
IBM Netfinity Servers
IBM Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
Models 12Y, 1SY, 22Y, 2SY, 31Y, 3RY, 41Y, 4RY,
51Y, 5RY, 61Y, 6RY, 71Y, 7RY, 81Y, 8RY
Hardware Maintenance Manual
January 2000
We Want Your Comments!
(Please see page 206)
S10L-9837-04


IBM Netfinity Servers
IBM Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
Models 12Y, 1SY, 22Y, 2SY, 31Y, 3RY, 41Y, 4RY,
51Y, 5RY, 61Y, 6RY, 71Y, 7RY, 81Y, 8RY
Hardware Maintenance Manual
January 2000
We Want Your Comments!
(Please see page 206)
S10L-9837-04
IBM

Note
Before using this information and the product it
supports, be sure to read the general information
under “Notices” in the manual.
Fifth Edition (January 2000)
The following paragraph does not apply to the United
Kingdom or any country where such provisions are
inconsistent with local law: INTERNATIONAL
BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION PROVIDES THIS
PUBLICATION “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY
KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT
NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer of
express or implied warranties in certain transactions,
therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This publication could include technical inaccuracies or
typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to
the information herein; these changes will be incorporated
in new editions of the publication. IBM may make
improvements and/or changes in the product(s) and/or the
program(s) described in this publication at any time.
This publication was developed for products and services
offered in the United States of America. IBM may not offer
the products, services, or features discussed in this
document in other countries, and the information is subject
to change without notice. Consult your local IBM
representative for information on the products, services,
and features available in your area.
Requests for technical information about IBM products
should be made to your IBM reseller or IBM marketing
representative.
Copyright International Business Machines
Corporation 1997, 2000. All rights reserved.
Note to U.S. Government users–Documentation related to
Restricted rights–Use, duplication, or disclosure is subject
to restrictions set forth in GSA ADP Schedule Contract
with IBM Corp.
ii Netfinity Server HMM

About this manual
This manual contains diagnostic information,
Symptom-to-FRU Indexes, service information, error
codes, error messages, and configuration information for
the Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659.
Important
This manual is intended for trained servicers who are
familiar with IBM PC Server products.
Important safety information
Be sure to read all caution and danger statements in this
book before performing any of the instructions.
Leia todas as instruções de cuidado e perigo antes de
executar qualquer operação.
Prenez connaissance de toutes les consignes de type
Attention et
Danger avant de procéder aux opérations décrites par les
instructions.
Lesen Sie alle Sicherheitshinweise, bevor Sie eine
Anweisung ausführen.
iii

Accertarsi di leggere tutti gli avvisi di attenzione e di
pericolo prima di effettuare qualsiasi operazione.
Lea atentamente todas las declaraciones de precaución y
peligro ante
de llevar a cabo cualquier operación.
Online support
Use the World Wide Web (WWW) or the IBM BBS to
download Diagnostic, BIOS Flash, and Device Driver files.
File download address is:
http://www.ibm.com/pc/files.html
The IBM BBS can be reached at (919) 517-0001.
IBM online addresses:
The IBM Support Page is:
http://www.ibm.com/support/
The IBM Home Page is:
http://www.ibm.com/pc/
iv Netfinity Server HMM

Contents
About this manual ................. iii
Important safety information .......... iii
Online support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iv
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 ............ 1
General Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Diagnostic tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Additional service information ........... 16
Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Symptom-to-FRU index . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Undetermined problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Parts listing (Type 8659) ............ 167
Related service information .......... 175
Safety information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Send us your comments! ............ 206
Problem determination tips ........... 207
Phone numbers, U.S. and Canada ........ 208
Trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Copyright IBM Corp. 2000 v

vi Netfinity Server HMM

Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
General Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Diagnostic tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Diagnostic tools overview ........... 8
Diagnostic LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Diagnostic test programs .......... 8
Power-on self-test (POST) ......... 9
POST beep codes ............. 10
Error messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
POST error messages and beep codes . . 10
Diagnostic error messages ........ 10
Software-generated error messages . . . 10
Option diskettes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Diagnostic test programs ............ 10
Navigating through the diagnostic tests . . . 11
Running Diagnostic test programs ...... 12
Viewing the test log ............. 13
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Additional service information ........... 16
Checking the system for damage ........ 17
After dropping it .............. 17
After spilling liquid on it ........... 17
Configuration overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Configuration/Setup utility . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Configuration/Setup utility usage ........ 22
System summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
System information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Product data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
System card data ............ 23
PCI routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Devices and I/O ports ............ 23
Date and time ............... 24
System security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Using the power-on password menu . . . 26
Using the administrator password menu . 27
Defining a system owner's name ..... 28
Start options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Advanced setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Core chipset control ........... 29
PCI bus control ............. 30
Cache control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Memory settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Advanced ISA settings .......... 30
Service Processor IRQ settings ..... 30
Plug and Play ............... 31
Error log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Configuring PCI features and options .... 31
Configuring the Ethernet controller ....... 32
Ethernet controller messages .......... 34
Novell NetWare or IntraNetWare Server ODI
driver messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
NDIS 2.01 (OS/2) driver messages ..... 36
Copyright IBM Corp. 2000 1

NDIS 4.0 (Windows NT) driver messages . . 38
UNIX messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Failover for redundant Ethernet ......... 41
Configuring Failover on OS/2 ........ 41
Configuring Failover on Windows NT .... 42
Configuring Failover on IntraNetWare .... 42
Identifying problems using status LEDs ..... 44
Power supply LEDs ............. 44
LED diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Recovering BIOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Resolving configuration conflicts ........ 49
Resolving memory-address conflicts ..... 49
Changing the software configuration setup . . 49
Changing the hardware configuration setup . 49
Resolving resource conflicts .......... 50
Resolving hardware configuration conflicts . . 50
Resolving software configuration conflicts . . 51
Using the SCSISelect utility program ...... 52
Starting the SCSISelect utility program .... 52
SCSISelect utility program choices ...... 52
Configure/View host adapter settings . . . 52
SCSI disk utilities ............ 53
Performing a low-level disk format .... 54
When to use the format disk program . . . 54
Starting the low-level format ....... 54
Verifying the disk media ......... 54
Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Adapter considerations . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Installing or removing adapters ....... 57
Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Bays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Types of cables .............. 65
SCSI devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
SCSI IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Termination requirements . . . . . . . . 67
Preinstallation steps (all bays) ........ 67
Installing or removing drives in bays A and B
(removable media) . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Installing or removing a drive in bay C (diskette
drive) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Installing or removing drives in bays 1 through 5
(hard disk drives) ............. 72
Changing jumper positions ........... 75
Two-pin jumper blocks ........... 75
Completing the installation ........... 77
Completing the tower model installation ..... 77
Completing the rack model installation .... 80
Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Front panel indicators ............ 85
DASD fan assembly removal .......... 90
Ethernet connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Expansion bays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
External options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
2 Netfinity Server HMM

Adding External SCSI devices ........ 94
Attaching external options .......... 95
Hot-swap backplane assembly removal ..... 96
Input/Output connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Installing a server in a rack enclosure ...... 99
Before you begin ............. 100
Installing the rack model in a rack enclosure 102
Preparing the server .......... 102
Preparing the rack enclosure ...... 104
Installing the server in the rack enclosure 108
Removing the rack model from a rack
enclosure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Internal drives installation or removing .... 113
Keyboard and mouse connectors ....... 114
Management port C ............. 115
Memory modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Installing or removing memory modules . . 116
Microprocessors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Installing microprocessor upgrades .... 118
Installing or replacing a microprocessor . . 119
Option installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Preparing a tower model ......... 126
Preparing a rack model .......... 128
Parallel port connector ............ 131
Power supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Power supply removal ............ 133
Rear fan assembly removal ......... 134
SCSI connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Internal SCSI connector .......... 135
External SCSI connector ......... 135
SCSI jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
DASD backplane jumper block location . 138
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Installing a U-bolt and security cable .... 139
Serial port connectors ............ 141
System board illustration ........... 142
System board LEDs ........... 142
System board connectors ......... 143
System board removal/replacement ...... 145
System board switches ............ 147
Bypassing an unknown power-on password 148
Universal serial bus ports .......... 149
Updating the server configuration ....... 150
Video port connector ............. 151
Symptom-to-FRU index . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Beep symptoms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
No beep symptoms ............. 155
Diagnostic error codes ............ 156
Error symptoms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
POST error codes .............. 160
SCSI error codes .............. 165
Undetermined problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Parts listing (Type 8659) ............ 167
System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 3

Keyboards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Power cords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
4 Netfinity Server HMM

General Checkout
The server diagnostic programs are stored in nonvolatile
random-access memory (NVRAM) on the system board.
These programs are the primary method of testing the
major components of the server: the system board,
Ethernet controller, video controller, RAM, keyboard,
mouse (pointing device), diskette drive, serial port, and
parallel port. You can also use them to test some external
devices.
Also, if you cannot determine whether a problem is caused
by the hardware or by the software, you can run the
diagnostic programs to confirm that the hardware is
working properly.
When you run the diagnostic programs, a single problem
might cause several error messages. When this occurs,
work to correct the cause of the first error message. After
the cause of the first error message is corrected, the other
error messages might not occur the next time you run the
test.
A failed system might be part of a shared DASD cluster
(two or more systems sharing the same external storage
device(s)). Prior to running diagnostics, verify that the
failing system is not part of a shared DASD cluster.
A system might be part of a cluster if:
The customer identifies the system as part of a
cluster.
One or more external storage units are attached to
the system and at least one of the attached storage
units is additionally attached to another system or
unidentifiable source.
One or more systems are located near the failing
system.
If the failing system is suspected to be part of a shared
DASD cluster, all diagnostic tests can be run except
diagnostic tests which test the storage unit (DASD residing
in the storage unit) or the storage adapter attached to the
storage unit.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
5

Notes
1. For systems that are part of a shared DASD
cluster, run one test at a time in looped mode.
Do not run all tests in looped mode, as this could
enable the DASD diagnostic tests.
2. If multiple error codes are displayed, diagnose
the first error code displayed.
3. If the computer hangs with a POST error, go to
the “Symptom-to-FRU index” on page 152.
4. If the computer hangs and no error is displayed,
go to “Undetermined problems” on page 165.
5. Power Supply problems, see “No beep
symptoms” on page 155.
6. Safety information, see “Safety information” on
page 176.
7. For intermittent problems, check the error log;
see, “Error log” on page 31.
001
IS THE SYSTEM PART OF A CLUSTER?
Yes No
002
Go to Step 004.
(CONTINUED)
003
Schedule maintenance with the customer. Shut down all
systems related to the cluster. Run storage test.
004
– Power-off the computer and all external devices.
– Check all cables and power cords.
– Set all display controls to the middle position.
– Power-on all external devices.
– Power-on the computer.
– Check the error log, see “Error log” on page 31. If an
error was recorded by the system, see
“Symptom-to-FRU index” on page 152.
– Start the Diagnostic Programs. See “Running
Diagnostic test programs” on page 12.
– Check for the following responses:
1. No beep.
2. Readable instructions or the Main Menu.
DID YOU RECEIVE THE CORRECT RESPONSES?
Yes No
005
Find the failure symptom in “Symptom-to-FRU index”
on page 152.
6 Netfinity Server HMM

006
– Run the Diagnostic Programs. If necessary, refer to
“Running Diagnostic test programs” on page 12.
If you receive an error, go to “Symptom-to-FRU index”
on page 152.
If the diagnostics completed successfully and you still
suspect a problem, see “Undetermined problems” on
page 165.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 7

Diagnostic tools
Server problems can be caused by the hardware, the
software, or a user error. An example of a user error is
pressing the wrong key on the keyboard.
You can check the hardware by using the diagnostic test
programs and the information in this section.
Note
When you run the diagnostic test programs, a single
problem can cause several error messages to occur.
When this happens, work to correct the cause of the
first error message. After the cause is corrected, the
other error messages probably will not occur the next
time you run the tests.
If the hardware is OK and you have not made an error,
you might have a software problem. If you suspect that
you have a software problem, refer to the information that
comes with that software package.
Diagnostic tools overview
The following tools are available to help identify and
resolve hardware-related problems:
LEDs on the system board and power supplies
Diagnostic test programs
Power-on self-test (POST)
POST beep codes
Error messages
Troubleshooting charts
Option diskettes
Diagnostic LEDs: When a system error occurs, the
relevant LEDs on the system board are lighted to identify
where the errors are (see “System board LEDs” on
page 142). When you see the System Error LED
illuminated on the operator LED (status) panel on the front
of the server, check the LEDs on the power supplies and
at any Ethernet adapters, then open the cover and see
which LEDs are illuminated on the system board.
Diagnostic test programs: The server
diagnostics test programs are stored in nonvolatile
random-access memory (NVRAM) on the system board.
These programs are the primary method of testing the
system board, memory, and other standard features of the
Netfinity 5000. You can also use them to test some
external devices.
Also, if you cannot determine whether a problem is caused
by the hardware or by the software, you can run the test
programs to confirm that the hardware is working properly.
8 Netfinity Server HMM

The server diagnostic test programs can identify most
problems associated with major components of the server:
the system board, Ethernet controller, video controller,
RAM, diskette drive, serial port, parallel port, keyboard,
and mouse.
You can start the diagnostic test programs from the
Startup panel, when the message Press F2 for
Diagnostics appears. Test options let you batch groups of
tests, specify test parameters (for example, which memory
DIMM you want to test), and specify the number of passes
that you want to run (1 through 9999).
You can also view the server configuration information
from the Diagnostic Utility menu. For example, you can
view the interrupt request (IRQ) and direct memory access
(DMA) assignments, memory usage, device drivers, and so
on.
Power-on self-test (POST): When you turn on
the server, it performs a series of tests to check the
operation of server components and some options. This
series of tests is called the power-on self-test, or POST.
POST does the following:
Checks the operation of some basic system board
operations
Checks the memory
Compares the current server configuration with the
stored server configuration information
Configures PCI adapters
Starts the video operation
Verifies that drives (such as the diskette, CD-ROM,
and hard disk drives) are connected properly
If you have a power-on password or administrator
password set, you must type the password and press
Enter before POST will continue.
While the memory is being tested, the amount of available
memory appears on the screen. These numbers advance
as the system progresses through POST and the final
number that appears on the screen represents the amount
of memory available. If POST finishes without detecting
any problems, a single beep sounds, the POST OK on the
front LED panel comes on, and the first screen of the
operating system or application program appears.
If POST detects a problem, an error message appears on
the screen. A single problem can cause several error
messages to appear. When this occurs, work to correct
the cause of the first error message. After the cause is
corrected, the other error messages probably will not
appear the next time you turn on the system.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
9

