Page 1

1
4
5
6
1
5
-2
5
f
t
4
.
5
-7
.
5
m
3
5
-5
0
f
t
1
2
-1
5
m
6
.
0
B
A
R
5
.
0
4
.
0
P
S
I
8
0
7
0
5
0
6
0
8
0
A
M
P
S
1
2
0
9
2
6
1
2
0
9
2
5
1
2
0
9
7
8
1
2
0
9
2
7
1
2
0
9
2
8
1
2
0
9
2
8
1
2
0
9
2
9
1
2
0
9
7
7
1
1
0
3
7
8
Re
v
.
A
6.0
BAR
5.0
4.0
PSI
80
70
50
60
60
40
AM
PS
80
25
AC
+
_
2
3
1
4
5
6
1
5
5
0f
t
4
.
5
1
5m
1
5
2
5f
t
4
.
5
7
.
5m
3
5
5
0f
t
1
2
-
1
5m
6
.
0
B
A
R
5
.
0
4
.
0
P
S
I
8
0
7
0
5
0
6
0
8
0
A
M
P
S
8
0
A
M
P
S
powermax1000
Plasma Arc
Cutting System
Service Manual
804300 – Revision 1
®
Page 2

powermax1000
Service Manual
(P/N 804300)
Revision 1 – May, 2006
Hypertherm, Inc.
Hanover, NH USA
www.hypertherm.com
© Copyright 2006 Hypertherm, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Hypertherm and Powermax are trademarks of Hypertherm, Inc.
and may be registered in the United States and/or other countries
Page 3

6/15/05
H
ypertherm, Inc.
Etna Road, P.O. Box 5010
Hanover, NH 03755 USA
6
03-643-3441 Tel (Main Office)
603-643-5352 Fax (All Departments)
info@hypertherm.com (Main Office Email)
8
00-643-9878 Tel (Technical Service)
technical.service@hypertherm.com (Technical Service Email)
800-737-2978 Tel (Customer Service)
c
ustomer.service@hypertherm.com (Customer Service Email)
Hypertherm Automation
5 Technology Drive, Suite 300
West Lebanon, NH 03784 USA
603-298-7970 Tel
603-298-7977 Fax
Hypertherm Plasmatechnik, GmbH
Technologiepark Hanau
Rodenbacher Chaussee 6
D-63457 Hanau-Wolfgang, Deutschland
49 6181 58 2100 Tel
49 6181 58 2134 Fax
49 6181 58 2123 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm (S) Pte Ltd.
No. 19 Kaki Bukit Road 2
K.B. Warehouse Complex
Singapore 417847, Republic of Singapore
65 6 8
41 2
489 Tel
65 6 841 2490 Fax
65 6 841 2489 (Technical Service)
Hyper
therm (Shanghai) T
r
ading Co., Ltd.
Unit 1308-09, Careri Building
432 West Huai Hai Road
Shanghai, 2
000
52
PR China
86-21 5258 3330/1 Tel
8
6-21 52
5
8 3332 Fax
Hypertherm
Branc
h of Hyper
therm, U
K, U
C
PO Box 244
Wigan, Lancashire, England WN8 7WU
00 8
00 332
4 9
7
3
7 T
el
00 8
00 4973 7329 Fax
00 800 4973 7843 (Technical Service)
F
rance (Representative office)
15 Impasse des Rosiers
95610 Eragny, France
0
0 800 3324 9737 Tel
00 800 4973 7329 Fax
H
ypertherm S.r.l.
Via Torino 2
20123 Milano, Italia
3
9 02 725 46 312 Tel
39 02 725 46 400 Fax
39 02 725 46 314 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm Europe B.V.
Vaartveld 9
4704 SE Roosendaal, Nederland
31 165 596907 Tel
31 165 596901 Fax
31 165 596908 Tel (Marketing)
31 165 596900 Tel (Technical Service)
00 800 49 73 7843 Tel (Technical Service)
Japan (Representative office)
1952-14 Yata-Natsumegi
Mishima City, Shizuoka Pref.
411-0801 Japan
81 0 559 75 7387 Tel
81 0 559 75 7376 Fax
HYPERTHERM BRASIL LTDA.
Rua Jati, 33
CEP 07180-350 Cumbica
Guarulhos, SP - Brasil
5
5 11 6
4
82 1087 Tel
55 11 6482 0591 Fax
Page 4

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY (EMC)
EMC INTRODUCTION
Hypertherm's CE-marked equipment is built
in compliance with standard EN50199. The
equipment should be installed and used in
accordance with the information below to
achieve electromagnetic compatibility.
The limits required by EN50199 may not be
adequate to completely eliminate interference when the affected equipment is in
close proximity or has a high degree of
sensitivity. In such cases it may be necessary to use other measures to further
reduce interference.
This plasma equipment is designed for use
only in an industrial environment.
INSTALLATION AND USE
The user is responsible for installing and
using the plasma equipment according to
the manufacturer's instructions. If electromagnetic disturbances are detected then it
shall be the responsibility of the user to resolve the situation with the technical assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases
this remedial action may be as simple as
earthing the cutting circuit, see Earthing of
Workpiece. In other cases it could involve
constructing an electromagnetic screen
enclosing the power source and the work
complete with associated input filters. In all
cases electromagnetic disturbances must
be reduced to the point where they are no
longer troublesome.
ASSESSMENT OF AREA
Before installing the equipment the user
shall make an assessment of potential electromagnetic problems in the surrounding
area. The following shall be taken into
account:
a. Other supply cables, control cables,
signalling and telephone cables; above,
below and adjacent to the cutting equipment.
b. Radio and television transmitters and
receivers.
c. Computer and other control equipment.
d. Safety critical equipment, for example
guarding of industrial equipment.
e. Health of the people around, for
example the use of pacemakers and hearing aids.
f. Equipment used for calibration or measurement.
g. Immunity of other equipment in the environment. User shall ensure that other
equipment being used in the environment is
compatible. This may require additional
protection measures.
h. Time of day that cutting or other activities
are to be carried out.
Earthing of Workpiece
Where the workpiece is not bonded to earth
for electrical safety, nor connected to earth
because of its size and position, for example,
ship's hull or building steelwork, a connection
bonding the workpiece to earth may reduce
emissions in some, but not all instances.
Care should be taken to prevent the earthing
of the workpiece increasing the risk of injury
to users, or damage to other electrical equipment. Where necessary, the connection of
the workpiece to earth should be made by a
direct connection to the workpiece, but in
some countries where direct connection is
not permitted, the bonding should be
achieved by suitable capacitances selected
according to national regulations.
Note. The cutting circuit may or may not be
earthed for safety reasons. Changing the
earthing arrangements should only be authorized by a person who is competent to
assess whether the changes will increase
the risk of injury, for example, by allowing
parallel cutting current return paths which
may damage the earth circuits of other
equipment. Further guidance is given in
IEC/TS 62081 Arc Welding Equipment
Installation and Use.
Screening and Shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other
cables and equipment in the surrounding
area may alleviate problems of interference.
Screening of the entire plasma cutting
installation may be considered for special
applications.
The size of the surrounding area to be
considered will depend on the structure of
the building and other activities that are taking place. The surrounding area may extend
beyond the boundaries of the premises.
METHODS OF REDUCING EMISSIONS
Mains Supply
Cutting equipment must be connected to the
mains supply according to the manufacturer's recommendations. If interference
occurs, it may be necessary to take
additional precautions such as filtering of
the mains supply. Consideration should be
given to shielding the supply cable of permanently installed cutting equipment, in
metallic conduit or equivalent. Shielding
should be electrically continuous throughout
its length. The shielding should be connected to the cutting mains supply so that good
electrical contact is maintained between the
conduit and the cutting power source
enclosure.
Maintenance of Cutting Equipment
The cutting equipment must be routinely
maintained according to the manufacturer's
recommendations. All access and service
doors and covers should be closed and
properly fastened when the cutting
equipment is in operation. The cutting
equipment should not be modified in any
way except for those changes and adjustments covered in the manufacturer's
instructions. In particular, the spark gaps of
arc striking and stabilizing devices should
be adjusted and maintained according to
the manufacturer's recommendations.
Cutting Cables
The cutting cables should be kept as short
as possible and should be positioned close
together, running at or close to the floor
level.
Equipotential Bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the
cutting installation and adjacent to it should
be considered. However, metallic components bonded to the workpiece will increase
the risk that the operator could receive a
shock by touching these metallic
components and the electrode at the same
time. The operator should be insulated from
all such bonded metallic components.
Hypertherm Plasma Systems i
01/25/05
Page 5

WARRANTY
ii Hypertherm Plasma Systems
9-01
WARNING
Genuine Hypertherm parts are the factory-recommended
replacement parts for your Hypertherm system. Any damage
caused by the use of other than genuine Hypertherm parts may
not be covered by the Hypertherm warranty.
WARNING
You are responsible for the safe use of the Product.
Hypertherm does not and cannot make any guarantee or
warranty regarding the safe use of the Product in your
environment.
GENERAL
Hypertherm, Inc. warrants that its Products shall be free from
defects in materials and workmanship, if Hypertherm is notified
of a defect (i) with respect to the power supply within a period
of two (2) years from the date of its delivery to you, with the
exception of Powermax Series power supplies, which shall be
within a period of three (3) years from the date of delivery to
you, and (ii) with respect to the torch and leads within a period
of one (1) year from its date of delivery to you. This warranty
shall not apply to any Product which has been incorrectly
installed, modified, or otherwise damaged. Hypertherm, at its
sole option, shall repair, replace, or adjust, free of charge, any
defective Products covered by this warranty which shall be
returned with Hypertherm’s prior authorization (which shall not
be unreasonably withheld), properly packed, to Hypertherm’s
place of business in Hanover, New Hampshire, or to an
authorized Hypertherm repair facility, all costs, insurance and
freight prepaid. Hypertherm shall not be liable for any repairs,
replacement, or adjustments of Products covered by this
warranty, except those made pursuant to this paragraph or with
Hypertherm’s prior written consent. The warranty above is
exclusive and is in lieu of all other warranties, express,
implied, statutory, or otherwise with respect to the
Products or as to the results which may be obtained
therefrom, and all implied warranties or conditions of
quality or of merchantability or fitness for a particular
purpose or against infringement. The foregoing shall
constitute the sole and exclusive remedy for any breach
by Hypertherm of its warranty. Distributors/OEMs may offer
different or additional warranties, but Distributors/OEMs are
not authorized to give any additional warranty protection to you
or make any representation to you purporting to be binding
upon Hypertherm.
PATENT INDEMNITY
Except only in cases of products not manufactured by
Hypertherm or manufactured by a person other than
Hypertherm not in strict conformity with Hypertherm’s
specifications and in cases of designs, processes, formulae, or
combinations not developed or purported to be developed by
Hypertherm, Hypertherm will defend or settle, at its own
expense, any suit or proceeding brought against you alleging
that the use of the Hypertherm product, alone and not in
combination with any other product not supplied by
Hypertherm, infringes any patent of any third party. You shall
notify Hypertherm promptly upon learning of any action or
threatened action in connection with any such alleged
infringement, and Hypertherm’s obligation to indemnify shall be
conditioned upon Hypertherm’s sole control of, and the
indemnified party’s cooperation and assistance in, the defense
of the claim.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
In no event shall Hypertherm be liable to any person or
entity for any incidental, consequential, indirect, or
punitive damages (including but not limited to lost profits)
regardless of whether such liability is based on breach of
contract, tort, strict liability, breach of warranties, failure of
essential purpose or otherwise and even if advised of the
possibility of such damages.
LIABILITY CAP
In no event shall Hypertherm’s liability, whether such
liability is based on breach of contract, tort, strict liability,
breach of warranties, failure of essential purpose or
otherwise, for any claim action suit or proceeding arising
out of or relating to the use of the Products exceed in the
aggregate the amount paid for the Products that gave rise
to such claim.
INSURANCE
At all times you will have and maintain insurance in such
quantities and types, and with coverage sufficient and
appropriate to defend and to hold Hypertherm harmless in
the event of any cause of action arising from the use of the
Products.
NATIONAL AND LOCAL CODES
National and Local codes governing plumbing and electrical
installation shall take precedent over any instructions
contained in this manual. In no event shall Hypertherm be
liable for injury to persons or property damage by reason of any
code violation or poor work practices.
TRANSFER OF RIGHTS
You may transfer any remaining rights you may have
hereunder only in connection with the sale of all or substantially
all of your assets or capital stock to a successor in interest who
agrees to be bound by all of the terms and conditions of this
Warranty.
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
powermax1000 Service Manual iii
1
Electromagnetic Compatibility.......................................................................................................................................i
Warranty.......................................................................................................................................................................ii
Section 1 Safety
Recognize safety information ...................................................................................................................................1-2
Follow safety instructions..........................................................................................................................................1-2
Cutting can cause fire or explosion...........................................................................................................................1-2
Electric shock can kill................................................................................................................................................1-3
Cutting can produce toxic fumes ..............................................................................................................................1-3
A plasma arc can cause injury and burns.................................................................................................................1-4
Arc rays can burn eyes and skin...............................................................................................................................1-4
Grounding safety ......................................................................................................................................................1-4
Compressed gas equipment safety ..........................................................................................................................1-5
Gas cylinders can explode if damaged.....................................................................................................................1-5
Noise can damage hearing.......................................................................................................................................1-5
Pacemaker and hearing aid operation......................................................................................................................1-5
A plasma arc can damage frozen pipes....................................................................................................................1-5
Additional safety information.....................................................................................................................................1-5
Warning label............................................................................................................................................................1-6
Section 1a Sécurité
Identifier les consignes de sécurité.........................................................................................................................1a-2
Suivre les instructions de sécurité ..........................................................................................................................1a-2
Danger Avertissement Précaution ........................................................................................................................1a-2
Le coupage peut provoquer un incendie ou une explosion ....................................................................................1a-2
Prévention des incendies, Prévention des explosions...................................................................................1a-2
Risque d’explosion argon-hydrogène et méthane..........................................................................................1a-2
Détonation de l’hydrogène lors du coupage de l’aluminium...........................................................................1a-2
Les chocs électriques peuvent être fatals...............................................................................................................1a-3
Prévention des chocs électriques ..................................................................................................................1a-3
Le coupage peut produire des vapeurs toxiques....................................................................................................1a-3
L’arc plasma peut provoquer des blessures ou des brûlures .................................................................................1a-4
Torches à allumage instantané ......................................................................................................................1a-4
Les rayons de l’arc peuvent brûler les yeux et la peau...........................................................................................1a-4
Protection des yeux, Protection de la peau, Zone de coupage ....................................................................1a-4
Mise à la masse et à la terre...................................................................................................................................1a-4
Câble de retour, Table de travail, Alimentation ...............................................................................................1a-4
Sécurité des bouteilles de gaz comprimé ...............................................................................................................1a-5
Les bouteilles de gaz comprimé peuvent exploser en cas de dommages .............................................................1a-5
Le bruit peut provoquer des problèmes auditifs......................................................................................................1a-5
Pacemakers et prothèses auditives........................................................................................................................1a-5
Un arc plasma peut endommager les tuyaux gelés................................................................................................1a-5
Étiquette de sécurité ...............................................................................................................................................1a-6
Page 7

TABLE OF CONTENTS
iv powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Seccíon 1b Seguridad
Reconocimiento de información de seguridad........................................................................................................1b-2
Siga las instrucciones de seguridad .......................................................................................................................1b-2
Peligro…Advertencia…Precaución ........................................................................................................................1b-2
Los cortes pueden provocar incendios o explosiones ............................................................................................1b-2
Prevención ante el fuego, Prevención ante explosiones ...............................................................................1b-2
Peligro de explosión argón-hidrógeno y metano............................................................................................1b-2
Detonación de hidrógeno con el corte de aluminio........................................................................................1b-2
El choque eléctrico puede provocar la muerte .......................................................................................................1b-3
Prevención ante el electrochoque..................................................................................................................1b-3
Los cortes pueden producir humos tóxicos ............................................................................................................1b-3
El arco de plasma puede causar lesiones y quemaduras ......................................................................................1b-4
Antorchas de encendido instantáneo.............................................................................................................1b-4
Los rayos del arco pueden producir quemaduras en los ojos y en la piel ..............................................................1b-4
Protección para los ojos, Protección para la piel, Área de corte....................................................................1b-4
Seguridad de toma a tierra .....................................................................................................................................1b-4
Cable de trabajo, Mesa de trabajo, Potencia primaria de entrada.................................................................1b-4
Seguridad de los equipos de gas comprimido........................................................................................................1b-5
Los cilindros de gas pueden explotar si están dañados .........................................................................................1b-5
El ruido puede deteriorar la audición ......................................................................................................................1b-5
Operación de marcapasos y de audífonos .............................................................................................................1b-5
Un arco plasma puede dañar tubos congelados ....................................................................................................1b-5
Etiqueta de advertencia ..........................................................................................................................................1b-6
Section 2 Specifications
Power supply ............................................................................................................................................................2-2
Dimensions and weight ....................................................................................................................................2-3
T60 torches...............................................................................................................................................................2-4
Dimensions ......................................................................................................................................................2-5
Symbols and markings .............................................................................................................................................2-6
S Mark............................................................................................................................................................2-6
IEC symbols .....................................................................................................................................................2-6
Section 3 Maintenance
Controls and indicators .............................................................................................................................................3-3
Indicator LEDs..................................................................................................................................................3-3
Theory of operation...................................................................................................................................................3-4
General ............................................................................................................................................................3-4
Functional description ......................................................................................................................................3-4
Sequence of operation .....................................................................................................................................3-5
Troubleshooting preparation.....................................................................................................................................3-6
Test equipment.................................................................................................................................................3-6
Troubleshooting procedures and sequence.....................................................................................................3-6
External inspection...........................................................................................................................................3-6
Internal inspection ............................................................................................................................................3-7
Initial resistance check..............................................................................................................................................3-7
Page 8

