Page 1

45
Plasma arc cutting system
Service Manual – 806110
Revision 2
Page 2

Register your new Hypertherm system
Register your product online at www.hypertherm.com/registration for easier technical
and warranty support. You can also receive updates on new Hypertherm products and a free
gift as a token of our appreciation.
For your records
Serial number:________________________________________________________________
Purchase date: _______________________________________________________________
Distributor: __________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Maintenance notes:
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Page 3

Service Manual
45
(P/N 806110)
Revision 2 – April, 2013
Hypertherm, Inc.
Hanover, NH USA
www.hypertherm.com
© Copyright 2013 Hypertherm, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Hypertherm and powermax are trademarks of Hypertherm, Inc.
and may be registered in the United States and/or other countries.
Page 4

Hypertherm, Inc.
Etna Road, P.O. Box 5010
Hanover, NH 03755 USA
603-643-3441 Tel (Main Office)
603-643-5352 Fax (All Departments)
info@hypertherm.com (Main Office Email)
800-643-9878 Tel (Technical Service)
technical.service@hypertherm.com (Technical Service Email)
800-737-2978 Tel (Customer Service)
customer.service@hypertherm.com (Customer Service Email)
866-643-7711 Tel (Return Materials Authorization)
877-371-2876 Fax (Return Materials Authorization)
return.materials@hypertherm.com (RMA email)
Hypertherm Plasmatechnik GmbH
Technologiepark Hanau
Rodenbacher Chaussee 6
D-63457 Hanau-Wolfgang, Deutschland
49 6181 58 2100 Tel
49 6181 58 2134 Fax
49 6181 58 2123 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm (S) Pte Ltd.
82 Genting Lane
Media Centre
Annexe Block #A01-01
Singapore 349567, Republic of Singapore
65 6841 2489 Tel
65 6841 2490 Fax
65 6841 2489 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd.
Unit 301, South Building
495 ShangZhong Road
Shanghai, 200231
PR China
86-21-60740003 Tel
86-21-60740393 Fax
Hypertherm Europe B.V.
Vaartveld 9
4704 SE
Roosendaal, Nederland
31 165 596907 Tel
31 165 596901 Fax
31 165 596908 Tel (Marketing)
31 165 596900 Tel (Technical Service)
00 800 4973 7843 Tel (Technical Service)
Hypertherm Japan Ltd.
Level 9, Edobori Center Building
2-1-1 Edobori, Nishi-ku
Osaka 550-0002 Japan
81 6 6225 1183 Tel
81 6 6225 1184 Fax
Hypertherm Brasil Ltda.
Rua Bras Cubas, 231 – Jardim Maia
Guarulhos, SP - Brasil
CEP 07115-030
55 11 2409 2636 Tel
55 11 2408 0462 Fax
Hypertherm México, S.A. de C.V.
Avenida Toluca No. 444, Anexo 1,
Colonia Olivar de los Padres
Delegación Álvaro Obregón
México, D.F. C.P. 01780
52 55 5681 8109 Tel
52 55 5683 2127 Fax
Hypertherm Korea Branch
#3904 Centum Leaders Mark B/D,
1514 Woo-dong, Haeundae-gu, Busan
Korea, 612-889
82 51 747 0358 Tel
82 51 701 0358 Fax
07/18/12
Page 5

Safety information
Before operating any Hypertherm equipment, read the separate Safety and Compliance Manual (80669C) included
with your product for important safety information.
Page 6

Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY EMC .......................................................................................................EMC1
WARRANTY ............................................................................................................................................................................ W1
SECTION 1
SPECIFICATIONS
System description ....................................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Where to find information ........................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Power supply dimensions and weights ................................................................................................................................................1-3
Dimensions .......................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Weights .............................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Power supply ratings .................................................................................................................................................................................1-4
T45v torch dimensions .............................................................................................................................................................................1-5
T45m torch dimensions ............................................................................................................................................................................1-5
T45v and T45m torch specifications .....................................................................................................................................................1-6
Symbols and marks ...................................................................................................................................................................................1-7
IEC symbols ................................................................................................................................................................................................1-8
SECTION 2
POWER SUPPLY SETUP
Unpack the Powermax45 .........................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Claims ................................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Contents ............................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Position the power supply........................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Prepare the electrical power ...................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Voltage configurations ....................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Install a line-disconnect switch ....................................................................................................................................................2-4
Requirements for grounding .........................................................................................................................................................2-4
powermax
45
Service Manual
i
Page 8

Table of ConTenTs
Power cord considerations ......................................................................................................................................................................2-4
Extension cord recommendations ...............................................................................................................................................2-5
Generator recommendations ........................................................................................................................................................2-6
Prepare the gas supply .............................................................................................................................................................................2-6
Connect the gas supply .................................................................................................................................................................2-7
Additional gas filtration ...................................................................................................................................................................2-7
SECTION 3
TORCH SETUP
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Consumable life ..........................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Hand torch setup .......................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Choose the consumables ..............................................................................................................................................................3-3
Install the consumables ..................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Machine torch setup..................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Mount the torch ................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Choose the consumables (cut charts) .......................................................................................................................................3-8
Using the cut charts ........................................................................................................................................................................3-8
T45m shielded consumables ........................................................................................................................................................3-8
Align the torch ............................................................................................................................................................................... 3-24
Connect the remote-start pendant ...........................................................................................................................................3-25
Connect a machine interface cable .........................................................................................................................................3-25
Accessing raw arc voltage ......................................................................................................................................................... 3-27
Connect the torch lead .......................................................................................................................................................................... 3-30
SECTION 4
OPERATION
Controls and indicators ............................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Front controls and LEDs ................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Rear controls ....................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Operate the Powermax45 ........................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Connect the electrical power and gas supply ..........................................................................................................................4-3
Power ON the system ....................................................................................................................................................................4-4
Set the mode switch .......................................................................................................................................................................4-4
Adjust the gas pressure .................................................................................................................................................................4-4
Check the indicator LEDs .............................................................................................................................................................4-6
Attach the work clamp ...................................................................................................................................................................4-6
Understand duty-cycle limitations ..........................................................................................................................................................4-6
How to use the hand torch ......................................................................................................................................................................4-7
Operate the safety trigger .............................................................................................................................................................4-7
Hand torch cutting hints ................................................................................................................................................................4-7
Start a cut from the edge of the workpiece...............................................................................................................................4-8
ii powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 9

Table of ConTenTs
Pierce a workpiece ..........................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Gouge a workpiece .....................................................................................................................................................................4-10
Common hand-cutting faults ..................................................................................................................................................... 4-12
How to use the machine torch .............................................................................................................................................................4-12
Ensure the torch and table are set up correctly .................................................................................................................... 4-12
Understand and optimize cut quality ........................................................................................................................................4-13
To pierce a workpiece using the machine torch ................................................................................................................... 4-14
Common machine-cutting faults ............................................................................................................................................... 4-15
SECTION 5
TROUBLESHOOTING AND SYSTEM TESTS
Theory of operation ....................................................................................................................................................................................5-2
General ..............................................................................................................................................................................................5-2
200–240V CSA and 230V CE 1-phase power supply functional description..............................................................5-2
400V CE 3-phase power supply functional description .......................................................................................................5-2
480V CSA 3-phase power supply functional description ....................................................................................................5-3
Sequence of operation ...................................................................................................................................................................5-4
Troubleshooting preparation ...................................................................................................................................................................5-5
Test equipment ................................................................................................................................................................................5-5
Troubleshooting procedures and sequence .............................................................................................................................5-5
External inspection ..........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Internal inspection ...........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Initial resistance check ..............................................................................................................................................................................5-7
200–240V CSA and 230V CE power supply overview ................................................................................................................5-8
400V CE power supply overview .........................................................................................................................................................5-9
480V CSA power supply overview ...................................................................................................................................................5-10
Troubleshooting guide ........................................................................................................................................................................... 5-11
Control Board LEDs ............................................................................................................................................................................... 5-16
Use the control board Error and Reset LEDs to troubleshoot ...........................................................................................5-17
System tests.............................................................................................................................................................................................5-18
Test 1 – voltage input ..................................................................................................................................................................5-18
Test 2 – power board voltage checks ..................................................................................................................................... 5-19
Test 3 – VBUS and voltage balance .......................................................................................................................................5-20
Test 4 – solenoid valve ...............................................................................................................................................................5-24
Test 5 – torch stuck open (TSO) or torch stuck closed (TSC) ........................................................................................5-25
Test 6 – plasma start ................................................................................................................................................................... 5-26
Test 7 – torch cap sensor .......................................................................................................................................................... 5-27
Test 8 – fan ....................................................................................................................................................................................5-27
Test 9 – pressure transducer .................................................................................................................................................... 5-28
Test 10 – power switch trip coil ............................................................................................................................................... 5-28
powermax
45
Service Manual
iii
Page 10

Table of ConTenTs
SECTION 6
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
Remove and replace the cover and Mylar® barrier .............................................................................................................................6-2
Removal .............................................................................................................................................................................................6-2
Replacement .....................................................................................................................................................................................6-3
Replace the work lead (CSA and CE) ..................................................................................................................................................6-3
Replace the power cord (200–240V CSA) .......................................................................................................................................6-5
Replace the power cord (230V CE) ....................................................................................................................................................6-6
Replace the power cord (400V CE) ....................................................................................................................................................6-8
Replace the power cord (480V CSA) .............................................................................................................................................. 6-10
Replace the fan .......................................................................................................................................................................................6-12
Replace the gas filter element .............................................................................................................................................................6-13
Replace the air filter and regulator ...................................................................................................................................................... 6-15
Replace the control board .................................................................................................................................................................... 6-16
Replace the power board (200–240V CSA and 230V CE) ......................................................................................................6-17
Replace the power board (400V CE and 480V CSA) ................................................................................................................ 6-21
SECTION 7
PARTS
Power supply parts ....................................................................................................................................................................................7-2
Exterior ...............................................................................................................................................................................................7-2
Interior, power board side .............................................................................................................................................................7-4
Interior, fan side ...............................................................................................................................................................................7-5
Interior, heat sink side .....................................................................................................................................................................7-6
T45v hand torch parts...............................................................................................................................................................................7-7
T45v hand torch consumables .....................................................................................................................................................7-8
T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables ...................................................................................................................................7-8
T45m machine torch parts .......................................................................................................................................................................7-9
T45m machine torch consumables .......................................................................................................................................... 7-10
Accessory parts.......................................................................................................................................................................................7-10
Safety-critical parts.................................................................................................................................................................................7-11
Recommended spare parts .................................................................................................................................................................. 7-12
Powermax45 labels ................................................................................................................................................................................ 7-13
SECTION 8
WIRING DIAGRAMS
Control board diagram: 200–240V CSA and 230V CE ...............................................................................................................8-2
Control board diagram: 400V CE and 480V CSA ..........................................................................................................................8-3
Power board wiring diagram: 200–240VCSA and 230VCE .....................................................................................................8-5
Power board wiring diagram: 400VCE ..............................................................................................................................................8-6
Power board wiring diagram: 480VCSA ...........................................................................................................................................8-7
iv powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 11

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY EMC
Introduction
Hypertherm’s CE-marked equipment is built in compliance
with standard EN60974-10. The equipment should be
installed and used in accordance with the information
below to achieve electromagnetic compatibility.
The limits required by EN60974-10 may not be adequate
to completely eliminate interference when the affected
equipment is in close proximity or has a high degree of
sensitivity. In such cases it may be necessary to use other
measures to further reduce interference.
This cutting equipment is designed for use only in an
industrial environment.
Installation and use
The user is responsible for installing and using the plasma
equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
If electromagnetic disturbances are detected then it shall
be the responsibility of the user to resolve the situation
with the technical assistance of the manufacturer. In some
cases this remedial action may be as simple as earthing
the cutting circuit, see Earthing of the workpiece. In other
cases, it could involve constructing an electromagnetic
screen enclosing the power source and the work
complete with associated input filters. In all cases,
electromagnetic disturbances must be reduced to the
point where they are no longer troublesome.
Assessment of area
Before installing the equipment, the user shall make an
assessment of potential electromagnetic problems in
the surrounding area. The following shall be taken into
account:
a. Other supply cables, control cables, signaling and
telephone cables; above, below and adjacent to the
cutting equipment.
b. Radio and television transmitters and receivers.
c. Computer and other control equipment.
d. Safety critical equipment, for example guarding
ofindustrial equipment.
e. Health of the people around, for example the use
ofpacemakers and hearing aids.
f. Equipment used for calibration or measurement.
g. Immunity of other equipment in the environment. User
shall ensure that other equipment being used in the
environment is compatible. This may require additional
protection measures.
h. Time of day that cutting or other activities are to be
carried out.
The size of the surrounding area to be considered
will depend on the structure of the building and other
activities that are taking place. The surrounding area may
extend beyond the boundaries of the premises.
Methods of reducing emissions
Mains supply
Cutting equipment must be connected to the mains
supply according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
If interference occurs, it may be necessary to take
additional precautions such as filtering of the mains
supply.
Compliance Information EMC-1
7/ 10
Page 12

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY
Consideration should be given to shielding the supply
cable of permanently installed cutting equipment,
in metallic conduit or equivalent. Shielding should
be electrically continuous throughout its length. The
shielding should be connected to the cutting mains
supply so that good electrical contact is maintained
between the conduit and the cutting power source
enclosure.
Maintenance of cutting equipment
The cutting equipment must be routinely maintained
according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. All
access and service doors and covers should be closed
and properly fastened when the cutting equipment is in
operation. The cutting equipment should not be modified
in any way, except as set forth in and in accordance with
the manufacturer’s written instructions. For example,
the spark gaps of arc striking and stabilizing devices
should be adjusted and maintained according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations.
Cutting cables
The cutting cables should be kept as short as possible
and should be positioned close together, running at or
close to the floor level.
Earthing of the workpiece
Where the workpiece is not bonded to earth for
electrical safety, nor connected to earth because of its
size and position, for example, ship’s hull or building
steel work, a connection bonding the workpiece to earth
may reduce emissions in some, but not all instances.
Care should be taken to prevent the earthing of the
workpiece increasing the risk of injury to users, or
damage to other electrical equipment. Where necessary,
the connection of the workpiece to earth should be
made by a direct connection to the workpiece, but
in some countries where direct connection is not
permitted, the bonding should be achieved by suitable
capacitances selected according to national regulations.
Note: The cutting circuit may or may not be earthed for
safety reasons. Changing the earthing arrangements
should only be authorized by a person who is competent
to assess whether the changes will in crease the risk of
injury, for example, by allowing parallel cutting current
return paths which may damage the earth circuits
of other equipment. Further guidance is provided
in IEC60974-9, Arc Welding Equip ment, Part 9:
Installation and Use.
Screening and shielding
Equipotential bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the cutting
installation and adjacent to it should be considered.
However, metallic components bonded to the workpiece
will increase the risk that the operator could receive a
shock by touching these metallic components and the
electrode (nozzle for laser heads) at the same time.
The operator should be insulated from all such bonded
metallic components.
Selective screening and shielding of other cables
and equipment in the surrounding area may alleviate
problems of interference. Screening of the entire plasma
cutting installation may be considered for special
applications.
EMC-2 Compliance Information
7/ 10
Page 13

WARRANTY
Attention
Genuine Hypertherm parts are the factoryrecommended replacement parts for your Hypertherm
system. Any damage or injury caused by the use of other
than genuine Hypertherm parts may not be covered by
the Hypertherm warranty, and will constitute misuse of
the Hypertherm Product.
You are solely responsible for the safe use of the
Product. Hypertherm does not and cannot make any
guarantee or warranty regarding the safe use of the
product in your environment.
General
Hypertherm, Inc. warrants that its Products shall be
free from defects in materials and workmanship for the
specific periods of time set forth herein and as follows: if
Hypertherm is notified of a defect (i)with respect to the
plasma power supply within a period of two (2) years
from the date of its delivery to you, with the exception of
Powermax brand power supplies, which shall be within
a period of three (3) years from the date of delivery to
you, and (ii)with respect to the torch and leads within
a period of one (1) year from its date of delivery to you,
and with respect to torch lifter assemblies within a
period of one (1) year from its date of delivery to you,
and with respect to Automation products one (1) year
from its date of delivery to you, with the exception of
the EDGE Pro CNC and ArcGlide THC, which shall be
within a period of two (2) years from the date of delivery
to you, and (iii)with respect to HyIntensity fiber laser
components within a period of two (2) years from the
date of its delivery to you, with the exception of laser
heads and beam delivery cables, which shall be within a
period of one (1) year from its date of delivery to you.
Hypertherm provides repair, replacement or adjustment
of the Product as the sole and exclusive remedy, if
and only if the warranty set forth herein properly is
invoked and applies. Hypertherm, at its sole option,
shall repair, replace, or adjust, free of charge, any
defective Products covered by this warranty which
shall be returned with Hypertherm’s prior authorization
(which shall not be unreasonably withheld), properly
packed, to Hypertherm’s place of business in Hanover,
New Hampshire, or to an authorized Hypertherm repair
facility, all costs, insurance and freight pre paid by the
customer. Hypertherm shall not be liable for any repairs,
replacement, or adjustments of Products covered by this
warranty, except those made pursuant to this paragraph
and with Hypertherm’s prior written consent.
The warranty set forth above is exclusive and is in
lieu of all other warranties, express, implied, statutory,
or otherwise with respect to the Products or as to
the results which may be obtained therefrom, and
all implied warranties or conditions of quality or of
merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose or
against infringement. The foregoing shall constitute the
sole and exclusive remedy for any breach by Hypertherm
of its warranty.
Distributors/OEMs may offer different or additional
warranties, but Distributors/OEMs are not authorized
togive any additional warranty protection to you or make
any representation to you purporting to be binding upon
Hypertherm.
This warranty shall not apply to any Powermax brand
power supplies that have been used with phase
converters. In addition, Hypertherm does not warranty
systems that have been damaged as a result of poor
power quality, whether from phase converters or
incoming line power. This warranty shall not apply to any
product which has been incorrectly installed, modified,
or otherwise damaged.
Compliance Information W-1
9/10
Page 14

WARRANTY
Patent indemnity
Except only in cases of products not manufactured by
Hypertherm or manufactured by a person other than
Hypertherm not in strict conformity with Hypertherm’s
specifications and in cases of designs, processes,
formulae, or combinations not developed or purported
to be developed by Hypertherm, Hypertherm will have
the right to defend or settle, at its own expense, any
suit or proceeding brought against you alleging that
the use of the Hypertherm product, alone and not in
combination with any other product not supplied by
Hypertherm, infringes any patent of any third party. You
shall notify Hypertherm promptly upon learning of any
action or threatened action in connection with any such
alleged infringement (and in any event no longer than
fourteen (14) days after learning of any action or threat
of action), and Hypertherm’s obligation to defend shall
be conditioned upon Hypertherm’s sole control of, and
the indemnified party’s cooperation and assistance in,
the defense of the claim.
Limitation of liability
In no event shall Hypertherm be liable to any
person or entity for any incidental, consequential
direct, indirect, punitive or exemplary damages
(including but not limited to lost profits)
regardless of whether such liability is based on
breach of contract, tort, strict liability, breach
of warranty, failure of essential purpose, or
otherwise, and even if advised of the possibility
of such damages.
Liability cap
In no event shall Hypertherm’s liability, if any,
whether such liability is based on breach of
contract, tort, strict liability, breach of warranties,
failure of essential purpose or otherwise, for
any claim, action, suit or proceeding (whether
in court, arbitration, regulatory proceeding or
otherwise) arising out of or relating to the use of
the Products exceed in the aggregate the amount
paid for the Products that gave rise to such claim.
Insurance
At all times you will have and maintain insurance in such
quantities and types, and with coverage sufficient and
appropriate to defend and to hold Hypertherm harmless
in the event of any cause of action arising from the use
of the products.
Transfer of rights
You may transfer any remaining rights you may have
hereunder only in connection with the sale of all or
substantially all of your assets or capital stock to a
successor in interest who agrees to be bound by all of
the terms and conditions of this Warranty. Within thirty
(30) days before any such transfer occurs, you agree to
notify in writing Hypertherm, which reserves the right of
approval. Should you fail timely to notify Hypertherm and
seek its approval as set forth herein, the Warranty set
forth herein shall be null and void and you will have no
further recourse against Hypertherm under the Warranty
or otherwise.
National and local codes
National and local codes governing plumbing and
electrical installation shall take precedence over any
instructions contained in this manual. In no event shall
Hypertherm be liable for injury to persons or property
damage by reason of any code violation or poor work
practices.
W-2 Compliance Information
9/10
Page 15

