
Hypermedia HG-3000
Product Manual
3U and 6U Cellular / PRI Gateways
Release 5.3 (June 2013)

Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
2b, Professor Bergman St., Rabin Science Park,
Rehovot, 7670504, Israel
Telephone: (+972)-77-4445000
Fax: (+972)-8-936-3066
For general inquiries: info@hyperms.com
For sales inquiries: sales@hyperms.com
For Technical Support: support@hyperms.com
Web site: http://www.hyperms.com/
PROPRIETARY AND CONFIDENTIAL
Copyright © 2013 by Hypermedia Systems Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced, transmitted or copied in any form or by any
means- graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, typing or information
retrieval systems- without the express written permission of Hypermedia Systems Ltd.

Hypermedia Systems
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. LICENSE AGREEMENT AND WARRANTY
IMPORTANT — READ CAREFULLY
This Hypermedia Systems Ltd. License Agreement (the "AGREEMENT") is a legal agreement between you
(either an individual or a single entity) and Hypermedia Systems Ltd. for the product accompanying this
AGREEMENT. The product includes computer software, associated media and printed materials, and may
include "online" or electronic documentation (the "SOFTWARE"). The PRODUCT may also include hardware (the
“HARDWARE”). The SOFTWARE and the HARDWARE are referred to, collectively, as the PRODUCT.
BY INSTALLING AND/OR USING THE PRODUCT YOU AGREE TO BE BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS
AGREEMENT.
IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, PROMPTLY ERASE ALL COPIES OF THE
SOFTWARE IN YOUR POSSESSION, AND RETURN THE SOFTWARE AND ANY ACCOMPANYING
HARDWARE TO THE PLACE FROM WHICH YOU OBTAINED IT.
COPYRIGHT.
All title and copyrights in and to the PRODUCT are owned by Hypermedia Systems Ltd. The PRODUCT is
protected by copyright laws and international copyright treaties, as well as other intellectual property laws and
treaties.
GRANT OF LICENSE FOR THE SOFTWARE.
The SOFTWARE is licensed, not sold. Hypermedia Systems Ltd. grants to you a non-exclusive, non-transferable,
royalty-free right to install and use the SOFTWARE, provided that the SOFTWARE will be used by a single
person on a single computer and for personal non-commercial, internal use only. If accompanied by a proof-ofpurchase document specifying "site license," "company license," or any other multiple-user type license scheme,
then the terms of that document shall override this single-user restriction. Any rights not expressly granted herein
are retained by Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
OTHER RESTRICTIONS.
This AGREEMENT is your proof of license to exercise the rights granted herein and must be retained by you.
You may not rent, lease, reverse engineer, decompile, modify, or disassemble the PRODUCT, or create
derivative works based on the PRODUCT.
LIMITED HARDWARE WARRANTY
The HARDWARE is protected against defects in material and workmanship, under normal use, for one (1) year
from the original purchase date.
If the HARDWARE fails to perform within the abovementioned warranty period, you must return the PRODUCT to
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. and prepay any shipping charges, export taxes, custom duties and taxes, or any
charges associated with transportation of the Product. In addition, you are responsible for insuring the PRODUCT
shipped or returned and assume the risk of loss during shipment.
All returned PRODUCTS must be accompanied by a description of the problem, a proof of the place and date of
purchase, and the original shipping and packing materials.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. shall, at its sole discretion, either repair the PRODUCT or replace it with a product of
the same functionally. Replacement products may be refurbished or contain refurbished materials. If Hypermedia
Systems Ltd. cannot repair or replace the PRODUCT, Hypermedia Systems Ltd. will refund the depreciated
purchase price of the PRODUCT.
This limited warranty does not apply to any PRODUCT not purchased from Hypermedia Systems Ltd., or from a
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. authorized reseller, or on which the serial number has been removed or defaced. This
limited warranty also does not cover any PRODUCT that has been damaged or rendered defective as a result of
(a) improper transportation or packing when returning the PRODUCT to Hypermedia Systems Ltd.; (b) use of the
PRODUCT other than in accordance with its instructions, or other misuse or abuse of the PRODUCT; (c)
modification of the PRODUCT; (d) service by anyone other than a Hypermedia Systems Ltd.-approved agent; (e)
unusual physical or electrical stress or interference, failure or fluctuation of electrical power, lightning, static
electricity, improper temperature or humidity, fire, or acts of God.
The maximum liability of Hypermedia Systems Ltd. under this limited warranty is limited to the purchase price of
the PRODUCT covered by the warranty.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
iii

