Page 1

IntelliStation POWER 9112 Model 265
Service Guide
SA38-0609-00
IBM
Page 2

Page 3

IntelliStation POWER 9112 Model 265
Service Guide
SA38-0609-00
IBM
Page 4

First Edition (February 2002)
Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Safety Notices” on page ix,
Appendix A, “Environmental Notices” on page 305, and Appendix B, “Notices” on page 307.
A reader’s comment form is provided at the back of this publication. If the form has been removed, address comments
to Information Development, Department H6DS-905-6C006, 11400 Burnet Road, Austin, Texas 78758-3493. To send
comments electronically, use this commercial internet address: aix6kpub@austin.ibm.com. Any information that you
supply may be used without incurring any obligation to you.
© International Business Machines Corporation, 2002. All rights reserved. Note to U.S. Government Users -Documentation related to restricted rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth is GSA
ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp.
Page 5

Contents
Safety Notices ........................ix
Electrical Safety........................ix
Laser Safety Information .....................x
Laser Compliance ......................x
Data Integrity and Verification ..................xi
About This Book ......................xiii
ISO 9000 .........................xiii
Related Publications ......................xiii
Trademarks.........................xiv
Chapter 1. Reference Information .................1
System Unit Locations......................1
Front View.........................1
Rear View.........................2
Power Supply Locations ....................3
Fan Locations .......................4
System Board Locations ....................5
Memory DIMMs Location ....................6
Power Backplane ......................7
Operator Panel .......................8
SCSI IDs and Bay Locations ..................9
System Logic Flow Diagram ...................10
Location Codes........................11
Physical Location Codes ...................11
Location Code Format ....................11
AIX Location Codes .....................12
AIX and Physical Location Code Table ................15
System Cables........................19
Specifications ........................20
Power Cables ........................21
Service Inspection Guide ....................22
Chapter 2. Diagnostic Overview .................23
Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)...............23
Attention LED and Lightpath LEDs .................24
Indicator Panel .......................24
Component LEDs ......................25
Resetting the LEDs .....................25
Checkpoints.........................26
FRU Isolation ........................27
Electronic Service Agent for the RS/6000 ...............27
Using the Service Processor and Electronic Service Agent Features ......27
Service Processor......................27
Electronic Service Agent ...................28
iii
Page 6

Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) ..........31
Quick Entry MAP .......................32
Quick Entry MAP Table of Contents ................32
MAP 1020: Problem Determination .................40
MAP 1240: Memory Problem Resolution ...............45
General Memory Information ..................46
MAP 1520: Power.......................49
MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration .................59
Chapter 4. Checkpoints ....................81
Unresolved Checkpoint Problems .................81
Service Processor Checkpoints ..................82
Firmware Checkpoints .....................88
Boot Problems/Concerns ....................106
Chapter 5. Error Code to FRU Index ...............109
Performing Slow Boot .....................109
Considerations for Using the Error Code to FRU Index ..........109
Firmware/POST Error Codes ...................110
Memory DIMM Present Detect Bits (PD-Bits) .............169
Error Codes E0A0, E0B0, E0C0, E0E0, E0E1 and 40A00000 Recovery Procedure 170
Bus SRN to FRU Reference Table .................171
Typical Boot Sequence for 9112 Model 265 ..............172
Chapter 6. Loading the System Diagnostics .............175
Performing Slow Boot .....................175
Loading Standalone Diagnostics .................175
Loading Online Diagnostics ...................175
Default Boot List and Service Mode Boot List .............176
Chapter 7. Using the Service Processor ..............177
Service Processor Menus ....................179
Service Processor Menu Inactivity ................179
Accessing Service Processor Menus Locally ............179
Accessing Service Processor Menus Remotely............179
Saving and Restoring Service Processor Settings ...........179
General User Menu ......................180
Privileged User Menus .....................182
Main Menu........................182
Service Processor Setup Menu .................183
Passwords........................183
Serial Port Snoop Setup Menu .................186
System Power Control Menu..................187
System Information Menu ...................191
Language Selection Menu ..................194
Call-In/Call-Out Setup Menu ..................195
Modem Configuration Menu ..................196
Serial Port Selection Menu ..................196
Serial Port Speed Setup Menu .................197
Telephone Number Setup Menu.................197
iv Service Guide
Page 7

Call-Out Policy Setup Menu ..................199
Customer Account Setup Menu .................200
Call-Out Test .......................200
System Power-On Methods ...................200
Service Processor Call-In Security .................201
Service Processor Reboot/Restart Recovery .............202
Boot (IPL) Speed .....................202
Failure During Boot Process ..................202
Failure During Normal System Operation..............202
Service Processor Reboot/Restart Policy Controls...........202
Processor Boot-Time Deconfiguration (CPU Repeat Gard) ........202
Memory Boot-Time Deconfiguration (Memory Repeat Gard) .......203
Service Processor System Monitoring - Surveillance ...........204
System Firmware Surveillance .................204
Operating System Surveillance .................204
Call Out.........................205
Console Mirroring ......................206
System Configuration for Console Mirroring .............206
Service Processor Firmware Updates ................207
Service Processor Error Log ...................207
Service Processor Operational Phases ...............208
Pre-Standby Phase .....................208
Standby Phase ......................208
Bring-Up Phase ......................209
Run-time Phase ......................209
Service Processor Procedures in Service Mode ............210
Chapter 8. Using System Management Services ...........211
Graphical System Management Services ...............211
Config ..........................214
Multiboot .........................215
Utilities ..........................218
Password ........................220
Spin Delay........................224
Error Log ........................225
RIPL..........................226
SCSI ID.........................231
Firmware Update.......................232
Firmware Recovery .....................232
Text-Based System Management Services ..............233
Select Language.......................234
Change Password Options ...................235
Set Privileged-Access Password ................235
Unattended Start Mode ...................235
View Error Log .......................236
Setup Remote IPL (Initial Program Load)...............237
Change SCSI Settings .....................240
Select Console .......................240
Select Boot Options......................241
Select Boot Device .....................242
Contents v
Page 8

Configure Nth Boot Device ..................243
View System Configuration Components ...............245
System/Service Processor Firmware Update .............246
Firmware Recovery ......................246
Chapter 9. Removal and Replacement Procedures ..........247
Handling Static-Sensitive Devices .................248
Stopping the System .....................248
Front Door .........................249
Removal ........................249
Replacement .......................250
Service Access Cover .....................251
Removal ........................251
Replacement .......................252
Bezels ..........................253
Removal ........................253
Replacement .......................253
Processor and Memory Card Cover ................254
Removal ........................254
Replacement .......................254
CEC Cage .........................255
Removal ........................255
Replacement .......................255
Memory Card and Memory DIMMs.................256
Memory Card Removal....................256
Memory Card Replacement ..................261
Processor Card .......................263
Removal ........................263
Replacement .......................264
Adapters .........................266
Removal ........................266
Replacement .......................267
System Board........................270
Removal ........................270
Replacement .......................271
Power Supply........................272
Removal ........................272
Replacement .......................274
Operator Panel .......................277
Removal ........................277
Replacement .......................277
System Vital Product Data (VPD) Update Procedure ..........278
Power Backplane ......................280
Removal ........................280
Replacement .......................280
SCSI Backplane .......................281
Removal ........................281
Replacement .......................281
Media Devices (CD-ROM, Tape, or Disk Drive).............282
Removal ........................282
vi Service Guide
Page 9

Replacement .......................283
Battery ..........................284
Removal ........................284
Replacement .......................285
Hot-Swap Disk Drives .....................286
Deconfiguring (Removing) or Configuring a Disk Drive .........286
Deconfiguring (Removing)...................286
Configuring (Replacing) ...................287
Removal ........................288
Replacement .......................289
Hot-Swap Fan Assembly ....................290
Removal ........................290
Replacement .......................291
Chapter 10. Parts Information ..................293
System Parts ........................294
System Internal Cables ....................296
SCSI Cables ........................298
Keyboards and Mouse (White) ..................302
Keyboards and Mouse (Black) ..................303
Appendix A. Environmental Notices................305
Product Recycling and Disposal..................305
Environmental Design .....................305
Acoustical Noise Emissions ...................305
Declared Acoustical Noise Emissions ...............305
Appendix B. Notices .....................307
Appendix C. Service Processor Setup and Test ...........309
Service Processor Setup Checklist .................309
Testing the Setup ......................310
Testing Call-In ......................310
Testing Call-Out ......................310
Serial Port Configuration ...................311
Appendix D. Modem Configurations ...............313
Sample Modem Configuration Files ................313
Generic Modem Configuration Files ...............313
Specific Modem Configuration Files ...............313
Configuration File Selection ...................314
Examples for Using the Generic Sample Modem Configuration Files ....316
Customizing the Modem Configuration Files.............316
IBM 7852-400 DIP Switch Settings ................317
Xon/Xoff Modems .....................317
Ring Detection ......................317
Terminal Emulators .....................318
Recovery Procedures ....................318
Transfer of a Modem Session ..................318
Recovery Strategy .....................319
Contents vii
Page 10

Prevention Strategy .....................320
Modem Configuration Sample Files ................321
Sample File modem_m0.cfg ..................321
Sample File modem_m1.cfg ..................323
Sample File modem_z.cfg...................325
Sample File modem_z0.cfg ..................327
Sample File modem_f.cfg ...................329
Sample File modem_f0.cfg ..................332
Sample File modem_f1.cfg ..................335
Appendix E. Firmware Updates .................339
Checking the Current Firmware Levels ...............339
Updating System Firmware ...................339
Index ..........................341
viii Service Guide
Page 11

Safety Notices
A
danger
notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing
death or serious personal injury. Danger notices appear on the following pages:
v ix
v 49
v 50
v 247
v 272
A
caution
notice indicates the presence of a hazard that has the potential of causing
moderate or minor personal injury. Caution notices appear on the following pages:
v ix
v x
v 49
v 247
v 284
Note: For a translation of these notices, see
System Unit Safety Information
, order
number SA23-2652.
Electrical Safety
Observe the following safety instructions any time you are connecting or disconnecting
devices attached to the workstation.
DANGER
To prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect all power cables from the
electrical outlet before relocating the system.
CAUTION:
This product is equipped with a three–wire power cable and plug for the user’s
safety. Use this power cable with a properly grounded electrical outlet to avoid
electrical shock.
DANGER
To prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect all power cables from the
electrical outlet before relocating the system.
ix
Page 12

Laser Safety Information
CAUTION:
This product may contain a CD-ROM which is a class 1 laser product.
Laser Compliance
All lasers are certified in the U.S. to conform to the requirements of DHHS 21 CFR
Subchapter J for class 1 laser products. Outside the U.S., they are certified to be in
compliance with the IEC 825 (first edition 1984) as a class 1 laser product. Consult the
label on each part for laser certification numbers and approval information.
CAUTION:
All IBM laser modules are designed so that there is never any human access to
laser radiation above a class 1 level during normal operation, user maintenance,
or prescribed service conditions. Data processing environments can contain
equipment transmitting on system links with laser modules that operate at
greater than class 1 power levels. For this reason, never look into the end of an
optical fiber cable or open receptacle. Only trained service personnel should
perform the inspection or repair of optical fiber cable assemblies and receptacles.
x Service Guide
Page 13

Data Integrity and Verification
IBM computer systems contain mechanisms designed to reduce the possibility of
undetected data corruption or loss. This risk, however, cannot be eliminated. Users who
experience unplanned outages, system failures, power fluctuations or outages, or
component failures must verify the accuracy of operations performed and data saved or
transmitted by the system at or near the time of the outage or failure. In addition, users
must establish procedures to ensure that there is independent data verification before
relying on such data in sensitive or critical operations. Users should periodically check
the IBM support websites for updated information and fixes applicable to the system and
related software.
xi
Page 14

xii Service Guide
Page 15

About This Book
This book provides maintenance information that is specific to the 9112 Model 265 as
well as adapters and attached devices that do not have their own service information. It
also contains Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) that are not common to other
systems. In this book, the 9112 Model 265 are hereafter referred to as the ″system.″
MAPs that are common to all systems are contained in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
This book is used by the service technician to repair system failures. This book
assumes that the service technician has had training on the system unit.
ISO 9000
ISO 9000 registered quality systems were used in the development and manufacturing
of this product.
Related Publications
The following publications provide additional information about your system unit:
v The
IntelliStation POWER 9112 Model 265 Installation Guide
, order number
SA38-0607, contains information on how to set up and cable the system, install and
remove options, and verify system operation.
v The
IntelliStation POWER 9112 Model 265 User’s Guide
, order number SA38-0608,
contains information to help users use the system, use the service aids, and solve
minor problems.
v The
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
,
order number SA38-0509, contains diagnostic information, service request numbers
(SRNs), and failing function codes (FFCs).
v The
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Adapters, Devices, and Cable Information for
Multiple Bus Systems
, order number SA38-0516, contains information about
adapters, devices, and cables for your system. This manual is intended to
supplement the service information found in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
v The
Site and Hardware Planning Guide
, order number SA38-0508, contains
information to help you plan your installation.
v The
System Unit Safety Information
, order number SA23-2652, contains translations
of safety information used throughout this book.
v The
PCI Adapter Placement Reference
, order number SA38-0538, contains
information regarding slot restrictions for adapters that can be used in this system.
xiii
Page 16

Trademarks
The following terms are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in
the United States, other countries, or both:
v AIX
v IBM
v PowerPC
v pSeries
v e (logo)
v IntelliStation
Other company, product, and service names may be trademarks or service marks of
others.
xiv Service Guide
Page 17

