Page 1

1060E-1409
LQ-201CL
RGB Color & NIR
4CMOS Line Scan Camera
Document Version:1.1
LQ-201CL_Ver.1.1_Dec2014
User's Manual
Page 2

LQ-201CL
2
Notice
The material contained in this manual consists of information that is proprietary to JAI Ltd., Japan
and may only be used by the purchasers of the product. JAI Ltd., Japan makes no warranty for the
use of its product and assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear or for damages
resulting from the use of the information contained herein. JAI Ltd., Japan reserves the right to
make changes without notice.
Company and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective owners.
Warranty
For information about the warranty, please contact your factory representative.
Certifications
CE compliance
As defined by the Directive 2004/108/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, EMC
(Electromagnetic compatibility), JAI Ltd., Japan declares that LQ-201CL complies with the following
provisions applying to its standards.
CISPR Pub.22 (EN55022) (Emission admissible value and measuring method)
CISPR Pub.24 (EN55024) (Immunity admissible value and measuring method)
IEC61000-4-2(Electrostatic discharge immunity test)
FCC
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Warning
Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for FCC compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
Page 3

LQ-201CL
Supplement
The following statement is related to the regulation on “ Measures for the Administration
of the control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products “ , known as “ China RoHS “.
The table shows contained Hazardous Substances in this camera.
mark shows that the environment-frien dly u se period of containe d Hazard ous
Substances is 15 years.
嶷勣廣吭並㍻
嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕
功象嶄鯖繁酎慌才忽佚連恢匍何〆窮徨佚連恢瞳麟半陣崙砿尖一隈〇云恢瞳ゞ 嗤蕎嗤
墾麗嵎賜圷殆兆各式根楚燕 〃泌和
桟隠聞喘豚㍉
窮徨佚連恢瞳嶄根嗤議嗤蕎嗤墾麗嵎賜圷殆壓屎械聞喘議訳周和音氏窟伏翌
亶賜融延、窮徨佚連恢瞳喘薩聞喘乎窮徨佚連恢瞳音氏斤桟廠夛撹冢嶷麟半
賜斤児繁附、夏恢夛撹冢嶷鱒墾議豚㍉。
方忖仝15々葎豚㍉15定。
Page 4

LQ-201CL
3
- Table of contents –
1. General ........................................................................................................ 6
2. Camera composition ........................................................................................ 6
3. Main features ................................................................................................. 7
4. Locations and functions .................................................................................... 8
4.1. Locations and functions ............................................................................... 8
4.2. Rear Panel ............................................................................................... 9
5. Connectors and pin assignment .......................................................................... 10
5.1. 12-Pin Connector ...................................................................................... 10
5.1.1 Pin assignment ..................................................................................... 10
5.1.2 Conformable connector (Example) ............................................................. 10
5.2. Digital Output / Interface Connectors for Camera LinkTM ...................................... 10
5.2.1 Pin assignment ..................................................................................... 10
5.2.2 Conformable connector and cable assembly ................................................. 11
5.3.3 Camera Link Interface (Bit allocation) ........................................................ 11
5.3.4 Camera link output port ......................................................................... 13
5.3.5 Bit allocation of the output video .............................................................. 14
6. Functions and Operation .................................................................................. 14
6.1. Basic functions ......................................................................................... 14
6.2 Key functions ............................................................................................ 15
6.2.1 Line rate (Command LR) ......................................................................... 16
6.2.2 Electronic shutter (Exposure) (Command PER, PEG, PEB, PEIR) .......................... 16
6.2.3 External Trigger ................................................................................... 16
6.2.4 Serial communication ............................................................................ 16
6.2.3 EEN (Exposure Enable) function ................................................................ 17
6.2.4 White balance ..................................................................................... 17
6.2.5 Gain control ........................................................................................ 17
6.2.6 Black level .......................................................................................... 19
6.2.7 PRNU (Pixel Response Non-Uniformity ) correction ......................................... 19
6.2.8 DSNU (Dark Signal Non-Uniformity) correction ............................................... 20
6.2.10 Shading correction ................................................................................ 21
6.2.11 Lateral chromatic aberration ................................................................... 22
6.2.12 Aperture filter ..................................................................................... 25
6.2.13 Binning .............................................................................................. 25
6.2.14 Sub-sampling ....................................................................................... 25
6.2.15 Windowing .......................................................................................... 26
6.2.16 Test pattern generator ........................................................................... 26
6.3. Operation modes ...................................................................................... 27
6.3.1 Camera Default Settings ......................................................................... 27
6.3.2 No-Shutter mode with Internal Trigger ........................................................ 28
6.3.3 No-Shutter mode with external trigger ....................................................... 30
6.3.4 Shutter-Select mode with internal trigger .................................................... 32
6.3.5 Shutter-Select mode with external trigger ................................................... 35
6.3.6 Pulse Width Control (PWC) mode .............................................................. 37
6.3.7 Compatibility of trigger modes and functions ................................................ 39
6.3.8 Trigger modes and auto white balance modes matrix table ............................... 39
7. Functions listed alphabetically by command acronyms .............................................. 40
7.1 Command AHRS – Request Status After One-Push AWB......................................... 40
7.2 Command AL – Automatic Line Rate Reference Level .......................................... 40
7.3 Command AR – Automatic Line Rate Setting ..................................................... 40
7.4 Command ARST – Auto Reset Mode ................................................................ 40
7.5 Command AH - Activate One-Push Auto White Balance (AWB) - Shutter .................... 42
7.6 Command AW – Activate One-Push Auto White Balance (AWB) - Gain ....................... 43
7.7 Command BA – Bit Allocation ....................................................................... 43
7.8 Command BI – Binning ................................................................................ 43
Page 5

LQ-201CL
4
7.9 Command BL – Master Black Level ................................................................. 43
7.10 Commands BLR, BLB and BLIR – Black Level Red, Blue and NIR............................... 44
7.11 Command BLM - Black Level Mode ............................................................... 44
7.12 Command CABR, CABB and CABIR Chromatic aberration Red, Blue NIR ..................... 44
7.13 Command EI – Interlocked R, G, B & NIR Exposure .............................................. 44
7.14 Command GA – Master Gain Level .................................................................. 45
7.15 Commands GAR, GAB and GAIR – Gain Level Red, Blue and NIR. ............................. 45
7.16 Command GM - Gain Mode ...................................................................... 45
7.17 Command HPFC – Aperture Control ................................................................ 45
7.18 Command LR - Line Rate (Scan Rate) ............................................................. 45
7.19 Command MAV – Chromatic Aberration Control ................................................. 46
7.20 Command MAVCG – Chromatic Aberration Select ............................................... 46
7.21. Command NR - Noise Reduction ............................................................. 46
7.22 Command OS1,2,3,4,5,6 – Camera Link Video Output Select ................................. 46
7.22 Command PBC – Enable Pixel Black (FPN) Correction .......................................... 46
7.23 Command PBR – Run Pixel Black Correction and Store to User Area .......................... 47
7.24 Command PBS - Request Status After Pixel Black Correction ............................... 47
7.25 Command PER,PEG,PEB and PEIR – Programmable Exposure for R,G,B,and NIR ............ 47
7.26 Command PGC – Select pixel gain correction mode .............................................. 47
7.27 Command PGR – Pixel Gain Correction and Store in User Area................................. 48
7.28 Command PGS - Request Status After Pixel Gain Correction ............................... 48
7.29 Command SCB – Select cable ....................................................................... 48
7.30 Command SDC – Select Shading Correction Mode ................................................. 48
7.31 Command SDR – Run Shading Correction and store to user area ............................. 48
7.32 Command SDS – Request Status After Executing Shading Correction Command ........... 49
7.33 Command SRO – Sensor Read Out .................................................................. 49
7.34 Command SGR, SGG, SGB, SGIR – Sensor Gain Set R, G, B and NIR ........................ 49
7.35 Command TG – Trigger Origin ....................................................................... 49
7.36 Command TI – Trigger Input ......................................................................... 49
7.37 Command TP – Trigger Polarity ..................................................................... 49
7.38 Command TR – Trigger Mode ........................................................................ 50
7.39 Command TS – Test Pattern ......................................................................... 50
7.40 Command WB – White Balance ..................................................................... 50
8. Serial communication and command list ............................................................... 51
8.1. Serial communication ................................................................................. 51
8.2. Command list .......................................................................................... 52
9. Camera Control Tool for LQ-201CL ...................................................................... 59
9.1. Software Install ........................................................................................ 59
9.2. Open the Control Tool ................................................................................ 59
9.3. Connect a camera ..................................................................................... 59
9.4. Camera control window .............................................................................. 60
9.5 Menus ...................................................................................................... 60
9.5.1 File menu ........................................................................................... 60
9.5.2 Settings menu ...................................................................................... 61
9.5.3 Line Correction menu ............................................................................ 61
9.5.4 Help menu .......................................................................................... 62
10. External appearance and Dimensions .................................................................. 63
11. Specifications ............................................................................................. 65
11.1 Typical data ............................................................................................... 65
11.2 Camera Spectral sensitivity ......................................................................... 67
Appendix ............................................................................................................ 68
1. Precautions ............................................................................................... 68
2. Typical Sensor Characteristics ......................................................................... 68
3. Caution when mounting a lens on the camera ...................................................... 68
4. Caution when mounting the camera.................................................................. 69
5. Exportation ............................................................................................... 69
6. References ................................................................................................ 69
Page 6

LQ-201CL
5
Change history ..................................................................................................... 70
User's Record ....................................................................................................... 71
Page 7

LQ-201CL
6
1. General
The LQ-201CL is a 4CMOS line scan camera using four 2048 pixel line sensors mounted on a prism,
for the R, G, B and NIR channels. It operates with an 84 MHz pixel clock, resulting in a maximum
line rate of 33,014 lines per second.
The camera outputs digital data in 4 x 8 bits or 4 x 10 bits format via Camera Link. The camera is
configured by software through the serial communication port of the Camera Link interface, or via
RS-232C through a 12-pin connector.
The camera accepts an M52 mount or F-mount lens, depending on the version selected.
The LQ-201CL is a suitable camera for various applications such as inspection of fruits,
vegetables ,circuits boards or electronic/mechanical parts, as the NIR image can catch scratches or
blemishes on object surfaces which the RGB color image cannot find.
The latest version of the operation manual can be downloaded from www.jai.com .
The latest camera control tool for the LQ-201CL can be downloaded from www.jai.com .
For camera revision history, please contact your local JAI distributor
2. Camera composition
Two camera versions are available
LQ-201CL-M52 M52 mount
LQ-201CL-F F mount
The standard camera composition is as follows.
Camera body 1
Sensor protection cap 1
Dear Customer (sheet) 1
The following optional accessories are available.
Power supply unit
PD-12 series
Page 8

LQ-201CL
7
3. Main features
4CMOS line scan camera with 2048 pixel resolution
Dichroic beam splitter prism to separate R,G,B and NIR wavelengths
33,014 lines per second scan rate
84 MHz pixel clock
4 x 8 bits or 4 x 10 bits output through Camera Link interface
PRNU and DSNU Flat-field correction
Individual gain control in the range of -4dB to +14dB with a fine gain control
Flat shading correction and color shading compensation
One-push auto white balance using gain control or shutter control
Binning function to increase sensitivity
Sub-sampling and windowing functions for faster line rate
Auto reset function
Noise reduction function
Test pattern generator(color bar, gray, white) for setup and trouble shooting
Electronic shutter (for selected modes)
Short ASCII commands set up via RS 232C or Camera Link
M52 mount and F mount versions
Field upgrade function by using exclusive update tool
Page 9

LQ-201CL
8
4. Locations and functions
4.1. Locations and functions
Fig. 1 Location of external features
1 Lens mount M52 mount (*1)Note)
2 Camera Link connector 1 base connector (1) (*2)Note)
3 Camera Link connector 2 medium connector (2) (*2)Note)
4 12-pin Hirose connector DC +12, External trigger and RS-232C
5 DIP switch SW-1 ( refer to chapter 4.2 for the details)
6 Button For one-push auto white balance (Gain based)
7 LED indicator Power, trigger input and operation indications
8 Camera mounting holes 8 x M3, depth 5mm (*3) Note)
*1) Note: Rear protrusion on M52 mount lens must be less than 13mm.
F mount is also available. Rear protrusion for F mount lens is the same as M52 mount.
*2) Note: When a Camera LinkTM cable is connected to the camera, please do not excessively tighten
screws by using a driver. The Camera Link receptacle on the camera might be damaged.
For security, the strength to tighten screws is less than 0.291 Newton meter (Nm).
Tightening by hand is sufficient in order to achieve this.
*3) Note: The depth of mounting hole is 5 mm. If the longer screws than 5 mm are used, they may
damage the circuit board inside.
Page 10