TABLE OF CONTENTS
powermax1000 Service Manual v
1
Check power switch .........................................................................................................................................3-8
Hypertherm IGBT tester ...................................................................................................................................3-9
Indicator LEDS and device tests ......................................................................................................................3-9
IGBT test preparation.....................................................................................................................................3-10
IGBT device test using the Hypertherm tester ...............................................................................................3-10
Troubleshoot the Hypertherm IGBT tester .....................................................................................................3-11
Schematic for building an IGBT tester............................................................................................................3-11
IGBT device test using non-Hypertherm tester ..............................................................................................3-12
Troubleshooting guide ............................................................................................................................................3-14
Control board LEDs........................................................................................................................................3-18
Test 1 – voltage input .....................................................................................................................................3-19
Test 2 – voltage balance ................................................................................................................................3-20
Test 3 – output diodes ....................................................................................................................................3-21
Test 4 – pilot arc IGBT (Q8) ...........................................................................................................................3-22
Test 5 – inverter IGBT (Q6) and PFC IGBT (Q7) ...........................................................................................3-23
Test 6 – flyback circuit ....................................................................................................................................3-24
Test 7 – torch stuck open (TSO) ....................................................................................................................3-25
Test 8 – plasma start ......................................................................................................................................3-26
Test 9 – torch cap sensor ...............................................................................................................................3-26
Test 10 – gas solenoid ...................................................................................................................................3-27
Test 11 – incoming line voltage (VACR) .........................................................................................................3-27
Test 12 – pressure switch...............................................................................................................................3-27
Test 13 – fan...................................................................................................................................................3-27
Test 14 – AUX switch .....................................................................................................................................3-28
Test 15 – flyback circuit failure .......................................................................................................................3-28
T60 hand torch connector pinouts and assembly ...................................................................................................3-29
T60M machine torch connector pinouts and assembly ..........................................................................................3-30
Component replacement ........................................................................................................................................3-31
Power cord replacement ................................................................................................................................3-31
Torch replacement..........................................................................................................................................3-32
Filter element replacement.............................................................................................................................3-34
Work cable replacement ................................................................................................................................3-35
Capacitor replacement ...................................................................................................................................3-36
Heat sink component replacement.................................................................................................................3-37
Section 4 Parts – power supply
Exterior .....................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Interior right side .......................................................................................................................................................4-3
Back interior right side ..............................................................................................................................................4-4
Interior fan side .........................................................................................................................................................4-5
Heat sink assembly...................................................................................................................................................4-6
Recommended spare parts ......................................................................................................................................4-7
Section 5 Parts – torch and consumables
T60 hand torch assembly .........................................................................................................................................5-2
T60M machine torch assembly.................................................................................................................................5-4
Page 9

TABLE OF CONTENTS
vi powermax1000 Service Manual
T60 consumable configurations................................................................................................................................5-6
T60M consumable configurations.............................................................................................................................5-7
Recommended spare parts ......................................................................................................................................5-8
Section 6 Wiring diagrams
Timing diagrams .......................................................................................................................................................6-2
Electrical schematic ..................................................................................................................................................6-5
Page 10

Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-1
Section 1
SAFETY
In this section:
Recognize Safety Information...................................................................................................................................1-2
Follow Safety Instructions.........................................................................................................................................1-2
Cutting Can Cause Fire or Explosion .......................................................................................................................1-2
Electric Shock Can Kill..............................................................................................................................................1-3
Cutting Can Produce Toxic Fumes ...........................................................................................................................1-3
A Plasma Arc Can Cause Injury and Burns ..............................................................................................................1-4
Arc Rays Can Burn Eyes and Skin ...........................................................................................................................1-4
Grounding Safety......................................................................................................................................................1-4
Compressed Gas Equipment Safety ........................................................................................................................1-5
Gas Cylinders Can Explode If Damaged ..................................................................................................................1-5
Noise Can Damage Hearing.....................................................................................................................................1-5
Pacemaker and Hearing Aid Operation ....................................................................................................................1-5
A Plasma Arc Can Damage Frozen Pipes ................................................................................................................1-5
Additional Safety Information....................................................................................................................................1-5
Warning Label...........................................................................................................................................................1-6
Page 11

SAFETY
1-2 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
11-98
SAFETY
RECOGNIZE SAFETY INFORMATION
The symbols shown in this section are used to
identify potential hazards. When you see a safety
symbol in this manual or on your machine, understand
the potential for personal injury, and follow the related
instructions to avoid the hazard.
FOLLOW SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Read carefully all safety messages in this manual and
safety labels on your machine.
• Keep the safety labels on your machine in good
condition. Replace missing or damaged labels
immediately.
• Learn how to operate the machine and how to use
the controls properly. Do not let anyone operate it
without instruction.
• Keep your machine in proper working condition.
Unauthorized modifications to the machine may
affect safety and machine service life.
DANGER WARNING CAUTION
A signal word DANGER or WARNING is used with a
safety symbol. DANGER identifies the most serious
hazards.
• DANGER and WARNING safety labels are located
on your machine near specific hazards.
• WARNING safety messages precede related
instructions in this manual that may result in injury
or death if not followed correctly.
• CAUTION safety messages precede related
instructions in this manual that may result in
damage to equipment if not followed correctly.
Fire Prevention
• Be sure the area is safe before doing any cutting.
Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
• Remove all flammables within 35 feet (10 m) of the
cutting area.
• Quench hot metal or allow it to cool before handling
or before letting it touch combustible materials.
• Never cut containers with potentially flammable
materials inside – they must be emptied and
properly cleaned first.
• Ventilate potentially flammable atmospheres before
cutting.
• When cutting with oxygen as the plasma gas, an
exhaust ventilation system is required.
Explosion Prevention
• Do not use the plasma system if explosive dust or
vapors may be present.
• Do not cut pressurized cylinders, pipes, or any
closed container.
• Do not cut containers that have held combustible
materials.
CUTTING CAN CAUSE FIRE OR EXPLOSION
WARNING
Explosion Hazard
Argon-Hydrogen and Methane
Hydrogen and methane are flammable gases that
present an explosion hazard. Keep flames away from
cylinders and hoses that contain methane or hydrogen
mixtures. Keep flames and sparks away from the torch
when using methane or argon-hydrogen plasma.
WARNING
Hydrogen Detonation with Aluminum Cutting
• When cutting aluminum underwater, or with the
water touching the underside of the aluminum, free
hydrogen gas may collect under the workpiece and
detonate during plasma cutting operations.
• Install an aeration manifold on the floor of the water
table to eliminate the possibility of hydrogen
detonation. Refer to the Appendix section of this
manual for aeration manifold details.
Page 12

Touching live electrical parts can cause a fatal shock
or severe burn.
• Operating the plasma system completes an
electrical circuit between the torch and the
workpiece. The workpiece and anything touching
the workpiece are part of the electrical circuit.
• Never touch the torch body, workpiece or the water
in a water table when the plasma system is
operating.
Electric Shock Prevention
All Hypertherm plasma systems use high voltage
in the cutting process (200 to 400 VDC are
common). Take the following precautions when
operating this system:
• Wear insulated gloves and boots, and keep your
body and clothing dry.
• Do not stand, sit or lie on – or touch – any wet
surface when using the plasma system.
• Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry
insulating mats or covers big enough to prevent any
physical contact with the work or ground. If you must
work in or near a damp area, use extreme caution.
• Provide a disconnect switch close to the power
supply with properly sized fuses. This switch allows
the operator to turn off the power supply quickly in
an emergency situation.
• When using a water table, be sure that it is correctly
connected to earth ground.
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
• Install and ground this equipment according to the
instruction manual and in accordance with national
and local codes.
• Inspect the input power cord frequently for damage
or cracking of the cover. Replace a damaged power
cord immediately. Bare wiring can kill.
• Inspect and replace any worn or damaged torch
leads.
• Do not pick up the workpiece, including the waste
cutoff, while you cut. Leave the workpiece in place
or on the workbench with the work cable attached
during the cutting process.
• Before checking, cleaning or changing torch parts,
disconnect the main power or unplug the power
supply.
• Never bypass or shortcut the safety interlocks.
• Before removing any power supply or system
enclosure cover, disconnect electrical input power.
Wait 5 minutes after disconnecting the main power
to allow capacitors to discharge.
• Never operate the plasma system unless the power
supply covers are in place. Exposed power supply
connections present a severe electrical hazard.
• When making input connections, attach proper
grounding conductor first.
• Each Hypertherm plasma system is designed to be
used only with specific Hypertherm torches. Do not
substitute other torches which could overheat and
present a safety hazard.
Cutting can produce toxic fumes and gases that
deplete oxygen and cause injury or death.
• Keep the cutting area well ventilated or use an
approved air-supplied respirator.
• Do not cut in locations near degreasing, cleaning or
spraying operations. The vapors from certain
chlorinated solvents decompose to form phosgene
gas when exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
• Do not cut metal coated or containing toxic materials, such as zinc (galvanized), lead, cadmium or
CUTTING CAN PRODUCE TOXIC FUMES
beryllium, unless the area is well ventilated and the
operator wears an air-supplied respirator. The
coatings and any metals containing these elements
can produce toxic fumes when cut.
• Never cut containers with potentially toxic materials
inside – they must be emptied and properly cleaned
first.
• This product, when used for welding or cutting,
produces fumes or gases which contain chemicals
known to the State of California to cause birth
defects and, in some cases, cancer.
Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-3
8-99
SAFETY
Page 13

SAFETY
1-4 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
5/6/02
SAFETY
Instant-On Torches
Plasma arc comes on immediately when the torch
switch is activated.
A PLASMA ARC CAN CAUSE INJURY AND BURNS
The plasma arc will cut quickly through gloves and
skin.
• Keep away from the torch tip.
• Do not hold metal near the cutting path.
• Never point the torch toward yourself or others.
Eye Protection Plasma arc rays produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays that
can burn eyes and skin.
• Use eye protection in accordance with applicable
national or local codes.
• Wear eye protection (safety glasses or goggles with
side shields, and a welding helmet) with appropriate
lens shading to protect your eyes from the arc’s
ultraviolet and infrared rays.
Lens Shade
Arc Current AWS (USA) ISO 4850
Up to 100 A No. 8 No. 11
100-200 A No. 10 No. 11-12
200-400 A No. 12 No. 13
Over 400 A No. 14 No. 14
ARC RAYS CAN BURN EYES AND SKIN
Skin Protection Wear protective clothing to protect
against burns caused by ultraviolet light, sparks and
hot metal.
• Gauntlet gloves, safety shoes and hat.
• Flame-retardant clothing to cover all exposed areas.
• Cuffless trousers to prevent entry of sparks and
slag.
• Remove any combustibles, such as a butane lighter
or matches, from your pockets before cutting.
Cutting Area Prepare the cutting area to reduce
reflection and transmission of ultraviolet light:
• Paint walls and other surfaces with dark colors to
reduce reflection.
• Use protective screens or barriers to protect others
from flash and glare.
• Warn others not to watch the arc. Use placards or
signs.
Work Cable Attach the work cable securely to the
workpiece or the work table with good metal-to-metal
contact. Do not connect it to the piece that will fall
away when the cut is complete.
Work Table Connect the work table to an earth
ground, in accordance with appropriate national or
local electrical codes.
GROUNDING SAFETY
Input Power
• Be sure to connect the power cord ground wire to
the ground in the disconnect box.
• If installation of the plasma system involves
connecting the power cord to the power supply, be
sure to connect the power cord ground wire
properly.
• Place the power cord's ground wire on the stud first,
then place any other ground wires on top of the
power cord ground. Fasten the retaining nut tightly.
• Tighten all electrical connections to avoid excessive
heating.
Page 14

SAFETY
Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-5
11-98
SAFETY
• Never lubricate cylinder valves or regulators with oil
or grease.
• Use only correct gas cylinders, regulators, hoses
and fittings designed for the specific application.
• Maintain all compressed gas equipment and
associated parts in good condition.
• Label and color-code all gas hoses to identify the
type of gas in each hose. Consult applicable
national or local codes.
GAS CYLINDERS CAN EXPLODE IF DAMAGED
COMPRESSED GAS EQUIPMENT SAFETY
Gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure. If
damaged, a cylinder can explode.
• Handle and use compressed gas cylinders in
accordance with applicable national or local codes.
• Never use a cylinder that is not upright and secured
in place.
• Keep the protective cap in place over valve except
when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.
• Never allow electrical contact between the plasma
arc and a cylinder.
• Never expose cylinders to excessive heat, sparks,
slag or open flame.
• Never use a hammer, wrench or other tool to open
a stuck cylinder valve.
Prolonged exposure to noise from cutting or gouging
can damage hearing.
• Use approved ear protection when using plasma
system.
• Warn others nearby about the noise hazard.
NOISE CAN DAMAGE HEARING
Pacemaker and hearing aid operation can be affected
by magnetic fields from high currents.
Pacemaker and hearing aid wearers should consult a
doctor before going near any plasma arc cutting and
gouging operations.
To reduce magnetic field hazards:
• Keep both the work cable and the torch lead to one
side, away from your body.
• Route the torch leads as close as possible to the
work cable.
• Do not wrap or drape the torch lead or work cable
around your body.
• Keep as far away from the power supply as
possible.
PACEMAKER AND HEARING AID OPERATION
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION
1. ANSI Standard Z49.1, Safety in Welding and Cutting, American
Welding Society, 550 LeJeune Road
P.O. Box 351020, Miami, FL 33135
2. ANSI Standard Z49.2, Fire Prevention in the Use of Cutting and
Welding Processes, American National Standards Institute
1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018
3. ANSI Standard Z87.1, Safe Practices for Occupation and
Educational Eye and Face Protection, American National
Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018
4. AWS F4.1, Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for
Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping That Have Held
Hazardous Substances, American Welding Society
550 LeJeune Road, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, FL 33135
5. AWS F5.2, Recommended Safe Practices for Plasma Arc
Cutting, American Welding Society
550 LeJeune Road, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, FL 33135
6. CGA Pamphlet P-1, Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders, Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202
7. CSA Standard W117.2, Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting,
Canadian Standards Association Standard Sales
178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario M9W 1R3, Canada
8. NFPA Standard 51B, Cutting and Welding Processes, National
Fire Protection Association
470 Atlantic Avenue, Boston, MA 02210
9. NFPA Standard 70–1978, National Electrical Code, National Fire
Protection Association, 470 Atlantic Avenue, Boston, MA 02210
10. OSHA, Safety and Health Standards, 29FR 1910
U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402
A PLASMA ARC CAN DAMAGE FROZEN PIPES
Frozen pipes may be damaged or can burst if you
attempt to thaw them with a plasma torch.
Page 15

SAFETY
1-6 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
8-99
SAFETY
WARNING LABEL
This warning label is affixed to some power supplies. It is
important that the operator and maintenance technician
understand the intent of these warning symbols as described.
The numbered text corresponds to the numbered boxes on
the label.
1. Cutting sparks can cause explosion or fire.
1.1 Keep flammables away from cutting.
1.2 Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, and have
a watchperson ready to use it.
1.3 Do not cut on any closed containers.
2. The plasma arc can cause injury and
burns.
2.1 Turn off power before disassembling torch.
2.2 Do not hold the material near cutting path.
2.3 Wear complete body protection.
3. Electric shock from torch or wiring can kill.
Protect yourself from electric shock.
3.1 Wear insulating gloves. Do not wear wet or
damaged gloves.
3.2 Insulate yourself from work and ground.
3.3 Disconnect input plug or power before
working on machine.
4. Breathing cutting fumes can be hazardous
to your health.
4.1 Keep your head out of the fumes.
4.2 Use forced ventilation or local exhaust to
remove the fumes.
4.3 Use ventilating fan to remove the fumes.
5. Arc rays can burn eyes and injure skin.
5.1 Wear hat and safety glasses. Use ear
protection and button shirt collar. Use
welding helmet with correct shade of filter.
Wear complete body protection.
6. Become trained and read the instructions
before working on the machine or cutting.
7. Do not remove or paint over (cover)
warning labels.
110391 Rev A
Page 16

Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-1
2/12/01
Section 1a
SÉCURITÉ
Dans cette section :
Identifier les consignes de sécurité.........................................................................................................................1a-2
Suivre les instructions de sécurité ..........................................................................................................................1a-2
Danger Avertissement Précaution ........................................................................................................................1a-2
Le coupage peut provoquer un incendie ou une explosion ....................................................................................1a-2
Prévention des incendies, Prévention des explosions...................................................................................1a-2
Risque d’explosion argon-hydrogène et méthane..........................................................................................1a-2
Détonation de l’hydrogène lors du coupage de l’aluminium...........................................................................1a-2
Les chocs électriques peuvent être fatals...............................................................................................................1a-3
Prévention des chocs électriques ..................................................................................................................1a-3
Le coupage peut produire des vapeurs toxiques....................................................................................................1a-3
L’arc plasma peut provoquer des blessures ou des brûlures .................................................................................1a-4
Torches à allumage instantané ......................................................................................................................1a-4
Les rayons de l’arc peuvent brûler les yeux et la peau...........................................................................................1a-4
Protection des yeux, Protection de la peau, Zone de coupage ....................................................................1a-4
Mise à la masse et à la terre...................................................................................................................................1a-4
Câble de retour, Table de travail, Alimentation...............................................................................................1a-4
Sécurité des bouteilles de gaz comprimé ...............................................................................................................1a-5
Les bouteilles de gaz comprimé peuvent exploser en cas de dommages .............................................................1a-5
Le bruit peut provoquer des problèmes auditifs......................................................................................................1a-5
Pacemakers et prothèses auditives........................................................................................................................1a-5
Un arc plasma peut endommager les tuyaux gelés................................................................................................1a-5
Étiquette de sécurité ...............................................................................................................................................1a-6
Page 17

