
®
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3
MODULATING GAS BOILERS
(Natural Gas or Propane)
WARNING: If the information in this manual is not followed exactly, a re or
explosion may result causing property damage, personal injury, or loss of life.
Do not store or use gasoline or other ammable vapors and liquids or other
combustible materials in the vicinity of this or any other appliance.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS:
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electrical switch; do not use any phone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a nearby phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the re department.
Installation and service must be performed by a qualied installer, service
agency or the gas supplier.
This Manual is also available in French - contact IBC or visit our web site www.ibcboiler.com
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
SL 40-399 G3
www.ibcboiler.com

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
WARNING
If the information in this manual
is not followed exactly, a re or
explosion may result causing
property damage, personal
injury, or loss of life.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation, start-up and servicing of IBC boilers must be performed by competent,
qualied, licensed and trained heating technicians.
Failure to read and comply with all instructions and applicable National and local codes
may result in hazardous conditions that could result in property damage and injury to
occupants which in extreme cases might result in death.
HAZARDS & PRECAUTIONS
DANGER
Points out an immediately
hazardous situation which must
be avoided in order to prevent
serious injury or death.
WARNING
Points out a potentially
hazardous situation which must
be avoided to prevent serious
injury or death.
CAUTION
Points out a potentially
hazardous situation which must
be avoided to prevent possible
moderate injury and/or property
damage
Supplied with the boiler - The IBC boiler is shipped with an accessory parts kit
consisting of the following items:
• 1 x Wall mounting bracket
• 1 x Condensate trap assembly
• 1 x 30 psig pressure relief valve
• 1 x Outdoor temperature sensor
• 6 x 1/4” x 2 1/2” Lag screws/w at
washers
• Installation and Operating Instructions
• User Manual
• V10 Touchscreen Operating Instructions
NOTE
Points out installation,
maintenance and operation
details that will result in
enhanced efciency, longevity
and proper operation of your
boiler.
Manual
Manual
2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATION SL 26-260 G3 SL 40-399 G3
CSA Input (Natural Gas or Propane) - MBH
CSA Input (Natural Gas or Propane) - kW
CSA Output - MBH
CSA Output - kW
A.F.U.E
Combustion Efciency BTS-2000
Thermal Efciency
Minimum gas supply pressure (Natural Gas or
Propane) - inch w.c.
Maximum gas supply pressure (Natural Gas or
Propane) - inch w.c.
Ambient temperature - Low °F / °C
High °F / °C
Max. relative humidity (non-condensing)
Minimum water temp.
Maximum water temp. (electronic hi-limit)
Max. ΔT - supply/return (electronic fence)
Power use (120Vac/60Hz) @ full re - Watts
26 - 260
7.6 - 76.2
24.9 - 239
7.30 - 70.0
95%
4
14
32°F / 0°C
122°F / 50°C
90%
34°F / 1°C
190°F/ 88°C
40°F
127 (less pumps)
40 - 399
11.7 - 117
38.4 - 383
11.2 - 112
96%
96%
4
14
32°F / 0°C
122°F / 50°C
90%
34°F / 1°C
190°F/ 88°C
40°F
345 (less pumps)
Weight (empty) - lbs/Kg
2
Heating Surface Area - ft
Pressure vessel water content - USG/Litres
Maximum boiler ow rate - USgpm
Minimum boiler ow rate - USgpm
Maximum operating water pressure* - psig
Minimum water pressure - psig
Approved installation altitude - ASL
Maximum equivalent vent length
Each side (Vent & Air Intake))
(Natural Gas or Propane)
Air intake options: either direct vent or indoor
supply
* boilers are shipped with 30 psig pressure relief valve.
/ m
2
162 / 74
22.71 / 2.11
5 / 19
25
6
30
8
0 - 12,000’
200’ (3")
240 / 110
36.56 / 3.40
7 / 26
45
20
80
8
0 - 12,000’
200’ (4")
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
3

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
4
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
Contents
1.0 INSTALLATION....................................................1-1
1.1 GENERAL........................................................1-1
1.2 CODE REQUIREMENTS ............................................1-3
1.3 LOCATION .......................................................1-3
1.4 EXHAUST VENTING AND AIR INTAKE .................................1-4
1.4.1 Applications ...................................................1-6
1.4.2 Exhaust Vent Material ...........................................1-6
1.4.3 Vent Travel ....................................................1-7
1.4.4 Venting Passage Through Ceiling and Floor ..........................1-9
1.4.5 Rooftop Vent Termination .........................................1-9
1.4.6 Sidewall Vent Termination .......................................1-10
1.4.7 “Direct Vent” Combustion Air Intake Piping ..........................1-15
1.4.8 “Indoor Air” Combustion Air Intake .................................1-16
1.4.9 Combustion Air Filtration ........................................1-17
1.4.10 Closet Installations ............................................1-17
1.5 CONDENSATE REMOVAL ..........................................1-18
1.5.1 Condensate Trap ..............................................1-18
1.5.2 Condensate Trap Assembly - Installation ............................1-18
1.5.3 Condensate Trap Assembly - cleaning procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-19
1.5.4 Further installation details .......................................1-19
1.6 WATER PIPING ..................................................1-21
1.6.1 General Piping Issues ..........................................1-21
1.6.2 Installation Rules ..............................................1-24
1.7 GAS PIPING .....................................................1-28
1.8 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS ......................................1-29
1.8.1 120 VAC Line Voltage Hook-up ...................................1-29
1.8.2 Power Quality and Electrical Protection .............................1-30
1.8.3 Zone Valve Hook-up............................................1-30
1.8.4 Thermostat / Sensor Wiring ......................................1-30
1.8.5 Other Wiring ..................................................1-30
1.8.6 Thermostat Heat Anticipator......................................1-31
2.0 IBC BOILER CONTROLLER .........................................2-1
2.1 GENERAL........................................................2-1
2.2 CONTROL .......................................................2-1
2.3 CONTROL INTERFACE .............................................2-2
3.0 STARTUP & COMMISSIONING .......................................3-1
3.1 BOILER SHUTDOWN & LIGHTING ....................................3-1
3.2 PRIOR TO START-UP ..............................................3-2
3.2.1 Pre-Ignition Checks .............................................3-2
3.2.2 Test Ignition Safety Shutoff .......................................3-2
3.3 COMMISSIONING .................................................3-2
3.3.1 Gas Valve and Fan Diagrams .....................................3-4
3.4 FUEL CONVERSION ...............................................3-5
3.4.1 Gaining access to combustion chamber and burner removal instructions....3-6
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
5

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
4.0 MAINTENANCE ...................................................4-1
4.1 BOILER MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.1 General Care ..................................................4-1
4.1.2 Inspection.....................................................4-1
4.1.3 Venting .......................................................4-1
4.1.4 Condensate Traps ..............................................4-1
4.1.5 Burner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.6 Heat Exchanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.7 Pump ........................................................4-2
4.1.8 Gas Piping ....................................................4-2
4.1.9 Touchscreen Boiler Controller .....................................4-2
4.1.10 Water .......................................................4-2
4.1.11 Freeze Protection ..............................................4-2
4.1.12 Boiler Treatment...............................................4-2
4.1.13 Relief Valve - Maintenance and Testing .............................4-3
4.2 GEOGRAPHY & COMPONENTS......................................4-4
4.2.1 Fan and gas valve removal instructions..............................4-6
4.2.2 Fan and gas valve re-installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.2.3 Replacing the gas valve ..........................................4-8
5.0 TROUBLESHOOTING ..............................................5-1
5.1 PRELIMINARY CHECKS ............................................5-1
5.2 ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS .......................................5-2
5.2.1 Temperature Sensors............................................5-2
5.2.2 Fan ..........................................................5-3
5.2.3 Water Pressure Sensor ..........................................5-3
5.2.4 Safety and Ignition Module (SIM)...................................5-3
5.2.4.1 Low water cutoff function: reset and test............................5-4
5.2.4.2 Water Temperature function: reset and test .........................5-5
5.3 TROUBLESHOOTING ..............................................5-6
5.3.1 Using Control Module Errors Displayed ..............................5-6
5.3.2 Ignition Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
5.3.3 Cycling Problems ...............................................5-9
5.3.4 Temperature Problems..........................................5-10
5.3.5 Miscellaneous.................................................5-11
6.0 DIAGRAMS.......................................................6-1
6.1 PARTS DIAGRAMS ................................................6-2
6.2 WIRING DIAGRAMS ...............................................6-9
6.3 SEQUENCE OF OPERATION .......................................6-11
INSTALLATION & COMMISSIONING REPORT.............................6-12
INSTALLER SET-UP..................................................6-13
SERVICE RECORD ..................................................6-14
NOTES ....................................................6-15
REVISION HISTORY .................................................6-17
6
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

DANGER
Should overheating occur or the
gas supply fails to shut off, do
not turn off or disconnect the
electrical supply to the pump.
Instead shut off the gas supply
at a location external to the
appliance
WARNING
Do not use this boiler if any
part has been under water.
Immediately call a qualied
service technician to inspect the
boiler and to replace any part
of the control system and any
gas control that has been under
water.
CAUTION
Care must be taken to properly
size the boiler for its intended
use. Prolonged full re run time,
over-sizing or under-sizing, and
incorrect ow rates through
the boiler can lead to increased
maintenance costs, equipment
stress and premature failure.
WARNING
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
The Installer must carefully read this manual to ensure that all installation details can
be adhered to. Special attention is to be paid to clearances and access, vent travel and
termination, gas supply, condensate removal and combustion air supply.
The Installer should do a pre-installation check to ensure that the following precautions
can be observed:
• The boiler should be installed in areas where the combustion air source is not subject
to chemical fouling or agricultural vapors. Exposure to corrosive chemical fumes
such as chlorinated and/or uorinated hydrocarbons can reduce the life of a boiler.
Cleaners, bleaches, air fresheners, refrigerants, aerosol propellants, dry-cleaning
uids, de-greasers and paint-removers all contain vapors which can form corrosive
acid compounds when burned in a gas ame. Airborne chlorides such as those
released with the use of laundry detergents are also to be avoided.
• The boiler should be located where water leakage will not result in damage to the area.
If a location such as this cannot be found, a suitable drain pan should be installed
under the appliance. The boiler is not to be installed above carpeting.
• At a new construction site, or during renovations, action must be taken to protect
the boiler from drywall dust or other construction related contaminants; combustion
air should be drawn from a CLEAN source (e.g. outdoors) and the boiler should be
isolated from interior dust sources. Do not seal boiler case openings directly when
ring - allow for air circulation and ventilation in the immediate area.
• When the boiler is in operation, the impact of the steam plume normally experienced at
the exhaust terminal of a condensing boiler should be assessed. Generally, intake and
exhaust pipes should terminate at a rooftop or sterile wall location. Boiler condensate
is corrosive. Protective measures must be taken to prevent corrosion damage to
metal roofs or other metal building components in contact with the condensate. Keep
exhaust plumes well away from all building air intakes including those of neighboring
properties.
• The exhaust outlet should be placed so as to reach 12” minimum above the downturned intake - to avoid exhaust re-ingestion.
• For sidewall venting options: Both the inlet and exhaust terminations should normally
be located on the same plane (side) of the building. The elevation of both pipes can
be raised in “periscope style” after passing through the wall to gain required clearance
above grade and snow level.
• If the indoor combustion air option is used, ensure combustion air openings to the
boiler room remain unblocked and free of obstructions.
• Examine the condensate outlet to ensure proper disposal of condensate will occur
during operation. If condensates are to be discharged into building drain piping
materials that are subject to corrosion, a neutralization package must be used.
• Ensure that the pressure relief valve will be installed with no valves or other means of
isolation between its inlet and the boiler. Make sure the relief valve outlet will be piped
with unobstructed piping (minimum 3/4” diameter) to a safe discharge location.
If the boiler can become exposed
to uid temperatures below 34°F
(1°C), a method of protection to
prevent freezing of condensate
should be employed. Contact the
factory for further information.
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
7

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
8
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
1.0 INSTALLATION
1.1 GENERAL
The gas-red modulating boilers are low pressure, fully condensing units having a variable
input range. Approved as “Category IV” vented appliances, the boilers use either Direct
Vent (sealed combustion) or indoor combustion air, providing a great degree of installation
exibility.
The following table displays the required connection specications for each model.
DESCRIPTION SL 26-260 G3 SL 40-399 G3
A Flue Outlet 3” Schedule 40 4" Schedule 40
B Combustion Air Inlet 3” Schedule 40 4" Schedule 40
C Safety Relief Valve and Air Vent 3/4" NPT - F 3/4" NPT - F
D Touchscreen display 2-1/4” x 4” 2-1/4" x 4"
E Water Outlet 1-1/2” NPT-M 1-1/2" NPT - M
F Water Inlet 1-1/2” NPT-M 1-1/2" NPT - M
G Knock-outs (8) 1/2” 1/2"
H Gas Inlet 3/4” NPT-F 3/4" NPT - F
I Condensate Outlet 3/4” Hose 3/4" Hose
Table 1: Connections
Figures 1A and 1B show outer case dimensions, piping and electrical holes. Refer to
these gures to help with nding a suitable location for the boiler. See also Section 1.3
Location.
INSTALLATION
1-1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
Figure 1A: Dimensions / Connections for SL 26-260 G3
9.7in
[246mm]
Figure 1B: Dimensions / Connections for SL 40-399 G3
1-2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

WARNING
Keep boiler area free and clear of
combustible materials, gasoline,
and other ammable vapors and
liquids.
WARNING
Combustion air must not be
drawn from areas containing
corrosive air from swimming
pools or spas, including air
directly next to outdoor pools
and spas.
WARNING
The boiler shall not be exposed
to water leaks from piping or
components located overhead.
This includes condensation
dropping from un-insulated cold
water lines overhead.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
1.2 CODE REQUIREMENTS
The boilers are tested and certied under CSA 4.9-2014 / ANSI Z21.13-2014.
Installation must conform to local codes, or in the absence of these, with the latest editions
of CAN/CGA B149.1 and the Canadian Electrical Code Part 1 CSA C22.2 No. 1.
In the US, installations must conform to the current National Fuel Gas Code ANSI
Z223.1 and the National Electrical Code ANSI/NFPA 70. Where required by jurisdiction,
installation must conform to the Standard for Controls and Safety Devices for
Automatically Fired Boilers, ANSI/ASME CSD-1. If there is any conict, then the more
stringent requirement will apply.
1.3 LOCATION
The boilers are designed and approved for indoor installation (wall or rack mounting), with
signicant exibility of location provided with the available venting options. The boiler can
be placed in an alcove, basement, closet or utility room. Surrounding conditions shall be
32°F (0°C) to 122°F (50°C) and less than 90% relative humidity.
Install the boiler in areas where the combustion air source is not subject to chemical
fouling or agricultural vapors. Exposure to corrosive chemical fumes such as chlorinated
and/or uorinated hydrocarbons can reduce the life of a boiler. Cleaners, bleaches, air
fresheners, refrigerants, aerosol propellants, dry-cleaning uids, de-greasers and paint-
removers all contain vapors which can form corrosive acid compounds when burned in a
gas ame. Airborne chlorides such as those released with the use of laundry detergents
are also to be avoided. For this reason, the indoor air venting option using air surrounding
the boiler should not be used in a laundry room. Similarly, ensure any direct vent air
source is not adjacent to a clothes dryer exhaust terminal. Avoid agricultural applications
where the boiler and/or the intake air source are affected by ammonia and/or dust.
Locate the boiler where water leakage will not result in damage to the area. If a location
such as this cannot be found, a suitable drain pan should be installed under the appliance.
The boiler is not to be installed above carpeting.
Boiler weight – without water and any effect of system piping and components – is up to
approx. 240 lbs/110 kg. For support fasteners, use the supplied 6 x 1/4” x 2 1/2" long lag
screws. Installer to supply 1/4" bolts if metal mounting systems are used. Fasteners are to
be attached to solid material capable of supporting the combined weight of the boiler and
piping assembly components.
Other factors to consider for mounting sites:
• Adhere to the minimum clearance requirements for combustible materials (see Table
2).
• A minimum 24" clearance at the front and 12” above the boiler is recommended for
adequate servicing. Check local codes for additional access and service clearance
requirements.
WARNING
Ensure the gas ignition system
components are protected from
water (dripping, spraying, rain,
etc.) during appliance operation
and when servicing (pump
replacement, condensate trap
servicing, control replacement,
etc.)
INSTALLATION
1-3