LQ-201CL
9
4.2. Rear Panel
Fig2. Rear panel
① LED
Green (Steady)
Operating, but not receiving external trigger input
Green (Flashing)
Operating and receiving external trigger input.
Note that the flashing frequency does not correspond to the frequency of the trigger
signal. The flashing does not occur in the No-shutter internal and Shutter-Select internal
modes.
Orange
Initializing and cannot operate
1) Initializing for approx. 800 ms
2) One-push auto white balance is engaged.
② DIP switch
SW-1 function
No
Function
Settings
ON
OFF
1
Serial communication
12-Pin
Camera Link (CC1)
2
Termination of External trigger
75Ω
TTL
Note: Factory default settings for both functions are “OFF”.
Fig.3 DIP switch
DIG ITAL I /O - 1
DIG ITAL I /O - 2
POW ER/
TRIG
W .B .
DC IN
/TRIG
S W1
①
②
OFF
ON
Serial
Communication
75 Ω
Page 11

LQ-201CL
10
5. Connectors and pin assignment
5.1. 12-Pin Connector
5.1.1 Pin assignment
Type: HR10A-10R-12PB-01 (Male) or equivalent
Use the part number HR10A-10P-12S or equivalent for the cable side
Pin No.
Signal
Remarks
1
GND
2
DC in
+12V to +24V
3
GND
4
Reserved
Do not connect
5
GND
6
RxD in
RS-232C
7
TxD out
RS-232C
8
GND
9
XEEN out
10
Trigger in
11
DC in
+12V to +24V
12
GND
5.1.2 Conformable connector (Example)
No.
Manufacture
Type name
Note
Camera side
HIROSE
HR10A-10R-12PB(71)
Cable side
HIROSE
HR-10A-10P-12S
Plug
5.2. Digital Output / Interface Connectors for Camera LinkTM
5.2.1 Pin assignment
Type: 26P MRD Connector 3M 10226-1A10PL
Fig. 5 Camera Link connector
This camera can be used with all Camera Link products that comply with the AIA Camera Link
standard. Cables, transmission systems and frame grabbers/acquisition boards that do not comply
with the Camera Link standard may work with this camera, but JAI Camera Solutions cannot be
held responsible for loss in performance or damage of equipment, including the camera.
Connector 1 (4 x 8-Bit, 4 x 10-Bit)
Pin No
In/Out
Name
Note
1,14 Shield
GND
2(-),15(+)
O
TxOUT0
Data out
3(-),16(+)
O
TxOUT1
4(-),17(+)
O
TxOUT2
5(-),18(+)
O
TxClk
Clock for CL
6(-),19(+)
O
TxOUT3
Data out
7(+),20(-)
I
SerTC (RxD)
LVDS Serial Control
8(-),21(+)
O
SerTFG (TxD)
9(-),22(+)
I
CC1 (Trigger)
Trigger
10(+),23(-)
I
CC2 (Reserved)
11,24 N.C
12,25 N.C
13,26
Shield
GND
Fig. 4 12-pin Hirose connector
Page 12

LQ-201CL
11
Connector 2 ( Used only for 4 x 10-Bit output)
Pin No
In/Out
Name
Note
1,14 Shield
GND
2(-),15(+)
O
TxOUT0
Data out
3(-),16(+)
O
TxOUT1
4(-),17(+)
O
TxOUT2
5(-),18(+)
O
TxClk
Clock for CL
6(-),19(+)
O
TxOUT3
Data out
7(+),20(-)
N.C
8(-),21(+)
N.C
9(-),22(+)
N.C
10(+),23(-)
N.C
11,24 N.C
12,25 N.C
13,26
Shield
GND
5.2.2 Conformable connector and cable assembly
No.
Manufacture
Type name
Note
Camera side
3M
10226-1A10PL
Cable
assembly
3M
14B26-SZLB-xxx-
0LC
Standard
Note1: In the above table, xxx shows cable length. Applicable length is 0.5m to 10m.
Note2: If the used cable does not comply with Camera Link standards or it is 14B26-SZ3B-
xxx-03C (Thin diameter type) or 14B26-SZ3B-xxx-04C (High flex type), the cable
length for transmission is limited.
5.3.3 Camera Link Interface (Bit allocation)
The LQ-201CL follows the Camera Link standard in all respects.
Out1_D9~Out1_D0 : Out1_Camera Data (Out1_D9=MSB, Out1_D0=LSB)
Out2_D9~Out2_D0 : Out2_Camera Data (Out2_D9=MSB, Out2_D0=LSB)
Out3_D9~Out3_D0 : Out3_Camera Data (Out3_D9=MSB, Out3_D0=LSB)
Out4_D9~Out3_D0 : Out4_Camera Data (Out4_D9=MSB, Out4_D0=LSB)
Out5_D7 ~Out3_D0 : Out5_Camera Data (Out5_D7=MSB, Out5_D0=LSB)
Out6_D7 ~Out3_D0 : Out6_Camera Data (Out6_D7=MSB, Out6_D0=LSB)
× : Don’t Care
8-
bitx6output
10-
bitx4output
Connector
Pin Name
Port A0
Out1_D0
Out1_D0
1
Tx0
Port A1
Out1_D1
Out1_D1
1
Tx1
Port A2
Out1_D2
Out1_D2
1
Tx2
Port A3
Out1_D3
Out1_D3
1
Tx3
Port A4
Out1_D4
Out1_D4
1
Tx4
Port A5
Out1_D5
Out1_D5
1
Tx6
Port A6
Out1_D6
Out1_D6
1
Tx27
Port A7
Out1_D7
Out1_D7
1
Tx5
Port B0
Out2_D0
Out1_D8
1
Tx7
Port B1
Out2_D1
Out1_D9
1
Tx8
Port B2
Out2_D2
× 1 Tx9
Port B3
Out2_D3
× 1 Tx12
Page 13

LQ-201CL
12
Port B4
Out2_D4
Out2_D8
1
Tx13
Port B5
Out2_D5
Out2_D9
1
Tx14
Port B6
Out2_D6
× 1 Tx10
Port B7
Out2_D7
× 1 Tx11
Port C0
Out3_D0
Out2_D0
1
Tx15
Port C1
Out3_D1
Out2_D1
1
Tx18
Port C2
Out3_D2
Out2_D2
1
Tx19
Port C3
Out3_D3
Out2_D3
1
Tx20
Port C4
Out3_D4
Out2_D4
1
Tx21
Port C5
Out3_D5
Out2_D5
1
Tx22
Port C6
Out3_D6
Out2_D6
1
Tx16
Port C7
Out3_D7
Out2_D7
1
Tx17
Port D0
Out4_D0
Out4_D0
2
Tx0
Port D1
Out4_D1
Out4_D1
2
Tx1
Port D2
Out4_D2
Out4_D2
2
Tx2
Port D3
Out4_D3
Out4_D3
2
Tx3
Port D4
Out4_D4
Out4_D4
2
Tx4
Port D5
Out4_D5
Out4_D5
2
Tx6
Port D6
Out4_D6
Out4_D6
2
Tx27
Port D7
Out4_D7
Out4_D7
2
Tx5
Port E0
Out5_D0
Out3_D0
2
Tx7
Port E1
Out5_D1
Out3_D1
2
Tx8
Port E2
Out5_D2
Out3_D2
2
Tx9
Port E3
Out5_D3
Out3_D3
2
Tx12
Port E4
Out5_D4
Out3_D4
2
Tx13
Port E5
Out5_D5
Out3_D5
2
Tx14
Port E6
Out5_D6
Out3_D6
2
Tx10
Port E7
Out5_D7
Out3_D7
2
Tx11
Port F0
Out6_D0
Out3_D8
2
Tx15
Port F1
Out6_D1
Out3_D9
2
Tx18
Port F2
Out6_D2
×
2
Tx19
Port F3
Out6_D3
×
2
Tx20
Port F4
Out6_D4
Out4_D8
2
Tx21
Port F5
Out6_D5
Out4_D9
2
Tx22
Port F6
Out6_D6
×
2
Tx16
Port F7
Out6_D7
×
2
Tx17
LVAL 1
1
Tx24
FVAL 1
1
Tx25
LVAL 2
2
Tx24
FVAL 2
2
Tx25
DVAL
1
Tx26
EEN
1
Tx23
Note: LVAL 1, LVAL 2and FVAL 1, FVAL 2 will show the same signal
Page 14
LQ-201CL
13
(Output timing)
TxCLK
A7 A6 EEN C7 B7 B6 A7 A6C6
C3 C2 DVAL FVAL C5 C4 C3 C2LVAL
B2 B1 C1 C0 B4 B3 B2 B1B5
A1 A0 B0 A5 A3 A2 A1 A0A4
TxOUT3
TxOUT2
TxOUT1
TxOUT0
1 pixel cycle
Fig.6 Camera Link output timing
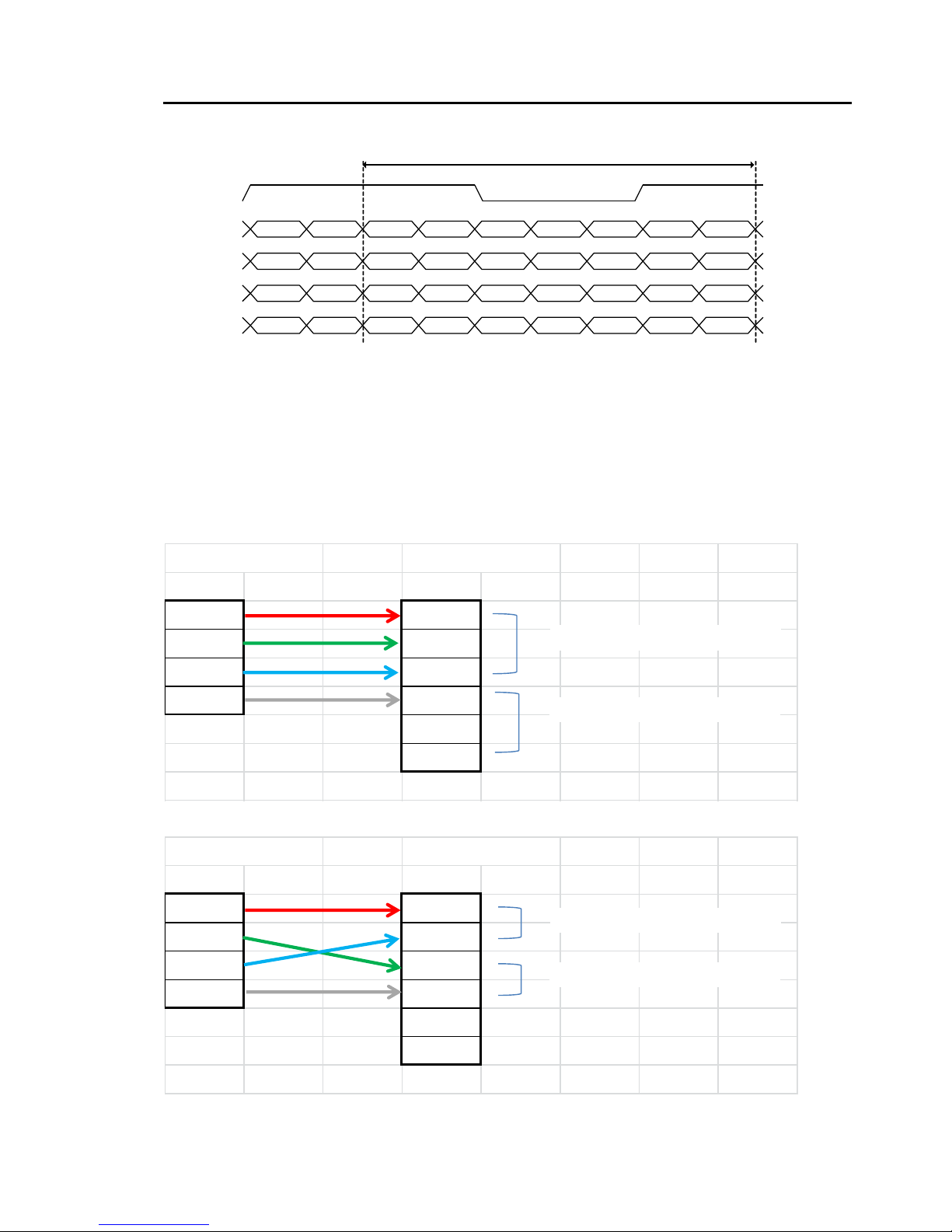
5.3.4 Camera link output port
LQ-201CL handles R, G, B and NIR channels. The output ports for 8-bit and 10-bit are different.
The following drawings show the default settings for the Camera Link Video Output Select
(Command OS1 to OS6). Camera Link output can be configured by command OS.
8-bit output
10-bit output
Fig. 7 Camera Link output configuration (Default)
Input signal Camera Link output
RED Out 1
GREEN Out 2
BLUE Out 3
Near IR Out 4
Out 5
Out 6
Camera Link 1 Port a - c
Camera Link 2 Port d - f
Input signal Camera Link output
RED Out 1
GREEN Out 2
BLUE Out 3
Near IR Out 4
Out 5
Out 6
Camera Link 1 Port a - c
Camera Link 2 Port d - fc
Page 15

