Page 1

HyPerformance
®
Plasma HPR260
®
Auto gas
Instruction manual
805000 – Revision 5
Page 2

Register your new Hypertherm system
Register your product on-line at www.hypertherm.com/registration for easier technical
and warranty support. You can also receive updates on new Hypertherm products and a
free gift as a token of our appreciation.
For your records
Serial number: ______________________________________________________
Purchase date: ______________________________________________________
Distributor: ______________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Maintenance notes:
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Page 3

HyPerformance Plasma
HPR260 Auto Gas
Instruction Manual
(P/N 805000)
Revision 5 – April, 2008
© Copyright 2008 Hypertherm, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Hypertherm, HyPerformance, HyDefinition, LongLife and CommandTHC are trademarks of Hypertherm, Inc.
and may be registered in the United States and/or other countries
Hypertherm, Inc.
Hanover, NH USA
www.hypertherm.com
Page 4

1/19/07
Hypertherm, Inc.
Etna Road, P.O. Box 5010
Hanover, NH 03755 USA
603-643-3441 Tel (Main Office)
603-643-5352 Fax (All Departments)
info@hypertherm.com (Main Office Email)
800-643-9878 Tel (Technical Service)
technical.service@hypertherm.com (Technical Service Email)
800-737-2978 Tel (Customer Service)
customer.service@hypertherm.com (Customer Service Email)
Hypertherm Automation
5 Technology Drive, Suite 300
West Lebanon, NH 03784 USA
603-298-7970 Tel
603-298-7977 Fax
Hypertherm Plasmatechnik GmbH
Technologiepark Hanau
Rodenbacher Chaussee 6
D-63457 Hanau-Wolfgang, Deutschland
49 6181 58 2100 Tel
49 6181 58 2134 Fax
49 6181 58 2123 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm (S) Pte Ltd.
No. 19 Kaki Bukit Road 2
K.B. Warehouse Complex
Singapore 417847, Republic of Singapore
65 6 841 2489 Tel
65 6 841 2490 Fax
65 6 841 2489 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm (Shanghai) Trading Co., Ltd.
Unit 1308-09, Careri Building
432 West Huai Hai Road
Shanghai, 200052
PR China
86-21 5258 3330/1 Tel
86-21 5258 3332 Fax
Hypertherm
Branch of Hypertherm, UK, UC
PO Box 244
Wigan, Lancashire, England WN8 7WU
00 800 3324 9737 Tel
00 800 4973 7329 Fax
00 800 4973 7843 (Technical Service)
France (Representative office)
15 Impasse des Rosiers
95610 Eragny, France
00 800 3324 9737 Tel
00 800 4973 7329 Fax
Hypertherm S.r.l.
Via Torino 2
20123 Milano, Italia
39 02 725 46 312 Tel
39 02 725 46 400 Fax
39 02 725 46 314 (Technical Service)
Hypertherm Europe B.V.
Vaartveld 9
4704 SE Roosendaal, Nederland
31 165 596907 Tel
31 165 596901 Fax
31 165 596908 Tel (Marketing)
31 165 596900 Tel (Technical Service)
00 800 49 73 7843 Tel (Technical Service)
Hypertherm Japan Ltd.
801 Samty Will Building
2-40 Miyahara 1-Chome,
Yodogawa-ku, Osaka
532-0003, Japan
81 6 6170 2020 Tel
81 6 6170 2015 Fax
HYPERTHERM BRASIL LTDA.
Avenida Doutor Renato de
Andrade Maia 350
Parque Renato Maia
CEP 07114-000
Guarulhos, SP Brasil
55 11 6409 2636 Tel
55 11 6408 0462 Fax
Page 5

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY (EMC)
Hypertherm i
6-07
EMC Introduction
Hypertherm’s CE-marked equipment is built in compliance
with standard EN60974-10. The equipment should be
installed and used in accordance with the information
below to achieve electromagnetic compatibility.
The limits required by EN60974-10 may not be adequate
to completely eliminate interference when the affected
equipment is in close proximity or has a high degree of
sensitivity. In such cases it may be necessary to use other
measures to further reduce interference.
This cutting equipment is designed for use only in an
industrial environment.
Installation and use
The user is responsible for installing and using the plasma
equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
If electromagnetic disturbances are detected then it shall
be the responsibility of the user to resolve the situation
with the technical assistance of the manufacturer. In some
cases this remedial action may be as simple as earthing
the cutting circuit, see Earthing of Workpiece. In other
cases it could involve constructing an electromagnetic
screen enclosing the power source and the work
complete with associated input filters. In all cases
electromagnetic disturbances must be reduced to the
point where they are no longer troublesome.
Assessment of area
Before installing the equipment the user shall make an
assessment of potential electromagnetic problems in the
surrounding area. The following shall be taken into
account:
a. Other supply cables, control cables, signalling and
telephone cables; above, below and adjacent to the
cutting equipment.
b. Radio and television transmitters and receivers.
c. Computer and other control equipment.
d. Safety critical equipment, for example guarding of
industrial equipment.
e. Health of the people around, for example the use of
pacemakers and hearing aids.
f. Equipment used for calibration or measurement.
g. Immunity of other equipment in the environment. User
shall ensure that other equipment being used in the
environment is compatible. This may require additional
protection measures.
h. Time of day that cutting or other activities are to be
carried out.
The size of the surrounding area to be considered will
depend on the structure of the building and other
activities that are taking place. The surrounding area may
extend beyond the boundaries of the premises.
Methods of reducing emissions
Mains supply
Cutting equipment must be connected to the mains
supply according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
If interference occurs, it may be necessary to take
additional precautions such as filtering of the mains supply.
Consideration should be given to shielding the supply
cable of permanently installed cutting equipment, in
metallic conduit or equivalent. Shielding should be
electrically continuous throughout its length. The shielding
should be connected to the cutting mains supply so that
good electrical contact is maintained between the conduit
and the cutting power source enclosure.
Maintenance of cutting equipment
The cutting equipment must be routinely maintained
according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. All
access and service doors and covers should be closed
and properly fastened when the cutting equipment is in
operation. The cutting equipment should not be modified
in any way except for those changes and adjustments
covered in the manufacturer’s instructions. In particular,
the spark gaps of arc striking and stabilizing devices
should be adjusted and maintained according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations.
Cutting cables
The cutting cables should be kept as short as possible
and should be positioned close together, running at or
close to the floor level.
Equipotential bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the cutting
installation and adjacent to it should be considered.
However, metallic components bonded to the workpiece
will increase the risk that the operator could receive a
shock by touching these metallic components and the
electrode (nozzle for laser heads) at the same time.
The operator should be insulated from all such bonded
metallic components.
Page 6

ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY (EMC)
ii Hypertherm
8-06
Earthing of workpiece
Where the workpiece is not bonded to earth for electrical
safety, nor connected to earth because of its size and
position, for example, ship’s hull or building steelwork, a
connection bonding the workpiece to earth may reduce
emissions in some, but not all instances. Care should be
taken to prevent the earthing of the workpiece increasing
the risk of injury to users, or damage to other electrical
equipment. Where necessary, the connection of the
workpiece to earth should be made by a direct
connection to the workpiece, but in some countries where
direct connection is not permitted, the bonding should be
achieved by suitable capacitances selected according to
national regulations.
Note: the cutting circuit may or may not be earthed for
safety reasons. Changing the earthing arrangements
should only be authorized by a person who is competent
to assess whether the changes will increase the risk of
injury, for example, by allowing parallel cutting current
return paths which may damage the earth circuits of other
equipment. Further guidance is given in IEC/TS 62081
Arc Welding Equipment Installation and Use.
Screening and shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables
and equipment in the surrounding area may alleviate
problems of interference. Screening of the entire
plasma cutting installation may be considered for
special applications.
Page 7

WARRANTY
Hypertherm iii
6-07
Attention
Genuine Hypertherm parts are the factory-recommended
replacement parts for your Hypertherm system. Any
damage caused by the use of other than genuine
Hypertherm parts may not be covered by the
Hypertherm warranty.
You are responsible for the safe use of the Product.
Hypertherm does not and cannot make any guarantee
or warranty regarding the safe use of the Product in
your environment.
General
Hypertherm, Inc. warrants that its Products shall be free
from defects in materials and workmanship, if Hypertherm
is notified of a defect (i) with respect to the power supply
within a period of two (2) years from the date of its delivery
to you, with the exception of Powermax Series power
supplies, which shall be within a period of three (3) years
from the date of delivery to you, and (ii) with respect to the
torch and leads within a period of one (1) year from its date
of delivery to you, and with respect to torch lifter
assemblies within a period of one (1) year from its date of
delivery to you, and with respect to laser heads within a
period of one (1) year from its date of delivery to you. This
warranty shall not apply to any Product which has been
incorrectly installed, modified, or otherwise damaged.
Hypertherm, at its sole option, shall repair, replace, or
adjust, free of charge, any defective Products covered by
this warranty which shall be returned with Hypertherm’s
prior authorization (which shall not be unreasonably
withheld), properly packed, to Hypertherm’s place of
business in Hanover, New Hampshire, or to an authorized
Hypertherm repair facility, all costs, insurance and freight
prepaid. Hypertherm shall not be liable for any repairs,
replacement, or adjustments of Products covered by this
warranty, except those made pursuant to this paragraph or
with Hypertherm’s prior written consent. The warranty
above is exclusive and is in lieu of all other
warranties, express, implied, statutory, or otherwise
with respect to the Products or as to the results
which may be obtained therefrom, and all implied
warranties or conditions of quality or of
merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose or
against infringement. The foregoing shall constitute
the sole and exclusive remedy for any breach by
Hypertherm of its warranty. Distributors/OEMs may
offer different or additional warranties, but Distributors/
OEMs are not authorized to give any additional warranty
protection to you or make any representation to you
purporting to be binding upon Hypertherm.
Certification test marks
Certified products are identified by one or more
certification test marks from accredited testing laboratories.
The certification test marks are located on or near the data
plate. Each certification test mark means that the product
and its safety-critical components conform to the relevant
national safety standards as reviewed by that testing
laboratory. Hypertherm places a certification test mark on
its products only after that product is manufactured with
safety-critical components that have been authorized by the
accredited testing laboratory.
Once the product has left the Hypertherm factory, the
certification test marks are invalidated if any of the following
occurs:
• The product is significantly modified in a manner that
creates a hazard or non-conformance.
• Safety-critical components are replaced with
unauthorized spare parts.
• Any unauthorized assembly or accessory that uses or
generates a hazardous voltage is added.
• There is any tampering with a safety circuit or other
feature that is designed into the product as part of the
certification.
CE marking constitutes a manufacturer’s declaration of
conformity to applicable European directives and
standards. Only those versions of Hypertherm products
with a CE Marking located on or near the data plate have
been tested for compliance with the European Low Voltage
Directive and the European EMC Directive. EMC filters
needed to comply with the European EMC Directive are
incorporated within versions of the power supply with a
CE Marking.
Patent indemnity
Except only in cases of products not manufactured by
Hypertherm or manufactured by a person other than
Hypertherm not in strict conformity with Hypertherm’s
specifications and in cases of designs, processes,
formulae, or combinations not developed or purported to
be developed by Hypertherm, Hypertherm will defend or
settle, at its own expense, any suit or proceeding brought
against you alleging that the use of the Hypertherm
product, alone and not in combination with any other
product not supplied by Hypertherm, infringes any patent of
any third party. You shall notify Hypertherm promptly upon
learning of any action or threatened action in connection
with any such alleged infringement, and Hypertherm’s
Page 8

WARRANTY
iv Hypertherm
6-07
obligation to indemnify shall be conditioned upon
Hypertherm’s sole control of, and the indemnified party’s
cooperation and assistance in, the defense of the claim.
Limitation of liability
In no event shall Hypertherm be liable to any person
or entity for any incidental, consequential, indirect,
or punitive damages (including but not limited to
lost profits) regardless of whether such liability is
based on breach of contract, tort, strict liability,
breach of warranties, failure of essential purpose or
otherwise and even if advised of the possibility of
such damages.
Liability cap
In no event shall Hypertherm’s liability, whether such
liability is based on breach of contract, tort, strict
liability, breach of warranties, failure of essential
purpose or otherwise, for any claim action suit or
proceeding arising out of or relating to the use of
the Products exceed in the aggregate the amount
paid for the Products that gave rise to such claim.
Insurance
At all times you will have and maintain insurance in such
quantities and types, and with coverage sufficient and
appropriate to defend and to hold Hypertherm harmless
in the event of any cause of action arising from the use of
the Products.
National and Local codes
National and Local codes governing plumbing and
electrical installation shall take precedent over any
instructions contained in this manual. In no event shall
Hypertherm be liable for injury to persons or property
damage by reason of any code violation or poor work
practices.
Transfer of rights
You may transfer any remaining rights you may have
hereunder only in connection with the sale of all or
substantially all of your assets or capital stock to a
successor in interest who agrees to be bound by all of the
terms and conditions of this Warranty.
Proper disposal of Hypertherm
products
Hypertherm plasma cutting systems, like all electronic
products, may contain materials or components, such as
printed circuit boards, that cannot be discarded with
ordinary waste. It is your responsibility to dispose of any
Hypertherm product or component part in an
environmentally acceptable manner according to national
and local codes.
• In the United States, check all federal, state, and local
laws.
• In the European Union, check the EU directives, national,
and local laws. For more information, visit
www.hypertherm.com/weee.
• In other countries, check national and local laws.
Page 9

TABLE OF CONTENTS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual v
4
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ...................................................................................................................................i
Warranty........................................................................................................................................................................................ii
Section 1 SAFETY ..............................................................................................................................................................1-1
Recognize safety information...................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Follow safety instructions .........................................................................................................................................................................1-2
Cutting can cause fire or explosion........................................................................................................................................................1-2
Electric shock can kill................................................................................................................................................................................1-3
Static electricity can damage circuit boards........................................................................................................................................1-3
Toxic fumes can cause injury or death...................................................................................................................................................1-4
A plasma arc can cause injury and burns.............................................................................................................................................1-5
Arc rays can burn eyes and skin.............................................................................................................................................................1-5
Grounding safety........................................................................................................................................................................................1-5
Compressed gas equipment safety .......................................................................................................................................................1-6
Gas cylinders can explode if damaged.................................................................................................................................................1-6
Noise can damage hearing ......................................................................................................................................................................1-6
Pacemaker and hearing aid operation...................................................................................................................................................1-6
A plasma arc can damage frozen pipes................................................................................................................................................1-6
Additional safety information....................................................................................................................................................................1-6
Warning labels.............................................................................................................................................................................................1-7
Section 1a SÉCURITÉ ......................................................................................................................................................1a-1
Identifier les consignes de sécurité .....................................................................................................................................................1a-2
Suivre les instructions de sécurité .......................................................................................................................................................1a-2
Le coupage peut provoquer un incendie ou une explosion ...........................................................................................................1a-2
Les chocs électriques peuvent être fatals..........................................................................................................................................1a-3
L’électricité statique peut endommager les cartes de circuits imprimés ....................................................................................1a-3
Les vapeurs toxiques peuvent provoquer des blessures ou la mort ............................................................................................1a-4
L’arc plasma peut provoquer des blessures ou des brûlures ........................................................................................................1a-5
Les rayons de l’arc peuvent brûler les yeux et la peau....................................................................................................................1a-5
Mise à la masse et à la terre..................................................................................................................................................................1a-5
Sécurité des bouteilles de gaz comprimé ..........................................................................................................................................1a-6
Les bouteilles de gaz comprimé peuvent exploser en cas de dommages .................................................................................1a-6
Le bruit peut provoquer des problèmes auditifs...............................................................................................................................1a-6
Pacemakers et prothèses auditives .....................................................................................................................................................1a-6
Un arc plasma peut endommager les tuyaux gelés..........................................................................................................................1a-6
Étiquettes de sécurité..............................................................................................................................................................................1a-7
Section 1b SEGURIDAD .................................................................................................................................................1b-1
Reconocimiento de información de seguridad .................................................................................................................................1b-2
Siga las instrucciones de seguridad ...................................................................................................................................................1b-2
Los cortes pueden provocar incendios o explosiones....................................................................................................................1b-2
El choque eléctrico puede provocar la muerte.................................................................................................................................1b-3
Electricidad estática puede dañar tablillas de circuito....................................................................................................................1b-3
Humos tóxicos pueden causar lesiones o muerte ...........................................................................................................................1b-4
El arco de plasma puede causar lesiones y quemaduras ..............................................................................................................1b-5
Los rayos del arco pueden producir quemaduras en los ojos y en la piel .................................................................................1b-5
Seguridad de toma a tierra....................................................................................................................................................................1b-5
Page 10

TABLE OF CONTENTS
vi HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Seguridad de los equipos de gas comprimido.................................................................................................................................1b-6
Los cilindros de gas pueden explotar si están dañados.................................................................................................................1b-6
El ruido puede deteriorar la audición ..................................................................................................................................................1b-6
Operación de marcapasos y de audífonos........................................................................................................................................1b-6
Un arco plasma puede dañar tubos congelados .............................................................................................................................1b-6
Etiquetas de advertencia........................................................................................................................................................................1b-7
Section 2 SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................................................................................2-1
System description ....................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
General...............................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Power supply ...................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Ignition console ................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Selection console ............................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Metering console .............................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Torch ...................................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Specifications..............................................................................................................................................................................................2-4
System gas requirements ..............................................................................................................................................................2-4
Power supply ....................................................................................................................................................................................2-5
Ignition console – 078172.............................................................................................................................................................2-6
Selection console – 078185 ........................................................................................................................................................2-8
Metering console – 078184 .........................................................................................................................................................2-9
Torch – 128818.............................................................................................................................................................................2-10
Section 3 INSTALLATION...................................................................................................................................................3-1
Upon receipt................................................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Claims ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Installation requirements...........................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Noise levels..................................................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Placement of system components .........................................................................................................................................................3-3
Torque specifications ......................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Installation requirements...........................................................................................................................................................................3-4
System components........................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Cables and hoses............................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Supply gas hoses ............................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Customer supplied power cable..................................................................................................................................................3-5
Recommended grounding and shielding practices............................................................................................................................3-6
Introduction..................................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Types of grounding ..........................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Steps to take.....................................................................................................................................................................................3-7
Grounding diagram.......................................................................................................................................................................3-10
Placement of the power supply..................................................................................................................................................3-11
Install the ignition console...........................................................................................................................................................3-12
Placement of the selection console..........................................................................................................................................3-14
Install the metering console ........................................................................................................................................................3-15
Power supply to ignition console leads..............................................................................................................................................3-16
Pilot arc lead...................................................................................................................................................................................3-16
Negative lead..................................................................................................................................................................................3-16
Page 11