Hypermedia Systems
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. reserves the right to refuse PRODUCTS (i) that are not covered by the warranty; or (ii)
for which there is no problem found. Such PRODUCTS shall be returned to the purchaser at purchaser’s
expense.
DISCLAIMER.
EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY STATED ABOVE OR AS REQUIRED BY LAW, Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTY FOR THE PRODUCT. THE PRODUCT IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT
REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NONINFRINGEMENT. Hypermedia Systems Ltd. ASSUMES NO RISK ARISING
OUT OF THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
IN NO EVENT SHALL Hypermedia Systems Ltd., ITS AGENTS OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY
DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL OR OTHER
CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES; DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, OR ANY OTHER PECUNIARY LOSS) ARISING
DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY OUT OF THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT, EVEN IF
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. HAS BEEN ADVISED IN ADVANCE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Because some states or jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability for consequential or
incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to you.
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS.
For purchases made in the United States: The SOFTWARE and any accompanying documentation are provided
with restricted rights. Use, duplication or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in
subparagraph (b) (3) and (c) (1) (ii) of The Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS
252.227-7013 or subparagraphs (c) (1) and (2) of the Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights at 48
CFR 52.227-19, as applicable.
AMENDMENTS.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd. may amend these terms and conditions at any time by posting a notice on one or more
of its websites. Your continued use of the PRODUCT shall constitute your acceptance of such amended terms.
Accordingly, we urge you to visit our websites periodically to review the current and effective terms and
conditions for use of our products. Certain provisions of these terms and conditions may be superseded by
expressly designated legal notices or terms outlined on our websites.
GOVERNING LAW.
This AGREEMENT and any and all claims relating to the PRODUCT shall be governed by the laws of the State
of Israel, without regard to or application of choice of law or principles, and the courts of Tel-Aviv Jaffa shall have
sole and exclusive jurisdiction over any dispute arising in connection with this Agreement and/or the use of the
PRODUCT.
NO WAIVER.
No delay or failure to take action under these terms and conditions will constitute a waiver by Hypermedia
Systems Ltd. unless expressly waived in writing by a duly authorized officer of Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
iv
Hypermedia Systems
Symbol
Description
Note:
Information given in a note describes how the System functions or provides
a tip on how best to use it.
Caution:
Information given in a message labeled “caution” refers to the safe
operation of the System and provides warnings where the possibility for
loss of data or damage to the equipment exists.
Danger:
Information given in a message labeled “danger” warns of possible hazard
to personnel and extreme hazard to the System.
Before You Begin
Before You Begin
Conventions
The following symbols have been inserted on the left hand side of the operating
instructions in order to make it easier for the User to perform procedures:
Notice
Information given in this document is subject to change without any notice.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
v

Hypermedia Systems
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1 Hardware and Installation .................................... 1
1.1 Overview .................................................................................... 2
1.1.1 Contents of Package ..................................................................................... 2
1.2 Safety Information ................................ ..................................... 3
1.3 System Components ................................................................. 4
1.4 Installation .................................................................................. 6
1.4.1 Pre-Installation and Preparation .................................................................... 6
1.4.2 Installing the Hybrid (HBD or HBS) Card ...................................................... 7
1.4.3 Preparing the PRI Connection ....................................................................... 8
1.4.4 Inserting the SIM Cards .............................................................................. 10
1.4.5 Inserting the SD Card .................................................................................. 11
1.5 Powering Up and LEDs ........................................................... 12
1.5.1 Powering Up................................................................................................ 12
1.5.2 LEDs ........................................................................................................... 13
1.6 Cable Connections .................................................................. 15
1.6.1 Hybrid Cards (HBS/HBD) ............................................................................ 15
1.6.2 PC ............................................................................................................... 18
2 HMC Quick Start ................................................. 19
2.1 Installation ................................................................................ 20
2.2 Setting the IP Address ............................................................ 22
2.3 Start-up and Initial Connection ............................................... 24
2.4 Save, Backup and Restore ...................................................... 27
2.4.1 Save All ....................................................................................................... 27
2.4.2 Save All Settings on Cards ......................................................................... 27
2.4.3 Backup/Restore ........................................................................................... 27
3 Configuring a Cellular Card ............................... 29
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
vi

Hypermedia Systems
Table of Contents
3.1 Cellular Card and System Terminology ................................. 30
3.2 Volume Settings....................................................................... 31
3.3 Media Connections .................................................................. 32
3.3.1 Associating/Linking Cellular Channels ........................................................ 32
3.3.2 Auto Linking ................................................................................................ 33
3.3.3 Unlinking Cellular Allocations ...................................................................... 34
3.4 PIN Codes ................................................................................. 35
3.5 MSN Values .............................................................................. 36
3.6 Reset ......................................................................................... 37
3.7 Information Screens ................................................................ 38
3.7.1 Module Info ................................................................................................. 38
3.7.2 Serial Numbers ........................................................................................... 38
3.8 Locks ........................................................................................ 39
3.9 SIM Select................................................................................. 40
3.10 SIM Counters ........................................................................... 41
3.11 SIM Auto Manage ..................................................................... 42
3.12 Call Counter Steps ................................................................... 43
3.13 CLI Blocking ............................................................................. 44
3.14 Call Limits ................................ ................................................ 45
3.15 Cell Selection ........................................................................... 46
3.16 Settings .................................................................................... 47
3.17 Network Parameters ................................................................ 48
3.18 USSD SIM Balance ................................................................... 49
3.19 Monitoring Cellular Cards ....................................................... 50
3.19.1 All Cells ....................................................................................................... 50
3.19.2 Reception .................................................................................................... 51
3.19.3 Status .......................................................................................................... 52
4 Configuring LCR ................................................. 53
4.1 Overview .................................................................................. 54
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
vii