Section 1
SPECIFICATIONS
In this section:
System description ....................................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Where to find information ........................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Power supply dimensions and weights ................................................................................................................................................1-3
Dimensions .......................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Weights .............................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Power supply ratings .................................................................................................................................................................................1-4
T45v torch dimensions .............................................................................................................................................................................1-5
T45m torch dimensions ............................................................................................................................................................................1-5
T45v and T45m torch specifications .....................................................................................................................................................1-6
Symbols and marks ...................................................................................................................................................................................1-7
IEC symbols ................................................................................................................................................................................................1-8
powermax
45
Service Manual 1-1
Page 16

SpecificationS
System description
The Powermax45 is a highly portable, 45-amp, handheld and mechanized plasma cutting system appropriate for a
wide range of applications. The Powermax45 uses air or nitrogen to cut electrically conductive metals, such as mild
or stainless steel or aluminum. With it, you can cut thicknesses up to 25.4mm (1inch) and pierce thicknesses up to
9.5mm (3/8inch).
The standard Powermax45 includes one complete set of the consumables needed for cutting (shield, retaining cap,
swirl ring, nozzle, electrode), 2spare electrodes, 2spare nozzles, gouging consumables (handheld configurations only),
a quick-disconnect air fitting (1/4NPT on CSA units and 1/4NPT x G-1/4BSPP on CE units), a consumables box,
a shoulder strap, an Operator Manual, a Quick Setup Card, and a Setup DVD. Mechanized configurations include a
remote-start pendant as well.
You can order additional consumables and accessories – such as the plasma cutting guide – from any Hypertherm
distributor. See the Parts section for a list of spare and optional parts.
The power cords on the 200–240V CSA power supplies are shipped with a 50A, 250V plug (NEMA6-50P) on the
power cord. The CE units and the 480V CSA units are shipped without a plug on the power cord. See Prepare the
electrical power in the Power Supply Setup section for more information.
Where to find information
System specifications, such as size, weight, detailed electrical specifications, and cut speeds can be found in this
section. For information on:
• Safety information – see the Safety and Compliance Manual for detailed safety information.
• Setup requirements, including power requirements, grounding, power cord configurations, extension cord
requirements, and generator recommendations – see the Power Supply Setup section.
• Handheld and machine torch consumables, cut charts, and torch setup information – see the Torch Setup section.
• Information about the controls and LEDs, steps for system operation, and hints for improving cut quality – see the
Operation section.
• Troubleshooting – see the Troubleshooting and System Tests section.
• Maintenance and repair instructions – see the Component Replacement section.
• Part numbers and ordering information for accessories, consumables, and replacement parts – see the Parts
section.
• Wiring and timing diagrams – see the Wiring Diagrams section.
1-2 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 17
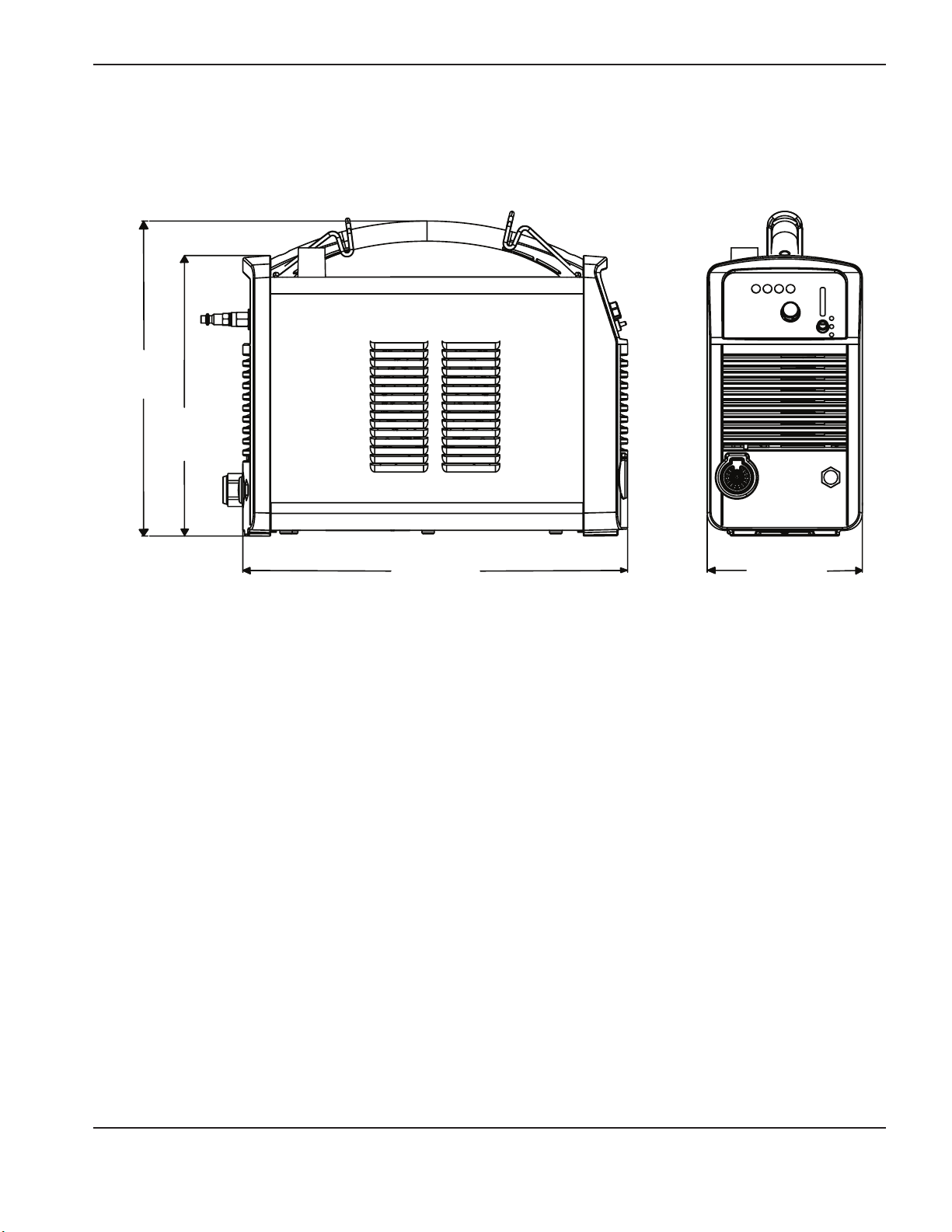
Power supply dimensions and weights
Dimensions
34.8 cm
(13.7 in)
31 cm
(12.19 in)
SpecificationS
42.6 cm
(16.75 in)
17.2 cm
(6.75 in)
Weights
Power supply weights given below include the hand torch with 6.1m (20foot) lead, a 6.1m (20foot) work lead, and a
3m (10foot) power cord.
• CSA 200–240V power supply: 16.8 kg (37 pounds)
• CSA 480V power supply: 15.9 kg (35 pounds)
• CE 230V power supply: 16.6 kg (36.5 pounds)
• CE 400V power supply: 15.9 kg (35 pounds)
powermax
45
Service Manual 1-3
Page 18
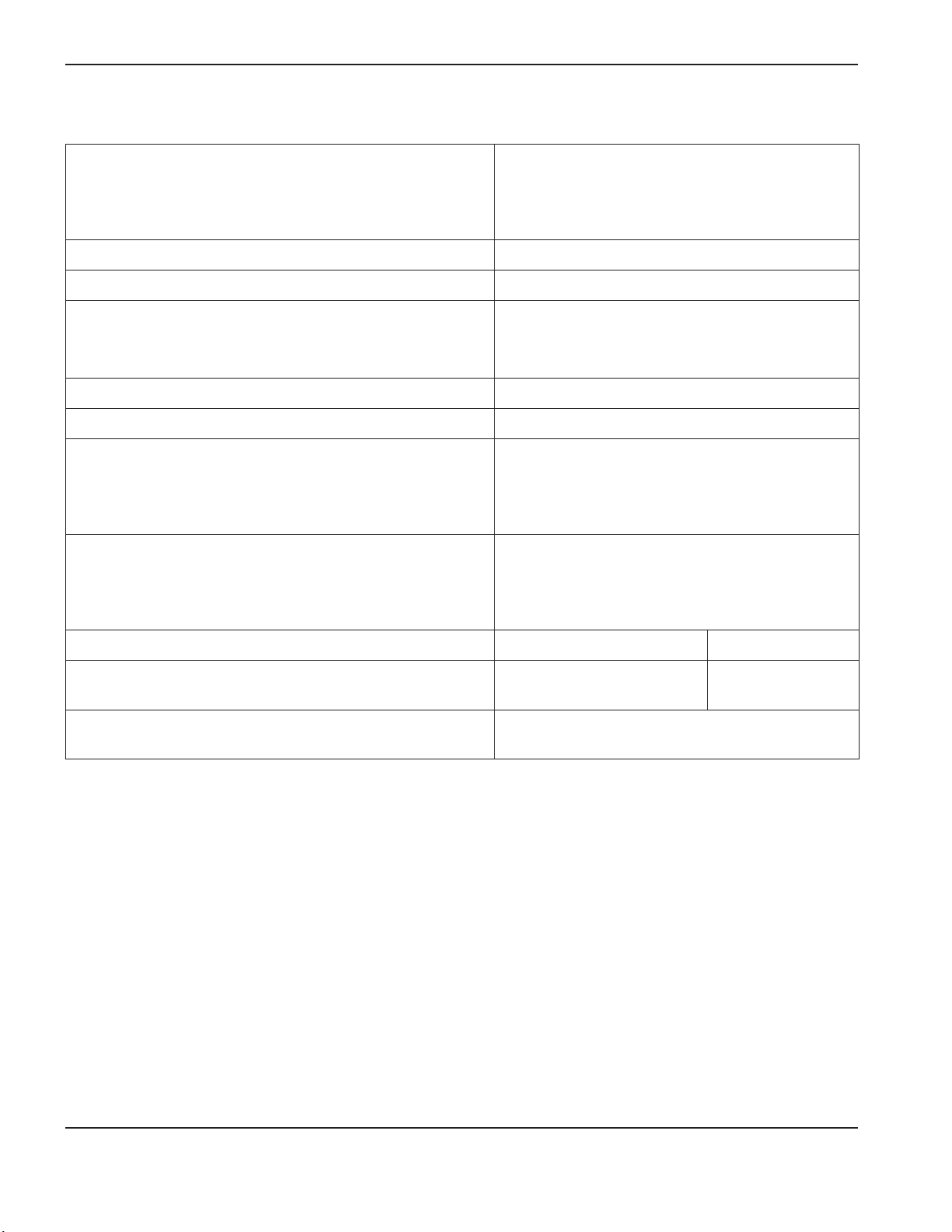
SpecificationS
Power supply ratings
Rated open-circuit voltage (U0)
CSA/CE, single-phase
CE, 3-phase
CSA, 3-phase
275VDC (CSA/CE single-phase)
275VDC (CE 3-phase)
278VDC (CSA 3-phase)
Rated output current (I2) 20 A to 45 A
Rated output voltage (U
Duty cycle at 40° C
(See data plate on power supply for moreinformation on
dutycycle.)
) 132VDC
2
50% (I
=45 A, U2=132V)
2
60% (I2=41 A, U2=132V)
100% (I2=32 A, U2=132V)
Operating temperature -10° to 40° C (14° to 104° F)
Storage temperature -25° to 55° C (-13° to 131° F)
Power factor
200–240V CSA, 230V CE, 1-phase
400V CE, 3-phase
480V CSA, 3-phase
Input voltage (U
ratedoutput(U
) / Input current (I1) at
1
,I
2MAX
)
2MAX
(See Voltage configurations in the Power Supply Setup
section for more information.)
200–240VAC / 34–28 A (200–240V CSA)
230VAC / 30 A (230V CE)*
400VAC / 10 A (400V CE)**
480VAC / 8.5A (480V CSA)
0.99
0.94
0.93
Gas type Air Nitrogen
Gas quality Clean, dry, oil-free per ISO
99.995% pure
8573-1 Class 1.2.2
Recommended gas inlet flow and pressure 170 l/min at 6.2 bar (360 scfh at 90 psi)
* Equipment complies with IEC 61000-3-12.
** Equipment complies with IEC 61000-3-12 provided that the short-circuit power S
is greater than or equal to
sc
692KVA at the interface point between the user’s supply and the public system. It is the responsibility of the installer
or user of the equipment to ensure, by consultation with the distribution network operator if necessary, that the
equipment is connected only to a supply with a short-circuit power Ssc greater than or equal to 692 KVA.
1-4 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 19
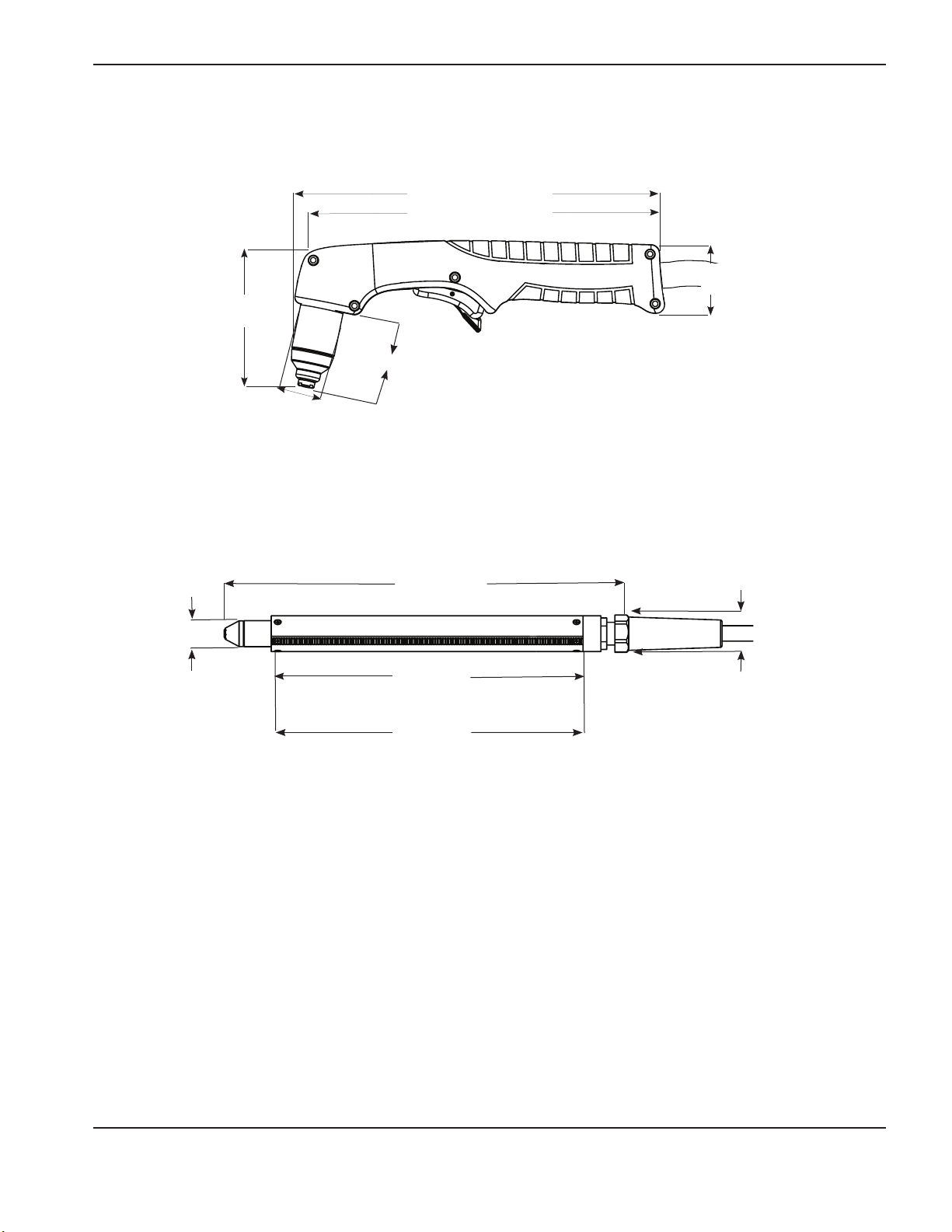
T45v torch dimensions
8.3 cm
(3.28 in)
2.5 cm
(1 in)
SpecificationS
22.1 cm (8.72 in)
21.6 cm (8.5 in)
4.0 cm
(1.58 in)
4.9 cm (1.91 in)
T45m torch dimensions
2.5 cm
(1 in)
36.5 cm
(14.36 in)
(30.5 cm)
12 in
33.0 cm
(13 in)
3.6 cm (1.43 in) outer dimension,
3.3 cm (1.3 in) flat sides
powermax
45
Service Manual 1-5
Page 20
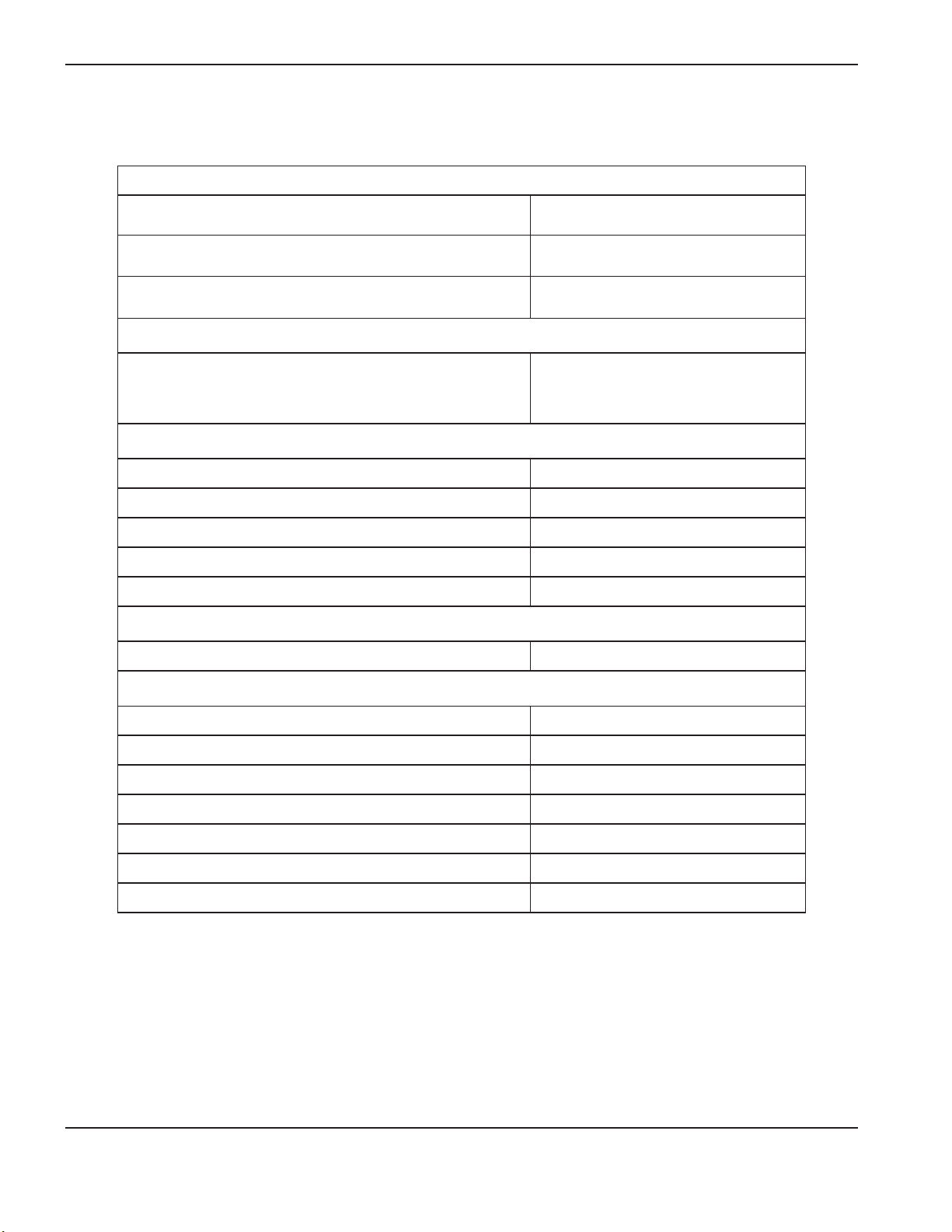
SpecificationS
T45v and T45m torch specifications
Handheld cut capacity (material thickness)
Recommended cut capacity (hand cutting) 12.7 mm (1/2 inch)
Maximum cut capacity (hand cutting or mechanized
edgestart)
Severance capacity (hand cutting or mechanized edgestart) 25.4 mm (1 inch)
Mechanized pierce capacity (material thickness)
Pierce capacity
(for edge starts, the capacities are the same as the handheld
capacities)
Recommended cut speed (on mild steel)
6.35 mm (1/4 inch) 1524 mm/min (60 ipm)
9.53 mm (3/8 inch) 813 mm/min (32 ipm)
12.7 mm (1/2 inch) 508 mm/min (20 ipm)
19.1 mm (3/4 inch) 203 mm/min (8 ipm)
25.4 mm (1 inch) 102 mm/min (4 ipm)
Gouging capacity
Metal removal rate on mild steel 2.8 kg/hr (6.2 lbs/hr)
Weight
T45v torch only 0.27 kg (0.6 lb)
19.1 mm (3/4 inch)
9.5 mm (3/8 inch)
T45v with 6.1 m (20 foot) lead 1.55 kg (3.4 lb)
T45v with 15.24 m (50 foot) lead 3.54 kg (7.8 lb)
T45m torch only 0.45 kg (1.0 lb)
T45m with 7.62 m (25 foot) lead 2.27 kg (5.0 lb)
T45m with 10.7 m (35 foot) lead 2.90 kg (6.4 lb)
T45m with 15.24 m (50 foot) lead 3.85 kg (8.5 lb)
1-6 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 21
SpecificationS
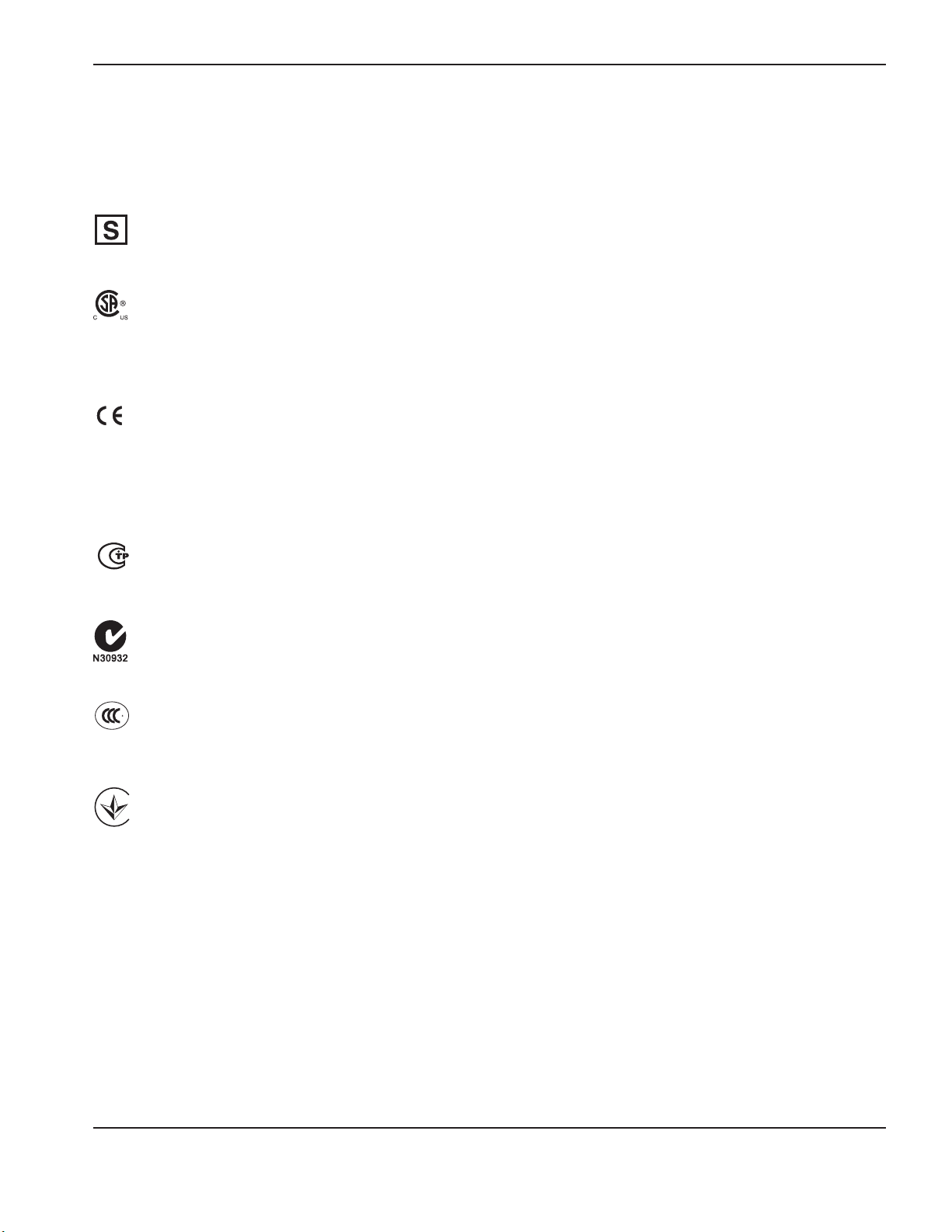
Symbols and marks
Your Hypertherm product may have one or more of the following markings on or near the data plate. Due to differences
and conflicts in national regulations, not all marks are applied to every version of a product.
S mark symbol
The S mark symbol indicates that the power supply and torch are suit able for operations carried out in
environments with in creased hazard of elec tri cal shock per IEC 60974-1.
CSA mark
Hypertherm products with a CSA mark meet the United States and Canadian regulations for product safety.
The products were evaluated, tested, and certified by CSA-International. Alternatively the product may have
amark by one of the other Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories (NRTL) accredited in both the United
States and Canada, such as Underwriters Laboratories, Incorporated (UL) or TÜV.
CE marking
The CE marking signifies the manufacturer’s declaration of conformity to applicable European directives
andstandards. Only those versions of Hypertherm products with a CE marking located on or near the
dataplate have been tested for compliance with the European Low Voltage Directive and the European
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive. EMC filters needed to comply with the European EMC
Directive are incorporated within versions of the product with a CE marking.
GOST-TR mark
CE versions of Hypertherm products that include a GOST-TR mark of conformity meet the product safety
andEMC requirements for export to the Russian Federation.
C-Tick mark
CE versions of Hypertherm products with a C-Tick mark comply with the EMC regulations required for sale
inAustralia and New Zealand.
CCC mark
The China Compulsory Certification (CCC) mark indicates that the product has been tested and found
compliant with product safety regulations required for sale in China.
UkrSEPRO mark
CE versions of Hypertherm products that include a UkrSEPRO mark of conformity meet the product safety and
EMC requirements for export to the Ukraine.
powermax
45
Service Manual 1-7
Page 22
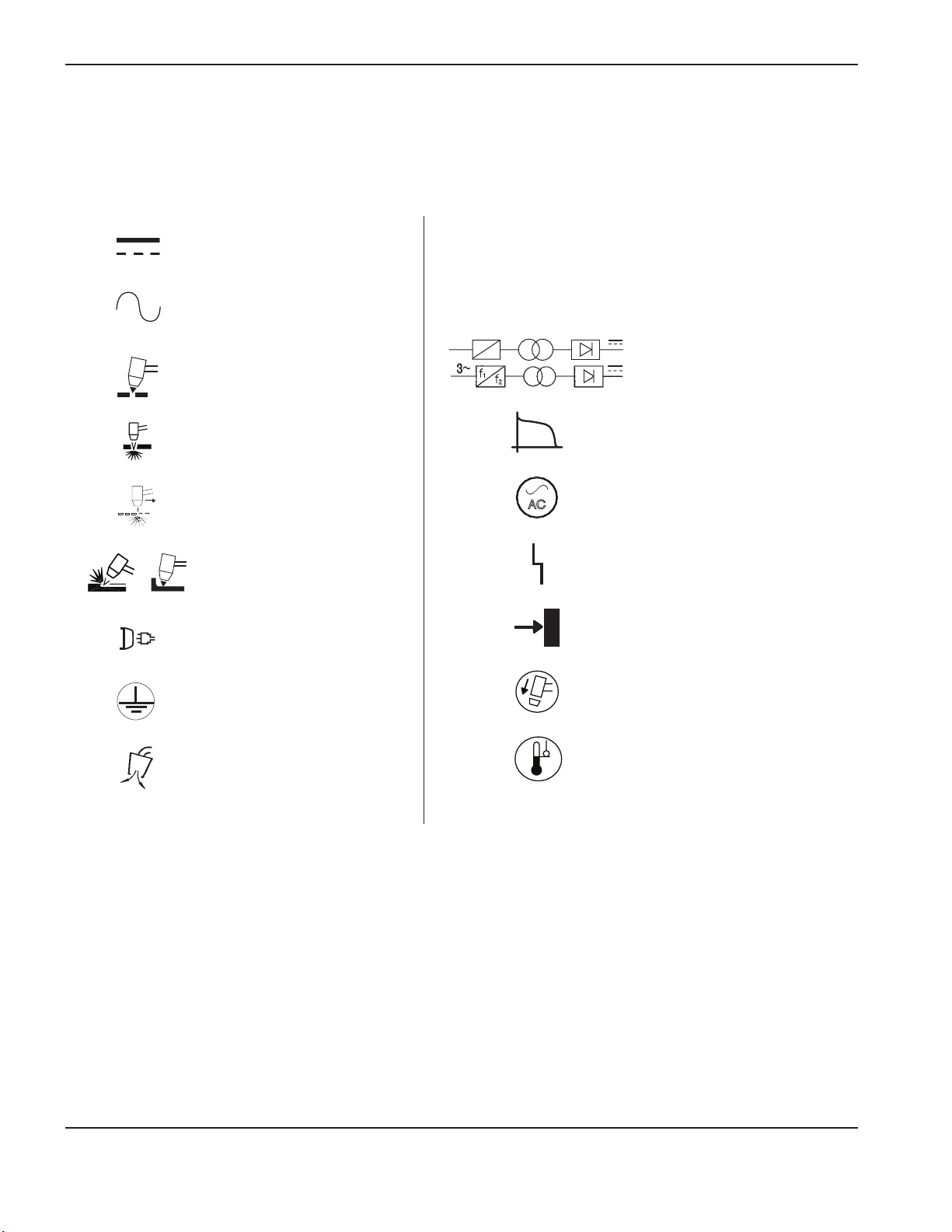
SpecificationS
IEC symbols
The following symbols may appear on the power supply data plate, control labels, switches, and LEDs.
Direct current (DC)
Alternating current (AC)
Plasma torch cutting
Plate metal cutting
Expanded metal cutting
Gouging
AC input power connection
The terminal for the external
protective (earth) conductor
l
O
1~
f
1
f
2
AC
Power is ON
Power is OFF
An inverter-based power
source, either 1-phase or
3-phase
Volt/amp curve, “drooping”
characteristic
Power is ON (LED)
System fault (LED)
Inlet gas pressure fault (LED)
Missing or loose consumables
(LED)
Power supply is out of
Gas test mode
temperature range (LED)
1-8 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 23

