Page 1

Installation/User’s Guide
Agilent 4986B LanProbe
Page 2

Consumer Warranty Statement
Consumer Warranty Statement
AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES, INC. LIMITED WARRANTY STATEMENT
AGILENT PRODUCT DURATION OF LIMITED WARRANTY
LanProbe 1 year
Agilent warrants to you, the end-user customer, that Agilent hardware, accessories
and supplies will b e fre e from defect s in materi als a nd workman ship a fter the d ate
of purchase, for the period specified above. If Agilent receives notice of such
defects during the warranty period, Agilent will, at its option, either repair or
replace products which prove to be defective. Replacement products may be
either new or like-new.
Agilent war rants to you that Agilent soft ware will not fail to execute its
programming instructions after the date of purchase, for the period specified
above, due to defects in material and workmanship when properly installed and
used. If Agilent receives notice of such defects during the warranty period,
Agilent will replace software media which does not execute its programming
instructions due to such defects.
Agilent does not warrant that the operation of Agilent products will be
uninterrupted or error free. If Agilent is unable, within a reasonable time, to repair
or replace any produc t to a condi tion a s warra nted, y ou will be ent itled t o a re fund
of the purchase price upon prompt return of the product.
Agilent products may contain remanufactured parts equivalent to new in
performance or may have been subject to incidental use.
Warranty does not apply to defects resulting from (a) improper or inadequate
maintenance or calibration, (b) software, interfacing, parts or supplies not
supplied by Agilent, (c) unauthorized modification or misuse, (d) operation
outside of the published environmental specifications for the product, or (e)
improper site preparation or maintenance.
ii
Page 3

Consumer Warranty Statement
AGILENT MAKES NO OTHER EXPRESS WARRANTY OR CONDITION
WHETHER WRITTEN OR ORAL. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL
LAW, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF
MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTORY QUALITY, OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE IS LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE
EXPRESS WARRANTY SET FORTH ABOVE. Some countries, states or
provinces do not allow limitations on the duration of an implied warranty, so the
above limitation or exclusion might not apply to you. This warranty gives you
specific legal rights an d you might also have other rig hts th at vary fr om country t o
country, state to state, or province to province.
TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE REMEDIES IN THIS
WARRANTY STATEMENT ARE YOUR SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE
REMEDIES. EXCEPT AS INDICATED ABOVE, IN NO EVENT WILL
AGILENT OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR LOSS OF DATA OR FOR
DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL (INCLUDING LOST
PROFIT OR DATA), OR OTHER DAMAGE, WHETHER BASED IN
CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE. Some countries, States or provinces do
not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so
the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to you.
FOR CONSUMER TRANSACTIONS IN AUSTRALIA AND NEW
ZEALAND: THE WARRANTY TERMS CONTAINED IN THIS STA TEMENT,
EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT LAWFULLY PERMITTED, DO NOT EXCLUDE,
RESTRICT OR MODIFY AND ARE IN ADDITION TO THE MANDATORY
ST ATUTORY RIGHTS APPLICABLE TO THE SALE OF THIS PRODUCT TO
YOU.
iii
Page 4

Operating Restrictions
The following warnings and operating information are shown in French followed
by the English translation.
MISE ENGARDE
MISE ENGARDE
Restrictions d'utilisation
L'utilisateur se doit d'observer les mesures de précaution
énumérées ci-dessous pour tou tes les ph ases d 'u tili sati on ,
de service et de réparation de cet appareil. Le fait de ne
pas s'y conformer équivaut à ne pas respecter les mises en
gardes spécifique s contenu es da ns ce manu el et cons titue
une violation des normes de sécurité relatives à la
conception, la fabrication et l'utilisation prévue de cet
appareil. La société Agilent Technologies, Inc. n'assume
aucune responsabilité envers un client qui manquerait de
se conformer à ces exigences.
Mise à la t erre
Afin de minimiser les risques de choc électrique, le
chÀssis et le cabinet de l'apparei l doivent être mis à la
terre. L'appareil est équipé d'un cordon d'alimentation
muni d'une fiche hom oloqu é e à trois lames, com patib le
c.a. La prise murale et la prise femelle de la rallonge
électrique doivent respecter les normes de sécurité de la
«Commision électrotechnique internationale» (IEC).
Cet appareil répond aux normes
de la «Classe de sécurité I» et
est muni d'un fil de mise à la
terre pour votre protection.
Pour prévenir les risques de
choc électrique, la broche de
mise à la terre du cordon
d'alimentation ne doit pas être
désactivée.
WARNING
WARNING
Operating Restrictions
The following general safety precatuions must be observed
during all phases of oper ation, service, and re pair of this
instrument. Failure to comply with these precautions with
specific warnings in this manual violate safety standards of
design, manufacture, an d intended use of this instru ment.
Grounding
To minimize shock hazard, the instrument chassis and
cabinet must be connected to an electrical ground. The
instrument is equipped with a three-conductor AC power
cable compatible with an approved three-contact electrical
outlet. The power jack and mating plug of th e power cord
must meet International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
safety standards.
This product is a Safety Class I
instrument with a protective earth
terminal.
For protection f rom electric shock
hazard, power cord ground must
not be defeated.
iv
Page 5

Environnement
Ne faites pas fonctionner cet appareil en présence de gaz
inflammables ou de vapeurs dangereuses. L'utilisation de
n'importe quel appareil électrique dans ces conditions
constitue un risque élevé pour votre sécurité.
Service et ajustement
Des «tensions dangereuses» résident dans cet appareil. Par
conséquent, le service et l'ajustement doivent être effectués
uniquement par une personne qualifiée.
Ne remplacez pas de composantes lorsque le cordon
d'alimentation est sous tension. Il pourrait y avoir présence
de «tensions dangereuses» même lorsque l'appare il est
déconnecté.
Environment
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of flammable
gases or fumes. Operation of any electrical instrument in
such an environment constitutes a definite safety hazard.
Service and Adjustment
Dangerous voltages exist within this instrument. Service
and adjustment of this instrumen t is to be perfor med only by
trained service personnel.
Do not replace components with the power cable connected.
Dangerous voltages may be present even when the power
cable is disconnected.
Ne faites pas de service interne ou d'ajustement sauf en
présence d'une autre personne, capable de prodiguer les
premiers soins et de pratiquer la réanimation.
Service non aut orisé
L'installation de pièces étrangères, ou toute modification
apportée à l'appareil sans le consentement de Agilent
Technologies, Inc. est formellement interdit. Le fait de
procéder à de tels modifications sans autorisation pourrait
entraîner l'annulation de la garantie de l'appareil ou de tout
contrat de service.
Pour un service et des réparations autori sées, retournez
l'appareil à un point de vente et service Agilent
Technologies, Inc..
Do not perform internal servicing or adjustment unless
another person, c apable of rendering first aid and
resuscitation is present.
Unauthorized Service
The installation of substitute parts or the installation of any
instrument modification not authorized by Agilent
Technologies, Inc. is specifically forbidden. The
performance of such unauthori zed service can negate the
instrument warranty or any maintenance agreements.
Return the instrument to a Agilent Technologies, Inc. Sales
and Service Office for authorized service and repair.
v
Page 6

Notice
Notice
© Copyright Agilent
All Rights Reserved
Reproduction, adapta tion, or tran slation without prior written permis sion is
prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Agilent makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material,
including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and
fitness for a particular purpose.
herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the
furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Agilent a ssumes no responsibility for the use or reliabili ty of its software on
equipment that is not furnished by Agilent .
Agilent shall not be liable for errors contained
This document contains pro prietary in formation that is protected by c opyright. All
rights are reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or
translated to another language without the prior written consent of Agilent
Technologies, Inc.
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
NetMetrix Division
5070 Centennial Boulevard
Colorado Springs, Colorado 80919-2497
vi
Page 7

Safety Information
Safety Information
Before you use thi s instru ment, be sure to pa y speci al att ention to the “S afety” an d
“Warning” topics in this Manual. Failure to comply with the precautions or with
specific warnings in this book violates safety standards of design, manufacture,
and intended use of this instrument. Agilent assumes no liability for the
customer’s failure to comply with these requirements.
Electric Shock Hazard.
Do not remove the system covers. To avoid electric
shock, use only the supplied power cords and connect only to properly grounded
(3-pin) wall outlets.
Explosion Hazard.
Fire Hazard.
Do not operate in the presence of flammable gases.
For continued protection against fire hazard replace only with fuse
of same type and rating.
Indoor Use.
Cleaning.
solution of soap and water.
This instrument is designed for indoor use.
To clean the instrument, use a damp cloth moistened with a mild
Do not
use harsh chemicals.
Do not
let water get into
the instrument.
Product Damage.
the product shows visible damage,
fails to perform,
has been stored in unfavorable conditions, or
has been subject to severe transport stresses.
Do not use this product when:
Make the product inoperative and secure it against any unintended operation.
Contact yo ur nearest Agilent Sales office for assistance.
Defects and Abnormal Stresses.
Whenever this inst rument has be en damaged or
wet, make the product inoperative and secure it against any unintended operation.
vii
Page 8

Warning Symbols Used in This Book
Warning Symbols Used in This Book
Instruction book symbol: the product will be marked with this symbol when it is
necessary for the user to refer to the instruction book in order to protect against
damage.
Indicates potential for electrical shock.
WARNING
CAUTION
An operating procedure, prac tice, etc. which, if not correctly foll owed could result
in personal injury or loss of life.
An operating procedure, practice, etc. which, if not strictly observed, could result
in damage to, or destruction of, equipment or software.
viii
Page 9

Conventions Used in this Book
g
Conventions Used in this Book
NOTE
An operating procedure, prac tice, or informat ion of impor tance , is separ ated fr om
normal text as shown in this NOTE.
Terminology and conventions in this manual are handled with the following
methods:
z
Keys on the keyboard such as
(page down) or F1 (function key #1)
P
Dn
are printed in the characters you see here.
z
Text that you should type is printed in characters such as:
Filename.ext
z
In some cases, you must press two keys simultaneously. This is represented
as
CTRL + Q
.
ix
Page 10

Trademarks
Trademarks
Agilent is a registered trademark and OpenView is a trademark of
Hewlett-Packard Company.
Microsoft, LAN Manager, MS-DOS, and Windows are either registered
trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or
other countries.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed
exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Hayes is a registered trademark of Hayes MicroComputer Products, Inc.
IBM and Token-Ring are trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation.
Sun and Solaris are registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
SPARC is a registered trademark of SPARC International, Inc. Products bearing
the SPARC trademark are based on an architecture developed by Sun
Microsystems, Inc.
Novell and NetWare are registered trademarks of Novell Inc.
x
Page 11
Printing History
Printing History
New editions are complete revisions of this book. Update packages may contain
new or additional material and be released between editions. See the date of the
current edition on the back cover of this book.
First Edition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . December 1996 04986-99502
Second Edition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . September 1997 04986-99503
Third Edition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . January 1998 04986-99505
Fourth Edition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . June 1998 04986-99505
Additional Help
You can obtain additional assistance in the U.S. by calling U.S. Response Center
at 888 699 7280, or Internationally by calling your local Agilent Sales Office.
xi
Page 12

xii
Page 13

Contents
Consumer Warranty Statement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ii
Operating Restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iv
Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .vi
Safety Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Warning Symbols Used in This Book . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .viii
Conventions Used in this Book . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ix
Trademarks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Printing History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xi
Additional Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xi
1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Installation and Configuration Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Local Terminal Configuration and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Installation and Bootp Server Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
LanProbe Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Supported MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Management Stations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Access Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
CONFIG Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Included Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Optional Accessories. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2 Local Terminal Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Probe Configuration Using a Local Terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Using a Local Terminal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Modify/View Configuration Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Modify/View Security Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Modify/View Interface Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Display Interface Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Modify/View Serial Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
xiii
Page 14