Hypermedia Systems
Table of Contents
4.2 Linking to LCR ......................................................................... 55
4.2.1 Linking from a Media Branch....................................................................... 55
4.2.2 Linking from the LCR Branch ...................................................................... 57
4.2.3 Editing a Target Link ................................................................................... 59
4.2.4 Breaking a Link (Unlink) .............................................................................. 59
4.3 Groups ...................................................................................... 60
4.3.1 Creating a Group ......................................................................................... 60
4.3.2 Using the Default Group Settings ................................................................ 61
4.4 Resource Map .......................................................................... 62
4.4.1 Sample Assignment .................................................................................... 62
4.4.2 Assigning LCR Resources .......................................................................... 63
4.5 Rules ......................................................................................... 65
4.5.1 Creating a Rule ........................................................................................... 65
4.5.2 Deleting a Rule ................................................................ ............................ 66
4.6 Filters ........................................................................................ 67
4.7 Advanced Call Routing (ACR)................................................. 69
4.7.1 Modifying the Existing ACR Number List .................................................... 69
4.7.2 Creating a New ACR Number List File ........................................................ 70
4.7.3 ACR Rules .................................................................................................. 72
4.8 Number Filters ......................................................................... 75
4.8.1 Creating a Number Filter ............................................................................. 75
4.9 CDR ........................................................................................... 77
4.9.1 Enabling Collection of CDR ......................................................................... 77
4.9.2 Downloading a CDR File ............................................................................. 78
4.9.3 Deciphering the CDR File ........................................................................... 78
4.10 Activating LCR ......................................................................... 80
5 Configuring the PRI Card ................................... 83
5.1 PRI Media Connections ........................................................... 84
5.1.1 Associating/Linking PRI Channels .............................................................. 84
5.1.2 Unlinking PRI Allocations ............................................................................ 86
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
viii

Hypermedia Systems
Table of Contents
5.2 Connection Settings ................................................................ 87
5.3 PRI Card Dial Plan ................................................................... 89
5.4 Monitoring PRI Card Status .................................................... 90
6 Managing via the HMC ........................................ 91
6.1 Scheduler ................................................................................. 92
6.1.1 Switch SIM per Slot ..................................................................................... 92
6.1.2 Switch SIM per System ............................................................................... 95
6.1.3 Reset SIM Counter ...................................................................................... 96
6.1.4 Set Multi SIM ............................................................................................... 98
6.1.5 Manual Command ..................................................................................... 100
7 Console Suite and other Tools ........................ 101
7.1 Service Console ..................................................................... 102
7.2 PRI Cause Conversion .......................................................... 103
7.3 Hypermedia Gateway Server List ......................................... 105
7.3.1 Adding a New Server ................................................................................ 105
7.3.2 Accessing Other Tools via the Server List ................................................ 106
7.4 Troubleshooting .................................................................... 107
8 Index ................................ ................................ .. 109
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
ix

Hypermedia Systems
Table of Contents
This page is intentionally blank
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
x

Hypermedia Systems
Hardware and Installation
1 Hardware and Installation
Note: Hardware and installation vary depending upon the features included with the
Hypermedia Gateway system. Skip the sections that do not apply to your system.
This section includes:
Contents of Package on page 2
Safety Information on page 3
System Components on page 4
Pre-Installation and Preparation on page 6
Installing the Hybrid (HBD or HBS) Card on page 7
Preparing the PRI Connection on page 8
Inserting the SIM Cards on page 10
Inserting the SD Card on page 11
Powering Up and LEDs12 on page 12
LEDs on page 13
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
1