TABLE OF CONTENTS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual vii
5
Ignition console power cable......................................................................................................................................................3-18
Ignition console coolant hoses...................................................................................................................................................3-19
Power supply to selection console cables.........................................................................................................................................3-20
Control cable..................................................................................................................................................................................3-20
Power cable....................................................................................................................................................................................3-20
Selection console to metering console connections ......................................................................................................................3-22
Cable and gas hose assembly ...................................................................................................................................................3-22
Power supply to CNC interface cable................................................................................................................................................3-24
Optional multi-system CNC interface cable ...........................................................................................................................3-24
Notes to CNC interface cable run list ......................................................................................................................................3-25
Examples of output circuits.........................................................................................................................................................3-26
Examples of input circuits............................................................................................................................................................3-27
Remote ON/OFF switch........................................................................................................................................................................3-28
Torch lead assembly................................................................................................................................................................................3-29
Work lead ..................................................................................................................................................................................................3-30
Torch connections....................................................................................................................................................................................3-31
Connect the torch to the torch lead assembly.......................................................................................................................3-31
Connect the torch to the quick-disconnect.............................................................................................................................3-34
Torch mounting and alignment..............................................................................................................................................................3-35
Mounting the torch........................................................................................................................................................................3-35
Torch alignment..............................................................................................................................................................................3-35
Torch lifter requirement...........................................................................................................................................................................3-35
Power requirements................................................................................................................................................................................3-36
General............................................................................................................................................................................................3-36
Line disconnect switch ................................................................................................................................................................3-36
Power cable....................................................................................................................................................................................3-36
Connect the power..................................................................................................................................................................................3-37
Torch coolant requirements...................................................................................................................................................................3-38
Standard installation.....................................................................................................................................................................3-38
Coolant for cold operating temperatures.................................................................................................................................3-39
Coolant for hot operating temperatures...................................................................................................................................3-40
Water purity requirements.....................................................................................................................................................................3-40
Fill the power supply with coolant........................................................................................................................................................3-41
Gas requirements ....................................................................................................................................................................................3-42
Setting the supply regulators......................................................................................................................................................3-42
Gas regulators..........................................................................................................................................................................................3-43
Supply gas plumbing ..............................................................................................................................................................................3-44
Connect the supply gases ..........................................................................................................................................................3-44
Supply gas hoses ....................................................................................................................................................................................3-45
Section 4 OPERATION........................................................................................................................................................4-1
Daily start-up................................................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Check torch.......................................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Power indicators.........................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
General...............................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Power supply ...................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Selection console ...........................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Page 12

TABLE OF CONTENTS
viii HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Metering console .............................................................................................................................................................................4-3
CNC controller requirements ..................................................................................................................................................................4-4
CNC screen examples ..............................................................................................................................................................................4-5
Main (control) screen......................................................................................................................................................................4-5
Diagnostic screen............................................................................................................................................................................4-6
Test screen.........................................................................................................................................................................................4-7
Cut chart screen...............................................................................................................................................................................4-8
Consumable selection...............................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Mild steel............................................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Stainless steel................................................................................................................................................................................4-10
Aluminum.........................................................................................................................................................................................4-10
Install consumables.................................................................................................................................................................................4-11
Cut charts..................................................................................................................................................................................................4-12
Bevel cutting...................................................................................................................................................................................4-12
Marking ............................................................................................................................................................................................4-12
Consumables for mirror-image cutting.....................................................................................................................................4-12
Estimated kerf width compensation..........................................................................................................................................4-13
Changing consumable parts .................................................................................................................................................................4-42
Remove consumables..................................................................................................................................................................4-42
Inspect consumables....................................................................................................................................................................4-43
Inspect torch...................................................................................................................................................................................4-44
Inspect electrode pit depth.........................................................................................................................................................4-45
Replace torch water tube.......................................................................................................................................................................4-46
Common cutting faults............................................................................................................................................................................4-47
How to optimize cut quality...................................................................................................................................................................4-48
Tips for table and torch................................................................................................................................................................4-48
Plasma set-up tips.........................................................................................................................................................................4-48
Maximize the life of consumable parts......................................................................................................................................4-48
Additional factors of cut quality..................................................................................................................................................4-49
Additional improvements .............................................................................................................................................................4-50
Section 5 MAINTENANCE .................................................................................................................................................5-1
Introduction..................................................................................................................................................................................................5-3
Routine maintenance.................................................................................................................................................................................5-3
System description ....................................................................................................................................................................................5-4
Control and signal cables ..............................................................................................................................................................5-4
Sequence of operation..............................................................................................................................................................................5-5
Gas system purge cycle ...........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Gas system valve usage ...........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Marking process...............................................................................................................................................................................5-8
PCB block diagram....................................................................................................................................................................................5-9
Error codes................................................................................................................................................................................................5-10
Error code troubleshooting – 1 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-11
Error code troubleshooting – 2 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-12
Error code troubleshooting – 3 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-13
Error code troubleshooting – 4 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-14
Error code troubleshooting – 5 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-15
Page 13

TABLE OF CONTENTS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual ix
5
Error code troubleshooting – 6 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-16
Error code troubleshooting – 7 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-17
Error code troubleshooting – 8 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-18
Error code troubleshooting – 9 of 10.......................................................................................................................................5-19
Error code troubleshooting – 10 of 10 ....................................................................................................................................5-20
Power supply states................................................................................................................................................................................5-21
Plasma system operation with pump time-out ..................................................................................................................................5-22
CNC operation with pump time-out ....................................................................................................................................................5-23
Initial checks..............................................................................................................................................................................................5-24
Power measurement ...............................................................................................................................................................................5-25
Power supply coolant system servicing..............................................................................................................................................5-26
Draining the coolant system. ......................................................................................................................................................5-26
Coolant system filter................................................................................................................................................................................5-27
Filter replacement..........................................................................................................................................................................5-27
Coolant flow troubleshooting chart .....................................................................................................................................................5-28
Coolant flow tests....................................................................................................................................................................................5-29
Before testing.................................................................................................................................................................................5-29
Using the Hypertherm flow meter (128933) ..........................................................................................................................5-29
Manual pump operation...............................................................................................................................................................5-30
Test 1 – return line......................................................................................................................................................................5-31
Test 2 – supply line at ignition console .................................................................................................................................5-31
Test 3 – change the torch.........................................................................................................................................................5-32
Test 4 – supply line to the torch receptacle .........................................................................................................................5-32
Test 5 – return line from the torch receptacle......................................................................................................................5-32
Test 6 – bucket test at the pump ............................................................................................................................................5-33
Test 7 – bypass the check valve .............................................................................................................................................5-33
Pump and motor troubleshooting..............................................................................................................................................5-34
Testing the flow switch.................................................................................................................................................................5-35
Gas leak tests...........................................................................................................................................................................................5-36
Power supply control board PCB3 .....................................................................................................................................................5-38
Power supply power distribution board PCB2.................................................................................................................................5-39
Start circuit PCB1 ...................................................................................................................................................................................5-40
Operation ........................................................................................................................................................................................5-40
Start circuit functional schematic ..............................................................................................................................................5-40
Start circuit troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................................................5-40
Pilot arc current levels..................................................................................................................................................................5-42
Selection console control board PCB2 .............................................................................................................................................5-43
Selection console power distribution board PCB1.........................................................................................................................5-44
Selection console AC valve-driver board PCB3 ..............................................................................................................................5-45
Metering console control board PCB2 ..............................................................................................................................................5-46
Metering console power distribution board PCB1 ..........................................................................................................................5-47
Chopper tests...........................................................................................................................................................................................5-48
Phase-loss detection test ......................................................................................................................................................................5-50
Torch lead test ..........................................................................................................................................................................................5-51
Preventive maintenance..........................................................................................................................................................................5-52
Page 14

TABLE OF CONTENTS
x HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Section 6 PARTS LIST ........................................................................................................................................................6-1
Power supply...............................................................................................................................................................................................6-2
Ignition console ..........................................................................................................................................................................................6-7
Selection console – 1 of 2.......................................................................................................................................................................6-8
Selection console – 2 of 2.......................................................................................................................................................................6-9
Metering console........................................................................................................................................................................................6-9
HyPerformance torch..............................................................................................................................................................................6-10
Torch assembly ..............................................................................................................................................................................6-10
Torch leads......................................................................................................................................................................................6-10
Consumable parts kit – 228027..........................................................................................................................................................6-11
Consumables for mirror-image cutting ...............................................................................................................................................6-12
Recommended spare parts...................................................................................................................................................................6-13
Section 7 WIRING DIAGRAMS........................................................................................................................................7-1
Introduction..................................................................................................................................................................................................7-1
Wiring Diagrams.........................................................................................................................................................................................7-5
Appendix A BENZOTRIAZOLE / PROPYLENE GLYCOL SAFETY DATA ...............................................................a-1
Section 1 Chemical Product and Company Identification..............................................................................................................a-2
Section 2 Composition / Information on Ingredients.......................................................................................................................a-2
Section 3 Hazards Identification...........................................................................................................................................................a-2
Section 4 First Aid Measures................................................................................................................................................................a-3
Section 5 Fire Fighting Measures.........................................................................................................................................................a-3
Section 6 Accidental Release Measures............................................................................................................................................a-3
Section 7 Handling and Storage..........................................................................................................................................................a-3
Section 8 Exposure Controls / Personal Protection ........................................................................................................................a-4
Section 9 Physical and Chemical Properties ....................................................................................................................................a-4
Section 10 Stability and Reactivity.........................................................................................................................................................a-4
Section 11 Toxicological Information .....................................................................................................................................................a-4
Section 12 Ecological Information..........................................................................................................................................................a-5
Section 13 Disposal Considerations .....................................................................................................................................................a-5
Section 14 Transport Information ...........................................................................................................................................................a-5
Section 15 Regulatory Information.........................................................................................................................................................a-5
Section 16 Other Information..................................................................................................................................................................a-5
Freezing point of Propylene Glycol solution.........................................................................................................................................a-6
Appendix B CNC INTERFACE PROTOCOL ...................................................................................................................b-1
Interface hardware......................................................................................................................................................................................b-2
Signal list......................................................................................................................................................................................................b-2
Signals................................................................................................................................................................................................b-2
Hardware ...........................................................................................................................................................................................b-3
Multi-drop wiring...............................................................................................................................................................................b-4
Multi-drop addressing.....................................................................................................................................................................b-5
Serial commands........................................................................................................................................................................................b-5
Format.................................................................................................................................................................................................b-5
Framing...............................................................................................................................................................................................b-5
Commands ........................................................................................................................................................................................b-5
Page 15

TABLE OF CONTENTS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual xi
5
Command tables..............................................................................................................................................................................b-6
Error responses..............................................................................................................................................................................b-19
Calculating checksums................................................................................................................................................................b-19
Error codes................................................................................................................................................................................................b-20
Status codes.............................................................................................................................................................................................b-22
Gas type codes........................................................................................................................................................................................b-22
CNC requirements ..................................................................................................................................................................................b-23
Auto gas console...........................................................................................................................................................................b-23
Serial interface guidelines......................................................................................................................................................................b-24
Application notes .....................................................................................................................................................................................b-24
Appendix C CUT CHARTS FOR PREVIOUS SYSTEM REVISIONS........................................................................c-1
Appendix D BEVEL CUTTING ...........................................................................................................................................d-1
Bevel torch dimensions.............................................................................................................................................................................d-2
Bevel cutting definitions............................................................................................................................................................................d-3
Cut charts.....................................................................................................................................................................................................d-4
Torch connections....................................................................................................................................................................................d-12
Connect the torch lead assembly to the quick-disconnect assembly...............................................................................d-12
Parts list......................................................................................................................................................................................................d-14
Consumables..................................................................................................................................................................................d-14
Part selection..................................................................................................................................................................................d-15
Page 16

Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-1
8-06
Section 1
SAFETY
In this section:
Recognize safety information ...................................................................................................................................1-2
Follow safety instructions..........................................................................................................................................1-2
Cutting can cause fire or explosion...........................................................................................................................1-2
Electric shock can kill................................................................................................................................................1-3
Static electricity can damage circuit boards..............................................................................................................1-3
Toxic fumes can cause injury or death......................................................................................................................1-4
A plasma arc can cause injury and burns.................................................................................................................1-5
Arc rays can burn eyes and skin...............................................................................................................................1-5
Grounding safety ......................................................................................................................................................1-5
Compressed gas equipment safety ..........................................................................................................................1-6
Gas cylinders can explode if damaged.....................................................................................................................1-6
Noise can damage hearing.......................................................................................................................................1-6
Pacemaker and hearing aid operation......................................................................................................................1-6
A plasma arc can damage frozen pipes....................................................................................................................1-6
Additional safety information.....................................................................................................................................1-6
Warning labels..........................................................................................................................................................1-7
Page 17

1-2 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
11-98
SAFETY
RECOGNIZE SAFETY INFORMATION
The symbols shown in this section are used to identify
potential hazards. When you see a safety symbol in this
manual or on your machine, understand the potential
for personal injury, and follow the related instructions to
avoid the hazard.
FOLLOW SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Read carefully all safety messages in this manual and
safety labels on your machine.
• Keep the safety labels on your machine in good
condition. Replace missing or damaged labels
immediately.
• Learn how to operate the machine and how to use
the controls properly. Do not let anyone operate it
without instruction.
• Keep your machine in proper working condition.
Unauthorized modifications to the machine may
affect safety and machine service life.
DANGER WARNING CAUTION
A signal word DANGER or WARNING is used with a
safety symbol. DANGER identifies the most serious
hazards.
• DANGER and WARNING safety labels are located
on your machine near specific hazards.
• WARNING safety messages precede related
instructions in this manual that may result in injury
or death if not followed correctly.
• CAUTION safety messages precede related
instructions in this manual that may result in
damage to equipment if not followed correctly.
Fire prevention
• Be sure the area is safe before doing any cutting.
Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
• Remove all flammables within 35 feet (10 m) of the
cutting area.
• Quench hot metal or allow it to cool before handling
or before letting it touch combustible materials.
• Never cut containers with potentially flammable
materials inside – they must be emptied and
properly cleaned first.
• Ventilate potentially flammable atmospheres
before cutting.
• When cutting with oxygen as the plasma gas, an
exhaust ventilation system is required.
Explosion prevention
• Do not use the plasma system if explosive dust or
vapors may be present.
• Do not cut pressurized cylinders, pipes, or any
closed container.
• Do not cut containers that have held combustible
materials.
CUTTING CAN CAUSE FIRE OR EXPLOSION
WARNING
Explosion Hazard
Argon-Hydrogen and Methane
Hydrogen and methane are flammable gases that
present an explosion hazard. Keep flames away from
cylinders and hoses that contain methane or hydrogen
mixtures. Keep flames and sparks away from the torch
when using methane or argon-hydrogen plasma.
WARNING
Hydrogen Detonation
with Aluminum Cutting
• When cutting aluminum underwater, or with the
water touching the underside of the aluminum, free
hydrogen gas may collect under the workpiece and
detonate during plasma cutting operations.
• Install an aeration manifold on the floor of the water
table to eliminate the possibility of hydrogen
detonation. Refer to the Appendix section of this
manual for aeration manifold details.
Page 18

Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-3
8-06
SAFETY
Touching live electrical parts can cause a fatal shock
or severe burn.
• Operating the plasma system completes an
electrical circuit between the torch and the
workpiece. The workpiece and anything touching
the workpiece are part of the electrical circuit.
• Never touch the torch body, workpiece or the
water in a water table when the plasma system
is operating.
Electric shock prevention
All Hypertherm plasma systems use high voltage
in the cutting process (200 to 400 VDC are
common). Take the following precautions when
operating this system:
• Wear insulated gloves and boots, and keep your
body and clothing dry.
• Do not stand, sit or lie on – or touch – any wet
surface when using the plasma system.
• Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry
insulating mats or covers big enough to prevent any
physical contact with the work or ground. If you must
work in or near a damp area, use extreme caution.
• Provide a disconnect switch close to the power
supply with properly sized fuses. This switch allows
the operator to turn off the power supply quickly in
an emergency situation.
• When using a water table, be sure that it is correctly
connected to earth ground.
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
• Install and ground this equipment according to the
instruction manual and in accordance with national
and local codes.
• Inspect the input power cord frequently for damage
or cracking of the cover. Replace a damaged power
cord immediately. Bare wiring can kill.
• Inspect and replace any worn or damaged torch
leads.
• Do not pick up the workpiece, including the waste
cutoff, while you cut. Leave the workpiece in place
or on the workbench with the work cable attached
during the cutting process.
• Before checking, cleaning or changing torch parts,
disconnect the main power or unplug the power
supply.
• Never bypass or shortcut the safety interlocks.
• Before removing any power supply or system
enclosure cover, disconnect electrical input power.
Wait 5 minutes after disconnecting the main power
to allow capacitors to discharge.
• Never operate the plasma system unless the power
supply covers are in place. Exposed power supply
connections present a severe electrical hazard.
• When making input connections, attach proper
grounding conductor first.
• Each Hypertherm plasma system is designed to be
used only with specific Hypertherm torches. Do not
substitute other torches which could overheat and
present a safety hazard.
Use proper precautions when handling printed
circuit boards.
STATIC ELECTRICITYCAN DAMAGE CIRCUIT BOARDS
• Store PC boards in anti-static containers.
• Wear a grounded wrist strap when handling
PC boards.
Page 19

