Page 1
Horizontal Articulated Robot – IX Series
Tabletop Type, Clean-room Specification
Arm Length 500/600/700/800
IX-NNC50 /60 /70 /80
Operation Manual Fourth Edition
Page 2

Page 3

Please Read Before Use
Thank you for purchasing an IAI product.
This operation manual explains the handling methods, structure and maintenance of this product, among
others, providing the information you need to know to use the product safely.
Before using the product, be sure to read this manual and fully understand the contents explained herein
to ensure safe use of the product.
The CD or DVD that comes with the product contains operation manuals for IAI products.
When using the product, refer to the necessary portions of the applicable operation manual by printing
them out or displaying them on a PC.
After reading the operation manual, keep it in a convenient place so that whoever is handling this product
can reference it quickly when necessary.
[Important]
The product cannot be operated in any way unless expressly specified in this operation
manual. IAI shall assume no responsibility for the outcome of any operation not specified
herein.
Information contained in this operation manual is subject to change without notice for the
purpose of product improvement.
This operation manual is original.
If you have any question or comment regarding the content of this manual, please contact
the IAI sales office near you.
Unauthorized use or reproduction of this operation manual, whether in whole or in part, is strictly
prohibited.
Page 4

CE Marking
If a compliance with the CE Marking is required, please follow Overseas Standards Compliance Manual
(ME0287) that is provided separately.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Safety Guide ······················································································································1
Caution in Handling ···········································································································8
1. Names of Robot Parts ································································································9
1.1 Names of Parts ·····························································································································9
1.2 Labels ·········································································································································10
1.3 Label Positions ··························································································································· 11
2. Transportation and Handling ··················································································· 12
2.1 Handling of the Carton ················································································································12
2.2 Packing Condition of the Robot ··································································································12
2.3 Handling of Individual Components ····························································································13
2.4 Checking after Unpacking ··········································································································13
2.5 Transporting the Robot ···············································································································14
3. Installation Environment and Storage Environment ················································ 15
3.1 Installation Environment ·············································································································15
3.2 Installation Platform ····················································································································15
3.3 Storage Environment ··················································································································16
4. How to Install ··········································································································· 17
4.1 Installation Posture ·····················································································································17
4.2 Installing the Robot ·····················································································································18
4.3 Connecting the Controller ···········································································································19
4.4 Checking after Installation ··········································································································21
5. Precautions for Use ································································································· 22
5.1 Reference Acceleration/Deceleration Settings ···········································································22
5.2 Tools ···········································································································································24
5.3 Carrying Load ·····························································································································25
5.4 User Wiring and Piping ···············································································································26
5.5 Suction Rate ·······························································································································28
6. Inspection/Maintenance ·························································································· 29
6.1 Inspection/Maintenance ··············································································································29
6.2 How to Replace Bellows ·············································································································31
6.3 How to Check/Adjust Belt Tension ······························································································37
6.4 Battery Replacement ··················································································································44
6.5 Absolute Reset Procedure ··········································································································47
7. Specifi cations ·········································································································· 63
7.1 Specifi cation Table ······················································································································63
7.2 External Dimensions ···················································································································71
7.3 Robot Operation Area ·················································································································75
7.4 Wiring Diagram ···························································································································77
7.5 230V Circuit Components ···········································································································78
Page 6

8. Warranty ·················································································································· 79
8.1 Warranty Period ··························································································································79
8.2 Scope of Warranty ······················································································································79
8.3 Honoring the Warranty ················································································································79
8.4 Limited Liability ···························································································································79
8.5 Conditions of Conformance with Applicable Standards/Regulations, Etc., and Applications ·····80
8.6 Other Items Excluded from Warranty ·························································································80
Change History ··············································································································· 81
Page 7
Safety Guide
“Safety Guide” has been written to use the machine safely and so prevent personal injury or property
damage beforehand. Make sure to read it before the operation of this product.
Safety Precautions for Our Products
The common safety precautions for the use of any of our robots in each operation.
No.
1 Model
Operation
Description
Selection
Description
This product has not been planned and designed for the application where
high level of safety is required, so the guarantee of the protection of
human life is impossible. Accordingly, do not use it in any of the following
applications.
1) Medical equipment used to maintain, control or otherwise affect human
life or physical health.
2) Mechanisms and machinery designed for the purpose of moving or
transporting people (For vehicle, railway facility or air navigation facility)
3) Important safety parts of machinery (Safety device, etc.)
Do not use the product outside the specifications. Failure to do so may
considerably shorten the life of the product.
Do not use it in any of the following environments.
1) Location where there is any inflammable gas, inflammable object or
explosive
2) Place with potential exposure to radiation
3) Location with the ambient temperature or relative humidity exceeding
the specification range
4) Location where radiant heat is added from direct sunlight or other large
heat source
5) Location where condensation occurs due to abrupt temperature
changes
6) Location where there is any corrosive gas (sulfuric acid or hydrochloric
acid)
7) Location exposed to significant amount of dust, salt or iron powder
8) Location subject to direct vibration or impact
For an actuator used in vertical orientation, select a model which is
equipped with a brake. If selecting a model with no brake, the moving part
may drop when the power is turned OFF and may cause an accident such
as an injury or damage on the work piece.
1
Page 8
No.
Operation
Description
Description
2 Transportation When carrying a heavy object, do the work with two or more persons or
utilize equipment such as crane.
When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is
to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with
each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
When in transportation, consider well about the positions to hold, weight
and weight balance and pay special attention to the carried object so it
would not get hit or dropped.
Transport it using an appropriate transportation measure.
The actuators available for transportation with a crane have eyebolts
attached or there are tapped holes to attach bolts. Follow the instructions
in the instruction manual for each model.
Do not step or sit on the package.
Do not put any heavy thing that can deform the package, on it.
When using a crane capable of 1t or more of weight, have an operator
who has qualifications for crane operation and sling work.
When using a crane or equivalent equipments, make sure not to hang a
load that weighs more than the equipment’s capability limit.
Use a hook that is suitable for the load. Consider the safety factor of the
hook in such factors as shear strength.
Do not get on the load that is hung on a crane.
Do not leave a load hung up with a crane.
Do not stand under the load that is hung up with a crane.
3 Storage and
Preservation
The storage and preservation environment conforms to the installation
environment. However, especially give consideration to the prevention of
condensation.
Store the products with a consideration not to fall them over or drop due to
an act of God such as earthquake.
4 Installation
and Start
(1) Installation of Robot Main Body and Controller, etc.
Make sure to securely hold and fix the product (including the work part). A
fall, drop or abnormal motion of the product may cause a damage or injury.
Also, be equipped for a fall-over or drop due to an act of God such as
earthquake.
Do not get on or put anything on the product. Failure to do so may cause
an accidental fall, injury or damage to the product due to a drop of
anything, malfunction of the product, performance degradation, or
shortening of its life.
When using the product in any of the places specified below, provide a
sufficient shield.
1) Location where electric noise is generated
2) Location where high electrical or magnetic field is present
3) Location with the mains or power lines passing nearby
4) Location where the product may come in contact with water, oil or
chemical droplets
2
Page 9
No.
Operation
Description
4 Installation
and Start
Description
(2) Cable Wiring
Use our company’s genuine cables for connecting between the actuator
and controller, and for the teaching tool.
Do not scratch on the cable. Do not bend it forcibly. Do not pull it. Do not
coil it around. Do not insert it. Do not put any heavy thing on it. Failure to
do so may cause a fire, electric shock or malfunction due to leakage or
continuity error.
Perform the wiring for the product, after turning OFF the power to the unit,
so that there is no wiring error.
When the direct current power (+24V) is connected, take the great care of
the directions of positive and negative poles. If the connection direction is
not correct, it might cause a fire, product breakdown or malfunction.
Connect the cable connector securely so that there is no disconnection or
looseness. Failure to do so may cause a fire, electric shock or malfunction
of the product.
Never cut and/or reconnect the cables supplied with the product for the
purpose of extending or shortening the cable length. Failure to do so may
cause the product to malfunction or cause fire.
(3) Grounding
The grounding operation should be performed to prevent an electric shock
or electrostatic charge, enhance the noise-resistance ability and control
the unnecessary electromagnetic radiation.
For the ground terminal on the AC power cable of the controller and the
grounding plate in the control panel, make sure to use a twisted pair cable
with wire thickness 0.5mm
2
(AWG20 or equivalent) or more for grounding
work. For security grounding, it is necessary to select an appropriate wire
thickness suitable for the load. Perform wiring that satisfies the
specifications (electrical equipment technical standards).
Perform Class D Grounding (former Class 3 Grounding with ground
resistance 100: or below).
3
Page 10
No.
4 Installation
Operation
Description
and Start
Description
(4) Safety Measures
When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is
to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with
each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
When the product is under operation or in the ready mode, take the safety
measures (such as the installation of safety and protection fence) so that
nobody can enter the area within the robot’s movable range. When the
robot under operation is touched, it may result in death or serious injury.
Make sure to install the emergency stop circuit so that the unit can be
stopped immediately in an emergency during the unit operation.
Take the safety measure not to start up the unit only with the power turning
ON. Failure to do so may start up the machine suddenly and cause an
injury or damage to the product.
Take the safety measure not to start up the machine only with the
emergency stop cancellation or recovery after the power failure. Failure to
do so may result in an electric shock or injury due to unexpected power
input.
When the installation or adjustment operation is to be performed, give
clear warnings such as “Under Operation; Do not turn ON the power!” etc.
Sudden power input may cause an electric shock or injury.
Take the measure so that the work part is not dropped in power failure or
emergency stop.
Wear protection gloves, goggle or safety shoes, as necessary, to secure
safety.
Do not insert a finger or object in the openings in the product. Failure to do
so may cause an injury, electric shock, damage to the product or fire.
When releasing the brake on a vertically oriented actuator, exercise
precaution not to pinch your hand or damage the work parts with the
actuator dropped by gravity.
5 Teaching When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is
to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with
each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Perform the teaching operation from outside the safety protection fence, if
possible. In the case that the operation is to be performed unavoidably
inside the safety protection fence, prepare the “Stipulations for the
Operation” and make sure that all the workers acknowledge and
understand them well.
When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection fence,
the worker should have an emergency stop switch at hand with him so that
the unit can be stopped any time in an emergency.
When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection fence,
in addition to the workers, arrange a watchman so that the machine can
be stopped any time in an emergency. Also, keep watch on the operation
so that any third person can not operate the switches carelessly.
Place a sign “Under Operation” at the position easy to see.
When releasing the brake on a vertically oriented actuator, exercise
precaution not to pinch your hand or damage the work parts with the
actuator dropped by gravity.
* Safety protection Fence : In the case that there is no safety protection
fence, the movable range should be indicated.
4
Page 11

No.
Operation
Description
Description
6 Trial Operation When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is
to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with
each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
After the teaching or programming operation, perform the check operation
one step by one step and then shift to the automatic operation.
When the check operation is to be performed inside the safety protection
fence, perform the check operation using the previously specified work
procedure like the teaching operation.
Make sure to perform the programmed operation check at the safety
speed. Failure to do so may result in an accident due to unexpected
motion caused by a program error, etc.
Do not touch the terminal block or any of the various setting switches in
the power ON mode. Failure to do so may result in an electric shock or
malfunction.
7 Automatic
Operation
Check before starting the automatic operation or rebooting after operation
stop that there is nobody in the safety protection fence.
Before starting automatic operation, make sure that all peripheral
equipment is in an automatic-operation-ready state and there is no alarm
indication.
Make sure to operate automatic operation start from outside of the safety
protection fence.
In the case that there is any abnormal heating, smoke, offensive smell, or
abnormal noise in the product, immediately stop the machine and turn
OFF the power switch. Failure to do so may result in a fire or damage to
the product.
When a power failure occurs, turn OFF the power switch. Failure to do so
may cause an injury or damage to the product, due to a sudden motion of
the product in the recovery operation from the power failure.
5
Page 12

No.
8 Maintenance
Operation
Description
and Inspection
Description
When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who is
to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well with
each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Perform the work out of the safety protection fence, if possible. In the case
that the operation is to be performed unavoidably inside the safety
protection fence, prepare the “Stipulations for the Operation” and make
sure that all the workers acknowledge and understand them well.
When the work is to be performed inside the safety protection fence,
basically turn OFF the power switch.
When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection fence,
the worker should have an emergency stop switch at hand with him so that
the unit can be stopped any time in an emergency.
When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection fence,
in addition to the workers, arrange a watchman so that the machine can
be stopped any time in an emergency. Also, keep watch on the operation
so that any third person can not operate the switches carelessly.
Place a sign “Under Operation” at the position easy to see.
For the grease for the guide or ball screw, use appropriate grease
according to the Instruction Manual for each model.
Do not perform the dielectric strength test. Failure to do so may result in a
damage to the product.
When releasing the brake on a vertically oriented actuator, exercise
precaution not to pinch your hand or damage the work parts with the
actuator dropped by gravity.
The slider or rod may get misaligned OFF the stop position if the servo is
turned OFF. Be careful not to get injured or damaged due to an
unnecessary operation.
Pay attention not to lose the cover or untightened screws, and make sure
to put the product back to the original condition after maintenance and
inspection works.
Use in incomplete condition may cause damage to the product or an injury.
* Safety protection Fence : In the case that there is no safety protection
fence, the movable range should be indicated.
9 Modification
and Dismantle
Do not modify, disassemble, assemble or use of maintenance parts not
specified based at your own discretion.
10 Disposal When the product becomes no longer usable or necessary, dispose of it
properly as an industrial waste.
When removing the actuator for disposal, pay attention to drop of
components when detaching screws.
Do not put the product in a fire when disposing of it.
The product may burst or generate toxic gases.
11 Other Do not come close to the product or the harnesses if you are a person
who requires a support of medical devices such as a pacemaker. Doing so
may affect the performance of your medical device.
See Overseas Specifications Compliance Manual to check whether
complies if necessary.
For the handling of actuators and controllers, follow the dedicated
instruction manual of each unit to ensure the safety.
6
Page 13
Alert Indication
The safety precautions are divided into “Danger”, “Warning”, “Caution” and “Notice” according to the
warning level, as follows, and described in the Instruction Manual for each model.
Level Degree of Danger and Damage Symbol
Danger
Warning
Caution
Notice
This indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if the
product is not handled correctly, will result in death or serious injury.
This indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if the product
is not handled correctly, could result in death or serious injury.
This indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if the product
is not handled correctly, may result in minor injury or property
damage.
This indicates lower possibility for the injury, but should be kept to
use this product properly.
Danger
Warning
Caution
Notice
7
Page 14