3 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Selecting a Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Installing the Probe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Rack or Cabinet Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Connecting the Probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Connecting to the Network (In-Band) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Connecting to 10Base-T Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Connecting Out-of-Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Direct Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Modem Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Data Switch Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Starting the Probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Verifying the Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Troubleshooting the Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4 Bootp Server Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Probe Configuration Using a Bootp Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Starting the Bootp Server on an HP or Sun System . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Bootp Server Setup on a PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Using Microsoft LAN Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Using Novell NetWare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Starting the PC Bootp Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Configuring the Bootptab File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Example Bootptab File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
5 LanProbe Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Restarting the Probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Warm Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Cycling Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Selecting the Warm Start Menu Item. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Cold Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Pressing the CONFIG Button Twice. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Selecting the Cold Start Menu Item. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
xiv
Page 15

6 Download New Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Downloading Firmware using an HP-UX Workstation and a Terminal 80
Install New Download Firmware on an HP-UX Workstation . . . . 80
Download Firmware to LanProbe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Downloading Firmware using a Networked PC and a Terminal . . . . 84
Setup TFTP Server for Downloading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Download Firmware to LanProbe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Xmodem Download of Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
A Cables and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Serial Port Interface Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Cable Connector Pin-Outs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
LanProbe’s RS-232 Port Pin-Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
LanProbe RS-232 Modem Cable Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
9-pin Terminal/PC Cable Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
10Base-T Network Connector Pin-Out. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
B LanProbe Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Probe Memory Allocation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
RMON-2 Protocol Directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Index
Agilent Technologies, Inc. Offices
xv
Page 16

xvi
Page 17

Figures
Figure 1-1: LanProbe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Figure 1-2: LanProbe System Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 1-3: Front Panel LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 2-4: LanProbe’s Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 2-5: LanProbe’s Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 2-6: Modify/View Configuration Values Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 2-7: Modify/View Security Values Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 2-8: Modify/View Interface Values Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 2-9: Display Interface Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 2-10: Modify/View Serial Port Settings Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 3-11: Installing LanProbe in the Rack Support Shelf . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 3-12: LanProbe Installed in the Rack Support Shelf . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 3-13: Ethernet LanProbe Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 3-14: Connecting LanProbe to 10Base-T Networks . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 3-15: LanProbe Direct Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 3-16: LanProbe Modem Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 3-17: LanProbe Data Switch Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 5-18: LanProbe’s Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Figure 6-19: LanProbe Main Menu (HP-UX Workstation) . . . . . . . . . 82
Figure 6-20: LanProbe TFTP Download Menu (HP-UX Workstation) 82
Figure 6-21: LanProbe Main Menu (Networked PC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Figure 6-22: LanProbe TFTP Download Menu (Networked PC) . . . . 86
Figure 6-23: LanProbe Main Menu (XMODEM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 6-24: LanProbe XMODEM Download Menu (Networked PC) 89
xvii
Page 18

xviii
Page 19

Tables
Table 1-1: Private MIB Access Security Privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 4-2: Minimum Requirements for a Bootp Server . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 4-3: Bootp Server bootptab Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 4-4: Bootptab File Tags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 4-5: Bootp Process Verification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 5-6: Probe Data and Parameters Reset by Warm or Cold Start . . 72
Table A-1: Serial Port Interface Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Table A-2: LanProbe RS-232 Port Pin-Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Table A-3: LanProbe to Modem Cable Min. Pin-Out (9-Pin to 9-Pin) 95
Table A-4: LanProbe to Modem Cable Min. Pin-Out (25-Pin to 9-Pin) 96
Table A-5: LanProbe to 9-Pin Terminal Cable Min. Pin-Out . . . . . . 96
Table A-6: 10Base-T Network Connector Pin-Outs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Table B-7: LanProbe Memory Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Table B-8: RMON-2 Protocol Directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
xix
Page 20

xx
Page 21

1
Introduction
Page 22

Introduction
Introduction
This chapter introduce s the Agil ent 498 6B Etherne t LanPro be (shown i n Figu re 11 on page 2), including its installation and configuration options.
You can use your LanProbe with NetMetrix/UX (for HP-UX and Solaris) The
term “NetMetrix” is used in this manual to refer to Agilen t NetMetrix/UX.
The following sections are included in this chapter:
z
“Installation and Configuration Overview” on page 4
z
“LanProbe Overview” on page 5
The Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe is a Motorola 68040-based, SNMPmanaged segment monitor fo r distrib uted Ethernet net works. Its netwo rk interface
(port) consists of a single RJ-45 connector.
Figure 1-1: LanProbe
2
Page 23

Introduction
The Ethernet LanProbe has 16 MB of memory (optionally 32 MB), and uses
FLASH EPROM. Future upgrades to La nProbe’s firmware are easily do wnloaded
over the LAN to multiple probes simultaneously. You can also download
firmware using LanProbe’s serial port.
LanProbe maintains a variety of statisti cal measurements on network
performance, continuously keeping track of traffic levels, errors, and other
important trends. Alarm thresholds can be set on any of these parameters,
immediately alerting the network manager or initiating a packet trace to capture
the details of the event for later analysis. Traffic and error levels are also
monitored per node for each station on the segment.
Private MIB extensions give LanProbe additional capabilities beyond RMON.
Multiple SNMP trap addresses, or groups of addresses, can be defined for event
notification. The probe maps MAC addresses to IP addresses for node
identification, and provides duplicate IP address detection. A real time utilization
variable has been added, which provides the ability to alarm on instantaneous
peaks of network load . An additional Out-of -Ban d connection to the pr obe ca n be
established using Serial Link Internet Protocol (SLIP), either directly, using a
modem, or by using a data switch.
You can configure the LanProbe to perform Echo Test Monitoring (tests to verify
communications) of network nodes from your network management station.
LanProbe allows the netw or k manag er t o select one or several no des t o pe rf orm a
one-time test or specify an interval for periodic testing. You can view the results
of the Echo Test Monitoring from your NetMetrix management console. This can
be very useful for monitoring critical nodes to verify connectivity. This test can
also be performed from several points on the network (using several LanProbes)
to verify connectiv ity from each point . When a node becomes unr eachable an aler t
can be sent from LanProbe to your management station. To provide testing of a
large range of nodes, Echo Test Monitoring supports ICMP, IEEE 802.2, and
IEEE 802.3 for Novell IPX. This extension is supported by the NetMetrix
software.
3
Page 24
Introduction
Installation and Configuration Overview
Installation and Configuration Overview
To quickly install and configure your LanProbe, it is important for you to
understand the available configuration and installation options. Configuration
consists of setting the LanProbe parameters (IP address, for example). Installation
consists of physically installing the probe and connecting it to the network.
You will reference different chapters of this Installation/User’s Guide depending
on which of the following installation and configuration options you select:
z
“Local Terminal Configuration and Installation” below
z
“Installation and Bootp Server Configuration” below
Local Terminal Configuration and Installation
This method of installation and configuration requires that you configure the
probe first and then install the probe. These procedures are detailed in Chapter 2
“Local Terminal Configuration” and Chapter 3 “Installation”.
Installation and Bootp Server Configuration
This method of installation and configuration requires that you install the probe
first and then configure the probe. These procedures are detailed in Chapter 3
“Installation” and in Chapter 4 “Bootp Server Configuration”.
4
Page 25
LanProbe Overview
Introduction
LanProbe Overview
This section provides some general information on the Agilent 4986B Ethernet
LanProbe.
The LanProbe is a non-intrusive SNMP agent that monitors all packets and
network performance. This includes current and historical traffic statistics and
snapshots of selected packets.
The following topics are covered:
z
“System Overview” below
z
“Supported MIBs” on page 7
z
“Management Stations” on page 8
z
“Access Security” on page 8
z
“Status LEDs” on page 10
z
“CONFIG Button” on page 11
z
“Included Parts” on page 11
System Overview
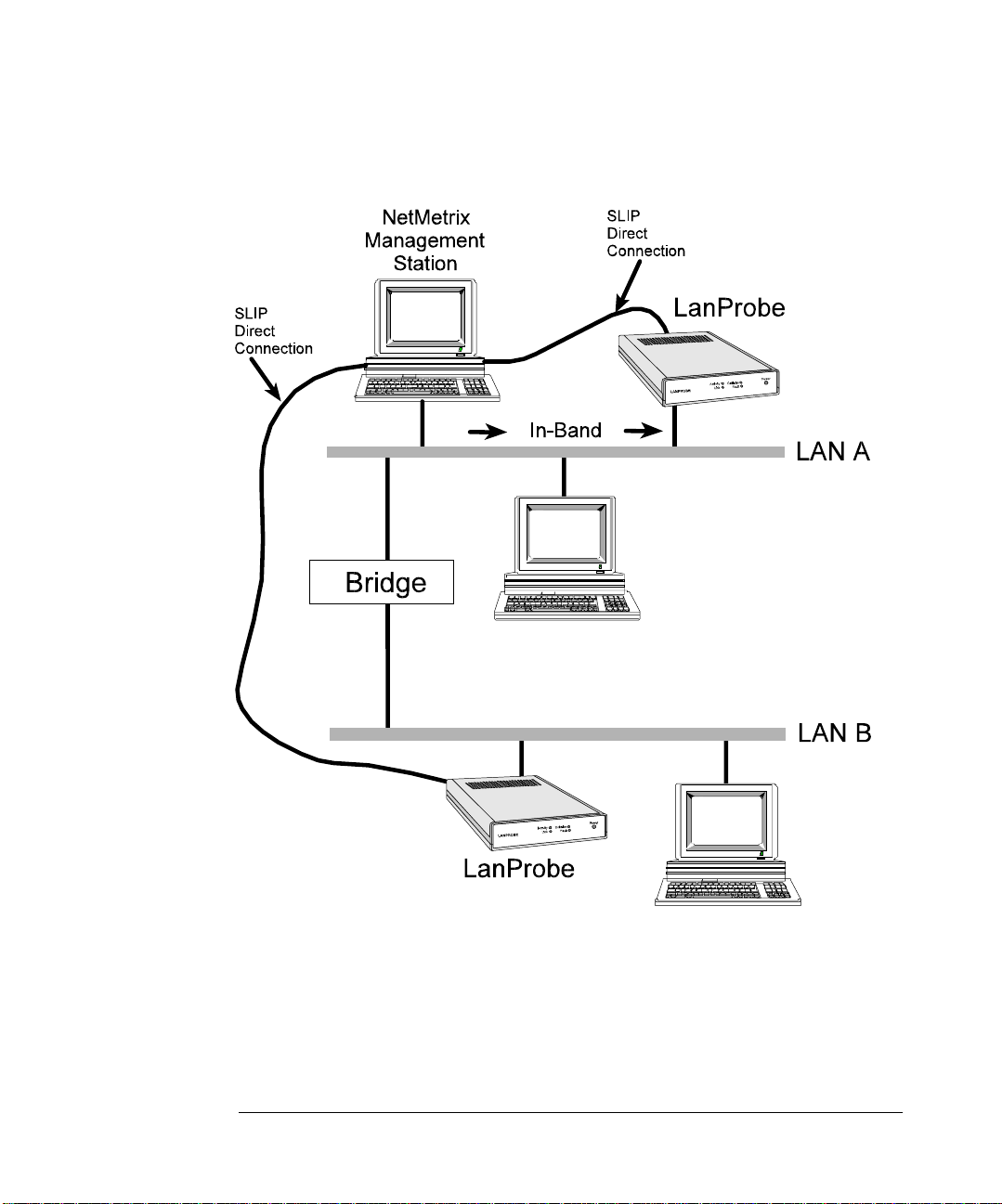
A typical LanProbe distributed monitoring system consists of the following:
z
One or more LanProbes
z
One or more NetMetrix management stations, using NetMetrix
Figure 1-2 on page 6 shows a LanProbe system example.
5
Page 26
Introduction
LanProbe Overview
Figure 1-2: LanProbe System Example
6
Page 27