1-4 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
8-06
SAFETY
The plasma arc by itself is the heat source used for
cutting. Accordingly, although the plasma arc has not
been identified as a source of toxic fumes, the
material being cut can be a source of toxic fumes or
gases that deplete oxygen.
Fumes produced vary depending on the metal that is
cut. Metals that may release toxic fumes include, but
are not limited to, stainless steel, carbon steel, zinc
(galvanized), and copper.
In some cases, the metal may be coated with a
substance that could release toxic fumes. Toxic
coatings include, but are not limited to, lead (in some
paints), cadmium (in some paints and fillers), and
beryllium.
Gases produced by plasma cutting vary based on the
material to be cut and the method of cutting, but may
include ozone, oxides of nitrogen, hexavalent
chromium, hydrogen, and other substances if such
are contained in or released by the material being cut.
Caution should be taken to minimize exposure to
fumes produced by any industrial process. Depending
upon the chemical composition and concentration of
the fumes (as well as other factors, such as
ventilation), there may be a risk of physical illness,
such as birth defects or cancer.
It is the responsibility of the equipment and site owner
to test the air quality in the area where the equipment
is used and to ensure that the air quality in the
workplace meets all local and national standards
and regulations.
TOXIC FUMES CAN CAUSE INJURYOR DEATH
The air quality level in any relevant workplace
depends on site-specific variables such as:
• Table design (wet, dry, underwater).
• Material composition, surface finish, and
composition of coatings.
• Volume of material removed.
• Duration of cutting or gouging.
• Size, air volume, ventilation and filtration of the
work area.
• Personal protective equipment.
• Number of welding and cutting systems in
operation.
• Other site processes that may produce fumes.
If the workplace must conform to national or local
regulations, only monitoring or testing done at the site
can determine whether the site is above or below
allowable levels.
To reduce the risk of exposure to fumes:
• Remove all coatings and solvents from the metal
before cutting.
• Use local exhaust ventilation to remove fumes from
the air.
• Do not inhale fumes. Wear an air-supplied
respirator when cutting any metal coated with,
containing, or suspected to contain toxic elements.
• Assure that those using welding or cutting
equipment, as well as air-supplied respiration
devices, are qualified and trained in the proper use
of such equipment.
• Never cut containers with potentially toxic materials
inside. Empty and properly clean the container first.
• Monitor or test the air quality at the site as needed.
• Consult with a local expert to implement a site plan
to ensure safe air quality.
Page 20
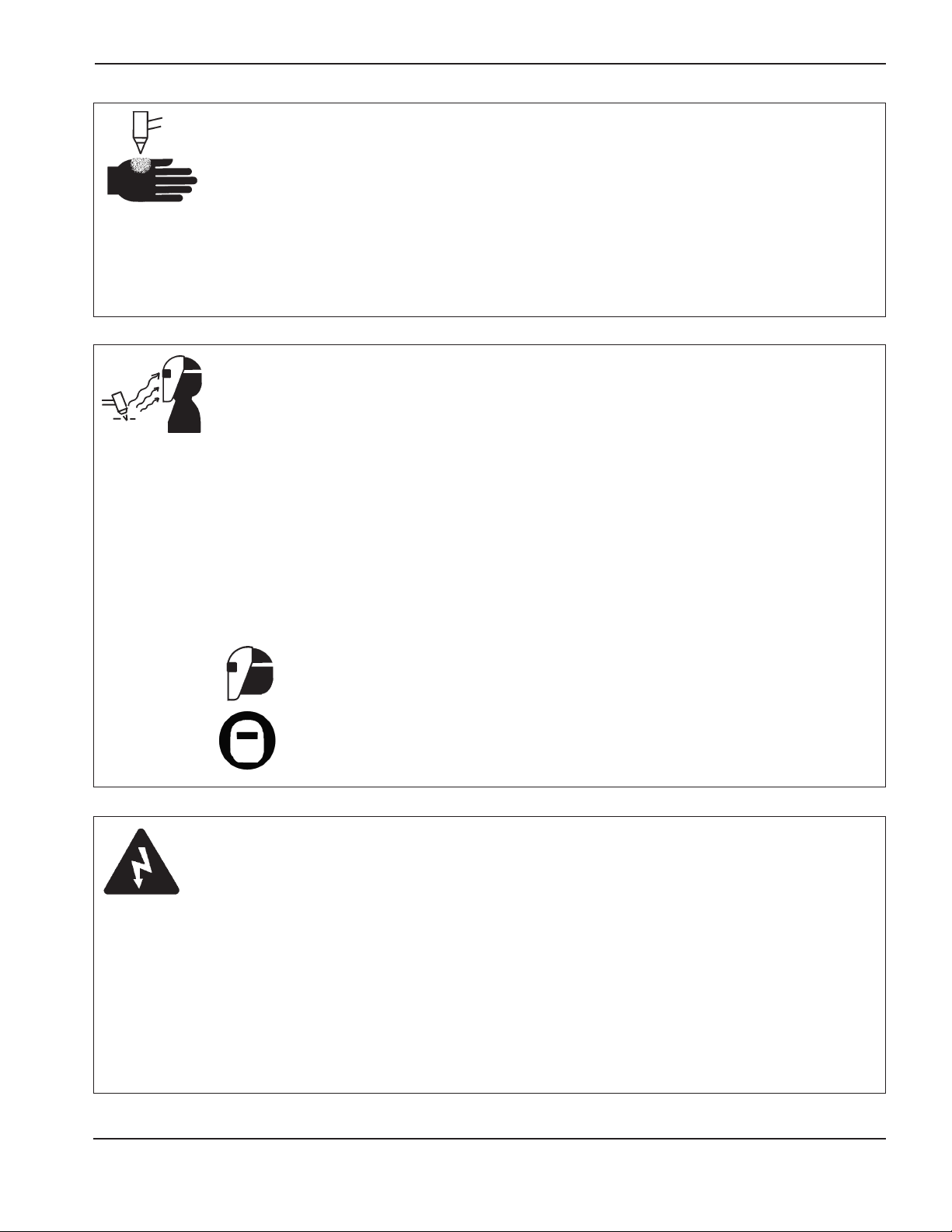
Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-5
5-02
SAFETY
Instant-on torches
Plasma arc comes on immediately when the torch
switch is activated.
A PLASMAARC CAN CAUSE INJURYAND BURNS
The plasma arc will cut quickly through gloves
and skin.
• Keep away from the torch tip.
• Do not hold metal near the cutting path.
• Never point the torch toward yourself or others.
Eye protection Plasma arc rays produce intense
visible and invisible (ultraviolet and infrared) rays that
can burn eyes and skin.
• Use eye protection in accordance with applicable
national or local codes.
• Wear eye protection (safety glasses or goggles with
side shields, and a welding helmet) with appropriate
lens shading to protect your eyes from the arc’s
ultraviolet and infrared rays.
Lens shade
Arc current AWS (USA) ISO 4850
Up to 100 A No. 8 No. 11
100-200 A No. 10 No. 11-12
200-400 A No. 12 No. 13
Over 400 A No. 14 No. 14
ARC RAYS CAN BURN EYES AND SKIN
Skin protection Wear protective clothing to protect
against burns caused by ultraviolet light, sparks and
hot metal.
• Gauntlet gloves, safety shoes and hat.
• Flame-retardant clothing to cover all exposed areas.
• Cuffless trousers to prevent entry of sparks and
slag.
• Remove any combustibles, such as a butane lighter
or matches, from your pockets before cutting.
Cutting area Prepare the cutting area to reduce
reflection and transmission of ultraviolet light:
• Paint walls and other surfaces with dark colors to
reduce reflection.
• Use protective screens or barriers to protect others
from flash and glare.
• Warn others not to watch the arc. Use placards
or signs.
Work cable Attach the work cable securely to the
workpiece or the work table with good metal-to-metal
contact. Do not connect it to the piece that will fall
away when the cut is complete.
Work table Connect the work table to an earth
ground, in accordance with appropriate national or
local electrical codes.
GROUNDING SAFETY
Input power
• Be sure to connect the power cord ground wire to
the ground in the disconnect box.
• If installation of the plasma system involves
connecting the power cord to the power supply, be
sure to connect the power cord ground wire
properly.
• Place the power cord's ground wire on the stud first,
then place any other ground wires on top of the
power cord ground. Fasten the retaining nut tightly.
• Tighten all electrical connections to avoid excessive
heating.
Page 21
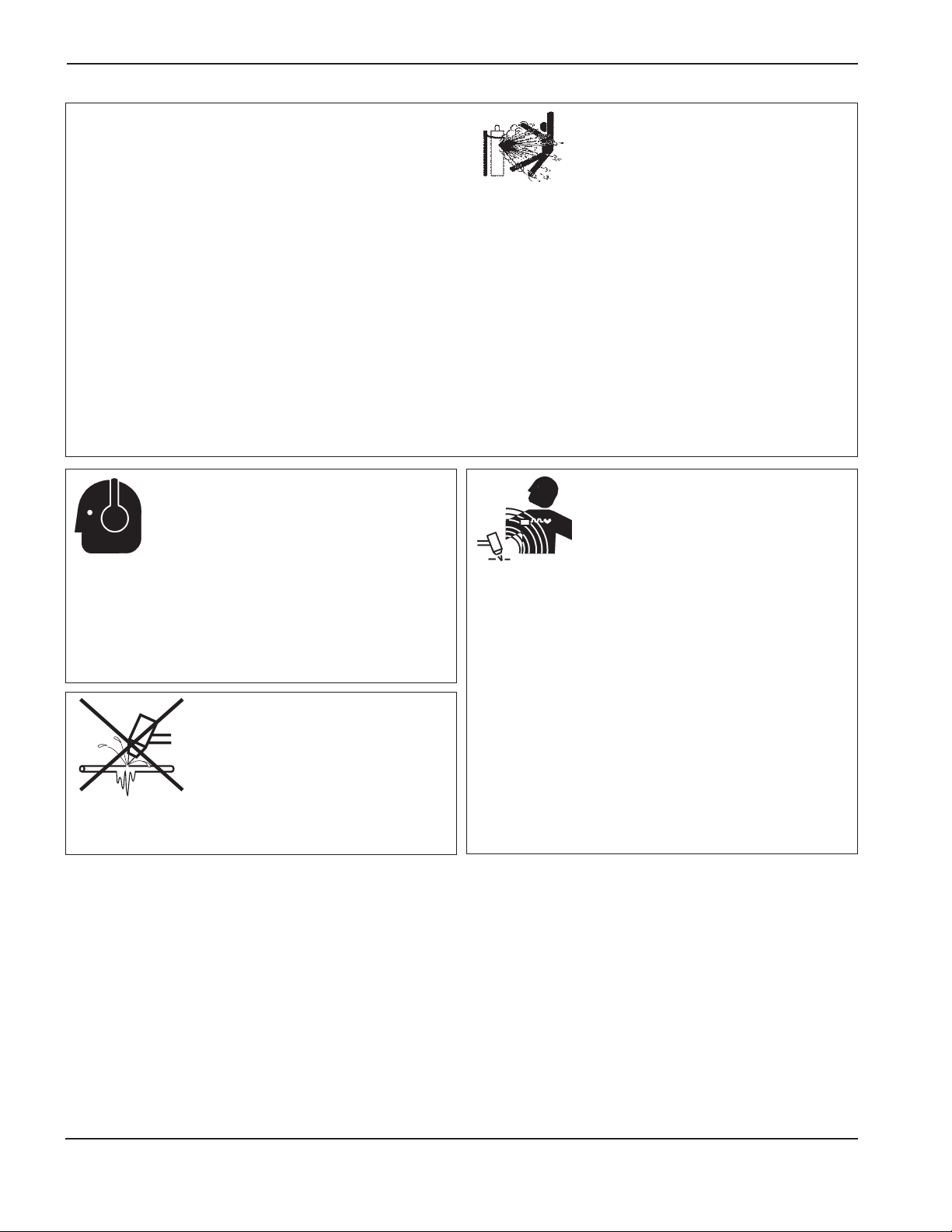
1-6 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
11-98
SAFETY
• Never lubricate cylinder valves or regulators with oil
or grease.
• Use only correct gas cylinders, regulators, hoses
and fittings designed for the specific application.
• Maintain all compressed gas equipment and
associated parts in good condition.
• Label and color-code all gas hoses to identify the
type of gas in each hose. Consult applicable
national or local codes.
GAS CYLINDERS CAN
EXPLODE IF DAMAGED
COMPRESSED GAS EQUIPMENT SAFETY
Gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure. If
damaged, a cylinder can explode.
• Handle and use compressed gas cylinders in
accordance with applicable national or local codes.
• Never use a cylinder that is not upright and secured
in place.
• Keep the protective cap in place over valve except
when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.
• Never allow electrical contact between the plasma
arc and a cylinder.
• Never expose cylinders to excessive heat, sparks,
slag or open flame.
• Never use a hammer, wrench or other tool to open
a stuck cylinder valve.
Frozen pipes may be damaged or can burst if you
attempt to thaw them with a plasma torch.
NOISE CAN DAMAGE HEARING
A PLASMAARC CAN
DAMAGE FROZEN PIPES
Pacemaker and hearing aid operation can be affected
by magnetic fields from high currents.
Pacemaker and hearing aid wearers should consult a
doctor before going near any plasma arc cutting and
gouging operations.
To reduce magnetic field hazards:
• Keep both the work cable and the torch lead to one
side, away from your body.
• Route the torch leads as close as possible to the
work cable.
• Do not wrap or drape the torch lead or work cable
around your body.
• Keep as far away from the power supply as
possible.
PACEMAKER AND
HEARING AID OPERATION
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION
1. ANSI Standard Z49.1,
Safety in Welding and Cutting,
American
Welding Society, 550 LeJeune Road
P.O. Box 351020, Miami, FL 33135
2. ANSI Standard Z49.2,
Fire Prevention in the Use of Cutting and
Welding Processes,
American National Standards Institute
1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018
3. ANSI Standard Z87.1,
Safe Practices for Occupation and
Educational Eye and Face Protection,
American National
Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018
4. AWS F4.1,
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for
Welding and Cutting of Containers and Piping That Have Held
Hazardous Substances,
American Welding Society
550 LeJeune Road, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, FL 33135
5. AWS F5.2,
Recommended Safe Practices for Plasma Arc
Cutting,
American Welding Society
550 LeJeune Road, P.O. Box 351040, Miami, FL 33135
6. CGAPamphlet P-1,
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in
Cylinders,
Compressed Gas Association
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA22202
7. CSAStandard W117.2,
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting,
Canadian Standards Association Standard Sales
178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario M9W 1R3, Canada
8. NFPA Standard 51B,
Cutting and Welding Processes,
National
Fire Protection Association
470 Atlantic Avenue, Boston, MA 02210
9. NFPA Standard 70–1978,
National Electrical Code,
National Fire
Protection Association, 470 Atlantic Avenue, Boston, MA 02210
10. OSHA,
Safety and Health Standards,
29FR 1910
U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402
Prolonged exposure to noise from cutting or gouging
can damage hearing.
• Use approved ear protection when using plasma
system.
• Warn others nearby about the noise hazard.
Page 22

Hypertherm Plasma Systems 1-7
8-99
SAFETY
WARNING LABEL
This warning label is affixed to some power supplies. It is
important that the operator and maintenance technician
understand the intent of these warning symbols as described.
Page 23
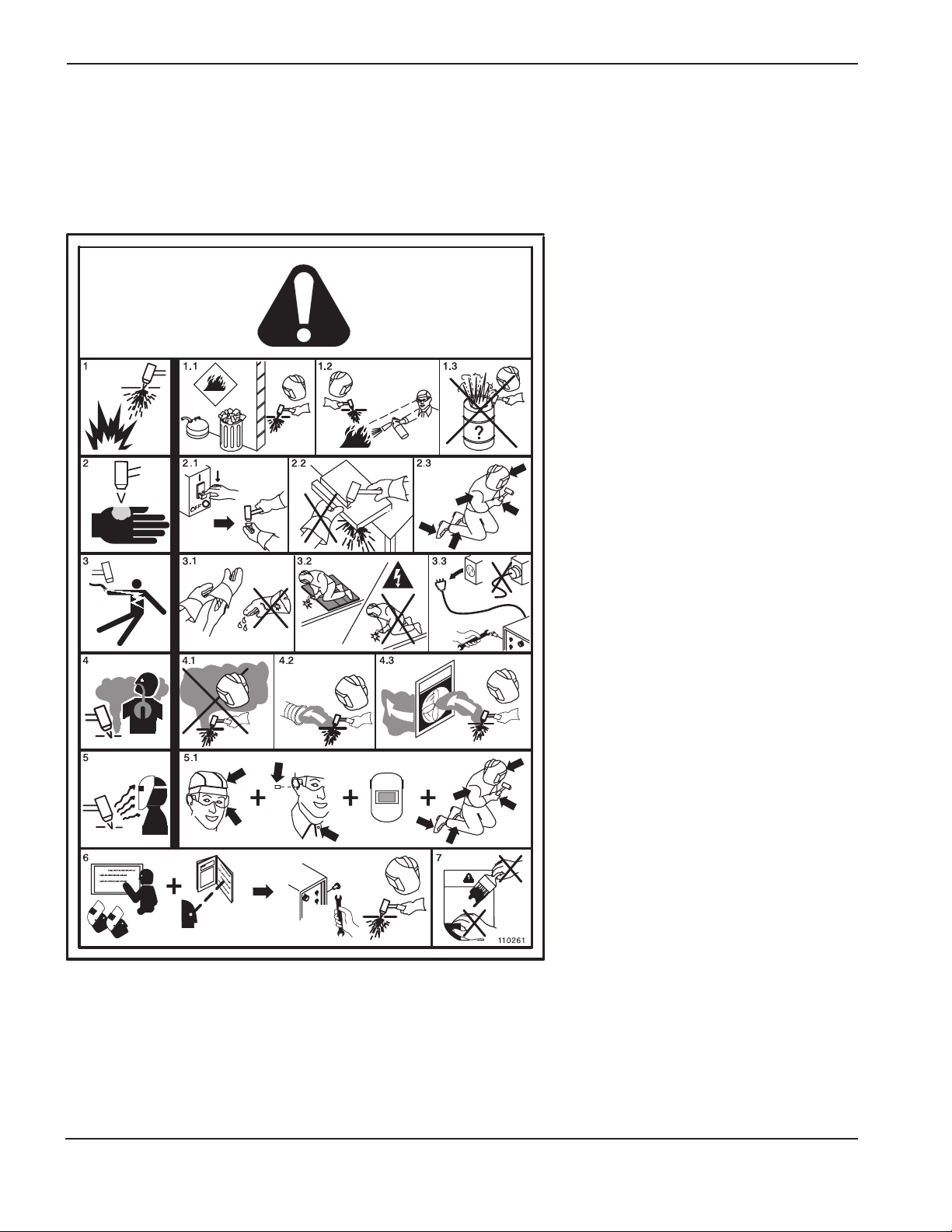
1-8 Hypertherm Plasma Systems
8-99
SAFETY
WARNING LABEL
This warning label is affixed to some power supplies. It is
important that the operator and maintenance technician
understand the intent of these warning symbols as described.
The numbered text corresponds to the numbered boxes on
the label.
1. Cutting sparks can cause explosion
or fire.
1.1 Keep flammables away from cutting.
1.2 Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, and
have a watchperson ready to use it.
1.3 Do not cut on any closed containers.
2. The plasma arc can cause injury
and burns.
2.1 Turn off power before disassembling
torch.
2.2 Do not hold the material near cutting
path.
2.3 Wear complete body protection.
3. Electric shock from torch or wiring
can kill. Protect yourself from electric
shock.
3.1 Wear insulating gloves. Do not wear
wet or damaged gloves.
3.2 Insulate yourself from work and
ground.
3.3 Disconnect input plug or power before
working on machine.
4. Breathing cutting fumes can be
hazardous to your health.
4.1 Keep your head out of the fumes.
4.2 Use forced ventilation or local exhaust
to remove the fumes.
4.3 Use ventilating fan to remove the
fumes.
5. Arc rays can burn eyes and injure skin.
5.1 Wear hat and safety glasses. Use ear
protection and button shirt collar. Use
welding helmet with correct shade of
filter. Wear complete body protection.
6. Become trained and read the
instructions before working on the
machine or cutting.
7. Do not remove or paint over (cover)
warning labels.
Page 24

8-06
Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-1
Section 1a
SÉCURITÉ
Dans cette section :
Identifier les consignes de sécurité.........................................................................................................................1a-2
Suivre les instructions de sécurité ..........................................................................................................................1a-2
Le coupage peut provoquer un incendie ou une explosion ....................................................................................1a-2
Les chocs électriques peuvent être fatals...............................................................................................................1a-3
L’électricité statique peut endommager les cartes de circuits imprimés.................................................................1a-3
Les vapeurs toxiques peuvent provoquer des blessures ou la mort.......................................................................1a-4
L’arc plasma peut provoquer des blessures ou des brûlures .................................................................................1a-5
Les rayons de l’arc peuvent brûler les yeux et la peau...........................................................................................1a-5
Mise à la masse et à la terre...................................................................................................................................1a-5
Sécurité des bouteilles de gaz comprimé...............................................................................................................1a-6
Les bouteilles de gaz comprimé peuvent exploser en cas de dommages .............................................................1a-6
Le bruit peut provoquer des problèmes auditifs......................................................................................................1a-6
Pacemakers et prothèses auditives........................................................................................................................1a-6
Un arc plasma peut endommager les tuyaux gelés................................................................................................1a-6
Étiquettes de sécurité .............................................................................................................................................1a-7
Page 25