Caution in Handling
1. Make sure to attach the vertical articulated robot properly by following this operation
manual.
Using the product with the vertical articulated robot not being certainly retained or affixed may
cause abnormal noise, vibration, malfunction or shorten the product life.
8
Page 15
1 Names of Robot Parts
A
I
A
A
A
A
1.1 Names of Parts
User connector
LM (indicator)
Spacer for user
part installation
BK SW
(Brake-release switch)
Bellows
(rotational axis)
Axis 3
(vertical axis)
Cover
(arm 2)
Axis 4
Panel
I4 joint for user piping, black
I6 joint for user piping, red
6 joint for user piping, yellow
I4 joint for user piping, white
Mechanical
stopper for arm 2
xis 2
1. Names of Robot Parts
Suction joint
Top cover (arm 1)
Wiring duct
xis 1
Mechanical stopper
for arm 1/arm 2
Bellows
Ball screw
spline shaft
rm 2
End cover (arm 1)
rm 1
Reference
surface
Cover (base)
Base
M cable (outside robot)
PG cable (outside robot)
U cable (outside robot)
BK power cable (outside robot)
Air tubes (I4: 2 pcs., I6: 2 pcs.)
9
Page 16
1.2 Labels
The following labels are attached on the robot and controller. Be sure to observe the instructions and
cautions written on the labels to ensure the correct use of the robot/controller.
Labels on the Robot
1. Names of Robot Parts
Prohibition of entry into
the operation area
Warning on handling of
the vertical axis
Warning against
electric shock
Robot serial number
Labels on the Controller
Caution/warning on handling
of the controller
Controller serial number
(Other than CE-certified models)
CE-certified robot (Provided only for
CE-certified models)
Rated
Designation of the connected robot
Controller serial number
(CE-certified models)
Danger
z Failure to observe the cautionary information provided on the labels may result in serious injury or
damage to the robot.
10
Warning
Caution
Page 17
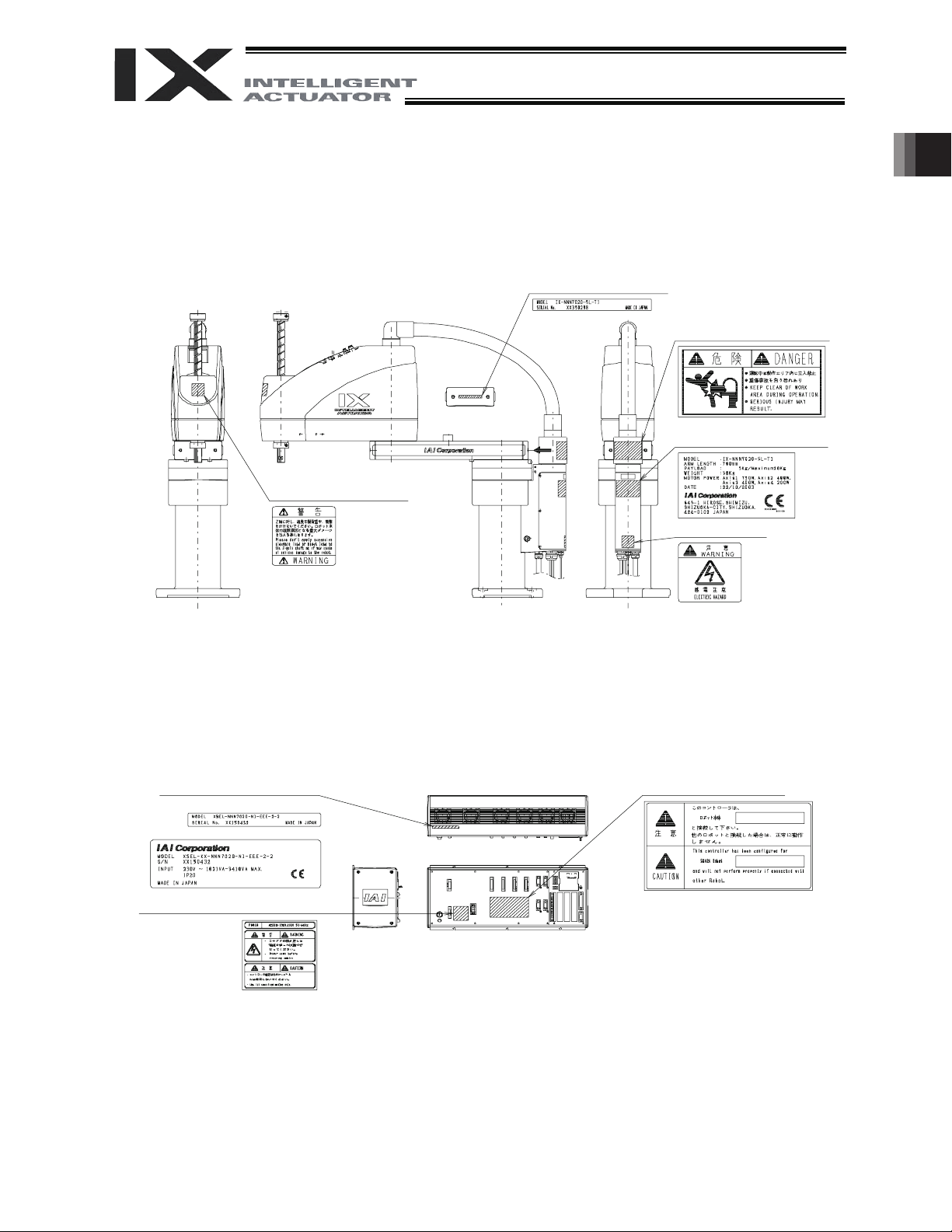
1.3 Label Positions
Label Positions on the Robot
1. Names of Robot Parts
Robot serial number
Prohibition of entry into
the operation area
Warning on handling of
the vertical axis
Label Positions on the Controller
Controller serial number
Other than CE-certified models
CE-certified models
View A
CE-certified robot (Provided
only for CE-certified models)
Rated
Warning against electric shock
Designation of the connected robot
Caution/warning on handling of the controller
11
Page 18

2 Transportation and Handling
2.1 Handling of the Carton
Each robot is packed with a controller prior to shipment.
When transporting the carton containing the robot and controller, observe the following items and be
careful not to drop the carton or apply impact due to forcible contact:
x If the carton is heavy, one operator should not attempt to carry it alone.
x Place the carton on a level surface if it is to be left there for a while.
x Do not climb upon the carton.
x Do not place on the carton any heavy object that may cause the carton to deform, or an article
whose shape allows a load to be concentrated at one point.
2.2 Packing Condition of the Robot
2. Transportation and Handling
Robot
Controller, accessories and other
items (except for the robot)
Arm fixing plate
Warning
z The robot and controller are very heavy. When transporting the carton containing the robot and
controller, handle it with extra care so as not to drop the carton or apply impact due to forcible
contact, as it may cause injury or damage to the robot or controller.
z Serious injury may result if the carton is dropped onto a person during transportation.
z Never stand below the carton as it is hoisted.
z Use a carrier device with sufficient loading capacity.
z If a machine or method is used that requires specified skills, it must be operated/performed by a
person having the proper qualifications.
Caution
12
Page 19
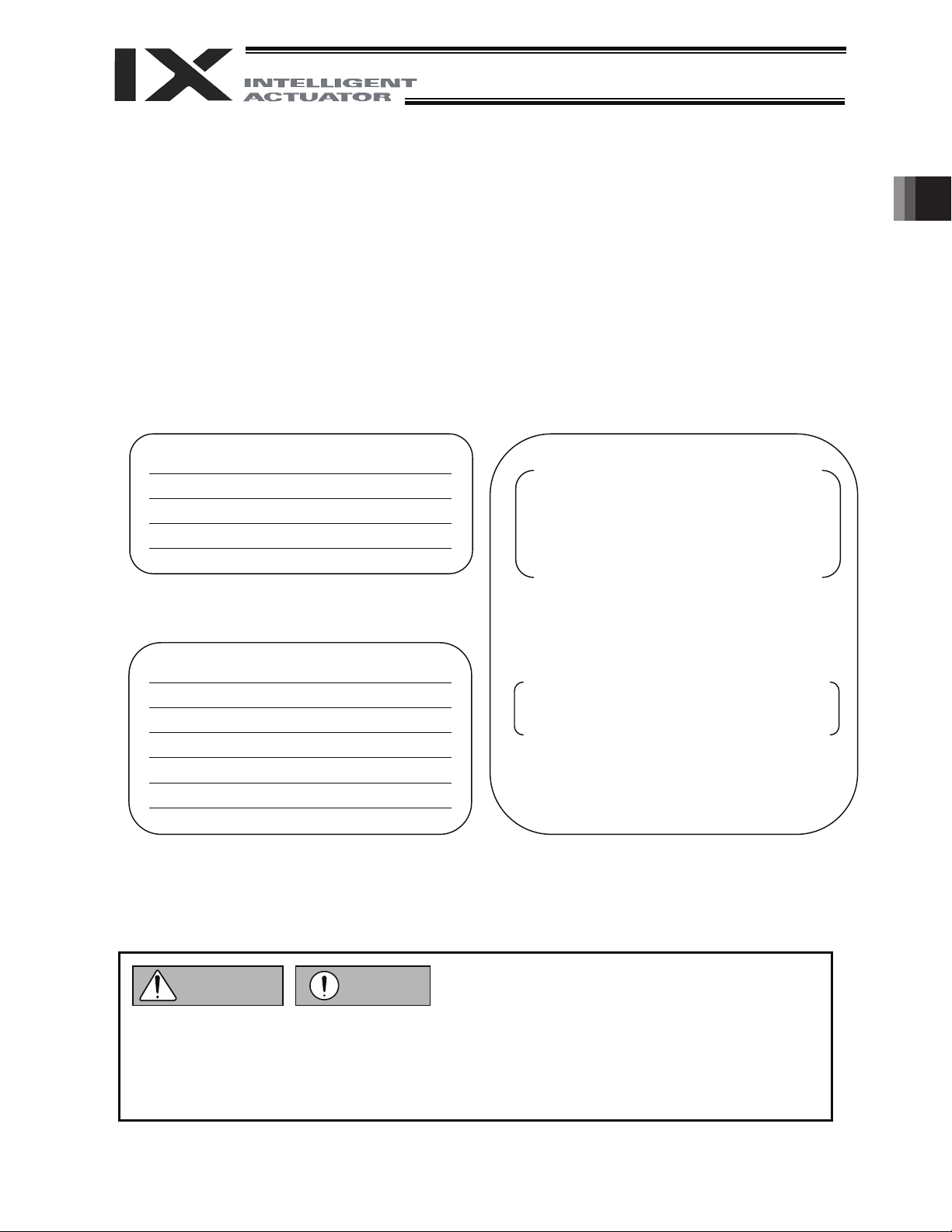
2.3 Handling of Individual Components
The robot and controller are supplied as a set.
Your robot cannot be used with the controller supplied with another robot.
When handling multiple robots, be careful not to lose their correct pairings with the controllers.
The robot will not stand on its own after being unloaded from the carton pallet.
Hold it by hand, or place a cushioning material on the floor and place the robot on its side upon the cushion.
2.4 Checking after Unpacking
After unpacking the carton, check the condition of the robot and other items contained in the carton.
Standard parts Optional parts
Robot 1 PC software (type: IA-101-X-MW)
Controller 1 Floppy disk 2
Operation manual for robot 1 PC connection cable 1
Operation manual for controller 1 Hand-held emergency-stop switch 1
Operation manual for PC software 1
2. Transportation and Handling
Absolute reset adjustment jig
Accessories
Type: JG-1 (IX-NNC50, IX-NNC60)
Eyebolt 2 JG-3 (IX-NNC70, IX-NNC80)
D-sub connector 1 Positioning jig for axes 1 and 2 1
Hood set (for D-sub connector) 1 Positioning jig for axis 4 1
Caution label 2
Positioning label 1
PIO flat cable 1
Caution
z Always operate the robot using the controller supplied with the robot in the same carton. Using
another controller may result in an unexpected operation, damaged motor or other problem.
z After unpacking, be sure to confirm the condition of the robot and other items contained in the
carton. Should you find a damaged or missing part, please contact IAI immediately.
Note
13
Page 20
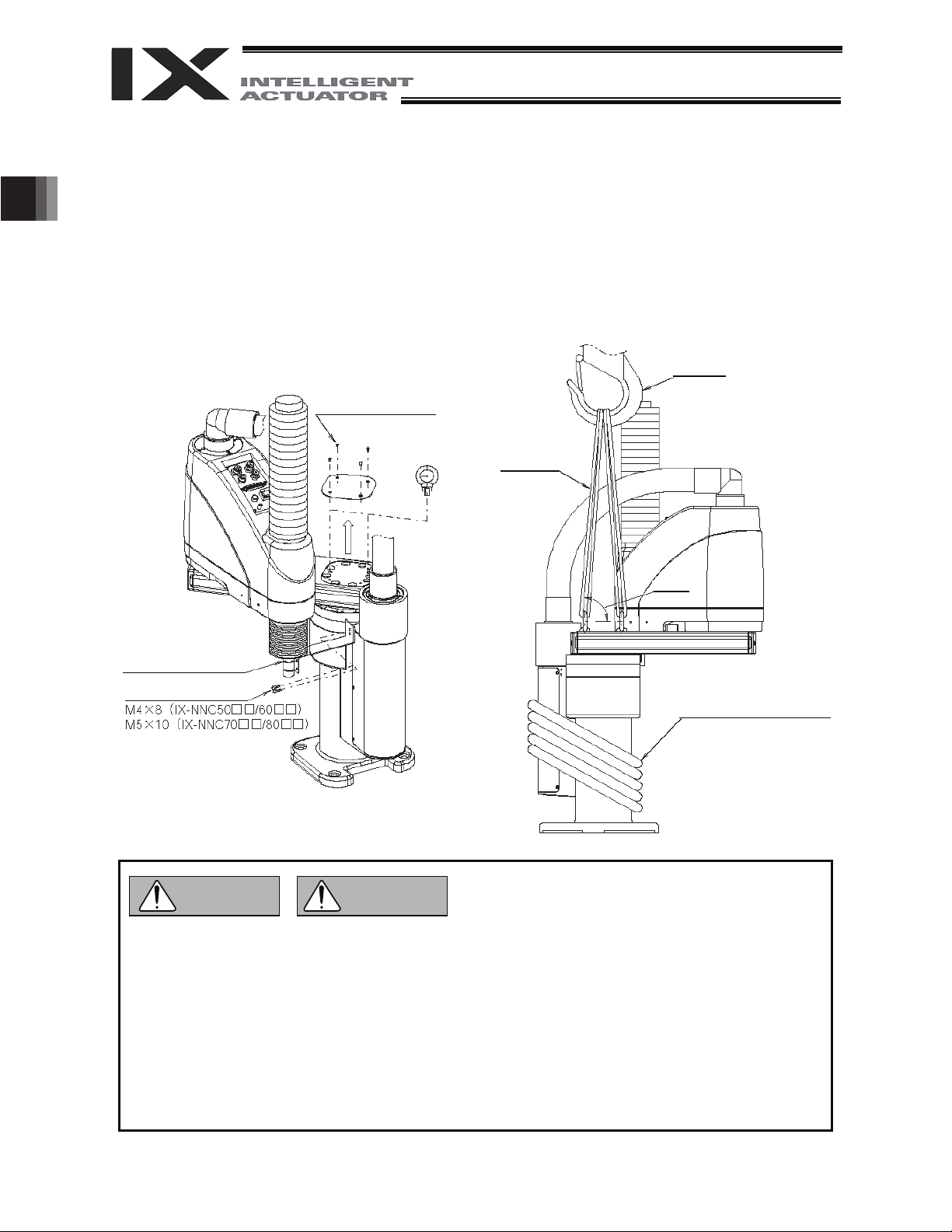
2.5 Transporting the Robot
When transporting the robot, affix the arms using the supplied arm fixing plate. Additionally, wrap the cables
around the base and secure them with gummed tape or other means.
Use a dolly, forklift, crane or other appropriate equipment for transportation. When transporting the robot,
move it slowly so that it maintains its balance. Also, safeguard the robot against vibration or impact.
When a crane is used, install the supplied eyebolts on the robot for the pass-through of ropes. Install the
eyebolts following removal of the top cover.
2. Transportation and Handling
Cross-recessed countersunk
head screw, M3 x 8
Eyebolt
(supplied)
String,
rope, etc.
Hoisting hook
with lock
45 degrees
or more
Fix with a tie wrap.
Hex bolt
Danger
Warning
Cables
(Wrap around the base.)
z If the arms and cables remain free, the arms may turn unexpectedly and pinch a hand, or a person
may be tripped by the trailing cables.
z Do not attempt to carry the robot by hand, as it may injure the back. Additionally, an injury may
result if the robot is dropped onto the feet.
z Serious injury may result if a person is caught under a fallen robot during transportation.
z Never stand below the robot as it is hoisted.
z Use a hoist and ropes that can comfortably support the weight of the robot.
z If a machine or method is used that requires specified skills, it must be operated/performed by a
person having the proper qualifications.
14
Page 21
3 Installation Environment and Storage Environment
3.1 Installation Environment
Install the robot in an environment that satisfies the following conditions:
x Away from direct sunlight
x Not subject to radiated heat from a high-capacity energy source such as a heat-treating furnace
x Ambient temperature: 0qC to 40qC
x Humidity: 85% or less (non-condensing)
x Not exposed to corrosive or flammable gases
x Not subject to impact or vibration
x Not exposed to a significant amount of electromagnetic waves, ultraviolet rays or radiation
x Sufficient space is available to ensure safety in teaching and maintenance/inspection operations
Generally, the robot must be installed where the operator need not wear protective gear in order to work.
3.2 Installation Platform
The platform on which to install the robot receives a significant reactive force. Be certain the platform has
sufficient rigidity to withstand the anticipated force.
x The surface on which the robot is fixed must have a thickness of 25 mm or more.
The levelness of the robot installation surface must be at least r0.05 mm.
x Drill and tap holes, as indicated below, into the installation surface of the platform.
3. Installation Environment and Storage Environment
Type Tap size Remarks
IX-NNC50/60 M10
IX-NNC70/80 M12
x The platform must have sufficient rigidity to withstand not only the weight of the robot but also the
dynamic moment of inertia that is generated when the robot is operated at maximum speed.
x Secure the platform to the floor or other rigid structure in a manner that prevents any movement due
to operation of the robot.
x The installation platform must allow the robot to be mounted on a level surface.
Effective thread: 10 mm or longer for steel (20 mm or
longer for aluminum)
Effective thread: 12 mm or longer for steel (24mm or
longer for aluminum)
15
Page 22