LanProbe Overview
Introduction
Supported MIBs
LanProbe uses the SNMP, RMON-1, and RMON-2 MIB standards together with
private MIB extensions to provide the following features:
Segment Statistics
z
History
z
Alarms
z
Host Table
z
Host Top N
z
Traffic Matrix
z
Filters
z
Packet Capture
z
Events
z
Log
z
Tra p
z
Echo Test
z
Protocol Directory
z
Protocol Distribution
z
Address Map
z
Network Layer Host Table
z
Network Layer Traffic Matrix
z
Application Layer Host Table
z
Application Layer Traffic Matrix
z
User History
z
Probe Configuration
z
RMON Conformance
z
The LanProbe implements groups 1 through 9 of RFC 1757 and groups 11
through 20 of RFC 2021. Refer to RFC 1757 for more informati on on the Remo te
Network Monitoring Manage ment Inf ormati on Base Pr otocol I dentif iers (RMON1 MIB), to RFC 2021 for information on the RMON-2 MIB, and to RFC 2074 for
information on Protocol Identifiers. LanProbe also supports MIB-II.
7
Page 28

Introduction
LanProbe Overview
LanProbe also contains the Agilent Private MIB which allows for configuration
and administration of the probe. It provides enhanced authentication features,
specification of trap destinations, remote download of new firmware revisions,
serial line control, and other features. The Agilent Private MIB is available
electronically with NetMetrix.
You can refer to Table B-8 on page 104 for specific information on your probe’s
protocol directory.
Management Stations
Management stations gather network data collected by Agilent LanProbes. They
present this information in easy-to-use and easy-to-understand text and graphic
formats. You can use a management station to communicate with your LanProbe
after it has been installed and configured.
The LanProbe communicates with the NetMetrix software running on your
management station. NetMetrix management applications allow you to review
and reconfigure LanProbe parameters (such as IP address, trap destinations,
filters, and packet captures), to manage the information collected by LanProbe
(including statistics, historical studies, alarms, packet size distribution, and
captured packet traces), and to monitor local or remote networks (by gathering
network statistics from Agilent LanProbe agents as network monitors).
Refer to your NetMetrix docu mentation fo r more information.
Access Security
The LanProbe configuration menu allows network administrators to disable
standard RMON functions which c ould be consi dered a se curity risk . The securit y
menu allows network administrators to disable the RMON-1 packet capture
capabilities of LanProbe to prevent network users from viewing network traffic.
TFTP firmware downloads can be disabled to prevent users from downloading
earlier versions of the LanProbe firmware which did not support these new
security features. For more information, refer to “Modify/View Security Values”
on page 20.
8
Page 29
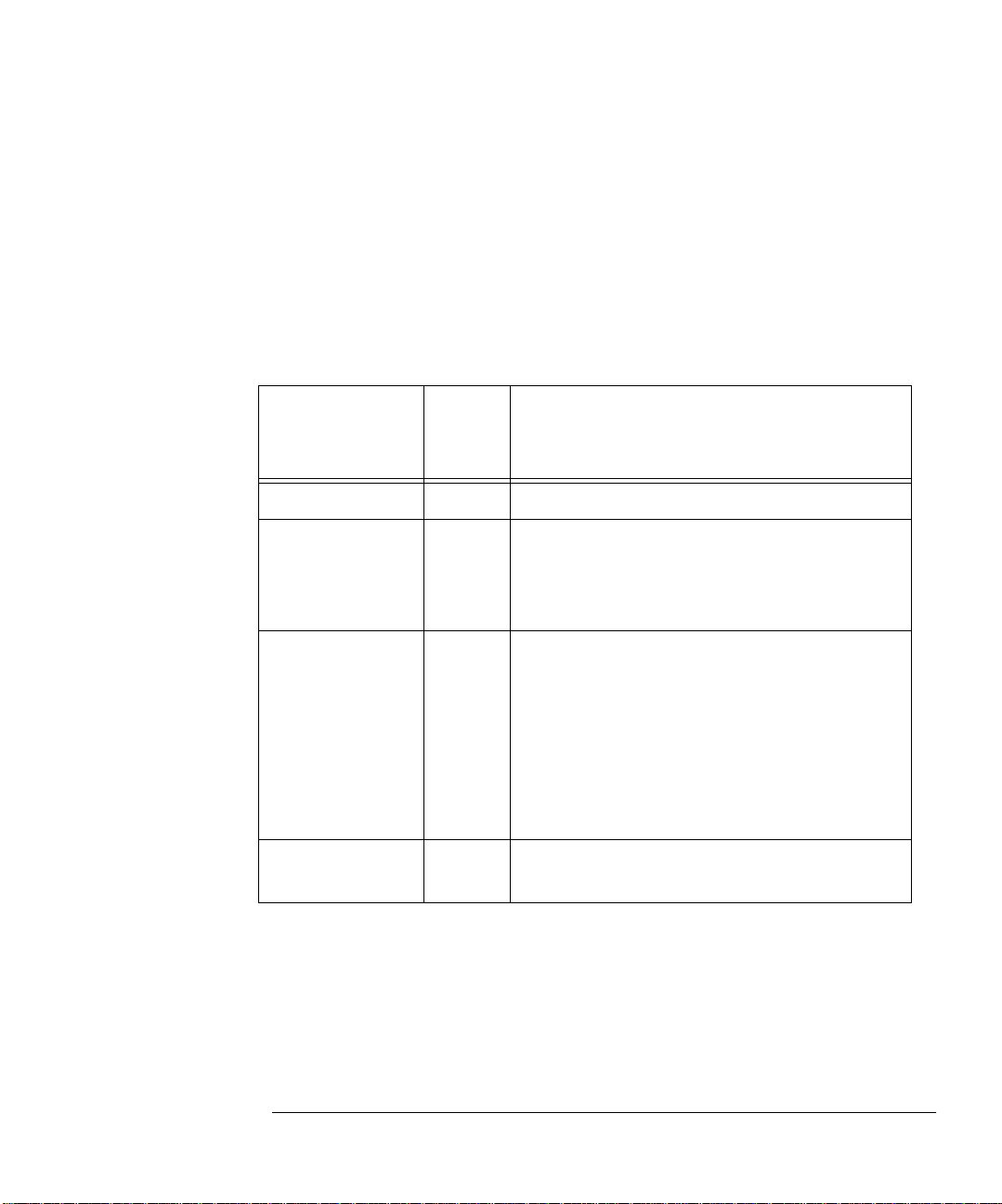
LanProbe Overview
Introduction
The LanProbe private MIB uses a four-level access control scheme. An access
level is assigned for each communi ty stri ng to be used with Lan Probe. The acc ess
level is an integer value between one and four, with increasing degrees of
authorization granted for higher authorization numbers. Each higher level is
granted the rights of all lower levels in addition to the specific privileges of that
level. Table 1-1 shows specific access privileges by level.
Table 1-1: Private MIB Access Security Privileges
Default
Community
Name Level Permissions
public 1 Read access to MIB-II objects.
rmon 2 Read access to MIB-II, RMON* MIB, and
LanProbe MIB objects, excluding the objects
in the accessControl group and in the
captureBuffer Table.
rmon_admin 3 Write access to RMON* MIB and LanProbe
MIB objects, excluding the objects in the
probeAdmin, interface, and accessControl
groups.
Read access to MIB-II, RMON* MIB
(including the captureBuffer Table), and
LanProbe MIB objects, exc lu ding those in the
accessControl group.
Agilent_admin 4 Read and write access to all MIB-II, RMON*
MIB, and LanProbe MIB objects.
* RMON implies RMON-1 and RMON-2.
9
Page 30

Introduction
LanProbe Overview
Status LEDs
The status LEDs are visible on the front of LanProbe. Figure 1-3 shows the
orientation of the LEDs on the front of LanProbe.
~ Line On
power.
Link.
This green LED is turned on when LanProbe is attached to an 10Base-T
network.
Collision.
network.
Activity
network or transmitted by LanProbe. When flashing, the frequency shows the
amount of traffic. During periods of steady traffic, it may appear to stay on solid.
Fault
. This yellow LED is turned on when LanProbe needs to be reset, repaired,
or replaced or when new firmware is downloaded. The Fault LED is normally on
during the power-on self-test, but turns off after a successful self-test or when a
cold or warm start is completed. The Fault LED will blink when a collision is
detected on the network.
Power
or
This yellow LED is turned on when LanProbe det ects collisions on the
. This green LED is turned on when data is being received from the
. This green LED is turned on when LanProbe is receiving
10
Page 31

Figure 1-3: Front Panel LEDs
LanProbe Overview
Introduction
CONFIG Button
The CONFIG button is used to configure LanProbe from a terminal or to restart
the probe. The CONFIG button is recessed and located on the back of the probe
near the RS-232C connector. You will need to use a narrow, pointed object (like a
pen) to press the CONFIG button.
To configure LanProbe using a local terminal (or PC emulating a terminal),
connect a terminal to LanProbe using a null modem cable and push the CONFIG
button to display La nProbe’s Main Menu. This operation i s describe d in Chapte r 2
“Local Terminal Configuration”.
You can restart the probe (with a warm start or cold start) using the CONFIG
button. These functions are described in Chapter 5 “LanProbe Operation”.
Included Parts
The following items are included with your :Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe:
11
Page 32

Introduction
LanProbe Overview
Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe
z
Bootp Software 3 1/2-inch Disk, for PCs
z
Power Module (0950-2546)
z
Power Cord, one of the following:
z
Australian (8120-1369)
Danish (8120-2957)
European (8120-1689)
Japanese (8120-4753)
South Africa (8120-4600)
Swiss (8120-2104)
United Kingdom (8120-1351)
United States/Canada 125 V (8120-1378)
United States/Canada 250 V (8120-0698)
Optional Accessories
The following Agilent LanProbe accessories can be purchased from Agilent:
Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe Installation/User’s Guide—this manual
z
(04986-99505)
Null Modem Cable—9 pin to 25 pin (24542G)
z
Null Modem Cable—9 pin to 9 pin (24542U)
z
Rack Mount Kit (J2886-94001)
z
Female-Male Power Cable (8120-1575)
z
12
Page 33

2
Local Terminal Configuration
Page 34

Local Terminal Configuration
Local Terminal Configuration
This chapter describes how to use a local terminal to configure your Agilent
4986B Ethernet LanProbe so that it can communicate over a network. If you plan
to use the Bootp server method of configuration, then skip this chapter and
continue with Chapter 3 “Installation”.
The following sections are covered in this chapter:
z
“Probe Configuration Using a Local Terminal” on page 15
z
“Using a Local Terminal” on page 16
14
Page 35