SÉCURITÉ
1a-2 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
2/12/01
IDENTIFIER LES CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
Les symboles indiqués dans cette section sont utilisés pour
identifier les risques éventuels. Si vous trouvez un symbole
de sécurité, que ce soit dans ce manuel ou sur
l’équipement, soyez conscient des risques de blessures et
suivez les instructions correspondantes afin d’éviter ces
risques.
SUIVRE LES INSTRUCTIONS DE SÉCURITÉ
Lire attentivement toutes les consignes de sécurité dans le
présent manuel et sur les étiquettes de sécurité se trouvant
sur la machine.
• Les étiquettes de sécurité doivent rester lisibles.
Remplacer immédiatement les étiquettes manquantes ou
abîmées.
• Apprendre à faire fonctionner la machine et à utiliser
correctement les commandes. Ne laisser personne utiliser
la machine sans connaître son fonctionnement.
• Garder la machine en bon état. Des modifications non
autorisées sur la machine peuvent engendrer des
problèmes de sécurité et raccourcir la durée d’utilisation
de l’équipement.
DANGER AVERTISSEMENT PRÉCAUTION
Les signaux DANGER ou AVERTISSEMENT sont utilisés
avec un symbole de sécurité, DANGER correspondant aux
risques les plus sérieux.
• Les étiquettes de sécurité DANGER et AVERTISSEMENT
sont situées sur la machine pour signaler certains
dangers spécifiques.
• Les messages d’AVERTISSEMENT précèdent les
instructions d’utilisation expliquées dans ce manuel et
signalent les risques de blessures ou de mort au cas où
ces instructions ne seraient pas suivies correctement.
• Les messages de PRÉCAUTION précèdent les
instructions d’utilisation contenues dans ce manuel et
signalent que le matériel risque d’être endommagé si les
instructions ne sont pas suivies correctement.
Prévention des incendies
• Avant de commencer, s’assurer que la zone de coupage
ne présente aucun danger. Conserver un extincteur à
proximité.
• Éloigner toute matière inflammable à une distance d’au
moins 10 m du poste de coupage.
• Tremper le métal chaud ou le laisser refroidir avant de
le manipuler ou avant de le mettre en contact avec des
matériaux combustibles.
• Ne jamais couper des récipients pouvant contenir des
matières inflammables avant de les avoir vidés et
nettoyés correctement.
• Aérer toute atmosphère potentiellement inflammable
avant d’utiliser un système plasma.
• Lors de l’utilisation d’oxygène comme gaz plasma, un
système de ventilation par aspiration est nécessaire.
Prévention des explosions
• Ne pas couper en présence de poussière ou de vapeurs.
• Ne pas couper de bouteilles, de tuyaux ou autres
récipients fermés et pressurisés.
• Ne pas couper de récipients contenant des matières
combustibles.
LE COUPAGE PEUT PROVOQUER UN INCENDIE
OU UNE EXPLOSION
AVERTISSEMENT
Risque d’explosion
argon-hydrogène et méthane
L’hydrogène et le méthane sont des gaz inflammables et
potentiellement explosifs. Conserver à l’écart de toute
flamme les bouteilles et tuyaux contenant des mélanges à
base d’hydrogène ou de méthane. Maintenir toute flamme
et étincelle à l’écart de la torche lors de l’utilisation d’un
plasma d’argon-hydrogène ou de méthane.
AVERTISSEMENT
Détonation de l’hydrogène lors du
coupage de l’aluminium
• Lors du coupage de l’aluminium sous l’eau, ou si l’eau
touche la partie inférieure de la pièce d’aluminium, de
l’hydrogène libre peut s’accumuler sous la pièce à couper
et détonner lors du coupage plasma.
• Installer un collecteur d’aération au fond de la table à eau
afin d’éliminer les risques de détonation de l’hydrogène.
Se référer à l’annexe du manuel pour plus de
renseignements sur les collecteurs d’aération.
Page 18

SÉCURITÉ
Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-3
2/12/01
Toucher une pièce électrique sous tension peut provoquer
un choc électrique fatal ou des brûlures graves.
• La mise en fonctionnement du système plasma ferme un
circuit électrique entre la torche et la pièce à couper. La
pièce à couper et tout autre élément en contact avec cette
pièce font partie du circuit électrique.
• Ne jamais toucher le corps de la torche, la pièce à couper
ou l’eau de la table à eau pendant le fonctionnement du
système plasma.
Prévention des chocs électriques
Tous les systèmes plasma Hypertherm utilisent des hautes
tensions pour le coupage (souvent de 200 à 400 V). On
doit prendre les précautions suivantes quand on utilise le
système plasma :
• Porter des bottes et des gants isolants et garder le corps
et les vêtements au sec.
• Ne pas se tenir, s’asseoir ou se coucher sur une surface
mouillée, ni la toucher quand on utilise le système plasma.
• S’isoler de la surface de travail et du sol en utilisant des
tapis isolants secs ou des couvertures assez grandes
pour éviter tout contact physique avec le travail ou le sol.
S’il s’avère nécessaire de travailler dans ou près d’un
endroit humide, procéder avec une extrême prudence.
• Installer un sectionneur avec fusibles appropriés, à
proximité de la source de courant. Ce dispositif permet à
l’opérateur d’arrêter rapidement la source de courant en
cas d’urgence.
• En cas d’utilisation d’une table à eau, s’assurer que cette
dernière est correctement mise à la terre.
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES PEUVENT ÊTRE FATALS
• Installer et mettre à la terre l’équipement selon les
instructions du présent manuel et conformément aux
codes électriques locaux et nationaux.
• Inspecter fréquemment le cordon d’alimentation primaire
pour s’assurer qu’il n’est ni endommagé, ni fendu.
Remplacer immédiatement un cordon endommagé.
Un câble dénudé peut tuer.
• Inspecter et remplacer les câbles de la torche qui sont
usés ou endommagés.
• Ne pas saisir la pièce à couper ni les chutes lors du
coupage. Laisser la pièce à couper en place ou sur la
table de travail, le câble de retour connecté lors du
coupage.
• Avant de vérifier, de nettoyer ou de remplacer les pièces
de la torche, couper l’alimentation ou débrancher la prise
de courant.
• Ne jamais contourner ou court-circuiter les verrouillages
de sécurité.
• Avant d’enlever le capot du système ou de la source de
courant, couper l’alimentation électrique. Attendre en
suite
5 minutes pour que les condensateurs se déchargent.
• Ne jamais faire fonctionner le système plasma sans que
les capots de la source de courant ne soient en place.
Les raccords exposés de la source de courant sont
extrêmement dangereux.
• Lors de l’installation des connexions, attacher tout d’abord
la prise de terre appropriée.
• Chaque système plasma Hypertherm est conçu pour être
utilisé uniquement avec des torches Hypertherm
spécifiques. Ne pas utiliser des torches inappropriées qui
pourraient surchauffer et présenter des risques pour la
sécurité.
Le coupage peut produire des vapeurs et des gaz toxiques
qui réduisent le niveau d’oxygène dans l’air et peuvent
provoquer des blessures, voire la mort.
• Conserver le poste de coupage bien aéré ou utiliser un
masque respiratoire homologué.
• Ne pas procéder au coupage près d’endroits où
s’effectuent le dégraissage, le nettoyage ou la vaporisation. Certains solvants chlorés se décomposent sous
l’effet des rayons ultraviolets et forment du phosgène.
• Ne pas couper des métaux peints ou contenant des
matières toxiques comme le zinc (galvanisé), le plomb, le
cadmium ou le béryllium, à moins que la zone de travail
LE COUPAGE PEUT PRODUIRE DES VAPEURS TOXIQUES
soit très bien ventilée et que l’opérateur porte un masque
respiratoire. Les revêtements et métaux contenant ces
matières peuvent produire des vapeurs toxiques lors du
coupage.
• Ne jamais couper de récipients pouvant contenir des
matières inflammables avant de les avoir vidés et
nettoyés correctement.
• Quand on utilise ce produit pour le soudage ou le
coupage, il dégage des fumées et des gaz qui
contiennent des produits chimiques qui, selon l’État de
Californie, provoquent des anomalies congénitales et,
dans certains cas, le cancer.
Page 19

SÉCURITÉ
1a-4 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
5/6/02
Torches à allumage instantané
L’arc plasma s’allume immédiatement après que la torche
soit mise en marche.
L’ARC PLASMA PEUT PROVOQUER DES BLESSURES OU DES BRÛLURES
L’arc plasma coupe facilement les gants et la peau.
• Rester éloigné de l’extrémité de la torche.
• Ne pas tenir de métal près de la trajectoire de coupe.
• Ne jamais pointer la torche vers soi ou d’autres
personnes.
Protection des yeux Les rayons de l’arc plasma
produisent de puissants rayons visibles ou invisibles
(ultraviolets et infrarouges) qui peuvent brûler les yeux et la
peau.
• Utiliser des lunettes de sécurité conformément aux codes
locaux ou nationaux en vigueur.
• Porter des lunettes de protection (lunettes ou masque
muni d’écrans latéraux et encore masque de soudure)
avec des verres teintés appropriés pour protéger les yeux
des rayons ultraviolets et infrarouges de l’arc.
Puissance des verres teintés
Courant de l’arc AWS (É.-U.) ISO 4850
Jusqu’à 100 A No8N
o
11
100-200 A No10 No11-12
200-400 A No12 No13
Plus de 400 A No14 No14
Protection de la peau Porter des vêtements de sécurité
pour se protéger contre les brûlures que peuvent causer les
rayons ultraviolets, les étincelles et le métal brûlant :
LES RAYONS DE L’ARC PEUVENT BRÛLER LES YEUX ET LA PEAU
• Gants à crispin, chaussures et casque de sécurité.
• Vêtements ignifuges couvrant toutes les parties exposées
du corps.
• Pantalon sans revers pour éviter que des étincelles ou
des scories puissent s’y loger.
• Avant le coupage, retirer de ses poches tout objet
combustible comme les briquets au butane ou les
allumettes.
Zone de coupage Préparer la zone de coupage afin de
réduire la réverbération et la transmission de la lumière
ultraviolette :
• Peindre les murs et autres surfaces de couleur sombre
pour réduire la réflexion de la lumière.
• Utiliser des écrans et autres dispositifs de protection afin
de protéger les autres personnes de la lumière et de la
réverbération.
• Prévenir les autres personnes de ne pas regarder l’arc.
Utiliser des affiches ou des panneaux.
Câble de retour Bien fixer le câble de retour (ou de
masse) à la pièce à couper ou à la table de travail de façon
à assurer un bon contact métal-métal. Ne pas fixer le câble
de retour à la partie de la pièce qui doit se détacher.
Table de travail Raccorder la table de travail à la terre,
conformément aux codes de sécurité locaux ou nationaux
appropriés.
MISE À LA MASSE ET À LA TERRE
Alimentation
• S’assurer que le fil de terre du cordon d’alimentation est
connecté à la terre dans le coffret du sectionneur.
• S’il est nécessaire de brancher le cordon d’alimentation à
la source de courant lors de l’installation du système,
s’assurer que le fil de terre est correctement branché.
• Placer tout d’abord le fil de terre du cordon d’alimentation
sur le plot de mise à la terre puis placer les autres fils de
terre par-dessus. Bien serrer l’écrou de retenue.
• S’assurer que toutes les connexions sont bien serrées
pour éviter la surchauffe.
Page 20

SÉCURITÉ
Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-5
2/12/01
• Ne jamais lubrifier les robinets des bouteilles ou les
régulateurs avec de l’huile ou de la graisse.
• Utiliser uniquement les bouteilles, régulateurs, tuyaux et
accessoires appropriés et conçus pour chaque application
spécifique.
• Entretenir l’équipement et les pièces d’équipement à gaz
comprimé afin de les garder en bon état.
• Étiqueter et coder avec des couleurs tous les tuyaux de
gaz afin d’identifier le type de gaz contenu dans chaque
tuyau. Se référer aux codes locaux ou nationaux en
vigueur.
LES BOUTEILLES DE GAZ COMPRIMÉ PEUVENT EXPLOSER EN CAS DE DOMMAGES
SÉCURITÉ DES BOUTEILLES DE GAZ COMPRIMÉ
Les bouteilles de gaz contiennent du gaz à haute pression.
Si une bouteille est endommagée, elle peut exploser.
• Manipuler et utiliser les bouteilles de gaz comprimé
conformément aux codes locaux ou nationaux.
• Ne jamais utiliser une bouteille qui n’est pas placée à la
verticale et bien assujettie.
• Le capuchon de protection doit être placé sur le robinet
sauf si la bouteille est en cours d’utilisation ou connectée
pour utilisation.
• Éviter à tout prix le contact électrique entre l’arc plasma et
une bouteille.
• Ne jamais exposer des bouteilles à une chaleur
excessive, aux étincelles, aux scories ou aux flammes
nues.
• Ne jamais utiliser des marteaux, des clés ou d’autres
outils pour débloquer le robinet des bouteilles.
Une exposition prolongée au bruit du coupage ou du
gougeage peut provoquer des problèmes auditifs.
• Utiliser un casque de protection homologué lors de
l’utilisation du système plasma.
• Prévenir les personnes aux alentours des risques
encourus en cas d’exposition au bruit.
LE BRUIT PEUT PROVOQUER DES
PROBLÈMES AUDITIFS
Les champs magnétiques produits par les courants à haute
tension peuvent affecter le fonctionnement des prothèses
auditives et des pacemakers. Les personnes portant ce
type d’appareil doivent consulter un médecin avant de
s’approcher d’un lieu où s’effectue le coupage ou le
gougeage plasma.
Pour réduire les risques associés aux champs magnétiques :
• Garder loin de soi et du même côté du corps le câble de
retour et le faisceau de la torche.
• Faire passer le faisceau de la torche le plus près possible
du câble de retour.
• Ne pas s’enrouler le faisceau de la torche ou le câble de
retour autour du corps.
• Se tenir le plus loin possible de la source de courant.
PACEMAKERS ET PROTHÈSES AUDITIVES
Les tuyaux gelés peuvent être endommagés ou éclater
si l'on essaie de les dégeler avec une torche plasma.
UN ARC PLASMA
PEUT ENDOMMAGER
LES TUYAUX GELÉS
Page 21

SÉCURITÉ
1a-6 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
2/12/01
Étiquette de sécurité
Cette étiquette est affichée sur la source de courant. Il est important
que l’utilisateur et le technicien de maintenance comprennent la
signification des symboles de sécurité. Les numéros de la liste
correspondent aux numéros des images.
1. Les étincelles produites par le coupage
peuvent provoquer une explosion ou un
incendie.
1.1 Pendant le coupage, éloigner toute matière
inflammable.
1.2 Conserver un extincteur à proximité et
s’assurer qu’une personne soit prête à
l’utiliser.
1.3 Ne jamais couper de récipients fermés.
2. L’arc plasma peut provoquer des blessures
et des brûlures.
2.1 Couper l’alimentation avant de démonter la
torche.
2.2 Ne pas tenir la surface à couper près de la
trajectoire de coupe.
2.3 Porter des vêtements de protection
couvrant tout le corps.
3. Un choc électrique causé par la torche ou
les câbles peut être fatal. Se protéger
contre les risques de chocs électriques.
3.1 Porter des gants isolants. Ne pas porter de
gants mouillés ou abîmés.
3.2 S’isoler de la surface de travail et du sol.
3.3 Débrancher la prise ou la source de
courant avant de manipuler l’équipement.
4. L’inhalation des vapeurs produites par le
coupage peut être dangereuse pour la
santé.
4.1 Garder le visage à l’écart des vapeurs.
4.2 Utiliser un système de ventilation par
aspiration ou d’échappement localisé pour
dissiper les vapeurs.
4.3 Utiliser un ventilateur pour dissiper les
vapeurs.
5. Les rayons de l’arc peuvent brûler les yeux
et provoquer des lésions de la peau.
5.1 Porter un casque et des lunettes de
sécurité. Se protéger les oreilles et porter
une chemise dont le col peut être
déboutonné. Porter un casque de soudure
dont la protection filtrante est suffisante.
Porter des vêtements protecteurs couvrant
la totalité du corps.
6. Se former à la technique du coupage et lire
les instructions avant de manipuler
l’équipement ou de procéder au coupage.
7. Ne pas retirer ou peindre (recouvrir) les
étiquettes de sécurité.
110391 Rev A
Page 22

HYPERTHERM Sistemas plasma 1b-1
2/12/01
Seccíon 1b
SEGURIDAD
En esta sección:
Reconocimiento de información de seguridad........................................................................................................1b-2
Siga las instrucciones de seguridad .......................................................................................................................1b-2
Peligro…Advertencia…Precaución ........................................................................................................................1b-2
Los cortes pueden provocar incendios o explosiones ............................................................................................1b-2
Prevención ante el fuego, Prevención ante explosiones ...............................................................................1b-2
Peligro de explosión argón-hidrógeno y metano............................................................................................1b-2
Detonación de hidrógeno con el corte de aluminio........................................................................................1b-2
El choque eléctrico puede provocar la muerte .......................................................................................................1b-3
Prevención ante el electrochoque..................................................................................................................1b-3
Los cortes pueden producir humos tóxicos ............................................................................................................1b-3
El arco de plasma puede causar lesiones y quemaduras ......................................................................................1b-4
Antorchas de encendido instantáneo.............................................................................................................1b-4
Los rayos del arco pueden producir quemaduras en los ojos y en la piel ..............................................................1b-4
Protección para los ojos, Protección para la piel, Área de corte....................................................................1b-4
Seguridad de toma a tierra .....................................................................................................................................1b-4
Cable de trabajo, Mesa de trabajo, Potencia primaria de entrada.................................................................1b-4
Seguridad de los equipos de gas comprimido........................................................................................................1b-5
Los cilindros de gas pueden explotar si están dañados .........................................................................................1b-5
El ruido puede deteriorar la audición ......................................................................................................................1b-5
Operación de marcapasos y de audífonos .............................................................................................................1b-5
Un arco plasma puede dañar tubos congelados ....................................................................................................1b-5
Etiqueta de advertencia ..........................................................................................................................................1b-6
Page 23