Hardware and Installation
Overview
1.1 Overview
The HyperGateway family of scalable platforms empowers cost-effective corporate
telephony over fixed, cellular and IP networks. HyperGateway systems provide
integrated voice communications for both on-site and remote users of small-to-large
enterprises. Acting as legacy PBX VoIP enablers, the flexible systems are easily
expanded to meet evolving corporate telephony needs over time.
The Hypermedia Gateway unit is a 19" x 6U or 19" x 3U rack-mount unit that
connects to the local PBX or network via a PRI card or VoIP card. It also connects
to the cellular network via up to 8 cellular cards, each card with 4 modules of
cellular channels. The system enables any combination of connectivity between its
various interfaces.
Running on the HyperGateway family of platforms, the HyperConnect package is a
corporate communications software add-on that minimizes expenses of local,
national and international calls. The scalable system provides secure and flexible
control of on-site and remote calls over fixed, cellular and IP networks. Leveraging
organizational communications resources, Web-based management capabilities, and
operators' various service tariffs, the HyperConnect package empowers significant
savings in corporate telephony expenses.
The HyperConnect package includes a number of service combinations, such as:
Call-Through, Call-Back, SMS Call-Back, Web Call-Back, 2-ways SMS messenger
and Smart-phones applications.
1.1.1 Contents of Package
Depending upon configuration, the package should contain some or all of the
following:
The Hypermedia Gateway unit
PRI cables
Ethernet cables
1 or 2 power cords, depending upon configuration
1 to 8 indoor antennas, depending upon configuration
The warranty certificate
Hypermedia Software CD-ROM
1 SD Card
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
2

