Page 1

MaxLoader User’s Guide
1. INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................... 7
P
ROGRAMMER MODELS FOR PC USB INTERFACE ....................................................................................... 7
ROGRAMMER MODELS FOR PC USB INTERFACE MULTI-SOCKETS ............................................................ 8
P
ROGRAMMER MODELS FOR PC PARALLEL INTERFACE............................................................................... 8
P
BOUT THIS MANUAL ................................................................................................................................. 9
A
ENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................... 9
G
2. GETTING STARTED / INSTALLATION ......................................................................................... 10
NSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS ................................................................................................................. 10
I
ARDWARE INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................................... 10
H
To Install the software from a CD drive .............................................................................................. 10
O START THE WINDOWS SOFTWARE ......................................................................................................... 10
T
O INSTALL SOFTWARE AND CONNECT TO PC FOR USB PROGRAMMERS ................................................... 10
T
O INSTALL THE SOFTWARE FOR PARALLEL PORT PROGRAMMERS ............................................................ 17
T
To download the software from the www.eetools.com web site .......................................................... 17
ELECT PRODUCT ...................................................................................................................................... 18
S
3. FAMILIES OF PROGRAMMABLE DEVICES ................................................................................ 19
NVM: NON VOLATILE MEMORY ............................................................................................................ 19
ROM: READ ONLY MEMORY ................................................................................................................. 19
OTP: ONE TIME PROGRAMMABLE ROM ................................................................................................ 19
EPROM: ERASABLE PROGRAMMABLE ROM ......................................................................................... 19
EEPROM: ELECTRICALLY ERASABLE & PROGRAMMABLE ROM .......................................................... 19
HIERARCHY ..................................................................................................................................... 19
NVM
ERIAL FLASH EEPROM........................................................................................................................... 21
S
ERIAL EEPROM ...................................................................................................................................... 21
S
ON-TYPICAL DEVICES ............................................................................................................................. 22
N
BIT 1-MEGABITS ..................................................................................................................................... 22
8-
16-bit 1-Megabits .................................................................................................................................. 23
RASING AN EPROM ................................................................................................................................ 23
E
PLD ........................................................................................................................................................... 23
1
Page 2

MaxLoader User’s Guide
PLD Features ....................................................................................................................................... 24
ICROCONTROLLER .................................................................................................................................. 25
M
BOUT “DEVICE ID” AND “AUTO SELECT” ON EE TOOLS PROGRAMMERS ............................................... 26
A
4. TERMS AND SYMBOLS USED IN THE GUIDE ............................................................................. 28
AFETY NOTE CONVENTIONS .................................................................................................................... 28
S
THER TERMS AND DEFINITIONS ARE AS FOLLOWS .................................................................................... 28
O
HOOSING A RIGHT ADAPTER ................................................................................................................... 29
C
Different Device Packages .................................................................................................................... 30
Different Programming Adapters ......................................................................................................... 31
5. QUICK START EXAMPLES ............................................................................................................... 32
ROGRAMMING AN EPROM WITH DATA ................................................................................................... 32
P
UPLICATING AN EPROM FROM A MASTER IC DEVICE ............................................................................. 34
D
6. MAXLOADER OPERATIONS ............................................................................................................ 35
ASIC MENU SCREEN INFORMATION ......................................................................................................... 35
B
Option Information .............................................................................................................................. 35
(Additional Option Information for Non PLD Devices) ..................................................................... 36
System Information .............................................................................................................................. 36
Counter ................................................................................................................................................. 36
File ........................................................................................................................................................ 37
Binary Format ................................................................................................................................ 38
Intel HEX Format .......................................................................................................................... 38
Motorola S HEX Format ........................................................................................................... 39
TEKTRONIX HEX FORMAT ......................................................................................................... 40
ASCII HEX format .................................................................................................................. 40
JEDEC Standard <PLD devices only> ............................................................................................. 41
POF file <Altera EPMxxx devices only> ........................................................................................ 43
File / Load ......................................................................................................................................... 43
File / Reload ..................................................................................................................................... 44
File / Save ......................................................................................................................................... 45
2
Page 3
MaxLoader User’s Guide
File/ Load Project ............................................................................................................................. 45
File/ Save Project .............................................................................................................................. 45
File/ Save Log ................................................................................................................................... 46
File/ Save All Messages ................................................................................................................... 47
Buffer ................................................................................................................................................... 48
Buffer / Edit Buffer ........................................................................................................................... 49
Find ................................................................................................................................................... 49
Find Next .......................................................................................................................................... 50
Fill Buffer ......................................................................................................................................... 50
Fill random data ................................................................................................................................ 50
Copy buffer ....................................................................................................................................... 51
Fill Buffer ......................................................................................................................................... 51
Clear buffer ...................................................................................................................................... 52
Print buffer ........................................................................................................................................ 53
Set editor to view mode .................................................................................................................... 53
Set editor to edit mode ...................................................................................................................... 54
Set Editor to binary mode ................................................................................................................. 54
Set editor to 8 bit(byte) Hex ............................................................................................................. 55
Set editor to 16 bit(word) Hex .......................................................................................................... 55
Set editor to 32 bit(double word) Hex .............................................................................................. 56
Set default editor mode ..................................................................................................................... 56
Set default Reset Editor .................................................................................................................... 57
Swap nibble ...................................................................................................................................... 57
Swap byte ......................................................................................................................................... 58
Swap Word ..................................................................................................................... .................. 58
Swap double word ............................................................................................................................ 59
Jedec editor ....................................................................................................................................... 59
Clear ................................................................................................................................................. 60
Close ................................................................................................................................................. 61
Buffer / Edit UES ............................................................................................................................. 61
Device ................................................................................................................................................... 61
3
Page 4
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Select by history ................................................................................................................. 62
Select ................................................................................................................................................ 63
Select / E (E)PROM, FLASH ........................................................................................................... 64
Select / PLD ...................................................................................................................................... 64
Select / Microcontroller .................................................................................................................... 64
Select / PROM .................................................................................................................................. 64
Select / Auto Select........................................................................................................................... 64
Select / Device information .............................................................................................................. 65
Device / Change Algorithm .............................................................................................................. 66
Device / Auto Menu Option ............................................................................................................. 67
Device / Blank Check ....................................................................................................................... 67
Device / Program .............................................................................................................................. 69
Device / Read ................................................................................................................................... 72
Device / Verify ................................................................................................................................. 72
Device / Data Compare ..................................................................................................................... 73
Device / Erase ................................................................................................................................... 73
Device / Security .............................................................................................................................. 73
Device / Encryption .......................................................................................................................... 74
Device / Option ................................................................................................................................. 74
Device / Auto .................................................................................................................................... 75
Test (This feature is for only TopMax, TopMaxII) ................................................................................ 75
Test / RAM Test ............................................................................................................................... 75
Test / Vector Test ............................................................................................................................. 76
Test / IC Test .................................................................................................................................... 77
Config Config / Select Product ......................................................................................... 78
Config / Config Option ......................................................................................................................... 79
Config Option / Buffer Clear Before File Loading ................................................................. 79
Config Option / Blank Check Before Programming ............................................................... 80
Config Option / Verify After Reading ...................................................................................... 80
Config Option / verify after programming .............................................................................. 80
Config Option / Byte order swapping ...................................................................................... 80
4
Page 5
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Config Option / Device Insert Test .......................................................................................... 82
Config Option / Device ID Check ............................................................................................ 82
Config Option / Sound ............................................................................................................. 83
Config Option / Default Buffer Value ..................................................................................... 83
Config Option / 32 Bit Checksum ............................................................................................ 83
Config Option / Port (TopMax, ChipMax) ....................................................................................... 84
Config Option / USB Option (USB programmer) ............................................................................ 85
USB option / Enable START button ........................................................................................ 85
th
If you want to choose the master socket in 4
th
socket among 8 sequential serial numbers. i.e the 4th socket serial number is P8-0057. ..... 86
4
location in 8 sockets, select the serial number for
USB option / Good LED off on socket open ............................................................................ 86
USB option / Enable “START ALL” button ........................................................................... 86
Config Option / Gang Split Select .................................................................................................... 87
Split ........................................................................................................................................... 88
Device Address ......................................................................................................................... 90
File Load .................................................................................................................................. 90
File Save ................................................................................................................................... 91
Config Option / Auto Inc .................................................................................................................. 91
Config / Hardware test ...................................................................................................................... 92
Config / Concurrent (gang) mode ..................................................................................................... 92
How to program (write) one file into different sockets ? ........................................................ 96
How to program (write) buffer ( blocks) data into different sockets ? ................................ 99
Config / Enter Production Mode ..................................................................................................... 102
Config / Set Password ..................................................................................................................... 103
Config / Language .......................................................................................................................... 103
7. TROUBLE SHOOTING & TECHNICAL SUPPORT .................................................................... 104
1.
REGISTRATION ..................................................................................................................................... 104
SOFTWARE UPDATES ........................................................................................................................... 104
2.
TESTING THE HARDWARE .................................................................................................................... 104
3.
QUICK SELF-DIAGNOSTICS .................................................................................................................. 105
4.
5
Page 6

MaxLoader User’s Guide
5. CONTACTING CUSTOMER SUPPORT ...................................................................................................... 106
SERVICE INFORMATION ........................................................................................................................ 107
6.
LIMITED ONE-YEAR WARRANTY ......................................................................................................... 108
7.
USEFUL WEB SITE ADDRESSES/ PHONE NUMBERS .............................................................................. 109
8.
PROGRAMMING ADAPTER MANUFACTURERS ...................................................................................... 110
9.
EPROM EMULATOR MANUFACTURERS ............................................................................................ 110
10.
8. OTHER PRODUCTS .......................................................................................................................... 110
Optional EPROM Emulator ............................................................................................................ 110
9. ABOUT NAND FLASH MEMORY ................................................................................................... 111
OMPARISON OF NOR AND NAND FLASH TECHNOLOGIES ..................................................................... 111
C
HY NAND FLASH ................................................................................................................................ 112
W
OW TO PROGRAM NAND FLASH ........................................................................................................... 112
H
OW TO READ NAND FLASH ................................................................................................................ 113
H
10. GLOSSARY ....................................................................................................................................... 113
6
Page 7

1. INTRODUCTION
This manual describes the operation of EE Tools’ programmers.
TopMax/ChipMax/ChipMax2/TopMaxII/UniMax/ProMax8G (4G) are software,
MaxLoader, driven device programmers. The information contained in this
manual has been reviewed for accuracy, clarity, and completeness.
Please report in writing any errors or suggestions to support@eetools.co m
EE Tools, Inc.
4620 Fortran Drive Suite 102
San Jose, CA 95134, USA.
www.eetools.com
Tel : (408)263-2221 Fax : (408)263-2230
EE Tools reserves the right to use and distribute any information supplied
without obligation.
Programmer Models for PC USB Interface
MaxLoader User’s Guide
7
Page 8

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Programmer Models for PC USB Interface Multi-Sockets
Programmer Models for PC parallel Interface
8
Page 9

MaxLoader User’s Guide
About This Manual
TopMax/ChipMax/ChipMax 2/To pMaxII/UniMax/ProMax-8G (4G) Us er Guide
explains how to install and run the programming software in your computer.
Chapter 2 contains instructions for installing and running MaxLoader.
Chapter 3 describes the most popular programmable devices.
Chapter 4 contains all terms and symbols used in the manual.
Chapter 5 describes basic operating examples of programmers.
Chapter 6 is organized by main operating commands and gives detailed
instructions on each command.
Chapter 7 provides troublesh ooting information for identifying and
solving problems with programmers. It provides a detailed guide for
EE Tools’ technical support and return material procedures.
Chapter 8 introduces a useful product, EPROM Emulator.
Chapter 9 describes the recent information of NAND Flash
Chapter 10 contains glossary about programmable devices and package
types.
This Manual assumes that you have a working knowledge of your personal
computer and its operating conventions.
General Description
TopMax/ChipMax/ChipMax2/ To pM ax II/UniMax/ProMax-8G /4G are software
driven device programmers that support a wide variety of programmable
devices including: EPROM, EEPROM, Serial PROM, EPLD, PEEL, GAL,
FPGA, and single chip Microcontroller.
TopMax/ChipMax easily connects to the parallel printer port of any IBM PC,
and can operate with a full spectrum of IBM compatibles: PC 386, 486, Pentium,
PS/2, portable (laptop), and clone computers. TopMaxII/UniMax/ProMax-8G
(4G) connects to the USB(2.0) port of any IBM PC, and can operate with a full
spectrum of IBM compatibles.
9
Page 10

MaxLoader User’s Guide
The great advantage of a programmer is their programming speed and
superior software. All programmers are controlled via a host IBM PC computer.
The operating software has a user-friendly interface that includes window pulldown menus and virtual memory management to deal with very large files.
2. GETTING STARTED / INSTALLATION
Installation Requirements
MaxLoader is designed to operate with any 386, 486, Pentium, PS/2, Portable
(notebook), compatibles running WIN 95/98/ ME/NT/2000/XP and Vista. The
computer requires a CD-ROM drive, but a hard disk drive is also recommended.
Hardware Installation
The following section details the procedure for accomplishing the hardware
installation procedure. TopMax / ChipMax easily connect to any parallel printer
port in your computer and TopMaxII / ChipMax2/ UniMax / ProMax-8G (4G)
connects to USB 2.0 port in your PC.
To Install the software from a CD drive
Place CD-ROM in the CD-ROM or DVD drive.
Choose a programmer model from the list of files located on the menu
screen. The SETUP program will then launch the installation
procedure.
To Start the windows software
To run the windows software, select your product model shortcut in the
Windows Start Menu / Programs list.
From Configuration Menu, you can choose one of the
TopMax/ChipMax/ChipM a x 2/ To pMaxII/UniMax/ProMax-8G (4 G) that y ou
use.
To install software and connect to PC for USB programmers
The software works with Windows OS 98, SE, Me, 2000, XP and Vista.
10
Page 11

