Page 1

IBM Infoprint 1532 MICR 35
Secure MICR Printer
User’s Guide
Source Technologies
2910 Whitehall Park Drive
Charlotte, NC 28273
www.sourcetech.com
techsupport@sourcetech.com
800-922-8501
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide i © Source Technologies
February 2006 All Rights Reserved
Page 2

This manual serves as a reference for Source Technologies Secure MICR Printers. The user
manual that ships with your printer contains details on printer setup and operations and should be
read first. This manual should be used as a reference for learning more about MICR technology,
and developing MICR printing applications. This guide was produced to assist IS Technicians and
Engineers in the use Source Technologies’ programmed printers with their custom MICR
applications. The guide also contains information on MICR related error messages that post to the
operator panel.
Every effort has been made to ensure that all the information contained in this booklet is complete
and accurate. Changes, typos, and technical inaccuracies will be corrected in subsequent
publications. This publication is subject to change without notice. The information and descriptions
contained in this manual cannot be copied, disseminated, or distributed without the express written
consent of Source Technologies, Inc. No liability, expressed or implied, will be assumed by Source
Technologies, Inc. or its dealers or affiliates for any damage resulting from use of this information.
Additional copies of this publication can be received through the Marketing Department of Source
Technologies.
All other trade names or products used in this manual are for identification purposes only and may
be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide ii © Source Technologies
February 2006 All Rights Reserved
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Printer Installation ...........................................................1
2 MICR Overview ................................................................2
The Check Processing System.....................................2
MICR Printing Today.....................................................2
3 MICR Check Design.........................................................4
General Features of Check Design...............................4
Position and Dimension Gauge ....................................4
Design Elements in Detail.............................................4
Figure 3.1 Sample Check .............................................9
4 Quality Issues ..................................................................10
Printer Features ............................................................10
MICR Toner ..................................................................10
MICR Check Stock........................................................11
5 Security Issues ................................................................13
Check Stock Security Features.....................................13
Security Note ................................................................14
6 MICR Features .................................................................16
MICR Mode...................................................................16
MICR Fonts...................................................................16
Secure Fonts ................................................................16
MicroPrint......................................................................16
Bi-Directional Feedback................................................17
Resource Storage.........................................................17
MICR Menu...................................................................18
Entering MICR Mode ....................................................18
MICR Mode Commands ...............................................20
DES and AES Decryption .............................................24
MFP Copy Defeat Commands ......................................25
Custom Character Conversion Commands ..................26
Special Alert and Custom Beep Command...................27
MICRpoint.....................................................................28
7 IBM Host Programming Features and Examples..........30
Hex Transfer .................................................................30
Figure 7.1: MICR Mode Command Example ................32
Escape Character Transition ........................................34
Figure 7.2: Sample Check ............................................35
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide iii © Source Technologies
February 2006 All Rights Reserved
Page 4

8 Audit Trail Report ............................................................36
Report Details ...............................................................36
Audit Trail Menu............................................................36
Audit Trail Command Set..............................................37
Figure 8.1: Audit Trail Command Example ...................41
Figure 8.2: Audit Trail Check Sample ...........................42
Figure 8.3 Audit Trail Report.........................................45
9 Error Messages................................................................46
MICR Error Messages ..................................................46
Appendix A: E-13B MICR Font Mapping.................................A1
Appendix B: CMC7 MICR Font Mapping ................................A2
Appendix C: Secure Numeric Font Mapping...........................A4
Appendix D: ICR Secure Numeric Font Mapping....................A7
Appendix E: MICR Mode Command Summary.......................A8
Appendix F: Audit Report Command Summary ......................A10
Appendix G: PJL Based MICR Commands……………………A11
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide iv © Source Technologies
February 2006 All Rights Reserved
Page 5

1. Printer Installation
For complete information on how to unpack and setup your printer, see your printer’s user’s
guide. Please read the following if you are going to install the printer driver shipped with
your printer.
1. Locate the CD that was shipped with your printer.
Note: If you do not have a CD-ROM drive on the host PC, locate another
computer with a CD-ROM drive, start the CD-ROM utility, and then follow the
instructions on the screen to create printer driver diskettes.
2. Follow the instructions in the CD booklet to start the printer setup utility
appropriate for your operating system, i.e. Windows 95, NT, etc. The setup utility
will install printer driver and utilities to manage Source Technologies printer(s)
attached to your PC or Network.
3. The Source Technologies MICR printer, in most cases, assumes the printer
driver is set to the internal DEFAULT values. The following Default values
should not be changed for best overall printer performance and data stream
requirements of the ST Secure MICR printer.
- Print Resolution under the Graphic Tab should be set to the Default value of
600 DPI.
- Form Source under the Paper Tab should be set to Default value of By
Source.
- Print Quality and Picture Grade under the Graphic Tab should be set to the
Default values of Use Printer Default.
The ST Secure MICR Printer requires a PCL5 or PCL5e data stream. Current
level printer drivers require Graphic Mode under the Graphic Tab be set to either
Raster or GL/2. We recommend Raster. This is the only required non-Default
value that needs to be set in the printer driver.
A majority of other driver options can be set for your particular requirements. The most
obvious of these would be a Paper Tray selection if your application uses the Print Driver
Setting.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
1 All Rights Reserved
Page 6
2. MICR Overview
MICR stands for Magnetic Ink Character Recognition. All MICR documents have a MICR
line with numbers and symbols printed in a MICR font with magnetically chargeable toner.
Each character of the MICR font has a unique waveform when sensed magnetically.
Financial institutions and the Federal Reserve use the MICR line to identify and sort
checks. The high-speed automated processing of checks and other financial documents
depends on the accuracy and the integrity of the data printed in the MICR line. Your new
Source Technologies’ Secure MICR Printer is specifically designed to produce high quality
MICR documents.
The Check Processing System
As a MICR document travels through the check clearing system it is processed an average
of about seven times by high speed reader/sorter machines. Some checks are read up to
30 times or more by these machines. Reader/sorter machines charge the toner in the
MICR line and then read the line with a magnetically sensitive reader.
The MICR line contains numbers and symbols to indicate the check serial number, the
routing number of the drawee institution and the makers’ account number. The institution
of first deposit encodes the check amount in the MICR line to be read by the reader/sorter
equipment. Checks travel through reader/sorters at up to 20 miles-per-hour (2,400
documents per minute) with each MICR line read in three hundredths of a second.
MICR Printing Today
Congress established the Federal Reserve System (FRS) in 1913. Today most commercial
banks in the United States belong to the FRS. Many other depository institutions provide
banking and checking account services to the public. These other institutions, such as
some credit unions, savings and loan associations and nonmember banks, are not formally
part of the FRS. However, they have access to the payment services it provides and are
subject to many of the FRS regulations.
In 1958, because of the explosive growth of check usage, the American Bankers
Association selected the E-13B MICR font and the MICR system as the technology for
high-speed check processing. Today, check standards are determined by the American
National Standards Institute (ANSI) Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) X9B of which
Source Technologies is a voting member. The latest versions of the standards and
technical guidelines are available from Global Engineering Documents.
Hardcopy Standards Softcopy Standards
Global Engineering Documents X9 Electronic Bookstore
Phone 800-854-7179 or 303-397-7956 www.x9.org - click ESS
Fax 303-397-2740 www.ansi.org - click ESS
global@ihs.com or
http://global.ihs.com
http://webstore.ansi.org
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
2 All Rights Reserved
Page 7

The key standards that address check documents are as follows:
ANSI X9.7 Specifications for Bank Check Background and Convenience Amount Field
ANSI X9.13 Specifications for Placement and Location of MICR Printing
ANSI X9.18 Paper Specifications for Checks
ANSI X9.27 Print and Test Specifications for Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR)
Note: These standards are being re-numbered as new versions are published:
ANSI X9.7 will become ANSI X9.100-110
ANSI X9.13 will become ANSI X9.100-110, Parts 1 & 2
ANSI X9.18 will become ANSI X9.100-10
ANSI X9.27 will become ANSI X9.100-20
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
3 All Rights Reserved
Page 8
3. MICR Check Design
General Features of Check Design
To be a legal and negotiable document, the necessary elements required on a check are
the date, amount, payee, drawee institution, and payer’s signature.
Other elements included in a good check design are: the amount in words, account title,
check serial number, fractional routing number and MICR line.
A good check design contains security features and is formatted to be easily read by both
machines and the human eye. If the format is complicated, the depositor, bank employee
or reader/sorter machine may make an error in reading the data.
Position and Dimension Gauge
A MICR position and dimension gauge (Source Technologies’ part number 205-1000MGE
or 220-M1027-34) is an important tool for use in designing checks. During check design,
check your output against this gauge to determine if the data elements are correctly
positioned on your document.
Design Elements in Detail
Paper
The ideal paper for check production is 24 lb. laser bond. Our MICR lab has tested
paper stock from most major manufacturers and has compiled a list of products that
produce superior results. Contact your sales representative for this information. For
a fee, Source Technologies will test your paper for proper MICR adherence and
check reader/sorter performance. There are also many security features available to
aid in the overall security of your MICR documents. See Chapter 3 for more
information on check stock specifications and security features.
Size
The size of check documents must be:
Between 6.00 inches and 8.75 inches in length
Between 2.75 inches and 3.66 inches in height
We recommend standard 8.5" X 11" letter size stock or 8.5" X 14" legal size stock for
proper feeding through your ST Secure MICR Printer. The number of checks per
page is determined by your application. Custom size stock other than letter or legal
can be done with proper planning and application programming within the paper size
specifications for the base printer.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
4 All Rights Reserved
Page 9

Duplexing
Use caution if printing on both sides of the paper (duplexing) when printing checks.
MICR toner on the back of a check can cause read failures in the MICR Line. Order
your check stock with any necessary information preprinted on the back. If duplex
is necessary, we suggest a more aggressive test plan be developed to ensure print
quality consistently conforms to the ANSI/ABA specifications.
MICR Clear Band
The MICR clear band is an area at the bottom of the check where the MICR line
prints. No other magnetic printing should appear in this area on both the font and
back of document. The clear band is an area 0.625 (5/8) inches high from the
bottom of the check running the entire length of the check. Exact MICR line
placement in this area is very important. See Figure 3.1 for more information on
MICR line placement.
Data Elements
Date
The date is a required data element for a check. It represents the day on or after the
transfer of the check amount may take place. It is usually placed in the upper right
portion of the check so it does not interfere with the convenience amount field. The
common format is Month, Day and Year, however, the military format of Day, Month
and Year is also acceptable.
Amount
The amount of the check is a required element. The amount usually appears at
least twice on the check. The amount printed in numbers is called the convenience
amount. The amount printed in words is sometimes referred to as the legal amount,
since this is the amount that applies if there is a difference between the two amount
fields. The amount may also be printed a third time on the check in a secure font,
intended to make alteration of the amount field difficult. See Chapter 5 and Appendix
C for information on Source Technologies’ Secure Numeric Font.
Convenience Amount
The convenience amount location is specified in ANSI X9.7. The basic location is
illustrated in Figure 3.1. Since this amount can be machine scanned, its location and
design should be kept within the specifications. The amount beginning with the
dollar sign should be left justified within the scan area with numbers spaced normally
to the right. The dollars and cents should be separated by a decimal point with the
cents printed in the same size font as the rest of the field. Embedded commas
should not be used. The convenience amount background should have good
reflectance so it does not interfere with optical scanning (see ANSI X9.7).
The convenience amount should be printed in a simple, fixed pitch font. We
recommend our ICR Secure Numeric Font (see Appendix D). It was designed to be
easily read by image capture equipment and is also a fraud deterrent. A fixed pitch
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
5 All Rights Reserved
Page 10