3.3 Storage Environment
The storage environment conforms to the installation environment. If the robot is to be stored for a
prolonged period of time, be sure the robot will not be exposed to dew condensation.
Unless otherwise specified, desiccant is not placed in the carton when shipped. If the robot is to be kept in
an environment subject to condensation, provide preventive measures from over the carton or directly to
the robot after unpacking.
The maximum storage temperature is 60qC for a short storage period. If the robot is to be stored for more
than a month, the ambient temperature should not exceed 50qC.
Danger
z Failure to provide a proper environment for installation and storage may shorten the service life of
the robot, reduce its operation accuracy, or cause a malfunction or failure.
z Never use the robot in a flammable atmosphere. The robot may explode or ignite.
3. Installation Environment and Storage Environment
Warning
16
Page 23
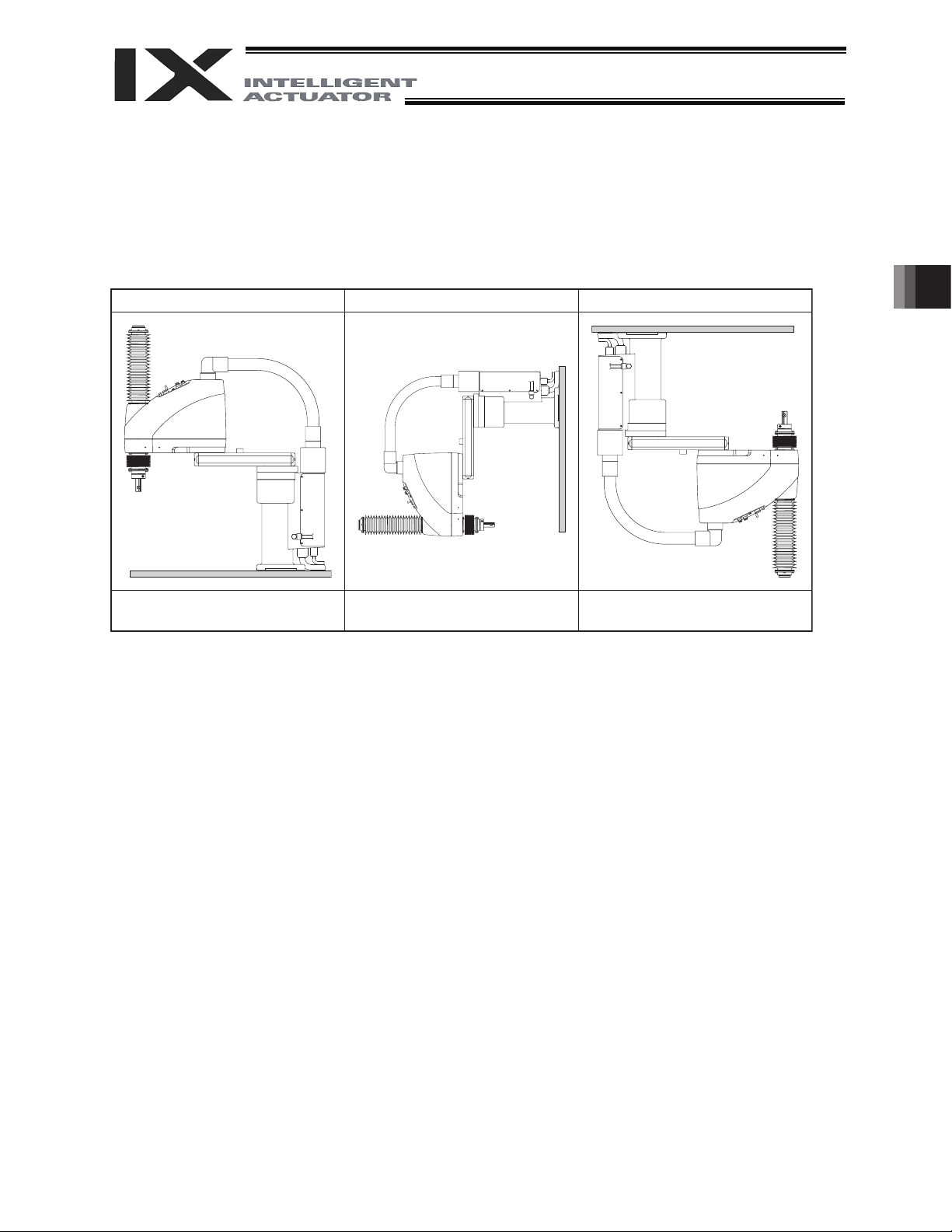
17
How to Install
4.
Shown below is how to install SCARA Robot.
4.1
: Available s : Not available
ż
Installation Posture
ż
Ceiling-MountWall-MountHorizontally Oriented Mount
4. How to Install
ss
Page 24
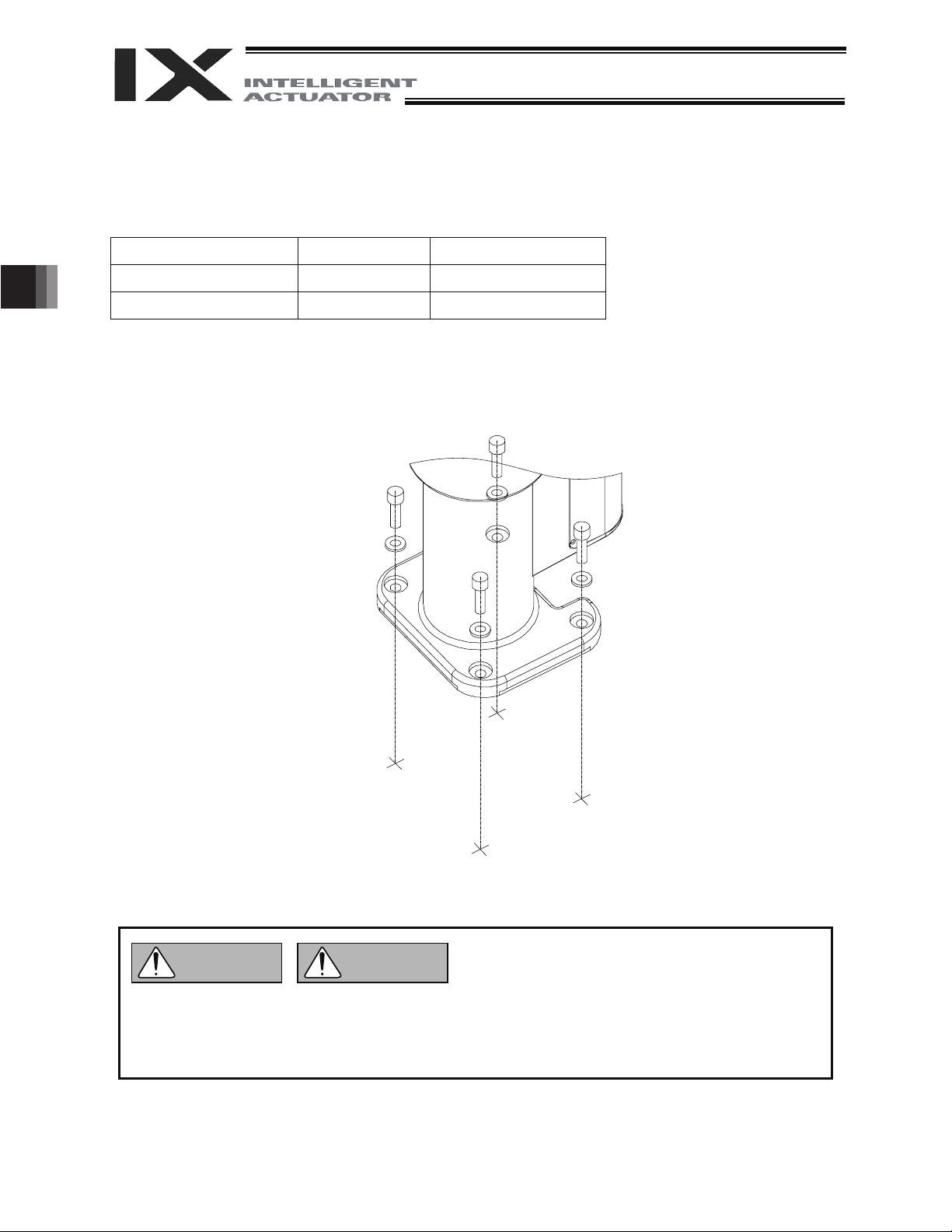
4.2
4.1 Installing the Robot
Install the robot on a level surface.
Secure the robot using hex bolts and washers.
IX-NNC50/60 M10 60 Nxm
IX-NNC70/80 M12 104 Nxm
For the hex bolts, use high-tension bolts with an ISO rating of 10.9 or higher.
4. How to Install
Type Bolt size Tightening torque
Warning
z Always insert a washer below each bolt. Without a washer, the bolt-bearing surface may sink.
z Tighten the hex bolts securely to the correct torque. Improperly tightened bolts may reduce the
accuracy of robot operation, and in the worst case cause the robot to overturn.
18
Caution
Page 25
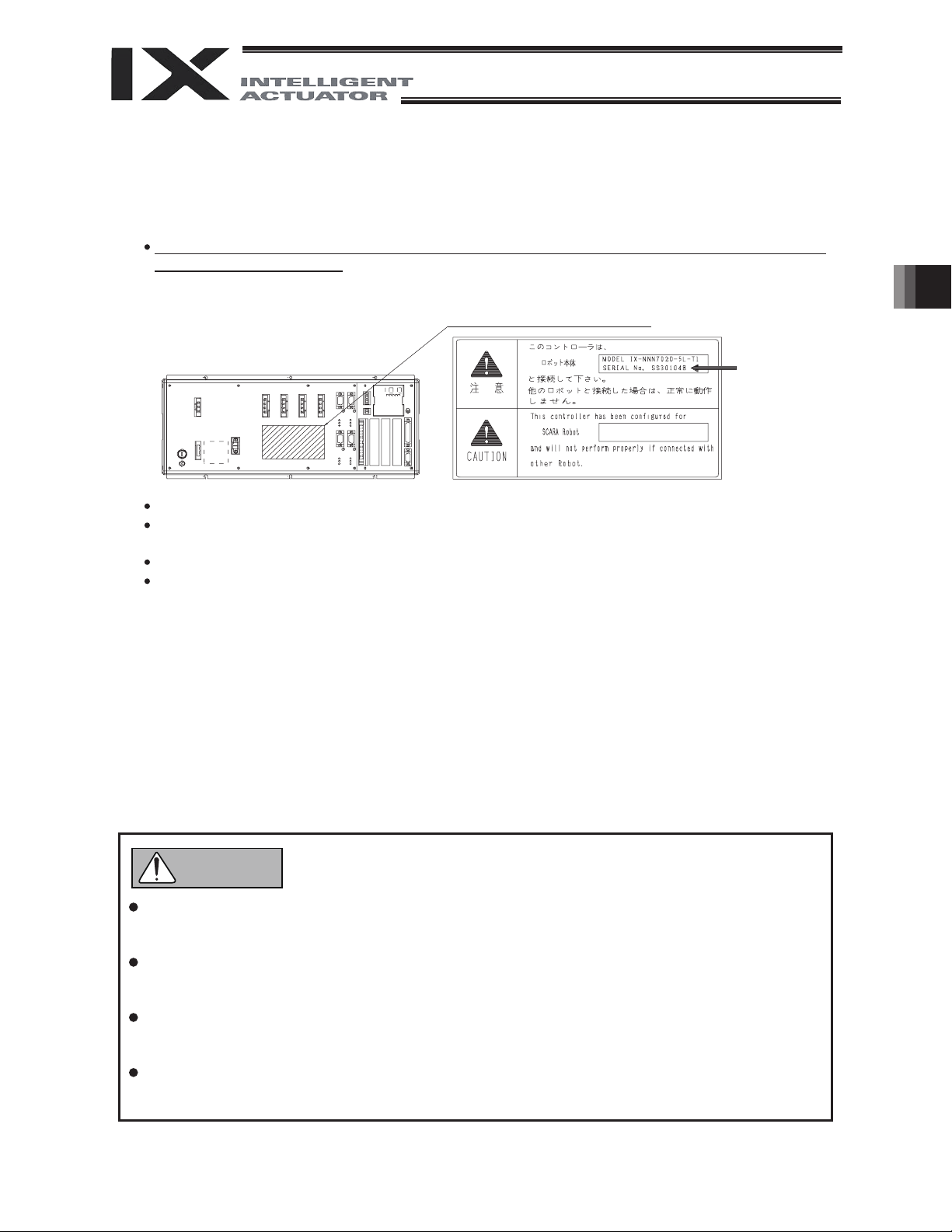
4.3 Connecting the Controller
The controller connection cables are attached on the robot (standard cable: 5 m, to air-tube joint: 150 mm).
Pay attention to the following items when connecting the controller:
Connect to the robot of the serial number specified on the robot designation label provided on the
front panel of the controller.
Robot designation label
Robot serial
number
Connect the cables securely after confirming that they are free from damage or bent connector pins.
Connect each cable by aligning the indication on the marking tube on the cable with the indication on
the controller panel.
When installing the PG connector (D-sub connector), ensure correct orientation of the connector.
The brake power circuit is provided on the primary side (high-voltage side). Therefore, provide a
dedicated 24 VDC power supply for the brake.
sources such as I/O power source.
The brake power to be supplied to Horizontal Articulated Robot should be 24V DC ±10% and the
voltage source capacity 20W.
The brake power to be supplied to the XSEL-PX/QX controller should be 24V DC ±10% and the
voltage source capacity 9W.
(Note) It is necessary to increase the voltage source capacity of the brake power source if brake
actuators are to be connected to the 5th and 6th axes of the XSEL-PX/QX controller.
[Refer to the section of the voltage source capacity and heat generation in the controller
operation manual.]
Do not attempt to share the secondary circuit power
4. How to Install
Refer to the operation manuals for the controller and PC software for the procedures to connect the I/O
cable, controller power cable, PC connection cable, etc.
Warning
Be sure to connect to the robot of the serial number specified on the front panel of the controller.
The controller will not operate properly if any other robot is connected. Failure to observe this
warning may cause the robot to malfunction, resulting in a serious accident.
Before connecting or disconnecting a cable, always turn off the power to the controller.
Connecting/disconnecting a cable with the power supplied to the controller may cause the robot to
malfunction, resulting in a serious accident.
Installing the connectors into the wrong sockets may cause the robot to malfunction. Be sure to
check the designation on the cable with that on the controller panel before plugging in any
connector.
If the connectors are not inserted securely, the robot may malfunction and generate the risk of
danger. Be sure to affix each connector with the supplied screws.
19
Page 26
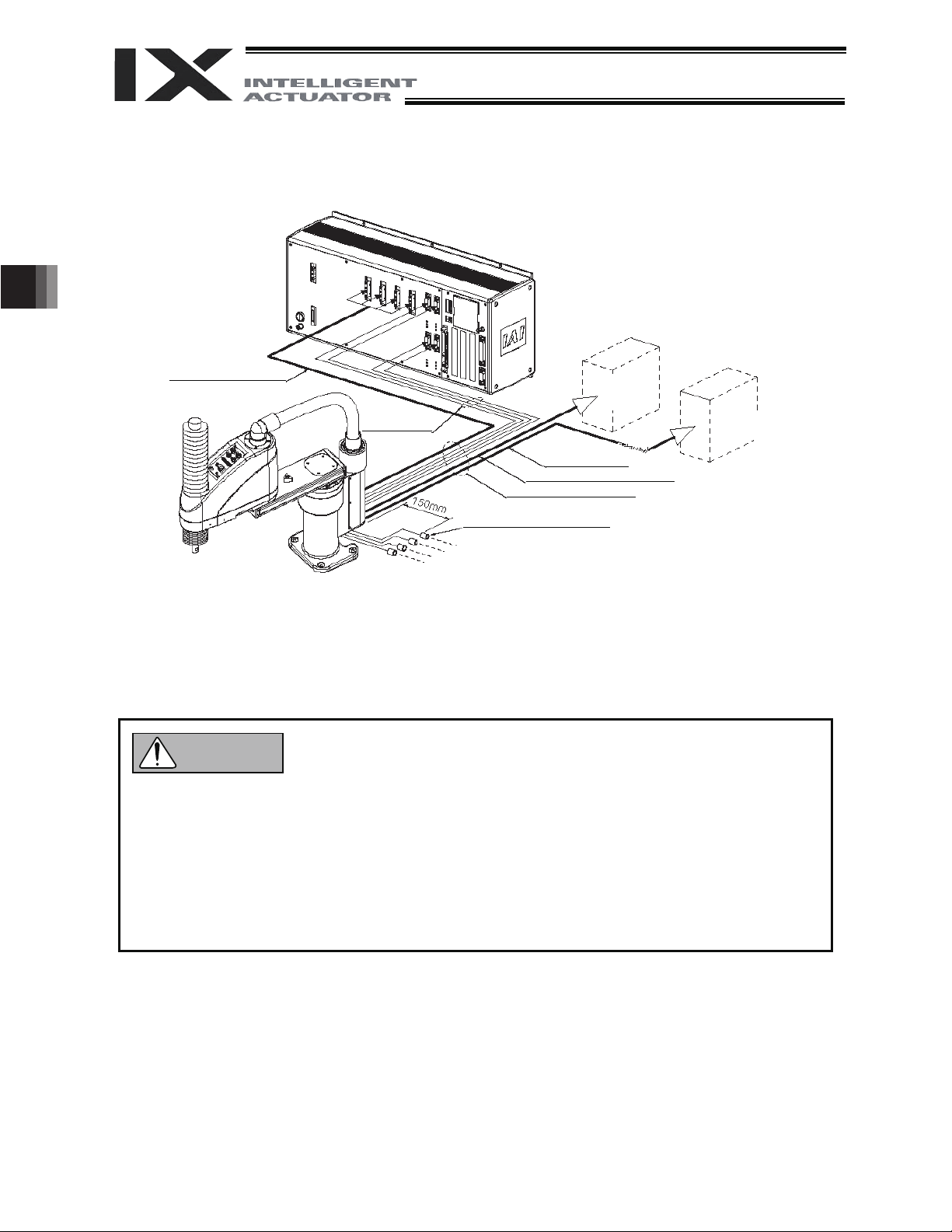
Output voltage: 24 VDC r 10%
Current capacity: 20 to 30 W
4. How to Install
z Before connecting or disconnecting a cable, always turn off the power to the controller.
z Installing the connectors into the wrong sockets may cause the robot to malfunction. Be sure to
z If the connectors are not inserted securely, the robot may malfunction and generate the risk of
M cable (outside robot)
PG cable
(outside robot)
Standard cable length: 5 m
I4, I
6 quick joint (2 pcs. each)
To air tube
(provided by user)
U cable (outsid e ro bot)
(cable for user wiring)
BK power cable (outside robot)
24 VDC power
supply for brake
(provided by
user)
Tool, control
unit, etc.
(provided by
user)
Warning
Connecting/disconnecting a cable with the power supplied to the controller may cause the robot to
malfunction, resulting in a serious accident.
check the designation on the cable with that on the controller panel before plugging in any
connector.
danger. Be sure to affix each connector with the supplied screws.
20
Page 27