POST beep codes: POST generates beep codes to
indicate successful completion or the detection of an error.
One beep indicates successful completion of POST.
More than one beep indicates that POST detected an
error, see “Beep symptoms” on page 152
Error messages: Error messages indicate that a
problem exists; they are not intended to be used to identify
a failing part.
Hardware error messages that occur can be text, numeric,
or both. Messages generated by the software generally
are text messages, but they also can be numeric.
POST error messages and beep codes:
error messages and beep codes occur during startup when
POST finds a problem with the hardware or detects a
change in the hardware configuration, see
“Symptom-to-FRU index” on page 152.
Diagnostic error messages:
messages occur when a test finds a problem with the
server hardware. These error messages are alphanumeric
and they are saved in the Test Log.
Diagnostic error
Software-generated error messages:
messages occur if a problem or conflict is found by an
application program, the operating system, or both.
Messages are generally text messages, but they also can
be numeric. For information about these error messages,
refer to the documentation that comes with the software.
POST
These
Option diskettes: An optional device or adapter
might come with an Option Diskette. Option Diskettes
usually contain option-specific diagnostic test programs or
configuration files.
If the optional device or adapter comes with an Option
Diskette, follow the instructions that come with the option.
Different instructions apply depending on whether the
Option Diskette is startable or not.
Diagnostic test programs
This section includes useful information about navigating
through the diagnostic test programs, as well as
procedures for starting and stopping them. These
programs are designed to test the IBM Netfinity 5000. If
you want to test a non-IBM product, refer to the
information that comes with that product.
You can start the diagnostic test programs from the
Startup panel, when the message Press F2 for
Diagnostics appears.
10 Netfinity Server HMM

Note
When you run the diagnostic test programs, a single
problem can cause several error messages to occur.
When this happens, work to correct the cause of the
first error message. After the cause is corrected, the
other error messages probably will not occur the next
time you run the tests.
Navigating through the diagnostic tests:
Error messages in the Test Log are stored by diagnostic
test session. A diagnostic test session is defined as
running one, all, or a selection of tests, one or more times.
You can use the following keys to maneuver within the test
program:
Enter Selects an item.
Down Arrow (↓) Moves the cursor down.
Up Arrow (↑) Moves the cursor up.
Left Arrow (←) Toggles test selection between
Yes and No.
Right Arrow (→) Toggles test selection between
Yes and No.
Page Down (PgDn) Moves to the next diagnostic
test session in the log (if any).
Page Up (PgUp) Moves to the previous
diagnostic test session in the
log (if any).
F1 Displays the appropriate Help
information. Use the Up Arrow
(↑) or Down Arrow (↓) key to
scroll through the information.
Pressing F1 from within a Help
screen provides a help index
from which you can select
different categories. Pressing
Esc exits Help and returns to
where you left off.
Esc Returns to the previous menu.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
11

Running Diagnostic test programs: When
you start the diagnostic test programs from the Diagnostic
Utility menu, you can select the tests, the way the tests
run, and the number of times the tests run.
Notes
1. To run the diagnostic test programs, you must
start the server with the highest level password.
That is, if you enter the power-on password, and
an administrator password is set, you cannot run
the test programs. You can only view the error
messages in the test log.
If an administrator password is set, you must
enter the administrator password to run the
diagnostic test programs.
2. If the server stops during testing and you cannot
continue, restart the server and try running the
tests again. If the problem persists, see “Error
symptoms” on page 159 and look for the
problem symptom.
3. If the diagnostic tests do not find a problem, see
“Error symptoms” on page 159 and look for the
problem symptom.
4. You might need a scratch diskette to obtain
accurate test results when testing the diskette
drive.
5. The keyboard and mouse tests assume that a
keyboard and mouse are attached to the server.
To start the diagnostic tests:
1. Turn on the server and watch the screen.
If the system is turned on already, shut down the
operating system and restart the server.
2. When the message Press F2 for Diagnostics
appears, press F2.
If a power-on password or administrator password is
set, the system prompts you for it. Type in the
appropriate password; then, press Enter.
3. The Diagnostic Programs screen appears.
4. Select Extended or Basic from the top of the screen.
5. Select the test you want to run from the list that
appears; then, follow the instructions that appear on
the screen. The actions available include specifying
the options for the tests to be run, such as the
number of times to run the test, whether to stop on
error, or whether to use a predefined overlay that
describes the tests to be run.
When the tests have completed, you can view the
Test Log by selecting Utility from the top of the
screen.
12 Netfinity Server HMM

Also, you can view server configuration information
(such as system configuration, memory contents,
interrupt request (IRQ) use, direct memory access
(DMA) use, device drivers, and so on) by selecting
Hardware Info from the top of the screen.
If the hardware checks out OK but the problem persists
during normal server operations, a software error might be
the cause. If you suspect a software problem, refer to the
information that comes with the software package.
Viewing the test log: If you are already running
the diagnostic programs, continue with step 4 in this
procedure.
To view the Test Log:
1. Turn on the server and watch the screen.
If the system is turned on already, shut down the
operating system and restart the server.
2. When the message Press F2 for Diagnostics
appears, press F2.
If a power-on password or administrator password is
set, the system prompts you for it. Type in the
appropriate password; then, press Enter.
3. The Diagnostic Programs screen appears. After you
run diagnostic tests or abort the diagnostic tests, the
utility option appears at the top of the screen.
4. Select Utility from the top of the screen.
5. Select View Test Log from the list that appears; then,
follow instructions on the screen.
6. Press Esc to return to the Diagnostic Programs
screen.
7. Select Quit from the top of the screen; then, select
Exit Diags to exit from the diagnostic programs. The
server restarts.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
13

Features
The following table summarizes the features of the
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659.
Microprocessor
Intel Pentium II microprocessor
with MMX technology
512 KB of level-2 cache (min)
Memory
Standard: 64 MB (min), expandable to 1 GB
100 MHz, error correcting code (ECC) registered
synchronous dynamic random access memory
(SDRAM)
Four dual-inline memory-module (DIMM) sockets
Diskette Drive
One 3.5-inch, 1.44 MB
Hard Disk Drives
Up to five hot-swappable internal hard disk drives are
supported
CD-ROM Drive
Standard: IDE
Keyboard and Auxiliary Device (tower models)
Keyboard
Mouse
Expansion Slots
Supports up to five adapters
One ISA slot
Two shared PCI/ISA slot
Three dedicated PCI slots
Expansion Bays
One 3.5-inch diskette drive bay
Two 5.25-inch drive bays, open bay supports
half-high SCSI tape drive
Five 3.5-inch drive bays, hot-swappable
Upgradable Microcode
BIOS, diagnostics, and Netfinity Advanced System
Management Processor code upgrades (when
available) can update EEPROMs on the system board
Power Supply
350W with voltage auto-selection (110, 120, 220,
240 V ac) and power redundancy
– Standard—350W non-redundant, 175 W
redundant
14 Netfinity Server HMM

– Optional—Additional 175W power supply
available for 350W redundancy
Built-in overload and surge protection
Automatic restart after a momentary loss of power
Integrated Functions
Two serial ports
Two universal serial bus (USB) ports
System management port (C)
Advanced system management processor on system
board
One IDE internal connector, supports the system IDE
CD-ROM drive
One parallel port
Mouse port
Keyboard port
16-bit UltraSCSI controller
– One external connector (16-bit)
– One internal connector (16-bit)
Full-duplex 10/100 Mbps Ethernet controller
– 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX port
– Redundant Ethernet capability, through the use
of an optional network interface card (NIC)
Video controller port, super video graphics array
(SVGA)
1 MB video memory
Security Features
Bolt-down capability
Door lock (tower model only)
Power-on and administrator passwords
Selectable startup sequence
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 15

Additional service information
The following additional service information supports
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659.
“Checking the system for damage” on page 17.
“Configuration overview” on page 18.
“Configuration/Setup utility” on page 20.
“Configuration/Setup utility usage” on page 22.
“Configuring the Ethernet controller” on page 32.
“Ethernet controller messages” on page 34.
“Failover for redundant Ethernet” on page 41.
“Identifying problems using status LEDs” on page 44.
“Recovering BIOS” on page 48.
“Resolving configuration conflicts” on page 49.
“Resolving resource conflicts” on page 50.
16 Netfinity Server HMM

Checking the system for damage
This section provides instructions on what to do if the
system might be damaged.
After dropping it: Look for loose cables and
obvious damage. If any cables are loose, reconnect them
securely.
If you see no damage, turn on the system. If it works
correctly, the system probably did not suffer any damage.
If the system does not work correctly, turn it off and check
the adapters and memory modules to ensure that they are
connected correctly. Reseat all adapters and memory
modules.
If the system still does not work correctly, run the
diagnostic tests from diagnostic utility menu. For
information about running tests, see “Running Diagnostic
test programs” on page 12.
After spilling liquid on it: If liquid gets on the
keyboard:
1. Turn off the server.
2. Unplug the keyboard from the back of the server.
3. Turn the keyboard upside down to drain excess liquid.
4. Dry off the keyboard with a lint-free cloth.
After the keyboard is completely dry, plug it in and turn on
the server. If it does not work correctly, replace the
keyboard.
If liquid gets inside the monitor:
1. Turn off the monitor.
2. Turn off the server.
3. Unplug the monitor from the server and the electrical
outlet.
4. Let the monitor dry out.
If liquid gets inside the server:
1. Turn off the server and all attached devices.
2. Unplug the server from the electrical outlet and all
attached devices.
3. Let the server dry out.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
17

Configuration overview
You play a key role in how the server allocates resources
to organize and interconnect hardware devices and
software programs. This allocation process is referred to
as
configuration
server depend on the number and types of devices and
programs that you install.
The server supports several types of adapters. Because
of this flexibility, you can choose from among thousands of
adapters and devices that comply with any of the following
standards:
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA)
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
In general, the greater the number and variety of hardware
devices and software programs that you install in the
server, the more you will have to interact with the server
and the devices to correctly configure the system.
The server comes with the following hardware
configuration utility programs:
Configuration/Setup Utility
With the built-in Configuration/Setup Utility program,
you can configure system board functions, such as
serial and parallel port assignments; change interrupt
request settings; and change the startup sequence for
drives that you install. You can also use this utility
program to set passwords for starting up the server
and accessing the Configuration/Setup Utility
program.
SCSISelect Utility
With the built-in SCSISelect Utility program, you can
configure the SCSI devices that you install in the
server. You can use SCSISelect to change default
values, resolve configuration conflicts, and perform a
low-level format on a SCSI hard disk drive.
Before installing a new device or program, read the
documentation that comes with it. Reading the instructions
helps you determine the steps required for installation and
configuration. The following actions are typically, but not
always, required to configure the server.
. The steps required to configure the
18 Netfinity Server HMM

1. Run the Configuration/Setup Utility program and
record the current configuration settings.
2. Set switches on the server system board.
See “System board switches” on page 147 for the
meanings of the system board switches.
3. Set jumpers or switches on the device.
See the device installation instructions.
4. Install the device in the server, see “Locations” on
page 55.
5. Install software programs.
Refer to the information provided with the
“ServerGuide and Netfinity Manager Information”
section of this
Server Library
and with the operating
system for more information.
6. Resolve configuration conflicts.
See “Resolving resource conflicts” on page 50.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
19

Configuration/Setup utility
For most configurations, the server will operate using the
default system settings. You need to change the settings
only to resolve configuration conflicts or to enable or
change device functions.
When you want or need to change the default settings, the
Configuration/Setup Utility program provides a convenient
way to display and change the settings.
After you run and exit the Configuration/Setup Utility
program, configuration information is stored in nonvolatile
random-access memory (NVRAM). While the server is
powered off, the configuration information remains
available for the next system startup.
Always run the Configuration/Setup Utility program if you
add or remove any hardware option, or if you receive an
error message instructing you to do so. Review this
chapter and the information that comes with the option
before making changes. Also, record the current settings
before making any changes.
To start the Configuration/Setup Utility program:
1. Turn on the server and watch the screen.
2. When the messages Press F1 for
Configuration/Setup and Press F2 for Diagnostics
appear, select the action you need.
To configure the server, press F1 to select
Configuration/Setup Utility.
The Configuration/Setup Utility main menu
appears. For information about the menus, see
“Configuration/Setup utility usage” on page 22.
Note
If you enter a power-on password and an
administrator password has been set, a
limited menu appears on the screen. To
access the full Configuration/Setup Utility
menu, you must enter the administrator
password.
To run the system diagnostics, press F2 to
select Diagnostic Utility.
The Diagnostic Utility main menu appears. For
information about running the system
diagnostics, see “Diagnostic test programs” on
page 10.
20 Netfinity Server HMM

Important
If a defective PCI adapter is causing the system
to stop responding during startup, you can press
Alt+F1 here. This will cause the server to
bypass PCI device initialization (except video)
and go directly to the Configuration/Setup
Utility, where you can disable the defective PCI
adapter. Disabling the defective PCI adapter
should enable you to complete a normal startup
when you restart the server.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 21

Configuration/Setup utility usage
From the Configuration/Setup Utility program main menu
you can select settings you want to change.
Pressing F1 displays Help information for a selected menu
item.
Notes
1. If you enter only the power-on password and an
administrator (supervisor-level) password is also
set, a limited version of the menu appears. To
view the full Configuration/Setup Utility menu you
must enter the administrator password.
2. The choices on some menus might differ slightly,
depending on the BIOS version that comes with
the server.
To change configuration settings:
1. Use the Up Arrow (↑) key to select the item you want
to change; then, press Enter.
2. Select the configuration setting you want to change.
Use the Right Arrow (→) or Left Arrow (←) key to
highlight the menu, if needed.
3. Use the Right Arrow (→) or Left Arrow (←) key to
select the appropriate setting for the selected item.
4. Repeat Steps 1 through 3 for each setting that you
want to change. Press Esc to return to the
Configuration/Setup Utility main menu.
5. After making changes, you can select:
Save Settings to save the selected changes.
Restore Settings to delete the selected
changes.
Load Default Settings to cancel the changes
and restore the factory settings.
6. To exit from the Configuration/Setup Utility main
menu, select Exit Setup.
7. The system prompts you to confirm your choice. You
can return to the Configuration/Setup Utility main
menu, or exit.
System summary: Select this choice to display
configuration information, such as the type and speed of
the microprocessor, and amount of memory.
Changes that you make to configuration settings appear on
this summary screen. You cannot edit the fields.
22 Netfinity Server HMM