courier font, or if available OCR-B, are also acceptable fonts to print the
convenience amount.
Note: The Source Technologies’ Secure Numeric Font (see Appendix C) should not
be used in the convenience amount since it is not a machine readable font.
Amount In Words
The amount in words (sometimes called the legal amount) is normally located either
above or below and to the left of the convenience amount. The area for the amount
in words should be entirely filled to make alteration difficult. The amount should start
at the far left of the line with the words placed immediately adjacent to each other.
The cents need not be written out. They may be expressed as a fraction (60/100),
and should be placed immediately to the right of the dollar amount and followed by a
line or other space filler to inhibit alteration.
Example: One hundred forty-four and 62/100---------------DOLLARS
Given the available area on the document, you may need to use a smaller font when
printing larger value amounts.
Payee Area
The payee is a necessary element for a negotiable document. The payee area is
generally to the left side of the document either above or below the amount in words.
It is often preceded by the words “Pay to the Order Of.” The payee data should not
enter the MICR clear band which extends 5/8 of an inch above the bottom of the
check.
Signature Area
A signature is a required element for a negotiable document. The signature or
signatures authorize the bank to honor the check; therefore, it must match the
bank’s records. The signature area should be beneath the convenience amount area
but the signatures should not enter the convenience amount area nor the MICR
clear band. This is especially true if you print the signature with MICR toner.
We recommend using our MicroPrint font for the signature line as a fraud deterrent.
Information on how to utilize this font is in section 5: MICR Features.
Drawee Institution Name
The name of the institution where the maker’s account is located is referred to as the
drawee institution. The bank’s name, city, and state are required.
Account Title
The account title is normally printed in the upper left corner of the check. It includes
the name of the account holder and other information such as addresses, telephone
numbers, and logos. The data in the title should be legible and sufficiently complete
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
6 All Rights Reserved
Page 11

so that if the MICR data account number is destroyed, the drawee institution can
refer to the account title in order to trace the account number.
Memo Line
This line is located in the lower left quadrant of the check, and is not required. Data
printed here does not contain any legal significance. Printing in this area with
th
magnetic toner should not extend downward into the MICR clear band which is 5/8
of an inch above the bottom of the check.
Check Serial Number
The check serial number is generally printed in the upper right quadrant of the
check. Although the check number is not required for the check to be negotiable,
the account holder and financial institution use these numbers to reconcile
statements and stop payments. The check serial number should also appear a
second time in the MICR line, and these numbers should match. The number of
digits in the check serial number is controlled by the financial institution and the
MICR line format. Consult your banking institution for their requirements.
Fractional Routing Number
The fractional routing number should be printed in a fractional format in the upper
right quadrant of the check. This number is assigned to identify the Federal Reserve
District and drawee institution. Consult with your bank for the proper routing number
and format for each of your accounts.
MICR Line
Accurate high-speed processing of your checks by financial institutions is enabled by
the accuracy and integrity of the data in the MICR line. Refer to figure 3.1 for the
location of the following MICR line fields. The MICR line is read from right to left with
position one being the right most position proceeding to position sixty-five on the left.
The MICR line must be printed at exactly eight characters per inch.
Auxiliary On-Us Field Positions 65 to 45
This field usually contains the check serial number for commercial size checks
and possibly account control information. It is bounded by On-Us symbols. (;). It
is not included on personal, small size checks.
External Processing Code (EPC) Field Position 44
This one digit field is position 44 of the MICR line. This field is usually left blank.
The use of this field is controlled by the ASC X9B Standards Committee.
Routing Field Positions 43 to 33
The routing field is bounded by Transit Symbols (:) in positions 43 and 33. It
contains fixed format information about the drawee institution. Consult with your
bank for the specific data field to be placed here for each of your accounts.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
7 All Rights Reserved
Page 12

On-Us Field Positions 32 to 14
The On-us field contains the makers’ account number. The structure and content
of this field is left to the drawee bank. On personal checks this field also contains
the check serial numbers. The On-Us field may not consist of more than 19
characters. An On-Us (;) symbol must appear immediately to the right of the
account number.
Blank Field Position 13
Position 13 is always left blank.
Amount Field Positions 1 to 12
The amount field is the right most field in the MICR line. It remains blank until it is
printed by the bank of first deposit. When the check enters the banking system,
the bank of first deposit encodes this field from data in the convenience amount
field. It will be bounded by Amount Symbols (/).
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
8 All Rights Reserved
Page 13

Figure 3.1: Sample Check
A. Serial Number: Must be in the upper right corner and match the serial number in the
MICR line (see D for further explanation).
B. Fractional Routing Transit Number: Should be in the upper right corner and must
match the routing transit number in the MICR line with the exception of the state prefix
number (ex. 66 = NC, 67 = SC, 64 = GA, etc.) and the preceding zeros.
C. Bank Name, State, City: The bank logo is optional. Name of bank, city and state
where the account will be assigned/opened is a required field.
D. Aux On Us (46-55): This is a required field if the customer desires services offered by
the bank which require a serial number. The serial number format is controlled by the
payer’s bank. A & D should match.
E. Routing Number (34-42): Designates the Federal Reserve district and financial
institution. Each city, state or region that the bank serves has a unique institution
identifier. IMPORTANT: positions 35-42 is the Routing Number, position 34 is the
check digit.
F. Account Number: This is a unique number assigned to the customer’s account.
G. Optional Serial Number: Used for personal accounts (checks only). A 4 digit zero
filled field that should match the serial number in the upper right corner.
H. Convenience Amount Area should be in the general location shown above in the
diagram. The illustrated box in the diagram is optional and if used, should conform to
ANS X9.7. A single stroke dollar sign is required.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
9 All Rights Reserved
Page 14

4. Quality Issues
A high quality MICR document can be read by bank reader/sorter equipment many times
with no readability issues and does not result in damage to bank equipment. This quality is
the result of a well designed printer, an originally manufactured MICR toner cartridge and
high quality check stock.
Printer Features
Your Secure MICR Printer is equipped with some features to ensure high quality MICR
documents.
Paper Type
We recommend paper trays with check stock be set to “bond” paper type. The
associated “weight” and “texture” settings should be set to “heavy” and “rough.” See
the base printers User’s Guide. If more than one input tray has check stock and
they are the same stock, set all to “bond” and they will be linked. If different stock is
used in more than one input tray, use “custom” type, “rough” and “heavy” to block
Linking.
MICR Toner Low Alarm
When MICR toner is low, the printer stops and the user is prompted to load a new
MICR toner cartridge. We do not recommend shaking the cartridge to prolong its
life. Once low toner is sensed, there may not be enough MICR toner left to produce
quality MICR documents.
MICR Toner Sensing
When the printer enters MICR mode and attempts to print a MICR font, it checks to
ensure a MICR toner cartridge is loaded in the printer. If a regular cartridge is
present, an alarm will sound and the user must load a MICR cartridge before their
print job will resume. A message “load MICR Toner” will appear on the Operator’s
Panel.
MICR Toner
Use only Source Technologies MICR toner when printing MICR documents. It is
specifically engineered to print quality MICR documents with your printer. The printers’
MICR toner sensor is designed to work with the Source Technologies MICR toner cartridge
to prevent printing checks with regular toner present. You may choose to use this printer for
general office printing, which is acceptable. If a MICR print job begins and the printer has a
regular toner cartridge present, the printer will stop and prompt the operator to install a
MICR toner cartridge.
Source Technologies does not recommend the use of refilled MICR toner cartridges.
Although refilled cartridges are generally less expensive, they may result in expensive
printer repairs and bank check reject fees due to inferior MICR toner formulation.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
10 All Rights Reserved
Page 15

MICR Check Stock
Check stock has a large impact on the resulting quality and security of your MICR
document. Here are a few features that should be considered when selecting a check
stock. Please see Chapter 4 for more information on check stock security features.
Quality
Quality MICR check printing with your ST Secure MICR Printer requires check stock
that matches the printer’s requirements. Source Technologies can supply paper
specifically made for our printers. If you wish to order check stock from other
suppliers, please show the following requirements to your sales representative. We
will test other suppliers’ paper for a nominal fee.
Layout
Layout your check design before any paper is purchased or layout your design to
existing check stock. Keep in mind, perforations, orientation, special logos and any
color elements. The printer can print just about anything as long as it is black.
Weight
We recommend 24 lb. - 29 lb. paper.
Stiffness
We recommend taber M.D. 2.5 and C.D. 1.1 minimum.
Smoothness
For best toner fusing, we recommend rougher surfaces within the base printers’
specifications and the Paper Specifications for Checks X9.18. We recommend a
smoothness range of 150 to 200 - Sheffield.
Paper Grain Direction
When using 24 lb. - 29 lb. bond paper we generally support either long or short
paper grain. Overall performance in the banks reader/sorters is best when the
resultant grain direction is left to right when viewing the check.
Perforations
All perforations in the stock should be Micro-Perfs (20 or more cuts per inch). Larger
perforations can produce excessive paper chaff and result in damage to the toner
cartridge. Perforations should be ironed by the paper supplier to reduce nesting and
potential double feeding.
Moisture
The paper moisture content should be between 4.7 and 5.5%. Storage conditions
have much to do with the final moisture content of most papers. Store your check
stock in a cool, dry, environmentally stable and secure area. Protective wrappings
should be removed just prior to use.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
11 All Rights Reserved
Page 16

5. Security Issues
Printing negotiable documents from blank paper on desktop MICR laser printers makes
security a top priority for any company embarking on a desktop check printing project.
Good security programs integrate hardware, software, your employees and your financial
institution into a secure check production system. Recent changes relative to the
responsibilities of banks and their customers have a bearing on the ultimate liability for
fraudulent documents. Customers must have systems designed and documented to show
“Ordinary Care and Good Faith Effort” is in place to avoid liability. In the past, financial
institutions generally credited corporations when fraud was discovered. New regulations
attempt to define who may have been negligent in the transaction and put the liability on
that party or parties. Clearly, if a fraudulent occurrence can be traced to a corporation’s
lack of security procedures, or the design of their negotiable documents, the regulations will
protect the banks, or at best case the loss will be shared.
Check Stock Security Features
We have found the following check stock security features to be of merit:
Artificial Watermarks - White on white printing generally on the back reveals words
or patterns when held at an angle. You should state on the front of the check that
this feature is present. It cannot be copied.
Laid Lines - Evenly spaced background lines that make cut and paste alteration
difficult.
Void Pantograph - Background printing of the word VOID or COPY which appears
on photocopies. Some paper suppliers offer enhanced versions of pantographs
which provide more protection from the latest in color copier technology.
Chemical Additives - If an ink eradicator (bleach, acetone, etc.) is applied to the
document, the eradicator creates a permanent stain.
Numbered Check Stock - Sequential numbering printed in dye that penetrates to
the reverse side of the check can be used to verify authenticity. This number may
not relate to the check serial number. This also provides for inventory control of
blank check stock.
NOTE: These quality issues serve as a general guide for check production. You should not
consider these features as an all inclusive list. We recommend consulting with your local
paper supplier for any additional comments or suggestions.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
12 All Rights Reserved
Page 17

Security Note
Check fraud in the United States is a continuing problem. We have attempted to identify
security features that can be incorporated into the base check stock. However, these may
not prove 100% fraud preventative. Over time, technology will continue to develop new and
improved measures to address check fraud.
The following internal and external security measures will help minimize your risk of check
fraud.
1. Financial institutions should train tellers to look at the check, not the person
presenting the check. The check, not the person, is the item that must be
verified.
2. Firms accepting checks should be aware of damaged MICR lines. Intentionally
damaging the MICR line can increase the time necessary to process an item,
giving the forger enough time to leave town. Also be sensitive to discoloration,
this could be an indication of alteration.
3. Incorporate security features into your base check stock and utilize printed
security features that address both alteration and counterfeiting of original items.
A short list of these features would be:
• Warning Bands, or other methods that alert recipients to visual security
features;
• Artificial or genuine watermarks in the base paper;
• Chemical additives in the base paper that react to chemical alteration
attempts;
• Void Pantographs that address attempts to copy original items;
• Unique security fonts that deter attempts to alter payee or amount
information.
4. When generating final negotiable items,
• The document always includes the amount value in words;
• The document should not include information that limits the value range,
i.e. “Not valid over $500.” This only guides the fraudulent attempt. Use
your application software to detect out of range items;
• All levels of hardware and software password protection should be
utilized.
5. Safeguard check stock paper, and limit access only to necessary employees.
6. Understand and approve the security procedures of your check stock suppliers to
safeguard stock in their custody.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
13 All Rights Reserved
Page 18

7. Use “Positive Pay” check services from your financial institution that match check
number and dollar amounts to known information. Financial institutions should
encourage full participation of corporate clients.
8. Move methods of fraud detection to the item’s point of entry into the clearing
system. For example, low cost readers can detect low magnetic strength in the
MICR line which is a good indication of attempts to copy an original.
9. Always verify the home address and place of employment of new account
applicants. Use public sources such as phone books to verify phone numbers.
Ask new account applicants why they are opening an account with your
institution. Be suspect of unusual answers or delays in responding.
10. Stay abreast of current check fraud methods and the latest in fraud detection.
Offer seminars to educate corporate clients.
11. Review and document your internal negotiable document printing procedures.
Investigate employee backgrounds before assigning security authority. Split
responsibilities, for example, an accounts payable production/security officer
should not also balance the account.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
14 All Rights Reserved
Page 19