Chapter 1. Reference Information
System Unit Locations
Front View
1
2
3
4
5
6
1 Diskette drive
2 Hot-swap disk drives (optional on some systems)
3 Cover release lever
4 CD-ROM drive
5 Media bay
6 Operator panel
1
Page 18
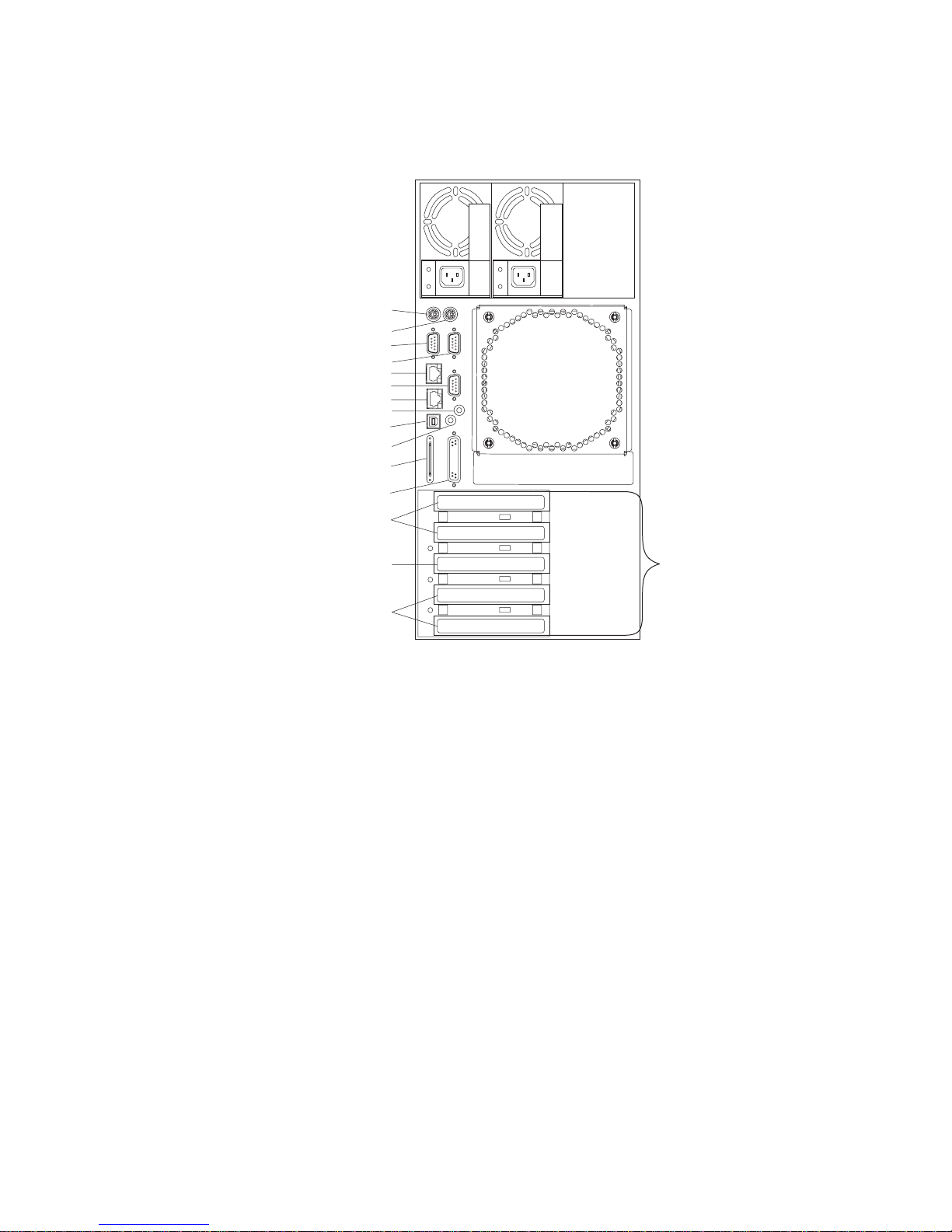
Rear View
1
4
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1 PCI slots
2 PCI slots 1-2 (64-Bit/3.3V)
3 PCI slot 3 (64-Bit/5V)
4 PCI slots 4-5 (32-Bit/5V)
5 Parallel connector
6 SCSI connector
7 Attention LED
8 Rack indicator connector
9 Power LED
10 Ethernet connector 2
11 Serial connector 1
12 Ethernet connector 1
13 Serial connector 3
14 Serial connector 2
15 Mouse connector
16 Keyboard connector
2 Service Guide
Page 19
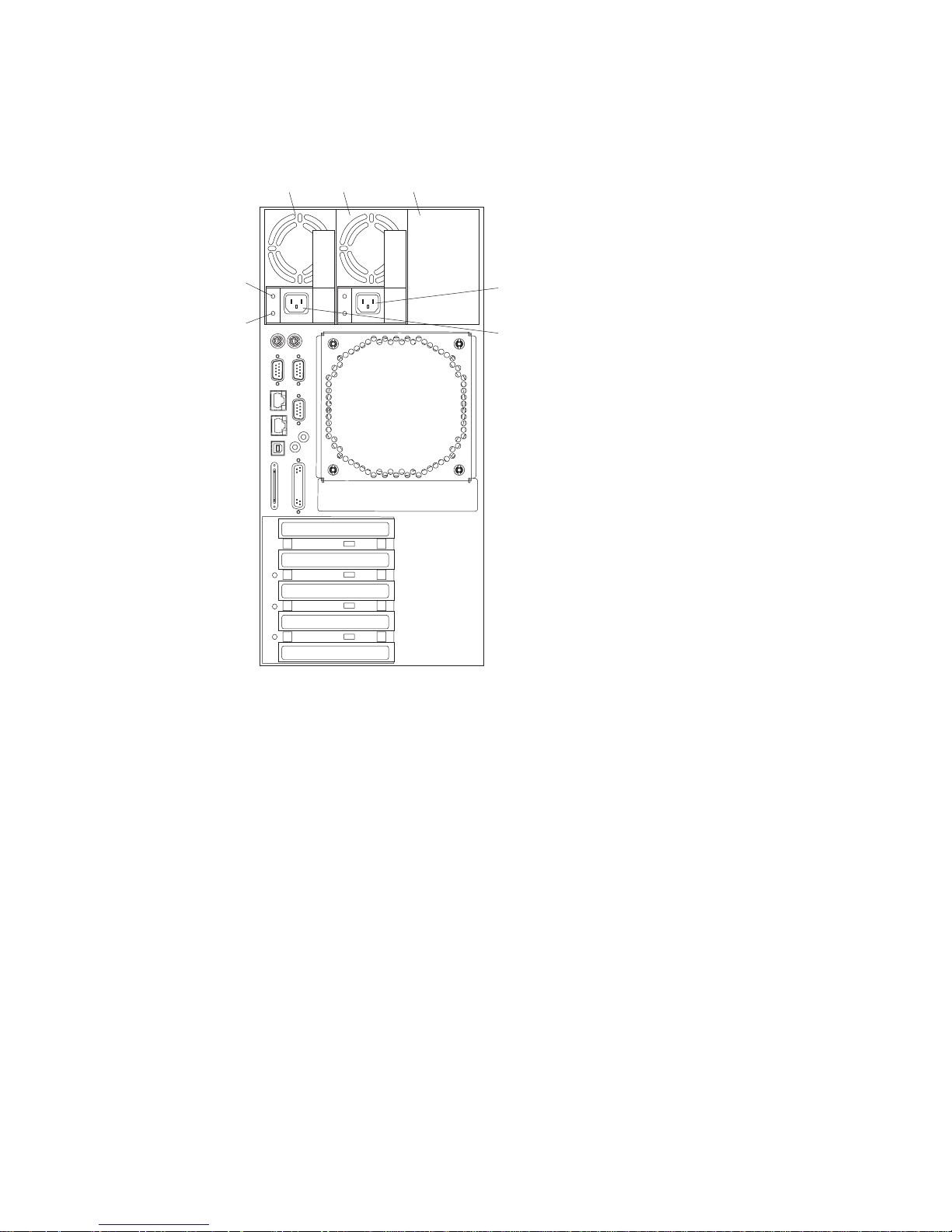
Power Supply Locations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1 Power supply 1
2 Power supply 2
3 Filler panel or power supply 3
4 Power supply 2 power connector
5 Power supply 1 power connector
6 DC power light
7 AC power light
Chapter 1. Reference Information
3
Page 20
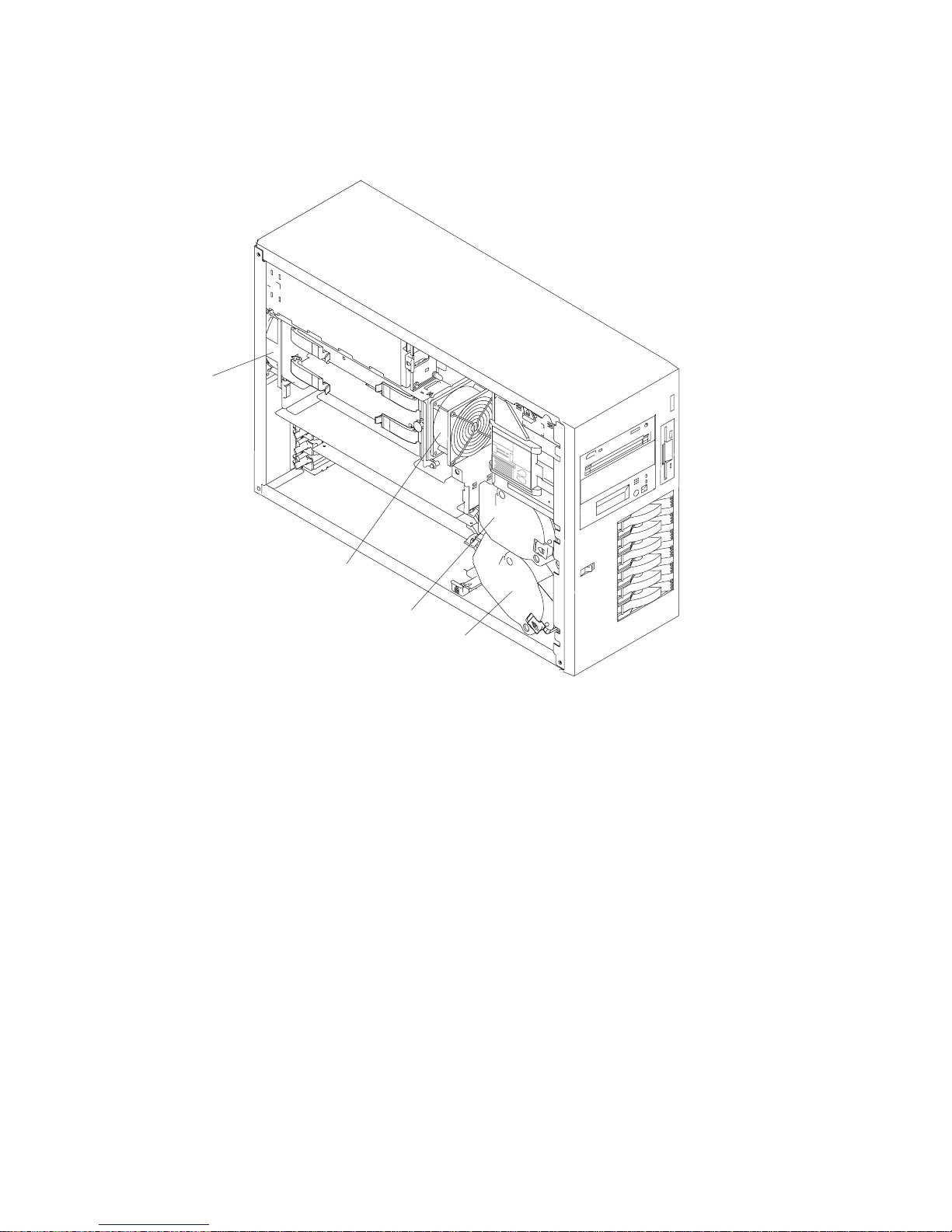
Fan Locations
1
2
3
4
1 Fan #1
2 Fan #2
3 Fan #3
4 Fan #4
4 Service Guide
Page 21
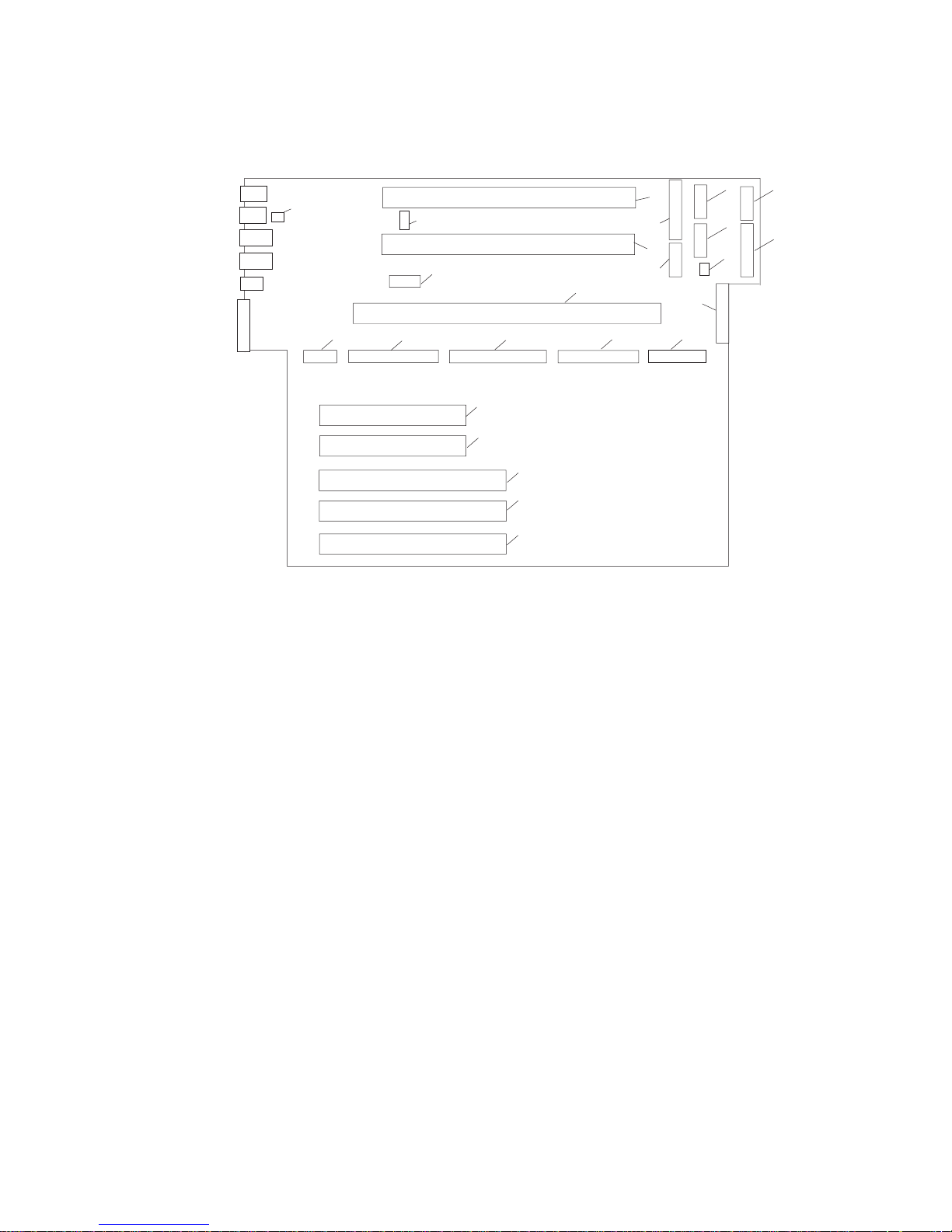
System Board Locations
2
3
6
4
5
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
17
15
18
16
19
20
21
22
23
24
7
1
1 Rear serial port (#1) connector 2 Rear power and attention LED connector
3 Processor power connector 4 Processor #2 card connector
5 Processor #1 card connector 6 Power connector
7 Power connector 8 Power connector
9 Power connector 10 Light path card connector
11 Processor fans 12 Blowers
13 Diskette connector 14 Memory card connector
15 Front serial port connector 16 Operator panel connector
17 CD-ROM IDE connector 18 Internal SCSI connector
19 - 20 32-bit PCI connectors
(33MHz, 5V)
21 64-bit PCI connector
(33MHz, 5V)
22 - 23 64-bit PCI connector
(50MHz, 3.3V)
24 Battery connector
Chapter 1. Reference Information
5
Page 22
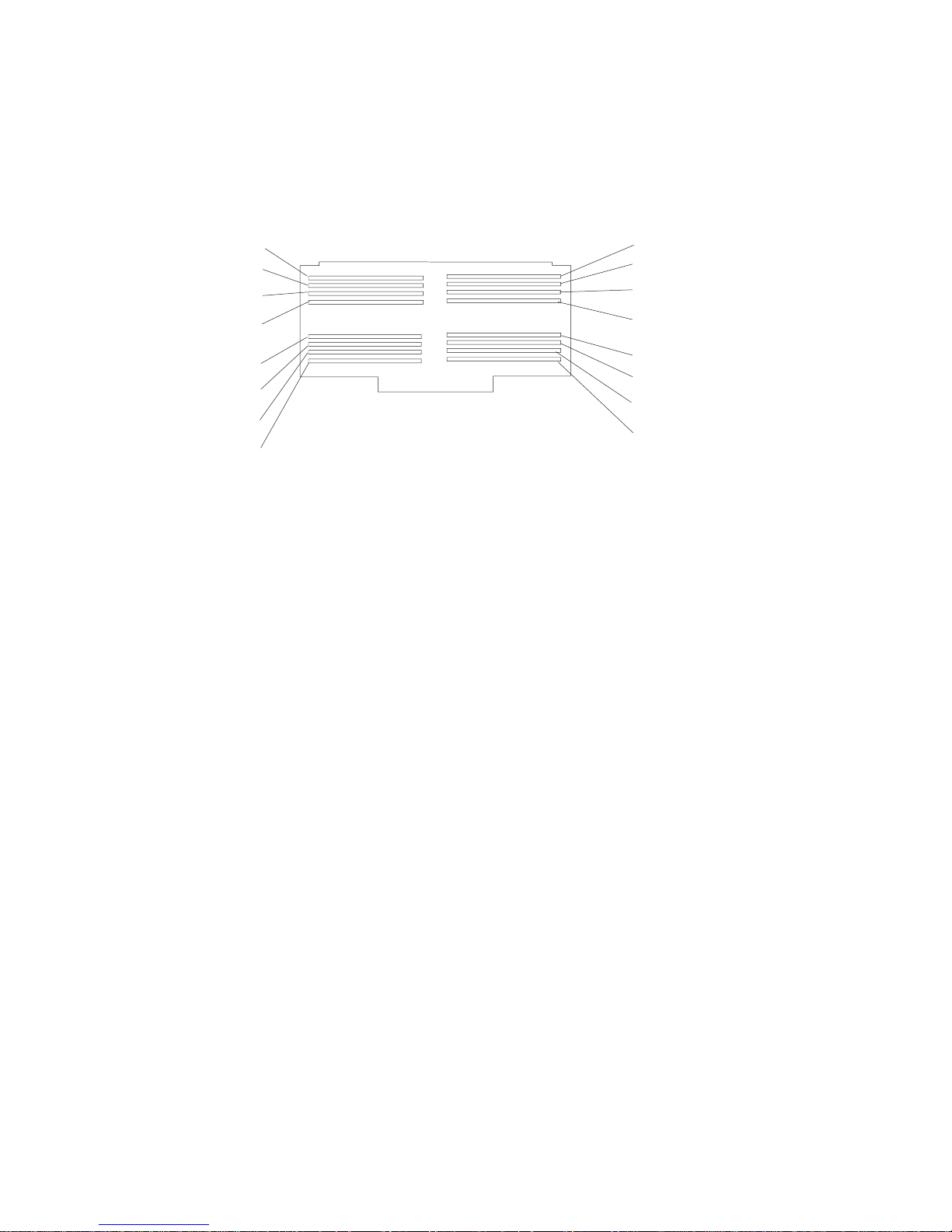
Memory DIMMs Location
Note: Memory DIMMs must be installed and removed in pairs and in the correct slots.
(Slots J1 and J2, J3 and J4, J5 and J6, and so on.)
Slot J1
Slot J3
Slot J4
Slot J2
Slot J5
Slot J6
Slot J9
Slot J10
Slot J11
Slot J12
Slot J13
Slot J14
Slot J15
Slot J16
Slot J7
Slot J8
Slot J1 Location P1-M1.1 Slot J2 Location P1-M1.2
Slot J3 Location P1-M1.3 Slot J4 Location P1-M1.4
Slot J5 Location P1-M1.5 Slot J6 Location P1-M1.6
Slot J7 Location P1-M1.7 Slot J8 Location P1-M1.8
Slot J9 Location P1-M1.9 Slot J10 Location P1-M1.10
Slot J11 Location P1-M1.11 Slot J12 Location P1-M1.12
Slot J13 Location P1-M1.13 Slot J14 Location P1-M1.14
Slot J15 Location P1-M1.15 Slot J16 Location P1-M1.16
6 Service Guide
Page 23

