solid failures.
microprocessors
Performs real-time functions, such as power
management.
The L2 and L3 caches in the POWER8 processor and L4 cache in the memory buffer chip are
protected with double-bit detect, single-bit correct ECC.
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 35
Page 50

Special Uncorrectable Error handling
Special Uncorrectable Error (SUE) handling prevents an uncorrectable error in memory or
cache from immediately causing an MC with uncorrectable error (UE). The system marks the
data such that if the data ever is read again, it generates an MC with UE. Termination may be
limited to the program / partition or hypervisor owning the data. If the data is referenced by an
I/O adapter, it freeze if data is transferred to an I/O device.
Processor Instruction Retry and other try again techniques
Within the processor core, soft error events might occur that interfere with the various
computation units. When such an event can be detected before a failing instruction is
completed, the processor hardware might try the operation again by using the advanced RAS
feature that is known as
Processor Instruction Retry allows the system to recover from soft faults that otherwise result
in outages of applications or the entire server. Try-again techniques are used in other parts of
the system as well. Faults that are detected on the memory bus that connects processor
memory controllers to DIMMs can be tried again. In POWER8 processor-based systems, the
memory controller is designed with a replay buffer that allows memory transactions to be tried
again after certain faults internal to the memory controller faults are detected. This function
complements the try-again abilities of the memory buffer module.
Processor Instruction Retry.
Other processor chip functions
Within a processor chip, there are other functions besides just processor cores.
POWER8 processors have built-in accelerators that can be used as application resources to
handle such functions as random number generation. POWER8 also introduces a controller
for attaching cache-coherent adapters that are external to the processor module. The
POWER8 design contains a function to “freeze” the function that is associated with some of
these elements, without taking a system-wide checkstop. Depending on the code that uses
these features, a “freeze” event might be handled without an application or partition outage.
As indicated elsewhere, single-bit errors, even solid faults, within internal or external
processor
processor-to-processor module fabric buses also use a spare data lane so that a single
failure can be repaired without calling for the replacement of hardware.
2.3.4 Serviceability
The server is designed for system installation and setup, feature installation and removal,
proactive maintenance, and corrective repair that is performed by the client:
Customer Install and Setup (CSU)
Customer Feature Install (CFI)
Customer Repairable Units (CRU)
Warranty service upgrades are offered for an onsite repair (OSR) by an IBM System Services
Representative (SSR), or an authorized warranty service provider.
The system is designed with a 5 year MTBF. If something needs to be serviced or relocated,
Table 2-2 on page 37 lists whether an item is able to be concurrently repaired, and if it
requires an IBM SSR to repair.
fabric buses, are corrected by the ECC that is used. POWER8
36 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 51

Table 2-2 Major component repair matrix
Element Concurrent Repair Customer Repair SSR Replace
SATA HD D Ye s Yes Ye s
SATA SSD Yes Yes Yes
Power supply Yes Yes Yes
Cooling fans Yes Yes Yes
DIMM riser Yes
DIMM Yes
Processor Yes
PCIe adapter Yes Yes
Storage adapter Yes Yes
GPU Yes Yes
Planer Yes
HDD/Fan card Yes
Fan power cable Yes Yes
DASD signal cable Yes Yes
Front USB Cable Yes Yes
Detection introduction
The first and most crucial component of a solid serviceability strategy is the ability to detect
accurately and effectively errors when they occur.
Although not all errors are a guaranteed threat to system availability, those errors that go
undetected can cause problems because the system has no opportunity to evaluate and act if
necessary. POWER processor-based systems employ IBM z™ Systems server-inspired error
detection mechanisms, extending from processor cores and memory to power supplies and
hard disk drives (HDDs).
Error checkers and fault isolation registers
POWER processor-based systems contain specialized hardware detection circuitry that is
used to detect erroneous hardware operations. Error-checking hardware ranges from parity
error detection that is coupled with Processor Instruction Retry and bus try again, to ECC
correction on caches and system buses.
Within the processor/memory subsystem error checker, error-checker signals are captured
and stored in hardware FIRs. The associated logic circuitry is used to limit the domain of an
error to the first checker that encounters the error. In this way, runtime error diagnostic tests
can be deterministic so that for every check station, the unique error domain for that checker
is defined and mapped to CRUs that can be repaired when necessary.
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 37
Page 52

Service processor
The service processor supports the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI 2.0) and
Data Center Management Interface (DCMI 1.5) for system monitoring and management. The
service processor provides the following platform system functions:
Power on/off
Power sequencing
Power fault monitoring
Power reporting
Fan/thermal control
Fault monitoring
VPD inventory collection
Serial over LAN (SOL)
Service Indicator LED management
Code update
Event reporting through System Event Logs (SELs)
All SELs can be retrieved either directly from the service processor or from the host OS
(Linux). The service processor monitors the operation of the firmware during the boot
process.
The firmware code update is supported through the service processor and IPMI interface.
Multiple firmware images exist in the system and the backup copy is used if the primary
image is corrupted and unusable.
Diagnosing
General diagnostic objectives are to detect and identify problems so that they can be resolved
quickly.
Using the extensive network of advanced and complementary error detection logic that is built
directly into hardware, firmware, and operating systems, Power Systems servers can perform
considerable self-diagnosis.
Host Boot IPL
In POWER8, the initialization process during IPL changed. The service processor is no longer
the only instance that initializes and runs the boot process. With POWER8, the service
processor initializes the boot processes, but on the POWER8 processor itself, one part of the
firmware is running and performing the central electrical complex chip initialization. A new
component that is called the PNOR chip stores the Host Boot firmware and the SBE is an
internal part of the POWER8 chip itself and is used to start the chip.
Device drivers
In certain cases, diagnostic tests are preferably performed by operating system-specific
drivers, most notably adapters or I/O devices that are owned directly by a logical partition. In
these cases, the operating system device driver often works with I/O device Licensed Internal
Code to isolate and recover from problems. Potential problems are reported to an operating
system device driver, which logs the error.
General problem determination
Accessing the Advanced System Management GUI interface provides a general overview of
sensor information and possible errors.
38 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 53