Section 2
POWER SUPPLY SETUP
In this section:
Unpack the Powermax45 .........................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Claims ................................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Contents ............................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Position the power supply........................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Prepare the electrical power ...................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Voltage configurations ....................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Install a line-disconnect switch ....................................................................................................................................................2-4
Requirements for grounding .........................................................................................................................................................2-4
Power cord considerations ......................................................................................................................................................................2-4
Extension cord recommendations ...............................................................................................................................................2-5
Generator recommendations ........................................................................................................................................................2-6
Prepare the gas supply .............................................................................................................................................................................2-6
Connect the gas supply .................................................................................................................................................................2-7
Additional gas filtration ...................................................................................................................................................................2-7
powermax
45
Service Manual 2-1
Page 24
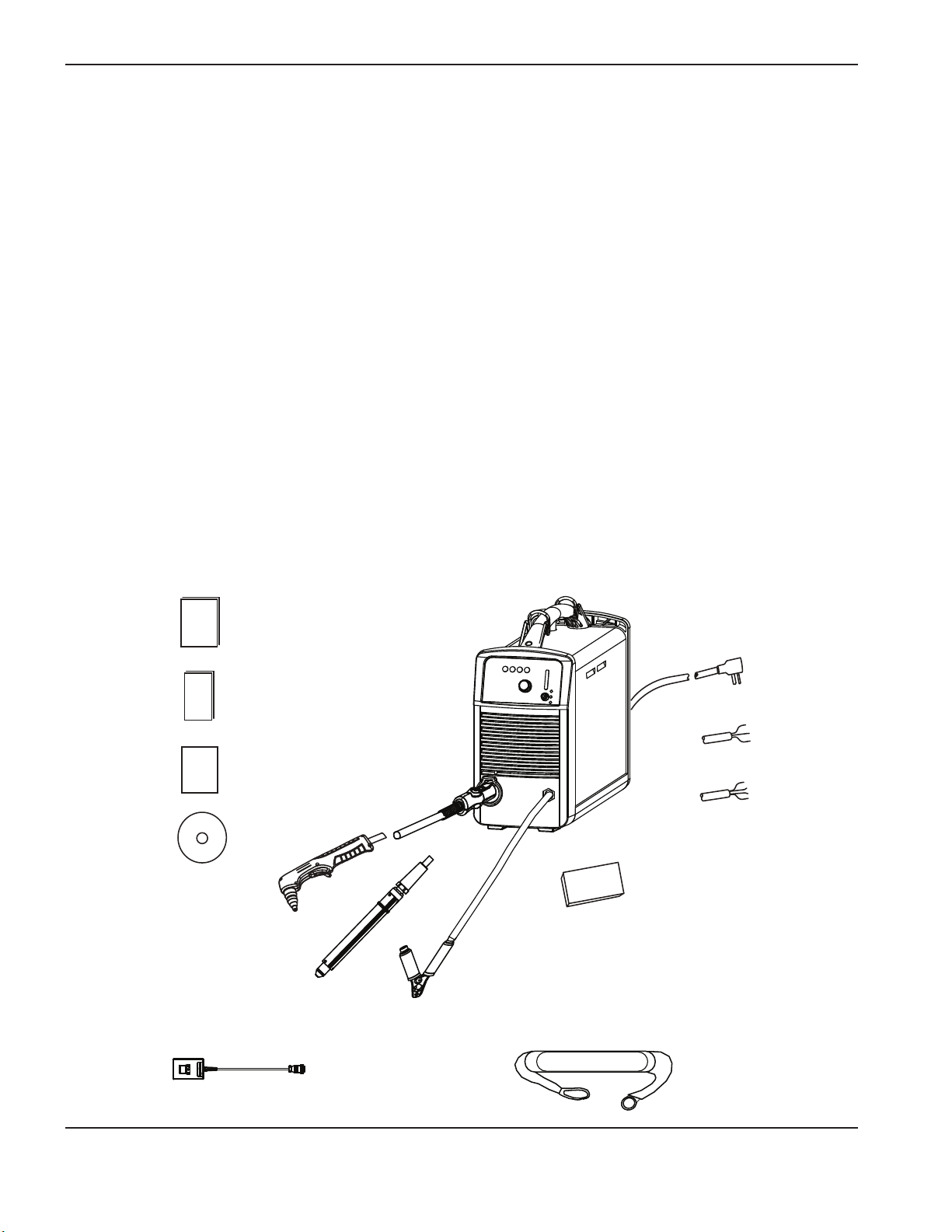
Power suPPly setuP
Unpack the Powermax45
1. Verify that all items on your order have been received in good condition. Contact your distributor if any parts are
damaged or missing.
2. Inspect the power supply for damage that may have occurred during shipping. If there is evidence of damage,
refer to Claims, below. All communications regarding this equipment must include the model number and the serial
number located on the bottom of the power supply.
3. Before you set up and operate this Hypertherm system, read the Safety and Compliance Manual.
Claims
• Claims for damage during shipment – If your unit was damaged during shipment, youmust file a claim
with the carrier. Hypertherm will furnish you with a copy of the bill oflading upon request. If you need additional
assistance, call the nearest Hypertherm office listed in the front of this manual.
• Claims for defective or missing merchandise – If any component is missing or defective, contact your
Hypertherm distributor. If you need additional assistance, call thenearest Hypertherm office listed in the front of
this manual.
Contents
Verify the items in the box against the illustration.
Operator Manual
Quick Setup Card
Registration Card
Setup DVD
or
200–240V (CSA)
(plug included)
230V (CE)
(plug not included)
400V (CE)
480V (CSA)
(plug not included)
Box with extra
consumables
Remote-start pendant (optional) Shoulder strap
2-2 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 25
power supply setup
Position the power supply
Locate the Powermax45 near an appropriate 200–240volt power receptacle for CSA or CE 1-phase power supplies,
a 400volt receptacle for 3-phase CE power supplies, or a 480volt receptacle for 3-phase CSA power supplies. The
Powermax45 has a 3m (10-foot) power cord. Allow at least 0.25m (10inches) of space around the power supply for
proper ventilation.
Prepare the electrical power
The maximum output voltage will vary based on your input voltage and the circuit’s amperage. Because the current
draw varies during startup, slow-blow fuses are recommended as shown in the following chart. Slow-blow fuses can
withstand currents up to 10times the rated value for short periods of time.
Voltage configurations
The following chart shows the maximum rated output for typical combinations of input voltage and amperage.
Acceptable input voltages can be ±10% of the values given below.
CAUTION
Protect the circuit with appropriately sized time-delay (slow-blow) fuses and a line-disconnect
switch.
Input
Model Input voltage Phase Rated output
200–240 VAC 1 45 A, 132V 34–28A 55–45A 50 A
CSA
CE
CE/CCC
* Use the higher amperage fuse for applications that require a long arc stretch.
208VAC 1 45 A, 132V 33 A 54.5 A 50 A
480VAC 3 45 A, 132V 8.5A 12A 15 or 20*A
200–240 VAC 1 45 A, 132V 34–28A 55–45A 35 or 50*A
400VAC 3 45 A, 132V 10 A 15.5 A 15 or 20*A
220VAC 1 45 A, 132V 31 A 53 A 35 or 50*A
380VAC 3 45 A, 132V 11 A 14 A 15 A
current at
6kw output
Input
current
during arc
stretch
Recommended
slow-blow fuse
size
powermax
45
Service Manual 2-3
Page 26