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
Exposed water piping and
associated components
(relief valves, circulators,
etc.) should not be in contact
with combustible materials.
Check local codes for required
clearances and/or provide
adequate insulation.
WARNING
DO NOT MOUNT THIS
BOILER TO HOLLOW WALL
STRUCTURES - The weight of the
boiler alone is 240 pounds. The
combined weight of the boiler, its
water contents and associated
piping components can exceed
300 pounds. Fasteners must be
rated for this strain, and must
be rmly anchored into solid
material that will support this
weight.
• At a new construction site, or during renovations, action must be taken to protect
the boiler from drywall dust or other construction related contaminants; combustion
air should be drawn from a CLEAN source (e.g. outdoors) and the boiler should be
isolated from interior dust sources. Do not seal boiler case openings directly when
ring - allow for air circulation and ventilation in the immediate area.
SURFACE
Front 1" 24”
Rear 0" 0”
Left Side 1" 0” - (to non-combustibles)
Right Side 1" 4” (for electric and gas if required
Top 12” 12” (for vent connection)
Bottom 12" 12” (for condensate trap and piping)
Table 2 - Clearance from boiler cabinet
A minimum distance below the boiler of 12" is required to provide clearance for the
supplied condensation trap assembly. More clearance will typically be required to
accommodate associated water and gas piping.
DISTANCE FROM
COMBUSTIBLES
DISTANCE FOR INSTALLATION
AND SERVICE
Installers are to take all
necessary precautions to avoid
injury during the installation of
this boiler.
DANGER
Do not common vent SL series
modulating boilers with any other
existing or new appliance.
Figure 2: Wall mounting of boiler
1.4 EXHAUST VENTING AND AIR INTAKE
It is important to carefully plan the installation to ensure the appropriate vent materials,
travel and termination decisions are included. Specic attention is warranted to manage
the impact of the steam plume normally experienced at the exhaust terminal of a
condensing boiler. Generally, intake and exhaust pipes should terminate at a rooftop or
sterile wall location, to maximize customer satisfaction. Keep exhaust plumes well away
from all building air intakes including those of neighboring properties.
1-4
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
Venting, condensate drainage,
and combustion air systems for
all IBC boilers must be installed
in compliance with all applicable
codes and the instructions of
their respective Installation
Manuals.
Inspect nished vent and air
piping thoroughly to ensure all
are airtight and comply with the
instructions provided and with
all requirements of applicable
codes.
Failure to comply will result in
severe personal injury or death.
All venting must be installed in accordance with the requirements of the jurisdiction having
authority: in Canada, Part 8, Venting Systems of the B149.1-10 Code and any other local
building codes are to be followed. In the USA, the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI 223.1,
latest edition, prevails. Where there is a discrepancy between the installation instructions
below, and the code requirements, the more stringent shall apply.
Figure 3: Flue gas venting
Provisions for the combustion and air ventilation must be in accordance with the section
“Air for Combustion and Ventilation” of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA
54, or Clause 8.2, 8.3 or 8.4 of the Natural Gas and Propane Installation Code, CAN/CSA
B149.1, or applicable provisions of the local building codes.
IMPORTANT:
When an existing boiler is removed from a common venting system, the common venting
system is likely to be too large for proper venting of the appliances that remain connected
to it.
When resizing any portion of the common venting system, the common venting system
should be resized to approach the minimum size using the appropriate tables in the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 - latest edition. In Canada, use the B149.1
Installation Code.
At the time of removal of an existing boiler the following steps shall be followed with each
appliance remaining connected to the common venting system placed in operation, while
the other appliances remaining connected to the common venting system are not in
operation.
• Seal any unused opening in the common venting system.
• Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and horizontal pitch and determine
there is no blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion and other deciencies that
could cause an unsafe condition.
• Insofar as is practical, close all building doors and windows and all doors between
the space in which the appliances remaining connected to the common venting
system are located and other spaces of the building. Turn on clothes dryers and
any appliance not connected to the common venting system. Turn on any exhaust
fans, such as range hoods and bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum
speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close replace dampers.
INSTALLATION
1-5

WARNING
Covering non-metallic vent
pipe and ttings with thermal
insulation shall be prohibited.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
• Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow the lighting instructions.
Adjust the thermostat so that the appliance operates continuously.
• After it has been determined that each appliance remaining connected to the common
venting system properly vents when tested as outlined above, return doors, windows,
exhaust fans, replace dampers and any other gas-burning appliance to their
previous condition.
• Any improper operation of the common venting system should be corrected so the
installation conforms with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 - latest edition.
In Canada, all installations must conform with the current CAN/CGA - B149.1-10
Installation Code and/or local codes.
1.4.1 Applications
All SL series boilers are approved with alternative venting options: either 2-pipe Direct
Vent or Vent pipe with Indoor Air, offering exibility to meet the specic requirements of
the installation. With the Direct Vent case, combustion air is piped directly to the boiler’s
air intake from outdoors (see Section 1.4.7 for air intake piping requirements). Using the
indoor air alternative, air for combustion is drawn from the indoor air surrounding the
boiler.
Provided the maximum overall vent length limit is not exceeded, the installer may choose
to vent the boiler through the wall, directly through the roof, or upward using an existing
- but otherwise unused - chimney as a vent raceway.
WARNING
Condensate can cause corrosion
of metal roong components
and other roong materials.
Check with the builder or
roong contractor to ensure
that materials will be resistant to
acidic condensate. pH levels can
be as low as 3.0
1.4.2 Exhaust Vent Material
Exhaust Vent Material – CANADA
Use PVC, CPVC or Polypropylene (PPs) vent component systems approved under
ULC-S636 Standard for Type BH Gas Venting Systems, or stainless steel Type BH venting
systems*. The vent temperature is limited with the use of a ue temperature sensor
and software to ensure the maximum temperature of the PVC venting material is not
exceeded. The temperatures are typically:
• ULC-S636 PVC: 158°F (70°C)
• ULC-S636 CPVC: 212°F (100°C)
• ULC-S636 PPs:- 249°F (120°C)
Exhaust Vent Material – USA
PVC, CPVC or PPs venting materials are approved for use with these boilers in the USA.
The vent temperature is limited with the use of ue temperature sensor and software to
ensure that the maximum temperature of the PVC venting material is not exceeded. PVC
venting material shall be certied to Sch. 40 ASTM D1785 or D2665. CPVC material shall
be certied to Sch. 40/ASTM F441.
Do not use ABS or any cellular core pipe for exhaust venting.
Use of cellular core PVC (ASTM F891), cellular core CPVC, or Radel®
(polyphenolsulfone) in venting systems shall be prohibited.
The boiler offers 3" or 4" venting connections. Fittings are to be used to adapt to the
appropriate diameter – see Vent Travel below. Exhaust venting is to be inserted directly
into the 3" or 4" female stainless steel tting (see Figure 3).
1-6
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
Do not mix PPs venting materials
from different Manufacturers.
These venting materials are
designed to be installed as part
of a complete system.
Failure to comply may result in
severe personal injury or death.
WARNING
Fully insert the approved venting
material into the boilers exhaust
outlet and tighten clamp to ensure
the venting connection is locked
in place.
For PPs material, use the transition / adaptor tting (Sch 40 to PPs) offered by the
respective PPs manufacturers Centrotherm / Innoue
ISAA0404) or M&G Dura Vent / PolyPro
TM
(# 3PPs-AD), (# 4PPs-AD) or Z-Flex/Z_DENS (#
TM
(their part # ISAA0303 or #
2ZDCPVCG3). For PPs material exposed to outdoor weather, follow the venting supplier’s
recommendations on UV protection.
Combustion air piping - if used - is inserted directly into the 3" or 4" female stainless steel
tting (see Section 1.4.7).
Venting shall be supported in accordance with the applicable code.
*Manufacturers of stainless steel Type BH venting systems must submit their approved
transition tting to IBC for evaluation and written approval.
1.4.3 Vent Travel
PVC/CPVC or PPs (Rigid Single Wall) or Schedule 40 approved piping is the standard
venting option; with this, the boilers can be sited up to 200 equivalent feet from the vent
termination. The actual vent travel allowance is reduced for ttings in accordance with the
following tables. For example, for an SL 40-399 G3 using 6 x 90º CPVC vent elbows, the
maximum lineal measure of pipe allowed is 152 feet (200' – (6 x 8' = 48) = 152').
SL 26-260 G3
EXHAUST PIPE SIZE MAXIMUM EQUIVALENT LENGTH
Sched.40; Rigid PPs
3" 200' (each side)
90° vent elbow allow 8' equivalent
90° long sweep elbow allow 5' equivalent
45° elbow allow 3' equivalent
PPs 87-90° elbows use 8' equivalent
3" Stainless Sidewall Terminal (SST)
IBC P/N 180-149 (P-257)
Flexible PPs
3" PPs Flexible 60' (max.) actual lineal x 3.33 = equivalent
allow 20' equivalent of 3" Sched. 40
INSTALLATION
Table 3A: Maximum Exhaust Venting Length for SL 26-260 G3
1-7

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
SL 40-399 G3
EXHAUST PIPE SIZE MAXIMUM EQUIVALENT LENGTH
Sched.40; Rigid PPs
4" CPVC / Rigid PPs 200' (each side)
90° vent elbow allow 8' equivalent
90° long sweep elbow allow 5' equivalent
45° elbow allow 3' equivalent
PPs 87-90° elbows use 8' equivalent
3" Stainless Sidewall Terminal (SST)
IBC P/N 180-149 (P-257)
allow 65' equivalent
3" CPVC (to adapt to the SST) for each 1' allow 3.2' equivalent
Flexible PPs
4" PPs Flexible 160' max, using 1.2 x for equivalent length
Table 3B: Maximum Exhaust Venting Length for SL 40-399 G3
For Flexible PPs, up to 160 actual lineal feet are allowed in a nominally vertical orientation
(>45°). The equivalent length of 4” Flex PPs shall be computed using a multiple of 1.2:1,
e.g.80' x 1.2 = 96’ equivalent (with such use of 80' of 4" Flex, up to 104' equivalent of 4" Rigid
PPs would still be allowed). PPs 87-90° elbows are considered equivalent to 8'.
NOTE: Unused intake travel cannot be added to the exhaust. Unequal intake and exhaust
piping is allowed - see Section 1.4.8.
Exhaust venting must slope down towards the boiler with a pitch of at least 1/4" per foot
(PPs vent: follow PPs manufacturer requirements for slope), so condensate runs back
towards the trap. Support should be provided for intake and vent piping, particularly so for
horizontal runs (follow local code).
Figure 4: Pipe and tting beveling
Ensure all venting components are clear of burrs/debris prior to assembly. Care is to be
taken to avoid ingestion into the fan of plastic debris left in the combustion air piping.
All joints must be secured using appropriate solvent cement to bond the respective
pipe material (Canada: CPVC cement approved under ULC-S636, in accordance
with its manufacturer instructions; USA: PVC (ASTM D2564), or PVC/ABS (D2235)
- Use transition glue anywhere that PVC and CPVC are joined. Follow the cement
manufacturer’s instructions closely when joining various components. For PPs,
connections shall be secured using approved retainer clips supplied by the respective PPs
manufacturer.
1-8
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
Follow all installation
instructions supplied by the pipe
and tting manufacturer.
Figure 5A: 26-260 Fan control
harness plug
Figure 5B: 40-399 Fan control
harness plug
BEST PRACTICES
To reduce the possibility of
expansion noise, allow a 1/4” gap
around the exhaust and air intake
piping.
WARNING
Condensate can cause corrosion
of metal roong components
and other roong materials.
Check with the builder or
roong contractor to ensure
that materials will be resistant to
acidic condensate. pH levels can
be as low as 3.0
All vent connections must be liquid and pressure tight. Prior to ring the boiler, and before
any of the venting run is concealed by the building construction, the installer must test the
exhaust joints under fan pressure with the vent blocked, using a soap and water solution.
The installer must ll the condensate trap prior to testing.
To drive the fan into manual high speed operation for vent leak testing, unplug the fan
control harness plug (see Figures 5A and 5B), and then block the vent outlet so that the
vent run will be under maximum fan pressure. Paint all joints with an approved leak test
solution just as you would joints in a gas line, and make sure there are no leaks. Good
practice would suggest that the installer attach a tag on the vent line near the condensate
drain tee indicating the type of test, the date and the installer’s name.
1.4.4 Venting Passage Through Ceiling and Floor
• Conrm material meets local codes including re stopping requirements.
• Some local jurisdictions require a minimum initial length of pipe be exposed or
accessible for inspection.
• Pipe clearances - no IBC requirements; follow local codes.
• All piping must be liquid and pressure tight.
1.4.5 Rooftop Vent Termination
a) Rooftop vents must terminate as follows:
• The exhaust pipe can terminate in an open vertical orientation without concern about
rain inltration; rain will drain away through the condensate trap.
• Optional bird screen may be placed in a termination tting. Leave unglued, and hold in
place with a short nipple. This permits easy access for cleaning.
• DO NOT exhaust vent into a common venting system.
b) For Rooftop Direct Vent systems:
• Rooftop, two pipe, direct vent congurations, including typical clearance requirements,
are shown in Figure 8.
• The intake air pipe is not typically drained, so it must be terminated with a down-turned
elbow (see Figure 8).
• The intake pipe does not need to penetrate the roof at the same elevation as the
exhaust (as shown); lower down on the roof is acceptable.
• For roof top venting of multiple boiler sets, group all intake terminals together for a
common penetration through a custom cap. Alternatively, place in the closest proximity
achievable using commonly available pipe ashing. Similarly group the exhaust pipes
and place the two separate groups of pipes at least 3' apart (the closest intake and
exhaust pipes shall be 36", or more, apart). Use the same 12" (minimum) vertical
separation for all termination options. For alternate group terminations, contact the IBC
Factory for written guidance.
• Roof Top Concentric Termination kits are approved for use with the boiler model. The
installation of the vertical roof top concentric termination must follow the installation
instructions supplied with the venting material manufacturer. Care must be taken to
install the termination kit a minimum horizontal distance of 10’ (305cm) away from
any portion of the building and a minimum of 2’ (61cm) above the roof line plus the
anticipated snow line.
INSTALLATION
1-9

Figure 6: IBC recommended
minimum vent terminal clearance
under ventilated soft
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
Figure 8: Rooftop vent terminal congurations
Figure 7: Prohibited installation
Rooftop vent termination with
sidewall combustion air
1.4.6 Sidewall Vent Termination
a) Vent terminal clearance minimums are as follows:
• The exhaust vent terminal is to be placed 18” minimum (12” in USA) above the grade
or anticipated snow level.
• Clearance above grade, veranda, porch, deck or balcony – 12” (0.3m), but check local
code also (anticipated snow levels may supersede).
• Clearance to openable window or door – 36” (0.91m) (USA – 12”)
• Vertical clearance to ventilated soft located above the terminal - 48” (1.2m)See
Caution note in this section.
• Clearance to each side of centre line extended above meter/regulator assembly: - 3’
(0.91m) within a height of 15’ (4.6m) above the meter/regulator.
• Clearance to service regulator vent outlet: - 3’ (0.91m)
• Clearance to non-mechanical air supply inlet to building or the combustion air intake to
any other appliance: - 3’ (0.91m) (USA – 12” (0.3m))
• Clearance to a mechanical air supply inlet: - 6’ (1.82m) (USA - 3’ (0.91m) above if
within 10’ (3.1m) horizontally)
• Clearance above paved sidewalk or paved driveway located on public property: - 7’
(2.2m) Note: Cannot terminate directly above a paved sidewalk or paved driveway that
is located between two single family dwellings and serves both dwellings
• Clearance under veranda, porch, deck or balcony: - 12” (0.3m) IBC strongly
recommends a minimum of 24” with the boilers to avoid damage to the structure. Note:
Prohibited unless fully open on a minimum of two sides below the oor.
• Vents must be installed such that ue gas does not discharge towards neighbor’s
windows, or where personal injury or property damage can occur.
• It is important to ensure proper condensate management from vent terminations.
Condensate shall not be discharged in a manner that will cause damage to external
building nishes or components, or inltrate building envelopes, including adjacent
structures.
1-10
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
Figure 10: Vent terminal clearances
Figure 9: Sidewall vent termination indoor combustion air applications
CAUTION
Vent termination clearances in
this section are code minimum,
or IBC recommended minimum
requirements, and may be
inadequate for your installation.
Building envelope details must
be examined carefully, and
ingress of moisture into building
structures is to be avoided.
Serious structural damage may
occur if adequate precautions
and clearances are not allowed
for.
These precautions are to be
observed for neighboring
structures as well as for the
structure the boiler(s) are
installed in.
Figure 11: Vent terminal clearances
b) Sidewall vent termination for indoor combustion air applications shall be as follows:
• The vent shall be terminated with a tee tting as illustrated - See Figure 9.
• Bird screen of 1/4” stainless steel or plastic mesh (IPEX System 636 drain grate)
should be installed in both open ends of the tee.
INSTALLATION
1-11