System information: Select this choice to display
information about the Netfinity 5000,
Changes that you make on other menus might appear on
this summary screen.
Product data:
information such as the machine type and model, the
system serial number, the system board identifier, and the
revision level or issue date of the flash electronically
erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM) and BIOS.
System card data:
system board model, submodel, system serial number,
system board identifier, DASD backplane identifier, and
identifiers for power supply 1 and power supply 2.
Select this choice to view system
Select this choice to view the
PCI routing:
Select this choice to view the interrupt request (IRQ)
settings for PCI adapters and for the Ethernet, SCSI, and
other controllers on the system board. See “PCI bus
control” on page 30 for information about changing the
PCI IRQ settings.
Devices and I/O ports: Software recognizes ports
from their port assignments. Each port must have a
unique port assignment. The Configuration/Setup Utility
program normally handles this, but you might have special
hardware or software that requires you to change these
assignments.
Note
Serial port A can be shared by the system
management processor and operating system. Serial
port B is used by the operating system only.
Management port C is controlled exclusively by the
system management processor, cannot be used by
the operating system, and cannot be configured using
the Configuration/Setup Utility program. See the
“Advanced System Management Information” section
of this
Server Library
serial ports A and C.
for information about configuring
Select the Devices and I/O Ports choice to view or
change the assignments for devices and input/output ports.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 23

You can add serial ports by installing a serial adapter in an
expansion slot. See the documentation that comes with
the serial adapter for information about port assignments.
You can configure the parallel port as standard, as
bidirectional, as an Extended Capabilities Port (ECP), or as
an Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP). Bidirectional, ECP, and
EPP are all bidirectional modes; in all three modes, data
can be both read from and written to a device. ECP and
EPP are industry-standard, high-performance bidirectional
modes. Which one of these modes you choose depends
on what mode the device supports.
Note
When you configure the parallel port as bidirectional,
ECP, or EPP, use an IEEE 1284-compliant cable.
The maximum length of the cable must not exceed 3
meters (9.8 feet).
You can configure the mouse and diskette controller as
enabled or disabled, and configure the type of diskette
drive.
You can view the type of video controller and the amount
of video memory installed.
You can configure the IDE channel (enabled or disabled)
and view the IDE Primary Master Device (type, size,
transfer selection and mode, and logical block addressing
(LBA) mode).
To display or change the port assignments:
1. Select Devices and I/O Ports.
2. Select a device or port; then, use the Left Arrow (←)
or Right Arrow (→) key to advance through the
settings available.
Date and time: Select this choice to set the system
date and time.
The system time is in a 24-hour format:
hour/minute/second. The system date is in standard
format for your country. For example, in the United States,
the format is MM/DD/YYYY (Month/Day/Year).
Select Date and Time; then, use the Left Arrow (←) or
Right Arrow (→) key to advance through each data field.
Type the new information; the system saves the
information as you type it.
System security: To control access to the
information in the server, you can implement security
features, such as adding passwords and defining a system
owner's name that displays during startup. Implementing
these security measures helps you to ensure the integrity
of the data and programs that are stored in the server.
24 Netfinity Server HMM

After setting a power-on password, you can enable the
unattended-start mode. This locks the keyboard and
mouse, but allows the server to start the operating system.
The keyboard and mouse remain locked until you enter the
correct password.
To set, change, or delete a password:
1. Select System Security.
2. Select the password that you want to change.
3. Follow the instructions on the screen.
After you have set a power-on or administrator password,
you must enter the password whenever you turn on the
server. (The passwords do not appear on the screen as
you type them.)
Type of Password Results
No password set No password required to start system.
Power-on password
only
Administrator
password only
Administrator
power-on password
and
You can access all choices on the
Configuration/Setup Utility program main
menu.
You must enter the password to complete
the system startup.
You can access all choices on the
Configuration/Setup Utility program main
menu.
If you forget the power-on password, you
can regain access to the server by using
switch 8 on the system board. See “Using
the power-on password menu” on page 26
for details.
You must enter the password to enter the
Configuration/Setup Utility program.
You can access all choices on the
Configuration/Setup Utility program main
menu.
If the administrator password is forgotten, it
cannot be overridden or removed. You
must replace the system board.
You can enter either password to complete
the system startup.
– Administrator password provides
access to all choices on the
Configuration/Setup Utility program
main menu. You can set, change, or
delete both the administrator and
power-on passwords, and allow a
power-on password to be changed by
the user.
– Power-on password provides access to
a limited set of choices on the
Configuration/Setup Utility program
main menu. This might include
changing or deleting the power-on
password.
If you forget the power-on password, and
the administrator password has been set,
use the administrator password at the
password prompt. Then, start the
Configuration/Setup Utility program and
change the power-on password.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 25

Using the power-on password menu:
power-on password is set, you must enter a password
each time you start the system.
To set a power-on password:
1. Select Power-on Password from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
The Power-on Password menu appears.
2. Type the password in the Enter Power-on Password
data field.
You can use any combination of up to seven
characters (A–Z, a–z, and 0–9) for the power-on
password. Keep a record of the password in a
secure place.
3. Move the cursor to the Enter Power-on Password
Again data field and type the password again.
Note
A message appears if the two passwords do not
match. If this happens, press Enter to return to
the Power-On Password menu.
4. Select Change Power-on Password to save the new
password; then, press Enter.
5. A confirmation window appears. Press Enter to
change the power-on password. Press Esc to return
to the System Security menu.
When a power-on password is set, POST does not
complete until you enter the password. If you forget the
power-on password, you can regain access to the server
through one of the following methods:
If an administrator password has been set, enter the
administrator password at the power-on prompt (see
“Using the administrator password menu” on page 27
for details). Start the Configuration/Setup Utility
program and change the power-on password as
described in steps 1 through 5 above.
Use the Bypass-Power-On-Password switch on the
system board to temporarily bypass the power-on
password.
1. See “Option installation” on page 125 through
“Preparing a tower model” on page 126 or
through “Preparing a rack model” on page 128
for instructions on powering off the server and
removing the cover. Then, refer to the system
board diagram inside the server for the location
of the switch block.
2. Locate switch 8 (see “System board switches” on
page 147).
3. Set switch 8 on the switch block to On, to
bypass the power-on password.
4. Restart the server, then start the
Configuration/Setup Utility program and change
When a
26 Netfinity Server HMM

the power-on password as described in steps 1
through 5 above.
5. Turn the server off again.
6. Set switch 8 back to Off.
7. Restart the server.
To delete a power-on password:
1. Select Power-on Password from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
The Power-on Password menu appears.
2. Select Delete Power-on Password; then, press
Enter.
3. A confirmation window appears. Press Enter to
delete the power-on password. Press Esc to cancel
the request and return to the System Security menu.
To allow the server to start in unattended mode when
a power-on password is set:
Note
If the password data field is set to On, the
Unattended Start and Stop modes are not
supported.
1. Select Power-on Password from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
The Power-on Password menu appears.
2. Select Allow for unattended boot with password.
Press the Left Arrow (←) or Right Arrow (→) key to
toggle the entry to On.
If no power-on password is set on the server, this option
has no effect.
Using the administrator password menu:
administrator password (sometimes called a
supervisor-level password) controls access to some
features of the server, including the Configuration/Setup
Utility program.
Important
If an administrator password is set and then forgotten,
it cannot be overridden or removed. You must replace
the system board.
To set an administrator password:
1. Select Administrator Password from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
2. Type the password in the Enter Administrator
Password data field.
A password can contain any combination of up to
seven alphanumeric characters (A–Z, a–z, and 0–9).
Keep a record of the password in a secure place.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
The
27

3. Move the cursor to the Enter Administrator
Password Again data field and type the password
again.
Note
A message appears if the two passwords do not
match. If this happens, press Enter to return to
the Administrator Password menu.
4. Select Change Administrator Password to save the
new password; then, press Enter. The password
becomes effective immediately.
To delete an administrator password:
1. Select Administrator Password from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
2. Select Delete Administrator Password; then, press
Enter.
3. A confirmation window appears. Press Enter to
delete the administrator password. Press Esc to
return to the System Security menu.
To enable a user to change the power-on password:
1. Select Administrator Password from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
2. Select Power-on password changeable by user.
Press the Left Arrow (←) or Right Arrow (→) key to
toggle the entry to Yes.
When this choice is enabled, System Security appears on
the limited Configuration/Setup menu. The System
Security menu contains the Power-on Password choice.
Defining a system owner's name:
a system owner's name that displays during POST each
time that the server is started. If you set an administrator
password, only the administrator can set, change, or delete
the system owner's name.
To set the system owner's name:
1. Select System Owners Name from the System
Security menu; then, press Enter.
The System Owners Name screen appears.
2. Type the name in the Enter System Owners Name
String data field. You can use any combination of up
to 15 characters and spaces in the system owner's
name.
3. Press the Down Arrow (↓) key to select the Set or
Change System Owners Name data field.
4. Press Enter to set the name or change a previously
defined name.
To delete the system owner's name, select Delete Stored
System Owners Name; then, press Enter.
You can specify
28 Netfinity Server HMM

Start options: Start options take effect when you
start the server.
You can select keyboard operating characteristics, such as
the keyboard speed. You also can specify whether the
keyboard number lock (NumLock) starts on or off. You
also can enable the server to run in disketteless and
monitorless operation.
You can specify the startup sequence the server is to use
to determine the device from which the operating system
loads. For example, you can define a startup sequence
that checks for a CD-ROM, then checks an installed hard
disk drive, and then checks a network adapter.
Attention: If the CD-ROM drive contains a startable CD,
you must remove the CD if you want to use a startup
sequence that begins with a startable diskette.
You can enable a virus-detection test that checks at
startup for changes in the master boot record. You also
can also choose to run POST in the enhanced mode or in
the quick mode.
Select Start Options; then, use the Left Arrow (←) or
Right Arrow (→) key to advance through each data field.
Advanced setup: Select Advanced Setup to
change values for advanced hardware features, such as
cache control, PCI bus control, memory settings, and
advanced ISA settings.
Note
A warning message displays above the choices on
this menu, to alert you that the system may
malfunction if these options are configured incorrectly.
Follow the instructions on the screen carefully.
Use the Left Arrow (←) or Right Arrow (→) key to highlight
the options for the selected menu item.
Core chipset control:
settings that control features of the core chip set on the
system board. The chipset control choices are:
IOQ Depth Use this setting to control the in order queue
(IOQ) depth in the system. The value can be
varied from 1 to 8. This value should
normally be set at 8 (default)
Grant Timers Use this setting to enable or disable the
grant timer mechanism for each of the 5 PCI
slots. Enabling this will cause grant to be
asserted to a PCI bus agent for a minimum
of two clocks. This setting should normally
be set to disable (default)
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
Select this choice to modify
29

PCI bus control
Note
This page shows the interrupts and the correct
interrupt assigned to the devices.
Select PCI Bus Control to:
Change the master latency timer values for PCI bus 1
and PCI bus 2.
Specify the system board interrupt routing (IRQs) for
SCSI, Ethernet, video, and USB.
Specify the slot interrupt routing (IRQs) for PCI slots.
Enable and disable PCI device types (SCSI, video,
Ethernet) and slots. When a PCI adapter is defective,
you can use Alt+F1 at startup and then disable the
PCI adapter in order to enable the system to start up
successfully.
Note
Any changes you make to IRQs will not be reflected in
the PCI Interrupt Routing selection of this menu until
you restart the server.
Cache control:
microprocessor cache state as enabled or disabled, and to
define the microprocessor cache type as Write-back or
Write-through.
Selecting write-back mode will provide the maximum
system performance.
Memory settings:
banks of memory and to enable or disable selected rows
of memory within those banks.
If a memory error is detected during POST or memory
configuration, the server can automatically disable the
failing row of memory and continue operating with reduced
memory capacity. If this occurs, you must manually
enable the row of memory after the problem is corrected.
Choose Memory Settings from the Advanced Setup
menu; then use the the Up Arrow (↑) or Down Arrow (↓)
key to highlight the row that you want to enable. Use the
Left Arrow (←) or Right Arrow (→) key to select Enable.
Advanced ISA settings:
timer delay for ISA I/O recovery.
Service Processor IRQ settings:
to specify the IRQ the system-management processor is to
use and to synchronize the service processor clock to the
system clock.
Select this choice to define the
Select this choice to view the server
Use this selection to set the
Use this selection
30 Netfinity Server HMM

Plug and Play: Most adapters designed for PCI slots
are Plug and Play devices that are auto-configuring.
However, many ISA adapters are not Plug and Play
devices and you must allocate the system resources that
the adapter will use. Select Plug and Play to identify the
available system resources:
Memory
I/O ports
DMA
Interrupt
Note
The menus do not contain resources that are used by
the system or by previously installed Plug and Play
adapters.
Select Plug and Play; then, use the Up Arrow (↑) and
Down Arrow (↓) key to highlight the system resource that
you want to change. Use the Left Arrow (←) or Right
Arrow (→) key to toggle from Plug and Play to ISA
Legacy for the selected menu choice.
Error log: Select Error Log to view the three most
recent power-on self-test (POST) errors the system has
generated, or to view the system error log. You can clear
both error logs from this screen by selecting Clear Error
Logs.
Configuring PCI features and options: PCI
devices automatically communicate with the server
configuration information. This usually results in automatic
configuration of a PCI device. If a conflict does occur, see
“Resolving resource conflicts” on page 50.
Multiple-function PCI adapters use more than one interrupt.
When you install one of these adapters, review the IRQ
assignments in the Configuration/Setup utility programs
(see “PCI bus control” on page 30). Verify that the IRQ
assignments are correct.
The Netfinity 5000 server uses a rotational interrupt
technique to configure PCI adapters. This technique
enables you to install a variety of PCI adapters that
currently do not support sharing of PCI interrupts. For
information on manually overriding the interrupt setting,
see “PCI bus control” on page 30.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
31