Probe Configuration Using a Local Terminal
Local Terminal Configuration
Probe Configuration Using a Local Terminal
Some initial configuration information must be entered into LanProbe before it
can communi cate over the network interface or serial port. This initial
configuration for network communication consists of the following parameters:
z
IP Address (for each Telemetry and Monitor/Transmit port)
z
Default Gateway IP Address (if requ ired)
z
Subnet Mask (if required)
z
Autodiscovery Echo Interval
LanProbe uses the following configuration parameters to display time and date
information in the user interface only. LanProbe uses a separate internal clock to
time-stamp dat a collected from the network.
z
Date
z
Time
z
Time Zone
The initial configuration for communication over the serial port consists of the
following parameters:
z
Serial Port IP Address
z
Serial Port Subnet Mask (if required)
z
Serial Port Speed
z
Serial Port Mode
z
Modem Control String (if required)
15
Page 36

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Using a Local Terminal
You can configure LanProbe by connecting a terminal directly to LanProbe and
using the LanProbe’s Main Menu. Refer to the following sections for additional
information on configuring LanProbe after you access the LanProbe’s Main
Menu:
z
“Modify/View Configuration Values” on page 18
z
“Modify/View Security Values” on page 20
z
“Modify/View Interface Values” on page 21
z
“Display Interface Summary” on page 23
z
“Modify/View Serial Port Settings” on page 24
NOTE
The LanProbe is not available to the network when you are in it’s configuration
menus.
Use the following procedure to access LanProbe’s Main Menu:
1. Connect a terminal or a personal computer (PC) emulating a terminal to the
LanProbe’s RS-232 connector using a null modem cable. For more
information on cables, refer to Appendix A “Cables and Connectors”.
2. Configure the terminal for 8 bits/character, 1 stop bit, no parity, Xon/Xoff
handshaking, and a baud rate of 9600.
3. Connect the Agilent Power Module (0950-2546) to the LanProbe and to a
power source (either 100-120/VAC or 220-240/VAC). The LanProbe does
not have a power switch, but is turned on by connecting power.
4. Start the configuration by quickly pressing the CONFIG button on the back
of LanProbe one time only. After about 10 seconds, LanProbe displays its
Main Menu on the terminal. Figure 2-4 on page 17 shows LanProbe’s Main
Menu. If the Main Menu is not displayed, verify that the previous steps in
this procedure have been performed correctly.
16
Page 37

Main Menu - Revision
1. Modify/View configuration values ->
2. Modify/View security values ->
3. Modify/View interface values ->
4. Display interface summary
5. TFTP Download new firmware ->
6. XMODEM Download new firmware ->
7. Warm start and Exit
8. Cold start and Exit
Figure 2-4: LanProbe’s Main Menu
Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
NOTE
Item 5 in Figure 2-4 is not displayed if the
menu item is not enabled. Refer to “Modify/View Security Values” on page 20 for
more information on enabling this menu item.
If item 5 (TFTP Download new firmware) is not displayed, the number used to
access items 6, 7, and 8 will be different.
Allow TFTP firmware downloads
Figure 2-5: LanProbe’s Rear Panel
17
Page 38

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
NOTE
The LanProbe CONFIG button is recessed. This requires the use of a narrow,
pointed object (like a pen) to press the CONFIG button.
LanProbe executes a cold start if you press the CONFIG button twice within one
second. If th is happens, wait for the cold start to be comp leted and press the
CONFIG button again to reenter the configuration mode.
A warm start or cold start is completed when the Fault LED goes off. If traffic is
present, the Activity LED flashes to show traffic.
Modify/View Configuration Values
Use the following proced ure to configure items in the Mod ify/V ie w Configuration
Values menu:
1. Press 1 to access the
Modify/View Configuration Values menu is displayed, as shown in Figure
2-6.
Modify/View Configuration Values Menu - Firmware Rev
Modify/View configuration values
menu item. The
Memory configuration x Mbytes
1. Autodiscovery Echo Interval (sec.) 1800
2. Date Wed 05/05/97
3. Time 09:12:00
4. Time zone PST8PDT
S. Save changes and exit
0. Cancel changes and exit
Figure 2-6: Modify/View Configuration Values Menu
2. Select each field requiring configuration (one at a time) by pressing its
corresponding number and then entering the values that are appropriate for
your network.
18
Page 39

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Autodiscovery Press 1 and enter the autodiscovery echo interval, in
Echo Interval seconds, as desired for your pro be (o pti onal). This parameter
sets the time interval for the probe to transmit an
autodiscovery frame, which is used by HP OpenView
NetMetrix to maintain its network map.
The default value is 30 minutes (1800 seconds). A value of
zero results in no transmission of autodiscovery frames.
Date Press 2 and enter the day of the week and then the date in
month/day/year format (mm/d d/y y, through 1999 or
mm/dd/yyyy, starting 2000).
Time Press 3 and enter the time of day in hours, minutes, seconds
(hh:mm:ss) format.
Time Zone Press 4 and enter your time zone in one to 15 characters
(optional).
The Time Zone characters are stored for your convenience
and are used only to time-stamp probe information.
Recommended practice is to use the format of Time Zone,
hours from Greenwich mean time, and then Daylight Saving
Time, such as PST8PDT for Pacific Standard Time (the
default). The probe does not automatically update the Time
field when your local time changes from standard time to
daylight savings and back.
The values you en te r for date and time take effect as soon as you enter the m.
All other parameters do not take effect until you select the Save Changes
and Exit menu item.
3. Press S to save the configuration changes and return to LanProbe’s Main
Menu. If you want to cancel your current changes and return to the
LanProbe’s Main Menu, press 0.
19
Page 40

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
NOTE
The other Main Menu items are explained in other chapters of this manual. The
TFTP Download new firmware and XMODEM Download new firmware
menu item is described in Chapter 6 “Download New Firmware”. The Warm
start and Exit and Cold start and Exit menu items are explained in Chapter 5
“LanProbe Operation”.
Modify/View Security Values
Use the following procedure to configure items in the Modify/View Security
Values menu:
1. If you want to restri ct access t o the probe pr ess 2 to access the Modify /V iew
security v alues menu item, otherwise skip this section. The Modify/View
Security Values menu is displayed, as shown in Figure 2-7.
Modify/View Security Values Menu - Firmware Rev
1. Allow packet capture Yes
2. Allow TFTP firmware downloads Yes
S. Save changes and exit
0. Cancel changes and exit
Figure 2-7: Modify/View Security Values Menu
2. Select each field requiring configuration (one at a time) by pressing its
corresponding number and then entering the values that are appropriate for
your network. See “Access Security” on page 8. for more information on
security.
Allow Packet Press 1 and enter Yes to allow or enter No to not allow
Capture packet capture.
Allow TFTP Press 2 and enter Yes to allow or enter No to not allow
20
Page 41

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Firmware Downloads TFTP firmware downloading.
3. Press S to save the configuration changes and return to LanProbe’s Main
Menu. If you want to cancel your current changes and return to the
LanProbe’s Main Menu, press 0.
Modify/View Interface Values
After you access the Modif y/V ie w Interface Values menu, you mu st first sele ct the
port that you want to configure and then configure that port. For example, the
possible options for the port parameter could be the following:
[1] 1.1/Ethernet
z
[2] 1.2/Serial
z
Use the following procedure to configure items in the Modify/View Interface
Values menu:
1. Press 3 to access the
Modify/View interface v alues
menu item. The
Modify/V i ew Int erface Values men u is di splayed, a s shown i n Figur e 2-8 o n
page 21.
Modify/View Interface Values Menu - Firmware Rev
MAC Address 00 00 C6 XX XX XX
Interface Type Ethernet
1. Port 1.1/Ethernet
2. Port Type Telemetry
3. IP address 0.0.0.0
4. Default gateway IP address 0.0.0.0
5. Subnet mask 255.0.0.0
S. Save changes and exit
0. Cancel changes and exit
Figure 2-8: Modify/View Interface Values Menu
21
Page 42

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
2. Select each field requiring configuration (one at a time) by pressing its
corresponding number and then entering the values that are appropriate for
your network.
Port Press
and enter the port number to be configured. Refer to
1
“Display Interface Summary” on page 23 for interface
summary information. After you enter a port number, the
configuration parameters are shown along with their current
settings for the specified port number. You can then view or
configure the port’s parameters. The following are your port
choices:
[1] 1.1/Ethernet
z
[2] 1.2/Serial
z
Refer to “Modify/View Serial Port Settings” on page24 for
information on configuring the Serial Port settings.
Port Type Press
and select the port type as Telemetry or Serial Port.
2
IP Address Press 3 and enter the IP address for the probe. If the IP
address is 0.0.0.0, LanProbe will transmit Bootp Requests
for configuration information (including IP address) over the
network.
Default Gateway Press 4 and enter the def ault gate way IP a ddress for the prob e
IP Address (optional).
Subnet Mask Press 5 and enter the subnet mask for the probe.
Parameters do not take effect until you select the Save Changes and Exit
menu item.
3. Press S to save the configuration changes and return to LanProbe’s Main
Menu. If you want to cancel your current changes and return to the
LanProbe’s Main Menu, press 0.
22
Page 43

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Display Interface Summary
Use the following procedure to view the Display Interface Summary screen for
your LanProbe. Refer to Figure 2-9 on page 24.
NOTE
1. Press 4, the
Summary item displays the number and type of ea ch interf ace, the port type,
and each port’s IP address.
2. Press Enter to continue.
3. From LanProbe’s Main Menu, press 7 to execute a warm start or press 8 to
execute a cold start. A cold start is required if you change the IP Address,
Default Gateway or Subnet Mask. For either menu choice, LanProbe exits
the Main Menu and restarts normal operations.
A warm start resets all data collected by the probe. A cold start resets all data
collected by the pr obe and also resets an y user-configuration information, such as
history studies, filters, and alarms to their default values. Refer to Chapter 5
“LanProbe Operation” for more information on what is reset by warm and cold
starts.
After the probe restarts (boots), it operates normally using the new
configuration information. The warm start or cold start occurs immediately
and there is no visual indication of when it finishes.
4. If you are performing the initial probe configuration, prepare LanProbe for
installation by disconnecting the power cord. You will not lose your initial
configuration information.
Display Interface Summary
item. The Display Inte rface
23
Page 44

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Display Interface Summary
Interface Port Type IP Address
------------ ---------- -----------
1.1/Ethernet Telemetry 15.6.72.216
1.2/Serial Not Applicable 0.0.0.0
Figure 2-9: Display Interface Summary
Modify/View Serial Port Settings
You can view or modify LanProbe’s serial port settings by en teri ng the Se rial Port
number (port 2) into the Modify/View Interface Values Menu’s Port parameter.
The Serial Po rt configuration parameters are then show n along with their current
settings. Use the following procedure to configure LanProbe’s serial port:
1. Enter the LanProbe’s Serial Port number (port 2) into the Modify/View
Interface Values Menu’s Port parameter as shown in Figure 2-8 on page 21.
24
Page 45

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Modify/View Interface Values Menu - Firmware Rev
Interface Type Serial
1. Port 1.2/Serial
2. Port Type Not Applicable
3. Serial port IP address 0.0.0.0
4. Serial port subnet mask 255.255.252.192
5. Serial port speed 9600
6. Serial port mode Direct
7. Serial port hardware flow control On
8. Modem Init String ^s^M^d1^sATE0Q0V1X4 S0=1...
9. Modem Hangup String ^d2^s+++^d2^sATH0^M^d2
10. Modem Connect Responses /CONNECT/300/CONNECT/1200/...
11. Modem No-Connect Responses /NO CARRIER/BUSY/NO DIALT...
S. Save Changes and Exit
0. Cancel Changes and Exit
Figure 2-10: Modify/View Serial Port Settings Menu
2. Select each field requiring configuration (one at a time) by selecting its
corresponding number as shown in Figure 2-10 and then ente ri ng the values
that are appropriate for your modem’s serial port.
Serial port IP address Press 3 and then ente r the serial port IP address for the
probe. The default Serial Port IP Address is 0.0.0.0.
Serial port Press 4 and then enter the serial port subnet mask for
subnet mask the probe (optional). It is recommended that you
change the serial port subnet mask unless there is a
conflict. The default Serial Port Subnet Mask is
255.255.255.192.
do not
25
Page 46