LQ-201CL
14
5.3.5 Bit allocation of the output video
CMOS
out
Digital
8-Bit
(LSB)
Digital
10-Bit
(LSB)
Black
8
32
200mV
222
890
230mV
255
1023
Fig.8 Video output
6. Functions and Operation
6.1. Basic functions
Fig.9 Signals flow
The LQ-201CL uses four high-performance CMOS line scan image sensors mounted on a prism
block.
During exposure, the incoming light is converted to electrons (electric charge) in the photodiodes
(active pixels). The transfer gate controls the transfer of charge from photodiodes to the shift
register. Activating the transfer gate terminates the exposure cycle, transfers the charge to the
Horizontal Shift Register (2-phase buried channel CMOS shift register) and starts a new exposure
cycle. The line is subsequently read out in a single sequence starting with pixel 1.
The exposure time is normally the same as the cycle time (in No-shutter mode). By using the
Exposure Control Gate (in Shutter-Select or Pulse Width Control trigger modes) the exposure time
can be individually set to be shorter than the cycle time (the inverse of line rate). This also allows
a fixed exposure time, independent of the line rate. In the LQ-201CL the exposure time can be set
individually for all four channels.
Dichroic
Prism
Color
Separation
Light
AMP
ADC
Auto black, DSNU, PRNU, Shading,
Fine Gain, Line Matrix, Knee, Noise
reduction, User black
MPX
Digital Binning
MUX / Camera link IF
AMP
ADC
Auto black, DSNU, PRNU, Shading,
Fine Gain, Line Matrix, Knee, Noise
reduction, User black
AMP
ADC
Auto black, DSNU, PRNU, Shading,
Fine Gain, Line Matrix, Knee, Noise
reduction, User black
AMP
ADC
Auto black, DSNU, PRNU, Shading,
Fine Gain, Line Matrix, Knee, Noise
reduction, User black
OUT
PUT
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
32
0
CCD_out( mV)
Di gi tal _out ( mV)
Anal og ( mV)
230
1740
2000
200
0
8/32
222/ 890
255/1023
8-bit /10-bit
Page 16

LQ-201CL
15
Fig.10 Sensor layout
DMDMDMDMDMDMDMDMDMDMDMDMDM
DM
DM0
DM1
DM2
DM3
DM4
DM5
DM6
DM7
AP0
AP1
AP2
AP3
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
DM8
DM9
DM10
DM11
DM12
DM13
DM14
DM15
AP2047
AP2046
AP2045
AP2044
・・・・・・・・・・・・・
・
DM
DM
・
2048
LVAL
DVAL
Data
DM : Dummy or Transfer_data Pixels
AP : Active Pixels
LVAL: Line Valid
DVAL: Data Valid
1CLK = 11.9ns
2544
Fig.11 Video output timing
6.2 Key functions
Important note:
LQ-201CL has many functions explained in this chapter. In order to use these functions
properly and to get proper image, please follow the procedure described below.
Setting procedure:
1. Set the shutter and line rate
2. Set the master gain (refer to the chapter 6.3.5 for the details)
3. Set the white balance (refer to the chapter 6.3.4 for the details)
4. Activate DSNU compensation (refer to the chapter 6.3.9 for the details)
5. Activate PRNU compensation (refer to the chapter 6.3.8 for the details)
6. Activate the shading compensation (refer to the chapter 6.3.10 for the details)
After completing the above, adjust black level, lateral chromatic aberration and knee
adjustments. For these adjustments, there is no specific order required.
Effective Pixel
474
DM8
DM9
DM10
DM11
DM12
DM13
DM14
DM15
DM4
DM0
DM1
DM2
DM3
DM5
DM6
DM7
Digital Processor
CDS, PGA, ADC
Serializer
8 82048
Dummy Pixels Dummy Pixels
PD0<0>
PD0<1>
PD0<2>
Transfer Data
DM : Dummy Pixels
480
Page 17

LQ-201CL
16
6.2.1 Line rate (Command LR)
This function can set the line rate longer than 1L. Accordingly, it is possible to set the camera scan
rate with the object running speed or to boost up the sensitivity by setting longer exposure time.
Adjusting range: 30.29 µs(1L) to 15.0 ms
Adjusting unit: 11.9 ns
Operation mode: No Shutter/Internal Trigger and
Shutter Select/Internal Trigger
The line rate can be automatically configured (one-push auto line set) (Command:AR). This function
will calculate and set the line rate of the camera based on the Automatic Line Rate Reference Level
(Command :AL) and the scene illumination. This function is available on No Shutter/Internal Trigger
and Shutter Select/Internal Trigger modes.
6.2.2 Electronic shutter (Exposure) (Command PER, PEG, PEB, PEIR)
This function sets the exposure time regardless of line rate setting. The exposure time can be set
for red, blue, green, and NIR, respectively.
Command PER, PEG, PEB and PEIR
Adjusting range: 9.52 μs to 14.99 ms (RGB and NIR individually)
Adjusting unit: 11.9 ns (1clock) (RGB and NIR individually)
Operation mode: Shutter Select/Internal Trigger and
Shutter Select/External Trigger
Note: Upper limit of operable line rate
On Shutter Select/internal trigger mode
The line rate setting is the maximum line rate for operation
On Shutter Select/external trigger mode:
The trigger interval is the maximum value.
6.2.3 External Trigger
The external trigger can be input through the 12-pin connector or Camera Link CC1.
These cannot be used at the same time.
The external trigger signal can be terminated by 75 ohms inside the camera (Refer to Chapter 4.2).
6.2.4 Serial communication
The camera can communicate by serial interface through the 12-pin or Camera Link interface. The
default baud rate is 9600 bps. The serial interface of the 12-pin or Camera Link interface cannot be
used at the same time. The selection of the communication interface can be done via the DIP switch
located on the rear panel. (Refer to Chapter 4.2)
OFF
ON
Serial
Communication
75 Ω
OFF
ON
Serial
Communication
75 Ω
Page 18

LQ-201CL
17
6.2.3 EEN (Exposure Enable) function
This function outputs the timing for image accumulation in all operating modes except test pattern
output. The output can be through both the 12-pin and Camera Link connectors. The polarity of this
output is negative from the 12-pin connector and positive from the Camera Link connector. These
polarities cannot be changed. The following drawing shows the output through Camera Link.
Fig.12 EEN function
6.2.4 White balance
In this function, the green channel video level is used as the reference. Red and blue channel levels
are adjusted to match with that of the green channel.
There are two ways to adjust white balance: one is gain white balance and the other is shutter
white balance.
White balance
Control tool
Command
Rear panel
switch
WB
AH
Gain
○ ○ ☓
○
Shutter
○ ☓ ○
☓
Gain white balance
Calculates the difference between green and red video levels, and green and blue levels, and adjusts
the red and blue channels’ video level so that the video level of all three channels becomes equal.
Command WB=0 Manual/One push AWB
WB=1 4000K
WB=2 4600K
WB=3 5600K
Shutter white balance (only for Shutter Select mode)
Calculates the difference between green and red video levels, and green and blue levels, and adjusts
the red and blue channels’ shutter speed so that the video level of all three channels becomes equal.
Command AH=0 Activate one-push shutter AWB
Note:
If gain and shutter white balance are used in the External Trigger mode, external trigger pulses
should be continuously provided while white balance adjustment is executing.
6.2.5 Gain control
The LQ-400CL has two ways of setting gain - one for master mode and the other for individual mode.
Each setting also has two analog gain modes - one is GAIN LOW and the other is GAIN HIGH. Gain
Low is the default output setting. The following shows the setting procedures and adjustable range.
Exposure B
Exposure G
Exposure R
EEN
(I nternal/External )
Tri gger
EEN represents with the longets exposure time among R,G and B
Page 19

LQ-201CL
18
1. Master mode (Default setting)
Gain Low mode:
Reference value: 0dB
Master gain control range : 0dB to 8dB
R,B and NIR adjusting range :-4dB to +6dB (at the master gain setting value)
Gain High mode:
Reference value: +6dB
Master gain control range : 0dB to 8dB
R, B and NIR adjusting range :-4dB to +6dB (at the master gain setting value)
Fig.13 Master gain mode with Gain Low and High
2. Individual gain mode
Gain Low mode:
Reference value: 0dB
R, G, B and NIR adjusting range :-4dB to +14dB (at the master gain setting value)
Gain High mode:
Reference value: +6dB
R, G, B and NIR adjusting range :-4dB to +14dB (at the master gain setting value)
+4dB
+6dB
+6dB
+6dB
-4dB
-4dB
+6dB
-4dB
0
0+6dB
+2dB
-4dB
0dB
+14dB
+20dB
+8dB 800
800
Analog Gain = LOW Analog Gain = HIGH
Blue Red NIR
Blue Red
Master
Master NIR
Page 20

LQ-201CL
19
Fig.14 Individual gain mode with gain low and gain high
6.2.6 Black level
The setup level of the LQ-400CL is set at 8LSB in 4 x 8-bit output mode as the factory default setting
(32LSB for 4 x 10-bit output mode)
In order to adjust, the following commands are available.
BLM= 0 Master mode
BLM= 1 Individual mode
BL= 0 to 64
BLR= -64 to 63
BLB= -64 to 63
BLIR= -64 to 63
If the gain is set at Master mode:
Adjusting range Master(green) : 0LSB to 64LSB (16LSB)
Red : -64(-16) LSB to +64(16) LSB
Blue : -64(-16) LSB to +64(16) LSB
NIR : -64(-16) LSB to +64(16) LSB
Figures in ( ) are for 8-bit output
If the gain is set at Individual mode:
Adjusting range Red : 0LSB to 64(16) LSB
Green : 0LSB to 64(16) LSB
Blue : 0LSB to 64(16) LSB
NIR : 0LSB to 64(16) LSB
Figures in ( ) are for 8-bit output
Note: Red, green, blue and NIR can be adjusted individually
6.2.7 PRNU (Pixel Response Non-Uniformity ) correction
PRNU (Pixel Response Non-Uniformity) is, as the name implies, a non-uniformity of the response of
each individual pixel. This means that for a fixed light level each pixel will have a slightly
different output level (response).
Blue Red
Blue Red
1400
0
-400
-400
0
1400
Analog Gain = LOW Analog Gain = HIGH
+6dB
+2dB
-4dB
0dB
+14dB
+20dB
Green
Green NIR
NIR
Page 21

LQ-201CL
20
Fig.15 Conceptual drawing for PRNU correction (1)
To correct for PRNU, the camera’s internal correction circuit captures one or several lines of data
under non-saturated illuminated conditions which are not more than 80% of maximum
(recommend level is half of maximum), and the average across the line is calculated. Based on
this average, coefficients are then generated for each individual pixel. The coefficient has the
function of multiplying the pixel output with a factor greater or less than 1. These coefficients are
stored in a non-volatile memory, and are therefore maintained after power down.
Fig.16 Conceptual drawing for PRNU correction (2)
6.2.8 DSNU (Dark Signal Non-Uniformity) correction
DSNU (Dark Signal Non-Uniformity) is, as the name implies, a non-uniformity of offset level of
each pixel, which is not dependent on the incoming light.
Fig.17 Conceptual drawing of DSNU correction
To correct for DSNU, the camera internal correction circuit captures one or several lines of data
under dark conditions (the lens must be covered by a lens cap), and the average across the line is
calculated. Based on the average, coefficients are then generated for each individual pixel. The
coefficient has the function of adding or subtracting a value to the pixel output. These
coefficients are stored in a non-volatile memory, and are therefore maintained after power down.
As the dark signal is highly dependent on the exposure time, this correction must be performed
under the operating conditions (exposure time and line rate) that will be used by the application.
Max
Before correction: dark signal non-uniformity from pixel to pixel
Subtract factor
Add factor
Min
Average
Max
Min
Multiply
by
Factor > 1
Multiply
by
Factor < 1
Before correction: Non-uniform response from pixel to pixel
Average
After correction: flat response from pixel to pixel
Average
Page 22