Hypermedia Systems
Hardware and Installation
1.2 Safety Information
The Hypermedia Gateway works with a nominal mains supply voltage of 110–240
VAC. Hazardous voltages are present inside the equipment. Some parts may also
have high operating temperatures.
To avoid injury and prevent equipment damage, observe the following safety
precautions:
Installation, service, and maintenance of the Hypermedia Gateway should be
done by qualified technicians only.
Do not connect the Hypermedia Gateway to any power source other than the
indicated nominal source.
The power supply cord must be connected to a socket with a valid ground. This
equipment should only be used in buildings with proper safety ground.
When connecting the equipment, first, ensure that the ground connection is
connected to the rack ground or building ground.
When disconnecting the equipment, disconnect the ground connection last.
Opening the housing may be dangerous and invalidates the warranty. Only a
qualified technician should open the housing. Before opening, disconnect the
power cable from the equipment.
The Hypermedia Gateway complies with all necessary safety standards.
Equipment connected to the Hypermedia Gateway must also comply with the
applicable safety standards.
The packaging is designed to protect against mechanical damage and should be
stored. Do not ship equipment unless it is properly packed in its original
wrapping and shipping containers.
Make sure that the equipment top and bottom are not blocked to air movement.
Leave 1U under and on top of the equipment for proper ventilation.
Do not operate the Hypermedia Gateway in close proximity to potentially
hazardous areas. These include areas such as, but not exclusively, fuel stations,
fuel depots, chemical works or during blasting.
The operation of radio transmitters, which includes cellular engines, can impair
the function of medical devices that have not been properly shielded. Ask the
advice of your doctor or the manufacturer of the medical device.
To avoid moisture condensation, allow time for the unit to adapt to the ambient
temperature before switching it on.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
3
Hardware and Installation
Power Supply
CG Boards
HBS/HBD Board
HBS/HBD Board
CG Boards
Power Supply
6U
3U
System Components
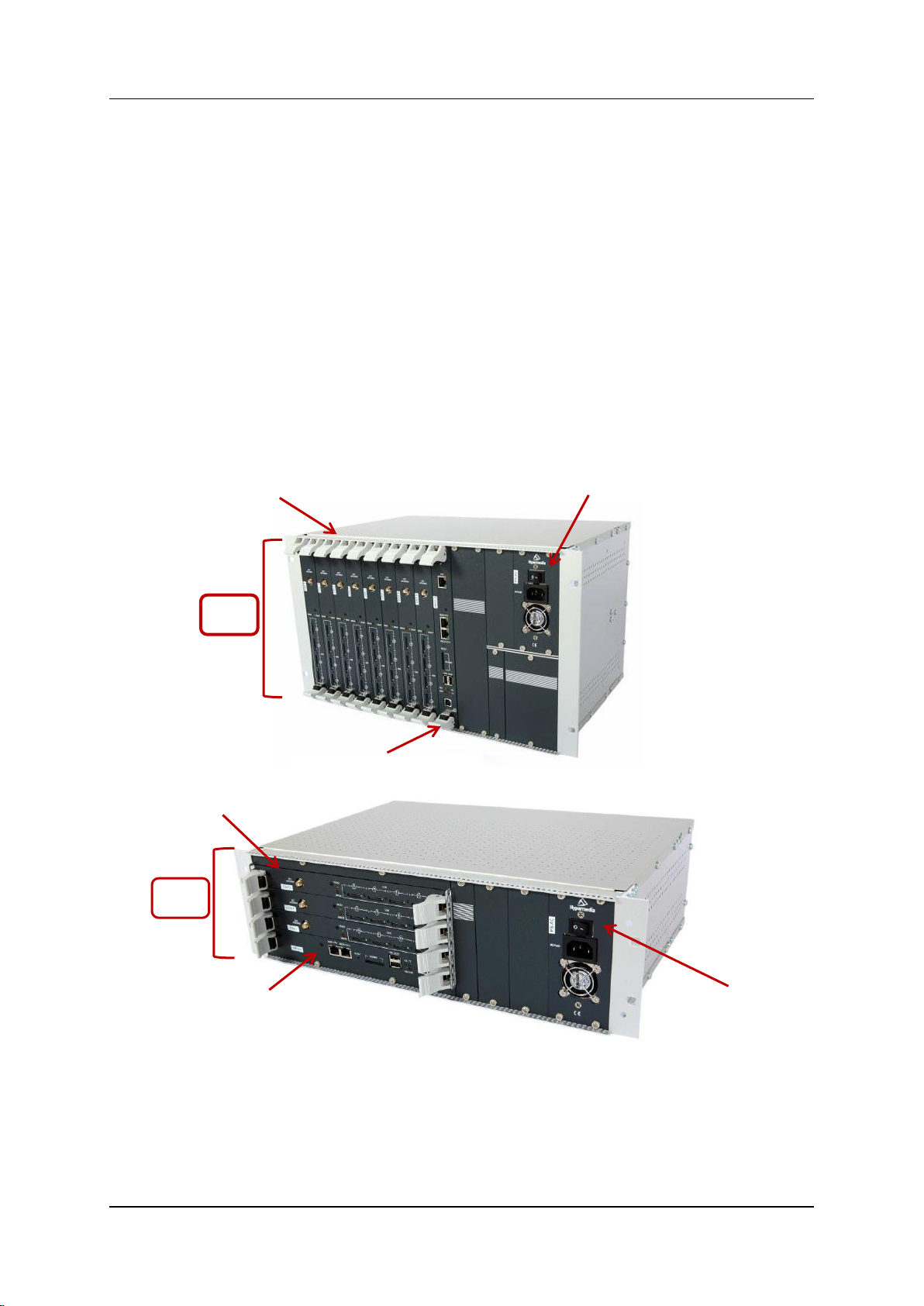
1.3 System Components
The Hypermedia Gateway system consists of the components described below:
The Hypermedia Gateway is a 19" x 6U or 19" x 3U rack-mount unit that
connects to the local PBX or network. The system enables any combination of
connectivity between its PRI and cellular interfaces (VoIP and BRI are
optional).
The unit is built of a backplane and slots for the system boards, as described in
the following Table 1. Placement of the boards varies according to product
configuration.
The unit contains a single power supply module. A dual power supply module
is also available.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
4
Figure 1. Examples of Boards in a Hypermedia Gateway
Depending upon system configuration, the Hypermedia Server is an
application that is embedded on the HBS, HBD or on the PC1/2 board. The
Hypermedia Server is controlled and managed by the browser-based
Hypermedia Management Console.
Hypermedia Systems
Board Name
Description
CG41/CC41/CU41
Cellular Cards
CG41 for GSM, CC41 for CDMA and CU41 for UMTS
is a single-slot card that enables inbound and outbound
cellular voice calls for the various cellular networks.
HBD and HBS
Hybrid Cards
These cards provide both the gateway management
function as well as PRI connectivity. Optionally, these
cards can also support VoIP functionality. The HBD
supports dual PRI ports and the HBS supports a single
PRI port.
MC1.1 and MC1.2 card
These cards provide the PRI connectivity function.
Installed on PC-based systems where the above Hybrid
Cards do not exist. The MC1.2 card supports dual PRI
ports and the MC1.1 card supports a single PRI port.
PC1/PC2 cards
The PC card provides the gateway management function.
Installed on HG3xxx systems along with an MC card
instead of a Hybrid card on specific gateway
configurations.
Hardware and Installation
The Hypermedia Management Console (HMC) is used by the system
administrator for remote configuration and monitoring of the Hypermedia
Gateway system. It connects to the gateway using TCP/IP and is accessed via a
standard WEB browser.
Table 1. Hypermedia Gateway Boards
The HG3xxx systems come in two main configurations:
Hybrid-based: with an HBS/HBD card (depending on the amount of PRI ports)
and cellular cards.
PC-based: with a PC1/2 card, an MC1.1/1.2 card (depending on the amount of
PRI ports) and cellular cards.
Additional boards might be added to provide various capabilities, such as VoIP, SIM
server connectivity, etc.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
5