SEGURIDAD
2/12/01
1b-2 HYPERTHERM Sistemas plasma
RECONOCIMIENTO DE INFORMACIÓN DE SEGURIDAD
Los símbolos que se muestran en esta sección se utilizan
para identificar los posibles peligros. Cuando vea un
símbolo de seguridad en este manual o en su máquina,
recuerde que existe la posibilidad de que se produzcan
lesiones personales y siga las instrucciones
correspondientes para evitar el peligro.
SIGA LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
Lea atentamente todos los mensajes de seguridad de este
manual y las etiquetas de seguridad en su máquina.
• Mantenga las etiquetas de seguridad de su máquina en
buen estado. Reemplace las etiquetas que se pierdan o
se dañen inmediatamente.
• Aprenda a utilizar la máquina y a utilizar los controles de
la manera correcta. No permita que sea utilizada por
alguien que no conozca su funcionamiento.
• Mantenga su máquina en buenas condiciones de
funcionamiento. La realización de modificaciones no
autorizadas a la máquina puede comprometer la
seguridad y la vida útil de la máquina.
PELIGRO ADVERTENCIA PRECAUCIÓN
Las palabras PELIGRO y ADVERTENCIA se utilizan
conjuntamente con un símbolo de seguridad. La palabra
PELIGRO se utiliza para identificar los mayores peligros.
• Encontrará etiquetas de seguridad con las inscripciones
PELIGRO y ADVERTENCIA en su máquina, junto a
peligros específicos.
• En este manual, la palabra ADVERTENCIA va seguida de
instrucciones que, si no se siguen correctamente, pueden
provocar lesiones e inclusive la muerte.
• En este manual, la palabra PRECAUCIÓN va seguida de
instrucciones que, si no se siguen correctamente, pueden
provocar daños en el equipo.
Prevención ante el fuego
• Asegúrese de que el área sea segura antes de proceder
a cortar. Tenga a mano un extinguidor de incendios.
• Retire todos los materiales inflamables, colocándolos a
por lo menos 10 metros del área de corte.
• Remoje los metales calientes o permita que se enfríen
antes de que entren en contacto con materiales
combustibles.
• Nunca corte depósitos que contengan materiales
inflamables – primero es necesario vaciarlos y limpiarlos
debidamente.
• Antes de realizar cortes en atmósferas potencialmente
inflamables, asegúrese de ventilar bien.
• Al realizar cortes utilizando oxígeno como gas plasma, se
requiere tener un sistema de ventilación de escape.
Prevención ante explosiones
• No corte en atmósferas que contengan polvo o vapores
explosivos.
• No corte depósitos o tubos a presión ni cualquier depósito
cerrado.
• No corte depósitos que hayan contenido materiales
combustibles.
LOS CORTES PUEDEN PROVOCAR INCENDIOS O EXPLOSIONES
ADVERTENCIA
Peligro de explosión
Argón-Hidrógeno y metano
El hidrógeno y el metano son gases inflamables que
suponen un peligro de explosión. Mantenga el fuego lejos
de los cilindros y las mangueras que contengan mezclas de
hidrógeno o metano. Mantenga la llama y las chispas lejos
de la antorcha al utilizar metano o argón-hidrógeno como
plasma.
ADVERTENCIA
Detonación de hidrógeno con
el corte de aluminio
• Al cortar aluminio bajo agua o con agua en contacto con
el lado inferior del aluminio, puede acumularse gas
hidrógeno bajo la pieza a cortar y detonar durante la
operación de corte por plasma.
• Instale un múltiple de aireación en el fondo de la mesa de
agua para eliminar la posibilidad de la detonación del
hidrógeno. Consulte la sección del apéndice de este
manual para conocer detalles acerca del múltiple de
aireación.
Page 24

SEGURIDAD
4/11/03
HYPERTHERM Sistemas plasma 1b-3
El contacto directo con piezas eléctricas conectadas puede
provocar un electrochoque fatal o quemaduras graves.
• Al hacer funcionar el sistema de plasma, se completa un
circuito eléctrico entre la antorcha y la pieza a cortar. La
pieza a cortar es una parte del circuito eléctrico, como
también cualquier cosa que se encuentre en contacto con
ella.
• Nunca toque el cuerpo de la antorcha, la pieza a cortar o
el agua en una mesa de agua cuando el sistema de
plasma se encuentre en funcionamiento.
Prevención ante el electrochoque
Todos los sistemas por plasma de Hypertherm usan alto
voltaje en el proceso de corte (son comunes los voltajes CD
de 200 a 400). Tome las siguientes precauciones cuando se
utiliza el equipo de plasma:
• Use guantes y botas aislantes y mantenga el cuerpo y la
ropa secos.
• No se siente, se pare o se ponga sobre cualquier superficie húmeda cuando esté trabajando con el equipo.
• Aíslese eléctricamente de la pieza a cortar y de la tierra
utilizando alfombrillas o cubiertas de aislamiento secas lo
suficientemente grandes como para impedir todo contacto
físico con la pieza a cortar o con la tierra. Si su única
opción es trabajar en una área húmeda o cerca de ella,
sea muy cauteloso.
• Instale un interruptor de corriente adecuado en cuanto a
fusibles, en una pared cercana a la fuente de energía.
Este interruptor permitirá al operador desconectar
rápidamente la fuente de energía en caso de emergencia.
• Al utilizar una mesa de agua, asegúrese de que ésta se
encuentre correctamente conectada a la toma a tierra.
EL CHOQUE ELÉCTRICO PUEDE PROVOCAR LA MUERTE
• Instale este equipo y conéctelo a tierra según el manual
de instrucciones y de conformidad con los códigos locales
y nacionales.
• Inspeccione el cordón de alimentación primaria con
frecuencia para asegurarse de que no esté dañado ni
agrietado. Si el cordón de alimentación primaria está
dañado, reemplácelo inmediatamente. Un cable pelado
puede provocar la muerte.
• Inspeccione las mangueras de la antorcha y
reemplácelas cuando se encuentren dañadas.
• No toque la pieza ni los recortes cuando se está
cortando. Deje la pieza en su lugar o sobre la mesa de
trabajo con el cable de trabajo conectado en todo
momento.
• Antes de inspeccionar, limpiar o cambiar las piezas de la
antorcha, desconecte la potencia primaria o desenchufe
la fuente de energía.
• Nunca evite o descuide los bloqueos de seguridad.
• Antes de retirar la cubierta de una fuente de energía o del
gabinete de un sistema, desconecte la potencia primaria
de entrada. Espere 5 minutos después de desconectar la
potencia primaria para permitir la descarga de los
condensadores.
• Nunca opere el sistema de plasma sin que las tapas de la
fuente de energía estén en su lugar. Las conexiones
expuestas de la fuente de energía presentan un serio
riesgo eléctrico.
• Al hacer conexiones de entrada, conecte el conductor de
conexión a tierra en primer lugar.
• Cada sistema de plasma Hypertherm está diseñado para
ser utilizado sólo con antorchas Hypertherm específicas.
No utilice antorchas diferentes, que podrían recalentarse
y ser peligrosas.
Los cortes pueden producir gases y humos tóxicos que
agotan el oxígeno y causan lesiones o inclusive la muerte.
• Mantenga el área de corte bien ventilada o utilice un
respirador con suministro de aire aprobado.
• No realice sus cortes en sitios que se hallen cerca de
operaciones de desengrasado, limpieza o aplicación de
aerosoles. Los vapores de ciertos solventes clorados se
descomponen y forman gas fosgeno al quedar expuestos
a la radiación ultravioleta.
• No corte metales que contengan materiales tóxicos o que
estén recubiertos con ellos, tales como el cinc
(galvanizado), el plomo, el cadmio o el berilio, a menos
LOS CORTES PUEDEN PRODUCIR HUMOS TÓXICOS
que el área se halle bien ventilada y el operador lleve
puesto un respirador con suministro de aire. Los
recubrimientos y todo metal que contenga estos
elementos pueden producir gases o humos tóxicos al ser
cortados.
• Nunca corte depósitos con materiales potencialmente
tóxicos en su interior – primero es necesario vaciarlos y
limpiarlos debidamente.
• Este producto, cuando se lo usa para soldar o cortar,
produce humo y gases que se conocen en el estado de
California como causantes de defectos de nacimiento, y
en algunos casos, cáncer.
Page 25

SEGURIDAD
4/11/03
1b-4 HYPERTHERM Sistemas plasma
Antorchas de encendido instantáneo
El arco de plasma se enciende inmediatamente después de
activarse el interruptor de la antorcha.
EL ARCO DE PLASMA PUEDE CAUSAR LESIONES Y QUEMADURAS
El arco de plasma puede cortar a través de guantes y de la
piel con rapidez.
• Manténgase alejado de la punta de la antorcha.
• No sostenga el metal junto al trayecto de corte.
• Nunca apunte la antorcha hacia Ud. mismo o hacia otras
personas.
Protección para los ojos Los rayos del arco de plasma
producen rayos intensos visibles e invisibles (ultravioleta e
infrarrojo) que pueden quemar los ojos y la piel.
• Utilice protección para los ojos de conformidad con los
códigos locales o nacionales aplicables.
• Colóquese protectores para los ojos (gafas o anteojos
protectores con protectores laterales, y bien un casco de
soldar) con lentes con sombreado adecuado para
proteger sus ojos de los rayos ultravioleta e infrarrojos del
arco.
Número del cristal
Corriente del arco AWS (EE.UU.) ISO 4850
Hasta 100A No. 8 No. 11
100-200 A No. 10 No. 11-12
200-400 A No. 12 No. 13
Más de 400 A No. 14 No. 14
LOS RAYOS DEL ARCO PUEDEN PRODUCIR QUEMADURAS
EN LOS OJOS Y EN LA PIEL
Protección para la piel Vista ropa de protección para
proteger la piel contra quemaduras causadas por la
radiación ultravioleta de alta intensidad, por las chispas y
por el metal caliente:
• Guantes largos, zapatos de seguridad y gorro.
• Roipa de combustión retardada y que cubra todas las
partes expuestas.
• Pantalones sin dobladillos para impedir que recojan
chispas y escorias.
• Retire todo material combustible de los bolsillos, como
encendedores a butano e inclusive cerillas, antes de
comenzar a cortar.
Área de corte Prepare el área de corte para reducir la
reflexión y la transmisión de la luz ultravioleta:
• Pinte las paredes y demás superficies con colores
oscuros para reducir la reflexión.
• Utilice pantallas o barreras protectoras para proteger a
los demás de los destellos.
• Advierta a los demás que no debe mirarse el arco. Utilice
carteles o letreros.
Cable de trabajo La pinza del cable de trabajo debe
estar bien sujetada a la pieza y hacer un buen contacto de
metal a metal con ella o bien con la mesa de trabajo. No
conecte el cable con la parte que va a quedar separada por
el corte.
Mesa de trabajo Conecte la mesa de trabajo a una
buena toma de tierra, de conformidad con los códigos
eléctricos nacionales o locales apropiados.
SEGURIDAD DE TOMA A TIERRA
Potencia primaria de entrada
• Asegúrese de que el alambre de toma a tierra del cordón
de alimentación está conectado al terminal de tierra en la
caja del interruptor de corriente.
•
Si la instalación del sistema de plasma supone la conexión
del cordón de alimentación primaria a la fuente de energía,
asegúrese de conectar correctamente el alambre de toma
a tierra del cordón de alimentación primaria.
• Coloque en primer lugar el alambre de toma a tierra del
cordón de alimentación primaria en el espárrago luego
coloque cualquier otro alambre de tierra sobre el
conductor de tierra del cable. Ajuste firmemente la tuerca
de retención.
• Asegúrese de que todas las conexiones eléctricas están
firmemente realizadas para evitar sobrecalentamientos.
Page 26

SEGURIDAD
2/12/01
HYPERTHERM Sistemas plasma 1b-5
• Nunca lubrique reguladores o válvulas de cilindros con
aceite o grasa.
• Utilice solamente cilindros, reguladores, mangueras y
conectores de gas correctos que hayan sido diseñados
para la aplicación específica.
• Mantenga todo el equipo de gas comprimido y las piezas
relacionadas en buen estado.
• Coloque etiquetas y códigos de color en todas las
mangueras de gas para identificar el tipo de gas que
conduce cada una. Consulte los códigos locales o
nacionales aplicables.
LOS CILINDROS DE GAS PUEDEN EXPLOTAR SI ESTÁN DAÑADOS
SEGURIDAD DE LOS EQUIPOS DE GAS COMPRIMIDO
Los cilindros de gas contienen gas bajo alta presión. Un
cilindro dañado puede explotar.
• Manipule y utilice los cilindros de gas comprimido de
acuerdo con los códigos locales o nacionales aplicables.
• No use nunca un cilindro que no esté de pie y bien sujeto.
• Mantenga la tapa de protección en su lugar encima de la
válvula, excepto cuando el cilindro se encuentre en uso o
conectado para ser utilizado.
• No permita nunca el contacto eléctrico entre el arco de
plasma y un cilindro.
• No exponga nunca los cilindros a calor excesivo, chispas,
escorias o llamas.
• No emplee nunca martillos, llaves u otro tipo de
herramientas para abrir de golpe la válvula del cilindro.
La exposición prolongada al ruido propio de las
operaciones de corte y ranurado puede dañar la audición.
• Utilice un método de protección de los oídos aprobado al
utilizar el sistema de plasma.
• Advierta a las demás personas que se encuentren en las
cercanías acerca del peligro que supone el ruido
excesivo.
EL RUIDO PUEDE DETERIORAR LA AUDICIÓN
Los campos magnéticos producidos por las elevadas
corrientes pueden afectar la operación de marcapasos y de
audífonos. Las personas que lleven marcapasos y
audífonos deberán consultar a un médico antes de
acercarse a sitios donde se realizan operaciones de corte y
ranurado por plasma.
Para reducir los peligros de los campos magnéticos:
• Mantenga el cable de trabajo y la manguera de la
antorcha a un lado, lejos del cuerpo.
• Dirija la manguera antorcha lo más cerca posible del
cable de trabajo.
• No envuelva el cable de trabajo ni la manguera de la
antorcha en su cuerpo.
• Manténgase tan lejos de la fuente de energía como sea
posible.
OPERACIÓN DE MARCAPASOS Y DE AUDÍFONOS
Se puede hacer daño a los tubos congelados, o se
los puede reventar, si uno trata de descongelarlos
con una antorcha por plasma.
UN ARCO PLASMA PUEDE DAÑAR TUBOS CONGELADOS
Page 27

SEGURIDAD
2/12/01
1b-6 HYPERTHERM Sistemas plasma
Etiqueta de advertencia
Esta etiqueta de advertencia se encuentra adherida a la fuente de energía.
Es importante que el operador y el técnico de mantenimiento comprendan
el sentido de estos símbolos de advertencia según se describen. El texto
numerado corresponde a los cuadros numerados de la etiqueta.
1. Las chispas producidas por el corte
pueden causar explosiones o incendios.
1.1 Mantenga los materiales inflamables lejos
del lugar de corte.
1.2 Tenga a mano un extinguidor de incendios
y asegúrese de que alguien esté preparado
para utilizarlo.
1.3 No corte depósitos cerrados.
2. El arco de plasma puede causar
quemaduras y lesiones.
2.1 Apague la fuente de energía antes de
desarmar la antorcha.
2.2 No sostenga el material junto al trayecto de
corte.
2.3 Proteja su cuerpo completamente.
3. Los electrochoques provocados por la
antorcha o el cableado pueden ser fatales.
Protéjase del electrochoque.
3.1 Colóquese guantes aislantes. No utilice
guantes dañados o mojados.
3.2 Aíslese de la pieza de trabajo y de la tierra.
3.3 Antes de trabajar en una máquina,
desconecte el enchufe de entrada o la
potencia primaria.
4. La inhalación de los humos provenientes
del área de corte puede ser nociva para la
salud.
4.1 Mantenga la cabeza fuera de los gases
tóxicos.
4.2 Utilice ventilación forzada o un sistema
local de escape para eliminar los humos.
4.3 Utilice un ventilador para eliminar los
humos.
5. Los rayos del arco pueden producir
quemaduras en los ojos y en la piel.
5.1 Utilice un sombrero y gafas de seguridad.
Utilice protección para los oídos y
abróchese el botón del cuello de la camisa.
Utilice un casco de soldar con el filtro de
sombreado adecuado. Proteja su cuerpo
completamente.
6. Antes de trabajar en la máquina o de
proceder a cortar, capacítese y lea las
instrucciones completamente.
7. No retire las etiquetas de advertencia ni las
cubra con pintura.
110391 Rev A
Page 28

Section 2
SPECIFICATIONS
In this section:
Power supply ............................................................................................................................................................2-2
Dimensions and weight ....................................................................................................................................2-3
T60 torches...............................................................................................................................................................2-4
Dimensions ......................................................................................................................................................2-5
Symbols and markings .............................................................................................................................................2-6
S Mark............................................................................................................................................................2-6
IEC symbols .....................................................................................................................................................2-6
powermax1000 Service Manual 2-1
1
Page 29