LQ-201CL
21
Fig.18 Conceptual drawing of DSNU correction
6.2.10 Shading correction
Shading is caused either by illumination with uneven distribution of light across the surface, or by
reductions in the light transmission ratio towards the edges of a lens.
The shading correction incorporated in the camera will compensate for this effect by as much as
20% of the brightest signal.
Shading is not compensated for each individual pixel. The signal is averaged across groups of 8 pixels
in relation to the whole line. The pixel response non-uniformity will be superimposed on the output
also after shading correction has been performed. Therefore, it is recommended to perform PRNU
correction before shading correction.
Fig.19 Shading correction
The shading correction has two ways to compensate, flat shading correction and color shading
correction.
Flat shading correction (SDR=0):
Flat shading correction compensates red, blue, green and NIR signals to be flat output. The range
of compensation is within plus-or-minus 20% as compared the brightest signal level. It may not
compensate enough according to the lenses and/or lighting in use.
As the default, the data which is activated in the factory is stored.
Fig.20 Flat shading correction concept drawing
Note:
Depending on the optics and/or illumination used together with the camera, it may not
be possible to fully compensate for shading.
Average
After correction: Flat dark signal response from pixel to pixel
Shading caused by uneven illumination or transmission at the edges of the lens.
Pixel response non-uniformity will be superimposed on the output signal
Page 23

LQ-201CL
22
Operating procedure for individual R, G ,B and NIR channel shading correction:
1. Before making adjustment, approximately 30 minutes of warm up is required.
2. Make sure the output signal is not saturated (<80% of full output is recommended)
3. Set command PGC=2 and SDC=2.
4. Set command SDR to 0 to initiate shading correction.
5. If desired, set command PGR to 0 to activate flat-field (pixel gain) correction to
correct for pixel response non-uniformity.
6. Again set SDR=0 after running the flat-field (pixel gain) correction
Color shading correction (SDR=1):
Color shading correction compensates red, blue and NIR signals to match with green signal
characteristics. The camera does not store the reference data for color shading.
Fig.21 Color shading correction concept drawing
Note:
For this function, no reference value is stored in the camera.
Operating procedure for individual R, ,B and NIR channel shading correction:
1. Before making adjustment, approximately 30 minutes of warm up is required.
2. Make sure the output signal is not saturated (<80% of full output is recommended)
3. Set command PGC=2 and SDC=2.
4. Set command SDR to 1 to initiate shading correction.
5. If desired, set command PGR to 0 to activate flat-field (pixel gain) correction to
correct for pixel response non-uniformity.
6. Again set SDR=1 after running the flat-field (pixel gain) correction
Please note that before adjusting the shading, the white balance must be adjusted.
6.2.11 Lateral chromatic aberration
This function compensates for lateral chromatic aberration of lenses. Lateral chromatic aberration
causes different line lengths for the R, G, B and NIR rays at the focal point. This function enables
compensation data for up to three lenses to be stored. The compensation data specifies how many
pixels the R, B and NIR channels should be stretched or shortened to match the line length of the G
channel which is the reference. The range of correction is minus three pixels to plus three pixels.
In order to realize this function, the LQ-201CL uses an FIR (finite impulse response) filter for R, B
and NIR channels. The filter’s response is determined by a set of 7 types of filter coefficients. The
2048 pixels that make up a line are divided in 16 blocks, with each block having 128 pixels.
To compensate lateral chromatic aberration, the 7 types of coefficients are set for each block.
In the factory, a default set of 112 data elements (7 types x 16 blocks) are calculated and stored.
Page 24

LQ-201CL
23
Pixel number in each block: 128 pixels
Note: Restrictions for this function
In order to adjust properly lateral chromatic aberration, the difference between G and R or B or
NIR on right and left sides should be equal. Otherwise, the compensation may not be properly
executed.
The following screen is used for creating up to three user-defined sets of lateral chromatic
aberration data in the camera control tool.
Fig. 22 Setting screen for lateral chromatic aberration
Setting procedure:
Please use the following steps.
1. Chromatic Aberration Enable
2. Select Lens 1, 2 or 3
3. Set the left side pixel
4. Set the area
5. Set the second block pixel
6. Set the third block pixel
Enable : Set chromatic aberration function ON or OFF.
Command MAV=0(OFF) and MAV=1(ON).
Lens 1,2,3 : Select a data set to use. Data for three lenses can be stored.
2048th Pixel
Page 25

LQ-201CL
24
Change name : Instead of Lens 1, 2 and 3, specific names such as 28mm can be
displayed. Max. 16 alpha-numeric characters can be used.
Left side pixel : Specifies by how many pixels the left edge of the image should
be shifted. The maximum value is 3 pixels. A negative value
extends the image by 1, 2 or 3 pixels. A positive value, narrows
the image.
Values to set are L3,L2,L1,R1,R2 and R3.
L3 says to shift 3 pixels to the left and R3 says to shift 3 pixels to the
right.
In case of Red, CABLR=[User Lens],[Shift value]
In case of Blue, CABLB=[User Lens],[Shift value]
In case of NIR, CABLIR=[User Lens],[Shift value]
The range of the shift value is -3 to +3.
The following is the result of a negative setting
The following is the result of a positive setting.
Fig. 23 Operation of the compensation
Area : This command specifies the area in which pixel shifting will be applied.
The image is divided into 16 blocks, with each block representing 256
pixels. Enter a number from 1 to 8 to specify the inner edge of the pixel
shifted area. The value is automatically mirrored on both the left and right
sides of the image. If the left side pixel value is +/-1, only Area setting (1
to 6 blocks in fig. 25) is used and all pixels in this area will be shifted by 1
pixel. All pixels outside this area (7 and 8, white blocks) will remain unshifted. If the left side pixel value is +/-2 or +/-3 use the 2nd Pixel Block
and 3rd Pixel block fields to define a gradual shift from the edge to the
center of the image.
2nd pixel block : If the left side pixel value is 2 or more pixels, enter a number in this field
to specify the block where the compensation will transition from a 2-pixel
shift to a 1-pixel shift. The value entered is automatically mirrored on
both the left and right sides of the image. Blocks 1 to 4 in fig.25, are
where the 2 to 1-pixel shift will be applied.
3rd pixel setting : If the left side pixel value is set at +/-3, enter a value in this field to
specify the block where the compensation will transition from a 3-pixel
shift to a 2-pixel shift. The value entered is automatically mirrored on
both the left and right sides of the image. Blocks shown in blue (1 and 2
block) are where the 3-pixel shift will be applied.
Setting example:
Left side = -3 or 3
Area : 6, 2nd : 4, 3rd : 2
Page 26

LQ-201CL
25
Fig. 24 Setting example
Note: 1) If left side pixel is set at -2 or +2, only Area and 2nd can be configured.
3rd cannot be set.
2) If left side pixel is set at -1 or +1, only Area can be configured.
Caution on calibration:
The object must be charts or materials which have clear and sharp discrimination of white and black
edges. The volume of color difference in peripheral area is measured by using the image analysis
software. Check how many pixels of R and B channels are shifted against G channel. In this function,
maximum three pixels are compensated.
For instance, if R channel is shifted 1 pixel to the left in the left end of the image, this means “-1”
and set the command CABLR to 1.
The compensation for the right side is automatically effected.
6.2.12 Aperture filter
LQ-400CL has a circuit for image enhancement in order to improve visible MTF. The compensation
coefficient is a fixed value and cannot be changed. The factory default for this function is OFF. This
function does not depend on the operating mode.
6.2.13 Binning
In this mode, the camera combines the charge collected in two adjacent pixels. This halves the
effective resolution to 2048 pixels, but doubles the sensitivity. The line rate is not affected by
binning. This function does not depend on the operating mode.
Fig.25 Binning reads out adjacent pixels at the same time
6.2.14 Sub-sampling
In this mode, every two effective pixels are read out. Accordingly, the read out rate is doubled. The
FOV (Field Of View) is not changed versus full scan mode but the resolution becomes half.
4092 4093
4094
4095
4096409140904089408840871 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
20482047204620452044
5
4321
Page 27

LQ-201CL
26
Fig.26 Sub-sampling reads out every two pixels
6.2.15 Windowing
In this mode, only the effective 2048 pixels in the center portion can be read out and accordingly,
the readout rate is doubled. FOV becomes half as compared to the full pixel read out. 2048 pixels
are a fixed number and cannot be varied by the user.
Fig.7 Windowing reads out only 2048 pixels at the center
6.2.16 Test pattern generator
LQ-400CL has four test pattern generators.
In the following drawings, figures shown in ( ) are for 8 bits output.
Color bar
Fig.28 Color bar test pattern
Gray 1
Fig.29 Gradation test pattern
Gray 2
1 3 5 7 9 40964094409240904088
20482047204620452044
5
4321
2 4 6 8 10
4087
4089
4091 4093
4095
20482047204620452044
5
4321
1025 1026 1027 1028 1029 30723071307030693068102410231 2 3073 3074 40964095
0
4095
32(8)
0
890(222)
DVAL
Page 28

LQ-201CL
27
Fig.30 Multi burst test pattern
White
Fig.31 White test pattern
6.3. Operation modes
The LQ-400CL has the following operation modes.
Trigger Mode
Trigger origin
Command
Description
Command
Description
1
TR=0
No-Shutter
TG=0
Internal
2
TG=1
External
3
TR=1
Shutter select
TG=0
Internal
4
TG=1
External
5
TR=2
Pulse width control
TG=1
-
6.3.1 Camera Default Settings
The following table shows the default settings of LQ-201CL
Item
Default setting
Value
Gain
Master mode B/G/R/NIR
0dB
Black
Master mode B/G/R/NIR
8LSB
Trigger Mode
No-shutter
Trigger Origin
Internal
Auto Reset Mode
ON Input
Camera Link
Polarity
Active Low
Line Rate
24000
Bit Allocation
8-bit
Binning
OFF Test Pattern
OFF Noise Reduction
OFF
0
32(8)
0
890(222)
DVAL
Si gnal (RGB
16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16・・・
4095
0
32(8)
0
890(222)
DVAL
4095
Page 29

LQ-201CL
28
6.3.2 No-Shutter mode with Internal Trigger
In this mode, the exposure and readout are activated by the trigger pulse generated internally.
As the accumulation control is done by the internal counter, the accumulation is not affected by
the trigger jitter.
In this mode, the accumulation period depends on the trigger interval. Accordingly, if trigger
interval becomes longer, the sensitivity is increased.
To use this mode:
Set function Trigger mode, No-Shutter TR=0
Trigger origin, Internal TG=0
Line rate LR=2544 to 1260000
(30.29 µs to 15.0 ms in 11.9 ns increments)
Optional functions when using this mode:
One-push auto line rate AR=0
Auto line rate reference AL=0 to 1023
One-push white balance WB
Important Note
The “one-push auto line rate” function is not recommended for continuous web applications,
as the speed of motion needs to be adjustable in order to maintain the aspect ratio of the
image.
Only gain based one-push white balance functions (WB) are available with this mode.
Fig.32 No-Shutter / Internal Trigger mode
451clk
EEN
LVAL
137clk
611clk
8clk
2048clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
Page 30

LQ-201CL
29
Fig.33 No-Shutter mode / Binning/ Internal
Fig.34 No-Shutter /Sub-sampling and Window/ Internal
451clk
EEN
611clk
LVAL
8clk
2048clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
451clk
EEN
611clk
LVAL
8clk
1024clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP1023
Page 31

LQ-201CL
30
6.3.3 No-Shutter mode with external trigger
In this mode, the accumulation and readout is activated by an external trigger pulse. The
exposure period depends on the trigger interval and if the trigger interval becomes longer, the
sensitivity is increased.
To use this mode:
Set function Trigger mode, No-Shutter TR=0
Trigger origin, external TG=1
Trigger input TI=0 or 1
Important note:
In this mode, the shutter cannot be used.
Only gain based one-push white balance functions (WB) are available with this mode.
The jitter generated in the trigger input causes a variation of exposure time.
Minimum trigger interval
Scan mode
Trigger input via
Minimum interval (µs)
Full/Binning
Camera link
30.8
12-pin
35.3
Sub-sampling/windowing
Camera link
18.9
12-pin
23.4
Minimum trigger pulse width
Trigger input via
Minimum trigger pulse width
Camera link
500 ns
12-pin
5 µs
Fig. 35 No-Shutter mode with external trigger
TG
653c lk
EEN
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
2048 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
Page 32

LQ-201CL
31
Fig. 36 No-Shutter mode /Binning/ External
Fig.37 No-Shutter mode /Sub-sampling and Window/ External
TG
653clk
EEN
1043clk
LVAL
8clk
2048clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
TG
653c lk
EEN
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
1024 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP1023
Page 33