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
It is extremely important to
maintain at least the minimum
separation of exhaust vent
termination from boiler intake
air as illustrated in gures 12
and 13. Failure to do so can
result in a dangerous situation
where exhaust gasses are reingested with combustion air.
Damage to the boiler can result
from a failure to maintain these
separations. Third party vent
termination kits and concentric
wall penetration kits that do
not maintain these minimum
separations shall NOT be
used. Improper installation will
void the warranty. Do not use
proprietary InnoFlue or PolyPro
PPs terminals available without
specic approval from IBC.
•
Figure 12: Sidewall vent termination
c) Sidewall Direct Vent with separate vent and air pipes shall be terminated as follows:
• Both the intake air and exhaust vent terminations shall be located on the same plane
(side) of the building.
• The exhaust vent termination is to be placed so as to reach 12” minimum above the
down-turned intake to avoid exhaust re-ingestion.
• The elevation of both terminations can be raised in “periscope style” after passing
through the wall, then congured as in Figure 12 to gain the required clearance.
• Use a 45° elbow on the exhaust termination to launch the plume up and off the sidewall
(for protection of wall).
• Bird screen of 1/4" stainless steel or plastic mesh (IPEX System 636 drain grate) is
useful to guard against foreign objects.
Figure 13: Sidewall vent termination options - multiple vent piping congurations
1-12
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
In areas of high snowfall, users
must be advised to check
side wall vent and air intake
terminations on a regular basis
to ensure blockage does not
occur.
CAUTION
Take care installing Concentric
Side Wall Termination kits.
Blockage of the combustion
air intake can occur when the
outdoor temperature drops below
5°F/-15°C.
d) Sidewall Direct Vent with Stainless Sidewall Terminal shall be terminated as follows:
• The Stainless Sidewall Terminal (SST) 3 inch IBC part number 180-149 (sold
separately included with the IBC kit P-257 ), is the only direct vent sidewall terminal
approved for use with the IBC boiler model.
• The boiler’s controller is required to be the Touchscreen type and have software
version 1.02.2 or later installed for SST to be used.
• The SST shall be installed in compliance with the minimum vent clearances listed in a)
above.
• The installation instructions included with the kit shall be carefully followed.
• The SST shall only be installed with the vent and intake pipes horizontally beside
each other or vertically with the vent pipe on top as shown in Figure 14. The vent pipe
cannot be installed below the intake. The vent cap must be installed with the openings
directed up and down, as shown in Figure 14, and not side to side.
• The SST vent/air connections t Sched. 40 three inch PVC/CPVC pipe. PPs pipe
cannot be used with the SST. The pipes must extend completely through the wall as
shown in Figure 15 and immediately inside the wall adapt up to a 4 inch pipe using
a standard reducing coupling tting. Do not use a bushing. The SST is an external
xture, and is not part of the sealed vent system that runs inside the building.
• Ensure that the vent termination location does not exceed the allowed maximum
equivalent vent length, including the allowance for the SST, dened in this document
section 1.4.3 Vent Travel and section 1.4.7 “Direct Vent” Combustion Air Intake Piping.
• Multiple vent SST installations must be installed level with one another, and maintain
at least the minimum separation distances shown in Figures 16 and 17. The Terminals
shall not be stacked vertically.
•
The two basic methods for supplying combustion air to an IBC boiler are described in
sections 1.4.7 and 1.4.8.
e) Approved PVC Side Wall Termination kits are listed below:
• Ipex # 196984 2"
• Ipex # 196985 3"
• Ipex # 196986 4"
These kits are sold separately through the manufacturer.
INSTALLATION
Ipex # 196984 2" PVC, #196985 3" PVC, and # 196986 4" PVC
1-13

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
Figure 14: Allowed SST installation orientations
Figure 15: Pipes extend completely through the wall (Vertical orientation shown).
Figure 16: Minimum separation for multiple vent installation - vertical orientation
Figure 17: Minimum separations for multiple vent installation - horizontal orientation
1-14
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
In addition to preventing
ingestion of chemical
contaminants, care must be
taken to ensure air intake
terminals are not installed in
locations where contamination
might occur due to ingestion of
particulate foreign material (dust,
dirt and debris).
WARNING
Intake air openings must be
congured such that rain or
other forms of moisture cannot
enter the air intake piping
system. Otherwise serious
damage to the boiler may result.
NOTE
Care must be taken when
installing air intake piping to
ensure that a “trap” is not formed
in the piping so as to allow a
build-up of water, and blockage
of intake air.
1.4.7 “Direct Vent” Combustion Air Intake Piping
The direct vent option uses piping from the outside to supply combustion air directly to the
boiler’s combustion air connection.
Figure 18: Direct vent combustion air intake
SL 26-260 G3
Such blockage will result in a
boiler safety shut-down.
NOTE
Combustion fan blockages
can occur when environmental
particulate and foreign matter
contaminants (leaves, dust,
dandelion & cottonwood uff,
etc) are drawn into the air intake.
In areas where this problem
is suspected to be an issue,
intake air ltration should be
considered. Contact Factory.
Filters should be checked and
cleaned or replaced on a regular
schedule based on the severity
of the problem.
INTAKE PIPE SIZE MAXIMUM EQUIVALENT LENGTH
Sched.40; Rigid PPs
3" 200' each side
90° vent elbow allow 8' equivalent
90° long sweep elbow allow 5' equivalent
45° elbow allow 3' equivalent
PPs 87-90° elbows use 8' equivalent
3" Stainless Sidewall Terminal
IBC P/N 180-149 (P-257)
Flexible PPs
3" PPs Flexible (SL 26-260
G3)
Table 4A: Maximum Intake Pipe Venting Length for SL 26-260 G3
No additional allowance required
60' max., actual lineal x 3.33 = equivalent
INSTALLATION
1-15

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
NOTE
It is not permitted to add to the
exhaust length by transfer of
unused intake allowance.
NOTE
Combustion air piping - if used - is
inserted directly into the 4” female
stainless steel tting on the top,
right side of the boiler and run
horizontally or vertically to the
outdoors. Screen material can be
placed at the inlet as appropriate for
the environment (e.g. insects, dust).
SL 40-399 G3
INTAKE PIPE SIZE MAXIMUM EQUIVALENT LENGTH
Sched.40; Rigid PPs
4" CPVC / Rigid PPs 200' (each side)
90° vent elbow allow 8' equivalent
90° long sweep elbow allow 5' equivalent
45° elbow allow 3' equivalent
PPs 87-90° elbows use 8' equivalent
3" Stainless Sidewall Terminal
IBC P/N 180-149 (P-257)
3" PVC (to adapt to SST) for each 1' allow 3.2' equivalent
Flexible PPs
4" PPs Flexible 160' max, using 1.2 x for equivalent length
Table 4B: Maximum Intake Pipe Venting Length for SL 40-399 G3
For the inlet air – 4" Schedule 40 PVC, CPVC, ABS, or PPs piping of any type is
permitted.
Care must be taken to ensure adequate separation is maintained between the air intake
inlet and the vent terminal. Refer to the vent terminal conguration drawings in the Vent
Termination section above.
Support should be provided for intake piping, particularly so for horizontal runs (follow
local code).
No additional allowance required
WARNING
When using Indoor Air options,
adequate combustion air must
be supplied to the boiler room
according to the requirements of all
applicable codes.
1.4.8 “Indoor Air” Combustion Air Intake
An “Indoor Combustion Air installation”, as described herein, is one in which air for
combustion is taken from the ambient air around the boiler.
Figure 19: Indoor combustion air intake
1-16
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
To support combustion, an ample air supply is required. This may require direct openings
in the boiler room to the outside. If the boiler is not in a room adjacent to an outside wall,
air may be ducted from outside wall openings.
Provisions for combustion and ventilation air must be made as follows:
• in the USA, in accordance with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 (latest
edition), or applicable provisions of the local building codes
• in Canada, in compliance with B149.1
1.4.9 Combustion Air Filtration
If combustion air contamination from ingested particulate matter is a concern in any
installation, an optional air intake lter may be installed.
IMPORTANT: Under no circumstances should a third-party air lter be installed on
an IBC boiler without proper evaluation and written approval of the IBC Engineering
Department.
Figure 20: Air Intake Filter
Assembly P-172
INSTALLATION
Figure 21: Combustion air intake
1.4.10 Closet Installations
For installations in a conned space (such as a closet), ventilation openings may be
needed through a door or wall to prevent excessive heat from building up inside the
space.
The boiler shall not be exposed to ambient conditions above 122°F (50°C) or below 32°F
(0°C).
1-17

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
1. Install condensate
2. Slide retainer around trap and
4. Secure trap with nut and
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
Fill trap with water before boiler
is rst red to prevent exhaust
fumes from entering room. Never
operate the boiler unless the trap
is lled with water.
Failure to comply will result in
severe personal injury or death.
trap and tube.
slide retainer tabs into cabinet.
3. Pass tube through retainer.
1.5 CONDENSATE REMOVAL
IBC’s specied vent conguration promotes the safe drainage of moisture from the boiler
and exhaust venting without owing liquids back through the heat exchanger (as done by
some other condensing boilers).
Reliable system operation requires (1) proper design and installation of exhaust venting
to allow condensate to run back to the drain/trap; (2) acid neutralization as appropriate. To
achieve these:
• Allow for a 1/4” per foot slope back to the vent connection, with appropriate hangers
to maintain that gradient.
• Ensure the supplied trap is correctly installed and lled with water.
• When required, add (and maintain in good condition) a neutralization tank.
1.5.1 Condensate Trap
The condensate trap must be installed on the drain connection at the base of the boiler as
shown in Figure 22.
1.5.2 Condensate Trap Assembly - Installation
1. Remove the boiler door and remove the condensate trap door by removing the 2 nuts
and washers, lower the front of the trap door and slide forward. Undo the Drain Spout
Compression Nut (E), remove the Drain Hose (G) from Trap Drain Outlet (F). Place
the Vacuum breaker cap (J) over the Vacuum breaker opening and push rmly home.
Remove the Upper Compression Nut and Washer (C) and slide over the Boiler Drain
Outlet (A).
2. Fill the trap with water and slide
the trap body (D) over the Boiler Drain Outlet (A) and tighten.
Attach the Drain Hose (G) and tighten the Drain Spout Compression Nut (E).
3. Install the Condensate Trap Door and tighten the 2 hex screws. Check for leaks.
washer.
Figure 22: Condensate trap installation
WARNING
The Trap Door must be installed
as instructed and all trap ttings
must be tightened as instructed
to prevent leakage of ue gasses.
Failure to comply may result in
severe personal injury or death.
1-18
Condensate Trap, as shipped and
disassembled
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

NOTE
It is the responsibility of
the installing and/or service
Contractor to advise and instruct
the end User in how to perform
the Trap cleaning procedure,
and to advise that the Trap
be checked at least every two
months and cleaned as required.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
INSTALLATION
1.5.3 Condensate Trap Assembly - cleaning procedure
1. Turn off the power to the boiler and allow it to cool down.
2. Remove the trap from the boiler (reverse the installation procedure above).
3. Remove the Trap Cleanout Assembly (H) from the Trap Body and clean and ush the
debris out.
4. Re-assemble the trap components, re-ll the trap, and replace on the boiler as
described in the installation instructions above.
1.5.4 Further installation details
• The condensate drain must be piped to within 1” of a drain or connected to a
condensate pump.
• Drainage line must slope down to the drain at a pitch of 1/4” per foot so condensate
runs towards the drain.
• Condensate traps should be checked every two months, and cleaned and relled as
necessary.
1-19

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
Figure 23: Condensate trap
disassembly for cleaning
WARNING
If condensates are to be
discharged into building drain
piping materials that are subject
to corrosion, a neutralization
package must be used.
CAUTION
When a condensate
neutralization package
is installed, the pH of the
condensate discharge must be
measured on a regular schedule
to ensure the neutralizing agent
is active and effective.
DANGER
The water in the condensate
neutralizer can cause severe
burns to the skin. Use extreme
caution when servicing the
condensate neutralizer. Wear
protective gloves and eyewear.
Figure 24 Condensate trap drainage
Figure 25: Condensate neutralization tank
1-20
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
During operation, the relief valve
may discharge large amounts
of steam and/or hot water.
Therefore, to reduce the potential
for bodily injury and property
damage, a discharge line MUST
be installed that it:
1. is connected from the
valve outlet with no intervening
valve and directed downward
to a safe point of discharge.
2. allows complete
drainage of both the valve and
the discharge line.
3. is independently
supported and securely
anchored so as to avoid
applied stress on the valve.
4. is as short and straight
as possible
5. terminates freely
to atmosphere where any
discharge will be clearly visible
and is at no risk of freezing.
6. terminates with a plain
end which is not threaded.
7. is constructed of a
material suitable for exposure
to temperatures of 375°F or
greater.
8. is, over its entire length,
of a pipe size equal to or
greater than that of the valve
outlet.
1.6 WATER PIPING
1.6.1 General Piping Issues
Primary/secondary piping, or the use of a hydraulic separator is recommended for
maximum exibility in multi-load applications, but piping loads in parallel is also
encouraged in systems that only have two loads, or when loads are operating
simultaneously. The extremely low pressure drop through the SL Series heat exchanger
allows many options not available in other designs. In short – IBC has built a boiler that
will allow you to pipe the system the way you prefer, rather than try and dictate your piping
practices from boiler to radiator.
SL 26-260 G3
These boilers are designed for use within a closed loop, forced circulation, low pressure
system. A 30 psi pressure relief valve (3/4” NPT) is supplied for eld installation at one
of the locations shown in the following illustrations. Relief valve discharge piping must
terminate between 6” (15cm) and 12” (30cm) above the oor or per local Code.
SL 40-399 G3
These boilers are designed for use within a closed loop, forced circulation, low pressure
system. A 30 psi pressure relief valve (3/4" NPT) is supplied for eld installation in the
relief valve tting on top of the boiler. An optional 75 Psig relief valve can be used where
required on closed loop systems within multi-level buildings. Relief valve discharge piping
must terminate between 6" (15cm) and 12” (30cm) above the oor or per local Code.
DO NOT CAP, PLUG OR OTHERWISE
OBSTRUCT THE DISCHARGE PIPE
OUTLET!
CAUTION
Installers should inquire of
local water purveyors as to the
suitability of their supply for use
in hydronic heating systems.
If water quality is questionable,
a local water treatment expert
must be consulted for testing,
assessment and, if required,
treatment.
Alternatively, water or hydronic
uid of known quality can be
brought to the site.
INSTALLATION
Figure 26: Boiler trim options - Single boiler
System piping is connected to the boiler using the 1 1/2" NPT-M threaded ttings.
Unions and gate or ball valves at the boilers supply and return water connections are
recommended to simplify servicing. Un-insulated hot water pipes must be installed with a
minimum 1/4" clearance from combustible materials.
1-21

WARNING
Close ll valve after any addition
of water to the system, to reduce
risk of water escapement.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
Fluid ll is most often accomplished by using a boiler regulator & ll valve set at 12 psig
or more, with the appropriate backow prevention device as required by local code. This
is acceptable in areas where municipal water or well water has been treated and ltered
to remove excessive minerals and sediment, and water chemistry is known to be suitable
for closed loop hydronic systems. In areas where water quality is in question, or when
chemical treatment or glycol is required, other options should be considered. Follow the
applicable codes and good piping practice.
There are a number of boiler feed and pressurization devices on the market today that
may be a better choice than a raw water ll from the mains. When regular maintenance
requires relief valve blow-off, the discharge may be directed back into the pressurization
unit for recycling of boiler uid and chemicals back into the system. In buildings that may
be unoccupied for long periods of time, pressurization units are useful to prevent ood
damage should leakage occur from any component in the system. An additional benet is
that backow prevention devices are not required when using these devices.
Do not place any water connections above the boiler; leaks can damage the fan and
controls. If needed, create a shield over the top of the cover, but allow clearance for airow
and service access.
For best results, use a Primary/Secondary piping system, with a pumped boiler loop using
2" piping. Refer to Tables 5A and 5B for boiler head loss information.
Supply stack upper tapping - 3/4”
FIP to accept relief valve and air
vent assembly
Relief valve and air vent assembly
(recommended conguration)
For example, the minimum ow rate required through the heat exchanger is 20 gpm and
a maximum of 45 gpm is allowed. Primary/Secondary piping ensures adequate ow and
de-couples Δ°T issues (boiler vs. distribution). Aim for a 20° to 30° F Δ°T across the heat
exchanger at high re (there is a boiler protection throttle fence limiting the Δ°T to 40°F).
NOTE
Full sized application drawings
can be downloaded from our web
site.
Figure 27: Primary/Secondary piping concept with hydraulic separator
The boilers can supply multiple heating loads with compatible supply temperature
requirements. Always ensure that loads sensitive to high temperatures are protected using
means such as mixing valves.
www.ibcboiler.com
1-22
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
WARNING
Water quality has a signicant
impact on the lifetime and
performance of an IBC Boiler
heat exchanger.
Improperly prepared water in
a heating circuit may cause
damage to the heat exchanger
through corrosion or fouling.
Repeated or uncontrolled water
lls will increase the potential
for damage.
High levels of dissolved solids
or minerals may precipitate
out of the uid onto the hottest
part of the heat exchanger,
impairing heat transfer and
resulting in overheating and
premature failure. The amount
of solids that may form on the
heat exchanger will depend
on the degree of hardness and
the total water volume in the
system. A high water volume
system with a low hardness
count may cause as much
damage as a system with less
volume and higher hardness, so
it is recommended to treat water
so as to remove all dissolved
solids. Other water chemistry
allowable limits are as follows:
Acidity pH is to be between 6.6
and 8.5
Chloride is to be less than 125
mg/l
Iron is to be less than 0.3 mg/l
Cu less than 0.1 mg/l
Conductivity is to be less than
400μS/cm (at 77°F (25°C))
Hardness is to be 7 Grains or
less
IMPORTANT: Ensure that these
limits are acceptable for the
other water-side components in
the system.
BOILER HEAD LOSS
BOILER HEAD LOSS SL 26-260 G3
Flow rate (gpm) 6 10 15 20 25
Head @ ow (ft wc) 2’ 3.5’ 5.5’ 8’ 13’
Table 5A: Boiler Head Loss
BOILER HEAD LOSS - SL 40-399 G3
Flow rate (gpm) 20 25 30 35 40 45
Head @ ow (ft wc) 1 1.5 2 3 4 6
Table 5B: Boiler Head Loss
Ensure that the pump is rated for the design circulating water temperatures; some pumps
have a minimum water temperature rating above the low temperature potential of the
boiler. Following installation, conrm the actual performance by measuring Δ°T (under high
and low ow conditions) after establishing the correct ring rate.
We require water ow after burner shutdown to utilize legacy heat – this is signicant
due to the mass of the heat exchanger plus its internal water volume. Default software
values will run the boiler’s primary pump for up to 5 minutes (300 seconds) after burner
shutdown. Secondary pumps can be set to run up to 15 minutes after burner shutdown
(for the last calling load). As shipped, the default software will run the Load 1 pump for 5
minutes to place the legacy heat where it is useful. Any secondary pump can be set to run
for 0 – 900 seconds in the heat purge mode. Guard against deadheading pumps when all
zone valves are closed (see Section 2.7 Set Up & Load Denition).
The primary pump must be under the control of the boiler to allow pump purge after burner
shut-down.
Schematics for several piping layouts are provided, and additional drawings are
available at www.ibcboiler.com. Installers shall conform the piping design to one of the
provided congurations to simplify the control application, promote good loads and ow
management.
Propylene glycol solution is commonly used in a closed loop where freeze protection is
required. Its density is lower than that of water, resulting in lower thermal performance at a
given ow and pressure. As a rule of thumb, a 50%:50% solution of propylene glycol and
water will require an increased system circulation rate (gpm up 10%), and system head
(up 20%) to provide performance equivalent to straight water.
INSTALLATION
1-23