SPECIFICATIONS
Power supply
ated open circuit voltage (U
R
)
0
300 VDC
Output characteristic* Drooping
*Defined as a plot of output voltage
versus output current
ated output current (I
R
)
2
20A – 60A
Hypertherm standard rated output 140 VDC
voltage (U2)
Duty cycle (X*) at 104°F (40°C) at U1– Volts AC rms X
rated conditions (U1, I1, U2, I2) 200-208 VAC 1PH 40%
230-240 VAC 1PH 50%
*X = T
on/Tbase
T
= time, minutes 200-208 VAC 3PH 40%
o
n
T
base
, 480 VAC 1PH 50%
= 10 minutes 230-240 VAC 3PH 50%
380/400/415 VAC 3PH 50%
480 VAC 3PH 50%
600 VAC 3PH 50%
Operating temperature 14° to 104° F (-10° to 40° C)
Rated
AC phases (PH) and line frequency (Hz) PH Hz
Standard model 1-3 50-60
CE model 3 50-60
Rated input voltage (U1), rated input U1– Volts AC rms I1-Amps rms I1eff
current (I1) and I1eff* at rated output 200-208 VAC 1PH 50 32
U2and I2– cutting only. 230-240 VAC 1PH 44 31
480 VAC 1PH 22 15.5
200-208 VAC 3PH 30 19
*I1eff = (I1) X used to determine 230-240 VAC 3PH 26 18
rating of power cord. 380/400/415 VAC 3PH 15 10.5
480 VAC 3PH 12 8.5
600 VAC 3PH 11 8
Power factor U1– Volts AC rms Harmonic power factor Displacement
power factor
200-208 VAC 1PH 0.99 0.99
230-240 VAC 1PH 0.99 0.99
480 VAC 1PH 0.91 0.99
200-208 VAC 3PH 0.94 0.99
230-240 VAC 3PH 0.94 0.99
380/400/415 VAC 3PH 0.94 0.99
480 VAC 3PH 0.94 0.99
600 VAC 3PH 0.80 0.99
R
– short circuit ratio—CE model only U1– Volts AC rms, 3PH R
sce
sce
400 VAC 153
230 VAC 97
This equipment conforms to IEC 61000-3-12, provided that
code—degree of protection provided by
IP
R
IP23CS*
= 153 at 400 VAC 3PH and 97 at 230 VAC 3PH.
sce min
enclosure IP – “International Protection”
2 – No ingress foreign objects >=12.5mm (0.5 in)
3 – No harmful ingress spraying water
C – AC line circuits protected against ingress of tool >=2.5 mm
dia. x 100 mm long (0.1 in x 4.0 in)
S – fan stationary during water test
*
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE IN THE RAIN
oppling, Tilting (with or without wheel kit) Up to 15° incline
T
.
Gas type Air Nitrogen
Gas quality Clean, moisture-free, oil-free
Gas inlet pressure and flow 90 psig (6.1 bar) 400 scfh/6.7 scfm (189 l/min)
2-2 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 30

6
.
0
BAR
5
.
0
4
.
0
PSI
8
0
7
0
5
0
6
0
6
0
4
0
AM
PS
8
0
2
5
AC
+
_
Dimensions and weight
76 lb
(34.5 kg)
Weight of power supply
without torch
SPECIFICATIONS
10.5 in
(267 mm)
23 in
(584 mm)
19.5 in
(495 mm)
powermax1000 Service Manual 2-3
1
Page 31

SPECIFICATIONS
T60 torches
Handheld cutting capacity at 60 amps
Recommended capacity 3/4 inch (19 mm)
Maximum capacity 1 inch (25 mm)
Severance capacity 1-1/4 inch (32 mm)
Mechanized cutting capacity at 60 amps
Recommended capacity 3/8 inch (10 mm)
Maximum capacity 1/2 inch (12 mm)
Gouging capability
(metal removal rate on mild steel)
Weight
6.9 pounds (3.1 kg) with 25 ft (7.5 m) lead
T60 13.6 pounds (6.2 kg) with 50 ft (15 m) lead
20.6 pounds (9.4 kg) with 75 ft (22.5 m) lead
10.0 pounds (4.5 kg) hour
4.5 pounds (2.0 kg) with 15 ft (4.5 m) lead
T60M 8.3 pounds (3.8 kg) with 25 ft (7.5 m) lead
9.9 pounds (4.5 kg) with 35 ft (10.7 m) lead
15.0 pounds (6.8 kg) with 50 ft (15 m) lead
21.7 pounds (9.9 kg) with 75 ft (22.5 m) lead
2-4 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 32

Dimensions
T60 hand torch dimensions
3.9"
(99 mm)
2.25"
(57 mm)
SPECIFICATIONS
8.9" (226 mm)
1.5"
(38 mm)
1.00"
(25 mm)
T60M machine torch dimensions
1.00"
(25 mm)
2.03"
(52mm)
15.25"
(387 mm)
8"
(203 mm)
32 pitch 0.125" (3.2 mm) width
0.125" (3.2 mm) height
1.38"
(35 mm)
powermax1000 Service Manual 2-5
1
Page 33

SPECIFICATIONS
Symbols and markings
S MARK
The S mark indicates that the power supply and torch are suitable for use in environments with increased hazard
of electrical shock. The hand torches must have shielded consumable parts to maintain S mark compliance.
IEC symbols
The following symbols may appear on the power supply data plate, control labels and switches.
Direct current (DC)
Alternating current (AC)
Plasma torch cutting and gouging
AC input power connection
The terminal for the external
protective (earth) conductor
l
O
An inverter-based power
source
Plasma torch in the
position (cooling and cutting
gas exiting nozzle)
Power is on
Power is off
Volt/amp curve, “drooping”
characteristic
TEST
2-6 powermax1000 Service Manual
Page 34

Section 3
MAINTENANCE
In this section
Controls and indicators .............................................................................................................................................3-3
Indicator LEDs..................................................................................................................................................3-3
Theory of operation...................................................................................................................................................3-4
General ............................................................................................................................................................3-4
Functional description ......................................................................................................................................3-4
Sequence of operation .....................................................................................................................................3-5
Troubleshooting preparation.....................................................................................................................................3-6
Test equipment.................................................................................................................................................3-6
Troubleshooting procedures and sequence.....................................................................................................3-6
External inspection...........................................................................................................................................3-6
Internal inspection ............................................................................................................................................3-7
Initial resistance check..............................................................................................................................................3-7
Check power switch .........................................................................................................................................3-8
Hypertherm IGBT tester ...................................................................................................................................3-9
Indicator LEDS and device tests ......................................................................................................................3-9
IGBT test preparation.....................................................................................................................................3-10
IGBT device test using the Hypertherm tester ...............................................................................................3-10
Troubleshoot the Hypertherm IGBT tester .....................................................................................................3-11
Schematic for building an IGBT tester............................................................................................................3-11
IGBT device test using non-Hypertherm tester ..............................................................................................3-12
Troubleshooting guide ............................................................................................................................................3-14
Control board LEDs........................................................................................................................................3-18
Test 1 – voltage input .....................................................................................................................................3-19
Test 2 – voltage balance ................................................................................................................................3-20
T
est 3 – output diodes ....................................................................................................................................3-21
Test 4 – pilot arc IGBT (Q8) ...........................................................................................................................3-22
Test 5 – inverter IGBT (Q6) and PFC IGBT (Q7) ...........................................................................................3-23
T
est 6 – flyback circuit ....................................................................................................................................3-24
Test 7 – torch stuck open (TSO) ....................................................................................................................3-25
Test 8 – plasma start ......................................................................................................................................3-26
T
est 9 – torch cap sensor ...............................................................................................................................3-26
Test 10 – gas solenoid ...................................................................................................................................3-27
Test 11 – incoming line voltage (VACR) .........................................................................................................3-27
T
est 12 – pressure switch
est 13 – fan
T
...................................................................................................................................................3-27
...............................................................................................................................3-27
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-1
1
Page 35

MAINTENANCE
Test 14 – AUX switch .....................................................................................................................................3-28
Test 15 – flyback circuit failure .......................................................................................................................3-28
T60 hand torch connector pinouts and assembly ...................................................................................................3-29
60M machine torch connector pinouts and assembly ..........................................................................................3-30
T
Component replacement ........................................................................................................................................3-31
Power cord replacement ................................................................................................................................3-31
Torch replacement..........................................................................................................................................3-32
Filter element replacement.............................................................................................................................3-34
Work cable replacement ................................................................................................................................3-35
Capacitor replacement ...................................................................................................................................3-36
Heat sink component replacement.................................................................................................................3-37
3-2 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 36

Controls and indicators
6.0
B
AR
5.04.0
PSI
80705060
6
0
40
AMPS
80
25
V
AC
+
_
AC
V
Current
(amps)
adjustment
knob
ndicator
I
EDs
L
MAINTENANCE
ON (I) / OFF (O)
switch (S1)
Mode switch
Pressure
gauge
Pressure
regulator
Indicator LEDs
Green power ON LED
When illuminated, indicates that power is applied to the system and the power switch is ON (I).
Note: The LED should illuminate when the power is ON (|).
Gas pressure LED
Yellow: When flashing, indicates that the gas pressure is below 60 psig (4.1 bar) for cutting, or 40 psig
Green: When illuminated, indicates acceptable gas pressure for torch operation.
ellow torch cap LED
Y
When illuminated, indicates that the retaining cap is loose or not installed.
Note: Turn the power OFF, correct this fault condition, then turn ON the power to extinguish the LED.
Yellow temp LED
When illuminated, indicates that the power supply’s temperature is too hot.
Red fault LED
When illuminated, indicates that a fault condition exists, which prevents system operation.
Yellow low line voltage LED
When illuminated, indicates that line voltage is below 170 VAC or above 680 VAC. On CE units, it can
also indicate a missing phase.
(2.8 bar) for gouging.
Note: The LED should illuminate when the power is ON (|).
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-3
1
Page 37

MAINTENANCE
Theory of operation
General
Refer to the
Functional description
and
Sequence of operation
sections below, and to Section 6,
Wiring diagrams
.
Functional description
AC power enters the system through the power switch (S1) to the input diode bridge (D24). The voltage from the
diode bridge supplies the Power Factor Correction (PFC) Boost Converter, which provides a 750 VDC bus voltage.
The bus voltage then supplies voltage and current to the inverter and the flyback circuit power supply (DC-to-DC
converter) on the power board (PCB2). The power board provides noise suppression and spike protection. A “soft
start” is implemented via the power board resistor and relay (K1).
The PFC Boost Converter consists of an isolated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT Q7), choke and control circuit. It
provides a 750 VDC bus voltage when the input AC voltage is between 170 and 540 VAC. When the input voltage
is above 540 VAC, the bus voltage will rise to (V
The inverter consists of an IGBT (Q6), the power transformer (T2), a current sense transformer, and sections of the
power board. The inverter operates as a pulse-width, modulator-controlled bridge circuit that is rectified by the
output diode.
The output circuitry consists of 2 current
the output choke.
The control board’s microprocessor monitors and regulates system operation and safety circuits. The current
adjustment knob is used to set to the current to the desired value. The system compares the set point to the output
current by monitoring the current sensor and adjusting the pulse width output of the inverter IGBT (Q6).
-transfer sensors located on the power board, the pilot-arc IGBT (Q8), and
)( 2).
in
The control board (PCB3) includes a pilot arc control switch, which allows the operator to turn ON the pilot arc
(useful when cutting expanded metal), turn OFF the pilot arc (for maximum life of consumables), or to increase the
pilot arc to 20A (useful for gouging or non-transferred-arc cutting).
3-4 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 38

Sequence of operation
MAINTENANCE
Power OFF
• Connect the gas supply to the filter on the power unit.
• Connect the torch to the power supply.
• Connect the work lead to the workpiece.
• Apply power at the line-voltage disconnect box.
• Set the ON/OFF switch (S1) to ON (I)
• The power ON LED and the gas pressure LED illuminate
green, indicating the system is ready for operation.
• The fault LEDs should be extinguished (see
Troubleshooting guide
• Turn the current adjustment knob fully counterclockwise, to
the gas test position.
• Check the air pressure setting.
for more information).
Set the power switch (S1) to OFF (O).
• The gas solenoid valve (V1) closes.
• The gas flow stops.
• The arc extinguishes.
• Postflow continues for
10 seconds.
• Move the torch to make a cut.
• The workpiece drops after the cut.
• Release the plasma start trigger on
the hand torch or the remote start
switch for the machine torch.
The gas solenoid valve (V1)
opens to purge the system and
to allow the setting of pressure.
• Set the gas pressure (see the
Setup
section in the Operator
Manual).
• Select the desired cutting
amps with the current
adjustment knob.
• Gas solenoid valve (V1) closes.
The gas flow stops.
•
• Position the torch above the workpiece.
• Pull the plasma start trigger on the hand torch or
press the remote start switch for the machine torch.
• The gas solenoid valve (V1) opens.
• The gas flow starts.
• The cutting arc starts.
The power circuits are ready.
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-5
1
Page 39

MAINTENANCE
Troubleshooting preparation
The complexity of the circuits requires that service technicians have a working knowledge of inverter power supply
theory. In addition to being technically qualified, technicians must perform all testing with safety in mind.
If questions or problems arise during servicing, call the nearest Hypertherm Technical Services Department listed in
the front of this manual.
Test equipment
• Multimeter
• IGBT tester (part number 128883)
Troubleshooting procedures and sequence
When performing the troubleshooting procedures,
• Refer to Section 6 for the system wiring diagram;
• Refer to Section 4 to locate power supply components;
• Refer to Section 5 for torch components.
After the problem has been located and repaired, refer to the
test the power supply for proper operation.
Power OFF and disconnected
External inspection
Internal inspection
Resistance checks
Power ON
External inspection
Sequence of Operation
Troubleshooting guide
Troubleshooting tests
flow diagram in this section to
1. Inspect the exterior of the power supply for damage to the cover and external components.
2. Inspect the torch and the torch lead for damage.
3-6 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 40

MAINTENANCE
DANGER
LECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
E
• Turn off the power and remove the input power plug from its receptacle before removing the
cover from the power supply. If the power supply is connected directly to a line disconnect
box, switch the line disconnect to OFF (O). In the U.S., use a “lock-out / tag-out” procedure
until the service or maintenance work is complete. In other countries, follow appropriate
national or local safety procedures.
• Do not touch live electrical parts! If power is required for servicing, use extreme caution
when working near live electrical circuits. Dangerous voltages exist inside the power supply
that can cause serious injury or death.
• Do not attempt to repair the power board or control board. Do not cut away or remove any
protective conformal coating from either board. To do so will risk a short circuit between the
AC input circuit and the output circuit and may result in serious injury or death.
HOT PARTS CAN CAUSE SEVERE BURNS
• Allow the power supply to cool before servicing.
MOVING BLADES CAN CAUSE INJURY
• Keep hands away from moving parts.
STATIC ELECTRICITY CAN DAMAGE CIRCUIT BOARDS
• Put on a grounded wrist strap before handling PC boards.
Internal inspection
1. Set the ON/OFF switch (S1) to O (OFF), unplug the power cord and disconnect the gas supply.
2. Remove the power supply’s cover by removing the 12 securing screws.
3. Inspect the inside of the power supply, especially on the side with the power board. Look for broken or loose
wiring connections, burn and char marks, damaged components,
and so on
. Repair or replace as necessary
.
Initial resistance check
All resistance values must be taken with the power cord disconnected and all internal power supply wires attached.
Perform the steps in
Internal inspection
before continuing in this section.
• If resistance values are not close (±25%) to the values given in this section, isolate the problem by
removing wires attached to the resistance check points or component until the problem is found.
• After the problem has been located and repaired, refer to the
section to test the power supply for proper operation.
Sequence of operation
flow diagram in this
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-7
1
Page 41