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Follow the steps below for Windows.
1. Make sure a programmer is not connected when turning on your computer.
2. Note: If you see New Hardware Wizard screen then disconnect your
programmer. You cannot install programmer software that way.
3. Insert the CD-ROM from factory (EE Tools) in your CD-ROM or DVD
driver.
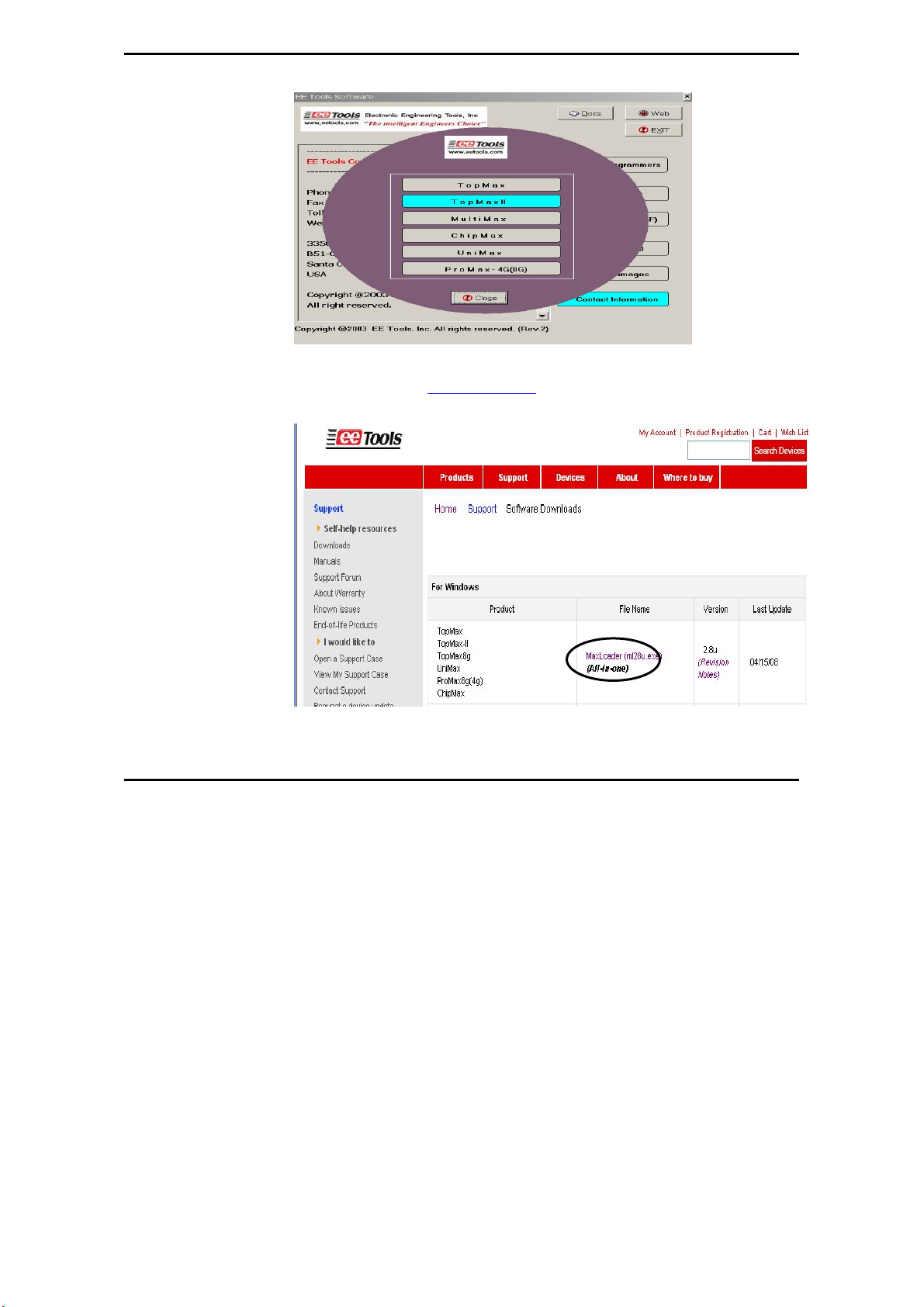
4. Wait until you see the following screen then Click on Device Programmers
and choose a programmer name. The executable file name for the installation
is in the CD-ROM.
11
Page 12
MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Customers who want to install the latest software may download the
MaxLoader file from www.eetools.com
12
Page 13
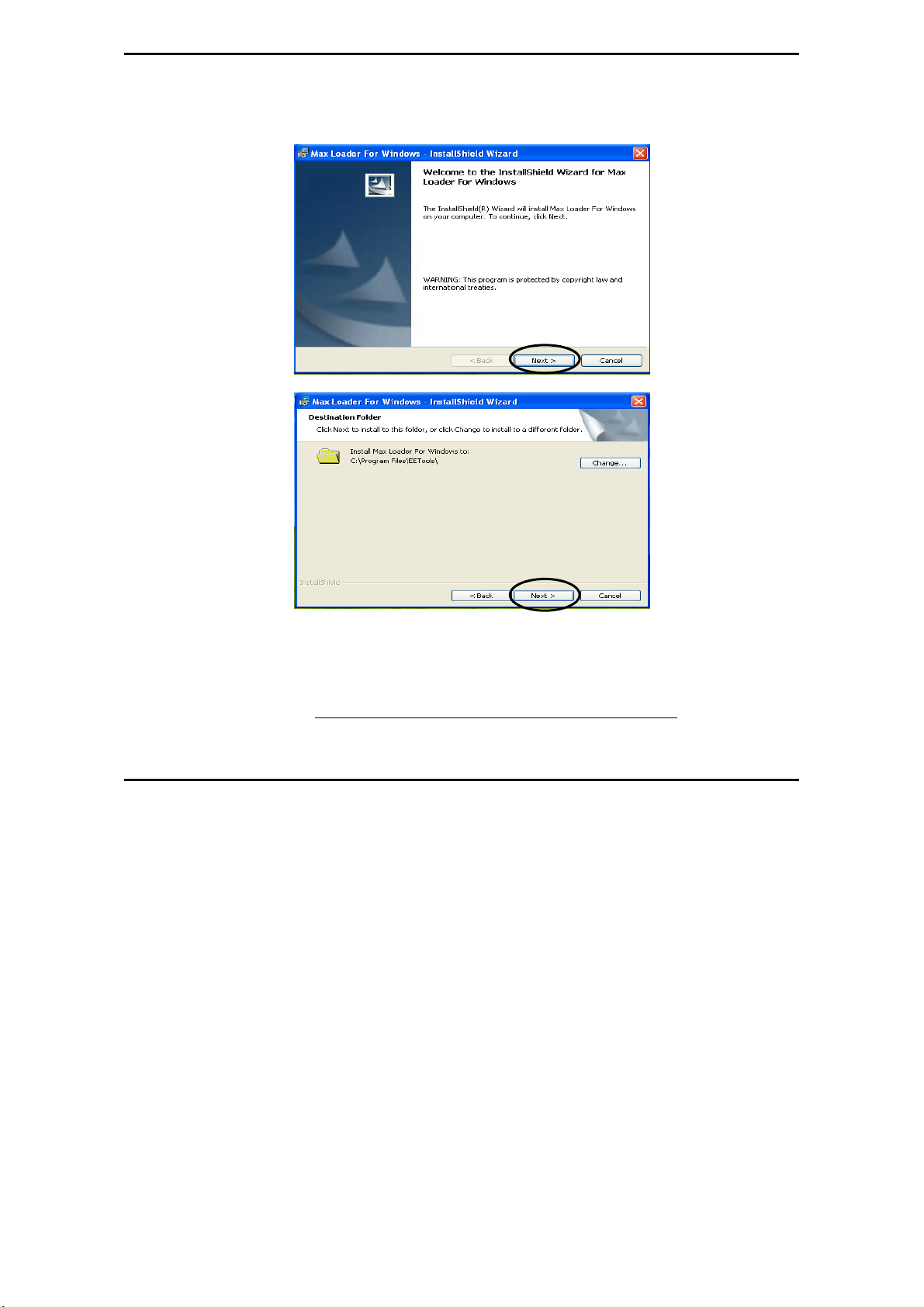
MaxLoader User’s Guide
5. Set up MaxLoader software
6. Install MaxLoader and the MaxLoader icon and USB driver (eetusb.inf and
eetusb.sys files) will be generated in directory C:\program files\EE Tools\.
Follow the steps below for installation for USB 2.0 driver.
13
Page 14

MaxLoader User’s Guide
7. Connect a USB cable between programmer and your computer and turn the
power switch ON after connecting the power cord in the programmer.
14
NOTE: In Windows2000, you need to choose “specific location” when the
“Found New Hardware Wizard” appears. The USB driver files are generated
Page 15
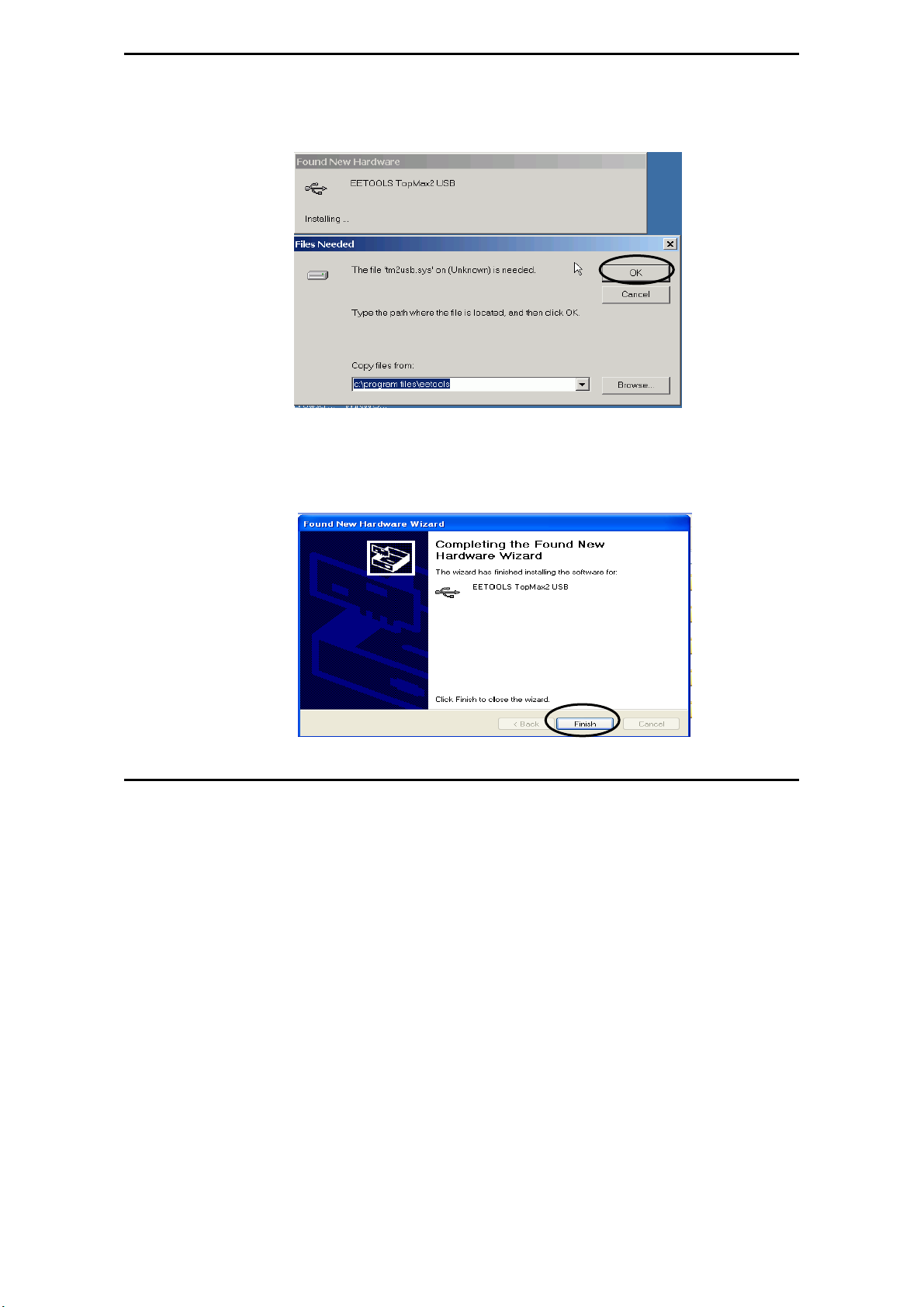
MaxLoader User’s Guide
in directory C:\program files\EE Tools. Or you can find the USB driver files in
the CD-ROM comes in the product package.
8. Click on the Finish button on the Wizard screen and you can confirm the
USB driver in Device Manager in your computer system.
15
Page 16
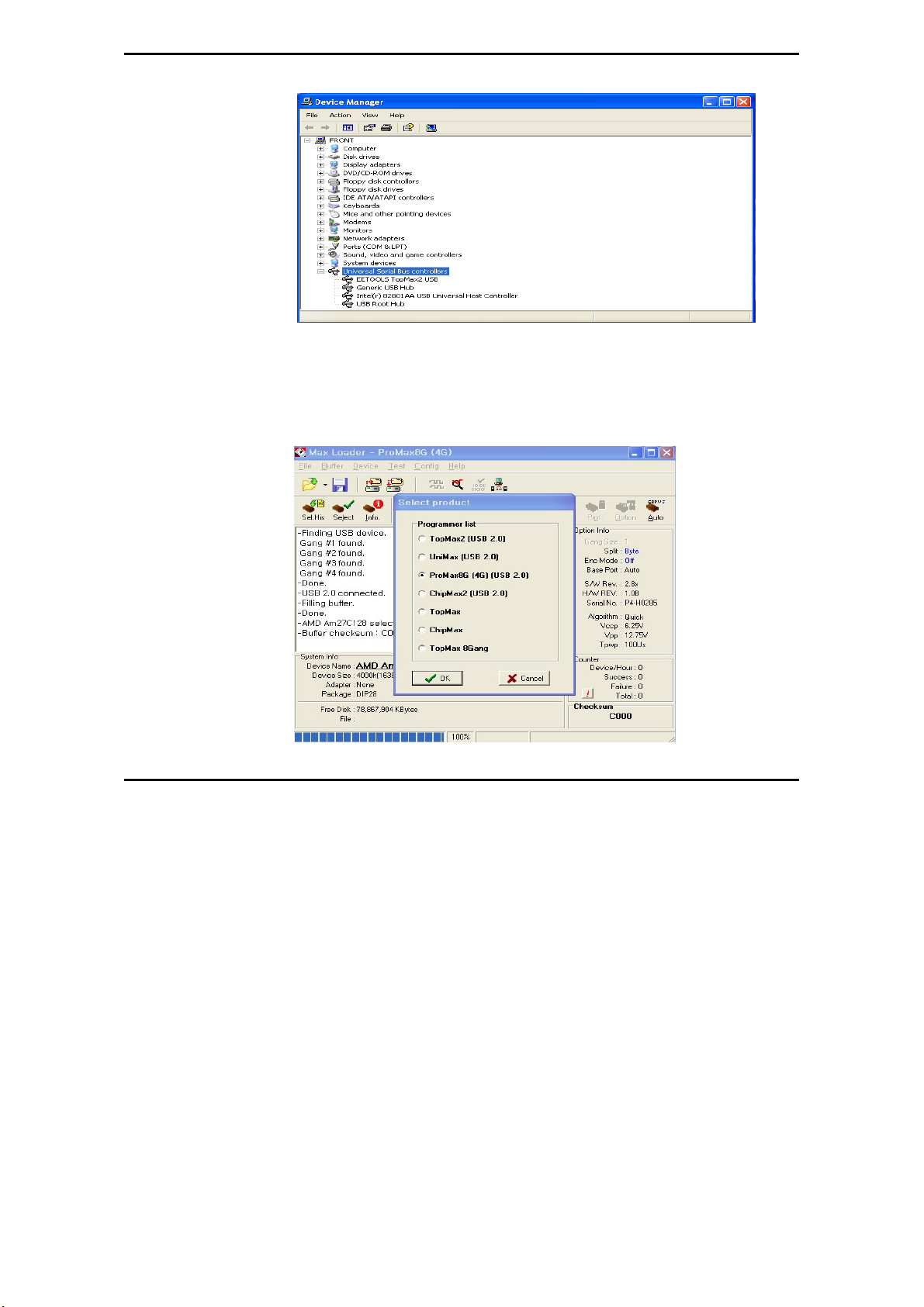
MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: For a computer that doesn’t installed USB 2.0 controller, you need to
install USB 2.0 driver for the particular product vendor.
9. Execute MaxLoader and choose Programmer model
10. Choose your programmer that is ready to be use in your computer.
16
Page 17