11-98
1a-2 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
SÉCURITÉ
IDENTIFIER LES CONSIGNES
DE SÉCURITÉ
Les symboles indiqués dans cette section sont utilisés pour
identifier les risques éventuels. Si vous trouvez un symbole
de sécurité, que ce soit dans ce manuel ou sur l’équipement,
soyez conscient des risques de blessures et suivez les
instructions correspondantes afin d’éviter ces risques.
SUIVRE LES INSTRUCTIONS
DE SÉCURITÉ
Lire attentivement toutes les consignes de sécurité dans le
présent manuel et sur les étiquettes de sécurité se trouvant
sur la machine.
• Les étiquettes de sécurité doivent rester lisibles. Remplacer
immédiatement les étiquettes manquantes ou abîmées.
• Apprendre à faire fonctionner la machine et à utiliser
correctement les commandes. Ne laisser personne utiliser
la machine sans connaître son fonctionnement.
• Garder la machine en bon état. Des modifications non
autorisées sur la machine peuvent engendrer des
problèmes de sécurité et raccourcir la durée d’utilisation
de l’équipement.
DANGER AVERTISSEMENT PRÉCAUTION
Les signaux DANGER ou AVERTISSEMENT sont utilisés
avec un symbole de sécurité, DANGER correspondant aux
risques les plus sérieux.
• Les étiquettes de sécurité DANGER et AVERTISSEMENT
sont situées sur la machine pour signaler certains
dangers spécifiques.
• Les messages d’AVERTISSEMENT précèdent les
instructions d’utilisation expliquées dans ce manuel et
signalent les risques de blessures ou de mort au cas où
ces instructions ne seraient pas suivies correctement.
• Les messages de PRÉCAUTION précèdent les
instructions d’utilisation contenues dans ce manuel et
signalent que le matériel risque d’être endommagé si les
instructions ne sont pas suivies correctement.
Prévention des incendies
• Avant de commencer, s’assurer que la zone de coupage
ne présente aucun danger. Conserver un extincteur à
proximité.
• Éloigner toute matière inflammable à une distance d’au
moins 10 m du poste de coupage.
• Tremper le métal chaud ou le laisser refroidir avant de
le manipuler ou avant de le mettre en contact avec des
matériaux combustibles.
• Ne jamais couper des récipients pouvant contenir des
matières inflammables avant de les avoir vidés et
nettoyés correctement.
• Aérer toute atmosphère potentiellement inflammable
avant d’utiliser un système plasma.
• Lors de l’utilisation d’oxygène comme gaz plasma, un
système de ventilation par aspiration est nécessaire.
Prévention des explosions
• Ne pas couper en présence de poussière ou de vapeurs.
• Ne pas couper de bouteilles, de tuyaux ou autres
récipients fermés et pressurisés.
• Ne pas couper de récipients contenant des matières
combustibles.
LE COUPAGE PEUT PROVOQUER UN INCENDIE
OU UNE EXPLOSION
AVERTISSEMENT
Risque d’explosion
argon-hydrogène et méthane
L’hydrogène et le méthane sont des gaz inflammables et
potentiellement explosifs. Conserver à l’écart de toute
flamme les bouteilles et tuyaux contenant des mélanges à
base d’hydrogène ou de méthane. Maintenir toute flamme et
étincelle à l’écart de la torche lors de l’utilisation d’un plasma
d’argon-hydrogène ou de méthane.
AVERTISSEMENT
Détonation de l’hydrogène lors du
coupage de l’aluminium
• Lors du coupage de l’aluminium sous l’eau, ou si l’eau
touche la partie inférieure de la pièce d’aluminium, de
l’hydrogène libre peut s’accumuler sous la pièce à couper
et détonner lors du coupage plasma.
• Installer un collecteur d’aération au fond de la table à eau
afin d’éliminer les risques de détonation de l’hydrogène.
Se référer à l’annexe du manuel pour plus de
renseignements sur les collecteurs d’aération.
Page 26

8-06
Toucher une pièce électrique sous tension peut provoquer
un choc électrique fatal ou des brûlures graves.
• La mise en fonctionnement du système plasma ferme un
circuit électrique entre la torche et la pièce à couper. La
pièce à couper et tout autre élément en contact avec cette
pièce font partie du circuit électrique.
• Ne jamais toucher le corps de la torche, la pièce à couper
ou l’eau de la table à eau pendant le fonctionnement du
système plasma.
Prévention des chocs électriques
Tous les systèmes plasma Hypertherm utilisent des hautes
tensions pour le coupage (souvent de 200 à 400 V). On
doit prendre les précautions suivantes quand on utilise le
système plasma :
• Porter des bottes et des gants isolants et garder le corps
et les vêtements au sec.
• Ne pas se tenir, s’asseoir ou se coucher sur une surface
mouillée, ni la toucher quand on utilise le système plasma.
• S’isoler de la surface de travail et du sol en utilisant des
tapis isolants secs ou des couvertures assez grandes
pour éviter tout contact physique avec le travail ou le sol.
S’il s’avère nécessaire de travailler dans ou près d’un
endroit humide, procéder avec une extrême prudence.
• Installer un sectionneur avec fusibles appropriés, à
proximité de la source de courant. Ce dispositif permet à
l’opérateur d’arrêter rapidement la source de courant en
cas d’urgence.
• En cas d’utilisation d’une table à eau, s’assurer que cette
dernière est correctement mise à la terre.
LES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES PEUVENT ÊTRE FATALS
• Installer et mettre à la terre l’équipement selon les
instructions du présent manuel et conformément aux
codes électriques locaux et nationaux.
• Inspecter fréquemment le cordon d’alimentation primaire
pour s’assurer qu’il n’est ni endommagé, ni fendu.
Remplacer immédiatement un cordon endommagé.
Un câble dénudé peut tuer.
• Inspecter et remplacer les câbles de la torche qui sont
usés ou endommagés.
• Ne pas saisir la pièce à couper ni les chutes lors du
coupage. Laisser la pièce à couper en place ou sur la
table de travail, le câble de retour connecté lors du
coupage.
• Avant de vérifier, de nettoyer ou de remplacer les pièces
de la torche, couper l’alimentation ou débrancher la prise
de courant.
• Ne jamais contourner ou court-circuiter les verrouillages
de sécurité.
• Avant d’enlever le capot du système ou de la source de
courant, couper l’alimentation électrique. Attendre en
suite
5 minutes pour que les condensateurs se déchargent.
• Ne jamais faire fonctionner le système plasma sans que
les capots de la source de courant ne soient en place.
Les raccords exposés de la source de courant sont
extrêmement dangereux.
• Lors de l’installation des connexions, attacher tout d’abord
la prise de terre appropriée.
• Chaque système plasma Hypertherm est conçu pour être
utilisé uniquement avec des torches Hypertherm
spécifiques. Ne pas utiliser des torches inappropriées qui
pourraient surchauffer et présenter des risques pour la
sécurité.
On doit prendre les précautions qui s’imposent
quand on manipule les circuits imprimés.
L’ÉLECTRICITÉ STATIQUE PEUT ENDOMMAGER
LES CARTES DE CIRCUITS IMPRIMÉS
• On doit ranger les cartes de circuits imprimés dans
des contenants antistatiques.
• On doit porter un bracelet antistatique quand on
manipule les cartes de circuits imprimés.
Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-3
SÉCURITÉ
Page 27

8-06
1a-4 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
SÉCURITÉ
L’arc plasma est lui-même la source de chaleur
utilisée pour le coupage. Par conséquent, bien que
l’arc plasma n’ait pas été reconnu comme une source
de vapeurs toxiques, le matériau coupé peut être une
source de vapeurs ou de gaz toxiques qui épuisent
l’oxygène.
Les vapeurs produites varient selon le métal coupé.
Les métaux qui peuvent dégager des vapeurs
toxiques comprennent, entre autres, l’acier
inoxydable, l’acier au carbone, le zinc (galvanisé) et le
cuivre.
Dans certains cas, le métal peut être revêtu d’une
substance susceptible de dégager des vapeurs
toxiques. Les revêtements toxiques comprennent
entre autres, le plomb (dans certaines peintures), le
cadmium (dans certaines peintures et enduits) et le
béryllium.
Les gaz produits par le coupage plasma varient selon
le matériau à couper et la méthode de coupage, mais
ils peuvent comprendre l’ozone, les oxydes d’azote, le
chrome hexavalent, l’hydrogène et autres substances
présentes dans le matériau coupé ou en émanent.
On doit prendre les précautions qui s’imposent pour
réduire au minimum l’exposition aux vapeurs
produites par tout processus industriel. Selon la
composition chimique et la concentration des vapeurs
(ainsi que d’autres facteurs comme la ventilation), il
peut y avoir un risque de maladie physique, comme
des malformations ou le cancer.
Il incombe au propriétaire du matériel et du site de
vérifier la qualité de l’air dans le secteur où l’on utilise
le matériel et de s’assurer que la qualité de l’air sur
les lieux de travail répond aux normes et
réglementation locales et nationales.
LES VAPEURS TOXIQUES PEUVENT PROVOQUER
DES BLESSURES OU LA MORT
Le niveau de qualité de l’air dans tout lieu de travail
dépend des variables propres au site comme :
• Type de table (humide, sèche, sous l’eau).
• Composition du matériau, fini de la surface et
composition des revêtements.
• Volume de matériau enlevé.
• Durée du coupage ou du gougeage.
• Dimensions, volume d’air, ventilation et filtration de
la zone de travail.
• Équipement de protection individuelle.
• Nombre de systèmes de soudage et de coupage en
fonctionnement.
• Autres procédés du site qui peuvent produire des
vapeurs.
Si les lieux de travail doivent être conformes aux
règlements nationaux ou locaux, seuls les contrôles
ou les essais effectués au site peuvent déterminer si
celui-ci se situe au-dessus ou au-dessous des
niveaux admissibles.
Pour réduire le risque d’exposition aux vapeurs :
• Éliminer tout revêtement et solvant du métal avant
le coupage.
• Utiliser la ventilation d’extraction locale pour
éliminer les vapeurs de l’air.
• Ne pas inhaler les vapeurs. Porter un respirateur à
adduction d’air quand on coupe des métaux revêtus
d’éléments toxiques ou qui en contiennent ou sont
susceptibles d’en contenir.
• S’assurer que les personnes qui utilisent un
matériel de soudage ou de coupage ainsi que les
dispositifs de respiration par adduction d’air sont
qualifiés et ont reçu la formation sur la bonne
utilisation d’un tel matériel.
• Ne jamais couper les contenants dans lesquels il
peut y avoir des matériaux toxiques. En premier
lieu, vider et nettoyer correctement le contenant.
• Contrôler ou éprouver la qualité de l’air au site
selon les besoins.
• Consulter un expert local pour mettre en œuvre un
plan du site afin d’assurer une qualité de l’air sûre.
Page 28
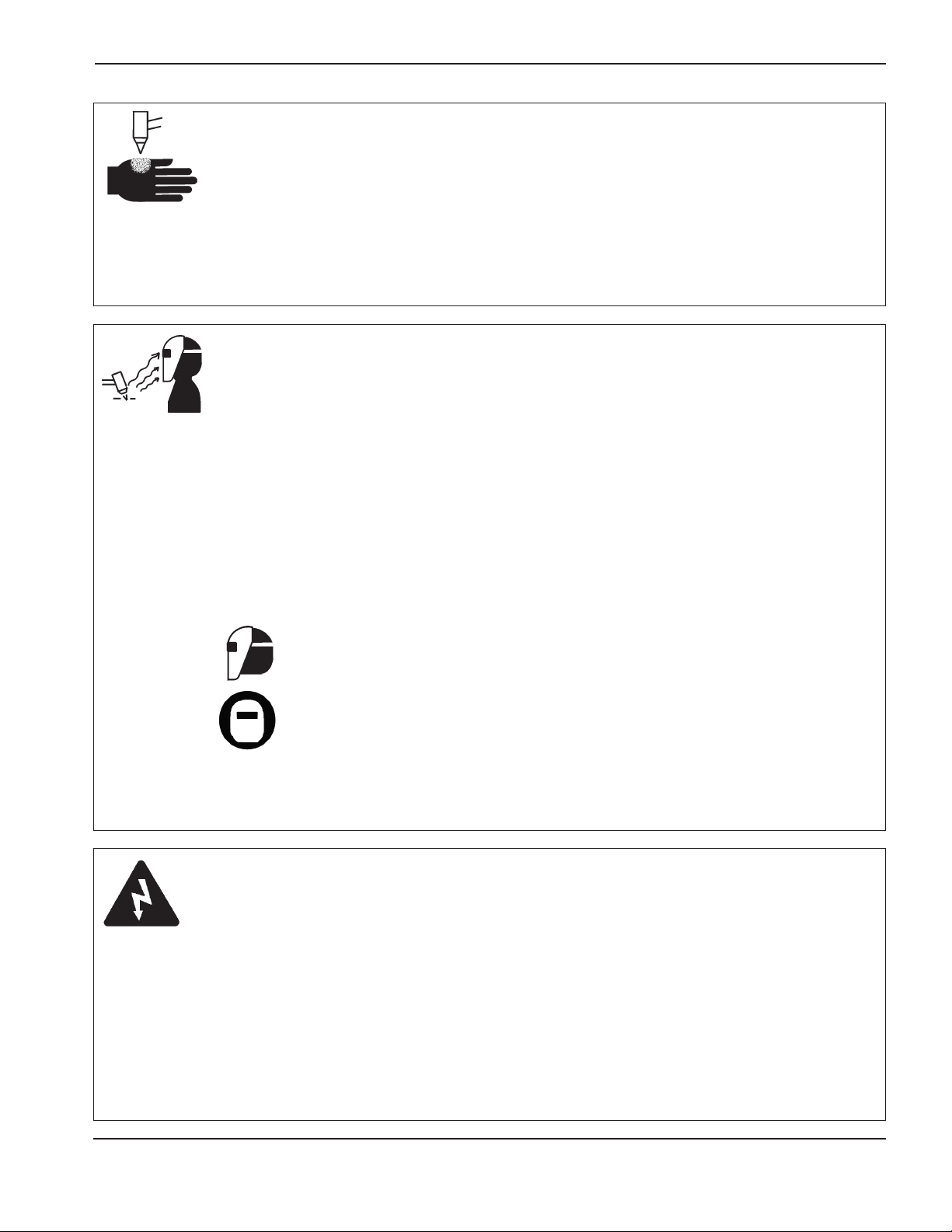
5-02
Torches à allumage instantané
L’arc plasma s’allume immédiatement après que la torche
soit mise en marche.
L’ARC PLASMAPEUT PROVOQUER DES BLESSURES OU DES BRÛLURES
L’arc plasma coupe facilement les gants et la peau.
• Rester éloigné de l’extrémité de la torche.
• Ne pas tenir de métal près de la trajectoire de coupe.
• Ne jamais pointer la torche vers soi ou d’autres
personnes.
Protection des yeux Les rayons de l’arc plasma produisent
de puissants rayons visibles ou invisibles (ultraviolets et
infrarouges) qui peuvent brûler les yeux et la peau.
• Utiliser des lunettes de sécurité conformément aux codes
locaux ou nationaux en vigueur.
• Porter des lunettes de protection (lunettes ou masque muni
d’écrans latéraux et encore masque de soudure) avec des
verres teintés appropriés pour protéger les yeux des rayons
ultraviolets et infrarouges de l’arc.
Puissance des verres teintés
Courant de l’arc AWS (É.-U.) ISO 4850
Jusqu’à 100 A No8N
o
11
100-200 A No10 No11-12
200-400 A No12 No13
Plus de 400 A No14 No14
LES RAYONS DE L’ARC PEUVENT BRÛLER LES YEUX ET LA PEAU
Protection de la peau Porter des vêtements de sécurité
pour se protéger contre les brûlures que peuvent causer les
rayons ultraviolets, les étincelles et le métal brûlant :
• Gants à crispin, chaussures et casque de sécurité.
• Vêtements ignifuges couvrant toutes les parties exposées
du corps.
• Pantalon sans revers pour éviter que des étincelles ou
des scories puissent s’y loger.
• Avant le coupage, retirer de ses poches tout objet
combustible comme les briquets au butane ou les
allumettes.
Zone de coupage Préparer la zone de coupage afin de
réduire la réverbération et la transmission de la lumière
ultraviolette :
• Peindre les murs et autres surfaces de couleur sombre
pour réduire la réflexion de la lumière.
• Utiliser des écrans et autres dispositifs de protection afin
de protéger les autres personnes de la lumière et de la
réverbération.
• Prévenir les autres personnes de ne pas regarder l’arc.
Utiliser des affiches ou des panneaux.
Câble de retour Bien fixer le câble de retour (ou de
masse) à la pièce à couper ou à la table de travail de façon
à assurer un bon contact métal-métal. Ne pas fixer le câble
de retour à la partie de la pièce qui doit se détacher.
Table de travail Raccorder la table de travail à la terre,
conformément aux codes de sécurité locaux ou nationaux
appropriés.
MISE À LA MASSE ET À LATERRE
Alimentation
• S’assurer que le fil de terre du cordon d’alimentation est
connecté à la terre dans le coffret du sectionneur.
• S’il est nécessaire de brancher le cordon d’alimentation à
la source de courant lors de l’installation du système,
s’assurer que le fil de terre est correctement branché.
• Placer tout d’abord le fil de terre du cordon d’alimentation
sur le plot de mise à la terre puis placer les autres fils de
terre par-dessus. Bien serrer l’écrou de retenue.
• S’assurer que toutes les connexions sont bien serrées
pour éviter la surchauffe.
Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-5
SÉCURITÉ
Page 29
11-98
1a-6 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
SÉCURITÉ
• Ne jamais lubrifier les robinets des bouteilles ou les
régulateurs avec de l’huile ou de la graisse.
• Utiliser uniquement les bouteilles, régulateurs, tuyaux et
accessoires appropriés et conçus pour chaque application
spécifique.
• Entretenir l’équipement et les pièces d’équipement à gaz
comprimé afin de les garder en bon état.
• Étiqueter et coder avec des couleurs tous les tuyaux de
gaz afin d’identifier le type de gaz contenu dans chaque
tuyau. Se référer aux codes locaux ou nationaux en
vigueur.
LES BOUTEILLES DE GAZ
COMPRIMÉ PEUVENT EXPLOSER
EN CAS DE DOMMAGES
SÉCURITÉ DES BOUTEILLES DE
GAZ COMPRIMÉ
Les bouteilles de gaz contiennent du gaz à haute pression.
Si une bouteille est endommagée, elle peut exploser.
• Manipuler et utiliser les bouteilles de gaz comprimé
conformément aux codes locaux ou nationaux.
• Ne jamais utiliser une bouteille qui n’est pas placée à la
verticale et bien assujettie.
• Le capuchon de protection doit être placé sur le robinet
sauf si la bouteille est en cours d’utilisation ou connectée
pour utilisation.
• Éviter à tout prix le contact électrique entre l’arc plasma et
une bouteille.
• Ne jamais exposer des bouteilles à une chaleur
excessive, aux étincelles, aux scories ou aux flammes
nues.
• Ne jamais utiliser des marteaux, des clés ou d’autres
outils pour débloquer le robinet des bouteilles.
Les tuyaux gelés peuvent être endommagés ou éclater si
l'on essaie de les dégeler avec une torche plasma.
LE BRUIT PEUT PROVOQUER DES
PROBLÈMES AUDITIFS
UN ARC PLASMA
PEUT ENDOMMAGER LES
TUYAUX GELÉS
Les champs magnétiques produits par les courants à haute
tension peuvent affecter le fonctionnement des prothèses
auditives et des pacemakers. Les personnes portant ce
type d’appareil doivent consulter un médecin avant de
s’approcher d’un lieu où s’effectue le coupage ou le
gougeage plasma.
Pour réduire les risques associés aux champs magnétiques :
• Garder loin de soi et du même côté du corps le câble de
retour et le faisceau de la torche.
• Faire passer le faisceau de la torche le plus près possible
du câble de retour.
• Ne pas s’enrouler le faisceau de la torche ou le câble de
retour autour du corps.
• Se tenir le plus loin possible de la source de courant.
PACEMAKERS ET
PROTHÈSES AUDITIVES
Une exposition prolongée au bruit du coupage ou du
gougeage peut provoquer des problèmes auditifs.
• Utiliser un casque de protection homologué lors de
l’utilisation du système plasma.
• Prévenir les personnes aux alentours des risques
encourus en cas d’exposition au bruit.
Page 30

8-99
Étiquette de sécurité
Cette étiquette est affichée sur la source de courant. Il est important
que l’utilisateur et le technicien de maintenance comprennent la
signification des symboles de sécurité.
Hypertherm Systèmes plasma 1a-7
SÉCURITÉ
Page 31

