
IBC
IBC Technologies Inc.
Vancouver, Canada
VFC Series Fixed Firing Gas Boiler
Model VFC 160
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING: If the information in this manual is not followed exactly, a fire or
explosion may result causing property damage, personal injury, or loss of life.
Do not store or use gasoline or other flammable vapours and liquids or other
combustible materials in the vicinity of this or any other appliance.
Should overheating occur or the gas supply fail to shut off, do not turn off or
disconnect the electrical supply to the pump. Instead shut off the gas supply at a
location external to the appliance
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS:
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electrical switch; do not use any phone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a nearby phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire department.
• Installation and service must be performed by a qualified installer, service
agency or the gas supplier.
VFCF160-v1.0

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INSTALLATION ...................... 3
1.1 GENERAL..........................................3
1.2 CODE REQUIREMENTS ................3
1.3 Location ..............................................4
1.4 Venting ................................................5
1.4.1 Applications................................5
1.4.2 Category IV Venting ................10
1.4.3 Closet Installations ...................10
1.5 Water Piping.....................................10
1.6 Gas Piping.........................................12
1.7 Electrical Connections .....................13
1.7.1 Mains Hook-up.........................13
1.7.2 Thermostat wiring.....................13
1.7.3 Thermostat Heat Anticipator ....14
2. STARTUP.............................. 15
2.1 PRIOR TO START-UP ...................16
2.1.1 Test Ignition System Safety
Shutoff Device.............................................16
2.4 CHECK BOILER INPUT .............. 17
2.5 SET OPERATOR LIMIT .............. 17
3. MAINTENANCE AND
TROUBLESHOOTING..................18
3.1 BOILER OPERATION .................. 18
3.1.1 Normal Operation .................... 18
3.1.2 Post-Purge Cycle ..................... 18
3.1.3 Boiler Safety System ............... 18
3.2 BOILER MAINTENANCE............ 19
3.2.1 General Care ............................ 19
3.2.2 Inspection................................. 19
3.3 COMPONENT DESCRIPTION.... 20
3.3.1 Pressure Switch........................ 20
3.3.2 Flow Switch............................. 20
3.3.3 Operator ................................... 20
3.3.4 Hi-Limit ................................... 20
3.3.5 Transformer ............................. 21
3.3.6 Gas Valve ................................ 21
3.3.7 Blower ..................................... 21
3.3.8 Ignition Control Module(ICM) 21
3.3.9 Igniter Probe/Flame Sensor ..... 21
3.3.10 DC Power /Enunciator Panel... 21
3.3.11 Detailed System Checks .......... 22
2.2 GAS VALVE ADJUSTMENT........16
2.3 BLOWER ADJUSTMENT .............17
IBC Technologies Inc. - 2 - VFC 160

1. INSTALLATION
1.1 GENERAL
The VFC 160 boiler is a low pressure,
fully condensing unit having a fixed
firing rate input of 160 MBH (160,000
Btu/hr). The boiler is approved for
either Direct Vent (sealed combustion)
or Category IV (indoor air) applications,
providing a great degree of installation
flexibility.
The installer must clearly indicate the
vent category for the installation on
the rating plate using an indelible
marker. See section 1.4 - Venting.
Figure 1. shows outer case dimensions
and piping and electrical holes. Use this
diagram to find a suitable location for
the boiler. (see also Section 1.3 Location.)
22.5" [572mm]
12" [305mm]
Table 1 - Connections
Description Size
A water outlet 1” NPT
B water inlet 1” NPT
C gas ½” NPT
D electrical power 3/4”
E thermostat 3/4”
F pump 3/4”
G combustion air 4.0"
H exhaust vent 4.0"
1.2 CODE REQUIREMENTS
Gas manifold and controls met safe
lighting and other performance criteria
when boiler underwent tests specified in
ANSI Z21.13-2000.
Installation must conform to local codes,
A
or in the absence of these, with the latest
editions of the National Fuel Gas Code
ANSI Z223.1 and the National
Electrical Code ANSI/NFPA 70.
34" [864mm]
Where required by jurisdiction,
installation must conform to the
Standard for Controls and Safety
Instructions to put the boiler in operation
are located on the inside surface of this
cover panel.
FOR YOUR SAFETY
Do not store or use gasoline of other
flammable vapors and liquids in the
vicinity of this or any other appliance.
Devices for Automatically Fired Boilers,
ANSI/ASME CSD-1. If there is any
22.5" [572mm]
conflict in the above requirements, then
the more stringent requirement will
apply.
12" [305mm]
G
H
In Canada, installations must conform to
the current CAN/CGA B149 and the
Canadian Electrical Code Part 1 CSA
Figure 1. Dimensions/Connections
C22.2 No. 1.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 3 - VFC 160
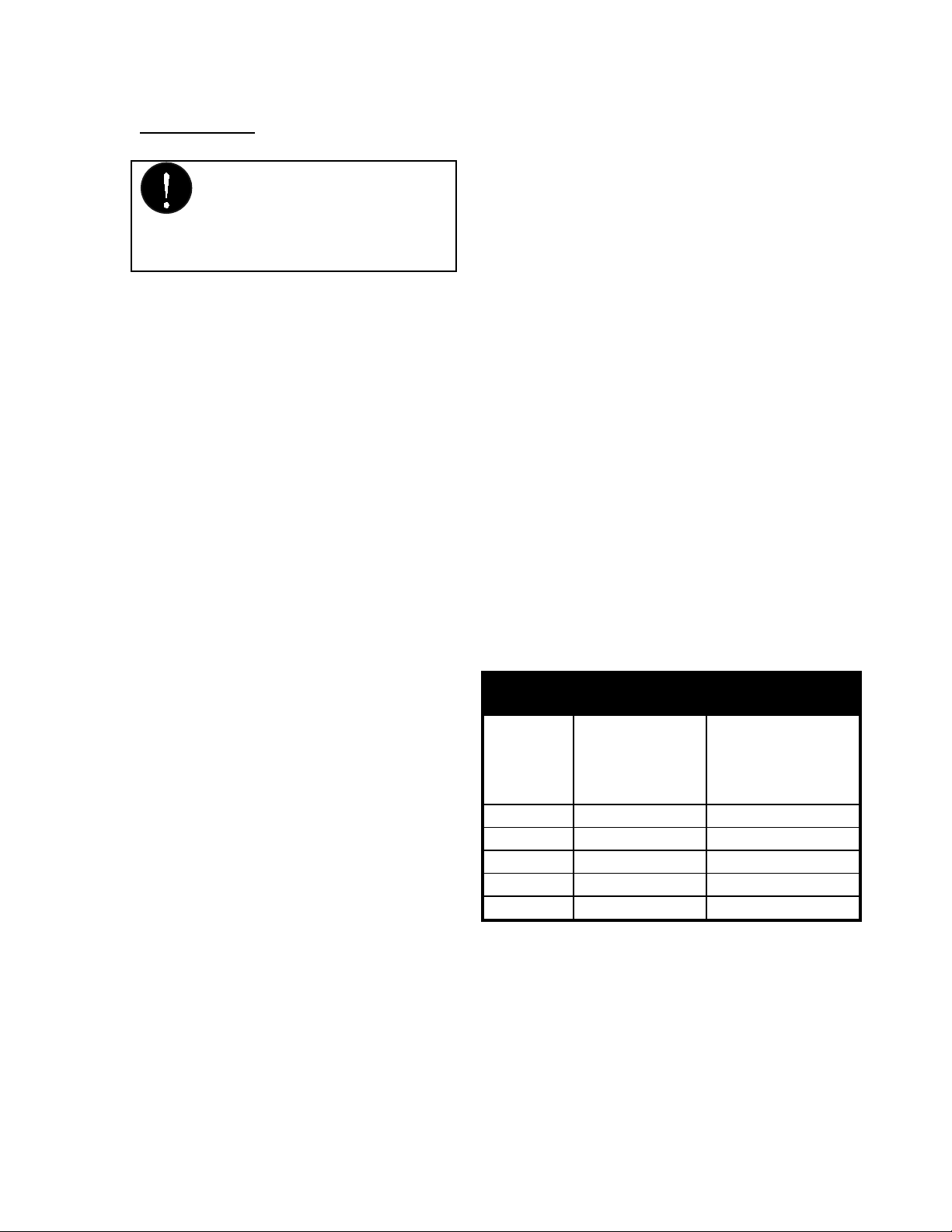
1.3 Location
Keep boiler area free and
clear of combustible
materials, gasoline, and other
flammable vapours and
liquids.
The VFC-series boilers are designed and
approved for wall or floor installation
(on combustible flooring), with
significant flexibility of location
provided with the available venting
options. The boiler can be placed in an
alcove, basement, closet or utility room.
Care must be taken not install the boiler
in areas where the combustion air source
is subject to chemical fouling.
Experience has shown that exposure to
corrosive chemical fumes such as
chlorinated and/or fluorinated
hydrocarbons can reduce the life of a
boiler. Cleaners, bleaches, air fresheners,
refrigerants, aerosol propellants, drycleaning fluids, de-greasers and paintremovers all contain vapours which can
form corrosive acid compounds when
burned in a gas flame. Airborne chorides
such as those released with the use of
laundry detergents are also to be
avoided. For this reason, the Category
IV (indoor air) venting option using air
surrounding the boiler should not be
used in a laundry room installation.
It is recommended that the boiler be
located in an area where water leakage
will not result in damage to the area. If a
location such as this cannot be found, a
suitable drain pan, should be installed
under the appliance. The boiler is not to
be installed above carpeting.
In addition to the foregoing, other
factors determining potential mounting
sites:
• ensure minimum clearance
requirements for combustible
materials(see Table 2) are satisfied
• 36” clearance at the front is
recommended for adequate servicing
• gas ignition system components
should be protected from water
(dripping, spraying, rain, etc.)
• boiler should not be exposed to
water leaks from piping or
components located overhead
• in a new construction installation,
particular action must be taken to
protect the boiler from dust;
combustion air should be drawn
from a CLEAN source (e.g.
outdoors) and the boiler must be
isolated from interior dust sources.
Do not seal boiler case openings
directly - allow for air circulation
and ventilation in the immediate
area.
Table 2 - Clearance from Boiler Cabinet
Surface Distance
from
Combustible
Surfaces
Front 2” 24”
Rear 0” 0”
L. Side 0” 12”
R. Side 2” 18”
Top 10” 10”
Below the boiler, 12” is required to
rovide clearance for the inlet and
exhaust venting together with the
required condensation trap. Legs are
available as an accessory for floormounting of the boiler; the 14” legs
provide the necessary clearance.
Recommended
Distance for
Service
IBC Technologies Inc. - 4 - VFC 160