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Watch the model name in left-up corner screen and the ProMax4G(8G) won’t be ready if “DEMO mode” appears in the screen. Check the
USB cable and turn on the AC switch in the back side of unit.
To install the Software for parallel port programmers
There are three different addresses for the parallel port. When you select an
address from LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, one of them should be valid without a
communication error message. Turn the AC switch ON before running the
MaxLoader software. Make sure you connect the prin ter (IEEE) cable between
TopMax/ChipMax and your available printer port and lock the shields in each
side of the cable. Be sure that your programmer recognizes your computer’s
parallel port address when you execute the MaxLoader icon. (MEMO mode is
indicated that your programmer has a “communication error”)
1. Connect print cable between PC and programmer.
2. Connect AC cord to programmer.
3. Turn on AC switch located on the back side of TopMax
4. Install programmer software that comes in a CD-R (or download the latest
software (all-in-one) from www.eetools.com
5. After the MaxLoader is installed, you choose a programmer name in the very
first screen menu
To download the software from the www.eetools.com web site
1. Click on “Software download” button on left at www.eetools.com and
download MaxLoader software. The file will be saved to your hard disk. The
MaxLoader can be operated for All-in-one (all programmers-in-one software).
2. Once the download is complete, double-click on the file name to install the
software.
17
Page 18

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Select Product
NOTE: For the latest software upgrade, remove the old MaxLoader in
“Add/Remove Program” of “Setting / Control Panel” in 2000/XP/VISTA before
installing a new MaxLoader in your PC.
After MaxLoader is installed, choose a programmer among TopMax, TopMax8G, ChipMax/ChipMax2, TopMaxII, UniMax, and ProMax8G (4G) hardware
in the very first MaxLoader screen menu. Or Click on Config / Select product
Make sure to select the right model and turn the switch on. (TopMaxII, ProMax,
TopMax) or connect the AC cord (UniMax, ChipMa x/ ChipMax2)
Trouble Shooting In Installation
A communication error may occur on the screen if the hardware / software are
not correctly installed.
Be sure that the following steps are checked:
Make sure the USB driver is installed after MaxLoader software is set up in
PC.
18
Page 19
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Make sure that the programmer hardware unit is connected to your PC
printer port or USB port directly. A programmer for parallel port interface will
not work with multiple port connectors.
Be sure your printer cable is firmly connected to your computer and
programmer. Plug in the AC power cord to your programmer and turn on the
switch in the back of the unit before clicking on the MaxLoader icon.
NOTE: The MaxLoader detects the printer port address when you install the
new software. When you see “Cannot find the programming module,” go to
CONFIG/PORT and select all three parallel port addresses. If the same error
message continues, contact technical support.
3. FAMILIES OF PROGRAMMABLE DEVICES
The devices that are supported on the EE Tools, Inc programmers are:
NVM: Non Volatile Memory
ROM: Read Only Memory
OTP: One Time Programmable ROM
EPROM: Erasable Programmable ROM
EEPROM: Electrically Erasable & Programmable ROM
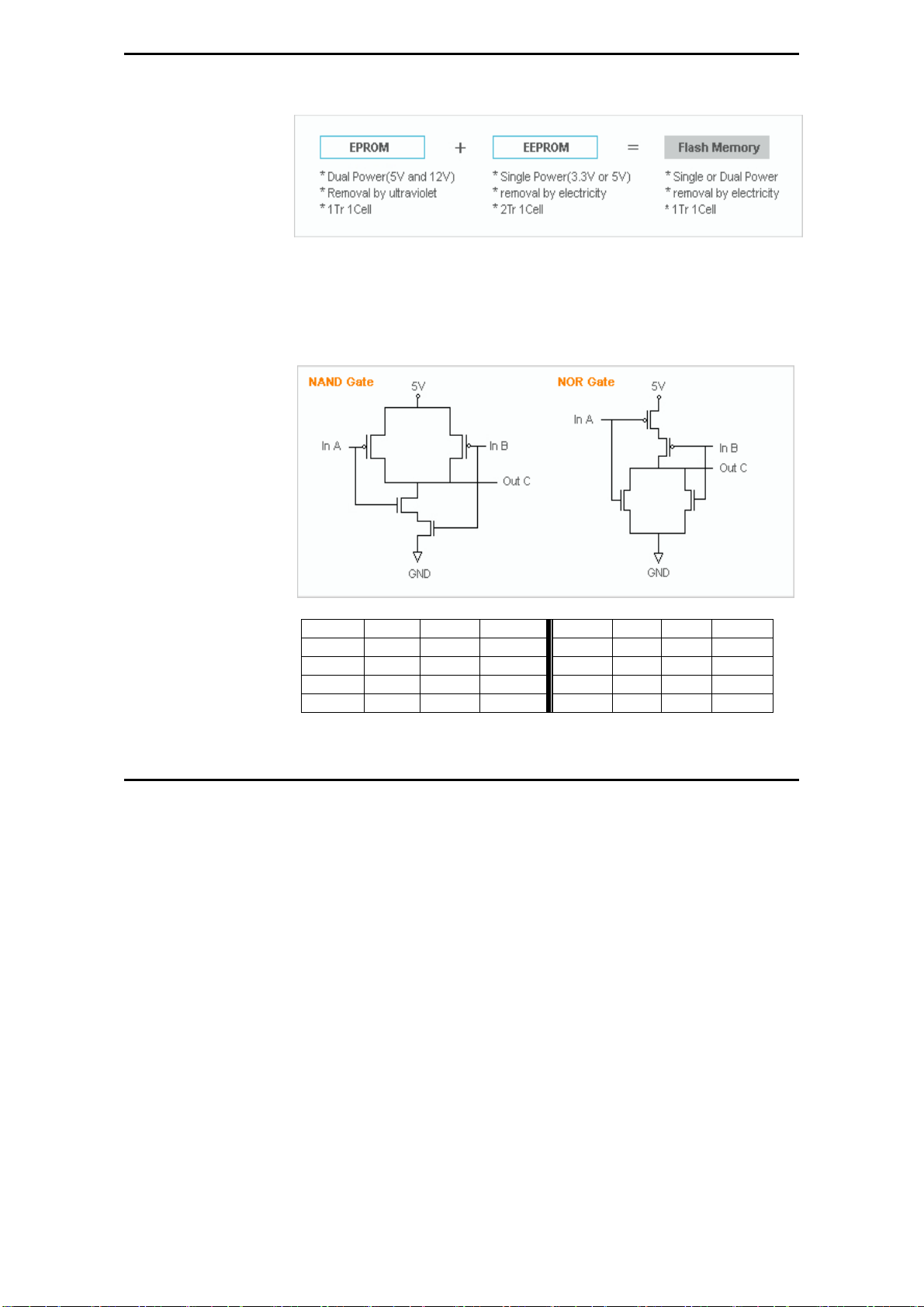
NVM Hierarchy
the
19
Page 20
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Flash Memory
Flash Memory Technologies
20
A B C(and) C(nand) A B C(or) C(nor)
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0
Page 21
MaxLoader User’s Guide
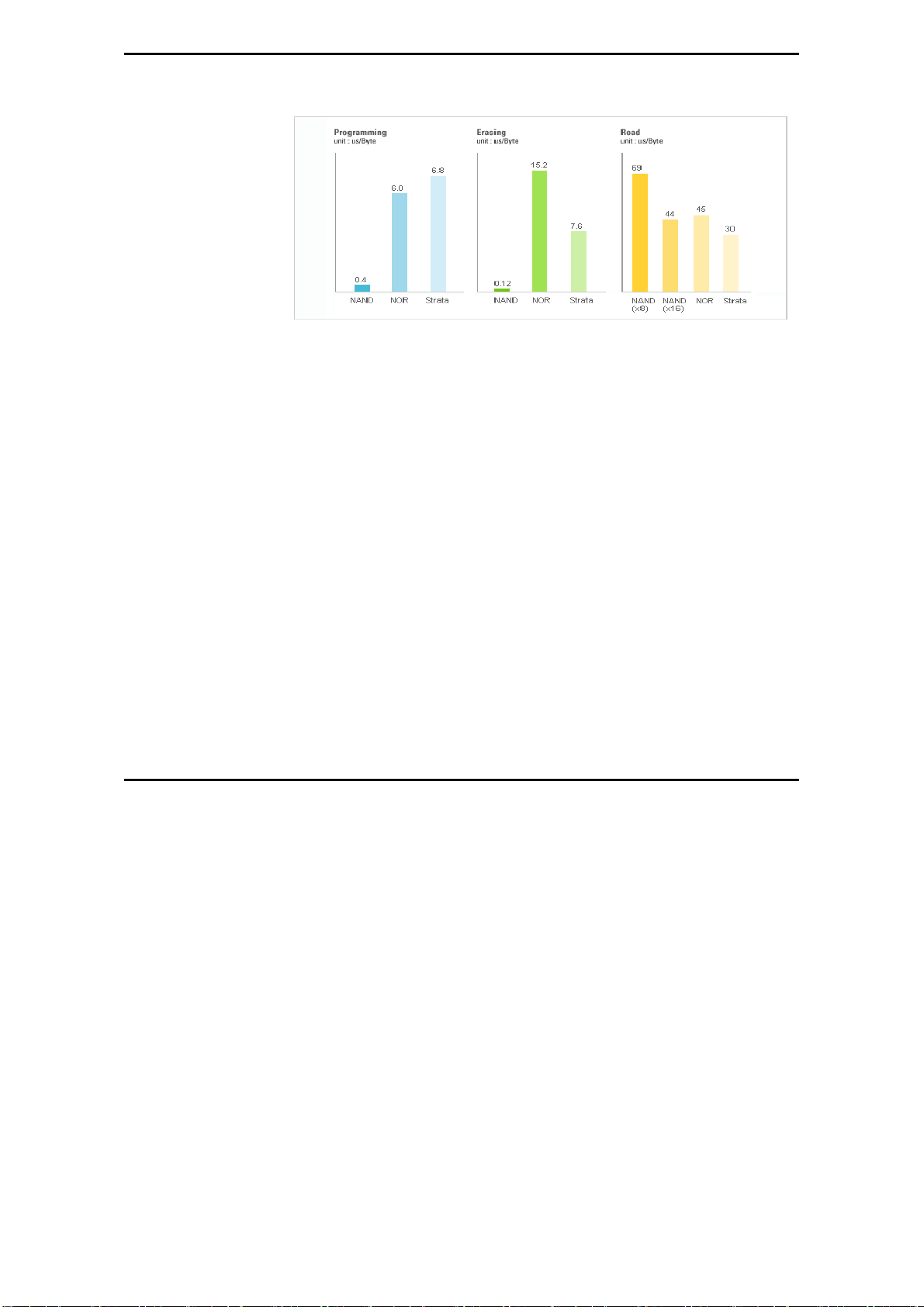
Performance Comparison
* NAND Flash: High Wright Performance
Serial Flash EEPROM
The non-volatile Serial Flash Memory is widely used for code storage and user
settings in cost-sensitive applications such as CD and DVD players, set-topboxes (STB), digital-TV and cameras, graphic cards, printers, PC motherboards
and flat panel displays. These products typically run their operating code from
fast Random Access Memory (RAM), after downloading the code from the
low-cost Serial Flash Memory at power-up. Several semiconductor
manufacturers produce this device family named as 25xxx.
Serial EEPROM
These devices are electrically erasable, but they operate in a series rather than in
parallel.
Xilinx 17xx family
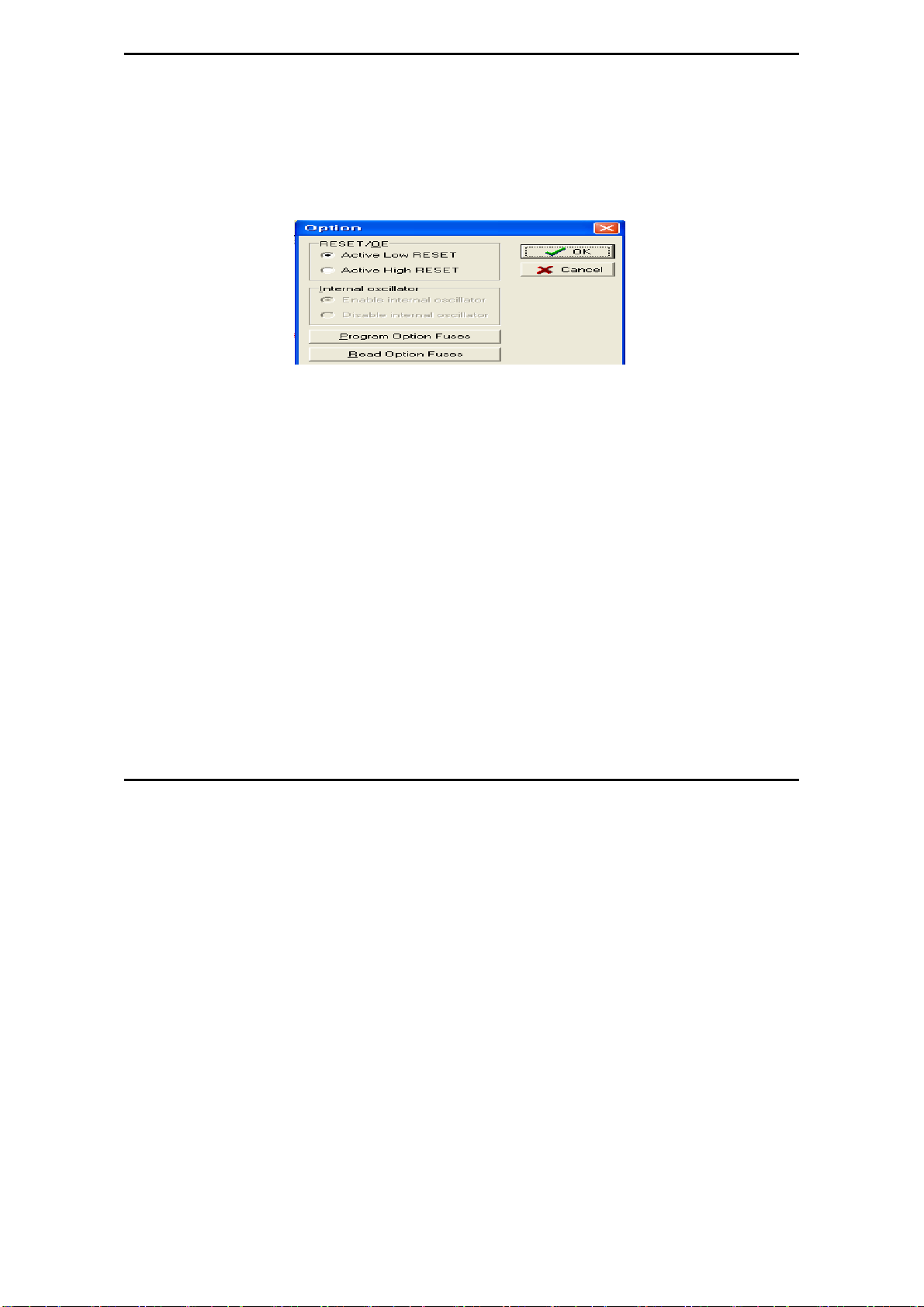
From the Xilinx 17xx series, the RESET Polarity can be changed only on Xilinx
17xxD/L and 17128. On devices with EPROM po rtion already programmed or
on new blank devices, RESET polarity is HIGH.
The current status of the Reset pin polarity is determined and displayed on the
screen after Reading the device. The polarity of the Reset pin can ONLY be
21
Page 22
MaxLoader User’s Guide
changed from HIGH to LOW, but not vice versa. To change the polarity, click
on the Option button and check the Reset bit box before programming your
device. To make certain that the RESET Polarity has been changed, read the
device again. On the other serial EEPROM devices (but NOT Xilinx 17xxD/L
& 17128) the RESET polarity is always HIGH and it cannot be changed to
LOW.
Non-Typical Devices
8-bit 1-Megabits
There are four types of 1 Megabits EPROMS. One set has the A16 and OE lines
swapped. However, this device will still program and verify like normal 1
Megabits. Once this device is placed into the circuit, it will appear as if it has
not been programmed correctly. This is not due to the MaxLoader software or
the programmer, but the difference between these 1 Megabits. When selecting a
1 Megabit, it is important to determine which one you have. Here is a list of 1
Megabits and their equivalents:
27010 (normal pin-out -- program as GENERIC or INTEL 27010):
Equivalents: INTEL 27010, HITACHI 27101, TOSHI BA 5710 00, NE C 271001,
MITSUBISHI 27101, 27301 (non-standard pin-out -- program as HITACHI
27301's):
Equivalents: HITACHI 27301, NEC 271000, MITSUBISHI 27100, TOSHIBA
571001, INTEL 27C100
22
Page 23