Using an event sensor display as a primary interface for problem determination
This function has the following aspects:
Covers 90% of typical failures
Does not handle transient failure scenarios
Using SEL logs or operating system syslog records for remainder
This function has the following aspects:
Sensors can be enabled/disabled by a client.
The “Get Sensor Event Enable” IPMI command is available.
SEL events: Platform-related events
The following platform-related events are available under the SEL events:
SELs link to eSELs
eSEL represents a service action required event:
– SELs linked to the eSEL represent “service action required” and a part to be replaced.
– You may have multiple SELs that are linked to the eSEL.
– SELs not linked to eSEL may not represent a service action required event.
– Without an eSEL Event, the System Attention LED does not turn on.
For an SEL event that is associated with a eSEL event, see Example 2-1. In this case, events
63 and 64 are the SEL events and event 62 is the associated eSEL event.
Example 2-1 SEL and eSEL events
60 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:27 | Power Supply #0xcd | Presence detected | Asserted
61 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:27 | Power Supply #0xce | Presence detected | Asserted
62 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:35 | OEM record df | 040020 | 0c2207aaaaaa
63 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:35 | Memory #0x22 | Transition to Non-recoverable | Asserted
64 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:36 | Memory #0x23 | Transition to Non-recoverable | Asserted
65 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:54 | System Firmware Progress #0x05 | Memory initialization | Asserted
OEM vendor SELs: Platform-related events
The following platform-related events are available under the OEM vendor SELs:
SELs are developed to provide specific OEM information in the error record.
Not interpretable by IPMI.
No corresponding IPMI SEL events.
Generic system event SELs
Here are some of the generic system event SELs:
Firmware
Isolates and symbolics as highest priority FRUs
Syslog events: OS-detected events
PCI adapters and devices are OS-deteced events.
Error handling and reporting
If there is a system hardware or environmentally induced failure, the system error capture
capability systematically analyzes the hardware error signature to determine the cause of
failure.
The central electrical complex recoverable errors are handled through central electrical
complex diagnostic capability in a Linux application and generates a System Event Log
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 39
Page 54

(SEL). There is also an eSEL that contains extra First Failure Data Capture (FFDC) from the
Host Boot, OCC, and OPAL subsystems that are associated with each SEL. For system
checkstop errors, OCC collects FIR data to PNOR, and Host Boot central electrical complex
diagnostic tests creates a SEL based on the FIR data in PNOR.
When the system can be successfully restarted either manually or automatically, or if the
system continues to operate, the host Linux OS can monitor the SELs on the service
processor through IPMI tool. Hardware and software failures are recorded in the SELs and
can be retrieved through IPMI interface. There is a plan to report SELs in the system log of
the operating system.
The system can report errors that are associated with PCIe adapters/devices.
For some example SEL events, see Example 2-2.
Example 2-2 Example of SEL events
31 | 09/04/2015 | 15:11:40 | Power Unit #0x1c | Power off/down | Asserted
32 | 09/04/2015 | 15:11:40 | Power Supply #0xcd | Presence detected | Deasserted
33 | 09/04/2015 | 15:11:40 | Power Supply #0xce | Presence detected | Deasserted
34 | 09/04/2015 | 15:11:43 | Power Supply #0xcd | Presence detected | Asserted
35 | 09/04/2015 | 15:11:43 | Power Supply #0xce | Presence detected | Asserted
36 | 09/04/2015 | 15:11:47 | System Firmware Progress #0x05 | Motherboard initialization | Asserted
37 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:11 | Fan #0xd4 | Upper Non-critical going high | Asserted
38 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:11 | Fan #0xd4 | Upper Critical going high | Asserted
39 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:11 | Fan #0xd4 | Upper Non-recoverable going high | Asserted
3a | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:12 | Fan #0xd5 | Upper Non-critical going high | Asserted
3b | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:12 | Fan #0xd5 | Upper Critical going high | Asserted
3c | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:12 | Fan #0xd5 | Upper Non-recoverable going high | Asserted
3d | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:12 | Fan #0xd6 | Upper Non-critical going high | Asserted
3e | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd6 | Upper Critical going high | Asserted
3f | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd6 | Upper Non-recoverable going high | Asserted
40 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd7 | Upper Non-critical going high | Asserted
41 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd7 | Upper Critical going high | Asserted
42 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd7 | Upper Non-recoverable going high | Asserted
43 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd4 | Upper Non-recoverable going high | Deasserted
44 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd4 | Upper Critical going high | Deasserted
45 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd4 | Upper Non-critical going high | Deasserted
46 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd5 | Upper Non-recoverable going high | Deasserted
47 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:13 | Fan #0xd5 | Upper Critical going high | Deasserted
48 | 09/04/2015 | 15:12:14 | Fan #0xd5 | Upper Non-critical going high | Deasserted
To service a Linux system end to end, Linux service and productivity tools must be installed.
You can find them at the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/customercare/sas/f/lopdiags/home.html
The tools are automatically loaded if IBM manufacturing installs the Linux image or IBM
Installation Toolkit. PowerPack is the preferred way to install required service packages from
the website. The Linux call home feature is also supported in a stand-alone system
configuration to report serviceable events.
Locating and servicing
The final component of a comprehensive design for serviceability is the ability to locate and
replace effectively parts requiring service. POWER processor-based systems use a
combination of visual cues and guided maintenance procedures to ensure that the identified
part is replaced correctly every time.
40 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 55