Configuring the Ethernet controller
The Netfinity 5000 comes with an Ethernet controller on
the system board. The Ethernet controller provides
10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX support through the RJ-45
connector on the back of the server.
When you connect the server to the network, the Ethernet
controller automatically detects the data-transfer rate
(10 Mbps or 100 Mbps) on the network and then sets the
controller to operate at the appropriate rate. That is, the
Ethernet controller will adjust to the network data rate,
whether the data rate is standard Ethernet (10BASE-T),
Fast Ethernet (100BASE-TX), half duplex (HDX), or full
duplex (FDX). This process is also known as
auto-negotiation
software intervention. The controller supports half-duplex
(HDX) and full-duplex (FDX) modes at both speeds.
Auto-negotiation works only if the hub or switch to which
the server is connected also supports auto-negotiation. If
the hub or switch does not support auto-negotiation, the
speed (10 Mbps or 100 Mbps) will still be detected
correctly, but half-duplex mode will always be selected. A
full-duplex switch that does not support auto-negotiation
will not attach to the Netfinity 5000 in full-duplex mode.
In this case, if you want the network to operate in
full-duplex mode, you must manually override the settings
to obtain a full-duplex connection. To do this, the server
must have a device driver that supports manual overrides.
Use the ServerGuide CDs to install this device driver.
Refer to the “ServerGuide and Netfinity Manager
Information” section of this
on installing device drivers. The ServerGuide CDs contain
IBM Update Connector, a dial-up1 program that keeps the
BIOS and device drivers current. Verify that you have
installed the appropriate device driver. Also, refer to the
Ethernet documentation for additional information on
operating modes, manual overrides, and device drivers.
Attention:
The 10BASE-T Ethernet and the 100BASE-TX Fast
Ethernet cabling in the network must be Category 5
or higher to meet various standards, including
electromagnetic compatibility.
You must install a device driver to enable the
operating system to address the Ethernet controller.
Use the ServerGuide CDs to install this device driver.
Refer to the information in the “ServerGuide and
Netfinity Manager Information” section of this
. This auto-negotiation occurs without
Server Library
for instructions
Server
1
Response time will vary, depending on the number and nature
of calls received.
32 Netfinity Server HMM

Library
for instructions on installing device drivers, or
for more information about the ServerGuide CDs.
Fast Ethernet operates at a data rate of up to 100 Mbps.
However, except for the different operating speeds, Fast
Ethernet and standard Ethernet are structurally identical.
Most applications and protocols that are currently installed
on a standard Ethernet system can be seamlessly
migrated to a Fast Ethernet system. Because of the
equivalence of the two types of Ethernet, mixed Ethernet
and Fast Ethernet systems also can be designed and
implemented.
The bandwidth required at each workstation connected to
a server is generally far less than the bandwidth required
at the server. This is because the server might have to
handle the bandwidth of multiple workstations at the same
time. A cost-effective solution to the bandwidth
requirements of this type of system is a mixed Ethernet
and Fast Ethernet network. This mixed network consists
of standard Ethernet connections at the workstations and
Fast Ethernet connections at the servers.
The Ethernet controller is a PCI device, and is therefore a
Plug and Play device. You do not have to set any jumpers
or configure the controller for the operating system before
you use the Ethernet controller.
Notes
1. The Ethernet controller supports the operating
systems that the server supports. To find out
which operating systems the server supports, go
to the following World Wide Web address:
http://www.ibm.com/pc/us/compat/
If you need additional Ethernet connections, you can install
an Ethernet adapter, such as an IBM 10/100 Ethernet
adapter. Review the network-adapter documentation for
any additional configuration requirements.
Note
If you are installing an IBM 10/100 Ethernet adapter,
be sure to run the Ethernet controller diagnostics and
record the Ethernet controller configuration information
before you install the adapter.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 33

Ethernet controller messages
The integrated Ethernet controller might display messages
from the following device drivers:
Novell NetWare or IntraNetWare Server ODI
NDIS Adapter for level 2.01 (OS/2)
NDIS Adapter for level 4.0 (Windows NT)
SCO UNIX LLI
Novell NetWare or IntraNetWare Server ODI
driver messages: The following error messages are
for the Novell NetWare or IntraNetWare server ODI driver.
The explanation and recommended action are included
with each message.
PCNTNW-NW-026 The MSM is unable to parse a required custom
Explanation: The user entered an incorrect parameter keyword.
Action: Reload the driver using the correct keyword.
PCNTNW-NW-054 The adapter did not respond to the initialization
Explanation: The adapter did not respond when the driver tried to initialize it.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) setting in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
PCNTNW-NW-058 The adapter did not respond to the initialization
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) setting might not be valid or the
EEPROM information might be incorrect.
Action: Make sure the IRQ settings are correct in the Configuration/Setup
utility programs. See “PCI bus control” on page 30 for information on setting
the interrupt requests. If the IRQ settings are correct, replace the system
board.
PCNTNW-NW-066 The cable might be disconnected from the adapter.
Explanation: The cable might be disconnected from the server Ethernet port.
Action: Verify that a cable is connected to the Ethernet port.
PCNTNW-NW-071 The matching virtual adapter could not be found.
Explanation: You tried to load another instance of the driver with a different
I/O address. This new adapter could not be found.
Action: If you installed an Ethernet adapter, such as an IBM Netfinity 10/100
Fault Tolerant Adapter, as part of Ethernet redundancy (failover), make sure
that the adapter is seated correctly. If the adapter is seated correctly, replace
the adapter.
PCNTNW-NW-072 A resource tag is unavailable.
Explanation: The driver tried to allocate some resources that were not
available.
Action: Add or free some memory in the server. Then, restart the server.
PCNTNW-NW-073 Unable to allocate memory.
Explanation: The driver failed to allocate the memory needed for normal
operation.
Action: Add more memory, or free some memory resources in the server.
Then, restart the server.
keyword.
command.
command.
34 Netfinity Server HMM

PCNTNW-NW-074 The hardware interrupt cannot be set.
Explanation: An attempt was made to initialize a given hardware interrupt.
The attempt was not successful.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30).
Make sure that the interrupt request numbers are set correctly. If you are
using an ISA adapter, make sure resources are reserved as ISA Legacy in the
Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “Plug and Play” on page 31.)
PCNTNW-NW-075 The Multiple Link Interface Driver (MLID) cannot be
Explanation: An error occurred while the driver was trying to register with the
LSL.
Action: Check the version of the NetWare or IntraNetWare Operating
System. Make sure that this driver is correct for the version of NetWare or
IntraNetWare that you are using. Restart the server.
PCNTNW-NW-079 The Multiple Link Interface Driver (MLID) did not
Explanation: The MSMTx Free Count is not initialized correctly.
Action: Restart the server.
PCNTNW-NW-086 The driver parameter block is too small.
Explanation: The driver parameter block is too small.
Action: Restart the server.
PCNTNW-NW-087 The media parameter block is too small.
Explanation: The driver media parameter block is too small.
Action: Restart the server.
PCNTNW-NW-091 The hardware configuration conflicts.
Explanation: You tried to load a new frame type for the existing controller.
The hardware assumptions made in doing so are incorrect. This error can
also occur if you try to specify a mode (such as, redundancy) that conflicts
with another specified mode.
Action: Make sure that the hardware configuration matches the software
settings. See “PCI bus control” on page 30 for information on viewing and
changing interrupt requests.
PCNTNW-NW-126 The group bit in the node address override was
Explanation: The IEEE address has a group bit indicating that an address
belongs to a group of stations. This bit is used only as a destination address;
it cannot be used as a source address. You tried to enter a source address
with this bit set. The driver cleared the group bit of the source address.
Action: None necessary, message is for information only.
PCNTNW-NW-127 The local bit in the node address override was set.
Explanation: The local bit in the IEEE address format indicates that the
addresses are being managed locally. If you use the node address override
capabilities of this driver to enter a new address, the local bit must be set.
You entered an address without the local bit set. The driver has set the local
bit.
Action: None necessary, message is for information only.
PCNTNW-NW-164 The device was not found.
Explanation: The driver cannot find an Ethernet controller in the server.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
registered with the Link Support Layer (LSL).
initialize MSMTx Free Count.
cleared.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 35

PCNTNW-NW-165 The device was not found at IOADDRESS.
Explanation: The Ethernet controller cannot be found at the I/O address
specified.
Action: The Ethernet controller does not require a parameter for the I/O
address. Remove the I/O address parameter.
PCNTNW-NW-167 PCI scan specified, device not found.
Explanation: The driver cannot locate the Ethernet controller on the PCI bus.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30).
If the problem persists, go to “Diagnostic test programs” on page 10 to run the
diagnostic utility.
PCNTNW-NW-180 The DMA parameter is not necessary for PCI device.
Explanation: The Ethernet controller does not require a DMA setting.
Action: None necessary, message is for information only.
NDIS 2.01 (OS/2) driver messages: The
following error messages are for the NDIS 2.01 (OS/2)
drivers. The explanation and recommended action are
included with each message.
PCNTND-1 Unable to open the Protocol Manager.
Explanation: The NDIS stack is not configured correctly.
Action: Check and correct the configuration.
PCNTND-6 Out of memory while allocating buffers.
Explanation: The driver could not allocate the requested buffers.
Action: Check the system configuration. Edit the PROTOCOL.INI file to
reduce the number of Txbuffers and Rxbuffers specified for the driver.
PCNTND-7 A Protocol Manager device error occurred.
Explanation: The NDIS stack is not configured correctly.
Action: Check and correct the configuration.
PCNTND-8 Bad status for the Protocol Manager.
Explanation: The NDIS stack is not configured correctly in the
PROTOCOL.INI file.
Action: Check and correct the configuration.
PCNTND-9 Cannot find the PROTOCOL.INI entry.
Explanation: The NDIS stack is not configured correctly in the
PROTOCOL.INI file.
Action: Check and correct the configuration.
PCNTND-10 The Protocol Manager Input Output Control (IOCTL)
Explanation: The NDIS stack is not configured correctly in the
PROTOCOL.INI file.
Action: Check and correct the configuration.
PCNTND-11 Protocol Manager registration failed.
Explanation: The NDIS stack is not configured correctly.
Action: Check and correct the configuration.
failed.
36 Netfinity Server HMM

PCNTND-15 Device not found.
Explanation: The driver cannot find an Ethernet controller in the server.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
PCNTND-16 PCI scan specified, device not found.
Explanation: The driver cannot locate the Ethernet controller on the PCI bus.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
PCNTND-21 The adapter failed the checksum test.
Explanation: The driver cannot find an Ethernet controller.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
PCNTND-23 WARNING: PCNET IRQ found =
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) setting (xx) in the PROTOCOL.INI
file does not match the hardware IRQ setting.
Action: Remove the IRQ setting from the PROTOCOL.INI file or change the
IRQ setting in the PROTOCOL.INI file to match the IRQ setting shown in the
PCI Routing selection of the System Information menu in the
Configuration/Setup Utility. (See “PCI routing” on page 23.)
PCNTND-24 WARNING: PCNET IRQ does not match PROTOCOL.INI.
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) setting in the PROTOCOL.INI file
does not match the hardware IRQ setting.
Action: Remove the IRQ setting from the PROTOCOL.INI file or change the
IRQ setting in the PROTOCOL.INI file to match the IRQ setting shown in the
PCI Routing selection of the System Information menu in the
Configuration/Setup Utility. (See “PCI routing” on page 23.)
PCNTND-25 PCI scan specified, PCI bus not found!
Explanation: The driver cannot locate the PCI bus on the server.
Action: Go to “Diagnostic test programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic
utility.
PCNTND-29 WARNING: DMA number is not necessary for PCI
Explanation: The Ethernet controller does not require a DMA setting.
Action: Remove the DMA setting in the PROTOCOL.INI file.
PCNTND-33 PCNET device with specified IOBASE is already in use.
Explanation: The specified I/O address number is already in use by another
Ethernet controller or device.
Action: Remove the I/O address setting in the PROTOCOL.INI file.
device.
xx
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 37

NDIS 4.0 (Windows NT) driver messages:
The following error messages are for the NDIS 4.0 drivers.
The explanation and recommended action are included
with each message.
PermaNet(tm) Server: No Secondary Adapter Found. Grouping Mode is
Explanation: The failover option requires an adapter that is compatible with
the device driver of the Ethernet controller on the system board. No such
adapter was found.
Action: Make sure the correct adapter is installed. .
PermaNet(tm) Server: Problem Occurs on the Primary Adapter. Switching
Explanation: The system detected a problem with the primary Ethernet
connection and has transferred all network traffic to the secondary Ethernet
controller.
Action: Identify the cause of the failure on the primary Ethernet connection.
Restoring the operational state of the primary connection will cause the
network traffic to automatically transfer to the primary Ethernet controller.
PermaNet(tm) Server: Switching back to Primary Adapter.
Explanation: The primary Ethernet connection is now operating correctly.
Network traffic will automatically transfer to the primary Ethernet controller.
Action: None needed, message is for information only. .
disabled.
over to the Secondary Adapter.
UNIX messages: The following error messages are
for the SCO UNIX LLI driver.
pnt0-2 PCI search specified, PCI device not found!
Explanation: The driver cannot locate the Ethernet controller on the PCI bus.
Action: Run the NETCONFIG program to search for another Ethernet
controller.
Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default (enabled) position
in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus control” on page 30).
If the problem persists, go to “Diagnostic test programs” on page 10 to run the
diagnostic utility.
pnt0-6 Cannot allocate memory for the adapter during an
Explanation: On a SunSoft Solaris system, this message indicates that the
system is out of Streams memory blocks.
Action: Use the CRASH utility to increase the number of Streams memory
blocks.
Modify the interrupt request (IRQ) settings in the Configuration/Setup utility
programs, or run the NETCONFIG program to match the hardware settings.
pnt0-7 Cannot allocate memory for the adapter during reset.
Explanation: The system is out of Streams memory blocks.
Action: Use the CRASH utility to increase the number of Streams memory
blocks.
pnt0-11 Device not found!
Explanation: The driver cannot find an Ethernet controller.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
interrupt. Please check the Streams parameters.
Please check the Streams parameters.
38 Netfinity Server HMM