LQ-201CL
32
6.3.4 Shutter-Select mode with internal trigger
In this mode, the exposure and readout is activated by the trigger pulse generated internally.
As the accumulation control is done by the internal counter, the accumulation is not affected by
the trigger jitter.
In this mode, the exposure time of R, G, B and NIR channel can be adjusted independently.
To use this mode:
Set function
Trigger mode, Shutter-Select TR=1
Line rate LR=2544 to 1260000
(30.29 μs to 15.0 ms in 11.9 ns increments)
Trigger origin, internal TG=0
Individual R, G, B and NIR exposure EI=0(individual)
EI=1(tracking with G)
Programmable exposure PER/PEG/PEB/PEIR=800 to 1259549
(9.52 µs to 14.99 ms in 11.9 ns increments)
Important note:
If using individual exposure, the EEN signal represents the channel with the longest exposure
time
For one-push white balance, both shutter gain (AH) and gain( AW) are effective.
Note: EEN uses channel with the largest exposure value
Fig.38 Shutter-Select mode / Internal
EEN
*Note
Exposure R
Exposure G
Exposure B
Exposure NIR
611clk
LVAL
8clk
2048c lk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
Page 34

LQ-201CL
33
Note: EEN uses channel with the largest exposure value
Fig. 39 Shutter-Select mode / Binning /Internal
EEN
*Note
Exposure R
Exposure G
Exposure B
Exposure NIR
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
2048 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
Page 35

LQ-201CL
34
Note: EEN uses channel with the largest exposure value
Fig.40 Shutter–Select mode/Sub-sampling and Window/ Internal
EEN
*Note
Exposure R
Exposure G
Exposure B
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
1024 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP1023
Page 36

LQ-201CL
35
6.3.5 Shutter-Select mode with external trigger
In this mode, the exposure and readout is activated by the external trigger pulse.
In this mode, the exposure time of R, G, B and NIR channel can be adjusted independently.
To use this mode:
Set function
Trigger TR=1
Trigger origin, external TG=1
Individual R, G, B and NIR exposure EI=0(individual)
EI=1(tracking with G)
Programmable exposure PER/PEG/PEB/PEIR=800 to 1259549
(9.52 µs to 14.99 ms in 11.9 ns increments)
Important note:
If using individual exposure, the EEN signal represents the channel with the longest exposure time
The minimum trigger interval
Scan mode
Trigger input via
Minimum interval (µs)
Full/Binning
Camera link
30.8
Hirose 12-pin
35.3
Sub-sampling/windowing
Camera link
18.9
Hirose 12-pin
23.4
The minimum trigger pulse width
Trigger input via
Minimum trigger pulse width
Camera link
500 ns
Hirose 12-pin
5 µs
For one-push white balance, both shutter gain (AH) and gain (AW) are effective.
Note: EEN uses channel with the largest exposure value
Fig. 41 Shutter-Select mode with external trigger (and individual exposure)
TG
146clk
EEN *Note
Exposure R
Exposure G
Exposure B
611clk
LVAL
8clk
2048c lk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
Page 37

LQ-201CL
36
Note: EEN uses channel with the largest exposure value
Fig.42 Shutter-Select mode /Binning /External
Note: EEN uses channel with the largest exposure value
Fig.43 Shutter-Select /Sub-sampling and Window/ External
TG
146clk
EEN
*Note
Exposure R
Exposure G
Exposure B
Exposure NIR
611clk
LVAL
8clk
2048c lk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
TG
146clk
EEN
*Note
Exposure R
Exposure G
Exposure B
Exposure NIR
611clk
LVAL
8clk
1024c lk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP1023
Page 38

LQ-201CL
37
6.3.6 Pulse Width Control (PWC) mode
In this mode, the exposure time and readout are activated by the external trigger pulse. The
exposure time depends on the pulse width provided.
To use this mode:
Set function Trigger mode, PWC TR=2
Important Note:
The minimum trigger interval
Scan mode
Trigger input via
Minimum interval (µs)
Full/Binning
Camera link
Exposure time + 30.8
12-pin
Exposure time + 35.3
Sub-sampling/windowing
Camera link
Exposure time + 18.9
12-pin
Exposure time + 23.4
The available input trigger pulse width
Trigger input via
available input trigger pulse width
Camera link
2µs ~ 1s
12-pin
50µs ~ 1s
One-push white balance by gain setting only.
When the one-push white balance has been initiated and the rear panel LED shows orange, the
camera must receive continuous external trigger pulses corresponding to the frequency and
duty cycle used in the application.
Fig. 44 Pulse Width Control mode
TG
174c lk
154c lk
EEN
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
2048 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
Page 39

LQ-201CL
38
Fig.45 PWC mode /Binning
Fig.46 PWC mode /Sub-sampling and Window
TG
174c lk
154c lk
EEN
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
2048 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP2047
TG
174c lk
154c lk
EEN
611c lk
LVAL
8clk
1024 clk
8clk
DVAL
Data
AP0
AP1023
Page 40

LQ-201CL
39
6.3.7 Compatibility of trigger modes and functions
Trigger
Image output format
Gain
Offset
Mode
Origin
Full
resolution
Binning
Sub
sampling
Windowing
Master
Tracking
Individual
Master
tracking
Individual
No-shutter
Internal
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎
External
ShutterSelect
Internal
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎
External
PWC
External
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎
Trigger
Shading
correction
AWB
Test
pattern
Auto Line
Rate
Mode
Origin
FLAT
COLOR
Gain
Shutter
Noshutter
Internal
◎ ◎ ◎ × ◎
◎
External
○ ○ ○ ○ ×
ShutterSelect
Internal
◎ ◎ ◎ ◎ ◎
◎
External
○ ○ ○ ○ ○
×
PWC
External
○ ○ ○ × ○
×
Note: ◎ They can be used together.
○ They can be used together but when the compensation data is acquiring or test signal
is displaying, the trigger pulse should be continuously input.
× They cannot be used together.
6.3.8 Trigger modes and auto white balance modes matrix table
Trigger
Control
One-push
gain
One-push
shutter
No-shutter
Internal
yes
No
External
yes
No
Shutter-Select
Internal
yes
yes
External
yes
yes
PWC
Internal
yes
No
Page 41

LQ-201CL
40
7. Functions listed alphabetically by command acronyms
The following is not a complete list. Please refer to Chapter 8, Serial Communication and Command
List, for the details.
7.1 Command AHRS – Request Status After One-Push AWB
This command returns the status of the one-push AWB function, with the following parameters:
0=AWB not completed yet
1=Succeeded
2=Error1: Green image too bright
3=Error2: Green image too dark
4=Error3: Timeout occurred
7.2 Command AL – Automatic Line Rate Reference Level
This command sets a target luminance level when command AR is activated.
Settings: 0 to 1023 (for 40-bit)
Applicable modes: No-shutter with internal trigger
Shutter-Select with internal trigger
Associated functions: Command AR
7.3 Command AR – Automatic Line Rate Setting
The line rate can be adjusted from 1L to 1024L. This function will calculate and set the line rate of
the camera based on the Automatic Line Rate Reference Level (as set in command AL) and the scene
illumination. Please note that the aspect ratio of the scanned object will change as the line rate is
changed.
Settings: 0 (activate automatic process)
Applicable modes: No-shutter with internal trigger
Shutter-Select with internal trigger
Associated functions: Command AL
Note
The data can be stored in the camera memory for next start up.
7.4 Command ARST – Auto Reset Mode
This function sets the reset mode to be used
Settings 0: OFF
1: Auto Reset
2: Auto Interval
Factory default is 0 (off).
1. Auto Reset Mode
In No Shutter External mode, when a trigger pulse does not occur after more than 52 ms,
and the first trigger pulse is input after this absence, the video signal which was exposed
during the trigger absence is output. If Auto Reset Mode is set to ON, the video, LVAL and
DVAL during the trigger absence are not output and when the second trigger is input, the
video, LVAL and DVAL are output again.
Page 42

LQ-201CL
41
t > 52ms
TG
EEN
LVAL
1 2
32
3
1
t > 52ms
TG
EEN
LVAL
1 2 3
1 2 3
In Shutter Select mode, when the first trigger is input, the camera is exposed during setting
exposure time and the video is output regardless of the setting of Auto Reset Mode.
The following shows the timing.
Auto Reset OFF
Auto Reset ON
Fing.47 Auto Reset Mode timing
2. Auto Interval
In Shutter-Select External mode, if a trigger pulse does not occur after more than
52 ms, the signal-to-noise ratio may deteriorate due to the increasing dark current.
If Auto Interval is enable, an internal trigger is generated every 52 ms and the
accumulated electrons are discharged. This prevents deterioration of the signal-to-noise
ratio.
1. If the trigger interval is less than 52 ms
Ext Trigger
EEN
LVAL
Int Trigger
52ms
①
①
②
Page 43

LQ-201CL
42
2. If the trigger interval is longer than 52 ms
3. If the external trigger timing happens to be the same as the internal trigger timing,
the internal trigger is generated again as shown below. In this case, jitter may
occur.
Fig. 48 Auto Interval Timing
7.5 Command AH - Activate One-Push Auto White Balance (AWB) - Shutter
By sending this command via the serial communication, the shutter based One-Push AWB function
is activated. The white balance function takes approximately 3 seconds to complete. During this
time the rear panel LED will show orange.
This function operates in two steps. First the red-to-green channel difference and the blue-togreen channel difference are calculated separately. Then the exposure times of the blue and red
channels are automatically adjusted, to obtain the same output level on all three channels.
Settings: 0 = activate automatic process
Applicable modes: Shutter-Select mode only
Associated functions: Command WB
Note:
When color temperature of illumination exceeds the range of adjustment, proper white
balance may not be obtained.
The data can be stored in camera memory for use at next start up.
This function can work in external trigger mode.
The S/N ratio of the output will remain constant for all channels
Ext Trigger
Sensor EEN
LVAL
Int Trigger
52ms
52ms
Ext Trigger
Exposure
Video Out
Int Trigger
① ① ② ① ① ② ②
②
Page 44

LQ-201CL
43
7.6 Command AW – Activate One-Push Auto White Balance (AWB) - Gain
By sending this command via the serial communication, the gain based One-Push AWB function is
activated. This function can also be initiated by pressing the rear panel button. The white balance
function takes approximately 3 seconds to complete. During this time the rear panel LED will show
orange.
This function operates in two steps. First the red-to-green channel difference and the blue-togreen channel difference are calculated separately. Then the gains of the blue and red channels
are automatically adjusted, to obtain the same output level on all three channels.
Settings: 0 = activate automatic process
Applicable modes: All
Associated functions: Command WB
Rear panel one-push WB button.
Note:
When color temperature of illumination exceeds the range of adjustment, proper white
balance may not be obtained.
The data can be stored in camera memory for use at next start up.
This function can work in external trigger mode.
The S/N ratio of the output will change as a result of this function.
7.7 Command BA – Bit Allocation
This function lets the user select whether the video data is presented as 4 x 8 (32)-bit or 4 x 10
(40)-bit in the Camera Link output. The internal processing in the camera is based on a 12-bit A/D
signal. The 32-bit and 40-bit function removes the least significant bits from the 12-bit signal.
Settings: 0= 4 x 8-bit, 1= 4 x 10-bit
Applicable modes: All
7.8 Command BI – Binning
This function reduces the number of pixels to 2048 without affecting the line rate. Two adjacent
pixels are combined at the output stage and read out as one pixel. Sensitivity is doubled as a
result of binning.
Settings: 1=binning on, 0=binning off
Applicable modes: All
Note
Setting data is stored in camera memory for use at next start up
This function is available for all modes.
7.9 Command BL – Master Black Level
This command is a global black level adjustment for all channels. There are two adjustment ways,
one is “Master Tracking” and the other is “Individual”. The adjustable range for master black is 0
LSB to 64 (16) LSB. The number in parenthesis is valid for 40-bit output.
Master Tracking
Settings: Master (G): 0 to 64
Page 45