Packaging for service
The following service enhancements are included in the physical packaging of the systems to
facilitate service:
Color coding (touch points)
Terracotta-colored touch points indicate that a component (FRU or CRU) can be
concurrently maintained.
Blue-colored touch points delineate components that may not be concurrently maintained
(they might require that the system is turned off for removal or repair).
Positive retention
Positive retention mechanisms help ensure proper connections between hardware
components, such as from cables to connectors, and between two adapters that attach to
each other. Without positive retention, hardware components risk becoming loose during
shipping or installation, which prevents a good electrical connection. Positive retention
mechanisms such as latches, levers, thumb-screws, pop Nylatches (U-clips), and cables
are included to help prevent loose connections and aid in installing (seating) parts
correctly. These positive retention items do not require tools.
Service Indicator LEDs
The Service Indicator LED function is for scale-out systems, including Power Systems such
as the Power S812LC server, that can be repaired by clients. In the Service Indicator LED
implementation, when a fault condition is detected on the POWER8 processor-based system,
an amber FRU fault LED is illuminated (turned on solid), which is then rolled up to the system
fault LED.
When the ID LED button on the front panel is pressed, the blue LED on the front panel and
the blue ID LED on the rear panel light up. The technical personnel can easily locate the
system on the rack, disconnect cables from the system, and remove it from the rack for later
repair.
The Service Indicator operator panel contains the following items:
Power On LED (Green LED: Front)
– Off: Enclosure is off.
– On Solid: Enclosure is powered on.
– On Blink: Enclosure is in the standby-power state.
Enclosure Identify LED (Blue LED: Front)
– Off: Normal.
– On Solid: Identify state.
– On Blink: Reserved.
System Information/Attention LED (Amber LED: Front)
– Off: Normal.
– On Solid: System Attention State.
Enclosure Fault Roll-up LED (Amber LED: Front)
– Off: Normal.
– On Solid: Fault.
– Power On/Off Switch.
– Pin-hole Reset Switch.
– USB Port.
– Beeper.
– Altitude Sensor with Ambient Thermal Sensor.
– VPD Module.
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 41
Page 56

Concurrent maintenance
The following components can be replaced without powering off the server:
Drives in the front bay
Power supplies
Fans
The POWER8 processor-based systems are designed with the understanding that certain
components have higher intrinsic failure rates than others. These components can include
fans, power supplies, and physical storage devices. Other devices, such as I/O adapters, can
wear from repeated plugging and unplugging. For these reasons, these devices are
concurrently maintainable when properly configured. Concurrent maintenance is facilitated
because of the redundant design for the power supplies and physical storage.
IBM Knowledge Center
IBM Knowledge Center provides you with a single place where you can access product
documentation for IBM systems hardware, operating systems, and server software.
The purpose of IBM Knowledge Center, in addition to providing client-related product
information, is to provide softcopy information to diagnose and fix any problems that might
occur with the system. Because the information is electronically maintained, changes
because of updates or the addition of new capabilities can be used by service representatives
immediately.
The IBM Knowledge Center provides the following up-to-date documentation to service
effectively the system:
Quick Install Guide
User’s Guide
Trouble Shooting Guide
Boot Configuration Guide
The documentation can be downloaded in PDF format or used online through an internet
connection.
The IBM Knowledge Center can be found at:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/
Supporting information for the Power S822LC (8335-GTB) server is available online at the
following websites:
8335-GCB:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/HW4L4/p8hdx/8335_gcB_landing.htm
Warranty and spare parts
The system comes with a 3-year warranty for parts. The replacement parts can be ordered
through the Advanced Part Exchange Warranty Service, which can be found at the following
website:
http://www.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=877/ENUSZG15-0194&infotype=
AN&subtype=CA&appname=skmwww
2.3.5 Manageability
Several functions and tools help you can efficiently and effectively manage your system.
42 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 57

Service user interfaces
The service interface allows support personnel or the client to communicate with the service
support applications in a server by using a console, interface, or terminal. Delivering a clear,
concise view of available service applications, the service interface allows the support team to
manage system resources and service information in an efficient and effective way.
Applications that are available through the service interface are carefully configured and
placed to give service providers access to important service functions.
Various service interfaces are used depending on the state of the system and its operating
environment. Here are the primary service interfaces:
Service Indicator LEDs (See “Service Indicator LEDs” on page 41 and “Concurrent
maintenance” on page 42.)
Service processor
Service Interface
The service interface allows the client and the support personnel to communicate with the
service support applications in a server by using a browser. It delivers a clear, concise view of
available service applications. The service interface allows the support client to manage
system resources and service information in an efficient and effective way. Different service
interfaces are used depending on the state of the system, hypervisor, and operating
environment. Here are the primary service interfaces:
Service processor: Ethernet Service Network with IPMI Version 2.0
Service Indicator LEDs: System attention and system identification (front and back)
Host operating system: Command-line interface (CLI)
The service processor is a controller that is running its own operating system.
IBM Power Systems Firmware maintenance
The IBM Power Systems Client-Managed Licensed Internal Code is a methodology that you
can use to manage and install Licensed Internal Code updates on a Power Systems server
and its associated I/O adapters.
Firmware updates
System firmware is delivered as a release level or a service pack. Release levels support the
general availability (GA) of new functions or features, and new machine types or models.
Upgrading to a higher release level is disruptive to customer operations. These release levels
are supported by service packs. Service packs are intended to contain only firmware fixes
and not introduce new functions. A
IBM is increasing its clients’ opportunity to stay on a given release level for longer periods.
Clients that want maximum stability can defer until there is a compelling reason to upgrade,
such as the following reasons:
A release level is approaching its end of service date (that is, it has been available for
about a year, and soon service will not be supported).
Move a system to a more standardized release level when there are multiple systems in
an environment with similar hardware.
A new release has a new function that is needed in the environment.
A scheduled maintenance action causes a platform restart, which provides an opportunity
to also upgrade to a new firmware release.
service pack is an update to an existing release level.
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 43
Page 58