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
WARNING
Do not use automotive-type
ethylene or other types of
automotive glycol antifreeze,
or undiluted antifreeze of
any kind. This may result in
severe boiler damage. It is the
responsibility of the Installer to
ensure that glycol solutions are
formulated to inhibit corrosion
in hydronic heating systems
of mixed materials. Improper
mixtures and chemical additives
may cause damage to ferrous
and non-ferrous components
as well as non-metallic, wetted
components, normally found
in hydronic systems. Ethylene
glycol is toxic, and may be
prohibited for use by codes
applicable to your installation
location. For environmental
and toxicity reasons, IBC
recommends only using nontoxic propylene glycol.
1.6.2 Installation Rules
If the installation involves small loads, as in typical zoned baseboard heating applications,
use of a buffer tank is recommended. To aid in temperature transition from hot to cool
loads, a 3-way mixing valve can be placed at the entrance to the cool load (this will also
provide oor protection). This will permit immediate circulation of mixed ow into the cool
loop.
NOTE
The boiler, when used in
connection with a refrigeration
system, must be installed so
the chilled medium is piped
in parallel with the boiler with
appropriate valves to prevent the
chilled medium from entering the
boiler.
NOTE
The boiler piping system of a hot
water boiler connected to heating
coils located in air handling units
where they may be exposed to
refrigerated air circulation must
be equipped with ow control
valves or other automatic means
to prevent gravity circulation
of the boiler water during the
cooling cycle.
Figure 28: Primary/Secondary piping concept with simultaneous setpoint calls. Always
ensure that loads sensitive to high temperatures (e.g. radiant oor) are protected using
appropriate means such as a manual mixing valve, or an aquastat (set to130°F, for
example) wired to the boiler’s auxiliary interlocks.
Figure 29: Two pump, two load - parallel piping concept
1-24
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
Compared with the Primary/Secondary approach, the above design saves one pump. Lost
is the simplicity of constant head and ow at the boiler.
Check valves or thermal traps should be used to isolate both the supply and return piping
for each load - to avoid thermal siphoning and reverse ow.
To ensure adequate water ow through the boiler under high-head / single zone space
heating conditions, a pressure activated bypass or other means of bypass must be used
on any load where the ow rate might drop below minimum requirements (20 gpm).
For further information and details, consult our Application Notes – which provide detail on
specic single and multiple boiler applications “Piping”, “Wiring” and “Settings”. (available
at www.ibcboiler.com or from your IBC Representative).
INSTALLATION
1-25

NOTE
The piping drawings in this
manual are simple schematic
guides to a successful
installation. There are many
necessary components not
shown, and details such as
thermal traps are left out so the
drawings have greater clarity.
We require that our boilers
be installed by licensed and
experienced trades people who
are familiar with the applicable
local and national codes. System
design is to be completed by an
experienced hydronic designer
or Engineer. It is necessary to
carefully read and follow these
installation instructions along with
the application drawing that ts
your system.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
1-26
Figure 30: Trim for multiple boiler installations
Figure 31: Mulit-Plex Racking System
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

NOTE
When using the sequential
load feature of the IBC boiler,
attention must be paid to the
operation of system components
in order to ensure they are
compatible.
Many air handlers (fan coils)
for instance have a thermostat
connection that will energize an
internal relay to operate the air
handler circulator and its fan on
a call for heat. This may result in
operation of these components
when other loads are running at
a higher priority, resulting in cold
air blowing, or robbing heat from
another load.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
Some wiring alteration may
be required to divorce both of
these functions from thermostat
control in favour of more
effective control from the IBC
boiler.
NOTE
For further information and
details regarding Multiple
Boiler application, consult our
Technical Notes - Multiple Boiler
Systems. These notes provide
necessary detail on specic
single and multiple boiler
applications “Piping”, “Wiring”
and “Settings”. (available at
www.ibcboiler.com or from your
IBC Representative).
Figure 32: Multiple boiler piping
Figure 33: Jumper
INSTALLATION
Figure 34: Multiple boiler inter-wiring
1-27

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
NOTE
Due to the precision of modern
modulating boilers it is important
to pay special attention to gas
pressure regulation.
It is essential to check gas
supply pressure to each boiler
with a manometer or other high-
quality precision measuring
device. Pressure should be
monitored before ring the
boiler, when the regulator is
in a “lock-up” condition and
during operation, throughout the
boiler’s full modulation range.
Pay special attention to retrot
situations where existing
regulators may have an oversized orice and/or worn seats,
causing pressure “creep” and
high lock up pressures.
A high quality regulator will
maintain constant pressure
above the boiler’s minimum
specication at all ring rates,
and will not exceed the boiler’s
maximum pressure rating when
locked-up with no load.
1.7 GAS PIPING
The boilers require an inlet gas supply pressure of at least 4.0" w.c. for natural gas or
propane during high re operation. This will ensure that gas pressure measured at the gas
valve inlet pressure tap does not droop below 3.5" w.c. at high re. For either fuel, the inlet
pressure shall be no greater than 14.0" w.c. Conrm this pressure range is available with
your local gas supplier.
The inlet gas connection to the boiler is 3/4" NPT (female).
Adequate gas supply piping shall be provided with no smaller than 3/4" Sched 40 (e.g.
Iron Pipe Size (IPS)) and using a 1" w.c. pressure drop, in accordance with the following
chart:
MODEL
SL 26-260 G3 (Natural Gas) 20' 80' 300' 600'
SL 26-260 G3 (Propane) 70' 200' 800' 1600'
SL 40-399 G3 (Natural Gas) 10' 40' 150' 300'
SL 40-399 G3 (Propane) 30' 100' 400' 900'
Table 6: Maximum Pipe Length (ft)
Gas piping must have a sediment trap ahead of the boiler’s gas valve (see Figure 34). A
manual shutoff valve must be located outside the boiler, in accordance with local codes/
standards. All threaded joints in gas piping should be made with an approved piping
compound resistant to the action of natural gas/propane. Use proper hangers to support
gas supply piping as per applicable codes.
The boiler must be disconnected or otherwise isolated from the gas supply during any
pressure testing of the system at test pressures in excess of 1/2 psig. Dissipate test
pressure prior to reconnecting. The boiler and its gas piping shall be leak tested before
being placed into operation.
3/4"
IPS
1" IPS 1 1/4" IPS 1 1/2" IPS
The gas valve is provided with pressure taps to measure gas pressure upstream (supply
pressure) and downstream (manifold pressure) of the gas valve (see Figures 35A and
35B). Note that manifold pressure varies slightly in accordance with ring rates with the
modulating series boilers, but will always be close to 0” w.
Figure 35: Typical gas piping
1-28
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

Line voltage leads for power supply,
primary pump and VS output
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
1.8 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
All electrical wiring to the boiler (including grounding) must conform to local electrical
codes and/or to the National Electrical Code, ANS/NFPA No. 70 – latest edition, or to the
Canadian Electrical Code, C22.1 - Part 1.
1.8.1 120 VAC Line Voltage Hook-up
Line-voltage wiring is done within the eld-wiring box. (Refer to Section 6.2.Wiring
Diagram on page 6-4). Connect the boiler to the grid power using a separate, fused circuit
and on/off switch within sight of the boiler. Use 14-gauge wire in BX cable or conduit
properly anchored to the boiler case for mains supply and pump circuits.
Connect a 120 VAC / 15 amp supply to the “AC IN” tagged leads in the wiring box. The
max. actual draw (with 5 typical residential size pumps) is less than 4 amps.
The 120 VAC power supply to the load pumps (P/V1, P/V2, P/V3, and P/V4) has been
factory installed and connected to P/V-L and P/V-N for your convenience. If you use the
P/V relay connections for zone valves, then the 120 VAC connections at P/V-L and P/V-N
will have to be removed and properly capped off. 24 VAC can then be applied using an
external transformer to supply power to zone valves. The upper 4 pairs of contacts on this
green connector strip are then powered to manage up to 4 load pumps – the top pair for
Load 1, the second pair for #2 etc. Once the controller is programmed for the respective
loads, the boiler manages all the loads without need of further relays (for loads up to 1/3
HP; for more – use a protective relay).
Line voltage load pump terminals
CAUTION
The internal pump relays are
protected with 5 Amp fuses. The
maximum recommended load
on each fuse is 4 Amps (80% of
rating). The maximum combined
pump load is 10 Amps. Isolation
relays or contactors MUST be
used if the loads exceed these
maximums.
The boiler (primary) pump is connected to the White/Yellow pair labeled Primary Pump.
This lead is factory wired to the controller (and its 120 VAC supply) at the upper right
backside of the controller board. Do not attempt to connect the primary pump to the Pump/
Zone Valve Terminal Block along the controller’s right edge. This is for the secondary
pumps and/or zone valves only. Connect the pump’s Black wire to the Yellow of this
pair (switched Hot). The White/ Yellow pair should be individually capped if the primary
pump does not obtain its power from this pair (e.g. if a variable speed primary pump is
connected to the mains power).
Pumps can be switched on/off using the touchscreen controller, so there is no need for
temporary pump wiring during system lling / air purging. If pumps are hard-wired to the
panel during the system ll/purge phase, re-wire the boiler pump to the primary pump
leads inside the wiring box so the primary pump purge function is active.
In a new construction application, use a construction thermostat, or jumper with an in-line
on/off switch – for on/off management of the boiler. Do not just pull power from the unit,
or its moisture management routine will be interrupted (fan turns at ultra low rpm for 90
minutes after burner shutdown). Treat it like a computer, where you do not just pull the
plug when done. If a “low airow / check vent” error signal shows, check for (and remove)
any water in the clear vinyl air reference tubes. This has been seen occasionally at
construction sites where the boiler has been repeatedly de-powered wet.
The combined current of all pumps connected through the on-board pump relays
should not exceed 10 amps. The control circuit board is protected using on-board eld
replaceable fuses. Each pump is fused with a separate 5 Amp fuse. The Alarm contact is
fused with a 5 Amp fuse and the 24 VAC boiler control circuit is protected with a 2 Amp
fuse.
INSTALLATION
1-29

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
NOTE
The IBC boiler (like any modern
appliance that contains
electronic equipment), must have
a “clean” power supply, and is
susceptible to power surges
and spikes, lightning strikes and
other forms of severe electrical
“noise”. Power conditioning
equipment (surge protectors,
APC or UPS devices) may be
required in areas where power
quality is suspect.
1.8.2 Power Quality and Electrical Protection
In areas of unreliable power, appropriate surge protectors and or power conditioning
equipment should be installed in powers supply wiring circuits.
1.8.3 Zone Valve Hook-up
If zone valves rather than pumps are used to manage multiple heating loads, then 24
VAC for the zone valves should be provided to the power contacts on the Pump/ Zone
Valve Terminal Block. Disconnect the 120 VAC leads connected to PV-L/PV-N and cap off.
Use a separate transformer – the 40 VA unit inside the wiring box is for internal systems
only. The individual load/zone valves are then to be wired to their associated contacts on
the secondary pump/zone valve connector. Do not confuse such “load/zone valves” with
similar valves used to segregate a single load type (e.g. those used on a zoned radiant
oor) – see next section.
1.8.4 Thermostat / Sensor Wiring
Dry contacts for thermostats for each of the four loads are provided as marked on the
lower connector strip (e.g. “Therm 1”). Gang lines from a multiple-zoned load (e.g. off
the end-switches for each radiant oor zone) present a common thermostat signal to the
controller. Ensure that there are no disturbing inuences on the call-for-heat lines - e.g.,
that no coils to switch an air handler motor. Most power stealing thermostats can be
connected directly to the Therm terminals.
manual for
more detailed instructions.
See the
V-10 Touchscreen Boiler Controller
DANGER
Do not connect thermistor
sensors to “Therm” terminals.
An overheating hazard can result
in serious personal injury and/or
property damage. See Controller
Manual section 2.1.1 for detailed
instructions.
NOTE
The IBC Touch-Screen controller
has the ability to connect to most
power stealing thermostats. See
the V-10 Touchscreen Boiler
Controller manual for details.
1.8.5 Other Wiring
Other optional low voltage connections to the control board include:
• Two auxiliary interlocks - for external safety devices as may be required by some
jurisdictions, such as a low water cutoff or a low gas pressure cut-out (for off-grid
propane). A oor-protecting aquastat (water temperature control) can use one of these,
to cause a full boiler shutdown in the case of excess oor temperature.
• Contacts for indoor and outdoor temperatures sensors associated with reset heating.
A 10K ohm thermister (resistor dependent on temperature) for outdoor reset sensing is
supplied with the boiler for improved comfort and combustion efciency.
• One pair for a DHW tank sensor. Connect to “DHW S” (not the respective Therm.
1,2,3,4 location) and the boiler automatically detects and calls a smart DHW routine.
• One pair of contacts for remote secondary loop temperature control.
• One pair (marked BoilerNet) for network connection – this is used for connecting
multiple SL and/or VFC modulating units for autonomous staging.
• The bottom pair of contacts receives a 0-10VDC (default) or 4-20 mA signal from an
external boiler controller for direct throttle control. The boiler’s own sensors act as high
limits only. The user must enter maximum and minimum boiler supply temperatures.
NOTE: Sensors connected to any sensor input contacts must be of the NTC Thermister
type with a resistance of 10,000 ohms at 77°F (25°C) and β = 3892. We do not
recommend using 3rd party supplied sensors. Compatible water temperature sensors and
outdoor sensors can be supplied by your IBC distributor.
1-30
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
1.8.6 Thermostat Heat Anticipator
IBC “Therm.” contacts draw no power, so an anticipator setting for the thermostat is not
applicable with the SL modulating series boilers. In the case of a single temperature / heat
load where zone valves are used to manage individual thermostatically controlled zones,
each room thermostat’s heat anticipator should be adjusted to the current draw of its
associated zone valve.
BOILER SYSTEMS AND OPERATION
Figure 36 : Electric wiring connections (full-page wiring diagram on the back of this manual}
1-31