Power suPPly setuP
Install a line-disconnect switch
Use a line-disconnect switch for each power supply so that the operator can turn off the incoming power quickly in an
emergency. Locate the switch so that it is easily accessible to the operator. Installation must be performed by a licensed
electrician according to national and local codes. The interrupt level of the switch must be equal to or exceed the
continuous rating of the fuses. In addition, the switch should:
• Isolate the electrical equipment and disconnect all live conductors from the incoming supply voltage when in the
OFF position.
• Have one OFF and one ON position that are clearly marked with O (OFF) and I (ON).
• Have an external operating handle that can be locked in the OFF position.
• Contain a power-operated mechanism that serves as an emergency stop.
• Have slow-blow fuses installed as recommended in the table on the previous page.
Requirements for grounding
To ensure personal safety, proper operation, and to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), the Powermax45 must
be properly grounded:
• The power supply must be grounded through the power cord according to national and local electrical codes.
• Single-phase service must be of the 3-wire type with a green or green/yellow wire for the protective earth ground
and must comply with national and local requirements. Do not use a 2-wire service.
• Three-phase service must be of the 4-wire type with a green or green/yellow wire for the protective earth ground
and must comply with national and local requirements.
• Refer to the Safety and Compliance Manual for more information.
Power cord considerations
Powermax45 power supplies are shipped with CSA and CE power cord configurations.
The power cords on the 200–240V CSA power supplies are shipped with a 50 amp, 250V plug (NEMA 6-50P) on the
power cord.
The CE power supplies and the 480V CSA power supplies are shipped without a plug on the power cord. Obtain
the correct plug for your unit (230V CE, 400V CE, or 480V CSA) and location and have it installed by a licensed
electrician.
2-4 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 27
power supply setup
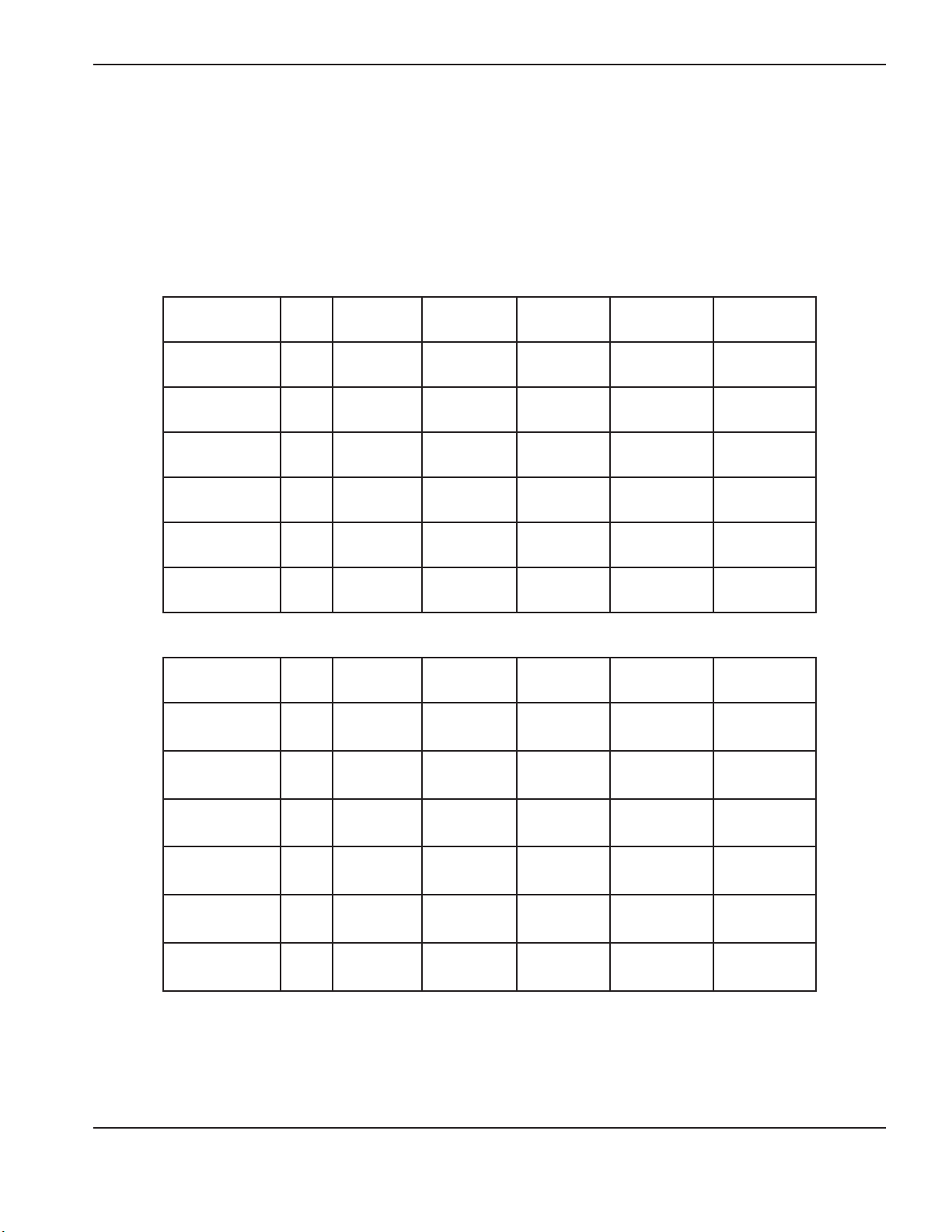
Extension cord recommendations
Use an extension cord of an appropriate wire size for the cord length and system voltage. Usea cord that meets national
and local codes.
The following tables provide the recommended gauge size for various lengths and input voltages. The lengths in the
tables are the length of the extension cord only; they do not include the power supply’s power cord.
Metric
Input voltage Phase < 3 m 3–7.5 m 7.5–15 m 15–30 m 30 –45 m
208VAC 1 10 mm
220VAC
200–240VAC
380VAC
400VAC
480VAC
1
1
3
3
3
10 mm
10 mm
4 mm
4 mm
4 mm
2
10 mm
2
10 mm
2
10 mm
2
2
2
4 mm
4 mm
4 mm
2
2
2
2
2
2
10 mm
10 mm
10 mm
4 mm
4 mm
4 mm
2
2
2
2
2
2
16 mm
16 mm
16 mm
6 mm
6 mm
6 mm
2
2
2
2
2
2
25 mm
25 mm
25 mm
6 mm
6 mm
6 mm
2
2
2
2
2
2
English
Input voltage Phase < 10 feet 10–25 feet 25–50 feet 50–100 feet 100–150 feet
208VAC 1 8 AWG 8 AWG 8 AWG 6 AWG 4 AWG
220VAC 1 8 AWG 8 AWG 8 AWG 6 AWG 4 AWG
200–240VAC 1 8 AWG 8 AWG 8 AWG 6 AWG 4 AWG
380VAC 3 12 AWG 12 AWG 12 AWG 10 AWG 10 AWG
400VAC 3 12 AWG 12 AWG 12 AWG 10 AWG 10 AWG
480VAC 3 12 AWG 12 AWG 12 AWG 10 AWG 10 AWG
powermax
45
Service Manual 2-5
Page 28
Power suPPly setuP
Generator recommendations
Generators used with the Powermax45 should satisfy the following requirements:
CSA
• 1-phase, 50/60Hz, 230/240VAC
• 3-phase, 50/60Hz, 480VAC
CE
• 1-phase, 50/60Hz, 230VAC
• 3-phase, 50/60Hz, 380/400VAC (400VAC recommended for best performance)
Engine drive outputcurrent
Engine
driverating
8 KW 33 A 11.5A 10A Good arc stretch at 45A cutting current
1-phase
(CSA/CE)
3-phase
(CE)
3-phase
(CSA)
Performance
(arc stretch)
6 KW 25 A 9A 7A
Notes: Based on the generator rating, age, and condition, adjust the cutting current as needed.
If a fault occurs while using a generator, turning the power switch quickly to OFF and then to ON again
(sometimes called a “quick reset”) may not clear the fault. Instead, turn the power supply off and wait 30 to
45seconds before turning it on again.
Limited arc stretch at 45A cutting current
Good arc stretch at 30A cutting current
Prepare the gas supply
The gas supply for the Powermax45 can be shop-compressed or cylinder-compressed.A high-pressure regulator must
be used on either type of supply and must be capable of delivering gas to the filter on the power supply at 170l/min at
6.2bar (360scfhat90psi).
WARNING
Do not allow the gas supply pressure to exceed 9.3 bar (135 psi). The filter bowl may explode if this
pressure is exceeded.
If gas supply quality is poor, cut speeds decrease, cut quality deteriorates, cutting thickness capability decreases, and
the life for consumables shortens. For optimum performance, the gas should have a maximum particle size of 0.1micron
at a maximum concentration of 0.1mg/m3, a maximum dew point of -40°C (-40°F), and a maximum oil concentration of
0.1mg/m3 (per ISO8573-1 Class1.2.2).
2-6 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 29
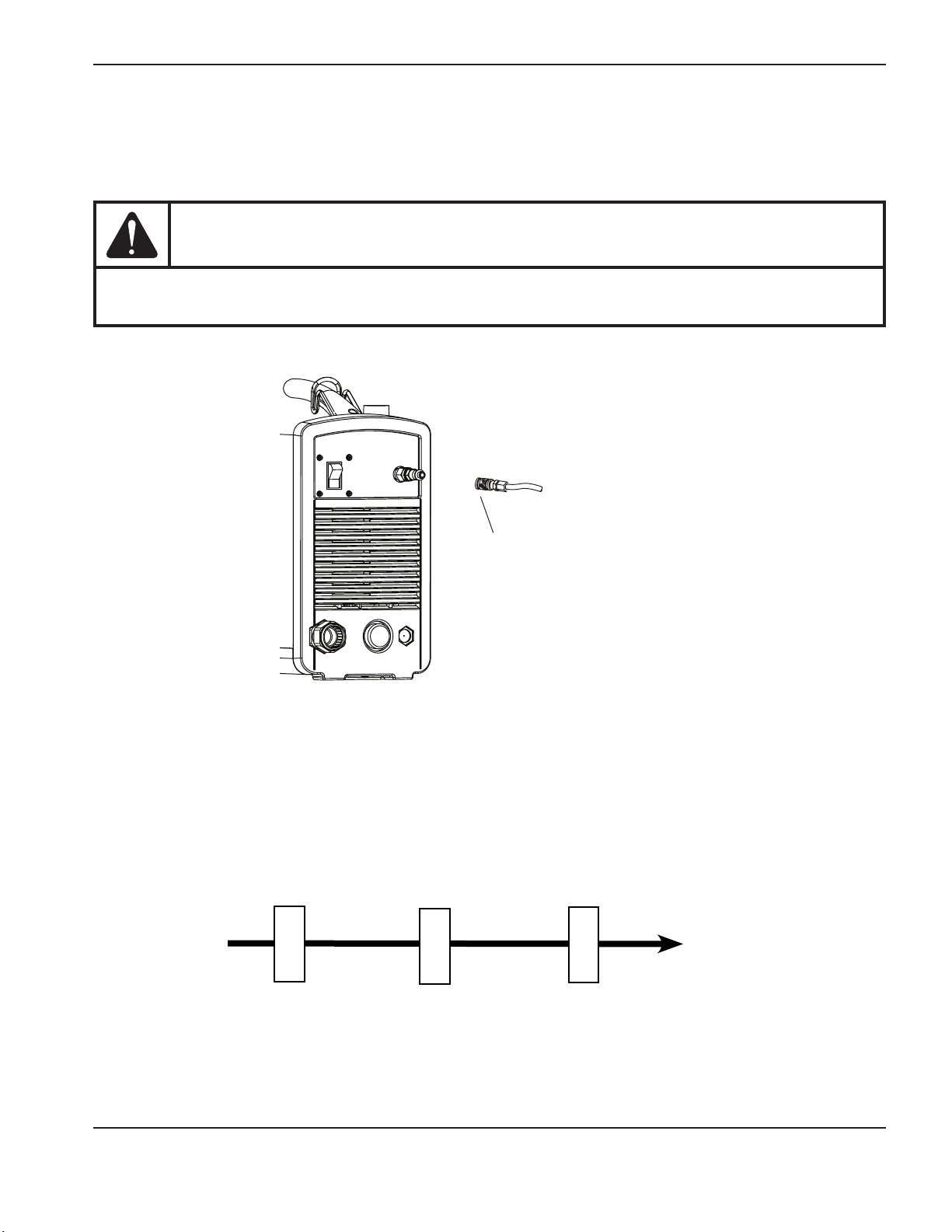
power supply setup
Connect the gas supply
Connect the gas supply to the power supply using an inert gas hose with a 9.5mm (3/8 inch) internal diameter and a
1/4NPT quick-disconnect coupler or a 1/4NPTxG-1/4 BSPP (CE units) quick-disconnect coupler.
CAUTION
Synthetic lubricants containing esters that are used in some air compressors will damage
polycarbonates used in the air regulator bowl.
5.5 – 6.9 bar (80 – 100 psi) gas supply
(maximum 9.3 bar or 135 psi) with a flow
rate of at least 165.2 l/min (350 scfh). The
recommended flow rate and pressure is 170 l/min
at 6.2 bar (360scfh at 90 psi).
Additional gas filtration
When site conditions introduce moisture, oil, or other contaminants into the gas line, use a three-stage coalescing
filtration system, such as the Eliminizer filter kit (128647) available from Hypertherm distributors. A three-stage filtering
system works as shown below toclean contaminants from the gas supply.
Oil vapor filter
Powermax45
Gas supply
Water and particle filter
Oil filter
The filtering system should be installed between the quick-disconnect coupler and the power supply.
powermax
45
Service Manual 2-7
Page 30

Power suPPly setuP
2-8 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 31

Section 3
TORCH SETUP
In this section:
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Consumable life ..........................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Hand torch setup .......................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
Choose the consumables ..............................................................................................................................................................3-3
Install the consumables ..................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Machine torch setup..................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Mount the torch ................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Choose the consumables (cut charts) .......................................................................................................................................3-8
Using the cut charts ........................................................................................................................................................................3-8
T45m shielded consumables ........................................................................................................................................................3-8
Align the torch ............................................................................................................................................................................... 3-24
Connect the remote-start pendant ...........................................................................................................................................3-25
Connect a machine interface cable .........................................................................................................................................3-25
Accessing raw arc voltage ......................................................................................................................................................... 3-27
Connect the torch lead .......................................................................................................................................................................... 3-30
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-1
Page 32

torch setup
Introduction
Both the T45v hand torch and the T45m machine torch are available for the Powermax45. The torch FastConnect™
system makes it easy to remove the torch for transport or to switch from one torch to the other if your applications
require the use of both torches.
This section explains how to set up your torch and choose the appropriate consumables for the job.
Consumable life
How often you will need to change the consumables on your Powermax45 will depend on a number of factors:
• The thickness of the metal being cut.
• The length of the average cut.
• Whether you are doing machine or hand cutting.
• The air quality (presence of oil, moisture, or other contaminants).
• Whether you are piercing the metal or starting cuts from the edge.
• Proper torch-to-work distance when gouging or cutting with unshielded consumables.
• Proper pierce height.
• Which consumables you are using. The T30v (Powermax30) 30 amp consumables will have a shorter life when
used on the T45v. However, they provide optimum cut quality for certain applications.
Under normal conditions, the electrode will wear out first during machine cutting, and the nozzle will wear out first when
hand cutting.
A good rule of thumb is that a set of consumables will last approximately 1to2hours of actual “arc on” time for hand
cutting, depending on these factors. For cutting with a machine torch, consumables may last up to 3to5hours.
You will find more information about proper cutting techniques in the Operation section.
Hand torch setup
Consumables
Safety trigger
3-2 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 33

torch setup
Choose the consumables
The Powermax45 with the T45v handheld torch comes with a full set of consumables for cutting installed on the torch,
spare electrodes and nozzles in the consumables box, and consumables for gouging in the consumables box. In nonCE-regulated countries, you can also purchase unshielded consumables that are useful for certain applications.
With shielded consumables, you drag the torch tip along the metal to cut. With unshielded consumables, you must
keep the torch a small distance, about 2mm (0.08inch), away from the metal. Unshielded consumables generally have
a shorter life than shielded consumables; however, you may find that visibility and accessibility are better for some
applications.
Consumables for hand cutting are shown below. Notice that the retaining cap, swirl ring, and electrode are the same for
shielded, unshielded, and gouging applications. Only the shield (deflector for unshielded consumables) and the nozzle
are different.
For the best cut quality on thin gauge stainless steel, you may prefer to reduce the amperage setting to 30amps and
use the T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables available from Hypertherm.
T45v shielded consumables
220674
Shield
220713
Retaining cap
T45v gouging consumables
220675
Shield
220713
Retaining cap
220671
Nozzle
220672
Nozzle
220670
Swirl ring
220670
Swirl ring
220669
Electrode
220669
Electrode
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-3
Page 34

torch setup
T45v unshielded consumables*
220717
Deflector
220713
Retaining cap
220718
Nozzle
220670
Swirl ring
* Unshielded consumables are not available for use in CE-regulated countries.
T30v (Powermax30) 30 A consumables
220569
Optional deflector
220483
Retaining cap
220480
Nozzle
220479
Swirl ring
220669
Electrode
220478
Electrode
3-4 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 35

Install the consumables
torch setup
WARNING
INSTANTON TORCHES
PLASMA ARC CAN CAUSE INJURY AND BURNS
I
O
The plasma arc comes on im me di ate ly when the torch trigger is activated. Makesure
the power is OFF before changing consumables.
To operate the T45v torch, it must have a complete set of consumable parts installed: a shield or deflector, retaining
cap, nozzle, swirl ring and electrode.
With the power switch in the OFF (O) position, verify that the torch consumables are installed as shown.
Electrode
Swirl ring
Nozzle
Retaining cap
Shield or deflector
Note: Tighten only to finger-tight. Overtightening
will cause the torch to misfire.
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-5
There should be a small gap
between the consumables and the
torch handle. Air will blow out from
this gap during normal operation.
Page 36

torch setup
Machine torch setup
Consumables
Before using the T45m, you must:
• Mount the torch on your cutting table or other equipment.
• Choose and install the consumables.
• Align the torch.
• Attach the torch lead to the power supply.
• Set up the power supply for remote starting with either the remote-start pendant or a machine interface cable.
Positioning sleeve
Gear rack
Brass strain relief
Strain relief
Mount the torch
Depending on the type of cutting table you have, you may or may not need to disassemble the torch to route it through
the track and mount it. If your cutting table’s track is large enough for you to thread the torch through it without removing
the torch body from the lead, do so and then attach the torch to the lifter per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Note: The T45m can be mounted on a wide variety of X-Y tables, track burners, pipe bevelers, and other equipment.
Install the torch per the manufacturer’s instructions and following the instructions below for disassembly if
necessary.
If you need to disassemble the torch, follow these steps:
1. Disconnect the torch lead from the power supply and remove the consumables from the torch.
2. Remove the gear rack from the positioning sleeve by removing the 2black screws that secure it to the positioning
sleeve. Remove the 6screws (3 at each end) that secure the positioning sleeve to the brass strain relief ring and to
the torch body. Slide the positioning sleeve off the torch.
3-6 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 37