The updating and upgrading of system firmware depends on several factors, such as the
current firmware that is installed, and what operating systems is running on the system.
These scenarios and the associated installation instructions are comprehensively outlined in
the firmware section of Fix Central, found at the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/fixcentral/
Figure 2-2 shows the ASM dashboard where service professionals can maintain the system.
Figure 2-2 Advanced System Management Dashboard
When updating firmware, a service professional can find a window that shows which
components will be overwritten or preserved, as shown in Figure 2-3. For this example, the
network settings will be preserved.
Figure 2-3 Firmware Update window
44 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 59
4. The next window prompts whether you want to continue to the update mode, as shown in
Figure 2-4. Until the firmware update is completed, no other activities can be performed in
the Advanced System Management Interface. If you want to proceed, click OK.
Figure 2-4 Confirm firmware update mode
5. Select the firmware update file from your local disk by selecting Browse and Parse HPM
firmware page, clicking Browse, and selecting the file, as shown in Figure 2-5,
Figure 2-5 Select the firmware image
Chapter 2. Management, Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability 45
Page 60

6. When the correct firmware image is selected, the GUI shows a list of components that will
be updated, as shown in Figure 2-6 on page 46. By default, all the components are
selected. To update the firmware, click Proceed.
Figure 2-6 Start the firmware upgrade
7. After the firmware update is complete, the system restarts. After the restart, you can verify
that the systems firmware was updated by opening the Advanced System Management
Dashboard window.
46 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 61

Appendix A. Server racks and energy
A
management
This appendix provides information about the racking options and energy
management-related concepts that are available for the IBM Power Systems 822LC server.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. 47
Page 62

IBM server racks
The Power S812LC server mounts in the 36U 7014-T00 (#0551) rack, the 42U 7014-T42
(#0553) rack, the 42U Slim Rack (7965-94Y), or the IBM 25U entry rack 7014-S25 (#0555).
These racks are built to the 19-inch EIA 310D standard.
Order information: Power 822LC servers cannot be integrated into these racks during the
manufacturing process, and are not orderable together with servers. If the Power 822LC
server and any of the supported IBM racks are ordered together, they are shipped at the
same time in the same shipment, but in separate packing material. IBM does not offer
integration of the server into the rack before shipping.
If a system is installed in a rack or cabinet that is not an IBM rack, ensure that the rack meets
the requirements that are described in “OEM racks” on page 54.
Responsibility: The client is responsible for ensuring that the installation of the drawer in
the preferred rack or cabinet results in a configuration that is stable, serviceable, safe, and
compatible with the drawer requirements for power, cooling, cable management, weight,
and rail security.
Water cooling option
IBM 7014 Model S25 rack
The 1.3-meter (49-in.) Model S25 rack has the following features:
Twenty-five EIA units
Weights:
– Base empty rack: 100.2 kg (221 lb.)
– Maximum load limit: 567.5 kg (1250 lb.)
The S25 racks do not have vertical mounting space to accommodate FC 7188 PDUs. All
PDUs that are required for application in these racks must be installed horizontally in the rear
of the rack. Each horizontally mounted PDU occupies 1U of space in the rack, and therefore
reduces the space that is available for mounting servers and other components.
IBM 7014 Model T00 rack
The 1.8-meter (71-in.) Model T00 rack is compatible with past and present Power Systems
servers. The T00 rack offers these features:
36U (EIA units) of usable space.
Optional removable side panels.
Optional side-to-side mounting hardware for joining multiple racks.
Increased power distribution and weight capacity.
Support for both AC and DC configurations.
48 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 63