6. MICR Features
Source Technologies’ Secure MICR Printers are designed to allow both general office
document printing and secure MICR document printing. You may print a variety of
conventional jobs with regular Lexmark toner using all of the printer features available such
as MarkNet and MarkVision network attachment interfaces and network printer utilities.
These printers come standard with HP PCL5, PCL6 and PostScript Level 2 emulations and
others. Source Technologies has designed features to enhance these printers with MICR
mode specific operation that allows you to securely print high quality negotiable documents.
MICR Mode
Your Secure MICR Printer has two operational states: normal and MICR mode. When the
printer is in normal printing mode your MICR resources cannot be accessed. Once the
printer enters into MICR mode your secure resources are available and the printer starts
the process of confirming readiness to print a negotiable document. There are two
conditions which must be met before MICR mode is activated:
If the front panel combination lock feature is activated, the correct eight digit
combination must be entered from the front panel.
The correct password command must be received by the printer from the software
application prior to printing any MICR documents.
MICR Fonts
The E-13B and CMC7 MICR fonts are resident in your printer. Examples of these fonts are
in the Appendix of this manual. They can only be accessed after MICR mode is activated
by your software. A MICR toner cartridge must be present to print the MICR fonts.
Secure Fonts
Two Source Technologies designed secure fonts: Secure Numeric Font and ICR Secure
Numeric Font are resident in your printer. Examples of these fonts are in the Appendix of
this manual. Like the MICR fonts, these secure fonts can only be accessed after MICR
mode is activated by your software.
The ICR Secure Numeric Font is designed for the convenience area of your check. It can
be read by the imaging equipment used by many financial institutions. The Secure
Numeric Font should not be used in this area since the reverse image aspect of this font
prevents it from being read by this equipment. We recommend using both of these fonts on
your checks as they are designed to deter check fraud.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
15 All Rights Reserved
Page 20

MicroPrint
Your Secure MICR Printer also contains the MicroPrint font. MicroPrint is text less than
.010” tall. It can easily be read with a magnifying glass but appears to be a solid line to an
unaided
eye. This font provides protection against reproduction by most scanners and copiers
because they cannot successfully print the tiny letters.
Most check printers use this font in the signature area of their preprinted checks. We
recommend using this font to help deter check fraud. The text in this font can either be
fixed, such as the name of your organization, or it can be variable, such as the check
amount and payee name. The use of variable text provides an additional method of
protection against check counterfeiters.
Use of the “MP” designate symbol to identify the line as MicroPrint is optional. The
MicroPrint font only contains alphanumeric characters. Punctuation marks and spaces are
ignored by this font and do not print.
Bi-Directional Feedback
Your Secure MICR Printer can provide MICR status messages to the check printing
application. This feature is valuable in a networked environment with multiple printers or
with users utilizing a printer located in another area. The application can get information on
MICR settings such as toner cartridge type (MICR or regular), locked trays (which trays are
locked to non-MICR applications), resident fonts/macros and audit trail settings. The
printer can send the application MICR error messages such as “load MICR toner.”
When the printer receives the “@PJL INFO STVARIABLES” command it will report all
MICR variables to the host. The MICR variables can also be seen by accessing the
printer’s front panel menu. Select Reports > Menu Settings Page. The second page of this
menu shows the current MICR variable configuration.
If USTATUS DEVICE=On, the printer will report PJL error 40020 for any MICR error which
causes the printer to go off-line. It will appear in this format:
@PJL USTATUS DEVICE
CODE=40020
DISPLAY=”MICR Password Error Press Go”
ONLINE=FALSE (formfeed----HEX 0C)
The code will always be 40020, only the display line will change to indicate the specific
error.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
16 All Rights Reserved
Page 21

Resource Storage
Check-related resources, such as form overlays and signatures, are stored in your printer
with unique identification numbers. ID numbers must be less than 32767. Number 5001 is
reserved for the Audit Trail overlay. Your Secure MICR Printer has two areas where you
may store these resources: FLASH and RAM Memory.
Flash Memory is an optional feature. It is user managed and resources can be designated
as “secure” or “unsecure.” Secure resources are loaded to flash with the STL command
and have ID numbers greater than or equal to 10000. They can only be accessed by using
the STP command when the printer is in MICR mode. Unsecure resources do not require a
password and should be assigned an ID number less than 10000. Resources stored in
flash memory are not deleted when the printer is powered off. Flash memory is required for
all Audit Trail features.
Storing resources in RAM is also an option. Resources in RAM are deleted when the
printer is powered off or reset. For this reason check-related resources may need to be
loaded frequently. Resources stored in RAM cannot be password protected.
We recommend storing all check-related resources in secured flash memory.
MICR Menu
Your Secure MICR Printer contains a front panel menu specific to MICR applications. The
complete menu is as follows:
Option Card Menu > MICR Menu
Security Lock
Audit Menu
Audit Location - Flash/Disk
Record Sorting
Overlay
Sum Field 4
Print Report
Setup Menu
MICR Type - Normal/Optraforms
Hex Transfer
Density Control
MICRpoint
Use the menu button on the front of your printer to toggle through the menu options. To
select an option press the select (√) button. An item is selected when it has an asterisk (*)
after it.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
17 All Rights Reserved
Page 22

The Security Lock option allows the user to activate and set a front panel combination for
additional security. This feature prevents anyone from printing checks without the proper 8digit combination. See the MICR Mode Commands section of this chapter for more
information.
MICR Type designates the printer as a “normal” Source Technologies Secure MICR Printer
or as a Secure MICR OptraForms Printer. The default is “normal.” Hex Transfer and
Density Control are normally reserved for ST Technical Support.
MICRpoint is a feature that allows for fine positioning of the MICR line by the operator.
The Audit Menu deals with the optional Audit Trail Report settings. See chapter 7 for more
information.
Entering MICR Mode
To print MICR documents, your Secure MICR Printer uses special alphanumeric text
commands called MICR Mode commands.
There are two different commands which activate MICR mode printing:
&%STFPASSWORD$ and &%STHPASSWORD$. The &%STF is the default command
and is recommended for most applications.
To use the &%STF command, it must be entered at the beginning of the job datastream.
The &%STH command can be entered anywhere prior to accessing secured resources.
The &%STH command is not as powerful as the &%STF command because it does not set
as many parameters for MICR printing. Both commands and descriptions are as follows:
&%STF Command
When entering MICR mode with the &%STF mode, the printer will:
• Check to see if the proper Front Panel Combination has been entered (when
enabled).
• Allow access to secure check printing resources such as MICR fonts and
secure fonts stored in printer ROM.
• Allow access to protected signatures, overlays, logos and other important
resources stored in password protected nonvolatile flash memory.
• Display “MICR Mode Active” on the printer’s front panel.
• Disable the printer’s front panel menu system.
• Set printer resolution to 600 dpi for printing MICR fonts.
• Disable Jam Recovery.
• Set the copies parameter to 1.
• Sets Toner Low Alarm.
• Turn Hex Transfer ON.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
18 All Rights Reserved
Page 23

NOTE: The &%STF command must be entered at the beginning of the print job
before any other print data is received.
&%STH Command
The &%STH command does not set-up the printer for check printing activity as
completely as the &%STF command mode. This alternate MICR mode command
forces the user to manually program some commands through their host application.
It is used when programmers cannot place &%STFPASSWORD$ at the beginning of
their job. Use the &%STH command if you experience page ejects while in &%STF
mode.
When entering MICR mode with the &%STH command, the printer will:
• Check to see if the proper Front Panel Combination has been entered (when
enabled).
• Allow access to secure check printing resources such as MICR fonts and
secure fonts which are stored in printer ROM. It also allows access to
protected signatures, overlays, logos and other important resources stored in
password protected nonvolatile flash memory.
• Turn Hex Transfer ON.
NOTE: The &%STH command can occur within a datastream after the page has
started. The &%STH command, unlike the &%STF command, can be issued
anywhere on the page.
MICR Mode Commands
Password Command &%STFPASSWORD$ or &%STHPASSWORD$
&%STF or &%STH Lead in sequence
PASSWORD User defined password, 8 characters, case sensitive,
unprintable characters allowed. Factory default is
PASSWORD. See also New Password Command.
$ Command terminator
MICR Definition Command &%SMCPxxxx$ (optional)
&%SMCP Lead in sequence
xxxx MICR count, the number of MICR lines to be printed during
this print job. (4 bytes in hex)
$ Command terminator
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
19 All Rights Reserved
Page 24

Example: &%SMCP0010$
Prints 16 (Hex 10) MICR lines before disabling MICR mode. This command defines how
many MICR lines may print in the current job. When the count decrements to zero, MICR
mode is terminated.
Set New Password Command &%STExxxxxxxx$
&%STE Lead in sequence
xxxxxxxx New password, must be 8 characters either printable or non
printable. Dollar ($) sign is an invalid password character.
$ Command terminator.
In order to set a new password the current password must first be sent. Caution: Errors
made in sending the new password command could lead to setting it to an unknown value.
If the Password is unknown the printer must be returned to Source Technologies to be
reset to PASSWORD.
Activate/Set Front Panel Combination Lock &%STSxxxxxxxx$ (optional)
&%STS Lead in sequence
xxxxxxxx Eight digit sequence, valid characters 0-9
$ Command terminator
Sets and activates the front panel MICR combination lock. If this feature is activated, MICR
mode cannot be entered until the front panel combination is entered correctly. All MICR
features will be inaccessible until this combination is entered. Sending an &%STS
command and eight zeros deactivates the security lock.
Caution: If the front panel combination is set and then forgotten, the printer must be
returned to Source Technologies for the combination to be deactivated.
Print MICR E-13B Font &%SMDddd...ddd$
&%SMD Lead in sequence
ddd...ddd Data to be printed in E-13B MICR font
$ Command terminator
Prints the specified data in the E-13B MICR font which is used in the United States,
Canada and Mexico. The correct spacing begins at the cursor position modified by the
MICRpoint adjustment setting at the start of the command. After the terminator is sent, the
printer is returned to its default font. After each Print E-13B command, the MICR count is
decremented by one. Upon receiving this command the printer will check to ensure a
MICR toner cartridge is installed and set the copies parameter to 1. See Appendix A for
MICR E-13B font character mapping.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
20 All Rights Reserved
Page 25

Print MICR CMC7 Font &%SM7ddd...ddd$
&%SM7 Lead in sequence
ddd...ddd Data to be printed in CMC7 font
$ Command terminator
Prints the specified data in the CMC7 MICR font which is used in Europe and South
America. The font and its correct spacing begins at the current cursor position modified by
the MICRpoint adjustment setting at the start of the command. After the terminator is sent,
the printer will return to its default font, and the MICR count will be decremented by one.
Upon receiving this command the printer will check to ensure a MICR toner cartridge is
installed and set the copies parameter to 1. See Appendix B for CMC7 character mapping.
Print Secure Numeric Font &%SMFddd..ddd~
&%SMF Lead in sequence
ddd...ddd Data to be printed in this font
~ Command terminator
The dollar sign ($) is not a command terminator for this command. For both security fonts
the tilde ~ (hex 7E) is the command terminator since the dollar sign is a valid character.
Print ICR Secure Numeric Font &%SMIxxxxxx~
&%SMI Lead in sequence
xxxxxxxx Data variables to be printed in this font
~ Command terminator
Print MicroPrint Line &%SMMxxxxxxxxx!$
&%SMM Lead in sequence
xxxxxx Data to be printed in this font
! MP designator (optional)
$ Command terminator
If the exclamation point (!) is used, the “MP” designate will print just above and to the right
of the last character. This is optional and is typically used to notify the check recipient of
the presence of MicroPrinting. Only 0-9, A-Z (upper and lower case) print. Special
characters and spaces disappear.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
21 All Rights Reserved
Page 26