8-99
1a-8 Hypertherm Systèmes plasma
SÉCURITÉ
Étiquette de sécurité
Cette étiquette est affichée sur la source de courant. Il est important
que l’utilisateur et le technicien de maintenance comprennent la
signification des symboles de sécurité. Les numéros de la liste
correspondent aux numéros des images.
1. Les étincelles produites par le coupage
peuvent provoquer une explosion ou un
incendie.
1.1 Pendant le coupage, éloigner toute matière
inflammable.
1.2 Conserver un extincteur à proximité et
s’assurer qu’une personne soit prête à
l’utiliser.
1.3 Ne jamais couper de récipients fermés.
2. L’arc plasma peut provoquer des blessures
et des brûlures.
2.1 Couper l’alimentation avant de démonter la
torche.
2.2 Ne pas tenir la surface à couper près de la
trajectoire de coupe.
2.3 Porter des vêtements de protection
couvrant tout le corps.
3. Un choc électrique causé par la torche ou
les câbles peut être fatal. Se protéger
contre les risques de chocs électriques.
3.1 Porter des gants isolants. Ne pas porter de
gants mouillés ou abîmés.
3.2 S’isoler de la surface de travail et du sol.
3.3 Débrancher la prise ou la source de
courant avant de manipuler l’équipement.
4. L’inhalation des vapeurs produites par le
coupage peut être dangereuse pour la
santé.
4.1 Garder le visage à l’écart des vapeurs.
4.2 Utiliser un système de ventilation par
aspiration ou d’échappement localisé pour
dissiper les vapeurs.
4.3 Utiliser un ventilateur pour dissiper les
vapeurs.
5. Les rayons de l’arc peuvent brûler les yeux
et provoquer des lésions de la peau.
5.1 Porter un casque et des lunettes de
sécurité. Se protéger les oreilles et porter
une chemise dont le col peut être
déboutonné. Porter un casque de soudure
dont la protection filtrante est suffisante.
Porter des vêtements protecteurs couvrant
la totalité du corps.
6. Se former à la technique du coupage et lire
les instructions avant de manipuler
l’équipement ou de procéder au coupage.
7. Ne pas retirer ou peindre (recouvrir) les
étiquettes de sécurité.
Page 32

8-06
Hypertherm Sistemas plasma 1b-1
Seccíon 1b
SEGURIDAD
En esta sección:
Reconocimiento de información de seguridad........................................................................................................1b-2
Siga las instrucciones de seguridad .......................................................................................................................1b-2
Los cortes pueden provocar incendios o explosiones............................................................................................1b-2
El choque eléctrico puede provocar la muerte .......................................................................................................1b-3
Electricidad estática puede dañar tablillas de circuito ............................................................................................1b-3
Humos tóxicos pueden causar lesiones o muerte..................................................................................................1b-4
El arco de plasma puede causar lesiones y quemaduras ......................................................................................1b-5
Los rayos del arco pueden producir quemaduras en los ojos y en la piel..............................................................1b-5
Seguridad de toma a tierra .....................................................................................................................................1b-5
Seguridad de los equipos de gas comprimido........................................................................................................1b-6
Los cilindros de gas pueden explotar si están dañados.........................................................................................1b-6
El ruido puede deteriorar la audición......................................................................................................................1b-6
Operación de marcapasos y de audífonos.............................................................................................................1b-6
Un arco plasma puede dañar tubos congelados ....................................................................................................1b-6
Etiquetas de advertencia ........................................................................................................................................1b-7
Page 33

11-98
SEGURIDAD
1b-2 Hypertherm Sistemas plasma
RECONOCIMIENTO DE
INFORMACIÓN DE SEGURIDAD
Los símbolos que se muestran en esta sección se utilizan
para identificar los posibles peligros. Cuando vea un símbolo
de seguridad en este manual o en su máquina, recuerde que
existe la posibilidad de que se produzcan lesiones personales
y siga las instrucciones correspondientes para evitar el
peligro.
SIGA LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE
SEGURIDAD
Lea atentamente todos los mensajes de seguridad de este
manual y las etiquetas de seguridad en su máquina.
• Mantenga las etiquetas de seguridad de su máquina en
buen estado. Reemplace las etiquetas que se pierdan o se
dañen inmediatamente.
• Aprenda a utilizar la máquina y a utilizar los controles de la
manera correcta. No permita que sea utilizada por alguien
que no conozca su funcionamiento.
• Mantenga su máquina en buenas condiciones de
funcionamiento. La realización de modificaciones no
autorizadas a la máquina puede comprometer la
seguridad y la vida útil de la máquina.
PELIGRO ADVERTENCIA PRECAUCIÓN
Las palabras PELIGRO y ADVERTENCIA se utilizan
conjuntamente con un símbolo de seguridad. La palabra
PELIGRO se utiliza para identificar los mayores peligros.
• Encontrará etiquetas de seguridad con las inscripciones
PELIGRO y ADVERTENCIA en su máquina, junto a
peligros específicos.
• En este manual, la palabra ADVERTENCIA va seguida de
instrucciones que, si no se siguen correctamente, pueden
provocar lesiones e inclusive la muerte.
• En este manual, la palabra PRECAUCIÓN va seguida de
instrucciones que, si no se siguen correctamente, pueden
provocar daños en el equipo.
Prevención ante el fuego
• Asegúrese de que el área sea segura antes de proceder
a cortar. Tenga a mano un extinguidor de incendios.
• Retire todos los materiales inflamables, colocándolos a
por lo menos 10 metros del área de corte.
• Remoje los metales calientes o permita que se enfríen
antes de que entren en contacto con materiales
combustibles.
• Nunca corte depósitos que contengan materiales
inflamables – primero es necesario vaciarlos y limpiarlos
debidamente.
• Antes de realizar cortes en atmósferas potencialmente
inflamables, asegúrese de ventilar bien.
• Al realizar cortes utilizando oxígeno como gas plasma, se
requiere tener un sistema de ventilación de escape.
Prevención ante explosiones
• No corte en atmósferas que contengan polvo o vapores
explosivos
.
• No corte depósitos o tubos a presión ni cualquier depósito
cerrado.
• No corte depósitos que hayan contenido materiales
combustibles.
LOS CORTES PUEDEN PROVOCAR INCENDIOS O EXPLOSIONES
ADVERTENCIA
Peligro de explosión
Argón-Hidrógeno y metano
El hidrógeno y el metano son gases inflamables que
suponen un peligro de explosión. Mantenga el fuego lejos de
los cilindros y las mangueras que contengan mezclas de
hidrógeno o metano. Mantenga la llama y las chispas lejos
de la antorcha al utilizar metano o argón-hidrógeno como
plasma.
ADVERTENCIA
Detonación de hidrógeno con
el corte de aluminio
• Al cortar aluminio bajo agua o con agua en contacto con el
lado inferior del aluminio, puede acumularse gas
hidrógeno bajo la pieza a cortar y detonar durante la
operación de corte por plasma.
• Instale un múltiple de aireación en el fondo de la mesa de
agua para eliminar la posibilidad de la detonación del
hidrógeno. Consulte la sección del apéndice de este
manual para conocer detalles acerca del múltiple de
aireación.
Page 34

8-06
El contacto directo con piezas eléctricas conectadas puede
provocar un electrochoque fatal o quemaduras graves.
• Al hacer funcionar el sistema de plasma, se completa un
circuito eléctrico entre la antorcha y la pieza a cortar.
La pieza a cortar es una parte del circuito eléctrico,
como también cualquier cosa que se encuentre en
contacto con ella.
• Nunca toque el cuerpo de la antorcha, la pieza a cortar o
el agua en una mesa de agua cuando el sistema de
plasma se encuentre en funcionamiento.
Prevención ante el electrochoque
Todos los sistemas por plasma de Hypertherm usan alto
voltaje en el proceso de corte (son comunes los voltajes CD
de 200 a 400). Tome las siguientes precauciones cuando se
utiliza el equipo de plasma:
• Use guantes y botas aislantes y mantenga el cuerpo y la
ropa secos.
• No se siente, se pare o se ponga sobre cualquier superficie húmeda cuando esté trabajando con el equipo.
• Aíslese eléctricamente de la pieza a cortar y de la tierra
utilizando alfombrillas o cubiertas de aislamiento secas lo
suficientemente grandes como para impedir todo contacto
físico con la pieza a cortar o con la tierra. Si su única
opción es trabajar en una área húmeda o cerca de ella,
sea muy cauteloso.
• Instale un interruptor de corriente adecuado en cuanto a
fusibles, en una pared cercana a la fuente de energía.
Este interruptor permitirá al operador desconectar
rápidamente la fuente de energía en caso de emergencia.
• Al utilizar una mesa de agua, asegúrese de que ésta se
encuentre correctamente conectada a la toma a tierra.
EL CHOQUE ELÉCTRICO PUEDE PROVOCAR LA MUERTE
• Instale este equipo y conéctelo a tierra según el manual
de instrucciones y de conformidad con los códigos locales
y nacionales.
• Inspeccione el cordón de alimentación primaria con
frecuencia para asegurarse de que no esté dañado ni
agrietado. Si el cordón de alimentación primaria está
dañado, reemplácelo inmediatamente. Un cable pelado
puede provocar la muerte.
• Inspeccione las mangueras de la antorcha y
reemplácelas cuando se encuentren dañadas.
• No toque la pieza ni los recortes cuando se está
cortando. Deje la pieza en su lugar o sobre la mesa de
trabajo con el cable de trabajo conectado en todo
momento.
• Antes de inspeccionar, limpiar o cambiar las piezas de la
antorcha, desconecte la potencia primaria o desenchufe
la fuente de energía.
• Nunca evite o descuide los bloqueos de seguridad.
• Antes de retirar la cubierta de una fuente de energía o del
gabinete de un sistema, desconecte la potencia primaria
de entrada. Espere 5 minutos después de desconectar la
potencia primaria para permitir la descarga de los
condensadores.
• Nunca opere el sistema de plasma sin que las tapas de la
fuente de energía estén en su lugar. Las conexiones
expuestas de la fuente de energía presentan un serio
riesgo eléctrico.
• Al hacer conexiones de entrada, conecte el conductor de
conexión a tierra en primer lugar.
• Cada sistema de plasma Hypertherm está diseñado para
ser utilizado sólo con antorchas Hypertherm específicas.
No utilice antorchas diferentes, que podrían recalentarse
y ser peligrosas.
Use precauciones adecuadas cuando maneje
tablillas impresas de circuito
ELECTRICIDAD ESTÁTICA PUEDE DAÑAR TABLILLAS DE CIRCUITO
• Almacene las tablillas PC en recipientes
antiestáticos.
• Use la defensa de muñeca conectada a tierra
cuando maneje tablillas PC.
SEGURIDAD
Hypertherm Sistemas plasma 1b-3
Page 35

8-06
SEGURIDAD
1b-4 Hypertherm Sistemas plasma
El arco plasma es por si solo la fuente de calor que
se usa para cortar. Según esto, aunque el arco de
plasma no ha sido identificado como la fuente de
humo tóxico, el material que se corta puede ser la
fuente de humo o gases tóxicos que vacían el
oxígeno.
El humo producido varía según el metal que está
cortándose. Metales que pueden liberar humo tóxico
incluyen, pero no están limitados a, acero inoxidable,
acero al carbón, cinc (galvanizado), y cobre.
En algunos casos, el metal puede estar recubierto
con una sustancia que podría liberar humos tóxicos.
Los recubrimientos tóxicos incluyen, pero no están
limitados a, plomo (en algunas pinturas), cadmio (en
algunas pinturas y rellenos), y berilio.
Los gases producidos por el corte por plasma varían
basándose en el material a cortarse y el método de
cortar, pero pueden incluir ozono, óxidos de
nitrógeno, cromo hexavalente, hidrógeno, y otras
substancias, si están contenidas dentro o liberadas
por el material que se corta.
Se debe tener cuidado de minimizar la exposición del
humo producido por cualquier proceso industrial.
Según la composición química y la concentración del
humo (al igual que otros factores, tales como
ventilación), puede haber el riesgo de enfermedad
física, tal como defectos de natividad o cáncer.
Es la responsabilidad del dueño del equipo y
instalación el comprobar la calidad de aire en el lugar
donde se está usando el equipo para garantizar que
la calidad del aire en el lugar de trabajo cumpla con
todas las normas y reglamentos locales y nacionales.
HUMOS TÓXICOS PUEDEN CAUSAR LESIONES O MUERTE
El nivel de la calidad del aire en cualquier lugar de
trabajo relevante depende en variables específicas al
sitio tales como:
• Diseño de mesa (mojada, seca, bajo agua).
• La composición del material, el acabado de la
superficie, y la composición de los recubrimientos.
• Volumen que se quita del material.
• La duración del corte o ranura.
• Tamaño, volumen del aire, ventilación y filtración
del lugar de trabajo.
• Equipo de protección personal.
• Número de sistemas de soldar y cortar en la
operación.
• Otros procesos del lugar que pueden producir
humo.
Si el lugar de trabajo debe cumplir reglamentos
nacionales o locales, solamente el monitoreo o las
pruebas que se hacen en el lugar pueden determinar
si el sitio está encima o debajo de los niveles
permitidos.
Para reducir el riesgo de exposición a humo:
• Quite todos los recubrimientos y solventes del
metal antes de cortar.
• Use ventilación extractora local para quitar humo
del aire.
• No inhale el humo. Use un respirador con fuente
propia de aire cuando corte cualquier metal
recubierto con, o sospechado de contener,
elementos tóxicos.
• Garantice que aquéllos usando equipo de soldar o
cortar, al igual que aparatos de respiración con aire
propio de aire, estén capacitados y entrenados en
el uso apropiado de tal equipo.
• Nunca corte recipientes con materiales
potencialmente tóxicos adentro. Primero, vacíe y
limpie el recipiente adecuadamente.
• Monitoree o compruebe la calidad del aire en el
sitio como fuera necesario.
• Consulte con un experto local para realizar un plan
al sitio para garantizar la calidad de aire seguro.
Page 36

5-02
Antorchas de encendido instantáneo
El arco de plasma se enciende inmediatamente después de
activarse el interruptor de la antorcha.
EL ARCO DE PLASMAPUEDE CAUSAR LESIONES Y QUEMADURAS
El arco de plasma puede cortar a través de guantes y de la
piel con rapidez.
• Manténgase alejado de la punta de la antorcha.
• No sostenga el metal junto al trayecto de corte.
• Nunca apunte la antorcha hacia Ud. mismo o hacia otras
personas.
Protección para los ojos Los rayos del arco de plasma
producen rayos intensos visibles e invisibles (ultravioleta e
infrarrojo) que pueden quemar los ojos y la piel.
• Utilice protección para los ojos de conformidad con los
códigos locales o nacionales aplicables.
• Colóquese protectores para los ojos (gafas o anteojos
protectores con protectores laterales, y bien un casco de
soldar) con lentes con sombreado adecuado para
proteger sus ojos de los rayos ultravioleta e infrarrojos del
arco.
Número del cristal
Corriente del arco AWS (EE.UU.) ISO 4850
Hasta 100A No. 8 No. 11
100-200 A No. 10 No. 11-12
200-400 A No. 12 No. 13
Más de 400 A No. 14 No. 14
LOS RAYOS DEL ARCO PUEDEN PRODUCIR QUEMADURAS
EN LOS OJOS Y EN LAPIEL
Protección para la piel Vista ropa de protección para
proteger la piel contra quemaduras causadas por la
radiación ultravioleta de alta intensidad, por las chispas y
por el metal caliente:
•
Guantes largos, zapatos de seguridad y gorro.
•
Roipa de combustión retardada y que cubra todas las
partes expuestas.
•
Pantalones sin dobladillos para impedir que recojan
chispas y escorias.
•
Retire todo material combustible de los bolsillos, como
encendedores a butano e inclusive cerillas, antes de
comenzar a cortar.
Área de corte Prepare el área de corte para reducir la
reflexión y la transmisión de la luz ultravioleta:
•
Pinte las paredes y demás superficies con colores
oscuros para reducir la reflexión.
•
Utilice pantallas o barreras protectoras para proteger a
los demás de los destellos.
•
Advierta a los demás que no debe mirarse el arco. Utilice
carteles o letreros.
Cable de trabajo La pinza del cable de trabajo debe
estar bien sujetada a la pieza y hacer un buen contacto de
metal a metal con ella o bien con la mesa de trabajo. No
conecte el cable con la parte que va a quedar separada por
el corte.
Mesa de trabajo Conecte la mesa de trabajo a una
buena toma de tierra, de conformidad con los códigos
eléctricos nacionales o locales apropiados.
SEGURIDAD DE TOMAA TIERRA
Potencia primaria de entrada
• Asegúrese de que el alambre de toma a tierra del cordón
de alimentación está conectado al terminal de tierra en la
caja del interruptor de corriente.
•
Si la instalación del sistema de plasma supone la conexión
del cordón de alimentación primaria a la fuente de energía,
asegúrese de conectar correctamente el alambre de toma
a tierra del cordón de alimentación primaria.
• Coloque en primer lugar el alambre de toma a tierra del
cordón de alimentación primaria en el espárrago luego
coloque cualquier otro alambre de tierra sobre el
conductor de tierra del cable. Ajuste firmemente la tuerca
de retención.
• Asegúrese de que todas las conexiones eléctricas están
firmemente realizadas para evitar sobrecalentamientos.
SEGURIDAD
Hypertherm Sistemas plasma 1b-5
Page 37

11-98
SEGURIDAD
1b-6 Hypertherm Sistemas plasma
•
Nunca lubrique reguladores o válvulas de cilindros con
aceite o grasa.
•
Utilice solamente cilindros, reguladores, mangueras y
conectores de gas correctos que hayan sido diseñados
para la aplicación específica.
•
Mantenga todo el equipo de gas comprimido y las piezas
relacionadas en buen estado.
•
Coloque etiquetas y códigos de color en todas las
mangueras de gas para identificar el tipo de gas que
conduce cada una. Consulte los códigos locales o
nacionales aplicables.
LOS CILINDROS DE GAS PUEDEN
EXPLOTAR SI ESTÁN DAÑADOS
SEGURIDAD DE LOS EQUIPOS DE GAS
COMPRIMIDO
Los cilindros de gas contienen gas bajo alta presión. Un
cilindro dañado puede explotar.
•
Manipule y utilice los cilindros de gas comprimido de
acuerdo con los códigos locales o nacionales aplicables.
•
No use nunca un cilindro que no esté de pie y bien sujeto.
•
Mantenga la tapa de protección en su lugar encima de la
válvula, excepto cuando el cilindro se encuentre en uso o
conectado para ser utilizado.
•
No permita nunca el contacto eléctrico entre el arco de
plasma y un cilindro.
•
No exponga nunca los cilindros a calor excesivo, chispas,
escorias o llamas.
•
No emplee nunca martillos, llaves u otro tipo de
herramientas para abrir de golpe la válvula del cilindro.
Se puede hacer daño a los tubos congelados, o se los
puede reventar, si uno trata de descongelarlos con una
antorcha por plasma.
EL RUIDO PUEDE DETERIORAR
LAAUDICIÓN
UN ARCO PLASMA PUEDE
DAÑAR TUBOS
CONGELADOS
Los campos magnéticos producidos por las elevadas
corrientes pueden afectar la operación de marcapasos y de
audífonos. Las personas que lleven marcapasos y
audífonos deberán consultar a un médico antes de
acercarse a sitios donde se realizan operaciones de corte y
ranurado por plasma.
Para reducir los peligros de los campos magnéticos:
•
Mantenga el cable de trabajo y la manguera de la
antorcha a un lado, lejos del cuerpo.
•
Dirija la manguera antorcha lo más cerca posible del
cable de trabajo.
•
No envuelva el cable de trabajo ni la manguera de la
antorcha en su cuerpo.
•
Manténgase tan lejos de la fuente de energía como sea
posible.
OPERACIÓN DE MARCAPASOS
Y DE AUDÍFONOS
La exposición prolongada al ruido propio de las
operaciones de corte y ranurado puede dañar la audición.
•
Utilice un método de protección de los oídos aprobado al
utilizar el sistema de plasma.
•
Advierta a las demás personas que se encuentren en las
cercanías acerca del peligro que supone el ruido
excesivo.
Page 38

8-99
Etiqueta de advertencia
Esta etiqueta de advertencia se encuentra adherida a la fuente de energía.
Es importante que el operador y el técnico de mantenimiento comprendan
el sentido de estos símbolos de advertencia según se describen. El texto
numerado corresponde a los cuadros numerados de la etiqueta.
SEGURIDAD
Hypertherm Sistemas plasma 1b-7
Page 39