1.4 Venting
All venting must be installed in
accordance with the requirements of the
jurisdiction having authority: in the USA
Part 7, Venting of Equipment of the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI 223.1,
latest edition, and any other local
building codes are to be followed. In
Canada, Part 7 - Venting Systems of the
B149 Code prevails. Where there is a
discrepancy between the installation
instructions below, and the code
requirements, the more stringent shall
apply.
IMPORTANT
When an existing boiler is removed from
a common venting system, the common
venting system is likely to be too large
for proper venting of the appliances
remaining connected to it.
At the time of removal of an existing
boiler the following steps shall be
followed with each appliance remaining
connected to the common venting
system placed in operation, while the
other appliances remaining connected to
the common venting system are not in
operation.
a) seal any unused opening in the
common venting system.
b) Visually inspect the venting system
for proper size and horizontal pitch
and determine there is no blockage
or restriction, leakage, corrosion and
other deficiencies which could cause
an unsafe condition.
any appliance not connected to the
common venting system. Turn on
any exhaust fans, such as range
hoods and bathroom exhausts, so
they will operate at maximum speed.
Do not operate a summer exhaust
fan. Close fireplace dampers.
d) Place in operation the appliance
being inspected. Follow the lighting
instructions. Adjust thermostat so
appliance will operate continuously.
e) After it has been determined that
each appliance remaining connected
to the common venting system
properly vents when tested as
outlined above, return doors,
windows, exhaust fans, fireplace
dampers and any other gas-burning
appliance to their previous
conditions of use.
f) Any improper operation of the
common venting system should be
corrected so the installation
conforms with the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1 - latest edition.
In Canada, all installations must
conform with the current CAN/CGA
- B149 Installation Code and/or local
codes.
When resizing any portion of the
common venting system, the common
venting system should be resized to
approach the minimum size as
determined using the appropriate tables
in the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1 - latest edition. In Canada, use
the CAN/CGA - B149 Installation Code.
c) Insofar as is practical, close all
building doors and windows and all
doors between the space in which the
appliances remaining connected to
the common venting system are
located and other spaces of the
building. Turn on clothes dryers and
IBC Technologies Inc. - 5 - VFC 160
1.4.1 Applications
The VFC 160 boiler is approved with
alternative venting options: either Direct
Vent or Category IV venting can be used
offering flexibility to meet the specific
requirements of the installation. With the
Direct Vent case, combustion air is
piped directly to the boiler’s air intake
from outdoors. Using the Category IV
alternative, air for combustion is drawn
from the indoor air surrounding the
boiler or drawn from ventilated attic or
crawl spaces.
The VFC 160 is shipped with a high
water temperature limit switch set for
200°F.
Provided the maximum overall vent
length limit is not exceeded, the installer
may choose to vent the boiler through
the wall, directly through the roof or
upward using an existing - but otherwise
unused - chimney as a vent raceway (see
below).
All boilers are shipped with connectors
permitting attachment of 2” intake
piping.
It is a code requirement that the
rating plate reflect the nature of the
boiler vent configuration as installed.
To facilitate such venting installation
flexibility, VFC boilers are shipped
with the rating plate unmarked. The
installer shall indelibly mark the
appropriate box on the rating plate to
recognize the venting alternative
chosen.
Exhaust venting is to be connected
directly to the 2” NPT male threaded
stainless steel fitting on the bottom of
the pressure vessel using a 2” CPVC
NPT x Socket fitting (female threaded
adaptor or 90° elbow). A condensate
trap of CPVC and PVC shall be spliced
into the CPVC exhaust pipe at or near
the base of the boiler (see Figure 2).
Combustion air piping is connected at
the base of the boiler using a standard 2"
PVC coupler or elbow. Screen material
shall be placed at the inlet termination as
appropriate for the environment (e.g.
insects, dust).
1.4.1.2 Vent Travel
With the specified 2 1/2" or 3” piping
(after 10' of 2" CPVC on the exhaust
side), the boiler can be sited up to 90
equivalent feet from the vent
termination. The actual vent travel is
reduced for fittings in accordance with
Table 3. - for example, using 5 x 90º
long-sweep* ABS elbows, the maximum
lineal measure is 65 feet.
Table 3 - Max. Venting Length
Pipe Size
( * = long sweep)
Max.
Equiv.Length
1.4.1.1 Intake/Exhaust Vent Material
The approved materials of construction:
For the exhaust vent-
• 2" CPVC Sch. 40 or 80 pipe (per
ASTM F441) and Sch. 40 or 80 fittings
for the initial 10 lineal feet of travel
• 2 1/2" or 3" Sch 40 CPVC or PVC, or
3" ABS (Sch. 40/ASTM D2661 or F628)
and fittings thereafter;
For the inlet air - ABS and PVC (ASTM
D1785 or D2665) are permitted.
See Vent Travel- below.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 6 - VFC 160
3” (after 10' of 2") 90’ (incl 1st 10')
90° elbow(CPVC/PVC) Allow 8’ equiv.
45° elbow(CPVC/PVC) Allow 4’ equiv.
90° elbow*(ABS) Allow 5’ equiv.
45° elbow*(ABS) Allow 2.5’ equiv.
A 3” x 2” (or 2.5" x 2" as appropriate)
bushing is to be used in the inlet piping
within 3 feet of the combustion air line
clearance hole at the base of the boiler.
The 3’ interval (which is part of the 90’
max. travel distance) is allowed to