3. Disconnect the wires for the cap-sensor switch at the connector in the middle.
Gas supply line connection
torch setup
Screw to connect the power cable
to the plunger
4. Use a #2Phillips screwdriver and a 6mm (1/4inch) nut driver (or adjustable wrench) to remove the screw and nut
that secure the torch’s power cable to the plunger. (Turn the plunger if necessary to gain access to the screw.)
5. Use 6mm (1/4inch) and 10mm (3/8inch) or adjustable wrenches to loosen the nut that secures the gas supply
line to the torch lead. Set the torch body aside.
Note: Cover the end of the gas line on the torch lead with tape to keep dirt and other contaminants from getting
in the gas line when you route the lead through the track.
6. Route the torch lead through the cutting table’s track.
7. Reattach the torch’s power cable to the torch plunger using the screw and nut. Rotate the plunger so that the screw
does not interfere with the cap-sensor switch.
8. Reconnect the gas line to the torch lead.
9. Press the two halves of the cap-sensor switch’s wire connector together.
10. Slide the positioning sleeve over the torch body and check the alignment of the screw holes. Replace the three
screws at each end.
Cap-sensor switch’s wireconnector
11. If you will be using the gear rack, re-attach it with the 2 black screws you removed earlier.
12. Attach the torch to the lifter per the manufacturer’s instructions.
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-7
Page 38

torch setup
Choose the consumables (cut charts)
PLASMA ARC CAN CAUSE INJURY AND BURNS
WARNING
INSTANTON TORCHES
I
O
The plasma arc comes on im me di ate ly when the torch trigger is activated. Make
sure the power is OFF before changing consumables.
A complete set of shielded consumables is shipped with the T45m machine torch. In addition, an ohmic sensing
retaining cap is available for use with the T45m shielded consumables. Unshielded consumables and the T30v
(Powermax30) 30A consumables are also available for use with the T45m.
Using the cut charts
The following sections provide illustrations of the consumable sets and cut charts for each set. Maximum cut speeds are
the fastest speeds possible to cut material without regard to cut quality. Recommended cut speeds are a good starting
point for finding the best quality cut (best angle, least dross, and best cut surface finish). You will need to adjust the
speeds for your application and your table to obtain the desired cut quality.
When cutting thin metal (3mm/10Ga or thinner), you may achieve a higher cut quality by using the T30v (Powermax30)
30A consumables and cut charts.
T45m shielded consumables
220673
Shield
220713
Retaining cap
or
220719
Ohmic sensing retaining cap
220671
Nozzle
220670
Swirl ring
220669
Electrode
The cut charts for these consumables are shown on the following pages.
3-8 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 39

torch setup
T45m shielded consumables
Mild steel
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 8650 116 10160* 117
0.9 8100 115 10160* 117
1.5 0.2 5650 111 7100 115
0.9
1.5 8890 116 10160* 115
1.9 0.1 7100 117 9144 115
2.7 0.3 4800 117 6096 115
3.4 0.4 3550 117 4445 115
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
1.5 3.8 mm 250%
Initial pierce
height
3.8 mm 250%
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.0
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 151
Cold 165.2
Recommended Maximum
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
9150 117 10160* 118
9652 115 10160* 112
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
4.8 0.5 2150 118 2794 115
45
6.4 0.6 1500 120 1905 116
9.5 0.9 510 122 101 6 116
12.7
15.9 280 138 356 127
19.1 200 140 254 131
25.4 10 0 146 127 142
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
1.5
Edge start recommended
510 132 635 125
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-9
Page 40

torch setup
T45m shielded consumables
Mild steel
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
0.018 in
(26 Ga)
0.030 in
(22 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.105 in
(12 Ga)
0.135 in
(10 Ga)
0.188 in
(3/16 in)
0.250 in
(1/4 in)
0.375 in
(3/8 in)
0.500 in
(1/2 in)
0.625 in
(5/8 in)
0.750 in
(3/4 in)
1.000 in
(1 in)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.06 0.15 in 250%
0.06
Initial pierce
height
0.15 in 250%
Edge start recommended
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 320
Cold 360
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2 225 111 280 115
0.0
0.1 280 117 360 115
0.3 190 117 240 115
0.4 140 117 175 115
0.5 85 118 110 115
0.6 60 120 75 116
0.9 32 122 40 116
Cut Speed
(ipm)
360 117 400* 118
340 116 400* 117
320 115 400* 117
380 115 400* 112
350 116 400* 115
20 132 25 125
11 138 14 127
8 140 10 131
4 146 5 142
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
3-10 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 41

torch setup
T45m shielded consumables
Stainless steel
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 8650 117 10160* 121
0.9 8100 115 10160* 119
1.5 0.2 3750 113 4700 118
0.9
1.5 8100 112 10160* 125
1.9 0.1 7100 118 9144 115
2.7 0.3 4050 118 5080 116
3.4 0.4 3050 121 3 810 118
4.8 0.5 1780 122 2159 118
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
1.5 3.8 mm 250%
1.5
Initial pierce
height
3.8 mm 250%
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.0
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 151
Cold 165.2
Recommended Maximum
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
9150 119 10160* 123
7600 112 10160* 10 9
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
6.4 0.6 1100 124 1397 120
9.5 0.8 760 126 813 121
12.7
Edge start recommended
19.1 175 136 229 131
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test able’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
350 132 457 128
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-11
Page 42

torch setup
T45m shielded consumables
Stainless steel
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
0.018 in
(26 Ga)
0.030 in
(22 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.105 in
(12 Ga)
0.135 in
(10 Ga)
0.188 in
(3/16 in)
0.250 in
(1/4 in)
0.375 in
(3/8 in)
0.500 in
(1/2 in)
0.750 in
(3/4 in)
Torch-
to-work
distance
0.06 0.15 in 250%
0.06
(in)
Initial pierce
height
0.15 in 250%
Edge start recommended
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 320
Cold 360
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2 145 111 185 118
0.0
0.1 280 117 360 115
0.3 160 117 200 116
0.4 120 117 150 118
0.5 70 118 85 118
0.6 44 120 55 120
0.8 30 122 32 121
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
360 117 400* 123
340 116 400* 121
320 115 400* 119
300 115 400* 10 9
320 116 400* 125
14 132 18 128
7 140 9 131
Voltage
(V)
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
3-12 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 43

torch setup
T45m shielded consumables
Aluminum
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
(mm)
1.2
1.5
1.9 5450 118 6860 121
1.5
1.9 8650 117 1016 0 116
2.7 7100 120 9144 119
3.4 0.1 5600 122 7112 120
4.8 0.2 2550 123 3302 120
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
1.5 3.8 mm 250%
1.5
Initial pierce
height
3.8 mm 250%
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 151
Cold 165.2
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0 9150 117 10160* 120
0.2
0.0
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
8650 118 10160* 121
9150 116 10160* 114
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
6.4 0.3 2050 123 2540 120
9.5 0.5 840 130 10 67 125
12.7
Edge start recommended
19.1 200 143 254 138
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
510 134 635 130
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-13
Page 44

torch setup
T45m shielded consumables
Aluminum
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
0.018 in
(26 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.105 in
(12 Ga)
0.135 in
(10 Ga)
0.188 in
(3/16 in)
0.250 in
(1/4 in)
0.375 in
(3/8 in)
0.500 in
(1/2 in)
0.750 in
(3/4 in)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.06 0.15 in 250%
0.06
Initial pierce
height
0.15 in 250%
Edge start recommended
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 320
Cold 360
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0 360 117 400* 120
0.2
0.0
0.1 220 122 280 120
0.2 100 123 130 120
0.3 80 123 10 0 120
0.5 33 130 42 125
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
340 118 400* 121
215 118 270 121
360 116 400* 114
340 117 400* 116
280 120 360 119
20 134 25 130
8 143 10 138
Voltage
(V)
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
3-14 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 45

T45m unshielded consumables
torch setup
220717
Deflector
Mild steel
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
220713
Retaining cap
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 8650 118 10160* 116
0.9 8100 117 10160* 120
1.5 0.2 5800 113 7250 119
0.9
1.5 8900 114 10160* 113
1.9 6100 114 7620 114
2.7 0.3 4450 116 5588 114
3.4 0.4 3400 118 4318 116
4.8 0.4 2150 118 2794 116
6.4 0.5 1500 118 1905 118
9.5 0.7 810 120 101 6 118
12.7
15.9 280 132 356 126
19.1 200 138 254 132
25.4 10 0 145 127 140
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
2.0 5.0 mm 250%
2.0
220718
Nozzle
Initial pierce
height
5.0 mm 250%
Edge start recommended
220670
Swirl ring
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.0
220669
Electrode
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 151
Cold 165.2
Recommended Maximum
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
9150 118 10160* 114
9650 118 10160* 110
510 130 635 124
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-15
Page 46

torch setup
T45m unshielded consumables
Mild steel
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
0.018 in
(26 Ga)
0.030 in
(22 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.105 in
(12 Ga)
0.135 in
(10 Ga)
0.188 in
(3/16 in)
0.250 in
(1/4 in)
0.375 in
(3/8 in)
0.500 in
(1/2 in)
0.625 in
(5/8 in)
0.750 in
(3/4 in)
1.000 in
(1 in)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.08 0.2 in 250%
0.08
Initial pierce
height
0.2 in 250%
Edge start recommended
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 320
Cold 360
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2 225 113 285 119
0.0
0.3 175 116 220 114
0.4 135 118 170 116
0.4 85 118 110 116
0.5 60 118 75 118
0.7 32 120 40 118
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
360 118 400* 114
340 118 400* 116
320 117 400* 120
380 118 400* 1 10
350 114 400* 113
240 114 300 114
20 130 25 124
11 132 14 126
8 138 10 132
4 145 5 140
Voltage
(V)
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
3-16 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 47

torch setup
T45m unshielded consumables
Stainless steel
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 8128 115 10160* 128
0.9 7000 114 9000 125
1.5 0.2 3650 112 4800 118
0.9
1.5 8100 115 10160* 113
1.9 0.1 7112 116 9144 114
2.7 0.3 4100 118 5080 116
3.4 0.4 2800 120 3556 118
4.8 0.5 1650 120 2032 118
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
2.0 5.0 mm 250%
2.0
Initial pierce
height
5.0 mm 250%
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.0
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 151
Cold 165.2
Recommended Maximum
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
9144 113 10160* 125
8900 112 10160* 110
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
6.4 0.6 1010 121 1270 118
9.5 0.8 610 125 762 120
12.7
Edge start recommended
19.1 175 133 229 138
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
355 130 457 126
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-17
Page 48

torch setup
T45m unshielded consumables
Stainless steel
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
0.018 in
(26 Ga)
0.030 in
(22 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.036 in
(20 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.105 in
(12 Ga)
0.135 in
(10 Ga)
0.188 in
(3/16 in)
0.250 in
(1/4 in)
0.375 in
(3/8 in)
0.500 in
(1/2 in)
0.750 in
(3/4 in)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.08 0.2 in 250%
0.08
Initial pierce
height
0.2 in 250%
Edge start recommended
Pierce time
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 320
Cold 360
Recommended Maximum
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2 145 112 180 118
0.0
0.1 280 116 360 114
0.3 160 118 200 116
0.4 110 120 140 118
0.5 64 120 80 118
0.6 40 121 50 118
0.8 24 125 30 120
Cut Speed
(ipm)
400* 113 400* 125
400* 115 400* 128
345 114 345 125
350 112 400* 110
320 115 400* 113
14 130 18 126
7 133 9 138
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
3-18 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 49

torch setup
T45m unshielded consumables
Aluminum
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
(mm)
1.2
1.5 0.1 8100 120 10160* 118
1.9 0.2 5700 121 7100 119
1.5
1.9 8100 120 10160* 116
2.7 7200 122 9144 118
3.4 0.1 5500 123 6858 118
4.8 0.3 2540 123 3175 118
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
2.0 5.0 mm 250%
2.0
Initial pierce
height
5.0 mm 250%
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 151
Cold 165.2
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0 8900 122 10160* 121
0.0
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
8900 120 10160* 116
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
6.4 0.3 1820 128 2286 124
9.5 0.5 710 130 914 124
12.7
Edge start recommended
19.1 200 148 254 143
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
510 131 635 125
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-19
Page 50

torch setup
T45m unshielded consumables
Aluminum
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
45
Material
thickness
0.018 in
(26 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.060 in
(16 Ga)
0.075 in
(14 Ga)
0.105 in
(12 Ga)
0.135 in
(10 Ga)
0.188 in
(3/16 in)
0.250 in
(1/4 in)
0.375 in
(3/8 in)
0.500 in
(1/2 in)
0.750 in
(3/4 in)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.08 0.20 in 250%
0.08
Initial pierce
height
0.20 in 250%
Edge start recommended
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 320
Cold 360
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0 350 122 400* 121
0.1 320 120 400* 118
0.2 225 121 280 119
0.0
0.1 215 123 270 118
0.3 100 123 125 118
0.3 72 128 90 124
0.5 28 130 36 124
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
350 120 400* 116
320 120 400* 116
285 122 360 118
20 131 25 125
8 148 10 143
Voltage
(V)
Cut
Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
3-20 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 51

T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables
torch setup
220569
Optional deflector
Mild steel
Metric
Arc
current
(amps)
30
220483
Retaining cap
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 8100 10 2 10160* 103
0.9 7100 101 8900 10 0
1.5 0.2 4450 97 5600 100
1.9
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
0.5 2.5 mm 500%
220480
Nozzle
Initial pierce
height
220479
Swirl ring
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
220478
Electrode
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 131.2
Cold 146.3
Recommended Maximum
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
8900 10 5 10160* 98
3050 98 3800 97
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
2.7 2050 96 2550 96
3.4 1270 10 0 1650 101
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (10160 mm/min).
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-21
0.4
Page 52

torch setup
T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables
Mild steel
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
Material
thickness
(in)
0.018
(26 Ga)
0.030
(22 Ga)
0.036
(20 Ga)
0.060
(16 Ga)
0.075
(14 Ga)
0.105
(12 Ga)
0.135
(10 Ga)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.02 0.1 in 500%
Initial pierce
height
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 280
Cold 3 10
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2 175 97 220 10 0
0.4
Cut Speed
(ipm)
350 105 400* 98
320 102 400* 103
280 101 350 10 0
120 98 150 97
80 96 100 96
50 10 0 65 101
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables
Stainless steel
Metric
Recommended Maximum
Arc
current
(amps)
30
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm or 10160 mm/min).
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 8100 98 10160* 100
0.9 7600 97 6850 98
1.5 0.2 3800 99 4800 98
1.9
2.7 1500 101 1900 98
3.4 1150 10 2 1400 97
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
0.5 2.5 mm 500%
Initial pierce
height
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.4
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
8900 10 3 10160* 102
2800 101 3450 97
Voltage
(V)
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 131.2
Cold 146.3
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
3-22 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 53

torch setup
T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables
Stainless steel
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
Material
thickness
(in)
0.018
(26 Ga)
0.030
(22 Ga)
0.036
(20 Ga)
0.060
(16 Ga)
0.075
(14 Ga)
0.105
(12 Ga)
0.135
(10 Ga)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.02 0.1 in 500%
Initial pierce
height
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 280
Cold 3 10
Recommended Maximum
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2 150 99 190 98
0.4
Cut Speed
(ipm)
350 103 400* 10 2
320 98 400* 10 0
300 97 380 98
110 101 135 97
60 101 75 98
45 102 55 97
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables
Aluminum
Metric
Recommended Maximum
Arc
current
(amps)
30
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm or 10160 mm/min).
Material
thickness
(mm)
0.5
0.8 6100 10 4 7650 103
0.9 4800 10 4 6100 103
1.5
1.9 2400 101 3050 101
Torch-
to-work
distance
(mm)
0.5 2.5 mm 500%
Initial pierce
height
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
8100 107 10160* 105
3700 10 3 4550 103
Voltage
(V)
Air flowrate (lpm)
Hot 131.2
Cold 146.3
Cut Speed
(mm/min)
Voltage
(V)
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-23
Page 54

torch setup
T30v (Powermax30) 30A consumables
Aluminum
English
Arc
current
(amps)
30
*Maximum cut speed is limited by the test table’s maximum speed (400 ipm).
Material
thickness
(in)
0.036
(20 Ga)
0.060
(16 Ga)
0.075
(14 Ga)
0.105
(12 Ga)
0.135
(10 Ga)
Torch-
to-work
distance
(in)
0.02 0.10 in 500%
Initial pierce
height
Pierce time
delay
(sec)
0.0
0.2
Air flowrate (scfh)
Hot 280
Cold 3 10
Recommended Maximum
Cut Speed
(ipm)
320 107 400* 105
240 104 300 10 3
190 104 240 10 3
145 103 180 10 3
95 101 120 101
Voltage
(V)
Cut Speed
(ipm)
Voltage
(V)
Align the torch
Mount the machine torch perpendicular to the workpiece in order to get a vertical cut. Use a square to align the torch at
0° and 90°.
Torch
0°
90°
3-24 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 55

torch setup
Connect the remote-start pendant
Configurations of a Powermax45 with a T45m also can include a 7.62m/25-foot (128650), 15.24m/50-foot
(128651), or 22.86m/75-foot (128652) remote-start pendant. To use the Hypertherm remote-start pendant, plug it
into the receptacle on the rear of the power supply.
Note: The remote-start pendant is for use only with a machine torch. It will not operate if a hand torch is installed.
Receptacle for the
remote-startpendant or a
machineinterfacecable.
Connect a machine interface cable
The Powermax45 is equipped with a factory-installed voltage divider that is designed to be safely connected without
tools. The built-in voltage divider provides a 50:1 arc voltage. A receptacle on the rear of the power supply provides
access to the 50:1 arc voltage and signals for arc transfer and plasma start.
CAUTION
The factory-installed internal voltage divider provides a maximum of 7V under open circuit
conditions. This is an impedance-protected functional extra low voltage (ELV) output to prevent
shock, energy, and fire under normal conditions at the machine interface receptacle and under single
fault conditions with the machine interface wiring. The voltage divider is not fault tolerant and ELV
outputs do not comply with safety extra low voltage (SELV) requirements for direct connection to
computer products.
Hypertherm offers several choices of machine interface cables for the Powermax45:
• To use the built-in voltage divider that provides a 50:1 arc voltage in addition to signals for arc transfer and
plasma start:
— Use kit number 228350 (7.62m, 25feet) or 228351 (15.24m, 50feet) for 6wires terminated with spade
connectors. (The following diagram shows an example of spade connectors.)
— Use part number 223048 (7.62m, 25feet) or 123896 (15.24m, 50feet) for a cable terminated with a
D-sub connector. (Compatible with Hypertherm’s EDGE®ProTi and Sensor™PHC products.)
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-25
Page 56

torch setup
• To use signals for arc transfer and plasma start only, use either part number 023206 (7.62m, 25feet) or part
number 023279 (15.24m, 50feet). These cables have spade connectors as shown here:
Note: The cover on the machine interface receptacle prevents dust and moisture from damaging the receptacle
when not in use. This cover should be replaced if damaged or lost (127204).
Installation of the machine interface cable must be performed by a qualified service technician. To install a machine
interface cable:
1. Turn OFF the power and disconnect the power cord.
2. Remove the machine interface receptacle’s cover from the rear of the power supply.
3. Connect the Hypertherm machine interface cable to the power supply.
4. If you are using a cable with a D-sub connector on the other end, plug it into the appropriate pin connector on the
torch height controller or CNC. Secure it with the screws on the D-sub connector.
If you are using a cable with wires and spade connectors on the other end, terminate the machine interface cable
inside the electrical enclosure of listed and certified torch height controllers or CNC controllers to prevent operator
access to the connections after installation. Verify that the connections are correct and that all live parts are
enclosed and protected before operating the equipment.
Note: The integration of Hypertherm equipment and customer-supplied equipment including interconnecting
cords and cables, if not listed and certified as a system, is subject to inspection by local authorities at the
final installation site.
The connector sockets for each type of signal available through the machine interface cable are shown below. The table
on page 3-27 provides details about each signal type.
6
3
14
5
4
12
13
3-26 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 57