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Serial port speed Press 5 and then enter a serial port speed (300 to 38,400
baud) for LanProbe’s SNMP connection. The default is
9600 baud. This speed is used only for Out-of-Band
access to LanProbe using SNMP. It does not affect the
serial connection for the local terminal, which is fixed at
9600 baud.
Make sure that the serial port speed is set to less than or
equal to the maximum speed of the modem to be used.
Serial port mode Press 6 and then select the ser ial port mode by pres sing 1
for direct connection (the default) or 2 for modem
connection.
Serial port hardware Press 7 and then select hardware flow control Off by
flow control pressing 1 or hardware flow control On (the default) by
pressing 2.
Modem Init St ring Press 8 to enter the modem initialization string. Only the
first 20 characters of the 256 character maximum will be
displayed in the Modify/View Serial Port Settings menu.
The defaul t is ^s^M^d1^sATEOQOV1X4 S0=1
S2=43^M.
Modem Hangup Press 9 to enter the modem hang-up string. Only the
String first 20 characters of the 256 character maximum will be
displayed in the Modify /View Serial Port Settings menu.
The defaul t is ^d2^s+++^d2^sATHO^M^d2.
Modem Connect Press 10 to enter the modem connect responses. Only
Responses the first 20 characters of the 256 character ma ximum will
be displayed in the Modify/View Serial Port Settings
menu. The default is /CONNECT/300/CONNECT
1200/1200/CONNECT 2400/2400/CONNECT
4800/4800/CONNECT 9600/9600/CONNECT
14400/14400/CONNECT 19200/19200/
CONNECT 38400/38400/.
26
Page 47

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
Modem No-Connect Press 11 to enter the modem no-connect responses.
Responses Only the first 20 characters of the 256 character
maximum will be displayed in the M odify/View Serial
Port Settings menu. The default is /NO CARRIER/
BUSY/NO DIALTONE/NO ANSWER/ERROR/.
3. Press S to save the serial port configuration changes and return to
LanProbe’s Main Menu. If you want to cancel these changes and return to
LanProbe’s Main Menu, press 0.
If you need to configure any other LanProbe parameters, make your selection
from LanProbe’s Main Menu.
27
Page 48

Local Terminal Configuration
Using a Local Terminal
28
Page 49

3
Installation
Page 50

Installation
Installation
This chapter describes how to install the Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe
Installing the Agilent LanProbe consists of the following tasks:
z
“Selecting a Location” on page 31
z
“Installing the Probe” on page 32
z
“Connecting the Probe” on page 37
z
“Starting the Probe” on page 47
z
“Verifying the Installation” on page 48
If you plan to configure the probe from a local ter mina l and have not yet done so,
go to Chapter 2 “Local Terminal Configuration”, and perform the configuration
now.
30
Page 51

Selecting a Location
Installation
Selecting a Location
Select a location for your LanProbe where it will be the most useful. The
LanProbe can only monit or tr affic that is present on the LAN where it i s attached.
Because interconne ct device s (bridges , for ex ample) fil ter tra ffi c, a LanP robe may
need to be attached on each si de of an int erconne ct devi ce fo r complet e colle ction
of network statistics. In this respect, the placement of LanProbe affects the
statistics collected.
Consider the following installation requirements when selecting a location for
your probe:
NOTE
NOTE
The Fault and Activity LEDs on the front of LanProbe will light if any of the
individual port LEDs on the rear panel l igh t. To determine which port has activity
or a fault, you are requ ired to lo ok at the por t LEDs on the ba ck panel. Thi s should
be considered when selecting a location or LanProbe’s orientation in a rack.
z
A flat surface that i s lar ge enough to suppo rt the probe (requires clear ance at
rear and sides for cooling and rear panel access), adequate wall space, or
space in a 19 inch rack or cabinet.
z
A grounded power outlet (either 100-120/VAC or 220-240/VAC).
z
Access to one or more Ethernet connection taps.
z
Access to an RS-232C connection (required only for Out-of-Band
communication).
z
Access to a phone line and a modem within 50 feet (required only for Outof-Band communication using a modem connection).
The MAC address for the probe can be found on the rear labe l. It is a good id ea to
make a note of this address
prior
to installing your LanProbe because some
installation methods make it difficult to see the rear label without removing the
probe.
31
Page 52

Installation
Installing the Probe
Installing the Probe
This section describes how to install your LanProbe. First decide which
installation metho d you are going to use and then in stall the probe usi ng one of the
following methods:
z
“Table Installation” on page 33
z
“Rack or Cabinet Installation” on page 33
CAUTION
not
Do
attach the power cord and Agilent Power Module to LanProbe until the
probe is completely installed. If the power cord and Agilent Power Module are
already attached to LanProbe, remove them now (you will not lose any
configuration parameters). The probe does not have a power switch but becomes
operational when the power is attached.
32
Page 53

Installing the Probe
Installation
Table Installation
Place the probe on a flat surface or table (refer to the requirements listed in
“Selecting a Location” on page 31).
Rack or Cabinet Installation
The LanProbe Rack Mount Kit is optional. The Agilent J2886A Rack Mount Kit
provides a suppo rt shel f and ha rdware for mount ing LanPr obe i n a rac k or ca binet.
The rack mounting kit requires a 3 1/2” slot in your rack and you will need a
POZIDRIV #1 screwdriver. The LanProbe Rack Mount Kit includes the
following:
One Support Shelf
z
One TORX‚T10 wrench
z
Four Clip-on sheet metal nuts
z
Four 0.55” (14 mm) 10-32 POZIDRIV‚ screws
z
Four 0.75” (19 mm) #M4 self-tapping POZIDRIV‚ screws
z
One LanProbe slot Cover
z
Two 0.312” (7.93 mm) #M3 machine screws
z
Four Dual Lock Reclosable Fasteners‚ strips
z
Optional Accessories
Support Rail Kit (12679C)
z
Female-Male Power Cable, 30” (8120-1575)
z
Use the following procedure to install LanProbe in a rack or cabinet (refer to the
requirements as listed in “Selecting a Location” on page 31 for additional
information):
1. Place LanProbe on its top with the front facing you.
2. Remove th e two screws that are in the low er right-hand corner and in the
upper left-hand corner (looking down on LanProbe).
33
Page 54

Installation
Installing the Probe
3. Place LanProbe in the left support shelf slot while aligning the two empty
screw holes (from Step 2 on page 33) with the two screw holes in the
support shelf. The corre ct alignment has the front of LanProbe fac ing out the
front of the support shelf, refer to Figure 3-11 on page 35.
4. Attach LanProbe to the support shelf with two 0.75” #M4 self-tapping
POZIDRIV screws. Refer to Figure 3-11 on page 35 for the correct
alignment.
5. Attach one Dual Lock Reclosable Fasteners‚ strip to the top of LanProbe,
being careful to place it in a location that will both allow for the alignment
of the power module to be inside the support shelf and to not block the
LanProbe vent holes, refer to Figure 3-11 on page 35.
34
Page 55

Installing the Probe
Installation
Figure 3-11: Installing LanProbe in the Rack Support Shelf
6. Attach the LanProbe power module to the top of LanProbe by pressing the
two Dual Lock Reclosable Fas tener s st rips t ogethe r while complyi ng with
the alignment restrictions as stated in Step 5 on page 34.
7. Attach the power module’s power line to LanProbe.
35
Page 56

Installation
Installing the Probe
8. Attach the support shelf cover to the right LanProbe slot using two 0.312”
(7.93 mm) #M3 machine screws, or repeat steps 1 through 9 to install a
second LanProbe in the support shelf.
9. Insert the support shelf into the rack (or cabinet) and attach it with four clipon sheet metal nuts (use if required) and four 0.55” (14 mm) 10-32
POZIDRIV screws. Figure 3-12 shows the completed LanProbe, power
module, and support shelf.
10. Attach the power cord to the power module and to a power source. If this is
the second LanProbe installed in the support shelf, you can use the optional
Female-Male Power Cable (8120-1575) to attach power from one power
module to the other.
Figure 3-12: LanProbe Installed in the Rack Support Shelf
36
Page 57

Connecting the Probe
Installation
Connecting the Probe
LanProbe communicates with Agilent NetMetrix either through the In-Band
network connection or by using an Out-of-Band serial connection. You can
establish both In-Band and Out-of-Band connections to give you the option of
communicating with the probe either over the network or over the serial link,
respectively.
The In-Band connection adds a slight amount of traffic to the network, but is
faster than the Out-of-Band connection. The disadvantage of using only the
In-Band connection is th at certain networ k or component fai lures can resul t in loss
of communication with LanProbe.
The Out-of-Band serial connection can be used as the primary means of
communication or as a ba ckup link in case of a network failure. The dis advantage
of using only the Out-of-Band connection is that it is a slower means of
communications.
CAUTION
Connecting to the Network (In-Band)
You can connect LanProbe to the network by connecting the 10Base-T (RJ-45)
port. Figure 3-13 on page 38 shows the rear panel of LanProbe.
Do not touch the probe connector pins or the cable connector pins. Static
discharge may damage equipment.
37
Page 58

Installation
Connecting the Probe
Figure 3-13: Ethernet LanProbe Rear Panel
Connecting to 10Base-T Networks
Connect LanProbe’s 10Base-T (RJ-45) port, located on the rear panel, to the
network by using a UTP cable. Figure 3-14 on page 39 shows how to connect
LanProbe to a 10Base-T network.
38
Page 59

Connecting the Probe
Figure 3-14: Connecting LanProbe to 10Base-T Networks
Installation
Connecting Out-of-Band
Out-of-Band communications with LanProbe are conducted through the serial
port, not over the network. This mode of communications is optional.
The following methods are available for Out-of-Band connections:
“Direct Connection”, below
z
“Modem Connection” on page 40
z
“Data Switch Connection” on page 45
z
Direct Connection
To make a direct connection to LanProbe, connect the NetMetrix management
station’s serial port to LanProbe’s RS-232C port using a null modem cable
(Agilent part number 24542G—9-to-25 pin, 24542U—9-to-9 pin, or equivalent).
Figure 3-15 on page 40 shows the direct connection to the probe.
39
Page 60

Installation
Connecting the Probe
Figure 3-15: LanProbe Direct Connection
Modem Connection
You can use a modem connection to increase the distance between the probe and
the NetMetrix management statio n. Perform the followi ng tasks to make a modem
connection between a NetMetrix management station and LanProbe. Figure 3-16
on page 41 shows the modem connection to the probe.
“Install the Management Station Modem” on page 41
z
“Install the LanProbe Modem” on page 42
z
“Configure the Management Station and LanProbe” on page 42
z
40
Page 61

Connecting the Probe
Installation
Figure 3-16: LanProbe Modem Connection
Install the Management Station Modem
You need the following list of equipment to install the management station’s
modem:
Hayes-compatible 300 to 38.4 K baud modem
z
RS-232C (straight through) modem cable
z
Modular phone cable with RJ-11 connectors or equivalent
z
CAUTION
Use the following procedure to install the management station’s modem:
Turn off all equipment prior to making cable connections.
1. Place the modem close enough to the management station to not violate the
50-foot RS-232C distance limitation.
2. Connect the RS-232C cable from the modem’s RS-232C port to the
management station’s serial port. Take care in selecting the appropriate
serial port on the management station (COM1 or COM2, for example).
3. Connect the RJ-11 modular phone cable from the modem
To Line
port to
the telephone jack.
4. Connect power to the modem and turn on the modem power switch (not
required for a PC internal m odem).
41
Page 62