provide space for splicing in an optional
2” compatible air filter unit.
The junction between the initial 2" vent
section (e.g. 10' of CPVC ), the vent line
diameter is increased through use of a
3”- 2” (or 2.5" x 2") reducer. It shall be
placed in a vertical section of the flue
gas vent to avoid pooling of condensate.
Exhaust venting must slope back to the
trap/drain with a pitch of at least ¼” per
foot so condensate runs towards the trap.
Support should be provided every 2 to 3
feet for each of the intake and vent
piping. Insulate exhaust piping where it
passes through unheated space with
appropriate pipe insulation to prevent
freezing of condensates.
Ensure all venting components are clean
of burrs/debris prior to assembly.
Particular care is to be taken to avoid
ingestion into the fan of CPVC/ABS
debris left in the combustion air piping.
straight 2" tee or a 2” x ½” x 2” reducing
tee). The trap itself is formed using ½”
CPVC pipe for the drop leg, with ½”
PVC pipe, elbows and threaded union
fittings. The trap must be installed as
follows:
• Have 5” minimum neck depth
• Piped to within 3” of a drain or be
connected to a condensate pump
• Drainage line must slope down to the
drain at a pitch of ¼” per foot so
condensate runs towards the trap
• IMPORTANT! Fill trap with
water before boiler is first fired to
prevent exhaust fumes from
entering room. Never operate the
boiler unless the trap is filled with
water.
• Trap should be checked every 6
months. Clean and refill as
necessary.
All joints must be secured using CPVC,
ABS or ABS/PVC solvent cement to
bond the respective pipe material. Use
solvent cement on the connector located
at the CPVC/ABS junction (e.g. 10’
along the exhaust piping). Follow the
cement manufacturer’s instructions
closely when joining various
components.
All vent connections must be liquid and
pressure tight. Test exhaust venting
connections, under fan pressure with
vent blocked, using a soap/water
solution prior to firing.
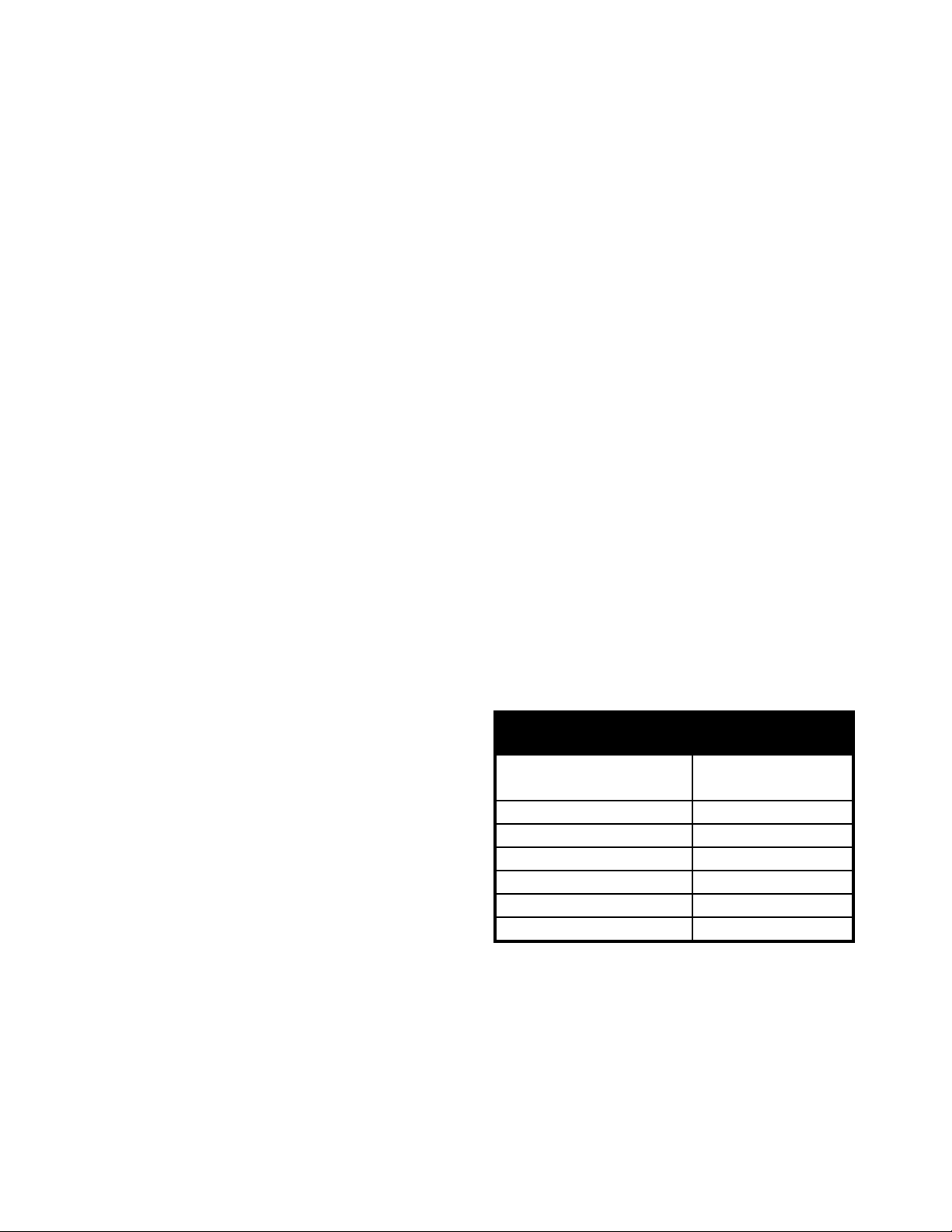
1.4.1.3 Condensate Trap
A condensate trap must be installed at
the base of the boiler (or within 12” of
the first 90° exhaust line elbow), as
shown in Figures 2. (e.g. spliced into
the 2” CPVC exhaust vent using a
¼" vertical per
horizontal foot
fill wit h wat er
(CP VC D rop leg)
to drain or condensate trap
5" min.
Figure 2 -Condensation Trap Alternatives
IBC Technologies Inc. - 7 - VFC 160