torch setup
Refer to the following table when connecting the Powermax45 to a torch height controller or CNC with a machine
interface cable.
Signal Type Notes
Normally open.
Start (start plasma) Input
Transfer
(startmachinemotion)
Ground Ground 13
Voltage divider Output
Output
18VDC open circuit voltage at START
terminals. Requires dry contact closure to
activate.
Normally open. Dry contact closure when
the arc transfers.
120VAC/1A maximum at the machine
interface relay or switching device
(supplied by the customer).
Divided arc signal of 50:1 (provides a
maximum of 7V).
Connector
sockets
3, 4 Green, black
12, 14 Red, black
5(-), 6(+) Black(-), white(+)
External cable
wires
Accessing raw arc voltage
Connecting a cable to the Powermax45 power board to bypass the voltage divider and access raw arc voltage must be
done by a qualified service technician.
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE AND CURRENT
Connecting directly to the plasma circuit for access to raw arc voltage increases the risk of shock
hazard, energy hazard, and fire hazard in the event of a single fault. The output voltage and the
output current of the circuit are specified on the data plate.
To access raw arc voltage on a Powermax45, you will need kit number 228352 and an 18 AWG, 2 wire, non-shielded
cable similar to OLFLEX
equipment plus an additional 45.72cm (18 inches).
1. On the end of the cable that will be attached to the power supply, strip the outer jacket 11.43cm (4.5 inches). Cut
6.35cm (2.5 inches) off of wire2 so that wire1 is 11.43cm (4.5inches) long and wire2 is 5.08cm (2inches)
long. Then strip 1.27cm (0.5 inches) of wire insulation off of each wire.
2. Crimp a #8insulated ring on the end of wire1 and a #10insulated ring on the end of wire2.
3. Use a #2 Phillips screwdriver to remove the 2 screws from the handle on the top of the power supply. Tip the end
panels back slightly so that you can get the edges of the handle out from underneath them. Lift the cover off the
power supply. Remove the Mylar barrier that protects the power board.
®
190 (601802) in the length needed to go between the power supply and the CNC or other
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-27
Page 58

torch setup
4. Separate the rear panel from the Powermax45 by removing the screw from the bottom and backing the end panel
away from the base so that there is enough room to drill out the access point without risk of hitting the interior
components.
Rear end panel
Access point
5. Use a drill with a 19/32inch drill bit to drill out the access point on the rear panel.
6. Route the cable through the strain relief and tighten it down so that 45.72cm (18inches) of insulated wire is on the
side of the strain relief that will go inside the power supply.
7. Thread the 45.72cm (18inches) of wire through the hole you drilled in the rear panel and fit the strain relief into the
hole. If necessary, drill out any remaining rough spots so that the strain relief fits snugly.
8. Tighten the strain relief nut on the inside of the rear panel to hold the strain relief in place.
9. Find the grommet closest to the rear panel and at the bottom of the center panel. Route the 2wires through the
grommet to the power board side of the power supply.
Rear panel pulled slightly
away from the base
Grommet in center panel
3-28 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 59

torch setup
10. Route the wires along the base of the unit and behind the cables connected to the power board.
11. Remove the work lead connector screw at J21 and the white wire connector screw at J19 (J18 for 400V CE and
480V CSA power supplies).
12. Connect wire1 to J19 (J18 for 400V CE and 480V CSA power supplies) with the ring connector for wire1
closest to the power board and the connector for the white wire closest to the head of the screw. Turn the ring
connector for wire1 upside down so that the slight bend in the ring connector base creates a little space between
the wire and the board. Tighten the screw to 23.0kgcm (20 inch-pounds).
13. Connect wire2 to J21. This time, put the connector for the work lead closest to the power board and put the ring
connector for wire2 closest to the head of the screw. Torque the screw to 23.0kgcm (20 inch-pounds).
J19 or J18
(white wire)
192 VDC
TP 19
TP 18
192 VDC
TP 17
R
B
-
+
W
-
+
J21 (work lead)
14. Replace the rear panel and secure it with the screw. Replace the Mylar barrier in front of the power board. Replace
the cover.
15. Connect the other end of the cable to the equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
NOTE: The integration of Hypertherm equipment and customer-supplied equipment including interconnecting
cords and cables, if not listed and certified as a system, is subject to inspection by local authorities at the
final installation site.
powermax
45
Service Manual 3-29
Page 60

torch setup
Connect the torch lead
The Powermax45 has a FastConnect system for connecting and disconnecting the hand and machine torches. When
connecting or disconnecting a torch, first power OFF the system. To connect either torch, push the connector into
receptacle on the front of the power supply.
To remove the torch, press the red button on the connector and pull the connector out of the receptacle.
Red button
3-30 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 61

Section 4
OPERATION
In this section:
Controls and indicators ............................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Front controls and LEDs ................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Rear controls ....................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Operate the Powermax45 ........................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Connect the electrical power and gas supply ..........................................................................................................................4-3
Power ON the system ....................................................................................................................................................................4-4
Set the mode switch .......................................................................................................................................................................4-4
Adjust the gas pressure .................................................................................................................................................................4-4
Check the indicator LEDs .............................................................................................................................................................4-6
Attach the work clamp ...................................................................................................................................................................4-6
Understand duty-cycle limitations ..........................................................................................................................................................4-6
How to use the hand torch ......................................................................................................................................................................4-7
Operate the safety trigger .............................................................................................................................................................4-7
Hand torch cutting hints ................................................................................................................................................................4-7
Start a cut from the edge of the workpiece ..............................................................................................................................4-8
Pierce a workpiece ..........................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Gouge a workpiece ..................................................................................................................................................................... 4-10
Common hand-cutting faults ..................................................................................................................................................... 4-12
How to use the machine torch .............................................................................................................................................................4-12
Ensure the torch and table are set up correctly .................................................................................................................... 4-12
Understand and optimize cut quality ........................................................................................................................................4-13
To pierce a workpiece using the machine torch .................................................................................................................... 4-14
Common machine-cutting faults ............................................................................................................................................... 4-15
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-1
Page 62

operation
Controls and indicators
The Powermax45 has an ON/OFF switch, an amperage adjustment knob, a pressure regulator knob, a mode switch,
4indicator LEDs, and a gas pressure LED, which are described below.
Front controls and LEDs
Pressure regulator knob
Gas pressure LED and pressure bar
Indicator LEDs
Amperage adjustment knob
30
20
AMPS
40
45
Mode switch
AC
Temperature LED (yellow)
When illuminated, this LED indicates that the power supply temperature is outside the acceptable range.
Torch cap sensor LED (yellow)
When illuminated, this LED indicates that the consumables are loose, improperly installed, or missing.
For information on the possible fault conditions, refer to the Troubleshooting guide topic in the
Troubleshooting and System Tests section. If this LED illuminates, the power must be turned OFF, the
consumables installed properly, and the system turned ON again to reset it.
Fault LED (yellow)
When illuminated, this LED indicates that there is a fault with the power supply. Some fault conditions
will cause one or more of the LEDs to blink. For information on what these fault conditions are and how
to correct them, refer to the Troubleshooting guide topic in the Troubleshooting and System Tests
section.
Power ON LED (green)
When illuminated, this LED indicates that the power switch has been set to I (ON) and that the safety
interlocks are satisfied.
Gas pressure LED and pressure bar (yellow/green)
When the LED indicator in the pressure bar illuminates green and is centered in the vertical bar, the gas
pressure is set correctly for the mode of cutting selected with the mode switch. If the pressure is too
high for the selected mode, the indicator in the pressure bar will be above the mid-point of the bar. If
it is too low, the indicator will be below the mid-point. At the highest and lowest points on the bar, the
indicator will illuminate yellow.
If the indicator is at the lowest part of the bar and is flashing, then the gas pressure is less than the
minimum required pressure.
4-2 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 63

30
Amperage adjustment knob
40
Set this knob to the gas test position (fully counter-clockwise) before adjusting the gas pressure with
the pressure regulator knob on the top of the power supply. Once the gas pressure is set, turn the knob
45
clockwise to set the output amperage. The torch will not fire when the knob is in gas-test position.
Mode switch and LEDs
The mode switch can be set in one of three positions:
• Continuous pilot arc to cut expanded metal or grate (top).
• Non-continuous pilot arc to cut metal plate (middle).
• Gouging (bottom).
After you change the mode switch, verify that the gas pressure is still set correctly. Different modes of
cutting require different pressure settings.
Rear controls
200–240V CSA / 230V CE 400V CE / 480V CSA
I
I
O
O
operation
ON (I)/OFF (O) power switch
Activates the power supply and its control circuits.
Operate the Powermax45
Follow the steps below to begin cutting or gouging with the Powermax45.
Connect the electrical power and gas supply
Plug in the power cord and connect the gas supply line. For more information about the electrical requirements and the
gas supply requirements of the Powermax45, see the Power Supply Setup section.
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-3
Page 64

operation
Power ON the system
Set the ON/OFF switch to the ON (I) position.
I
I
O
200–240V CSA / 230V CE 400V CE / 480V CSA
Set the mode switch
Use the mode switch to select the type of work you will be doing:
To cut expanded metal or grate (top position). Use this setting to cut metal
with holes in it or for any job requiring a continuous pilot arc. Leaving the mode
switch on this setting when cutting standard metal plate will result in reduced
consumable life.
To cut metal plate (middle position). Use this setting to cut metal up to 25.4mm
(1-inch) thick or pierce metal up to 12.7mm (1/2-inch) thick.
O
I
O
Gouging (bottom position). Use this setting to gouge metal. Leaving the mode
switch on this setting while cutting results in poor cut quality.
Adjust the gas pressure
Look at the gas pressure LED. If it illuminates green in the center of the pressure bar, the incoming gas pressure is
correct for the mode you have selected. If the LED illuminates yellow, either above or below the center, the gas pressure
needs to be adjusted.
4-4 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 65

operation
To adjust the pressure:
1. Turn the amperage knob counter-clockwise to the gas-test position as shown below.
30
40
45
2. With the amperage knob in the gas test position, pull up on the pressure regulator knob on top of the system to
unlock it.
Pressure regulator knob
30
20
40
AMPS
45
3. Turn the pressure regulator knob until the gas pressure LED shows a green bar in the center of the pressure bar.
4. Press down on the pressure regulator knob to lock it in position.
5. Turn the amperage knob to the cutting current appropriate for your application. If you are using T30v
(Powermax30) 30A consumables, do not set the amperage knob above 30A.
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-5
Page 66

operation
Check the indicator LEDs
Verify that the green power ON LED on the front of the power supply is illuminated, that the gas pressure LED shows a
green bar in the center of the gauge, and that none of the other LEDs are illuminated or blinking. If the temperature,
torch cap sensor, or fault LEDs are illuminated or blinking, or if the power ON LED blinks, correct the fault condition
before continuing. See the Troubleshooting guide topic in the Troubleshooting and System Tests section for more
information.
Attach the work clamp
The work clamp must be attached to the workpiece while you are cutting.
Note: If you are using the Powermax45 with a cutting table, you can ground it through the table instead of using
the work clamp. See your table manufacturer’s instructions for more information.
• Ensure that the work clamp and the workpiece make good metal-to-metal contact.
• For the best cut quality, attach the work clamp as close as possible to the area being cut.
• Donot attach the work clamp to the portion of the workpiece to be cut away.
Work clamp
When the power ON LED is illuminated, none of the other LEDs are illuminated or blinking, the gas pressure LED
indicates pressure is in the correct range, the amperage knob is set, and the work clamp is attached, the system is ready
for use.
Understand duty-cycle limitations
The duty cycle is the amount of time, in minutes, that a plasma arc can remain on within a 10-minute period when
operating at an ambient temperature of 40°C (104°F). With a Powermax45:
• At 45A, the arc can remain on for 5minutes out of 10minutes without causing the unit to overheat (50%duty
cycle).
• At 41A, the arc can remain on for 6minutes out of 10 (60%).
• At 32A, the arc can remain on for 10minutes out of 10 (100%).
If the power supply overheats because the duty cycle is exceeded, the temperature LED will illuminate, the arc will shut
off, and the cooling fan will continue to run. To resume cutting, wait for the temperature LED to extinguish.
4-6 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 67

operation
The next section explains how to operate the hand torch. To use the machine torch, see How to use the machine torch
on page 4-12.
How to use the hand torch
WARNING
INSTANTON TORCHES
PLASMA ARC CAN CAUSE INJURY AND BURNS
Plasma arc comes on im me di ate ly when the torch trigger is activated. The plasma arc will cut quickly
through gloves and skin.
• Keep away from the torch tip.
• Do not hold the workpiece and keep your hands clear of the cutting path.
• Never point the torch toward yourself or others.
Operate the safety trigger
The T45v is equipped with a safety trigger to prevent accidental firings. When you are ready to cut with the torch, flip
the yellow safety trigger forward (toward the torch head) and press the red torch trigger as show below.
1
2
3
Hand torch cutting hints
• With shielded consumables, drag the nozzle lightly along the workpiece to maintain a steady cut. With unshielded
consumables, maintain an approximate 2mm (0.08-inch) distance between the tip of the torch and the workpiece.
(This is between 1.6–3.2mm, or between 1/16th and 1/8th of an inch.)
• While cutting, make sure that sparks exit from the bottom of the workpiece. The sparks should be lagging slightly
behind the torch as you cut (15°–30° angle from vertical).
• If sparks are spraying up from the workpiece, move the torch more slowly, or set the output current higher.
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-7
Page 68

operation
• Hold the torch nozzle perpendicular to the
workpiece so that the nozzle is at a 90°angle to the
cutting surface, and watch the arc as it cuts along
the line.
• If you fire the torch unnecessarily, you shorten the
life of the nozzle and electrode.
• Pulling, or dragging, the torch along the cut is easier
than pushing it.
• For straight-line cuts, use a straight edge as a
guide. To cut circles, use a template or a radius
cutter attachment (a circle cutting guide). See the
Parts section for part numbers for the Hypertherm
plasma cutting guides for cutting circles and making
bevel cuts.
Start a cut from the edge of the workpiece
1. With the work clamp attached to the workpiece,
hold the torch nozzle perpendicular (90°) to
the edge of the workpiece. If you are using the
shielded consumables, no standoff is needed. With
unshielded consumables, maintain an approximate
2mm (0.08-inch) standoff.
4-8 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 69

2. Press the torch trigger to start the arc. Pause at the
edge until the arc has cut completely through the
workpiece.
3. Drag the nozzle lightly across the workpiece to
proceed with the cut. Maintain a steady, even pace.
operation
Pierce a workpiece
WARNING
SPARKS AND HOT METAL CAN INJURE EYES AND BURN SKIN. When firing the
torch at an angle, sparks and hot metal will spray out from the nozzle. Point the
torch away from yourself and others.
1. With the work clamp attached to the workpiece, hold the torch at an approximate 30° angle to the workpiece with the
nozzle within 1.5mm (1/16 inch) of it before firing the torch.
2. Fire the torch while still at an angle to the
workpiece, then slowly rotate the torch to a
perpendicular (90°) position.
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-9
Page 70

operation
3. Hold the torch in place while continuing to press
the trigger. When sparks exit from the bottom of the
workpiece, the arc has pierced the material.
4. When the pierce is complete, dragthe nozzle lightly
along the workpiece to proceed with the cut.
Gouge a workpiece
WARNING
SPARKS AND HOT METAL CAN INJURE EYES AND BURN SKIN. When firing the
torch at an angle, sparks and hot metal will spray out from the nozzle. Point the
torch away from yourself and others.
1. Hold the torch so that the nozzle is within 1.5mm (1/16 inch) from the workpiece before firing the torch.
2. Hold the torch at a 45° angle to the workpiece with a
small gap between the torch tip and the workpiece.
Press the trigger to obtain a pilot arc. Transfer the arc
to the workpiece.
4-10 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 71

3. Maintain an approximate 45° angle to the workpiece
as you feed into the gouge.
In other words, push the plasma arc in the direction of
the gouge you want to create. Keep a small distance
between the torch tip and the molten metal to avoid
reducing consumable life or damaging the torch.
operation
Changing the torch angle changes the dimensions of
the gouge.
Di rec tion of travel
Note: A heat shield is available for added hand and torch protection (220049).
You can vary the depth of the gouge by varying the angle of the torch to the workpiece. The following tables show the
gouging profile at 45° and 60° on mild steel and stainless steel.
Mild steel gouging profile
Torch angle Speed Width Depth
254 mm/min (10 ipm) 7.75 mm (0.3051 inch) 1.05 mm (0.0415 inch)
508 mm/min (20 ipm) 6.50 mm (0.2550 inch) 2.94 mm (0.1158 inch)
45°
60°
762 mm/min (30 ipm) 5.76 mm (0.2267 inch) 1.87 mm (0.0735 inch)
1016 mm/min (40 ipm) 5.30 mm (0.2087 inch) 1.31 mm (0.0517 inch)
1270 mm/min (50 ipm) 4.73 mm (0.1863 inch) 1.03 mm (0.0406 inch)
254 mm/min (10 ipm) 8.06 mm (0.3173 inch) 4.18 mm (0.1645 inch)
508 mm/min (20 ipm) 6.15 mm (0.2423 inch) 2.39 mm (0.0941 inch)
762 mm/min (30 ipm) 6.00 mm (0.2351 inch) 1.39 mm (0.0546 inch)
1016 mm/min (40 ipm) 5.80 mm (0.2281 inch) 1.21 mm (0.0476 inch)
1270 mm/min (50 ipm) 4.61 mm (0.1816 inch) 0.73 mm (0.0289 inch)
45°
Stainless steel gouging profile
Torch angle Speed Width Depth
254 mm/min (10 ipm) 6.37 mm (0.2508 inch) 3.05 mm (0.1200 inch)
508 mm/min (20 ipm) 5.74 mm (0.2258 inch) 1.96 mm (0.0772 inch)
45°
60°
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-11
762 mm/min (30 ipm) 5.28 mm (0.2077 inch) 1.09 mm (0.0428 inch)
1016 mm/min (40 ipm) 4.83 mm (0.1901 inch) 1.73 mm (0.0680 inch)
1270 mm/min (50 ipm) 4.42 mm (0.1739 inch) 1.47 mm (0.0580 inch)
254 mm/min (10 ipm) 6.55 mm (0.2580 inch) 5.92 mm (0.2330 inch)
508 mm/min (20 ipm) 6.42 mm (0.2526 inch) 2.01 mm (0.0792 inch)
762 mm/min (30 ipm) 5.92 mm (0.2329 inch) 1.45 mm (0.0569 inch)
1016 mm/min (40 ipm) 5.36 mm (0.2110 inch) 1.10 mm (0.0432 inch)
1270 mm/min (50 ipm) 5.09 mm (0.2003 inch) 0.82 mm (0.0322 inch)
Page 72

operation
Common hand-cutting faults
The torch sputters and hisses, but does not produce an arc. The cause can be:
• The consumables are too tight. Loosen the consumables about 1/8th of a turn and try again. Never tighten the
consumables beyond just finger-tight.
The torch does not cut completely through the workpiece. The causes can be:
• The cut speed is too fast.
• The consumables are worn.
• The metal being cut is too thick.
• Gouging consumables are installed instead of cutting consumables.
• The work clamp is not attached properly to the workpiece.
• The gas pressure or gas flow rate is too low.
Cut quality is poor. The causes can be:
• The metal being cut is too thick.
• The wrong consumables are being used (gouging consumables are installed instead of cutting consumables, for
example).
• You are moving the torch too quickly or too slowly.
The arc sputters and consumables life is shorter than expected. The cause can be:
• Moisture in the gas supply.
• The gas pressure is too low.
How to use the machine torch
Since the Powermax45 and the T45m can be used with a wide variety of cutting tables, track burners, pipe bevelers,
and such, you will need to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specifics on operating the machine torch in
your configuration. However, the information in the following sections can help you optimize cut quality and maximize
consumable life.
Ensure the torch and table are set up correctly
• Use a square to align the torch at right angles to the workpiece.
• The torch may travel more smoothly if you clean, check, and “tune” the rails and drive system on the cutting table.
Unsteady machine motion can cause a regular, wavy pattern on the cut surface.
• Ensure that the torch does not touch the workpiece during cutting. Contact with the workpiece can damage the
shield and nozzle and affect the cut surface.
4-12 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 73