pnt0-12 Device failed checksum test!
Explanation: The driver cannot find an Ethernet controller.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
pnt0-13 add_intr_handler failed! Interrupts already enabled.
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) that was specified, or the IRQ that
was found, conflicts with other devices in the server.
Action: Modify the hardware settings.
Run the NETCONFIG program to match the hardware settings.
pnt0-14 Cannot locate hardware.
Explanation: The SunSoft Solaris driver cannot find any Ethernet controller.
Action: Verify that the PCI Ethernet device type is set to the default
(enabled) position in the Configuration/Setup utility programs (see “PCI bus
control” on page 30). If the Ethernet adapter is enabled, go to “Diagnostic test
programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
pnt0-15 No more devices to open.
Explanation: The SunSoft Solaris driver cannot find any more Ethernet
controllers.
Action: Verify that additional Ethernet adapters are present or replace the
Ethernet adapter that fails to respond. If the problem persists, go to
“Diagnostic test programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
pnt0-17 Device fault...Reset initiated!
Explanation: The SunSoft Solaris driver has been reset due to a device
fault.
Action: Verify that additional Ethernet adapters are present or replace the
Ethernet adapter that fails to respond. If the problem persists, go to
“Diagnostic test programs” on page 10 to run the diagnostic utility.
pnt0-19 IRQ found for PCnet hardware does not match space.c
Explanation: This is a warning message referring to the interrupt request
(IRQ) that the SunSoft Solaris driver found in the system.
Action: Ignore this message if you are sure that this is what you want to do.
Otherwise, run the NETCONFIG program to match the hardware settings.
pnt0-20 add_intr_handler failed! Unknown interrupt type.
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) that was specified, or the IRQ that
was found, conflicts with other devices in the server.
Action: Modify the hardware settings.
Run the NETCONFIG program to search for another Ethernet controller.
pnt0-21 add_intr_handler failed! Out of range interrupt number.
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) that was specified, or the IRQ that
was found, conflicts with other devices in the server.
Action: Modify the hardware settings.
Run the NETCONFIG program to search for another Ethernet controller.
pnt0-22 add_intr_handler failed! Out of range IPL.
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) that was specified, or the IRQ that
was found, conflicts with other devices in the server.
Action: Modify the hardware settings.
Run the NETCONFIG program to search for another Ethernet controller.
(or pnt.conf)!
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 39

pnt0-23 add_intr_handler failed! Vector already occupied.
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) that was specified, or the IRQ that
was found, conflicts with other devices in the server.
Action: Modify the hardware settings.
Run the NETCONFIG program to search for another Ethernet controller.
pnt0-24 add_intr_handler failed! Vector already shared at
Explanation: The interrupt request (IRQ) that was specified, or the IRQ that
was found, conflicts with other devices in the server.
Action: Modify the hardware settings.
Run the NETCONFIG program to search for another Ethernet controller.
pnt0-26 The DMA number is not necessary for PCI device.
Explanation: The Ethernet adapter does not require a DMA setting.
Action: Edit the SPACE.C file to delete the DMA parameter.
pnt0-29 The IRQ number is already in use.
Explanation: The specified I/O address is already in use.
Action: Run the NETCONFIG program to modify the hardware settings.
pnt0-31 I/O address is not necessary for the PCI device.
Explanation: The I/O address specified is not required.
Action: Remove the assigned I/O address specified for the Ethernet
controller.
different IPL.
40 Netfinity Server HMM

Failover for redundant Ethernet
The Netfinity 5000 has an integrated Ethernet controller.
The IBM Netfinity 10/100 Fault Tolerant Adapter is an
optional redundant network interface card (NIC adapter)
that you can install in the server. If you install this NIC
adapter and connect it to the same logical segment as the
primary Ethernet controller, you can configure the server to
support a
integrated Ethernet controller or the NIC adapter as the
primary Ethernet controller. In failover mode, if the primary
Ethernet controller detects a link failure, all Ethernet traffic
associated with it is switched to the redundant (secondary)
controller. This switching occurs without any user
intervention. Applications with active sessions do not
experience any data loss. When the primary link is
restored to an operational state, the Ethernet traffic
automatically switches back to the primary Ethernet
controller.
failover
function. You can configure either the
Notes
1. Only one controller in the redundant pair is active
at any given time. For example, if the primary
Ethernet controller is active, then the secondary
Ethernet controller cannot be used for any other
network operation.
2. The operating system determines the maximum
number of IBM Netfinity 10/100 Fault Tolerant
Adapters that you can install in the server. See
the documentation that comes with the adapter
for more information.
The failover feature currently is supported by OS/2,
Windows NT, and IntraNetWare. The setup required for
each operating system follows.
Configuring Failover on OS/2
1. Install the redundant NIC adapter according to the
instructions provided with the adapter and in
“Installing or removing adapters” on page 57.
2. Use the ServerGuide CDs to install the AMD PCNet
Ethernet Family adapter device driver.
3. Using the MPTS utility program, select the driver from
the list and select the Edit button.
Note
Only one driver instance needs to be loaded for
each redundant pair of Ethernet controllers.
4. Change the PermaNet Server Feature keyword to
TRUE and specify the Primary and Standby slots that
contain the redundant pair. Refer to “System board
illustration” on page 142 for the locations and slot
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
41

numbers of the PCI slots. The integrated controller is
located in slot 9.
5. To enable the writing of messages to the
IBMCOM\LANTRAN.LOG file when a failover occurs:
a. Copy the file PCNETOS2.EXE from the OS2
directory of the diskette created by the
ServerGuide program to the hard disk drive.
b. Add the following statement to the CONFIG.SYS
file:
Run=d:\path\PCNETOS2.EXE
where d and
which you copied PCNETOS2.EXE.
6. Restart the server.
The failover function is now enabled.
path
are the drive and path to
Configuring Failover on Windows NT
1. Install the redundant NIC adapter according to the
instructions provided with the adapter and in
“Installing or removing adapters” on page 57.
2. Use the ServerGuide CDs to install the AMD PCNet
Ethernet Family adapter device driver.
3. From the Windows NT desktop, select Control Panel,
then select the Network icon, then the Adapters tab.
4. Highlight one of the adapters that will be in the
redundant pair and then select the Properties...
button.
5. Check the Grouping box. This will show the possible
combinations for redundant pairs.
6. Select the adapter pair you want and then select OK.
Note that the integrated Ethernet controller is located
at PCI bus 1, slot 9.
7. Select Close to exit from the Network setup.
When you restart the server, the failover function will
be in effect.
If a failover occurs, a message is written to the Windows
NT Event Viewer log. If the DMI instrumentation code for
the integrated Ethernet controller is active (PCNET.EXE
was run), a pop-up message is generated also.
Configuring Failover on IntraNetWare
1. Install the redundant NIC adapter according to the
instructions provided with the adapter and in
“Installing or removing adapters” on page 57.
2. Load the device driver by using the following
command:
LOAD d:\path\PCNTNW.LAN PRIMARY=x SECONDARY=y
where d and
driver is located, and x and y are the PCI slot
numbers where the redundant pair is located.
The slot number associated with the integrated
Ethernet controller can vary depending upon the
42 Netfinity Server HMM
path
are the drive and path where the

configuration of the server. To determine the slot
number, load the driver with no parameters. The
driver will display the available slot numbers. The slot
number that is greater than 10000 will be the slot
number of the integrated Ethernet controller. When
the slot number of the integrated Ethernet controller is
determined, reload the driver with the appropriate
parameters.
3. When the driver is loaded, bind it to a protocol stack.
The failover function is now enabled. If a failover occurs:
A message is generated to the operating system
console.
The custom counters for the device driver contain
variables that define the state of the failover function
and the location of the redundant pair. You can use
the NetWare Monitor to view the custom counters.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 43

Identifying problems using status LEDs
The server has LEDs to help you identify problems with
some server components. These LEDs are part of the
diagnostics built into the server. By following the path of
lights, you can quickly identify the type of system error that
occurred.
Status LEDs are located on the following components:
Operator LED panel
For more information, see “Front panel indicators” on
page 85.
Hard disk drive trays
For more information, see “Controls” on page 82.
Power supply
For more information, see “Power supply LEDs.”
System board
See “System board LEDs” on page 142 for locations
of the LEDs on the system board.
Power supply LEDs: The ac Power LEDs, located
on the rear of the power supply, provide status information
about the power supply. See “Front panel indicators” on
page 85 for the location of these LEDs.
The following table describes the ac Power LEDs.
AC Power LED Description and Action
On The power supply is on and operating
Off There is an ac power problem.
No beep, fans
running, and ac
power LED
blinking
correctly.
Possible causes:
1. There is no ac power to the power
supply.
Actions: Verify that:
The power cord is properly
connected to the server.
The power outlet functions properly.
2. The power supply has failed.
Action: Replace the power supply.
System held in reset
Possible causes:
1. If an optional VRM is installed and no
optional processor.
Action: Remove the optional VRM.
2. If optional VRM failed.
Action: Replace the optional VRM.
3. If primary VRM failed.
Action: Replace the system board.
4. If system board failed.
Action: Replace system board.
44 Netfinity Server HMM

LED diagnostics: The diagnostics built into the
server allow you to quickly identify the type of system error
that occurred. When the System Error LED on the
information LED panel is illuminated, use the following
information to isolate the problem. An error message
usually appears on the display monitor as well.
If the System Error LED on the information LED panel
on the front of the server is on, a system error was
detected. Check the LEDs on the power supplies and
at any Ethernet adapters, then open the cover and
check to see which of the LEDs on the system board
inside the server are on. (See “System board LEDs”
on page 142 for the location of the LEDs.)
System Board LED Description
Service Processor
Error LED on
NMI LED on A non-maskable interrupt occurred. The PCI
SMI LED on A system-management interrupt occurred.
PCI 1 LED on An error occurred on PCI bus 1. An adapter
PCI 2 LED on An error occurred on PCI Bus 2. An adapter
An error has occurred in the service
processor.
Actions:
1. Try a reset by turning off the
system, jumper/short J39, and
turn on the system.
2. Replace the system board.
1 or PCI 2 LED will probably also be on.
Actions:
1. If the PCI 1 or PCI 2 LED is on,
follow the instructions for those
LEDs.
2. If the PCI 1 or PCI 2 LED is not
on, restart the server. If the
problem persists (the NMI LED
stays on), go to “General
Checkout” on page 5.
This is an indication of service processor
activity, and is not an error.
Actions: No action is required.
in PCI slot 5 or the system board caused the
error.
Actions: Check the error log for additional
information. If the error log indicates
a problem with the integrated
Ethernet controller, replace the
system board.
in PCI slot 1, 2, 3, or 4 or the system board
caused the error.
Actions:
1. Check the error log for
additional information.
2. If you cannot correct the
problem from the information in
the error log, try to determine
the failing adapter by removing
one adapter at a time from the
primary PCI bus 2 (PCI slots
1–4) and restarting the server
after each adapter is removed.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 45

System Board LED Description
DIMM 1 Error LED
on
DIMM 2 Error LED
on
DIMM 3 Error LED
on
DIMM 4 Error LED
on
FAN 1 LED on Fan 1 has failed or is operating too slowly.
FAN 2 LED on Fan 2 has failed or is operating too slowly.
TEMP LED on The system temperature has exceeded the
Integrated Voltage
Regulator Error LED
on
Secondary
Processor VRM
Error LED on
Primary
Microprocessor Error
LED on
Secondary
Microprocessor Error
LED on
Power Supply 1 LEDonThe primary power supply has failed.
Power Supply 2 LEDonThe secondary power supply has failed.
The DIMM in DIMM slot 1 has failed.
Action: Replace the DIMM in DIMM slot 1.
The DIMM in DIMM slot 2 has failed.
Action: Replace the DIMM in DIMM slot 2.
The DIMM in DIMM slot 3 has failed.
Action: Replace the DIMM in DIMM slot 3.
The DIMM in DIMM slot 4 has failed.
Action: Replace the DIMM in DIMM slot 4.
Note: A failing fan can also cause the
TEMP and DASD 1 LEDs to be on.
Action: Replace fan 1.
Note: A failing fan can also cause the
TEMP and DASD 1 LEDs to be on.
Action: Replace fan 2.
maximum rating.
Actions:
1. Check to see if a fan has failed.
If it has, replace the fan.
2. Make sure the room
temperature is not too hot.
The voltage regulator for the primary
microprocessor slot has failed.
Actions: Replace the system board.
The voltage regulator module (VRM) for the
secondary microprocessor slot has failed.
Actions:
1. Turn off the server, reseat the
VRM, and restart the server.
2. If the problem persists, replace
the VRM.
The microprocessor in the primary
microprocessor slot has failed.
Actions:
1. Turn off the server, reseat the
microprocessor, and restart the
server.
2. If the problem persists, replace
the microprocessor.
The microprocessor in the secondary
microprocessor slot has failed.
Actions:
1. Turn off the server, reseat the
microprocessor and VRM; then
restart the server.
2. If the problem persists, replace
the microprocessor.
Action: Replace the primary power supply.
Action: Replace the secondary power
supply.
46 Netfinity Server HMM

System Board LED Description
DASD 1 LED on A hot-swap hard disk drive has failed.
Actions:
1. Check the error log for
additional information. If the
error log indicates a
temperature problem and the
fans are working correctly,
check the system for proper air
flow.
2. If the amber Hard Disk Status
LED on one of the hot-swap
hard disk drives is on, replace
the hard disk drive.
System Error LED on the information LED panel on
the front of the server is off. The diagnostics have
not detected a system error.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 47

Recovering BIOS
If the BIOS has become corrupted, such as from a power
failure during a flash update, you can recover the BIOS
using the recovery boot block and a BIOS flash diskette.
Note
You can obtain a BIOS flash diskette from one of the
following sources:
Use the ServerGuide program to make a BIOS
flash diskette.
Download a BIOS flash diskette from the World
Wide Web. Go to http://www.ibm.com/support/,
select IBM Server Support, and make the
selections for the server.
The flash memory of the server contains a protected area
that cannot be overwritten. The recovery boot block is a
section of code in this protected area that enables the
server to start up and to read a flash diskette. The flash
utility automatically recovers the system BIOS from the
BIOS recovery files on the diskette.
To recover the BIOS:
1. See “Option installation” on page 125 through
“Preparing a tower model” on page 126 or through
“Preparing a rack model” on page 128 for instructions
on powering off the server and removing the cover.
Then, refer to the system board diagram inside the
server for the location of the switch block.
2. Locate switch 5 (see “System board switches” on
page 147).
3. Set switch 5 on the switch block to On, to set boot
block recovery mode.
4. Insert the BIOS flash diskette in the diskette drive.
5. Restart the server.
Nothing appears on the display monitor, but the
diskette drive activity LED and periodic beeps
indicates that BIOS recovery is under way. Recovery
is complete when slow beeps are concluded by a
string of fast beeps and the Post Complete light on
the operator LED panel is on.
6. Remove the flash diskette from the diskette drive.
7. Turn the server off.
8. Set switch 5 to Off, to return to normal startup mode.
9. Restart the server. The system should start up
normally.
48 Netfinity Server HMM