Load Flash Resource &%STLxxxxxyyyyyyzdd....dd
&%STL Lead in sequence
xxxxx Resource number in decimal, must be 5 digits
yyyyyy Byte count of resource file in Hex, must be 6 positions
z Format of the resource file
S = Single byte binary format
D = Double byte text format
dd...dd Flash resource file. e.g. forms overlay, signatures etc.
Resource number values may be between 00001 to 32767. Values of 10000 and above
are password protected and will require the user to enter MICR mode with a valid password
before they can be unlocked with the STP command. Values below 10000 will be
unsecured.
Resource number 5001 is reserved for the Audit Trail overlay, see chapter 7.
Format Flash Memory &%SFF$
&%SFF Lead in sequence
$ Command terminator
This command formats flash memory. A valid password command must precede this
command.
Caution: All flash contents will be lost. This includes all electronic forms, signatures, logos,
etc.
Secure Flash Resource Unlock Command &%STPxxxxx$
&%STP Unlock flash resource command
xxxxx Flash resource number, must be 5 digits
$ Command terminator
Unlocks a secure flash resource.
Tray Lock Command &%STTL#$
&%STTL Lock tray command
# The tray to be locked (choose from 1, 2 or 3 only)
$ Command terminator
This command prevents other applications from accessing a particular printer paper tray.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
22 All Rights Reserved
Page 27

Tray Unlock Command &%STTU#$
&%STTU# Unlocks tray
# The tray to be unlocked (choose from 1, 2 or 3 only)
$ Command terminator
Tray Swapping Commands &%STTSON$ / &%STTSOFF$
&%STTSON Turns tray swapping on
&%STTSOFF Turns tray swapping off
$ Command terminator
This command allows you to redefine the PCL values for Trays 2 and 3 to allow software
and operational consistency with older printers in the system. Swapping ON causes any
<esc>&l4H to be replaced with 5H and vice-versa.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
23 All Rights Reserved
Page 28

DES and AES Decryption
Data Encryption Standard (DES) and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) are both
supported in the Source Technologies Secure MICR Printers. The minimum Code Level
support for AES is 8.5j. Levels 8.5i. and lower only support DES.
DES originated at IBM in 1977 and was adopted by the U.S. Department of Defense. The
controlling standards for DES are ANSI X3.92 and X3.106 and in the Federal FIPS 46-3
standard. An alternative to DES called Triple DES is not supported in our Secure MICR
printers.
AES is documented in a Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) standard
FIPS 197, dated 11/26/2001. Three key sizes are documented in the standard, 128-bit,
192-bit, & 256-bit. We currently only support the most commonly used 128-bit key size.
The algorithm selected for AES is Rijndael. Developed in Belgium, an English
pronunciation alternative is “Rain Doll”. In addition to U.S. Government implementations, it
is anticipated AES will be adopted by businesses, organizations, institutions, and
individuals outside of government, and outside of the United States as was the case for
DES.
We only support decryption for DES and AES. Encrypted printer data streams can be
decrypted using the key stored some time prior to the message. Keys for both DES and
AES are stored separately so that both AES and DES are supported simultaneously. The
keys messages themselves can be encrypted with either DES or AES for either DES or
AES. Only one DES and one AES key exists at any one point in time. Old keys are not
saved. To change either a DES or an AES key requires the MICR Password Command.
The Secure MICR printer does not have any capability to encrypt a return or Bi-directional
message.
Decryption Commands
Decryption requires printer processing overhead. In our testing encrypted printer data
steams near or below 100K bytes per page do not seem to affect printer speed in term of
pages per minute or first page out timings. Some testing done with print files from 500K to
1 Meg per page showed up to a 30% degradation in speed. It is therefore recommended
the encryption be reserved for the confidential portions of the data when large file sizes are
anticipated.
Set DES Decryption Key Command &%STSETDESKEY<16 Hex Characters>$
The command requires a MICR Password Command be sent prior to the Key Command.
The Key Command could itself be encrypted and then decrypted in the printer. The
command requires the key data be in a double-byte hex format. The 8 byte value must be
converted to the 16 byte format. The only values that can be contained in the 16 command
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
24 All Rights Reserved
Page 29

bytes are 0 through 9, A through F. Alpha key characters can be upper or lower case.
Command characters must be upper case. An example of a valid key command &%STSETDESKEY5f00FF7E3DA938eb$ The key value remains in the printer until
another key command is received. Printer power cycles and printer reset commands do
not affect the key value.
The dollar sign ($) is the command terminator and is required.
Set AES Decryption Key Command &%STSETAESKEY<32 Hex Characters>$
The command also requires a MICR Password Command be sent prior to the Key
Command.
The key data is similar to DES, but is twice in length with 32 Hex character format
representing the 16 byte or 128-bit key value.
Turn DES Decryption ON &%STDON$
Turn AES Decryption ON &%STAON$
All data following the $ command terminator will be decrypted using the current key value
stored in the printer and the DES or AES algorithm. Decryption continues until a Decryption
OFF command is received, a printer panel reset occurs, or printer power is cycled. Printer
software language resets do not stop decryption.
Turn DES Decryption OFF &%STDOFF$
Turn AES Decryption OFF &%STAOFF$
The OFF command resides within the encrypted data, and must also be encrypted. The
OFF occurs after an 8-byte block (DES) or 16-byte block (AES) is received and decrypted.
The last block containing the OFF should either have the command right justified or padded
out to the block boundary. Any padding bytes after the $ command terminator will be
discarded.
MFP Copy Defeat Commands
A Secure MICR printer with the Multi Function Printer (MFP) feature can scan and copy
documents. This allows the end users to copy MICR documents with MICR toner. The
Copy Defeat command will block the copy function when a MICR toner cartridge is
installed, but allow the copy function with standard toner.
MFP MICR Copy Defeat ON &%STMCDON$
MFP MICR Copy Defeat OFF &%STMCDOFF$
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
25 All Rights Reserved
Page 30

Both commands require the MICR Password Command. The ON command blocks the
copy function with MICR toner. The OFF command allows the copy function with MICR
toner. The factory default is OFF
Note – Postscript Language print jobs downloaded from a host will not print with MICR
toner if the Postscript job contains a copy count command. Copy Defeat = ON will reset
copy count to 0, and nothing prints. Either the Copy Defeat function needs to be set to OFF
or the copy count command needs to be removed if the user requires Postscript MICR
printing. We tested a few Postscript printer drivers and did not detect copy count
commands, but the specific data streams should be tested.
Customer Character Conversation Command
The Custom Character Conversion Command can be used to resolve some problems in
printer data streams. An example might be to remove a special command character in an
existing data stream that was used by your previous printer hardware. Without changing
your data stream, these special characters can either be removed, converted to Nulls, or
converted to other sets of data to accomplish what is required.
An example of this might convert a Skip Command used by an older generation printer to
multiple Carriage Return / Line Feed commands. You could also store a PCL5 command
in our SIMM and call it with one character in your data stream. Only one type of conversion
is permitted at any particular point in time, but the function can be modified within a data
stream multiple times.
The conversion information is stored in NVRAM and is retained through power off / power
on cycles. This means you could send the command one time and all future print jobs
would be converted. Special precautions are required if printer fonts and Macro’s are
downloaded to your printer. This might require you to disable the function during
downloads and re-enable prior to your print data.
&%STCxx[yy...]$ xx is a double-byte character to convert - the following characters are
not allowed:
&, %, S, T, C and $.
yy...is a double-byte string to convert to - can be 0 to 16 characters
long
$ command terminator
Example:
&%STC1E0D0A$ sets the convert character to 1E - the printer will replace any 1E
character in the data stream with 0D 0A (carriage return, line feed)
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
26 All Rights Reserved
Page 31

&%STC1E$ replace 1E with nothing - simply removes all 1E characters from the
data
&%STC00$ turn character conversion off
Special Alert and Custom Beep Command
Using the Beep Command, the printer data stream can alert printer operators that important
pages are currently being printed. The STBEEP1 command sounds its special beeps but
does not stop the printer. STBEEP2 stops the printing process and waits for the operator
to Press Go.
The Custom BEEP can be used to create an alternative beep pattern to STBEEP1. This
could be used to indicate a certain document, a custom signal to a different operator, or just
an alternative of your choice to STBEEP1. The Custom Beep command will not stop the
printing process.
NOTE: Beep Commands will not chain or link together. You cannot play Beethoven’s 5th
Symphony. During the execution of a beep pattern, all other beep commands are eaten.
Two important documents could be sent to the printer one after the other, both with beep
commands, but the pattern would only occur one time.
NOTE: The two digit frequency value is inverted. The higher the value, the lower the
frequency.
&%STBEEP1$ plays 3 long beeps, 3 short beeps, 3 long beeps and 3 short
beeps.
&%STBEEP2$ displays the message “Press Go to stop beeping” on the front
panel and repeatedly plays 5 long beeps.
&%STBEEPnnffdddd$ plays a custom beep -
nn is a two digit number of beeps (0-63)
ff is a two digit frequency (0-63)
dddd is a four digit duration (0-1023)
Example:
&%STBEEP02250300$ plays 2 long (duration 300) beeps at a frequency of 25.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
27 All Rights Reserved
Page 32

MICRpoint Feature
Fine positioning of the MICR Line characters is accomplished using the MICRpoint feature.
The feature only works with the SMD & SM7 MICR Print Commands using the printer’s
resident MICR fonts.
The exact location of the entire MICR Line can be moved left or right, up or down by the
printer operator through the printer’s front panel. Only the MICR Line is moved. All other
printed information is not affected. This allows the operator, using a MICR Positioning
Gauge and the MICRpoint feature, to precisely locate the MICR characters on the specific
printer in use to address slight print location variances.
Each value entered by the operator is equal to 1/10th of a Point, a decipoint ( 720
Decipoints = 1 inch ). The maximum value that can be entered is +/- 99 Decipoints
allowing the entire MICR Line to move up or down, left or right a maximum of 0.1375 inches
from the print data stream’s intended location.
The figure below shows proper MICR character placement using a MICR Positioning
Gauge. The best location has the right side of the characters at or near the right edge of
the location boxes. An operator may have to choose a compromise location that best
addresses the entire line.
To Enter MICRpoint values, enter the MICR Menu through the operator panel, select the
SETUP MENU, and then the MICRpoint Adjustment feature. Horizontal and Vertical
options are displayed. It’s through these Horizontal and Vertical options we can enter
maximum value of 99, and also choose + / - . A + horizontal value moves the characters to
the right. A + vertical value moves the characters down.
For instructional value let’s assume the current MICRpoint values are at 0, the default
values. For best positioning from using a gauge and the current printed output, the MICR
line needs to move up about 1/20th of an inch, and to the right what looks to be ¼ of the
typical character width. FYI, the MICR character 0 is 0.091 inches wide. Some quick math
tell us we want to move the line up 36 decipoints and to the right about 15 decipoints.
While in the MICR Menu with MICRpoint Adjustment selected, select Horizontal. You
should see two values, First a +/- choice followed by some value, in our case it’s 0 or
Default. To Move horizontal 15 points, use the UP/DOWN arrow keys to select +, a
positive value. Then press the RIGHT arrow key. Using the printer keypad enter 15. Then
select the center key to save the values. Again from the Horizontal / Vertical options, use
the DOWN arrow, and center key to enter Vertical values. Since we want to move the
MICR line UP, this requires a – or negative value. Use the UP/DOWN keys to select -, and
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
28 All Rights Reserved
Page 33

then use the RIGHT key to enter a value. In this instructional case it’s 36. Using the key
pad enter 36. Select the center key to save the value. The values are stored in internal
FLASH memory in the printer and will remain the same until changed by the operator.
Power ON/OFF cycles do not reset the values.
Assuming we did our measurements correctly at the beginning, when test or production
checks are now printed, the MICR Line should not be at the new location on the page.
If you wish to utilize the MICRpoint feature of the Infoprint 1532 MICR 35, please call Sales
Support at 1-800-922-8501 with your serial number on hand to receive the MICR
Positioning Gauge (shown above). The Positioning Gauge will be sent to you free of
charge.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
29 All Rights Reserved
Page 34

7. IBM Host Programming Features and Examples
Hex Transfer
The Hex Transfer feature allows the user to send PCL escape sequence printer commands
to the printer with simple text strings. You may send any valid command or string of
commands with no limit on the length or complexity. Form macros, signatures, or simple
commands may be passed through any platform to the printer since they are simple text.
The printer will convert them back to ESC (escape) sequences when they arrive at the
printer. Hex Transfer is automatically enabled while in MICR Mode. To enable it for all
applications use the following commands:
Turning Hex Transfer On
To enable Hex Transfer, send the following command:
&&??&%
Once Hex Transfer is enabled, the character sequence &% will act as a trigger sequence.
Any data following these trigger characters will not be printed and will be treated as Hex
Transfer data until the Hex Transfer ending character $ is encountered.
Turning Hex Transfer Off
To turn Hex Transfer off, send the following command:
&&??!!
This command will clear the trigger sequence and allow the &% characters to print. This
clear command may be sent at any time to assure that Hex Transfer is disabled. When
MICR Mode is entered, Hex Transfer will automatically be turned on, and when MICR
Mode is exited, Hex Transfer will be turned off unless it has previously been activated
outside of MICR Mode with the &&??&% string.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
30 All Rights Reserved
Page 35

