Page 1
IBM Informix
Version 11.50
IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide
for Windows
GC23-7753-05
Page 2

Page 3

IBM Informix
Version 11.50
IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide
for Windows
GC23-7753-05
Page 4

Note
Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page B-1.
This edition replaces GC23-7753-04.
This document contains proprietary information of IBM. It is provided under a license agreement and is protected
by copyright law. The information contained in this publication does not include any product warranties, and any
statements provided in this manual should not be interpreted as such.
When you send information to IBM, you grant IBM a nonexclusive right to use or distribute the information in any
way it believes appropriate without incurring any obligation to you.
© Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 1996, 2009.
US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract
with IBM Corp.
Page 5

Contents
Introduction ..................................v
IBM Informix Dynamic Server Editions ..........................v
About This Publication ................................v
Types of Users .................................vi
What’s New in IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation, Version 11.50 ...............vi
Documentation Conventions .............................viii
Technical Changes ................................ix
Feature, Product, and Platform Markup .........................ix
Example Code Conventions .............................ix
Additional Documentation...............................x
Compliance with Industry Standards ...........................x
Syntax Diagrams ..................................x
How to Read a Command-Line Syntax Diagram ......................xi
Keywords and Punctuation .............................xii
Identifiers and Names ..............................xiii
How to Provide Documentation Feedback .........................xiii
Chapter 1. Preparing to Install IDS on Windows ..................1-1
Online Notes ..................................1-1
Verifying System Requirements ............................1-1
Verifying Administrators Group Membership ........................1-1
Multiple Copies of IDS on One Computer .........................1-2
Choosing Your Installation Setup ............................1-3
Installable Features of IDS ..............................1-4
Demonstration Database Server ............................1-6
Instance Configuration Wizard.............................1-8
Planning Role Separation ..............................1-8
Installation Directory ................................1-9
Choosing between Local and Domain Installations ......................1-9
User informix ..................................1-10
Upgrading the Database Server ............................1-10
Chapter 2. Installing IDS on Windows ......................2-1
Installing IBM Informix Products ............................2-1
Installing a Copy of IDS on a Computer .........................2-1
||
Installing with the GUI Typical Setup ..........................2-2
Installing with the GUI Custom Setup ..........................2-3
Performing a Silent Installation ............................2-5
Using a Customized server.ini File for Silent Installation ...................2-6
Using a Response File for Silent Installation .......................2-6
Silent Installation Response Codes ...........................2-8
Setting Up Cluster Installations ............................2-9
Cluster Installations ...............................2-9
Upgrade of IDS by Overwriting an Existing Installation ....................2-12
||
Overwriting an Existing IDS Installation ........................2-12
||
Multiple Residency ................................2-13
Planning for Multiple Residency ...........................2-13
Creating a New Database Server Instance........................2-13
Server Instance Manager Command-Line Options .....................2-14
Troubleshooting Installation Problems ..........................2-15
Chapter 3. Post-Installation Tasks on Windows ..................3-1
Working with the Installation .............................3-1
Installation Automatic Actions ............................3-1
IDS Program Group ................................3-2
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 iii
Page 6

Initializing and Starting the Database Server ........................3-3
Stopping the Database Server ............................3-4
Database Server Configuration After Installation .......................3-4
Database Server Number .............................3-4
Database Server Name ..............................3-5
Service Name and Port Number ...........................3-5
Dbspace Name, Location, and Size ..........................3-5
Default Sbspace Name, Location, Size, and Page Size ....................3-6
Configuring IDS Manually .............................3-6
Chapter 4. Modifying IDS on Windows ......................4-1
Altering IDS Features ................................4-1
Uninstalling IDS .................................4-2
Reinstalling the Database Server ............................4-2
Performing Silent Uninstallations of IDS .........................4-2
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility ...............5-1
||
The Deployment Utility ...............................5-1
||
Rapid IDS Embeddability with the Deployment Utility ....................5-2
++
Creating a Snapshot for Deployment...........................5-4
||
Deploying a Snapshot with the Deployment Utility ......................5-4
||
ifxdeploy Command: The Deployment Utility........................5-5
||
ifxdeploy.conf File: The Deployment Utility Configuration File..................5-10
++
ifxdeploy.conf File Template ............................5-13
++
Removing a Snapshot with the Deployment Utility .....................5-15
++
Appendix. Accessibility ............................A-1
Accessibility features for IBM Informix Dynamic Server ....................A-1
Accessibility Features ..............................A-1
Keyboard Navigation ..............................A-1
Related Accessibility Information...........................A-1
IBM and Accessibility ..............................A-1
Dotted Decimal Syntax Diagrams ...........................A-1
Notices ...................................B-1
Trademarks ...................................B-3
Index ....................................X-1
iv
IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 7
Introduction
This introduction provides an overview of IBM®Informix®products and of this
publication as well as the conventions that it uses.
IBM Informix Dynamic Server Editions
IBM Informix Dynamic Server is available in different editions to fit different
business needs.
Some of the functionality described in IBM Informix documentation might not be
available for Workgroup Edition. For details on the differences between editions,
see the following Web site: http://www.ibm.com/software/data/informix/ids/
ids-ed-choice/
The license agreement has the specific restrictions for each edition. To view a
license for a particular edition, search for ″Informix Dynamic Server″ on the
following Web site: http://www.ibm.com/software/sla/sladb.nsf
About This Publication
This guide explains how to install, configure, and initialize IBM Informix Dynamic
Server on a computer running a Windows®operating system.
The following additional products can be installed from the installation media for
IDS:
v IBM Informix BladeManager
®
v IBM Informix DataBlade
v IBM Informix Connect (IConnect)
v IBM Informix Client Software Development Kit (Client SDK)
v IBM Informix ClusterIT
v The IBM Informix JDBC Driver is available on the installation media and needs
to be separately installed. For information on installing IBM Informix JDBC
Driver, see the IBM Informix JDBC Driver Programmer’s Guide.
v The IBM Informix ODBC Driver can be installed as part of IBM Informix Client
SDK. For information on installing IBM Informix Client SDK, see the IBM
Informix Client Products Installation Guide.
IBM Informix Server Administrator (ISA) is available for download at:
http://www.ibm.com/software/data/informix/downloads.html
OpenAdmin Tool for IDS is a PHP-based Web browser administration tool that can
administer multiple database server instances using a single installation on a Web
server. OpenAdmin Tool is available for download at: http://
www.openadmintool.com
For a description of client and other related products for IDS, see IBM Informix
Dynamic Server Getting Started Guide.
Developers Kit (DBDK)
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 v
Page 8

Types of Users
This publication is for database administrators (DBAs) who install IBM Informix
products. This guide assumes that you are familiar with the operating procedures
of your computer and with your operating system. For information about your
operating system, see your Microsoft
®
Windows documentation.
What’s New in IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation, Version 11.50
This publication includes information about new features and changes in existing
functionality.
The following changes and enhancements are relevant to this publication. For a
comprehensive list of all new features for this release, see the IBM Informix
Dynamic Server Getting Started Guide.
+
Table 1. What’s New in Version 11.50.xC6
+
++
Overview Reference
+
+
Simplified Deployment of an IDS Instance
+
+
You can set configuration parameters, essential
+
environment variables, and SQLHOST connectivity
+
information in a deployment utility configuration file
+
(ifxdeploy.conf). You can reuse the file to deploy
+
instances with the deployment utility. When you plan to
+
embed a snapshot of the same instance in multiple
+
locations, you can use the customized configuration file
+
to centralize the installation setup work and ensure that
+
the deployed instances are consistent.
See “ifxdeploy.conf File: The Deployment Utility
Configuration File” on page 5-10.
+
If you do not specify certain environment variables when
+
you run the ifxdeploy command, or set them in an
+
ifxdeploy.conf file, the deployment utility sets values
+
based on the process environment.
+
+
Dynamic dbspace Relocation when Deploying Snapshots
+
+
You can dynamically reconfigure the chunk paths of a
+
snapshot by using the -relocate option of the deployment
+
utility. The -relocate option initializes the dbspaces
+
required for deploying the template instance without a
+
separate step for disk space initialization.
See “Rapid IDS Embeddability with the Deployment
Utility” on page 5-2.
+
|
|
Table 2. What’s New in Version 11.50.xC5
||
Overview Reference
|
|
Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility (Windows)
|
|
This command-line utility facilitates faster deployment of
|
a configured IDS instance. This utility is currently
|
available on Windows. The utility can be called
|
programmatically or from a script as part of an
|
application installation, and therefore supports completely
|
silent IDS deployment.
See Chapter 5, “Deploying IDS with the Deployment
Utility,” on page 5-1.
vi IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 9
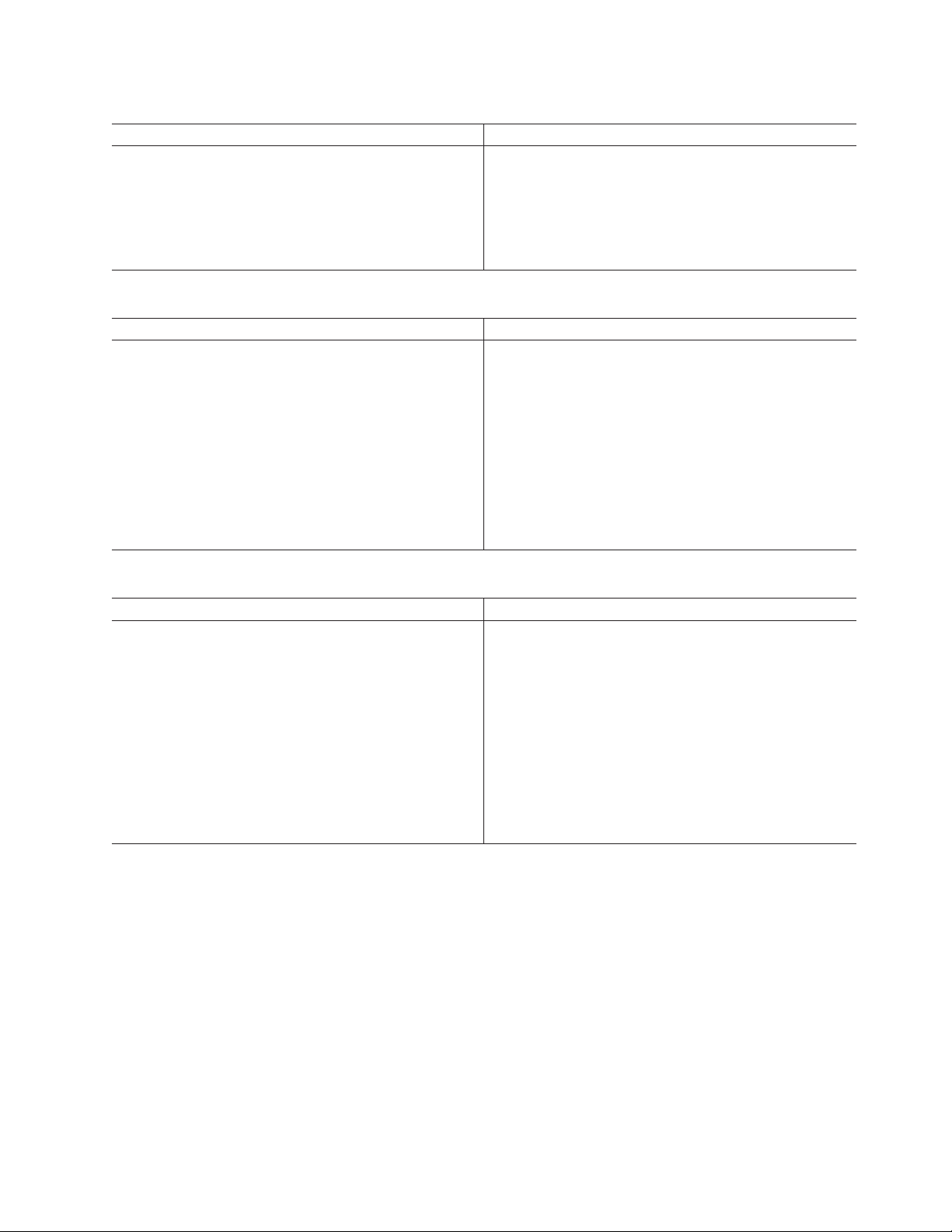
Table 2. What’s New in Version 11.50.xC5 (continued)
|
||
Overview Reference
|
|
Upgrading to IDS v11.50.xC5 in Silent Mode (Windows)
|
|
You can upgrade from IDS v11.50.xC4 or earlier to IDS
|
v11.50.xC5 in silent mode. You will need to record a
|
response file for IDS v11.50.xC5. You cannot use a
|
response file that was recorded when IDS v11.50.xC4 or
|
earlier versions were installed.
See “Using a Response File for Silent Installation” on
page 2-6.
|
|
|
Table 3. What’s New in Version 11.50.xC4
||
Overview Reference
|
|
Upgrade IBM Informix Dynamic Server by Overwriting
|
|
the Existing Installation
|
When you are upgrading IDS from one fix pack level to
|
another in the same product version, you can install the
|
product in the running database server installation
|
directory. You also can overwrite an existing installation
|
for training or specialized technical needs. Take all
|
necessary backup precautions before upgrading with this
|
method. It is recommended that most users follow the
|
IBM Informix Migration Guide for version-to-version
|
upgrades and migrations.
“Upgrade of IDS by Overwriting an Existing Installation”
on page 2-12
|
|
|
Table 4. What’s New in Version 11.50.xC2
||
Overview Reference
|
|
Multiple Copies of IBM Informix Dynamic Server on the
|
Same Windows Computer
|
In version 11.10, you could not install and run multiple
|
copies of the same version of IDS on the same Windows
|
computer. Now you can do so by using the graphical
|
user interface or by supplying installation parameters in a
|
file to perform a silent, non-interactive installation.
|
If the installation application detects that the same
|
version of IDS is already installed, you can choose to
|
install a new copy in another directory or you can choose
|
to modify the existing installation.
“Multiple Copies of IDS on One Computer” on page 1-2
|
Introduction vii
Page 10
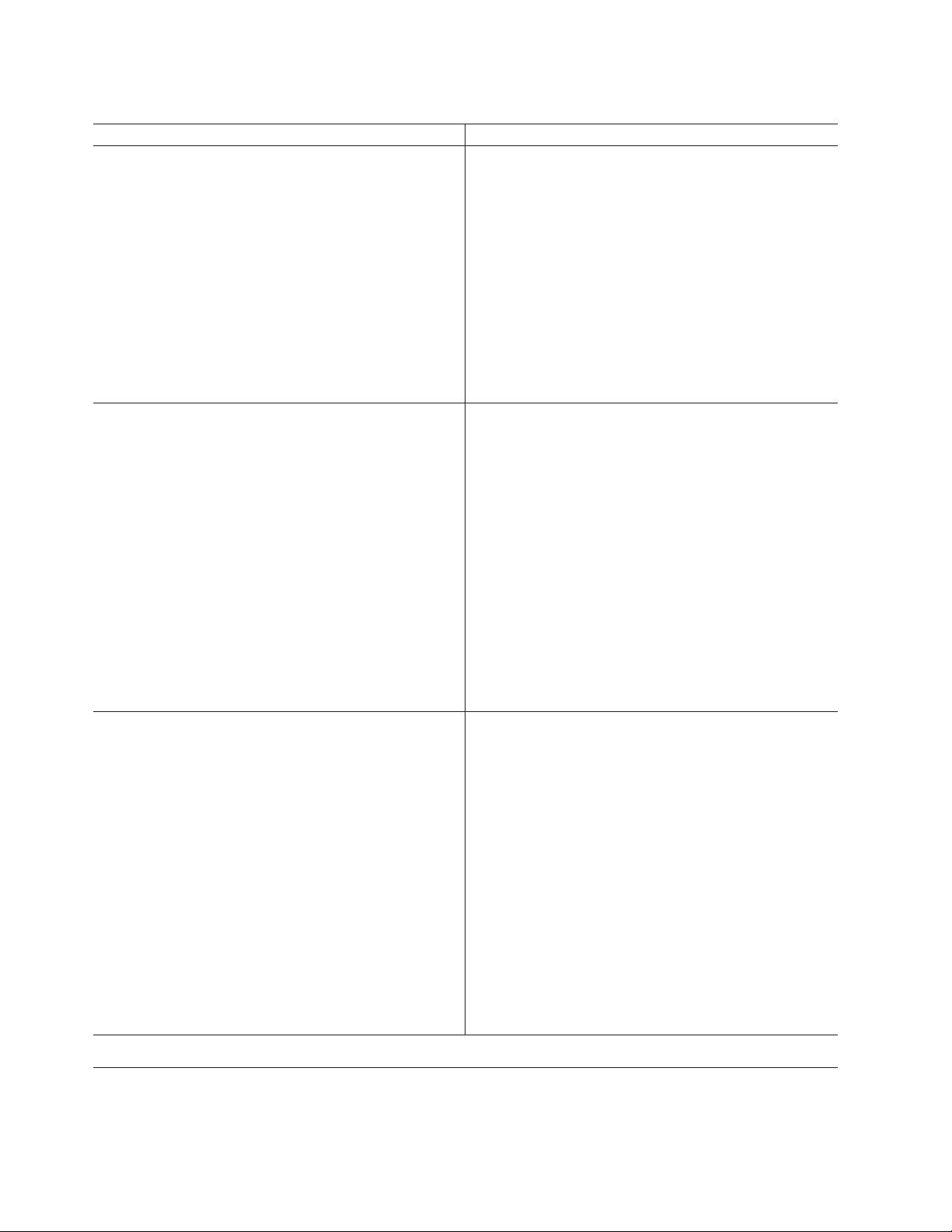
Table 5. What’s New in Version 11.50.xC1
Overview Reference
Enhanced Configuration Options During Installation
See “Instance Configuration Wizard” on page 1-8.
You can use the new Instance Configuration Wizard to
automatically create the database server configuration file
(ONCONFIG) during a custom installation in GUI mode.
Provide the information for the instance that you are
installing, such as the number of CPUs, memory, disk
space, and estimates of online transactions and query
clients. The wizard ensures that your settings are valid,
and it calculates values for other server configuration
parameters based on your settings. Your custom
configuration information is stored in the ONCONFIG file
so that when you start the instance after the product is
installed, the instance runs with your settings.
DRDA
®
Protocol Configuration During Installation
See “Installing with the GUI Custom Setup” on page 2-3.
It’s easier now than in past releases to set up an instance
to use a variety of database clients. When you install IBM
Informix Dynamic Server Version 11.50 the installer
enables you to configure a database server alias and a
port for clients that use the Distributed Relational
Database Architecture
™
(DRDA) protocol. By default,
those items are configured for you unless you deselect
DRDA support. DRDA is for open development of
applications that allow access of distributed data. DRDA
is interoperable with IBM Data Server clients.
If you disable DRDA support in the installation
application, you can still modify the instance to function
with the DRDA protocol after installation by using the
instmgr.exe utility (see ″Server Instance Manager
Command-Line Options″).
Install as the Local System Account Support
In past releases, the IBM Informix Dynamic Server
Windows Service was allowed to log on only as user
informix. Starting with version 11.50, you can install IDS
on Windows as the local system account.
Select the Local System User option in the installation
application. That option provides the same privileges as
the informix user account; however, it uses an internal
account that does not require a password. The local
system account is used by the operating system and
services running under Windows during the installation
of IDS.
You can choose not to create an informix user account at
all, but if you do so, you will not be able to use
Enterprise Replication between IDS on UNIX
®
and IDS on
Windows operating systems.
See “Installing with the GUI Custom Setup” on page 2-3.
Documentation Conventions
Special conventions are used in the product documentation for IBM Informix
Dynamic Server.
viii IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 11