Resolving configuration conflicts
The Configuration/Setup Utility program program
configures only the system hardware. It does not consider
the requirements of the operating system or the application
programs. For these reasons, memory-address
configuration conflicts might occur.
Resolving memory-address conflicts: The
Configuration/Setup Utility program might change the
memory-address space used by some hardware options.
If this happens, the new address might conflict with
addresses defined for use through expanded memory
specification (EMS). (EMS is used only with DOS.)
If a memory conflict exists, one or more of the following
conditions might exist:
The system cannot load the operating system.
The system does not work.
An application program does not operate, or it returns
an error.
Screen messages indicate that a memory-address
conflict exists.
You can resolve memory-address conflicts by changing
either the software or hardware configuration setup.
Changing the software configuration
setup: The best way to resolve memory-address
conflicts is to change the software configuration by
changing the addresses that the EMS device driver
defined. The SVGA video memory occupies 8 Kb (1 Kb =
approximately 1000 bytes) of space in the hex C0000 to
C7FFF EMS memory area. EMS device drivers must use
addresses different from those assigned to video read-only
memory (ROM). You can use the Configuration/Setup
Utility program to view or change the current setting for
video ROM. For information about using the
Configuration/Setup utility programs, see
“Configuration/Setup utility usage” on page 22.
If the SVGA or EMM386 device driver is causing the
memory-address conflict, refer to the DOS documentation.
For conflicts caused by device drivers supplied with
application programs instead of those supplied with DOS,
refer to the documentation that comes with the device
drivers.
Changing the hardware configuration
setup: An alternative way to resolve memory-address
conflicts is to change the address of the conflicting
hardware option.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 49

Resolving resource conflicts
The resources used by the server consist of IRQs, DMA,
I/O port addresses, and memory. This information is
useful when a resource configuration conflict occurs.
Conflicts in the configuration occur if:
A device is installed that requires the same resource
as another device. (For example, a conflict occurs
when two adapters try to write to the same address
space.)
A device resource is changed (for example, changing
jumper settings).
A device function is changed (for example, assigning
COM1
to two serial ports).
A software program is installed that requires the same
resource as a hardware device.
The steps required to resolve a configuration error are
determined by the number and variety of hardware devices
and software programs you install. If a hardware
configuration error is detected, a
message appears after the server completes POST and
before the operating system is loaded. You can bypass
the error by pressing Esc while the error message is
displayed.
The Configuration/Setup Utility program configures the
system hardware and PCI interrupt requests. The program
does not consider the requirements of the operating
system or the application programs. See “Resolving
software configuration conflicts” on page 51 for additional
information.
configuration error
Resolving hardware configuration
conflicts: Use the following information to help resolve
hardware configuration conflicts:
1. Run the Configuration/Setup Utility program to view
and change resources used by the system board
functions. Record the current settings before making
any changes. (See “Configuration/Setup utility” on
page 20 for instructions.)
2. Determine which adapter or device is causing the
conflict.
3. Change adapter jumpers or switches. Some devices
use jumpers and switches to define the system
resources that the device needs. If the settings are
incorrect or set to use a resource that cannot be
shared, a conflict occurs and the device will remain
deactivated by the configuration program.
4. Remove the device or adapter. Some configurations
are not supported. If you must remove an adapter,
see “Installing or removing adapters” on page 57.
50 Netfinity Server HMM

Resolving software configuration conflicts:
The memory-address space and IRQs used by some
hardware options might conflict with addresses defined for
use through application programs or the expanded memory
specification (EMS). (EMS is used only with DOS.)
If a conflict exists, one or more of the following conditions
might exist:
The system cannot load the operating system.
The system does not work.
An application program does not operate, or it returns
an error.
Screen messages indicate a conflict exists.
To resolve conflicts, you can change the software or
hardware configuration.
Note
Start the Configuration/Setup Utility program to view
the addresses used by the system board functions.
The best way to resolve memory-address conflicts is to
change the addresses used by the application program or
the device driver. You can use the Configuration/Setup
Utility program to change addresses.
If a device driver is causing a memory-address conflict,
refer to the operating-system documentation or the
documentation supplied with the device drivers.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
51

Using the SCSISelect utility program
The server comes with a menu-driven configuration utility
program, called SCSISelect, that you can use to view and
change SCSI settings.
You can use the SCSISelect Utility program to:
View and change the device configuration
Perform a low-level format or verify the media on a
SCSI hard disk drive.
Starting the SCSISelect utility program
Note
The SCSI controller in the server is a dual channel
device. Select channel B for internal devices, channel
A for external devices. The default selection is
channel A.
You can access this program when you start the server.
The SCSISelect prompt appears after the IBM Netfinity
Logo appears. Press Ctrl+A immediately after the
SCSISelect prompt appears; then, select channel B for
internal devices.
Use the Up Arrow (↑) and Down Arrow (↓) key to move
the highlight bar to the various menu choices. Press Esc
to return to the previous menu. Also, you can press the
F5 key to switch between color and monochrome modes (if
the monitor permits). To change the settings of the
displayed items, follow the directions on the screen.
SCSISelect utility program choices: The
following choices appear on the SCSISelect Utility program
menu:
Configure/View Host Adapter Settings
SCSI Disk Utilities
Configure/View host adapter settings:
change the SCSI controller settings, select
Configure/View Host Adapter Settings and follow the
directions on the screen. This menu has the following
choices:
Host Adapter SCSI ID
Select this choice to change the SCSI ID of the SCSI
controller from its default value of 7. Do not assign
the SCSI controller to a SCSI ID already in use, such
as 14, which is used by the daughterboard card
(SAF-TE) on the DASD backplane.
SCSI Parity Checking
The default value is
be changed.
Host Adapter SCSI Termination
Enabled.
This value should not
52 Netfinity Server HMM
To view or

The default value is
Enabled.
This value should not
be changed.
Boot Device Options
Select this choice to configure startable device
parameters. Before you can make updates, you must
know the ID of the device whose parameters you
want to configure.
SCSI Device Configuration
Select this choice to configure SCSI device
parameters. Before you can make updates, you must
know the ID of the device whose parameters you
want to configure.
Advanced Configuration Options
Select this choice to view or change the settings for
advanced configuration options. These options
include enabling support for large hard disk drives
and support for BIOS parameters if BIOS is enabled.
To reset to the the host adapter defaults, press F6; then,
follow the instructions on the screen.
SCSI disk utilities:
To see the IDs that are assigned
to each SCSI device, to format a SCSI device, or to scan
the disk for media defects, select SCSI Disk Utilities from
the SCSISelect Utility program menu.
To use the utility program, select a drive from the list.
Read the screens carefully before making a selection.
Note
If the following screen displays, you might have
pressed Ctrl+A before the selected drives were ready.
Restart the server, and watch the SCSISelect
messages as each drive spins up. After the drive that
you want to view or format spins up, press Ctrl+A.
à ð
Target SCSI ID: 4
SCSI CDB Sent: ð3 ðð ðð ðð ðE ðð ð7 ðð ð2 ðð
Host Adapter Status: ððh - No host adapter error
Target Status: ð2h - Check condition
Sense Key: ð2h - Not ready
+Sense Code: ð4h
+Sense Code Qualifier: ð2h
Unexpected SCSI Command Failure
Press 'Esc' to continue.
á
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 53
ñ

Performing a low-level disk format:
perform a low-level format on hard disk drives using the
Format Disk
Depending on the hard disk capacity, the low-level format
program could take up to two hours.
feature of the SCSISelect Utility program.
You can
When to use the format disk program:
Format Disk program:
When you are installing software that requires a
low-level format
When you get recurring messages from the diagnostic
tests directing you to run the Low-Level Format
program on the hard disk
As a last resort before replacing a failing hard disk
drive.
Note
For information about backing up all of the files, see
the operating-system documentation.
Use the
Starting the low-level format
Attention
The low-level format erases
1. If the hard disk drive is working, make a backup copy
of all the files and programs on the hard disk drive.
2. Select Format Disk; then, follow the instructions on
the screen.
Note
Hard disk drives normally contain more tracks
than their stated capacity, to allow for defective
tracks. A message appears on the screen if the
defect limit is reached. If this happens, replace
the drive.
all
data and programs.
3. To install an operating system after the hard disk
drive is formatted, refer to the ServerGuide
information in the “ServerGuide and Netfinity Manager
Information” section of this
with the server.
Verifying the disk media:
to scan the selected hard disk drive for media defects,
such as bad tracks. All recoverable defects will be
remapped.
The Verify Disk Media program takes about 15 to 20
minutes to complete.
Server Library
Select Verify Disk Media
that comes
54 Netfinity Server HMM

Locations
The following information supports the Netfinity 5000 Type 8659 server.
“Adapters” on page 56.
“Battery” on page 61.
“Bays” on page 64.
“Changing jumper positions” on page 75.
“Completing the installation” on page 77.
“Completing the tower model installation” on page 77.
“Controls” on page 82.
“DASD fan assembly removal” on page 90.
“Ethernet connector” on page 91.
“Expansion bays” on page 92.
“External options” on page 94.
“Hot-swap backplane assembly removal” on page 96.
“Input/Output connectors” on page 97.
“Installing a server in a rack enclosure” on page 99.
“Internal drives installation or removing” on page 113.
“Keyboard and mouse connectors” on page 114.
“Management port C” on page 115.
“Memory modules” on page 116.
“Microprocessors” on page 118.
“Option installation” on page 125.
“Parallel port connector” on page 131.
“Power supplies” on page 132.
“Power supply removal” on page 133.
“Rear fan assembly removal” on page 134.
“SCSI connectors” on page 135.
“SCSI jumpers” on page 137.
“Security” on page 139.
“Serial port connectors” on page 141.
“System board illustration” on page 142.
“System board removal/replacement” on page 145.
“System board switches” on page 147.
“Universal serial bus ports” on page 149.
“Updating the server configuration” on page 150.
“Video port connector” on page 151.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
55

Adapters
Adding an adapter, such as a communication adapter,
extends the capabilities and power of the server. For
example, you can add a RAID (redundant array of
independent disks) adapter that can enhance logical-drive
capacity and performance.
Adapter considerations: The Netfinity 5000
supports ISA and PCI adapters. You can install up to six
adapters in the connectors on the system board.
The system board in the server contains 16-bit, ISA-bus
expansion connectors and 32-bit, PCI-bus expansion
connectors. One of the expansion slots is a shared
PCI/ISA slot. One of the expansion slots supports only
ISA adapters. The remaining four slots support only PCI
adapters. The server supports only 5.0-volt adapters on
the PCI bus.
Notes
1. You can install PCI adapters in slots 1–5. Slots
1–4 are on PCI bus 2, slot 5 is on PCI bus 1.
Both PCI buses are primary buses; when the
system scans the buses to see what devices are
on them, it scans PCI bus 1 first.
2. You can install ISA adapters in the slots 1 and 2.
Note: If an ISA adapter is not a Plug and Play
device, you must allocate the system
resources that the adapter will use. Use
the Plug and Play choice in the Advanced
Setup selection of the Configuration/Setup
Utility program to allocate resources.
The following figure shows the location of the PCI and ISA
expansion slot connectors on the system board.
PCI
5
4
PCI
3
PCI
PCI
ISA
2
PCI
1
ISA
56 Netfinity Server HMM

Note
Expansion slots 1 and 2 are a shared slot. A shared
slot can be used by an adapter installed in either the
PCI connector or the adjacent ISA connector, but not
both.
The server comes with a video controller. This video
controller is an integrated component on the system board.
It is
not
in an expansion slot. The integrated video
controller has super video graphics array (SVGA)
technology.
The integrated video controller is not removable. If you
want to disable this controller and use a video adapter
instead, you can install a video adapter in an expansion
slot. When you install a video adapter, the server BIOS
automatically disables the integrated video controller.
Attention
To avoid possible damage to adapters and server
components, be sure that the adapters you install do
not touch each other or the other components (such
as the microprocessor) inside the server.
Installing or removing adapters: This section
gives the procedure for installing an adapter. If you want
to remove an adapter, reverse the following steps.
Before you begin
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Read the documentation that comes with the
option.
1. Review the instructions that come with the adapter to
determine if the adapter must be installed in a certain
slot; otherwise, use any available, bus-compatible
slot.
Note
If you install a video adapter, the server
automatically disables the video controller on the
system board. IBM recommends that the video
be installed in slot 5.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 57

2. If you have not done so, remove the server cover.
See “Option installation” on page 125.
3. Remove the expansion-slot cover.
a. Release the slot retaining clamp by pulling the
curved arm on the clamp away from the system
board.
Note
The slot retaining clamp might differ slightly
from this illustration.
b. Remove the expansion slot cover from the slot
opening.
4. If the adapter is a full-length card, continue with this
step. Otherwise, go to step 5 on page 59.
a. Remove the card support bracket retaining clip.
b. If the adapter is a full length card in slot 1 or 2,
ensure that the card support bracket has the
appropriate card support installed for that slot.
Card Type Card Support Color
ISA Black
PCI White
Each card support is also identified on the tab as
ISA or PCI.
58 Netfinity Server HMM

Note
You might find it easier to replace the card
support with the appropriate color card
support if you remove the card support
bracket from the server first.
1) To remove a card support from a slot .1/ or
storage location .2/, gently release the card
support tab .3/ and slide the card support
away from the system board until the card
support is free.
2) To insert a card support in a slot or a
storage location, place the card support in
the slot or storage opening and slide the
card support toward the system board until
the tab clicks into place.
c. If you removed the card support bracket from the
server, replace it in the server now.
5. Touch the static-protective package to any
unpainted
metal surface on the server; then, remove the adapter
from the package.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
59

6. Install the adapter:
a. Carefully grasp the adapter and align it with the
expansion slot (and with the card support
bracket if a full-length adapter).
b. Press the adapter
firmly
into the connector until
fully seated.
c. Fit the foot of the slot retaining clamp to the top
of the expansion slot.
d. Push the curved arm of the slot retaining clamp
toward the adapter until the clamp is locked into
place.
e. If necessary, connect any internal cables to the
adapter. Refer to the documentation that comes
with the option.
f. If you removed the card-guide retaining clip in
step 4a on page 58, reinstall it now.
7. If you want to install or remove any other options, do
so now. Otherwise, go to “Completing the
installation” on page 77.
60 Netfinity Server HMM