Hex Transfer Examples
&&??&% This command enables Hex Transfer On
&%1B 26 6C 34 48 $ Sends the PCL Esc sequence:
Or <Esc>&l4H
&% 1B $& l 4H which is a paper source command identifying what
tray the paper will be pulled from.
&% 1B 45$ This command is a printer reset PCL command
Or which consist of the Esc character and printable E
&% 1B $E character and may be sent by simply putting the
Esc character in Hex.
Note - Hex Transfer can now be set ON or OFF via the MICR Menu. See Section 6, MICR
Menu
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
31 All Rights Reserved
Page 36

Figure 7.1 MICR Mode Command Example
The following example shows the MICR Mode commands and Hex Transfer commands in
use. This datastream would print the check on the following page (assuming the check
macro and the signature are loaded as flash resources).
&%STFPASSWORD$ &%SMCP0001$
&%STP10001$ &%STP20000$
&%1B266C3178307331683261366346
306F3165316C372E3330431B266130
4C1B2873
3130481B266B31302E3030481B2666
3130303031793358$
1000
200 Vendor Systems
October 5, 2005
99999 Oct 1 05 1000.00 20.00 980.00
1234567 Oct 2 05 200.00 4.00 196.00
136784 Oct 3 05 800.00 16.00 784.00
555555 Oct 3 05 55.55 1.11 54.44
2055.55 41.11 2014.44
1000
200 Vendor Systems
October 5, 2005
99999 Oct 1 05 1000.00 20.00 980.00
1234567 Oct 2 05 200.00 4.00 196.00
136784 Oct 3 05 800.00 16.00 784.00
555555 Oct 3 05 55.55 1.11 54.44
2055.55 41.11 2014.44
&%1B$(s1p16v0s3b4148T 1000
&%1B$(3@
October 5, 2005
&%SMF$2014.44~
&%1B$(s0p12h1s0b4099T
*********** Two Thousand Fourteen and 44/100*******DOLLARS &%1B$(3@
$2014.44
Vendor Systems
927 Warehouse Road
Kansas City, MO 59782 &%1B$(20000X ! &%1B$(3@
&%1B$&f0S &%1B$*p296x3184Y &%SMD;00001000; :123456789:1234567890123:$
&%1B$&f1S
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
32 All Rights Reserved
Page 37

The commands in Figure 7.1 in order of appearance:
&%STFPASSWORD$ Password Command.
&%SMCP0001$ MICR Definition Command with the count set to one.
&%STP10001$ Unlock Flash Resource number 10001.
&%STP20000$ Unlock Flash Resource number 20000.
&%1B26...3358$ PCL sequence in hex which sets the page format and enables
macro number 10001.
&%1B$(s1p16v0s3b4148T PCL sequence which changes the font to Univers 16 point. After
the check serial number prints (1000), the printer is returned to
its default font with the following command.
&%1B$(3@ PCL command to return to default font.
&%SMF$2014.44~ Print Secure font command. Note: The tilde ~ is the
command terminator.
&%1B$(s0p12h1s0b4099T PCL command to change the font to Courier 12 pitch Italic. Print
PCL Fonts from the Front Panel menu for a list of fonts with
their call commands.
&%1B$(3@ PCL command to return to the default font.
&%1B$(20000X! PCL command to print font number 20000. In this example font
20000 is a signature previously loaded into flash memory. Here
we call it and print it with an exclamation point (!).
&%1B$(3@ PCL command to return to the default font.
&%1B$&f0S PCL command to Push (store) the current cursor position.
&%1B$*p296x3184Y PCL command to move the cursor to 296X , 3184Y. At 300
units of measure, this is .97 inches across and 10.61 inches
down. We are precisely positioning the MICR line.
&%SMD....$ Print E-13B MICR Command. Prints the MICR line. Note the
MICR font character mapping in Appendix A.
&%1B$&f1S PCL command to Pop (return) the cursor to the pushed position.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
33 All Rights Reserved
Page 38

Escape Character Translation
In many IBM host environments, the programmer cannot send an ESC character (ASCII hex
1B) to the printer from within the application. Your Secure MICR Printer allows you to define
the ESC character as a printable character or a combination of two printable characters. You
can select combinations of 1 or 2 characters which are translated to a Hex 1B when they are
sent to the printer.
The command &%STYxxyy$ is used to select the character or character combination. The
pair xx represents the first characters’ ASCII hex value, yy represents the second characters
hex value.
Example: The symbols @@ should be translated into the escape character:
&%STY4040$
After this is sent to the printer, anytime an @ @ is received in exact sequence, the pair is
translated into the ESC character (Hex 1B). A single @ would print normally.
If yy is equal to 00, only the first character is used for the escape character.
Example: The symbol @ should translate into the escape character:
&%STY4000$
After this is sent to the printer, anytime an @ is received it is translated into the ESC
character. This means that the printer will never print the @ character. The only invalid
single characters are the & (HEX 26) and a null (00).
Example: &%STY2300$ #&l8D
The printer would translate the number sign (Hex 23) to the ESC character and it would act
on the sequence Esc&l8D which will set line spacing to 8 lines per inch.
If you want to reset the ESC character translation from the previous settings then you can
send the &%STY Command to deactivate the translation.
Example: &%STY0000$ 8
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
34 All Rights Reserved
Page 39
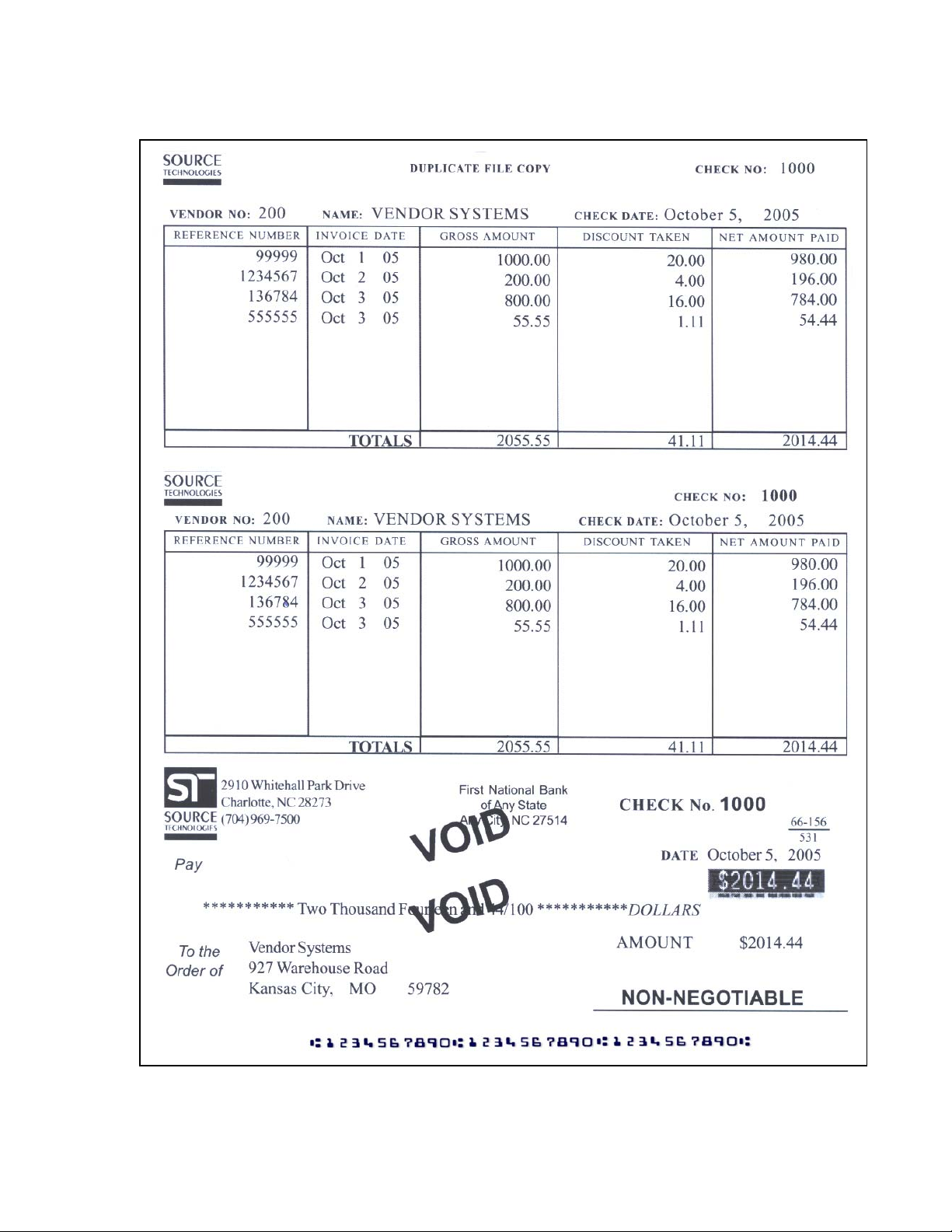
Figure 7.2: Sample Check
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
35 All Rights Reserved
Page 40

8. Audit Trail Reports
The Audit Trail Report feature provides a report of the printer’s MICR printing activity. The
printer must have flash memory to utilize this option. Details of each flagged check record
sent to the printer are provided since the last audit report was purged from flash memory.
Report Details
A record (check) must be bounded by a start of record command and an end of record
command. Within each record, fields to be included in the Audit Trail Report must be
flagged. The printer stores each record in flash memory. After the check is successfully
printed, its record is designated as a successfully printed document in flash.
The report is built by printing each one of these check records as a line item. At the end of
the report, an exception report is generated which highlights any records received by the
printer but not successfully printed.
Each record (check) has a maximum of seven fields with a total of 146 bytes. Two of the
flagged fields, SQ1 and SQ7 are Audit Report fields only. They are not printed on the
MICR document. Flagging other fields for inclusion in the Audit Report does not effect how
they print on a check.
Audit Trail Menu
The MICR menu contains a section for the Audit Trail options. Menu options are Audit
Location, Record Sorting, Overlay, Sum Field 4 and Print Report.
Audit Location
Choose to store audit data on flash or disk. The display will show “No Device” if neither is
installed. Flash is the default if both are present.
Audit Record Sorting
Enables sorting of the report by the first 20 digits in the MICR line field. In an unsorted report
the records are in the order in which they were printed.
Overlay
To assist in reading an Audit Trail report you have the option of using a form overlay. This
overlay can provide lines, boxes and shading for a more user friendly report format.
The Audit Trail Report overlay can be stored in printer flash or RAM. We recommend storing
it in flash. It must have an ID of 5001. It is enabled by accessing the MICR menu via the
printer’s front panel. Select Audit Menu>Overlay. This overlay will now be merged with the
record details every time the Audit Trail Report is printed.
Sum Field 4
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
36 All Rights Reserved
Page 41

The values in field four of the Audit Trail Report can be added together with the total provided
at the end of the report. This feature is activated through the MICR menu. Select Audit
Menu>Sum Field 4.
The values in field 4 must follow certain guidelines to be included in the column summation.
Dollar signs and commas must be properly located, no more than two numbers after a
decimal point, and no alpha characters. For example:
Valid Formats Invalid Formats
“$1,234,567.89” “$1,23,”
“4321234.56” “432.123”
“5,321” “34 test”
“$.89” “12$123”
If the value in field 4 is in an invalid format, that line will have a question mark to the right of
the field and it will not be added to the total. Under these circumstances, the total will print
with the notation “Fields flagged with ‘?’ not included in total.”
If the total exceeds $4,294,957,295.99 the printer will print an error message “Total exceeds
maximum value” instead of the total.
Print Audit Report
Prints an Audit Trail Report.
The Audit Trail Report is also part of the command set so the Audit Report can be printed
and purged via the host application. As a security control mechanism, purging is only
possible after entering a valid password.
The printer can store approximately 6,000 records or checks for each megabyte of flash. If
the Audit Report feature is activated, and the printer’s flash memory becomes full, an error
condition occurs. The printer will stop printing and prompt the operator to print and purge the
Audit Report memory. See the following section for purge instructions.
Audit Trail Report Command Set
&%SAR$ Start Audit Record
&%SAR Lead in sequence
$ Command terminator
Marks the start of an audit record and begins a PJL job.. This command must be inserted in
the datastream after MICR Mode is entered and before the first flagged field appears. It
should be sent at the beginning of each check record.
End Audit Record &%STORE$
&%STORE Lead in sequence
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
37 All Rights Reserved
Page 42