4.4
4.3 Checking after Installation
Once the robot has been installed, check the following items:
x Visually check the robot, controller and cables for dents and other abnormalities.
x Confirm that the cables are connected properly and that the connectors are inserted securely.
4. How to Install
Warning
z Failure to perform these checks may result in a malfunctioning robot or a damaged controller or
robot.
21
Page 28

5 Precautions for Use
5.1 Reference Acceleration/Deceleration Settings
Use the robot based on appropriate acceleration/deceleration settings by referring to the following graph:
(1) PTP operation (Set using the SEL language commands ACCS and DCLS.)
Reference acceleration/deceleration
100
50
5. Precautions for Use
Acceleration (%)
Reference range for continuous
0
0 5 10
IX-NNC50/60
settings for PTP operation
Reference range of
maximum setting
operation setting
Reference range of maximum setting when arm 1 is
operated over 125 degrees or more
Carrying load mass (kg)
Caution
IX-NNC70/80
Reference acceleration/deceleration
settings for PTP operation
100
Reference range of
50
maximum setting
cceleration (%)
Reference range for continuous
operation setting
Reference range of maximum setting when arm 1 is
0
0 5 10 15 20
operated over 125 degrees or more
Carrying load mass (kg)
z To operate the robot at the maximum acceleration, provide a stopping period of three seconds or
more after each acceleration/deceleration.
z When arm 1 is operated over 125 degrees or more, use the reference range for the continuous
operation setting as the reference range of the maximum setting. The continuous operation setting
value should be one-third the appropriate maximum value thus set.
z Start from the appropriate reference range for the continuous operation setting, and then gradually
raise the value for the purpose of adjustment.
z If an overload error occurs, lower the acceleration setting as appropriate or provide an appropriate
stopping time following each acceleration/deceleration.
z Depending on the position of the vertical axis, the robot may generate vibration when axis 1, axis 2
or the rotational axis turns. If vibration occurs, lower the acceleration as appropriate.
z To move the robot horizontally at high speed, keep the vertical axis as close as possible to the top
position. If the vertical axis is operated at the bottom position, the ball screw spline shaft will bend
and the vertical axis will be disabled.
z Be careful that the moment of inertia of axis 4 does not exceed the permissible value. (Refer to 5.3,
“Carrying Load.”)
z The carrying load indicates a load above the rotational center of axis 4.
z Operate the robot by using an appropriate acceleration coefficient as determined by the mass of
the tip. Failure to do so may cause the drive part to wear prematurely or may result in damage or
vibration.
22
Page 29

(2) CP operation (Set using the SEL language commands ACC and DCL.)
A
IX-NNC50/60
Reference acceleration/deceleration
settings for CP operation
1.0
Reference range of
maximum setting
1.0
0.5
0.5
cceleration (G)
Reference range for
continuous operation setting
0
Acceleration (G)
0
0 5 10
Carrying load mass (kg)
IX-NNC70/80
Reference acceleration/deceleration
settings for CP operation
Reference range of
maximum setting
Reference range for
continuous operation setting
0 5 10 15 20
Carrying load mass (kg)
5. Precautions for Use
Caution
z To operate the robot at the maximum acceleration, provide a stopping period of three seconds or
more after each acceleration/deceleration.
z Start from the appropriate reference range for the continuous operation setting, and then gradually
raise the value for the purpose of adjustment.
z If an overload error occurs, lower the acceleration setting as appropriate or provide an appropriate
stopping time following each acceleration/deceleration.
z Depending on the position of the vertical axis, the robot may generate vibration when axis 1, axis 2
or the rotational axis turns. If vibration occurs, lower the acceleration as appropriate.
z To move the robot horizontally at high speed, keep the vertical axis as close as possible to the top
position. If the vertical axis is operated at the bottom position, the ball screw spline shaft will bend
and the vertical axis will be disabled.
z Be careful that the moment of inertia of axis 4 does not exceed the permissible value. (Refer to 5.3,
“Carrying Load.”)
z The carrying load indicates a load above the rotational center of axis 4.
z Operate the robot by using an appropriate acceleration coefficient as determined by the mass of
the tip. Failure to do so may cause the drive part to wear prematurely or may result in damage or
vibration.
23
Page 30

5.2 Tools
The tool mounting part must have sufficient strength and rigidity, along with adequate fastening power to
prevent positional shift.
It is recommended that a tool be installed over a split ring, span ring or other appropriate part. A sample
configuration of tool installation is given below.
The diameter of each tool must not exceed 100 mm. A tool larger than this dimension will interfere with the
robot within the robot’s range of movement.
Adjust the position (direction) of axis 4 (rotational axis) using the D-cut surface at the tip of axis 4.
5. Precautions for Use
Warning
Tool diameter
I100 or less
D-cut surface
Center of axis 4
(rotational axis)
Caution
D-cut surface
Tool
Span ring, etc.
Pressure flange
z Turn off the power to the controller and robot before installing a tool.
z If the tool mounting part does not have sufficient strength, it may break while the robot is operating
and cause the tool to detach and fly off.
z If the tool diameter exceeds 100 mm, the tool will contact the robot within its range of movement
and cause damage to the tool, work and/or robot.
z Avoid attachment of the tool at the D-cut surface via thread fastening. Doing so may damage the
D-cut positioning surface.
24
Page 31