MAINTENANCE
Check power switch
1. With the power disconnected, set the ON/OFF switch (S1) to ON (I).
2. Check the resistance across the input leads.
. Check the resistance from the input leads to ground.
3
Notes: With the power disconnected and the ON/OFF switch (S1) set to OFF (O), all should read as open.
All electrical values shown are ±25%.
2.4 MΩ
2.4 MΩ2.4 MΩ
>20 MΩ
If no problems were found during the visual inspection or the initial resistance check, and the power supply still
does not operate correctly, see the
Note: The
Troubleshooting guide
Troubleshooting guide
.
provides most probable causes and solutions. Study the system wiring
diagram and understand the theory of operation before troubleshooting. Before purchasing a major
replacement component, verify the problem with Hypertherm T
echnical Service or the nearest
Hypertherm repair facility.
3-8 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 42
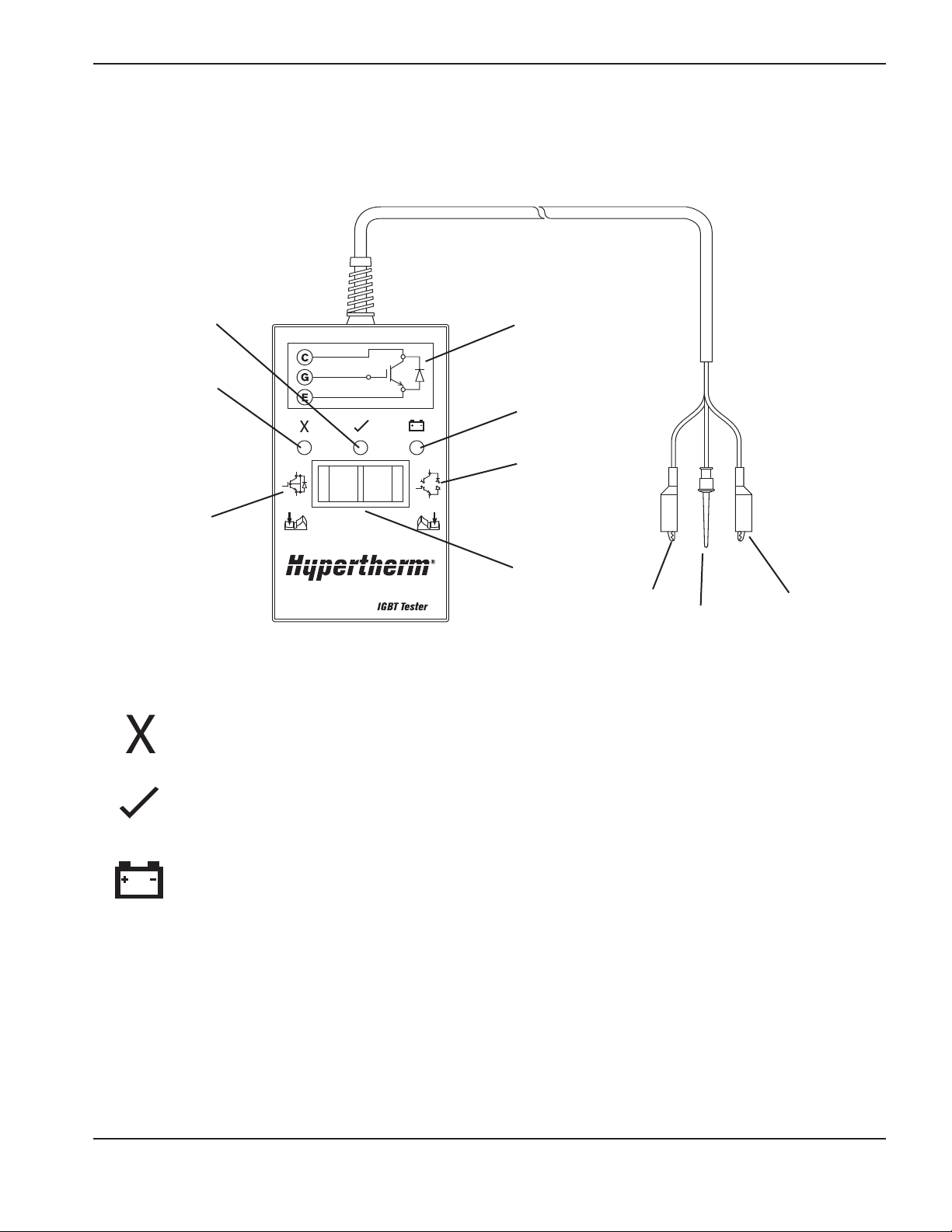
MAINTENANCE
128884
Hypertherm IGBT tester
Use the Hypertherm IGBT tester (part number 128883) as described in the following sections or assemble your
own IGBT tester from the schematic diagram shown in
IGBT tester schematic
and use it to test the IGBTs.
Pass LED
(green)
Fail LED
(red)
Test for
shorted IGBT
Indicator LEDs and device tests
Red “fail” LED
When illuminated, this LED indicates that the IGBT failed the test for an open IGBT when the switch
is pressed to the right or for a shorted IGBT when the switch is pressed to the left.
Circuit
diagram
Low battery
LED (red)
Test for
open IGBT
Rocker
switch
Collector
(red)
Gate
(yellow)
Emitter
(black)
Green “pass” LED
When illuminated, this LED indicates that the IGBT passed the test for an open IGBT when the
switch is pressed to the right or for a
shorted IGBT when the switch is pressed to the left.
Red “low battery” LED
When illuminated, this LED indicates that the remaining voltage in the battery is insuf
ficient to power
the test circuitry. Replace the battery.
Note:
The Hypertherm IGBT tester requires a minimum of 8V to properly power its circuitry.
IGBT test preparation
Before testing with the Hypertherm IGBT
Before an IGBT
can be tested, it must be electrically isolated from all circuits. If the IGBT
tester
onnect the colored leads to the IGBT
, c
supply, remove the power board and any lead connections before testing.
as shown below
is installed in a power
.
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-9
1
Page 43

MAINTENANCE
aution: Failure to isolate the IGBT may result in false readings and/or damage
C
to the IGBT tester.
The illustrations below depict three common IGBT configurations. Each connection on the IGBT is labeled with an
bbreviation. They may be labeled as C, E, G or 1, 2, 3 with a schematic that shows numbers and pin functions.
a
Yellow lead
Gate 2 (G2)
Black lead
Emitter 2 (E2)
Red lead
Collector 2 (C2)
Red lead
Collector 1, (C1)
Black lead
Emitter 1 (E1)
IGBT, Inverter,
Test 1
IGBT, Inverter,
Test 2
Yellow lead
Gate 1 (G1)
Yellow lead
Gate (G)
Black lead
Emitter (E)
Red lead
Collector (C)
IGBT, PFC
IGBT, Pilot arc
Yellow lead
Gate (G)
Black lead
Emitter (E)
Red lead
Collector (C)
IGBT device test using the Hypertherm tester
Using the Hypertherm IGBT tester, press and hold the switch in the desired position to perform the tests described
in the following table.
Switch
LED
position Fail Pass Battery This may mean Corrective action
Left X – – IGBT is shorted Replace IGBT
Left – X – IGBT passed short test None
Left – – X Battery below 8V Replace battery
Left – – – Dead battery Replace battery
Right X – – IGBT is open Replace IGBT
Right – X – IGBT passed open test None
Right
– – X Battery below 8V Replace battery
Right – – – Dead battery Replace battery
3-10 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 44

MAINTENANCE
Troubleshoot the Hypertherm IGBT tester
1. Inspect the leads and the IGBT tester for damage.
2. Verify that the battery voltage is greater than 8V.
. Test the IGBT Tester, itself, as shown below. If the results do not match the table, replace the lead connections.
3
Connect leads Short test Open test
None Pass Fail
Red to Black Fail Pass
Schematic for building an IGBT tester
R4
2.0K
009036
9 VDC
battery
N.O.
pushbutton
switch
R1
3.01M
009464
Black
Minigrabber
test clip
ellow
Y
Minigrabber
test clip 4
Legend
1. Collector 1 (C1)
2. Emitter 2 (E2)
R3
2.0K
009036
D1
Red LED lamp
109092
3. Collector 2, Emitter 1 (C2,E1)
4. Gate 1 (G1)
5. Emitter 1 (E1)
6. Emitter 2 (E2)
7. Gate 2 (G2)
Red Minigrabber
test clip
1
5
3
7
6
Q1
2
150A
1400V
109125
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-11
1
Page 45

MAINTENANCE
IGBT device test using non-Hypertherm tester
The device tester shown in
Schematic for building an IGBT tester
has one LED and one pushbutton switch that are
used in combination to perform two tests.
1. Visually inspect the IGBT for cracks or black marks. If damaged, replace the IGBT.
2. Verify that the 9V battery reads greater than (>) 8.0V.
3. Connect the test leads as shown below.
Note: The IGBT must be electrically isolated before the test is performed.
4. With the test leads connected and without pressing the pushbutton switch, the LED should not illuminate. If the
LED is illuminated, then the IGBT is shorted. Replace the IGBT.
5. With the test leads connected, press the push button switch. This time, the LED should illuminate. If the LED
does not illuminate, then the IGBT is open. Replace the IGBT.
Yellow lead
Gate 2 (G2)
IGBT, Inverter
Test 1
Yellow lead
Gate (G)
IGBT, PFC
Yellow lead
Gate (G)
IGBT, Pilot arc
Black lead
Emitter 2 (E2)
Red lead
Collector 2 (C2)
Red lead
Collector 1 (C1)
Black lead
Emitter 1 (E1)
IGBT, Inverter,
Test 2
Black lead
Emitter (E)
Red lead
Collector (C)
Yellow lead
Gate 1 (G1)
Black lead
Emitter (E)
Red lead
Collector (C)
3-12 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 46

MAINTENANCE
Power switch (S1)
Flyback circuit
Power factor circuit
Input diode
Gas manifold Inverter circuit
Inverter IGBT (Q6)
Board common (TP1) PFC IGBT (Q7)
orch (J18)
T
Work lead
Output diodes
Control board (PCB3)
Pilot arc IGBT (Q8)
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-13
1
Page 47

MAINTENANCE
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
No voltage, improper voltage applied to
unit, defective power switch (S1), or
defective input diode.
Perform Test 1.
Defective filter board (PCB1).
CE systems only: Measure the AC voltage at the CE filter. If no
voltage or low voltage, replace the filter board.
Defective power board (PCB2), fan, or
solenoid valve.
Disconnect J1 and J20 from power board and perform Test 6. If all
voltages are not present or if voltages are oscillating, replace the
power board. If the voltages are good, reconnect J1 and J20 one at a
time and perform Test 6. Replace the component that causes the
voltage to oscillate or drop.
Defective power board (PCB2) or IGBT
(Q6 or Q7).
Perform Tests 1 and 5.
Defective control board (PCB3). Replace the control board.
Defective power board (PCB2), fan, or
solenoid valve.
Disconnect J1 and J20 from power board and perform Test 6. If all
voltages are not present or if voltages are oscillating, replace the
power board. If the voltages are correct, reconnect J1 and J20 one at
a time and perform Test 6. Replace the component that causes the
voltage to oscillate or drop.
Defective power board (PCB2) or IGBT
(Q6 or Q7).
Perform Tests 1 and 5.
Defective control board (PCB3). Replace the control board.
System is in gas test mode.
The current adjustment knob is in the
gas test position.
Turn the knob clockwise until it is set at 20 amps or below.
Solenoid valve (V1) stuck open
or defective power board
(PCB2).
Faulty valve, power board (PCB2), or
control board (PCB3).
Perform Test 10.
Voltage below proper operating limits,
or phase is lost.
Verify the incoming line voltage and the circuit size according to the
Operator Manual.
Faulty power board or control board. Perform Tests 5, 6, and 11.
No air supplied to unit. Connect air supply.
Dirty air filter element. Replace air filter element.
Restriction in air supply line. Replace the air supply line.
Air pressure setting below operating
requirements or incoming air pressure
is dropping when trying to fire the torch.
Turn the current adjustment knob to gas test and set the pressure to
70 psi (4.8 bar) for cutting and 50 (3.4 bar) for gouging as required for
system operation. Verify the gas source is within the setup
specifications in Section 2.
Faulty pressure sensor assembly or
control board.
Perform Test 12.
Insufficient voltage to control
circuits, or shorted power
component.
Power On LED does not illuminate or
blinks when power switch is ON.
Insufficient air pressure.
Air pressure LED blinks yellow.
Improper line voltage or circuit
size.
Voltage LED illuminates.
Troubleshooting guide
Power On LED blinks, flashes, or
goes out while cutting.
Shorted power components.
Air flows from the torch at power-up
when neither the torch trigger nor
the start switch is activated.
3-14 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 48

MAINTENANCE
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
Consumables not installed, installed
improperly, or damaged.
Refer to the consumables diagram in Section 5 or to the Operator
Manual for proper installation. Try new consumables and turn off the
power and then turn it on again to clear the error.
Damage to cap sensing circuit. Perform Test 9.
Exceeded duty cycle. Allow unit to cool. Work within duty cycle limits in manual.
Fan not operating or operating
improperly.
Perform Test 13.
Defective heatsink temperature switch
(TP1) Check when system is cool, at
least 15 min after use.
Remove connector J2 from power board (PCB2). Check the
temperature PCB (PCB4) by checking the resistance on pins 1 and 2.
If the resistance is greater than 300 ohms on the heatsink and 458
ohms on the transformer, replace the control board (PCB3). If the
resistance is lower than stated, replace the temperature sensor PCB
(PCB4).
Defective power transformer (T2) or
temperature sensor (TS2). Check
these when system is cool, at least 60
min after use.
Check the transformer sensor (T2) by checking the resistance on J21
pins 1 and 2. If the resistance is greater than 300 ohms on the
heatsink and 458 ohms on the transformer, replace the control board
(PCB3). If the resistance is lower than stated, replace the
temperature sensor PCB (PCB4).
Damaged torch or lead
assembly.
Torch plunger stuck open or broken
torch leads.
Verify the TSO (Torch Stuck Open) LED illuminates (see
Control
Board LEDs
). Perform Test 7.
Pilot Arc IGBT (Q8) not working.
Faulty pilot arc IGBT (Q8), power board
(PCB2), or control board (PCB3).
Perform Test 4.
No output from power board
(PCB2).
Faulty inverter IGBT (Q6) or power
board (PCB2).
Perform Test 5.
No air flow when trying to fire the
torch and no fault LEDs are
illuminated. Air flows when in test.
Start signal not being received
by power supply. Start LED OFF
on control board (PCB3). See
Control Board LEDs
.
Damage to torch or lead assembly for
manual torch. Damage to interface
cable or no input from CNC for
mechanized applications.
Manual torch: check the start wires; see wiring diagram. Mechanized
torch, perform Test 8.
No air flow when trying to fire the
torch, no fault LEDs are illuminated,
and no air flows when in test.
Solenoid valve not working. Valve stuck or no voltage to valve. Perform Test 10.
Worn or damaged consumables.
Overused or improperly installed
consumables.
Replace consumables.
Insufficient air flow. Improper pressure setting.
Turn current adjustment knob to test flow and set pressure regulator
70 psi (4.7 bar) for cutting and 50 psi (3.4 bar) for gouging.
Damaged torch or lead
assembly.
Electrode is not moving properly in the
torch, or there is a short-circuit in the
torch leads.
Perform Test 7.
Faulty power board (PCB2).
Voltage imbalance across bus
capacitors.
Perform Test 2 while trying to fire the torch. If voltage across
capacitors is not balanced, then replace the power board (PCB2).
No air flow when trying to fire the
torch. Fault, Pressure, and AC LEDs
are illuminated.
Cap sensing circuit not satisfied.
Yellow cap-sensing LED illuminates.
Over temp LED illuminates.
Temperature sensors indicating
an over temperature condition.
When pressing the torch trigger or
start switch, air flows from the torch,
but the torch does not fire or fires
for only a short duration.
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-15
1
Page 49

MAINTENANCE
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
Arc lost contact with the
workpiece.
Faulty work lead, work lead connection,
or connection between the work lead
and cutting table.
Check the physical condition of the work lead. Check for loose
connections at the clamp and power supply. Reposition work lead
directly to the work piece. If the problem goes away, clean the cutting
table.
Faulty fan.
Fan could be loading down the Flyback
circuit.
Disconnect J1 and perform Test 6. If the voltage values are correct,
run with the fan disconnected. If system runs fine until the system
reaches over-temperature, replace the fan.
Worn consumables. Worn-out consumables. Replace consumables.
Improper air pressure setting or
low flow.
Insufficient supply or air leak on supply
line.
Turn the current adjustment knob to test flow and set the pressure
regulator to 70 psi (4.7 bar) for cutting or 50 psi (3.4 bar) for gouging.
If unable to adjust to the proper setting, check external air supply.
Poor quality air. Moisture or contaminates in air supply.
Add appropriate filtration and purge the lines with nitrogen to flush out
oil and moisture.
Insufficient input power (Low
voltage and fault LEDs may not
illuminate).
Undersized electrical supply
installation:
- Breaker or fuse
- Supply wire
- Extension cord
Verify that external electrical power is installed according to the
specifications in Section 2. Check the input voltage while trying to fire
the torch. A voltage drop indicates an undersized electrical supply
installation.
Inverter fault or interlock. Power board (PCB2) failure.
Check the fault LEDs on the back of the control board (see
Control
Board LEDs
). If "IF" is illuminated, disconnect J5 and place a jumper
between pins 1 and 2 on power board (PCB2). If the error clears,
replace the power switch (S1). If not, perform Test 5. If one of the two
tests fails, replace the power board and inverter IGBT (Q6).
Capacitor voltage imbalance
(C94/C98).
Faulty resistors on power board
(PCB2).
Perform Test 2 while trying to fire the torch. If voltage across the
capacitors is not balanced, then replace the power board (PCB2).
Poor work lead connection.
Verify that the work lead is attached to workpiece and the workpiece
is free of rust, paint, or other coatings.
Damaged work lead.
Check the resistance across the work lead. If the resistance is greater
than 3 ohms, replace or repair as required.
Defective pilot arc IGBT (Q8).
Turn power OFF, remove consumables, and check resistance
between the plunger and the work piece. If the resistance is less than
5k ohms, check the resistance across the pilot arc IGBT (two screws
on Q8). If resistance is less than 5k ohms, replace the pilot arc IGBT.
Defective control board (PCB3). Replace the control board.
Arc goes out while cutting or
intermittently will not refire.
Inadequate ground.
When pressing torch trigger or start
switch, pilot arc starts but then
extinguishes before the normal 5-
second time-out period. Fault LEDs
may illuminate.
Machine will not cut material well
(does not appear to be operating at
full cutting power), and the arc does
not time out after 5 seconds.
3-16 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 50

MAINTENANCE
Problem This may mean Cause Solution
Current adjustment set too low.
Verify that the current adjustment knob is at the proper setting (turn to
max, fully clockwise).
Defective power board current sensor.
Verify that the yellow wire connected to the bottom of Q6 is wired
through the bottom of L1. If so and the "IF" LED is illuminating (see
Control Board LEDs
), replace the power board and perform Test 5. If
one of the two tests fails, replace the power board (PCB2) and the
appropriate IGBT.
Defective control board.
Verify the Transfer LED illuminates properly (see
Control Board LEDs
)
on the control board (PCB3) and check the current on the work lead.
If the current is between 15 and 25 amps and the LED illuminates,
replace the control board.
Mode switch set wrong. Set the mode switch to the correct position.
Faulty control board (PCB3).
Verify that the Transfer LED illuminates on the control board and
verify that the "IF" LED is not illuminating (see
Control Board LEDs
).
If both are true, replace the control board (PCB3).
Fault LED on power-up.
Start signal illuminated on
control board.
CNC issuing plasma start in a machine
application or the torch trigger is
defective or engaged.
Remove the interface cable from the back of the power supply and
check the Start LED (see
Control Board LEDs
). If the Start LED goes
out, the problem is either a short circuit in the interface cable or the
CNC is issuing a plasma start signal. For a hand torch, check wiring
of the torch trigger (see
T80 Hand Torch
).
Red LED on power board (PCB2)
remains illuminated when input
voltage is between 200-540 VAC.
Faulty PFC circuit on the power
board or the inverter is going
into an over-current state.
Faulty inverter IGBT (Q6), PFC IGBT
(Q7), power board (PCB2).
Perform Test 5.
Major component damage on power
board (PCB2).
Shorted inverter IGBT (Q6) or
PFC IGBT (Q7).
Perform Test 5.
Machine will not cut material well
(does not appear to be operating at
full cutting power) and the arc does
not time out after 5 seconds.
Losing pilot arc when going off plate
while in continuous pilot mode.
Continuous pilot arc does not
work.
Low output from power supply.
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-17
1
Page 51