Installation
Connecting the Probe
5. Perform any other instructions as required by the modem manufacturer. If
you have any problems with the modem, contact the modem manufacturer
for assistance.
Install the LanProbe Modem
You need the following list of equipment to install the LanProbe modem:
Hayes-compatible 300 to 38.4 K baud modem
z
RS-232C (straight through) modem cable
z
Modular phone cable with RJ-11 connectors or equivalent
z
Use the following procedure to install the LanProbe modem:
1. Place the modem close enough to the probe to not violate the 50-foot RS-232C distance limitation.
2. Connect an RS-232C cable from the modem’s RS-232C port to the
LanProbe’s RS-232 port. A null modem cable
connection.
cannot
be used for this
3. Connect the RJ-11 modular phone cable from the modem
To Line
port to
the telephone jack.
4. Connect power to the modem and place the modem power switch to on.
5. Perform any other instructions as required by the modem manufacturer. If
you have any problems with the modem, contact the modem manufacturer
for assistance.
Configure the Management Station and LanProbe
Refer to your NetMetrix documentation for information on configuring the
management station for use with a modem. Verify that the packet retransmission
timeout is set appropriately. For example, a 1500-byte SNMP packet requires
about one second to transmit over a 9600 baud connection, with another one
second for the reply. A packet retransmission timeout of three to five seconds is
appropria te for this example.
42
Page 63

Connecting the Probe
Installation
The LanProbe can be configured for Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) link
communications either by using a local terminal through the serial port or by
using a NetMetrix management station over the network.
If you use the network to config ure LanProbe, make the network connection (r efer
to “Connecting to the Network (In-Band)” on page 37) and then refer to your
NetMetrix documentation to configure the following LanProbe parameters:
Serial Port IP Address
z
Serial Port Subnet Mask
z
Serial Port Speed
z
Hardware Flow Control (if unsure, consult your modem’s documentation)
z
Modem Init St ring
z
If you use an ASCII terminal to configure LanProbe as described in Chapter 2
“Local Terminal Configuration”, attach the terminal and configure the following
LanProbe parameters:
Serial Port IP Address
z
Serial Port Subnet Mask
z
Serial Port Speed
z
Hardware Flow Control (if unsure, ask your local network administrator)
z
Modem Init St ring
z
The Serial Port IP Address must be on the same IP subnet as the management
station’s serial IP address.
Normally, each company has one subnet mask that is used for all machines on
their network. Enter this subnet mask value into the Serial Port Subnet Mask
field. The Serial Subnet Mask used for the probe should match the subnet mask
used for the SLIP port on the management station.
Set the Serial Port Speed to a value that is less than or equal to the maximum
speed at which your modem can operate.
Set the Hardware Flow Control to Off (On is the default), unless you are using
high speed modems (14.4K baud or faster) with advanced features, such as error
correction and data compression. If the Hardware Flow Control is set to On, you
can set it to Off by using LanProbe’s menu or over the network from a NetMetrix
management station (refer to your NetMetrix documentation for details).
43
Page 64

Installation
Connecting the Probe
Verify that the Modem Init String is properly ini tialized for the attached modem
by referencing the modem’s documentation. The probe’s default modem
initialization string is configured to w ork with low-speed and medium-speed
Hayes compatible modems. The following modem setting s ar e r ec ommended for
low-speed to medium-speed modem connections:
Modem Flow Control: Off
Data Compression (if applicable): Off
Error Correction (if applicable): Off
Not all Hayes commands are the same for all Hayes-compatible modems. Refer
to your modem’s documentation to determine the commands required for each of
the above settings and append these commands to the end of the default Modem
Init String.
NOTE
Your modem’s documentation discusses the features that are relevant to your
modem. If your modem does not support a feature (data compression, for
example), you do not need to turn it off in the Modem Init String.
Some modems require you to set register values explicitly, rather than sending
Hayes style commands. In this case, follow your modem’s documentation to set
these registers.
If you are using a high-speed modem, you probably need to modify the default
modem initialization string. The following modem settings are recommended for
high-speed modem connections:
Modem Flow Control: Hardware Flow Control (RTS/CTS signaling)
Carrier Dete ct: Always On
Data Compression: Enabled
Error Correction: Enabled
After appending the appropriate commands to the modem initialization string,
warm start your LanProbe.
Refer to your NetMetrix docu mentation fo r information o n how to establ ish
communications with LanProbe over the SLIP link.
44
Page 65

Connecting the Probe
Installation
Data Switch Connection
Use the data switch connection to provide the flexibility of using more than one
management station to communicate with more than one LanProbe.
T o mak e a da ta switch co nnec tion to LanP robe, c onnect a NetMet rix manage ment
station to LanProbe’s RS-232C port through a data switch. Set the Serial Port
Mode to Direct, if your probe is directly connected to the data switch, or set it to
Modem, if your probe must dial through a modem to another modem that is
attached to the data switch.
To allow traps to be sent from the probe to your management station, specify a
Serial Trap Destination of type Switch or Modem Switch, using NetMetrix.
Refer to your data switch documentation for information on setting up your data
switch. There are many variations available for this connection method. Figure 317 on page 46 shows a possible data switch connection scheme.
45
Page 66

Installation
Connecting the Probe
Figure 3-17: LanProbe Data Switch Connection
46
Page 67

Starting the Probe
Starting the Probe
Installation
NOTE
If you are using the Bootp serv er method of configur ation, do not atta ch the power
cord and Agilent Power Module (0950-2546) to the probe until told to do so in
Chapter 4 “Bootp Server Configuration”.
If you used the local terminal method of configuration, attach the power cord and
Agilent Power Module to LanProbe. The probe doe s not have a power switc h, but
is powered on when power i s a tt ac hed. When powered on or re set , La nPr obe runs
self-tests and transmits ICMP echo frames to the default gateway for the purpose
of allowing the probe to be discovered by the routers (ARP cache). The probe
transmits four ICMP echo request packets about 10 seconds after booting and
again every autodiscove ry echo interval. Refer to Cha pter 5 “LanPro be
Operation” for more information on resetting the probe.
47
Page 68

Installation
Verifying the Installation
Verifying the Installation
You can verify the LanProbe installation by looking at the status LEDs on the
front of the pro be. Af t er the LanProbe restar ts (boots), it runs a power-on self-test
(POST) and then starts normal operations.
The Fault LED is briefly turned on (about three seconds) during the POST. After
LanProbe passes the POST, the Fault LED turns off. The Activity LED flashes
during network activit y . The ~ Line On or Power LED should be on to indicate that
power is applied to the probe.
After LanProbe has passed its self-tests, look at the status LEDs to verify your
installation. The status LEDs should be in the following states:
LED State
Activity Flashing, if connected to a network with traffic, or may
appear to stay on solid during periods of steady traffic.
~ Line On or Power On solid
Fault Off
Link On when attached to a 10Base-T network
Collision Off (or flashing if connected to a network with collisions)
You can use NetMetrix to verify that LanProbe can be reached (refer to your
NetMetrix documentation).
48
Page 69

Verifying the Installation
Installation
Troubleshooting the Installation
If the Activity LED is off, verify that LanProbe is properly connected to the
network and that there is traffic on the network.
If the ~ Line On or Power LED is off, verify that power is properly connected to
LanProbe and to the correct power source.
If the Fault LED is on, the probe failed the self-test. Repeat the installation
procedures and verification of installation.
If you are still having d iff iculty, call your local Agilent service represent ative.
49
Page 70

Installation
Verifying the Installation
50
Page 71

4
Bootp Server Configuration
Page 72

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Configuration
This chapter describes how to use the Bootp server method to configure the
Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe so that it can communicate over the network.
This chapter assumes that you have already installed LanProbe, but have not
attached the power cord and Agilent Power Module (0950-2546). If you plan to
use the loca l terminal m ethod of configuration, skip this cha pter and refer to
Chapter 2 “Local Terminal Configuration”.
The following sections are covered in this chapter:
z
“Probe Configuration Using a Bootp Server” on page 53
z
“Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System” on page 55
z
“Bootp Server Setup on a PC” on page 59
z
“Configuring the Bootptab File” on page 65
52
Page 73

Probe Configuration Using a Bootp Server
Bootp Server Configuration
Probe Configuration Using a Bootp Server
You can use a Bootstrap Protocol (Bootp*) server to load LanProbe’s IP
configuration. This method requires that a Bootp server maintains a file
containing client configuration information, maps from MAC addresses to IP
addresses, and responds to requests from clients. You can configure the probe
from an HP-UX, Solaris, or MS-DOS syst em acting as a Bootp server. The system
that is operat ing as t he Bootp server must be connected to your n etwork. Table 4-2
on page 54 shows the minimum requirements for a Bootp server operating on HP
9000, Sun SPARC, and PC systems.
Before you can use the Bootp server, you must edit the bootptab file to configure
the required LanProbe parameters. Refer to “Configuring the Bootptab File” on
page 65 for more information.
LanProbe’s MAC address is twelve characters long and is printed on a tag on the
back of the probe. You must determine the IP Address, Default Gateway IP
Address, and Subnet Mask from the network.
T o all ow LanProbe to use a Bootp ser ver tha t is not on th e same subnet , the router
involved must support Boot p Relay (the tra nsfer of a Bootp req uest). For exampl e,
if you have multiple LanProbes that you want to configure from a single Bootp
server, be sure that the routers in the path between your Bootp server and the
LanProbes support Bootp Relay. Otherwise, you will need to operate the Bootp
server on the same subnet as your LanProbes. You can configure multiple
LanProbes on one subnet and then place them on their respective segments.
53
Page 74

Bootp Server Configuration
Probe Configuration Using a Bootp Server
Table 4-2: Minimum Requirements for a Bootp Server
Bootp Server type
Item
HP Sun PC
Model or Processor HP 9000
Model 700
or 800
Operating System HP-UX 9.x
or later
Network Operating
System/Subsystem
Floppy Drive Not
System Memory No t
ARPA
Berkeley
Services
Applicable
Applicable
Sun SP ARC Model
1, 1+, 2, IPC, 5, 10,
20
Solaris 2.1 or later DOS 3.0 or later
Sun Networking
Services (Ethernet
and TCP/IP)
Not Applicable 3.5" Floppy Disk Drive
Not Applicable 10KB of free memory to
286 or above
Microsoft LAN Manager
1.0 or later
-orNovell NetWare
environment, including
LSL.COM v1.2,
IPXODI.COM v1.2,
NETX.COM v3.1
or later
run the installation
process. 100 KB of free
memory to run
BOOTPD.
54
Page 75

Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System
Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System
If your Bootp server is an HP-UX or Solari s system, use the followi ng instructions
to configure LanProbe:
1. Determin e the IP address to be used for LanProbe.
2. Determine the name to be used as LanProbe’ s Domain Name Servi ces (refer
to the HP ARPA Services manual) or configure an IP address and name for
LanProbe in your loca
3. Make sure that the Bootp server can communicate with LanProbe (if they
are separated by a router, the router must support Bootp Relay).
4. From the Bootp server, edit the client configuration file and enter the
following parameters to be used for LanProbe (do not specify any other
parameters):
l /etc/hosts file.
NOTE
z
MAC Address
z
IP Address
z
Default Gateway IP Address (if available)
z
Subnet Mask
The Bootp server must support the vendor specific subnet mask field and the
default gateway field.
5. Start the Bootp daemon as des cribed i n “Star ting t he Bootp Server on an HP
or Sun System” on page 57.
6. Connect the power cord and Agilent Power Module (0950-2546) to
LanProbe and to a power source (either 100-120/VAC or 220-240/VAC).
LanProbe does not have a power switch but becomes operational when
power is attached.
55
Page 76