Hardware and Installation
Installation
1.4 Installation
Note: Installation varies depending upon the boards included with the Hypermedia
Gateway system. Skip the sections that do not apply to your system.
This section is subdivided into:
Pre-Installation and Preparation (section 1.4.1)
Installing the Hybrid (HBD or HBS) Card (section 1.4.2)
Preparing the PRI Connection (section 1.4.3)
Inserting the SIM Cards (section 1.4.4)
Inserting the SD Card (section 1.4.5)
1.4.1 Pre-Installation and Preparation
1. Install the Hypermedia Gateway in a 19” rack. Depending upon the physical
configuration, the unit requires a height of either 3U or 6U. In addition, the
following should be noted:
Avoid installing the device near computer rooms, computer monitors,
electrical cabinets, metal objects, and windows with fold aluminum sheet.
Perform a cellular signal check before mounting the system. This can be
done by checking the Signal Strength and the Bit Error Rate on another
mobile phone's display from the same operator and system.
Ensure that the device is protected against direct sunlight and heat. This
increases both the reliability of the operation as well as its service life.
The antennas provided are for indoor use only. RF combiners and external
antennas are sold separately.
The cables to the devices should be installed so that they do not cause any
physical risk. Power cables should be installed separate from the signal
cables.
2. Depending upon the configuration of your system, verify that you have some or
all of the following:
An Ethernet or WAN socket and a pre-allocated fixed IP address
A spare PRI card in your PBX
SIM cards from your GSM operator. At least one SIM card is required for
each GSM channel
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
6

Hypermedia Systems
Hardware and Installation
1.4.2 Installing the Hybrid (HBD or HBS) Card
The Hybrid cards enable flexible, pre-defined, and dynamic allocation of GSM
channels, E1 and PRI B-channels. Optionally, these can also support VoIP
connectivity.
The HBD supports dual PRI channels and the HBS supports a single PRI channel.
Figure 2. A Hybrid Card
To install the card in the unit:
3. Slide the card into the unit.
4. Close the two side locking levers to lock the card in place.
Figure 3. Card in unit
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
7

Hardware and Installation
Pin1
Pin 8
Installation
1.4.3 Preparing the PRI Connection
Danger: The ISDN connection is regarded as a source of voltage that should be
inaccessible to user contact. Do not tamper with, or open, any public telephone operator
provided equipment or hardware. Any hard-wired connection (other than by a nonremovable, connect-one-time-only plug) must be made by trained engineers.
1. The Hypermedia Gateway’s PRI connection operates in a point-to-point
configuration. The default setting is NT, that is, the Hypermedia Gateway
assumes that it is connected to a PBX as a Network Terminal. Either leave it or
change it to TE.
2. Set the Clock Synchronization. The default setting is Slave; that is, the PBX
provides synchronization for the mutual PRI clock (see section 5.2, Connection
Settings).
Note: In most cases, the PBX is also configured as a Synchronization Slave. The Master
on the network is the telephone company which provides the PRI connection to the PBX.
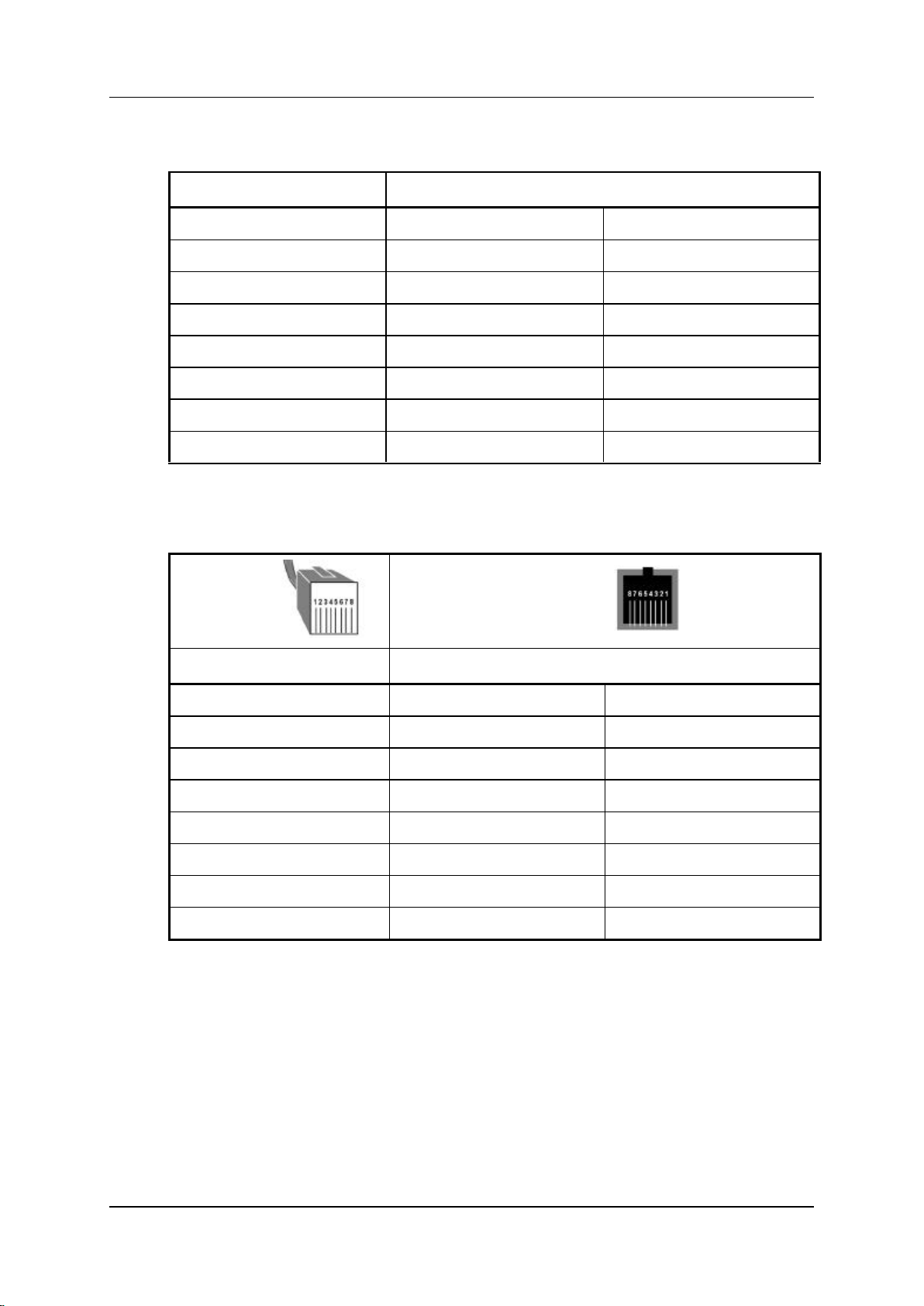
3. Check the RJ-45 connector that will be used to connect the PRI module to the
PBX or network operator. In most cases it must have the pin layout defined in
Table 2. In other cases it must have the pin layout defined in Table 3.
Figure 4. RJ-45 Connector Orientation
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
8
Hypermedia Systems
RJ-45 Pin
Straight Cable
1
Blue
Blue
2
Blue / White
Blue / White
3
n/a
n/a
4
Orange
Orange
5
Orange / White
Orange / White
6
n/a
n/a
7
n/a
n/a 8 n/a
n/a
RJ-45 Plug
RJ-45 Port
RJ-45 Pin
Cross Cable
1
Blue
Orange
2
Blue / White
Orange / White
3
n/a
n/a
4
Orange
Blue
5
Orange / White
Blue / White
6
n/a
n/a 7 n/a
n/a
8
n/a
n/a
Hardware and Installation
Table 2. Straight Cable PRI RJ-45 Pinout
Table 3. Cross Cable PRI RJ-45 Pinout
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
9