LQ-201CL
44
Individual
Settings: G ch: 0 to 64
Associated functions: Commands BLR, BLB, BLIR
7.10 Commands BLR, BLB and BLIR – Black Level Red, Blue and NIR
In conjunction with Command BL, these commands allow individual setting of the black level in all
channels.
Master Tracking
Settings: -64 to 63
This parameter is adjusted to Master setting value
Individual
Settings 0 to 64
Associated functions: Command BL
7.11 Command BLM - Black Level Mode
Select the black level adjustment method
Settings 0=Master tracking (Factory default)
1=Individual
7.12 Command CABR, CABB and CABIR Chromatic aberration Red, Blue NIR
These commands compensate the size of image on sensor. The size of image on the sensor may be
different on R,G,B and NIR channels due to the prism optics which is called lateral chromatic
aberration.
There are 112 data elements. In order to write all data, this command must be written 112 times.
Please refer to the chapter 6.2.11 for the details of this function
Associated commands: MAV, MAVCG,CABN1, CABN2, CABN3, CABLR, CABLB, CABLIR
CABAR, CABAB, CABAIR, CABSR, VABSB, CABSIR, CABTR, VABTB
CABTIR
7.13 Command EI – Interlocked R, G, B & NIR Exposure
When this function is enabled (interlocked), exposure time for all four channels is selected by
setting the green channel and the red, blue and NIR channels will track.
To obtain white balance, adjust red and blue channels using PER and PEB. Thereafter, it is
possible to adjust overall exposure time by using the command PEG. The red and blue channels
will track the green channel proportionally, thus maintaining white balance settings.
Settings: 0= OFF(independent R, G,B and NIR settings)
1= R, B and NIR channel tracking with G
Associated functions: Commands PER, PEG, PEB and PEIR – Programmable Exposure
Applicable modes: Shutter-Select mode only
Page 46

LQ-201CL
45
7.14 Command GA – Master Gain Level
This function is a global gain adjustment for all channels. There are two ways to adjust gain: one is
“Master Tracking” and the other is “Individual”. Command GM selects a required mode. The gain
setting is done in the analog domain where 1LSB equals 0.01dB.
Master Tracking
Settings: Master (G): 0 to 802
Individual
Settings: G: -402 to 1404
Associated functions: Commands GAR, GAB, GAIR - Gain level red, blue, and NIR.
7.15 Commands GAR, GAB and GAIR – Gain Level Red, Blue and NIR.
In conjunction with the Command GA, this function allows the individual setting of gain for
all channels, or it can be used for fine adjustment after one push white balance is executed.
It is important to note that increasing the gain will lead to an increased noise level and
reduced S/N-Ratio.
Master Tracking
Settings: -402 to 602(-4dB to +6dB)
Individual
Settings: -402 to 1404 (-4dB to +14dB)
Associated function: Command GA – Master gain level
Applicable modes: All modes
Note: Setting data is stored in camera memory for use at next start up
7.16 Command GM - Gain Mode
Selects gain mode.
Settings: 0=Master Tracking (Factory default)
1=Individual
7.17 Command HPFC – Aperture Control
This command enables Aperture Correction to enhance the edge of the picture. The level is pre-set
in the factory.
Settings: 0= OFF, 1= ON
7.18 Command LR - Line Rate (Scan Rate)
This function is used only when there is not an external trigger pulse (e.g. from an encoder) available.
It allows the user to program the line rate, in order to match the speed of the object being scanned.
In the No-shutter mode, the exposure time is directly proportional to the line rate (T
exp
= 1/line
rate)
Settings: Full resolution/Binning
2544 to 1260000, in 11.9 ns increments
Sub-sampling/Windowing
1520 to 1260000 in 11.9 ns increments
Page 47

LQ-201CL
46
Associated functions: Trigger origin, TG=0
Applicable modes: No-shutter with internal trigger (TR=0)
Shutter-Select with internal trigger (TR=1)
Note
The data can be stored in the camera memory for next start up.
7.19 Command MAV – Chromatic Aberration Control
This command enables or disables chromatic aberration adjustment for each channel.
Settings: = OFF, 1= ON
7.20 Command MAVCG – Chromatic Aberration Select
This command selects the lens to be used if the compensation data is stored. The data for three
lenses can be stored and used.
Settings: 0= User1 Lens
1= User2 Lens
2= User3 lens
Note: Name of User I, 2 or 3 can be modified to particular lens type name.
7.21. Command NR - Noise Reduction
Noise levels less than 16 LSB (4LSB) which are superimposed on the video signal will be
eliminated. The deterioration of spatial frequency is minimized. The improvement of
signal-to-noise ratio will be 3dB as the maximum although it depends on the object.
Figure in ( ) is for 8-bit output.
Settings: 0=ON, 1=OFF
7.22 Command OS1,2,3,4,5,6 – Camera Link Video Output Select
Settings: OS1 0= Rch 1= Gch 2=Bch 3= NIR ch (Default 0)
OS2 0= Rch 1= Gch 2=Bch 3= NIR ch (Default 1)
OS3 0= Rch 1= Gch 2=Bch 3= NIR ch (Default 2)
OS4 0= Rch 1= Gch 2=Bch 3= NIR ch (Default 3)
OS5 0= Rch 1= Gch 2=Bch 3= NIR ch (Default 0, only 8-bit)
OS6 0= Rch 1= Gch 2=Bch 3= NIR ch (Default 0, only 8-bit)
7.22 Command PBC – Enable Pixel Black (FPN) Correction
This command enables (or disables) the “pixel black level” correction function, which compensates
for Dark Signal Non Uniformity / Fixed Pattern Noise (DSNU / FPN) for individual pixels.
Settings: 0 = Off (Default)
1 = Factory setting
2 = user area
Associated functions: Command PBR
Applicable modes: All
Page 48

LQ-201CL
47
7.23 Command PBR – Run Pixel Black Correction and Store to User Area
This command initiates the “pixel black level” correction function, and stores the settings in the
user area. When this function is activated, lens must be capped.
Settings: 0 = Run this function
Associated functions: Command PBC must be set to 2
Note:
This function requires that no light reaches the image sensors. The lens must therefore
be covered by a lens cap, or put the F-mount protective cover on the camera, when
executing this function.
As the black level is influenced by the exposure time (especially for long exposure
times at slow scan rates) it is recommended to perform the pixel black correction at
the exposure time and line rate at which the camera will be operated.
7.24 Command PBS - Request Status After Pixel Black Correction
This command returns the status of the pixel black correction, with the following parameters:
0=Not completed yet
1=Succeeded
2=Error1: Image too bright
3=Error2: Image too dark
4=Error3: Timeout occurred
7.25 Command PER,PEG,PEB and PEIR – Programmable Exposure for R,G,B,and NIR
This command allows individual setting of the exposure time for each channel. It is only valid for
the Shutter-Select mode
Settings: 800(9.52μs) to 1259549(14.99ms) in 11.9 ns steps
Associated functions: EI =0 :OFF (R,G,B and NIR independent)
EI=1: ON (R , B and NIR exposure interlocked with G)
Applicable modes: Shutter-Select (internal/external trigger)
7.26 Command PGC – Select pixel gain correction mode
This command enables (or disables) the “pixel gain” (flat-field) correction function, which
compensates for Pixel Response Non Uniformity (PRNU) for individual pixels.
The algorithm for compensation is different in No-shutter mode and Shutter-Select mode.
If the operating mode is changed, an adjustment in the selected mode must be made. The factory
default is Shutter-Select mode.
Settings: 0=Off (Default)
1=Factory Setting
2=User area
Associated functions: Command PGR
Applicable modes: All
Page 49

LQ-201CL
48
7.27 Command PGR – Pixel Gain Correction and Store in User Area
This command initiates the pixel gain correction function, and stores the settings in the user area.
Settings: 0= activate automatic process
Associated functions: Command PGC must be set to 2
Note:
The image sensors must not be saturated when executing this function.
When executing this function, the exposure time and line rate should be the same as
when the camera is operated in the application.
7.28 Command PGS - Request Status After Pixel Gain Correction
This command returns the status of the pixel gain correction, with the following parameters:
0=Not completed yet
1=Succeeded
2=Error1: Image too bright
3=Error2: Image too dark
4=Error3: Timeout occurred
7.29 Command SCB – Select cable
This command sets if the length of a Camera Link cable to be used is changed.
Settings: 0= 1 to 5m
1= 5 to 10m
2= 10 to 15m
Note: the above lengths are if a standard type Camera Link cable is used.
7.30 Command SDC – Select Shading Correction Mode
This function enables (or disables) shading correction.
Settings: 0 = off (Bypass) (Default)
1 = Factory setting
2 = User area
Associated functions: Commands PGR, SDR and SDS
7.31 Command SDR – Run Shading Correction and store to user area
This function initiates automatic shading correction, and stores the result to the user area. This
function should be used together with the flat-field correction (commands PGC and PGR). There
are two types of shading correction: Individual R, G and B channel correction and chromatic
shading correction.
Run Flat shading correction (SDR=0)
Run Color shading correction (SDR=1)
Page 50

LQ-201CL
49
7.32 Command SDS – Request Status After Executing Shading Correction
Command
This command returns the status of the shading correction function, with the following parameters:
0=Not completed yet
1=Succeeded
2=Error1: Image too bright
3=Error2: Image too dark
4=Error3: Timeout occurred
7.33 Command SRO – Sensor Read Out
This command selects the readout format from the sensor.
Settings: 0= OFF (Full Frame)
1= Sub-sampling
2= Windowing
7.34 Command SGR, SGG, SGB, SGIR – Sensor Gain Set R, G, B and NIR
This command sets the reference gain for gain control.
Settings: 0= Low Gain
1= High Gain
Common for all channels
7.35 Command TG – Trigger Origin
Selects whether an external signal or an internal clock generator is used as a trigger source.
Settings: 0=Internal clock generator
1=External signal
Associated commands: TI
TP
7.36 Command TI – Trigger Input
Selects whether the External Trigger input signal is taken from the Camera Link connector, or
from the 12-pin connector. The 12-pin connector trigger input can be terminated by a 75 ohm
terminator. This is selected by a rear panel DIP-switch (SW1).
Settings: 0=Camera Link connector
1=12-pin connector
7.37 Command TP – Trigger Polarity
Settings: 0=Active Low (factory default)
1=Active High
Page 51

LQ-201CL
50
7.38 Command TR – Trigger Mode
Selects the trigger mode of the camera. Depending on the mode used, it allows the scan rate to
either be programmed by an internal timing generator or by and external trigger pulse. See
chapter 6 for details on the operation modes.
Settings: 0=No-shutter mode
1=Shutter-Select mode
2=Pulse Width Control (PWC) mode
Associated functions: Command TG (trigger origin)
Command TI (trigger input)
Command TP (trigger polarity)
7.39 Command TS – Test Pattern
This allows the camera to output a number of test patterns for set-up and troubleshooting.
Settings: 0=off
1=Color bar
2=Gray wedge
3=Gray bars
4=White (890LSB)
7.40 Command WB – White Balance
The white balance function can be used for manual setting, one-push automatic white balance
(AWB) and fixed color temperatures (3 selections)
Settings: 0=Manual / On-Push AWB
1=4000K
2=4600K
3=5600K
Applicable modes: All
Associated functions: Command AW (Gain)
Command AH (Shutter)
Command GAR – Gain Level red channel
Command GAB – Gain Level blue channel
Page 52

LQ-201CL
51
8. Serial communication and command list
8.1. Serial communication
The LQ-201CL can communicate by serial communication via the Camera Link connector
or via RS232C in the 12-pin Hirose connector. The Baud Rate is fixed at 9600 bps.
Switch SW1 at the rear panel of the camera is used to select which way the serial
communication is set up.
SW1
No
Function
Setting
ON
OFF (Default )
1
Select serial communication path
12-Pin
Camera link
2
External trigger input termination
75 ohm
TTL
Note: HIROSE 12-Pin and Camera Link cannot be used simultaneously.
Communication setting:
Protocol.
Transmit the setting command to camera:
NN is any kind of the commands.
NN=[Param.]<CR><LF>
e.g.
Send to camera: TR=0 <CR><LF>
Camera response: COMPLETE<CR><LF>
When the camera receives a valid command, camera will return 'COMPLETE'.
If the camera receives an invalid command, camera will return following:
e.g.
Send to camera: TRX=0 <CR><LF>
Camera response: 01 Unknown Command!!<CR><LF>
e.g.
Send to camera: TR=99 <CR><LF>
Camera response: 02 Bad Parameters!!<CR><LF>
1
2
ON
Default setting
OFF ON
Serial Communication
Baud Rate
9600
Data Length
8bit
Start Bit
1bit
Stop Bit
1bit
Parity
Non
Xon/Xoff Control
Non
Page 53