Battery
IBM has designed this product with safety in mind. The
lithium battery must be handled correctly to avoid possible
danger.
Caution
When replacing the battery, use only IBM Part
Number 33F8354 or an equivalent type battery
recommended by the manufacturer. If the system has
a module containing a lithium battery, replace it only
with the same module type made by the same
manufacturer. The battery contains lithium and can
explode if not properly used, handled, or disposed of.
Do not:
Throw or immerse into water
Heat to more than 100°C (212°F)
Repair or disassemble
Dispose of the battery as required by local ordinances
or regulations.
Note
In the U.S., please call 1-800-IBM-4333 for information
about battery disposal.
If you replace the original lithium battery with a
heavy-metal battery or a battery with heavy-metal
components, be aware of the following environmental
consideration. Batteries and accumulators that contain
heavy metals must not be disposed of with normal
domestic waste. They will be taken back free of charge by
the manufacturer, distributor, or representative, to be
recycled or disposed of in a proper manner.
Before you begin, be sure you have:
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Followed any special handling and installation
instructions supplied with the replacement
battery.
Removed the server side cover (see “Option
installation” on page 125).
Note
After you replace the battery, you must reconfigure the
system and reset the system date and time.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 61

To replace the battery:
1. Unplug the server.
2. Locate the battery on the system board (see “System
board illustration” on page 142).
3. Remove the battery:
a. Use one finger to lift the battery clip over the
battery.
b. Use one finger to slightly slide the battery toward
the front of the server. The spring mechanism
behind the battery will push it out toward you as
you slide it forward.
c. Use your thumb and index finger to pull the
battery from under the battery clip.
d. Ensure that the battery clip is touching the base
of the battery socket by pressing gently on the
clip.
4. Insert the new battery:
a. Tilt the battery so that you can insert it into the
front of the socket, under the battery clip.
b. As you slide it under the battery clip, press the
battery down into the socket.
5. Reinstall the server covers and complete the
installation (see “Completing the installation” on
page 77).
6. Start the Configuration/Setup Utility program and
reset configuration parameters as needed.
To reset the system date and time, go to “Date
and time” on page 24.
To reset the power-on password, go to “Using
the power-on password menu” on page 26.
62 Netfinity Server HMM

To reconfigure the system, follow the instructions
given in “Configuration/Setup utility” on page 20
(all models).
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 63

Bays
Internal drives are installed in
to as bay A, bay B, bay C, bay 1, bay 2, and so on.
The following illustrations show the locations of the bays in
the server.
Tower model
bays
. The bays are referred
A
B
C
1
2
3
4
5
Rack model
54321 CBA
The server comes with a CD-ROM drive installed in bay B
and a diskette drive installed in bay C.
64 Netfinity Server HMM
Bay Drive Width Drive Type Drive Height
A 5.25-inch Removable
B 5.25-inch CD-ROM 41.3 mm (1.6
C 3.5-inch Diskette drive 25.4 mm (1.0
1
through
5
Notes:
3.5-inch Hot-swap hard
1. Removable media includes CD-ROMs, optical discs, and tapes. It
does not include hard disk drives.
2. A 41.3 mm drive installed in bays 1 through 5 will occupy two
bays.
media drive
only
disk
1
41.3 mm (1.6
in.)
in.)
in.)
25.4 mm (1.0
in.) – Slim line
(SL)
41.3 mm (1.6
2
– Half
in.)
height (HH)
Table 1. Maximum Allowable Drive Sizes
Types of cables: Drives connect to the server with
cables. Each cable connector is designed to fit a
corresponding connector on a drive.
Three types of internal cables connect to the drives in the
server:
A four-wire power cable connects to each drive.
A flat-ribbon signal cable connects to IDE devices.
– One flat-ribbon cable connects the internal
diskette drive.
The connector on one end of this cable attaches
to the system board. The primary diskette drive
installed in the server (usually known as drive A)
is attached to the connector on the other end of
this cable.
Note
The primary diskette drive must always be
attached to the drive connector on the end
of this cable.
– A second flat-ribbon cable connects the
CD-ROM drive.
This cable has two drive connectors. A third
connector attaches to the system board. The
CD-ROM drive that comes with the server is
attached to the connector on the end of this
cable.
Another cable connects internal SCSI devices. This
SCSI cable has two connectors that connect to SCSI
devices:
– One to the backplane of the DASD hot-swap
enclosure
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 65

– One to a SCSI device you install in the open
5.25-inch bay
A third connector attaches to the SCSI connector on
the system board.
External SCSI devices usually come with a SCSI cable.
You attach one end of this SCSI cable to the SCSI
connector on the back of the server, and the other end to
the SCSI device. You usually can attach additional SCSI
devices to this cable.
SCSI devices: The Netfinity 5000 supports drives
that comply with American National Standards Institute
(ANSI) SCSI Standards X3.131-1986 (SCSI), X3.131-1994,
(SCSI-2), X3.277-1996 (SCSI-3 Fast-20 parallel interface),
and X3.253-1995 (SCSI-3 parallel interface).
For a complete list of the SCSI devices supported on the
Netfinity 5000, go to http://www.ibm.com/support/ on the
World Wide Web.
If you install additional SCSI devices, you must set a
unique identification (ID) for each SCSI device. This
enables the SCSI controller to identify the devices and
ensure that different devices do not attempt to transfer
data at the same time.
Note
Any information about SCSI drives also applies to
other SCSI devices, such as scanners and printers.
SCSI IDs:
unique identification (ID) for each SCSI device that you
connect to the server. This enables the SCSI controller to
identify the devices and ensure that different devices do
not attempt to transfer data at the same time.
The SCSI controller in the server supports SCSI IDs 0 to
15; ID 7 is reserved for the controller, ID 14 is reserved for
the daughterboard (SAF-TE) on the DASD backplane.
Use the SCSISelect Utility program to view the SCSI IDs
of SCSI devices in the server. (See “Using the SCSISelect
utility program” on page 52 for more information.)
Note
A daughterboard is a secondary adapter that can be
plugged into another adapter or the system board.
The SAF-TE daughterboard on the DASD backplane
makes available the status information about the
DASD drives that meet the following conditions:
The drives are part of a RAID environment
The status information comes from a supported
If you install SCSI devices, you must set a
IBM RAID adapter
66 Netfinity Server HMM

If you install wide (16-bit) SCSI devices, you can set the
IDs to any whole number between 0 and 6, or to any
whole number between 8 and 13, or to 15. If you install
narrow (8-bit) SCSI devices, you can set the IDs to any
whole number between 0 and 6.
The server automatically sets SCSI IDs for hot-swap hard
disk drives, according to the jumper settings on the DASD
backplane. The server uses the hard disk drive SCSI IDs
to send status information to the indicator lights on each
hard disk drive. See “Front panel indicators” on page 85
for the location and identification of the hard disk drive
status lights.
Table 2 shows the default SCSI IDs that the backplane
assigns for hot-swap hard disk drives.
Table 2. Automatically Assigned SCSI IDs
Bay 1 2 3 4 5
ID 0 1 2 3 4
You can change the default ID addresses of the drives by
changing the jumper settings on the DASD backplane.
See “SCSI jumpers” on page 137.
Termination requirements:
The UltraSCSI controller
and the backplane of the hot-swap bays provide
termination for the internal SCSI bus (cable) in the server.
There are no termination requirements for any SCSI
devices you install in the hard disk drive bays or attach to
this cable.
If you attach a SCSI cable and devices to the external
SCSI connector, set the termination for the last device on
that SCSI cable to Enabled. Refer to the instructions that
come with the SCSI device for more information about
termination.
Preinstallation steps (all bays)
Before you begin, be sure you have:
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Read the documentation that comes with the
option.
Read “Termination requirements.”
Verified that you have all cables, drive trays, and
any other equipment specified in the
documentation that comes with the internal drive.
Before you can install drives in the Netfinity 5000, you
might need to perform certain preinstallation activities.
Some of the steps are required only during the initial
installation of an option.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 67

1. Choose the bay in which you want to install the drive.
(Refer to Table 1 on page 65 for the drive types and
sizes available for each bay.)
Tower model
A
B
C
1
2
3
4
5
Rack model
54321 CBA
2. Touch the static-protective bag containing the drive to
any unpainted metal surface on the server; then,
remove the drive from the bag.
68 Netfinity Server HMM

3. Check the instructions that come with the drive if you
need to set any switches or jumpers on the drive, or if
you need to attach a tray to the drive.
What to do next
To install a removable-media drive, go to
“Installing or removing drives in bays A and B
(removable media).”
To install a diskette drive, go to “Installing or
removing a drive in bay C (diskette drive)” on
page 70.
To install a hard disk drive, go to “Installing or
removing drives in bays 1 through 5 (hard disk
drives)” on page 72.
Installing or removing drives in bays A and
B (removable media): This section gives the
procedure for installing a removable-media drive. If you
want to remove a drive, reverse the following steps.
Before you begin
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Read “Preinstallation steps (all bays)” on
page 67 and the instructions that come with the
option.
Read “Termination requirements” on page 67
1. If you have not done so already, remove the server
cover and the front bezel. See “Option installation”
on page 125.
2. Remove the bay cover plate, if present.
a. Remove the screws on either side of the cover
plate that secure the plate to the target bay.
b. Remove the cover plate from the server front
panel. (Save the cover plate for future use.)
3. Using the instructions that come with the drive,
together with these instructions, check that any
switches or jumpers on the drive are set correctly.
Change the settings if necessary. For information
about termination requirements, see “Termination
requirements” on page 67.
4. Position the drive with the connectors facing the rear
of the server.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 69

5. Slide the drive into the bay until it stops.
6. Reinstall and tighten the screws that you removed in
step 2 on page 69.
7. Connect the drive to the available connector on the
SCSI cable or the IDE cable, as appropriate.
Note
If you have difficulty connecting a cable, turn the
cable connector over and try again; cable
connectors are keyed to connect only one way.
8. Connect one of the 4-pin power cables to the drive.
9. If you want to install or remove any other options, do
so now. Otherwise, go to “Completing the
installation” on page 77.
Installing or removing a drive in bay C
(diskette drive): This section gives the procedure for
installing or removing a diskette drive.
Before you begin
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Read the documentation that comes with the
option.
70 Netfinity Server HMM

To remove a drive in bay C:
1. Locate the drive-release tab on the diskette drive.
2. Press the tab against the drive and hold it there while
pulling the drive out.
3. Disconnect the diskette drive cable and power cable
from the drive.
4. If you want to install or remove any other options, do
so now. Otherwise, go to “Completing the
installation” on page 77.
To install a drive in bay C:
1. If you have not done so, remove the server cover and
front bezel. See “Option installation” on page 125.
2. Using the instructions that come with the drive,
together with these instructions, check that any
switches or jumpers on the drive are set correctly.
Change the settings if necessary. For information
about termination requirements, see “Termination
requirements” on page 67.
3. Insert the drive into the bay.
a. Position the drive so that the connectors face the
rear of the server and the diskette eject button is
toward the outside of the server.
b. Connect the diskette drive cable and power
cable to the drive.
Note
If you have difficulty connecting a cable, turn
the cable connector over and try again;
cable connectors are keyed to connect only
one way.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 71

c. Locate the drive-release tab on the diskette
drive.
d. Press the tab against the drive and hold it there;
slide the drive into the bay until it clicks into
place.
4. If you want to install or remove any other options, do
so now. Otherwise, go to “Completing the
installation” on page 77.
Installing or removing drives in bays 1
through 5 (hard disk drives): This section gives
the procedure for installing a hard disk drive. If you want
to remove a drive, reverse the following steps.
Note
To minimize the possibility of damage to the hard disk
drives when you are installing a hard disk drive in a
rack model, install the rack model in the rack before
installing the hard disk drives.
Attention: To avoid damage to a hard disk drive,
remove the drive from the hot-swap bay until it has had
time to spin down (approximately 30 seconds). Handle the
drive gently.
Before you begin
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Read “Termination requirements” on page 67
The Netfinity 5000 contains hardware that lets you replace
a hard disk drive without turning off the Netfinity 5000.
These drives are known as
drives.
Each hot-swap drive that you plan to install must have a
hot-swap-drive tray attached. The drive must have a
single connector attachment (SCA) connector. Hot-swap
drives come with the hot-swap-drive tray attached.
Notes
1. The Netfinity 5000 EMI integrity and cooling are
both protected by having the hot-swap bays
covered or occupied. When you install a drive,
save the filler panel from the bay, in case you
later remove the drive and do not replace it with
another.
2. The hot-swap bays connect to a SCSI backplane.
This backplane is the printed circuit board behind
the hot-swap bays.
hot-swappable
or
hot-swap
do not
72 Netfinity Server HMM

To install a drive in a hot-swap bay:
1. Remove the filler panel .1/ from one of the empty
hot-swap bays by inserting your finger into the
depression at the top of the filler panel (tower model)
or left side of the filler panel (rack model) and pulling
it away from the server.
Attention
To maintain proper system cooling, do not
operate the Netfinity 5000 for more than two
minutes without either a drive or a filler panel
installed for each bay.
.1/ Filler panel
.2/ Drive
.3/ Tray handle
2. Install the hard disk drive .2/ in the hot-swap bay.
a. Ensure the tray handle .3/ is open (that is,
perpendicular to the drive).
b. Align the drive-tray assembly so that it engages
the guide rails in the bay.
c. Gently push the drive-tray assembly into the bay
until the drive connects to the backplane.
d. Push the tray handle toward the drive until the
handle locks.
3. Check the hard disk drive status indicators to verify
that the hard disk drives are operating properly. See
“Front panel indicators” on page 85 for details.
Notes
1. There are no termination requirements for
any SCSI hard disk drives installed in the
hard drive bays. Termination is achieved
through the DASD backplane.
2. If the Netfinity 5000 has a RAID adapter or
controller, you might want to reconfigure the
disk arrays after installing hard disk drives;
consult the documentation that came with
the adapter or controller.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 73

4. If you want to install or remove any other options, do
so now. Otherwise, go to “Completing the
installation” on page 77.
74 Netfinity Server HMM