16-bit 1-Megabits
Any devices with the number 27210, 271024 and the MITSUBISHI 27102.
27011: The 27011 is a 28-pin 1-megabit device that is organized into 8 pages of
16k-bytes. NOTE: The 27512 is 4 pages of 16k-bytes.
Erasing an EPROM
An EPROM has a quartz window located on the chip just above the die. Erasing
an EPROM is done by exposing the EPROM to high-frequency ultra-violet
(UV) light waves. Erasing an EPROM usually takes 15-20 minutes, but may be
shorter or longer, depending on the device. If you wish to purchase an Er aser,
call EE Tools at (408) 263-2221. When an EPROM is not being erased, th e
window may be covered with an opaque label. Sometimes (over a period of
years) an EPROM will start to erase due to the rooms level of fluorescent light.
Direct exposure to sunlight also has the same effect, but happens much more
rapidly
MaxLoader User’s Guide
.
PLD
A programmable logic device (PLD) consists of an array of logic gates and flipflops that can be programmed to implement an almost unlimited number of
logic designs. These are programmable logic arrays that can be EEPROM based,
EPROM based, fused link, anti-fuse, or Flash-based technology. They are
programmable by the user to implement logic circuits in order to reduce part
23
Page 24

MaxLoader User’s Guide
PLD Features
count and turnaround time. PLDs are programmed according to a fuse map,
which is typically contained in a JEDEC file.
NOTE: PLD compiler CUPL EE Tools offers PLD development tool for
engineers who want to generate a JEDEC file for data of PLD devices. Four
different tools are available in www.eetools.com
Many different PLDs are available from the IC manufacturers. PLDs are
fabricated using either bipolar or CMOS Processes. All PLDs are made up of
combinations of AND gates, OR gates, inverters, and flip-flops.
PAL
PAL’s AND gates connect to OR gates in a fixed pattern.
: The PAL is a PLD with a fuse-programmable AND array. The
24
PROM
though most of the smaller PROMs (i.e. 32 x 8 organization) were being used as
logic elements. The larger PROMs were still applied in bipolar microprocessor
designs to store microcode instructions. The PROM has an architecture similar
to the PAL, except that the PROM’s AND array is fixed while it’s OR array is
programmable.
FPLA
programmable AND array like the PAL, with a programmable OR array like the
PROM. The FPLA is therefore a more general PLD because any product ter m
may be connected to any output OR gate. Because the entire IC is
programmable, the FPLA can implement some functions which a PAL or
PROM may not be able to implement.
EPLD
: For many years, the PROM was not classified as a PLD, even
: The field-programmable logic array (FPLA) consists of a
: Several manufacturers produce PLDs which can be erased and
Page 25

reprogrammed like EPROMs. These ICs are called erasable programmable
logic devices or EPLDs. Internally, they have the same programmable ANDOR-register structures of the PAL and FPLA.
Microcontroller
These devices are CPU's with on-chip EPROM and RAM. They are typically
40 pins and are UV erasable. They have part numbers such as Intel's
8748,8749,8751,8752 etc. A micro -controller is generally a computer-on-a-chip
with RAM, ROM, and I/O ports. Microcontrollers are usually used for specific
purposes, such as keyboard decoders, printers, clocks, telephones, CD-players,
or any other application that requires a small, on-board computer.
Microcontrollers are used to take the place of in-circuit logic, as it can be less
expensive and take less space. Also, since it is software driven, the device may
be updated very easily. Micro-controllers have the ability to use internal as well
as external RAM. Also, micro-controller data may be encrypted or otherwise
secured to prevent copying of the data or program information. Microcontrollers
also have their own instruction set, usually very similar to familiar
Microprocessors (such as the 8080 or 8086). The INTEL MCS-51 family
features up to 64k each of internal and external memory, 32 I/O lines, interrupts,
timers, and bit-addressable RAM. Its instruction set contains 111 instructions.
However, for specific purposes, limited versions of the 51 family are available.
For instance, the Philips 87c751/87c752 families do not allow external RAM to
be used, and have limited I/O channels, etc. However, these devices still allow
for data/program encryption and security levels. They are also less expensive
than the MCS-51 micro-controllers.
See the help selection under MAIN-MENU COMMANDS for Encr yption and
Security-bit information.
MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Programming Microchip PIC family Microchip
PIC series are different from other Microcontrollers in that they have an
EPROM area as well as a Configuration Fuse. The Configuration Fuse in the
25
Page 26
MaxLoader User’s Guide
About “Device ID” and “Auto Select” on EE Tools programmers
PIC family is used to setup different Oscillator types, to set Memory Code
Protection and Watchdog timer, and etc. To program this fuse:
1. Program the EPROM portion of the device
2. Click on Option
3. Make any changes if necessary
4. Click on the Program Configuration Fuses button to program the fuse
information that you want to program
5. Click on the Read Current Configuration Fuses button to read back the
current status of the fuse
6. Press the Close bu tton
Most of the devices have their own manufacturer and device ID’s in each
programmable devices such as E(E)PROM / Flash Memory, PLD, and MCU.
However the old type of devices such as PAL, PROM, or 2816 does not come
with an ID because the IC makers didn’t put its ID for the older chip types.
26
(Auto Select)
As you can see the “warning” in the Auto Select menu in MaxLoader, we can
only guarantee the “auto select” function for 32-pin or less device in
E(E)PROM / Flash Memory. Since device library in programmer software has
information for these standard devices, users can utilize this feature as their
purpose. However, all other devices such as PLD, Serial Memory,
Microcontroller, and FPGA are not able to be recognized by programmer
software automatically. We use this feature as optional device selection menu.
Auto Select command allows you choose an unknown device through device
IDs which were recorded in MaxLoader library. Put a device up to 32-pin on
the ZIF socket of programmer and click on “Auto Select” in Select Device
Page 27

MaxLoader User’s Guide
menu. It will find out a correct device ID and choose a correct device for you.
(To Find a Device ID)
After selecting a certain device from Select Device menu and plug-in a
corresponding device in ZIF socket, you can see the ID(s) when you pressing
“Shift” and “F1” keys in your keyboard.
27
Page 28

MaxLoader User’s Guide
In the software menu, Chip (in socket) MFG (manufacturer) ID and DATA (in
software) ID must be identical if your target device is valid .
If it does not, check the socket with your device if you use NON-Standard (DIP)
device or use test other devices in case the first device may be defective. This
ID check must be passed before further operation on your device.
4. TERMS AND SYMBOLS USED IN THE GUIDE
Safety Note Conventions
NOTE assists the user in performing a task. It makes the job more easily
understood.
CAUTION alerts the user that unexpected results or damages to a device
may occur if an instruction is not followed.
Other terms and definitions are as follows
Toolbar : Clicking on a toolbar button manipulates operations or
commands for MaxLoader programmer software.
Bold/Italics : actions items/sof tware functions, i.e. Edit Button, IC Test,
or Change Algorithm.
28
Page 29