8-99
SEGURIDAD
1b-8 Hypertherm Sistemas plasma
Etiqueta de advertencia
Esta etiqueta de advertencia se encuentra adherida a la fuente de energía.
Es importante que el operador y el técnico de mantenimiento comprendan
el sentido de estos símbolos de advertencia según se describen. El texto
numerado corresponde a los cuadros numerados de la etiqueta.
1. Las chispas producidas por el corte
pueden causar explosiones o incendios.
1.1 Mantenga los materiales inflamables lejos
del lugar de corte.
1.2 Tenga a mano un extinguidor de incendios
y asegúrese de que alguien esté
preparado para utilizarlo.
1.3 No corte depósitos cerrados.
2. El arco de plasma puede causar
quemaduras y lesiones.
2.1 Apague la fuente de energía antes de
desarmar la antorcha.
2.2 No sostenga el material junto al trayecto de
corte.
2.3 Proteja su cuerpo completamente.
3. Los electrochoques provocados por la
antorcha o el cableado pueden ser fatales.
Protéjase del electrochoque.
3.1 Colóquese guantes aislantes. No utilice
guantes dañados o mojados.
3.2 Aíslese de la pieza de trabajo y de la tierra.
3.3 Antes de trabajar en una máquina,
desconecte el enchufe de entrada o la
potencia primaria.
4. La inhalación de los humos provenientes
del área de corte puede ser nociva para la
salud.
4.1 Mantenga la cabeza fuera de los gases
tóxicos.
4.2 Utilice ventilación forzada o un sistema
local de escape para eliminar los humos.
4.3 Utilice un ventilador para eliminar los
humos.
5. Los rayos del arco pueden producir
quemaduras en los ojos y en la piel.
5.1 Utilice un sombrero y gafas de seguridad.
Utilice protección para los oídos y
abróchese el botón del cuello de la camisa.
Utilice un casco de soldar con el filtro de
sombreado adecuado. Proteja su cuerpo
completamente.
6. Antes de trabajar en la máquina o de
proceder a cortar, capacítese y lea las
instrucciones completamente.
7. No retire las etiquetas de advertencia ni las
cubra con pintura.
Page 40

HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 2-1
Section 2
SPECIFICATIONS
In this section:
System description ....................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
General...............................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Power supply ...................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Ignition console ................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Selection console ............................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Metering console .............................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Torch ...................................................................................................................................................................................................2-3
Specifications..............................................................................................................................................................................................2-4
System gas requirements ..............................................................................................................................................................2-4
Power supply ....................................................................................................................................................................................2-5
Ignition console – 078172.............................................................................................................................................................2-6
Selection console – 078185 ........................................................................................................................................................2-8
Metering console – 078184 .........................................................................................................................................................2-9
Torch – 128818.............................................................................................................................................................................2-10
5
Page 41

SPECIFICATIONS
2-2 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
Page 42

SPECIFICATIONS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 2-3
System description
General
HyPerformance plasma systems are designed to cut a wide range of thicknesses of mild steel, stainless steel
and aluminum.
Power supply
The power supply is a 260-amp, 150-VDC constant-current supply. It contains the circuitry to ignite a torch, a heat
exchanger and pump to cool the torch. The power supply has a serial interface to provide communication with a CNC
controller.
Ignition console
The ignition console uses a spark-gap assembly. The ignition console converts 120 VAC control voltage from the power
supply into high-frequency and high-voltage pulses (9-10 kV) to break over the torch electrode-nozzle gap. The highvoltage, high-frequency signal is coupled to the cathode lead and pilot arc lead.
Selection console
The selection console manages the selection and mixing of the plasma gases. It contains motor valves, solenoid valves
and pressure transducers. It also contains a PC control board, an AC relay board and a power distribution board. The
selection console has an LED lamp that illuminates when power is supplied to the system.
Metering console
The metering console may be located up to 1.8 m (6 ft) away from the torch and controls the flow rate of the gases to
the torch in real time. It also controls the gas portion of the LongLife®process. The metering console contains
proportional control valves, a PC control board and a power distribution board.
Torch
The virtually dross-free cutting capacity of the torch is 32 mm (1.25 in) for HyDefinition cutting. The production pierce
capacity is 32 mm (1.25 in) for mild steel and stainless steel and 25 mm (1 in) for aluminum. The maximum cutting
capability (edge start) is 64 mm (2.5 in) for mild steel and stainless steel and 50 mm (2 in) for aluminum.
5
Page 43

SPECIFICATIONS
2-4 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Specifications
System gas requirements
Mild steel Stainless steel Aluminum
Gas types Plasma Shield Plasma Shield Plasma Shield
Cutting 30 to 50 A O
2
O
2
N2& F5 N
2
Air Air
Cutting 80 A O
2
Air F5 N
2
Cutting 130 A O
2
Air N2& H35 N
2
H35 & Air N2& Air
Cutting 200 A O
2
Air N2& H35 N
2
N2& H35 N
2
Cutting 260 A O
2
Air N2& H35 N2& Air N2& H35 N2& Air
Gas quality and pressure requirements
Quality Grade** Pressure +/- 10% Flow rate
O2Oxygen* 99.5% pure G 827 kPa / 8.3 bar 4250 l/h 150 scfh
Clean, dry, oil-free 115 psi
N2Nitrogen* 99.99% pure E 827 kPa / 8.3 bar 9910 l/h 350 scfh
Clean, dry, oil-free 115 psi
Air* *** Clean, dry, oil-free per K 827 kPa / 8.3 bar 9910 l/h 350 scfh
ISO 8573-1 Class 1.2.2 115 psi
H35 99.995% pure Ar = A 827 kPa / 8.3 bar 4250 l/h 150 scfh
Argon-hydrogen (H35 = 65% Argon, 35% Hydrogen) H2= A 115 psi
F5 99.98% pure N2= E 827 kPa / 8.3 bar 4250 l/h 150 scfh
Nitrogen-hydrogen (F5 = 95% Nitrogen, 5% Hydrogen) H2= A 115 psi
* Oxygen, nitrogen, and air are required for all systems. Nitrogen is used as a purge gas.
** This information can be found in the Handbook of Compressed Gases, 3rd edition, Compressed Gas Association,
Van Nostrand Reinhold.
*** ISO standard 8573-1 Class 1.2.2 requirements are:
• Particulates – no more than 100 particles per cubic meter of air at a Size of 0.1 to 0.5 microns in the largest
dimension and 1 particle per cubic meter of air at a Size of 0.5 to 5.0 microns in the largest
dimension.
• Water – there can not be more humidity in the air than in air at –40° C (–40° F).
• Oil – the concentration of oil can be no more than 0.1 mg per cubic meter of air.
Page 44

SPECIFICATIONS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 2-5
5
Power supply
133.4 mm
5.3"
1181.1 mm
46.5"
1143.0 mm
45.0"
803.3 mm
31.6"
554.7 kg
1223 lb
General
Maximum OCV (U0) 311 VDC
Maximum output current (I2) 260 Amps
Output voltage (U2) 50 – 175 VDC
Duty cycle rating (X) 100% @ 45.5 kw, 40° C (104° F)
Ambient temperature/Duty cycle Power supplies will operate between -10° C and +40° C (+14° and 104° F)
Power factor(cosϕ)
0.98 @ 260 ADC output
Cooling Forced air (Class F)
Insulation Class H
Part
number
AC Voltage
(U1)
Phase
Frequency
(Hz)
Amperage (I1)
Regulatory
approval
Power kW (+/- 10%)
(U1 x I1x 1.73)
078187 200/208 3 50/60 149/144 CSA 51.6
078202 220 3 50/60 136 CSA 51.6
078188 240 3 60 124 CSA 51.6
078192 380 3 50/60 79 CCC 51.6
078186 400 3 50/60 75 CE/GOST-R 51.6
078189 440 3 50/60 68 CSA 51.6
078190 480 3 60 62 CSA 51.6
078191 600 3 60 50 CSA 51.6
Note: Software verification is needed for field upgrade units. New systems ship with revision J software or
later.
Caution: Revision “J” software, or later, is required for the safe
operation of the automatic gas console.
Page 45

SPECIFICATIONS
2-6 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Ignition console – 078172
• The ignition console may be mounted locally on the power supply (LHF) or remotely on the cutting table’s bridge
(RHF). See Installation section for details.
• Maximum cable length from the ignition console to the torch lifter station is 20 m (65 ft). Allow room to remove
the top for servicing.
• The ignition console may be mounted horizontally or vertically.
9.1 kg
20 lb
283 mm
11.125"
219 mm
8.625"
194 mm
7.625"
152 mm
6"
216 mm
8.5"
Page 46

SPECIFICATIONS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 2-7
Horizontal mounting
Vertical mounting
LHF mounting (local)
Mounted on table
RHF mounting (remote)
Page 47

SPECIFICATIONS
2-8 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
Selection console – 078185
• Maximum cable length from the power supply to the selection console is 75 m (250 ft).
• Maximum cable length from the selection console to the metering console is 20 m (65 ft).
• Mount the selection console on top of the power supply or near the CNC on the cutting table. Allow room to
open the top for servicing.
355.6 mm
14.00"
285.75 mm
11.25"
311.15 mm
12.25"
314.5 mm
12.38"
254.0 mm
10.0"
13.6 kg
30 lb
0
38.1 mm
1.5"
0
76.2 mm
3.0"
Page 48

Metering console – 078184
• Maximum cable length from the metering console to the torch lifter station is 1.8 m (6 ft).
• Mount the metering console to the torch carriage on larger tables. On smaller tables it can be mounted to a
bracket just above the bridge.
• The vent hole on the console must be kept clear at all times.
SPECIFICATIONS
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 2-9
153.9 mm
6.1"
33.3 mm
1.3"
122.2 mm
4.8"
0
54.9 mm
2.2"
76.2 mm
3.0"
6.4 kg
14 lb
282.5 mm
11.1"
0
248.9 mm
9.8"
Vent hole. Do not block.
263.53 mm
10.375"
155.58 mm
6.125"
285.75 mm
11.25"
5
Page 49

SPECIFICATIONS
2-10 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Torch – 128818
• The outside diameter of the torch mounting sleeve is 50.8 mm (2.0 in).
• The maximum bend radius for the torch leads is 152.4 mm (6.0 in).
1.8 m
6'
2.11 kg
4.65 lb
193 mm
7. 5 9 "
27 mm
1.07"
116 mm
4.55"
51 mm
2.00"
48 mm
1.89"
107 mm
4.22"
51 mm
2.00"
57 mm
2.25"
336 mm
13.21"
5
Page 50

HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-1
Section 3
INSTALLATION
In this section:
Upon receipt................................................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Claims ...........................................................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Installation requirements...........................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Noise levels..................................................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Placement of system components .........................................................................................................................................................3-3
Torque specifications ......................................................................................................................................................................3-3
Installation requirements...........................................................................................................................................................................3-4
System components........................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Cables and hoses............................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Supply gas hoses ............................................................................................................................................................................3-5
Customer supplied power cable..................................................................................................................................................3-5
Recommended grounding and shielding practices............................................................................................................................3-6
Introduction..................................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Types of grounding ..........................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Steps to take.....................................................................................................................................................................................3-7
Grounding diagram.......................................................................................................................................................................3-10
Placement of the power supply..................................................................................................................................................3-11
Install the ignition console...........................................................................................................................................................3-12
Placement of the selection console..........................................................................................................................................3-14
Install the metering console ........................................................................................................................................................3-15
Power supply to ignition console leads..............................................................................................................................................3-16
Pilot arc lead...................................................................................................................................................................................3-16
Negative lead..................................................................................................................................................................................3-16
Ignition console power cable......................................................................................................................................................3-18
Ignition console coolant hoses...................................................................................................................................................3-19
Power supply to selection console cables.........................................................................................................................................3-20
Control cable..................................................................................................................................................................................3-20
Power cable....................................................................................................................................................................................3-20
Selection console to metering console connections ......................................................................................................................3-22
Cable and gas hose assembly ...................................................................................................................................................3-22
Power supply to CNC interface cable................................................................................................................................................3-24
Optional multi-system CNC interface cable ...........................................................................................................................3-24
Notes to CNC interface cable run list ......................................................................................................................................3-25
Examples of output circuits.........................................................................................................................................................3-26
5
Page 51

INSTALLATION
3-2 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Examples of input circuits............................................................................................................................................................3-27
Remote on/off switch..............................................................................................................................................................................3-28
Torch lead assembly................................................................................................................................................................................3-29
Work lead ..................................................................................................................................................................................................3-30
Torch connections....................................................................................................................................................................................3-31
Connect the torch to the torch lead assembly.......................................................................................................................3-31
Connect the torch to the quick-disconnect.............................................................................................................................3-34
Torch mounting and alignment..............................................................................................................................................................3-35
Mounting the torch........................................................................................................................................................................3-35
Torch alignment..............................................................................................................................................................................3-35
Torch lifter requirement...........................................................................................................................................................................3-35
Power requirements................................................................................................................................................................................3-36
General............................................................................................................................................................................................3-36
Line disconnect switch ................................................................................................................................................................3-36
Power cable....................................................................................................................................................................................3-36
Connect the power..................................................................................................................................................................................3-37
Torch coolant requirements...................................................................................................................................................................3-38
Standard installation.....................................................................................................................................................................3-38
Coolant for cold operating temperatures.................................................................................................................................3-39
Coolant for hot operating temperatures...................................................................................................................................3-40
Water purity requirements.....................................................................................................................................................................3-40
Fill the power supply with coolant........................................................................................................................................................3-41
Gas requirements ....................................................................................................................................................................................3-42
Setting the supply regulators......................................................................................................................................................3-42
Gas regulators..........................................................................................................................................................................................3-43
Supply gas plumbing ..............................................................................................................................................................................3-44
Connect the supply gases ..........................................................................................................................................................3-44
Supply gas hoses ....................................................................................................................................................................................3-45
5
Page 52

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-3
5
Upon receipt
• Verify that all system components on your order have been received. Contact your supplier if any items
are missing.
• Inspect the system components for any physical damage that may have occurred during shipping. If there is
evidence of damage, refer to Claims. All communications regarding claims must include the model number and
serial number located on the back of the power supply.
Claims
Claims for damage during shipment – If your unit was damaged during shipment, you must file a claim with the
carrier. Hypertherm will furnish you with a copy of the bill of lading upon request. If you need additional assistance, call
Customer Service listed in the front of this manual, or your authorized Hypertherm distributor.
Claims for defective or missing merchandise – If any of the merchandise is defective or missing, contact your
supplier. If you need additional assistance, call Customer Service listed in the front of this manual, or your authorized
Hypertherm distributor.
Installation requirements
All installation and service of the electrical and plumbing systems must conform to national or local
electrical and plumbing codes. This work should be performed only by qualified, licensed personnel.
Direct any technical questions to the nearest Hypertherm Technical Service Department listed in the front of this manual,
or your authorized Hypertherm distributor.
Noise levels
Acceptable noise levels as defined by national and local codes may be exceeded by this plasma system. Always wear
proper ear protection when cutting or gouging. See also Noise can damage hearing in the Safety section of this manual.
Data was taken while cutting 12.7 mm (0.5 in) mild steel at 260A using an O2/Air process 76.2 mm (3 in) above water.
The decibel readings at 914.4 mm (36 in) from the front of the torch and 330.2 mm (13 in) above the arc are:
120.7 Max Level, dBC (MaxP) and 98.6 Lav5, dBA.
Placement of system components
• Place all system components in position prior to making electrical, gas and interface connections. Use the
diagram in this section for component-placement guidelines.
• Ground all system components to earth. See Recommended grounding and shielding practices in this section
for details.
• To prevent leaks in the system, tighten all gas and water connections as shown below:
Torque specifications
Gas or water
hose size kgf-cm lbf-in lbf-ft
Up to 10 mm (3/8") 8.6-9.8 75-85 6.25-7
12 mm (1/2") 41.5-55 360-480 30-40
2WRENCHES
Page 53

INSTALLATION
3-4 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
Installation requirements
A
B
C
D
12345
6
7
8
9
10
11
E
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
Page 54

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-5
System components
Power supply
Ignition console
Selection console
Metering console
Torch
Cables and hoses
Pilot arc lead
Negative lead
Ignition console power cable
Ignition console coolant hoses
Gas control cable
Gas power cable
Selection console to metering console hose and lead assembly
CNC interface cable
Optional CNC interface cable for systems with multiple power supplies
Torch lead assembly
Work lead
Supply gas hoses
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Air
Argon-hydrogen (H5)
Argon-hydrogen (H35)
Nitrogen-hydrogen (F5)
Methane (CH4)
Customer-supplied power cable
Main power cable
11E10
98765
4
C
B
D
3
2
1
A
5
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
Page 55

INSTALLATION
3-6 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Recommended grounding and shielding practices
Introduction
This document describes the grounding and shielding necessary to protect a plasma cutting system installation against
radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference (EMI) noise. It addresses the 3 grounding systems
described below. There is diagram on page 5 for reference.
Note: These procedures and practices are not known to succeed in every case to eliminate RFI/EMI noise
issues. The practices listed here have been used on many installations with excellent results, and we
recommend that these practices be a routine part of the installation process. The actual methods
used to implement these practices may vary from system to system, but should remain as consistent
as possible across the product line.
Types of grounding
A. The safety (PE) or service ground. This is the grounding system that applies to the incoming line voltage. It prevents
a shock hazard to any personnel from any of the equipment, or the work table. It includes the service ground coming
into the plasma power supply and other systems such as the CNC controller and the motor drivers, as well as the
supplemental ground rod connected to the work table. In the plasma circuits, the ground is carried from the plasma
power supply chassis to the chassis of each separate console through the interconnecting cables.
B. The DC power or cutting current ground. This is the grounding system that completes the path of the cutting current
from the torch back to the power supply. It requires that the positive lead from the power supply be firmly connected
to the work table ground bus with a properly sized cable. It also requires that the slats, on which the workpiece rests,
make good contact with the table and the workpiece.
C. RFI and EMI grounding and shielding. This is the grounding system that limits the amount of electrical “noise”
emitted by the plasma and motor drive systems. It also limits the amount of noise that is received by the CNC and
other control and measurement circuits. This grounding/shielding process is the main target of this document.
DANGER
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
Disconnect electrical power before performing any maintenance. All work
requiring the removal of the power supply cover must be performed by a
qualified technician.
See Section 1 of the plasma system instruction manual for more safety
precautions.
Page 56

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-7
5
Steps to take
1. Unless noted, use only 6 AWG (16 mm2) welding cable (Hypertherm part no. 047040) for the EMI ground cables
shown on the diagram (blue).
2. The cutting table is used for the common, or star, EMI ground point and should have threaded studs welded to the
table with a copper bus bar mounted on them. A separate bus bar should be mounted on the gantry as close to
each drive motor as possible. If there are drive motors at each end of the gantry, run a separate EMI ground cable
from the far drive motor to the gantry bus bar. The gantry bus bar should have a separate, heavy EMI ground cable
(4 AWG part no. 047031) to the table bus bar. The EMI ground cables for the torch lifter and the RHF console
must each run separately to the table ground bus.
3. A ground rod that meets all applicable local and national electrical codes must be installed within 6 m (20 ft) of the
table. This is a PE ground and should be connected to the ground bus on the cutting table with 6 AWG
green/yellow grounding cable (Hypertherm part number 047121) or equivalent. All PE grounds are shown on the
diagram in green.
4. For the most effective shielding, use the Hypertherm CNC interface cables for I/O signals, serial communication
signals, power supply-to-power supply multi-drop connections, and interconnections between all parts of the
Hypertherm system.
5. All hardware used in the ground system must be brass or copper. The only exception is that the studs welded to the
table for mounting the ground bus can be steel. Under no circumstances should aluminum or steel hardware be used.
6. AC power, PE, and service grounds must be connected to all equipment according to local and national codes.
7. * The positive, negative, and pilot arc leads should be bundled together for as long a distance as possible.
The torch lead, work lead, and the pilot arc (nozzle) leads may only be run parallel to other wires or cables if they
are separated by at least 150 mm (6 in). If possible, run power and signal cables in separate cable tracks.
8. * The ignition console should be mounted as close as possible to the torch, and must have a separate ground cable
to the bus bar on the cutting table.
9. Each Hypertherm component, as well as any other CNC or motor-drive cabinet or enclosure, must have a separate
ground cable to the common (star) point on the table. This includes the ignition console, even if it is bolted to the
power supply or to the cutting machine.
10. The metal braided shield on the torch leads must be connected firmly to the ignition console and to the torch. It must
be electrically insulated from any metal and from any contact with the floor or building. The leads can be run in a
plastic cable tray (track) or covered with a plastic or leather sheath.
11. The torch holder and the torch breakaway mechanism – the part mounted to the lifter, not the part mounted on
the torch – must be connected to the stationary part of the lifter with copper braid at least 12.7 mm (1/2 in) wide.
A separate cable must run from the lifter to the bus bar on the gantry. The valve assembly should also have a
separate ground connection to the gantry bus bar.
* Applies to systems that use a remote high frequency (RHF) console
Page 57