1.4.1.4 Venting Passage Through
Ceiling and Floor
12" min.
24" min.
The following instructions apply to 2”,
2.5" and 3” piping:
• pipe clearances - no specific
requirements - follow local codes
• piping must be supported in the
flooring
• all piping must be liquid and
pressure tight.
1.4.1.5 Rooftop Vent Termination
Vents must terminate as follows:
• 12” above grade and normal snow
line to vent terminal bottom
• DO NOT exhaust vent into a
common venting system
(See Figures 3 & 4 for rooftop vent
terminations)
exhaust vent with s creen
air intake 1 80° elbow
with screen face down
12"min.
12" min.
snow line
2" min.
10 ft. or less
2 ft. min.
2" min.
Figure 3. Vent Terminations through
a Pitched Roof
1.4.1.6 Sidewall Vent Termination
Vents must terminate as follows:
• minimum 12” from any building
opening
36" min.
snow line
12" min.
2" min.
other than as listed, vents terminate in the sam
e manner as in figure 3. above.
Figure 4. Vent Terminations Through
a Flat Roof
• minimum 3’ above any forced air
intake located within 10’
• minimum 4’ horizontally from (and
in no case above or below unless 4’
horizontal distance is maintained),
from electric or gas meters,
regulators and relief equipment
• not to be located over public
walkway, in a confined space, or
under any overhang or deck
• vents must be installed such that flue
gas does not discharge towards
neighbor’s windows, or where
personal injury or property damage
can occur.
• For Direct Vent installations
employing sidewall vent
terminations, both the inlet and
exhaust terminations shall be located
on the same plane (side) of the
building, with the exhaust outlet
placed above the inlet to avoid reingestion (later point not applicable
to concentric vent termination).
(See Figures 5, 6 & 7 for side wall vent
terminations)
IBC Technologies Inc. - 8 - VFC 160
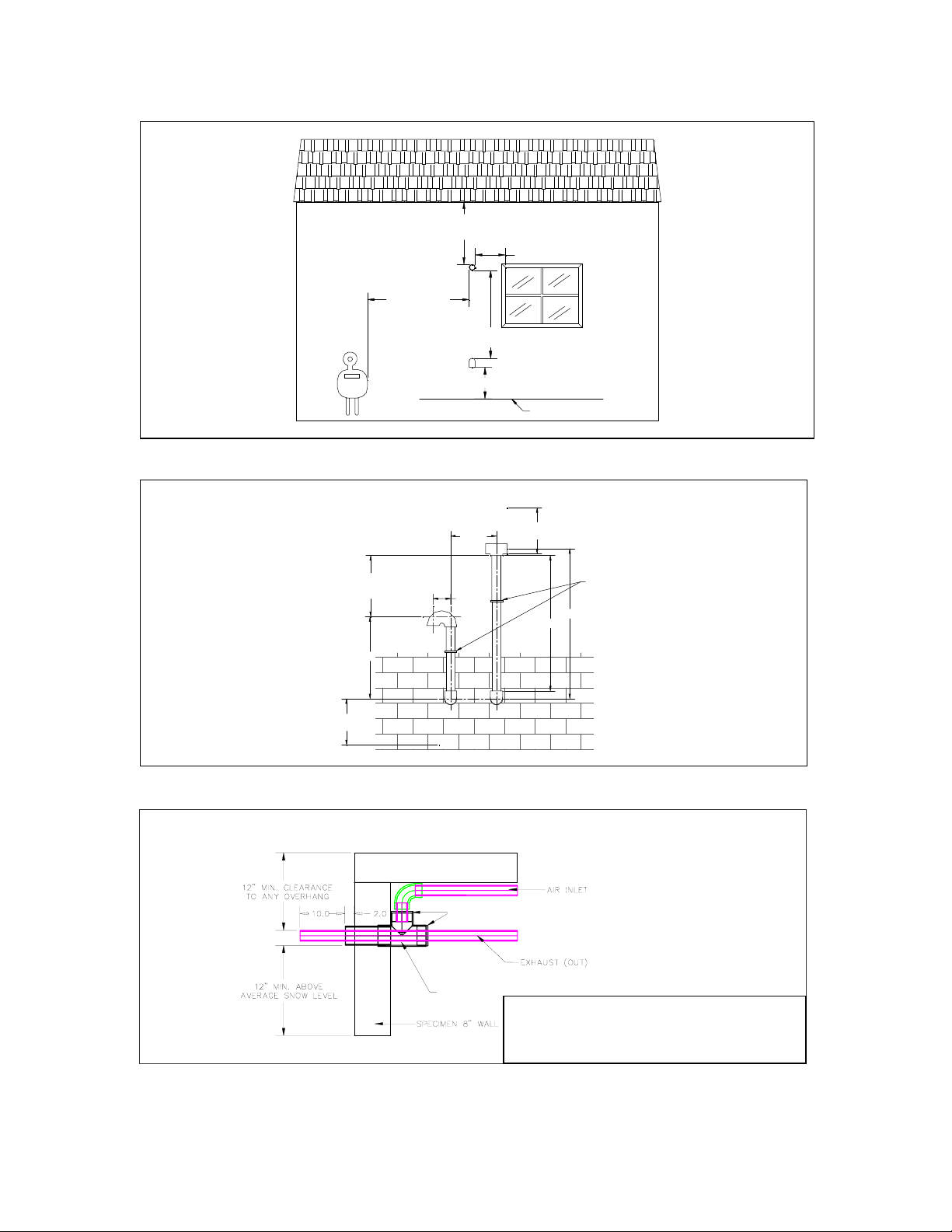
Figure 5. Side Wall Venting
vent tee sh ould be parallel to side wall.
intake should be swung to parallel
with side wall.
min. 12 " between
bottom of intake
and bottom of vent
MIN. 24" TO
ANY OVERHANG
MIN. 4’
HORIZONTAL
DISTANCE
FROM ANY
GAS OR
ELECTRICAL
METER
MIN 36" TO
INTAKE
MIN. 12"
installation below average snow level
4−3/8"
minimum
5−1/2"
12"
MIN. 12" TO ANY OPENING
SNOW LINE
12" m in. clearance
to any overhang
FIELD SUPPLIED PLASTIC
STRAPPING MUST BE USED
TO SECURE THE VENT TO
THE STRUCTURE
24−1/2"
18−1/2"
12" min. above
average snow leve l
Figure 6. Side Wall Vent Terminations (Configuration 1)
2.5" or 3" PVC or 3" ABS
"−
"
"
2.5"/3" PVC or 3" ABS or CPVC
4"x4"x4" ABS/PVCTee(alt: 4x4x3 Tee with approp.bushing)
If 3" venting is used, the exhaust line must be reduced
to 2½" immediately prior to entering the 4" termination
tee to allow adequate intake clearance. Use a 3 x 2½"
Figure 7. Side Wall Vent Terminations (Configuration 2)
IBC Technologies Inc. - 9 - VFC 160

1.4.2 Category IV Venting
A category IV venting system is one in
which air for combustion is take from
the ambient air around the boiler. Vent
piping is run horizontally or vertically to
the outdoors.
1.4.2.1 Ventilation and Air Supply
To support combustion, an ample air
supply is required. This may require
direct openings in the boiler room to the
outside. If the boiler is not in a room
adjacent to an outside wall, air may be
ducted from outside wall openings.
Provisions for combustion and
ventilation air must be made as follows:
in the USA, in accordance with Section
5.3 Air for Combustion and Ventilation
of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1 (latest edition), or applicable
provisions of the local building codes; in
Canada, in compliance with CAN 1.4.3.
The following lists are recommendations
for buildings of energy-saving
construction, fully caulked and weatherstripped:
• an opening to the outside, within 18”
of the floor, but no less than 6” off
the floor, should be provided in the
room. Each opening should be
covered in a grill, and have an area
of 1” per 1,000 BTUh for ALL
APPLIANCES in the area.
• Openings must not be closed or
reduced. Doors and windows used
for air supply must be locked open.
• Mechanical draft exhaust or supply
fans are not to be used in or near the
boiler area
• Boiler combustion and ventilation
airflow must not be obstructed
Category IV venting is installed in the
same manner as for the exhaust side of
Direct Vent installations.
1.4.3 Closet Installations
For installations in a confined space
(such as a closet), ventilation openings
must be provided through a door or wall
to prevent excessive heat from building
up inside the space.
Minimum requirements:
• one opening within 12” of the ceiling
(100 sq. in. opening)
• one opening within 12” of the floor
(100 sq. in. opening)
1.5 Water Piping
Follow applicable Codes and good
piping practice. Any uninsulated hot
water pipes must be installed with a
minimum 1” clearance from combustible
materials.
System piping is connected to the boiler
using the 1” NPT female threaded
fittings provided at the locations shown
on page 10. Typical piping systems are
shown in Figures 8,9, &10.
A 30 psi pressure relief valve (¾” NPT)
is supplied for field installation in the
flow supply line, in the manner shown in
Figures 8,9, & 10. Relief valve
discharge piping must terminate 6”
above a drain using plain un-threaded
end, or per local Code.
To avoid exposure to water damage,
system piping and components are not to
be located overhead the boiler.
Indoor combustion air must not expose
the boiler to contamination - see Section
1.3 - Location, above. In other respects,
IBC Technologies Inc. - 10 - VFC 160

(s)
stop & waste
(
)
backflow
or ball valve
boiler feedwater
preventer
Figure 8. Sample Piping Schematic (1)
cold supply
flow
check
system
supply
hydronic flow check(s) o
zone valves to prevent
thermal circulation
contractor
supplied
system
circulator
air purger
diaphragm
expansion tank
auto fill valve
12 psi min.
drain
air vent
12−18"
pressure
relief
valve
system supply piping
tee & boiler drain
for system purging
ball
valve
system return piping
system return piping
#30
#15
Figure 910. Sample Piping Schematic (2)
note: wire aquastat or control contacts in series wit
parallel wired zone control end switches or pump relay
air
eliminator
diaphragm
expansion
tank
pressure
relief
valve
pressure
relief
valve
contacts.
buffer/tempering
tank
flow
check
additional zones
zones
aquastat
indirect
T&P
domestic
relief
water
heater
wire to zone
valve end switches
or relay contacts
hot
cold
Figure 10. Sample Piping Schematic (3)
IBC Technologies Inc. - 11 - VFC 160