5.3 Carrying Load
Load capacity
Type Rated load capacity Maximum load capacity
IX-NNC50/60 2 kg 10 kg
IX-NNC70/80 5 kg 20 kg
Load’s permissible moment of inertia
Type Permissible moment of inertia Remarks
IX-NNC50/60 0.06 kgxm
IX-NNC70/80 0.10 kgxm
2
2
Load offset (from the center of axis 4 (rotational axis))
50 mm or less
50 mm or less
5. Precautions for Use
Both rated and maximum
Center of axis 4 (rotational axis)
Load’s center of gravity
Caution
z Set appropriate acceleration/deceleration according to the mass of the tip and moment of inertia.
Failure to do so may cause the drive part to wear prematurely or may result in damage or vibration.
z If vibration occurs, lower the acceleration/deceleration as appropriate.
z If the load gets offset, the robot becomes more likely to cause vibration. Design the tools so that
the load’s center of gravity aligns with the center of axis 4.
z Do not move the robot horizontally with axis 3 (vertical axis) extended. It may cause the vertical
axis to bend and disable the axis. To move the robot horizontally with axis 3 extended, adjust the
speed and acceleration/deceleration as appropriate.
25
Page 32

5.4 User Wiring and Piping
A
A
The robot comes with standard cables and tubes that the user can use in a desired wiring/piping
configuration.
Quick joint
I6 (red)
Quick joint
I4 (black)
User Connector
D-sub 25-pin
connector for user
wiring (socket),
fixing screw M2.6
LM indicator
Spacer for user
part installation
5. Precautions for Use
User connector specifications
Rated voltage 3.0 V
Permissible current 1.1 A
Conductor size and number of wires AWG 26 (0.15 mm
Other Twisted-pair cable (1 to 24), shielded
Piping specifications
Normal service pressure 0.8 MPa
Dimensions (outer diameter x inner
diameter) and number of tubes
Working medium Air
Quick joint I6 (yellow)
Quick joint I4 (white)
BK SW
Brake-release
switch
I4 mm x I2.5 mm, 2 pieces
I6 mm x I4 mm, 2 pieces
2
), 25 wires
Standard cable (5 m)
BK power cable (outside robot)
M cable (outside robot)
PG cable (outside robot)
To controller
Y-terminal at the end
U cable
(outside robot)
I4, I6 quick joint
(2 pcs. each)
ir tube
I4 (black, white)
I6 (red, yellow)
ALM (indicator) specifications
Rated voltage 24 VDC
Rated current 12 mA
Illumination color Red LED
Shape of Y-terminal Spacer for user part installation
I7
M4, depth 5
3.2
5.2
2.6 5.9
10
External force applied to the spacers must not
exceed 30 N in the axial direction or 2 Nm in
the rotating direction (for each spacer).
26
30 N or less
2 Nm or less
Page 33

The robot comes with a D-sub 25-pin mating plug for the user connector.
A
A
Solder a user-supplied cable to the D-sub connector (plug), attach the supplied hood, and then connect to
the user connector (socket). Use a shielded cable with an outer diameter of I11 or less.
To turn on the indicator, the user must configure a dedicated circuit that uses the controller I/O output signal,
etc.
User connector pins and corresponding Y-terminals
rm 2 side
Connection No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
D-sub,
25-pin
12
13
14
User Connector
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Indicator
LM
(LED)
To D-sub connector frame
Inside unit
Cable
Y-terminal designation
U1
U2
U3
U4
U5
U6
U7
U8
U9
U10
U11
U12
U13
U14
U15
U16
U17
U18
U19
U20
U21
U22
U23
U24
U25
LED +24V
LED G24V
FG
Controller side
Wire color
Orange 1 red
Orange 1 black
Light gray 1 red
Light gray 1 black
White 1 red
White 1 black
Yellow 1 red
Yellow 1 black
Pink 1 red
Pink 1 black
Orange 2 red
Orange 2 black
Light gray 2 red
Light gray 2 black
White 2 red
White 2 black
Yellow 2 red
Yellow 2 black
Pink 2 red
Pink 2 black
Orange 3 red
Orange 3 black
Light gray 3 red
Light gray 3 black
White 3 red
White 3 black
Yellow 3 red
Green
Connection
5. Precautions for Use
Y-terminal
To base
Warning
z Before commencing wiring/piping work, turn off the power to the controller and the power/air
supplies to the robot. Failure to do so may cause the robot to malfunction.
z Use cables and tubes within their specifications. Failure to do so may result in fire or short circuit
due to an overheated cable, or may cause air leaks.
z Connect the shielded cable to the hood. Otherwise, the robot may malfunction due to noise.
z Secure the supplied D-sub connector using the screws on the hood.
27
Page 34

5.5 Suction Rate
A
The robot will conform to cleanliness class 10 when air is sucked at a specified rate from the quick suction
joint provided on a side face of the base.
x The user must provide the suction device and suction air tube (I12).
Model Suction rate (Nl/min)
IX-NNC50/60 60
IX-NNC70/80 80
5. Precautions for Use
Quick suction joint
pplicable tube:
Outer diameter I12
(inner diameter I8)
Caution
z The clean room must be designed as a down-flow environment.
z Cleanliness class 10 corresponds to a particle size of 0.1 Pm.
z The robot will generate dust if suction is not provided.
28
Page 35

6 Inspection/Maintenance
6.1 Inspection/Maintenance
Your horizontal articulated robot must be inspected daily and on a regular basis to ensure safe, efficient
operation. Perform the necessary inspections after confirming the maintenance/inspection items required
for your IAI robot, as defined in this section.
The following items must be adjusted at our factory. Do not disassemble the following components or cut
cables at the user site:
Disassembly of servo motor
Disassembly of ball speed reducer
Disassembly of ball-screw spline
Disassembly of bearing
Disassembly of harmonic speed reducer
Disassembly of brake
Cutting of cable
IAI will not be responsible for any malfunction or damage resulting from the conduct of any operation cited
above.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Warning
Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
6.1.1 Daily Inspection
Check the following items daily before and after operating the robot.
Observe the precautions for work near the robot and for inspection/maintenance/adjustment operations
when carrying out each check.
Check location Description
Safety cage
Robot
Cables
Emergency-stop switch Confirm that the emergency-stop switch functions properly.
Correct the deformation or positional shift of the cage.
Confirm that the interlock mechanism is operating properly.
Check the robot mounting bolts for looseness.
Check the exterior for abnormality, loose covers, flaws, dents, etc.
(If the robot has flaws or other abnormalities, please contact IAI.)
Check for abnormal move, vibration or noise.
Check the cables for flaws.
Check the cable mounting parts for looseness.
29
Page 36

6.1.2 Six-Month Inspection
Check the following items on the robot every six months.
Observe the precautions for work near the robot and for inspection/maintenance/adjustment operations
when carrying out each check.
Check location Description
Check the arm mounting sections for looseness.
Robot
Ball-screw spline Add grease. (AFE Grease by THK or equivalent)
Timing belts of axes 3 and4• Check the belt tension for axes 3 and 4.
Connectors Check the connectors for looseness.
If the robot has flaws or other abnormalities, please contact IAI.
(If any of the arm mounting sections is loose, tighten the fastening parts
securely.)
• Check the belts for flaws, cracks, wear, etc.
Caution
In case the grease got into your eye, immediately go to see the doctor to get an appropriate care.
After finishing the grease supply work, wash your hands carefully with water and soap to rinse the
grease off.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
6.1.3 Yearly Inspection
Check the following items on the robot every year.
Observe the precautions for work near the robot and for inspection/maintenance/adjustment operations
when carrying out each check.
Check location Description
*Harmonic speed reducer Change the grease. (Contact IAI.)
Ball-screw spline Check the shaft for looseness. (Contact IAI if an abnormality is found.)
* Based on 24-hour operation. Change the grease every three years or so if the robot is operated eight
hours a day.
Warning
Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
30
Page 37

6.2 How to Replace Bellows
6.2.1 IX-NNC-50/60
Preparation
The following tools are required when replacing bellows in the IX-NNC-50/60:
x Hex wrenches (2, 2.5 and 4 mm)
x Replacement bellows (2 units)
Turn off the power to the controller. Do not cut off the 24 VDC power supply to the brake.
Disassembly
(1) Remove the bolts affixing the bellows.
(2) Remove the setscrews affixing the top stopper, as well as collar A and gasket A affixing the
bellows-turning unit at the bottom.
(4 pcs.)
(1 pc.)
M4 sets rew c
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(4 pcs.)
(4 pcs.)
(4 pcs.)
Gasket A
Collar A
Warning
Caution
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
z When removing the stopper bolts at the top, exercise caution not to let the spline shaft come off
from the nuts and drop.
z Disassembly of the bellows generates dust. Before disassembling the bellows, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
31
Page 38

(3) Remove the stopper at the top and bellows-turning unit at the bottom.
(4) Remove the bellows from the robot and separate affixing plates A and B from the bellows.
Plate B
Stopper unit at
top
Bellows-turning
unit at bottom
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(4 pcs.)
Warning
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
z When removing the stopper bolts at the top, exercise caution not to let the spline shaft come off
from the nuts and drop.
z Disassembly of the bellows generates dust. Before disassembling the bellows, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
Plate A
Plate B
Caution
32
Page 39

Assembly
(1) Assemble the bellows by following the disassembly procedure in reverse.
(2) Install the bellows by aligning the positioning mark labels attached on the turning unit and collar A.
Move the robot’s X-axis, Y-axis, vertical axis and rotational axis to 0, arm length, 0 and 0, respectively,
and install and affix the bellows in this position by aligning the arrow position on collar A with the mark
on the turning unit. If the marks do not align, reattach the labels.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
This completes the replacement of bellows.
Warning
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
z When removing the stopper bolts at the top, exercise caution not to let the spline shaft come off
from the nuts and drop.
Caution
33
Page 40

6.2.2 IX-NNC-70/80
Preparation
The following tools are required when replacing bellows in the IX-NNC-70/80:
x Hex wrenches (1.5 and 2 mm)
x Phillips screwdriver
x Replacement bellows (2 units)
Turn off the power to the controller. Do not cut off the 24 VDC power supply to the brake.
Disassembly
(1) Remove the bolts affixing the bellows.
(2) Remove the top and bottom bellows units.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
M3 sets rew c
(2 pcs.)
(4 pcs.)
(4 pcs.)
(4 pcs.)
(4 pcs.)
Collar C
Bellows unit
Gasket D
Gasket D
Gasket C
Collar B
Gasket B
Plate C
Warning
Caution
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
z Disassembly of the bellows generates dust. Before disassembling the bellows, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
34
Page 41

(3) Remove the bellows-turning unit (one unit each at the top and bottom).
(4) Remove affixing plate D from the bellows.
Bellows-turning
unit
Gasket D
(4 pcs.)
Plate D
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Plate D
Warning
Caution
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
z Disassembly of the bellows generates dust. Before disassembling the bellows, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
35
Page 42

Assembly
(1) Assemble the bellows by following the disassembly procedure in reverse.
(2) Install the bellows by aligning the positioning mark labels attached on the turning unit and collar A.
Move the robot’s X-axis, Y-axis, vertical axis and rotational axis to 0, arm length, 0 and 0, respectively,
and install and affix the bellows in this position by aligning the arrow position on collar A with the mark
on the turning unit. If the marks do not align, reattach the labels.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
This completes the replacement of bellows.
Warning
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
Caution
36
Page 43

6.3 How to Check/Adjust Belt Tension
6.3.1 Preparation
The following tools are required when checking/adjusting belt tension:
x Push-pull gauge (maximum measurement capability of 2 kg)
x Hex wrenches (2.5, 3 and 4 mm)
x Spanners (5.5 and 8 mm)
x Phillips screwdriver
x Scale
x Pin (I3, 40 to 80 mm in length)
Turn off the power to the controller. Do not cut off the 24 VDC power supply to the brake.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Warning
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z If inspections are neglected, the drive part may wear prematurely or the robot may malfunction
unexpectedly.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
Caution
37
Page 44

6.3.2 Removing the Cover
(1) With arms 1 and 2 extended as illustrated below, press the brake-release switch [1] to release the
brake and then push down the vertical axis until the stopper contacts the pulley.
(2) Remove the countersunk head screws [2], [3] and [4] (four pieces each), in that order.
(3) Remove all connectors (UA, UB, BK and LED) and air tubes (four pieces) from the back of the panel.
(4) Move the cover to the position shown in the photograph.
Rotary joint
[4] 4 - M3 x 12 (countersunk head screw)
Panel
[1] Brake-release switch
[3] 4 - M3 x 12 (countersunk head screw)
[2] 4 - M3 x 12 (countersunk head screw)
Vertical axis
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Caution
z Remove the four outer screws for the countersunk head screws [4].
z Do not remove the M/PG connectors at the rotary joint, since it will necessitate an absolute reset.
z The cover will not detach completely, since the M/PG connectors are still connected. Do not pull
the cover forcibly.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
38
Page 45

6.3.3 Checking the Belt Tension
A
Timing belt for vertical axis
Timing belt for rotational axis
6.3.4 Checking the Belt Tension for the Vertical Axis
Top view
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Bottom view
Using a push-pull gauge, push the timing belt for vertical axis with a force of A (gf) and measure the
amount of deflection.
If the deflection is B (mm), the belt tension is normal.
If not, adjust the belt tension by referring to 6.3.6, “Adjusting the Belt Tension for the Vertical Axis.”
Type A B
IX-NNC50/60 340 ~ 410 (gf) 1.35 (mm)
IX-NNC70/80 550 ~ 650 (gf) 2.2 (mm)
(gf)
B (mm)
Pulley
Belt
Pulley
Caution
z When measuring deflection, do not use a gauge with a sharp tip that may damage the belt.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
39
Page 46

6.3.5 Checking the Belt Tension for the Rotational Axis
A
(1) Remove one setscrew provided on a side face of arm 2.
Remove the screw at the center.
(2) Insert a I3 pin in the hole on the side face of arm 2 (pin length: 40 to 80 mm) until the pin lightly
contacts the belt, and then mark a point off C (mm) from the surface of arm 2.
(3) Using a push-pull gauge, push the pin with a force of D (kgf). The belt tension is normal if the mark on
the pin aligns with the surface of arm 2. If not, adjust the belt tension by referring to 6.3.7, “Adjusting
the Belt Tension for the Rotational Axis.”
Type C D
IX-NNC50/60 2.48 (mm) 1.3 ~ 1.5 (kgf)
IX-NNC70/80 3.60 (mm) 1.6 ~ 2.0 (kgf)
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Belt
Caution
Pulley
Pulley
rm 2
C (mm)
Mark here
Pin
Mark aligns with the
surface of arm 2.
D (kgf)
Pulley
z Do not use a pin with a sharp tip that may damage the belt.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
40
Page 47