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
1-32
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
2.0 IBC BOILER CONTROLLER
2.1 GENERAL
This boiler is equipped with the V-10 Touchscreen controller. The controller simplies the
programming of the boiler while providing greater exibility. For more detailed instructions,
reference the Touchscreen Boiler Controller manual.
The controller is equipped to provide:
• Control of up to 5 pumps – 1 boiler pump + 4 separate load pumps
• Outdoor Reset control
• Set Point temperature regulation
• Domestic Hot Water (DHW)
• External control via 0-10VDC or 4-20mA signaling
• Alarm dry contacts
• Load Combining – simultaneous operation of 2 similar water temperature loads
• The control can manage and/or operate in a network of up to 24 IBC VFC or SL boilers
Some of the new features available in the touchscreen control include:
NOTE
No sharp or metallic object
should be used on the
touchscreen as this will cause
damage. Use only a Stylus or a
clean nger.”
• Express Setup Menu for simple, quick programming
• Software updatable in the eld with an SD card or a USB stick
• Setup conguration back-up and cloning using an SD card or USB stick
• Superior warning messages while setting up the control
• Advanced Error messages with visual display on the Home Screen
• Internet/LAN connectivity
• BACnet (with activation)
2.2 CONTROL
When the boiler is rst energized, the controller will go through a power up sequence that
will take approximately 90 seconds. During this time the controller is completing a selfdiagnostic and loading all previous settings. In the event of a power interruption the boiler
will automatically resume operation when power is restored with all the previously stored
values. The controller provides overall management of the boiler operations including:
• Power-up, Self-diagnostics, easy Load parameter adjustments
• Burner operation, safety management systems, Call for Heat management and Load
Priority
• Real time boiler data
• Temperature and throttle operation
• Maintenance of operational and error service logs
• 2-way communication between other IBC boilers and controls
Operational and historical data may be accessed at any time using the System Status
and Load Proles sections of the control. Error logs are available in the Diagnostics
section and the controller is capable of recording any or all errors since original power-up
complete with the date and time of the error.
BOILER SYSTEMS AND OPERATION
2-1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
2.3 CONTROL INTERFACE
The control interface is provided through a 2-1/4 x 4 inch, color touchscreen display. The
touchscreen responds to a light nger touch on the screen. You can also use a stylus or
similar device to operate the touch controls. Do not use a sharp or metallic object such as
a screw driver to operate the control as it could damage the touchscreen.
The controller display is divided into two areas, the screen active area and the boiler
status bar. All screens have an active area consisting of the screen title bar at the top and
a border surrounding the active area. At the bottom of the display there is space reserved
for the boiler status bar.
Prior to any interaction with the touchscreen, the display shows the Home screen details
of the current boiler status. If the controller has been left on the Home screen long enough
(user adjustable, 10 minutes by default) the display will be dimmed to save power.
The control will automatically return to the home screen if left unattended. The screens will
step back one screen at a time in 10 minute increments if the touchscreen has not been
touched. The pop-up windows will also step back automatically in 2 minute intervals.
The boiler status bar indicates if the boiler is in a normal, warning or alarm state. When
no warning or alarm state is present, the bar will be green and the time will be displayed
inside the green area. The bar can also be yellow or red corresponding a warning or alarm
state. Text inside the bar will indicate the specic warning or alarm present. If more than
one alarm is present the text display will slowly change, rotating though whatever alarms
that are present.
2-2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
3.0 STARTUP & COMMISSIONING
3.1 BOILER SHUTDOWN & LIGHTING
STARTUP AND COMMISSIONING
3-1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
WARNING
Fill trap with water before boiler is
rst red to prevent exhaust fumes
from entering room. Never operate
the boiler unless the trap is lled
with water. Failure to comply will
result in severe personal injury or
death.
3.2 PRIOR TO START-UP
3.2.1 Pre-Ignition Checks
1. Ensure venting system is complete and seal tested. Conrm any common venting
system at the installation site is isolated and independent of the SL boiler. Also
conrm that any holes left from the removal of a previous boiler have been sealed,
and that any resizing of the old ue has been done. Fill condensation trap.
2. Check that the water piping system is fully ushed and charged, and that all air has
been discharged through loosened bleed caps. Note it is possible to switch all pumps
on/off from the touchscreen – without a call for heat. This greatly simplies system
lling and air bleeding (go to Installer Setup, System Settings, Site Settings, change
Manual Pump Purge to “ON”. When complete, return to Off, or this will automatically
occur with a call for heat). Use a minimum water pressure of 12 psig. And conrm that
the pressure relief valve is installed and safely drained.
3. Check to see that adequate gas pressure is present at the inlet gas supply test port.
Open the test port by turning its center-screw one full turn counterclockwise, using a
small (1/8” or 3 mm) at screwdriver.. Connect a manometer and open the gas control
valve. Requirements are minimum 5” w.c and maximum 14” w.c. Check that there are
no gas leaks.
4. Perform a nal check of electrical wiring, and provide power to the boiler to initialize
operation.
Error displayed after testing ignition
safety shut off
3.2.2 Test Ignition Safety Shutoff
With the boiler in operation, test the ignition system safety shutoff device by shutting the
gas control valve immediately outside the boiler case. Ensure the boiler has shut off and
the appropriate Error information is displayed on the Touchscreen. To restart the boiler,
reset power or press “Clear Errors” in the Advanced Diagnostics section.
3.3 COMMISSIONING
The SL boilers are factory calibrated to operate with natural gas (or propane if so ordered)
at sea level. The Low Fire (Zero Offset) valve adjustment cap has been factory sealed
using paint-seal compound. This cap must not be tampered with. The Low
Fire (Zero Offset) screw is not to be adjusted in the eld. The High Fire
(Gas:Air ratio) adjustment screw may have to be adjusted to attain optimum combustion
results if required, however, no mixture adjustment shall be performed unless done by
a qualied technician using properly functioning and calibrated combustion analyzing
equipment.
The controller will automatically detect the installation's altitude and make the appropriate
adjustments to operate the boiler up to 12,000 feet in elevation without de-ration. The
boiler will automatically de-rate at altitudes above 12,000 feet. Refer to the IBC Altitude
tables for further information.
3-2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
DANGER
Making adjustments to the IBC
gas valve without a properly
calibrated gas combustion
analyzer and by persons who
are not trained and experienced
in its use is forbidden. Failure to
use an analyzer can result in an
immediate hazard.
1. Turn off the gas supply. With a small (1/8” or 3 mm) at screwdriver, open the inlet gas
supply pressure test port by turning its center-screw one full turn counterclockwise.
Attach a manometer to the pressure test port, and turn on the gas to the appliance.
The static manometer reading should be ideally 7” w.c. for Natural Gas and 11” w.c. for
Propane. Minimum and maximum static pressure should be between 4” and 14” w.c.
Monitor pressure throughout the commissioning procedure. Pressure may drop up to 1”
to 2” w.c. at high re but under no circumstances should it drop below 4” w.c. at the gas
valve inlet test port.
2. Allow the boiler to ignite. Run against a large load, to maintain high re.
3. With a combustion analyzer probe in the ue gas test port, turn the High Fire (Gas:Air
Ratio) Adjustment screw (see Figure 37A and Figure 37B) (see Table 7 below for the
corresponding CO
values - set the CO2 target at high re). This screw offers very ne
2
adjustment, and may require several turns.
NOTE: This screw has signicant backlash. When changing direction of turn, it may
take up to a full turn before any change is indicated on the analyzer reading. Clock
the gas meter to conrm full maximum rating plate input.
4. Conrm the minimum re level settings. Re-dene the load as “Manual Control”.
Use Heat Output in “Congure Load x” to control the output as needed. The reading
should be within the Low re range. Re-test at high re.
5. Turn boiler off by removing the call for heat (use the Installer Setup screen to
turn load to off if no other ready means available). Turn off gas then remove the
manometer connections, and turn the centre-screw in the manifold pressure test port
clockwise until fully closed. Ensure fully closed, but not over-tightened. Restore gas
and soap test for leaks.
MODEL C
RANGE TARGET RANGE TARGET
Natural Gas
Propane
Note: Low Fire CO
should be at least 0.5% lower than High Fire CO
2
9.0 – 10.0 9.5 8.2 – 9.2 8.7 < 150
10.3 – 11.3 10.8 9.3 – 10.3 9.8 < 250
Table 7: Combustion test target ranges - CO
HIGH FIRE LOW FIRE
2
/ Maximum CO
2
CO MAX
PPM
STARTUP AND COMMISSIONING
3-3

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
3.3.1 Gas Valve and Fan Diagrams
Figure 37A: Gas Valve and Pressure Reference System - SL 26-260 G3
Figure 37B: Gas Valve and Pressure Reference System - SL 40-399 G3
3-4
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
WARNING
Check the rating plate of the
boiler to ensure it is congured
for the fuel you are using. If
the fuel is incorrect for the
appliance, a conversion kit must
be ordered from IBC and the
gas valve adjusted accordingly.
Failure to perform the required
fuel conversion can result in an
immediate hazard.
DANGER
Operating any IBC boiler using
a fuel other than the fuel listed
on its rating plate is prohibited.
If the information in this section
related to conversion to
alternate fuels is not followed
exactly, a dangerous situation
can result, leading to re or
explosion, which may cause
property damage, personal
injury, or loss of life.
3.4 FUEL CONVERSION
The SL boilers are factory re-tested to operate with natural gas or propane as ordered.
The rating plate will be marked to indicate which fuel the particular boiler has been set
up with. Firing a boiler with a fuel other than what is listed on the rating plate is prohibited
unless the following conversion procedure is completed by a qualied technician.
Refer to the previous section 3.3 - COMMISSIONING. The Low Fire (Zero offset) valve
adjustment cap on the gas valve has been factory sealed using paint-seal compound. This
cap must not be tampered with. The Low Fire (Zero offset) screw is not to be adjusted in
the eld.
The High Fire (Gas:Air ratio) adjustment screw will have to be adjusted to attain optimum
combustion results whenever fuel conversion is undertaken, however, no mixture
adjustment shall be performed unless done by a qualied technician using properly
functioning and calibrated combustion analyzing equipment.
Fuel conversions must be carried out by a qualied technician:
1. Ensure you are installing the correct fuel conversion kit for your boiler. Compare the
boiler model number with the Kit # found in Table 8.
2. Read the fuel conversion instructions supplied with the fuel conversion kit.
3. Carefully follow the procedures of the fuel conversion instructions on:
• Fuel Conversion
• Combustion Testing and Adjustment
• Placing conversion labels associated with the new fuel onto the boiler.
4. Carefully follow the “Prior to Start-Up” – Section 3.2 and “Commissioning” – Section
3.3 procedures on the preceding pages 3-2 and 3-3.
Fuel Conversion Kit Part Numbers
MODEL NUMBER
SL 26-260 G3
SL 40-399 G3
Table 8: Fuel Conversion Kits
NATURAL GAS
TO PROPANE
P-300 P-301
P-302 P-303
PROPANE TO
NATURAL GAS
STARTUP AND COMMISSIONING
3-5

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
NOTE
The safety warning regarding
burner refractory on page 4-2 of
this manual must be observed.
Heat Exchanger Lid removed
Refractory removed
3.4.1 Gaining access to combustion chamber and
burner removal instructions
SL 26-260 G3
1. Remove the fan and gas valve assembly. See “Fan and gas valve removal
instructions” on page 4-6 of this manual.
2. Disconnect the igniter cable, gas valve cable and the two fan plugs, and move them
out of the way.
3. Remove the two screws that secure the igniter to the lid using a # 2 Phillips
screwdriver.
4. Carefully remove the igniter by sliding it straight up.
5. Remove the igniter gasket, and place the parts on a clean dry area.
6. Remove the 8 hex nuts that attach the heat exchanger lid to the heat exchanger with
a 10 mm open-end wrench or socket.
7. With a permanent marker or equivalent, make an alignment mark between the lid,
gasket, and heat exchanger.
8. Before removing the lid, it is important to be positioned directly above it to ensure a
straight-up extraction. Failing to do this may result in refractory damage.
9. Slowly lift the lid-burner assembly off the heat exchanger. The refractory should
remain in place in the combustion chamber shoulder. Note that there is less than
1/8” (3 mm) clearance between the burner walls and the refractory. Care must
be observed to ensure minimal contact between these parts to prevent refractory
cracking.
10. Place the lid with the burner attached, on a clean dry area.
11. With a permanent marker or equivalent, make an alignment mark on the refractory,
lining it up with the same mark made earlier between the lid and heat exchanger.
12. Carefully remove the refractory, and place it in a clean dry area.
13. If the burner needs to be removed, gradually loosen the ve screws that secure the
burner to the heat exchanger lid with a # 2 Phillips screwdriver. Then remove the
screws and the burner.
Burner and Heat Exchanger Lid
3-6
SL 40-399 G3
1. Remove the fan and the gas valve assembly. See “Fan and gas valve removal
instructions” on page 4-6 of this manual.
2. Disconnect the igniter cable, and move it out of the way.
3. Remove the two screws that secure the igniter to the lid with a # 2 Phillips
screwdriver.
4. Carefully remove the igniter by sliding it straight up.
5. Remove the igniter gasket, and place the parts on a clean dry area.
6. Loosen the lid fasteners located around the top edge of the heat exchanger, and
swing the bolts off the lid and let them hang down.
7. With a permanent marker or equivalent, make an alignment mark between the lid and
heat exchanger.
8. Before removing the lid, it is important to be positioned directly above it to ensure a
straight-up extraction. Failing to do this may result in refractory damage.
9. Carefully lift the lid-burner assembly straight up and out of the heat exchanger, being
careful not to damage the refractory.
10. Place the lid with the burner attached, on a clean dry area.
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
11. With a permanent marker or equivalent, make an alignment mark on the refractory,
lining it up with the same mark made earlier between the lid and heat exchanger.
12. Carefully remove the refractory, and place in a clean dry area.
13. If the burner needs to be removed, gradually loosen the screws that secure the burner
to the heat exchanger lid with an M5 hex screwdriver. Then, remove the screws and
the burner.
Re-assembly
SL 26-260 G3
1. Inspect the burner gasket: look for cracks, deterioration or signs of gas bypass.
Replace if necessary.
2. Place the heat exchanger lid on a at surface, and position the gasket on the lid,
aligning it with the screw holes.
3. Install the burner in place with its four screws, tightening the screws gradually and in a
cross sequence. Do not over tighten;
good seal and to prevent deformation of the burner ange.
4. Inspect the refractory for cracks, degradation and atness. If in doubt, replace with a
new one.
5. If installing a new refractory, rst place it onto the lid, aligning it at the igniter hole,
then make an alignment mark on the refractory to correspond with the previously
made line on the lid.
6. Carefully insert the refractory into the heat exchanger combustion chamber, using the
alignment marks for proper positioning.
7. Ensure that the lid gasket is in good condition, and is in place and level.
8. Carefully insert the lid-burner assembly straight down. Ensure that there is limited
contact between the burner and the refractory as well as observe the alignment
markings.
9. Install the 8 hex nuts to secure the lid in place; tighten by hand plus an extra 1/2 to 1
turn. Caution! Over-tightening these nuts will cause the lid to warp and possibly leak
fumes or ames.
10. Re-install the igniter, tightening its screws by hand plus an extra 1/8 of a turn.
11. Re-attach the igniter wire to the igniter, gas valve cable and the two fan plugs.
tighten by hand
plus an 1/8 of a turn to maintain a
MAINTENANCE
SL 40-399 G3
1. Inspect the burner gasket: look for cracks, deterioration or signs of gas bypass.
Replace if necessary.
2. Place the heat exchanger lid on a at surface and position the gasket on the lid,
aligning it with the screw holes.
3. Install the burner in place with its screws, tightening the screws gradually and in a cross
sequence. Do not over tighten;
tighten by hand
plus a 1/2 turn to maintain a good seal
and prevent deformation of the burner ange.
4. Inspect the refractory for cracks, degradation and atness. If in doubt, replace with a
new one.
5. If installing a new refractory, rst place it onto the lid, aligning it at the igniter hole,
then make an alignment mark on the refractory to correspond with the previously
made marking on the lid.
6. Carefully insert the refractory onto the heat exchanger combustion chamber, using
the alignment marks for proper positioning.
3-7