Technical Changes
Technical changes to the text are indicated by special characters depending on the
format of the documentation.
HTML documentation
New or changed information is surrounded by blue @ and ! characters.
PDF documentation
A plus sign (+) is shown to the left of the current changes. A vertical bar
(│) is shown to the left of changes made in earlier shipments.
Feature, Product, and Platform Markup
Feature, product, and platform markup identifies paragraphs that contain
feature-specific, product-specific, or platform-specific information.
Some examples of this markup follow:
Dynamic Server only: Identifies information that is specific to IBM Informix
Dynamic Server
Windows only: Identifies information that is specific to the Windows operating
system
This markup can apply to one or more paragraphs within a section. When an
entire section applies to a particular product or platform, this is noted as part of
the heading text, for example:
Table Sorting (Windows)
Example Code Conventions
Examples of SQL code occur throughout this publication. Except as noted, the code
is not specific to any single IBM Informix application development tool.
If only SQL statements are listed in the example, they are not delimited by
semicolons. For instance, you might see the code in the following example:
CONNECT TO stores_demo
...
DELETE FROM customer
WHERE customer_num = 121
...
COMMIT WORK
DISCONNECT CURRENT
To use this SQL code for a specific product, you must apply the syntax rules for
that product. For example, if you are using an SQL API, you must use EXEC SQL
at the start of each statement and a semicolon (or other appropriate delimiter) at
the end of the statement. If you are using DB–Access, you must delimit multiple
statements with semicolons.
Tip: Ellipsis points in a code example indicate that more code would be added in
a full application, but it is not necessary to show it to describe the concept being
discussed.
For detailed directions on using SQL statements for a particular application
development tool or SQL API, see the documentation for your product.
Introduction ix
Page 12

Additional Documentation
Documentation about IBM Informix products is available in various formats.
You can view, search, and print all of the product documentation from the IBM
Informix Dynamic Server information center on the Web at http://
publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/idshelp/v115/index.jsp.
For additional documentation about IBM Informix Dynamic Server and related
products, including release notes, machine notes, and documentation notes, go to
the online product library page at http://www.ibm.com/software/data/informix/
techdocs.html. Alternatively, you can access or install the product documentation
from the Quick Start CD that is shipped with the product.
Compliance with Industry Standards
IBM Informix products are compliant with various standards.
IBM Informix SQL-based products are fully compliant with SQL-92 Entry Level
(published as ANSI X3.135-1992), which is identical to ISO 9075:1992. In addition,
many features of IBM Informix database servers comply with the SQL-92
Intermediate and Full Level and X/Open SQL Common Applications Environment
(CAE) standards.
The IBM Informix Geodetic DataBlade Module supports a subset of the data types
from the Spatial Data Transfer Standard (SDTS)—Federal Information Processing
Standard 173, as referenced by the document Content Standard for Geospatial
Metadata, Federal Geographic Data Committee, June 8, 1994 (FGDC Metadata
Standard).
IBM Informix Dynamic Server (IDS) Enterprise Edition, Version 11.50 is certified
under the Common Criteria. For more information, refer to Common Criteria
Certification: Requirements for IBM Informix Dynamic Server, which is available at
http://www.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg27015363.
Syntax Diagrams
Syntax diagrams use special components to describe the syntax for statements and
commands.
Table 6. Syntax Diagram Components
Component represented in PDF Component represented in HTML Meaning
>>----------------------
----------------------->
>-----------------------
-----------------------><
--------SELECT----------
Statement begins.
Statement continues on next
line.
Statement continues from
previous line.
Statement ends.
Required item.
x IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 13

Table 6. Syntax Diagram Components (continued)
Component represented in PDF Component represented in HTML Meaning
--+-----------------+--'------LOCAL------'
Optional item.
---+-----ALL-------+---
+--DISTINCT-----+
'---UNIQUE------'
---+------------------+---
+--FOR UPDATE-----+
'--FOR READ ONLY--'
.---NEXT---------.
----+----------------+---
+---PRIOR--------+
'---PREVIOUS-----'
.-------,-----------.
V|
---+-----------------+---
+---index_name---+
'---table_name---'
>>-| Table Reference |-><
Table Reference
|--+-----view--------+--|
+------table------+
'----synonym------'
Required item with choice.
One and only one item must
be present.
Optional items with choice
are shown below the main
line, one of which you might
specify.
The values below the main
line are optional, one of
which you might specify. If
you do not specify an item,
the value above the line will
be used as the default.
Optional items. Several items
are allowed; a comma must
precede each repetition.
Reference to a syntax
segment.
Syntax segment.
How to Read a Command-Line Syntax Diagram
Command-line syntax diagrams use similar elements to those of other syntax
diagrams.
Some of the elements are listed in the table in Syntax Diagrams.
Creating a No-Conversion Job
onpladm create job job
-t table
-p project
-n -d device -D database
Introduction xi
Page 14

-S server -T target
Notes:
1 See page Z-1
(1)
Setting the Run Mode
|
|
|
|
|
This diagram has a segment named “Setting the Run Mode,” which according to
the diagram footnote is on page Z-1. If this was an actual cross-reference, you
would find this segment in on the first page of Appendix Z. Instead, this segment
is shown in the following segment diagram. Notice that the diagram uses segment
start and end components.
Setting the Run Mode:
l
c
-f
d
p
a
u
n N
To see how to construct a command correctly, start at the top left of the main
diagram. Follow the diagram to the right, including the elements that you want.
The elements in this diagram are case sensitive because they illustrate utility
syntax. Other types of syntax, such as SQL, are not case sensitive.
The Creating a No-Conversion Job diagram illustrates the following steps:
1. Type onpladm create job and then the name of the job.
2. Optionally, type -p and then the name of the project.
3. Type the following required elements:
v -n
v -d and the name of the device
v -D and the name of the database
v -t and the name of the table
4. Optionally, you can choose one or more of the following elements and repeat
them an arbitrary number of times:
v -S and the server name
v -T and the target server name
v The run mode. To set the run mode, follow the Setting the Run Mode
segment diagram to type -f, optionally type d, p,ora, and then optionally
type l or u.
5. Follow the diagram to the terminator.
Keywords and Punctuation
Keywords are words reserved for statements and all commands except
system-level commands.
xii IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 15

When a keyword appears in a syntax diagram, it is shown in uppercase letters.
When you use a keyword in a command, you can write it in uppercase or
lowercase letters, but you must spell the keyword exactly as it appears in the
syntax diagram.
You must also use any punctuation in your statements and commands exactly as
shown in the syntax diagrams.
Identifiers and Names
Variables serve as placeholders for identifiers and names in the syntax diagrams
and examples.
You can replace a variable with an arbitrary name, identifier, or literal, depending
on the context. Variables are also used to represent complex syntax elements that
are expanded in additional syntax diagrams. When a variable appears in a syntax
diagram, an example, or text, it is shown in lowercase italic.
The following syntax diagram uses variables to illustrate the general form of a
simple SELECT statement.
SELECT column_name FROM table_name
When you write a SELECT statement of this form, you replace the variables
column_name and table_name with the name of a specific column and table.
How to Provide Documentation Feedback
You are encouraged to send your comments about IBM Informix user
documentation.
Use one of the following methods:
v Send e-mail to docinf@us.ibm.com.
v Go to the information center at http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/
idshelp/v115/index.jsp and open the topic that you want to comment on. Click
the feedback link at the bottom of the page, fill out the form, and submit your
feedback.
v Add comments to topics directly in the IDS information center and read
comments that were added by other users. Share information about the product
documentation, participate in discussions with other users, rate topics, and
more! Find out more at http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/idshelp/
v115/index.jsp?topic=/com.ibm.start.doc/contributing.htm.
Feedback from all methods is monitored by those who maintain the user
documentation. The feedback methods are reserved for reporting errors and
omissions in our documentation. For immediate help with a technical problem,
contact IBM Technical Support. For instructions, see the IBM Informix Technical
Support Web site at http://www.ibm.com/planetwide/.
We appreciate your suggestions.
Introduction xiii
Page 16

xiv IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 17

Chapter 1. Preparing to Install IDS on Windows
Read the following information and complete the tasks appropriate for your
installation environment.
v “Online Notes”
v “Verifying System Requirements”
v “Verifying Administrators Group Membership”
v “Multiple Copies of IDS on One Computer” on page 1-2
v “Choosing Your Installation Setup” on page 1-3
v “Installable Features of IDS” on page 1-4
v “Demonstration Database Server” on page 1-6
v “Instance Configuration Wizard” on page 1-8
v “Planning Role Separation” on page 1-8
v “Installation Directory” on page 1-9
v “Choosing between Local and Domain Installations” on page 1-9
v “User informix” on page 1-10
v “Upgrading the Database Server” on page 1-10
Online Notes
Read the online notes, which are located in the IIF/doc directory or at
http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/idshelp/v115/topic/
com.ibm.relnotes.doc/relnotes.htm.
Verifying System Requirements
Refer to the IBM Informix Dynamic Server machine notes for specific, supported
Windows operating systems.
Verify that your computer meets the minimum installation requirements:
v 256 MB of RAM.
v Sum of RAM and paging file must be at least 512 megabytes. (Some installation
choices require additional disk space. The installation application informs you of
the total disk space required by your setup before you copy the binary files to
your host computer.)
v Total of 350 MB of free disk space for installation of the product and all features
of a working system.
v Destination drive with a Windows file system (NTFS).
The installation program determines, at run time, the amount of disk space
required.
Verifying Administrators Group Membership
Verify that you are logged in as a member of the Windows Administrators group.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 1-1
Page 18

For information on how to create groups and add users to groups, see your
Windows documentation.
Multiple Copies of IDS on One Computer
|
|
Multiple copies of IBM Informix Dynamic Server can run on the same computer.
The copies can be the same or different versions of the product.
Multiple copies of different versions
If your computer hosts more than one installation of IDS, each instance has a
corresponding IBM Informix Dynamic Server program group on the Start >
Programs menu.
Do not install a newer version of IBM Informix Dynamic Server in the same
location where an earlier version of the product exists to avoid conflicts between
directories, .dll files, registry entries, and other Informix-related services. If you
wan to run different versions of IDS on the same host machine, keep the
installations in different paths.
To uninstall versions of IBM Informix products released before 11.50, refer to the
uninstallation documentation for that version.
To uninstall version 11.50 IDS and any of its components, refer to Chapter 4,
“Modifying IDS on Windows,” on page 4-1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multiple copies of the same version
You can install multiple copies of the same version of IBM Informix Dynamic
Server on one Windows operating system. A copy refers to an installation in a
different location on the same computer. The benefits of doing this include:
v The ability to test new features before using them in a production database
v The ability to have both 32-bit and 64-bit versions on the same computer
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To identify which installed copy you want to modify, use the unique location of
the installation or the installation number that was generated automatically when
the copy was installed.
The first copy that you install on a computer is, by default, installation number 1.
The subsequent copies that you install have installation numbers that increase by 1.
For example, the installation number of the second copy is 2 and the installation
number of the next copy is 3.
Note: If you uninstall copies, and then install additional copies, the installation
number will increase by 1 based on the highest installation number on that
computer. For example, if you have three copies on the computer and you delete
installation number 2, when you install another copy of the same version, the new
copy is installation number 4.
1-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 19

Related tasks
“Installing a Copy of IDS on a Computer” on page 2-1
Choosing Your Installation Setup
Using the installation application, you can choose a typical or custom setup for
loading IBM Informix Dynamic Server and other products to your system. Typical
setup installs the full IDS product, while custom setup lets you exclude product
features in order to minimize the installation footprint (disk size).
Installation Application Setup Types
The installation application has two setup options:
v Typical installation: A typical installation requires the most disk space and
memory. It is the recommended installation for most database servers. The
typical setup installs IDS (the base server) and all associated feature sets
(components), as well as a configured demonstration database server.
v Custom installation: A custom installation allows you to perform advanced
installation steps and configuration of the database server. The main
customization tool of this setup option is the Deployment Wizard, which lets
you omit components and features that you do not need to reduce the disk
space required by the installation (footprint).
You can run the installation application on Windows in either of the following
modes:
v graphical user interface (GUI)
v silent installation
Which setup type you choose depends your system architecture, your technical
expertise, and the needs of your implementation. There are some IDS installation
options for which you must choose a particular setup or installation mode:
v Instance Configuration Wizard: This wizard is only available with a custom setup
in GUI mode.
v Silent installation: Custom setup is recommended, but not required, for silent
installation. If you expect to replicate your installation configuration in other
machines, read “Performing a Silent Installation” on page 2-5 first. In the GUI
installation application, you can generate a response file for configuring other
instances’ installations in silent mode, but not when you use the Instance
Configuration Wizard. Parameters affected by the Instance Configuration Wizard
are not available for silent installation.
v Automatic startup of cluster utility after installation: You must select a custom IBM
Informix Dynamic Server installation and select the cluster utility checkbox if
you want the IBM Informix ClusterIT Utility to start running automatically after
you have completed installation. This option is only available if you have the
IDS installation media that is bundled with other IBM Informix products and if
the installation application detects the Microsoft Cluster Server on the host
computer. Read “Cluster Installations” on page 2-9 for more information.
v DRDA protocol support: To exclude support for DRDA connections in your IDS
instance, you must select a custom installation and complete the configuration
setup accordingly. DRDA (Distributed Relational Database Architecture) is
designed for interoperability among different IBM Data Server clients. If you
disable DRDA support in the installation application, you can still modify the
Chapter 1. Preparing to Install IDS (Windows) 1-3
Page 20

instance to function with the DRDA protocol after installation by using the
instmgr.exe utility (see “Server Instance Manager Command-Line Options” on
page 2-14).
v Installing database server to run as local system user: To install IDS as a local system
account on Windows, you must select a custom installation and complete the
configuration setup accordingly. This lets the IDS log in as a Windows service,
instead of user informix.
Read “Installing with the GUI Custom Setup” on page 2-3 for more information
about DRDA support and IDS as local system user.
Installable Features of IDS
You can install the following features with the base server: Database Server
Extensions, Global Language Support, Backup and Restore, Demos, Data-Loading
Utilities, and Administrative Utilities.
Base Server
The base server refers to the core database server for basic DBA operations without
optional extensions, libraries, or utilities. The minimum size of the base server
installation is 180 megabytes (MB). Every IBM Informix Dynamic Server
installation includes the components of the base server, regardless of whether you
choose a typical or custom installation.
The base server no longer contains the XML Publishing feature and must be
included in your Deployment Wizard selections if you want to install it. XML
Publishing is in the Database Server Extensions component.
Support for the Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA) protocol is
included in the Base Server. To use the DRDA support functionality with IBM Data
Server .NET Provider or IBM Data Server JDBC Driver, you must obtain and install
the .NET Provider or JDBC Driver separately.
|
|
The IBM Global Security Kit (GSKit) is included as a component of the IDS
installation.
Features
The following list describes features in IBM Informix Dynamic Server, Version
11.50. A typical installation setup installs all of these features. If you choose custom
installation setup, you can omit features that you do not want to install. You can
view the size of each component and feature on your system before you actually
proceed with installation when you select the component or feature in the GUI
setup.
Database Server Extensions
Database administration tools and programming extensions
J/Foundation
For writing user-defined routines in the Java
language
™
programming
Built-in DataBlade Modules
For providing large object location management, MQ transaction
support, binary user-defined types, the hierarchical node data type,
basic text search, and Web Feature Services for spatial data
1-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 21