The VFC boiler is designed for supply
water temperatures within the range
80°F to 180°F, with a 20°F rise. Water
flow rates and pressure drop (head in ft.
w.c.) associated with a 20°F maximum
rise (∆°T) for the respective VFC
models are as follows:
Table 4 - Flow Rate
Model Flow
(Usgpm)
VFC 160 16.0 12
Water flow rates must not be allowed to
fall below 8 gpm in any possible
operating condition (eg. Single zone in
use).
To achieve system flow rates and
temperatures within such limits, care
must be taken to select the appropriate
pump. Evaluate pressure drop across the
system, including the above head values
for the boiler itself. Ensure pump is
rated for the design circulating water
temperatures; some pumps have a
minimum water temperature rating
above the low temperature potential of
the boiler. Following installation,
confirm actual performance by
measuring ∆°T (under high and low flow
conditions) after establishing the correct
firing rate (see Section 2.2 – Check
Boiler Input).
VFC-series boilers are supplied with a
integral low-water flow switch, which
allows installation of the boiler above
radiation level. The flow switch is
calibrated to close with at 4.5 US gpm
and open at 4.0 US gpm.
When installed in a low mass heating
system such as an in-floor radiant
application, the VFC-series boilers may
benefit through use of a buffer tank to
Approx.
Head (ft. wc)
ensure a controlled supply temperature,
and to prevent short cycling. It is highly
recommended that a buffer tank be
included in any heating system in which
any single zone has radiative loading
lower than 1/3rd of the minimum input of
the boiler (i.e. at 160 000 BTU/hr, the
boiler should be buffered if any single
zone attached is below 55 000 Btu/hr).
Propylene glycol solution is commonly
used in a water heating loop where
freeze protection is required. Its density
is lower than that of water, resulting in
lower thermal performance at a given
flow and pressure. As a rule of thumb, a
50%:50% solution of propylene glycol
and water will require an increased
system circulation rate (gpm up 10%),
and system head (up 20%) to provide
performance equivalent to straight water.
Whether required by local Codes or
otherwise, it is recommended that piping
systems include a suitable check valve,
gate valve and feedwater regulator set at
12 psig. In the make-up water link with
the city main. Use of unions and gate or
ball valves at the boilers supply and
return water connections is
recommended to simplify servicing.
1.6 Gas Piping
The boiler requires an inlet gas pressure
of at least 3.5” w.c. and no greater than
14.0” w.c. Confirm this pressure range
is available with your local gas utility.
The inlet gas connection of the boiler’s
gas valve is 1/2” NPT (female).
Adequate gas supply piping shall be
provided with no smaller than 1/2” Iron
Pipe Size (IPS), in accordance with the
following chart:
IBC Technologies Inc. - 12 - VFC 160

Table 5 - Max. Pipe Length (ft)
Model 1/2” IPS 3/4” IPS 1” IPS
VFC 160
8 35 120
Gas piping must have a sediment trap
ahead of the boiler’s gas valve (see
Figure 11.). A manual shutoff valve
must be located outside the boiler, in
accordance with local codes/standards.
All threaded joints in gas piping should
be made with a piping compound
resistant to the action of natural gas - do
not use Teflon tape. Use proper hangers
to support gas supply piping.
union
gas valve inside
install manual
main shutoff
valve 5 ft.
above floor
when required
by local code
full size
sediment
trap
Figure 11. Typical Gas Piping
The boiler must be disconnected or
otherwise isolated from the gas supply
during any pressure testing of the system
at test pressures in excess of 1/2 psig.
Dissipate test pressure prior to
reconnecting.
The boiler and its gas piping shall be
leak tested before being placed into
operation.
The gas valve is provided with pressure
taps to measure gas pressure upstream
(supply pressure) and downstream
(manifold pressure) of the gas valve.
1.7 Electrical Connections
All Electrical wiring to the boiler
(including grounding) must conform to
local electrical codes and/or National
Electrical Code, ANS/NFPA No. 70 –
latest edition, or The Canadian Electrical
Code, C22.1 - Part 1.
1.7.1 Mains Hook-up
Line-voltage wiring is done within the
field-wiring box. Referring to Wiring
Diagram on page 26, connect the boiler
to the mains power using a separate,
fused circuit and a disconnect means
within sight of the boiler. Use 14-gauge
conductors in BX cable or conduit
appropriately anchored to the boiler case
for both mains supply and pump circuits.
The transformer primary (black wire) is
connected to the neutral and line (hot)
wires. The red conductors for the pump
contacts should be wired into the
ungrounded leg of the pump circuit.
Note: The combined current of all
pumps connected through the on-board
pump relay (red conductors) should not
exceed 10 amps.
1.7.2 Thermostat wiring
The Thermostat terminal block is located
on the control module. The thermostat
terminals should NOT be connected to
any other power source and should only
be connected to a room thermostat,
isolated, zone valve end switches or
circulator end switches. When using 3wire zone valves (non-isolated) the zone
valve end contacts must be isolated from
the thermostat terminals using an
appropriate relay.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 13 - VFC 160

1.7.3 Thermostat Heat Anticipator
When installed in a non-zoned system,
the heat anticipator setting is dependant
on the gas valve installed in the boiler:
Gas Valve Anticipator
Current
Setting
White-Rodgers 36E22 0.5 A
White-Rodgers 36E36 0.5 A
White-Rodgers 36F22 0.5 A
White-Rodgers 36G22 0.3 A
Honeywell VR8205A 0.7 A
For zoned systems, each room
thermostat’s heat anticipator should be
adjusted to the current draw of its
associated zone valve.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 14 - VFC 160

2. STARTUP
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire or
explosion may result causing property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
FOR YOUR SAFETY READ BEFORE OPERATING
A. This appliance does not have a pilot. It is equipped
with an ignition device which automatically lights the
burner. Do not try to light the burner by hand.
B. BEFORE OPERATING smell all around the
appliance area for gas. Be sure to smell next to the
floor because some gas is heavier than air and will
settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electric switch; do not use any
phone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a
neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas suppliers
instructions.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
1. STOP! Read the safety information above on this
label.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance by
selecting main power switch to Off.
4. This appliance is equipped with an ignition device
which automatically lights the burner. Do not try to
light the burner by hand.
Gas Inlet
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the
fire department.
C. Use only your hand to turn the gas control knob.
Never use tools. If the knob will not turn by hand,
don’t try to repair it, call a qualified service
technician. Force or attempted repair may result in
a fire or explosion.
Do not use this appliance if any part has been under
water. Immediately call a qualified service technician to
inspect the appliance and to replace any part of the
control system and any gas control which has been
under water.
6. Turn gas control knob clockwise ¬ to Off.
7. Wait five (5) minutes to clear out any gas. Then
smell for gas, including near the floor. If you smell
gas, STOP! Follow B in the safety information
above on this label. If you don’t smell gas, go to the
next step.
8. Turn gas control knob counterclockwise « to On.
9. Replace front cover on appliance.
10. Turn on electric power to appliance by selecting
main power switch to On.
Gas valve
shown in ON
position
11. Set thermostat to desired setting.
12. If the appliance will not operate, follow the
instructions “To Turn Off Gas To Appliance” and call
your service technician or gas supplier.
5. Remove front cover from appliance.
TO TURN OFF GAS APPLIANCE
1. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn of all electric power to the appliance by selecting main power switch to Off.
3. Remove front cover from appliance.
4. Turn gas control knob clockwise ¬ to Off.
5. Replace front cover on appliance
Also ensure items under the following caption 2.1 Prior to Start-up have been addressed.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 15 - VFC 160
2.1 PRIOR TO START-UP
Ensure venting system is complete and
seal tested. Confirm any common venting
system at the installation site is isolated
and independent of the VFC boiler and
that any holes left from removal of a
previous boiler have been sealed. Fill
condensation trap to full 5” (min.) neck
height. Check water piping system is fully
charged, and that all air has been
discharged through loosened bleed caps.
Use a minimum operating water pressure
of 12 psig. Perform a final check of
electrical wiring.
2.1.1 Test Ignition System Safety
Shutoff Device
With the boiler in operation, test the
ignition system safety shutoff device by
shutting the manual gas valve immediately
outside the boiler case. Ensure boiler has
shut off and error and gas valve lights are
flashing. To restart boiler, reset power.
setting (using manual Fan Speed
screw as shown in Figure 13) until
pressure switch indicator illuminates
5. Open gas supply and start boiler
6. Raise thermostat to trigger call-for-
heat. Within 40s, gas valve will open
and boiler will attempt to ignite
7. Once stable combustion has been
achieved, remove set screw on top of
gas valve. Turn calibration screw on
gas valve until pressure gauge reads
3.0” w.c. Ensure set screw has been
returned to its original position.
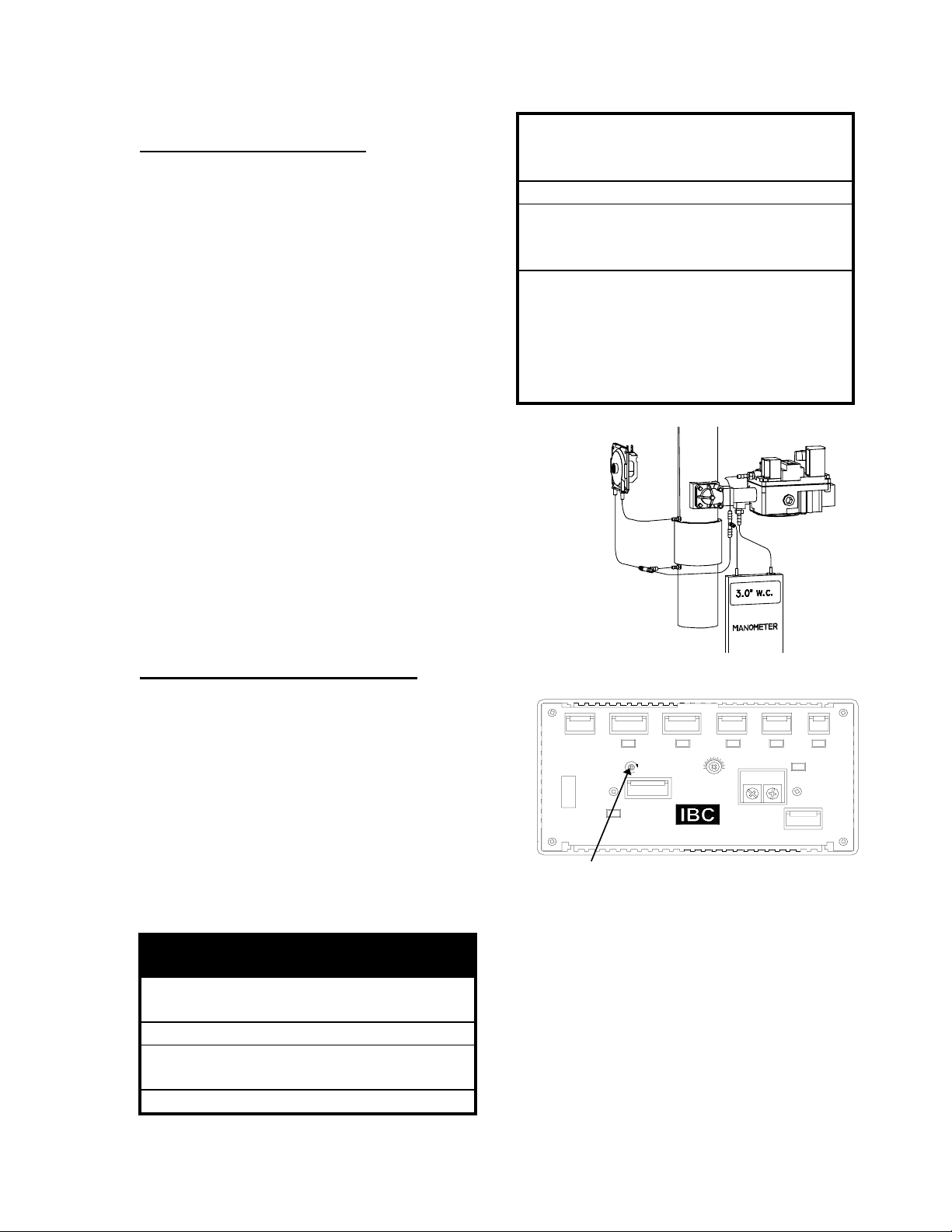
2.2 GAS VALVE ADJUSTMENT
The gas valve is factory pre-set for proper
gas/air mixing at mean sea-level pressure,
however some adjustment may be
required, e.g. for altitude.
To ensure gas input is set to the desired
boiler output, set the gas valve using the
method described in this section. A
pressure measurement gauge (with
0.1”w.c. divisions) should be used as
shown in Figure 13.
Table 6 - Gas Valve Adjustment
1. Ensure that vents are not obstructed
(see Troubleshooting Guide)
2. Set pressure measurement gauge to 0
3. Connect pressure measurement gauge
as shown in Figure 12
4. Increase blower speed from lowest
Figure 12. Gas Valve Adjustment
Ignition Module
Pump
Fan adjust
Pressure Switch
Power
H
Fan Speed
L
Fan
Operator
Flow Switch Vent Hi-Lim it W ater Hi-Lim it
180°F
80°F
Set Point
FXFR
Therm ostat
Figure 13. Fan Adjustment Screw
24 V
Call for Heat
AC
IBC Technologies Inc. - 16 - VFC 160