LQ-201CL
52
Transmit the request command to camera:
The status of the camera's settings can be queried by transmitting NN?<CR><LF>, where NN is
any one of the commands.
The camera will return the current setting data.
e.g.
Send to camera: TR? <CR><LF>
Camera response: TR=3<CR><LF>
8.2. Command list
Command
Name
Format
Parameter
Remarks
A – General settings and useful commands.
EB
Echo Back
EB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
EB?<CR><LF>
0=Echo off, 1=Echo on
Returns character
sent to the camera.
Off at power up
ST
Camera Status
Request
ST?<CR><LF>
Display current
settings of all
functions
HP
Online Help
Request
HP?<CR><LF>
Get a list of
available commands
VN
Firmware
Program
Version
Request
VN?<CR><LF>
3 digits
Example:
100 = Version 1.00
PV
FPGA Program
Version
Request
PV?<CR><LF>
3 digits
Example:
100 = Version 1.00
ID
Camera ID
Request
ID?<CR><LF>
Returns the camera’s
ID (?). Factory
setting.
MD
Model Name
Request
MD?<CR><LF>
Returns the camera’s
model name. Factory
setting.
UD
User ID
UD=[Param.]<CR><LF>
UD?<CR><LF>
User definable field.
Up to 16 characters.
B - Line Rate, Exposure
LR
Line Rate
LR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
LR?<CR><LF>
Full resolution
2544 to 1260000 clocks
Sub-sampling/Windowing
1520 to 1260000 clocks
- 1 clock is 11.9 ns
Only valid for TG=0
AR
One-push auto
line rate set
AR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
AR?<CR><LF>
0=Activate one-push auto
line rate set
Only valid for TG=0
AL
Auto line rate
reference
level
AL=[Param.]<CR><LF>
AL?<CR><LF>
0 to 1023
At 10-bit
EI
R/B/NIR
Exposure
interlocked
with G
EI=[Param.]<CR><LF>
EI?<CR><LF>
0=Off (independent)
1=On (interlocked)
Only valid for TR=1
Page 54

LQ-201CL
53
PER
Programmable
Exposure Red
PER=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
PER?<CR><LF>
Full resolution
Sub-sampling/Windowing
800 to 1259549 clocks
- 1 clock is 11.9 ns
Only valid for TR=1
PEG
Programmable
Exposure Green
PEG=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
PEG?<CR><LF>
Full resolution
Sub-sampling/Windowing
800 to 1259549 clocks
- 1 clock is 11.9 ns
Only valid for TR=1
PEB
Programmable
Exposure Blue
PEB=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
PEB?<CR><LF>
Full resolution
Sub-sampling/Windowing
800 to 1259549 clocks
- 1 clock is 11.9 ns
Only valid for TR=1
PEIR
Programmable
Exposure - NIR
PEIR=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
PEIR?<CR><LF>
Full resolution
Sub-sampling/Windowing
800 to 1259549 clocks
- 1 clock is 11.9 ns
Only valid for TR=1
AH
One-push AWB
shutter
AH=[Param.]<CR><LF>
0=Activate one-push AWB
shutter
Only valid for TR=1
AHRS
Inquire the
status after
one-push AWB
shutter
AHRS?<CR><LF>
<One of following values will
be replied from the camera>
0=AWB has not been finished
yet.
1=Succeeded.
2=Error1 - G image was too
bright.
3=Error2 - G image was too
dark.
4=Error3 - Timeout-error
occurred.
C - Trigger mode
TR
Trigger Mode
TR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TR?<CR><LF>
0=No-shutter mode
1=Shutter-Select mode
2=Pulse Width Control
mode
TG
Trigger Origin
TG=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TG?<CR><LF>
0=Internal
1=External
TG=0 is available
when TR=0 or TR=1
TI
Trigger Input
TI=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TI?<CR><LF>
0=Camera-Link
1=12pin
TP
Trigger
Polarity
TP=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TP?<CR><LF>
0=Active-Low
1=Active-High
ARST
Auto reset
mode
ARST=[Param.]<CR><LF>
ARST?<CR><LF>
0=OFF
1=Auto Reset
2=Auto Interval
D - Image format
BI
Binning
BI=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BI?<CR><LF>
0=Binning Off, 1=Binning
On
BA
Bit allocation
BA=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BA?<CR><LF>
0=24bit, 1=30bit
TS
Test Pattern
TS=[Param.]<CR><LF>
TS?<CR><LF>
0=Off
1=Color Bar
2=Gray Pattern 1
3=Gray Pattern 2
4=White
Off at power up
Page 55

LQ-201CL
54
SRO
Sensor read
out
SRO=[Param.]
<CR><LF>
SRO?<CR><LF>
0=off
1=Sub-sampling
2=Windowing
OS1
CameraLink
video1 Output
Select
OS1=[Param.]<CR><LF>
OS1?<CR><LF>
0=Rch,1=Gch, 2=Bch,
3=NIRch
Default 0
OS2
CameraLink
video2 Output
Select
OS2=[Param.]<CR><LF>
OS2?<CR><LF>
0=Rch,1=Gch, 2=Bch,
3=NIRch
Default 1
OS3
CameraLink
video3 Output
Select
OS3=[Param.]<CR><LF>
OS3?<CR><LF>
0=Rch,1=Gch, 2=Bch,
3=NIRch
Default 2
OS4
CameraLink
video4 Output
Select
OS4=[Param.]<CR><LF>
OS4?<CR><LF>
0=Rch,1=Gch, 2=Bch,
3=NIRch
Default 3
OS5
CameraLink
video5 Output
Select
OS5=[Param.]<CR><LF>
OS5?<CR><LF>
0=Rch,1=Gch, 2=Bch,
3=NIRch
Only BA=0(8bit)
Default 0
OD6
CameraLink
video6 Output
Select
OS6=[Param.]<CR><LF>
OS6?<CR><LF>
0=Rch,1=Gch, 2=Bch,
3=NIRch
Only BA=0(8bit)
Default 0
E - Gain, white balance and signal settings
GA
Gain Level Master
GA=[Param.]<CR><LF>
GA?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking Mode
0 to 802
Individual
-402 to 1404
GAR
Gain Level Red
GAR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
GAR?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking Mode
-402 to 602
Individual
-402 to 1404
GAB
Gain Level Blue
GAB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
GAB?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking Mode
-402 to 602
Individual
-402 to 1404
GAIR
Gain Level –
NIR
GAIR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
GAIR?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking Mode
-402 to 602
Individual
-402 to 1404
GM
Gain mode
GM=[Param.]<CR><LF>
GM?<CR><LF>
0=Master tracking
1=Individual
Default is 0
SGR
Sensor Gain
Set
Red
SGR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SGR?<CR><LF>
0=Low Gain
1=High Gain
SGG
Sensor Gain
Set
Green
SGG=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SGG?<CR><LF>
0=Low Gain
1=High Gain
SGB
Sensor Gain
Set
Blue
SGB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SGB?<CR><LF>
0=Low Gain
1=High Gain
Page 56

LQ-201CL
55
SGIR
Sensor Gain
Set
NIR
SGIR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SGIR?<CR><LF>
0=Low Gain
1=High Gain
BL
Black Level –
Master
BL=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BL?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking 0 to 64
Individual 0 to 64
BLR
Black Level –
Red
BLR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BLR?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking -64 to 63
Individual 0 to 64
BLB
Black Level –
Blue
BLB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BLB?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking -64 to 63
Individual 0 to 64
BLIR
Black Level –
NIR
BLIR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BLIR?<CR><LF>
Master Tracking -64 to 63
Individual 0 to 64
BLM
Black Level
mode
BLM=[Param.]<CR><LF>
BLM?<CR><LF>
0=Master Tracking
1=Individual
Default is 0
WB
White Balance
WB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
WB?<CR><LF>
0=Manual/One push AWB
1=4000K
2=4600K
3=5600K
AW
Activate Onepush AWB
AW=[Param.]<CR><LF>
0=Activate one-push AWB
AWRS
Inquire the
status after
one-push AWB
AWRS?<CR><LF>
<Camera replies >
0=AWB has not been
finished yet.
1=Succeeded.
2=Error1. Green image was
too bright.
3=Error2. Green image was
too dark.
4=Error3. Timeout-error
occurred.
NR
Noise
reduction
NR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
NR?
0 = OFF, 1= ON
F - Shading correction, pixel gain and pixel black correction
SDC
Select shading
correction
mode
SDC=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SDC?<CR><LF>
0=Off (Bypass)
1=Factory area
2=User area
SDR
Run shading
correction,
store to user
area
SDR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
0=Run flat shading
correction, store to user
area
1=Run color shading
correction, store to user
area
Store in user setting.
SDS
Inquire the
status after
shading
correction
SDS?<CR><LF>
0=Shading correction not
yet completed.
1=Succeeded.
2=Error 1 – Image too bright
3=Error 2 - Image too dark
4=Error 3 - Timeout error
occurred.
PGC
Select pixel
gain
correction
mode
PGC=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PGC?<CR><LF>
0=Off (Bypass)
1=Factory area
2=User area
Only valid for SHC=0.
Page 57

LQ-201CL
56
PGR
Run pixel gain
correction,
store to user
area
PGR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PGR?<CR><LF>
0=Run pixel gain correction,
store to user area
Store in user setting.
PGS
Inquire the
status after
pixel gain
correction
PGS?<CR><LF>
0=Pixel gain correction not
yet completed.
1=Succeeded
2=Error 1 – Image too bright
3=Error 2 - Image too dark
4=Error 3 - Timeout error
occurred.
PBC
Select pixel
black
correction
mode
PBC=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PBC?<CR><LF>
0=Off (Bypass)
1=Factory area
2=User area
PBR
Run pixel
black
correction,
store to user
area
PBR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
PBR?<CR><LF>
0=Run pixel black
correction, store to user
area
Store in user setting.
PBS
Inquire the
status after
pixel black
correction
PBS?<CR><LF>
0=Pixel black correction has
not been finished yet.
1=Succeeded.
2=Error1 - Timeout error
occurred.
SCB
Select Cable
SCB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
SCB?<CR><LF>
0 to 2
0:1~5m
1:5~10m
2:10~15m
MAVC
G
Chromatic
aberration
Select
MAVCG=[Param1]<CR><L
F>
MAVCG?<CR><LF>
0=User1 Lens
1=User2 Lens
2=User3 Lens
Available when MAV=1
CABR
Chromatic
aberration
Red
CABR=[Param.]<CR><LF>
CABR?<CR><LF>
-32768 to 32768
112 times writing make
all parameters to be
written.
112 times reading make
all parameters to be
read.
CABB
Chromatic
aberration
Blue
CABB=[Param.]<CR><LF>
CABB?<CR><LF>
-32768 to 32768
112 times writing make
all parameters to be
written.
112 times reading make
all parameters to be
read.
CABIR
Chromatic
aberration INR
CABIR=[Param.]<CR><LF
>
CABIR?<CR><LF>
-32768 to 32768
112 times writing make
all parameters to be
written.
112 times reading make
all parameters to be
read.
MAV
Chromatic
aberration
Control
MAV=[Param.]<CR><LF>
MAV?<CR><LF>
0=OFF, 1=ON
CABN
1
Chromatic
aberration
Input Name 1
CABN1=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
CABN1?<CR><LF>
User1 Lens Data Name
e.g.
BV28mmLens
Lens Data Name is 16
characters.
Page 58

LQ-201CL
57
CABN
2
Chromatic
aberration
Input Name 2
CABN2=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
CABN2?<CR><LF>
User2 Lens Data Name
e.g.
BV28mmLens
Lens Data Name is 16
characters.
CABN
3
Chromatic
aberration
Input Name 3
CABN3=[Param.]<CR><L
F>
CABN3?<CR><LF>
User3 Lens Data Name
e.g.
BV28mmLens
Lens Data Name is 16
characters.
CABL
R
Chromatic
aberration
Left Side Pixel
Red
CABLR=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABLR?[Param1]<CR><LF
>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:-3,-2,-1,1,2,3
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABL
B
Chromatic
aberration
Left Side Pixel
Blue
CABLB=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABLB?[Param1]<CR><LF
>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:-3,-2,-1,1,2,3
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABLI
R
Chromatic
aberration
Left Side Pixel
NIR
CABLIR=[Param1],[Para
m2]<CR><LF>
CABLIR?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:-3,-2,-1,1,2,3
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABA
R
Chromatic
aberration
Area No. Red
CABAR=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABAR?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 8
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABA
B
Chromatic
aberration
Area No. Blue
CABAB=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABAB?[Param1]<CR><LF
>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 8
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
VABAI
R
Chromatic
aberration
Area No. NIR
CABAIR=[Param1],[Para
m2]<CR><LF>
CABAIR?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 8
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABS
R
Chromatic
aberration 2nd
Pixel Red
CABSR=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABSR?[Param1]<CR><LF
>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 7
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABS
B
Chromatic
aberration 2nd
Pixel Blue
CABSB=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABSB?[Param1]<CR><LF
>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 7
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABSI
R
Chromatic
aberration 2nd
Pixel NIR
CABSIR=[Param1],[Para
m2]<CR><LF>
CABSIR?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 7
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
VABT
R
Chromatic
aberration 3rd
Pixel Red
CABTR=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABTR?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 6
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
CABT
B
Chromatic
aberration 3rd
Pixel Blue
CABTB=[Param1],[Param
2]<CR><LF>
CABTB?[Param1]<CR><LF
>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 6
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
VABTI
R
Chromatic
aberration 3rd
Pixel NIR
CABTIR=[Param1],[Para
m2]<CR><LF>
CABTIR?[Param1]<CR><L
F>
Param1:User No. 0 to 2
Param2:1 to 6
Param1:Correspond to
the value set in MAVCG
HPFC
HPF_CTRL
HPFC=[Param.]<CR><LF>
HPFC?<CR><LF>
0=off
1=on
Aperture Correction
G - Saving and loading data in EEPROM
Page 59