Conversion and Reversion Support
Framework required for migrating to and from other versions of
the database server
XML Publishing
Set of functions to publish SQL queries as XML
Global Language Support
The feature files to support languages, cultural conventions, and code sets.
These files are not required if your default locale uses American English,
which is the default language in IDS when no GLS feature is installed.
West European and Americas
Danish, Dutch, English, Finnish, French, German, Icelandic, Italian,
Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, and Swedish locales
East European and Cyrillic
Czech, Polish, Russian, and Slovak locales
Chinese
Traditional Chinese and simplified Chinese locales
Korean
Korean locales
Japanese
Japanese locales
Other Thai locales
Backup and Restore
Feature utilities for backing up and restoring database server data
ON-Bar Utilities
The onbar utility is a batch file (onbar.bat) that starts the
onbar-driver. Use this batch file to customize backup and restore
operations and check the storage-manager version.
Informix Interface for Tivoli
For implementing XBSA functions that use Tivoli Storage Manager
with ON-Bar
IBM Informix Storage Manager
For managing external storage devices and media that contain
backups
archecker Utility
For verifying backups and restoring portions of a database, a table,
a portion of a table, or a set of tables
Demos
Demonstration databases and examples
Data-Loading Utilities
For efficient loading and unloading of data in certain configurations
onunload and onload Utilities
For moving data quickly from one operating system or database
server to another without changing the database schema. Use the
onunload utility to unload data from the specified database or
table onto a tape or a file on disk in disk-page-sized units. Use the
onload utility to re-create the database or the table from the tape or
file that was created by the onload utility.
®
Storage Manager
Chapter 1. Preparing to Install IDS (Windows) 1-5
Page 22

dbload Utility
For loading data into databases or tables that IBM Informix
products created. Use the dbload utility to transfer data from one
or more text files into one or more existing tables.
High-Performance Loader (HPL)
For loading or unloading large quantities of data efficiently to or
from a database. Use HPL to exchange data with tapes, data files,
and programs, and convert data from these sources into a format
compatible with IBM Informix databases. Also use HPL to
manipulate and filter the data as you perform load and unload
operations.
Enterprise Replication
For replicating data between IDS database servers
Administrative Utilities
Additional administrative utility feature sets
Miscellaneous Monitoring Utilities
For displaying the logical log by using the onlog utility or
managing the database server with SNMP by using the onsnmp
utility.
Auditing Utilities
For administering audit masks, trails, and other auditing
information on the database server by using the onaudit and
onshowaudit utilities.
Database Import and Export Utilities
For unloading a database into text files, creating and populating a
database from those text files, or unloading a database schema into
a text file
Demonstration Database Server
The installation application can create and configure a ready-to-use database
server, which you can use as a production or testing instance.
The IDS Configuration File
To access the installed database server, a configuration file must exist in
INFORMIXDIR and must contain valid settings for your system. Setting up a
demonstration database server during installation establishes a basic, valid
configuration file, which can help users who are new to IBM Informix Dynamic
Server. The installation setup you choose determines how the demonstration
database server can be configured:
v Typical Installation: Setup of the demonstration database server is automatic and
requires no user input during installation. The installation application scans your
system and records necessary information to the configuration file shipped with
the installation media. The database server will be initialized after installation is
complete.
v Custom Installation: Custom installation lets you decide whether to configure a
database server or not, and if you do, gives you more options about the settings.
There are two ways in which you can utilize the default configuration file
during installation:
1-6 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 23

Basic demonstration database server: Select the Initialize Server checkbox in the
installation application and ensure that the settings for the server name,
service name, port, and server number are accurate.
Instance Configuration Wizard: A more customized database server can be
created with the Instance Configuration Wizard. Select the Initialize Server
and Enable the default configuration file checkboxes to use this feature. Read
the “Instance Configuration Wizard” on page 1-8 section for more
information.
Important: If you check the box by Initialize Server, the database server
initializes automatically after installation and deletes any existing data on the
host computer.
Alternatively, you can skip server configuration and configure the database
server manually after installation is complete using the Server Instance
Manager (instmgr.exe) utility.
Demonstration Database Server on Your System
The following information about the demonstration database server can help you
decide what installation setup and settings to choose:
v The demonstration database server should have on your system a server number
between 0 and 255 that is not shared with another instance. If all the valid
server numbers are used by other instances and you want to install the
demonstration server, it is recommended that you make one of the server
numbers available only for the IDS demonstration instance before launching the
installation.
v The installation application automatically searches for and assigns a unique,
unused server number for your demonstration database server. You can also
specify a server number between 0 and 255. If you enter a server number that is
used by another instance, the installation application does not accept it and does
one of the following:
1. If a server number between 0 and 255 is unused on your system, the
demonstration database server is assigned this number.
2. If the installation application is unable to find another unused server
number, then the number that you provided will be used.
v If you select the shipped configuration file, the name assigned to the
demonstration database server depends on what installation setup is being used:
Typical Setup: The installation application dynamically creates a database
server name, and the information about it is displayed in a message.
Custom Setup: You provide the database server name.
The ONCONFIG environment variable is set to the sample configuration file
located at %INFORMIXDIR%\etc\onconfig.demo_server_name. Details about
this are displayed before the installation application copies files. The information
is also stored in %INFORMIXDIR%\logs\IDS_install_date_time.log.
v When the installation application initializes the demonstration database server,
the following databases are built automatically: sysmaster, sysuser, sysutils, and
sysadmin.
v The message log regarding installation of the demonstration database server is
located in %INFORMIXDIR%\demo_server_name.log.
Chapter 1. Preparing to Install IDS (Windows) 1-7
Page 24

Instance Configuration Wizard
The Instance Configuration Wizard is an installation option that automatically
creates a database server configuration file customized to your system
environment.
You can use the Instance Configuration Wizard on a Windows computer when you
install using a custom setup in GUI mode. In the installation application, the
checkboxes for Initialize Server and for enabling a custom configuration file must
be selected to invoke the wizard.
Note: When the Initialize Server checkbox is selected, the installation will delete
any existing IDS data on the host computer.
The wizard is a utility that ensures your settings are valid, and it calculates values
for other server configuration parameters based on your settings. The configuration
information is stored in the ONCONFIG file so that when you start the instance
after the product is installed, the instance runs with settings appropriate for your
environment.
If you use this configuration utility, the installation’s settings cannot be recorded in
a response file for silent installation.
The Instance Configuration Wizard prompts for the following configuration
settings and system information:
v server name
v server number
v rootsize: the size of the root dbspace (in megabytes)
v number of central processing units (CPUs): a CPU is equivalent to a single
execution unit
v memory: system RAM dedicated to the server instance being created (in
megabytes)
v number of online transaction clients (applications used for modifying the state of
databases)
v number of query clients (applications used for returning result sets for decision
support; typically require more overhead than clients used for transaction
processing)
The number of ONCONFIG file parameters set by this wizard varies, depending
on your hardware and database system needs.
If the Instance Configuration Wizard encounters a problem while checking the
entered settings, the configuration file is created with standard, workable
configuration parameters and a message about this is displayed.
Planning Role Separation
You must choose Custom installation setup to enable role separation.
1-8 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 25
Role separation provides increased database security because the database server
splits administrative tasks into mutually exclusive roles. If you do not enable role
separation, the Informix-Admin group performs all administrative tasks. For
detailed information about the role separation feature, see the IBM Informix Security
Guide.
You cannot turn off role separation after you enable it. To remove role separation
from your system, you must use the uninstaller to remove all database instances
and related files. and then reinstall the database server without role separation.
If you choose to enable role separation during installation, you are prompted to
create groups and users and add the users to the corresponding groups.
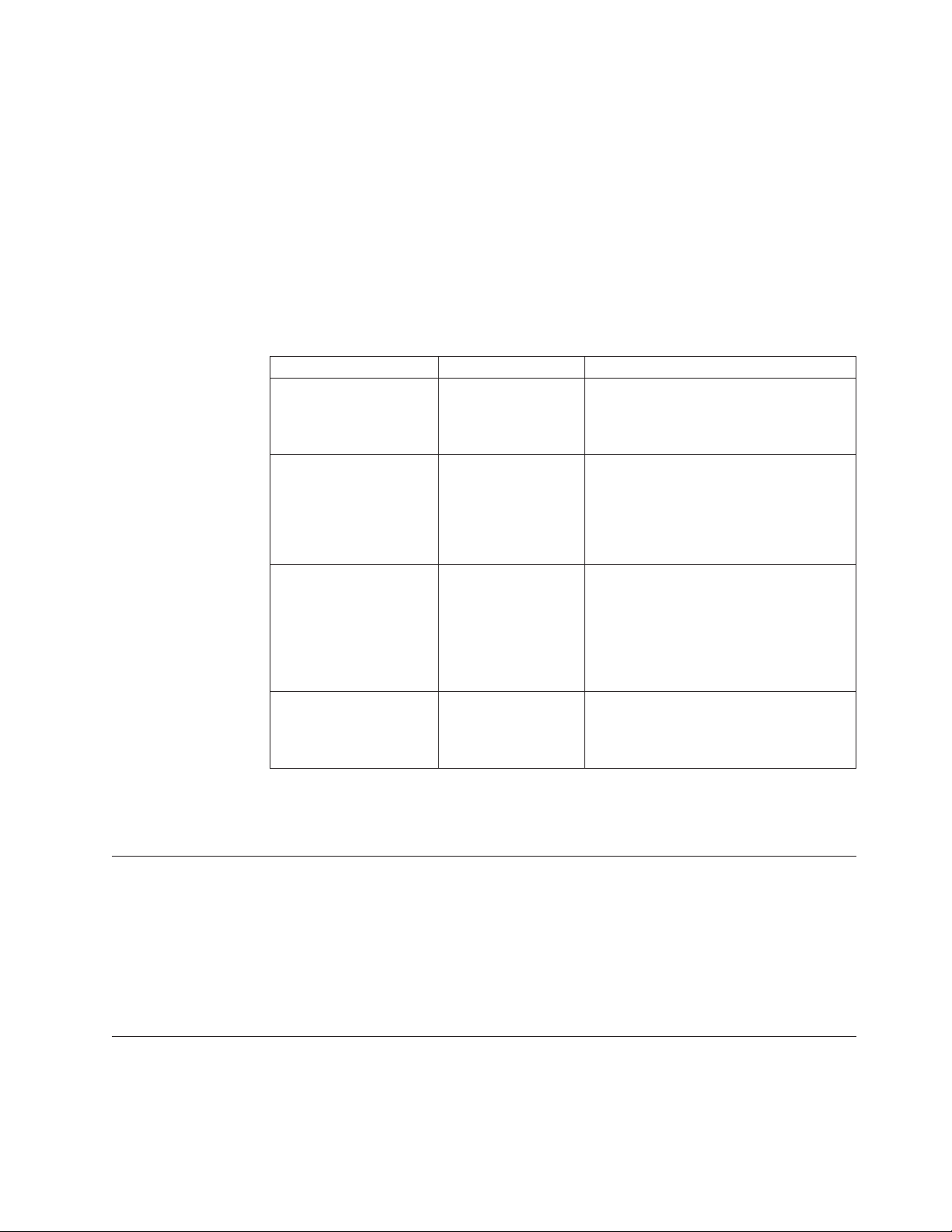
Table 1-1. Role Separation
Default Group Name Role Category Role Definition
Informix-Admin General Database
Administration
ix_dbsso Database System
Security Officer
ix_aao Auditing Analysis
Officer
ix_users Database Users Accesses the database to perform
Performs general administrative tasks,
such as archiving and restoring data,
monitoring use and performance, and
tuning the system.
Maintains the security of the database
server. Functions of this role include
audit adjustment and changing security
characteristics of storage objects. Creation
of this user role requires selection of a
password during installation.
Audits the records of specific types of
database activities. If someone attempts
to circumvent or corrupt the security
mechanism of the database, these actions
can be traced. Creation of this user role
requires selection of a password during
installation.
end-user tasks. Only users who are
designated as members of the ix_users
group can access the database.
During installation, you can replace these default users and groups with existing
users or groups.
Installation Directory
The drive on which the directory exists must be formatted using NTFS. You do not
need to create the directory before installation. IBM Informix software refers to this
installation directory as %INFORMIXDIR%, and often the INFORMIXDIR
environment variable is set to this directory. The installation application suggests a
default %INFORMIXDIR% path, which you can change by typing a different
path.
Choosing between Local and Domain Installations
You can install locally or in a domain.
Chapter 1. Preparing to Install IDS (Windows) 1-9
Page 26

User informix
Local Installation
If you do not plan to have workstations access a domain controller, install the
database server on a local computer. For a local installation, you should have
administrative privileges.
Domain Installation with Domain Administrator Privileges
Domain installation is useful if you run the database server on several computers
and want a central security mechanism. If several of your computers belong to the
same domain, and therefore share the same primary domain controller or domain
controllers, perform a domain installation on these computers. To install in a
domain, you must have administrative privileges and your computer must already
belong to a domain. Run the installation program and choose the Install in Domain
option when the installation wizard prompts you.
User informix is a user account with main authority over an IBM Informix
Dynamic Server instance.
User informix is required for most installations because it has the unique user
identifier (UID) to manage and maintain IDS instances and databases on the host
server. The only exception to this requirement is when you install IDS 11.50 as
local system user.
The password for this user account must be protected. Only let trusted database
and security administrators log in as user informix.
If you are installing IDS for the first time on your system and have not selected the
local system user option, the installation program prompts you to create the
informix user by providing a password. If user informix already exists on your
system, the installation program prompts you to confirm the password.
Important: The database server will not start if password standards for either
user informix or end users do not conform to local security standards.
Upgrading the Database Server
For information on migrating your database server from a previous version of IBM
Informix Dynamic Server to Version 11.50, and for information on migrating your
data, see the IBM Informix Migration Guide, Version 11.50.
|
|
See also “Upgrade of IDS by Overwriting an Existing Installation” on page 2-12 to
replace the earlier product.
1-10 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 27

Chapter 2. Installing IDS on Windows
The following topics explain your IBM Informix Dynamic Server and IBM Informix
products installation choices. Troubleshooting information is also included.
v “Installing IBM Informix Products”
v “Installing a Copy of IDS on a Computer”
v “Installing with the GUI Typical Setup” on page 2-2
v “Installing with the GUI Custom Setup” on page 2-3
v “Performing a Silent Installation” on page 2-5
v “Setting Up Cluster Installations” on page 2-9
v “Upgrade of IDS by Overwriting an Existing Installation” on page 2-12
v “Multiple Residency” on page 2-13
Installing IBM Informix Products
IBM Informix Dynamic Server for Windows includes a Windows launchpad, which
is a graphical interface with the options to view this publication, the release notes
or the Information Center, start the installation, or browse the installation media.
The launchpad will start automatically when the CD is inserted. To access the
launchpad from a downloaded product, from the main directory, select
Launch.exe.
If the Launch.exe file does not appear in the directory that first opens, click
setup.exe.
The IBM Informix JDBC Driver is available on the installation media and needs to
be separately installed. For information on installing IBM Informix JDBC Driver,
see the IBM Informix JDBC Driver Programmer’s Guide.
The IBM Informix ODBC Driver can be installed as part of IBM Informix Client
Software Development Kit (Client SDK) or Informix Connect. For information on
installing these products, see the IBM Informix Client Products Installation Guide.
Installing a Copy of IDS on a Computer
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You can install a copy of IBM Informix Dynamic Server in a different directory if
the same version of the product is already installed on the computer.
The following steps require IBM Informix Dynamic Server Version 11.50.xC2 or
later. They describe how to use a graphical user interface (GUI) to install a copy of
the product. If you prefer to install a copy without directly interacting with the
GUI, you can perform a silent installation instead.
To install a copy of IDS on a computer where the same version is already installed:
1. Prepare the installation media.
v Downloaded installation media: You must extract the files maintaining the
folder structure delivered in the media. Select Launch.exe.
v CD installation: Launch the CD.
|
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 2-1
The Launchpad opens.
Page 28

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Select Install Products from the Launchpad and click Next.
3. Select to install IBM Informix Dynamic Server and click Next.
4. Select the option to install a new instance when the installation application lists
existing IDS instances and click Next.
5. Select the option to install in a different directory and click Next. Complete the
prompts in the server installation application for a typical or custom setup.
Related concepts
“Multiple Copies of IDS on One Computer” on page 1-2
“Altering IDS Features” on page 4-1
Related reference
“Performing a Silent Installation” on page 2-5
Installing with the GUI Typical Setup
Launch the GUI installation application to complete a typical installation setup of
IBM Informix products, which will load IBM Informix Dynamic Server with all its
components and features.
Typical setup automates the installation by providing default settings for the
following:
v server name
v server number
v port
v user account (informix)
v general administrative group (Informix-Admin)
To install IBM Informix Dynamic Server using GUI Typical Setup:
1. Prepare the installation media.
v Downloaded installation media: You must extract the files maintaining the
folder structure delivered in the media. Select Launch.exe.
v CD installation: Launch the CD.
The Launchpad opens.
2. Select Install Products from the Launchpad and click Next.
3. Select the products that you want to install.
4. Read the license agreement. You must accept it to proceed.
5. Select the Typical option.
6. Enter user account information. You will need to enter your system’s user
informix password for these GUI windows. If no user informix exists yet, the
installation wizard creates one and will require you to create a password for it.
Enter a password and record it in a secure location.
7. Specify the installation directory if you do not want to accept the default
destination path that the GUI displays.
The destination drive must be formatted with a Windows file system (NTFS).
8. Review your installation settings. When the GUI displays a summary of your
installation settings, you have the opportunity to change the settings (Back
button) or to cancel the installation (Cancel button). Otherwise, if you are
satisfied with the settings, select Next to begin installation.
2-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 29