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device : The IC you are attempting to read, program, or verify.
Buffer : The work area in your computer memory to execute Read, Save,
Program, and Verify. The Buffer size may be from 64K to 32 Megabytes.
NOTE: If the size of a device is bigger than the buffer size in your computer,
MaxLoader will use the hard disk space (swapping). For this reason, the
MaxLoader software can handle devices up to unlimited size of E(E)PROMs
with your standard memory space ( a minimum of 512KB RAM memory is
required).
Choosing a Right Adapter
Most programming adapters are simple package converters. The y allow TSOP,
QFP, SOIC, or PLCC devices to plug into the same device’s DIP footprint.
These adapters are available for memory, logic, and Microcontrollers. They can
often be used with many devices from various manufacturers. For devices that
cannot use a generic footprint we have offered adapters to work with specific
programmers.
Here is what you need to know to select an appropriate adapter.
1) A part number and manufacturer of your device.
2) A device package. (TSOP, PLCC, DIP, QFP, SOIC, etc.)
(Refer to the following package drawings)
3) Pin numbers in your device.
4) In some cases you need to know your device package dimensions for SOIC,
SSOP, and TSOP packages.
29
Page 30
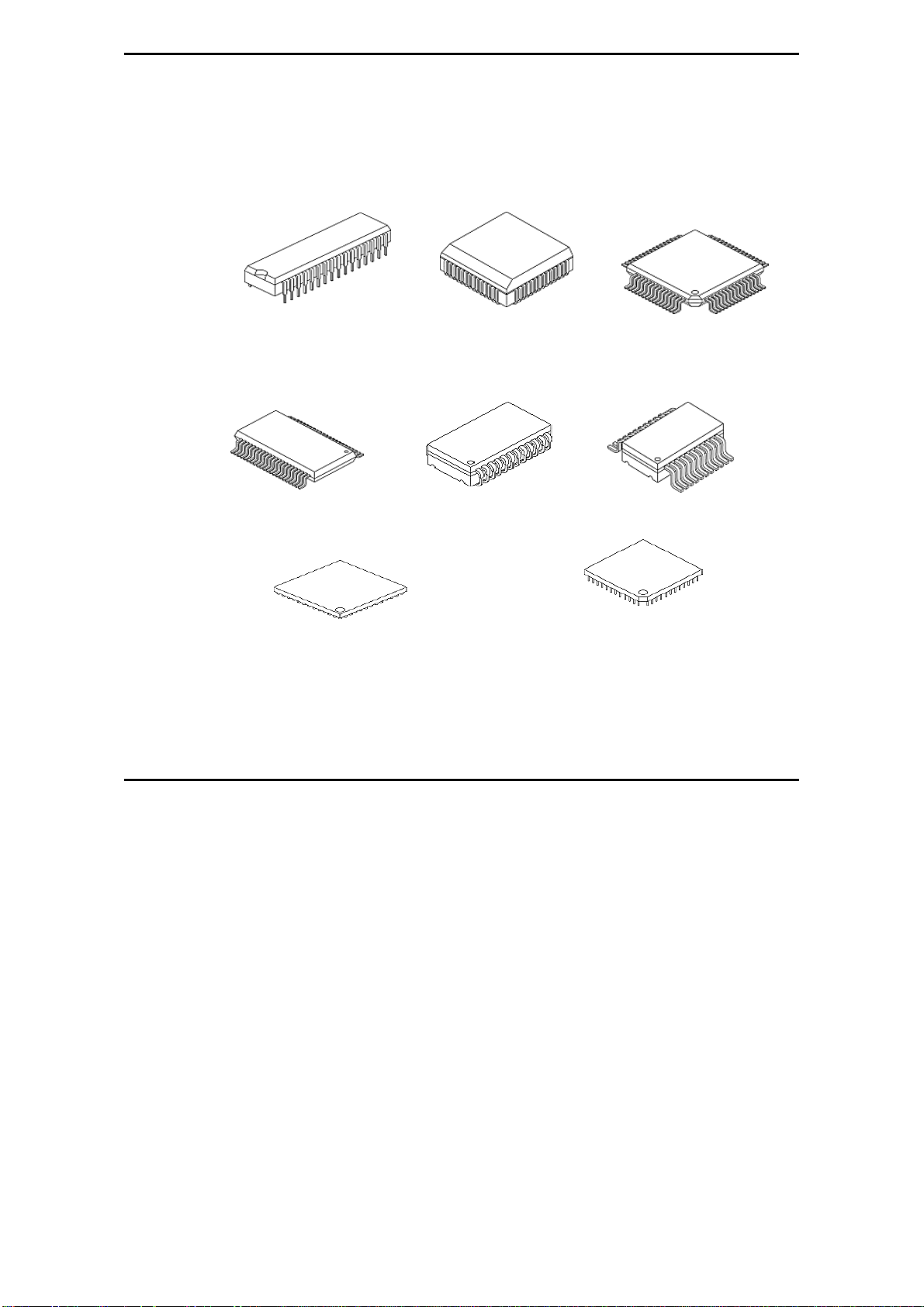
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Different Device Packages
DIP PLCC QFP
TSOP SOJ SOIC
BGA PGA
30
Page 31

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Different Programming Adapters
PLCC-TO-DIP TSOP-TO-DIP
QFP-T
QFP-TO-DIP SOIC-TO-PLCC
BGA-TO-DIP DIP-TO-PLCC (for Emulator)
31
Page 32

MaxLoader User’s Guide
5. QUICK START EXAMPLES
If you are using a programmer for the first time, this section will help you to
become familiar with the basic operating procedure. This section includes two
examples of device programming with your programmer.
Programming an EPROM with data
We selected an AMD 27C010 EPROM to show you how to program an
EPROM. The 27C010 EPROM needs to be erased (blank) before this
procedure begins.
NOTE: EPROMs have a quartz window that can be erased by exposing the
EPROMs to Ultra-Violet (UV) light. Erasing an EPROM usually takes 10-30
minutes.
1. Click on the MaxLoader icon in your desk top menu after installing the
MaxLoader.
2. Check the optional configuration before programming begins.
3. Click on the Select button. There are two different ways to select the target
device from the menu: 1) by choosing the device manufacturer type using the
arrow keys or 2) by typing the manufacturer and the device names on NAME
box. MaxLoader will display the names of the devices that have the best match
to your input. After selecting the device, the detailed device information box is
provided below the select menu screen.
32
Page 33

MaxLoader User’s Guide
4. Click on the Load to load a file from a floppy or hard disk into the buffer.
Change your file directory by choosing a directory in Look in box. Choose a file
name and type of the file. Make sure that the file type is selected; ”All Hex
File” or “Binary file” is located in the File of type box.
33
Page 34

MaxLoader User’s Guide
5. Insert the 27C010 device into the ZIF socket. After inserting the part, make
sure that the socket handle is down (close) to secure the chip.
See the illustration below:
6. Click on the highlighted cursor Blank Check.
NOTE: If an EPROM is not erased completely, it will not pass the Blank Check.
If an EPROM is damaged to begin with, it may not pass the blank check,
although it has been erased for a long time in UV eraser.
7. Click on the Program.
CAUTION: Do not touch the device while the BUSY green LED light is on
(programming is in progress).
After programming a device, the part is automatically verified. The Checksum
is calculated and displayed in the OPTION info. In order to verify your work,
read the programmed part again. If this Checksum value matches to that of the
programming checksum, then the 27C010 is programmed successfully.
Duplicating an EPROM from a master IC device
The following is an instruction on duplicating a program med device. In order
to do so a source device and an erased (blank) target device are necessary.
Source Device: Programmed AMD 27C256
34
Page 35

Target Device: Erased or blank INTEL 27C256
1. Make sure the MaxLoader is displayed without any communication error
(refer to programming section ).
2. Place the AMD 27C256 device into the ZIF socket.
3. Select the manufacturer and part names from the Select menu.
4. Click on the Read button. In order to make sure the device is read properly,
Click on the Verify button.
5. Remove the current chip from the socket and replace it with the erased or
blank Intel 27C256 device. Select the appropriate device fr om Select menu on
screen.
NOTE: You do not need to change the device information if you use the exact
same chip as the source device.
6. Click on the Blank button.
7. Click on the Program button. The part will be programmed and verified
automatically. If no error messages appear during the Programming or
Verification process, your duplicating work is done successfully. You have a
duplicated Intel 27C256 part from AMD 27C256 chip.
6. MAXLOADER OPERATIONS
This section describes the operation of the software. The Main standard
system-menu is divided into four display areas: Main operation menu screen,
Option Information, System information, and counter.
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Basic Menu Screen Information
Option Information
• Gang Size : Current socket size when MaxLoader is used
• Split : Current world format for split programming
• Enc Mode : Enable or Disable Encryption mode for
Microcontrollers
• Base Port : Current parallel port address
• Check-Sum : Check-Sum number of the data in current buffer
35
Page 36

MaxLoader User’s Guide
• H/W Rev : Hardware revision number for your programmer
• S/W Rev : Current MaxLoader software revision number
• Serial No : Serial number of MaxLoader hardware
(Additional Option Information for Non PLD Devices)
The following information presents programming information of the selected
device.
• Algorithm : Programming Algorithm
• Vccp : Main Power Supply Voltage
• Vpp : Programming Power Supply Voltage
• Tpwp : Programming Pulse Width
System Information
• Device Name : The current device number with manufacturer name
• Device Size : The size of device in HEX value
(Ending Address –Starting Address + 1)
• Free Disk : Check the free disk space for a big size E(E)PROM
programming.
• Adapter : Optional Adapter Name for Non-standard devices
• Pins : Number of device pin
• File : Current working directory path and file name after
loading a file
Counter
• Devices/HR : Displays the estimated number of devices that can be
programmed per hour. This feature can only be used
when choosing the Program or Auto selection unde r
the Device button.
• Success: This number indicates the device programmed
successfully.
• Failure: This number indicates the number of device
programming errors that occur during a programming cycle.
These could be either Blank Checking, Programming, or
36
Page 37

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Verification error.
• Count: This number indicates all devices executed successfully and
unsuccessfully.
NOTE: This feature is useful for repeat programming on the same device.
You can make an estimate time to perform the programming job and see
the successful and failed devices after finishing the Program or Auto
Repeat programming routine.
File
NOTE: The feature allows users to program a certain area that might contain
a serial number in the memory device with serialized number by a certain value.
Start : Start address of memory that contains serialized data
End : End address of memory
Inc Value : This value will be added to the previous data value
User must click on Auto Increment to program a memory with data increased
by one to the previous data.
MaxLoader uses three different file types: BINARY, ALL HEX, and . POF. In
the file type box, a file type can be selected and loaded to the buffer or saved
onto a disk. The default file type is the Binary file. The All HEX files can be
chosen by maneuvering the arrow button. All HEX files include INTEL HEX
(MCS-80/86/386, MOTOROLA S (1-9), Tektronix HEX and ASCII HEX. OPF
37
Page 38

MaxLoader User’s Guide
(Programmer Object File) is a binary file generated by Altera assembler
(Quartus and MAX+PLUS II). This file should be loaded for Altera MAX or
EPC family devices only.
Binary Format
Binary format does not specify the address or checksum of the file. The file
contains the actual binary data. An example of this format is a DOS
executable file with an .EXE or .COM extension. Binary format is generated
for programmable memory devices. It is recommended to save your EPROM
data as binary format in order to load the file as a standard file format later.
Intel HEX Format
Intel HEX format files are text files that include the file information in
hexadecimal.
1 : A record mark
2 – 3 Byte Record length in 2 digits HEX, Max 20 (64 in
ASCII)
4 – 7 Address 4 digits HEX Field. Most si g n i fi cant byte fi rs t
8 – 9 Byte 2 digit field record type:
01 End of file
02 Extended addresses
10 – N Data Data field in HEX digits
N+1 – N+2 Check-Sum Two digit HEX Check-Sum character computed
by two’s complementing the sum of previous
bytes except the ‘:’
INTEL HEX FILE EXAMPLE
:110000000444154414D414E2053332053455249414C73
:00000001FF
The extended address record specifies the index address where data will be
loaded into. The Extended Address will continue to offset data record address
until a new Extended Address record is specified.
38
Page 39

MaxLoader User’s Guide
:02 0000 02 4A29 02
Check Sum
Index address
Record type
Address
• The Address field is blank because this record is not data.
• The record length is '02' for index address (2 Bytes).
NOTE: If the address for the data record is '2B56', the actual address will be
4A290 + 2B56 or 4CDE6 (HEX).
Record Length
Motorola S HEX Format
The Motorola S format file is an ASCII-HEX file.
Position (Byte) Character Remarks
1 S Letter S indicates start of record
2 0, 1, 2, 3, or 9 A single character indicates the type of
record.
9: End-of-file
3: 32-bit address data record
2: 24-bit address data record
1: 16-bit address data record
0: Header
3 - 4 Bytes Byte COUNT in HEX (multiply by two
for number of characters). This count
includes the address, data, and
Checksum field.
5 - X Bytes Memory Address for the current record.
X will be:
8 : 16-bit addressing for files less than 64K.
39
Page 40

MaxLoader User’s Guide
10: 24-bit addressing for files greater than 64K.
12: 32-bit addressing for files greater than 64K in
length.
X+1 - N Bytes HEX Data (two per byte)
N+1 – N+2 Check-Sum Two digit HEX Check-Sum character
calculated by one’s complement
of DATA, ADDRESS and COUNT.
Motorola File Example
S325200000002F0000EA060000EA0B0000EA100000EA160000EA0000A0E11B0000EA210000
EA31
The file offset address is “20000000,” so you should put this value in the
“file offset” of “File Load ” config option / address menu.
TEKTRONIX HEX FORMAT
The Tektronix HEX format contains ASCII records, expressing bytes
ASCII pairs.
Position Character Remarks
1 / Slash character for start of line
2 - 5 2Bytes Address. MSB first load
6 - 7 Byte Number of data bytes (not checksums)
8 - 9 Byte Check-Sum of ADDRESS and COUNT
by character in HEX (not by by t e)
10 - N Data Data bytes as ASCII pairs
N+1 - N+2 Byte Check-Sum of Data by character (not as
bytes)
Tek Hex Example
/00001102444154414D414E2053332053455249414C8F
/01000001
ASCII HEX format
This selection generates an ASCII coded HEX format for either 4-bit or 8-bit
PROMs. Each record contains a four-digit HEX address (16-bit) followed by 16
data elements. A 16-bit checksum is at the end of the file.
40
Page 41