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
7. Ensure that the lid (orange) gasket is in place and level.
8. Carefully insert the lid-burner assembly straight down. Ensure that there is limited
contact between the burner and refractory, and observe the alignment markings.
9. Swing up the lid fasteners, ensuring the nuts and the washers are above the
lid. Evenly tighten the nuts in a cross pattern, and ensure that the lid is securely
tightened. Test for leaks around the gasket seal to ensure there are no ue gas leaks.
10. Re-install the igniter, tightening its screws by hand plus an extra 1/2 a turn.
11. Re-attach the igniter wire to the igniter.
3-8
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
4.0 MAINTENANCE
4.1 BOILER MAINTENANCE
4.1.1 General Care
CAUTION
The owner is responsible for
general care of the boiler.
Improper maintenance of the
boiler may result in a hazardous
condition.
CAUTION
Label all wires prior to
disconnection when servicing
controls. Wiring errors can
cause improper and dangerous
operation.
WARNING
Fill trap with water before boiler
is rst red to prevent exhaust
fumes from entering room. Never
operate the boiler unless the trap
is lled with water.
Failure to comply will result in
severe personal injury or death.
WARNING
Whenever the burner is removed
for inspection or boiler servicing,
the sealing gaskets must be
examined and replaced if
damaged. Upon re-assembly,
an approved leak test solution
must be applied around the
burner ange sealing area to
ensure there is no leakage of
combustible gas/air premix.
• Keep combustible materials and ammable liquids and vapors away from the boiler.
• Keep vent terminals clear of obstructions (snow, dirt, etc.).
4.1.2 Inspection
Inspection of the boiler is to be performed annually by a qualied service technician.
4.1.3 Venting
• Remove any obstructions to vent terminals (e.g. leaves, dust, other debris).
• Clean or replace intake air lters or screens as required.
• Check for holes or leaks in venting. Replace venting as needed.
• Examine for any signs of moisture caused by sweating intake air pipes; insulate as
required.
• Ensure proper resealing or reinstallation of venting on each servicing.
4.1.4 Condensate Traps
• The condensate trap must be examined every two months to see if cleaning is
necessary (refer to trap cleaning instructions, section 1.5.3 of this manual). Ensure that
the trap has been re-lled completely before ring boiler.
• If condensate neutralization is used, check the pH level of condensate discharge.
4.1.5 Burner
• Annually, remove the burner to inspect for fouling (refer to the burner removal and
reassembly instructions, section 3.4.1 of this manual). Blow clear using compressed
air. Evaluate the magnitude of clearing required, and establish a reasonable burner
inspection schedule. Some boiler / locations may call for annual service, others
showing clean burners will only need attention every 2 – 5 years. Consider adding air
ltration if the burner requires cleaning every year. In alternate years, visually inspect
the burner through the sight glass. Ensure that the ame is stable and is without
excessive uttering. Normal ame pattern is evenly distributed over the burner surface.
• If the burner is operating improperly, remove and clean or replace. Use a CO
to determine proper combustion. See Table 7 for correct values.
analyzer
2
4.1.6 Heat Exchanger
During annual inspection (with the burner removed), examine the heat exchanger for
signs of contamination and clean if necessary. In areas of poor gas quality, there may be a
buildup of black plaque (typically sulfur). Other fouling agents may include: airborne dust,
debris and volatiles.
Refer to the burner removal instructions in Section 3.4.1 for access to combustion
chamber and heat exchanger. Note that the safety warning regarding burner refractory on
this page must be observed.
MAINTENANCE
4-1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
WARNING
The IBC heat exchanger has a
small amount of combustion
chamber insulation (refractory),
which contains ceramic bers.
When exposed to extremely high
temperatures, the ceramic bers,
which contain crystalline silica,
can be converted into cristobalite - which is classied as a
possible human carcinogen.
Care should be taken to avoid
disturbing or damaging the refractory. If damage occurs, contact the factory for directions.
Avoid breathing and contact with
skin and eyes and follow these
precautions:
1. For conditions of frequent
use or heavy exposure, respirator protection is required. Refer
to the “NIOSH Guide to the
Selection and Use of Particulate
Respirators Certied under 42
CFR 84” for selection and use of
respirators certied by NIOSH.
For the most current information, NIOSH can be contacted at
1-800-356-4676 or on the web at
www.cdc.gov/niosh.
2. Wear long sleeved, loose tting clothing, gloves and eyes
protection.
3. Assure adequate ventilation.
4. Wash with soap and water
after contact.
5. Wash potentially contaminated clothes separately from
other laundry and rinse washing
machine thoroughly.
6. Discard used insulation in an
air tight plastic bag.
NIOSH stated rst aid:
Eye contact - Irrigate and wash
immediately.
Breathing - Provide fresh air.
4.1.7 Pump
Check that the pump is on in normal operation and that the water Δ°T is reasonable for a
given ring rate.
4.1.8 Gas Piping
Check for damage or leaks and repair as needed.
4.1.9 Touchscreen Boiler Controller
• Check that the boiler operation is consistent with the steps in the Touchscreen Boiler
Controller manual.
• Check that the water temperature targets and setpoint are satisfactory and that they
have not been adversely amended.
• Check the operating history via the boilers Logs menu and the Error Logs menu. The
controller tracks the duty cycle of the boiler in each of the four loads separately. This
information can be used to adjust the water temperatures of each load.
• If a problem exists with the control, consult the Troubleshooting section.
4.1.10 Water
• Check the water pressure and temperature. There should be no noticeable change if
the boiler is functioning normally. Check for any noise in the system.
• Check the water piping for damage or leaks. Repair as needed.
• Check for 12-15 psig in normal operation, and look to ensure pressure does not run up
toward 30 psig at high temperature. If pressure rises sharply, consider replacement of
the expansion tank. Check also for noise at high re, which may signal water quality
problems.
• Water chemistry shall be of a quality generally accepted as suitable for hydronic
applications.
• Ensure any direct “city ll” water connections are left in the closed position to minimize
exposure to leaks and ooding.
4.1.11 Freeze Protection
Check the freeze protection. Use only antifreeze made specically for hydronic systems.
Inhibited propylene glycol is recommended. Antifreeze volume must be between 25% and
50% of the total volume of water in the system.
4.1.12 Boiler Treatment
• Check consistency of any boiler treatment used, for appropriate mixture. Chemical
inhibitors are consumed over time, lowering their density.
• Verify proper operation after servicing.
4-2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
WARNING
Do not use automotive-type
ethylene or other types of
automotive glycol antifreeze,
or undiluted antifreeze of
any kind. This may result in
severe boiler damage. It is the
responsibility of the Installer to
ensure that glycol solutions are
formulated to inhibit corrosion
in hydronic heating systems
of mixed materials. Improper
mixtures and chemical additives
may cause damage to ferrous
and non-ferrous components
as well as non-metallic, wetted
components, normally found
in hydronic systems. Ethylene
glycol is toxic, and may be
prohibited for use by codes
applicable to your installation
location. For environmental
and toxicity reasons, IBC
recommends only using nontoxic propylene glycol.
4.1.13 Relief Valve - Maintenance and Testing
The relief valve manufacturer requires that under normal operating conditions a “try
lever test” must be performed every two months. Under severe service conditions, or if
corrosion and/or deposits are noticed within the valve body, testing must be performed
more often. A “try lever test” must also be performed at the end of any non-service period.
Test at or near the maximum operating pressure by holding the test lever fully open for at
least 5 seconds to ush the valve seat free of sediment and debris. Then release the lever
and permit the valve to snap shut.
If the lever does not activate, or there is no evidence of discharge, discontinue use of
equipment immediately and contact a licensed contractor or qualied service personnel.
If the relief valve does not completely seal, and uid continues to leak from the discharge
pipe - perform the test again to try and ush any debris that may be lodged in the valve.
If repeated tries fail to stop the leakage, contact a licensed contractor or qualied service
personnel to replace the valve.
While performing a “try lever test”, a quantity of heat transfer uid will be discharged from
the piping system and the system pressure will drop. This uid must be replaced. It is
highly recommended that a system pressurization unit, such as an Axiom Industries model
MF200 be employed to rell and pressurize your system. Capture the discharged uid
in a container and recycle it by returning it to the system feeder unit. This is particularly
important when your system contains treatment chemicals or glycol solutions. If the
system employs plain water, the boiler auto ll valve must be turned on in order to
recharge the lost uid.
CAUTION
Installers should inquire of
local water purveyors as to the
suitability of their supply for use
in hydronic heating systems.
If water quality is questionable,
a local water treatment expert
must be consulted for testing,
assessment and, if required,
treatment.
Alternatively, water or hydronic
uid of known quality can be
brought to the site.
CAUTION
Before testing the relief valve,
make certain the discharge pipe
is properly connected to the
valve outlet and arranged to
contain and safely dispose of
equipment discharge.
MAINTENANCE
4-3

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
4.2 GEOGRAPHY & COMPONENTS
Components of the SL 26-260 G3
ITEM NO. COMPONENT ITEM NO. COMPONENT
1
2
3
4
5
4-4
Pressure Relief Valve
Combustion Test Port
Safety Ignition Module
Ignitor
Flue Gas Temperature Sensor
10
6
7
8
9
Low Water Cutoff Probe
Site Glass
Tridicator
Supply Water Pipe
Gas Valve
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

Components of the SL 40-399 G3
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
ITEM NO. COMPONENT ITEM NO. COMPONENT
11
12
13
14
15
MAINTENANCE
Venturi Mixing Device
Fan
Supply Water Temperature Sensor
Air Intake Pipe
V-10 Touchscreen Controller
16
17
18
19
20
Water Pressure Sensor
Return Water Temperature Sensor
Return Water Pipe
Blocked Vent Pressure Switch
Vessel Hi-Limit Switch
4-5

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
4.2.1 Fan and gas valve removal instructions
SL 26-260 G3
1. Turn off the electric power and gas supply to the boiler.
2. Ensure the boiler cools down to the surrounding temperature. Do not drain the boiler
unless freezing conditions are expected during this procedure.
3. Remove the front cover, and then remove the boiler upper-front cover by removing
the screws at the top right and left corner of the boiler.
A ladder or step may be required to have a clear vertical view of the work area. Do not
attempt to reach from the front without a clear view, as damage to connectors, screws
or refractory may occur.
4. Unplug both electrical connectors from the fan.
5. Unplug the electrical connector from the gas valve.
6. Position the harnesses out of the way of the heat exchanger lid.
7. Undo the brass nut between the valve and the venturi mixing device.
8. Remove the four 8 mm hex bolts that attach the fan to the lid.
9. Remove the fan and air intake venturi assembly from the boiler.
10. Separate the fan and the venturi mixing device by removing the 3 Phillips head
screws that attach the venturi mixing device to the fan.
11. Attach the venturi mixing device to the new fan.
12. Bolt the fan to the lid of the heat exchanger.
13. Attach the gas valve to the venturi mixing device with the brass coupler nut, ensuring
that the gasket is in place.
14. Connect the electrical connectors to the fan and gas valve.
SL 40-399 G3
1. Turn off the electric power and gas supply to the boiler.
2. Ensure the boiler cools down to the surrounding temperature. Do not drain the boiler
unless freezing conditions are expected during this procedure.
3. Remove the front cover, and then remove the boiler's upper-front cover by removing
the two Phillips head screws at the top right and left corners of the boiler.
A ladder or step may be required to have a clear vertical view of the work area. Do not
attempt to reach from the front without a clear view, as damage to connectors, screws
or refractory may occur.
4. Unplug both the upper and lower electrical connectors from the fan.
5. Note the colors and positioning of the wire connectors, and then unplug the electrical
connector from the gas valve by removing the 1/4” spade connectors.
6. Position the harnesses out of the way of the heat exchanger lid.
7. Remove the 4 hex head bolts using a 4 mm hex key that attaches the gas valve to
the venturi mixing device. These screws should be rst loosened slightly in a cross
sequence to prevent deformation of the mating parts.
8. With the corrugated stainless steel gas line still attached to the gas valve, the gas
valve can now be separated from the venturi mixing device. There is an O-ring
installed between the gas inlet block and gas valve, and it should remain positioned
on the block’s groove. If it falls out it is important that it be positioned back on the
groove or saved for re-assembly.
9. Remove the 4 hex nuts that attach the fan to the heat exchanger lid. A 7 mm openended wrench or socket is required.
4-6
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
10. With the venturi mixing device still attached, remove the fan by pulling straight up
ensuring that no wires are caught and that the gas line remains in place. Place the
removed components in a clean, dry area.
11. Note how the venturi mixing device is positioned on the fan before removing it from
the fan. Remove the three Phillips head screws to separate the venturi mixing device
from the fan.
12. Attach the venturi mixing device to the new fan.
4.2.2 Fan and gas valve re-installation
SL 26-260 G3
1. If the gas valve was removed from the venturi, ensure the gasket is in the proper
position.
2. Attach the gas valve to the venturi mixing device with the brass coupler nut.
3. Re-install the fan and gas valve assembly onto the lid using the four 8 mm hex bolts
removed earlier.
• Ensure the black gasket is installed between the fan outlet and the lid.
• Tighten by hand plus an extra 1/8 of a turn the 4 hex bolts.
• Test for leaks around the fan and lid gasket.
4. Re-attach both fan harness connectors.
5. Re-attach the gas valve connector.
6. If a new gas valve is being installed, remove the protective cover from the gas inlet
now.
7. Re-attach the gas supply line JIC connector (are-tting nut).
8. Open up the gas supply, and check for possible leaks.
9. Return the electric power to the boiler, and perform the startup routine.
10. Check for gas or fume leaks after 10 minutes of continuous operation.
SL 40-399 G3
1. If the gas valve has been removed, reattach it to the corrugated gas line.
2. Re-attach the venturi mixing device to the new fan, observing the alignment marks
made during disassembly.
3. Ensure that the fan gasket is in place (between the heat exchanger lid and the fan).
4. Re-install the fan and venturi assembly onto the heat exchanger lid, tightening the
four hex nuts by hand plus an extra 1/2 turn.
5. Plug in both the upper and lower fan harness connectors.
6. Plug in the gas valve connector.
7. If a new gas valve is being installed, remove the protective cover from the gas inlet
now.
8. Re-attach the gas inlet block onto the gas valve, ensuring that the O-ring seal is in
place. If this O-ring is lost, it must be replaced with a factory supplied O-ring.
9. Tighten by hand plus an extra 1/2 turn in cross sequence the 4 gas inlet block screws.
10. Open up the gas supply valve, and check for possible leaks.
11. Return the electric power to the boiler, and perform the startup routine.
12. Check for gas or fume leaks after 10 minutes of continuous operation.
TROUBLESHOOTING
4-7