Hardware and Installation
SIM Card
SIM Drawer
Yellow button for drawer
Multi-SIM
Extender
Antenna Socket
Installation
1.4.4 Inserting the SIM Cards
1. Insert the GSM SIM Cards. One SIM card should be used per each cellular
channel.
Note: Some versions of the CG board have SIM drawers. Push the small yellow button for
the SIM drawer to exit. Remove the SIM drawer, place the SIM card in the SIM drawer and
replace the SIM drawer.
The SIM port is spring loaded. Slide the SIM card into the slot and it will latch
in place. To remove a SIM card, press the SIM card and it will pop out.
Optionally, use the CG board’s multi-SIM extender:
a. Pull out the CG board.
b. Slide back and pull up the SIM socket.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
10
Figure 5. CG Card Multi-SIM Extender

Hypermedia Systems
Hardware and Installation
Caution: Do not use force on the SIM sockets.
c. Slide in the SIM cards.
d. Lock the SIM sockets.
2. Install the antennas. Each cellular card requires one antenna.
a. Locate the antenna socket (see Figure 5).
b. Fasten the antenna using the SMA connector. Do not use excess force.
c. Tether all cables securely. Tethering helps prevents breakage of connectors
and damage to cellular cards.
Caution: The antennas are for indoor use only. The antennas will be irreversibly damaged
if placed outdoors.
d. Place the antenna indoors, where the reception level is high.
e. Optionally, to improve reception, place the magnetic back of the antenna on
a metal plate larger than 20 x 20 cm.
1.4.5 Inserting the SD Card
The Gateway saves Call Detail Records (CDRs) on a Secure Digital (SD) flash
memory card that is supplied by Hypermedia. Insert the SD card into the SD port of
the HBS/HBD card.
Figure 6. SD Card and Port
Insert or remove SD cards as required.
Note: CDRs are displaced on a FIFO basis.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
11