When this format is selected, the device base address must be specified. This
address represents the lowest address in the device. The file created contains an
entry for each location in this device. ASCII HEX format can be created for
programmable memory devices only.
JEDEC Standard <PLD devices only>
JEDEC (Joint Electronic Device Engineering Council) files are the standard
method for describing PLD fuse patterns and test vectors. JEDEC files contain
fuse data, test vectors, part numbers, and checksums. The checksum of the file
allows you to verify that a given file is intact and has not been unintentionally
modified. JEDEC files normally use the extension (last 3 letters) “.JED.”
For more information on the JEDEC standard, contact:
Global Engineering Documents Inc. at (800) 854-7179
Electronic Industries Association at (202) 457-4900.
Following is an example of a JEDEC file:
<STX>File for PLD 15S8 Created on 11-SEP-96 5:08PM
2754 memory decode 345-432-123
Seung Park PK Logic corp.
QP20* QF448* QV8*
F0*X0*
L0000111110111111111111111111111*
L0028101111111111111111111111111*
L0056111011111111111111111111111*
L0112010110110111101111111111111*
L0224011110111011101111111111111*
L0336010101110111011111111111111*
V0001000000XXXNXXXHHHLXXN*
V0002010000XXXNXXXHHHLXXN*
V0003100000XXXNXXXHHHLXXN*
V0004110000XXXNXXXHHHLXXN*
V0005111000XXXNXXXHLHHXXN*
V0006111010XXXNXXXHLHHXXN*
MaxLoader User’s Guide
41
Page 42

MaxLoader User’s Guide
V0007111100XXXNXXXHHLHXXN*
V0008111110XXXNXXXLHHLXXN*
C124E*<ETX>8646
STX The fuse map begins with an ASCII STX character (02 HEX)
Design Specification This item is user specific. While no format rules apply,
certain information, such as user’s name, company, design
date, part designation, revision and device part number,
should be entered. This field is illustrated by an asterisk
(*).
QP Specifies the number of pins in the devices.
QF Specifies the number of JEDEC fuses in the devices.
L The fuse list fields contain the state of all fuse links in the
devices. The starting fuse number follows the L specifying
the field type. The fuse list that follows contains a zero (0)
for each intact link and a one (1) for each blown link. An
L field is generated for each product term in the device.
C The checksum field contains the 16-bit sum of the link
stated in the 8-bit words.
ETX The fuse map ends with an ASCII ETX character (03
HEX).
Sum Check A 16-bit sum of the ASCII values of the characters from
STX to ETX inclusive. The sum check follows the ETX.
NOTE: LOGIC Compilers For PLD Devices: Software is available to help the
engineer develop designs using PLDs. Software tools called logic assemblers or
compilers translate a design file written in high-level language into a fuse
pattern stored in a JEDEC file. JEDEC files are produced by almost all PLD
development software’s and are accepted by the MaxLoader programmer.
There are many commercial software packages available to help you design
using PLDs.
42
Page 43

MaxLoader User’s Guide
POF file <Altera EPMxxx devices only>
The programming object file (.pof) for an EPM7128A or EPM7256A device
can be programmed into the EPM7128AE or EPM7256AE device, respectively,
using the MAX+PLUS
programming software from EE Tools programmers.
For further question on POF file, contact http://www.altera.com/support/spt-
index.html.
®
II software version 9.6 and later or with 3rd party
File / Load
Data can be loaded into the memory from a device or by opening a data file.
Load fills your buffer memory with the data from storage for viewing or editing.
This command loads the data from the selected file storage into the memory
buffer. In order to the use “All HEX File” selection, the HEX file must be one
of the file formats supported by the MaxLoader(TopMax/Chip Max), such as
Intel HEX(MCS-80/86/386, MOTOROLA S(1-9), Tektroni x HEX and ASCII
HEX.
43
Page 44

MaxLoader User’s Guide
The default selection on File Load menu is in Binary Format. To select any of
the HEX files mentioned above, choose “All HEX File” by pressing ⇓ button.
When you have selected the desired file, press the OPEN button to load the file
into the data buffer. If you are programming a PLD, you will want to load a
JEDEC file. The procedure is identical to loading a data file, except that the
files in the current directory will have the JED extension. If your selected
device is an Altera MAX family, the file you should load is a POF extension.
The MaxLoader uses a RAM buffer to hold data. After loading a file into the
buffer, you can edit the buffer data. If you load a JEDEC file, you may use (the
vector pattern edit) command to view or edit the fuse map and (test/vectors) for
any test vectors that may have been in the JEDEC file.
44
File / Reload
Page 45

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Data can be reloaded into the memory from the file directories that contains
previously loaded files. Reload remembers your file location and type (Binary
or All Hex) that has been loaded into the buffer.
File / Save
Save the current data in your memory buffer to disk storage by using one of the
current supported file formats.
Before saving a file, check the buffer and the file address ranges. The contents
of the buffer through the specified range will be written into the new file,
completely erasing any existing file with the same name. Before saving to a
disk, make sure that no file with the same name exists.
File/ Load Project
A project file that saved by SAVE PROJECT menu is loaded. The project files
use the extension (last 3 letters) “.prj.”
File/ Save Project
This feature allows you to create a job description such as “engineer name” and
other useful information for records.
It is very useful for future use when you set up all possible environments such
as selecting a device, loading a file, and setting other configurations for
programming jobs. A job description can be saved as a file name and the same
project environment will be ready once you load the same project name.
File Name: A file name can be entered with the 3 letter extension “.prj.”
Author: An engineer’s name [whom creates this project].
Description: A job explanation that you memorize for your future usage. A
device number, File name, and checksum number can be entered in the note pad.
Other programming menu descript i o ns, such as configurations can be described.
45
Page 46

MaxLoader User’s Guide
File/ Save Log
This function will record all operating procedure. Such as carrying out
preloaded tasks in maxloader software.
The .txt file can be saved in any folder, and opened in “Note Pad.”
46
Page 47

MaxLoader User’s Guide
File/ Save All Messages
This function will record all programming displayed messages from the
MaxLoader message window.
The .txt file can be saved in any folder, and opened in “Note Pad.”
47
Page 48

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Buffer
48
Page 49

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Buffer / Edit Buffer
This command allows the user to examine and modify the contents of the
memory buffer. This section applies to a non-JEDEC file (PROM, EPROM,
EEPROM, and Microcontroller) or to a memory chip. If a PLD is being loaded,
see the (vector pattern edit) section. The data is presented in HEX and ASCII
formats.
Find
This feature allows you to search the data (ASCII and HEX) in the current
Asc : The data looking for ASCII value.
HEX : The data looking for HEX value.
Direction / UP : The data searching from previous address than the current
location.
Direction / DOWN: The data searching from higher address than the current
location.
If you would like to see more & same data, click on the Find Next button.
49
Page 50

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Find Next
Press the Find Next button to locate the rest of the data that you entered in the
FIND box. The error “Search Pattern not Found” will be accursed when you
press this button without entering data in the FIND text box.
Fill Buffer
You can enter a certain character (data) in a certain buffer location.
Buffer Start: Starting address for the data to be filled in buffer.
Buffer End: Ending address for the data to be filled in buffer.
Fill Data: Two digits of HEX value to be filled between Start and End buffer.
50
Fill random data
Once you click this button, a random data stream will be filled in the entire. This
will be useful before programming a device with full buffer data.
Page 51

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Copy buffer
Copy certain data between 2 addresses to other location in the same buffer.
Fill Buffer
Enter certain data between 2 different buffer locations.
51
Page 52

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Clear buffer
Fill entire buffer with the same data in “default buffer value” which can be any
data. In most, it is “FF” but it can be “00” for Motorola S-record type.
52
Page 53

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Print buffer
The current buffer data can be printer in different formats. Also, you can review
buffer data with an editor in an utility software.
Set editor to view mode
This mode allows you not to modify data in the buffer.
53
Page 54

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Data in buffer can be modified in this mode.
Set editor to edit mode
54
Set Editor to binary mode
The data in current buffer will be changed as binary mode.
Page 55

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Set editor to 8 bit(byte) Hex
The data in current buffer will be changed as 8-bit hex value.
Set editor to 16 bit(word) Hex
The data in current buffer will be changed as 16-bit hex value.
55
Page 56

MaxLoader User’s Guide
The data in current buffer will be changed as 32-bit mode.
Set editor to 32 bit(double word) Hex
Set default editor mode
Make the current buffer mode as same data size as the selected device in the
current operation. It could be 8 or 16-bit depends on the de vi ce selecti on .
56
Page 57

Set default Reset Editor
The cursor mode will be the first data in address 0.
Swap nibble
Swap each character (nibble) in 8-bit(1 byte) block.
MaxLoader User’s Guide
57
Page 58

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Swap byte
Swap each 8-bit (1-byte) data in each 16-bit(4-byte) block.
Swap Word
Swap each 16-bit (2-byte) data in each 32-bit(4-byte) block.
58
Page 59

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Swap double word
Swap each 32-bit (4-byte) data in each 64-bit(8-byte) block.
Jedec editor
This buffer mode allows you to retrieve and modify data for PLD devices.
The data can be displayed in two different mode (unused-bit “0” or “X”, usedbit ”1”or “ –“.)
59
Page 60

MaxLoader User’s Guide
In the Jedec editor mode, you can still use all features in Buffer Edit Mode.
60
Clear
Pressing this button allows you to fill the buffer with the data located in
“Default Buffer Value” in Config Option Menu.
Page 61

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Close
Press to exit the HEX Editor.
Buffer / Edit UES
The UES Edit command creates or changes the User's Electronic Signature
(UES) array in GAL device. Each GAL device contains an electronic signature
word consisting of 64 bits of reprogrammable memory. The electronic
signature word can be programmed to contain any identification information
desired by the user. Some uses include pattern identification labels, version
numbers, dates, inventory control information, etc. These features give the user
the ability to view and edit the UES data before programming a GAL device.
When the UES edit command is invoked, an editing data window appears. If
the data fields are empty, you may create a new UES. You can enter the UES
up to eight characters in the HEX or ASCII data area. If you see any data from
the current UES window, it means the UES has been created and that you can
modify the data for a different reason. The UES data is not secured when you
execute the Function / Security command.
Device
61
Page 62

MaxLoader User’s Guide
This section presents the main operation menu for the target device that is
mounted on the ZIF socket. In order to process the following commands, make
sure that the device is correctly inserted into the ZIF socket and the latch is
down.
NOTE: The Device Information display area presents the device information of
the selected device.
Device / Select by history
Pressing this button allows you to review all devices that have selected
before. You don’t have to select the same device again and just select from
this menu.
62
Page 63

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Select
During operation, the first step is usually to select a device. This Select
command enables the user to define the manufacturer and the type of the device
that will be used. After you select a device, you can insert a device into the
programmer’s device socket and conduct various device operations such as
programming and verifying device data or reading data from the device. The
Select command contains both manual and automatic methods for selecting a
device. If your device is not identified by the Auto Device Select menu, you can
select the device list displayed in the Manufacturer & Device list. Scroll through
the manufacturers and device numbers until you find the manufacturer and
device you are looking for. You can use wildcards to help you “zoom” on the
device you are looking for.
NOTE: PAL Device Logic Symbols: The logic symbols for each of the
individual PAL device gives a concise functional description of the PAL device
63
Page 64

MaxLoader User’s Guide
logic function. This symbol makes a convenient reference when selecting the
PAL device that best fits a specific application
Select / E (E)PROM, FLASH
All EPROMs (27xxx), EEPROMs (28Cxxx, 29Cxxx), Serial E(E)PROMs
(17xxx, 24xxx, 32xxx, 33xxx, 35xxx, 59xxx), and Flash EPROM (2 8Fxxx,
29Fxxx, 29LVxxx, 29BVxxx, 29Wxxx, 49Fxxx) of 24/28/32/40/42 and up to
48 pins (1 Mbit, 2Mbit, 4Mbit, 8Mbit,16Mbit, 32Mbit, and up).
Select / PLD
EPLD, EEPLD, FPL, PEEL, GAL, MAX, MACH, PLS, PLD, PLC, PLUS,
EPM, ATFxxx, ATVxxxx, EPxxx, EPCxxx, 5Cxxx, 85Cxxx.
Select / Microcontroller
Intel 87xx, Phillips 87C75x, SGS-Thomson ST62xx, Atmel AT89Cxx, 89Sxx,
89LVxx, Microchip PIC12/16/17, Motorola MC60705xx,
MC68HC711xx/705xx/908xx; Zilog Z86Exx; NEC 8749H.
Select / PROM
AMD 27Sxx, Cypress CY7Cxxx, Fujitsu MB71xx, Fairchild 63Sxx,
NS
74Sxxx, Phillips 82Sxxx, WSI 57Cxx.
64
Select / Auto Select
Identify the device that is mounted on the ZIF socket.
This feature can only be applied to Memory and some Microcontroller devices.
Clicking the Auto Select button will enable the programmer to identify the ID
on the device and will select the matching device in the library automatically.
NOTE: If you have a “Device not found" message, select the device manually.
If you have old devices or defective devices, TopMax will not be able to
recognize the ID code from your device
Page 65

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Select / Device information
Pressing this button allows you to review the target device information
before selecting a device.
65
Page 66

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Change Algorithm
Users are provided with an option of changing the programming parameters of
most devices. Once you select the “Change Algorithm” option under the
DEVICE menu, the user will be presented with a list of device specific
programming parameters, such as Vccp, Vpp, Read Vcc, Verify Vcc Low,
Verify Vcc High, Pulse Width, Over Pulse Width, Over Pulse Mul, and Retry
number. Each of these parameters can be selected and edited individually by
changing the existing numbers in the parameter box and pressing the close
button. The user will then be prompted to enter the new value for that
parameter.
66
CAUTION: Please note that before deciding to modify any programming
parameter, the user must consult the manufacturer programming specification
for that device. EE Tools will not be responsible for any damages caused by
any unauthorized modified programming parameters. Any changes in
programming parameters are temporary an d the origi n al par a met er’s val ue
will be restored once the operation on that device is complete. However, the
user can store the modified programming parameter for a particular device by
using Macro command.
Page 67

Device / Auto Menu Option
Users can choose a operation stream for “Auto” button.
CAUTION: Clicking the Auto button makes the selected device secured. It is
highly recommended that customer should click on the “auto” button after
reviewing the “Auto Option” stream.
MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Blank Check
The Blank Check function is used to verify whether or not a device is in an
erased or unprogrammed state.
All EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory) devices should be
checked before programming. EEPROM (Electrical Erasable Programmable
Read Only Memory) based parts do not need this command because
EEPROM’s are erased automatically before programming.
PLD based parts are checked by verifying all of the fuses that are intact. Any
erased PLD’s should pass this test.
67
Page 68