$ Command terminator
Ends the Audit Record and the PJL job (ignored if there was no Start Audit Record
Command).
Audit Report Field One &%SQ1d..d$
&%SQ1 Lead in sequence
d..d Data to be stored
$ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the first column of the report. It is a
maximum of 14 characters in length. If less than 14 characters are sent, the printer fills the
field with spaces when the audit report is printed. This field is recorded in the audit report
only, it is not printed on the check.
Audit Report Field Two-MICR Line &%SMDd..d$ or &%SM7d..d$
&%SMD or &%SM7 Lead in sequence
d..d Data to be printed
$ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the second column of the report. It is a
maximum of 40 characters in length.
Audit Report Field Three &%SQ3d..d$
&%SQ3 Lead in sequence
d..d Data to be printed
$ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the third column of the report. It is a
maximum of 40 characters.
Audit Report Field Four &%SQ4d..d~
&%SQ4 Lead in sequence
d..d Data to be printed
~ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the fourth column of the report. It is a
maximum of 16 characters in length. Since a total of this field can be provided at the end of
the Audit Trail Report it is typically used for the convenience amount field. NOTE: This is the
only command where the $ is not a command terminator. The tilde ~ (hex 7E) acts as the
command terminator.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
38 All Rights Reserved
Page 43

Audit Report Field Five &%SQ5d..d$
&%SQ5 Lead in sequence
d..d Data to be printed
$ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the fifth column of the report. This field is a
maximum of eight characters.
Audit Report Field Six &%SQ6d..d$
&%SQ6 Lead in string
d..d Data to be printed
$ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the sixth column of the report. This field is
a maximum of 19 characters.
Audit Report Field Seven &%SQ7d..d$
&SQ&7 Lead in string
d..d Data to be stored
$ Command terminator
This command identifies the data to be printed in the seventh column of the report. This field
is a maximum of 12 characters. The data in this field is recorded for the Audit Report only.
Print and Purge Audit Report &%SPURGExx$
&%SPURGE Lead in string
x option(s)
$ Command terminator
This command prints and purges the Audit Report. All recorded information is deleted. The
optional field can be any combination of the following letters:
T Total Field 4
O Overlay
S Sort by MICR line
C Communicate - send report to host instead of printing - see additional
information below on SPRINT command
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
39 All Rights Reserved
Page 44

For example, the command &%SPURGES$ sorts the records by the MICR line while the
command &%SPURGESO$ sorts the records by the MICR line and prints an overlay with the
data.
Options can be forced on with these commands but they cannot be forced off. In other
words, if the front panel overlay setting is on, it cannot be forced off by a datastream
command. If the front panel overlay setting is off, however, a datastream command can
activate this feature. This command can only be accessed with a valid password command.
Print Audit Report &%SPRINTxx$
&%SPRINT Lead in string
x option(s)
$ Command terminator
Prints the Audit Report
The optional field can be any combination of the following letters:
T Total Field 4
O Overlay
S Sort by MICR line
U Unsuccessful report only
C Communicate - send report to host instead of printing
The report sent back to the host begins with SOH (0x01) and ends with EOT (04). Since the
reports can be quite long, they will likely be broken into separate buffers which may be
interspersed with non-audit buffers such as PJL JOB status. Each buffer will begin with an
STX character (0x02) and end with ETX (0x03).
Each record will be terminated with carriage return-line feed (0x0D 0A).
Start Audit Feedback Command
&%SAF$
The printer will report to the host that sent this command every time an audit job
successfully prints.
Each report will be a 151 byte string:
byte 1 STX (0x02)
bytes 2-15 field 1 of the audit record (from SQ1)
16-55 field 2 (from SMD)
56-95 field 3 (from SQ3)
96-111 SQ4
112-119 SQ5
120-138 SQ6
139-150 SQ7
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
40 All Rights Reserved
Page 45

151 ETX (0x03)
The printer will continue to report until it is powered off and back on.
Figure 8.1 Audit Trail Commands Example
The following example shows the Audit Trail, MICR Mode and Hex Transfer commands in
use.
&&??&% &%STFPASSWORD$ &%SMCP0001$ &%SAR$ &%STP10001$ &%STP20000$
&%1B266C317830733168326136346630
6F3165316C372E3330431B2661304C
1B28733130481B266B31302E3030481B
26663130303031793358$
1000
&%SQ1200$200 Vendor Systems
Oct. 5, 2005
99999 Oct 1 05 1000.00 20.00 980.00
1234567 Oct 2 05 200.00 4.00 196.00
36784 Oct 3 05 800.00 16.00 784.00
555555 Oct 3 05 5 5.00 1.11 54.44
2055.55 41.11 2014.4
1000
200 Vendor Systems Oct. 5, 2005
99999 Oct 1 05 1000.00 20.00 980.00
1234567 Oct 2 05 200.00 4.00 196.00
136784 Oct 3 05 800.00 16.00 784.00
555555 Oct 3 05 55.55 1.11 54.44
2055.55 41.11 2014.44
&%1B$(s1p16v0s3b4148T1000&%1B$(3@
&%SQ6October 5, 2005$
&%SMF$2014.44~
&%1B$(s0p12h10v1s0b4099T
***********Two Thousand Fourteen and 44/100*******DOLLARS &%1B$(3@
&%SQ4$2014.44~
&%SQ3 Vendor Systems$
927 Warehouse Road
Kansas City, MO 59782 &%1B$(20000X ! &%1B$(3@
&%1B$&f0S &%1B$*p296x3184Y &%SMD;00001000; :123456789:1234567890123:$
&%1B$&f1S &%SQ710:33:45 AM$ &%STORE$ &&??!!
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
41 All Rights Reserved
Page 46

Figure 8.2 Audit Trail Check Sample
The datastream in Figure 7.1 will print the following check (assuming the check macro and
signature are loaded as flash resources).
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
42 All Rights Reserved
Page 47

The commands in Figure 8.1 in order of appearance. (Audit Report fields shown in
bold)
&&??&% Hex transfer enable.
&%STFPASSWORD$ Password command.
&%SMCP0001$ MICR definition command with the count set to one.
&%SAR$ Activates Audit Report recording.
&%STP10001$ Unlock flash resource number 10001.
&%STP00200$ Unlock flash resource number 200.
&%1B26...3358$ PCL sequence in hex which sets the page format and enables
macro number 10001.
&%SQ1200$200 Stores the vendor number 200 in the first position of the Audit
Report. Note that this field will not be sent to the page to be
printed. Here we send the field again so that it will print.
&%1B$(s1p16v0s3b4148T PCL sequence which changes the font to Univers 16 point.
After the check serial numbers prints (100), the printer is
returned to its default font with the following command.
&%1B$(3@ PCL command to return to default font.
&%SQ6October 5, 2005$ Stores the date in the sixth position of the Audit Report.
&%SMF$2014.44~ Prints Secure Font command. NOTE: Tilde (~) is command
terminator.
&%1B$(s0p12h10v1s0b4099T PCL command to change the font to Courier 12 pitch Italic.
See print PCL Fonts on the Front Panel under the test menu
for a printout with their call commands.
&%1B$(3@ PCL command to return to the default font.
&%SQ4$2104.44~ Stores the amount in the fourth position of the Audit Report.
&%SQ3Vendor Systems $ Stores the payee, Vendor Systems, in the third position of the
Audit Trail report.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
43 All Rights Reserved
Page 48

&%1B$(200X! PCL command to print font number 200. In this example font
200 is a signature previously loaded into flash memory. Here
we call it and print it with an exclamation point (!).
&%1B(3@ PCL command to return to the default font.
&%1B$&f0S PCL command to push (store) the current cursor position.
&%1B$*p296x3184Y PCL command to move the cursor to 296X, 3184Y. At 300
dpi, this is .97 inches across and 10.61 inches down. We are
precisely positioning the MICR line.
&%SMD...$ Print E-13B MICR command. Prints the MICR line and stores
the MICR line information in the second position in the Audit
Report.
&%1B$&f1S PCL command to pop (return) the cursor to the pushed
position.
&%SQ710:33:45 AM$ Here we send the time of print to the printer. The data is
recorded in the Audit Report but this field is not printed on the
page.
&%STORE$ Signals the end of a check and the end of Audit Report
recording.
&%??!! Turns Hex Transfer off.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
44 All Rights Reserved
Page 49

Figure 8.3 Audit Trail Report
Audit Report page1 Records 1 through 10 of 10 *indicates check did not print **indicates gap in check numbers
200 :00001000; :123456789: 12345678912345678: Vendor Systems $2,014.44 February 10, 2001 10:33:44 AM
200 :00001001; :562478923: 12345678912345678: Classic Homes Construction $28,576.72 February 12, 2001 09:45:40 AM
200 :00001002; :285946731: 12345678912345678: Computer Source, Inc. $55,600.00 February 14, 2001 01:00:26 AM
MSMITH :00001003; :628499761: 12345678912345678: Eastern Cleaning Supplies $876.00 February 15, 2001 08:45:36 AM
MSMITH :00001004; :559873164: 12345678912345678: Dillon Consulting Company $1,200.00 February 15, 2001 08:46:50 AM
MSMITH ** :00001006; :578642315: 12345678912345678: Klaussen Enterprises $449,466,800.00 February 15, 2001 08:47:32 AM
MSMITH :00001007; :556791324: 12345678912345678: Woods Paper Products $89.95 February 15, 2001 08:49:45 AM
*PJONES :00001008; :256988974: 12345678912345678: Printers Quarterly $899.99 February 19, 2001 09:35:40 AM
Administrator :00001009; :123654987: 12345678912345678: XYZ Insurance $123,568.00 February 21, 2001 10:30:45 AM
T53DODER :00001010; :155554897: 12345678912345678: Carmine’s Deli $2,354.00 February 22, 2001 11:15:25 AM
SQ1=14 spaces SMD=40 spaces SQ3=40 spaces SQ4=16 spaces SQ5=8 spaces SQ6=19spaces
Q7=12 spaces
NOTE: Each of the seven fields in the Audit Report holds a maximum number of characters. Those numbers
are represented in BOLD above with their corresponding fields. Field 1 and Field 7 will not print on the check.
This Audit Report is just one example of a report format. Any of the seven fields can be
manipulated to show any information the user feels is appropriate. For example, the check
amount could be in field 3 rather than field 4; or field 5 could contain items such as taxes
drawn on the check, check numbers, year-to-date accumulations, etc.
Each line is a record of a check that was printed. The top of every Audit Trail Report shows
how many pages make up the report as well as the number of records that will print. The
Audit Report can be printed in two ways: a sorted report or an unsorted report. A sorted
report sorts all checks numerically by the first 20 characters in the MICR line field and prints
asterisks (**) beside checks printed out of sequence. Sorting can be done via the front panel
or by the commands &%SPRINTS$ or &%SPURGES$. An unsorted report lists checks in the
order they were printed. An asterisk(*) at the beginning of a line states that the check number
did not print.
In this example:
SQ1= The authorized user who accessed the Audit Trail Report.
SMD= Displays the client’s check number, the bank institution’s routing number, and
account number.
SQ3= The name of the payee (The name of the person or organization to whom the
check was made payable).
SQ4= The amount of the check.
SQ5= Not used in this report.
SQ6= The date the check was written.
SQ7= The time that the check was printed.
All of the above fields will be printed on the check with the exception of field 1 and field 7.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
45 All Rights Reserved
Page 50

9. Error Messages
Your Secure MICR Printer has a set of front panel error messages unique to MICR
applications. These messages appear if there is a MICR related problem. The printer may
also print an error message on the page near where the error occurred. In many cases you
can receive more information about a displayed error by pressing Go to print the job which
caused the error. Then inspect the printed page for a more detailed error message.
Error Message on Display Printed Message Description Action
Can’t Purge, password not
enabled
Can’t Sort Insufficient Memory This error indicates
Command Decode Error
Invalid Convert to Escape
Character
Flash Full Purge and Format This error message
Load MICR Toner Before printing a
This error indicates
that MICR mode has
not been enabled.
the printer does not
have sufficient
memory to sort the
Audit Report.
Decode error &%Sx
(where x is the
incorrect character)
Invalid Convert to
Escape Character
A syntax error was
detected in a MICR
command.
An error was
detected in the User
Programmable
Escape Character
Selection
Command. The
software tried to
specify a NULL or
an ampersand as
the first Escape
Character.
indicates that the
printer’s flash
memory is full. The
audit trail cannot
accept more jobs
until more space is
available in flash.
MICR font, the
printer checks for
MICR toner. If
Press Go. Enter
MICR mode, then reattempt the purge.
Press Go. The
printer may need to
be upgraded with
more RAM memory
to sort; otherwise an
unsorted Audit
Report may be
printed.
Check your software
for a syntax error in
the MICR command
that was being used
when the error
occurred.
Check the Command
(&%STY...) for errors.
Press Go then purge
the audit trail. Then
either defragment or
format flash memory
(Utilities Menu).
Replace standard
toner cartridge with a
MICR Toner. Go to
proceed. If MICR
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
46 All Rights Reserved
Page 51