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
4.2.3 Replacing the gas valve
SL 26-260 G3
1. Turn off the electric power and gas supply to the boiler.
2. Remove the electrical connection from the gas valve.
3. Ensure the boiler cools to the surrounding temperature. Do not drain the boiler unless
freezing conditions are expected during this procedure.
4. Remove the front cover, and then remove the boiler's upper-front cover by removing
the two Phillips head screws at the top right and left corners of the boiler.
A ladder or step may be required to have a clear vertical view of the work area. Do
not attempt to reach from the front without a clear view as damage to the connectors,
screws, or refractory may occur.
5. Support the male compression coupling on the inlet of the gas valve, and with a
wrench, undo the compression tting to separate the gas valve from the gas supply
pipe.
6. To separate the gas valve from the venturi mixing device, unscrew the brass coupler
nut and retain the gasket between the gas valve and the brass coupler.
7. Remove the male compression coupler from the old gas valve outlet, and install this
on the new gas valve outlet, using fuel-appropriate Teon tape on the threads.
8. Screw the brass coupler nut to the brass coupler ange on the left side of the gas
valve. Ensure that the gasket is in place.
9. Supporting the male compression coupling on the outlet of the gas valve, with a
wrench, tighten the compression tting to secure the gas valve to the gas supply pipe.
SL 40-399 G3
1. Turn off the electric power and gas supply to the boiler.
2. Ensure that the boiler cools down to the surrounding temperature. Do not drain the
boiler unless freezing conditions are expected during this procedure.
3. Remove the front cover, and then remove the boiler's upper-front cover by removing
the two Phillips head screws at the top right and left corner of the boiler.
A ladder or step may be required to have a clear vertical view of the work area. Do not
attempt to reach from the front without a clear view, as damage to connectors, screws
or refractory may occur.
4. Noting the color and orientation of the connectors, unplug the 4 spade connectors
from the gas valve.
5. To separate the aluminium gas block on the right side of the gas valve, remove the 4
hex head bolts with a 4 mm hex key.
6. To separate the gas valve from the venturi mixing device, remove the 4 hex head
bolts on the left side of the gas valve with a 4 mm hex key.
7. Bolt the gas valve to the venturi mixing device ange with the 4 mm hex bolts,
ensuring that the O-ring is positioned between the gas valve and the venturi mixing
device.
8. Bolt the gas block to the gas valve outlet, ensuring that the O-ring is positioned
between the gas block and the gas valve.
9. Connect the electrical connectors to the new gas valve.
4-8
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
NOTE
This boiler is equipped with a
blocked vent shutoff system,
which closes the gas supply
upon detection of an irregular
venting condition. In such
event, the electronic controller
will automatically carry out a
reset/ retry every 5 minutes. See
Section 5.3.1 Airow Error for
Troubleshooting steps.
5.0 TROUBLESHOOTING
The troubleshooting section is divided into 3 sections:
• Preliminary Checks
• Electronic Components
• Troubleshooting
Often, a problem can be identied and solved through simple checks of the basics:
conrming the electrical power supply, gas ow and resetting the thermostat control. To
extend the cover of such preliminary checks, the boiler’s touchscreen controller offers a
clear visual display of the status of the various control circuit components.
Should a problem remain unsolved after applying the preliminary checks, proceed to
the detailed system review, using the Troubleshooting section. It covers potential error
conditions grouped into the following categories:
• Using touchscreen controller errors displayed
• Ignition problems
• Cycling problems
• Temperature problems
• Miscellaneous
Below each section is a list of Symptoms, Diagnoses, and Remedies.
Also provided with this manual are a number of diagrams (see Section 6.0) for use with
troubleshooting including:
• Electrical wiring diagrams
• Sequence of operations owchart
• Boiler component diagrams
5.1 PRELIMINARY CHECKS
The rst step in troubleshooting this system should be a review of the touchscreen
controller. There are a number of diagnostic features incorporated in the software that
evaluate system integrity, display error conditions and provide initial remedial actions.
In addition to checking the display, the following list is a guideline for troubleshooting:
1. Conrm power to the boiler: check that the touchscreen controller display is on (e.g.
display is lit. The touchscreen controller’s display will be fully functional in 90 seconds
after power is restored to the boiler.)
2. Check that the boiler is not in a safety lockout.
3. Ensure wiring is clean and secure.
4. Check that gas is reaching the unit.
5. Conrm that the water system is properly charged to 12 and that the pump is
serviceable.
TROUBLESHOOTING
5-1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
5.2 ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
This section details the method for troubleshooting the non-standard electronic
components on the boiler.
5.2.1 Temperature Sensors
The resistance of the temperature sensors varies inversely with temperature. To test,
measure the temperature of the sensed environment and compare with the value derived
from the measurement of the resistance (obtained by connecting a good quality test meter
capable of measuring up to 5,000 kΩ (5,000,000Ω) at the controller end of the sensor
lead).
To obtain a resistance reading, remove power to the boiler, and return water. For the
supply water and vent temperature sensors, remove the wire leads by disconnecting their
respective Molex connectors. Place multi-meter probes into the sensor’s female Molex
connector socket. Do not apply voltage to the sensor as damage may result.
TEMPERATURE RESISTANCE TEMPERATURE RESISTANCE
°F °C Ω °F °C Ω
0 -18 85,362 100 38 5,828
5 -15 72,918 105 41 5,210
10 -12 62,465 110 43 4,665
15 -9 53,658 11 5 46 4,184
20 -7 42,218 120 49 3,760
25 -4 39,913 125 52 3,383
30 -1 34,558 130 54 3,050
35 2 29,996 135 57 2,754
40 4 26,099 140 60 2,490
45 7 22,763 145 63 2,255
50 10 19,900 150 66 2,045
55 13 17,436 155 68 1,857
60 16 15,311 160 71 1,689
65 18 13,474 165 74 1,538
70 21 11,883 170 77 1,403
75 24 10,501 175 79 1,281
80 27 9,299 180 82 1,172
85 29 8,250 185 85 1,073
90 32 7,334 190 88 983
95 35 6,532 195 91
903
Table 9: Temperature Sensor resistance values
5-2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
5.2.2 Fan
Operating power is provided by means of a separate 120 VAC connector (white/black/
green). Control of the fan is provided via a four lead connector. This connector feeds a
PWM control signal (black wire) from the controller and provides a tachometer signal
(white wire) back from the fan. Unplugging the control connector will cause the fan to go to
high speed and trigger a “Blocked Vent Error” within 6 seconds if the boiler is operating.
LEAD COLOR FUNCTION TROUBLESHOOTING
Red
Blue
Black Signal from controller
White Fan tach. 2 pulses/rev (freq x 30=rpm)
Table 10: Fan Operation
35 VDC Positive power
terminal
35 VDC Negative
power terminal
Fan will only operate at max.
speed if disconnected.
Fan will only operate at max.
speed if disconnected.
Fan will only operate at max.
speed if disconnected.
5.2.3 Water Pressure Sensor
The water pressure sensor ensures that there is adequate pressure in the heating system
for safe operation. The pressure is displayed in PSI as the default. If the system pressure
should drop below 8PSI the ring rate of the boiler is reduced. If the pressure drops to
4PSI or lower, the boiler will not re.
Check the operation of the sensor by isolating the boiler from its system piping, and close
the system ll valve, and then crack the pressure relief valve. The pressure displayed should
reect declining pressure. If it remains “xed”, drain the boiler and replace the sensor, or
dislodge any blocking debris from the sensor inlet channel and reinsert.
5.2.4 Safety and Ignition Module (SIM)
The SIM is a safety control that is certied to conform to the UL 60730-5-5 and ANSI
Z21.20-2014 • CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60730-2-5-14 Standards. The low water cutoff
function and the high-limit manual reset water temperature function also conform to these
standards.
TROUBLESHOOTING
The SIM directly controls the boiler’s gas valve and provides:
• Direct spark automatic ignition
• Flame detection and current measurement
• Supply water temperature sensing
• Flue gas temperature sensing
• Supply water maximum temperature shutdown
• Flue gas maximum temperature shutdown
• Low water cut-off.
5-3
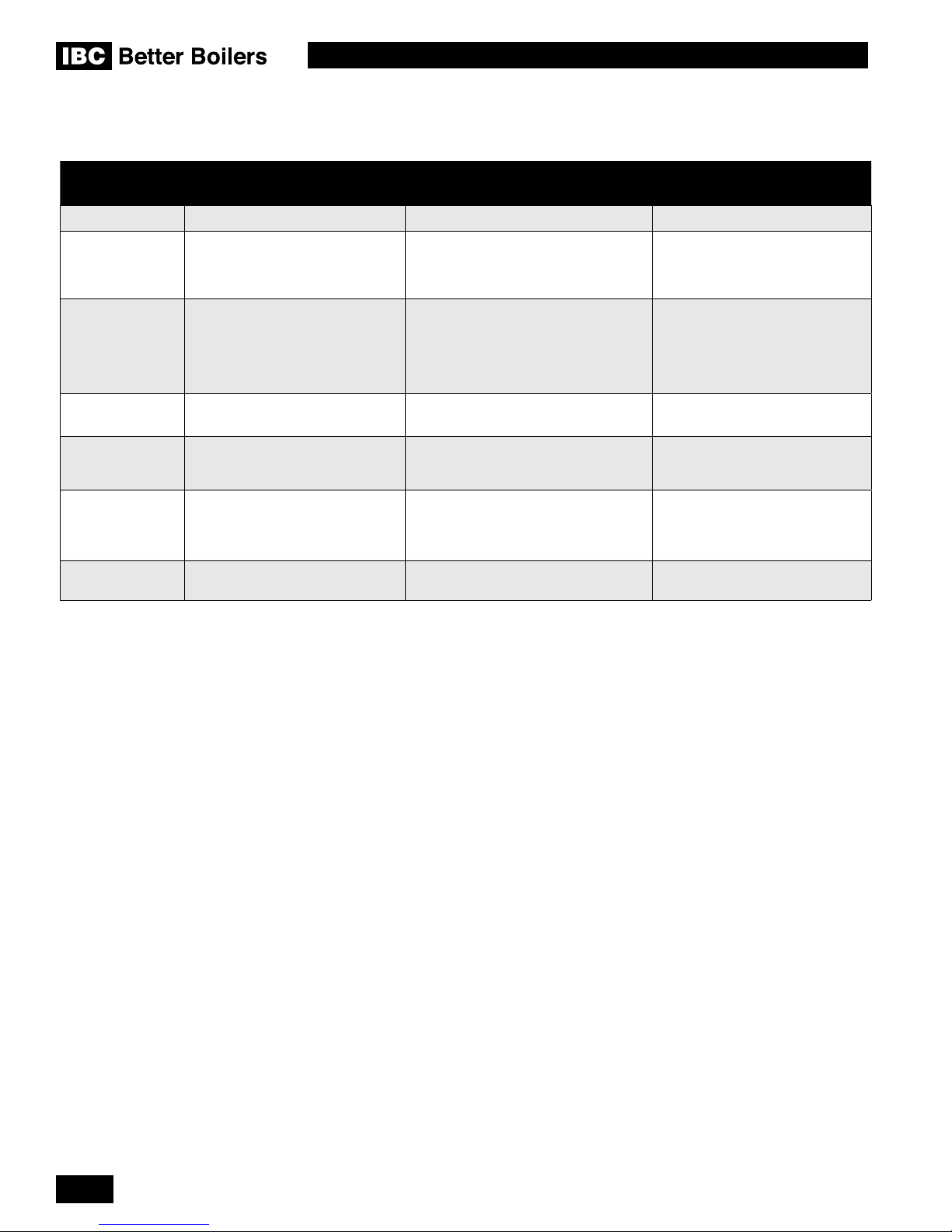
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
The SIM’s two status LEDs indicate the operating status as shown in the table below.
Status Indicators
LED 1 LED 2 STATE
DESCRIPTION, LED
STATUS INDICATION
Rapid Flash Rapid Flash Power up or Resetting Startup checks and initialization
LED1 Off = No Flame or
Off Off Standby
Sparking
LED 2 = Burner-On Call state
LED1 Off = No Flame or
Sparking
Off On Pre-Purge or Inter-Purge
On On Heating
LED 2 = Burner-On Call state
LED 1 On = Flame detected
LED 2 = Burner-On Call state
LED 1 ashing = Electrode
Rapid Flash On Igniting
Sparking, LED 2 = Burner-On
Call state
An operating limit was exceeded
Off Flashing Lockout
or a sequence failed or an
external sensor fault was
detected.
Flash Alternately
with LED 2
Flash Alternately with LED 1 Fail-Safe
A critical internal fault was
detected.
The SIM is continuously communicating with the boiler’s main controller reporting sensor
readings and status. The sensor readings and error status, if any are displayed on the boiler
controller’s screen.
5.2.4.1 Low water cutoff function: reset and test
The low water cutoff (LWCO) function provides continuous protection against a low water
incident.
If the SIM detects a low water incident, the boiler goes into a lockout condition.
Here, you will
need to reset the boiler. To test the LWCO on the boiler, you can also manually place the boiler
in a lockout condition (locks).
Resetting the boiler after a LWCO lockout
Before you reset the boiler, ensure that the boiler is pressurized and that the air has been
removed.
1. On the touchscreen controller, tap the Home screen.
2. On the Main Menu, tap the Diagnostics button.
3. Tap the Advanced Diagnostics button.
4. Tap the Clear Errors button.
5. Tap the Ye s radio button, and then tap OK.
The system clears the errors, and resets the boiler.
Testing the LWCO function
1. On the touchscreen controller, tap the Home screen.
2. On the Main Menu, tap the Diagnostics button.
3. Tap the SIM Module button.
5-4
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
4. Tap the LWCO Test button.
5. Disconnect the yellow wire from the LWCO function.
A message on the screen indicates that the boiler is in lockout mode.
6. To reset the boiler, reconnect the yellow wire to the LWCO function.
On the touchscreen controller, tap the Reset button.
The message: "The SIM Module has been reset" is displayed.
7. Tap the Close button, and then tap the Back button until you return to the Home
screen.
5.2.4.2 Water Temperature function: reset and test
The hi-limit temperature function monitors the hi-limit temperature set in the SIM. If
the water temperature exceeds the hi-limit temperature, the boiler goes into a lockout
condition (locks), requiring a manual reset. You can test the hi-limit cutoff temperature
function on the boiler.
Resetting the boiler after a Hi-Limit lockout
Before you reset the boiler, ensure that the boiler is pressurized and that the air has been
removed.
1. On the touchscreen controller, tap the Home screen.
2. On the Main Menu, tap the Diagnostics button.
3. Tap the Advanced Diagnostics button.
4. Tap the Clear Errors button.
5. Tap the Ye s radio button, and then tap OK.
The system clears the errors, and resets the boiler.
Testing the Hi-Limit cutoff temperature function
1. On the touchscreen controller, tap the Home screen.
2. On the Main Menu, tap the Diagnostics button.
3. Tap the SIM Module button.
4. Tap the Hi-Limit Test button.
You will need to enter a cutoff temperature below the Supply Temp. value currently
displayed. For example, if the Supply Temp. value is 180°F, enter 170°F in the Cut Off
Temp. box.
5. Tap inside the Cut-Off Temp. box, and then tap a number value.
6. Tap the OK button.
The message: "Hi-Limit Detected" is displayed.
TROUBLESHOOTING
7. To reset the boiler, select the Reset button.
The message: "The SIM module has been reset" is displayed.
8. Tap the Close button, and then tap the Back button until you return to the Home
screen.
5-5

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
5.3 TROUBLESHOOTING
WARNING
Never attempt to repair the
control module (circuit board). If
the control module is defective,
replace it immediately.
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
MAXIMUM IGNITION TRIALS
ERROR
Touchscreen Message:
Error – Ignition Failure after 3
tries
Boiler has failed to ignite on 3
successive attempts. Boiler in
lockout for 1 hour, then repeats
3-try seq. Consult service
technician if error recurs.
5.3.1 Using Control Module Errors Displayed
The bottom line of the touchscreen is reserved for displaying the boiler's error status. The
boiler status bar will normally be Green, but can change color to Yellow or Red. The colors
represent the following boiler operating status. The text inside the bar will indicate the
specic warning or alarm. If there is more than one alarm present the text will scroll slowly
through all current alarm conditions.
• Green – Normal
• Yellow – Warning
• Red – Alarm
No spark when igniting.
Igniter probe/ame
sensor disconnected.
Manual gas shutoff is
closed or gas line not
fully purged.
Gap between igniter
probe rods is too large
or too small.
Check that igniter lead is secure at the touchscreen
controller and at the probe.
Check for gas ow. Open manual gas shutoff and
reset boiler.
Adjust ignitor probe rod gap between 1/8th and
3/16th (3.2-4.7 mm)
HI LIMIT CUTOFF
TEMPERATURE ERROR
Touchscreen message:
Error – Water High-Limit
Exceeded
Spark, but no ignition.
Boiler ignites, but shuts
off at the end of the
ignition trial. Improperly
grounded pressure vessel/
burner or unserviceable
ignition lead or spark
module.
Water temperature
exceeds hi-limit. Boiler
in hard lockout.
Check spark module is sending power to gas valve
– close gas supply, then disconnect (black) electric
housing from face of gas valve, gently spread plastic
tabs to open, and look for 24vac voltage between blue
and brown wires during an ignition cycle. Replace
module if no current detected
• Ensure pressure vessel is grounded.
• Check the igniter probe/ame sensor is electrically
isolated from the vessel, and its ceramic insulator
is intact.
• Replace ignition lead
• Replace spark module
See Section 5.2.4.
5-6
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
LOW WATER CUTOFF ERROR
Touchscreen message:
Error - Low Water Cutoff
The Safety and Ignition
module has detected a
low water condition.
See Section 5.2.4.
TROUBLESHOOTING
5-7

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
ERROR
Touchscreen Message:
Error - Max. Inlet/Outlet Sensor
Temp. Exceeded. -> Check water
ow
Current outlet
temperature exceeds
operating limit.
Defective or
disconnected
temperature sensor.
• Check water ow.
• Check wiring to temperature sensor and control
module.
• Check temperature sensor. See Section 5.2.1.
Water temperature signal
not within acceptable range.
Potential ow or sensor failure.
Consult service technician.
MISCELLANEOUS
Touchscreen Message :
• Check transformer; replace if damaged.
• Check circuit board for visible damage.
Blank – screen dark, but fan
running Indicative of power-
surge damage to appliance
5.3.2 Ignition Problems
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
NOISY SPARK WHEN
IGNITING
BOILER RUMBLES WHEN
IGNITING.
BOILER WILL NOT ATTEMPT
TO IGNITE. FAN AND PUMP
ARE OPERATING NORMALLY.
BOILER WILL NOT ATTEMPT
TO IGNITE. FAN AND / OR
PUMP ARE OFF DISPLAY
NOT ILLUMINATED
Ignition lead is not rmly
Reconnect ignition lead.
connected.
Contaminants/moisture
on igniter probe/ame
Ensure probe is dry by re-running post-purge;
otherwise, clean or replace igniter probe.
sensor.
Fluctuating gas
Check CO
level via analyzer.
2
pressure/ gas pressure
too high/too low.
Check for proper gas
Check pressure with manometer during ignition.
piping.
No power to ignition
control module.
Igniter probe/ame
• Check system wiring.
• Check air reference tubing.
Reconnect probe.
sensor disconnected.
Defective Control
Check ignition output from control module.
Module.
No power to boiler. Check line voltage.
Defective transformer. Check transformer. Reconnect or replace as needed.
5-8
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
5.3.3 Cycling Problems
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
RAPID CYCLING Improper values entered
via keypad.
Excess Condensate in
venting.
Obstruction in
condensate trap.
Improper vent length or
improper slope to vent.
Incorrect settings or
defective thermostat.
Air in system or marginal
water ow.
Slow combustion air
blower.
Dirty burner/heat
exchanger.
Low water ow due to
improper piping.
Check load maximum temps are above target temps,
by 1/2 of the selected boiler differential. Ensure boiler
differential is OK (16-30°F is generally adequate)
Check venting slopes on horizontal runs. Look for
sags.
Inspect and clean condensate trap.
Check venting. Compare vent length and diameter to
Table 4A or Table 4B: Maximum Venting.
Check operation. Refer to manufacturer’s instructions.
Check setting with ammeter.
Bleed/purge system as required. Conrm adequate
pump size and temp rise in HX.
Check that CO
level is within specication.
2
Check pressure drop.
Refer to recommended piping in Section 1.6
Low water ow due to
undersized pump.
Low water ow due to
restrictions in water
Check manufacturer’s rating charts/check
temperature differential across heat exchanger.
Check temperature differential across zone/heat
exchanger.
pipe.
Low radiation. Check actual amount of radiation per zone and refer
to manufacturer’s rating tables.
Unit over-red. Clock gas meter/check gas pressure with manometer/
check CO
level.
2
Unit Oversized. Check load calculation vs. min. boiler output.
Improperly set or
Check operation with ohmmeter/voltmeter.
defective operating/
safety controls.
TROUBLESHOOTING
5-9