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Erasing EPROMs. In order to clear data in an EPROM, the chip
should be exposed to a short wave UV (Ultra violet) light. Most erasers require
between 5 and 30 minutes erasing an EPROM. So me types of chips take longer
to erase than others. An EPROM based part (a PLD or Microcontroller) with a
security bit feature is designed so that the security address is typically th e last
bit to be erased. If the window of a chip is not clear, try cleaning the window
with alcohol or a solvent. Erase chips if the chips are exposed to sunlight and
fluorescent light for months or years; your chips can be erased. You should
cover the window of the programmed chips with an opaque label to make th e
data permanent. Some EPROM based parts can't be erased because they do
not have a window. These chips are called one time programmable (OTP)
EPROMs.
An EPROM has a quartz window located on the chip just above the die. An
EPROM is erased by exposing it to high-frequency ultra-violet light waves.
Erasing an EPROM usually takes from 15-20 minutes, but may be shorter or
longer, depending on the device. Many manufacturers make EPROM erasers. If
you wish to purchase an eraser, call EE TOOLS at 408-263-2221,
sales@eetools.com. When an EPROM is not being erased, the window may be
covered with an opaque label. Sometimes (over a period of years) an EPROM
will start to erase due to the level fluorescent light in the room. Direct exposure
to sunlight also has this effect and happens much more rapidly and commonly.
NOTE: In order to decide if the device is blank, the user should read the target
device. If the buffer is filled with all FFs or 00s, the device is most likely in an
erased or unprogrammed state; otherwise, t he device is no t erase d.
CAUTION: Some devices such as Philips P98C52 can pass the BLANK
CHECK routine after they are secured even though they are not blank.
68
Page 69

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Program
Program command will enable you to place new data from the memory buffer
into the target device. The BUSY GREEN led will be blinking during
programming. Make sure the device is correctly inserted into the ZIF socket and
the latch is down. Then check the buffer device address range before you start.
The values will default to the size of the device.
NOTE: <MOTOROLA MICROCONTROLLERS>
The window of windowed devices must be covered with an opaque label
during operation at all times.
NOTE: For all DEVICE/FUNCTION operations, the ERROR YELLOW LED,
located at the bottom of the ZIF socket is used to indicate the status of the
complete operation. It will turn on if an error has occurred; otherwise it will
remain off.
The target device must be blank checked unless the part is electrically erasable.
Although most of EEPROMs and Flash Memory devices have the ERASE
function in the menu, some EEPROMs such as AT28CXXX or AT29CXXX
don’t have the ERASE function. Note that EEPROMs without the ERASE
function are automatically erased before programming.
After programming is complete, verification should be performed according to
the semiconductor manufacturer's specifications. In order to test vectors, a
vector test should be performed (See vector test under the TEST menu). Finally,
the part may be secured so that its content can no longer be examined or
modified. The security function will not execute if the device fails to verify or
pass the vector test properly.
Memory device
Programmable Logic Device operation
28C256, 28C010, etc.
69
Page 70

MaxLoader User’s Guide
28CXXX family devices support Software Data Protection. The user has an
option of either protecting or not protecting the data. This option must be
changed before the start of any programming operatio n. To change this option,
go to the Option selection under DEVICE/FUNCTION menu and make any
changes accordingly. To obtain more information about Software Data
Protection, please consult the device manufacturer’s specification.
Microchip PIC series is different from other Microcontrollers in that they have
an EPROM area as well as a CONFIGURATION FUSE. The configuration
fuse in the PIC family is used to setup Oscillator Type, Memory Code
Protection, Watchdog Timer, or Processor Mode, and etc. After
programming the EPROM portion, change the fuses of the items listed under
Option. Then you must progra m the configuration option in the Option menu.
Perform the following procedure:
1. Program the main memory
2. Click on the OPTION button
3. Set all of the configuration fuse in OPTION menu
4. Click on the Program configuration fuses button
You may also read the status of the Configuration Fuse under the OPTION
selection. In order to obtain more information about programming the
configuration fuse, contact Microchip technology at 602-786-7200 or consult
the appropriate data book.
Microchip PIC devices
Copy from a master chip to a new chip
1. Select the master device from select menu in Microcontroller.
2. Put the chip on the ZIF socket.
3. Click on the Device button and read the chip.
4. Click on the Option button and read the fuses.
5. Write down all of the option fuses [the memory protect must be
disabled] in order to copy the information from your master chip.
70
Page 71

MaxLoader User’s Guide
6. Place a new chip. It must be the same chip as the master chip.
7. The buffer still holds your master data and the memory portion.
8. Click on Option again and set all the fuses that you wrote.
9. (To change the option, use the arrow button in the selection box.)
10. In the same Option menu, Click on the program configuration fuses,
read and compare the fuses with your original device.
CAUTION: The PIC16C711, will be used as an OTP (one time programmable)
chip when you erase the secured device. You cannot reuse the chip after erasing
it, even though the PIC16C711 is an erasable device.
This device will require a security code in certain memory location when you
program a new device along with data and users must remember the security
data once read (copy)or verify the master device for duplication.
Serial EEPROMs
These devices are electrically erasable, but they operate serially rather than
parallel.
Atmel or Xilinx 17xxx
You need to set the POLARITY FUSE with this family via the Option menu.
After programming the main MEMORY, go to the OPTION menu and make
the appropriate change. On OTP (One Time Programmable) devices, the
POLARITY FUSE status cannot be reversed once it has been changed. Even
on some of the windowed 7xxx family devices (excluding Xilinx 17xxD/L &
17128), the POLARITY FUSE cannot be toggled. Consult the device
manufacturer for further instructions on how to handle the Polarity FUSE.
CAUTION: Do not touch or remove a device during an operation when the
BUSY green led is on.
MOTOROLA MC68HC908 devices
71
Page 72

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Read
Read the data in the source device mounted on the ZIF socket into the buffer for
examination.
The checksum will be displayed on the checksum line. The buffer may be
edited, saved to a disk, or used to duplicate the chip.
CAUTION: Reading the device into the buffer destroys the buffer contents
through the specified range. Make sure everything in the buffer that is needed
has been saved.
PLD test vectors are not stored in a logic device; therefore, they cannot be read.
The test vector buffer will be empty after reading the PLD.
72
NOTE: Devices that have been secured cannot be read properly. Secured chips
may appear all blank, fully programmed, or scrambled.
Device / Verify
Assure that data in the device matches data in the memory buffer. If your
device has the security fuse blown, a verification error is detected. The verify
operation requires that the exact data pattern or file that was used to program
the device be resident in the memory buffer.
Page 73

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Data Compare
Compares the data in device to the data in buffer and saves any difference into
the COMPARE.TXT file. When you have a verify error during the Verify
operation, the Data Compare command will be useful. It will detect a
difference between the device content and the buffer content and will write the
difference into the COMPARE.TXT file under the MaxLoader
(TopMax/TopMax 8Gang/ChipMax) directory. You may view the file using
edited utility software.
Device / Erase
This option erases the data in your socket before programming it. This operation
is valid for only limited devices such as EEPROM, Flash Memory, GAL, PEEL
devices. EPROMs that have a window should be erased by UV EPROM erasers
externally (see NOTE “Erasing EPROMs” in this manual).
Device / Security
Secure a PLD or Microcontroller so that their content can no longer be
examined or modified. Security is confirmed when valid data can no longer be
read or verified against a previously read pattern. To ensure that the security
fuse has been blown, the Security operation is preceded by a “read” of the
device and followed by a “verify.” Securing a device prevents the programmed
data pattern into the device from unauthorized access. This command appears
only when the selected device supports it. Some Microcontrollers and PLDs
can be secured by programming a special address location. The security bit will
be cleared when the device is erased. Once a device is secured, it cannot be
unsecured to read, verify, or duplicate. Also the secured device is seen as a
blank chip even though it is not actually blan k.
73
Page 74

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: When you click on OPTION, device security mode and option fuses will
be available for certain manufacture devices. Selecting these options,
programmer will program your device with the checked options continuously. It
is a useful feature for users who like to program devices in volume quantities.
The user does not have to set the fuses or security modes for every
programming.
CAUTION: Some devices, such as Philips P89C52, can pass the BLANK
CHECK routine after they are secured. Securing a device separates the
programmed data pattern from unauthorized access. This command appears
only when the selected device supports it. Some Microcontroller’s and PLDs
can be secured by programming a special address location. The security bit
will be cleared when the device is erased. Once a device is secured, it cannot
be unsecured to read, verify, or duplicate. Also the secured device is seen as a
blank chip even though it is not actually blank.
Device / Encryption
The encryption table is a feature of the 87C51/87C52 family Microcontroller
devices. The Encryption array of the Microcontroller is initially unprogra mmed
(all '1's). In order to protect the code from being easily read by anyone other
than the programmer, this feature allows you to program the encryption table
that is exclusive NO Read with the program code data as it is read out. You
have to know its content in order to correctly decode the program code data.
Thereafter you will have to use the same displayed encryption array an y time
you need to read back the device.
74
Device / Option
In most Microcontrollers, there are several option bits (or fuses) in order to
secure Microcontroller devices. Customer should understand how to set these
bit (fuses) after reviewing data sheet. This option fuses can be either loaded
though a file or entered by manually.
Page 75

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device / Auto
Auto command will enable you to execute a operation steam that are selected in
auto menu option It will execute all commands sequentially and it is useful to
program a volume quantity devices with the same data.
CAUTION: Some devices such as Philips P98C52 can be passed the BLANK
CHECK routine after they are secured even though it is not in blank status.
Test (This feature is for only TopMax, TopMaxII)
Test / RAM Test
TopMax, TopMaxII provide an additional memory test function. This operation
tests static and dynamic RAM memory chips. The following memories are
tested:
DRAM types tested
- 16K*4, 64K*1, 64K*4, 256K*1, 256K*4, 1M*1
SRAM type tested
- 2K*8, 8K*8, 32K*8, 128K*8
75
Page 76

MaxLoader User’s Guide
After inserting a memory device into the ZIF socket, select the memory type
from the device select “GENERIC RAM” selection screen and click on the
RAM test button, in the test menu.
The program will test each address of the memory. A "Defective memory"
message will be displayed with a current address if the memory has a defective
bit. "Good memory" will appear when the test has passed successfully.
76
Test / Vector Test
Verifies that the PLD (PAL, GAL EPLD, etc.) currently behaves without
having to prototype a circuit. In order to perform test vectors, test vectors
should be in the JEDEC file when the file is loaded. Most PLD development
software will generate valid test vectors automatically. Test vectors may be
examined and modified with Vector Pattern Edit/^F6 command in the buffer
menu screen.
Page 77

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Due to hardware’s limitation, Vector Test is only implemented on 24-
pin or less devices.
During the vector test, TopMax applies high and low signals to the input pins of
a tested PLD and observes signals at the output pins. The output results are
compared to the expected results from the test vectors. Any difference will
show up as an error message.
The following are valid characters for test vectors:
0 Apply input logic low (Vil) to an input pin
1 Apply input logic high (Vih) to an input pin
C Clock an input pin (Vil, Vih, Vil)
F Float pin
N Power pin or untested output pin
V VCC pin
X Don't care: output values are not tested
G GND pin
K Clock an inverted input pin (Vih, Vil, Vih)
H Expected result on output pin is Vih
L Expected result on output pin is Vil
Z Test for high impedance
Optional Operation
X value Optional valu e of “don’t care”
Vcc Test Vcc value on Vcc pin
Delay Test period of each vector in mill-second
Test / IC Test
This operation tests TTL or CMOS logic devices according to the test patterns
stored in the test pattern library.
77
Page 78

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Click on the Select button and enter a device name and click on Test to begin
the test function. A result message will be displayed after testing.
Config Config / Select Product
78
After the MaxLoader is installed, you can choose one of the programmer listed
in Select product menu.
Page 79

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Make sure that you select a right model and turn on the switch (TopMax /,
TopMaxII, ProMax-4/8G) or connect the AC cord (UniMax,
ChipMax/ChipMax2)
Config / Config Option
Config Option / Buffer Clear Before File Loading
When loading a file into the buffer, executing the ENABLE option fills the
buffer with the data that is defined in Default Buffer Value before the file is
loaded into the buffer. When you load a file that is smaller than the current
buffer size, the unfilled buffer will contain the Default Buffer Value so that you
may examine the buffer data more conveniently. DISABLE option keeps the
same data for the unfilled buffer area after Buffer Load command is executed.
79
Page 80

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Buffer Clear means that the current buffer will be filled with the Default
Buffer Value. It can be any data of Hexadecimal values such as FF, 00, or XX
Config Option / Blank Check Before Programming
Enabling Blank Check Before Programming verifies whether the device is
erased before programming. Disabling Auto Blank Check Before Programming
prevents this check from occurring.
Config Option / Verify After Reading
Setting the configuration menu to ENABLE will allow you to verify whether
the device data is the same as the data in your current buffer after reading the
source device.
Config Option / verify after programming
Setting the option to ENABLE will allow you to verify whether the device data
is the same as the one in your current buffer after programming a device.
Config Option / Byte order swapping
This option applies only to 16-bit wide (E)EPROMs or Flash Memory. User
data is displayed in the buffer according to the Intel convention with the default
value set at Disable. Enabling this option allows you to use data according to
the Motorola convention during Program and Verify operations under the
Device selection. However, the data in the buffer is not physically swapped
.
When enabled, the MSB (Most Significant Byte) of data is located to EVEN
addresses (0,2,4,...) and the LSB(Least Significant Byte) of data is located to
ODD addresses(1,3,5,...).
For example, Byte swap is useful if an assembler creates a file in Intel format,
in which the low byte is read before the high byte, but the file must be in
Motorola format, in which the high byte is read before the low byte.
Sample data file (Motorola EXORmacs Format, Code 87):
S00B00004441544120492F4FF3
S11300000123456789ABCDEF001122334455667750
S9030000FC
Data file opened with format 87 and displayed in the editor (8-bit addressing
mode):
80
Page 81