Power Backplane
J3
J2
J4
J1
J6
J5
J1 SCSI backplane power
J2 Media devices power
J3 System board power
J4 System board power
J5 System board power
J6 System board power
Chapter 1. Reference Information
7
Page 24
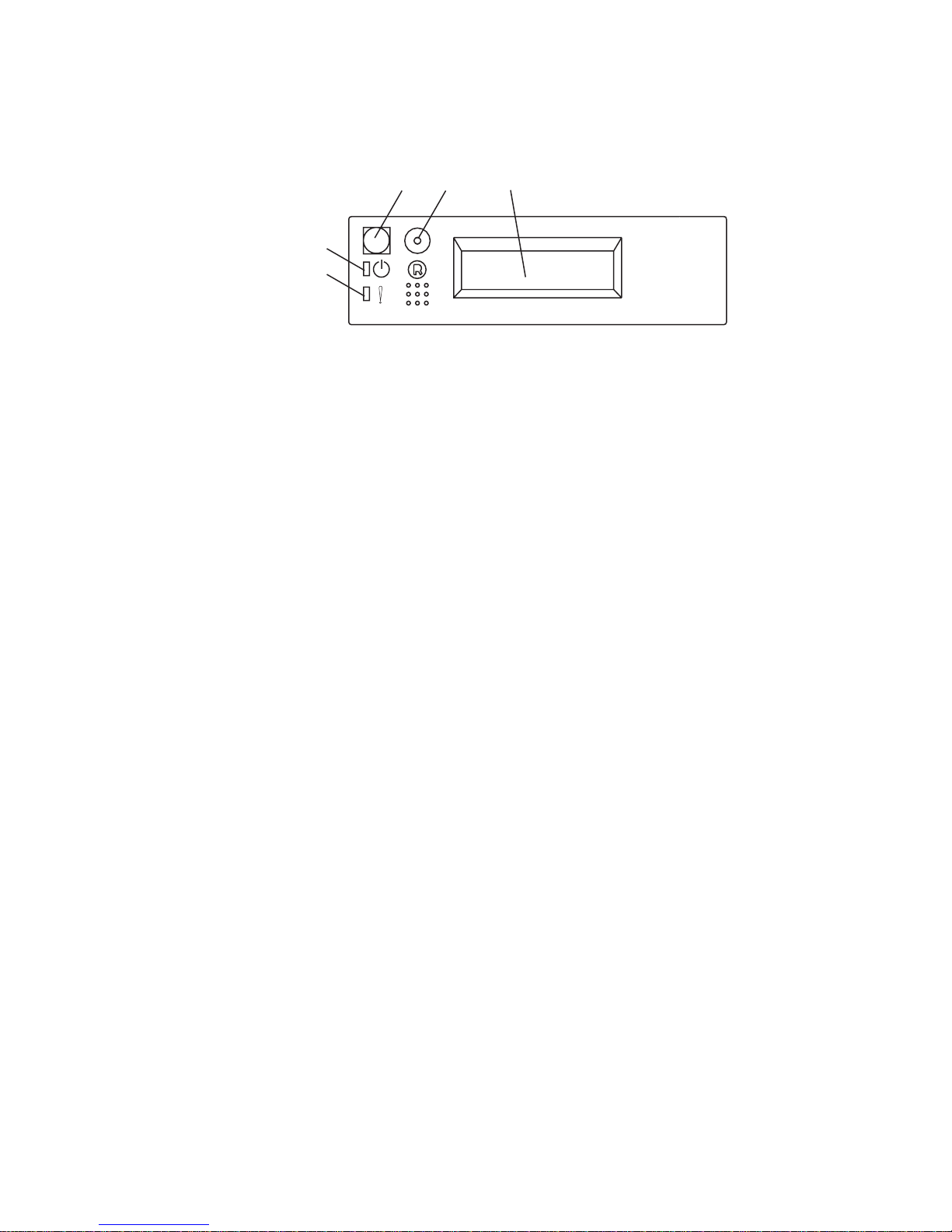
Operator Panel
4
5
1
2
3
1 Power-On Switch
2 Reset Switch
3 Display
4 Attention LED
5 Power-On LED
8 Service Guide
Page 25

SCSI IDs and Bay Locations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Index Bay Location Drive Name SCSI ID
1 D01 Disk Drive (behind operator
panel
SCSI ID 0
2 D02 Media SCSI ID 1
3 D03 IDE CD-ROM IDE (Non-SCSI)
3 D03 SCSI Device SCSI ID 2
4 D10 Disk Drive SCSI ID 10
5 D11 Disk Drive SCSI ID 11
6 D12 Disk Drive SCSI ID 12
7 D13 Disk Drive SCSI ID 13
8 D14 Disk Drive SCSI ID 14
9 D15 Disk Drive SCSI ID 15
Note: The SCSI bus IDs are the recommended values and indicate how the IDs are
set when the system is shipped from the factory. Field instaions might not
comply with these recommendations.
Chapter 1. Reference Information 9
Page 26
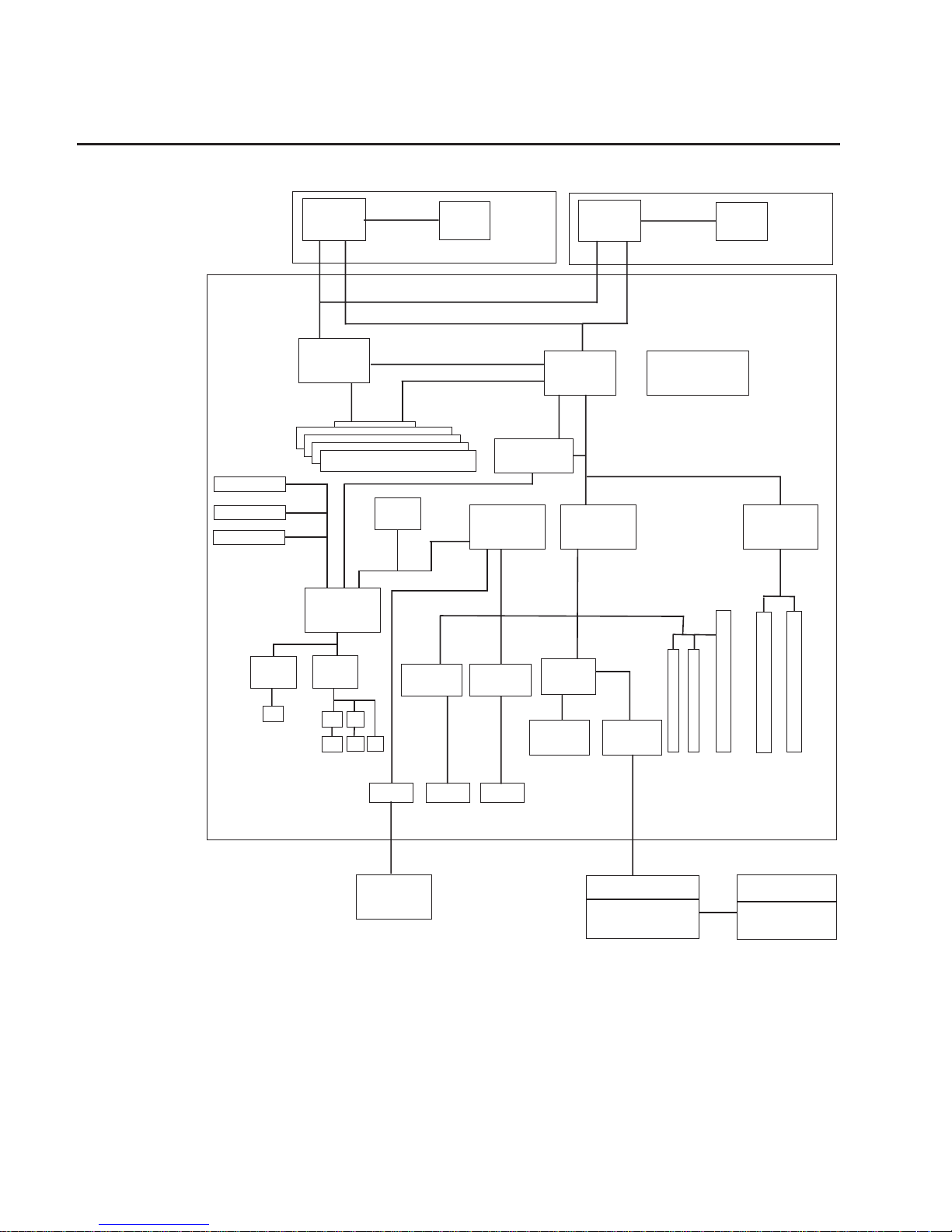
System Logic Flow Diagram
Power3-II
Power3-II
Processor Card
Processor Card
System Board
Addr/Cntl
Memory
Address
Memory Data Bus
16-bytes
6XX Address
CPU Data Bus 16-bytes
CPU-MX Bus
66MHz
Memory Modules
Data
System Clock
Arbiter
(Misc Logic)
S4
S3 S2 S1
S5
PCI Bridge
(0)
ISA Bridge
SCSI
CD-ROM
Drive
SCSI Backplane
SCSI Repeater
Hot-Swap
Disk Drives
SCSI Media
Devices
Internal
Ultra 160
External
Ultra 160
RJ45
RJ45
IDE
10/100
Ethernet
10/100
Ethernet
Boot
ROM
SP CPU
SP Flash
SP SRAM
SP
Interface
Super
I/O
UART
S3
P
K
S1
S2
M
PCI Bridge
(1)
L2
Cache
L2
Cache
32-Bytes
32-Bytes
10 Service Guide
Page 27

Location Codes
This system unit uses physical location codes in conjunction with AIX location codes to
provide mapping of the failing field replaceable units. The location codes are produced
by the system unit’s firmware and AIX.
Physical Location Codes
Physical location codes provide a mapping of logical functions in a platform (or
expansion sites for logical functions, such as connectors or ports) to their specific
locations within the physical structure of the platform.
Location Code Format
The location code is an alphanumeric string of variable length, consisting of a series of
location identifiers, separated by a dash (-), or slash (/), or a pound sign (#) character.
The series is hierarchical; that is, each location identifier in the string is a physical or
logical child of the one preceding it.
v The - (dash) separator character represents a normal structural relationship where
the child is a separate physical package and it plugs into (or is connected to) the
parent. For example, P1-C1 is a processor card (C1) plugged into a planar (P1), or
P1-M1 is a memory card (M1) plugged into a planar (P1).
v The / (slash) separator character separates the base location code of a function from
any extended location information. A group of logical devices can have the same
base location code because they are all on the same physical package, but may
require extended location information to describe the connectors they support. For
example, P2/S1 describes the location of the serial port 1 controller and its connector
(S1), which is located on planar P2 (its base location code), but the / indicates that
further devices can be connected to it at the external S1 serial connector. The
keyboard controller and its connector likewise have location code P2/K1, which
means they have the same base location code (P2) as serial port 1, but a different
external connector. In contrast, the location code P2-K1 actually points to the device
connected to connector K1; that is, the keyboard. The location code P2/Z1 indicates
an integrated SCSI controller which drives connector Z1, while location codes of
P2-Z1-... point to the actual SCSI bus and devices.
v The # (pound sign) separator character indicates a cable connection between a
connector and parent.
The following are examples:
v P1-C1 identifies processor card C1 plugged into planar P1.
v P1-M1 identifies memory card M1 plugged into planar P1.
v P2/S1 identifies serial port 1 controller on I/O board P2 or the connector for serial
port 1.
v P1-K1 identifies a keyboard attached to connector K1 on planar P1.
v P2/Z1 identifies an integrated SCSI port controller on planar P2 which drives
connector Z1.
v P2-Z1-... points to the actual SCSI bus and devices attached to Z1.
Chapter 1. Reference Information 11
Page 28