6.3.6 Adjusting the Belt Tension for the Vertical Axis
(1) Loosen the four M5 nuts [4] slightly, making sure the fastened points do not become overly loose.
(2) Loosen the lock nut [5], and then turn the bolt with urethane stopper [6] to tension the belt properly.
(3) Check the belt tension by referring to 6.3.4, “Checking the Belt Tension for the Vertical Axis.”
(4) Tighten the M5 nuts [4] loosened in step 1, and then tighten the lock nut [5].
(5) Check the belt tension again by referring to 6.3.4, “Checking the Belt Tension for the Vertical Axis.”
(If the deflection has changed, perform the adjustment again.)
6.3.7 Adjusting the Belt Tension for the Rotational Axis
(1) Loosen the bolts [1] and [2] (four pieces each) slightly, making sure the fastened points do not become
overly loose.
(2) Turn the bolts [3] (two pieces) to tension the belt.
(3) Check the belt tension by referring to 6.3.5, “Checking the Belt Tension for the Rotational Axis.”
(4) Tighten the bolts [1] and [2] loosened in step 1.
(5) Finally, tighten the bolts [3] securely.
(6) Check the belt tension again by referring to 6.3.5, “Checking the Belt Tension for the Rotational Axis.”
(If the deflection has changed, perform the adjustment again.)
[2] 4 - M5 x 18 (IX-NNC50/60)
4 - M6 x 25 (IX-NNC70/80)
[1] 4 - M4 x 10 (IX-NNC50/60)
4 - M5 x 10 (IX-NNC70/80)
[4] 4 - M5 nut
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Tightening torque
[3] 2 - M3 x 15 (IX-NNC50/60)
2 - M3 x 20 (IX-NNC70/80)
[5] Lock nut
[6] Bolt with urethane stopper
Caution
z Be careful not to overtighten screws [1], [2] and [4].
z After fixing the axis center, be sure to confirm once again that the deflection meets the specified
value.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
41
Page 48

6.3.8 Installing the Cover
(1) Place the cover on the robot and connect the connectors, cables and air tubes installed as illustrated
below. (Absolute reset, as described on the following page, is not required after the belt tension is only
checked.)
[2] 4 - M3 x 12
[1] 4 - M3 x 12
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Caution
z Check the marking tubes to prevent improper connections.
z Be careful not to bend the air tubes.
z Be careful not to let the cables contact the pulley.
z Check if the connectors are fully inserted.
z Be careful not to pinch the cables.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
Installation position
of PG connector
PG cable
42
Page 49

M cable
Installation position
of M connector
[3] 4 - M3 x 12
6. Inspection/Maintenance
U cables
Be careful not to let them contact the pulley.
Installation position
of U connectors
(2) Install the M4 setscrew on the side face of arm 2.
(3) Perform an absolute reset for the rotational axis and vertical axis. This completes the procedure for
installation of the cover.
(Refer to 6.5, “Absolute Reset Procedure.”)
Caution
z Check the marking tubes to prevent improper connections.
z Be careful not to bend the air tubes.
z Be careful not to let the cables contact the pulley.
z Check if the connectors are fully inserted.
z Be careful not to pinch the cables.
z Perform an absolute reset for the rotational axis and vertical axis only after adjustment of the belt
tension.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
43
Page 50

6.4 Battery Replacement
6.4.1 Preparation
The following items are required when replacing the batteries:
x Phillips screwdriver
x New dedicated batteries for IX: AB-3 (4 pieces)
Before replacing the batteries, turn off the power to the controller, control panel and other relevant units.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Warning
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
z Use dedicated batteries for IX. Batteries for the old model (IH) cannot be used.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
Caution
44
Page 51

6.4.2 Battery Replacement Procedure
(1) Remove the countersunk head screws [1] (six pieces) and detach the cover (base).
(2) Remove the batteries from the battery holder.
(3) Remove the battery connectors and connect new batteries.
x After removing the old batteries, quickly connect new batteries (roughly within 5 minutes x
number of batteries).
x If new batteries are not connected for a longer period, the rotation data will be lost and an
absolute reset will become necessary.
x Replace batteries one axis at a time. If the batteries for all axes are replaced at once, the work
may not be completed within the specified time.
(4) Install the batteries into the battery holder.
[1] 6 - M3 x 8
Cover (base)
Battery connector 1
(for axis 1)
Battery
(for axis 1)
Battery connector 3
(for axis 3)
Battery
(for axis 3)
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Battery connector 2
(for axis 2)
Battery
(for axis 2)
Battery connector 4
(for axis 4)
Battery
(for axis 4)
Battery holder
45
Page 52

(5) Affix the cover (base) using the countersunk head screws [1] (six pieces) (tightening torque: 0.74
Nm).
[1] 6 - M3 x 8
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Caution
z When installing the cover (base), be careful not to pinch the cables inside.
z Disassembly of the cover generates dust. Before disassembling the cover, move the robot to a
location where dust will not cause problem, or cover the robot with a plastic sheet, etc., to prevent
dust from scattering.
Do not tighten the screws to the specified torque in one go. First
tighten the screws to the position shown to the left, and while
pushing the cover in the direction of the arrow tighten the screws
on both sides evenly to ensure tight sealing.
46
Page 53

6.5 Absolute Reset Procedure
6.5.1 Preparation for Absolute Reset
The following jig is required when performing an absolute reset: (Included with robot at time of shipment).
x Absolute reset adjustment jig Model: JG-1 (IX-NNC50/60)
JG-3 (IX-NNC70/80)
Connect the cables for the robot, controller and PC, so the robot can be operated from the PC.
Before commencing the work, always confirm that the emergency-stop switch is functioning properly.
An absolute reset adjustment jig is always required when performing an absolute reset of the rotational axis
or vertical axis. However, the jig is not always necessary when performing an absolute reset of arm 1 or
arm 2.
(Rotation data can be reset as long as a positioning accuracy of “center of positioning mark label r1
graduation” is ensured.)
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Plate
Pin
Absolute reset adjustment jig (type: JG-1)
Warning
z Performing inspection or maintenance without fully understanding the details of work may result in
a serious accident.
z Display a “Work in Progress” sign so that other operators will not operate the controller, operation
panel, etc.
47
Page 54

6.5.2 Starting the Absolute Reset Menu
A
A
(1) Open the absolute reset window from the PC software.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(2) The absolute reset window opens.
x One of three absolute reset screens—for arm 1, arm 2 and rotational axis + vertical axis—is
displayed when a corresponding tab is clicked.
bsolute reset screen
for arm 1 or 2
bsolute reset
screen for rotational
axis + vertical axis
48
Page 55

6.5.3 Absolute Reset Procedure for Arm 1 or 2
(1) Click the “Encoder Rotation Data Reset1” button.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(2) Click the “Reset Controller Error” button.
49
Page 56

(3) Click the “Servo ON” button.
(4) Jog the arm to near the reference position (see reference position drawing in step 7), and click the
“Jog end” button.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(5) Click the “Servo-OFF” button.
50
Page 57

(6) Press the emergency-stop switch.
A
(7) Set an adjustment jig (pin) in arm 1 or 2 to fix the arm at the reference position.
x Set the jig after confirming that the emergency-stop switch is pressed.
x Set the jig after adjusting the arm to the reference position, using the positioning mark label as a
guide.
x Arm 1 has a cover (not arm 2), which is fixed with setscrews. Remove the setscrews and detach
the cover before setting the jig.
x It is recommended that an adjustment jig be used to perform an absolute reset. With arm 1 or 2,
however, rotation data can be reset as long as a positioning accuracy of “center of positioning mark
label r1 graduation” is ensured.
Positioning mark label
for arm 1
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Arm 1
Arm 2
Warning
Positioning mark label
for arm 1
Reference position drawing
Positioning
mark label for
arm 2
djust arm 1 or 2 to a position
within ± 1 graduation of the center.
z Always press the emergency-stop switch before setting an adjustment jig. Failure to do so may
cause the robot to malfunction and result in a serious accident.
51
Page 58

(8) Click the “OK” button.
(9) Click the “Encoder Rotation Data Reset2” button.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
52
Page 59

(10) Remove the adjustment jig.
x If you are working on arm 1, install the cover and secure it with the setscrews (not required for arm
2).
(11) Release the emergency-stop switch.
(12) Click the “OK” button.
x An arrow is shown next to the “Home pos. automatic update” button. Do not set this item. (In
particular, be sure this item is not set when performing an absolute reset without using a jig).
x If the home position is updated automatically when a reset is performed without using an
adjustment jig, the home position will become offset.
x If the home position has been updated by mistake, perform an absolute reset again using an
adjustment jig. (This time, end the procedure before home position automatic update).
x Always click the “OK” button after removing the jig and releasing the emergency-stop switch.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(13) Click “X” in the top right-hand corner to exit the absolute reset window.
x Once the absolute reset is complete, be sure to reset the controller.
Caution
z Be careful not to perform a reset using an incorrect sequence, since it may cause the arm position
to become offset.
z When home position automatic update has been performed, be sure to write the flash ROM.
53
Page 60

6.5.4 Absolute Reset Procedure for the Rotational Axis + Vertical Axis
(1) Click “Encoder Rotation Data Reset1” button.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(2) Click the “Reset Controller Error” button.
54
Page 61

(3) Click the “Servo ON” button.
(4) Click the “Temp. Standard posture standby” button.
x The vertical axis returns to its home position. Exercise caution so as not to be injured by the axis
during movement.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(5) Jog the rotational axis to the reference position (see reference position drawing in step 8), and click
the “Jog end” button.
55
Page 62

(6) Click the “Servo-OFF” button.
(7) Press the emergency-stop switch.
(8) Affix the rotational axis at the reference position by setting the plate and pin of the adjustment jig as
illustrated below.
x Set the jig after confirming that the emergency-stop switch is pressed.
x Set the jig after adjusting the rotational axis to the reference position, using the positioning mark
label as a guide.
x The top face of the stopper should roughly align with the bottom face of arm 2.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
Warning
The plate and pin should
make light contact.
Positioning mark label
for rotational axis
Location of positioning seal
on IX-NNC50/60
D-cut surface
D-cut surface
Location of positioning seal
on IX-NNC70/80
z Always press the emergency-stop switch before setting an adjustment jig. Failure to do so may
cause the robot to malfunction and result in a serious accident.
z Pay attention to the orientation of the D-cut surface of the plate jig.
56
Page 63

(9) Click the “OK” button.
(10) Click the “Encoder Rotation Data Reset2” button.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
57
Page 64

(11) Click the “Home pos. automatic update” button.
(12) Remove the adjustment jig.
(13) Release the emergency-stop switch.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(14) Click the “OK” button.
58
Page 65

(15) Click the “Servo ON” button.
(16) Click the “Standard posture standby” button.
x The vertical axis returns to its home position. Exercise caution so as not to be injured by the axis
during movement.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(17) Click the “Servo-OFF” button.
59
Page 66

(18) Click the “Encoder Rotation Data Reset3” button.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(19) Click the “Home pos. automatic update” button, and then click “X” in the top right-hand corner to exit
the absolute reset window.
x Once the absolute reset is complete, be sure to write the flash ROM and reset the controller.
60
Page 67

6.5.5 Writing the Flash ROM
(1) Following an absolute reset of the rotational axis and vertical axis, the following screen opens when
the absolute reset window is closed. Click the “Yes” button.
x Clicking “Yes” writes the information in the flash ROM.
x The flash ROM must also be written when home position automatic update has been performed for
arm 1 or 2.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(2) When the writing of flash ROM is complete, the following screen is displayed. Click the “Yes” button.
x The controller is restarted and the software is reset.
61
Page 68

6.5.6 Resetting the Controller
(1) Select “Software Reset” from the Controller menu on the tool bar.
6. Inspection/Maintenance
(2) Click the “Yes” button. The controller is reset and restarted.
62
Page 69

7 Specifications
7.1 Specification Table
IX-NNC50 (Arm Length 500, Clean-room Specification)
Item Specifications
Type IX-NNC50-L-T1
Degree of freedom Four degrees of freedom
Overall arm length 500
Arm 1 length 250
Arm 2 length
Drive method
Motor capacity
Movement range
Maximum
operating speed
(*2)
Positioning
repeatability (*3)
Cycle time (*4)
Load capacity
Push-in thrust of
axis 3 (vertical axis)
Permissible load
on axis 4
Permissible tool diameter (*6) mm
Origin detection Absolute
User wiring D-sub 25-pin connector with 25-core AWG26 shielded cable (socket)
Suction pipe joint
Alarm indicator (*7) One small, red LED indicator (rated voltage: 24 V)
User piping
Axis 1 (arm 1) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 2 (arm 2) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 3 (vertical axis) AC servo motor with brake + Belt + Ball-screw spline
Axis 4 (rotational axis) AC servo motor with brake + Speed reducer + Belt + Spline
Axis 1 (arm 1) 400
Axis 2 (arm 2) 200
Axis 3 (vertical axis) 200
Axis 4 (rotational axis)
Axis 1 (arm 1)
Axis 2 (arm 2)
Axis 3 (vertical axis) (*1) mm 200 (Optional: 300)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Axis 1 + Axis 2 (maximum composite speed)
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree/sec 1200
Axis 1 + Axis 2
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Rated 2
Maximum
Dynamic (*8) 152 (15.5)
Static (*9)
Permissible moment of inertia (*5)
Permissible torque
mm
W
degree
mm/sec
mm
kg
N (kgf)
2
kgm
Nm (kgfcm)
250
100
r120
r145
r360
6283
1393
r0.010
r0.010
r0.005
0.47/2 kg
10
108 (11.0)
0.06
3.3 (33.6)
I100
Applicable tube: Outer diameter I12 (inner diameter I8)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I6, inner diameter: I4) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I4, inner diameter: I2.5) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
7. Specifi cations
63
Page 70