2.3 BLOWER ADJUSTMENT
To ensure a proper gas/air ratio, adjust the
blower using the manometer as shown in
Figure 14.
Ignition Module
Pump
Fan adjust
Pressure Switch
Power
H
Fan Speed
L
Operator
Flow Switch Vent Hi-Limit Wa ter Hi-Limit
180°F
80°F
Set Point
Fan
FXFR
Therm osta t
24 V
Call for Heat
AC
Figure 15. Fan Adjustment
2.4 CHECK BOILER INPUT
To ensure that the boiler input is correct,
check the boiler input rate using the
following procedure:
Figure 14. Blower Adjustment
Connections
Table 7 - Blower Adjustment
1. Once again, ensure that vents are not
obstructed (see Troubleshooting Guide)
2. Connect manometer in the
configuration shown in Fig.14
3. Increase blower speed (using manual
Fan Speed screw as shown in Figure 15)
until 1.20”wc differential is achieved
4. Open gas supply and start boiler
5. Raise thermostat to trigger call-for-heat.
Within 40s, gas valve will open and
boiler will attempt to ignite
6. Once stable combustion has been
achieved, take CO2 sample at vent
termination
7. Turn Fan adjust screw on enunciator
panel to vary fan speed (and airflow)
until combustion analyzer reading of
9.2% CO2 is achieved
2.5 SET OPERATOR LIMIT
Adjust operator limit as temperature
demands require.
Table 8 - Check Boiler Input
1. Start boiler
2. Ensure other gas appliances are not
using the supply gas
3. Observe the number of cubic feet used
by the boiler in 1 minute
4. Consult gas supplier for gas heating
value(typically 1000 BTU/cu. ft.)
5. Verify output by using the formula at
the end of this section
6. If fuel flow is too high or low, check
the orifice plate size. Adjust gas valve
(per Section 2.2) as required to
achieve Rating gas plate input;
recheck flue gas composition at 9.2%
CO2 if adjustment is made.
Boiler Input Formula
3600
INPUTHV
=×
time
time = seconds for 1 cu. ft. of
natural gas through meter
HV = heating value of gas as
provided by gas supplier
INPUT = gas input(in BTU/hr)
Table 9 - Operator Setting
Dial Colour "A" to "E" Temp. Range
Red 130°F - 170°F
Black 100°F - 140°F
IBC Technologies Inc. - 17 - VFC 160

3. MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING
commanded to an ultra-lowflow mode for
3.1 BOILER OPERATION
3.1.1 Normal Operation
1. On power-up, the boiler exercises the
fan and pump by entering into a postpurge routine - see below.
up to 90 minutes to act as a vent-damper.
The pump maintains normal circulation
throughout the phase. This low intensity
mode is a simple way of ensuring moisture
does not migrate and re-condense around
and above the burner area (e.g. fouling the
igniter) during the off-cycle.
2. On a call for heat, the blower and
pump switch on.
3. After 20-40 seconds, the gas valve
opens and the igniter probe sparks.
The ignition module will issue a spark
to the burner for approximately 10
seconds. If no flame is present, the gas
valve closes, and locks out until there
is a new call for heat.
4. On successful ignition, the spark is
discontinued and the gas valve remains
open.
5. If water or vent temperature conditions
exceed safe operating limits, or vent
pressure falls below the calibrated
value, the gas valve closes and the
burner remains off until a safe
condition exists. A post-purge cycle
follows.
6. If the call for heat ends, the gas valve
closes and the boiler will enter a postpurge cycle.
The post-purge is immediately interrupted
by a new call for heat, or return to safe
condition of a tripped limit switch (in the
case of a shutdown caused by an open hilimit). In such case the mode ends and the
boiler enters an ignition cycle. The
interrupt is deferred however, to allow a 2
minute low-flow interval prior to return to
the ignition routine in the event of an
opening of the control circuit at the air
pressure switch; this is to allow for
clearance of any excess buildup of
condensates in the vent.
3.1.3 Boiler Safety System
There are 5 safety devices that can cause
the boiler to shut down:
1. Outlet Water Limit: closes gas-valve
when outlet water exceeds 200°F.
2. Vent Hi-Limit: closes gas-valve when
vent temperature exceeds 230°F.
3. Pressure Switch: closes gas-valve
when air pressure drops below 0.9”wc.
3.1.2 Post-Purge Cycle
The post-purge cycle employs the variable
speed fan to clear exhaust gases from the
boiler and its venting, and the pump to
utilize residual heat from the boiler vessel
during cool-down. The fan and pump
provide normal flow rates for an initial 10
second period; subsequently the fan is
IBC Technologies Inc. - 18 - VFC 160
4. Flow Switch: Shuts boiler off if water
flow drops below US 4 gpm
5. Flame Presence: the ignition module
will lockout if no flame is detected
during its 21 second trial period.
Causes for this can be found in Section
4 - Troubleshooting Guide under
Lockout.