The . (period) identifies sublocations (DIMMs on a memory card or SCSI addresses).
The following are examples:
v P1-M1.4 identifies memory DIMM 4 on memory card 1 plugged into planar P1.
v P1-C1.1 identifies processor 1 on processor card 1 plugged into planar P1.
v P2-Z1-A3.1 identifies a SCSI device with SCSI address of LUN 1 at SCSI ID 3
attached to SCSI bus 1, which is integrated on planar P2.
v P2.1 identifies a riser card plugged into planar P2.
AIX Location Codes
The basic formats of the AIX location codes are as follows:
v For non-SCSI devices/drives:
– AB-CD-EF-GH
v For SCSI devices/drives:
– AB-CD-EF-G,H
Non-SCSI Devices/Drives
For planars, cards, and non-SCSI devices, the location code is defined as follows:
AB-CD-EF-GH
||||
| | | Device/FRU/Port ID
| | Connector ID
| devfunc Number, Adapter Number or Physical Location
Bus Type or PCI Parent Bus
v The AB value identifies a bus type or PCI parent bus as assigned by the firmware.
v The CD value identifies adapter number, the adapter’s devfunc number, or physical
location. The devfunc number is defined as the PCI device number times 8, plus the
function number.
v The EF value identifies a connector.
v The GH value identifies a port, address, device, or FRU.
Adapters and cards are identified only with AB-CD.
The possible values for AB are:
00 Processor bus
01 ISA bus
02 EISA bus
03 MCA bus
04 PCI bus used in the case where the PCI bus cannot be identified
05 PCMCIA buses
xy For PCI adapters where x is equal to or greater than 1. The x and y are characters in the
range of 0-9, A-H, J-N, P-Z (O, I, and lower case are omitted) and are equal to the parent
bus’s ’ibm, aix-location’ open firmware property.
The possible values for CD depend on the adapter/card:
12 Service Guide
Page 29

v For pluggable PCI adapters/cards, CD is the device’s devfunc number (PCI device
number times 8, plus the function number). The C and D are characters in the range
of 0-9, and A-F (hex numbers). Location codes therefore uniquely identify multiple
adapters on individual PCI cards.
v For pluggable ISA adapters, CD is equal to the order of the ISA cards
defined/configured either by SMIT or the ISA Adapter Configuration Service Aid.
v For an integrated ISA adapters, CD is equal to a unique code identifying the ISA
adapter. In most cases, this code is equal to the adapter’s physical location code. In
cases where a physical location code is not available, CD will be FF.
EF is the connector ID. It is used to identify the adapter’s connector to which a resource
is attached.
GH is used to identify a port, device, or FRU. For example:
v For async, devices GH defines the port on the fanout box. The values re 00 a to 15.
v For a diskette drive, H identifies either diskette drive 1 or 2. G is always 0.
v For all other devices, GH is equal to 00.
For an integrated adapter, EF-GH is the same as the definition for a pluggable adapter.
For example, the location code for a diskette drive is 01-D1-00-00. A second diskette
drive is 01-D1-00-01.
SCSI Devices/Drives
For SCSI devices, the location code is defined as follows:
AB-CD-EF-G,H
| | |||
| | | | Logical Unit address of the SCSI Device
| | | Control Unit Address of the SCSI Device
| | Connector ID
| devfunc Number, Adapter Number or Physical Location
Bus Type or PCI Parent Bus
Where AB-CD-EF are the same as non-SCSI devices.
G defines the control unit address of the device. Values of 0 to 15 are valid.
H defines the logical unit address of the device. Values of 0 to 255 are valid.
A bus location code is also generated as ’00-XXXXXXXX’ where XXXXXXXX is
equivalent to the node’s unit address.
Examples of physical location codes displayed by AIX are as follows:
v First processor card plugged into planar 1:
P1-C1
Chapter 1. Reference Information
13
Page 30

v Second memory card in planar P1:
P1-M2
v Memory DIMM 12 on second memory card plugged into planar P1:
P1-M2.12
Examples of AIX location codes displayed are as follows:
v Integrated PCI adapter:
10-80 Ethernet
10-60 Integrated SCSI Port 1 (internal)
10-88 Integrated SCSI Port 2 (external)
v Pluggable PCI adapters:
20-58 to 20-5F Any PCI card in slot 1
20-60 to 20-67 Any PCI card in slot 2
10-68 to 10-6F Any PCI card in slot 3
10-70 to 10-77 Any PCI card in slot 4
10-78 to 10-7F Any PCI card in slot 5
v Integrated ISA adapters:
01-D1 Diskette adapter
01-R1 Parallel port adapter
01-S1 Serial port 1 adapter
01-S2 Serial port 2 adapter
01-S3 Serial port 3 adapter
01-K1 Keyboard adapter
v Device attached to SCSI controller:
10-60-00-4,0 Device attached to integrated SCSI Port 1
14 Service Guide
Page 31

AIX and Physical Location Code Table
AIX
Location
Codes
Physical
Location
Codes
10-78 to 10-7F
or
1F-XX
10-70 to 10-77
or
1E-XX
10-68 to 10-6F
or
1D-XX
20-60 to 20-67
or
2C-XX
20-58 to 20-5F
or
2B-XX
P1-I1
P1-I2
P1-I3
P1-I4
P1-I5
P1-C2
00-02
00-00
00-00
01-D1
10-60
10-58
01-K1-00
01-S2
01-S3
10-80
10-88
01-S1
10-61
01-R1
01-K1-01
P1-C1
P1-V2
P1-M1
P1/D1
P1/Z1
P1/Q1
P1/L1
P1/O1
P1/S2
P1/S3
P1/E1
P1/E2
P1/S1
P1/Z2
P1/R1
P1/K1
Chapter 1. Reference Information 15
Page 32

Component Name AIX Location Code Physical Location
Code
Logical Identification
Central Electronics Complex (CEC)
System Board 00-00 P1
Processor Card 1 00-00 P1-C1 Processor 0
Processor Card 2 00-02 P1-C2 Processor 2
Memory Card 00-00 P1-M1
Memory DIMMs on
Memory Card
00-00 P1-M1.1 thru
P1-M1.16
Extents:
0H, 0L, 2H, 2L, 4H,
4L, 6H, 6L, 1H, 1L,
3H, 3L, 5H, 5L, 7H, 7L
Integrated Devices
Diskette Drive 01-D1-00-00 P1-D1
Keyboard 01-K1-00-00 P1/K1-K1
Mouse 01-K1-01-00 P1/O1-O1
Diskette Port 01-D1 P1/D1
Keyboard Port 01-K1-00 P1/K1
Mouse Port 01-K1-01 P1/O1
Serial Port 1 01-S1 P1/S1
Serial Port 2 01-S2 P1/S2
Serial Port 3 01-S3 P1/S3
Parallel Port 01-R1 P1/R1
Ethernet Port 1 10-80 P1/E1
Ethernet Port 2 10-88 P1/E2
Internal SCSI Port 10-60 P1/Z1
External SCSI Port 10-61 P1/Z2
IDE Port 10-58 P1/Q1
Base CD-ROM (IDE)
in bay D03
10-59 P1/Q1–A2
Pluggable Adapters
PCI Host Bridge 1 00-FEE00000 P1
Card in PCI Slot 1 20-58 to 20-5F or
2B-xx
P1-I1
Card in PCI Slot 2 20-60 to 20-67 or
2C-xx
P1-I2
PCI Host Bridge 0 00-FEF00000 P1
Card in PCI Slot 3 10-68 to 10-6F or
1D-xx
P1-I3
Card in PCI Slot 4 10-70 to 10-77 or
1E-xx
P1-I4
16 Service Guide
Page 33

Component Name AIX Location Code Physical Location
Code
Logical Identification
Card in PCI Slot 5 10-78 to 10-7F or
1F-xx
P1-I5
SCSI Devices
SCSI Backplane N/A P2
SCSI Repeater
Backplane
N/A N/A
SCSI Device in bay
D01
10-60-00-0,0 P1/Z1–A0 Internal SCSI Bus ID 0
SCSI Device in bay
D02
10-60-00-1,0 P1/Z1-A1 Internal SCSI Bus ID 1
SCSI Device in bay
D03
10-60-00-2,0 P1/Z1-A2 Internal SCSI Bus ID 2
SAF-TE Controller 10-60-00-9-0 P1/Z1–A9 SCSI Enclosure
Services Controller
Hot-swap DASD bay 1 10-60-00-10,0 P1/Z1-Aa Primary SCSI Bus ID
10
Hot-swap DASD bay 2 10-60-00-11,0 P1/Z1-Ab Primary SCSI Bus ID
11
Hot-swap DASD bay 3 10-60-00-12,0 P1/Z1-Ac Primary SCSI Bus ID
12
Hot-swap DASD bay 4 10-60-00-13,0 P1/Z1-Ad Primary SCSI Bus ID
13
Hot-swap DASD bay 5 10-60-00-14,0 P1/Z1-Ae Primary SCSI Bus ID
14
Hot-swap DASD bay 6 10-60-00-15,0 P1/Z1-Af Primary SCSI Bus ID
15
Fans
Fan 1 F1 Fan
Fan 2 F2 Fan
Fan 3 F3 Fan
Fan 4 F4 Fan
Operator Panel
Operator panel L1
Lightpath
LED panel
L2
Power Supply
Power backplane P3
Power supply 1 P3-V1
Power supply 2 P3-V2
Power supply 3 P3-V3
Chapter 1. Reference Information
17
Page 34

Component Name AIX Location Code Physical Location
Code
Logical Identification
Battery
Battery P1-V2
System VPD module
System VPD module L1-N1
Notes:
1. The physical location code for the PCI slots, when empty, uses the P1/Ix notation, where the
’/’ identifies an integrated device (in this case the empty slot). A PCI device plugged into the
slot uses the P1-Ix notation, where the ’-’ identifies a plugged device.
2. The SCSI bus IDs are the recommended values. The SCSI IDs shown for media devices
indicate how the devices are set when they are shipped from the factory. Field installations
may not comply with these recommendations.
18 Service Guide
Page 35

System Cables
J6
J5
J3
J4
J1
J2
T
Fan
Fan
Power
Backplane
System Board
Processor Slot
Processor Slot
Diskette
DASD
Operator
Panel
CD-ROM
Tape
Power
Power
SCSI
SCSI
Power
IDE
Power
Signal
Power
SCSI
SCSI
Backplane
Blower
Light
Path
LEDs
RJ45
Serial
Rear
Serial
Port #1
Rear
LEDs
Blower
Chapter 1. Reference Information 19
Page 36

Specifications
Dimensions
Height 426 mm (16.8 in.)
Width 215 mm (8.5 in..
Depth 617 mm (24 in.).
Weight
Minimum configuration 35.5 kg 78 lbs.
Maximum configuration 43.1 kg 94.8 lbs.
Electrical
Power source loading
(maximum in kVA)
0.46
Power source loading (typical in
kVA)
0.31
Voltage range (V ac) 100 to 127 or 200 to 240 (autoranging)
Frequency (hertz) 50 / 60
Voltage range (V dc) Not supported
Thermal output (maximum) 1536 Btu/hr
Thermal output (typical) 1024 Btu/hr
Power requirements (maximum) 450 watts
Power requirements (typical) 300 watts
Power factor - US, World Trade,
Japan
0.98
Inrush current² 70 amps
Maximum altitude³,⁴ 2135 m (7000 ft.)
Temperature Requirements³ Operating
10 to 40°C
(50 to 104°F)
Non-Operating
10 to 52°C
(50 to 126°F)
Humidity Requirements⁴ Operating Non-Operating
(Noncondensing) 8 to 80% 8 to 80%
Wet Bulb 27°C (80°F) 27°C (80°F)
Noise Emissions¹,⁵ Operating Idle
L
WAd
6.1 bels 6.1 bels
<L
pA>m
42 dBA 41 dBA
Install/Air Flow Maintenance of proper service clearance should allow proper
air flow.
1. Inrush currents occur only at initial application of power, no inrush occurs during normal
power off-on cycle.
2. The upper limit of the dry bulb temperature must be derated 1 degree C per 137 m (450 ft.)
above 915 m (3000 ft.).
3. The upper limit of the wet bulb temperature must be derated 1 degree C per 274 m (900 ft. )
above 305 m (1000 ft.).
4. Levels are for a single system installed in a T00 32 EIA rack with the center of the unit
approximately 1500 mm (59 in.) off the floor.
20 Service Guide
Page 37

Power Cables
To avoid electrical shock, a power cable with a grounded attachment plug is provided.
Use only properly grounded outlets.
Power cables used in the United States and Canada are listed by Underwriter’s
Laboratories (UL) and certified by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). These
power cords consist of the following:
v Electrical cables, Type SVT or SJT.
v Attachment plugs complying with National Electrical Manufacturers Association
(NEMA) 5-15P, that is:
″For 115 V operation, use a UL listed cable set consisting of a minimum 18 AWG, Type
SVT or SJT three-conductor cord a maximum of 15 feet in length and a parallel blade,
grounding type attachment plug rated at 15 A, 125 V.″
″For 230 V operation in the United States use a UL listed cable set consisting of a
minimum 18 AWG, Type SVT or SJT three-conductor cable a maximum of 15 feet in
length, and a tandem blade, grounding type attachment plug rated at 15 A, 250 V.″
v Appliance couplers complying with International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
Standard 320, Sheet C13.
Power cables used in other countries consist of the following:
v Electrical cables, Type HD21.
v Attachment plugs approved by the appropriate testing organization for the specific
countries where they are used.
″For units set at 230 V (outside of U.S.): use a cable set consisting of a minimum 18
AWG cable and grounding type attachment plug rated 15 A, 250 V. The cable set
should have the appropriate safety approvals for the country in which the equipment will
be installed and should be marked `HAR’.″
Refer to Chapter 10, “Parts Information” on page 293 to find the power cables that are
available.
Chapter 1. Reference Information 21
Page 38

Service Inspection Guide
Perform a service inspection on the system when:
v The system is inspected for a maintenance agreement.
v Service is requested and service has not recently been performed.
v An alterations and attachments review is performed.
v Changes have been made to the equipment that may affect the safe operation of the
equipment.
v External devices with their own power cables have those cables attached.
If the inspection indicates an unacceptable safety condition, the condition must be
corrected before anyone can service the machine.
Note: The owner of the system is responsible to correct any unsafe conditions.
Perform the following checks:
1. Check the covers for sharp edges and for damage or alterations that expose the
internal parts of the system.
2. Check the covers for proper fit to the system. They should be in place and secure.
3. Gently rock the system from side to side to determine if it is steady.
4. Set the power switch of the system to Off.
5. Remove the covers.
6. Check for alterations or attachments. If there are any, check for obvious safety
hazards, such as broken wires, sharp edges, or broken insulation.
7. Check the internal cables for damage.
8. Check for dirt, water, and any other contamination within the system.
9. Check the voltage label on the back of the system to ensure that it matches the
voltage at the outlet.
10. Check the external power cable for damage.
11. With the external power cable connected to the system, check for 0.1 ohm or less
resistance between the ground lug on the external power cable plug and the metal
frame.
12. Perform the following checks on each device that has its own power cables:
a. Check for damage to the power cord.
b. Check for the correctly grounded power cable.
c. With the external power cable connected to the device, check for 0.1 ohm or
less resistance between the ground lug on the external power cable plug and
the metal frame of the device.
13. Install the covers.
22 Service Guide
Page 39

Chapter 2. Diagnostic Overview
The system uses an integrated set of software diagnostic procedures to facilitate
isolation of failing components and system maintenance. This book, along with the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
,isthe
basis of the diagnostic procedures for the system. In particular, Chapter 4,
“Checkpoints” on page 81, Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU Index” on page 109,
Chapter 6, “Loading the System Diagnostics” on page 175, and Chapter 10, “Parts
Information” on page 293, in this book are important for the trained service
representative to understand and use when isolating a failure on the system.
The manufacturer recommends that systems configured with 4 GB of memory or
greater have access to a 4-mm or 8-mm tape drive for submission of system dump
information if required. This function can be accomplished through locally attached or
network-attached devices, as appropriate.
Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) guide the trained service person through the
system. These MAPs are the entry point for all isolation and error recovery procedures.
The MAPs are consistent with existing procedures and methods. The system uses a set
of integrated procedures, mentioned earlier, to which the MAPs are the primary entry
point.
The MAPS are as follows:
v Entry MAP
v Quick Entry MAP
v Problem Determination MAP
v Power MAP
v Minimum Configuration MAP
The Entry Map is the starting point for problem determination. The purpose of this MAP
is to quickly point to the appropriate MAP or service reference information either in this
book, or in the common book set, which includes the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
and
PCI Adapter Placement
Reference
.
The Quick Entry MAP is a subset of the Entry MAP and helps to save time for some
types of problems.
The Problem Determination MAP provides a structured analysis method to get an error
code if one is not provided by the customer, or if diagnostics cannot be loaded.
The Power MAP deals with isolation of components to diagnose a power problem.
Power problems can be related to powering on and powering off the system, or power
failures that occur after power is turned on.
23
Page 40

The Minimum Configuration MAP is used to locate defective components not found by
normal diagnostics or error-isolation methods. This MAP provides a systematic method
of isolation to the failing item or items.
Attention LED and Lightpath LEDs
The Attention and Lightpath LEDs provide a means to identify failing components in
your server. When a failing component is detected in your server, the Attention LED is
turned on. To further help you identify the failing component, go to the indicator panel
(see “Indicator Panel”) inside the server and check which LEDs are on.
Indicator Panel
The panel provides enough information to identify the area that needs attention. The
panel contains a group of amber LEDs that indicate which functional area of the system
is experiencing the fault (such as power, CPUs, memory, fans). If one of these LEDs is
on, the user or service representative is directed to the physical area of the server
where an additional LED on will be on, indicating the component that is responsible for
the current fault.
Indicator
Panel
24 Service Guide
Page 41