Up to four power distribution units (PDUs) can be mounted in the PDU bays (see
Figure A-2 on page 52), but others can fit inside the rack. For more information, see “The
AC power distribution unit and rack content” on page 51.
For the T00 rack, three door options are available:
– Front Door for 1.8 m Rack (#6068)
This feature provides an attractive black full height rack door. The door is steel with a
perforated flat front surface. The perforation pattern extends from the bottom to the top
of the door to enhance ventilation and provide visibility into the rack.
– A 1.8 m Rack Acoustic Door (#6248)
This feature provides a front and rear rack door that are designed to reduce acoustic
sound levels in a general business environment.
– A 1.8 m Rack Trim Kit (#6263)
If no front door is used in the rack, this feature provides a decorative trim kit for the
front.
Ruggedized Rack Feature
For enhanced rigidity and stability of the rack, the optional Ruggedized Rack Feature
(#6080) provides additional hardware that reinforces the rack and anchors it to the floor.
This hardware is for use in locations where earthquakes are a concern. The feature
includes a large steel brace or truss that bolts into the rear of the rack.
It is hinged on the left side so that it can swing out of the way for easy access to the rack
drawers when necessary. The Ruggedized Rack Feature also includes hardware for
bolting the rack to a concrete floor or a similar surface, and bolt-in steel filler panels for any
unoccupied spaces in the rack.
The following weights apply to the T00 rack:
– T00 base empty rack: 244 kg (535 lb.).
– T00 full rack: 816 kg (1795 lb.).
– Maximum weight of drawers is 572 kg (1260 lb.).
– Maximum weight of drawers in a zone 4 earthquake environment is 490 kg (1080 lb.).
This number equates to 13.6 kg (30 lb.) per EIA.
Important: If additional weight is added to the top of the rack, for example, by adding
#6117, the 490 kg (1080 lb.) weight must be reduced by the weight of the addition. As an
example, #6117 weighs approximately 45 kg (100 lb.), so the new maximum weight of the
drawers that the rack can support in a zone 4 earthquake environment is 445 kg (980 lb.).
In the zone 4 earthquake environment, the rack must be configured starting with the
heavier drawers at the bottom of the rack.
IBM 7014 Model T42 rack
The 2.0-meter (79.3-in.) Model T42 addresses the client requirement for a tall enclosure to
house the maximum amount of equipment in the smallest possible floor space. The following
features are for the Model T42 rack (which differ from the model T00):
The T42 rack has 42U (EIA units) of usable space (6U of additional space).
The model T42 supports AC power only.
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management 49
Page 64

The following weights apply to the T42 rack:
Trim kit (no front
door)
FC 6272
Plain front door
FC 6069
Acoustic doors
(front & rear)
FC 6249
Optional
front door
FC ERG7
– T42 base empty rack: 261 kg (575 lb.)
– T42 full rack: 930 kg (2045 lb.)
The available door options for the Model T42 rack are shown in Figure A-1.
Figure A-1 Door options for the T42 rack
Where:
The 2.0-meter Rack Trim Kit (#6272) is used if no front door is used in the rack.
The Front Door for a 2.0-meter Rack (#6069) is made of steel with a perforated flat front
surface. The perforation pattern extends from the bottom to the top of the door to enhance
ventilation and provide visibility into the rack. This door is non-acoustic and has a depth of
about 25 mm (1 in.).
The 2.0-meter Rack Acoustic Door (#6249) consists of a front and rear door to reduce
noise by approximately 6 dB(A). It has a depth of approximately 191 mm (7.5 in.).
The #ERG7 provides an attractive black full height rack door. The door is steel with a
perforated flat front surface. The perforation pattern extends from the bottom to the top of
the door to enhance ventilation and provide visibility into the rack. The non-acoustic door
has a depth of about 134 mm (5.3 in.).
Rear Door Heat Exchanger
To lead away more heat, a special door that is named the Rear Door Heat Exchanger
(#EC15) is available. This door replaces the standard rear door on the rack. Copper tubes
that are attached to the rear door circulate chilled water, which is provided by the client. The
chilled water removes heat from the exhaust air being blown through the servers and
attachments that are mounted in the rack. With industry-standard quick couplings, the water
lines in the door attach to the client-supplied secondary water loop.
50 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 65

For more information about planning for the installation of the IBM Rear Door Heat
Exchanger, see the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/api/redirect/powersys/v3r1m5/index.jsp?
topic=/iphad_p5/iphadexchangeroverview.html
IBM 42U SlimRack 7965-94Y
The 2.0-meter (79-inch) Model 7965-94Y is compatible with past and present Power Systems
servers and provides an excellent 19-inch rack enclosure for your data center. Its 600 mm
(23.6 in.) width combined with its 1100 mm (43.3 in.) depth plus its 42 EIA enclosure capacity
provides great footprint efficiency for your systems and allows it to be easily placed on
standard 24-inch floor tiles.
The IBM 42U Slim Rack has a lockable perforated front steel door that provides ventilation,
physical security, and visibility of indicator lights in the installed equipment within. In the rear,
either a lockable perforated rear steel door (#EC02) or a lockable Rear Door Heat Exchanger
(RDHX)(1164-95X) is used. Lockable optional side panels (#EC03) increase the rack’s
aesthetics, help control airflow through the rack, and provide physical security. Multiple 42U
Slim Racks can be bolted together to create a rack suite (indicate feature code #EC04).
Up to six optional 1U PDUs can be placed vertically in the sides of the rack. Additional PDUs
can be placed horizontally, but they each use 1U of space in this position.
The AC power distribution unit and rack content
For rack models T00 and T42, 12-outlet PDUs are available. These PDUs include the AC
power distribution unit #7188 and the AC Intelligent PDU+ #7109. The Intelligent PDU+ is
identical to #7188 PDUs, but it is equipped with one Ethernet port, one console serial port,
and one RS232 serial port for power monitoring.
The PDUs have 12 client-usable IEC 320-C13 outlets. Six groups of two outlets are fed by six
circuit breakers. Each outlet is rated up to 10 amps, but each group of two outlets is fed from
one 15 amp circuit breaker.
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management 51
Page 66