INSTALLATION
3-8 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
12. If the gantry runs on rails that are not welded to the table, then the rails need to be connected with a ground cable
from each end of both rails to the table. These need not go to the common (star) point, but could take the shortest
path to the table.
13. If the OEM is installing a voltage divider to process arc voltage for use in the control system, the voltage divider
board should be mounted as close as possible to the point where the arc voltage is sampled. One acceptable
location is inside the plasma power supply. If the Hypertherm voltage divider board is used, the output signal is
isolated from all other circuits. The processed signal should be run in twisted, shielded cable (Belden type 1800F
or equivalent). The cable used must have a braided shield, not a foil shield. The shield should be connected to the
chassis of the power supply and left unconnected at the other end.
14. All other signals (analog, digital, serial, encoder) should run in twisted pairs inside a shielded cable. Connectors on
these cables should have a metal housing and the shield, not the drain, should be connected to the metal housing
of the connectors at each end of the cable. Never run the shield or the drain through the connector on any of the
pins.
Example of a good cutting table ground bus. The picture above shows the connection from the
gantry ground bus, the connection from the ground rod, the power supply positive lead, the RHF
console*, the CNC enclosure, the torch holder, and the power supply chassis.
* Applies to systems that use a remote high frequency (RHF) console
Gantry
Ground rod
Power
supply
lead (+)
Remote
high frequency
(RHF) console
CNC enclosure
Torch holder
Power supply
chassis
Page 58

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-9
5
Example of a good gantry ground bus. It is bolted to the gantry, close to the motor. All of the individual
ground cables from the components mounted on the gantry go to the bus except those from the RHF
console* and the torch holder. A single heavy cable then goes from the gantry ground bus to the
ground bus bolted to the table.
* Applies to systems that use a remote high frequency (RHF) console
Component
ground cables
Cable to ground
bus on the
cutting table
Page 59

INSTALLATION
3-10 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
AC earth/service ground
Ground rod
Chassis and RFI ground
The lifter assembly and the RHF console each
require a separate path to the cutting table
ground bus bar.
Cutting table
Plasma
power supply
Positive DC
Command
THC
Bus bar
Bus bar
Command
THC
RHF
console
Metering
console
Gas/Selection
console
CNC
console
Grounding diagram (some systems will not include all the components shown)
Gantry
**
**
**
Page 60

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-11
5
Placement of the power supply
A
DANGER
ELECTRICAL SHOCK CAN KILL
Remove all electrical connections to power supply before moving or positioning. Transporting unit
can cause personal injury and equipment damage.
The power supply can be moved by forklift but the forks must be long enough to extend the entire length of the base.
Take care when lifting so that the underside of the power supply is not damaged.
• Place the power supply in an area that is free of excessive moisture, has proper ventilation and is relatively clean.
Allow 1 m (3 ft) of space on all sides of the power supply for ventilation and service.
• Cooling air is drawn in through the front panel and is exhausted through the rear of the unit by a cooling fan. Do
not place any filter device over the air intake locations, which reduces cooling efficiency and VOIDS
THE WARRANTY.
• Do not place the power supply on an incline greater than 10° to prevent it from toppling.
Page 61

INSTALLATION
3-12 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Install the ignition console
• Mount the ignition console on the gantry (bridge) for the RHF configuration.
• Mount the ignition console on the power supply for the LHF configuration.
• Allow room to remove the top for servicing.
B
Ignition console grounding
7 mm
.028"
(4 places)
32 mm
1.25"
32 mm
1.25"
184 mm
7.25"
279 mm
11.00"
248 mm
9.75"
216 mm
8.50"
Page 62

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-13
LHF mounting
Horizontal RHF mounting
Vertical RHF mounting
Page 63

INSTALLATION
3-14 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
Placement of the selection console
• Mount the selection console near the cutting table. Allow room to remove the top and right side cover for
servicing. Preferred orientation is shown in the figure below. The maximum length of cables between the power
supply and selection console is 75 m (250 ft). The maximum length of cables and hoses between the selection
console and the metering console assembly is 20 m (65 ft).
C
Preferred selection
console orientation
Selection console grounding
314.5 mm
12.38"
254.0 mm
10.0"
0
38.1 mm
1.5"
0
76.2 mm
3.0"
Page 64

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-15
Install the metering console
• Mount the metering console near the torch lifter station. The maximum length of the gas hoses between the
metering console and the torch is 1.8 m (6 ft).
D
Metering console grounding
153.9 mm
6.1"
33.3 mm
1.3"
122.2 mm
4.8"
0
54.9 mm
2.2"
76.2 mm
3.0"
282.5 mm
11.1"
0
248.9 mm
9.8"
Vent hole:
Do not block
5
Page 65

INSTALLATION
3-16 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Power supply to ignition console leads
Pilot arc lead
1
Negative lead
2
Pilot arc lead
Negative lead
Ignition console
Power supply
Ignition console
I/O board
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123829* 1.5 m (5 ft) 123819 20 m (65 ft)
123816 3 m (10 ft) 123775 25 m (82 ft)
123817 4.5 m (15 ft) 123776 35 m (115 ft)
123773 7.5 m (25 ft) 123777 45 m (150 ft)
123818 10 m (35 ft) 123778 60 m (200 ft)
123774 15 m (50 ft) 123779 75 m (250 ft)
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123683* 1.5 m (5 ft) 123823 20 m (65 ft)
123820 3 m (10 ft) 123735 25 m (82 ft)
123821 4.5 m (15 ft) 123668 35 m (115 ft)
123666 7.5 m (25 ft) 123669 45 m (150 ft)
123822 10 m (35 ft) 123824 60 m (200 ft)
123667 15 m (50 ft) 123825 75 m (250 ft)
*Cable numbers 123683 and 123829 are for use with systems that have the ignition console mounted on the power supply
Page 66

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-17
Pilot arc lead
Negative lead
Pilot arc lead
Negative lead
2
Work lead
2
2
1
1
1
2
Page 67

INSTALLATION
3-18 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Ignition console power cable
3
Cable signal list – power supply to ignition console
Power supply end Ignition console end
Pin # I/O Description Pin # I/O Function
1 120 Vac Hot 1
2 120 Vac Return 2
3 Ground 3
4 Not connected 4
3
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123865* 2.1 m (7 ft) 123836 20 m (65 ft)
123419 3 m (10 ft) 123736 25 m (82 ft)
123834 4.5 m (15 ft) 123672 35 m (115 ft)
123670 7.5 m (25 ft) 123673 45 m (150 ft)
123835 10 m (35 ft) 123837 60 m (200 ft)
123671 15 m (50 ft) 123838 75 m (250 ft)
*Cable number 123865 is for use with systems that have the ignition console mounted on the power supply
Page 68

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-19
3
Ignition console coolant hoses
4
Red
Green
Green
Red
4
Part no. Length Part no. Length
228031* 1.1 m (3.8 ft) 128984 20 m (65 ft)
028652 3 m (10 ft) 128078 25 m (82 ft)
028440 4.5 m (15 ft) 028896 35 m (115 ft)
028441 7.5 m (25 ft) 028445 45 m (150 ft)
128173 10 m (35 ft) 028637 60 m (200 ft)
028442 15 m (50 ft) 128985 75 m (250 ft)
*Hose set number 228031 is for use with systems that have the ignition console mounted on the power supply
Page 69

INSTALLATION
3-20 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
Power supply to selection console cables
Control cable
5
Power cable
6
Cable signal list – power supply to selection console
Power supply end Selection console end
Pin # Input/Output Description Pin # Input/Output Function
1 unused 1
6 unused 6
2 Input/Output CANL 2 Input/Output CAN serial communication
7 Input/Output CANH 7 Input/Output CAN serial communication
3 CAN Ground 3 CAN ground reference
9 unused 9 unused
8 unused 8
4 unused 4
5 unused 5
Cable signal list – power supply to selection console
Power supply end Selection console end
Pin # I/O Description Pin # I/O Function
1 120 VAC-Hot 1
2 120 VAC-Return 2
3 Ground 3
4 unused 4
5 unused 5
6 24 VAC-Hot 6
7 24 VAC-Return 7
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123784* 3 m (10 ft) 123737 25 m (82 ft)
123839 4.5 m (15 ft) 123738 35 m (115 ft)
123691 7.5 m (25 ft) 123739 45 m (150 ft)
123840 10 m (35 ft) 123842 60 m (200 ft)
123711 15 m (50 ft) 123843 75 m (250 ft)
123841 20 m (65 ft)
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123785* 3 m (10 ft) 123740 25 m (82 ft)
123846 4.5 m (15 ft) 123676 35 m (115 ft)
123674 7.5 m (25 ft) 123677 45 m (150 ft)
123847 10 m (35 ft) 123849 60 m (200 ft)
123675 15 m (50 ft) 123850 75 m (250 ft)
123848 20 m (65 ft)
*Cable numbers 123784 and 123785 are for use with systems that have the selection console mounted on the power supply
Page 70

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-21
1X5
J103
J300
Female
Male
5
656
3X1
3X2
3X3
3X4
5
Page 71

INSTALLATION
3-22 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Cable and gas hose assembly
7
Selection console to metering console connections
Female end to metering console Male end to selection console
Power cable signal list – 9-pin connectors
Metering console end Selection console end
Pin # Input/Output Description Pin # Input/Output Function
1 Input 120 VAC power 1 Output AC in, return
2 Input 120 VAC power 2 Output AC in, hot
3 Input Chassis ground 3 Output Chassis ground
6 unused 6
7 unused 7
4 unused 4
5 unused 5
Communication cable signal list – 9-pin DSUB connectors
Metering console end Selection console end
Pin # I/O Description Pin # I/O Function
9 I unused 9 O unused
3 I CAN ground 3 O Power ground
7 I/O CAN H 7 I/O CAN communication
2 I/O CAN L 2 I/O CAN communication
Typical female DSUB connector
Part no. Length
128992 3 m (10 ft)
128993 4.5 m (15 ft)
128952 7.5 m (25 ft)
128994 10 m (35 ft)
128930 15 m (50 ft)
128995 20 m (65 ft)
Page 72

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-23
7
Page 73

INSTALLATION
3-24 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Wire Input/ Input/
color Pin # Output Signal name Function Output Notes
Black 1 Input Rx - RS-422 serial receiver Output
Red 20 Input Rx + RS-422 serial receiver Output
Black 2 Output Tx - RS-422 serial transmitter Input
Green 21 Output Tx + RS-422 serial transmitter Input
Black 3 RS-422 ground RS-422 serial ground
Blue 22 None Not used
Black 4 Output Motion 1 E (-) Notifies the CNC that an arc transfer has occurred and to begin Input 2 & 3
Yellow 23 Output Motion 1 C (+) machine motion once the CNC’s pierce delay has timed out. Input
Black 5 Output Error E (-) Notifies the CNC that an error has occurred. Input 2
Brown 24 Output Error C (+) Input
Black 6 Output Rampdown error E (-) Notifies the CNC that a rampdown error has occurred Input 2
Orange 25 Output Rampdown error C (+)
Red 7 Output Not ready E (-) Notifies the CNC that the plasma system is not ready to fire an arc Input 2
White 26 Output Not ready C (+)
Red 8 Output Motion 2 E (-) Notifies the CNC that an arc transfer has occurred and to begin Input 2 & 3
Green 27 Output Motion 2 C (+) machine motion once the CNC’s pierce delay has timed out. Input
Red 9 Output Motion 3 E (-) Notifies the CNC that an arc transfer has occurred and to begin Input 2 & 3
Blue 28 Output Motion 3 C (+) machine motion once the CNC’s pierce delay has timed out. Input
Red 10 Output Motion 4 E (-) Notifies the CNC that an arc transfer has occurred and to begin Input 2 & 3
Yellow 29 Output Motion 4 C (+) machine motion once the CNC’s pierce delay has timed out. Input
Red 11 None Not used
Brown 30 None Not used
Red 12 Input Corner - CNC Notifies the plasma system that a corner is approaching and to Output 1
Orange 31 Input Corner + reduce cut current (Cut current is CNC selectable or defaults to 50%. Output
of cut current)
Green 13 Input Pierce - CNC Notifies the plasma system to maintain the shield preflow until Output 1
White 32 Input Pierce + the CNC releases the signal.
Green 14 Input Hold - Not required without CommandTHC. CommandTHC requires signal Output 1
Blue 33 Input Hold + to preflow gases during IHS.
Green 15 Input Start - CNC initiates the plasma arc. Output 1
Yellow 34 Input Start + Output
Green 16 None Not used
Brown 35 None Not used
Green 17 None Not used
Orange 36 Power ground Ground
White 18 Power ground Ground
Black 37 CNC +24 VDC Available 24 VDC (200 milliamps maximum) See notes 4
19 CNC + 24 VDC Not connected
Power supply to CNC interface cable
8
To J 300
Power supply CNC
Optional multi-system CNC interface cable
(see schematics for installation information)
9
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123210 3 m (10 ft) 123741 25 m (82 ft)
123211 4.5 m (15 ft) 123742 35 m (115 ft)
123022 7.5 m (25 ft) 123220 45 m (150 ft)
123214 10 m (35 ft) 123852 60 m (200 ft)
123023 15 m (50 ft) 123853 75 m (250 ft)
123851 20 m (65 ft)
Page 74

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-25
5
Caution: The CNC cable must be constructed using cable with 360-degree shield and
metal housing connectors at each end. The shield must be terminated to the
metal housings at each end to ensure proper grounding and to provide the
best shield.
Notes to CNC interface cable run list
Note 1. Inputs are optically isolated. They require 24 VDC at 7.3 mA, or dry-contact closure. The external relay’s life
may be improved by adding a metallized-polyester capacitor (0.022µF 100V or higher) in parallel with the
relay contacts
Note 2. Outputs are optically isolated, open collector, transistors. The maximum rating is 24 VDC at 10 mA.
Note 3. Machine motion is selectable and is used for configurations with multiple plasma systems.
Note 4. CNC +24 VDC provides 24 VDC at 200 mA maximum. A jumper is required on J304 to use 24 V power.
Page 75

INSTALLATION
3-26 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Examples of output circuits
1. Logic interface, active-high
2. Logic interface, active-low
3. Relay interface
4. Do not use this configuration. Warranty will be void.
High-impedance (≤10mA)
10K
(optional)
CNC/PLC
5 VDC-24 VDC
C
HPR
E
+
-
HPR
C
E
+
-
5 VDC-24 VDC
High-impedance (≤10mA)
CNC/PLC
10K
(optional)
CNC/PLC
CNC +24 V
+24 VDC
CNC +24 V
HPR
C
E
+
-
Power
ground
External relay
24 VDC low-power coil
≤10 mA or ≥2400 ohm
High-current
contact closure
inputs (AC or DC)
°t
Any voltage
VOIDS
WARRANTY
HPR
Install a
Jumper
108056
J304
C
E
+
-
Page 76

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-27
3
Examples of input circuits
Output from
CNC/PLC
External relay
(AC or DC)
1. Relay interface
+24 VDC
HPR
Power
ground
2. Optocoupler interface
CNC/PLC
+24 VDC
HPR
Power
ground
Transistor-output
optocoupler
12V-24 VDC
CNC/PLC
+24 VDC
HPR
Power
ground Power
ground
Active-high drive
3. Amplified-output interface
Note: The external relay's life may be improved by adding a
metallized-polyester capacitor (0.022µF 100V or higher) in
parallel with the relay contacts.
Page 77

INSTALLATION
3-28 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
1. Locate terminal block 2 (TB2) in the power supply.
2. Remove wire 1 and wire 3 as shown. These wires do not need to be reconnected.
3. Connect switch to terminals 1 and 3 as shown.
TB2 location
123
TB2
13
Note: Use a switch, relay or solid-state relay that is compatible with 24 VAC @ 100 mA. It must be a
maintained contact switch, not a momentary contact switch.
Remote ON/OFF switch (provided by customer)
5
DANGER
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL
Disconnect electrical power before performing any maintenance.
See the Safety section in this manual for more safety precautions.
13
TB2
123
1
3
Page 78

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-29
5
Torch lead assembly
10
Plasma-gas vent hose
10
Part no. Length
128986 2 m (6 ft)
128935 3 m (10 ft)
128934 4.5 m (15 ft)
128784 7.5 m (25 ft)
128987 10 m (35 ft)
128785 15 m (50 ft)
128988 20 m (65 ft)
Caution: Locate the exposed end of the plasma-gas vent hose away from sparks caused
by piercing to avoid ignition and possible damage to the torch leads.
Grey
Page 79

INSTALLATION
3-30 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
Work lead
11
Work lead
Work lead
Lower frame of work table (typical).
Work table
Power supply
Part no. Length Part no. Length
123816 3 m (10 ft) 123775 25 m (82 ft)
123817 4.5 m (15 ft) 123776 35 m (115 ft)
123773 7.5 m (25 ft) 123777 45 m (150 ft)
123818 10 m (35 ft) 123778 60 m (200 ft)
123774 15 m (50 ft) 123779 75 m (250 ft)
123819 20 m (65 ft)
Page 80

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-31
5
Torch connections
Connect the torch to the torch lead assembly
1. Uncoil the first 2 meters (6.5 ft) of the leads on a flat surface.
2. Hold the torch assembly in place with the spanner wrench (104269) and remove the mounting sleeve from the torch
assembly.
3. Push back the braided cover and slide the sleeve over the leads. Align the torch with the hoses in the lead assembly.
The hoses must not be twisted. They are taped together to help prevent twisting.
4. Connect the coolant IN hose (green) to the torch.
Braided cover
Sleeve
Coolant IN hose
2WRENCHES
Page 81

INSTALLATION
3-32 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5c. Slide the sleeve forward until it clicks into place.
5. Connect the pilot arc lead.
Note: Be careful not to damage or remove the small slotted metal band at the end of the pilot arc cable.
5a. Pull the sleeve back until the connector is exposed.
5b. Screw the connector onto the pilot arc connection from the torch. Tighten by hand until it is firmly seated.
6. Connect the plasma-gas vent hose.
5
Page 82

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-33
5
7. Connect the coolant return hose (red).
8. Connect the plasma gas hose.
9. Connect the shield gas hose.
10. Slide the torch sleeve over connections and screw it onto the torch body.
11. Slide the braided cover up to the torch sleeve. Make sure that the plasma, shield and vent hoses are routed through
the hole in the braided cover. Loosen the hose clamp on the braided cover, slide the braided cover and clamp over
the sleeve and tighten the clamp.
Page 83

INSTALLATION
3-34 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Connect the torch to the quick-disconnect
Installation note
Align the torch body to the torch leads and secure by
screwing completely together. Be certain that there is no
space between the torch body and the o-ring on the torch
leads. See also Torch connections earlier in this section for
torch lead connections to ignition console.
Apply a thin film of silicone
lubricant to each o-ring
Torch body
220162
Torch quick-disconnect receptacle
220163
5
Page 84