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
5.3.4 Temperature Problems
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
LOW HEAT
Operating temperature
Increase temperature target.
too low.
Priority parameters
Review load conguration parameters.
or load conguration
improperly set up.
Unit undersized. Refer to Load Calculation vs. Boiler Output.
Air trapped within
Bleed system as required.
system.
Improper system
Refer to recommended piping in Section 1.6
piping.
System pump
undersized.
Poor gas/air mixing. Check CO
Check pump manufacturer’s data/check temp
differential across heat exchanger.
level.
2
Defective thermostat. Refer to manufacturer’s instructions.
Obstruction in
Inspect and clean condensate drain.
condensate drain.
Unit cycling on
Check operation with Ohmmeter/Voltmeter.
operating/ safety
controls.
TEMPERATURE EXCEEDS
THERMOSTAT SETTING
ONE OR MORE ZONES DO
NOT HEAT PROPERLY
System radiation
undersized.
Incorrect anticipator
Check manufacturer’s rating tables for capacity per
foot.
Check with Ammeter.
setting.
Thermostat not level. Check level.
Air trapped within
Vent system/zone as required.
zone(s) piping
Low radiation/
excessive heat loss.
Low ow rate to
Check actual length of pipe using radiation / heat loss
calculation.
Check temperature drop across zone.
zone(s).
Defective zone valve/
Check operation per manufacturer’s instructions.
zone circulator.
5-10
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS
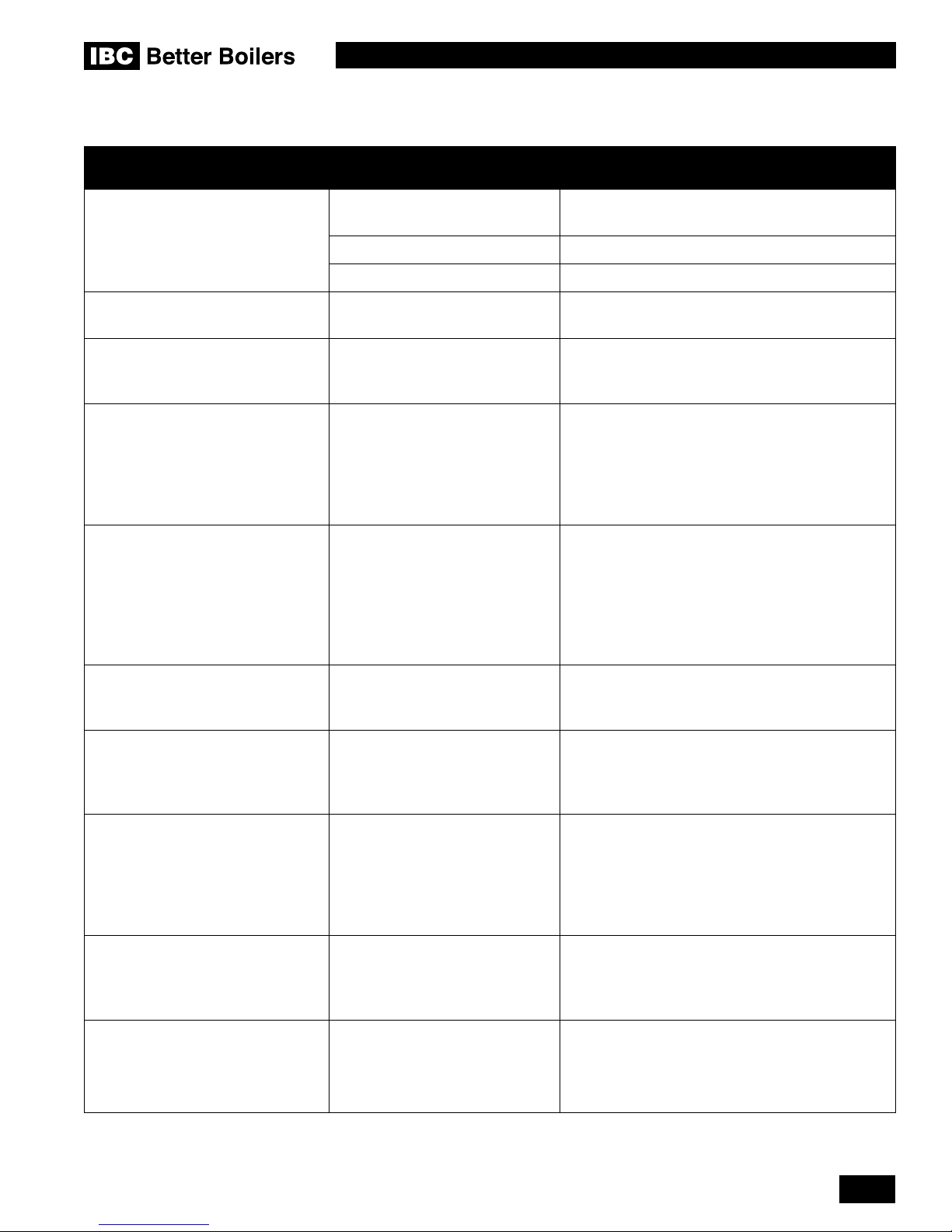
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
5.3.5 Miscellaneous
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS REMEDY
FUMES AND HIGH HUMIDITY
BOILER STUCK ON
INITIALIZE
TOUCHSCREEN MESSAGE:
Unknown Error
BOILER REMAINS IN
STANDBY DURING CALL FOR
RESET HEATING OR SETPOINT (DHW OPERATION
WORKS AS NORMAL). (5
BUTTON CONTROLLER)
‘GHOST’ CALL FOR HEAT.
Improperly installed
Refer to installation/operation instructions
condensate trap
Leak in vent piping Inspect using soap solution
Flue gas leak within boiler Visually inspect all mechanical connections
Fan board failure Replace fan.
Temperature sensor input
problem.
Test each temperature sensor for appropriate
readings and Replace defective temperature
sensor.
Boiler may be in Warm Weather
Shut-down.
In Installer Setup / Heat Load Conguration
/ Congure Load (Heating) adjust Summer
Shutdown Temperature to a temperature above
that registered by outdoor sensor.
Triac or ‘Power-robbing’
thermostat sending current to
boiler.
Remove Therm. connections from boiler to conrm
that stray voltage, or current induced in thermostat
wiring, is source of nuisance signal. Replace the
Power Robbing thermostat, isolate the thermostat
with a relay or install a properly sized resistor
(consult the thermostat manufacturer rst then IBC
for instructions).
ERROR: WATER HIGH LIMIT /
LOW WATER CUTOFF WON’T
CLEAR.
DHW TAKING TOO LONG TO
HEAT.
BOILER OUTPUT NOT
MODULATING UP TO
MAXIMUM DESPITE TARGET
NOT BEING REACHED.
PRIMARY PUMP RUNS BUT
LOAD PUMPS DO NOT.
PRIMARY PUMP RUNS
DURING PARALLEL-PIPED
DHW CALL.
Boiler is in 1 hour safety
lockout.
Sensor may be under-reading
actual water temp.
Reset safety device and cycle boiler power off and
on to reset error.
Check sensor engagement; note well is 15cm /
almost 6 inches deep and sensor must be fully set
to back. Check programmed settings boiler temp
set too close to the required DHW temp
Possible ow issue: check for
35 or 40 degree F temperature
difference between boiler
Conrm that primary pump is able to overcome
head loss of boiler and primary loop piping at the
required ow rate.
supply and return water
temperatures (evokes
electronic fence).
Wiring not complete. Supply power to the PV/L and PV/N terminals
from the incoming power supply to the boiler.
(Factory wired on boilers with a factory installed
Touchscreen Controller)
Load denition as DHW. Re-dene DHW load as DHW Loop 2 (5 button
Controls) to turn off primary pump during domestic
hot water calls. On Touchscreen Controllers set the
boiler pump to off in the Installer Set-up Menu.
TROUBLESHOOTING
5-11

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
5-12
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
6.0 DIAGRAMS
This section includes:
• Parts diagrams
• Wiring diagrams
• The sequence of operation
DIAGRAMS
6-1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
6.1 PARTS DIAGRAMS
SL 26-260 G3 Boiler - Parts assembly
Diagram 6.1-1: Boiler assembly parts - SL 26-260 G3
6-2
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

Table : Boiler assembly parts list
(refer to Diagram
Some parts are available only in
Kits. Please visit www.ibcboiler.
com for more information.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY
10 240-113 FAN 1
20 150-073 MIXER O-RING 1
30 180-161 FUEL MIXER, NG 1
180-162 FUEL MIXER, LP
40 250-742 GASKET, GAS VALVE COUPLER 1
50 250-768 GAS VALVE COUPLER 1
60 250-741 NUT, GAS VALVE COUPLER 1
70 180-166 GAS VALVE 1
80 190-157 GAS LINE 1
90 190-162 AIR INTAKE ASSEMBLY 1
100 250-859 AIR INTAKE ASSEMBLY, MOUNTING CLIP 1
110 250-322 GASKET, FAN TO LID 1
120 250-050 GASKET, IGNITOR 1
130 240-002 IGNITOR 1
140 250-057 SIGHT GLASS HOUSING 1
150 255-025 GASKET, HOUSING-GLASS 1
160 250-059 SIGHT GLASS 1
170 255-023 GASKET, SIGHT GLASS-H.Ex. 1
180 255-026 GASKET, H.Ex. LID-H.Ex. 1
190 255-034 GASKET, BURNER-H.Ex. 1
200 180-186 BURNER 1
210 250-761 HEAT EXCHANGER REFRACTORY 1
220 500-044 V10.0 CONTROL MODULE 1
230 250-488 CONTROLLER, TERMINAL BLOCK COVER 1
240 500-021 DOOR ASSEMBLY 1
250 240-006 PRESSURE SENSOR, RETURN WATER 1
260 250-258 RETURN WATER PIPE 1
270 250-682 WATER PIPE SPACER 1
280 255-024 GASKET, WATER PIPE 2
290 180-013 CONDENSATE TRAP 1
300 250-664 CONDENSATE TRAP RETAINER 1
310 240-134 TEMPERATURE SENSOR, RETURN WATER 1
320 240-133 TEMPERATURE SENSOR, SUPPLY WATER 1
330 170-032 HEAT EXCHANGER 1
340 250-259 SUPPLY WATER PIPE 1
350 240-010 LOW WATER CUT OFF PROBE 1
360 180-005 PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE 1
370 250-187 RATING LABEL, PANEL 1
380 250-254 BRACKET, VESSEL LIMIT SWITCH 1
390 240-030 VESSEL TEMP. HIGH LIMIT SWITCH 1
DIAGRAMS
6-3

SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY
400 250-867
BRACKET, BLOCKED VENT PRESS.
SWITCH
410 240-138 BLOCKED VENT PRESSURE SWITCH 1
420 240-008 TRANSFORMER 1
430 500-105 IGNITION MODULE 1
440 240-132 FLUE TEMPERATURE SENSOR 1
450 250-855 FLUE TEMPERATURE SENSOR FITTING 1
460 250-804 EXHAUST DUCT 1
470 250-856 INTAKE DUCT 1
480 250-800 ACCESS COVER 1
1
6-4
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.
TROUBLESHOOTING
6-5

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 40-399 G3 Boiler - Parts assembly
Diagram 6.1-2: Boiler assembly parts - SL 40-399 G3
6-6
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

Table : Boiler assembly parts list
(refer to Diagram 6.1-2 on opposite
page)
Some parts are available only in
Kits. Please visit www.ibcboiler.
com for more information.
SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
ITEM PART # DESCRIPTION QTY
10 240-113 FAN 1
20 150-073 MIXER, NG 1
180-164 MIXER, LP
30 150-232 MIXER O-RING 1
40 190-160 GAS VALVE ELBOW 1
50 150-259 GAS VALVE ELBOW O-RING 1
60 250-869 NATURAL GAS ORIFICE 12.0 1
250-865 PROPANE ORIFICE 11.2
70 255-035 ORIFICE/COUPLER GASKET 2
80 180-150 GAS VALVE 1
90 250-755 GAS INLET BLOCK 1
100 150-001 GAS INLET BLOCK O-RING 1
110 250-794 GAS VALVE COUPLER ROTATION LOCK 1
120 250-793 GAS VALVE COUPLER BOTTOM PLATE 1
130 190-162 AIR INTAKE ASSEMBLY 1
140 250-859 AIR INTAKE MOUNTING CLIP 1
150 190-158 GAS LINE 1
160 250-322 FAN GASKET 1
170 240-002 IGNITER 1
180 250-050 IGNITER GASKET 1
190 250-057 SIGHT GLASS FRAME 1
200 255-023 SIGHT GLASS LOWER GASKET 1
210 250-059 SIGHT GLASS 1
220 255-025 SIGHT GLASS UPPER GASKET 1
230 255-048 BURNER GASKET 1
240 255-009 HEAT EXCHANGER LID GASKET 1
250 180-185 BURNER 1
260 250-753 HEAT EXCHANGER REFRACTORY 1
270 500-044 V10.0 CONTROL MODULE 1
280 250-488 CONTROLLER TERMINAL BLOCK COVER 1
290 500-079 DOOR ASSEMBLY 1
300 240-006 RETURN WATER PRESSURE SENSOR 1
310 250-748 RETURN WATER PIPE ASSEMBLY 1
320 255-027 GASKET, WATER PIPE 2
330 240-133
TEMPERATURE SENSOR, SUPPLY
WATER
1
DIAGRAMS
340 240-134
TEMPERATURE SENSOR, RETURN
WATER
350 180-065 CONDENSATE TRAP 1
360 250-664 CONDENSATE TRAP RETAINER 1
370 HEAT EXCHANGER 1
6-7
1

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
ITEM PART # DESCRIPTION QTY
170-028
80 PSI CAPACITY, 316Ti STAINLESS
STEEL
170-029 80 PSI CAPACITY, 439 STAINLESS STEEL
380 250-853 SUPPLY WATER PIPE ASSEMBLY 1
390 180-189 TRIDICATOR 1
400 240-010 LOW WATER CUT-OFF SENSOR 1
410 180-005 PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE 30 PSIG 1
420 500-081 CABINET 1
430 240-008 TRANSFORMER 1
440 250-187 RATING LABEL PANEL 1
450 500-105 SAFETY IGNITION MODULE 1
460 240-132 FLUE TEMPERATURE SENSOR 1
470 250-024 EXHAUST DUCT 1
480 250-025 INTAKE DUCT 1
490 250-693 UPPER ACCESS PANEL 1
500 250-870 SWITCH BRACKET 1
510 240-138 BLOCKED VENT PRESSURE SWITCH 1
520 240-030 VESSEL TEMP. HIGH LIMIT SWITCH 1
6-8
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
6.2 WIRING DIAGRAMS
Diagram 6.2-1: Ladder wiring diagram
DIAGRAMS
6-9

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
Better
Boilers
P 101
blue
3
red
4
red
10
blue
9
orange
15
orange
2
blue
1
P 102
IBC Control Board
P 501
P 702
TB1
10
17
16
22
13
27
28
black
1
brown
2
black
5
white
6
yellow
3
orange
4
white
black
9
white
orange
white
white
2 x plug
red
white
red
6
yellow
4
black
5
yellow
6
black
5
Diagram 6.2-2: Internal wiring diagram
5 x plug
Exhaust
Pressure
Switch
VS Out 0-10VDC
NG150
Combustion
Transformer
24 Vac
Upper Vessel
High Limit
Switch
Inlet Water
Temperature
Sensor
Inlet Water
Pressure
Sensor
Fan
3 x plug
120 Vac
black
white
black
white
SL 40-399 G3 and SL 26-260 G3
INTERNAL WIRING DIAGRAM
Outlet Water
Temperature
Sensor
Flue Gas
Temperature
Sensor
black
white
black
black
black
green
brown
blue
Gas
Valve
green
white
white
white
120Vac
Mains
Power Supply
yellow
To Boiler Pump
4 x plug
4 x plug
LWCO Probe
orange
orange
Replacement internal wiring
must meet or exceed the
ratings of the wiring supplied
from the factory.
green
green green
white
white
1
white
2
blue
3
blue
4
white
5
white
6
red
7
red
8
yellow
green
brown
green
green
9
11
red
1
2
white
3
4
5
blue
7
8
9
blue
10
Spark
Electrode
and Flame
Sensing Rod
Assembly
Grounded
to case
P3
P2
IBC SIM Ignition Module
T1b
100-025A
6-10
INSTALLATION AND OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS

SL 26-260 G3, SL 40-399 G3 MODULATING GAS BOILERS
SL 80-399 MODULATING GAS BOILER
6.3 SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
Diagram 6.3: Sequence of operation diagram
DIAGRAMS
6-11

INSTALLATION & COMMISSIONING REPORT
Boiler Details:
Model Number _____________________ Serial Number ______________________________________________
Date of Installation ______________ Address of installation __________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
User contact information _______________________________________________________________________
Installer Information Company ___________________________________________________________________
Address ______________________________________________________________________________________
Phone/Fax/E mail ______________________________________________________________________________
Fuel
Gas Supply Pressure (high re) _______ Inches w.c. Measured Rate of Input (high re) ____________ Btu/hr
Instructions).
Instructions).
Neutralization? Yes/No
µA
Combustion Readings:
Natural Gas Propane
Installation instructions have been followed and completed (Section 1 of Installation and Operating
Check-out procedures have been followed and completed (Section 3 of Installation and Operating
Leak testing completed gas piping venting system Fan and combustion components
System Cleaned and Flushed (type of cleaner used) ________________________________________________
System Filled (type/concentration of any glycol/chemicals used) _______________________________________
Air purge completed
Relief Valve correctly installed and piped
Condensate trap lled
Ignition Safety Shutoff test completed. Flame current reading - High re _______ µA - Low re _______
Owner advised and instructed in the safe operation and maintenance of the boiler and system.
Information regarding the unit and installation received and left with owner
Condensate drain clear and free owing Condensate
Relief valve “try lever” test performed
CO
_____________ % O2 ______________ % CO ____________ ppm
2
Flue temperature _________ Return water temperature (measure simultaneously with ue temp.)
_______________
Installers: send this completed sheet - Fax to 604 877 0295 - or - scan and Email to info@ibcboiler.com, and earn an extra
year’s Parts Warranty coverage (User to submit corresponding Installation Record from User Guide).
Commissioning has been completed as listed on this report - Installer Signature _____________________________

INSTALLER SET-UP
Load Denition - Load #1 _______________________________________________________________________
Load Conguration - Load #1
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Load Denition - Load #2 _______________________________________________________________________
Load Conguration - Load #2
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Load Denition - Load #3 _______________________________________________________________________
Load Conguration - Load #3
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
Load Denition - Load #4 _______________________________________________________________________
Load Conguration - Load #4
_____________________________________________________________________________________________

SERVICE RECORD
DATE LICENSED CONTRACTOR DESCRIPTION OF WORK DONE

NOTES

As referenced on page 2-7 of this manual, the following message is relevant to users in the USA:
IMPORTANT
This Boiler is equipped with a feature that saves energy by reducing the boiler water
temperature as the heating load decreases. This feature is equipped with an override
which is provided primarily to permit the use of an external energy management system
that serves the same function. THIS OVERRIDE MUST NOT BE USED UNLESS AT
LEAST ONE OF THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS IS TRUE:
• An external energy management system is installed that reduces the boiler
water temperature as the heating load decreases.
• This boiler is not used for any space heating.
• This boiler is part of a modular or multiple boiler system having a total input
300,000 BTU/hr or greater.
of
• This boiler is equipped with a tankless coil (not applicable to IBC’s SL boilers).
US installers should contact IBC for any further information required.

REVISION HISTORY
R1 (March 2017) Initial release
R2 (AVRIL 2017) Corrections to text (Specications table and part number tables)

IBC Technologies Inc.
8015 North Fraser Way
Burnaby, BC
Canada V5J 5M8
Tel: 604-877-0277
Fax: 604-877-0295
Toll Free: 1-844-432-8422
www.ibcboiler.com
April 2017
© IBC Technologies Inc. 2017
 Loading...
Loading...