Four PDUs can be mounted vertically in the back of the T00 and T42 racks. Figure A-2 shows
Rack Rear View
43
21
Circuit breaker reset
Status LED
the placement of the four vertically mounted PDUs. In the rear of the rack, two additional
PDUs can be installed horizontally in the T00 rack and three in the T42 rack. The four vertical
mounting locations are filled first in the T00 and T42 racks. Mounting PDUs horizontally
consumes 1U per PDU and reduces the space that is available for other racked components.
When mounting PDUs horizontally, the preferred approach is to use fillers in the EIA units that
are occupied by these PDUs to facilitate the correct airflow and ventilation in the rack.
Figure A-2 PDU placement and PDU view
The PDU receives power through a UTG0247 power-line connector. Each PDU requires one
PDU-to-wall power cord. Various power cord features are available for various countries and
applications by varying the PDU-to-wall power cord, which must be ordered separately. Each
power cord provides the unique design characteristics for the specific power requirements. To
match new power requirements and save previous investments, these power cords can be
requested with an initial order of the rack or with a later upgrade of the rack features.
52 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 67
Table A-1 shows the available wall power cord options for the PDU and iPDU features, which
must be ordered separately.
Table A-1 Wall power cord options for the PDU and iPDU features
Feature
code
6653 IEC 309,
6489 IEC309
6654 NEMA L6-30 200 - 208, 240 1 24 amps US, Canada, LA, and Japan
6655 RS 3750DP
6656 IEC 309,
6657 PDL 230 - 240 1 32 amps Australia and New Zealand
6658 Korean plug 220 1 30 amps North and South Korea
6492 IEC 309, 2P+G,
6491 IEC 309, P+N+G,
Wall plug Rated voltage
(Vac)
230 3 16 amps/phase Internationally available
3P+N+G, 16A
230 3 32 amps/phase EMEA
3P+N+G, 32A
200 - 208, 240 1 24 amps US, Canada, LA, and Japan
(watertight)
230 1 24 amps EMEA
P+N+G, 32A
200 - 208, 240 1 48 amps US, Canada, LA, and Japan
60A
230 1 63 amps EMEA
63A
Phase Rated amperage Geography
Notes: Ensure that the correct power cord feature is configured to support the power that
is being supplied. Based on the power cord that is used, the PDU can supply 4.8 - 19.2
kVA. The power of all of the drawers that are plugged into the PDU must not exceed the
power cord limitation.
The Universal PDUs are compatible with previous models.
To better enable electrical redundancy, each server has two power supplies that must be
connected to separate PDUs, which are not included in the base order.
For maximum availability, a preferred approach is to connect power cords from the same
system to two separate PDUs in the rack, and to connect each PDU to independent power
sources.
For detailed power requirements and power cord details about the 7014 racks, see the
“Planning for power” section in the IBM Power Systems Hardware IBM Knowledge Center
website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/api/redirect/powersys/v3r1m5/topic/p7ha
d/p7hadrpower.htm
For detailed power requirements and power cord details about the 7965-94Y rack, see the
“Planning for power” section in the IBM Power Systems Hardware IBM Knowledge Center
website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/api/redirect/powersys/v3r1m5/topic/p7ha
d/p7hadkickoff795394x.htm
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management 53
Page 68

Rack-mounting rules
Consider the following primary rules when you mount the system into a rack:
The system can be placed at any location in the rack. For rack stability, start filling a rack
from the bottom.
Any remaining space in the rack can be used to install other systems or peripheral devices
if the maximum permissible weight of the rack is not exceeded and the installation rules for
these devices are followed.
Before placing the system into the service position, be sure to follow the rack
manufacturer’s safety instructions regarding rack stability.
Useful rack additions
This section highlights several rack addition solutions for Power Systems rack-based
systems.
OEM racks
The system can be installed in a suitable OEM rack if that the rack conforms to the EIA-310-D
standard for 19-inch racks. This standard is published by the Electrical Industries Alliance. For
more information, see the IBM Power Systems Hardware IBM Knowledge Center at the
following website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/api/redirect/systems/scope/hw/index.jsp
54 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 69

The website mentions the following key points:
571mm (22.50 in.)
Drawer Rail
Mounting
Flanges
Back, No Door
494mm (19.45 in.)
Front, No Door
203mm (8.0 in.)
719mm (28.31 in.)
51mm (2.01 in.)
451mm (17.76 in.)
494mm (19.45 in.)
The front rack opening must be 451 mm wide ± 0.75 mm (17.75 in. ± 0.03 in.), and the
rail-mounting holes must be 465 mm ± 0.8 mm (18.3 in. ± 0.03 in.) apart on-center
(horizontal width between the vertical columns of holes on the two front-mounting flanges
and on the two rear-mounting flanges). Figure A-3 is a top view that shows the
specification dimensions.
Figure A-3 Top view of rack specification dimensions (not specific to IBM)
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management 55
Page 70
The vertical distance between the mounting holes must consist of sets of three holes
Hole Diameter =
7.1 +/- 0.1mm
Rack Mounting Holes Center-to-Center
Rack Front Opening
450 +/- 0.75mm
465 +/- 0.8mm
EIA Hole Spacing
6.75mm min
15.9mm
15.9mm
12.7mm
15.9mm
15.9mm
12.7mm
6.75mm min
15.9mm
15.9mm
12.7mm
15.9mm
15.9mm
12.7mm
Top Front of Rack
Top Front of Rack
spaced (from bottom to top) 15.9 mm (0.625 in.), 15.9 mm (0.625 in.), and 12.67 mm (0.5
in.) on-center, which makes each three-hole set of vertical hole spacing 44.45 mm
(1.75 in.) apart on center. Rail-mounting holes must be 7.1 mm ± 0.1 mm (0.28 in. ±
0.004 in.) in diameter. Figure A-4 shows the top front specification dimensions.
Figure A-4 Rack specification dimensions top front view
Energy management
The Power S822LC servers have features to help clients become more energy efficient.
EnergyScale technology enables advanced energy management features to conserve power
dramatically and dynamically and further improve energy efficiency. Intelligent Energy
optimization capabilities enable the POWER8 processor to operate at a higher frequency for
increased performance and performance per watt, or to reduce dramatically the frequency to
save energy.
56 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 71