Macro Definition Error Invalid decode
mode specified
Macro Definition Error Macro ID greater
than 32767 limit.
Macro Definition Error Macro size exceeds
available space
Non-hexadecimal Value
Received
Non-hexadecimal
value received.
Non Integer Value Received Non integer value
received.
Integer string incorrect length Integer string
incorrect length
MICR Definition Line Count
The number of digits
Error
MICR Password Error
Password Length
Error.
regular toner is
present, the printer
will stop all printing
and display this
message.
The Load Flash
Resource Command
contained an invalid
character specifying
the format of the file.
Must be either a D
or S.
The resource
number in the Load
Flash Resource
Command
(&%STL...) was over
the 32767 limit.
Flash resource file
size specified in the
Load Flash
Resource Command
is too large for the
available space
remaining in the
flash module.
A command
contained a nonhexadecimal value
in a parameter.
A parameter in a
command was not
an integer.
A parameter in a
command was not
the correct length.
in the MICR
definition Command
is not equal to four,
or there is a nonhexadecimal
character in the
count.
Password length is
not equal to eight
toner is not available,
you must power-off
your printer and
restart the print job at
a later time when
MICR toner is
available.
Check the Command
(&%STL...) for syntax
errors.
Check the Load
Flash Resource
Command for
syntax/numbering
errors.
Format flash memory
to remove all existing
resources or upgrade
flash memory to a
larger module.
Check the Command
(&%STL, STY)
syntax for errors.
Check the command
(&%STL, STS,
STP)
numbering errors.
Check the Command
(&%STP, STS) for
syntax/numbering
errors.
Check your software
for errors in the MICR
definition Command
(SMCP).
Check the Password
Command in your
for syntax/
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
47 All Rights Reserved
Page 52

characters.
MICR Password Error Password Match
Error
Password sent does
not match the
current stored
password.
Password Not Enabled Error
A secure command
was sent without the
password being sent
first
Invalid AES/DES key Invalid hex digit or
length of decryption
key
Purge Audit Report, Then
Format
An SFF command
was received, but
there is audit data in
flash which should
not be erased
File System Error Can’t Open
File
There was an
internal error while
trying to access
flash for audit trail
Can’t Create Node There was
insufficient memory
to track another
audit job
Secure File Not
Unlocked/Opened/Written/Read
There was an
internal error while
trying to access
Flash for an STL or
STP command
software, it must be
eight characters long.
Check the Password
Command in your
software.
Check software to
ensure that password
is sent before any
secure commands
Check syntax of
SETAESKEY or
SETDESKEY
command
Purge the audit data,
then resend the SFF
command
Check that Flash is
installed and not full
Turn printer off and
back on, then retry. If
the problem recurs,
call Tech Support
Print the menus to
ensure that Flash is
installed. Print a
directory of Flash to
ensure that is it not
write protected or full.
If error occurs on
STP command,
check to confirm that
the resource is stored
in Flash.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
48 All Rights Reserved
Page 53

Appendix A: E13B MICR Font Mapping
Command &%SMDddd..ddd$
MICR Font Description Alpha/Numeric Hex Values
Character Values
1
/ Amount Symbol A a / 41 61 2F
: Transit Symbol T t B b : 54 74 42 62 3A
; On-Us Symbol O o C c ; 4F 6F 43 63 3B
= Dash Symbol V v D d - = 56 76 44 64 2D 3D
0 Zero 0 30
1 One 1 31
2 Two 2 32
3 Three 3 33
4 Four 4 34
5 Five 5 35
6 Six 6 36
7 Seven 7 37
8 Eight 8 38
9 Nine 9 39
Example: &%SMD ;00001234; T01234567T3210987654321;$ will print:
1
Select only one alphanumeric character to call the font.
;00001234; :01234567:3210987654321;
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A1 All Rights Reserved
Page 54

Appendix B: CMC7 MICR Font Mapping
Command &%SM7ddd..ddd$
Description Alpha/Numeric Hex Values CMC7 Font
Characters Values
1
Zero 0 30
One 1 31
Two 2 32
Three 3 33
Four 4 34
Five 5 35
Six 6 36
Seven 7 37
Eight 8 38
Nine 9 39
Colon : 3A
Semi-Colon ; 3B
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A2 All Rights Reserved
Page 55

Less Than < 3C
Equal = 3D
Greater Than > 3E
The CMC7 Font in the example above is magnified for purposes of clarity.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A3 All Rights Reserved
Page 56

Appendix C: Secure Numeric Font Mapping
Command &%SMFddd...dd~
Description Alpha/Numeric Hex Value Secure Font Character
Character
Dollar Sign $ 23
Left Bracket ( 28
Right Bracket ) 29
Asterisk * 2A
Comma , 2C
Dash - 2D
Period . 2E
Slash / 2F
Zero 0 30
One 1 31
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A4 All Rights Reserved
Page 57

Appendix C continued: Secure Numeric Font Mapping
Description Alpha/Numeric Hex Value Secure Font Character
Character
Two 2 32
Three 3 33
Four 4 34
Five 5 35
Six 6 36
Seven 7 37
Eight 8 38
Nine 9 39
Arrow > 3E
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A5 All Rights Reserved
Page 58

Example: &%SMF($>>>15,575.00)~
NOTE: The secure fonts in the example are magnified for purposes of clarity.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A6 All Rights Reserved
Page 59
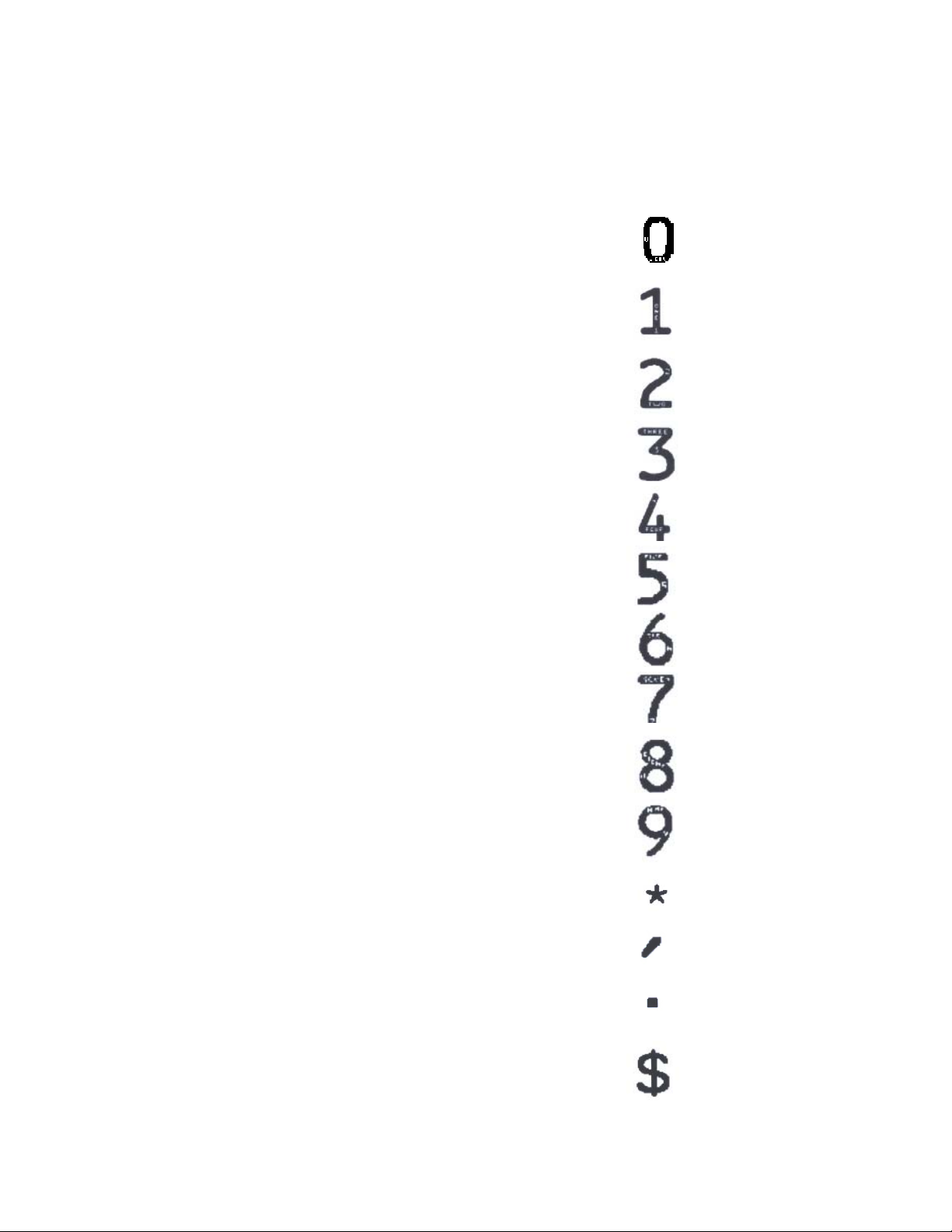
Appendix D: ICR Secure Numeric Font Mapping
Command &%SMIxxxxxx~
Description Alpha/Numeric Hex Value Secure Font Character
Character
Zero 0 30
One 1 31
Two 2 32
Three 3 33
Four 4 34
Five 5 35
Six 6 36
Seven 7 37
Eight 8 38
Nine 9 39
Asterisk * 2A
Comma , 2C
Period . 2E
Dollar Sign $ 23
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A7 All Rights Reserved
Page 60

Appendix E: MICR Mode Command Summary
Description Command Structure Function
Password &%STFPASSWORD$ Must be sent to enable
&%STHPASSWORD$ MICR Mode
MICR Definition &%SMCPxxxx$ MICR Line Count command
Set New Password &%STExxxxxxxx$ Sets new password, must be
preceded by current password
Activate/Set Front Panel &%STSxxxxxxxxx$ Turns on and sets Front Panel
Combination Combination Lock, must be 8 integers
Print MICR E13B Font &%SMDddd...ddd$ Prints E13-B MICR Font at the current
print position, see Appendix A
Print MICR CMC7 &%SM7ddd...ddd$ Prints CMC-7 MICR font at the current
print position, see Appendix B
Print Secure Numeric Font &%SMFddd...ddd~ Prints the Secure Numeric Font at the
current print position Note: The tilde is
the command terminator, see
Appendix C
Print ICR Secure Numeric Font &%SMIxxxxxx~ Prints the ICR Secure Numeric Font at
the current print position, see
Appendix D
Print in MicroPrint &%SMMxxxxxx$ Prints data in MicroPrint font.
Load Flash Resource &%STLxxxxxyyyyyyzddd...dd$ Loads a Flash Resource file into
password protected Flash Memory
Format Flash Memory &%SFF$ Formats Flash Memory Caution: All
flash contents will be lost
Flash Resource Unlock &%STPxxxxx$ Makes Flash Resource Command
available to be called, must be 5
integers
Tray Lock Command &%STTL#$ Locks Tray 1, 2 or 3 for MICR printing
Unlock Tray Command &%STTU#$ Locks Tray 1, 2, or 3
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A8 All Rights Reserved
Page 61

Tray Swapping Commands &%STTSON Turns tray swapping ON
&%STTSOFF$ Turns tray swapping OFF
Quit MICR MODE Command &%STQ$ Terminates MICR Mode
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A9 All Rights Reserved
Page 62