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System
The probe automatically broadcasts Bootp requestswhen its IP address is
0.0.0.0 (the default). The probe broadcasts Bootp requests to signal its
need to be configured.
7. For HP-UX systems: Log in as root , then use SAM to fol low the i nstructi ons
presented on the screen.
For HP-UX 9.x, choose:
Networking/Communications -> Service:Enable/Disable
For HP-UX 10.x and 11.x, choose:
Networking and Communications -> Network Services
NOTE
NOTE
If the last screen presented in Step 7 displays bootp server enabled, (for
either HP-UX 9.x, HP-UX 10.x, or HP-UX 11.x) then your machi ne is already set
up as a bootp server.
8. Edit the /etc/bootptab file to configure the probe and add descriptive
comments to the file for reference. Refer to “Configuring the Bootptab File”
on page 65, the bootpd(1M) man page or the HP ARPA Services manual
for more information on configuring the /etc/bootptab file.
9. Use tail -f to check the system log file to ensure that the Bootp server
responded correctly to the Bootp request. The log file is /var/adm/
messages (Solaris), /usr/adm/syslog (HP-UX 9.x), or /usr/
adm/syslog/syslog.log (HP-UX 10.x and 11.x).
10. If you are using HP OpenView, you can verify that LanProbe has been
assigned the correct IP address and shows up on the management station
map as a network analyzer. The discovery process that places LanProbe in
the management station map can take several minutes to complete.
You may be able to decrease the required time for discovery of LanProbe by
pinging it continuously from your Agilent NetMetrix management station. You
can also ping LanProbe to verify that it responds to the new IP address.
56
Page 77

Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System
Bootp Server Configuration
Starting the Bootp Server on an HP or Sun System
You can start the Bootp server on an HP or Sun system in one of the following
ways. Refer to “Configuring the Bootptab File” on page 65 if you need to
configure the bootptab file.
Bootp for Solaris is shipped on the NetMetrix CD-ROM but it is not part of the
operating system.
standalone
z
z
z
inetd
. Become superuser and give one of the following commands:
/etc/bootpd -s for HP-UX v. 9.x
/usr/lbin/bootpd -s for HP-UX v. 10.x & 11.x
/usr/netm/sun4s/bootpd -s for Solaris
. Become superuser and use the following procedure:
1. Edit the file /etc/inetd. conf. Sea rc h fo r a line like the followi ng a nd
ensure that the line is uncommented (does not contain a # character). If
necessary, add the line to the file.
bootps dgram udp wait root path/bootpd bootpd
Where path is one of the following:
/etc for HP-UX v. 9.x
/usr/lbin for HP-UX v. 10.x & 11.x
/usr/netm/sun4s for Solaris
For HP-UX
2.
, give one of the following commands to force inetd to re-read
the inetd.conf file that you modified in Step 1 on page 57:
/etc/inetd -c for HP-UX v. 9.x
/usr/sbin/inetd -c for HP-UX v. 10.x & 11.x
57
Page 78

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on an HP or Sun System
3. For Solaris, determine the process ID for inetd by entering the followin g
command:
ps -ef | grep inetd
Then force inetd to re-rea d the inetd.co nf fil e that you modi fied i n Step 1 on
page 57 by giving the following command:
kill -HUP process_id
For additional information, refer to the man pages for bootpd(1M),
inetd(1M), inetd.conf(4M), ps(1M) and kill.
58
Page 79

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
Bootp software for a PC is included (on a 3.5" floppy disk) with your Agilent
LanProbe. Bootp software implements an internet Bootstrap Protocol (Bootp)
server as defined in RFC 951 and RFC 1048. It is run from the DOS prompt
either as a standalone executable or as a terminate-and-stay-resident (TSR)
program and communicates to a ne twork in terf ace car d using t he Microsoft NDIS
(LAN Manager), or Novell ODI (NetWare), network stack. Bootp software does
not support Microsoft Windows.
Refer to “Configuring the Bootptab File” on page 65 if you need to configure the
bootptab configuration file.
Use the following procedure to setup the Bootp server software on a PC:
1. Insert the 3.5" floppy disk into your disk drive.
2. Change the prompt to indicate your floppy disk drive volume and enter
setup
Bootp Setup
===========
Setup helps you install the Bootp server software for
use with either Microsoft LAN Manager or Novell ODI
version 3.1 software by:
- copying to your setup drive software for interfacing
the Bootp program to your networking software.
- modifying your CONFIG.SYS, AUTOEXEC.BAT, and
PROTOCOL.INI or NET.CFG files. (A copy of these files
are saved in CONFIG.BTP, AUTOEXEC.BTP, PROTOCOL.BTP
and NET.BTP, respectively.)
- copying the Bootp software to BOOTPD directory on your
startup drive.
- providing a README file that contains more information.
(Press return to continue or press ‘E’ to exit.)
. The following screen is displayed:
59
Page 80

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
3. Press Return to cont inue. The following scre en is then displayed:
Please specify startup drive to install Bootp on [C:\]:
4. Specify the drive where you want to install the Bootp software and press
Return. The d efault is to install the Bootp software in C:\. The following
screen is then displayed:
Install Bootp Software for use with:
0: Microsoft LAN Manager 1.0 or later
1: Novell NetWare v3.1 or later
2: Exit this setup program
Enter choice [0 - 2]:
5. Specify the Network Operating System that you are using and then refer to
either “Using Microsoft LAN Manager” below or “Using Novell NetWare”
on page 62.
There will be different setup screens displayed depending on the Network
Operating System that you are using (Microsoft LAN Manager or Novell
NetWare).
Using Microsoft LAN Manager
If you have selected
NetWare” on page 62.
If you have selected
use the following procedure to setup your Bootp installation.
60
Novell NetWare v3.1 or later
, skip to “Using Novell
Microsoft LAN Manager 1.0 or la ter
from the setup menu,
Page 81

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
1. Skip this step if you only have one LAN interface in your system (the
following screen wil l n ot b e di splayed.) Specify the driver that will be use d
for the Bootp server. This is an example; your driver may be different.
Bootp Installation for Microsoft LAN Manager:
=============================================
Setup has found multiple drivers that it can bind the
bootp software to.
Choose one of the following:
0: HPLAN
1: HPLANB
2: Exit this setup program
Enter number [0 - 2]:
2. The final screen looks like the following:
The following file has been copied to the directory
C:\LANMAN.DOS\:
- DISPKT10.DOS
The CONFIG.SYS and the PROTOCOL.INI files have been
modified. Unmodified backups have been saved as
C:\CONFIG.BTP and C:\LANMAN.DOS\PROTOCOL.BTP.
The following files have been copied to the directory
C:\BOOTPD:
- BOOTPD.EXE
- BOOTPTAB
- README.TXT
BOOTPTAB is a sample configuration file which you must
modify before executing BOOTPD.EXE.
Bootp Setup is complete.
Please read the README.TXT file for additional
information. You will need to restart your computer
before running the Bootp software.
3. Modify the sample bootptab configuration file and restart your computer
before running the Bootp software.
61
Page 82

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
Using Novell NetWare
If you have selected
Microsoft LAN Manager 1.0 or later
, go back to “Using
Microsoft LAN Manager” on page 60.
If you have selected
Novell NetWare v3.1 or later
from the setup menu, use the
following procedure to setup your Bootp installation.
1. Press return to continue from the following screen.
Bootp Installation for Novell networks:
=======================================
In order to use this product using the NetWare protocols,
you need to be running client versions of NetWare that
include:
- LSL.COM v1.20 or later
Your NET.CFG file must specify a FRAME type of
ETHERNET_II. For example, your NET.CFG should include
something like:
LINK DRIVER HPWDSA8
FRAME ETHERNET_II
Bootp also requires that you do not have Novell TCP/IP
software (LAN Workplace for DOS) installed.
(Press return to continue or ‘E’ to Exit.)
2. Specify the location of the NET.CFG file. The default is for the NET.CFG
file to be located at C:\NOVELL\NET.CFG.
Setup could not find the NET.CFG file.
Please specify a full path and filename
(e.g. C:\NOVELL\NET.CFG):
62
Page 83

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
3. The final screen looks like the following:
The following file has been copied to the directory C:\:
- ODIPKT13.COM
The AUTOEXEC.BAT and the NET.CFG files have been modified.
A copy of the original files have been saved as
C:\AUTOEXEC.BTP and C:\NETWARE\NET.BTP.
The following files have been copied to the directory
C:\BOOTPD:
- BOOTPD.EXE
- BOOTPTAB
- README.TXT
BOOTPTAB is a sample configuration file which you must
modify before executing BOOTP.EXE
Bootp Setup is compete.
Please read the README.TXT file for additional
information. You will need to restart your computer before
running the Bootp software.
Starting the PC Bootp Server
You can start the PC Bootp server in one of the following ways:
As a standalone executable program by entering the following:
z
bootpd -a IP address -s
As a TSR (terminate-and-stay-resident) program by entering the following:
z
bootpd -a IP address
63
Page 84

Bootp Server Configuration
Bootp Server Setup on a PC
Where:
-a IP address is required and specifies the IP address of the PC where you are
running bootpd.
-s specifies that you are running bootpd as a standalone executable (not as a
TSR). You may want to use the -s option if you do not need t he Bootp daemon
to continually service boo tp reques ts. This is pre ferable , since the Boot pd TSR
may consume a large amount of memory (depending on the size of your
bootptab file).
Upon startup, Bootpd reads the bootptab file and then listens for bootp request
packets from the network. Bootpd re-reads the bootptab file when it receives a
bootp request packe t and detec ts tha t the fi le has been u pdated. If hosts a re added,
deleted, or modified, their entries in Bootpd’s internal database are also updated
when the bootptab file is re-read. All Bootp status messages are logged to the
BOOTPD.LOG file.
You can now attach the power cord and Agilent Power Module (0950-2546) to
LanProbe and to a power source (either 100-120/VAC or 220-240/VAC).
LanProbe does not have a power switch but becomes operational when power is
attached. When powered on and when its IP address is 0.0.0.0 (the default),
LanProbe automatically broadcasts Bootp request s that trigge r the Bootp ser ver to
provide its configuration parameters.
64
Page 85

Bootp Server Configuration
Configuring the Bootptab File
Configuring the Bootptab File
Configure the bootptab file by using the following procedure and any ASCII text
editor to edit one of the files from Table 4-3.
Table 4-3: Bootp Server bootptab Files
Bootp Server: Bootptab File Location
HP 9000 System /etc/bootptab
Sun SPARC system /usr/netm/config/bootptab
PC C:\bootpd\bootptab
1. Enter your IP parameters into the bootptab file for each LanProbe that you want to configure.
Use this format.
nodename:\
tag=value:\
tag=value:\
...
tag=value
The
nodename
40 characters long using alpha- numeric s, dash es, and dot s.
or underscores in the nodename.
Each
tag
LanProbe. Valid tags are listed in Table 4-4 on page 66. You
set of these tags for each LanProbe that you want to configure (some tags are
optional).
is the host name of the Lan Probe. The nodename can b e up to
Do not use spaces
and its associated value is an IP parameter configured for a
must
provide a
65
Page 86