3.2 BOILER MAINTENANCE
blockage exists, trap must be cleared and
refilled.
The installer is responsible to ensure the
owner aware of the importance of regular
maintenance, and that improper
maintenance may result in a hazardous
condition.
Unless otherwise specified, boiler must be
inspected at the beginning of each heating
season by a qualified technician.
CAUTION: Label all wires prior to
disconnection when servicing controls.
Wiring errors can cause improper and
dangerous operation.
3.2.1 General Care
Keep combustible materials and
flammable liquids and vapours away from
the boiler.
Keep vent terminals clear of obstructions
(snow, dirt, etc.).
3.2.2 Inspection
Burner
Visually inspect burner through sight
glass. Ensure flame is stable and without
excessive fluttering. Normal flame pattern
is evenly distributed over the burner
surface.
Annual inspection of the burner is not
necessary. If operating improperly,
remove burner and clean or replace.
Use a CO2 analyzer to determine proper
combustion. CO2 level should be 9.2%.
Pump
Check that the pump is on in normal
operation.
Heat Exchanger
In the unlikely event of boiler flue passage
blockage, service to remedy situation must
be performed only by an authorized IBC
representative.
Annual inspection of the boiler to be
performed by a qualified technician.
Venting
Check vent terminals and vent piping for
and remove any obstructions.
Check for holes or leaks in venting.
Examine for any signs of moisture caused
by sweating intake air pipes; insulate as
required.
If any of these conditions exists, contact a
qualified technician.
Air Filter
Replace or clean air filter annually.
Condensate Traps
Check condensate traps every 6 months
for water seal and blockages. If a
Gas Piping
Check for damage or leaks and repair as
needed.
Ignition Module/Igniter Probe
Check that boiler ignites 40s after a call
for heat. Ensure that fan and pump are on
when a call for heat occurs.
There should be no unusual crackling
noise when igniting the boiler. If there is,
consult Section 4 - Troubleshooting.
Enunciator
Check that the blower is on in normal
operation, and pump remains on and
blower operates at normal speed for 10
seconds then ultra-low speed (for 90 min.
max.) after boiler shuts off.
Water
IBC Technologies Inc. - 19 - VFC 160
Check water pressure and temperature.
There should be no noticeable change if
boiler is functioning normally. Check for
any noise in the system.
Check water piping for damage or leaks
and repair as needed.
volume must not exceed 50% of the total
volume of water in the system.
WARNING: Do not use Ethylene
Glycol, automotive-type
antifreeze, or undiluted
antifreeze. This may result in
severe boiler damage.
Freeze Protection
Use only antifreeze made specifically for
hydronic systems. Inhibited propylene
glycol is recommended. Antifreeze
3.3 COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
A diagram of components and their
placement can be found at the end of this
manual.
For a list of supplier for all components,
contact IBC Technologies or visit our
website at www.ibcboiler.com.
The following list provides a summary
description of major components:
3.3.1 Pressure Switch
Part#/Type: #VFCF-P011-NO4 /
Honeywell C6065D Differential Pressure
Switch, calibrated to 0.88” (Alt: Micro
Pneumatics 9300-0.88)
Function: used to confirm adequate flow
of combustion air; shuts boiler off when
intake air pressure differential drops below
0.9” at measurement point -
Verify proper operation after servicing.
Installation: Ensure that arrow points
towards the pressure vessel; shift bar to
“NO” position.
3.3.3 Operator
Part#/Type: #VFCF-P010-150 or -120 /
High range (red face): calibrated for 150°F
centerpoint, 20°F differential; low range
(black face): 120°F centerpoint, 20°F diff.
Function: Switch closes/opens to
enable/prevent boiler operation to provide
desired water temperature range.
Installation: Mount with Honeywell
Tradeline #107408 Heat Conductive
Compound between the base of the
operator and the surface of the tee. Set to
desired operating temperature - see
Section 3.5 - Set Operator Limit above.
Installation: see diagram at the end of
the manual for correct installation.
3.3.2 Flow Switch
Part#/Type: #VFCX-P002 / ½" NPT
paddle type brass/spst reed switch
Function: for confirmation of adequate
circulating water flow; shuts boiler off
when flowrate drops below US 4.0 gpm
IBC Technologies Inc. - 20 - VFC 160
3.3.4 Hi-Limit
Part#/Type: #VFCX-HL200 / Therm-ODisc 37T_21, calibrated for 200°F, 15°F
differential.
Function: Shuts boiler off when water
temperature exceeds safety limit. Two hilimits are available depending on the
desired maximum.
Installation: Mount with Honeywell
Tradeline #107408 Heat Conductive

Compound between the base of the
operator and the mounting surface.
3.3.5 Transformer
Part#/Type: #VFCX-P006 /Hammond
DG2G control transformer; Alternate: Rex
CS100AW/X Primary- 120VAC; Sec.- 24
VAC; 100VA
Function: Provides 24 VAC for (1) the
control circuit and (2) AC to DC power
converter, to drive the brushless DC fan
Installation: see wiring & ladder
diagrams.
3.3.6 Gas Valve
Type: White-Rodgers 36E22 (alts:
36E36; 36F22 or 36G22) Fast-Opening
Valve. Alternative: Honeywell VR8205A
Function: regulates and supplies gas for
gas:air mixing; opens/closes on signal
from the ignition control module.
Installation: see Section 2.2 Gas Valve
Adjustment.
3.3.7 Blower
1. 30 second (approx.) prepurge on a call
for heat
2. opens gas valve
3. provides ignition spark (30,000 V open
circuit, which provides approx 8,000 V
on a formed-arc basis) for a single
trial-for-ignition period of 20 second.
Checks for flame presence; locks out if
no flame by end of ignition trial. See 4
- Troubleshooting, under Lockout.
4. discontinues spark if flame present
5. on loss of flame, a timed trial-for-
ignition is repeated (locks out if trialfor-ignition period ends before flame
is re-established)
Installation: see wiring diagram.
3.3.9 Igniter Probe/Flame Sensor
Part#/Type: #VFCX-P004 / single probe
of Kanthal A1 and Alumina ceramic.
Function: Transmits spark from ICM
to burner for ignition, and sends electrical
signal back to ICM for flame proving.
Installation: Set gap between burner and
probe end must be between 3/16 - 1/4”.
Part#/Type: #VFCX-P005 / RG130/0800
24V DC blower
Function: Moves combustion air and flue
gas products through the boiler and
venting.
Installation: see Section 2.3 Blower
Adjustment.
3.3.8 Ignition Control Module(ICM)
Type: #VFCF-M003 / Honeywell S87J1034 Direct Spark Ignition Control
Module.
Function: Boiler ignition, flame proving
and gas valve control.
On a call for heat, the S87J-1034 performs
the following functions:
3.3.10 DC Power /Enunciator Panel
Ignition Module
Pump
Pressure Switch
Power
H
Fan Speed
L
Fan
Operator
Flow Switch Vent Hi-Limit Water Hi-Limit
180°F
80°F
Set Point
FXFR
Thermostat
24 V
Call for Heat
AC
Figure 16. DC Power & Enunciator
Part#/Type: #VFCF-M002 / combination
dc power supply and wiring bus
Function: Provides DC power supply for
fan operation and a PWM electronic signal
for fan speed variation. Also acts as a
IBC Technologies Inc. - 21 - VFC 160