operation
Understand and optimize cut quality
There are several factors to consider in cut quality:
• Cut angle – The degree of angularity of the cut edge.
• Dross – The molten material that solidifies on the top or bottom of the workpiece.
• Straightness of the cut surface – The cut surface can be concave or convex.
The following sections explain how these factors can affect cut quality.
Cut or bevel angle
• A positive cut angle, or bevel, results when more material is removed from the top of the cut than from the bottom.
• A negative cut angle results when more material is removed from the bottom of the cut.
Problem
Negative cut angle
Square cut
Positive cut angle
Notes: The squarest cut angle will be on the right side with respect to the forward motion of the torch. The left side
will always have some degree of bevel.
To determine whether a cut-angle problem is being caused by the plasma system or the drive system, make a test cut
and measure the angle of each side. Next, rotate the torch 90° in its holder and repeat the process. If the angles are the
same in both tests, the problem is in the drive system.
If a cut-angle problem persists after “mechanical causes” have been eliminated (see Ensure the torch and table are set
up correctly on page 4-12), check the torch-to-work distance, especially if the cut angles are all positive or all negative.
Also consider the material being cut. If the metal is magnetized or hardened, you are more likely to experience cut angle
problems.
Dross
Some amount of dross will always be present when cutting with air plasma. However, you can minimize the amount and
type of dross by adjusting your system correctly for your application.
Cause
The torch is too low.
The torch is too high.
Solution
Raise the torch; or if you are using a torch
height control, increase the arc voltage.
Lower the torch; or if you are using a torch
height control, decrease the arc voltage.
Dross appears on the top edge of both pieces of the plate when the torch is too low (or voltage is too high if using a
torch height control). Adjust the torch or the voltage in small increments (5 volts or less) until the dross is reduced.
Low-speed dross forms when the torch’s cutting speed is too slow and the arc shoots ahead. It forms as a heavy,
bubbly deposit at the bottom of the cut and can be removed easily. Increase the speed to reduce this type of dross.
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-13
Page 74

operation
High-speed dross forms when the cutting speed is too fast and the arc lags behind. It forms as a thin, linear bead of
solid metal attached very close to the cut. It is welded to the bottom of the cut and is difficult to remove. To reduce
high-speed dross:
• Decrease the cutting speed.
• Decrease arc voltage to decrease the torch-to-work distance.
Notes: Dross is more likely to form on warm or hot metal than on cool metal. For example, the first
cut in a series of cuts will likely produce the least dross. As the workpiece heats up, more
dross may form on subsequent cuts.
Dross is more likely to form on mild steel than on stainless steel or aluminum.
Worn or damaged consumables may produce intermittent dross.
Straightness of the cut surface
A typical plasma cut surface is slightly concave.
The cut surface may become more concave or convex. Correct torch height is required to keep the cut surface
acceptably close to straight. Worn consumables also affect the straightness of the cut.
A strongly concave cut surface occurs when the torch-to-work distance is too low. Increase the torch-to-work
distance to straighten the cut surface.
A convex cut surface occurs when the torch-to-work distance is too great or the cutting current is too high.
First, try lowering the torch, then reduce the cutting current.
To pierce a workpiece using the machine torch
As with the hand torch, you can start a cut with the machine torch at the edge of the workpiece or by piercing the
workpiece. Piercing will result in a shorter consumable life than with edge starts.
The cut charts include a column for the height at which the torch should be when starting a pierce. For the Powermax45,
the pierce height is generally 2.5 times the torch cutting height. Refer to the cut charts for specifics.
The pierce delay must be sufficiently long that the arc can pierce the material before the torch moves, but not so long
that the arc “wanders” while trying to find the edge of a large hole.
When piercing maximum thicknesses, the ring of dross that forms during the pierce may become high enough to contact
the torch when the torch begins to move after the pierce is complete.
4-14 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 75

operation
Common machine-cutting faults
The torch pilot arc will initiate, but will not transfer. Causes can be:
• The work cables connection on the cutting table is not making good contact or the table is not properly grounded.
• The torch-to-work distance is too great.
The workpiece is not totally penetrated, and there is excessive sparking on the top of the workpiece. Causes can be:
• The work cable’s connection on the cutting table is not making good contact or the table is not properly grounded.
• The amperage is set too low. See the cut charts in the Torch Setup section for more information.
• The cut speed is too high. See the cut charts in the Torch Setup section for more information.
• The consumables are worn and need to be replaced.
• The metal being cut exceeds the maximum capacity. See T45v and T45m torch specifications in the Specifications
section.
Dross forms on the bottom of the cut. Causes can be:
• The cutting speed is not correct. See the cut charts in the Torch Setup section for more information.
• The amperage is set too low. See the cut charts in the Torch Setup section for more information.
• The consumables are worn and need to be changed.
The cut angle is not square. Causes can be:
• The direction of the torch travel is incorrect. The high-quality cut is always on the right with respect to the forward
motion of the torch.
• The distance between the torch and the workpiece is not correct.
• The cutting speed is not correct. See the cut charts in the Torch Setup section for more information.
• The consumables are worn and need to be replaced.
The consumable life is shortened. Causes can be:
• The arc current, arc voltage, travel speed, and other variables are not set as specified in the cut charts.
• Firing the arc in the air (beginning or ending the cut off of the plate surface). Starting at the edge is acceptable as
long as the arc makes contact with the workpiece when started.
• Starting a pierce with an incorrect torch height. For the Powermax45, the pierce height is generally 2.5times the
torch cutting height. Refer to the cut charts for specifics.
powermax
45
Service Manual 4-15
Page 76

operation
4-16 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 77

Section 5
TROUBLESHOOTING AND SYSTEM TESTS
In this section:
Theory of operation ....................................................................................................................................................................................5-2
General ..............................................................................................................................................................................................5-2
200–240V CSA and 230V CE 1-phase power supply functional description .............................................................5-2
400V CE 3-phase power supply functional description .......................................................................................................5-2
480V CSA 3-phase power supply functional description ...................................................................................................5-3
Sequence of operation ...................................................................................................................................................................5-4
Troubleshooting preparation ....................................................................................................................................................................5-5
Test equipment .................................................................................................................................................................................5-5
Troubleshooting procedures and sequence..............................................................................................................................5-5
External inspection ..........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Internal inspection ...........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Initial resistance check ..............................................................................................................................................................................5-7
200–240V CSA and 230V CE power supply overview ................................................................................................................5-8
400V CE power supply overview .........................................................................................................................................................5-9
480V CSA power supply overview ................................................................................................................................................... 5-10
Troubleshooting guide ...........................................................................................................................................................................5-11
Control Board LEDs............................................................................................................................................................................... 5-16
Use the control board Error and Reset LEDs to troubleshoot .......................................................................................... 5-17
System tests.............................................................................................................................................................................................5-18
Test 1 – voltage input .................................................................................................................................................................. 5-18
Test 2 – power board voltage checks .....................................................................................................................................5-19
Test 3 – VBUS and voltage balance ....................................................................................................................................... 5-20
Test 4 – solenoid valve ................................................................................................................................................................ 5-24
Test 5 – torch stuck open (TSO) or torch stuck closed (TSC) .........................................................................................5-25
Test 6 – plasma start ................................................................................................................................................................... 5-26
Test 7 – torch cap sensor ........................................................................................................................................................... 5-27
Test 8 – fan .................................................................................................................................................................................... 5-27
Test 9 – pressure transducer ..................................................................................................................................................... 5-28
Test 10 – power switch trip coil ................................................................................................................................................ 5-28
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-1
Page 78

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Theory of operation
General
Refer to the following functional description topics, to Sequence of operation on page 5-4, and to the Wiring
Diagrams section.
200–240V CSA and 230V CE 1-phase power supply functional description
AC power enters the system through the power switch (S1) to the input diode bridge (D48). The voltage from the diode
bridge supplies the power factor correction (PFC) boost converter, which provides a nominal 385VDC bus voltage. The
bus voltage then supplies voltage and current to the inverter and the flyback circuit power supply (DC to DC converter)
on the power board (PCB2). The power board provides noise suppression and spike protection. A “soft start” is
implemented via the power board resistor and relays (K1, K2).
The PFC boost converter consists of an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT Q2), PFC choke, and control circuit.
Itprovides a 385VDC bus voltage when the input AC voltage is between 200 and 240VAC.
The inverter consists of a dual IGBT package (Q3), the power transformer, a current sense transducer, and the control
circuit. The inverter operates as a pulse-width modulated half-bridge circuit driving an isolation transformer. The
secondary of the isolation transformer is rectified by the output bridge (D38).
The output circuitry consists of 2 current sense transducers located on the power board, the pilot arc IGBT (inside the
D38module), and the output choke.
The control board’s digital signal processor (DSP) monitors and regulates the system’s operation and safety circuits.
The amperage adjustment knob is used to set the output current to the desired value between 20 and 45 amps. The
system compares the set-point to the output current by monitoring the current sense transducers and adjusting the
pulse-width output of the inverter IGBTs (Q3). A trip coil on the power switch provides over-voltage protection.
400V CE 3-phase power supply functional description
AC power enters the system through the power switch (S1) to the input diode bridge (D48). The voltage from the
diode bridge supplies the power factor correction (PFC) choke, which provides a nominal 560VDC bus voltage. The
bus voltage then supplies voltage and current to the inverter and the flyback circuit power supply (DC to DC converter)
on the power board (PCB2). The power board provides noise suppression and spike protection. A “soft start” is
implemented via the power board resistor and relays (K2).
The inverter consists of a dual IGBT package (Q2), the power transformer, a current sense transducer, and the control
circuit. The inverter operates as a pulse-width modulated half-bridge circuit driving an isolation transformer. The
secondary of the isolation transformer is rectified by the output bridge (D40).
The output circuitry consists of 2 current sense transducers located on the power board, the pilot arc IGBT (inside the
D40module), and the output choke.
The control board’s digital signal processor(DSP) monitors and regulates the system’s operation and safety circuits.
The amperage adjustment knob is used to set the output current to the desired value between 20 and 45amps. The
system compares the set-point to the output current by monitoring the current sense transducers and adjusting the
pulse-width output of the inverter IGBT(Q2).
5-2 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 79

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
480V CSA 3-phase power supply functional description
AC power enters the system through the power switch (S1) to the input diode bridge (D48). The voltage from the
diode bridge supplies the power factor correction (PFC) choke, which provides a nominal 670VDC bus voltage. The
bus voltage then supplies voltage and current to the inverter and the flyback circuit power supply (DC to DC converter)
on the power board (PCB2). The power board provides noise suppression and spike protection. A “soft start” is
implemented via the power board resistor and relays (K2).
The inverter consists of a dual IGBT package (Q2), the power transformer, a current sense transducer, and the control
circuit. The inverter operates as a pulse-width modulated half-bridge circuit driving an isolation transformer. The
secondary of the isolation transformer is rectified by the output bridge (D40).
The output circuitry consists of 2 current sense transducers located on the power board, the pilot arc IGBT (inside the
D40module), and the output choke.
The control board’s digital signal processor (DSP) monitors and regulates the system’s operation and safety circuits.
The amperage adjustment knob is used to set the output current to the desired value between 20 and 45 amps. The
system compares the set-point to the output current by monitoring the current sense transducers and adjusting the
pulse-width output of the inverter IGBT (Q2).
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-3
Page 80

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Sequence of operation
Power OFF
•Connect the gas supply to the air fitting on the power supply.
•Connect the work lead to the workpiece.
•Plug in the power supply and make sure incoming power is ON if using a
line-disconnect box.
•Set the ON/OFF switch(S1) to ON(I).
•The green power ON LED illuminates, indicating the system is ready for
operation.
•All the fault LEDs should be extinguished (see the Troubleshooting guide
on page 5-11 for more information).
•Set the mode switch to the desired mode for cutting or gouging.
•Set the power switch(S1) to OFF(O).
•The gas solenoid valve(V1) closes.
•The gas flow stops.
•The arc extinguishes.
•Gas continues to flow for 20seconds.
•Drag the torch lightly across the workpiece to
make a cut.
•The workpiece drops after the cut.
•Release the plasma start trigger on the hand
torch or the remote start switch for the machine
torch.
•Turn the amperage adjustment knob to the gas test position.
•The gas solenoid valve(V1) opens to purge the system and to allow the
gas pressure to be set.
•Verify that the gas pressure LED illuminates green and is centered in the
pressure bar.
•Set the amperage adjustment knob to the desired output current (between
20 and 45amps) based on the thickness of the metal to be cut.
•The gas solenoid valve(V1) opens.
•The gas flow starts.
•The cutting arc starts.
•Position the torch on the workpiece.
•Pull the plasma start trigger on the hand torch
or press the remote start switch for the machine
torch.
•The gas solenoid valve(V1) closes.
•The gas flow stops.
•The power circuits are ready.
5-4 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 81

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Troubleshooting preparation
The complexity of the circuits requires that service technicians have a working knowledge of inverter power supply
theory. In addition to being technically qualified, technicians must perform all testing with safety in mind.
If questions or problems arise during servicing, call the Hypertherm Technical Services team listed in the front of this
manual.
Test equipment
• Multimeter with a variety of jumper leads, including E-ZHooks®.
Troubleshooting procedures and sequence
When performing the troubleshooting procedures,
• Read the Safety and Compliance Manual for detailed safety information;
• Refer to the Wiring Diagrams section for the system’s electrical schematic;
• Refer to the Component Replacement section for part replacement procedures;
• Refer to the Parts section to locate power supply components and torch components.
After the problem has been located and repaired, refer to the Sequence of operation flow diagram on page 5-4 to test
the power supply for proper operation.
Power OFF and disconnected
External inspection
Internal inspection
Resistance checks
Power ON
Troubleshooting guide
powermax
Troubleshooting tests
45
Service Manual 5-5
Page 82

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
• Turn off the power and remove the input power plug from its receptacle before
removing the cover from the power supply. If the power supply is connected directly to
a line disconnect box, switch the line disconnect to OFF(O). In the U.S., use a “lockout / tag-out” procedure until the service or maintenance work is complete. In other
countries, follow appropriate national or local safety procedures.
• Do not touch live electrical parts! If power is required for servicing, use extreme caution
when working near live electrical circuits. Dangerous voltages exist inside the power
supply that can cause serious injury or death.
• Do not attempt to repair the power board or control board. Do not cut away or remove
any protective conformal coating from either board. To do so will risk a short circuit
between the AC input circuit and the output circuit and may result in serious injury or
death.
DANGER
HOT PARTS CAN CAUSE SEVERE BURNS
• Allow the power supply to cool before servicing.
MOVING BLADES CAN CAUSE INJURY
• Keep hands away from moving parts.
STATIC ELECTRICITY CAN DAMAGE CIRCUIT BOARDS
• Put on a grounded wrist strap before handling PC boards.
External inspection
1. Inspect the exterior of the power supply for damage to the cover and external components, such as the power
cord and plug.
2. Inspect the torch and the torch lead for damage.
Internal inspection
1. Turn OFF the power, disconnect the power cord, and disconnect the gas supply.
2. Use a #2Phillips screwdriver to remove the 2 screws from the handle on the top of the power supply. Gently pull
on the end panel nearest the screw you are removing to keep pressure on the screw. When the screw is almost
out, tilt the screwdriver slightly to help pull the screw out of the recessed hole.
3. Tip the end panels back slightly so that you can get the edges of the handle out from underneath them. Set the
handle and screws aside. Continue to tilt the end panels outward to release the fan side of the cover from its track.
Then lift the cover off the power supply.
5-6 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 83

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
4. Remove the Mylar barrier from the power board side of the power supply. Be certain to replace the barrier when
you are finished working on the power supply.
5. Inspect the inside of the power supply, especially on the side with the power board. Look for broken or loose
wiring connections, burn and char marks, damaged components, and so on. Repair or replace as necessary.
Initial resistance check
All resistance values must be taken with the power cord disconnected and all internal power supply wires attached.
Perform the steps in Internal inspection on page 5-6 before continuing in this section.
• If resistance values are not close (±25%) to the values given in this section, isolate the problem by removing wires
attached to the resistance check points or component until the problem is found.
• After the problem has been located and repaired, refer to the Sequence of operation flow diagram on page 5-4
to test the power supply for proper operation.
1. With the power disconnected and the torch removed from the power supply, set the ON/OFF switch(S1) to
ON(I).
2. Check the resistance across the input leads (the leads are identified with “AC” printed on the power board).
• 200–240V CSA and 230V CE: resistance across the input leads = 75kΩ.
• 400V CE and 480V CSA: resistance across the input leads = 2.5MΩ.
3. Check the resistance from the input leads to ground to verify that it reads as open. For all power supplies, the
resistance from input to ground should read as > 20MΩ.
Note: With the power disconnected and the ON/OFF switch(S1) set to OFF(O), all circuits should read
asopen.
The electrical values shown are ±25%.
4. Check the output resistance for the values shown in the following table.
200–240V CSA and
Measure resistance from
Work lead to nozzle J21 to J17 J21 to J16 100 kΩ
Work lead to electrode J21 to J19 J21 to J18 20 kΩ
Electrode to nozzle J19 to J17 J18 to J16 120 kΩ
Output to ground > 20 MΩ
If no problems were found during the visual inspection or the initial resistance check, and the power supply still does not
operate correctly, see the Troubleshooting guide on page 5-11.
230V CE power board
location
400V CE and 480V
CSA power board
location
Approximate
values
Note: The Troubleshooting guide provides most probable causes and solutions. Study the system wiring diagram
and understand the theory of operation before troubleshooting. Before purchasing any major replacement
component, verify the problem with Hypertherm Technical Service or the nearest Hypertherm repair facility.
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-7
Page 84

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
200–240V CSA and 230V CE power supply overview
Control board (PCB1)
Flyback circuit
TP 19
W
192 VDC
+
PE (ground)
Power switch (S1)Power board (PCB2)
TP 18
TP 17
R
192 VDC
-
B
-
+
Inverter IGBT
Work lead connection (J21)
(Q3)
Test points
PFC IGBT (Q2)
Newer power board
Output diode and pilot arc
IGBT module (D38)
Input diode bridge
(D48)
Older power board
Input diode bridges
(D29, D39)
5-8 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 85

400V CE power supply overview
Control board (PCB1)
Power board (PCB2)
Flyback circuit
TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
PE (ground)
Power switch (S1)
Work lead connection (J21)
Output diode and pilot arc
IGBT module (D40)
Inverter IGBT (Q2)
TP17
W
~280 VDC
+
TP16
R
TP18
-
~280 VDC
Test points
B
-
+
Newer power board
Input diode bridge
(D48)
Older power board
Input diode bridges
(D28, D38)
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-9
Page 86

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
480V CSA power supply overview
Control board (PCB1)
Power board (PCB2)
Flyback circuit
PE (ground)
Power switch (S1)
Work lead connection (J21)
Output diode and pilot arc
IGBT module (D40)
Inverter IGBT (Q2)
TP17
W
~280 VDC
+
TP16
R
TP18
~280 VDC
-
Test points
B
-
+
Power board
Input diode bridge
(D48)
5-10 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 87