MaxLoader User’s Guide
CURSOR AT LOCATION: 00000000 8 BIT ADDRESSING
HEXADECIMAL ASCII
ADDRESS -0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 -A -B -C -D -E -F 0123456789ABCDEF
00000000 01 23 45 67 89 AB CD EF 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 .#Eg . . ”3Duf w
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Example #1: Programming one 16-bit device (Data word width = 16, Odd/even
byte swap = disabled)
The user data is allocated as follows:
Device
MSB LSB
Device Address: 0 23 01
1 67 45
2 AB 89
3 EF CD
Sample data file (Motorola EXORmacs Format, Code 87):
S00B00004441544120492F4FF3
S11300000123456789ABCDEF001122334455667750
S9030000FC
Data file opened with format 87 and displayed in the editor (8-bit addressing
mode):
CURSOR AT LOCATION: 00000000 8 BIT ADDRESSING
HEXADECIMAL ASCII
ADDRESS -0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 -A -B -C -D -E -F 0123456789ABCDEF
00000000 01 23 45 67 89 AB CD EF 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 .#E.g. . . ”3DUf w
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Example #2: Programming one 16-bit device (Data word width = 16, Odd/even
byte swap = Enabled)
The user data is allocated as follows
81
Page 82

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device
MSB LSB
Device Address: 0 01 23
1 45 67
2 89 AB
3 CD EF
Config Option / Device Insert Test
When enabled, this test will allow the MaxLoader to first examine the physical
position of a device as it is sitting in the programming socket when the user
attempts to take any action to that device. Once it has finished examining, the
MaxLoader will prompt the user for corrective steps if needed depending upon
the position of the device. Once you click on “Device Insert Test,” MaxLoader
will display “Incorrect device ID” if your target device contains ID or if wrong
device is placed inside the socket. You may see the same message if the device
has been secured or if the device ID has been erased. Click on “Yes” if you
want to ignore the manufacturer’s device ID and proceed.
Config Option / Device ID Check
Check the device with both manufacturer and device part number
before run any operation for the target device in the socket. If you
program an EPROM, you may allow to skip the device ID check
routine when the device size and programming voltage between the
EPROM in socket and the part in menu.
82
Page 83

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Pressing “Shift F1” allows you confirm the device ID from
actual chip and MaxLoader algorithm.
Config Option / Sound
A default sound comes when you need attention du ring programming ti me such
as “blank check error,” “program error,” or “Verification error.”
Config Option / Default Buffer Value
Fill the buffer value (hexadecimal) with the initial data that you type in this
field. This feature helps the user who wants to have different initial values ('00'
or 'FF') in the buffer. In most case, the default buffer value should be set up as
“00” before loading a hex file.
Config Option / 32 Bit Checksum
The digit of Checksum value appears in 4 (hex) numbers as standard checksum
Value.
For 8 digit checksum value, click on the option box “32 Bit check sum” and
MaxLoader display 8 (hex) numbers in the Check sum location.
83
Page 84

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Config Option / Port (TopMax, ChipMax)
84
A parallel port address can be determined by the MaxLoader (TopMax /
ChipMax) software.
Page 85

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Auto : TopMax / ChipMax will select a valid parallel port as the default
address in your PC.
LPT1 : The parallel port 378 in HEX will be chosen for TopMax/ChipMax
address.
LPT2 : The parallel port 3BC in HEX will be chosen for TopMax/ChipMax
address.
LPT3 : The parallel port 278 in HEX will be chosen for TopMax/ChipMax
address.
Port Speed: Because the ISA-bus clock speed is not as fast as that of the CPU,
we designed this option to facilitate the problem caused when using a fast
computer such as Pentium 90/133/166 MHz The default value is 0. For
computers that have CPU speed of greater or equal to 133 MHz, we recommend
that you set the Port Delay to 40. In most cases, this option will help to solve the
communication problem between your PC and TopMax / ChipMax).
NOTE: TopMax / ChipMax power switch should be ON. The Parallel cable is
connected between TopMax / ChipMax and your PC parallel port. Make sure
that the shields on each side of the cable are locked. See section 6
Troubleshooting if you are having difficulty with installation and
communication.
Config Option / USB Option (USB programmer)
USB option / Enable START button
This option allows you to use a start key in USB programmer hardware rather
than PC control software. Once you check in the option and choose a master
socket, the socket location will be selected as a master socket without opening
the gang program mode (separate menu screen). So you can use the multiple
programmer, ProMax-4G (8G), as a single-socked programmer. We can see the
socket number in either beginning menu screen or gang program mode menu.
85
Page 86

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Enabling #4 socket to be master socket
86
If you want to choose the master socket in 4th location in 8 sockets, select the
th
serial number for 4
socket among 8 sequential serial numbers. i.e the 4th socket
serial number is P8-0057.
USB option / Good LED off on socket open
This option enables the LED light to not blink after finishing an operation.
So, user can recognize the empty socket as not being effective for any operation.
USB option / Enable “START ALL” button
This option enables any of the START button in multi-site programmer to be a
start button for all others. So, customers don’t need to press individual button as
an auto programming mode. Customers who want to operate a separate
operation for individual Start Button key must un-checked this option.
Page 87

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Enabling any button to be a “Start Key”
Config Option / Gang Split Select
87
Page 88

MaxLoader User’s Guide
All programmers except TopMax and ChipMax must use the
Concurrent Gang Mode for multiple socket operations.
Split
When programming devices for a 16-bit or 32-bit environment, you will need to
split your data onto two or four devices.
NOTE: Do not run this operation in “Concurrent Mode”.
EXAMPLE 1: PROGRAMMING TWO 8-BIT EPROM AS FOLLOWS:
Byte $0000
Byte $0001
Byte $0002
Byte $0003
Byte $0000 Byte $0001
Byte $0002 Byte $0003
88
: :
1. Load a 16-bit file into the buffer.
2. Select the target device from menu.
3. Insert the target device (#1) into the ZIF socket.
4. Click on EVEN in Split data menu.
5. Program the device (#1).
6. Remove the device (#1) and insert the second device (#2) into the ZIF socket.
7. Click on ODD.
8. Program the second device.
Page 89

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Now, you have two 8-bit EPROMs that have been programmed. The first
EPROM (#1) contains all the even address or low bytes and the second (#2)
device contains all the odd address or high bytes.
EXAMPLE 2: PROGR AMMING FOUR 8-BIT EPROMS AS FOLLOWS:
Byte $0000
Byte $0001
Byte $0002
Byte $0003
Byte $0004
Byte $0005
Byte $0006
Byte $0007
:
Byte $0000 Byte $0001 Byte $0002 Byte $0003
Byte $0004 Byte $0005 Byte $0006 Byte $0007
: : : :
1. Select the target EPROM.
2. Load the HEX file (32-bit file) into the buffer.
3. Insert the first EPROM (#1) into the socket.
4. Invoke Word 0 in Split Data menu.
5. Program the mounted device.
6. Remove the programmed device (#1) and insert the second device (#2) into
the socket.
7. Follow the same steps as above.
After programming the 4th EPROM with Word 3, you will have four 8-bit
programmed EPROMs. The original file (32-bit) is split into four EPROMs that
contain 8-bit data in each device.
Config Option / Address
89
Page 90

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Device Address
These addresses will be applied for programming the buffer data.
-Chip Start: Device Starting address for the data to be programmed in buffer.
-Chip End: Device Ending address for the data to be programmed in buffer.
-Buffer Start: Buffer Starting address for the data to be programmed.
-Buffer End: Buffer Ending address for the data to be programmed.
NOTE: Device size for different devices
Device Device Address
2716 0 - 7FF
2732 0 - FFF
2764 0 - 1FFF
27128 0 - 3FFF
27256 0 - FFFF
27010/1024 0 - 1FFFF
27020/2048 0 - 3FFFF
27040/4096 0 – 7FFFF
File Load
90
These address will be applied for programming the buffer data.
Page 91

MaxLoader User’s Guide
-File Offset is subtracted from addresses from the file downloaded to the
programmer. For example, if you set File Offset to 1000h, then the downloaded
data minus 1000h would be placed into the buffer at the address specified by the
Buffer Start Address.
-Buffer Start Address is the address in the buffer where you want your
downloaded data to start. For example, if you set Buffer Start Address to 800h,
then the downloaded data only appears in the buffer beginning at address 800h.
File Save
These addresses will be applied for programming the buffer data.
-Buffer Start: Starting address for data to be saved.
-Buffer End: Ending address for data to be saved.
Config Option / Auto Inc
The feature allows users to program a certain area that might contain a serial
number in the memory device with serialized number by a certain value.
Start: Start address of memory that contains serialized data
End: End address of memory
91
Page 92

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Inc Value: This value will be added to the previous data value
User must click on Auto Increment to program a memory with data increased
by one to the previous data.
Config / Hardware test
A hardware test is designed to assist customers in confirming and diagnosing
problems relating to all programmers. If a hardware defect with a programmer
is suspected, we recommend the users to run this test in order to confirm
whether or not a problem has occurred with the programmer.
92
Config / Concurrent (gang) mode
Since the technology for USB allows to make a hub port available in a PC, we
introduce multiple socket programmers, ProMax (4G, 8G), also multiple singlesocked programmers can be operated as GANG PROGRAM MOD E while the
same model are connected in a USB hub(4 or 8) . With the Start key in USB
programmer, a programmer command stream such as
Erase/Blank/Program/Verify/Security can be executed without PC software
Page 93

MaxLoader User’s Guide
control. You can execute individual socket with corresponding start button or
all sockets together with pressing any of START button.
Do not touch the device in socket until the operation stream is not finished
(stopped). Each operation in different socket can be displayed with blue color
bar in menu screen.
This picture illustrates how to set any of Start key enable all 8 sockets.
This option enables any of the START button in multi-site programmer to be a
start button for all others. So, customers don’t need to press individual button as
an auto programming mode
93
Page 94

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Enabling any button to be a “Start Key”
The individual socket with a serial number can be executed once the Start
button is pressed. After check the Enables START ALL button box in Config
option, all 8 sockets will be executed when you click on any of the “START”
key in Gang program. The START ALL button make all socket If the box is not
checked, individual socket will be executed once the button that contains a
serial number (actual programming socket) is clicked.
94
Page 95

MaxLoader User’s Guide
Wait 10 – 30 seconds for recognizing all sockets and you can see each socket’s
serial number in GANG PROGRAM MODE. There two different features in the
ProMax programmer operations. One feature is that Data in buffer memory can be
simply duplicated into more one socket (duplication). Other feature is splitting
data in buffer to the sockets by same size (set) as much as the same buffer size of
selected 8-bit memory device. It calls “Set Programming.”
Program Opt.: Program options for automation programming. This operation
steam will be executed once click on individual socket or START ALL button is
clicked.
Serial NO.: Indicates all hardware serial numbers.
STATUS: Indicates executable command status in each programming location.
PASS: Indicates the number of devices passed.
FAIL: Indicates the number of devices failed.
Reset : Set 0 in all of PASS / FAIL number.
Close : Quite the current menu windows.
95
Page 96

MaxLoader User’s Guide
How to program (write) one file into different sockets ?
If the target device is 8-bit EPROM such as 2764,128,256,512,101, make
the Set Program Mode disabled. The Set Program menu button will not be
appeared for all other (non-8 bit) device selection.
96
Set “Disable” in Set Program option which is not available for non-8 bit
EPROM.
Page 97

MaxLoader User’s Guide
EXAMPLE 1: PROGRAM 8 OF 27128 EPROMS WITH SAME DATA:
1. Select the target device (27128) and Load a file that should be same size as
the selected Device size. The target devices could be any devices.
2. Click on the “Gang Program Mode” button.
3. Set Disable for the “Set program” in menu screen.
4. Insert as many as devices in the open sockets.
5. Click a button with serial number or the “START ALL” button and a
programming steam will be executed.
This diagram illustrates how to write (program) buffer data(0000-3FFF for
27128 selection) in eight sockets with same data. All devices in 8 sockets must
be identical and data in devices will be same after programming. If a device in a
group failed during programming, the remaining devices will b e programmed;
then, a replacement device must be placed in the same socket as the failed
device
97
Page 98

MaxLoader User’s Guide
The next diagram illustrates how to travel the same buffer data(0000-3FFF
for 27128 selection) to the eight sockets.
Click for individual socket
operation
98
Click for operating all
sockets at once,
concurrent mode
Page 99

MaxLoader User’s Guide
How to program (write) buffer ( blocks) data into different sockets ?
This option is not available for all other devices that are not 8-bit EPROMs. The
menu screen below illustrates that there is no Set Program button because the
device selected DA28F320J5 is not 8-bit EPROM.
Set “Enable” in Set Program options that make all sockets with an EPROM are
available for “Set Programming.”
99
Page 100

MaxLoader User’s Guide
NOTE: Who may need the “set Programming?”
A file can be fit in an EPROM and the file size becomes bigger than the EPROM,
so the large file should be split into more than one EPROMs. The ProMax
software will split a file up to 8 blocks and program them in different EPROMs.
If the data blocks in buffer are less than the total socket numbers (4, 8), same data
block can be programmed in different sockets. You can assign the same data
block in different socket because there will be empty sockets. So, you can assign
each socket for different data block.
EXAMPLE 2: SET PROGRA M FOR 8 OF 27128 EPROMS:
1. Select the target part 27128 and Load a file that should bigger than the
selected EPROM size(3FFF).
2. Click on the “Gang Program Mode” button.
3. Set Enable for the “Set program” menu
4. Assign a block file for each socket as
(Customer must know the total length of file and how split the buffer data into
the EPROMs in sockets).
100
 Loading...
Loading...