Changing jumper positions
The DASD backplane, which is the Netfinity 5000 SCSI
backplane, contains two-pin jumper blocks, which are
behind the daughterboard (SAF-TE) on the DASD
backplane. Jumper block J4 controls the addressing of the
SCSI hard disk drive hot-swap bays. See “SCSI jumpers”
on page 137 for details.
Two-pin jumper blocks: Covering both pins with
a jumper specifies one function of the jumper block.
Covering one pin only or removing the jumper entirely
changes the function of the jumper block. To change a
jumper's position for a two-pin jumper block:
1. Turn off the server; then disconnect the server power
cord.
2. Remove the server cover (see “Option installation” on
page 125).
3. Locate the jumper block, removing any adapters or
components that may hinder access to the jumper
block.
4. Do one of the following:
Remove a jumper by performing either action:
– Lift the jumper straight off the pin block.
– Align one of the holes in the bottom of the
jumper with one of the pins on the pin
block, and then slide the jumper onto that
pin only.
Place a jumper by aligning the holes in the
bottom of the jumper with the two pins on the pin
block, and then sliding the jumper onto these
pins.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
75
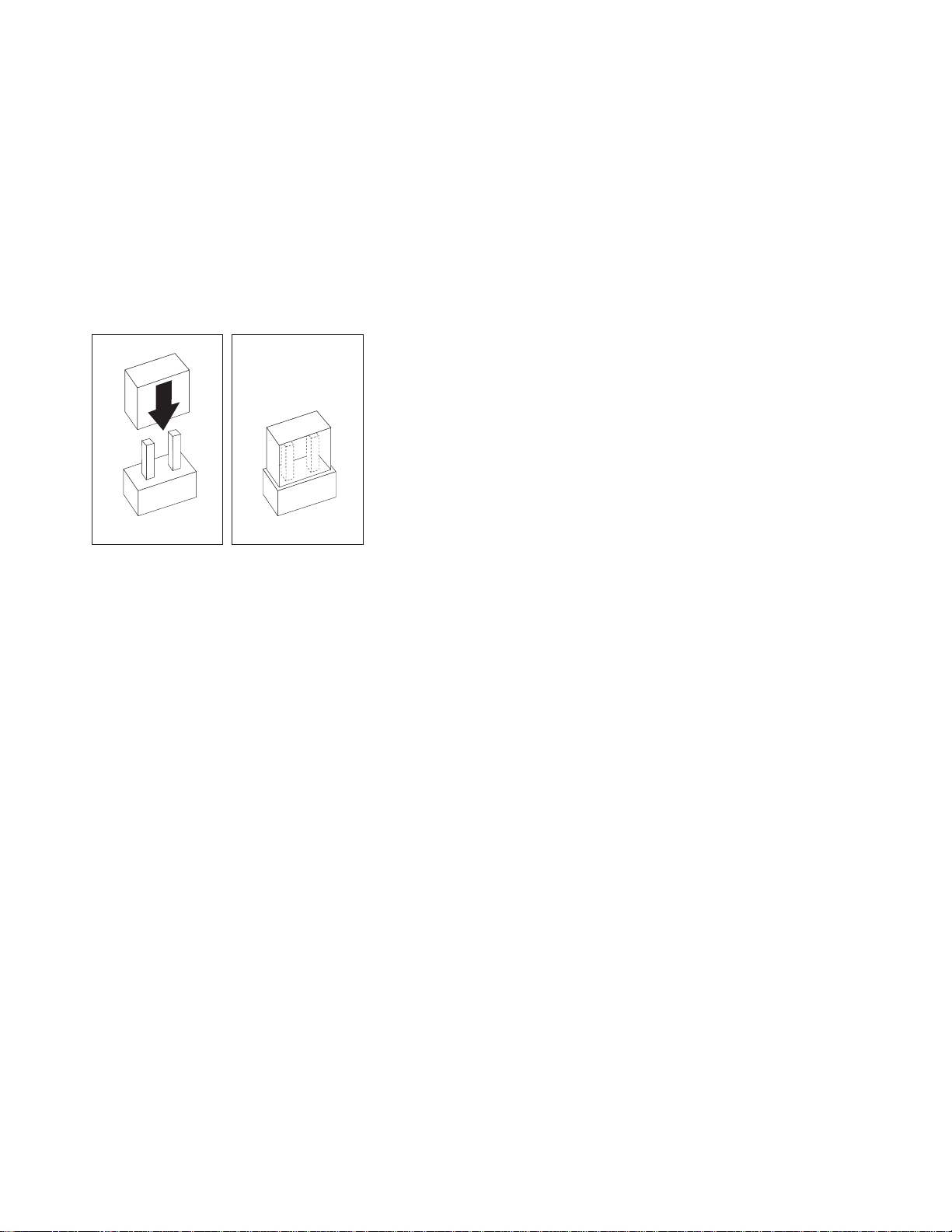
5. Replace any components or adapters that you might
have removed.
6. Reinstall the server cover and connect the cables
(see “Completing the installation” on page 77 for
instructions).
76 Netfinity Server HMM

Completing the installation
Before you begin
Complete all the installation procedures for the
internal options you have chosen to install.
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
If you have a tower model, continue with “Completing
the tower model installation.”
If you have a rack model, go to “Completing the rack
model installation” on page 80.
Completing the tower model installation
1. Install the cover on the server.
a. Align the left-side cover with the left side of the
server, about 25 mm (1 inch) from the front of
the server; place the bottom of the left-side cover
on the bottom rail of the left-side frame.
b. Insert the tabs at the top of the cover into the
slots at the top of the server side.
c. Hold the cover against the server and slide the
cover toward the front of the server until the
cover clicks into place.
Note
Be sure the front edge of the cover is flat
against the server.
2. Replace the bezel, if it was removed.
a. Place the bezel tabs .1/ in the slots at the
bottom front of the server.
b. Press the top of the bezel toward the server front
until the bezel clicks into place.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
77

3. Replace the server door, if it was removed.
a. Set the door on the bottom hinge.
b. Press the flange downward while pressing the
top of the door toward the server, until the flange
connects with the top hinge. Release the flange.
4. Close and lock the server door.
78 Netfinity Server HMM

Attention
Be sure to maintain a clearance of at least 127
mm (5 inches) on the front and rear of the server
to allow for air circulation.
5. Reconnect the cables to the back of the server; then,
plug the power cords into properly grounded electrical
outlets.
6. If you have a modem or fax machine attached to the
server, reconnect the telephone line to the wall outlet
and the server.
What to do next
When you have completed installing the covers and
cables, go to “Updating the server configuration” on
page 150.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 79

Completing the rack model installation
1. Replace the top cover:
a. Align the top cover with the top of the server,
about 25 mm (1 inch) from the front of the
server.
b. Hold the cover against the server and slide the
cover toward the front of the server until the
cover clicks into place.
Note
Be sure the front edge of the cover is flat
against the server.
c. Turn the captive thumbscrew .1/ until the cover
is secured.
2. Replace the bezel, if it was removed.
a. Place the bezel tabs .2/ in the slots at the left
front of the server.
b. Press the right end of the bezel toward the
server front until the bezel clicks into place.
80 Netfinity Server HMM

3. Attach the monitor, keyboard, and power cables to
the corresponding connectors on the server. Refer to
the rack documentation for instructions.
4. If you have a modem or fax machine attached to the
server, reconnect the telephone line to the wall outlet
and the server.
k32 kg (70.5 lbs) k55 kg (121.2 lbs)
Caution
Use safe lifting practices when lifting the
machine.
5. If you are installing the rack model in the rack for the
first time, go to “Installing the server in the rack
enclosure” on page 108, and then go to “Updating
the server configuration” on page 150. Otherwise,
continue with the following instructions to secure the
rack model in the rack.
a. Slide the rack model into the rack.
b. Locate the screws that you removed in step 3 on
page 128.
c. Insert the screws through the bracket, mounting
rail, and cage nut.
What to do next
When you have completed installing the cover and
cables, go to “Updating the server configuration” on
page 150.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 81

Controls
Tower model
Rack model
.1/ Diskette-Eject Button: Press this button to
release a diskette from the drive.
.2/ Diskette Drive In-Use Light: This light comes on
when the diskette drive is accessed.
.3/ CD-ROM Manual Tray-Release Opening: Insert a
straightened paper clip in the opening to release the
CD-ROM tray when using the CD-ROM eject button
is not successful.
82 Netfinity Server HMM

.4/ CD-ROM Eject Button: Press this button to
release a CD from the CD-ROM drive.
Note
If the CD-ROM tray does not extend out, insert
the end of a straightened paper clip into the
manual tray-release opening and gently pull the
tray open.
.5/ Reset Button: Press this button to reset the
server.
.6/ Power-on switch: Use this switch to turn on the
server, or to return the server to
Standby mode
(power is present but the server is not turned on).
Important
After you plug the server power cord into an
outlet, wait 20 seconds before pressing the
power switch. (During this time, the
system-management processor is initializing
and the power-on switch does not respond.)
Caution
The Power-On button on the front of the server
does not turn off the electrical current supplied
to the server. The server also might have
more than one power cord. To remove all
electrical current from the server, ensure that
all power cords are disconnected from the
power source.
The automatic restart feature, which enables the
server to restart following a momentary power loss,
means that the server is never completely turned
off. Do not set the server to the Standby mode if
any drive in-use light is on. This might damage the
information stored on a hard disk drive or on a
diskette. A Power-On Switch protector, which
prevents the Power-On Switch from being pushed
accidentally, is shipped with the server.
To toggle the server between Standby mode and
actively running, press and release the Power-On
Switch.
.7/ Side-Cover Release Lever: Use this lever to
release the left-side cover.
.8/ CD-ROM Drive In-Use Light: This light comes on
when the CD-ROM drive is accessed.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659
83

.9/ Operator LED Panel This panel contains LEDs
that light to indicate conditions on the server, such
as power on or a system error (see “Front panel
indicators” on page 85).
84 Netfinity Server HMM

Front panel indicators: The following illustrations
identify the indicators located on the front panel of the
server.
Tower model
Rack model
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 85

.1/ Power-On Light: This green LED blinks
when the server is in Standby mode
(power is present but the server is not
turned on). The blinking changes to a
solid (continuous) light when you turn on
the server remotely (Unattended mode) or
by pressing the Power-On Switch. If this
light is not on, the power cord is not
connected or the power supply has failed.
.2/
POST Complete Light: This green LED
lights when the server completes the
power-on self-test (POST) without any
errors.
.3/
SCSI Hard Disk Drive In-Use Light: This
green LED lights when the server is
accessing a SCSI device. If this light
remains illuminated, it might indicate that
either the SCSI bus or the system
microprocessor has stopped.
.4/
Primary Microprocessor Activity Light:
This green LED blinks to indicate the
activity of a microprocessor installed in the
primary microprocessor socket. The LED
comes on during POST to indicate the
presence of the microprocessor.
.5/
Secondary Microprocessor Activity
Light: This green LED blinks to show the
activity of a microprocessor installed in the
secondary microprocessor socket. The
LED lights during POST to indicate the
presence of the microprocessor. When you
install a secondary microprocessor, it
becomes the startup microprocessor.
.6/
System Error Light: This amber LED
shows that a system error occurred.
System errors can include high
temperature, excess current, or failure or
errors in the microprocessor, system fan,
memory, PCI bus, SCSI bus, USB, hard
disk drive, diskette drive, serial port,
keyboard interface, or power supply.
When this LED is on, one or more LEDs
on the system board also might be on,
indicating where the error occurred (see
“System board LEDs” on page 142).
.7/
Reserved: This LED is reserved for future
use.
86 Netfinity Server HMM

.8/ Hard Disk Drive Status Light (Amber): In
a RAID environment, this amber LED lights
continuously when the drive is faulty and
needs to be replaced. You can replace
these hot-swappable drives without turning
off the server. If you do not have a RAID
environment, this LED is not operational.
.9/
Hard Disk Drive Activity Light (Green):
This green LED lights when the hard disk
drive is being accessed.
.1ð/
Ethernet Transmit/Receive Activity
Light: This green LED shows
transmission and reception activity on the
network.
.11/
Ethernet Link Status Light: This green
LED shows an active link connection on
the 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX interface.
.12/
Ethernet Speed Light: This green LED
lights when the Ethernet LAN speed is 100
Mbps.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 87

The following illustrations identify the indicators located on
the back of the server.
Tower model
Rack model
.1/ Power Supply Lights: These green LEDs indicate
a power good status for each of the 175-watt
modules in the power supply. If any power supply
light is not illuminated when the Power-On Light on
the front of the server is on, there is a problem with
that power supply. The power supply shipped with
the server has two lights, one for each module in
88 Netfinity Server HMM

the power supply. The optional additional power
supply has one power module and one green LED.
See “Power supplies” on page 132 for more
information about the power supplies.
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 89

DASD fan assembly removal
Before you begin
Read “Safety information” on page 176.
Turn off the server, if it is on.
Attention
When removing or replacing the fan, be sure to route
the cables correctly to avoid damage to the SCSI
cables and connectors.
To remove the DASD fan assembly, do the following:
1. Remove the side cover, see “Option installation” on
page 125.
2. Release the fan assembly latch and slide the fan
assembly out of the server.
90 Netfinity Server HMM

Ethernet connector
The system board in the Netfinity 5000 contains an
Ethernet
controller
connector on the rear of the server that is used with a
category 3, 4, or 5 twisted-pair cable. The connector
enables an Ethernet network to attach to the internal
transceiver in the server. The 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
standard requires that the cabling in the network be
Category 5 or higher.
See “Configuring the Ethernet controller” on page 32 for
additional information about the Ethernet controller.
Table 3 shows the pin-number assignments for the RJ-45
connector. These assignments apply to both 10BASE-T
and 100-BASETX devices.
. The controller has an external RJ-45
10BASE-T or 100 BASE-TX
UTP Cable
1
Pins
2
3
6
RJ-45 Modular Plug Connector
Table 3. Ethernet Connector Pin-Number
Assignments
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Transmit data+ 5 Reserved
2 Transmit data− 6 Receive data−
3 Receive data+ 7 Reserved
4 Reserved 8 Reserved
Netfinity 5000 - Type 8659 91

Expansion bays
The server comes with one 3.5-inch, 1.44 MB diskette
drive, and one 5.25-inch CD-ROM drive. The following
illustrations show the server front view with the door (if
any) removed.
Tower model
Rack model
.1/ CD-ROM Drive: The server comes with an IDE
CD-ROM drive.
.2/ Open Bay (5.25-inch): The design of the server
accommodates an additional 5.25-inch half-height
device, such as tape or a rewritable optical disk
drive.
92 Netfinity Server HMM
 Loading...
Loading...