The following illustration shows the LEDs on the indicator panel, located inside the
server.
Memory
CPU
PCI
Fan
Fan
System Board
Power Board
1
2
3
4 3
2
1
Component LEDs
In addition to the indicator panel or display, individual LEDs are located on or near the
failing components. The LEDs are either on the component itself or on the carrier of the
component (memory card, fan, memory module, CPU).
The LEDs are amber, except for the power supplies. For the power supplies, two green
LEDs (ac power good and dc power good) indicate the fault condition for the power
supply.
Resetting the LEDs
To reset the LEDs:
1. Replace the failing component with the new component.
2. Log in as root user.
3. At the command line, type diag.
4. Select Task Selection.
5. Select Log Repair Action.
6. Select the device that was repaired. (If the device is not listed, select sysplanar0.)
Chapter 2. Diagnostic Overview 25
Page 42

Checkpoints
The system uses various types of checkpoints, error codes, and SRNs, which are
referred to throughout this book (primarily in Chapter 4, “Checkpoints” on page 81,
Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU Index” on page 109, Chapter 6, “Loading the System
Diagnostics” on page 175, and Chapter 10, “Parts Information” on page 293). These
codes may appear in the service processor boot progress log, the AIX error log, and the
operator panel display. Understanding the definition and relationships of these codes is
important to the service personnel who are installing or maintaining the system.
Codes that can appear on the operator panel or in error logs are as follows:
Checkpoints
Checkpoints display in the operator panel from the time ac power is connected
to the system until the AIX login prompt is displayed after a successful
operating system boot. These checkpoints have the following forms:
E000 - E075
These checkpoints display from the time ac power is connected to the
system until the OK prompt displays on the operator panel display.
During this time, the service processor performs self-test and NVRAM
initialization.
E0A0 - E0E1
When power on is initiated, the service processor starts built-in
self-test (BIST) on the central electronics complex (CEC). VPD data is
read.
E0E2 - E2xx
This range indicates that the system processor is in control and is
initializing system resources.
E3xx These codes indicate that the system processor is running memory
tests.
E1xx The system firmware attempts to boot from devices in the boot list.
Control is passed to AIX when E105 (normal mode boot) or E15B
(service mode boot) displays on the operator panel display.
0xxx and 2xxx
0xxx codes are AIX checkpoints and configuration codes. Location
codes may also be shown on the operator panel display during this
time.
Error Codes
If a fault is detected, an 8-digit error code is displayed in the operator panel
display. A location code may be displayed at the same time on the second line
of the display.
Checkpoints can become error codes if the system fails to advance past the
point at which the code was presented.
For a list of checkpoints, see Chapter 4, “Checkpoints” on page 81. Each entry
provides a description of the event and the recommended action if the system
fails to advance.
26 Service Guide
Page 43

SRNs Service request numbers, in the form xxx-xxx, may also be displayed on the
operator panel display and be noted in the AIX error log.
SRNs are listed in the
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
FRU Isolation
For a list of error codes and recommended actions for each code, see Chapter 5, “Error
Code to FRU Index” on page 109. These actions can refer to Chapter 10, “Parts
Information” on page 293, Chapter 3, “Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)” on
page 31, or provide informational message and directions. If a replacement part is
indicated, direct reference is made to the part name. The respective AIX and physical
location codes are listed for each occurrence as required. For a list of locations codes,
see “Location Codes” on page 11.
To look up part numbers and view component diagrams, see Chapter 10, “Parts
Information” on page 293. The beginning of that chapter provides a parts index with the
predominant field replaceable units (FRUs) listed by name. The remainder of the
chapter provides illustrations of the various assemblies and components that make up
the system.
Electronic Service Agent for the RS/6000
Service support for the system can be enhanced through the use of the application
program, Electronic Service Agent for the RS/6000. This application provides a number
of advantages for the customer, including automatic error reporting and analysis without
customer intervention. The Electronic Service Agent kit ships with the system and
includes the following:
v Electronic Service Agent for the RS/6000 program on CD-ROM
v The manual
Electronic Service Agent for the RS/6000 User’s Guide
.
If the manual is not included, it can be downloaded from the following Web site:
ftp://ftp.software.ibm.com/aix/.
Using the Service Processor and Electronic Service Agent Features
The service processor and Electronic Service Agent features protect users against
unnecessary system downtime by advising support personnel (both internal and
external) of any unexpected changes in the system environment. In combination, the
two features provide a flexible solution to automated system maintenance.
Service Processor
The service processor runs on its own power boundary and continually monitors
hardware attributes, the AIX operating system, and the environmental conditions within
the system. Any system failure which prevents the system from coming back to an
operational state (a fully functional AIX operating system) is reported by the service
processor. The service processor is controlled by firmware and does not require the AIX
Chapter 2. Diagnostic Overview 27
Page 44

operating system to be operational to perform its tasks. If any system failures are
detected, the service processor can take predetermined corrective actions. The
methods of corrective actions are:
v Surveillance
v Call home
v AIX operating system monitoring
Surveillance is a function in which the service processor monitors the system through
heartbeat communication with the system firmware. The
heartbeat
is a periodic signal
that the firmware can monitor. During system startup, the firmware surveillance monitor
is automatically enabled to check for heartbeats from the firmware. If a heartbeat is not
detected within a default period, the service processor cycles the system power and
attempts to restart until the system either restarts successfully, or a predetermined retry
threshold is reached. In the event the service processor is unsuccessful in bringing the
system online (or in the event that the user asked to be alerted to any service
processor-assisted restarts), the system can call home to report the error.
The call home function can be initialized to call either a service center telephone
number, a customer administration center, or a digital pager telephone number. The
service processor can be configured to stop at the first successful call to any of the
numbers listed, or can be configured to call every number provided. If connected to the
service center, the service processor transmits the relevant system information (the
system’s serial number and model type) and service request number (SRN). If
connected to a digital pager service, the service processor inputs a customer voice
telephone number defined by the customer. An established sequence of digits or the
telephone number to a phone near the failed system could be used to signal a system
administrator to a potential system failure.
During normal operations, the service processor can also be configured to monitor the
AIX operating system. If AIX does not respond to the service processor heartbeat, the
service processor assumes the operating system is hung. The service processor can
automatically initiate a restart and, if enabled, initiate the call home function to alert the
appropriate people to the system hang. Enabling operating system surveillance also
enables AIX to detect any service processor failures and report those failures to the
Electronic Service Agent application.
Unlike the Electronic Service Agent, the service processor cannot be configured in a
client/server environment where one system can be used to manage all dial-out
functionally for a set of systems.
Prior to installing the Electronic Service Agent feature, ensure that you have the latest
level of system firmware. You also need a properly configured modem. For more
information on configuring a modem, see Appendix D, “Modem Configurations” on
page 313.
Electronic Service Agent
The Electronic Service Agent is a software extension to the AIX operating system that
monitors the system while the AIX operating system is running. The Electronic Service
28 Service Guide
Page 45

Agent monitors and analyzes all recoverable system failures, and, if needed, can
automatically place a service call to a service center (without user intervention).
The service center receives the machine type/serial number, host name, SRN, and a
problem description. The service center analyzes the problem report and, if warranted,
dispatches a service person to the customer site. The service center also determines if
any hardware components need to be ordered prior to the service person’s arrival.
The Electronic Service Agent code also gives the user the option to establish a single
system as the problem reporting server. A single system, accessible over the user
network, can be used as the central server for all the other systems on the local area
network (LAN) that are running the Electronic Service Agent application. If the
Electronic Service Agent application on a remote client decides a service request needs
to be placed, the client forwards the information to the Electronic Service Agent server,
which dials the service center telephone number from its locally attached modem. In
this scenario, the user only needs to maintain a single analog line for providing call-out
capabilities for a large set of servers.
When used in a Scalable Parallel (SP) environment, a client/server type implementation
is configured. The Electronic Service Agent client code runs on each of the SP nodes.
The server component runs on the control workstation. In the event of any system
failures, the relevant information is transmitted to the control workstation through the
integrated Ethernet. Once alerted to the system failure, the control workstation initiates
actions to prepare and send the service request.
A modem is required for enabling automated problem reporting to the IBM service
center. Configuration files for several types of modems are included as part of the
Electronic Service Agent package. Refer to Appendix D, “Modem Configurations” on
page 313 for more information on configuring your modem.
Chapter 2. Diagnostic Overview 29
Page 46

30 Service Guide
Page 47

Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
This chapter contains Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) for the system.
Notes:
1. If you replace a FRU, go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
to verify correct system
operation.
2. When possible, run online diagnostics in service mode. Online diagnostics perform
additional functions compared to standalone diagnostics. This ensures that the error
state of the system that has been captured in nonvolatile random access memory
(NVRAM) is available for your use in fixing the problem. The AIX error log and SMIT
are only available when diagnostics are run from the hard drive.
3. If more than eight digits are displayed in the operator panel, use only the first eight
digits to find the error in the tables. The digits that display beyond the first eight
digits are location codes that can assist you in diagnosing the problem. See
“Location Codes” on page 11.
4. Licensed programs frequently rely on system information stored on the vital product
data (VPD) on the operator panel control assembly. If the MAPs indicate that the
operator panel should be replaced, update the VPD as described in “System Vital
Product Data (VPD) Update Procedure” on page 278.
5. If a network adapter or the system board is replaced, the network administrator
must be notified so that the client IP addresses used by the server can be changed.
In addition, the operating system configuration of the network controller might need
to be changed in order to enable system startup. Also check to ensure that any
client or server that addresses this system is updated.
6. If you are not able to isolate the problem, try loading standalone diagnostics from
the CD-ROM or NIM.
31
Page 48

Quick Entry MAP
Use the following table to determine your starting point.
Quick Entry MAP Table of Contents
Problem Description Page No.
Service Actions 33
System Stops With an 8-Digit Number Displayed 33
System Stops With a 4-Digit Number Displayed 33
OK Does Not Appear in the Operator Panel Display Before Pressing the
Power On Button
33
System Stops or Hangs With Alternating Numbers Displayed in the Operator
Display Panel.
34
There Appears to be a Display Problem (Distortion, Blurring,Etc.) 34
Power and Cooling Problems 34
Flashing 888 in Operator Panel Display 36
Other Symptoms or Problems 36
You Cannot Find the Symptom in this Table 39
32 Service Guide
Page 49

Symptom Action
Service Actions
You have parts to exchange or a
corrective action to perform.
1. Go to Chapter 9, “Removal and Replacement Procedures”
on page 247.
2. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
.
You need to verify that a part
exchange or corrective action
corrected the problem.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
You need to verify correct system
operation.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
System Stops With An 8-Digit Number Displayed
The system stops with an 8-digit
error code displayed in the
operator panel display or on the
console.
Record the error code. Go to Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU
Index” on page 109.
System Stops With A 4-Digit Number Displayed
The system stops and a 4-digit
number is displayed in the
operator panel display or on the
console.
If the number displayed has the format ″E0xx″ then go to
“Service Processor Checkpoints” on page 82.
If the number displayed is in the range ″E1xx-EFFF″, make
note of any location code that is displayed on the second line
of the operator panel. If the location code indicates a card slot
(for example, P2-I3), replace the card in the indicated slot. If
this does not correct the problem, then go to “Firmware
Checkpoints” on page 88.
For all other numbers, record SRN 101-xxx, where xxx is the
last three digits of the four-digit number displayed in the
operator panel, then go to the ″Fast Path MAP″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple
Bus Systems
.
Note: If the operator panel displays 2 sets of numbers, use
the bottom set of numbers as the error code.
OK does not appear in the operator panel display before pressing the power on button
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
33
Page 50

Symptom Action
A bouncing or scrolling ball
remains on the operator panel
display, or the operator panel
display is filled with dashes or
blocks.
If an ASCII terminal IS available, connect it to the system
through serial port 1.
1. If the service processor menu is displayed:
a. Replace the operator panel assembly. Refer to
“Operator Panel” on page 277.
b. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
2. If the service processor menu is not displayed, replace the
system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
If an ASCII terminal is NOT available, replace the following,
one at a time.
1. Operator panel assembly. Refer to “Operator Panel” on
page 277.
2. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
System Stops or Hangs With Alternating Numbers Displayed in the Operator Display Panel
The operator panel display
alternates between the code
″E1FD″ and another ″Exxx″
code.
Record both codes. Go to ″E1FD″ in “Firmware Checkpoints”
on page 88.
The operator panel display
alternates between the codes
″E1DE″ and ″E1AD″.
Record both codes. Go to ″E1DE″ in “Firmware Checkpoints”
on page 88.
Display Problem (Blank, Distortion, Blurring, Etc.).
All display problems.
v If using a graphics display:
1. Go to the Problem Determination Procedures for the
display.
2. If you do not find a problem, replace the display
adapter, then go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in
the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information
for Multiple Bus Systems
.
3. If you do not find a problem, suspect the system board.
Go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59.
v If the problem is with the ASCII terminal:
1. Make sure that the ASCII terminal is connected to S1.
2. If problems persist, go to the Problem Determination
Procedures for the terminal.
3. If you do not find a problem, suspect the system board.
Go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59.
Power and Cooling Problems
34 Service Guide
Page 51

Symptom Action
The power LEDs on the operator
panel and power supplies do not
start blinking within 30 seconds
of ac power application and the
operator panel display is blank.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-2” on page 51.
The power LEDs on the operator
panel and power supplies are
blinking and the operator panel
display is blank.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
The power LED on the operator
panel is on solid, the power
LEDs on the power supplies are
blinking and the operator panel
display is blank.
When the power on switch on
the operator panel is pressed,
there is no indication of activity.
The power LED on the power
supply does not change from
blinking to solid and none of the
fans, including the fan in the
power supplies, start to turn.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
The power LEDs on the operator
panel and power supplies are
blinking and OK, STBY or DIAG
STBY is displayed on the
operator panel display.
When the power on switch on
the operator panel is pressed,
there is no indication of activity.
None of the power LEDs change
from blinking to solid and none of
the fans, including the fan in the
power supplies, start to turn.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
The power LEDs on the operator
panel and power supplies are
blinking and OK, STBY or DIAG
STBY is displayed on the
operator panel display.
When the power on switch on
the operator panel is pressed,
the power LEDs change from
blinking to solid and the system
begins to power on, but the
power LEDs on the operator
panel and power supplies do not
stay on and the system powers
off.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
35
Page 52

Symptom Action
The power LED on the operator
panel is on solid, the power LED
on the power supply is blinking
and OK, STBY or DIAG STBY is
displayed on the operator panel
display.
When the power on switch on
the operator panel is pressed,
there is no indication of activity.
The power LED on the power
supply does not change from
blinking to solid and none of the
fans, including the fans in the
power supplies, start to turn.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
The power LEDs on the operator
panel and power supplies are
blinking and OK, STBY or DIAG
STBY is displayed on the
operator panel display.
When the power on switch on
the operator panel is pressed,
the power LEDs change from
blinking to solid, the fans come
on and stay on, but the system
does not power on.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
The power LED on the operator
panel is on solid, the power LED
on the power supplies are
blinking and OK, STBY or DIAG
STBY is displayed on the
operator panel display.
When the power on switch on
the operator panel is pressed,
the power LED on the operator
panel changes from blinking to
solid, the fans come on and stay
on, but the system does not
power on.
Go to ″MAP 1520: Power″, “Step 1520-3” on page 51
Flashing 888 in Operator Panel Display
888 is displayed in the operator
panel.
Go to the ″Fast Path MAP″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Other Symptoms or Problems
You have OK displayed. Fans
and blowers are off.
The service processor is ready. The system is waiting for
power-on.
36 Service Guide
Page 53