MAINTENANCE
7050456055 65 75 80 85
STAR T
STAR T
XFR
SDF
STAR T
IF
STAR T
TSO
STAR T
SP
.
.
.
.
Control board LEDs
If the red Fault LED illuminates, no yellow LEDs are illuminated, and the green AC and Gas pressure LEDs remain
illuminated, check the LEDs on the rear of the control board (PCB3).
Diagnostic LEDS
P
GAS
S
TATU S
URRENT
C
UP
MID
DOWN
1
CPA
NORMAL
GOUGE
START
START SIGNAL VALID
XFR
TRANSFER
SELF DIAGNOSTICS FAILURE
SDF
(Blinking at 1 sec. rate)
INVERTER INTERLOCK
IF
(Visible for 10 sec. after event)
TORCH STUCK OPEN
TSO
(Visible for 10 sec. after event)
SP
SPARE
3-18 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 52

MAINTENANCE
Test 1 – voltage input
• Check the line voltage to the top of the power switch (S1).
• Check the input voltage to the input diode bridge.
• The AC voltage between any 2 input wires should equal the line voltage.
• If there is proper voltage to the power switch and low voltage to the input diode, replace the power switch.
• For CE systems, check the voltage at the CE filter. If there is proper voltage to the CE filter and low
voltage to the input diode, replace the CE filter.
• Check the output voltage of the input diode bridge.
• Output VDC = Line Voltage x 1.414 VDC.
Note: All values can be ±15%.
Standard unit CE unit
L1 Black Black (U)
L2 White Blue (V)
L3 Red Brown (W)
PE Green Green/Yellow
Input diode bridge
L1 (U)
Ground (PE)
L2 (V)
L3 (W)
Power switch (S1)
= Line voltage*
= Line voltage
= Line voltage*
* Single phase
Line voltage x 1.414
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-19
1
Page 53

MAINTENANCE
Test 2 – voltage balance
Test to check the balance of the bus voltage, the power-factor circuit, and the soft-start circuit.
Verify the system’s serial number. Serial numbers lower than 1000-016236 have a different power board
•
from systems with serial numbers higher than 1000-016236.
• Remove screws from capacitors C94 and C98 before measuring the resistors listed below.
• Check the voltage across the inverter IGBT (Q6).
• Check the voltage across the capacitors (C94, C98) before and during torch operation.
• Voltage across both capacitors should be 375 VDC.
On systems with serial numbers below 1000-016236, if the capacitors are not balanced at 375 VDC, install the
RCD resistor kit (PN 128963). For systems with higher serial numbers, replace the power board.
Note: All values can be ±15%.
Bus-bleed and soft-start
resistors for serial numbers
below 1000-016236.
R118 = 3Ω
R119 = 25kΩ
R120 = 25kΩ
Inverter IGBT (Q6)
750 VDC
375 VDC
Bus-bleed and soft-start
resistors for serial numbers
above 1000-016236.
R124 = 75kΩ
R125 = 75kΩ
R126 = 75kΩ
R127 = 75kΩ
Note: Bulk capacitors must be
out of circuit.
R126 = 20.8k R120 = 21.2k
R125 = 21.0k R127 = 21.2k
R124 = 24.1k
R119 = 24.1k
375 VDC
C94
375 VDC
C98
375 VDC
3-20 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 54

MAINTENANCE
80
C
100
Test 3 – output diodes
• Check each diode (connection 1 and 3) with an ohm meter in diode test mode.
• For each diode, the value should be open with the meter leads in one direction and 0.1V to 1.0V with the
meter leads reversed.
he diode is shorted if the value is less than 0.1V. Replace the diode.
T
The diode is open if the value is greater than 1.0V in both directions. Replace the diode.
Note: In each case, common (black) should be on 3.
To p
3 2 1
3 to 2 = .179V
3 to 1 = 1.8V
3
2
1
3 2 1
Bottom
3 to 2 = .180V
3 to 1 = 1.8V
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-21
1
Page 55

MAINTENANCE
80
Test 4 – pilot arc IGBT (Q8)
• Check the resistance of the gate drive circuit (R108, R110).
• If the values are not ±15% of the values shown below, replace the power board (PCB2) and the pilot arc
IGBT (Q8).
• If the values are correct, check the pilot arc IGBT (Q8) with an IGBT Tester. If it fails, replace the power
board (PCB2) and the pilot arc IGBT (Q8).
Gate drive resistors
R108 = 1kΩ
R110 = 10kΩ
Pilot arc IGBT
(Q8)
3-22 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 56

MAINTENANCE
C100
Test 5 – inverter IGBT (Q6) and PFC IGBT (Q7)
• Check the resistance of the gate-drive circuit.
• If the values are not ±25% of the values shown below, replace the power board (PCB2) and the appropriate
IGBT.
• If the values are correct, check both IGBTs with an IGBT tester. If one IGBT fails, replace the power board
(PCB2) and the failed IGBT.
o o
Inverter IGBT (Q6)
o o
Inverter
R82 = 994Ω
R83 = 6.1Ω
R65
R65 = 995Ω
R75 = 6.1Ω
PFC
R87 = 994Ω
R56 = 4.1Ω
R98 = 1Ω
R84 = 10.4Ω
R82
R96 = .4Ω
PFC IGBT (Q7)
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-23
1
Page 57

MAINTENANCE
Test 6 – flyback circuit
DC power supply circuit (+5 VDC, +10 VDC, +18 VDC, and +24 VDC)
20 = 0.75Ω
R
Verify that the diodes listed below are not short-circuited by checking their resistance (approximately 2kΩ).
Note: Check voltage to ground (TP1).
D4 = 24 VDC R1 = 24 VDC
D5 = 24 VDC R2 = 18 VDC
D7 = 10 VDC R9 = -6 VDC
D9 = 18 VDC R18 = 5 VDC
D17 = 5 VDC R26 = 18 VDC
R55 = 18 VDC
Visually inspect for damage.
TP1
3-24 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 58

MAINTENANCE
Test 7 – torch stuck open (TSO)
• Check the resistance between the pilot arc IGBT (Q8) and J17. The value should be less than (<) 100Ω.
• Switch to Gas Test mode and check the resistance again. The value should be greater than (>) 1kΩ.
• If the value is less than (<) 100Ω all the time, check resistance between pilot arc IGBT (Q8) and J17 with
the torch removed. If the value is less than (< )100KΩ, replace the pilot arc IGBT (Q8).
• If the resistance is always greater than (>) 100Ω, then the electrode/nozzle circuit is open.
• Check the wiring to the torch.
• Replace all consumables and verify that the torch will fire.
Note: The retaining cap should be snug and not over-tightened.
• If the torch plunger does not move freely in the torch head, replace the torch head.
• Check to see if the pilot arc IGBT (Q8) is open by putting a jumper wire from J14 to the Pilot Arc IGBT (Q8).
Then attempt to fire the torch. If the torch fires, replace the Pilot Arc IGBT (Q8).
Note: All values are ±25%.
Pilot arc IGBT
Q8
J14
J17
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-25
1
Page 59

MAINTENANCE
Test 8 – plasma start
• After turning ON the power, put a jumper wire between red and white on the machine interface (J19). The
torch should produce an arc. Note: This only applies to the machine torch.
If the torch fires, inspect the machine interface cable and verify the start signal from the CNC by verifying
•
that the START LED on the control board illuminates (see
• If torch does not fire, verify that the Start LED on the control board (PCB3) also is not illuminating.
• To verify hand torch operation, pull the trigger and verify that the Start LED illuminates (see
LEDs
).
• If the Start LED is OFF, verify continuity between the purple and orange wires on the Easy Torch Removal
(ETR) connector of the torch lead.
• If the Start LED is OFF and the trigger works correctly, put a jumper wire between pins 3 and 4 of U22. If
the Start LED illuminates, replace the power board (PCB2). If it does not illuminate, replace the control
board (PCB3).
Control board LEDs
).
Control board
Test 9 – torch cap sensor
• Remove the ETR connector (J18) from the power supply.
• Check the continuity of pins 11 and 12 at the connector
end of the torch with consumables installed in torch.
• If open, check the wiring in the torch leads and cap
sensing switch.
• Put a jumper wire between pins 3 and 4 of U23 with the
power OFF.
• Turn ON the power. If the torch cap sensor LED goes out,
replace the power board (PCB2). If the LED remains
illuminated, replace the control board (PCB3).
ETR connector
(J18)
3-26 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 60

MAINTENANCE
J4
J1
Q1
R7
R25
R50
TP1
Q7
J20
J2
Test 10 – gas solenoid
• If the air is continuously running, disconnect the gas solenoid connector (J20) from the power board
(PCB2). If the air does not shut off, replace the valve.
• If the air does shut off, disconnect the ribbon cable (J4) from the power board (PCB2) and reconnect J20. If
the air remains off, replace the control board (PCB3). If the air flow returns, replace the power board
(PCB2).
Test 11 – incoming line voltage (VACR)
• Check the voltage on output of the input diode, which
should equal 1.414 multiplied by the input voltage.
• If the value is low, check the input voltage or replace
the diode.
• If the value is correct, check the voltage between the
left side of R25 and ground (TP1). It should read
4.969 mV/V.
• If the value is correct, replace the control board
(PCB3). If not, replace the power board (PCB2) and
the PFC IGBT (Q7).
Test 12 – pressure switch
• Check the voltage from the right side of R50 to ground
(TP1). It should be approximately equal to 0.0463 VDC
multiplied by psi. For example, when the air regulator is
set to 80 psi, the voltage should be approximately 3.7
VDC.
• If the value is correct, replace the control board
(PCB3). If not, replace the pressure switch.
Test 13 – fan
• Force the fan into an over-temperature condition (place a jumper wire from J2 pin 1 to pin 2 to short it).
Check the voltage across the fan on the power board (PCB2) J1 pins 1 and 2.
•
voltage on the power
voltage should read 24 VDC, if not remove fan connector (J1) and check
The
•
board (PCB2) J1 pins 1 and 2 again.
• If the voltage is 24 VDC, continue to the next step, if not perform Test 6 – flyback circuit.
• Place a jumper wire between the fan transistor (Q1) case to ground (TP1). If the fan turns on, continue to
the next step. If not, replace the fan.
• Check the voltage between the left side of R7 and ground (TP1). If the VDC is zero (0), replace the control
replace the power board (PCB2).
board (PCB3).
If the value is 5
VDC,
the
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-27
1
Page 61

MAINTENANCE
Test 14 – AUX switch
If the AUX switch on the I/O switch (S1) is open when the system is powered up, the IF LED on the control board
will illuminate when the torch trigger is pulled or the start switch is pressed.
• Remove the J3 connector from the power board.
With the ON/OFF switch in the OFF (O) position and the unit unplugged from electrical power, the AUX
•
switch should read as open.
• With the I/O switch in the ON (I) position, the AUX switch should read as closed.
Test 15 – flyback circuit failure
Multiple flashing indicator LEDs can signal a failure in the flyback circuit.
• Unplug the fan. If the LEDs no longer flash, replace the fan. If the lights are still flashing, plug the fan in
again and perform the next step.
• Unplug the solenoid valve. If the LEDs no longer flash, replace the solenoid valve. If the lights are still
flashing, plug the solenoid valve in again and perform the next step.
• Unplug the CNC interface cable or the ON/OFF pendant on the back of the machine.
• If the lights are still flashing, measure for 5 VDC on the power board (R15 or J5 pin 2 to TP1). If the value is
not a constant 5 VDC (±0.5V), disconnect the control board and measure for 5 VDC again. If it is still not a
constant 5 VDC, replace the power board (PCB2).
• If no problems are found while completing the previous steps, replace the control board (PCB3).
3-28 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 62

T60 hand torch connector pinouts and assembly
WHITE
RED
J18
VIOLET
ORANGE
BLUE
E
LECTRODE
NOZZLE
CAP
STAR T
KEY
NOTE: PIN 6 IS THE KEYING FEATURE FOR 60AAND 80A TORCHES
X
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
MAINTENANCE
Not used
Red dot
Pin 10 violet wire (trigger)
Red wire (nozzle)
Orange wire (cap sensor/trigger)
Pin 12 blue wire (cap sensor)
Left
handle
Blue rubber seal
Pin 1
White wires (plunger)
Pin 3
Right
handle
Torch
body
Spring
rigger
T
Screws (5)
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-29
1
Page 63

MAINTENANCE
J18
W
HITE
1
2
3
12
10
1
1
C
AP
8
9
6
7
4
5
RED
ORANGE
O
RANGE
BLUE
W
HITE
NOZZLE
ELECTRODE
T60M machine torch connector pinouts and assembly
Blue rubber seal
Pin 1
White wires (plunger)
Pin 3
Red wires (nozzle)
Red dot
Pin 10 not used
Orange wire (cap sensor)
Pin 12 blue wire (cap sensor)
Strain
relief
Strain
relief
lock
Torch
3-30 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Mounting
sleeve
Screws (3)
body
O-ring
Positioning
sleeve
Page 64

MAINTENANCE
Component replacement
DANGER
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
• Use extreme caution when working near live electrical circuits. Dangerous voltages exist inside the
power supply that can cause serious injury or death.
• See warnings on page 3-7 before proceeding.
Power cord replacement
Disconnect the electrical power and the gas supply before removing the old power cord.
1. Insert the new power cord through the strain relief.
2. Install the power cord connections where shown.
3. Tighten the strain relief onto the power cord.
4. Install the power supply cover.
5. Reconnect the electrical power and the gas supply.
L1 L2
Ground (PE)
Single phase
Ground (PE)
L1 (U)
L2 (V) L3 (W)
Three phase
Standard unit
Black
L1
L2 White
PE Green
Standard unit CE unit
L1 Black Black (U)
L2 White Blue or Grey (V)
Red
L3
PE Green Green/Yellow
Brown (W)
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-31
1
Page 65

MAINTENANCE
1
2
3
Torch replacement
Turn OFF (O) the power switch.
ON
OFF
Unplug the power cord from the power receptacle.
Open the ETR door and route the lead through the end cap.
ETR door
End cap
3-32 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 66

Align the mark on the strain relief with the mark on the end cap.
4
5
6
7
Pull back the quick-release collar and insert the lead’s gas fitting.
MAINTENANCE
Quick-release collar
Slide the quick-release collar forward to lock in the gas fitting. Verify that the gas fitting is secure.
Verify that the red dot on the connector is on top, then plug in the electrical connector. Close the ETR door.
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-33
1
Page 67

MAINTENANCE
A
B
C
A
B
C
3
1
2
Filter element replacement
isconnect the electrical power and the gas supply.
D
Remove the filter bowls from both the new and old filters.
A. Pull down and hold the black release tab.
B. Rotate the filter bowl in either direction until it releases.
C. Pull the filter bowl down to remove it. Do not discard
the o-ring .
If the o-ring shows signs of wear or otherwise needs
replacement, verify that you have the correct o-ring for
the filter. (Each filter has a label on the side of the filter
body.)
• For AF30 filters, use part number 011105.
• For NAF3000 filters, use part number 011094.
Use a screwdriver to remove the old filter element from the
filter housing. Then install the new filter element.
Note: Do not allow the filter element to turn when
loosening the screw.
Re-install the
Slide
A.
Align
B.
body.
C. Rotate the filter bowl until it locks in place.
filter bowl
the filter bowl over the filter element.
the marks on the filter bowl and the filter
over the new filter element.
3-34 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 68

Work cable replacement
Disconnect the electrical power, gas supply and torch lead before removing the old work cable.
1. Install the strain relief on the power supply and secure it with a nut.
2. Tighten the strain relief collar onto the cable.
MAINTENANCE
3. Connect the work cable to the power board
at J14. Tighten the nut to 10 in-lb (12 kg cm)
of torque.
4. Install the ETR barrier.
5. Install the power supply cover.
Connect to J14
Caution: This is a high-current connection.
Proper torque is critical.
Strain relief
ETR
barrier
Work cable
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-35
1
Page 69

MAINTENANCE
Capacitor replacement
Removal
1. Disconnect the electrical power and the gas supply, then remove the power supply cover.
2. Remove the two screws that secure the capacitor (either C94 or C98) to the PC board.
3. Remove the fan assembly.
4. Remove the capacitor from the fan side of the power supply.
Installation
1. Align the bleeder hole on the capacitor with the view hole
on the power board.
2. Install the new capacitor and secure it with 2 screws.
Tighten the screws to 20 in-lb (24 kg cm) of torque.
3. Install the power supply cover.
Remove and install
capacitors from fan side.
Screws
for C94
Screws for
C98
Remove and install screws
from power board side.
Correct installation
3-36 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 70