connector bus for control circuit wiring.
The integrity of the series control circuit is
preserved in the FXFR module’s internal
circuitry. Finally, the module comprises
the circuitry supporting the optional
Electronic Operator.
The Enunciator panel carries seven
indicator lamps (LEDs) pertaining to the
various control circuit components wired
to the module. The LEDs provide a visual
aid for locating open switches within the
control circuit. on the boiler showing the
states of the boiler:
1. power
2. airflow
3. water temperature operating range
(Operator)
4. water flow
5. vent temperature limit
6. water temperature limit
7. thermostat
The remaining indicators light up in series
from right to left, beginning with the
thermostat. If an indicator is off, all
indicators to the left of it will be off. The
first unlit indicator shows an open circuit
at that point. If the boiler is heating, all
indicators will be on.
Output of the fan may be adjusted during
installation using the fan speed adjustment
screw. This allows optimization of fan
speed to minimize electrical consumption
and noise for each installation. Fan
adjustment should only be done by a
qualified technician with appropriate
equipment (incl. combustion analyzer)
during installation or servicing.
The DC Power / Enunciator module
circuitry also manages the Post-Purge
cycle - see 3.1.2 Post-Purge Cycle above.
The power indicator light always remains
on except when there is no power to the
boiler.
3.3.11 Detailed System Checks
Should overheating occur or the gas supply fail to shut off, do not turn off or disconnect the
electrical supply to the pump. Instead shut off the gas supply at a location external to the
appliance.
Do not use this boiler if any part has been under water. Immediately call a qualified service
technician to inspect the boiler and to replace any part of the control system and any gas
control which has been under water.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 22 - VFC 160
4. Detailed Systems Troubleshooting
Cycling Problems
Symptom Diagnosis Remedy
Rapid Cycling
i) Gas valve clicks on and
off repeatedly when
igniting.
ii) Water noise in exhaust
venting
no other symptoms
Obstruction in Intake/
Exhaust venting.
Excess Condensate in
venting.
•
Obstruction in
condensate trap.
•
Improper vent length.
•
Improper slope to vent.
Incorrect anticipator setting
or defective thermostat.
Air in system (check for
flashing flowswitch lamp),
of marginal water flow.
Slow combustion air blower. Check that CO2 level is 9.2%.
Dirty burner/heat exchanger. Check pressure drop.
Insufficient water flow.
•
Improper piping.
•
Undersized pump.
•
Restriction in water
pipe.
Insufficient radiation. Check actual amount of
Unit overfired. Clock gas meter/check gas
Unit Oversized. Refer to Load Calculation vs.
Improperly set or defective
operating/safety controls
Inspect vent terminals and
tubing. Clear any obstructions.
Check venting angles
Inspect and clean condensate
trap.
Check venting. Compare vent
length and diameter to
Maximum Venting
Check operation. Refer to
manufacturer’s instructions.
Check setting with ammeter.
Bleed/purge system as required.
Confirm adequate pump size
and temp rise in HX
Refer to recommended piping in
ection 1.5
S
Check manufacturer’s rating
charts/check temperature
differential across heat
exchanger.
Check temperature differential
across zone/heat exchanger.
radiation per zone and refer to
manufacturer’s rating tables.
pressure with manometer/ check
level.
CO
2
Boiler Output
Check operation with
Ohmmeter/Voltmeter
.
Table 3-
.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 23 - VFC 160
Ignition Problems
Symptom Diagnosis Remedy
Noisy spark when igniting. Ignition lead is not firmly
connected.
Contaminants/moisture
on igniter probe/flame
sensor.
Boiler rumbles when igniting. Poor gas/air mixture. Check CO2 in exhaust. Check
Fluctuating gas pressure/
gas pressure too high/too
low.
Boiler will not attempt to ignite.
i) Fan and pump are
operating normally.
ii) Fan and pump are off
No lights on display
iii) Fan off and pump on
Boiler ignites but shuts off
within seconds
No power to ignition
control module.
Igniter probe/flame
sensor disconnected.
Blown fuse in ignition
module.
Defective Control
Module.
No power to boiler Check line voltage
Defective transformer. Check transformer.
Bad electrical grounding
of vessel defeats flame
rectification
Loose or bad igniter
cable
Reconnect ignition lead
Ensure probe is dry by rerunning post-purge;
otherwise, clean or replace
igniter probe.
mass airflow sensor.
Check pressure with
manometer during ignition.
Check mass airflow sensor.
Check system wiring.
Check airswitch & air tubing.
Reconnect probe.
Check fuse.
If blown, replace.
Check ignition output from
control module.
Reconnect or replace as
needed.
Confirm continuity between
pressure vessel and ground
terminal on Control Module.
Check and replace as required
Miscellaneous
Symptom Diagnosis Remedy
Fumes and High Humidity Improperly installed
condensate trap
Leak in CPVC/ABS/PVC
vent piping
Flue gas leak in heat
exchanger
IBC Technologies Inc. - 24 - VFC 160
Refer to installation/operation
instructions
Visually inspect using soap
solution
Visually inspect all
mechanical connections
Temperature Problems
Symptom Diagnosis Remedy
Insufficient heat. Operating temp. too low
Unit undersized Refer to Load Calculation vs.
Air trapped within system Bleed system as required.
Improper system piping Refer to recommended piping
System pump undersized Check pump manufacturer’s
Poor gas/air mixing Check CO2 level.
Defective thermostat. Refer to manufacturer’s
Incorrect gas/air orifices. Refer to orifice sizing table
Obstruction in condensate
drain.
Unit cycling on operating/
safety controls.
System radiation
undersized
Temperature exceeds thermostat
setting
One or more zones do not heat
properly.
One or more zones do not heat
properly.
Incorrect anticipator
setting
Thermostat not level. Check level.
Air trapped within
zone(s)
piping
Insufficient radiation/
excessive heat loss.
Insufficient flow rate to
zone(s).
Defective zone valve/
zone circulator.
Defective zone
thermostat.
Improper control wiring. Check wiring per
Improper/obstructed
baseboard radiation.
Operating limit set
improperly.
Boost setpoint per Section
2.3.1 above
Boiler Output
in Section 1.5.
data/check temp differential
across heat exchanger.
instructions.
Inspect and clean condensate
drain.
Check operation with
Ohmmeter/Voltmeter.
Check manufacturer’s rating
tables for capacity per foot.
Check with Ammeter.
Vent system/zone as required.
Check actual length of pipe
using radiation / heat loss
calculation.
Check temperature drop
across zone.
Check operation per
manufacturer’s instructions.
Check operation per
manufacturer’s instructions.
manufacturer’s instructions.
Check baseboard
manufacturer’s instructions/
check at zone.
Check limit setting/operation.
IBC Technologies Inc. - 25 - VFC 160

IBC Technologies Inc. - 26 - VFC 160

pressure
switch
w
b
o
operator
+25V
(GND)
b
valve
valve
+25V
gnd
(burner)
b
b
r
r
b
b
b
G
flow
switch
vent
limit
r
w
b
b
water
limit
b
b
Ignition Module
r
r
Pump
pump
Pressure Switch
Power
Fan Speed
Operator
Flow Switch Vent Hi-Limit Water Hi-Limit
°
°
Set Point
Thermostat
FXFR
Call for Heat
G
b
b
r
r
rwbry
thermostat
pwm−V tac +v
blower
jb1
(control)
n
n
l
115V AC
G
24V AC
l
Wiring Diagram for IBC VFC 160 Boiler
IBC Technologies Inc. - 27 - VFC 160

Component Layout Diagram
1. Igniter Probe/Flame Sensor
2. Blower
3. Tridicator
4. Water Hi-Limit
5. Operator
6. Gas Valve
7. Pressure Switch
8. Ignition Control Module (ICM)
9. Enunciator
10. Transformer
11. Flow Switch
12. Vent Hi-Limit
IBC Technologies Inc. - 28 - VFC 160

Installation Checklist
Model#: Water Tank #:
Dealer Name: Serial#: Installation Date:
Heat Loss: BTUhr ft. of Radiation: # of Zones:
BTU/ft.: Total Radiation Output: BTUhr
Electrical Information
Thermostat: Anticipator Setting: Amps
Supply Voltage: Volts Combusti on Air Blower Amp Draw: Amps
Boiler Information
Type of Gas: Operating Gas Inlet Pressure: in. w.c.
CO
reading: % Air Intake Orifice Size:
2
Air Pressure Differential Across Air Intake Orifice Plate: in. w.c.
Exhaust Vent Piping: in. ft.
Air Intake Piping: in. ft.
Temperature Rise Through Boiler
Space Heating: °F
Domestic Hot Water: °F Flue Gas Temp.: °F Operating Temp.: °F
Water Manifold Pipe Size
Supply: DHW Tank Aquastat Setting: °F Two-Way:
Return: Differential Setting: °F Three-W ay:
System Pump Model #: Additonal Pump Model #:
Expansion Tank Model #: Expansion Tank Size:
Type of Air Elimination
Spirovent Honeywell
Manual Air Bleed Manual
Pipe Size
perator Setting(A-E): Operating Pressure: psig
Pipe Size to DHW Tank: Valve Type to DHW Tank
Vent/Intake Piping
Water Pressure/Temperature
Water Piping
Actual Length # of 90 and 45 Elbows
Tridicator Gauge
System Bypass Type
None
Notes:
IBC Technologies Inc. - 29 - VFC 160

Air Switch Reference Line Connections
IBC Technologies Inc. - 30 - VFC 160
 Loading...
Loading...