Appendix F: Audit Report Command Summary
Description Command Structure Function
Start Audit Record &%SAR$ Activates Audit Trail and begins PJL job
Audit Report Field One &%SQ1.d$ Records first field on the Audit Report - does not
print
Print MICR E13B Font &%SMD..d$ Print and records MICR line
Audit Report Field Three &%SQ3d..$ Records third field on the Audit Report
Print the Check Amount &%SQ4d..d~ Records fourth field of the
Audit Report and prints the check amount
Audit Report Field Five &%SQ5d..d$ Records fifth field of Audit Report
Audit Report Field Six &%SQ6d..d$ Records sixth field of Audit Report
Audit Report Field Seven &%SQ7d..d$ Records seventh field of
Audit Report - does not print
Print Audit Report &%SPRINT$ Prints Audit Report
End Audit Record &%STORE$ Ends Audit Record and PJL Job
Print and Purge &%SPURGE$ Prints and purges the Audit Report Caution: All
previous Audit Report information will be lost.
Format Flash Memory &%SFF$ Formats flash memory. An error will occur if
Audit Report has not been purged.
End MICR Mode &%STQ$ Ends MICR Mode
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A10 All Rights Reserved
Page 63

Appendix G: PJL Based MICR Commands
In addition to supporting the Text Based MICR Command Set described in Sections 6 and
7, this Secure MICR printer also supports the PJL based MICR Commands used on our
slower speed models. The MICR code functions emulate the presence of FLASH memory
for the 5 secured font resources. The FLASH Memory option is not required for the five
fonts. If you require the capability to store custom signature fonts, Logo fonts, or overlay
MACRO’s in Secure FLASH Memory the FLASH memory option is required.
The following are the key PJL and PCL commands required to access MICR resources in
the printer. For the complete source of information on PJL and PCL languages, consult the
Lexmark Technical Reference documentation.
Fonts and Secured Resources
The ST Secure MICR printer has five fonts password protected in FLASH memory. The
printer requires PJL commands with the correct password value to unlock the font
resources, followed by PCL to print the fonts. They are then re-locked by PJL commands or
by a printer power cycle.
The PJL commands to unlock the fonts must precede all PCL commands. The re-lock PJL
commands must follow the PCL commands and final form feed command. The PCL
commands could print an unlimited number of pages between the unlock and re-lock
sequences. We will use <ESC> in the following examples to indicate the Escape
character, ASCII 27. Values shown in parentheses () are hexadecimal.
PJL Unlock Sequence
<ESC>%-12345X@PJL LDECLARE LRESOURCE:”flash:”
LRWLOCK=”PASSWORD”(0D)(0A) @PJL ENTER LANGUAGE=PCL(0A)
The sequence contains a UEL (Universal Exit Language) command followed by the unlock
and enter language commands. The commands are case sensitive. PASSWORD is the
initial ship default password value. The command delimiter is a Line Feed (hex 0A) with
Carriage Return (hex 0D) being optional. Spaces are required as shown. The ENTER
LANGUAGE command is optional but recommended. The command should also end with a
LF (hex 0A). At this time all secured resources including any resources that are customer
unique in FLASH are unlocked and available to PCL.
The password value is limited to no more than 8 alphanumeric case sensitive characters.
PJL Re-Lock Sequence
<ESC>%-12345X@PJL LDELETEPASSWORD LRESOURCE:flash:”(0D)(0A)
<ESC>%-12345X
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A11 All Rights Reserved
Page 64

Sent after PCL, this sequence re-locks the resources with no change in the password
value. The PJL syntax of LDELETEPASSWORD is not the password. The command
sequence terminates with the UEL command (Universal Exit Language). This is optional
but recommended.
PJL Re-Lock Sequence With A New Password Value
<ESC>%-12345X@PJL DEFAULT LRESOURCE:”flash:” LRWLOCK=”xxxxxxxx”(0D)(0A)
<ESC>%-12345X
This command requires the resources to be previously unlocked. The new password is
represented by the value xxxxxxxx. The UEL is again optional but recommended.
After consulting Lexmark Technical Reference materials you may wish to expand the PJL
sequences to include more than the examples above. To chain multiple PJL commands
follow the following format:
(UEL)(PJL COMMAND)(0A)(PJL COMMAND)(0A)(PJL COMMAND)(0A)(UEL or ENTER
LANGUAGE)
The normal printer action to any format problems or missing or extra symbols is to ignore
the PJL command. This does make troubleshooting format errors difficult. Have patience!
PCL Font Call Commands
After PJL has unlocked the MICR FLASH resources, the ST-9116 uses standard PCL5e
commands to print. The five resident Source Technologies MICR font resources are all
bitmapped fonts and therefore cannot be scaled larger or smaller than the bitmapped
images. These fonts can be called by either a PCL Font Selection String or by their ID. The
commands are:
E13B MICR FONT <ESC>(10O<ESC>(s0p8h8v0s7b360T The Selection String
<ESC>(30802X The ID Call
SECURE NUMERIC <ESC>(16C<ESC>(s0p5h36.24v0s112T The Selection String
<ESC>(30043X The ID Call
ICR SECURE <ESC>(1O<ESC>(s1p12v0s0b110T The Selection String
<ESC>(30066X The ID Call
MICROPRINT <ESC>(2Q<ESC>(s1p0.96v0s0b1023T The Selection String
<ESC>(30055X The ID Call
CMC7 MICR FONT <ESC>14Y<ESC>(s0p8h8v0s0b361T The Selection String
<ESC>(30803X The ID Call
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A12 All Rights Reserved
Page 65

MICR FONT NOTE – The E-13B and CMC7 Fonts are 8 characters per inch. To position
correctly at an exact 8 characters per inch, the printer must be set to an internal Unit of
Measure of 600 DPI or greater or must have a horizontal motion index command at 8 CPI
be issued after the font call. This is true even if the base printer is at 600 DPI. The default
character positioning is at 300 DPI and 8 into 300 is 37.5 pixels. The printer will either
round down to 37 or up to 38 pixels causing characters to creep. To resolve this there are
multiple options.
1. If you are using a printer driver that is set to 600 DPI, the printer data stream should
include a Unit of Measure PCL command set to 600. The command is
<ESC>&u600D
2. If the application controls the printer data stream, add the Unit of Measure command
early in the data stream. The command also affects X & Y positioning commands.
Add <ESC>&u600D
3. After calling the E-13B MICR font, issue a HMI (Horizontal Motion Index) command
set to 8 characters per inch. The command must be included with every E-13B
MICR font call using either the Selection String or ID call. The command string is:
<ESC>(10O<ESC>(s0p8h8v0s7b360T<ESC>&k15H font data The Selection String
<ESC>(30802X<ESC>&k15H font data The ID Call
See Font Mapping Appendix pages for specific character set data for each font.
PJL INFO MICR COMMAND
The ST Secure MICR Printer supports an optional custom bi-directional PJL Inquiry
Command. The command provides printer information and cartridge information for
network management. The command format is; @PJL INFO MICR
The command should be sent with UEL (Universal Exit Language) commands. Example:
<ESC>%-12345X UEL
@PJL INFO MICR INFO MICR Command
<ESC>%-12345X UEL
The following data is returned
@PJL INFO MICR
PRINTER STATE = READY
= BUSY
= NOT READY
SERIAL NUMBER = XXXXXXXX
PAGECOUNT = 123456
CARTRIDGE TYPE = NORMAL
= MICR
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A13 All Rights Reserved
Page 66

CARTRIDGE STATUS = UNKNOWN
= OK
= LOW
= EMPTY
CARTRIDGE SERIAL# = XXXXXXXX
TONER LEVEL = 0-9
= UNKNOWN
CARTRIDGE COUNT = XXXX
LOW THRESHOLD = XXXX
EMPTY THRESHOLD = XXXX
• Printer State
o “Ready” is the expected return
• Serial Number = Printer Serial Number
• Page Count = Printer Page Count
• Cartridge Type
o “MICR” is the expected return. “Normal” could mean the command was sent
to a non-MICR printer
• Cartridge Status
o “OK, Low, and Empty” are the expected returns. “Unknown” is possible if the
cartridge had just been installed.
• Cartridge Serial = Cartridge Serial Number
• Toner Level
o A single digit return giving a rough estimate of toner remaining
o 9 = Full, 0 = Empty
• Cartridge Count = xxxx
o Data indicating toner usage by counting pixels printed
• Low Threshold = xxxx
o The Toner Low point based on cartridge count value
• Empty Threshold = xxxx
o A cartridge count value that determines when printing must stop to ensure
quality MICR documents
PJL MICR Command Example
Figure 8.1, is an illustration of an Accounts Payable check and remittance information. The
page used a PCL MACRO for the static data and background design. This manual does not
address MACRO design and programming, but the variable text information including all
the PJL and PCL commands used to print the example are on the page following the
sample check. For illustrative purposes there are some extra spaces in the text preceding
the printable data. The following paragraphs describe the command functions. The
commands are a minimal set chosen to produce the example. Please consult Lexmark
Technical publications for the complete descriptions of PJL and PCL printer commands.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A14 All Rights Reserved
Page 67

PJL Unlock Sequence
The first two lines of the variable text example are PJL commands that unlock the MICR
font resources and enter PCL language processing. The password used is PASSWORD,
the initial ship default. These commands and all following commands are all case sensitive.
<ESC> is used to illustrate the ASCII Escape Character, ASCII 27, hex 1B. An actual data
stream requires the Escape Character, not <ESC>.
PCL Initial Set-Up
The next two commands set up some printer PCL variables. These commands are
normally early in the data stream. We chose a minimal set. <ESC>&l2a1h6d1e64F sets the
paper size to LETTER, the input tray to TRAY 1, the lines per inch to 6, the top margin to 1,
and the lines per page to 64. The next command, <ESC>&u600D, is the Unit of Measure
command set to 600 dots per inch mentioned in Section 7. This affects proper MICR line
spacing and X and Y cursor positioning.
PCL MACRO Call
The next command calls MACRO 100 that was previously loaded in RAM memory. When
called the graphic background, logos, and static data is written to the internal print buffer.
PCL Font Calls, Positioning Commands and Variable Print Data
The next eleven lines of data in the example call printer resident fonts, position the cursor,
and print the variable information. We are again using the minimal data required,
particularly the font selection strings, <ESC>(s4099t0b10H being a very short version to
call Courier, Normal Weight, 10 Pitch.
<ESC>*p300x600Y is a PCL positioning command. In this case its values are 600 pixels
down and 300 pixels to the right of the upper left corner of the page. The Unit of Measure
command determines the exact distance.
The next 4 lines call our secured MICR font resources. We are using the ID for the font call.
The Form Feed prints the page.
PJL Re-Lock Sequence
The last two lines re-lock the secured fonts. The password is not changed in this example.
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A15 All Rights Reserved
Page 68

FIGURE 8.1 SAMPLE ACCOUNTS PAYABLE CHECK
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A16 All Rights Reserved
Page 69

PJL and PCL commands used to print the sample check:
<ESC>%-12345X@PJL LDECLARE LRESOURCE:"flash:" LRWLOCK="PASSWORD"
@PJL ENTER LANGUAGE = PCL
<ESC>&l2a1h6d1e64F
<ESC>&u600D
<ESC>&f100y3X
<ESC>(s4099t0b10H
<ESC>*p300x600Y xxxxxxxxx xx/xx/xxxx $x,xxx.xx 3% $x,xxx.xx
<ESC>*p300x2775Y xxxxxxxxx xx/xx/xxxx $x,xxx.xx 3% $x,xxx.xx
<ESC>*p3250x75Y<ESC>(s4099t3b8H 123456
<ESC>*p3250x2200Y 123456
<ESC>*p4250x4450Y 123456
<ESC>*p3650x4775Y xx/xx/xxxx
<ESC>*p400x5225Y<ESC>(s4099t0b15H xxxxx Thousand xxxxx Hundred xxxxx Dollars
and xx/100 Cents
<ESC>*p600x5600Y<ESC>(s10H ABC TOOL & DIE
<ESC>*p600x5700Y 123 Main Street
<ESC>*p600x5800Y Yourcity, ST 12345-6789
<ESC>*p900x6325Y<ESC>(30802X<ESC>&k15H O123456O T123456780T
12345D67890O
<ESC>*p1500x5100Y<ESC>(30043X ($**1,234.56)
<ESC>*p3650x5400Y<ESC>(30066X $**1,234.56
<ESC>*p3000x6000Y<ESC>(30055X PAY ABC TOOL & DIE x THOUSAND XXX
HUNDRED AND XX CENTS PAY etc.
<0C> Form Feed
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A17 All Rights Reserved
Page 70

<ESC>%-12345X@PJL LDELETEPASSWORD LRESOURCE:"flash:"
<ESC>%-12345X
Secure MICR Printer User’s Guide © Source Technologies
September 2005
A18 All Rights Reserved
 Loading...
Loading...