Completing the installation program loads a configured database server with a
typical setup. For information on changing the configuration or configuring a
database server manually, see “Database Server Configuration After Installation”
on page 3-4 and “Configuring IDS Manually” on page 3-6.
The installation creates a log file in %INFORMIXDIR%\logs\ which contains
installation activity of the IDS installation. In addition, there is a manifest file
(%INFORMIXDIR%\etc\manifest.inf). This other ″log file″ can help you see
quickly what features and components are currently installed. Do not modify the
content of this file.
The informix user account, under which the database server runs, is assigned to
the Informix-Admin group.
Installing with the GUI Custom Setup
Custom installation in GUI mode lets you exclude some IBM Informix Dynamic
Server features and offers you other ways to configure installation variables for the
needs of your system.
Use the GUI custom setup if you want to generate a response file for replicating
the installation setup on other instances in silent mode. The silent installation
process will function in this way if you choose to install IBM Informix Dynamic
Server only (that is, you cannot choose any other IBM Informix products available
on the installation media). Read the topics “Performing a Silent Installation” on
page 2-5 and “Using a Response File for Silent Installation” on page 2-6 before you
start the installation application if you want to generate a response file.
To install IDS using GUI Custom Setup:
1. Prepare the installation media.
v Downloaded installation media: You must extract the files maintaining the
folder structure delivered in the media. Select Launch.exe.
v CD installation: Launch the CD.
The Launchpad opens.
2. Select Install Products from the Launchpad and click Next.
3. Select the products that you want to install.
4. Read the license agreement. You must accept it to proceed.
5. Select Custom installation setup.
6. Specify the installation directory if you do not want to accept the default
destination path that the GUI displays.
The destination drive must be formatted with a Windows file system (NTFS).
7. Select the features you want to install.
a. Components are at the top level of the tree-nesting hierarchy.
b. Click the + character by component feature sets–features grouped together
by similar functionality–to view individual features. The components
without + characters next to them do not have individual features.
c. Deselect components and features that you do not want to install. The
wizard enforces dependencies among features and all components. If you
cannot configure the selected/deselected features exactly as you want, it is
probably an unsupported installation configuration for your site.
d. Notice that a brief description of a selected component or feature appears
on the right side of the GUI window.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-3
Page 30

e. See the disk-size information about your selected component and feature
configuration, as well as the amount of free space on your drive, under the
GUI feature tree.
8. Enter applicable user account information and, optionally, enable role
separation. If the user informix account does not exist on your computer yet,
the installation application creates one and requires you to create a password
for it.
a. Enter the user informix password for your Windows computer, unless you
want to install IDS so that it runs as a local system user account without
creating user informix. If no user informix exists on your computer yet,
the installation application creates one but you are responsible for
providing the password and storing it in a secure location.
b. Optional: Click the first checkbox to install in a particular domain and
specify the domain controller administrator. You must have administrator
privileges for the domain to do this.
c. Optional: Click the Local System User checkbox if you want the IDS
instance to run as an internal Windows account, instead of logging in as a
Windows service.
d. Optional: Click the checkbox for ″Do not Create User informix″ if you are
sure that this does not interfere with your implementation goals.
e. Optional: Click the Enable Role Separation box if you want to activate this
configuration option. If you do not enable role separation, click Next and
go to step 10.
9. Specify role-based groups for IDS administration.
a. Select the name of the group to access the database server for general
administration tasks.
b. Select the name of the security administrator group and the password
twice for confirmation.
c. Select the name of the auditing administrator group and the password
twice for confirmation.
d. Select the name of the database end user group.
10. Enter the server name for the installation.
|
|
11. Optional: Select the Create Server option if you want to create the database
server but not initialize it.
12. Optional: Create the database server instance and set basic configuration
parameters in the GUI application.
Warning: Installing with the Initialize Server checkbox selected deletes all
existing IDS data, if any, on your host computer as part of the installation
process. However, to set basic configuration parameters in the installation
GUI, the Initialize Server checkbox must be selected. While using the
configuration features in the installation application are potentially very
useful, be sure to know your installation environment and proceed with
caution.
a. Deselect the Initialize Server checkbox if you do not want to overwrite
existing IDS data on your host computer by setting the configuration
parameters below. Regardless of whether this checkbox is selected or not,
the GUI program will provide a summary of your installation choices
before copying files to your computer.
b. Optional: Select the Enable a custom configuration file to suit your needs
and hardware checkbox if you want to activate the Instance Configuration
Wizard. You need to enter settings for the socket protocol fields, but you
will provide more detailed hardware and usage parameters in the GUI
2-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 31

window that appears directly afterwards. (See “Instance Configuration
Wizard” on page 1-8 for more information about this option.)
c. Optional: Select the Enable DRDA Support checkbox if you want the
instance to have a server alias and port for Distributed Relational Database
Architecture (DRDA) connections. DRDA is designed for interoperability
with IBM Data Server clients. If you install IDS without this option, you
can still add DRDA connectivity to the instance later without reinstalling.
13. Optional: Select the Start the ClusterIT Utility checkbox if you want the IBM
Informix ClusterIT Utility to start up after installation. You will need to
complete the tasks outlined in “Setting Up a Cluster Installation” on page
2-10. When the checkbox is disabled, the installation application does not
detect a supported cluster environment in the host computer or you are not
using the IDS installation media that is bundled with other IBM Informix
products.
14. If you chose to install other IBM Informix products bundled with IDS, verify
the GUI window for products selection reflects what you want to install.
15. Specify a domain installation type, if applicable.
16. Review your installation settings and select whether to begin copying the IBM
Informix files to your computer. When the GUI displays a summary of your
installation settings, you have the opportunity to change the settings (Back
button) or to cancel the installation (Cancel button). Otherwise, if you are
satisfied with the settings, select Next.
The installation program configures the database server with a custom setup. For
information on changing the configuration or configuring a database server
manually, see “Database Server Configuration After Installation” on page 3-4 and
“Configuring IDS Manually” on page 3-6
The installation creates a log file in %INFORMIXDIR%\logs\ , which records IDS
installation activity. In addition, there is a manifest file (%INFORMIXDIR%\etc\
manifest.inf). This other ″log file″ can help you see quickly what features and
components are currently installed. Do not modify the content of this file.
Performing a Silent Installation
You can perform a silent installation, an installation method requiring no user
interaction with the setup program, to install IBM Informix Dynamic Server and
other IBM Informix products separately. Silent installation is performed in the
command-line environment.
Before you can do a silent installation, you must provide IDS installation setup
information a .ini file. Then to complete silent installation, you invoke this .ini file
to repeat the same installation setup on a different computer or in a different
location on the same computer.
Choose one of the following methods to prepare the .ini file and to complete a
silent installation:
v Use the server.ini file provided on the installation media as a template for
entering your silent-installation settings. Specify your customized .ini file in the
silent installation command.
v While installing IDS with the GUI custom setup program, record your
installation settings in a response file. Use this response file for replicating the
custom installation in silent mode.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-5
Page 32

For information on how to silently install other IBM Informix products, see their
product documentation.
Related tasks
“Installing a Copy of IDS on a Computer” on page 2-1
“Performing Silent Uninstallations of IDS” on page 4-2
Using a Customized server.ini File for Silent Installation
Copy the server.ini file in the Dynamic Server installation media, customize it with
a different file name, and run the silent installation command.
You must have Windows administrator privileges to perform the silent installation.
To perform a silent installation using the server.ini file on the installation
media:
1. Create a copy of the server.ini file in the top directory of the database server
product folder (IIF by default), and keep your .ini file in the IIF folder.
Important: Do not overwrite the existing server.ini file, and do not move the
copy that you make from the IIF folder.
2. Customize the copy of the server.ini file.
|
|
|
3. Run the following command in the IIF directory to start the silent installation
and generate a log file.
setup.exe -s -f1"path\your_filename.ini" -f2"path\your_filename.log"
|
|
|
Where:
v path\your_filename is the full path and file name for your customized .ini file
in the -f1 flag and for the log file in the -f2 flag
The file specified by -f2 captures details about the silent installation. Because the
silent installation does not display error messages, it uses the .log file as an
installation log. If the silent installation fails for any reason, the failure is recorded
in this log file.
For example, if you have not changed the default database server product folder
name and its contents and you customize the .ini settings in a file named
new_server.ini, you would enter the following command to start the silent
installation of the database server:
setup.exe -s -f1"C:\IIF\new_server.ini" -f2"C:\IIF\new_server.log"
Using a Response File for Silent Installation
Record IBM Informix Dynamic Server installation settings in a response file, and
specify this file when you run the silent installation command.
You must have Windows administrator privileges to perform the silent installation.
If you plan to perform silent installation by replicating the settings of a completed
IDS installation done with the GUI custom setup program, use the following
method to start the installation application.
Note: The response file option does not function if you use the Instance
Configuration Wizard during the installation.
To perform a silent installation by using a response file:
2-6 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 33

1. Start the installation application by running the following command:
setup.exe -r -f1"path\response_filename.ini"
path\response_filename is the full path and file name of your response file
The f1 argument is optional. If you do not specify the location and name of the
response file with the f1 argument, by default the installation sequence is saved
in %WINDIR%\setup.iss.
2. Complete the GUI custom installation of the product.
3. Copy your .ini file to the directory where you want to use silent installation to
replicate the IDS installation setup that you just created.
|
|
|
|
4. Run the following command in the IIF directory. If the target computer already
hosts one or more IDS installations, see “Silent Installation on a Host with
Multiple Installations.”
setup.exe -s -f1"path\response_filename.ini" -f2"path\response_filename.log"
|
|
|
where:
v path\response_filename is the full path and file name for your response file in
the -f1 flag and for the log file in the -f2 flag
The file specified by -f2 captures details about the silent installation. Because the
silent installation does not display error messages, it uses the .log file as an
installation log. If the silent installation fails for any reason, the failure is recorded
in this log file.
For example, you want to complete an IDS installation and record the setup so that
you can replicate the installation in silent mode afterwards. First, you need to
record the installation setup in a response file. You run the following command:
setup.exe -r -f1"C:\temp\silent.ini"
Where:
v C:\temp\ is the path to the location where you want the response file to be
generated. This is not necessarily the same path as where you install IDS
because you indicate the path for the product installation in the GUI program
that launches after you run this command.
v silent is your response file name, to which you must append the .ini extension
After you have completed the installation, copy silent.ini to the directory where
you want to use silent installation to replicate the installation setup. For this
example, the following are conditions of the silent installation host environment:
v You are completing the silent installation on a different computer from where
you created the response file.
v The target computer does not already have another IDS installation.
v You want to install the product in an existing path named C:\AppDev.
Run the following command in the IIF directory:
setup.exe -s -f1"C:\AppDev\silent.ini" -f2"C:\AppDev\silent.log"
After silent installation completes, you can view the generated silent.log file for
troubleshooting in the path that you indicated in the -f2 option.
|
|
|
|
Silent Installation on a Host with Multiple Installations
Use a response file to direct the action of the silent installation on a computer that
already hosts a Dynamic Server installation. A command-line option lets you
specify location when maintaining or uninstalling an existing installation.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-7
Page 34

|
Specifying an Installation to Modify
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If the Dynamic Server version that you want to install matches the version on the
target computer, the information recorded in your response file determines
whether the silent installation adds a new copy of the database server or modifies
the existing installation. Therefore, if your response file recorded a new installation,
you do not need to include the -multiple option in the silent installation
command. Similarly, if you ran the setup.exe -r command to start the installation
application in maintenance mode, the response file records your intention to
modify features, repair binaries, or complete uninstallation of an existing database
server installation.
On a computer that hosts more than one installation of the database server, you
can direct which installation to modify by using the -path option in the silent
installation command.
If you do not specify a location with the -path option, the silent installation
randomly selects one of the existing installations on the target computer and
proceeds in maintenance mode.
The following is an example of how to include the -path option in the silent
installation command:
setup.exe -s –path C:\tmp\informix –f1”C:\tmp\install.ini” –f2”C\tmp\log.txt”
where -path C:\tmp\informix indicates the location of the installation to modify.
Silent Installation Response Codes
Response codes indicate success or errors during silent installation and they are
recorded in the file that is specified by the -f2 argument for the installation
command.
Table 2-1. Silent installation response codes
Code Description
0 Success.
-3 Required data not found in the Setup.iss file.
-5 File does not exist.
-6 Cannot write to the response file.
-7 Unable to write to the log file.
-8 Invalid path to the InstallShield Silent response (.iss) file.
-9 Not a valid list type (string or number).
-10 Data type is not valid.
-11 Unknown error during setup.
-51 Cannot create the specified folder.
-52 Cannot access the specified file or folder.
-53 Invalid option selected.
2-8 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 35

Setting Up Cluster Installations
Complete the following tasks to cluster two computers.
v “Cluster Installations”
v “Overview of Implementing a Cluster on Two Nodes”
v “Setting Up a Cluster Installation” on page 2-10
v “Preparing to Set Up a Cluster” on page 2-10
v “Implementing a Cluster on the Primary Node” on page 2-11
v “IDS as a Cluster on the Secondary Node” on page 2-11
v “Installing IDS as a Cluster on the Secondary Node” on page 2-11
v “IDS as a Cluster on the Secondary Node” on page 2-11
Cluster Installations
IBM Informix Dynamic Server supports Microsoft Cluster Server (MSCS), which
enables high availability on Microsoft Windows (Windows 2003, Windows XP and
Windows Vista). MSCS allows you to cluster two Windows computers as
redundant components, or nodes. When a failure occurs on one node in the cluster,
Windows restarts the failed applications (such as the database server) on the
surviving node in the pair.
MSCS includes the Cluster Administrator, which enables you to designate a cluster
and define resources, resource ownership, and dependencies on other resources. A
resource is a hardware component, such as a shared disk, or a software
application, such as the database server, that is shared between the two nodes in a
cluster.
The Cluster Administrator also enables you to define groups that specify resource
dependencies, so that the Microsoft Resource Manager can move groups of
dependent resources to the surviving node in the event of failover. The Microsoft
Resource Manager is a program that invokes specific start, restart, stop, and
monitoring functions for a resource.
You can install IDS either on one node of a cluster or on both nodes (in a fail-safe
mode). Installation on one node of a cluster is the same as regular installation on a
stand-alone computer. For more information about installing IBM Informix
Dynamic Server, see “Installing IBM Informix Products” on page 2-1.
Important: Stop IDS before shutting down the operating system during MSCS
setup to avoid any data loss.
Overview of Implementing a Cluster on Two Nodes
After you complete cluster-implementation preparation tasks, you implement IBM
Informix Dynamic Server in a cluster environment in three steps:
1. Install IBM Informix Dynamic Server on the primary node.
2. Install the ClusterIT utility.
3. Convert the database servers to a cluster configuration. This step is
implemented with the ClusterIT utilities:
v Use the clusterIT_a utility to configure IDS on the primary node for use in a
cluster.
v Use the clusterIT_b utility to install IDS and configure it for use in a cluster
on the secondary node.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-9
Page 36

Setting Up a Cluster Installation
To set up a cluster on the primary node:
1. Run the following command on the primary node: clusterIT_a.
The Informix ClusterIT - primary Node window appears.
2. Fill out the information about networking environment, machine names, and
configuration for installing IBM Informix Dynamic Server:
a. In the DBSERVERNAME to be clustered text box, enter the name of your
unclustered IDS instance.
b. In the DBSERVERNAME final (when clustered) text box, enter a name for
your IDS instance after it has been converted into a cluster configuration.
c. In the Physical hostname primary node text box, enter the physical host
name of the primary node.
d. In the Informix password text box, enter your password.
e. Fill in the Full path to the IDS directory on the Informix RDBMS CD
field.
f. Enter the location of the installation (the value of %INFORMIXDIR%,
which must be located on a local disk and must be identical for both nodes.
g. In the New virtual host name for the database host text box, enter the new
virtual host name.
h. In the virtual IP address for the database host text box, enter the IP
address for the new virtual host.
i. In the Subnetmask text box, enter the value of the Subnetmask for the new
virtual host.
j. Choose the network you want to use for the IP address from the Network
menu.
k. Choose the Number of shared disks where you have chunks located.
l. Enter the name of the shared disks you use as chunk locations for IDS from
the Shared disks for database text box. These disks are moved to the
Informix group that will be created by the ClusterIT utility. In the event of
failure, the disks you specify here will move over to the other node.
3. Click Convert to Cluster. After the ClusterIT utility completes, an IDS comes
back online, but it is now controlled by the Microsoft Cluster Service. The
resource group Informix has been created.
You can check the state of your IDS by running the onstat- command.
Preparing to Set Up a Cluster
To prepare to set up a cluster:
1. Install IBM Informix Dynamic Server on the primary node without
initialization.
2. Edit the onconfig file. For more information on the onconfig file, see the IBM
Informix Dynamic Server Administrator’s Reference.
3. Put the root dbspace on a shared disk.
4. Move all shared disks to the primary node.
5. Initialize the database server. For more information, see “Database Server
Configuration After Installation” on page 3-4.
6. Create additional dbspaces, if needed. For more information, see “Dbspace
Name, Location, and Size” on page 3-5. Additional dbspaces must be located
on shared disks.
2-10 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 37

7. Uninstall any previous IDS installations on the secondary node.
Implementing a Cluster on the Primary Node
When you run the clusterIT_a utility on the primary node, ClusterIT performs the
following tasks:
v Extracts the resource .dll (ifxdb920.dll)totheWINDOWS\Cluster directory
v Creates an IBM Informix resource group
v Moves all physical disks on which chunks are located to the IBM Informix group
v Creates a virtual IP address and a virtual host name
v Registers the resource type IFXDB920
v Creates the IDS cluster resource
v Sets dependencies
v Sets the IDS cluster resource to online
To use ClusterIT to implement a cluster, the INFORMIXDIR directory must be
located on a local disk, the (INFORMIXDIR directory must be on an identical local
path for each node, and any chunks must be on shared disks. It must be possible
to move the disks from one node to another.
IDS as a Cluster on the Secondary Node
When you run the clusterIT_b utility on the secondary node, the clusterIT_b
utility performs the following tasks:
v Installs IBM Informix Dynamic Server on the secondary node (silent installation)
v Copies registry entries from the primary node
v Copies the ONCONFIG file from the primary node
v Makes the resource .dll (ifxdb920.dll) available on the secondary node
Installing IDS as a Cluster on the Secondary Node
To install IBM Informix Dynamic Server in a cluster configuration on the secondary
node:
1. Run the following command on the secondary node: clusterIT_b The IBM
Informix ClusterIT - secondary node window appears.
2. Fill in the text boxes:
a. In the Physical hostname primary node field, enter the physical host name
of the primary node.
b. Fill in the Full path to the IDS directory on the Informix RDBMS CD
field.
c. Enter the Instance number that you choose for IDS on the secondary node.
This number is the same as that of IDS on the first node.
d. Enter the location of the installation (the value of %INFORMIXDIR%,
which must be located on a local disk and must be identical for both
nodes).
e. Enter your Informix password.
f. In the DBSERVERNAME final (when clustered) text box, enter the name of
the IDS instance in the cluster configuration. On this secondary node, IDS
will be installed directly with this name.
g. Check whether or not to enable Role separation. For more information, see
“Planning Role Separation” on page 1-8.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-11
Page 38