Symptom Action
You have STBY displayed. The service processor is ready. The operating system has
been terminated; the system is still powered on. This usually
indicates an operating system crash. The service processor
menus are available. Look for error codes related to the
operating system crash in the service processor error log.
The system POST indicators are
displayed on the system console,
the system pauses and then
restarts. The term ″POST
indicators″ refers to the icons
(graphic display) or device
mnemonics (ASCII terminal) that
appear during the power-on
self-test (POST).
Go to “Boot Problems/Concerns” on page 106.
The system stops and POST
indicators are displayed on the
system console. The term ″POST
indicators″ refers to the icons
(graphic display) or device
mnemonics (ASCII terminal) that
appear during the power-on
self-test (POST).
Go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59 to
isolate the problem.
The system stops and the
message ″STARTING
SOFTWARE PLEASE WAIT...″ is
displayed on the ASCII terminal,
or the boot indicator is displayed
on a graphics terminal.
Go to “Boot Problems/Concerns” on page 106.
The system does not respond to
the password being entered, or
the system login prompt is
displayed when booting in
service mode.
Verify that the password is being entered from the ASCII
terminal or keyboard defined as the firmware console. If so,
then the keyboard or its controller may be faulty.
v If entering the password from the keyboard that is attached
to the system, replace the keyboard. If replacing the
keyboard does not fix the problem, replace the system
board.
Location: P1
(See notes on page 31.)
v If entering the password from a keyboard that is attached
to an ASCII terminal, use the Problem Determination
Procedures for the ASCII terminal. Make sure the ASCII
terminal is connected to S1. Replace the system board if
these procedures do not reveal a problem.
v If the problem is fixed, go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″
in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for
Multiple Bus Systems
. If the problem persists, go to “MAP
1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59 to isolate the
problem.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
37
Page 54

Symptom Action
No codes are displayed on the
operator panel within a few
seconds of turning on the
system. The operator panel is
blank before the system is
powered on.
Reseat the operator panel cable. If the problem is not
resolved, replace these parts in the following order:
1. Operator panel assembly.
Location: L1
See 4 on page 31.
2. System board (See notes on page 31.)
If the problem is fixed, go to ″MAP 0410: Repair
Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
. If the problem
persists, go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on
page 59 to isolate the problem.
The SMS configuration list or
boot sequence selection menu
shows more SCSI devices
attached to a controller/adapter
than are actually attached.
A device may be set to use the same SCSI bus ID as the
control adapter. Note the ID being used by the
controller/adapter (this can be checked and/or changed via an
SMS utility), and verify that no device attached to the
controller is set to use that ID.
If settings do not appear to be in conflict:
1. Replace the SCSI cable.
2. Replace the device.
3. Replace the SCSI adapter (or system board if connected
to one of the two integrated SCSI controllers on the
system board). (See notes on page31 if the system board
is replaced.)
Note: In a ″twin-tailed″ configuration where there is more
than one initiator device (normally another system) attached
to the SCSI bus, it may be necessary to change the ID of the
SCSI controller or adapter with the System Management
Services.
The System Management
Services menu is displayed.
The device or media you are attempting to boot from may be
faulty.
1. Check the SMS error log for any errors. To check the error
log:
a. Choose error log from the utilities menu.
b. If an error is logged, check the time stamp.
c. If the error was logged during the current boot attempt,
record it.
d. Look up the error in Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU
Index” on page 109 and perform the listed action.
e. If no recent error is logged in the error log, continue to
the next step below.
2. Go to “Boot Problems/Concerns” on page 106.
3. Go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59.
You have a problem that does
not prevent the system from
booting.
Go to the ″Fast Path MAP″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
38 Service Guide
Page 55

Symptom Action
You have an SRN. Go to the ″Fast Path MAP″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
You suspect a cable problem. See the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Adapters, Devices, and
Cable Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
You do not have a symptom. Go to ″MAP 0020: Problem Determination Procedure″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple
Bus Systems
.
You have not determined a
symptom.
Go to “MAP 1020: Problem Determination” on page 40.
You Cannot Find the Symptom in this Table
All other problems. Go to “MAP 1020: Problem Determination” on page 40.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
39
Page 56

MAP 1020: Problem Determination
Purpose of This MAP
Use this MAP to get an error code if you were not provided one by the customer or you
are unable to load diagnostics. If you are able to load the diagnostics, go to MAP 0020
in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
The service processor may have recorded one or more symptoms in its error log. It is a
good idea to examine that error log before proceeding (see “System Information Menu”
on page 191).
Be prepared to record code numbers and use those numbers in the course of analyzing
a problem.
The service processor may have been set by the user to monitor server operations and
to attempt recoveries. You may wish to disable these actions while you diagnose and
service the system. If the system was set up according to the recommendations of the
User’s Guide, all the settings of the service processor (except language) were saved by
using the SAVE/RESTORE HARDWARE MAINTENANCE POLICIES service aid. You
can use that same service aid to restore the settings at the end of your service action.
In case the service processor settings were not saved by the user, if you disable them,
make notes of their current settings so that you can restore them before you leave.
In addition to the parameters in the table below, you might want to disconnect the
modem to prevent incoming signals that could cause the system to power on.
The following service processor settings may be of interest to you. The service
processor menus are described in “Service Processor Menus” on page 179.
Surveillance From the Service Processor Setup Menu, go to
the Surveillance Setup Menu and disable
surveillance.
Unattended Start From the Service Processor System Power
Control Menu, disable unattended start mode.
Reboot Policy From the System Power Control Menu, go to
the Reboot/Restart Policy Setup Menu and set:
1. Number of reboot attempts to 0 (zero)
2. Use OS-Defined restart policy to No
3. Enable supplemental restart policy to No.
Call Out From the Call-In/Call-Out Setup Menu, go to
the Serial Port Selection Menu and disable
call-out on both serial ports.
40 Service Guide
Page 57

Step 1020-1
The following steps analyze a failure to load the diagnostic programs.
Note: Before doing the following procedure be aware that:
v You are asked questions regarding the operator panel display.
v You are also asked to perform certain actions based on displayed POST
indicators.
1. Insert the diagnostic CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power.
3. Turn on the power.
4. When the keyboard indicator is displayed (the word keyboard on an ASCII terminal
or the keyboard icon on a graphical display), press the F5 key on the directly
attached keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal.
5. Enter a password, if requested.
6. Wait until the diagnostics are loaded or the system appears to stop.
7. Find your symptom in the following table. Then follow the instructions given in the
Action column.
Symptom Action
The diskette LED is blinking rapidly, or EIEA or
EIEB is displayed on the operator panel.
The flash EPROM data is corrupted. Run the
recovery procedure for the flash EPROM. See
“Firmware Recovery” on page 232.
The system stops with a prompt to enter a
password.
Enter the password. You are not allowed to
continue until a correct password has been
entered. When you have entered a valid
password, go to the beginning of this table and
wait for one of the other conditions to occur.
The diagnostic operating instructions are
displayed.
Go to ″MAP 0020: Problem Determination
Procedure″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
.
The system login prompt is displayed. You may not have pressed the correct key or
you may not have pressed the key soon
enough when initiating a service mode IPL of
the diagnostic programs. If this was the case,
start over at the beginning of this step.
Note: Perform the system shutdown procedure
before turning off the system.
If you are sure you pressed the correct key in a
timely manner, go to “Step 1020-2” on page 43.
The system does not respond when the
password is entered.
Go to “Step 1020-2” on page 43.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
41
Page 58

Symptom Action
The system stopped and a POST indicator is
displayed on the system console and an 8-digit
error code is not displayed.
If the POST indicator represents:
v Memory, record error code M0MEM002.
v Keyboard, record error code M0KBD000.
v SCSI, record error code M0CON000.
v Network, record error code M0NET000.
v Speaker (audio), record error code
M0BT0000.
Go to “Step 1020-3” on page 43.
The system stops and a 4-digit number is
displayed in the operator panel display.
If the number displayed has the format ″E0xx″,
then go to “Service Processor Checkpoints” on
page 82. If the number is in the range of
″E1xx-EFFF″ then go to “Firmware
Checkpoints” on page 88.
For all other numbers, record SRN 101-xxx,
where xxx is the last three digits of the
four-digit number displayed in the operator
panel, then go to the ″Fast Path MAP″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Note: If the operator panel displays 2 sets of
numbers, use the bottom set of numbers as the
error code.
The System Management Services is
displayed.
Go to “Step 1020-4” on page 44.
All other symptoms. If you were directed here from the Entry MAP,
go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on
page 59. Otherwise, find the symptom in the
“Quick Entry MAP” on page 32.
42 Service Guide
Page 59

Step 1020-2
There is a problem with the keyboard.
Find the type of keyboard you are using in the following table. Then follow the
instructions given in the Action column.
Keyboard Type Action
Type 101 keyboard (U.S.). Identify by the size of
the Enter key. The Enter key is in only one
horizontal row of keys.
Record error code M0KBD001; then go to
“Step 1020-3”.
Type 102 keyboard World Trade (W.T.). Identify
by the size of the Enter key. The Enter key
extends into two horizontal rows.
Record error code M0KBD002; then go to
“Step 1020-3”.
Type 106 keyboard. (Identify by the Japanese
characters.)
Record error code M0KBD003; then go to
“Step 1020-3”.
ASCII terminal keyboard Go to the documentation for this type of
ASCII terminal and continue problem
determination.
Step 1020-3
Take the following actions:
1. Find the 8-digit error code in Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU Index” on page 109.
Note: If the 8-digit error code is not listed in Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU Index”
on page 109, look for it in the following:
v Any supplemental service manual for the device
v The diagnostic problem report screen
v The Service Hints service aid
v The CEREADME file (by using the Service Hints service aid).
Note: Service aids can be found in
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
2. Perform the action listed.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 43
Page 60

Step 1020-4
1. Turn off, then turn on the system unit.
2. When the keyboard indicator appears, press the F1 key on a directly attached
keyboard or the 1 key on an ASCII terminal.
3. When the System Management Services menu appears, check the error log for any
errors.
v Choose Error Log from the utilities menu
v If an error is logged, check the time stamp.
v If the error was logged during the current boot attempt, record it.
v Look up the error in the Chapter 5, “Error Code to FRU Index” on page 109 and
perform the listed action.
v If no recent error is logged in the error log, go to “MAP 1540: Minimum
Configuration” on page 59.
44 Service Guide
Page 61

MAP 1240: Memory Problem Resolution
Note: The firmware checkpoint that sent you here could be one of the following: E122,
E213, E214, E218, E220 or E3xx. You may also have been sent here by an
8-digit error code.
Purpose of This MAP
This MAP is used to troubleshoot a problem during the memory test when the system
stops at a memory checkpoint and/or a error code is displayed on the operator panel.
Notes:
1. If the symptom changes while you are using this MAP, check for loose cards,
cables, and obvious problems. If you do not find a problem, go to “MAP 1540:
Minimum Configuration” on page 59.
2. The service processor may have recorded one or more symptoms in its error log. It
is a good idea to examine that error log before proceeding (see Service Processor
System Information Menu). If you find an obvious problem, fix the problem; then go
to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
3. The service processor may have been set by the user to monitor service operations
and to attempt recoveries. You might want to disable these actions while you
diagnose and service the system. If you disable them, make notes of their current
settings so that you can restore them before you leave. The following settings may
be of interest to you.
Surveillance From the Service Processor Setup Menu, go to
the Surveillance Setup Menu and disable
surveillance.
Unattended Start From the Service Processor System Power
Control Menu, disable unattended start mode.
Reboot Policy From the System Power Control Menu, go to
the Reboot/Restart Policy Setup Menu and set:
1. Number of reboot attempts to 0 (zero)
2. Use OS-Defined restart policy to No
3. Enable supplemental restart policy to No.
Call Out From the Call-In/Call-Out Setup Menu, go to
the Serial Port Selection Menu and disable
call-out on both serial ports.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
45
Page 62

General Memory Information
Be sure to unplug the power cables before removing or installing the memory DIMMs to
avoid damage to them.
Memory DIMMs must be installed in matched (size and speed) pairs. Refer to “Memory
Card and Memory DIMMs” on page 256 for labeling of the memory card and
instructions on DIMM removal and installation. (Do not, however, replace the covers as
directed while troubleshooting this problem.) A single memory DIMM pair may be
installed in module slots J1 and J2 (not slots J1 and J3). A second memory DIMM pair
could be installed in module slots J5 and J6 (slots J3 and J4 do not have to be
populated first). Along these same lines, there is no requirement that memory DIMM
slots J1 and J2 be populated before another slot pair.
Step 1240-1
1. Turn off the power.
2. Remove all installed memory DIMMs from the memory card. Record the positions of
the memory DIMMs so that when instructed to reinstall them they can be installed in
their original positions.
3. Install one pair of memory DIMMs.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with a memory checkpoint or memory error code displayed
on the operator panel?
NO If there are no more memory DIMMs to be installed, reseating the DIMMs on
the memory card has corrected the problem.
If there was more than one pair of memory DIMMs on the memory card, go to
“Step 1240-2” on page 47.
YES Go to “Step 1240-3” on page 47.
46 Service Guide
Page 63

Step 1240-2
1. Turn off the power.
2. Install a pair of memory DIMMs.
3. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with a memory checkpoint or error code displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Repeat this step until all the memory DIMMs are installed and tested.
If all the memory DIMMs have been installed, reseating the memory DIMMs on
the memory card has corrected the problem.
Go to ″Map 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Go to “Step 1240-3”.
Step 1240-3
The failure may be caused by the last pair of memory DIMMs installed or the memory
card. To isolate the failing FRU, do the following:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Exchange the last memory DIMM pair installed with another pair removed in “Step
1240-2” (or any other available pair).
3. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with a memory checkpoint or error code displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Go to “Step 1240-5” on page 48.
YES Go to “Step 1240-4” on page 48.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 47
Page 64

Step 1240-4
One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
1. Turn off the power.
2. Replace the following FRUs (one at a time) in the order listed.
v Memory card
v System board
v Processor card, processor #1, then processor #2
3. Turn on the power.
Note: Replacing any of the above listed FRUs may result in missing and new
resources.
Does the system stop with a memory checkpoint or error code displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all FRUs have been exchanged, go to
“MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59.
Step 1240-5
The memory DIMM(s) (may be both) you exchanged in the previous step may be
defective. To isolate the failing memory module, do the following:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Reinstall one of the memory DIMMs you exchanged in the previous step.
3. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with a memory checkpoint or error code displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Repeat this step with the second memory DIMM you exchanged in the
previous step.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Replace the memory DIMM.
If you have not tested both memory DIMMs, repeat this step with the second
memory module you exchanged in the previous step.
If the symptom did not change and both memory DIMMs have been
exchanged, go to “Step 1240-4”.
48 Service Guide
Page 65

MAP 1520: Power
Notes:
1. This is not a start-of-call MAP. Use this Power MAP only if you have been directed
here from another MAP, an SRN in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
, or an error code.
2. The 9112 Model 265 can accommodate three power supplies installed with separate
power receptacles on the rear of the system.
This procedure is used to locate power problems in system units. If a problem is
detected, this procedure helps you isolate the problem to a failing unit.
Observe the following safety notice during service procedures.
DANGER
An electrical outlet that is not correctly wired could place hazardous voltage
on metal parts of the system or the devices that attach to the system. It is the
responsibility of the customer to ensure that the outlet is correctly wired and
grounded to prevent an electrical shock.
Before installing or removing signal cables, ensure that the power cables for
the system unit and all attached devices are unplugged.
When adding or removing any additional devices to or from the system,
ensure that the power cables for those devices are unplugged before the
signal cables are connected. If possible, disconnect all power cables from the
existing system before you add a device.
Use one hand, when possible, to connect or disconnect signal cables to
prevent a possible shock from touching two surfaces with different electrical
potentials.
During an electrical storm, do not connect cables for display stations, printers,
telephones, or station protectors for communications lines.
CAUTION:
This product is equipped with a three–wire power cable and plug for the user’s
safety. Use this power cable with a properly grounded electrical outlet to avoid
electrical shock.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 49
Page 66