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-35
3
Torch mounting and alignment
Mounting the torch
Torch alignment
To align the torch at right angles to the workpiece, use a square. See figure above.
See also Changing consumables in Section 4 to install consumables in the torch.
Torch lifter requirement
The system requires a high-quality, motorized torch lifter with sufficient travel to cover all cutting thickness requirements.
The lifter must provide 203 mm (8 in) of vertical travel. The unit should have the capability of maintaining a constant
speed of up to 5080 mm/min (200 ipm) with positive braking. A unit which drifts through the stop point is not
acceptable.
Installation
1. Install the torch (with torch leads
attached) in the torch mounting bracket.
2. Position the torch below the mounting
bracket, so that the bracket is around the
lower portion of the torch sleeve but not
touching the torch quick-disconnect.
3. Tighten the securing screws.
Note: The bracket should be as low on the
torch sleeve as possible to minimize vibration
at the tip of the torch.
Lower torch sleeve
Torch mounting
bracket
(customer supplied)
Upper torch sleeve
Quick-disconnect
receptacle
Page 85

INSTALLATION
3-36 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Line disconnect switch
The line disconnect switch serves as the supply-voltage disconnecting (isolating) device. Install
this switch near the power supply for easy access by the operator.
Installation must be performed by a licensed electrician and according to applicable national or
local codes.
The switch should:
• Isolate the electrical equipment and disconnect all live conductors from the supply
voltage when in the “OFF” position
• Have one “OFF” and one “ON” position clearly marked with “O” (OFF) and “l” (ON)
• Have an external operating handle capable of being locked in the “OFF” position
• Contain a power-operated mechanism that serves as an emergency stop
• Have slow-blow fuses installed for the proper breaking capacity (see table above).
Power requirements
General
All switches, slow-blow fuses and power cables are customer-supplied and must be chosen as
outlined by applicable national or local electrical codes. Installation must be performed by a
licensed electrician. Use a separate primary line disconnect switch for the power supply.
Note: The main feed protection device (Circuit Breaker or Fuse) must be sized to handle all branch-feed loads
for both inrush and steady-state current. The power supply must be wired into one of the branch-feed
circuits. The power supply has a steady-state current listed in the table below and has an inrush current of
10 times the rated input current, which can last up to 0.20 seconds or 10 line cycles.
Power cable
Wire sizes vary based on the distance of the receptacle from the main box. The wire sizes listed in the table above were
taken from the National Electric Code 1990 handbook, table 310.16 (USA). Use a 4-conductor Type SO input power
cable with a conductor temperature rating of 60° C (140° F). Installation must be performed by a licensed electrician.
Note: Cable AWG recommendations taken from table 310-16 of the National Electric Code handbook (USA).
F
U
S
E
Input voltage Phase
Rated input
current
@ 45.5 kW output
Recommended
slow-blow fuse
size
Recommended Cable size for 15 m (50
ft) maximum length
Rated for 60°C Rated for 90°C
200/208 VAC
3 149/144 amps 175 amps N/A
67.5 mm2(2/0 AWG)
220 VAC
3 136 amps 175 amps N/A
67.5 mm2(2/0 AWG)
240 VAC
3 124 amps 150 amps
107.2 mm2(4/0 AWG) 53.5 mm2(1/0 AWG)
380 VAC
3 79 amps 95 amps
42.4 mm2(1 AWG) 26.7 mm2(3 AWG)
400 VAC
3 75 amps 90 amps
42.4 mm2(1 AWG) 26.7 mm2(3 AWG)
440 VAC
3 68 amps 80 amps
42.4 mm2(1 AWG) 21.2 mm2(4 AWG)
480 VAC
3 62 amps 75 amps
33.6 mm2(2 AWG) 21.2 mm2(4 AWG)
600 VAC
3 50 amps 60 amps
26.7 mm2(3 AWG) 13.3 mm2(6 AWG)
SWITCH BOX
Page 86

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-37
Connect the power
1. Insert the power cable through the strain relief at the rear of the power supply.
2. Connect the ground lead (PE) to the GROUND terminal of TB1 as shown below.
3. Connect the power leads to the terminals of TB1 as shown below.
4. Check that the line disconnect switch is in the OFF position and remains in the OFF position for the
remainder of the installation of the system.
5. Connect the power cord leads to the line disconnect switch following national or local electrical codes.
North American wire colors
U = Black
V = White
W = Red
(PE) Earth ground = Green/Yellow
DANGER
ELECTRICAL SHOCK CAN KILL
The line disconnect switch must be in the OFF position before making the power cable connections.
In the U.S., use a “lock-out/tag-out” procedure until installation is complete. In other countries,
follow appropriate national or local safety procedures.
Line
disconnect
switch
Power
cable
TB1
W
V
GND
U
European wire colors
U = Black
V = Blue
W = Brown
(PE) Earth ground = Green/Yellow
Page 87

INSTALLATION
3-38 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
DANGER
COOLANT CAN BE IRRITATING TO SKIN AND EYES AND
HARMFUL OR FATAL IF SWALLOWED
Propylene glycol and benzotriazole are irritating to skin and eyes, and harmful or fatal if
swallowed. Upon contact, flush skin or eyes with water. If swallowed, drink water and call a
physician immediately. Do not induce vomiting.
Torch coolant requirements
The power supply is shipped without any coolant in the tank. Before filling the coolant system, determine what coolant
mix is correct for your operating conditions.
Observe the warning and cautions below. Refer to the Material Safety Data Sheets Appendix for data on safety,
handling and storage of propylene glycol and benzotriazole.
Caution: Never use automotive anti-freeze in place of propylene glycol. Antifreeze
contains corrosion inhibitors that will damage the torch coolant system.
Always use purified water in the coolant mixture in order to prevent damage to
the pump and corrosion in the torch coolant system.
Standard installation
Use Hypertherm premixed coolant (028872) when operating in a temperature range of 0° C to 40° C
(32° F to 104° F). Refer to the non-standard installation recommendations, if temperatures during operation are ever
outside of this range.
Hypertherm premixed coolant consists of 69.9% water, 30% propylene glycol, and 0.1% benzotriazole.
Page 88

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-39
5
Temperature
% of Propylene Glycol
Caution: For operating temperatures colder than the temperature stated above,
the percentage of propylene glycol must be increased. Failure to do so
could result in a cracked torch head, hoses or other damage to the torch
coolant system due to freezing.
Hypertherm pre-mix (028872)
Maximum glycol percentage
°F°C
Coolant for cold operating temperatures (below 0° C / 32° F)
Use a custom coolant mix when operating in temperatures below 0° C (32° F).
Use the chart below to determine what percentage of propylene glycol to use in the mixture.
Mix 100% glycol (028873) with the premixed Hypertherm coolant (028872) to increase the percentage of glycol. The
100% glycol solution can also be mixed with purified water (see next page for water purity requirements) to achieve the
required protection from freezing.
Note: Maximum percentage of glycol should never exceed 50%.
-12
-18
-23
-29
-34
-40
-46
4
40
-1
30
-7
20
10
0
-1
0
-2
0
-3
0
-4
0
-5
0
-51
-6
0
-57
-7
0
0 102030405060
Page 89

INSTALLATION
3-40 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Water purity requirements
It is critical to maintain a low level of calcium carbonate in the coolant to avoid reduced performance of the torch or
cooling system.
Always use water that meets the minimum and maximum specifications in the table below when using a custom coolant
mix.
Water that does not meet the minimum purity specifications below can cause excessive deposits on the nozzle that will
alter the water flow and produce an unstable arc.
Water that does not meet the maximum purity specifications below can also cause problems. Deionized water that is too
pure will cause leaching problems with the coolant system plumbing.
Use water purified by any method (deionization, reverse osmosis, sand filters, water softeners, etc.) as long as the water
purity meets the specifications in the table below. Contact a water specialist for advice in choosing a water filtration
system.
Coolant for hot operating temperatures (above 38° C / 100° F)
Use a custom coolant mix when operating in temperatures above 38° C (100° F).
Treated water (with no propylene glycol) can only be used as coolant when operating temperatures are never below
0° C (32° F). For operations in very warm temperatures treated water will provide the best cooling properties.
Treated water refers to a mixture of purified water, that meets the specifications below, and 1 part benzotriazole (BZT) to
300 parts of water. BZT (128020) acts as a corrosion inhibitor for the copper based coolant system contained in the
plasma system.
Water purity measurement method
Water purity
Conductivity
S/cm
at 25° C
Resistivity
mΩ-cm
at 25° C
Dissolved solids
(ppm of NaCl)
Grains per gallon
(gpg of CaCO2)
Pure water (for reference only) 0.055 18.3 0 0
Maximum purity 0.5 2 0.206 0.010
Minimum purity 18 0.054 8.5 0.43
Maximum potable water
(for reference only)
1000 0.001 495 25
Page 90

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-41
Fill the power supply with coolant
The system will take 11.4 – 15.1 liters (3 to 4 gallons) of coolant depending on the length of the torch leads and
whether the system has a local or remote ignition console.
Locate the CNC screen for manual pump
control. The pump needs to run to fill the
leads.
3
Add coolant to the power supply
until the tank is full and replace the
filler cap.
4
Add coolant to the power supply until
the tank is full.
1
Turn ON the power supply using the
remote ON/OFF switch or the CNC.
2
Caution: Using the wrong coolant can cause damage to the system. Refer to torch
coolant requirements in this section for more information.
Do not over fill the coolant tank.
5
Page 91

INSTALLATION
3-42 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Gas requirements
The customer must furnish all gases and gas-supply regulators for the system. Use a high-quality, 2-stage pressure
regulator located within 3 m (10 ft) of the selection console. See gas regulators in this section for recommendations.
See Section 2 for gas and flow specifications.
Note: Oxygen, air and nitrogen are required for all systems. Nitrogen is used as a purge gas.
Caution: Gas supply pressures not within the specifications in Section 2 can cause poor cut
quality, poor consumable life and operational problems.
If the purity level of the gas is too low (or too high in the case of methane) or if
there are leaks in the supply hoses or connections,
• Cut speeds can decrease
• Cut quality can deteriorate
• Cutting thickness capability can decrease
• Parts life can shorten
Setting the supply regulators
1. Turn OFF the power to the system. Set all gas
regulator pressures to 8 bar (115 psi).
2. Turn ON the power to the system using the remote
ON/OFF switch or the CNC.
3. Set to Test Preflow.
4. While gas is flowing adjust the supply regulator for the
shield gas pressure to 8 bar (115 psi).
5. Turn OFF Test Preflow.
6. Set system to Test Cutflow.
7. While gas is flowing adjust the supply regulator for the
plasma gas to 8 bar (115 psi).
8. Turn OFF Test Cutflow.
Page 92

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-43
Gas regulators
Low-quality gas regulators do not provide consistent supply pressures and can result in poor cut quality and system
operation problems. Use a high-quality, 1-stage, gas regulator to maintain consistent gas supply pressure, if using liquid
cryogenic or bulk storage. Use a high-quality, 2-stage, gas regulator to maintain consistent gas supply pressure from
high pressure gas cylinders.
The high-quality gas regulators listed below are available from Hypertherm and meet U.S. Compressed Gas Association
(CGA) specifications. In other countries, select gas regulators that conform to national or local codes.
Part
Number
Description Qty.
128544 Kit: Oxygen, 2-stage * 1
128545 Kit: Inert Gas, 2-stage 1
128546 Kit: Hydrogen (H5, H35 and methane) 2-stage 1
128547 Kit: Air, 2-stage 1
128548 Kit: 1-stage (for use with cryogenic liquid nitrogen or oxygen) 1
022037 Oxygen, 2-stage 1
022038 Inert gas, 2-stage 1
022039 Hydrogen/methane, 2-stage 3
022040 Air, 2-stage 1
022041 Line regulator, 1-stage 1
* Kits include appropriate fittings
2-stage regulator
Single stage regulator
Page 93

INSTALLATION
3-44 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
5
Supply gas plumbing
Rigid copper plumbing or suitable flexible hose may be used for all gas supplies. Do not use steel or aluminum pipe.
After installation, pressurize the entire system and check for leaks.
Recommended hose diameters are 9.5 mm (3/8 in) for lengths < 23 m (75 ft) and 12.5 mm (1/2 in) for
lengths > 23 m (75 ft).
For flexible-hose systems, use a hose designed for inert gas to carry air, nitrogen or argon-hydrogen.
Connect the supply gases
Connect the supply gases to the selection console. Torch leads must be purged between gas changes.
WARNING
CUTTING WITH OXYGEN CAN CAUSE FIRE OR EXPLOSION
Cutting with oxygen as the plasma gas can cause a potential fire hazard due to the oxygen-enriched
atmosphere that it creates. As a precaution, Hypertherm recommends that an exhaust ventilation
system be installed when cutting with oxygen.
Flashback arrestors are required (unless not available for specific gases or required pressures) to
prevent fire from propagating back to supply gas.
Note: When cutting with oxygen as the plasma gas, air must also be connected to the selection console to
achieve the proper mixtures in the preflow and cutflow modes.
Caution: When configuring the selection console to the supply gases, make sure that all
hoses, hose connections and fittings are acceptable for use with oxygen,
argon-hydrogen and methane. Installation must be made in accordance with
national and local codes.
Fitting Size
N
2
5/8 – 18, RH, internal
(Inert Gas) “B”
Air 9/16 – 18, JIC, #6
F5, H35, H5 9/16 – 18 LH,
(Fuel Gas)“B”
O
2
9/16 – 18, RH
(oxygen) “B”
Page 94

INSTALLATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 3-45
Supply gas hoses
Oxygen hose
Air hose
H35 or F5 hose
Nitrogen hose
Part no. Length Part no. Length
024607 3 m (10 ft) 024738 25 m (82 ft)
024204 4.5 m (15 ft) 024450 35 m (115 ft)
024205 7.5 m (25 ft) 024159 45 m (150 ft)
024760 10 m (35 ft) 024333 60 m (200 ft)
024155 15 m (50 ft) 024762 75 m (250 ft)
024761 20 m (65 ft)
Part no. Length Part no. Length
024210 3 m (10 ft) 024739 25 m (82 ft)
024203 4.5 m (15 ft) 024451 35 m (115 ft)
024134 7.5 m (25 ft) 024120 45 m (150 ft)
024211 10 m (35 ft) 024124 60 m (200 ft)
024112 15 m (50 ft) 024764 75 m (250 ft)
024763 20 m (65 ft)
Part no. Length Part no. Length
024671 3 m (10 ft) 024740 25 m (82 ft)
024658 4.5 m (15 ft) 024744 35 m (115 ft)
024659 7.5 m (25 ft) 024678 45 m (150 ft)
024765 10 m (35 ft) 024680 60 m (200 ft)
024660 15 m (50 ft) 024767 75 m (250 ft)
024766 20 m (65 ft)
Part no. Length Part no. Length
024768 3 m (10 ft) 024741 25 m (82 ft)
024655 4.5 m (15 ft) 024742 35 m (115 ft)
024384 7.5 m (25 ft) 024743 45 m (150 ft)
024769 10 m (35 ft) 024771 60 m (200 ft)
024656 15 m (50 ft) 024772 75 m (250 ft)
024770 20 m (65 ft)
3
12
13
14
15
Page 95

5
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 4-1
Section 4
OPERATION
In this section:
Daily start-up................................................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Check torch.......................................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Power indicators.........................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
General...............................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Power supply ...................................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Selection console ...........................................................................................................................................................................4-3
Metering console .............................................................................................................................................................................4-3
CNC controller requirements ..................................................................................................................................................................4-4
CNC screen examples ..............................................................................................................................................................................4-5
Main (control) screen......................................................................................................................................................................4-5
Diagnostic screen............................................................................................................................................................................4-6
Test screen.........................................................................................................................................................................................4-7
Cut chart screen...............................................................................................................................................................................4-8
Consumable selection...............................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Mild steel............................................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Stainless steel................................................................................................................................................................................4-10
Aluminum.........................................................................................................................................................................................4-10
Install consumables.................................................................................................................................................................................4-11
Cut charts..................................................................................................................................................................................................4-12
Bevel cutting...................................................................................................................................................................................4-12
Marking ............................................................................................................................................................................................4-12
Consumables for mirror-image cutting.....................................................................................................................................4-12
Estimated kerf width compensation..........................................................................................................................................4-13
Changing consumable parts .................................................................................................................................................................4-42
Remove consumables..................................................................................................................................................................4-42
Inspect consumables....................................................................................................................................................................4-43
Inspect torch...................................................................................................................................................................................4-44
Inspect electrode pit depth.........................................................................................................................................................4-45
Replace torch water tube.......................................................................................................................................................................4-46
Common cutting faults............................................................................................................................................................................4-47
How to optimize cut quality...................................................................................................................................................................4-48
Tips for table and torch................................................................................................................................................................4-48
Plasma set-up tips.........................................................................................................................................................................4-48
Maximize the life of consumable parts......................................................................................................................................4-48
Additional factors of cut quality..................................................................................................................................................4-49
Additional improvements .............................................................................................................................................................4-50
Page 96

Daily start-up
Prior to start-up, ensure that your cutting environment and that your clothing meet the safety requirements outlined in the
Safety section of this manual.
Check torch
1. Turn main disconnect switch to the power supply OFF.
2. Remove the consumables from the torch and check for worn or damaged parts. Always place the consumables
on a clean, dry, oil-free surface after removing. Dirty consumables can cause the torch to malfunction.
• Refer to Changing consumable parts later in this section for details and for parts inspection tables.
• Refer to the Cut charts to choose the correct consumables for your cutting needs.
3. Replace consumable parts. Refer to Changing consumable parts later in this section for details.
4. Ensure that the torch is perpendicular to the workpiece.
WARNING
Before operating this system, you must read the Safety section thoroughly. Turn OFF the power
supply's main disconnect switch before proceeding with the following steps.
TorchCurrent ringElectrodeSwirl ring
Nozzle
OPERATION
4-2 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
3
ShieldRetaining cap
Inner retaining cap
Page 97

OPERATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 4-3
Power indicators
General
Power for the system is controlled by the CNC. The power supply, selection console and metering console each have
an LED lamp that illuminates when power is supplied to the component.
Green indicator
Power supply
Selection console
Metering console
Green indicator
Page 98

OPERATION
4-4 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
CNC controller requirements
Base required elements
The following elements should be able to be displayed and adjusted on the CNC for setup and basic system
information. The plasma system needs this group for basic setup and operation capability.
1. Remote ON/OFF
2. Ability to display and adjust the basic plasma process set-points (command ID #95)
a. Current set point
b. Plasma preflow
c. Plasma cutflow
d. Shield preflow
e. Shield cutflow
f. Plasma gas type
g. Shield gas type
h. Gas mixing set-points
3. Display basic system information
a. System error code
b. Gas and PS firmware version
4. Manual pump control
Required real time elements
The following elements should be able to be displayed in real time while cutting. This is necessary for trouble shooting
and diagnostic purposes.
5. Display line voltage
6. Display chopper current
7. Display work lead current
8. Display system status code
9. Display chopper temperature
10. Display transformer temperature
11. Display coolant temperature
12. Display coolant flow
13. Display pressure transducers
Required diagnostic elements
These elements provide additional diagnostic capability to the system for troubleshooting gas-delivery problems. The
CNC should be capable of executing these commands and displaying the relevant information for the respective test
according to the serial protocol guidelines.
14. Test preflow gases
15. Test cutflow gases
16. Inlet leak test
17. System leak test
18. System flow test
Page 99

OPERATION
HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual 4-5
CNC screen examples
The screens shown are for reference. The screens you work with may be different, but should include the functions
listed on the previous page.
Main (control) screen
Page 100

OPERATION
4-6 HPR260 Auto Gas Instruction Manual
Diagnostic screen
 Loading...
Loading...