3. Click Convert to Cluster. After the ClusterIT utility completes, IDS starts on the
secondary node.
After implementing a cluster environment on multiple nodes, you can find a
record of the ClusterIT utility activities in the clusterIT.log files, one for
clusterIT_a in the primary node directory, and one for clusterIT_b in the
secondary node directory where the ClusterIT executables were installed.
Upgrade of IDS by Overwriting an Existing Installation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use the installation application to overwrite an existing IBM Informix Dynamic
Server installation only when you are upgrading from a previous fix pack of the
same version number or for specialized technical environments.
When you place the IBM Informix Dynamic Server installation media on a
Windows computer that hosts an earlier version of the server, you will be
prompted as to whether you want to install in a different directory or upgrade by
installing in the same directory where the older version of the product already
exists.
For upgrading or migrating a production database server, choose to install in a
different directory as documented in the IBM Informix Migration Guide unless you
have specific goals or system constraints that require you to overwrite the older
installation completely. The following are some examples of when you might
upgrade by installing directly to the directory where an earlier version or fix pack
level are located:
v Upgrade an existing IDS installation that has the same version number as the
new product, but is an earlier fix pack. For example, if the host computer has
IDS 11.50.xC1 and you want to install IDS 11.50.xC4, then complete the upgrade
by installing in the same location.
v Capture the installation settings in a response file so that you can upgrade other
older IDS instances with silent installation.
v You have a computer hosting an older version of IDS that does not have
sufficient free space to hold two installations of the product.
v You plan to use a symbolic link to migrate the data to the new version.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overwriting an Existing IDS Installation
Ensure that you complete the prerequisites before you do an upgrade that installs
the product in a directory that already has an earlier version.
Important: Ensure that you have the installation media for the IBM Informix
Dynamic Server version that you are replacing, back up your databases, and
complete other preparation steps before you upgrade using the following method.
See the IBM Informix Migration Guide for details about supported upgrade paths
and data migration.
When you install using the procedure below, the old version or fix pack of the
product is uninstalled.
1. Open the IBM Informix Dynamic Server installation application of the version
or fix pack level that you want to install.
2. Select the option to install a new instance when the installation application lists
existing IDS instances and click Next.
3. Select the option to upgrade by replacing the product and click Next. Complete
the prompts in the server installation application for a typical or custom setup.
2-12 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 39

|
|
While the database server engine is upgraded by this task, the preceding steps do
not change your databases.
|
Multiple Residency
Planning for Multiple Residency
To start the IDS instance, you must initialize the server manually.
You can set up multiple independent database server environments on the same
computer
Complete the following tasks to set up multiple residency.
When you plan for multiple residency on a computer, consider the following
factors:
v Storage space
Each database server must have its own unique storage space. You cannot use
the same disk space for more than one instance of a database server. When you
prepare an additional database server, you need to repeat some of the planning
that you did to install the first database server. For example, you need to
consider these questions:
– Will you use mirroring? Where will the mirrors reside?
– Where will the message log reside?
– Can you dedicate a tape drive to this database server for its logical logs?
– What kind of backups will you perform?
v Memory
Each database server has its own memory. Can your computer handle the
memory usage that an additional database server requires?
Creating a New Database Server Instance
Before you set up multiple residency, you must install one database server as
described in Chapter 2, “Installing IDS on Windows,” on page 2-1. It is not
necessary to install more than one copy of the database server binary files. All
instances of the same version of the database server on one computer can share the
same executable files.
To set up multiple residency, use the Server Instance Manager. To use the Server
Instance Manager program, you must have administrative privileges on the
database server. However, local administrator privileges are sufficient, even if the
database server was installed for domain use.
Before you use the Server Instance Manager, verify that you are a member of the
Informix-Admin group. For more information, see “Verifying Administrators
Group Membership” on page 1-1.
The following steps are for using the Server Instance Manager GUI. See “Server
Instance Manager Command-Line Options” on page 2-14 for other ways you can
use this utility.
To create a new database server instance:
1. Choose Start → Programs → IBM Informix Dynamic Server 11.50 → Server
Instance Manager.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-13
Page 40

2. Select the Installation Method, and click Create New to create a new instance of
the database server.
3. Follow the prompts.
After you enter the required information, the Server Instance Manager installs
services, records environment variables, updates the registry, and creates an
onconfig file for the new database server instance.
Server Instance Manager Command-Line Options
The instmgr.exe utility extends the ability to configure an IBM Informix Dynamic
Server instance with command-line options.
Purpose
The instmgr.exe utility is a command-line version of the Server Instance Manager.
You must have administrative privileges on the database server. However, local
administrator privileges are sufficient, even if the database server was installed for
domain use.
The following table describes the instmgr.exe utility options.
Table 2-2. instmgr.exe Utility Options
Option Meaning
-alias
DRDA_server_alias
-drdaport DRDA_port
drdasvc
DRDA_service_name
-apw password Specifies the user informix password for a new instance.
-c -n servername -apw
informix_password
-rename -apw
informix_password -n
new_name old_name
-s .ini_filename Initialize the specified instance in silent mode.
-f .ini_ filename Retrieve some information from a partial initialization file, and the
-d -n servername Delete the specified instance. Warning: This removes related
-dall Delete all instances. Warning: This removes related dbspaces and
-uall -v version Upgrade all instances to the specified version. (Upgrading a single
-r -v version -n
servername
-rall -v version Revert all instances to the specified version.
-b64 Base64_password Specifies Base64–encoded password.
-l Indicates cluster installation.
Command line for standalone support of DRDA in the DBMS.
Creates an instance of the database server.
Rename an existing server name.
remainder from the user.
dbspaces and deletes the data.
deletes the data.
instance in a multi-instance environment is not supported.)
Revert the specified instance to the specified version.
2-14 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 41

Table 2-2. instmgr.exe Utility Options (continued)
Option Meaning
-system Create database server instance that runs as local system user
instead of user informix. (IDS must be installed as local system
user to use this option.)
Troubleshooting Installation Problems
This section describes some common installation problems and the corresponding
solutions for users who receive their product materials directly from IBM. You can
find more information about Client SDK and IConnect installation issues in the
IBM Informix Client Products Installation Guide.
You can find information that will help identify and resolve installation errors in
the IDS log file in the following location:
%INFORMIXDIR%\logs\IDS_Install_date_time.log
If any of the problems described in this section persist, contact IBM Technical
Support.
v Problem. If you enter an invalid database server name, you receive the following
message:
The database server name you entered is not valid. Please
note the following limitations: a database server name
cannot exceed 128 characters; it can only contain letters,
numbers, and underscores; and it must begin with a letter.
Solution. Enter a different name and note the limitations stated in the message.
v Problem. If you have insufficient virtual memory for the installation, you receive
the following message:
This installation of Dynamic Server requires number MB of
free page file space. After you install this product,
increase your page file size to properly use your virtual
memory with this product.
Solution. For information about how to increase the size of your page file, refer
to your Windows documentation.
v Problem. If you do not have the correct privileges to run the install program, you
receive the following message
You do not appear to be an administrator. In order to run
this program, you must belong to the Administrators group
on local computer.
Solution. Use the administrator account to log on or contact your system
administrator to add your user account to the Administrators group.
Chapter 2. Installing IDS (Windows) 2-15
Page 42

2-16 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 43

Chapter 3. Post-Installation Tasks on Windows
Review the following information after installing IBM Informix Dynamic Server.
v “Working with the Installation”
v “IDS Program Group” on page 3-2
v “Initializing and Starting the Database Server” on page 3-3
v “Database Server Configuration After Installation” on page 3-4
Working with the Installation
After installing IBM Informix Dynamic Server, determine how much of the
database server setup the installation application has completed and what actions
you must do before putting the server in production.
The installation sets up a database server that is ready to use and can run on your
system automatically. But you may still want to perform some basic enhancements
before you put the server in production. These tasks show you ways to control the
way IDS runs on your system.
If have completed a more advanced installation of IDS, these post-installation tasks
might be required in order to work with the database server.
Tip: When you initialize a server, a shortcut is added to the Start menu. To run
commands for an initialized server, click Start → All Programs → IBM Informix
Dynamic Server 11.50 → servername → .
The following tasks are covered in the next sections of the documentation:
v Starting the database server manually.
v Setting up the database server to start whenever Windows is launched.
v Stopping the database server.
Two IDS features that require post-installation configuration are the following:
– Global Language Support (GLS) is a feature that enables you to configure the
database server to use a locale other than the default locale, which is U.S.
English. For more information on how to create databases that use the
diacritics, collating sequence, and monetary and time conventions of a
different language, see the IBM Informix GLS User’s Guide.
– IBM Informix Storage Manager (ISM) is a feature that can be used for ON-Bar
backup-and-restores. See the IBM Informix Storage Manager Administrator’s
Guide for more information.
Installation Automatic Actions
Before you begin manual post-installation tasks, it is helpful to know some of the
major tasks the installation application has done. A typical installation (and
possibly a custom installation, depending on your choices during setup) performs
the following actions to make the database server ready to run on Windows:
v Configured and installed the database server as a Windows service.
v Created an informix user account and an Informix-Admin administrative group.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 3-1
Page 44

(Custom installations: If you enabled role separation when you installed the
database server, you could have changed the name of the Informix-Admin
group.)
v Automatically assigned the informix user account, under which the database
server runs, to the Informix-Admin group and to the Windows Administrators
group.
v Granted the following advanced privileges to the informix user account:
– Logon as service
– Act as part of the operating system
– Increase quotas
– Replace a process level token
– Debug programs
– Manage auditing and security log
IDS Program Group
An IBM Informix Dynamic Server program group is on the Windows Start Menu
after installation completes.
To access the following items on the database server program group, click Start →
Programs → IBM Informix Dynamic Server. The following table describes the
program group menu.
Table 3-1. IBM Informix Dynamic Server Program Group
Menu Item Description
Documentation Contains shortcuts to product documentation:
Information Center
A Web-based, powerful online interface
containing the technical information about the
IBM Informix products. Requires a connection
to the Internet. If you do not have a connection
to the Internet, you can find the product
documentation on the installation media.
Release Notes
Describes new features of IBM Informix
products. This file also contains information
about any changes to function from previous
releases, as well as any known problems and
their workarounds. Read this file before you
use the database server.
Error Messages Provides a complete list of all of the error messages and
their corrective actions.
Modify Installation Opens a wizard for modifying the installation:
Modify
Alter IDS components and features.
Repair Fix any corrupt or missing binaries for installed
features.
Remove
Remove all features of a working installation
and, optionally, remove related group and user
IDs. This selection launches the uninstallation
application.
3-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 45

Table 3-1. IBM Informix Dynamic Server Program Group (continued)
Menu Item Description
Server Instance Manager Creates and configures new server instances and
removes configured server instances.
server-name Opens a Command Prompt window for an initialized
database server instance. You can use that window to
run DB-Access and certain command-line utilities such
as onstat, oncheck, and onspaces. (The oninit utility is
designed to be started by a service rather than from this
window.) If you have more than one database server
instance, there is a shortcut menu for each of them.
Initializing and Starting the Database Server
After the database server is initialized once, you can start it manually or set it to
start automatically when Windows starts.
You can initialize and start the server from the Control Panel interface or from the
command line. If the server was initialized during installation, you do not need to
initialize it again.
Important: To complete these tasks from the Control Panel, you must be a member
of the Windows Administrators group. To complete them from the command line,
you must be a member of the Informix-Admin group. Do not use the oninit utility
to start the database server. For detailed information about how to start the
database server, see the IBM Informix Dynamic Server Administrator’s Guide.
To start the database server by using the Control Panel:
1. Choose one of the following options:
v Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools
v Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Component Services > Console
Root > Services (Local) (for a Domain Controller)
2. Double-click Services.
3. Double-click Informix IDS - server_name from the list and specify the
appropriate start options or accept the default ones. Verify the options on the
General page of the dialog box:
v If you want database server to start automatically when Windows starts,
make sure that Startup type is set to Automatic. The database server is set to
start automatically if you installed with a custom setup, or if you initialized
the database server during a typical setup.
v If the server is not initialized yet, type -iy in the Start Parameters field. This
option creates and initializes the root dbspace. You do not need to do this if
you chose to initialize the server during installation. The server needs to be
initialized only once before you can start it. Warning: If you run the -iy
switch on a database server that has IDS databases, the data is deleted.
v Click OK to save your options.
4. Click Start.
Alternatively, to perform the tasks from the command line, click Start > Run and
run the appropriate command from %INFORMIXDIR%\bin:
v To start a database server that was already initialized once, run this command:
starts server_name
Chapter 3. Post-Installation Tasks (Windows) 3-3
Page 46

v To initialize and then start the database server, run the command with the -iy
option.
starts server_name -iy
Warning: If you run the -iy switch on a database server that has IDS databases,
the data is deleted.
Stopping the Database Server
To stop the database server from the Control Panel, you must be a member of the
Windows Administrators group. To stop the database server from the command
line, you must be a member of the Informix-Admin group.
To stop the database server:
v From the Control Panel:
1. Choose Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools.
2. Double-click Services.
3. Select Informix IDS - server_name from the Service list box.
4. Click Stop.
v From the Command Prompt window:
1. Click Start > Programs > IBM Informix Dynamic Server 11.50 to display the
program group for the database server.
2. Click the database server instance (server_name) to display the Command
Prompt window.
3. In the Command Prompt window, type:
onmode -ky
Database Server Configuration After Installation
If you need to create a Dynamic Server instance after installation completes, you
can use the Server Instance Manager or use the standard configuration file
(onconfig.std) as a basis for a new configuration file.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The genoncfg utility is an alternative configuration method if you are comfortable
working in a command-line environment. With this utility, you set a short list of
parameters in an input file, from which the utility then generates a Dynamic
Server configuration file that is optimized for both your anticipated usage and
your host environment. You cannot use this utility to change a working
configuration file. The genoncfg utility is documented in the IBM Informix Dynamic
Server Administrator’s Reference.
The following information is provided for advanced users who must manually
start or change configuration of a database server instance.
Database Server Number
The database server number uniquely identifies a database server if more than one
instance of the database server is installed.
If only one instance of the database server is installed, set this number to 0. The
database server number that you specify is the value for the SERVERNUM
configuration parameter.
3-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 47

The database server uses configuration parameters, set in the onconfig file, during
initialization. For more information about configuration parameters and the
onconfig file, see the “Configuration Parameters” chapter of the IBM Informix
Dynamic Server Administrator’s Reference.
To determine how many instances of the database server are installed, run the
Server Instance Manager program. To run the Server Instance Manager program,
choose Start > Programs > IBM Informix Dynamic Server 11.50 > Server Instance
Manager.
Database Server Name
The database server name identifies the database server to client applications.
In most cases, you can choose the default database server name. The database
server name that you specify is the value for the DBSERVERNAME configuration
parameter.
Database server names must begin with a letter and can contain only letters,
numbers, and the underscore character.
Service Name and Port Number
The service name specifies the servicename entry and the port number specifies the
port entry for the database server in the sqlhosts registry.
Specify the service name and port number for the TCP/IP network protocol.
If only one database server instance exists on the computer, the installation
program provides default values. It is recommended that you use these default
values. For subsequent database server instances, you must provide unique values.
Dbspace Name, Location, and Size
A dbspace is a logical collection of chunks to which databases and tables are
assigned.
During installation, the root dbspace is created automatically. You can configure an
additional data dbspace, mirror location, or smart blob drive.
Specify the location and disk-space size for the dbspace:
v Primary Data Location
By default, the primary data location is the current drive. The installation
program displays the amount of available disk space; the default dbspace size is
200 megabytes.
v Smart blob Drive
A default smart blobspace can be configured optionally. The default size is 200
megabytes.
v Mirror Location
The mirrored location serves as the backup area if the primary storage device
fails. The mirrored location should be the same size as the primary location and
should be in a different drive. The data dbspace and the smart blob can be
mirrored on the same drive.
This mirrored location is also the value of the MIRRORPATH configuration
parameter.
Chapter 3. Post-Installation Tasks (Windows) 3-5
Page 48

Default Sbspace Name, Location, Size, and Page Size
An sbspace is a logical storage area that the database server uses to store smart
large objects (CLOB and BLOB data).
The default sbspace is the location in which the database server stores a smart
large object if you do not specify an sbspace name when you create the smart large
object. The database server also uses the default sbspace to store user-defined
statistics.
Specify the primary and mirror data-storage location for the default sbspace:
v Primary Data Location. By default, the Primary Data Location of the sbspace is
the current drive and must have a minimum of 200 megabytes. The installation
program displays the amount of available disk space. This location also specifies
the value of the SBSPACENAME configuration parameter.
v Mirror Location. The mirrored location serves as the backup area if the primary
storage device fails. The mirrored location should be the same size as the
primary location and should be in a different drive.
v Size. The size of the sbspace should be at least 200 megabytes.
v Page Size. The size of the sbpage should approximate the size of the most
frequently occurring smart large object that the sbspace holds. The default is one
page.
For more information about sbspaces, see the IBM Informix Dynamic Server
Administrator’s Guide.
Shared Server Definition Computer
The shared server definition computer is the machine hosting the database server
instance with which client computers connect if you are deploying Dynamic Server
in a networked Windows environment.
Specify where you want the sqlhosts registry information for the shared server
definition to be stored. You can choose either the local host machine or another
computer that hosts a central, shared repository of sqlhosts settings for multiple
database servers in the network.
If you specify another computer on the network, you must set the
INFORMIXSQLHOSTS environment variable on your local computer to the name
of the computer that stores the sqlhosts information.
Configuring IDS Manually
Use the Server Instance Manager if you want to configure the database server
manually after installation of the product.
To configure the installed database server:
1. Open the Server Instance Manager utility and specify the following:
v database server number
v database server name
v service name and port number for the TCP/IP network protocol
2. If you selected custom installation setup:
a. Specify a name for the root dbspace.
b. Specify the primary and mirror storage location and disk-space size for the
root dbspace.
3-6 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 49

c. Specify the name of the default sbspace.
d. Specify the primary and mirror storage location and disk-space size for the
default sbspace.
3. Specify the computer to use for shared server definition for your database
server and administrative tools.
The installation program installs services on the computer and configures the
database server.
4. If you configured a new instance of the database server, you are prompted to
initialize the database server:
v Click Ye s to initialize the database server and the root dbspace.
v Click No to skip initialization.
If you skip initialization, you must manually start the database server and
specify the root dbspace size later. For more information on manual
initialization, see “Initializing and Starting the Database Server” on page 3-3.
Note: Database server initialization might take several minutes.
A message indicates that the database server was successfully installed.
5. If you selected other products to install, the installation prompts you to
configure these products.
6. To update the members of the Informix-Admin group, log out and log back in.
This step enables you to run the IBM Informix administration tools.
7. Restart your computer, if prompted.
For more information about configuring the database server manually, see the IBM
Informix Dynamic Server Administrator’s Guide.
Chapter 3. Post-Installation Tasks (Windows) 3-7
Page 50