MAINTENANCE
3333112
1
2
3
Heat sink component replacement
1. Install the components to the heat sink as shown below.
2. Use new thermal pads on the temperature sensor.
3. Use thermal grease on all components. Apply a thin coat (3 mils or a thickness equivalent to a sheet of paper) to
the component, install with screws, and tighten to required torque.
4. Re-torque after 2 minutes. Repeat until torque is maintained.
5. Clean the excess grease from the heat sink.
Thermal grease, 10cc
Thermal pad
Notes:
Apply thermal grease and torque to 8 in-lb (9 kg cm).
Apply thermal grease and torque to 20 in-lb (23 kg cm).
Apply thermal grease and torque to 35 in-lb (40 kg cm).
powermax1000 Service Manual 3-37
1
Page 71

MAINTENANCE
3-38 powermax1000 Service Manual
4
Page 72

Section 4
PARTS – POWER SUPPLY
In this section:
Exterior .....................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Interior right side .......................................................................................................................................................4-3
Back interior right side ..............................................................................................................................................4-4
Interior fan side .........................................................................................................................................................4-5
Heat sink assembly...................................................................................................................................................4-6
Recommended spare parts ......................................................................................................................................4-7
powermax1000 Service Manual 4-1
1
Page 73

PARTS – POWER SUPPLY
6.
0
BAR
5.
0
4.
0
PSI
80
70
50
60
6
0
4
0
A
MP
S
8
0
2
5
AC
+
_
1876523
4
Exterior
Part
Item number Description Qty.
128686 Kit: Labels, domestic 1
128685 Kit: Labels, CE 1
1 128689 Kit: Front panel, domestic 1
2 008965 Current adjustment knob 1
3 128630 Kit: End panel screws 8
4
5 011096 Regulator knob 1
6 128629 Kit: Cover screws 12
128687
123645 Ground clamp 1
Kit: Front panel, CE 1
7 128690 Kit: Power supply cover with labels, domestic 1
128688 Kit: Power supply cover with labels, CE 1
8 128973 Kit: Rear panel 1
4-2 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 74

Interior right side
187109
121113
65234
PARTS –_ POWER SUPPLY
Part
Item number Description Designator Qty.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 128963 Kit: RCD resistor replacement (S/N < 1000-013717) 1
9
10
11 128665 Kit: Strain relief, arc voltage 1
12
13
128701 Kit: Control board, domestic
128702
128659 Kit: Pressure sensor 1
128801
123604
128622 Kit: Gas manifold with solenoid valve V1 1
128628 Kit: ETR Box
16 T
0461
1
10821
128662
128695
123602
Kit: Control board, CE
Kit: Pressure regulator
Pilot arc IGBT
ubing, 8mm OD, 6mm ID, nylon 3 ft.
f Knob 1
On/Of
Machine interface
Kit:
Kit: Power board
drive cables
Gate
cable
PCB3
PCB3
PCB2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
powermax1000 Service Manual 4-3
1
Page 75

PARTS – POWER SUPPLY
6.0
BAR
5
.0
4
.0
PSI
8
0
7
0
5
0
60
A
C
+
_
6
0
4
0
A
M
P
S
8
0
2
5
123
Back interior right side
Part
Item number Description Designator Qty.
1 128672 Kit: Power switch S1 1
2 128706 Kit: EMI filter PCB, CE only PCB1 1
3 128666 Kit: 8 ft (2.5 m) power cable, domestic 3PH 1
128705 Kit: 8 ft (2.5 m) power cable, CE 3PH 1
4-4 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 76

Interior fan side
12653
4
PARTS –_ POWER SUPPLY
Part
Item number Description Designator Qty.
1 128627 Kit: Filter 1
011093 Air filter element 1
011094 O-ring, NAF3000 filter 1
011105 O-ring, AF30 filter 1
2 128707 Kit: Fan M1 1
3 128693 Kit: Inductor, input choke L2 1
4 128691 Kit: Capacitor C94, C98 2
5 128692 Kit: Power transformer T2 1
6 128694 Kit: Inductor, output choke L1 1
powermax1000 Service Manual 4-5
1
Page 77

PARTS – POWER SUPPLY
1876523
4
Heat sink assembly
Part
Item number Description Designator Qty.
127128 Thermal grease, 10 cc 1
1 128677 Kit: Output diode bridge D25 1
2 128697 Kit: Inverter IGBT Q6 1
3 128700 Kit: Temperature Sensor PCB4 1
4 128708 Kit: PFC IGBT Q7 1
5 128696 Kit: Input diode bridge D24 1
6 128670 Kit: Snubber resister (7.5 Ω)1
7 128699 Kit: Pilot arc IGBT Q8 1
8 128669 Kit: Snubber resister (20 Ω)1
Reference Section 3,
Heat sink component replacement
, for torque specifications.
4-6 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 78

PARTS –_ POWER SUPPLY
Recommended spare parts
Part number Description Page
eference
r
008965............................................Current adjustment knob ..................................................................................4-2
128701............................................Kit: Control board, domestic .............................................................................4-3
128702............................................Kit: Control board, CE.......................................................................................4-3
128659............................................Kit: Pressure sensor .........................................................................................4-3
128801............................................Kit: Pressure regulator ......................................................................................4-3
128622............................................Kit: Gas manifold with solenoid valve ...............................................................4-3
123645............................................Work cable with clamp, 15 ft (4.6 m) ................................................................4-3
128695............................................Kit: Power board ...............................................................................................4-3
128963............................................Kit: RCD resistor replacement (S/N < 1000-013717) .......................................4-3
128672............................................Kit: Power switch ..............................................................................................4-4
128706............................................Kit: EMI Filter PCB, CE only .............................................................................4-4
128627............................................Kit: Filter............................................................................................................4-5
011093............................................Air filter element................................................................................................4-5
011094............................................O-ring, NAF3000 filter.......................................................................................4-5
011105 ............................................O-ring, AF30 filter..............................................................................................4-5
128707............................................Kit: Fan .............................................................................................................4-5
128691............................................Kit: Capacitor ....................................................................................................4-5
127128
128677............................................Kit: Output diode bridge ....................................................................................4-6
128697............................................Kit: Inverter IGBT ..............................................................................................4-6
128708............................................Kit: PFC IGBT ...................................................................................................4-6
128696............................................Kit: Input diode bridge.......................................................................................4-6
128699............................................Kit: Pilot arc IGBT .............................................................................................4-6
............................................Thermal grease, 10 cc .....................................................................................4-6
powermax1000 Service Manual 4-7
1
Page 79

PARTS – POWER SUPPLY
4-8 powermax1000 Service Manual
Page 80

powermax1000 Service Manual 5-1
1
Section 5
PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
In this section:
T60 hand torch assembly .........................................................................................................................................5-2
T60M machine torch assembly.................................................................................................................................5-4
T60 consumable configurations................................................................................................................................5-6
T60M consumable configurations.............................................................................................................................5-7
Recommended spare parts ......................................................................................................................................5-8
Page 81

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
5-2 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
T60 hand torch assembly
Item Part number Description Quantity
083172* T60 hand torch assembly with 25 ft (7.6 m) lead
083171* T60 hand torch assembly with 50 ft (15.2 m) lead
083208* T60 hand torch assembly with 75 ft (22.5 m) lead
1 128564 Kit: T60 torch main body replacement 1
2 027889 Retaining clip 1
3 058519 O-ring 1
4 128639 Kit: Cap-off sensor replacement 1
5 075571 Cap-off sensor screws 2
6 128521 Kit: T60/T60M torch head repair kit 1
7 128644 Kit: T60 torch handle replacement 1
8 075586 Handle screws 5
9 002244 Safety trigger 1
10 027254 Spring 1
11 128681 Kit: T60 25 ft (7.6 m) torch lead replacement 1
12 128682 Kit: T60 50 ft (15.2 m) torch lead replacement 1
13 128893 Kit: T60 75 ft (22.5 m) torch lead replacement 1
14 128638 Kit: ETR connector replacement 1
15 128642 Kit: T60 Start switch replacement 1
* Top assembly includes the following consumables (See
T60 consumable configurations
for descriptions of
consumable parts):
120926 Electrode 1
120925 Swirl ring 1
120928 Retaining cap 1
120929 Shield 1
120931 Nozzle 1
Page 82

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
powermax1000 Service Manual 5-3
1
8
7109
11
2
16534
13
14
12
15
Page 83

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
5-4 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
T60M machine torch assembly
Item Part number Description Quantity
083175* T60M machine torch assembly with 15 ft (4.6 m) lead
083174* T60M machine torch assembly with 25 ft (7.6 m) lead
083176* T60M machine torch assembly with 35 ft (10.7 m) lead
083177* T60M machine torch assembly with 50 ft (15.2 m) lead
083209* T60M machine torch assembly with 75 ft (22.5 m) lead
1 128640 Kit: T60M torch main body replacement 1
2 027889 Retaining clip 1
3 058519 O-ring 1
4 128639 Kit: Cap sensor replacement 1
5 075571 Cap sensor screws 2
6 128521 Kit: T60/T60M torch head repair 1
7 128643 Kit: T60M Torch Mounting Sleeve Replacement 1
8 075004 Torch mounting screws 3
9 128710 Torch positioning sleeve 1
10 128634 Kit: 15 ft (4.6 m) torch lead replacement 1
11 128633 Kit: 25 ft (7.6 m) torch lead replacement 1
12 128635 Kit: 35 ft (10.7 m) torch lead replacement 1
13 128641 Kit: 50 ft (15.2 m) torch lead replacement 1
14 128894 Kit: 75 ft (22.5 m) torch lead replacement 1
15 128638 Kit: ETR connector replacement 1
128645 Kit: T60M Torch mounting (for reassembly after installation) 1
* Top assembly includes the following consumables (See
T60M consumable configurations
for descriptions of
consumable parts):
120926 Electrode 1
120925 Swirl ring 1
120928 Retaining cap 1
120930 Shield 1
120931 Nozzle 1
Page 84

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
powermax1000 Service Manual 5-5
9
187
6
2
3
5
4
15
10
11
12
13
14
Page 85

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
5-6 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Hand-held, shielded
Gouging
T60 consumable configurations
120929
120925120926
120932120928
40A
O-ring
058519
120929 120931120928
60A
Shield NozzleRetaining cap
Swirl ringElectrode
120925120926
O-ring
058519
120977 220059120928
60A
220325*
220329120928
120926
120979
Hand-held, FineCut
220327
O-ring
058519
* For use with CE systems.
Page 86

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
powermax1000 Service Manual 5-7
1
T60M consumable configurations
Mechanized, shieldedUnshielded**
120930 120932120928
40A
O-ring
058519
120930 120931120928
60A
120925120926
120979 220006120928
40A
O-ring
058519
120979 220007120928
60A
120925120926
* For use with CE systems.
** In CE countries, unshielded
consumables may only be used in
mechanized torch applications.
Maintain torch-to-work distance of
approximately 3/16 inch (4.8 mm).
*** Use an ohmic sensing cap when a
compatible torch height controller is
installed.
220061***
Shield NozzleRetaining cap
Swirl ringElectrode
Ohmic sensing
retaining cap
220061***
220404
O-ring
058519
220325*
220329120928
120926
120979
120925
Mechanized, FineCut
Page 87

PARTS – TORCH AND CONSUMABLES
5-8 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Recommended spare parts
Part
number Description
058519 Torch o-ring
027055 Silicone lubricant, 1/4 oz. tube
128644 Kit: T60 torch handle replacement
128638 Kit: ETR connector replacement
075586 T60 torch handle screw (5 required)
002244 T60 torch trigger assembly with spring
027254 Replacement trigger spring, T60
128642 Kit: T60 start switch replacement
128564 Kit: T60 hand torch main body replacement
128640 Kit: T60M machine torch main body replacement
128639 Kit: T60/T60M torch cap sensor replacement
128888 Kit: FineCut consumables
128889 Kit: FineCut consumables – CE
083172 T60 hand torch assembly with 25 ft (7.6 m) lead
083175 T60M machine torch assembly with 25 ft (7.6 m) lead
Page 88

powermax1000 Service Manual 6-1
1
Section 6
WIRING DIAGRAMS
In this section:
Timing diagrams .......................................................................................................................................................6-2
Electrical schematics ................................................................................................................................................6-5
Page 89

6-2 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 90

powermax1000 Service Manual 6-3
1
Page 91

WIRING DIAGRAMS
6-4 powermax1000 Service Manual
1
Page 92

6-5
3
8 7 6 35 4 2 1
D
B
C
A
DOMESTIC UNIT
BLK
WHT
RED
GRN
(PE)
CE UNIT
BLK
BLU
BRN
GRN/YEL
(PE)
PCB3
INSTALL JUMPER 108056 CE UNITS ONLY
CONTROL BD
P1
CPA
UP
NORMAL
CURRENT
GAS
45 6055 65 75 80 85
INPUT VOLTAGE
Vbus (Vac<540vac) 750
Vbus (Vac>541vac)
CORD
MACHINE INTERFACE CABLE
POWER SWITCH (S1)
FILTER (PCB1)
POWER BD (PCB2)
CONTROL BD (PCB3)
TEMP SENSOR BD (PCB4) 041723 041723
TIMING DIAGRAM 013341 013341
MID
DOWN
GOUGE
7050STATUS
80 AMP UNIT
087000(DOMESTIC) 087007(CE) 083169(DOMESTIC) 083170(CE)
200-600vac
1/3PH
230-400vac
3PH
750
1.41 X Vac
129652
NA
129653
129683WIRE GROUP 123607
123603
003206
NA
041667
123603
003206
041660
041667
041663 041707
CORD
CORD
S1
AUX
S1
FILTER
J1
PCB1
AUX
DIAGNOSTIC LED'S
START SIGNAL VALID
START
XFR
TRANSFER
SELF DIAGNOSTICS FAILURE
SDF
(BLINKING @ 1 SEC. RATE)
INVERTER INTERLOCK
IF
(VISIBLE FOR 10 SEC. AFTER EVENT)
TORCH STUCK OPEN
TSO
(VISIBLE FOR 10 SEC. AFTER EVENT)
SP SPARE
40 POSITION RIBBON CABLE
60 AMP UNIT
200-600vac
1/3 PH
750 750
1.41 X Vac
129652 129726
129732
123603 123603
005257 005257
NA
041746 041746
041709 041710
041713 041713
013341 013341
J2
230-400vac
3PH
NA
129739
041773
POWER BD PCB2
K1
+
~
D24
~
INPUT
~
BRIDGE
-
MTG-4
PE
2
B
1
+24
Y
J3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
J4
108171
SOFT START
OUTA
OUTB
/IOC
+5
VBUS
VACR
ITF
IFB
T1
FLYBACK
SYSTEM
POWER
SUPPLY
C18
0.10uF
50V
009994
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
TP1
008924
+24
+10
+5
18PA
COMPA
18INV
COMINV
18T
COMT
18REG
-6
U1
ULN2003A
042188
1C1B
2B 2C
3B 3C
4B 4C
5C5B
6B 6C
7C
+V7B-V
D8
1N5231B
5.1V
109109
C1
0.10uF
50V
009994
16
15
14
13
12
11
107
9
CONTROL
GND
C41
0.01uF
100VDC
009990
PE
/PA
/SSR
/PREFLOW
/MM
+24
C13
0.10uF
50V
009994
1
R7
2.0K
009036
R22 R8
499
009414
R3
10
009115
VacR
R50
100
009073
PFC
CONTROL
CKT
2
3
2.21K
1/2W
009883
R4
10
009115
I Vbus
RT7
60V 0.20A
109024
t
Q1
IRLZ44N
55V
0.022ohm
109223
PFC CHOKE
Q6
IGBT
INVERTER
T2
POWER
TRANSFORMER
YEL
P2
YEL
J13
1R2
J2
Y
J1
B
FAN
SA
BRN
BRN
20 OHM
50W
+24
X
3 2R1
B
GAS SOLENOID
SA
7.5 ohm
J11
100W
OUTPUT
DIODES
J12
FEEDBACK
CURRENT
IFB
SENSOR
TRANSFER
SENSOR
ITF
CKT
+5
U22
COMT
+5
U23
COMT
J20
MATERIAL
THIS DRAWING AND ALL INFORMATION
CONTAINED THEREON IS CONSIDERED
PROPRIETARY AND MAY NOT BE USED
FOR MANUFACTURING OR FABRICATION
PURPOSES WITHOUT PERMISSION
FROM HYPERTHERM, INC.
18T
+24
/MM
+24
NOTES:
1. PIN 6 IS KEYING FEATURE ON 60A
2. PIN 9 IS LOCKOUT FEATURE
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED:
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES.
TOLERANCES ARE:
2 PL DECIMAL ±.01
3 PL DECIMAL ±.005
FRACTIONS ±1/64
ANGULAR ±.5∞
PART MUST BE FREE OF BURRS AND SHARP
EDGES. BREAK SHARP EDGES IF NECESSARY
WITH CHAMFER OR RADIUS .015 MAX.
R
B
NC
J14
J17
J18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
LOCKOUT
10
11
12
J19
1
2
3
4
5
6
WORK LEAD
RED
VIO
ORG
BLUE
WHT
RED
YEL
BLK
+
24VDC @100MA MAX
-
OUTPUT
INDUCTOR
PILOT ARC
IGBT
WHT
ELECTRODE
NOZZLE
START
CAP
4
3
14
MACHINE
INTERFACE
12
13
GRN/YEL
CHASSIS
GND
Box-5010 Hanover, NH 03755-5010 603/643-3441
PFC
IGBT
Q7
BY
PRESSURE
SENSOR
SA
Vbus
J7
1
+
C98
2
3
J6
+
C94
1
2
3
X
13 2
2
1 3B2
J5
R
B R
TEMP
SENSOR IN
XFMR
T2
J21
1
HEATSINK
TEMP
SENSOR BD
PCB4
J9
OR J10
J8
3
2
1
R116
10
009115
R117
10
009115
+5
C52
0.10uF
50V
009994
8 7 6 35 4 2 1
SCALE
1=1 1 OF 1
SHEET
D
C
B
A
C
 Loading...
Loading...