DANGER
To prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect all power cables from the
electrical outlet before relocating the system.
Step 1520-1
Check the power supply ac LEDs, the green LED on the rear of the system unit and the
power LED on the operator panel.
Note: If the condition exists that three power supplies are present, but only two are
working, you can verify this situation through the service processor and a
warning-level EPOW.
You might have been directed to this MAP for several reasons:
v The ac LEDs on the power supplies are not on, the green LED on the rear of the
system unit is not flashing and the operator panel is blank.
Go to “Step 1520-2” on page 51.
v The ac LEDs on the power supplies are on, the green LED on the rear of the system
unit is not flashing and the operator panel is blank.
Go to “Step 1520-7” on page 53.
v The ac LEDs on the power supplies are on, the green LED on the rear of the system
unit is flashing and OK, STBY or DIAG STBY is displayed on the operator panel.
When the power button on the operator panel is pressed:
– There is no indication of activity
– The power LED on the operator panel does not come on
– The green LED on the rear of the system unit does not come on
– The dc LEDs on the power supplies are not on
– None of the fans start to turn.
Go to “Step 1520-7” on page 53.
v The ac LEDs on the power supplies are on, the green LED on the rear of the system
unit is flashing and OK, STBY or DIAG STBY is displayed on the operator panel.
When the power button on the operator panel is pressed:
– The power LED on the operator panel comes on
– The green LED on the rear of the system unit comes on
– The dc LEDs on the power supplies are on
– All of the fans start to turn but the power LED on the operator panel, the green
LED on the rear of the system unit, the dc LEDs on the power supplies and the
fans do not stay on.
Go to “Step 1520-7” on page 53.
v An SRN in
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
listed “MAP 1520: Power” on page 49 in the ″Action/Description″ column for
a voltage sensor out of range.
50 Service Guide
Page 67

Step 1520-2
1. Turn off the power.
2. Unplug the power cables from the power outlet.
3. Unplug the power cables from the system.
4. Check that the power cables have continuity.
5. Check that the power outlet has been wired correctly with the correct voltage.
Did you find a problem?
NO Go to “Step 1520-3”.
YES Correct the problem. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Step 1520-3
1. Find all the cables connecting the power backplane to the system. Unplug these
cables from the system, but leave them attached to the power backplane.
2. Connect the power cables from the system unit to the power outlets.
Do the ac LEDs on the power supplies come on within 30 seconds after applying
ac power?
NO Go to “Step 1520-4”.
YES Go to “Step 1520-7” on page 53.
Step 1520-4
1. Unplug the power cord from the system unit.
2. Unplug all the cables from the power backplane.
3. Connect the power cables to the system unit.
Do the ac LEDs on the power supplies come on within 30 seconds after applying
ac power?
NO Go to “Step 1520-6” on page 52.
YES Go to “Step 1520-5” on page 52.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 51
Page 68

Step 1520-5
One of the cables you unplugged from the power backplane may be defective.
1. Unplug the power cables from the system.
2. Reconnect one of the cables to the power backplane.
3. Connect the power cables to the system.
Do the ac LEDs on the power supplies come on within 30 seconds after applying
ac power?
NO Replace the last cable that you connected to the power backplane.
Repeat this step until all the cables have been reconnected.
Replace the faulty cooling fan. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Repeat this step until the defective cable is identified or all the cables have
been reconnected.
Step 1520-6
Either the power supplies or the power backplane may be defective.
To test each FRU, exchange the FRUs that have not already been exchanged in the
following order.
v Power supply 1.
v Power supply 2.
v Power supply 3 (if installed).
v Power backplane.
1. Turn off the power.
2. Unplug the power cables from the system.
3. Exchange one of the FRUs in the list.
4. Connect the power cables to the system.
Do the ac LEDs on the power supplies come on within 30 seconds after applying
ac power?
NO Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
your service support person for assistance.
YES Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
52 Service Guide
Page 69

Step 1520-7
1. Unplug the power cables from the system.
2. Exchange the operator panel electronics assembly.
3. Plug the power cables into the system and wait for OK, STBY or DIAG STBY on the
operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the power LED on the operator panel come on and stay on?
NO Reinstall the original operator panel electronics assembly.
Go to “Step 1520-8”.
YES Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Step 1520-8
1. Turn off the power.
2. Unplug the power cables from the system.
3. Record the slot numbers of all the adapters. Label and record the location of any
cables attached to the adapters. Disconnect any cables attached to the adapters
and remove all the adapters.
4. Remove the memory card.
5. Remove the second processor card (if installed).
6. Unplug the power cable from the 6-pack backplane.
7. Unplug the disk drives from the 6-pack backplane.
8. Unplug the power cables from all devices in the media bay.
9. Remove or unplug all the fans.
10. Plug the power cables into the system.
11. Turn on the power.
Does the power LED on the operator panel come on and stay on?
NO Go to “Step 1520-9” on page 54.
YES Go to “Step 1520-10” on page 55.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 53
Page 70

Step 1520-9
Note: Either the processor card, system board, or the power supplies may be
defective.
To test each FRU, exchange the FRUs that have not already been exchanged in the
following order:
v Power supply 1.
v Power supply 2.
v Power supply 3 (if installed).
v Power backplane.
v Processor board
1. Turn off the power.
2. Unplug the power cables from the system.
3. Exchange one of the FRUs in the list.
4. Connect the power cables to the system.
5. Turn on the power.
Does the power LED on the operator panel come on and stay on?
NO Repeat these steps until all the parts have been installed or connected.
If the symptom did not change and all the parts have been installed or
connected, call service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1520-1” on page 50 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
YES Repeat these steps until all the parts have been installed or connected.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
54 Service Guide
Page 71

Step 1520-10
One of the parts that was removed or unplugged is causing the problem. Install or
connect the parts in the following order:
1. Second processor card (if removed).
2. Memory card.
3. PCI adapters, lowest slot to highest slot.
4. Fans.
Turn the power on after each part is installed or connected. If the system does not
power on or the power LED on the operator panel does not stay on, the most recently
installed or connected part is causing the failure.
1. Turn off the power.
2. Unplug the power cable from the system.
3. Install or connect one of the parts in the list.
4. Plug the power cable into the system.
5. Turn on the power.
Does the power LED on the operator panel come on and stay on?
NO Replace the last part installed.
If the memory card was just installed, remove all of the memory DIMMs. If the
system does not come up, replace the memory card.
Reinstall the memory DIMMs, one pair at a time, until the problem recurs.
Replace the memory DIMM pair that was just installed.
Note: The memory DIMM pair must be installed in slots that are next to each
other. Refer to “Memory Card and Memory DIMMs” on page 256.
Repeat these steps until all the parts have been installed.
Go to “Step 1520-11”.
YES Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Step 1520-11
Does the system contain three power supplies?
NO Go to “Step 1520-12” on page 56.
YES Go to “Step 1520-14” on page 57.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 55
Page 72

Step 1520-12
Shut down the system and remove all power cables from the rear of the system.
Exchange the following FRUs in the order listed:
1. Power supply.
2. Power cables to system board.
3. System board.
4. Power backplane.
Restart the system and perform error log analysis.
Do you get an SRN indicating a voltage sensor is out of range?
NO The last FRU exchanged is defective. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in
the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
.
YES Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat the FRU replacement steps until a defective FRU is identified or all the
FRUs have been exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all FRUs have been exchanged, go to
“Step 1520-13”.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1520-1” on page 50 in
this MAP, and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
Step 1520-13
Check that the power outlet is properly wired and is providing the correct voltage.
Did you find a problem?
NO Go to “Step 1540-1” on page 60.
YES Correct the problem. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
56 Service Guide
Page 73

Step 1520-14
Because the 9112 Model 265 accommodate redundant power supplies, it is not
necessary to power off the system when replacing a power supply.
The power supplies are symmetrical, so replacement starts with power supply 1 (the
unit closest to the bottom in a Model 6C1 or to the top left in a Model 6E1). Refer to
“Power Supply” on page 272 for instructions on replacing a power supply.
Notes:
1. Always service first the power supply whose green LED, located on top of the
power supplies, is either blinking or out.
2. Before removing a power supply, be sure the redundant power supply is operational
by observing the green LED. The green LED must be steady and not blinking or
out.
Replace the following FRUs in order:
1. Power supply 1
2. Power supply 2
Perform error log analysis.
Do you receive an SRN indicating a voltage sensor out of range?
NO The last FRU exchanged is defective. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in
the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
.
YES Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat the FRU replacement steps until a defective FRU is identified or all the
FRUs have been exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all FRUs have been exchanged, go to
“Step 1520-13” on page 56.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1520-1” on page 50 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 57
Page 74

Step 1520-15
The problem lies within the system hardware or with the line voltage/wiring.
Shut down the system and remove the power cable from the system.
Exchange the following FRUs in order:
1. Power cables to system board.
2. System board.
3. Power backplane.
Restart the system and perform error log analysis.
Do you receive an SRN indicating a voltage sensor out of range?
NO The last FRU exchanged is defective. Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in
the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
.
YES Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat the FRU replacement steps until a defective FRU is identified or all the
FRUs have been exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all FRUs have been exchanged, go to
“Step 1520-13” on page 56.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1520-1” on page 50 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
58 Service Guide
Page 75

MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration
Notes:
1. Be sure to unplug the power cords before removing or installing processor card(s),
the memory card, or the system board to avoid damage to it.
2. This MAP assumes that a CD-ROM drive is installed and connected to the
integrated SCSI or IDE adapter, and a diagnostic CD-ROM is available.
3. If a power-on password or privileged-access password is installed, you are
prompted to enter the password before the diagnostic CD-ROM can load.
4. The term ″POST indicators″ refers to the icons (graphic display) or device
mnemonics (ASCII terminal) that appear during the power-on self-test (POST).
5. The service processor might have recorded one or more symptoms in its error log.
It is a good idea to examine that error log before proceeding (see “System
Information Menu” on page 191).
6. The service processor might have been set by the user to monitor server operations
and to attempt recoveries. You might want to disable these actions while you
diagnose and service the system. If you disable them, make notes of their current
settings so that you can restore them before you leave. The following settings may
be of interest to you.
Surveillance From the Service Processor Setup Menu, go to
the OS Surveillance Setup Menu and disable
surveillance.
Unattended Start Mode From the System Power Control Menu, disable
unattended start mode.
Reboot Policy From the System Power Control Menu, go to
the Reboot/Restart Policy Setup Menu and set:
a. Number of reboot attempts to 0 (zero)
b. Use OS-Defined restart policy to No
c. Enable supplemental restart policy to No.
Call Out From the Call-In/Call-Out Setup Menu, go to
the Serial Port Selection Menu and disable
call-out on both serial ports.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs)
59
Page 76

Purpose of this MAP
This MAP is used to locate defective FRUs not found by normal diagnostics. For this
procedure, diagnostics are run on a minimally configured system. If a failure is detected
on the minimally configured system, the remaining FRUs are exchanged one at a time
until the failing FRU is identified. If a failure is not detected, FRUs are added back until
the failure occurs. The failure is then isolated to the failing FRU.
When directed to exchange a FRU that is common to a FRU removed to create a
minimum configuration system, use one of the removed FRUs instead of a new FRU.
For example, if the system contains 16 memory modules and you are directed to
remove 14 of them to create a minimun configuration system, then use one of the
removed memory modules when exchanging the FRU. Once the failing FRU is isolated,
replace it with a new one.
Step 1540-1
1. Insert the diagnostic CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive.
Note: If you cannot insert the diagnostic CD-ROM, go to “Step 1540-2” on page 61.
2. Ensure that the diagnostics and the operating system are shut down.
3. Turn off the power.
4. Turn on the power.
5. When the keyboard indicator is displayed (the word keyboard on an ASCII terminal
or the keyboard icon on a graphical display), press the F5 key on the directly
attached keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal.
6. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO Go to “Step 1540-2” on page 61.
YES Go to “Step 1540-18” on page 75.
60 Service Guide
Page 77

Step 1540-2
1. Turn off the power.
2. If you have not already done so, configure the service processor with the
instructions in note 6 on page 59. Then return here and continue.
3. Exit the service processor menus and remove the power cords.
4. Disconnect all external cables (parallel, serial port 1, serial port 2, serial port 3,
keyboard, mouse, Ethernet, SCSI, and so on).
5. Remove the service access cover (Model 6E1) or place the drawer (Model 6C1)
into the service position and remove the service access cover.
6. Record the slot numbers of the PCI adapters. Label and record the locations of
any cables attached to the adapters. Disconnect any cables attached to the
adapters and remove all the adapters.
7. Remove the second processor (if installed). If the second processor is removed,
ensure the first processor is installed.
8. Record the slot numbers of the memory DIMMs. Remove all memory DIMMs
except for one pair from the memory card.
Notes:
a. Place the memory DIMM locking tabs in the locked (upright) position to prevent
damage to the tabs.
b. Memory DIMMs must be installed in pairs and in the correct connectors. For
example, install the pair in connectors J1 and J2.
9. Disconnect the SCSI cable from the SCSI connector on the system board.
10. Disconnect the IDE cable from the IDE connector on the system board.
11. If installed, disconnect the signal and power connectors from the disk drive cage
backplane.
12. If installed, remove the disk drive(s) from the disk drive cage.
13. Disconnect the signal and power connectors from all the SCSI devices.
14. Disconnect the signal and power connectors from all the IDE devices.
15. Disconnect the diskette drive cable from the diskette drive connector on the
system board.
16. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
17. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Go to “Step 1540-3” on page 62.
YES If a second processor card was removed, go to “Step 1540-4” on page 63.
If the system has only one processor card, go to “Step 1540-5” on page 63.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 61
Page 78

Step 1540-3
One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
Note: If a memory module is exchanged, ensure that the new DIMM is the same size
and speed as the original DIMM.
1. Turn off the power, remove the power cords, and exchange the following FRUs in
the order listed:
a. Processor card
b. Memory DIMM in odd-numbered slot (J1, J3, J5)
c. Memory DIMM in even-numbered slot (J2, J4, J6)
d. Memory card
e. System board (see notes on page 31)
f. Power supplies.
2. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
3. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat the FRU replacement steps until the defective FRU is identified or all
the FRUs have been exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
YES Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
62 Service Guide
Page 79

Step 1540-4
No failure was detected with this configuration.
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Reinstall the second processor card.
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged:
1. Processor card (last one installed)
2. System board (see notes on page 31)
Repeat this step until the FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
your service support person for assistance.
If the symptom changed, check for loose cards and obvious problems. If you
do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 and follow the
instructions for the new symptom.
YES Go to “Step 1540-5”.
Step 1540-5
No failure was detected with this configuration.
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Install a pair of memory DIMMs.
Note: Ensure that the new memory DIMMs are the same size and speed as the
original memory DIMMs.
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Go to “Step 1540-6” on page 64.
YES Repeat this step until all the memory DIMMs are installed and tested.
Go to “Step 1540-9” on page 66.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 63
Page 80

Step 1540-6
The failure may be caused by the last pair of memory DIMMs installed or the memory
card. To isolate the failing FRU, do the following:
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Exchange the last memory DIMM pair installed.
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Go to “Step 1540-8” on page 65.
YES Go to “Step 1540-7”.
Step 1540-7
The memory DIMM(s) (may be both) you exchanged in the previous step may be
defective. To isolate the failing DIMM, do the following:
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Reinstall one of the memory DIMMs you exchanged in the previous step.
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Replace the memory DIMM.
If you have not tested both memory DIMMs repeat this step with the second
memory module you exchanged in the previous step.
If the symptom did not change and both memory DIMMs have been
exchanged, go to “Step 1540-8” on page 65.
YES Repeat this step with the second memory DIMM you exchanged in the
previous step.
If both memory DIMMs have been tested, go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″
in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus
Systems
.
64 Service Guide
Page 81

Step 1540-8
One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Exchange the following FRUs in the order listed.
a. Memory card
b. System board (see notes on page 31)
c. Power supply
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with code E1F2, E1F3, STBY or 4BA00830 displayed on the
operator panel?
NO Reinstall the original FRU.
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all of the FRUs have
been exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in this MAP, and follow the
instructions for the new symptom.
YES Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 65
Page 82