IBM EnergyScale technology
IBM EnergyScale technology provides functions to help the user understand and dynamically
optimize processor performance versus processor energy consumption, and system
workload, to control Power Systems power and cooling usage.
EnergyScale uses power and thermal information that is collected from the system to
implement policies that can lead to better performance or better energy usage. EnergyScale
offers the following features:
Power trending
EnergyScale provides continuous collection of real-time server energy consumption.
Administrators can use it to predict power consumption across their infrastructure and to
react to business and processing needs. For example, administrators can use this
information to predict data center energy consumption at various times of the day, week,
or month.
Power saver mode
Power saver mode lowers the processor frequency and voltage a fixed amount, reducing
the energy consumption of the system while still delivering predictable performance. This
percentage is predetermined to be within a safe operating limit and is not
user-configurable. The server is designed for a fixed frequency drop of almost 50% down
from nominal frequency (the actual value depends on the server type and configuration).
Power saver mode is not supported during system start, although it is a persistent
condition that is sustained after the start when the system starts running instructions.
Dynamic power saver mode
Dynamic power saver mode varies processor frequency and voltage based on the usage
of the POWER8 processors. Processor frequency and usage are inversely proportional for
most workloads, implying that as the frequency of a processor increases, its usage
decreases, given a constant workload. Dynamic power saver mode takes advantage of
this relationship to detect opportunities to save power, based on measured real-time
system usage.
When a system is idle, the system firmware lowers the frequency and voltage to power
energy saver mode values. When fully used, the maximum frequency varies, depending
on whether the user favors power savings or system performance. If an administrator
prefers energy savings and a system is fully used, the system reduced the maximum
frequency to about 95% of nominal values. If performance is favored over energy
consumption, the maximum frequency can be increased to up to 111.3% of nominal
frequency for extra performance.
Dynamic power saver mode is mutually exclusive with power saver mode. Only one of
these modes can be enabled at a time.
Power capping
Power capping enforces a user-specified limit on power usage. Power capping is not a
power-saving mechanism. It enforces power caps by throttling the processors in the
system, degrading performance significantly. The idea of a power cap is to set a limit that
must never be reached but that frees extra power that was never used in the data center.
The
margined power is this amount of extra power that is allocated to a server during its
installation in a data center. It is based on the server environmental specifications that
usually are never reached because server specifications are always based on maximum
configurations and worst-case scenarios.
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management 57
Page 72

Soft power capping
There are two power ranges into which the power cap can be set: power capping, as
described previously, and soft power capping. Soft power capping extends the allowed
energy capping range further, beyond a region that can be ensured in all configurations
and conditions. If the energy management goal is to meet a particular consumption limit,
soft power capping is the mechanism to use.
Processor core nap mode
The POWER8 processor uses a low-power mode that is called
execution when there is no work to do on that processor core. The latency of exiting nap
mode is small, typically not generating any impact on applications that are running.
Therefore, the IBM POWER Hypervisor™ can use nap mode as a general-purpose idle
state. When the operating system detects that a processor thread is idle, it yields control of
a hardware thread to the POWER Hypervisor. The POWER Hypervisor immediately puts
the thread into nap mode. Nap mode allows the hardware to turn off the clock on most of
the circuits in the processor core. Reducing active energy consumption by turning off the
clocks allows the temperature to fall, which further reduces leakage (static) power of the
circuits and causes a cumulative effect. Nap mode saves 10 - 15% of power consumption
in the processor core.
Processor core sleep mode
To save even more energy, the POWER8 processor has an even lower power mode
referred to as
the cache is flushed, transition lookaside buffers (TLB) are invalidated, and the hardware
clock is turned off in the core and in the cache. Voltage is reduced to minimize leakage
current. Processor cores that are inactive in the system (such as capacity on demand
(CoD) processor cores) are kept in sleep mode. Sleep mode saves about 80% of the
power consumption in the processor core and its associated private L2 cache.
Processor chip winkle mode
sleep. Before a core and its associated private L2 cache enter sleep mode,
nap that stops processor
The most energy can be saved when a whole POWER8 chiplet enters the
this mode, the entire chiplet is turned off, including the L3 cache. This mode can save
more than 95% power consumption.
Fan control and altitude input
System firmware dynamically adjusts fan speed based on energy consumption, altitude,
ambient temperature, and energy savings modes. Power Systems are designed to
operate in worst-case environments, in hot ambient temperatures, at high altitudes, and
with high-power components. In a typical case, one or more of these constraints are not
valid. When no power savings setting is enabled, fan speed is based on ambient
temperature and assumes a high-altitude environment. When a power savings setting is
enforced (either Power Energy Saver Mode or Dynamic Power Saver Mode), the fan
speed varies based on power consumption and ambient temperature.
Processor folding
Processor folding is a consolidation technique that dynamically adjusts, over the short
term, the number of processors that are available for dispatch to match the number of
processors that are demanded by the workload. As the workload increases, the number of
processors made available increases. As the workload decreases, the number of
processors that are made available decreases. Processor folding increases energy
savings during periods of low to moderate workload because unavailable processors
remain in low-power idle states (nap or sleep) longer.
winkle mode. In
58 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 73