Item Specifications
7. Specifi cations
Operating
environment
Noise dB 73
Robot weight
Brake power source for main unit
Cleanliness class
Suction rate (*10)
Controller Power supply
Ambient temperature/humidity
Altitude m 1,000 or less
Nl/min 60
Allowable supply voltage fluctuation %
Overvoltage category (IEC60664-1) Category III
Pollution degree (IEC60664-1) Pollution degree 3
Temperature: 0 to 40 C, humidity: 20 to 85%RH or less (non-condensing)
kg
W
24V DC ±10% 20W
Class 10 (0.1-
230 V 50/60 Hz 8 A
31.5
m base, with suction)
10
*1 To move the robot horizontally at high speed, perform teaching so that the vertical axis stays as close to the top
position as possible. (Fig. 1)
To operate the robot with its vertical axis at the bottom position, the speed and acceleration must be reduced as
appropriate. (Fig. 2)
*2 Assuming PTP instruction operation.
*3 Measured at a constant ambient temperature of 20
C.
*4 Measured when the robot is operated at the maximum speed, carrying a rated load of 2 kg.
*5 The permissible moment of inertia converted to a value at the rotational center of axis 4. The offset from the
rotational center of axis 4 to the tool’ s centerof gravity is assumed to be 50 mm or less. (Fig. 3)
If the tool’ s center of gravity is further away from the rotational center of axis 4, the speed and acceleration must be
reduced as appropriate.
*6 If the tool exceeds the permissible diameter, it will contact the robot inside the robot’ s range of movement. (Fig. 4)
*7 To enable the alarm LED indicator, the user must provide a circuit that supplies 24 VDC to the LED terminal in the
user connector in response to the controller I/O output signal, etc.
*8 A force of up to three times the dynamic push-in thrust may be applied at any given moment.
*9 The static thrust refers to thrust generated within the robot’ s range of operation based on a PAPR command.
*10 The level of dust generation will vary depending on the operation pattern. The suction rate may have to be raised if
the robot is operated at high speed or high acceleration/deceleration.
Center of
rotational axis
Bottom
Top position
Tool
(Fig. 1) (Fig. 2) (Fig. 3) (Fig. 4)
position
Tool
50
Tool
Tool’ s center of
gravity
Center of
rotational axis
Tool
100
Reference design standards: Annex I to Machine Directives, EN292-1, EN292-2, EN1050, EN60204-1, EN775
64
Page 71

IX-NNC60 (Arm Length 600, Clean-room Specification)
Item Specifications
Type IX-NNC60-L-T1
Degree of freedom Four degrees of freedom
Overall arm length 600
Arm 1 length 350
Arm 2 length
Drive method
Motor capacity
Movement range
Maximum
operating speed
(*2)
Positioning
repeatability (*3)
Cycle time (*4)
Load capacity
Push-in thrust of
axis 3 (vertical axis)
Permissible load
on axis 4
Permissible tool diameter (*6) mm
Origin detection Absolute
User wiring D-sub 25-pin connector with 25-core AWG26 shielded cable (socket)
Suction pipe joint
Alarm indicator (*7) One small, red LED indicator (rated voltage: 24 V)
User piping
Axis 1 (arm 1) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 2 (arm 2) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 3 (vertical axis) AC servo motor with brake + Belt + Ball-screw spline
Axis 4 (rotational axis) AC servo motor with brake + Speed reducer + Belt + Spline
Axis 1 (arm 1) 400
Axis 2 (arm 2) 200
Axis 3 (vertical axis) 200
Axis 4 (rotational axis)
Axis 1 (arm 1)
Axis 2 (arm 2)
Axis 3 (vertical axis) (*1) mm 200 (Optional: 300)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Axis 1 + Axis 2 (maximum composite speed)
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree/sec 1200
Axis 1 + Axis 2
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Rated 2
Maximum
Dynamic (*8) 152 (15.5)
Static (*9)
Permissible moment of inertia (*5)
Permissible torque
mm
W
degree
mm/sec
mm
kg
N (kgf)
2
kgm
Nm (kgfcm)
250
100
r120
r145
r360
7121
1393
r0.010
r0.010
r0.005
0.54/2 kg
10
108 (11.0)
0.06
3.3 (33.6)
I100
Applicable tube: Outer diameter I12 (inner diameter I8)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I6, inner diameter: I4) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I4, inner diameter: I2.5) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
7. Specifi cations
65
Page 72

Item Specifications
7. Specifi cations
Operating
environment
Noise dB 73
Robot weight kg 32.5
Brake power source for main unit
Cleanliness class
Suction rate (*10) 60
Controller Power supply
Ambient temperature/humidity
Altitude m 1,000 or less
Allowable supply voltage fluctuation %
Overvoltage category (IEC60664-1) Category III
Pollution degree (IEC60664-1) Pollution degree 3
Temperature: 0 to 40 C, humidity: 20 to 85%RH or less (non-condensing)
W
24V DC ±10% 20W
Class 10 (0.1-
230 V 50/60 Hz 8 A
m base, with suction)
10
*1 To move the robot horizontally at high speed, perform teaching so that the vertical axis stays as close to the top
position as possible. (Fig. 1)
To operate the robot with its vertical axis at the bottom position, the speed and acceleration must be reduced as
appropriate. (Fig. 2)
*2 Assuming PTP instruction operation.
*3 Measured at a constant ambient temperature of 20
C.
*4 Measured when the robot is operated at the maximum speed, carrying a rated load of 2 kg.
*5 The permissible moment of inertia converted to a value at the rotational center of axis 4. The offset from the
rotational center of axis 4 to the tool’ s centerof gravity is assumed to be 50 mm or less. (Fig. 3)
If the tool’ s center of gravity is further away from the rotational center of axis 4, the speed and acceleration must be
reduced as appropriate.
*6 If the tool exceeds the permissible diameter, it will contact the robot inside
the
robot’ s range of movement. (Fig. 4)
*7 To enable the alarm LED indicator, the user must provide a circuit that supplies 24 VDC to the LED terminal in the
user connector in response to the controller I/O output signal, etc.
*8 A force of up to three times the dynamic push-in thrust may be applied at any given moment.
*9 The static thrust refers to thrust generated within the robot’ s range of operation based on a PAPR command.
*10 The level of dust generation will vary depending on the operation pattern. The suction rate may have to be raised if
the robot is operated at high speed or high acceleration/deceleration.
Center of
rotational axis
Bottom
Top position
Tool
(Fig. 1) (Fig. 2) (Fig. 3) (Fig. 4)
position
Tool
50
Tool
Tool’ s center of
gravity
Center of
rotational axis
Tool
100
Reference design standards: Annex I to Machine Directives, EN292-1, EN292-2, EN1050, EN60204-1, EN775
66
Page 73

IX-NNC70 (Arm Length 700, Clean-room Specification)
Item Specifications
Type IX-NNC70-L-T1
Cleanliness class (*10)
Degree of freedom Four degrees of freedom
Overall arm length 700
Arm 1 length 350
Arm 2 length
Drive method
Motor capacity
Movement range
Maximum
operating speed
(*2)
Positioning
repeatability (*3)
Cycle time (*4)
Load capacity
Push-in thrust of
axis 3 (vertical axis)
Permissible load
on axis 4
Permissible tool diameter (*6) mm
Origin detection Absolute
User wiring D-sub 25-pin connector with 25-core AWG26 shielded cable (socket)
Alarm indicator (*7) One small, red LED indicator (rated voltage: 24 V)
User piping
Axis 1 (arm 1) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 2 (arm 2) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 3 (vertical axis) AC servo motor with brake + Belt + Ball-screw spline
Axis 4 (rotational axis) AC servo motor with brake + Speed reducer + Belt + Spline
Axis 1 (arm 1) 750
Axis 2 (arm 2) 400
Axis 3 (vertical axis) 400
Axis 4 (rotational axis)
Axis 1 (arm 1)
Axis 2 (arm 2)
Axis 3 (vertical axis) (*1) mm 200 (Optional: 400)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Axis 1 + Axis 2 (maximum composite speed)
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree/sec 1200
Axis 1 + Axis 2
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Rated 5
Maximum
Dynamic (*8) 265 (27.0)
Static (*9)
Permissible moment of inertia (*5)
Permissible torque
mm
W
degree
mm/sec
mm
kg
N (kgf)
2
kgm
Nm (kgfcm)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I6, inner diameter: I4) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I4, inner diameter: I2.5) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
Class 10 (0.1 Pm)
350
200
r125
r145
r360
6597
1583
r0.015
r0.010
r0.005
0.52
20
188 (19.1)
0.1
6.7 (68.3)
I100
7. Specifi cations
67
Page 74

Item Specifications
7. Specifi cations
Operating
environment
Noise dB 74
Robot weight kg 60
Brake power source for main unit
Controller Power supply
Ambient temperature/humidity
Altitude m 1,000 or less
Allowable supply voltage fluctuation %
Overvoltage category (IEC60664-1) Category III
Pollution degree (IEC60664-1) Pollution degree 3
Temperature: 0 to 40 C, humidity: 20 to 85%RH or less (non-condensing)
W
24V DC ±10% 20W
230 V 50/60 Hz 15 A
10
*1 To move the robot horizontally at high speed, perform teaching so that the vertical axis stays as close to the top
position as possible. (Fig. 1)
To operate the robot with its vertical axis at the bottom position, the speed and acceleration must be reduced as
appropriate. (Fig. 2)
*2 Assuming PTP instruction operation.
*3 Measured at a constant ambient temperature of 20
C.
*4 Measured when the robot is operated at the maximum speed, carrying a rated load of 5 kg.
*5 The permissible moment of inertia converted to a value at the rotational center of axis 4. The offset from the
rotational center of axis 4 to the tool’ s centerof gravity is assumed to be 50 mm or less. (Fig. 3)
If the tool’ s center of gravity is further away from the rotational center of axis 4, the speed and acceleration must be
reduced as appropriate.
*6 If the tool exceeds the permissible diameter, it will contact the robot inside the robot’ s range of movement. (Fig. 4)
*7 To enable the alarm LED indicator, the user must provide a circuit that supplies 24 VDC to the LED terminal in the
user connector in response to the controller I/O output signal, etc.
*8 A force of up to three times the dynamic push-in thrust may be applied at any given moment.
*9 The static thrust refers to thrust generated within the robot’ s range of operation based on a PAPR command.
*10 Based on a suction rate of 80 Nl/min (-100 mmAq).
Center of
rotational axis
Bottom
Top position
Tool
(Fig. 1) (Fig. 2) (Fig. 3) (Fig. 4)
position
Tool
50
Tool
Tool’ s center of
gravity
Center of
rotational axis
Tool
100
Reference design standards: Annex I to Machine Directives, EN292-1, EN292-2, EN1050, EN60204-1, EN775
68
Page 75

IX-NNC80 (Arm Length 800, Clean-room Specification)
Item Specifications
Type IX-NNC80-L-T1
Cleanliness class (*10)
Degree of freedom Four degrees of freedom
Overall arm length 800
Arm 1 length 450
Arm 2 length
Drive method
Motor capacity
Movement range
Maximum
operating speed
(*2)
Positioning
repeatability (*3)
Cycle time (*4)
Load capacity
Push-in thrust of
axis 3 (vertical axis)
Permissible load
on axis 4
Permissible tool diameter (*6) mm
Origin detection Absolute
User wiring D-sub 25-pin connector with 25-core AWG26 shielded cable (socket)
Alarm indicator (*7) One small, red LED indicator (rated voltage: 24 V)
User piping
Axis 1 (arm 1) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 2 (arm 2) AC servo motor + Speed reducer
Axis 3 (vertical axis) AC servo motor with brake + Belt + Ball-screw spline
Axis 4 (rotational axis) AC servo motor with brake + Speed reducer + Belt + Spline
Axis 1 (arm 1) 750
Axis 2 (arm 2) 400
Axis 3 (vertical axis) 400
Axis 4 (rotational axis)
Axis 1 (arm 1)
Axis 2 (arm 2)
Axis 3 (vertical axis) (*1) mm 200 (Optional: 400)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Axis 1 + Axis 2 (maximum composite speed)
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree/sec 1200
Axis 1 + Axis 2
Axis 3 (vertical axis)
Axis 4 (rotational axis) degree
Rated 5
Maximum
Dynamic (*8) 265 (27.0)
Static (*9)
Permissible moment of inertia (*5)
Permissible torque
mm
W
degree
mm/sec
mm
kg
N (kgf)
2
kgm
Nm (kgfcm)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I6, inner diameter: I4) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
Two air tubes (outer diameter: I4, inner diameter: I2.5) (normal service pressure: 0.8 MPa)
Class 10 (0.1 Pm)
350
200
r125
r145
r360
7121
1583
r0.015
r0.010
r0.005
0.52
20
188 (19.1)
0.1
6.7 (68.3)
I100
7. Specifi cations
69
Page 76

Item Specifications
Operating
environment
Noise dB 74
Robot weight kg 62
Ambient temperature/humidity
Altitude m 1,000 or less
Temperature: 0 to 40 C, humidity: 20 to 85%RH or less (non-condensing)
7. Specifi cations
Brake power source for main unit
Controller
Power supply 230 V 50/60 Hz 15 A
Allowable supply voltage fluctuation %
Overvoltage category (IEC60664-1) Category III
Pollution degree (IEC60664-1) Pollution degree 3
W
24V DC ±10% 20W
10
*1 To move the robot horizontally at high speed, perform teaching so that the vertical axis stays as close to the top
position as possible. (Fig. 1)
To operate the robot with its vertical axis at the bottom position, the speed and acceleration must be reduced as
appropriate. (Fig. 2)
*2 Assuming PTP instruction operation.
*3 Measured at a constant ambient temperature of 20
C.
*4 Measured when the robot is operated at the maximum speed, carrying a rated load of 5 kg.
*5 The permissible moment of inertia converted to a value at the rotational center of axis 4. The offset from the
rotational center of axis 4 to the tool’ s centerof gravity is assumed to be 50 mm or less. (Fig. 3)
If the tool’ s center of gravity is further away from the rotational center of axis 4, the speed and acceleration must be
reduced as appropriate.
*6 If the tool exceeds the permissible diameter, it will contact the robot inside the robot’ s range of movement. (Fig. 4)
*7 To enable the alarm LED indicator, the user must provide a circuit that supplies 24 VDC to the LED terminal in the
user connector in response to the controller I/O output signal, etc.
*8 A force of up to three times the dynamic push-in thrust may be applied at any given moment.
*9 The static thrust refers to thrust generated within the robot’ s range of operation based on a PAPR command.
*10 Based on a suction rate of 80 Nl/min (-100 mmAq).
Center of
rotational axis
Bottom
Top position
Tool
(Fig. 1) (Fig. 2) (Fig. 3) (Fig. 4)
position
Tool
50
Tool
Tool’ s center of
gravity
Center of
rotational axis
Tool
100
Reference design standards: Annex I to Machine Directives, EN292-1, EN292-2, EN1050, EN60204-1, EN775
70
Page 77