3-8 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 51

Chapter 4. Modifying IDS on Windows
The uninstallation application facilitates uninstallation and reinstallation of IBM
Informix Dynamic Server, as well as modification of installed features of a database
server instance.
Review the following information to uninstall or modify IDS
v “Altering IDS Features”
v “Uninstalling IDS” on page 4-2
v “Reinstalling the Database Server” on page 4-2
v “Performing Silent Uninstallations of IDS” on page 4-2
Altering IDS Features
|
|
|
You can modify, repair, or remove installed features. You can also modify, repair, or
remove a particular copy of the product if you have multiple copies installed on
one computer.
To alter the features and components of your installation, IBM Informix Dynamic
Server provides a dynamic GUI that detects what features are on your server. This
part of the uninstall application not only lets you select and deselect features, but
also repairs any flawed binaries among installed features.
To alter the features of your IDS installation:
v Select Start > Programs > IBM Informix Dynamic Server 11.50 > Modify
Installation or launch the GUI maintenance wizard by opening the
Add/Remove Programs feature of the Control Panel.
v Select the Modify button to alter IDS components and features.
The wizard for modifying IDS features and components enforces certain
dependencies. For example, if you select a feature for removal but do not select
other components that rely on this feature, the wizard does not let you perform
this.
v Select the Repair button to fix any corrupt or missing binaries for installed
features.
v Select the Remove button to remove all features, including all required
components for a working installation. This selection launches the uninstall
program.
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 4-1
Altering Copies of IDS
If you have multiple copies of the same version of IBM Informix Dynamic Server
installed on a computer, you can use the maintenance wizard to modify, repair, or
remove one of the copies. You can also use one of the following command line
options to perform maintenance on a specific copy or uninstall the copy:
-path Specifies the installation path for which maintenance is required. You can
use this command line option with other maintenance options. For
example:
setup.exe -path installation path -s -f1"X:path\response file"
Page 52

|
|
|
|
-instnum
Specifies the installation number of the copy that requires maintenance. For
example:
setup.exe -instnum installation number -s -f1"X:path\response file"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Uninstalling IDS
Where:
v installation path is the full or relative path to the location of the IDS installation
that you want to alter.
v installation number is the unique number that identifies each copy; this number
was automatically generated when the copy was installed.
v X:path\response file is your drive, path, and response file name of the file
(uninstall.ini) where the uninstallation options were recorded or of the file
(maint.ini) where the maintenance options were recorded.
Related tasks
“Installing a Copy of IDS on a Computer” on page 2-1
Back up your IBM Informix Dynamic Server system before you uninstall.
Important: Any groups and user accounts that you used for this installation will
be removed in both local and domain installations, except when there are other
instances on the disk. The uninstallation application cannot remove groups and
user accounts if there are other IDS instances on the host computer.
To uninstall the database server:
1. Select Start > Programs > IBM Informix Dynamic Server > Modify
Installation > Remove
2. Choose one of the following options:
v Retains all databases, but removes all server binaries
This option is typically used when you upgrade the product because it
facilitates removing server binaries while preserving dbspace.
v Removes server binaries and all databases associated with them
This option removes all installed binaries and dbspaces. Use this option with
caution.
Reinstalling the Database Server
If an earlier version of the database server is already installed at a specific instance,
the installer provides options either to upgrade or to complete a fresh installation
at a different location. See “Multiple Copies of IDS on One Computer” on page 1-2.
Performing Silent Uninstallations of IDS
You can remove IBM Informix Dynamic Server without interactively providing
options. To do so, you must generate a response file for the uninstallation
application. Ensure that you have access to the original media files for this task.
To perform a silent uninstallation:
1. To uninstall an existing installation and record a response file, use this
command:
setup.exe -r -f1"X:path\uninstall.ini"
4-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 53

The command records the uninstallation options as you perform them and
stores them in a response file. If you do not specify the location of the response
file, by default the uninstallation sequence is saved in %WINDIR%\setup.iss.
2. To perform the silent uninstallation on another system, or to uninstall from the
same system at a later time, specify the appropriate response file with this
command:
setup.exe -s -f1"X:path\uninstall.ini"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. To uninstall an existing installation when there are multiple copies of a version
installed on the same computer, specify the appropriate response file with one
of the following commands:
setup.exe -s -path installation path -f1"X:path\uninstall.ini"
setup.exe -s -instnum installation number -f1"X:path\uninstall.ini"
Where:
v installation path is the full or relative path to the location of the IDS
installation that you want to alter.
v installation number is the unique number that identifies each copy; this
number was automatically generated when the copy was installed.
v X:path\uninstall.ini is your drive, path, and file name for the recorded file
that contains the uninstallation options.
Related reference
“Performing a Silent Installation” on page 2-5
Chapter 4. Modifying IDS (Windows) 4-3
Page 54

4-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 55

|
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility
|
|
|
|
+
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Deployment Utility
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use the command-line deployment utility to deploy a snapshot of IBM Informix
Dynamic Server and create a new instance as a quick alternative to traditional
installation, especially for deployments to many computers.
You can configure the snapshot so that the instance is ready to run for your needs
immediately after deployment.
Review the following information to use the deployment utility.
v “The Deployment Utility”
v “Rapid IDS Embeddability with the Deployment Utility” on page 5-2
v “Creating a Snapshot for Deployment” on page 5-4
v “Deploying a Snapshot with the Deployment Utility” on page 5-4
v “ifxdeploy Command: The Deployment Utility” on page 5-5
v “ifxdeploy.conf File: The Deployment Utility Configuration File” on page 5-10
v “Removing a Snapshot with the Deployment Utility” on page 5-15
The IBM Informix deployment utility can deploy snapshots of pre-configured IDS
instances (with or without data) on one or more computers.
A snapshot is an image that includes the IBM Informix Dynamic Server installation
directory, configuration settings, and any data spaces associated with the instance.
To take a snapshot, you must have installed IDS. The installation can be a working
instance, or simply an installation that you set up as a template from which to
deploy the instance on other computers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+
+
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 5-1
Deploying a snapshot is different from installing IDS with the silent installation
option. It is much quicker because you are simply recreating the installed instance
from a snapshot, you are not installing the product all over again. Similarly, if you
deployed a snapshot on a computer, you can replace the snapshot or remove it by
using the deployment utility.
The following list describes some scenarios for which the deployment utility can be
useful:
v You want to deploy a particular database server configuration on multiple
computers. You can tune only one instance as the template instance, and then
use the utility to deploy it on to other computers in silent mode.
v You want to clone an instance on the same computer or set up multiple
instances quickly.
v You want to upgrade multiple instances to a different fix pack or version level to
take advantage of newer product enhancements but this requires tuning certain
configuration parameters or environment variables. You can tune the template
instance, and then use the utility to upgrade other instances rapidly.
v You are embedding a IDS application on multiple computers and want to reduce
application installation and setup time. You can specify the installation location
Page 56

+
+
+
and a single path for all application files including the database server files
during deployment to avoid waiting for data loading and database server
initialization.
+
+
+
+
+
|
+
+
+
|
|
Rapid IDS Embeddability with the Deployment Utility
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Most deployment utility functionality can be invoked by using either
command-line options or setting options in a text-based template configuration
(.conf) file to accommodate your working preference. The .conf file also facilitates
easier reuse of an instance setup because you can save your settings in a copy of
the file.
To operate the deployment utility, run the ifxdeploy executable from a command
line or from a script as part of an application installation. (The full file name of the
executable is ifxdeploy.exe in the Windows version of IDS, but it will be referred
to as simply ifxdeploy throughout the documentation.) The utility can be run
without user interaction, in silent mode.
A snapshot of an instance can be reconfigured and initialized by running the
deployment utility with a combination of command line options or by setting
values in the ifxdeploy.conf file.
You can preinitialize the instance by indicating the location of the IBM Informix
Dynamic Server chunk paths on the target computer.
The ifxdeploy.conf file allows for more dynamic customization than the
command-line options because in the file you can specify any configuration
parameter values, set key environment variables, and create multiple database
server aliases.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
To apply configuration settings of the ifxdeploy.conf file to an instance you are
deploying, enter the file name as an argument to the -config option when you run
the ifxdeploy command.
If you set different values for the same instance in the ifxdeploy.conf file and as an
option to the ifxdeploy command option, the deployment utility uses the value
specified on the command line. For example, if you specify -p mypassword1 on the
command line but set the INFORMIXPASSWORD parameter to mypassword2 in the
ifxdeploy.conf file, the deployed instance requires mypassword1 for authentication.
Initialized dbspaces
If you create a snapshot with initialized dbspaces, you can deploy the snapshot as
an initialized instance without having to wait for disk space initialization on the
target system.
To deploy the dbspaces to different locations from where they were when the
snapshot was taken, use the -relocate option. In the -relocate option you specify
one or more parent directories for the chunks of the deployed instance.
If you want to relocate the chunk parent directories, verify the following before
you run the utility:
v The chunk files on the target computer exist in path locations that correspond
with your chunk parent directory relocation settings.
5-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 57

+
+
+
+
+
v Each chunk file has an ownership and permissions setting that allows you to
modify it.
v You know the ROOTPATH (and MIRRORPATH, if applicable) for the deployed
instance, and provide the path information in a configuration parameter setting
or by using the -rootpath option.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Database Server Configuration
You can set essential configuration parameters in the command-line options of the
ifxdeploy command, instead of setting the values in the onconfig file.
In the ifxdeploy.conf file, you can provide server configuration parameters in the
following ways:
v Edit essential configuration parameter settings for your instance; the parameter
options that appear in the file mirror those that are available as command-line
options.
v If you do not edit a configuration parameter setting listed in the file, accept the
default value.
v Indicate a pre-existing onconfig file for the instance to use.
v Customize configuration parameter settings in the ONCONFIG part of the
ifxdeploy.conf file, which overrides any onconfig file settings. This is
particularly useful if you have brought your snapshot to the target computer,
analyzed the environment, and know that there are a few specific parameters
that are easier to adjust through the deployment utility instead of manually
editing the onconfig file.
Attention: The values of any options that you pass on the ifxdeploy command
line supersede the corresponding settings of the ifxdeploy.conf file.
An onconfig file is generated from onconfig.std if you do not specify one and the
ONCONFIG environment variable is not set.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Environment Variables
You can specify INFORMIXDIR, INFORMIXSERVER, INFORMIXSQLHOSTS,
and ONCONFIG environment variables in the ifxdeploy.conf file.
The deployment utility can read the following environment variables from the
process environment and use them to configure the deployed instance:
v INFORMIXDIR
v INFORMIXSERVER
v CLIENT_LOCALE
v DB_LOCALE
v DBLANG
v GL_USEGLU
v SERVER_LOCALE
If the INFORMIXDIR and INFORMIXSERVER environment variables are not set
on the target computer, you must enter them in the configuration file or when
prompted by the deployment utility. No default values are provided for these two
environment variables.
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-3
Page 58

+
+
+
On Windows, the INFORMIXSQLHOSTS environment variable is used only if
you want to capture the connectivity settings stored in the registry of another
computer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
|
Creating a Snapshot for Deployment
|
|
|
|
+
|
|
If the ONCONFIG environment variable is not set, the utility creates one from a
combination of whatever parameter settings you provide in the configuration file
and onconfig.std. The file name format of the autogenerated ONCONFIG file is
onconfig.server_name.
Database Server Aliases
With the ifxdeploy.conf file, you can set up multiple database server aliases that
are equivalent to setting the DBSERVERALIASES configuration parameter in the
onconfig file. The ″ALIAS″ section of the file consists of fields in which you can
provide the SQLHOSTS connection information for each alias. The ″ALIAS″ setting
can expedite your deployment if you plan to use database server aliases because
you enter the connection information as part of the configuration file setup and do
not need to configure SQLHOSTS information separately.
Create a snapshot of IBM Informix Dynamic Server that you can use with the
deployment utility to place pre-configured instances on multiple computers.
Before you create a snapshot, you must meet the following prerequisites:
v Windows administrator privileges on the computer.
v Sufficient disk space to save the snapshot in a file. If space is limited, you might
want to store the snapshot in a compressed file.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deploying a Snapshot with the Deployment Utility
|
|
|
To create a snapshot, complete the following steps on the computer where you
installed the IDS instance:
1. Shut down the instance in a consistent state with onmode -kuy.
2. Create a snapshot of the following items:
v IDS installation directory
Tip: Ensure you include the IDSFILES.txt file, which is in the installation
directory. That file is required if you want to use the deployment utility to
remove the snapshot from the target computer after you deploy it.
v Configuration settings
v Optional: Data spaces associated with the instance
Tip: Store the components of the snapshot in a compressed file if you want
to save space. If you compress the snapshot with Gzip tar on UNIX or
®
Linux
decompressed by the deployment utility.
3. Optional: After you create the snapshot, you can restart the instance.
Deploy a snapshot of an instance by using the ifxdeploy command on the target
computer.
or into a zip file on Windows, the utility can be automatically
|
|
Before you deploy a snapshot, you must meet the following prerequisites:
v Windows administrator privileges on the target computer.
5-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 59

|
|
|
v If you are deploying data, the root dbspace is in the same absolute path on the
target computer as on the template computer.
v The target computer has sufficient disk space for the snapshot.
|
|
|
|
|
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
|
|
|
+
+
+
Tip: You need the same amount of space as was used on the template computer.
The space required depends on what you included in the snapshot, such as data,
extra files, or other applications.
To deploy the snapshot on the target computer:
1. Save a copy of the snapshot.
2. If not set, set the environment variables for INFORMIXDIR,
INFORMIXSERVER, and your locale. You can set the environment variables in
the ifxdeploy.conf file. The default locale is U.S. English. If the environment
variables or the locale are not set, the utility reads these settings from the
process environment and uses them to configure the instance.
3. If you want to provide your own configuration file, set the ONCONFIG
environment variable to the location of the file that you want to use. You can
set the ONCONFIG environment variable in the ifxdeploy.conf file. If you do
not set the ONCONFIG environment variable, or if the file specified by the
ONCONFIG environment variable cannot be found, the deployment utility
automatically creates a configuration file with standard configuration settings
(based on the onconfig.std file).
4. Optional: If there are specific parameter values in the onconfig file that you
want to modify, set them in the ″ONCONFIG″ option section of the
ifxdeploy.conf file.
5. Run the ifxdeploy command with the appropriate options. The utility is located
in the bin subdirectory of the installation path. See “ifxdeploy Command: The
Deployment Utility” for supported options.
|
ifxdeploy Command: The Deployment Utility
|
|
|
+
+++++++++++++++++++++
Use the ifxdeploy command to deploy a snapshot or remove a snapshot that you
already deployed.
Syntax
ifxdeploy Deployment Parameters
Uninstallation Parameters
+
+
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+
+
++++++++++++
+
+
Deployment Parameters:
-p password
(1) -config ″conf_file_name″ -extractcmd ″command″
-system -file ″file_name″
-silent
-verbose
-servernum server_number
-y -verbose -l ″log_file″
++
-sqliport port
-namedpipe
(2)
-drdaport port
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-5
Page 60

++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+
+
++++++++++++
+
-rootpath ″path″
-6432
-y
(4)
-relocate path
-installdrive ″drive″
(3)
(5)
;
old_path=new_path
;
old_path,old_offset=new_path,new_offset
-verbose -force -l ″log_file″
+
+
++++++++++++++++++++++++
+
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+
+
++++++++++++
+
Uninstallation Parameters:
-uninstall ″installation_path″
-silent
-y -verbose -l ″log_file″
-verbose
-y
-delifx (6)
-6432
-l ″log_file″
+
+
++
++
++
+
++
++
++
Notes:
1 -system functions on Windows only
2 -namedpipe functions on Windows only
3 -relocate can run without -rootpath option if ROOTPATH is set in an
ONCONFIG parameter
4 -6432 functions on Windows only
5 -installdrive functions on Windows only
6 -6432 functions on Windows only
+
|
|
|||
||
|
Command Options
Table 5-1. ifxdeploy Command Options
Element Purpose Key Considerations
-config ″conf_file_name″ Specifies deployment
|
|
||
|
|
|
-delifx Removes user informix and
|
|
|
||
-drdaport port Specifies the Distributed
|
|
|
|
5-6 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
configuration file to run with
utility.
the Informix-Admin group.
Relational Database
Architecture (DRDA) service
port for use with the IBM
Common Clients.
The -delifx option functions
when there is only one IDS
installation on the computer.
The default is 9089.
Page 61

|
|||
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Table 5-1. ifxdeploy Command Options (continued)
Element Purpose Key Considerations
-extractcmd ″command″ Extracts the snapshot that
you want to deploy or
modify.
-file ″file_name″ Extracts the snapshot from
the ″file_name″ file by using
7-Zip software.
Specify the command and
the file that contains the
snapshot files.
Use this option only if the
target computer has 7-Zip for
Windows or Gzip for UNIX
or Linux.
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
-force Overwrites the existing
instance settings on the target
computer.
-installdrive ″drive″ Note: This option is for
Windows only.
Specifies the drive for the
directory containing data
spaces (typically, this is the
IFMXDATA directory).
-l ″file_path″ Sends status messages to a
text file.
-namedpipe Note: This option is for
Windows only. Sets the
default database server
network protocol to a named
pipe connection.
-p password Specifies the user informix
password used to create the
IDS service.
-relocate path Specifies new parent
directory of chunks in the
deployed instance.
-rootpath ″path″ Indicates the location of the
root dbspace.
-servernum server_number Specifies the server number
of the instance.
The default drive is C:. You
must have enough space for
the IDS installation and
databases.
Indicate the full path and file
name for the log file that you
want to use. If the file does
not exist, it will be created
for you.
If you specify both
-namedpipe and -sqliport,
the deployment utility uses
only one of them.
Specify the password for user
informix on the target
computer. If you specify a
password and the user
informix does not exist on
the target computer, the user
will be created and will have
the specified password.
You can specify a single new
parent directory or map
multiple separate chunk
paths to different locations.
In addition, you can
substitute offsets of the old
paths with new values if you
are indicating multiple new
parent directories.
default path:drive:\
ifmxdata\server_name\
rootdbs_dat.000
The number must be an
integer from 0 to 255. The
default is 0.
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-7
Page 62

|
|||
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Table 5-1. ifxdeploy Command Options (continued)
Element Purpose Key Considerations
-silent Directs the utility to run in
silent mode.
-sqliport port Specifies the SQLHOSTS
service port for the server
instance.
-system Note: This option is for
Windows only.
When you use this option,
messages do not display on
the screen but are written in
a log file. If you use the
-silent option and -verbose
option together, you must
also include the -l argument.
The default port is 9088.
If you specify both
-namedpipe and -sqliport,
the deployment utility uses
only one of them.
|
|
|
||
|
-uninstall installation_path Removes a snapshot that was
|
|
||||
||||
|
||
|
|
-verbose Runs the command in
-y Runs the command without
-6432 Note: This option is for
|
|
|
|
Creates an IDS service that
logs in to the operating
system as system user.
originally deployed by the
deployment utility.
verbose mode.
prompting for confirmation.
Windows only.
Redirects registry access to
32-bit registry view.
Use this option if you are
deploying a 32-bit IDS
instance on a 64-bit
computer.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Usage
Before you use this command, create a snapshot and copy it to the computer
where you want to deploy the snapshot. See “Creating a Snapshot for
Deployment” on page 5-4 for more information.
Run this command, with options, on the computer where you want to deploy the
snapshot. When you specify a value for a parameter, if the value contains a space,
enclose the value in double quotation marks. You must run the command either as
an Administrator user or as the root user.
+
+
+
+
|
|
If you placed the snapshot in a compressed file, you must extract it. Use the
-extractcmd option to decompress a snapshot with a customized command or
script. Alternatively, if you have 7-zip software for Windows or Gzip for UNIX or
Linux installed, you can use the -file option to decompress the snapshot.
Use the -force parameter to deploy a snapshot to multiple computers and override
the database server instance settings on the target computer.
5-8 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 63