Step 1540-9
1. Turn off the power.
2. Reconnect the system console.
Notes:
a. If an ASCII terminal has been defined as the firmware console, attach the ASCII
terminal cable to the S1 connector on the rear of the system unit.
b. If a display attached to a display adapter has been defined as the firmware
console, install the display adapter and connect the display to the adapter. Plug
the keyboard into the keyboard connector on the rear of the system unit
3. Turn on the power.
4. If the ASCII terminal or graphics display (including display adapter) is connected
differently than it was before, the Console Selection screen appears and requires
that a new console be selected.
5. When the keyboard indicator is displayed, press the F1 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 1 key on an ASCII terminal.
6. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the SMS screen displayed?
NO One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged:
1. Go to the problem determination procedures (test procedures) for the
device attached to the S1 serial port or the display attached to the graphics
adapter, and test that device. If a problem is found, follow the procedures
to correct the problem on that device.
2. Graphics adapter
3. Cable (async or graphics)
4. System board (see notes on page 31)
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious problems.
If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 and follow the
instructions for the new symptom.
YES Go to “Step 1540-10” on page 67.
66 Service Guide
Page 83

Step 1540-10
1. Make sure the diagnostic CD-ROM is inserted into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
3. Plug the IDE cable into the IDE connector on the system board.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for the OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. After the keyboard indicator is displayed, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged:
1. IDE cable
2. CD-ROM drive
3. System board (see notes on page 31)
4. Processor card
5. Power supply.
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
YES Go to “Step 1540-11” on page 68.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 67
Page 84

Step 1540-11
The system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the SCSI devices that
you disconnected may be defective.
1. Make sure the diagnostic CD-ROM is inserted into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
3. Plug the SCSI cable into the SCSI connector on the system board.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. After the keyboard indicator is displayed, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged:
1. SCSI cable
2. Last SCSI device connected (disk drive, tape drive)
3. System board (see notes on page 31)
4. Power supply.
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
YES Repeat this step, adding one SCSI device at a time, until all the SCSI devices
that were attached to the integrated SCSI adapter, except the backplane, are
connected and tested.
If the SCSI 6-pack is installed, go to “Step 1540-12” on page 69.
If the SCSI 6-pack is not installed, go to “Step 1540-14” on page 71.
68 Service Guide
Page 85

Step 1540-12
The system is working correctly with this configuration. The backplane may be
defective.
1. Make sure the diagnostic CD-ROM is inserted into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
3. Connect the signal and power connectors to the backplane.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. If the Console Selection screen is displayed, choose the system console.
7. After the keyboard indicator is displayed, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
8. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective.
In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged:
1. SCSI cable
2. Disk drive cage backplane
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Go to “Step 1540-13” on page 70.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 69
Page 86

Step 1540-13
The system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the disk drives that you
removed is removed from the disk drive cage may be defective.
1. Make sure the diagnostic CD-ROM is inserted into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
3. Install a disk drive in the disk drive cage.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. After the keyboard indicator is displayed, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
No In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged:
1. Last disk drive installed
2. Disk drive cage backplane
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
Yes Repeat this step until all drives are installed and tested.
Go to “Step 1540-14” on page 71.
70 Service Guide
Page 87

Step 1540-14
The system is working correctly with this configuration. The diskette drive may be
defective.
1. Make sure the diagnostic CD-ROM is inserted into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
3. Plug the diskette drive cable into the diskette drive connector on the system board.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. After the keyboard indicator displays, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO One of the FRUs remaining in the system is defective.
In the following order, exchange the FRUs that have not been exchanged.
1. Diskette drive
2. Diskette drive cable
3. System board (see notes on page 31)
4. Power supply
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem return, to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
YES Go to “Step 1540-15” on page 72.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 71
Page 88

Step 1540-15
The system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the devices that you
disconnected from the system board may be defective.
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Attach a system board device (parallel, serial port 1, serial port 2, serial port 3,
keyboard, mouse, Ethernet, SCSI, keyboard or mouse) that had been removed.
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
5. If the Console Selection screen is displayed, choose the system console.
6. After the keyboard indicator displays, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO The last device or cable that you attached is defective.
To test each FRU, exchange the FRUs in the following order:
1. Device and cable (last one attached)
2. System board (see notes on page 31).
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem return, to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Go to “Step 1540-16” on page 73.
72 Service Guide
Page 89

Step 1540-16
The system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the FRUs (adapters) that
you removed may be defective.
1. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
2. Install a FRU (adapter) and connect any cables and devices that were attached to
the FRU.
3. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
4. Turn on the power.
5. If the Console Selection screen is displayed, choose the system console.
6. After the keyboard indicator displays, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Is the ″Please define the System Console″ screen displayed?
NO Go to “Step 1540-17” on page 74.
YES Repeat this step until all of the FRUs (adapters) are installed.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 73
Page 90

Step 1540-17
The last FRU installed or one of its attached devices is probably defective.
1. Make sure the diagnostic CD-ROM is inserted into the CD-ROM drive.
2. Turn off the power and remove the power cords.
3. Starting with the last installed adapter, disconnect one attached device and cable.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. If the Console Selection screen is displayed, choose the system console.
7. After the keyboard indicator displays, press the F5 key on the directly attached
keyboard or the number 5 key on an ASCII terminal keyboard.
8. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
NO Repeat this step until the defective device or cable is identified or all devices
and cables have been disconnected.
If all the devices and cables have been removed, then one of the FRUs
remaining in the system unit is defective.
To test each FRU, exchange the FRUs in the following order:
1. Adapter (last one installed)
2. System board (see notes on page 31)
3. Power supply
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious
problems. If you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in
this MAP and follow the instructions for the new symptom.
YES The last device or cable that you disconnected is defective.
Exchange the defective device or cable.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
74 Service Guide
Page 91

Step 1540-18
1. Follow the instructions on the screen to select the system console.
2. When the DIAGNOSTIC OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS screen is displayed, press
Enter.
3. Select Advanced Diagnostics Routines.
4. If the terminal type has not been defined, you must use the Initialize Terminal option
on the FUNCTION SELECTION menu to initialize the AIX diagnostic environment
before you can continue with the diagnostics. This is a separate operation from
selecting the firmware display.
5. If the NEW RESOURCE screen displays, select an option from the bottom of the
screen.
Note: Adapters or devices that require supplemental media are not shown in the
new resource list. If the system has adapters or devices that require
supplemental media, select option 1.
6. When the DIAGNOSTIC MODE SELECTION screen is displayed, select System
Verification and press Enter.
7. Select All Resources (if you were sent here from “Step 1540-19” select the
adapter/device you loaded from the supplemental media) and commit (F7) to start
test routines. Follow the instructions on the screen to get test results.
Did you get an SRN?
NO Go to “Step 1540-20” on page 76.
YES Go to “Step 1540-19”.
Step 1540-19
Look at the FRU part numbers associated with the SRN.
Have you exchanged all the FRUs that correspond to the failing function codes
(FFCs)?
NO Exchange the FRU with the highest failure percentage that has not been
changed.
Repeat this step until all the FRUs associated with the SRN have been
exchanged or diagnostics run with no trouble found. Run diagnostics after
each FRU is exchanged.
If the system board or a network adapter is removed, see notes on page 31.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call
service support for assistance.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 75
Page 92

Step 1540-20
Does the system have adapters or devices that require supplemental media?
NO Go to “Step 1540-21”.
YES Go to “Step 1540-22”.
Step 1540-21
Consult the PCI adapter configuration documentation for your operating system to verify
that all installed adapters are configured.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call service
support for assistance.
Step 1540-22
Select Task Selection.
Select Process Supplemental Media and follow the onscreen instructions to process
the media.
Supplemental media must be loaded and processed one at a time.
Did the system return to the TASKS SELECTION SCREEN after the supplemental
media was processed?
NO Go to “Step 1540-23” on page 77.
YES Press F3 to return to the FUNCTION SELECTION screen.
Go to “Step 1540-18” on page 75, substep 4.
76 Service Guide
Page 93

Step 1540-23
The adapter or device is probably defective.
If the supplemental medium is for an adapter, replace the FRUs in the following order:
1. Adapter
2. System board (see notes on page 31)
If the supplemental medium is for a device, replace the FRUs in the following order:
1. Device and any associated cables
2. The adapter to which the device is attached.
Repeat this step until the defective FRU is identified or all the FRUs have been
exchanged.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, call service
support for assistance.
If the symptom has changed, check for loose cards, cables, and obvious problems. If
you do not find a problem, return to “Step 1540-1” on page 60 in this MAP and follow
the instructions for the new symptom.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
Step 1540-24
1. Ensure that the diagnostics and the operating system are shut down.
2. Turn off the power.
3. If you have not already done so, configure the service processor with the
instructions in note 6 on page 59 and then return here and continue.
4. Exit the service processor menus and remove the power cords.
5. Remove the service access cover (Model 6E1) or place the drawer (Model 6C1) into
the service position and remove the service access cover.
6. Record the slot numbers of the PCI adapters. Label and record the locations of any
cables attached to the adapters. Disconnect any cables attached to the adapters
and remove all the adapters.
7. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
8. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with the same error code displayed on the operator panel
that directed you to this MAP step?
NO Go to “Step 1540-26” on page 78.
YES Go to “Step 1540-25” on page 78.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 77
Page 94

Step 1540-25
One of the FRUs remaining in the system unit is defective. Do the following:
1. Turn off the power.
2. Remove the power cords.
3. Replace the system board (see notes on page 31).
4. Plug in the power cable and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
Does the system stop with the same error code displayed on the operator panel
that directed you to this MAP step?
NO Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Reinstall the original FRU.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, return
to “Step 1540-2” on page 61 in this MAP.
Step 1540-26
The system is working correctly with this configuration. One of the FRUs (adapters) that
you removed is probably defective.
1. Turn off the power.
2. Remove the power cable.
3. Install a FRU (adapter) and connect any cables and devices that were attached to
it.
4. Plug in the power cable and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. If the Console Selection screen is displayed, choose the firmware console.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Does the system stop with the same error code displayed on the operator panel
that directed you to this MAP step?
NO Repeat this step until all of the FRUs (adapters) are installed, then go to ″MAP
0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic
Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Go to “Step 1540-27” on page 79.
78 Service Guide
Page 95

Step 1540-27
The last FRU installed or one of its attached devices is probably defective.
1. Turn off the power.
2. Remove the power cords.
3. Starting with the last installed adapter, disconnect one attached device and cable.
4. Plug in the power cords and wait for OK on the operator panel display.
5. Turn on the power.
6. If the Console Selection screen is displayed, choose the firmware console.
7. Enter the appropriate password if you are prompted to do so.
Does the system stop with the same error code displayed on the operator panel
that directed you to this MAP step?
NO The last device or cable that you disconnected is defective.
Exchange the defective device or cable.
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
YES Repeat this step until the defective device or cable is identified or all of the
devices and cables have been disconnected.
If all of the devices and cables have been removed, then one of the FRUs
remaining in the system unit is defective.
To test each FRU, exchange the FRUs in the following order:
1. Adapter (last one installed)
2. System board (see notes on page 31)
Go to ″MAP 0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries
Diagnostic Information for Multiple Bus Systems
.
If the symptom did not change and all the FRUs have been exchanged, return
to “Step 1540-2” on page 61 in this MAP.
Chapter 3. Maintenance Analysis Procedures (MAPs) 79
Page 96

80 Service Guide
Page 97

Chapter 4. Checkpoints
Checkpoints let users and service personnel know what the server is doing, with some
detail, while it initializes. These checkpoints are not intended to be error indicators, but
in some cases, a server could hang at one of the checkpoints without displaying an
8-character error code. It is for these hang conditions, only, that any action should be
taken regarding checkpoints. The most appropriate action is included with each
checkpoint.
Before taking actions listed with a checkpoint, it is a good idea to look for more
appropriate symptoms in the service processor error log. See “System Information
Menu” on page 191. To access the System Information Menu, refer to “Privileged User
Menus” on page 182.
Unresolved Checkpoint Problems
Go to “MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59 for any of the following
problems:
v A 4-digit code in the range of E000 through EFFF is displayed on the operator panel
display but is not listed in “Service Processor Checkpoints” on page 82 or “Firmware
Checkpoints” on page 88.
v A 4-digit code is displayed and is listed in “Service Processor Checkpoints” on
page 82 or “Firmware Checkpoints” on page 88, but there are no repair actions or
FRUs listed for the code.
v All of the FRUs listed in the repair actions have been replaced, and the problem has
not been resolved.
81
Page 98

Service Processor Checkpoints
Service processor checkpoints are in the range E010 to E0FF. The message OK
indicates successful service processor testing and initialization. Firmware checkpoints
are listed in “Firmware Checkpoints” on page 88.
If you replace FRUs or perform an action, and the problem is still unresolved, go to
“MAP 1540: Minimum Configuration” on page 59 unless otherwise indicated in the
tables.
If you replace FRUs or perform an action, and the problem is corrected, go to ″MAP
0410: Repair Checkout″ in the
RS/6000
Eserver
pSeries Diagnostic Information for
Multiple Bus Systems
.
Table 1. Service Processor Checkpoints.
Checkpoint Description Action/ Possible Failing FRU
DIAG STBY Service processor is ready. The system
unit was shut down in service mode by
the operating system; however, the
system unit is still powered on.
The service processor is ready. The
operating system has been terminated;
the system is still powered on. This
usually indicates an operating system
crash. The service processor menus are
available. Look for error codes related
to the operating system crash in the
service processor error log.
E000 System support controller begins
operation. This is an informational
checkpoint.
Call support.
E010 Starting service processor self-tests Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E011 Service processor self-tests completed
successfully
Call support.
E012 Begin to set up service processor helps Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E020 Configuring CMOS Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E021 Configuring NVRAM 1. Manually drain the NVRAM by
removing the battery. Short circuit
the battery leads for at least 30
seconds. Use a conductive object
such as a coin or a screwdriver for
this purpose.
2. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E022 Accessing system board VPD Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
82 Service Guide
Page 99

Table 1. Service Processor Checkpoints. (continued)
Checkpoint Description Action/ Possible Failing FRU
E023 Accessing memory card VPD Replace the memory card
Location: P1-M1
E025 Service processor accessing VPD. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E026 Service processor accessing VPD. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E030 Beginning to build I
2
C resources 1. Replace the processor card.
Location: P1-C1
2. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E031 Finished building I
2
C resources Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E032 JTAG self-test Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E040 Starting serial port tests Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E042 Configuring serial port 1 Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E043 Configuring serial port 2 Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E044 Preparing to set serial port line speed Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E045 Preparing to disconnect serial port Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E050 Reading system VPD Operator panel.
Location: L1
(See note 2 on page 109.)
Chapter 4. Checkpoints
83
Page 100

Table 1. Service Processor Checkpoints. (continued)
Checkpoint Description Action/ Possible Failing FRU
E051 Reading processor card VPD If one processor is installed:
v Replace processor card 1
Location P1-C1
v Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
If two processor cards are installed:
1. Remove processor card 2 (P1-C2)
and turn on the power. If the system
does not hang on E051, replace
processor card 2. If removing
processor card 2 does not fix the
system, continue to the next step.
2. Remove processor card 1 (P1-C1)
and install processor card 2 in slot 1
(P1-C1) and turn on the power. If
the system does not hang on E051,
replace processor card 1. If this
swap does not fix the system,
continue to the next step.
3. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E053 Reading system board VPD Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E054 Reading system board VPD Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
E055 Reading power supply VPD Power supply
Location: P3-V1
Location: P3-V2
Location: P3-V3
E060 Preparing to auto power-on (AC
restored)
1. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
2. Replace processor card 1
Location P1-C1
3. Replace processor card 2
Location P1-C2
E061 Preparing to auto power-on (Timer) 1. Replace the system board.
Location: P1
(See note 3 on page 109.)
2. Replace processor card 1
Location P1-C1
3. Replace processor card 2
Location P1-C2
84 Service Guide
 Loading...
Loading...