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Troubleshooting guide
See System tests on page 5-18 for detailed test procedures.
It is important to note, when troubleshooting a problem on the Powermax45, how the front panel LEDs operate. To help
diagnose transient problems, an illuminated or blinking LED, including the bottom bar on the gas pressure bar, may
continue to illuminate or blink for 10to 20seconds after the system is poweredOFF. Once the system is poweredON,
the LED should not illuminate or blink if the fault has been cleared.
Also, note that there is no static gas pressure reading. So the gas pressure LEDs may not indicate a low pressure
situation if the gas was not connected when the system was powered ON. Attempting to fire the torch without the gas
connected will cause the bottom yellow gas pressure LED to blink.
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
The ON/OFF power switch
is set to ON(I), but the
power ON LED is not
illuminated.
The power ON LED is
illuminated, the fault LED is
illuminated, and the bottom
LED on the gas pressure
bar is illuminated yellow and
is blinking.
AC
There is insufficient voltage
to the control circuits or
a short-circuited power
component.
There is insufficient gas
pressure to the machine.
•The system has no
incoming voltage or
an improper incoming
voltage.
•The power board is faulty.
•There is no gas attached
to the system.
•The gas supply line has a
restriction or the air filter
element is dirty.
•The reading at the
pressure transducer
is below the minimum
acceptable gas pressure.
•Check to see that the
system is plugged into
an appropriately-sized
circuit and that the circuit
breaker has not been
tripped.
•Perform Test 1 – voltage
input on page 5-18
to check the incoming
voltage and the power
switch.
•Ensure that the gas supply
is connected correctly.
•Check the gas supply line
for restrictions or damage.
•Check the air filter
element and replace it if
necessary.
•Perform Test 9 – pressure
transducer on page 5-28
to verify that the pressure
transducer functions
correctly.
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-11
Page 88

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
The power ON LED is
illuminated and the yellow
temperature LED is
illuminated.
AC
The power ON LED is
blinking.
The power ON LED is
illuminated and the torch
cap LED is illuminated.
AC
The internal system
temperature is either over
or under its operating range
(approximately -30°C to
80°C).
The incoming voltage is not
correct.
The cap-sensing circuit is
not satisfied.
•The power supply is too
cold.
•You have exceeded the
duty cycle. (For more
information about duty
cycle, see the Operation
section.)
•The incoming voltage
is either too high or too
low (a variance greater
than ±15% of the rated
voltage).
•The consumables are
loose, improperly installed,
or missing.
•The cap-sensor switch is
faulty.
•Allow the power supply
to warm up if it has been
extremely cold.
•Check the area around the
system to make sure that
the air flow is not blocked.
•If the duty cycle has been
exceeded, let the system
cool before using it again.
•Perform Test 8 – fan
on page 5-27 to make
sure the fan is operating
correctly.
•Perform Test 1 – voltage
input on page 5-18 to
check the incoming line
voltage.
•Correctly install the
consumables.
•Perform Test 7 – torch
cap sensor on page 5-27
to test the cap-sensor
switch.
The power ON LED is
illuminated and the torch
cap LED blinks.
AC
This indicates either a
“torch stuck open” or “torch
stuck closed” situation.
•The consumables are
installed incorrectly,
they are worn, or were
removed while the power
supply is ON.
•The torch plunger is stuck.
•The torch or lead has a
broken wire.
•Check the consumables
for wear and replace if
necessary.
•Make sure they are
properly installed.
•Verify that they are
finger-tight. Try loosening
them 1/8th of a turn and
restarting the power
supply.
•Perform Test 5 – torch
stuck open (TSO) or
torch stuck closed (TSC)
on page 5-25 and
replace the torch head
ifnecessary.
5-12 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 89

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
The power ON LED is
illuminated or is blinking
and the fault LED is
blinking.
AC
The power ON LED is
illuminated and the fault
LED and the temperature
LED alternately flash when
the system is powered ON.
AC
The power ON LED is
illuminated and no fault
LEDs are illuminated, but no
gas flows when the torch
trigger is pulled.
AC
A major fault has occurred
in the power supply.
The system was powered
on while the plasma start
signal was being sent.
The start signal is not
reaching the control board.
•Any of the fan, solenoid
valve, control board, or
power board may be
faulty.
•The system was powered
on while the torch trigger
was being pulled or the
trigger was activated too
soon after the system was
powered on.
•The start circuit is stuck
closed.
•The torch or torch lead
may be damaged.
•The power board may be
faulty.
•The control board may be
faulty.
•The error LED on the
control board should be
flashing. The number of
times it flashes between
pauses indicates which
components to test. See
Control Board LEDs on
page 5-16.
•Release the torch trigger
and turn OFF the power
supply and then turn it ON
again to reset the unit.
Be sure to allow time for
the soft start circuit to be
satisfied.
•Perform Test 6 – plasma
start on page 5-26 to test
the start signal.
•Ensure that the gas is
connected (gas pressure
LED will illuminate
yellow after the torch is
activated).
•Inspect the torch and
torch lead for damage.
•Verify that the control
board start LED
illuminates when the
trigger is pulled. If it
does not, perform Test
6 – plasma start on page
5-26 to check the start
signal from the power
board.
Gas flows when the system
is powered ON.
AC
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-13
The incoming gas pressure
is too high or the system is
in gas test mode.
•Verify that the mode
switch is not set to gas
test mode.
•The gas pressure from the
compressor or cylinder
may be too high.
•The gas solenoid valve
may be faulty.
•Check the gas supply to
make sure that it does not
exceed 9.3bar (135psi).
If necessary, reduce the
pressure.
•Perform Test 4 – solenoid
valve on page 5-24 to
verify that the gas solenoid
valve is functioning
correctly.
Page 90

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
When pulling the torch’s
trigger, gas flows from
the torch, but the torch
does not fire or fires only
for a short period of time,
or the pilot arc starts but
extinguishes before the
normal 5-second time-out
period.
Arc goes out while
cuttingor intermittently
willnot fire.
The consumables, torch,
or torch lead are not
functioning correctly, the
gas pressure may be too
low or too high, the air
quality may be poor, or
there is a voltage imbalance
on the power board.
The arc lost contact with
the workpiece.
•The consumables may be
worn or damaged.
•The torch or torch lead
may be damaged.
•The gas pressure is too
high or too low or the gas
supply is restricted.
•The gas filter element is
dirty.
•The power board is faulty.
•The work lead or work
lead connection may be
faulty.
•The material being cut
may require the use of
continuous pilot arc mode.
•Inspect the consumables,
torch, and lead. Replace
any damaged parts.
•Verify that the gas supply
is providing at least
4.5bar (65psi) and
does not exceed 9.3bar
(135psi).
•Repair any restrictions in
the supply line.
•Replace the gas filter
element if dirty.
•Perform Test 3 – VBUS
and voltage balance on
page 5-20 to test the
voltage balance on the
power board.
•If you are cutting
expanded metal, grate,
or any metal with holes,
set the mode switch to
continuous pilot arc mode.
•Check for loose
connections at the work
clamp and at the power
supply.
•Reposition the work lead
on the workpiece.
•Clean the cutting surface
to ensure a better
connection with the work
lead.
The cut quality is poor
orthe cut does not sever
the metal.
The consumables are worn,
there is a poor work lead
connection, the output from
the power supply is too
low, or the power board is
producing low current.
•The consumables need to
be replaced.
•The work lead may be
damaged or not properly
connected to the work
piece.
•The amps adjustment
knob may be set too low.
•The power board may be
faulty.
•Inspect the consumables
and replace if necessary.
•Inspect the work lead for
damage. Reposition it and
clean the work surface to
ensure good contact.
•Check the amps
adjustment knob setting. If
your input circuit is 200V,
34A; 240V, 28A; 400V,
10A; or 480V, 8.5A, turn
the knob to the highest
setting.
5-14 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 91

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
The pilot arc extinguishes
when you move the plasma
arc off the work piece while
still pulling the torch’s
trigger.
The continuous pilot arc
feature is not working.
•The mode switch may be
set incorrectly.
•The power board or the
control board may be
faulty.
•Verify that the mode
switch is set to continuous
pilot arc.
•Perform Test 2 – power
board voltage checks
on page 5-19 andTest
3 – VBUS and voltage
balance on page 5-20 to
verify that the power board
is functioning properly. If
the power board is faulty,
replace it. Otherwise,
replace the control board.
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-15
Page 92

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Control Board LEDs
The Powermax45 control board (PCB1) has 4 diagnostic LEDs.
Start
Transfer (XFR)
Error
Reset/watchdog
Control board
Ribbon cable
The control board LEDs are:
• Start – The power supply has a start signal. This LED illuminates when the power supply receives a start signal and
remains illuminated during normal operation.
• Transfer – This LED illuminates when there is proper arc transfer between the torch and the workpiece, and will flash
during continuous pilot arc operation (such as when cutting expanded metal or moving the arc off the plate
and then back on).
• Error – The Error LED illuminates whenever there is a fault in the system. If the Fault LED on the front panel flashes
and the Error LED on the control board also flashes, there is a major fault in the system. The number of
flashes between pauses indicates which component may have failed.
• Reset – This LED illuminates when the reset circuit is active or the watchdog circuit fires.
During normal operation, the power ON LED on the front of the power supply and the Start and Transfer LEDs on the
control board illuminate. When a problem occurs with the system, one or more of the LEDs on the front of the power
supply and the Error LED or the Reset LED on the control board may illuminate or flash.
5-16 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 93

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Use the control board Error and Reset LEDs to troubleshoot
The Error and Reset LEDs provide information to use when troubleshooting a system failure. If the LEDs on the front of
the power supply are flashing, look at the Error LED on the control board to determine where the fault may be. Count the
number of flashes and then look at the table below to determine the corrective action.
Reset LED
When the control board’s Reset LED illuminates, the voltages on the power board may be incorrect. Perform the
following tests at J7 on 200–240V CSA power supplies and 230V CE power supplies or J8 on 400V CE and 480V
CSA power supplies (the pin numbers are the same for all power supplies) on the power board (see Test 2 – power
board voltage checks on page 5-19):
• Test pin 25 to ground for 3.3VDC (±10%).
• Test pin 24 to ground for 5VDC (±10%).
• Test pin 12 to ground for 2.2VDC (±10%).
If the values you find are not within ±10% of the above values, detach the control board’s ribbon cable and perform
the tests again. If you find the correct values the second time, replace the control board. Otherwise, replace the power
board.
Error LED
The number of times the Error LED flashes indicates the problem detected. Each flash is a half-second long and each
series of flashes is separated by a 2-second pause. See System tests on page 5-18 for detailed test procedures.
The following table shows the meaning associated with each set of flashes.
Number of error
LED flashes
1 Faulty control board Replace the control board.
2 Faulty power board Replace the power board.
3
4 Faulty gas solenoid valve Replace the gas solenoid valve.
Problem indicated Solution
•Perform Test 3 – VBUS and voltage balance on page 5-20.
If any of the values are incorrect, replace the power board.
•Perform Test 2 – power board voltage checks on page
Either a faulty power board
or a faulty control board
5-19. If any of the values for pins 5, 7, or 12 are incorrect,
remove the control board and test again. If the values are
correct, replace the control board.
•When performing test 2, if the values for pins 5, 7, and 12
are correct, but any other values are incorrect, replace the
power board.
5 Faulty fan Replace the fan.
6 Machine motion relay fault Replace the power board.
powermax
45
Service Manual 5-17
Page 94

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
System tests
There is a ground clip near the top of the rear end cap that can be used as ground for any tests that require the
multimeter to be attached to ground. There is also a ground on the heat sink with access next to the power board and
below the power switch.
Ground wire clip
WARNING
Voltages of up to 50VDC continue to be present on the DC bus for at least 30 seconds after
disconnecting the input power. Allow bus voltages to dissipate before performing any tests.
Test 1 – voltage input
Check the incoming voltage and the line voltage to the top of the power switch (S1).
1. Disconnect the electrical power and set the ON/OFF switch to OFF (O).
2. Once you have your test leads in place, reconnect the electrical power. Leave the ON/OFF switch set to OFF. The
voltage should equal the line voltage of the incoming circuit.
3. If the AC voltage is incorrect, check to see that you have power to the unit. If you do have power, check the power
cord for damage.
4. With the electrical power connected, set the ON/OFF switch to ON (I), and measure the AC voltage from J1 to J2
(labeled “AC” on the power board). This value should be the same as the incoming line voltage. If it is not, check
the ON/OFF switch.
5. If the power ON LED is still illuminated, perform Test 2 – power board voltage checks on page 5-19 to determine
whether the power board or the control board is faulty.
Note: All values can be ±15%.
5-18 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 95

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Single phase Three phase (CE) Three phase (CSA)
Black (CSA)
L
Brown (CE)
White (CSA)
N
Blue (CE)
Green (CSA)
PE
Green/yellow (CE)
L1 Brown L1 Black
L2 Black L2 White
L3 Gray L3 Red
PE Green/yellow PE Green
Test 2 – power board voltage checks
With the power ON, use a meter to verify the voltages at the J7 pins (J8 on 400V CE and 480V CSA power supplies)
listed in the following table to be certain that the power board is functioning correctly. If any of the values are incorrect,
replace the power board.
CAUTION
Do not use -VBUS as ground – doing so could destroy the power supply. Instead ground to either the
ground wire clip on the rear panel or to the heat sink as shown below.
Note: All values can be ±10%.
J7 or J8 pin number to
ground
19
21
18
(200–240 and 230V
only)
20 IFB (output current) < 0.1VDC < 0.1VDC
22 ITF (transfer current) < 0.1VDC < 0.1VDC
25 3.3VDC 3.3VDC ±5% 3.3VDC ±5%
24 5VDC 5VDC ±5% 5VDC ±5%
Expected value
Test
VACR (rectified AC
line voltage)
VBUS (DC bus
voltage)
IPFC (input current) < 0.1VDC Not applicable
(200–240V CSA or
230V CE)
1.95V at 230 line
voltage
2.28VDC at 385VBUS
2.7V at 400 line voltage (CE)
2.016VDC at 480 line voltage (CSA)
2.178VDC at 560VBUS (CE)
2.016VDC at 670VBUS (CSA)
Expected value
(400V CE or 480V CSA)
12 24V sense pin 2.2VDC 2.2VDC
16 Start signal
powermax
3.2VDC closed
0VDC open
45
Service Manual 5-19
3.2VDC closed
0VDC open
Page 96

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
J7 (200–240V CSA / 230V CE)
J8 (400 V CE / 480V CSA)
1
2
25
26
Note: To test the values at pin 16, you must have the torch and power supply positioned such that you can safely pull
and release the torch’s trigger.
Ground to the ground wire clip or to the heat sink
TP 19
TP 18
TP 17
W
R
192 VDC
+
B
192 VDC
-
+
-
Test 3 – VBUS and voltage balance
Test the power board to ensure that the circuits are balanced. There are three procedures below. Use the first
procedure if you have a 200–240V CSA power supply or a 230V CE power supply. Use the second procedure if you
have a 400VCE power supply. Use the third procedure if you have a 480V CSA power supply.
For this test, you can use the test point loops or you can test on the capacitor screws. The test points are labeled on the
back of the power board, as are the voltages and positive and negative capacitor terminals.
CAUTION
To test using the test points, do not use a multimeter with test probes. Use E-Z Hook leads instead
and attach them to the test point loops.
5-20 powermax
45
Service Manual
Page 97

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
TP 19
W
-
+
-
+
TP 18
R
TP 17
B
192 VDC
192 VDC
Test for 200–240V CSA and 230V CE power supplies
1. Turn OFF the power.
2. Position the multimeter leads to measure the boosted bus voltage on the power board by attaching the test leads
to TP (test point)19 and TP18. Turn on the power. The multimeter should read 385VDC. If you get a value other
than 385VDC, multiply the reading by 0.00601. Compare that value to a reading at pin 21 on J7. They should
have the same value.
3. Turn the power OFF. Attach the E-ZHooks to TP19 and TP17. Turn the power ON after you have connected the
multimeter. This value should be 192.5VDC or one-half of whatever value you found in step2.
Note: All values can be ±10%.
4. Turn the power OFF and move the E-Z Hooks to TP18 and TP17. Turn the power ON after you have connected
the multimeter. This value should be 192.5VDC or one-half of whatever value you found in step2.
5. The values found in steps3 and4 should be approximately equal. If they differ by more than 30V, replace the
power board.
Step 3
powermax
TP 19
TP 18
W
192 VDC
+
Step 2
45
Service Manual 5-21
Step 4
TP 17
R
B
192 VDC
-
+
-
Page 98

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
TP17
W
+
-
+
-
TP18
B
TP16
R
~280 VDC
~280 VDC
Test for 400V CE power supplies
For this test, you can use the test point loops or you can test on the capacitor screws. The test points are labeled on the
back of the power board, as are the voltages and positive and negative capacitor terminals.
CAUTION
To test using the test points, do not use a multimeter with test probes. Use E-Z Hook leads instead
and attach them to the test point loops.
1. Turn OFF the power.
2. Position the multimeter leads to measure the voltage on the power board by attaching the test leads with the
negative lead on TP 17 and the positive lead on TP 16. Turn on the power. The multimeter should read 560VDC.
If you get a value other than 560VDC, multiply the reading by 0.00601. Compare that value to a reading at pin 21
on J8. They should have the same value.
3. Attach E-Z Hooks to TP (test point)17 and TP18. Turn the power ON after you have connected the multimeter.
This value should be 280VDC or one-half of whatever value you found in step2.
Note: All values can be ±10%.
4. Turn the power OFF and move the E-Z Hooks to TP18 and TP16. Turn the power ON after you have connected
the multimeter. This value should be 280VDC or one-half of whatever value you found in step2.
5. The values found in steps3 and4 should be approximately equal. If they differ by more than 30V, replace the
power board.
Step 2
Step 3
TP17
W
~280 VDC
-
+
Step 4
5-22 powermax
TP16
R
TP18
B
~280 VDC
-
+
45
Service Manual
Page 99

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
TP17
W
+
-
+
-
TP18
B
TP16
R
~280 VDC
~280 VDC
Test for 480V CSA power supplies
For this test, you can use the test point loops or you can test on the capacitor screws. The test points are labeled on the
back of the power board, as are the voltages and positive and negative capacitor terminals.
CAUTION
To test using the test points, do not use a multimeter with test probes. Use E-Z Hook leads instead
and attach them to the test point loops.
1. Turn OFF the power.
2. Position the multimeter leads to measure the voltage on the power board by attaching the test leads with the
negative lead on TP17 and the positive lead on TP16. Turn on the power. The multimeter should read 670VDC.
If you get a value other than 670VDC, multiply the reading by 0.003. Compare that value to a reading at pin21 on
J8. They should have the same value.
3. Attach E-Z Hooks to TP (test point)17 and TP18. Turn the power ON after you have connected the multimeter.
This value should be 335VDC or one-half of whatever value you found in step2.
Note: All values can be ±10%.
4. Turn the power OFF and move the E-Z Hooks to TP18 and TP16. Turn the power ON after you have connected
the multimeter. This value should be 335VDC or one-half of whatever value you found in step2.
5. The values found in steps3 and4 should be approximately equal. If they differ by more than 30V, replace the
power board.
Step 2
Step 3
powermax
TP16
~280 VDC
R
TP18
B
-
+
Step 4
45
Service Manual 5-23
TP17
W
~280 VDC
-
+
Page 100

TroubleshooTing and sysTem TesTs
Test 4 – solenoid valve
If gas is not flowing properly, test the solenoid valve for proper operation.
1. There is an LED on the solenoid valve that illuminates red when the torch is fired or when the amperage control
knob is set to gas text mode. It stays illuminated until postflow stops. Turn the amperage knob to gas test and
verify that the LED illuminates.
2. Place a jumper from pin4 of J3 (J4 for 400V CE and 480V CSA power supplies) on the power board to ground.
You should hear the valve click.
3. If you do not hear the valve click or the LED does not illuminate and a voltage check on pin4 of J3 (or J4) reads
24VDC, replace the solenoid valve.
Solenoid valve LED
J3 or J4
PE (ground)
TP 19
TP 18
192 VDC
TP 17
R
B
-
+
192 VDC
W
-
+
5-24 powermax
45
Service Manual
 Loading...
Loading...