|
Examples of Deployment Utility Usage on Windows
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deploying a IDS Instance in Silent Mode
In this example, the user informix is created on the target server and has the
password mypassw0rd. The command will run in silent mode, without prompting
for confirmation. The snapshot is decompressed from the my_archive.zip file by
7-zip software if it is installed on the operating system.
ifxdeploy.exe -p mypassw0rd -y -silent -file my_archive.zip
Deploying a IDS Instance as Local System User Where You Specify an
Extraction Method
In this example, the snapshot is extracted from the C:\my_archive.tar file on the
target computer:
ifxdeploy.exe -system -extractcmd "tar -xf C:\my_archive.tar c:\informix"
The extract command is enclosed in double quotation marks because it contains
spaces.
Creating a New Server Instance
In this example, the SQLHOSTS port number is 9090, the server number for the
instance is 2, and a full path is specified for the log file.
ifxdeploy.exe -silent -y -sqliport 9090 -servernum 2 -l C:\my_log.txt
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Creating an Instance as Local System User with DRDA Enabled
In this example, the SQLHOSTS port is 9090, the DRDA port is 9096, and the
command will run in verbose mode. The snapshot used here is not in a
compressed file format, so neither the -file option nor the -extractcmd option is
needed.
ifxdeploy.exe -system -y -sqliport 9090 -drdaport 9096 -verbose
Dynamic Relocation of Chunks to Single Parent Directory
In this example, the chunks are relocated to a single parent directory and indicate
location of the root dbspace:
ifxdeploy -rootpath D:\IFMX\ex1\rootdbs.001 -relocate D:\IFMX\ex2
Chunk Relocation to Multiple Paths
In this example, the location of the root dbspace has been specified with the
ROOTPATH configuration parameter, so the command does not need to be run
with the -rootpath option. Each mapping between the old path and the new path
is separated by a semicolon.
ifxdeploy -relocate C:\IFMXDATA=D:\IFMXDATA;C:\IFMXLOGSPACE=E:\IFMXLOGSPACE
Chunk Relocation to Multiple Paths with New Offsets
|
|
|
|
|
In this example, the location of the root dbspace has been specified with the
ROOTPATH configuration parameter, so the command does not need to be run
with the -rootpath option. The mapping of the old paths and the new paths
includes offset values (in kilobytes), which are indicated after the commas.
ifxdeploy -relocate C:\IFMXDATA,0=D:\IFMXDATA,4;C:\IFMXDATAB,3=D:\IFMXDATAB,5
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-9
Page 64

|
ifxdeploy.conf File: The Deployment Utility Configuration File
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
The ifxdeploy.conf file is a text-file template in which you can configure an
instance snapshot prior to deploying it with the ifxdeploy command.
Purpose
The ifxdeploy.conf file is in $INFORMIXDIR/etc/ on Linux and
%INFORMIXDIR%\etc on Windows.
By using the ifxdeploy.conf file, you can run the deployment utility with fewer
command-line options to configure the instance. You can save and reuse the file to
deploy instances to other locations. The file supports the same functionality as the
ifxdeploy command options, but also additional functionality that is useful for
embedding IDS when you are deploying a snapshot in multiple locations that
require minimal or no modification in instance setup. See “Rapid IDS
Embeddability with the Deployment Utility” on page 5-2 for a description of the
major embeddability features of the ifxdeploy.conf file.
Parameters
The ifxdeploy.conf file is value pair based. If there is a parameter with a default
value that you want to change, provide the value in an uncommented line.
Attention: The values of parameters that are set on the ifxdeploy command line
overwrite the values of the same parameters in the ifxdeploy.conf file.
+
+
+
+
++++
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
The following table explains the parameters in the same order that they appear in
the configuration template file.
Table 5-2. ifxdeploy.conf File Parameters
Example of Value Setting
Parameter Description
INFORMIXSERVER Primary database server
name. Must be set either
here or as environment
variable before deployment
(no default value is
provided).
PROTOCOL1 Primary network protocol.
This is equivalent to the
PROTOCOL field of the
SQLHOSTS registry.
PORT1 Number of the primary
listening port. No value
required for the onipcnmp
protocol. The range of
permissible values is from 1
to 32767.
SERVERNUM The server number.
Corresponds to the
SERVERNUM configuration
parameter. The range of
permissible values is from 0
to 255.
(Uncommented Line)
INFORMIXSERVER deploy3
PROTOCOL1 olscoctcp
PORT1 9094
SERVERNUM 100
5-10 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 65

+
++++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
Table 5-2. ifxdeploy.conf File Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
INFORMIXSQLHOSTS
BEGIN ALIAS...END
ALIAS
INFORMIXDIR Path for the deployed
ONCONFIG The onconfigfile name. If
SNAPSHOT Note: This parameter can
Pointer to remote computer
containing SQLHOSTS
registry settings that the
deployed instance is to use.
Specifies new database
server aliases and related
SQLHOSTS connectivity
settings for the deployed
instance. The optional
OPTIONS line sets a
SQLHOSTS parameter
value. In the example,
b=32767 sets buffers.
instance. Must be set here or
as environment variable (no
default path is provided).
none is specified here and
no ONCONFIG
environment variable is set,
a new file is created from
onconfig.std.
only be used if you are
deploying an instance from
a snapshot compressed as a
.tgz file on UNIX or Linux
or a .zip file on Windows.
Example of Value Setting
(Uncommented Line)
BEGIN ALIAS
SERVERNAME alias1
PROTOCOL drsoctcp
PORT 9091
OPTIONS b=32767
END ALIAS
C:\tmp\informix
onconfig.sample
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
RELOCATE Set chunk paths for the
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Indicates the location of a
supported, compressed
archive type containing the
snapshot. This parameter is
equivalent to the -file
command-line option.
deployed instance. You can
indicate a parent directory
for all chunk path names or
map them individually to
separate parent directories.
You can also deploy the
chunks with specific offset
values. Offset values are in
kilobytes.
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-11
Example 1: Relocate all chunk paths to
one directory:
C:\example1
Example 2: Select individual chunk
paths and specify the directories where
the paths are relocated:
C:\ex2=C:\ex3; C:\ex4=C:\ex5
Example 3: Change multiple chunk
paths and offsets:
C:\ex6,10=C:\ex7,100;
C:\ex8,20=C:\ex9,200
Page 66

+
++++
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
++++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Table 5-2. ifxdeploy.conf File Parameters (continued)
Parameter Description
INFORMIXPASSWORD Password for user informix
on the target computer. Sets
password to what you enter
as a value if no user
informix exists on the
computer.
SYSTEM
Note: This parameter
is for Windows only.
LOGFILE Sets the full path name for
LOGLEVEL Sets amount of information
SILENT Sets whether or not the
FORCE Overwrites existing
INSTALLDRIVE
Note: This parameter is
for Windows only.
ROOTPATH Sets the location of the root
WIN6432
Note: This parameter
is for Windows only.
BEGIN ONCONFIG...
END ONCONFIG
Sets whether the deployed
instance will log on to
Windows as local system
account. The default value is
0 (IDS logs on as user
informix).
the log file of the
deployment utility’s errors
and messages.
to write to log. Refer to the
ifxdeploy.conf file for
permissible values.
utility displays console
output while it is running.
environment variable and
onconfig file settings of the
target computer.
Specifies the directory in
which the deployed
instance’s dbspaces will be
created on Windows.
dbspace.
Set this to 1 if installing
32-bit IBM Informix
Dynamic Server on 64-bit
Windows.
Specify values for any
configuration file
parameters. Enter each
parameter and value exactly
as they would be entered in
the onconfig file.
Example of Value Setting
(Uncommented Line)
INFORMIXPASSWORD password
SYSTEM 1 (this directs instance to
log on as local system account but
user informix is created) SYSTEM 2
(this deploys instance without
creation of user informix)
LOGFILE c:\my_log.txt
LOGLEVEL 5
SILENT 1 (no console output)
SILENT 0 (displays console output)
FORCE 0 (Does not overwrite)
FORCE 1 (Overwrites existing
settings)
INSTALLDRIVE C
default path:drive:\ifmxdata\
server_name\rootdbs_dat.000
WIN6432 1
BEGIN ONCONFIG
LOCKS 10000
END ONCONFIG
+
+
+
+
+
Can be used to overwrite
specific onconfig file
parameter values or instead
of providing an onconfig
file.
+
5-12 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 67

+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
ifxdeploy.conf File Template
The following shows the contents of the ifxdeploy.conf file.
# Licensed Material - Property Of IBM
#
# "Restricted Materials of IBM"
#
# IBM Informix Dynamic Server
# Copyright IBM Corporation 2009 All rights reserved.
#
# Title: ifxdeploy.conf
# Description: Configuration file for the IDS Deployment Utility
#
# Uncomment any values that you want to change from the default values.
#
# Note that any parameters set on the command line will override these values.
+
+
+
+
+
# Primary server values
# - These values define the primary server name, protocol, and port.
# - Use the BEGIN ALIAS section to define additional sever names and
# protocols (such as DRDA).
+
+
+
+
# INFORMIXSERVER - Set the primary server name, or set it as an environment
# variable or command line parameter.
#INFORMIXSERVER
+
+
+
+
+
# PROTOCOL1 - Set the primary protocol (the sqlhosts NETTYPE field) for the
# primary server.
# - Values: onsoctcp, onipcnmp
#PROTOCOL1 onsoctcp
+
+
+
+
+
# PORT1 - Set the primary listening port for the primary server (not needed for
# onipcnmp).
# - Range: 1-32767
#PORT1 9088
+
+
+
+
+
# SERVERNUM - Set the primary server number (the value for the SERVERNUM
# configuration parameter).
# - Range: 0-255
#SERVERNUM
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# INFORMIXSQLHOSTS - Set a value for the INFORMIXSQLHOSTS environment
# variable. On UNIX this value specifies the sqlhosts file
# (default is $INFORMIXDIR/etc/sqlhosts). On Windows, this
# value is generally not used but can be used to point to a
# remote machine (for example, \\machinename) whose registry
# contains SQLHOSTS information.
#INFORMIXSQLHOSTS
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# Define additional server names and listeners with the BEGIN/END ALIAS
# statements.
# Each ALIAS results in a new SQLHOSTS entry and a new value for the
# DBSERVERALIASES configuration parameter in the onconfig file.
# For example:
#BEGIN ALIAS
#SERVERNAME alias1
#PROTOCOL drsoctcp
#PORT 9091
#OPTIONS # optional SQLHOSTS parameters (for example, b=32767 to set buffers)
#END ALIAS
+
+
+
+
# INFORMIXDIR - Set the location of the installation directory.
# - Alternatively, set the INFORMIXDIR environment variable.
#INFORMIXDIR
+
+
+
# ONCONFIG - Set the onconfig file.
# - If not specified and the ONCONFIG environment variable is not set,
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-13
Page 68

+
+
# a new onconfig file is created based on the onconfig.std file.
#ONCONFIG
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# SNAPSHOT - Set the location of the compressed archive. This parameter is the
# equivalent to the -file command line option. The archive must be a
# .tgz file on UNIX or Linux and a .zip file on Windows. Only set
# this value if you are supplying a compressed snapshot of an IDS
# instance.
#SNAPSHOT
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# RELOCATE - Set to the new location of dbspace chunks.
# Use one of these methods or a combination of methods 2 and 3:
# - Method 1: new_path (relocates all chunks to the specified path)
# - Method 2: old_path=new_path (relocates only chunks
# created in the old path to the new path)
# - Method 3: old_path,old_offset=new_path,new_offset;
# (relocates chunks and moves offsets)
# You can specify multiple paths with methods 2 and 3 by
# separating old and new path sets with a semicolon (;).
#
#RELOCATE
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# Authentication values
# INFORMIXPASSWORD - Set the password for the informix user.
# - If not set, can be supplied on command line or
# interactively.
# - Not required if the SYSTEM parameter is set to 2.
#INFORMIXPASSWORD
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# SYSTEM - Windows only - Set the IDS service to log on as the Windows
# Local System user.
# - Values:
# 0 - IDS service logs on as the informix user.
# 1 - IDS service logs on as the Local System user but creates the
# informix user.
# 2 - Do not create the informix user.
#SYSTEM 0
+
+
+
+
# Logging parameters
# LOGFILE - Set the file for Deployment Utility errors and messages.
#LOGFILE
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# LOGLEVEL - Set the amount of information to write to the log.
#
# 1 - FATAL - only print fatal errors.
# 3 - WARNING - print warnings and fatal errors.
# 5 - INFO - print informational messages, warnings, and fatal errors.
# 10 - DEBUG - print debugging information and all other messages.
#
#LOGLEVEL 5
+
+
+
+
+
# SILENT - Set to 1 to prevent console output sot that errors and
# messages only appear in the log file.
# - Range: 0,1
#SILENT 1
+
+
+
+
# FORCE - Set to 1 to overwrite existing settings
# - Range: 0,1
#FORCE 0
+
+
+
+
+
# INSTALLDRIVE - Windows only - Set to the drive where data spaces will be
# created
# - Range: C-Z
#INSTALLDRIVE C
+
+
+
# ROOTPATH - Set to the path for the root dbspace
# - Default is \ifmxdata\$INFORMIXSERVER\rootdbs_dat.000
5-14 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 69

+
#ROOTPATH
+
+
+
+
+
# WIN6432 - Windows only - Set this to 1 if installing a 32-bit version of IDS
# on a 64-bit Windows operating system.
# - Range: 0,1
#WIN6432 0
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
# Onconfig customization
# Use the BEGIN ONCONFIG and END ONCONFIG statements to add or override
# configuration parameters values in the onconfig file.
# Use instead of providing an onconfig file.
# Example:
#BEGIN ONCONFIG
#LOCKS 10000
#END ONCONFIG
+
Removing a Snapshot with the Deployment Utility
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Use the deployment utility to remove a snapshot that was originally deployed by
the deployment utility. In addition, you can use this utility to remove user
informix and the Informix-Admin group from the operating system.
You must have Windows administrator privileges to remove the snapshot or
remove the user and group objects.
You must have the IDSFILES.txt file in the etc subdirectory of the installation
path.
To remove a snapshot:
Run the ifxdeploy command with the uninstallation options on the computer
where the snapshot is deployed. See “ifxdeploy Command: The Deployment
Utility” on page 5-5 for details about the command syntax.
The following command is an example of how to use the deployment utility to
remove a snapshot and to display runtime status messages:
ifxdeploy.exe -u C:\tmp\informix -verbose
The following is an example of how to uninstall a snapshot and to remove user
informix and the administrative group:
ifxdeploy.exe -u C:\tmp\informix -verbose -delifx
+
Chapter 5. Deploying IDS with the Deployment Utility 5-15
Page 70

5-16 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 71

Appendix. Accessibility
IBM strives to provide products with usable access for everyone, regardless of age
or ability.
Accessibility features for IBM Informix Dynamic Server
Accessibility features help a user who has a physical disability, such as restricted
mobility or limited vision, to use information technology products successfully.
Accessibility Features
The following list includes the major accessibility features in IBM Informix
Dynamic Server. These features support:
v Keyboard-only operation.
v Interfaces that are commonly used by screen readers.
v The attachment of alternative input and output devices.
Tip: The IBM Informix Dynamic Server Information Center and its related
publications are accessibility-enabled for the IBM Home Page Reader. You can
operate all features using the keyboard instead of the mouse.
Keyboard Navigation
This product uses standard Microsoft Windows navigation keys.
Related Accessibility Information
IBM is committed to making our documentation accessible to persons with
disabilities. Our publications are available in HTML format so that they can be
accessed with assistive technology such as screen reader software.
You can view the publications for IBM Informix 4GL in Adobe
Format (PDF) using the Adobe Acrobat Reader.
IBM and Accessibility
See the IBM Accessibility Center at http://www.ibm.com/able for more information
about the commitment that IBM has to accessibility.
Dotted Decimal Syntax Diagrams
The syntax diagrams in our publications are available in dotted decimal format,
which is an accessible format that is available only if you are using a screen reader.
In dotted decimal format, each syntax element is written on a separate line. If two
or more syntax elements are always present together (or always absent together),
the elements can appear on the same line, because they can be considered as a
single compound syntax element.
Each line starts with a dotted decimal number; for example, 3 or 3.1 or 3.1.1.To
hear these numbers correctly, make sure that your screen reader is set to read
punctuation. All syntax elements that have the same dotted decimal number (for
example, all syntax elements that have the number 3.1) are mutually exclusive
®
Portable Document
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 A-1
Page 72