Bootp Server Configuration
Configuring the Bootptab File
Blank lines and lines beginning with # in the bootptab file are ignored. You
must include a colon and a backslash to continue a line. The ht tag must
precede the ha tag.
An example bootptab file is shown at the end of this procedure.
Table 4-4: Bootptab File Tags
Tag Description
hn send nodename (Boolean flag, no “=value” is needed)
ht hardware type (ether); must precede ha tag
vm vendor magic cookie selector (must comply with RFC 1048)
ha hardware address (link-level or MAC address expressed in
hexadecimal); the LanProbe’s hardware address is printed on a
label located on the Probe’s back panel.
ip Internet Protocol (IP) address for the Probe
sm subnet mask; this is required only if subnetting is being used
gw IP address of the gateway used when sending packets off the local
subnet; one default gateway may be configured
2. Save the bootptab file after you have entered parameters for all of your LanProbes.
3. Verify the bootp process by performing one of the items in Table 4-5 on
page 67.
66
Page 87

Table 4-5: Bootp Process Verification
Server Verification Process
Bootp Server Configuration
Configuring the Bootptab File
NOTE
HP-UX
Bootp Server
Solaris
Bootp Server
PC
Bootp Server
Only bootpquery with bootptab entries include the ba tag.
Test the Bootp process by entering one of the following:
For HP-UX 9.x:
/etc/bootpquery <hardware address>
For HP-UX 10.x and 11.x:
/usr/sbin/bootpquery <hardware address>
Where <hardware address> is the MAC address of the
HP-UX workstation’s LAN interface.
If available, test the Bootp process by entering:
/etc/bootpquery <hardware address>
where <hardware address> is the MAC address of the
Solaris workstation’s LAN interface.
Check the
“Starting bootpd...”
C:\bootpd\bootpd.log
file for the entry
67
Page 88

Bootp Server Configuration
Configuring the Bootptab File
Example Bootptab File
The following is an example of the C:\bootpd\bootptab file provided with
the PC Bootp software. At the end of this bootptab file, there are example IP
configuration entries for a LanProbe.
# Example bootptab: database for bootp server.
#
# Format:
# nodename: tag=value: ... : tag=value
#
# first field - nodename (hostname) of terminal followed by colon
# (should be full domain name)
#
# Blank lines and lines beginning with ‘#’ are ignored.
# Make sure you include a colon and a backslash to continue a line.
# Don’t put any spaces in the tag=value string.
# The ht tag MUST precede the ha tag.
#
# The options listed below are useful for Agilent LanProbes.
# They are specified as tag=value and delimited by colons.
# For a list of all possible options, see the
# C:\BOOTPD\README.TXT file.
#
# ba - broadcast bootp reply for testing with bootpquery
# hn - send nodename (Boolean flag, no “=value” needed)
# ht - hardware type (ether) (must precede the ha tag)
# ha - hardware address (link level address) (hex)
# vm - vendor magic cookie selector (should be rfc1048)
# ip - LanProbe IP address
# sm - network subnet mask
# gw - gateway IP address
#
# LanProbe example
#
# lanprobe1:\
# ba:\
# hn:\
# ht=ether:\
# vm=rfc1048:\
# ha=080009123456:\
# ip=15.6.72.210:\
# sm=255.255.248.0:\
# gw=15.6.72.1
68
Page 89

5
LanProbe Operation
Page 90

LanProbe Operation
LanProbe Operation
The Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe is designed to operate unattended once it
has been configured and successfully completes its self-tests. This chapter
describes how to re set the p robe an d the ef fect that dif fer ent rest arts have on prob e
data and measurement configuration settings.
70
Page 91

Restarting the Probe
LanProbe Operation
Restarting the Probe
The LanProbe can be restarted by performing a
warm start
or a
cold start
. In
either case, the p robe exec utes sel f-tests a nd re-init ializes . There ar e dif feren ces in
the effects of each type of restart.
z
A warm start resets LanProbe’s measurement data only.
z
A cold start resets all of LanProbe’s measurement data, filters, alarms, and
user-defined statistics studies (excluding communications configuration
parameters) back to default values.
Warm Start
A warm start resets LanProbe’s measurement data only. You can warm start
LanProbe by doing one of the following:
z
Cycling power (or a power outage).
z
Selecting the menu it em
when you have a local terminal conn ect ed to the probe, as describe d in St ep
3 on page 74.
z
Using Agilent NetMetrix to execute a LanProbe warm start. Refer to your
NetMetrix do cumentation f or details.
Warm start and Exit
from LanProbe’ s Ma in Menu
Table 5-6 on page 72 shows which data and parameters are reset during a warm
start and during a cold start of a LanProbe.
71
Page 92

LanProbe Operation
Restarting the Probe
Table 5-6: Probe Data and Parameters Reset by Warm or Cold Start
Category LanProbe Memory Contents
Measurement Data
Measurement
Configuration
Parameters
LanProbe
Configuration
Parameters
Captured frames
Counted frames
Historical Ethernet statistics
Current Ethernet stati st ic s
Host tables (RMON-1 & RMON-2)
Matrix tables (RMON-1 & RMON-2)
Host Top N statisti cs
Protocol distribution
Address map
User history
Logs
Echo Test counters
Alarm table
Filter table
Channel table
Buffer control table
Event table
Protocol directory
Community access table
Client tables
Historical study configuration
Echo Test table
Trap destination table
Serial connection tabl e
Serial configuratio n information for
outgoing connect ions, such as:
dial strings
Time period for utilization cal cu la ti ons
Other Serial configuration information,
such as:
SLIP address and subnet mask
serial port speed
modem initialization strings
Flow Control
Probe configuration information,
such as:
IP address
default gateway
subnet mask
TFTP server address
Download filename
Time zone
Security Settings
Interface Status
Crash data (used by Agilent support)
Warm Start
Status
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Cold Start
Status
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Reset
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
Saved
72
Page 93

LanProbe Operation
Restarting the Probe
Cycling Power
A power outage or cycling power to LanProbe causes a warm start. LanProbe
does not have a power switch; therefore, cycling the power consists of
disconnecting and reconnecting the power cord.
Selecting the Warm Start Menu Item
Use the following procedure to warm start the probe using LanProbe’s Main
Menu:
1. Connect a local terminal (or a PC emulating a terminal) to LanProbe. Refer
to Chapter 2 “Local Terminal Configuration” for informat io n on connecting
a local terminal.
2. Press the CONFIG button once (on the back of the probe) to place La nProbe
into the configuration mode. Use a narrow, pointed object (like a pen) to
press the recessed CONFIG button. LanProbe then displays its Main Menu
on the terminal. Figure 5-18 shows LanProbe’s Main Menu.
Main Menu - Revision
1. Modify/View configuration values ->
2. Modify/View security values ->
3. Modify/View interface values ->
4. Display interface summary
5. TFTP Download new firmware ->
6. XMODEM Download new firmware ->
7. Warm start and Exit
8. Cold start and Exit
Figure 5-18: LanProbe’s Main Menu
73
Page 94

LanProbe Operation
Restarting the Probe
3. Press 7 to execute a warm start and exit LanProbe’s Main Menu. The w arm
start occurs immedia te ly. The Activity and Fault LEDs are turn ed on during
a warm start. When the warm start completes, the Activit y LED flashes to
indicate traffic (if present), the Fault LED turns off, and the ~Line On (or
Power) LED is on.
Cold Start
A cold start resets a ll of La nPr obe’s measurement data as well as all al arm, event,
filter, and user-d efined statistics configuration to t heir default values. Basic
communications configuration parameters (IP address, default gateway IP
address, and subnet mask) are not reset.
You can cold start LanProbe by doing one of the following:
Pressing the CONFIG Button twice within one second.
z
Selecting the menu item
z
Cold start and Exit
from LanProbe’s Main Menu
when you have a local terminal connected to the probe, as described on
page 75.
Using Agilent NetMetrix to execute a LanProbe cold start. Refer to your
z
NetMetrix do cumentation f or details.
Table 5-6 on page 72 shows which data and parameters are reset during a cold
start or warm start of LanProbe.
Pressing the CONFIG Button Twice
Pressing the CONFIG button twice within one second causes the probe to cold
start.
74
Page 95

LanProbe Operation
Restarting the Probe
Selecting the Cold Start Menu Item
Use the following procedure to cold start the probe using LanProbe’s Main Menu:
1. Connect a local terminal (or a PC emulation a terminal) to LanProbe. Refer
to “LanProbe Operation” on page 69 for information on connecting a local
terminal.
2. Press the CONFIG button once (on the back of the probe) to place La nProbe
into the configuration mode. Use a narrow, pointed object (like a pen) to
press the recessed CONFIG button. LanProbe then displays its Main Menu
on the terminal. Figure 5-18 on page 73 shows LanProbe’s Main Menu.
3. Press 8 to execute a cold start and to exit LanProbe’s Main Menu. The cold
start occurs immedia te ly. The Activity and Fault LEDs are turn ed on during
a cold start. When the cold start completes, the Activity LED flashes to
indicate traffic (if present), the Fault LED turns off, and the ~Line On (or
Power) LED is on.
75
Page 96

LanProbe Operation
Restarting the Probe
76
Page 97

6
Download New Firmware
Page 98

Download New Firmware
Download New Firmware
The instructions in this chapter describe how to download new firmware to the
Agilent 4986B Ethernet LanProbe.
This download procedure is only necessary to upgrad e your LanProbe firmware to
a new firmware release.
New firmware for the LanProbe comes in the form of a binary file. This binary
file can be received in t he following ways:
z
Sent to you by an Agilent Support Representative, on 3.5" floppy disk.
z
Sent to you by an Agilent Support Representative via electronic means.
CAUTION
z
Included wi th Agilent NetMetrix.
z
Obtained via anonymous ftp from col.hp.com (15.255.240.16). The
/dist/netmetrix/lpfirmware
directory contains the latest version
of LanProbe firmware. A README file found in this directory provides
more details about the files contained in the
lpfirmware
directory.
Downloading new LanProbe firmware resets stored probe data and some probe
configuration information (like filters, traps, and channels). It can affect the IP
address, subnet mask, or default gateway IP address in some situations. Refer to
the Readme file on the new firmware media for more information.
The available procedures for downloading new firmware to LanProbe are
documented in this cha pter. You should first select a procedure and then go to that
section in this chapter and execute that procedure.
78
Page 99

Download New Firmware
The following download procedures are covered in this chapter:
“Downloading Firmware using an HP-UX Workstation and a Terminal” on
z
page 80
“Downloading Firmware using a Networked PC and a Terminal” on page 84
z
“Xmodem Download of Firmware” on page 88
z
You can also download firmware using NetMetrix. Refer to your NetMetrix
documentation for details.
79
Page 100

Download New Firmware
Downloading Firmware using an HP-UX Workstation and a Terminal
Downloading Firmware using an HP-UX Workstation
and a Terminal
The following instructions assume you are using HP-UX 9.0, or later. Before
upgrading firmware, you must first establish an IP connection between your
HP-UX workstation and LanProbe.
The following steps are required to download firmware to your LanProbe:
1. “Install New Download Firmware on an HP-UX Workstation” below
2. “Download Firmware to LanProbe” on page 81
Install New Download Firmware on an HP-UX Workstation
T o downl oad a new f irmware f ile t o LanProbe using an HP-UX work stati on and a
terminal, the new firmware file must be co pied into the
HP-UX workstation, and the file must be readable by
directory is
For more information on configuration and usage of
tftp
documentation (typically found in an ARPA Services manual).
80
/usr/tftpdir
.
~tftp
directory on your
tftp
. Typically, the
tftp
, refer to your HP-UX
~tftp
 Loading...
Loading...