LQ-201CL
58
LD
Load Setttings
(from Camera
EEPROM)
LD=[Param.]<CR><LF>
0=Factory area
1=User area1
2=User area2
Latest used DATA
AREA will become
default at next
power up.
SA
Save Settings
(to Camera
EEPROM)
SA=[Param.]<CR><LF>
1=User area1
2=User area2
Note the parameter 0 is
not allowed.
EA
EEPROM
Current Area
No. Request.
EA?<CR><LF>
0=Factory area
1=User area1
2=User area2
The camera returns
latest used DATA
AREA.
Note: To avoid malfunction, do not attempt writing commands not shown in the above list.
Page 60

LQ-201CL
59
9. Camera Control Tool for LQ-201CL
From www.jai.com Camera Control Tool for Windows XP/Vista/7 can be downloaded.
9.1. Software Install
Execute LQ-X01CL_Ver.XXX.exe in the downloaded file. The setup program starts and continues
according to the screen instructions.
9.2. Open the Control Tool
Connect the camera to the PC on which the software is installed and set the power ON. Then
select “All programs” in the Windows start menu, select “JAI A-S” and click “LQ-X01CL control
tool”.
LQ-X01CL Camera Control Tool and Communication windows will open.
If the Communication window does not open, click “Help” in the Download menu of “Camera Control
Tool” and click “Communication”.
9.3. Connect a camera
If the frame grabber board is already installed in the connected PC, it will appear in the “Category”
box in the “Communication port” pane. Click it if it is the appropriate one.
If the frame grabber board is not used, select the COM port to which the camera is connected, and
click “OK”. After the connection is established, the RED Off-line icon changes to GREEN and the RED
bar in the bottom changes to GREEN.
Page 61

LQ-201CL
60
9.4. Camera control window
When the connection between camera and PC is completed, the camera control tool shows the
current camera settings.
9.5 Menus
9.5.1 File menu
Open: Transfer the setting parameters in HDD
or other memory devices to the camera.
The extension is .cam
Save as: Store the setting parameters in HDD or
other memory devices. The extension
is .cam.
Exit: Close the software.
Page 62

LQ-201CL
61
9.5.2 Settings menu
9.5.3 Line Correction menu
The following windows are for Pixel Black, Pixel Gain and Shading adjustments.
Reload: Read the setting parameters from RAM
area of the camera.
Load settings: Read the setting parameters from
EEPROM area of the camera.
Select from Factory, User 1 or User2.
Store settings: Read the parameters in the EEPROM
area of the camera. Select from User 1
or User 2.
Page 63

LQ-201CL
62
9.5.4 Help menu
Display camera software version, model name, firmware version and camera ID.
Page 64

LQ-201CL
63
10. External appearance and Dimensions
Outside dimensions tolerance: ± 0.3mm
Fig.49 External Appearance and Dimensions (M52 mount)
Page 65

LQ-201CL
64
Outside dimensions tolerance: ± 0.3mm
Fig.50 External Appearance and Dimensions (F mount)
Page 66

LQ-201CL
65
11. Specifications
11.1 Typical data
Scanning system
Line Scan
Image Sensor
Effective pixels : 2048 pixels
Pixel Size : 14.0 μm × 14.0 μm
Effective image length : 28.672 mm
Pixel clock
84.00 MHz
Line Rate
Full
resolution
/Binning
Total number of pixels per line: 2544 clocks
Line rate: 30.29 μs (No-shutter mode with internal trigger)
Line Frequency: 33.02 kHz
Sub-
sampling
/Windowing
Total number of pixels per line: 1520 clocks
Line rate: 18.1 μs (No-shutter mode with internal trigger)
Line Frequency: 55.26 kHz
Sensor sensitivity
64nJ/cm2
Sensitivity
(Standard)
RGB : 2800 Lx ( 7800K White LED light)
Conditions: Line Rate=600μs, Gain=0dB, Shutter=OFF, Lens
iris=F2, 100% output)
NIR : 2.35μW/cm2 at 800nm
S/N
55 dB (Green channel, Gain=0dB)
Synchronization
Internal
Video output
Digital 8-Bit x 4 or 10-Bit x 4 (Camera Link)
* Default setting: 8-bit
* Built-in pre emphasis function makes 10m transmission possible
Gain range (Note1)
Mode select:
Master mode : Adjust master level and match R,G,B and NIR
Master(Green): 0dB to +8dB
R/B/NIR : -4dB to +6dB
Individual : Adjust each channel individually
R/G/B/NIR : -4dB to +14dB
* Default setting: Master mode
White balance
Adjustable range : 4000K to 9000K
Standard color temperature : 7800K
Black level
(User setup)
Mode select:
Master mode : Adjust master level and match R,G,B and NIR
Master(Green): 0 to 64 LSB(10-bit output)
R/B/NIR : -64 to 63 LSB (10-bit output)
Individual : Adjust each channel individually
R/G/B/NIR : 0 to 64 LSB (10-bit output)
* Default setting: Master mode 8-bit (8 LSB)
Line rate
(Variable) (Note2)
Range : 30.29 μs (1L) to 15.0 ms (SensReadout is OFF)
Adjustment increment : 11.9 ns (1clk)
This mode is available for No-shutter internal trigger and ShutterSelect internal trigger modes.
Electronic shutter
Available for Shutter-Select mode
Adjustable range : 9.52 μs to 14.99 ms
Adjustment increments : 11.9 ns (1 clk)
Binning
Available (line rate is not increased)
Page 67

LQ-201CL
66
Test pattern
0: Color Bar 1: Gray 1 2: Gray 2 3: White (890 LSB)
Signal processing
circuit
1. Pixel gain correction: Pixel Response Non
Uniformity(PRNU),Dark Signal Non Uniformity(DSNU)
2. Shading compensation : ON / OFF
Visible: Flat shading compensation or Color shading
compensation can be selected
NIR: Flat shading compensation or color shading compensation
(Adjust using G channel as the reference) can be selected
3. Linear matrix : R,G,B color compensation, no compensation for
NIR
4. Noise reduction
Operation mode
No-shutter, Shutter-Select, Pulse Width Control (PWC)
Trigger input
(note3)
12-Pin : 4.0±2.0Vp-p TTL or
Camera Link : LVDS (CC1)
Possible to change negative logic or positive logic
Minimum trigger width (Through Camera Link) :
External trigger: more than 500 ns,
PWC : more than 2 μs
Sync output
(open termination)
Camera Link LVAL, DVAL, EEN
Hirose 12-Pin XEEN (negative logic) 4.0Vp-p (no termination)
Communication
interface
(Note4)
EIA-644: Camera CC1 or
RS-232C: 12-Pin connector
Baud rate : 9600 bps
Interface is switched by SW1 located rear panel.
Field update
Available
Power
DC +12V to +24V±10%
700mA (internal trigger, line rate 58.85 μs, 0dB, lens covered,
+12V input)
Note: Use a power supply capable of providing more than 3A.
Lens Mount
M52 mount (Standard) or Nikon F-Mount(Optional)
Maximum allowed rear protrusion on lenses:
M52 Mount : 13mm
Nikon F-Mount: 13 mm
Flange back
M52 Mount : 46.5mm Nikon F-Mount : 46.5mm
Lenses without iris rings cannot be used.
Optical axis
Center ±0.1 mm (max)
Operating temperature
/humidity
- 5C to +45C / 20 to 80% (non-condensing)
Storage temperature
/humidity
-25C to +60C, 20 to 80% (non-condensing)
Vibration
3G (20Hz to 200Hz XYZ direction)
Shock
50G
Regulation
CISPR Pub.22 (EN55022)
CISPR Pub.24
FCC Part15 Class B
IEC61000-4-2 conforming to Level 4(Contact discharge:8 kV,
Air discharge:15 kV)
Page 68

LQ-201CL
67
Dimensions
90(W) x 90(H) x 120(D) mm (without connector and lens mount
protrusion)
Weight
1050 g
Connectors
Camera Link : 10226-1A10PL x2
Hirose 12-Pin : HR10A-10R-12PB or equivalent
Note 1: If the digital output is set to 10-bit, the gain setting of more than 2dB may cause the
Break in histogram.
Note 2: If the line rate becomes longer, the dark current will increase and as the result, the
black level will be unstable.
Note 3: 12P input and Camera Link input cannot be used at the same time.
Note 4: 12P input and Camera Link input cannot be used at the same time.
Note 5: The mentioned specifications is guaranteed when the cable and connector to be used are
ones JAI suggests.
Note 6: The above specifications are subject to change without notice.
11.2 Camera Spectral sensitivity
Fig. 27 Camera Spectral sensitivity
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Sensitivity
wavelength (nm)
LQ-201CL CAMERA Sensitivity
Bch
Gch
Rch
NIRch
Page 69

LQ-201CL
68
Appendix
1. Precautions
Personnel not trained in dealing with similar electronic devices should not service this camera.
The camera contains components sensitive to electrostatic discharge. The handling of these devices
should follow the requirements of electrostatic sensitive components.
Do not attempt to disassemble this camera.
Do not expose this camera to rain or moisture.
Do not face this camera towards the sun, extreme bright light or light reflecting objects.
When this camera is not in use, put the supplied lens cap on the lens mount.
Handle this camera with the maximum care.
Operate this camera only from the type of power source indicated on the camera.
Power off the camera during any modification, such as changes of jumper and switch settings.
2. Typical Sensor Characteristics
The following effects may be observed on the video monitor screen. They do not indicate any fault
of the camera, but are associated with typical sensor characteristics.
V. Aliasing
When the CMOS camera captures stripes, straight lines or similar sharp patterns, jagged image on
the monitor may appear.
Blemishes
All cameras are shipped without visible image sensor blemishes.
Over time some pixel defects can occur. This does not have a practical effect on the operation of
the camera. These will show up as white spots (blemishes).
Exposure to cosmic rays can cause blemishes to appear on the image sensor. Please take care to
avoid exposure to cosmic rays during transportation and storage. It is recommended using sea
shipment instead of air flight in order to limit the influence of cosmic rays on the camera. Pixel
defects/blemishes also may emerge due to prolonged operation at elevated ambient temperature,
due to high gain setting, or during long time exposure. It is therefore recommended to operate the
camera within its specifications.
Patterned Noise
When the sensor captures a dark object at high temperature or is used for long time integration,
fixed pattern noise may appear on the video monitor screen.
3. Caution when mounting a lens on the camera
When mounting a lens on the camera dust particles in the air may settle on the surface of the lens
or the image sensor of the camera. It is therefore important to keep the protective caps on the lens
and on the camera until the lens is mounted. Point the lens mount of the camera downward to
prevent dust particles from landing on the optical surfaces of the camera. This work should be done
in a dust free environment. Do not touch any of the optical surfaces of the camera or the lens.
Page 70

LQ-201CL
69
4. Caution when mounting the camera
When you mount the camera on your system, please make sure to use screws of the
recommended length described in the following drawing. Longer screws may cause serious
damage to the PCB inside the camera.
5. Exportation
When exporting this product, please follow the export regulation of your own country.
6. References
1. This manual and datasheet for the LQ-201CL can be downloaded from www.jai.com
2. Camera control software can be downloaded from www.jai.com
Camera chassis
Fixing plate
Mounting the camera to fixing plate
5.0mm ± 0.2mm
Page 71

LQ-201CL
70
Change history
Date
Revision
Changes
Nov. 2014
1.0
New Release
Dec. 2014
1.1
Correct default setting for PBC, PGC and SDC
Page 72

LQ-201CL
71
User's Record
Camera type: LQ-201CL
Revision: ……………..
Serial No. ……………..
Firmware version. ……………..
For camera revision history, please contact your local JAI distributor.
User's Mode Settings.
User's Modifications.
Company and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
JAI A-S cannot be held responsible for any technical or typographical errors and reserves the right to make changes to products
and documentation without prior notification.
Europe, Middle East & Africa
Asia Pacific
Americas
Phone +45 4457 8888
Fax +45 4491 3252
Phone +81 45 440 0154
Fax +81 45 440 0166
Phone (toll-free) +1 800 445 5444
Phone +1 408 383 0300
Visit our web site at www.jai.com
 Loading...
Loading...