EnergyScale for I/O
POWER8 processor-based systems automatically power off hot-pluggable PCI adapter
slots that are empty or not being used. System firmware automatically scans all pluggable
PCI slots at regular intervals, looking for those slots that meet the criteria for being not in
use and powering them off. This support is available for all POWER8 processor-based
servers and the expansion units that they support.
Dynamic power saver mode
On POWER8 processor-based systems, several EnergyScale technologies are
embedded in the hardware and do not require an operating system or external
management component. Fan control, environmental monitoring, and system energy
management are controlled by the On Chip Controller (OCC) and associated components.
On Chip Controller
POWER8 invested in power management innovations. A new OCC that uses an embedded
IBM PowerPC® core with 512 KB of SRAM runs real-time control firmware to respond to
workload variations by adjusting the per-core frequency and voltage based on activity,
thermal, voltage, and current sensors.
The OCC also enables more granularity in controlling the energy parameters in the processor,
and increases reliability in energy management by having one controller in each processor
that can perform certain functions independently of the others.
POWER8 also includes an internal voltage regulation capability that enables each core to run
at a different voltage. Optimizing both voltage and frequency for workload variation enables a
better increase in power savings versus optimizing frequency only.
Energy consumption estimation
Often, for Power Systems servers, various energy-related values are important:
Maximum power consumption and power source loading values
These values are important for site planning and are described in the POWER8
processor-based systems information IBM Knowledge Center at the following website:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/api/redirect/powersys/v3r1m5/index.jsp
Search for type and model number and “server specifications”. For example, for the Power
S822LC servers, search for “8335-GCB” .
An estimation of the energy consumption for a certain configuration
Calculate the energy consumption for a certain configuration in the IBM Systems Energy
Estimator at the following website:
http://www-912.ibm.com/see/EnergyEstimator
In that tool, select the type and model for the system, and enter details about the
configuration and CPU usage that you want. As a result, the tool shows the estimated
energy consumption and the waste heat at the usage that you want and also at full usage.
Appendix A. Server racks and energy management 59
Page 74

60 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 75

Related publications
The publications that are listed in this section are considered suitable for a more detailed
description of the topics covered in this paper.
IBM Redbooks
The following IBM Redbooks publications provide additional information about the topic in this
document. Some publications that are referenced in this list might be available in softcopy
only.
Cloud Security Guidelines for IBM Power Systems, SG24-8242
IBM PowerKVM Configuration and Use, SG24-8231
IBM Power System S824L Technical Overview and Introduction, REDP-5139
IBM PowerVC Version 1.2.3: Introduction and Configuration, SG24-8199
IBM z13 Configuration Setup, SG24-8260
NVIDIA CUDA on IBM POWER8: Technical Overview, Software Installation, and
Application, REDP-5169
Performance Optimization and Tuning Techniques for IBM Power Systems Processors
Including IBM POWER8, SG24-8171
You can search for, view, download, or order these documents and other Redbooks,
Redpapers, web docs, draft and additional materials, at the following website:
ibm.com/redbooks
Other publications
These publications are also relevant as further information sources:
Active Memory Expansion: Overview and Usage Guide
http://public.dhe.ibm.com/common/ssi/ecm/en/pow03037usen/POW03037USEN.PDF
IBM EnergyScale for POWER8 Processor-Based Systems
http://public.dhe.ibm.com/common/ssi/ecm/en/pow03039usen/POW03039USEN.PDF
IBM Power Facts and Features - IBM Power Systems, IBM PureFlex System, and Power
Blades
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/reports/factsfeatures.html
IBM Power Systems S812L server specifications
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/s812l-s822l/specs.html
IBM Power Systems S814 server specifications
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/s814/specs.html
IBM Power Systems S822 server specifications
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/s822/specs.html
© Copyright IBM Corp. 2016. All rights reserved. 61
Page 76

IBM Power Systems S822L server specifications
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/s812l-s822l/specs.html
IBM Power Systems S824 server specifications
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/s824/specs.html
IBM Power Systems S824L server specifications:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/s824l/specs.html
IBM Power Systems E850 server specifications:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/e850/specs.html
IBM Power Systems E870 server specifications:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/e870/specs.html
IBM Power Systems E870 server specifications:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/hardware/e870/specs.html
System RAS - Introduction to Power Systems Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability
http://public.dhe.ibm.com/common/ssi/ecm/en/pow03056usen/POW03056USEN.PDF
Online resources
These websites are also relevant as further information sources:
IBM Fix Central website
http://www.ibm.com/support/fixcentral/
IBM Knowledge Center
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/
IBM Power Systems website
http://www.ibm.com/systems/power/
IBM Power Systems Hardware IBM Knowledge Center:
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/api/redirect/powersys/v3r1m5/index.jsp
IBM Storage website
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/
IBM System Planning Tool website
http://www.ibm.com/systems/support/tools/systemplanningtool/
IBM Systems Energy Estimator
http://www-912.ibm.com/see/EnergyEstimator/
Current information about IBM Java and tested Linux distributions are available here:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/java/jdk/linux/tested.html
Additional information about the OpenJDK port for Linux on PPC64 LE, as well as some
pre-generated builds can be found here:
http://cr.openjdk.java.net/~simonis/ppc-aix-port/
Launchpad.net has resources for Ubuntu builds. You can find out about them here:
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/openjdk-9
https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/openjdk-8
62 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 77

https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/openjdk-7
Help from IBM
IBM Support and downloads
ibm.com/support
IBM Global Services
ibm.com/services
Related publications 63
Page 78

64 IBM Power Systems S822LC for High Performance Computing
Page 79

Page 80

ibm.com/redbooks
Back cover
REDP-5405-00
ISBN
Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...