alternatives. If you hear the lines 3.1 USERID and 3.1 SYSTEMID, your syntax can
include either USERID or SYSTEMID, but not both.
The dotted decimal numbering level denotes the level of nesting. For example, if a
syntax element with dotted decimal number 3 is followed by a series of syntax
elements with dotted decimal number 3.1, all the syntax elements numbered 3.1
are subordinate to the syntax element numbered 3.
Certain words and symbols are used next to the dotted decimal numbers to add
information about the syntax elements. Occasionally, these words and symbols
might occur at the beginning of the element itself. For ease of identification, if the
word or symbol is a part of the syntax element, the word or symbol is preceded by
the backslash (\) character. The * symbol can be used next to a dotted decimal
number to indicate that the syntax element repeats. For example, syntax element
*FILE with dotted decimal number 3 is read as 3 \* FILE. Format 3* FILE
indicates that syntax element FILE repeats. Format 3* \* FILE indicates that
syntax element * FILE repeats.
Characters such as commas, which are used to separate a string of syntax
elements, are shown in the syntax just before the items they separate. These
characters can appear on the same line as each item, or on a separate line with the
same dotted decimal number as the relevant items. The line can also show another
symbol that provides information about the syntax elements. For example, the lines
5.1*, 5.1 LASTRUN, and 5.1 DELETE mean that if you use more than one of the
LASTRUN and DELETE syntax elements, the elements must be separated by a comma.
If no separator is given, assume that you use a blank to separate each syntax
element.
If a syntax element is preceded by the % symbol, that element is defined elsewhere.
The string following the % symbol is the name of a syntax fragment rather than a
literal. For example, the line 2.1 %OP1 means that you should refer to a separate
syntax fragment OP1.
The following words and symbols are used next to the dotted decimal numbers:
? Specifies an optional syntax element. A dotted decimal number followed
by the ? symbol indicates that all the syntax elements with a
corresponding dotted decimal number, and any subordinate syntax
elements, are optional. If there is only one syntax element with a dotted
decimal number, the ? symbol is displayed on the same line as the syntax
element (for example, 5? NOTIFY). If there is more than one syntax element
with a dotted decimal number, the ? symbol is displayed on a line by
itself, followed by the syntax elements that are optional. For example, if
you hear the lines 5?, 5 NOTIFY, and 5 UPDATE, you know that syntax
elements NOTIFY and UPDATE are optional; that is, you can choose one or
none of them. The ? symbol is equivalent to a bypass line in a railroad
diagram.
! Specifies a default syntax element. A dotted decimal number followed by
the ! symbol and a syntax element indicates that the syntax element is the
default option for all syntax elements that share the same dotted decimal
number. Only one of the syntax elements that share the same dotted
decimal number can specify a ! symbol. For example, if you hear the lines
2? FILE, 2.1! (KEEP), and 2.1 (DELETE), you know that (KEEP) is the
default option for the FILE keyword. In this example, if you include the
FILE keyword but do not specify an option, default option KEEP is applied.
A default option also applies to the next higher dotted decimal number. In
A-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 73

this example, if the FILE keyword is omitted, default FILE(KEEP) is used.
However, if you hear the lines 2? FILE, 2.1, 2.1.1! (KEEP), and 2.1.1
(DELETE), the default option KEEP only applies to the next higher dotted
decimal number, 2.1 (which does not have an associated keyword), and
does not apply to 2? FILE. Nothing is used if the keyword FILE is omitted.
* Specifies a syntax element that can be repeated zero or more times. A
dotted decimal number followed by the * symbol indicates that this syntax
element can be used zero or more times; that is, it is optional and can be
repeated. For example, if you hear the line 5.1* data-area, you know that
you can include more than one data area or you can include none. If you
hear the lines 3*, 3 HOST, and 3 STATE, you know that you can include
HOST, STATE, both together, or nothing.
Notes:
1. If a dotted decimal number has an asterisk (*) next to it and there is
only one item with that dotted decimal number, you can repeat that
same item more than once.
2. If a dotted decimal number has an asterisk next to it and several items
have that dotted decimal number, you can use more than one item
from the list, but you cannot use the items more than once each. In the
previous example, you could write HOST STATE, but you could not write
HOST HOST.
3. The * symbol is equivalent to a loop-back line in a railroad syntax
diagram.
+ Specifies a syntax element that must be included one or more times. A
dotted decimal number followed by the + symbol indicates that this syntax
element must be included one or more times. For example, if you hear the
line 6.1+ data-area, you must include at least one data area. If you hear
the lines 2+, 2 HOST, and 2 STATE, you know that you must include HOST,
STATE, or both. As for the * symbol, you can only repeat a particular item if
it is the only item with that dotted decimal number. The + symbol, like the
* symbol, is equivalent to a loop-back line in a railroad syntax diagram.
Appendix. Accessibility A-3
Page 74

A-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 75

Notices
This information was developed for products and services offered in the U.S.A.
IBM may not offer the products, services, or features discussed in this document in
other countries. Consult your local IBM representative for information on the
products and services currently available in your area. Any reference to an IBM
product, program, or service is not intended to state or imply that only that IBM
product, program, or service may be used. Any functionally equivalent product,
program, or service that does not infringe any IBM intellectual property right may
be used instead. However, it is the user’s responsibility to evaluate and verify the
operation of any non-IBM product, program, or service.
IBM may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter
described in this document. The furnishing of this document does not grant you
any license to these patents. You can send license inquiries, in writing, to:
IBM Director of Licensing
IBM Corporation
North Castle Drive
Armonk, NY 10504-1785
U.S.A.
For license inquiries regarding double-byte (DBCS) information, contact the IBM
Intellectual Property Department in your country or send inquiries, in writing, to:
Intellectual Property Licensing
Legal and Intellectual Property Law
IBM Japan Ltd.
1623-14, Shimotsuruma, Yamato-shi
Kanagawa 242-8502 Japan
The following paragraph does not apply to the United Kingdom or any other
country where such provisions are inconsistent with local law: INTERNATIONAL
BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION ″AS IS″
WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or implied warranties in
certain transactions, therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This information could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
Changes are periodically made to the information herein; these changes will be
incorporated in new editions of the publication. IBM may make improvements
and/or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this
publication at any time without notice.
Any references in this information to non-IBM Web sites are provided for
convenience only and do not in any manner serve as an endorsement of those Web
sites. The materials at those Web sites are not part of the materials for this IBM
product and use of those Web sites is at your own risk.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009 B-1
Page 76

IBM may use or distribute any of the information you supply in any way it
believes appropriate without incurring any obligation to you.
Licensees of this program who wish to have information about it for the purpose
of enabling: (i) the exchange of information between independently created
programs and other programs (including this one) and (ii) the mutual use of the
information which has been exchanged, should contact:
IBM Corporation
J46A/G4
555 Bailey Avenue
San Jose, CA 95141-1003
U.S.A.
Such information may be available, subject to appropriate terms and conditions,
including in some cases, payment of a fee.
The licensed program described in this document and all licensed material
available for it are provided by IBM under terms of the IBM Customer Agreement,
IBM International Program License Agreement or any equivalent agreement
between us.
Any performance data contained herein was determined in a controlled
environment. Therefore, the results obtained in other operating environments may
vary significantly. Some measurements may have been made on development-level
systems and there is no guarantee that these measurements will be the same on
generally available systems. Furthermore, some measurements may have been
estimated through extrapolation. Actual results may vary. Users of this document
should verify the applicable data for their specific environment.
Information concerning non-IBM products was obtained from the suppliers of
those products, their published announcements or other publicly available sources.
IBM has not tested those products and cannot confirm the accuracy of
performance, compatibility or any other claims related to non-IBM products.
Questions on the capabilities of non-IBM products should be addressed to the
suppliers of those products.
All statements regarding IBM’s future direction or intent are subject to change or
withdrawal without notice, and represent goals and objectives only.
All IBM prices shown are IBM’s suggested retail prices, are current and are subject
to change without notice. Dealer prices may vary.
This information is for planning purposes only. The information herein is subject to
change before the products described become available.
This information contains examples of data and reports used in daily business
operations. To illustrate them as completely as possible, the examples include the
names of individuals, companies, brands, and products. All of these names are
fictitious and any similarity to the names and addresses used by an actual business
enterprise is entirely coincidental.
COPYRIGHT LICENSE:
This information contains sample application programs in source language, which
illustrate programming techniques on various operating platforms. You may copy,
B-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 77

Trademarks
modify, and distribute these sample programs in any form without payment to
IBM, for the purposes of developing, using, marketing or distributing application
programs conforming to the application programming interface for the operating
platform for which the sample programs are written. These examples have not
been thoroughly tested under all conditions. IBM, therefore, cannot guarantee or
imply reliability, serviceability, or function of these programs. The sample
programs are provided ″AS IS″, without warranty of any kind. IBM shall not be
liable for any damages arising out of your use of the sample programs.
Each copy or any portion of these sample programs or any derivative work, must
include a copyright notice as follows:
© (your company name) (year). Portions of this code are derived from IBM Corp.
Sample Programs.
© Copyright IBM Corp. _enter the year or years_. All rights reserved.
If you are viewing this information softcopy, the photographs and color
illustrations may not appear.
IBM, the IBM logo, and ibm.com®are trademarks or registered trademarks of
International Business Machines Corp., registered in many jurisdictions worldwide.
Other product and service names might be trademarks of IBM or other companies.
A current list of IBM trademarks is available on the Web at “Copyright and
trademark information” at http://www.ibm.com/legal/copytrade.shtml.
®
Adobe, the Adobe logo, and PostScript
are either registered trademarks or
trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States, and/or other
countries.
®
, Itanium®, and Pentium®are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel
Intel
Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Java and all Java-based trademarks are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the
United States, other countries, or both.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States, other
countries, or both.
®
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT
are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States, other countries, or both.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other
countries.
Other company, product, or service names may be trademarks or service marks of
others.
Notices B-3
Page 78

B-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 79

Index
Special characters
-relocate option 5-2
%INFORMIXDIR%
environment variable 1-9
A
Accessibility A-1
dotted decimal format of syntax diagrams A-1
keyboard A-1
shortcut keys A-1
syntax diagrams, reading in a screen reader A-1
Accessing database server program group 3-1
Accounts
informix user 3-1
Administrative
groups
adding members to 1-1
privileges, Server Instance Manager 2-13
Administrative Utilities 1-4
Administrator
privileges, incorrect 2-15
Administrators group
adding members 1-1
incorrect privileges 2-15
requirements for installing 1-1
Advanced privileges, granted to informix user 3-1
B
Backup and Restore 1-4
Backups
and multiple residency 2-13
configuring storage manager 3-1
base server 1-3, 1-4
BladeManager 1-4
BLOB data 3-6
C
chunks
location 5-2
relocating parent directories 5-2
CLOB data 3-6
clone 5-1
Cluster
installation
on multiple nodes 1-3, 2-3, 2-9
Cluster Administrator 2-9
ClusterIT, installing in a Microsoft cluster environment 1-3,
2-3, 2-9
Command line
deploying IDS snapshot 5-5
initializing database server 3-3
starting database server 3-3
stopping database server 3-4
compliance with standards x
components 1-3, 1-4
configuration file
and deployment utility 5-2
creating during installation 1-8, 2-3
for demonstration database server 1-6
response file 1-8
Configuration parameters
DBSERVERNAME 3-5
MIRRORPATH 3-5
SBSPACENAME 3-6
SERVERNUM 3-4
Control Panel
initializing database server 3-3
starting database server 3-3
stopping database server 3-4
Conversion and Reversion Support
Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA) 1-4
XML Publishing 1-4
Creating
database server instances 2-13
custom installation 1-3, 2-3
D
Data-Loading Utilities 1-4
database server
aliases 5-2
Database server name
description of 3-5
error message 2-15
fixing invalid 2-15
limitations 2-15
specifying 3-6
Database server number
description of 3-4
specifying 3-6
Database servers
creating new instances 2-13
fresh installation 4-2
initializing 3-6
installing
multiple instances 1-9
on multiple nodes 2-9
program group
accessing 3-1
reinstalling 4-2
silent uninstallation 4-2
stopping 3-4
uninstalling 4-2
DataBlade modules 1-4
DBSERVERNAME configuration parameter 3-5
dbspace
specifying 3-5
dbspaces 3-5
initializing 5-2
root 3-6
Default sbspace
definition of 3-6
specifying 3-6
demonstration database server 1-6
Demos 1-4
deploying to multiple computers 5-1
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1996, 2009
X-1
Page 80

deployment utility 5-1
removing a snapshot 5-15
syntax and options 5-5
using with ifxdeploy.conf file 5-10
Disabilities, visual
reading syntax diagrams A-1
Disability A-1
Disk space, installation requirements 1-1
Dotted decimal format of syntax diagrams A-1
DRDA (Distributed Relational Database Architecture) 1-3, 2-3
E
embeddability
database server 5-2
Enterprise Replication 1-4
Environment variable
%INFORMIXDIR% 1-9
Environment variables
INFORMIXSQLHOSTS 3-6
Error log 2-15
Error messages 2-15
installation 2-15
F
features 1-3, 1-4
modifying 4-1
removing 4-1
repairing 4-1
features installed with IDS 1-4
First-time installation
INFORMIXDIR directory 1-9
fix the installation 3-2
Fresh installation
database server 4-2
G
Global Language Support (GLS) 1-4, 3-1
GLS (Global Language Support) 1-4
Group names 1-8
I
IDS extensions 1-4
ifxdeploy command
syntax and usage 5-5
ifxdeploy.conf file 5-10
Incorrect privileges error message 2-15
industry standards x
information center 3-2
Informix Storage Manager (ISM) 3-1
informix user 1-10
advanced privileges 3-1
creation of 3-1
Informix-Admin account
creation of 3-1
Informix-Admin group 1-8
updating members 3-6
using Server Instance Manager 2-13
INFORMIXDIR directory
first-time installation 1-9
multiple installation 1-9
upgrade 1-9
INFORMIXSQLHOSTS
environment variable 3-6
Initializing database server 3-3, 3-6
installation 2-1
of selective features 1-4
prerequisites 1-1
Installation
custom 1-9
custom with GUI 2-3
domain 1-10
error messages 2-15
first-time 1-9
local 1-10
problems, troubleshooting 2-15
typical 1-9
typical with GUI 2-2
installation number 1-2
Installations
specialized 2-9
installing
multiple copies on 1 computer 1-2
Installing
database server
custom with GUI 2-3
multiple instances 1-9
on multiple nodes 2-9
typical with GUI 2-2
Instance Configuration Wizard 1-3, 1-6, 1-8, 2-3
Instance Manager utility 1-6
instmgr.exe 1-6
instnum option 1-2
Insufficient virtual memory error message 2-15
Invalid database server name 2-15
L
Large objects (LOBs), smart 3-6
Limitations, database server name 2-15
local system user
installing product as 1-3, 2-3
M
Memory requirements, and multiple residency 2-13
Memory, virtual 2-15
Message log, for multiple residency 2-13
Migrating 1-10
Mirror location 3-5
root dbspace 3-6
Mirroring, and multiple residency 2-13
MIRRORPATH configuration parameter 3-5
modify installation 3-2
Modifying
Dynamic Server 4-1
modifying a copy of Dynamic Server 4-1
modifying installed features 4-1
multiple copies on a computer 1-2
Multiple installations
INFORMIXDIR directory 1-9
using silent installation 2-8
Multiple nodes, installing on 2-9
Multiple nodes, installing with ClusterIT utility 2-9
Multiple residency 2-13
and backups 2-13
and mirroring 2-13
and multiple binaries, warning 2-13
X-2 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 81

Multiple residency (continued)
memory requirements 2-13
message log for 2-13
ONCONFIG file 2-13
planning for 2-13
storage-space requirements 2-13
tape drive 2-13
return codes 2-8
Role separation 1-8
Root dbspace
disk space requirements 1-1
primary and mirror storage locations 3-6
specifying name 3-6
N
Network protocol
TCP/IP 3-5
O
ON-Bar utility
configuring storage manager 3-1
onconfig file 1-6
and deployment utility 5-2
ONCONFIG file, and multiple residency 2-13
onmode utility 3-4
P
Page size
default sbspace 3-6
error message 2-15
Paging file, installation requirements 1-1
Parameters
DBSERVERNAME 3-5
MIRRORPATH 3-5
SBSPACENAME 3-6
SERVERNUM 3-4
Port numbers
defined 3-5
specifying 3-6
Post-Installation tasks 3-1
Primary storage location, root dbspace 3-6
Privileges
administrator 2-15
advanced 3-1
local 2-13
Server Instance Manager 2-13
Problems, installation 2-15
program group 3-2
Program, database server group 3-1
R
RAM, installation requirements 1-1
reinstall the installation 3-2
Reinstalling
database server 4-2
INFORMIXDIR directory 1-9
release notes 3-2
remove features or products 3-2
removing a copy of Dynamic Server 4-1
removing installed features 4-1
repair the installation 3-2
repairing a copy of Dynamic Server 4-1
repairing installed features 4-1
response codes 2-8
response file 1-3, 2-5, 2-6, 2-8
Restore
configuring storage manager 3-1
S
sbpage, size 3-6
SBSPACENAME configuration parameter 3-6
sbspaces
default
specifying location 3-6
specifying name 3-6
specifying storage location 3-6
defined 3-6
size 3-6
Screen reader
reading syntax diagrams A-1
server
modifying 4-1
removing a copy 4-1
repairing 4-1
Server Instance Manager 3-2
command-line options 2-14
DRDA (Distributed Relational Database Architecture) 2-14
Informix-Admin Group 2-13
privileges 2-13
starting 2-13
Server name 3-6
Server number 3-6
SERVERNUM configuration parameter 3-4
Service name
defined 3-5
specifying 3-6
Shared server
specifying 3-6
Shortcut keys
keyboard A-1
shortcut menus 3-2
silent installation 1-3, 2-5, 2-6
definition of 2-5
response codes 2-8
response file 2-6, 2-8
server.ini file 2-5, 2-6
Size
default sbspace 3-6
sbpage 3-6
Smart blob drive 3-5
Smart large objects 3-6
snapshot 5-1
creating for deployment 5-4
deploying 5-4
removing 5-15
Specialized installations 2-9
Specifying
database server name 3-6
database server number 3-6
default sbspace 3-6
root dbspace name 3-6
service name 3-6
sqlhosts registry
port entry 3-5
servicename entry 3-5
shared server definition computer 3-6
standards x
Index
X-3
Page 82

Start menu 3-2
Starting
database server automatically 3-3
starts utility 3-3
Storage locations, specifying 3-6
Storage-space requirements, and multiple residency 2-13
Syntax diagrams
reading in a screen reader A-1
T
Tape drives, for multiple residency 2-13
TCP/IP
port number 3-5
service name 3-5
specifying port number 3-6
specifying service name 3-6
Troubleshooting, installation problems 2-15
typical installation 1-3, 2-2
U
Uninstalling 4-1
database server 4-2
Updating Informix-Admin group 3-6
Upgrading 1-10
INFORMIXDIR directory 1-9
User accounts
informix
creating 3-1
User informix 1-10
utilities 1-4
Utilities
onmode 3-4
starts 3-3
V
Virtual memory, insufficient 2-15
Visual disabilities
reading syntax diagrams A-1
W
Windows Administrators group 1-1
Windows file system, installation requirements 1-1
wizard
see installation application, GUI mode 1-3
X-4 IBM Informix Dynamic Server Installation Guide for Windows
Page 83

Page 84

Printed in USA
GC23-7753-05
 Loading...
Loading...