7.2 External Dimensions
A
A
t
A
IX-NNC50
4 - I11 hole
I24 counterbore, depth 5
Section A-A
I14, hollow
5 (Mechanical end)
2-M4
depth 8
(*1)
5 (Mechanical end)
User Connector
D-sub 25-pin connector
for user wiring (socket),
fixing screw M2.6
BK SW
Brake-release switch
Spacer
Outer diameter I 7
Height 10 (M4)
Depth 5 (*2)
I6 quick
air-tube joint
I4 quick
air-tube joint
LM (*3)
Reference surface
Red
Yel l ow
Black
White
ir joint
(opposite side)
(*4)
pplicable tube:
Outer diameter I12
(inner diameter I8)
*1: The holes for the 2-M4 screws (depth 8) pierce through the
thickness of the arm’s side wall. If the mounting screws are
long, they will contact the internal parts. Exercise due
caution in this regard.
*2: External force applied to the spacers must not exceed 30 N
in the axial direction or 2 Nm in the rotating direction (for
each spacer).
*3: The LED operates only when the user provides a circuit tha
receives controller I/O output signal and supplies 24 VDC to
the LED terminal in the user connector.
*4: The joint can be installed on the opposite side. (To reverse
the direction, swap the PT3/8 plug and the joint.)
7. Specifi cations
Detailed view of panel (1/2)
71
Page 78

IX-NNC60
A
A
A
4 - I11 hole
I24 counterbore, depth 5
5 (Mechanical end)
7. Specifi cations
Section A-A
I14, hollow
2-M4
(*1)
5 (Mechanical end)
I 6 quick
air-tube joint
I 4 quick
air-tube joint
User Connector
D-sub 25-pin connector
for user wiring (socket),
fixing screw M2.6
LM (*3)
BK SW
Brake-release switch
Spacer
Outer diameter I 7
Height 10 (M4)
Depth 5 (*2)
Red
Yel l ow
Black
Detailed view of panel (1/2)
Reference surface
White
ir joint
(opposite side)
pplicable tube:
Outer diameter I12
(inner diameter I8)
*1: The holes for the 2-M4 screws (depth 8) pierce through the
thickness of the arm’s side wall. If the mounting screws are
long, they will contact the internal parts. Exercise due
caution in this regard.
*2: External force applied to the spacers must not exceed 30 N
in the axial direction or 2 Nm in the rotating direction (for
each spacer).
*3: The LED operates only when the user provides a circuit that
receives controller I/O output signal and supplies 24 VDC to
the LED terminal in the user connector.
72
Page 79

IX-NNC70
A
A
A
A
A
A
pplicable tube:
Outer diameter I12
(inner diameter I8)
4 - I14 hole
I30 counterbore, depth 5
rm 2
stopper
ir joint (*4)
7. Specifi cations
6 (Mechanical end)
rm 1
rm 2
stopper
I18, hollow
3-M4, depth 8 (same on
the opposite side)
Sealed by a setscrew
(*1)
PT3/8
plug
6 (Mechanical end)
Reference surface
I6 quick
air-tube joint
I4 quick
Section A-A
air-tube joint
User Connector
D-sub 25-pin connector
for user wiring (socket),
fixing screw M2.6
BK SW
Brake-release switch
LM (*3)
Spacer
Outer diameter I7
Height 10 (M4)
Depth 5 (*2)
Red
Yel l ow
White
Black
Detailed view of panel (1/2)
*1: The holes for the 3-M4 screws (depth 8) pierce through
the thickness of the arm’s side wall.
*2: External force applied to the spacers must not exceed
30 N in the axial direction or 2 Nm in the rotating
direction (for each spacer).
*3: The LED operates only when the user provides a
circuit that receives controller I/O output signal and
supplies 24 VDC to the LED terminal in the user
connector.
*4: The joint can be installed on the opposite side.
(To reverse the direction, swap the PT3/8 plug and
the joint.)
73
Page 80

7. Specifi cations
A
A
A
A
A
A
IX-NNC80
ir joint (*4)
rm 2
stopper
6 (Mechanical end)
rm 1
rm 2
stopper
pplicable tube:
Outer diameter I12
(inner diameter I8)
4 - I14 hole
I30 counterbore, depth 5
I18, hollow
3-M4, depth 8 (same on
the opposite side)
Sealed by a setscrew
(*1)
PT3/8
plug
6 (Mechanical end)
Reference surface
I6 quick
air-tube joint
I6 quick
Section A-A
air-tube joint
User Connector
D-sub 25-pin connector
for user wiring (socket),
fixing screw M2.6
BK SW
Brake-release switch
LM (*3)
Spacer
Outer diameter I7
Height 10 (M4)
Depth 5 (*2)
Red
Yel l ow
White
Black
Detailed view of panel (1/2)
*1: The holes for the 3-M4 screws (depth 8) pierce through
the thickness of the arm’s side wall.
*2: External force applied to the spacers must not exceed
30 N in the axial direction or 2 Nm in the rotating
direction (for each spacer).
*3: The LED operates only when the user provides a
circuit that receives controller I/O output signal and
supplies 24 VDC to the LED terminal in the user
connector.
*4: The joint can be installed on the opposite side. (To
reverse the direction, swap the PT3/8 plug and the
joint.)
74
Page 81

7.3 Robot Operation Area
IX-NNC50
(Operation prohibited area)
7. Specifi cations
IX-NNC60
Movement range
(Operation prohibited area)
Movement range Stopper position range
Stopper position range
75
Page 82

7. Specifi cations
IX-NNC70
IX-NNC80
(Operation prohibited area)
Movement range
Stopper position range
76
(Operation prohibited area)
Movement range
Stopper position range
Page 83

7.4 Wiring Diagram
A
A
A
Servo motor for axis 2
(arm 2)
Servo motor with brake
larm LED
ir joint, red (I6)
ir joint, yellow (I6)
ir joint, black (I4)
for axis 3 (Z-axis)
Servo motor with brake
for axis 4 (R-axis)
FG (to D-sub housing)
D-sub connector for user wiring (25-pin, socket )
Brake-release switch for axes 3/4 (Z/R-axes)
ir joint, white (I4)
PG cable (inside robot)
cable
Flexible
Servo motor for
axis 1 (arm 1)
U cable (inside robot)
7. Specifi cations
M cable (inside robot)
Board
FG (To base)
ir joint, red (I6)
ir joint, yellow (I6)
ir joint, black (I4)Air joint, white (I4)
Cable fix cap
(Capcon)
M cable (outside robot)
PG cable (outside robot)
Wiring/Piping Diagram (Arm Length: 500/600)
Controller Inside base Inside arm 2
Dedicated batteries for IX: AB-3
BK power cable (outside robot)
U cable (outside robot)
circuit. The 24 V power supply for I/O circuits used on the secondary side (low-voltage side) cannot be shared.
terminals
Brake power
terminals
User wiring
Notes
(1) The actual layout of board connectors varies from this drawing.
(2) Since the brake power circuit is provided on the primary side (high-voltage side), a dedicated 24 V power supply is required for this
(3) To operate the alarm LED, the user must provide a circuit that uses the controller I/O output signal.
77
Page 84

7. Specifi cations
), flexible cable, UL
2
), oil-resistant cable, UL
2
), flexible cable,
2
), oil-resistant cable,
2
AC servo motor, 60, 400 W, key groove, CE certified
AC servo motor, 60, 200 W, key groove, CE certified
AC servo motor, 60, 100 W, key groove, CE certified
AC servo motor, 60, 200 W, w/ brake, round shaft, CE certified
Wire: 300 V, 105qC (rated), AWG18 (0.84 mm
Seiki
Tamagawa
E200
E200
E200
E200
TS4609 N2027
TS4607 N2027
TS4607 N7027
TS4606 N7027
VW-1, c-UL FT-1
VW-1, c-UL FT-1
Wire: 300 V, 80qC (rated), AWG18 (0.89 mm
AC servo motor, 80, 750 W, key groove, CE certified
AC servo motor, 60, 400 W, key groove, CE certified
AC servo motor, 60, 200 W, key groove, CE certified
AC servo motor, 60, 400 W, w/ brake, round shaft, CE certified
Wire: 300 V, 105qC (rated), AWG18 (0.84 mm
Seiki
Tamagawa
E200
E200
E200
E200
TS4614 N2027
TS4609 N2027
TS4609 N7027
TS4607 N2027
UL VW-1, c-UL FT-1
UL VW-1, c-UL FT-1
Wire: 300 V, 80qC (rated), AWG18 (0.89 mm
78
1 Axis 1 servo motor
2 Axis 2 servo motor
3 Axis 3 servo motor w/ brake
7.5 230V Circuit Components
IX-NNC50/60
No. Code name Model Manufacturer Remarks
4 Axis 4 servo motor w/ brake
5 M cable (inside robot) IAI
6 M cable (outside robot) IAI
IX-NNC70/80
1 Axis 1 servo motor
No. Code name Model Manufacturer Remarks
2 Axis 2 servo motor
3 Axis 3 servo motor w/ brake
4 Axis 4 servo motor w/ brake
5 M cable (inside robot) IAI
6 M cable (outside robot) IAI
Page 85

8. Warranty
8.1 Warranty Period
One of the following periods, whichever is shorter:
y 18 months after shipment from IAI
y 12 months after delivery to the specified location
y 2,500 hours of operation
8.2 Scope of Warranty
Our products are covered by warranty when all of the following conditions are met. Faulty products
covered by warranty will be replaced or repaired free of charge:
(1) The breakdown or problem in question pertains to our product as delivered by us or our authorized
dealer.
(2) The breakdown or problem in question occurred during the warranty period.
(3) The breakdown or problem in question occurred while the product was in use for an appropriate
purpose under the conditions and environment of use specified in the operation manual and catalog.
(4) The breakdown of problem in question was caused by a specification defect or problem, or by a
quality issue with our product.
Note that breakdowns due to any of the following reasons are excluded from the scope of warranty:
[1] Anything other than our product
[2] Modification or repair performed by a party other than us (unless we have approved such
modification or repair)
[3] Anything that could not be easily predicted with the level of science and technology available at
the time of shipment from our company
[4] A natural disaster, man-made disaster, incident or accident for which we are not liable
[5] Natural fading of paint or other symptoms of aging
[6] Wear, depletion or other expected result of use
[7] Operation noise, vibration or other subjective sensation not affecting function or maintenance
Note that the warranty only covers our product as delivered and that any secondary loss arising from a
breakdown of our product is excluded from the scope of warranty.
8.3 Honoring the Warranty
As a rule, the product must be brought to us for repair under warranty.
8. Warranty
8.4 Limited Liability
(1) We shall assume no liability for any special damage, consequential loss or passive loss such as a
loss of expected profit arising from or in connection with our product.
(2) We shall not be liable for any program or control method created by the customer to operate our
product or for the result of such program or control method.
79
Page 86

8. Warranty
8.5 Conditions of Conformance with Applicable Standards/Regulations, Etc., and Applications
(1) If our product is combined with another product or any system, device, etc., used by the customer,
the customer must first check the applicable standards, regulations and/or rules. The customer is also
responsible for confirming that such combination with our product conforms to the applicable
standards, etc. In such a case we will not be liable for the conformance of our product with the
applicable standards, etc.
(2) Our product is for general industrial use. It is not intended or designed for the applications specified
below, which require a high level of safety. Accordingly, as a rule our product cannot be used in these
applications. Contact us if you must use our product for any of these applications:
[1] Medical equipment pertaining to maintenance or management of human life or health
[2] A mechanism or mechanical equipment intended to move or transport people (such as a
vehicle, railway facility or aviation facility)
[3] Important safety parts of mechanical equipment (such as safety devices)
[4] Equipment used to handle cultural assets, art or other irreplaceable items
(3) Contact us at the earliest opportunity if our product is to be used in any condition or environment that
differs from what is specified in the catalog or operation manual.
8.6 Other Items Excluded from Warranty
The price of the product delivered to you does not include expenses associated with programming, the
dispatch of engineers, etc. Accordingly, a separate fee will be charged in the following cases even during
the warranty period:
[1] Guidance for installation/adjustment and witnessing of test operation
[2] Maintenance and inspection
[3] Technical guidance and education on operating/wiring methods, etc.
[4] Technical guidance and education on programming and other items related to programs
80
Page 87

Change History
Revision Date Description of Revision
April 2011
March 2012
August 2012
Second edition
A page for CE Marking added
Third edition
Introduction, Safety Symbols and Safety Precautions are deleted
Pg. 1 to 7
Pg. 8
Pg. 18
Pg. 29
Pg. 63, 65, 67, 69
Pg. 78, 79
8. Contacting Us deleted
Fourth edition
4.1 Installation Posture added
Safety Guide added
Caution in Handling added
Brake voltage source capacity from 20W to 30W ĺ
changed to 20W
Caution notes added telling to go to see the doctor to have
an appropriate treatment when the grease got into an eye
Brake voltage source capacity 20W added to specifications
Contents changed in 8. Warranty
Change History
81
Page 88

Page 89

Page 90

Manual No.: ME3628-4A (August 2012)
Head Office: 577-1 Obane Shimizu-KU Shizuoka City Shizuoka 424-0103, Japan
TEL +81-54-364-5105 FAX +81-54-364-2589
website: www.iai-robot.co.jp/
Technical Support available in USA, Europe and China
Head Office: 2690 W. 237th Street, Torrance, CA 90505
TEL (310) 891-6015 FAX (310) 891-0815
Chicago Office: 1261 Hamilton Parkway, Itasca, IL 60143
TEL (630) 467-9900 FAX (630) 467-9912
Atlanta Office: 1220 Kennestone Circle, Suite 108, Marietta, GA 30066
TEL (678) 354-9470 FAX (678) 354-9471
website: www.intelligentactuator.com
Ober der Röth 4, D-65824 Schwalbach am Taunus, Germany
TEL 06196-88950 FAX 06196-889524
SHANGHAI JIAHUA BUSINESS CENTER A8-303, 808, Hongqiao Rd. Shanghai 200030, China
TEL 021-6448-4753 FAX 021-6448-3992
website: www.iai-robot.com
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice for purposes of
product improvement.
Copyright © 2012. Aug. IAI Corporation. All rights reserved.
12.08.000
 Loading...
Loading...