Hardware and Installation
Powering Up and LEDs
1.5 Powering Up and LEDs
1.5.1 Powering Up
1. Turn on the unit. The power panel is located at the top right corner of the
system.
Figure 7. Power Panel
Note: Redundant power supplies are optional. When installed, if one fails, or if the system
is powered up with just one power supply, an alarm will sound. To stop the alarm, press the
Alarm Reset button at the top left of the panel.
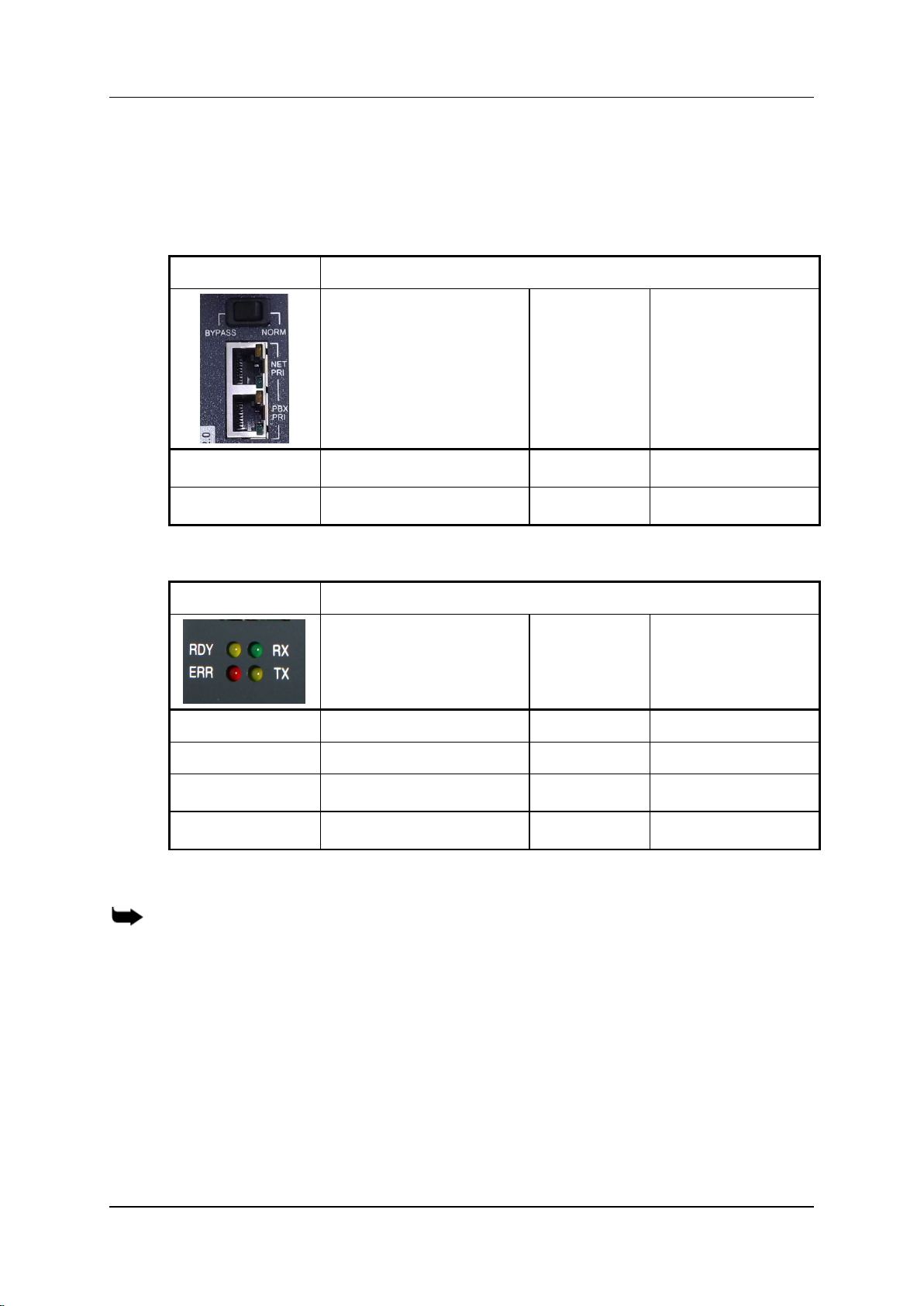
2. Check the LEDs:
For HBS/HBD PRI port LEDs, see Table 4.
For HBS/HBD status LEDs, see Table 5.
For Cellular Card Green SIM LEDs, see Table 6.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
12
Hypermedia Systems
LED
Status
On
Off
Blinking
Green
PRI connection OK
–
Powering-up
Yellow (Alarm)
Connection Error
Normal
Connection Error
LED
Status
On
Off
Blinking
1. Ready/Yellow
Connected on 95%
Power is off
Maintenance mode
2. Error/Red
Error
3. RX/Green
Internal communication
4. TX/Yellow
Internal communication
Hardware and Installation
1.5.2 LEDs
Following are explanations of LED behavior for each of the Hypermedia Gateway’s
cards.
Table 4. HBS/HBD PRI port LEDs
Table 5. HBS/HBD status LEDs
Note: the LED roles on MC1.1/MC1.2 cards are the same as on the above HBS/HBD
cards.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
13
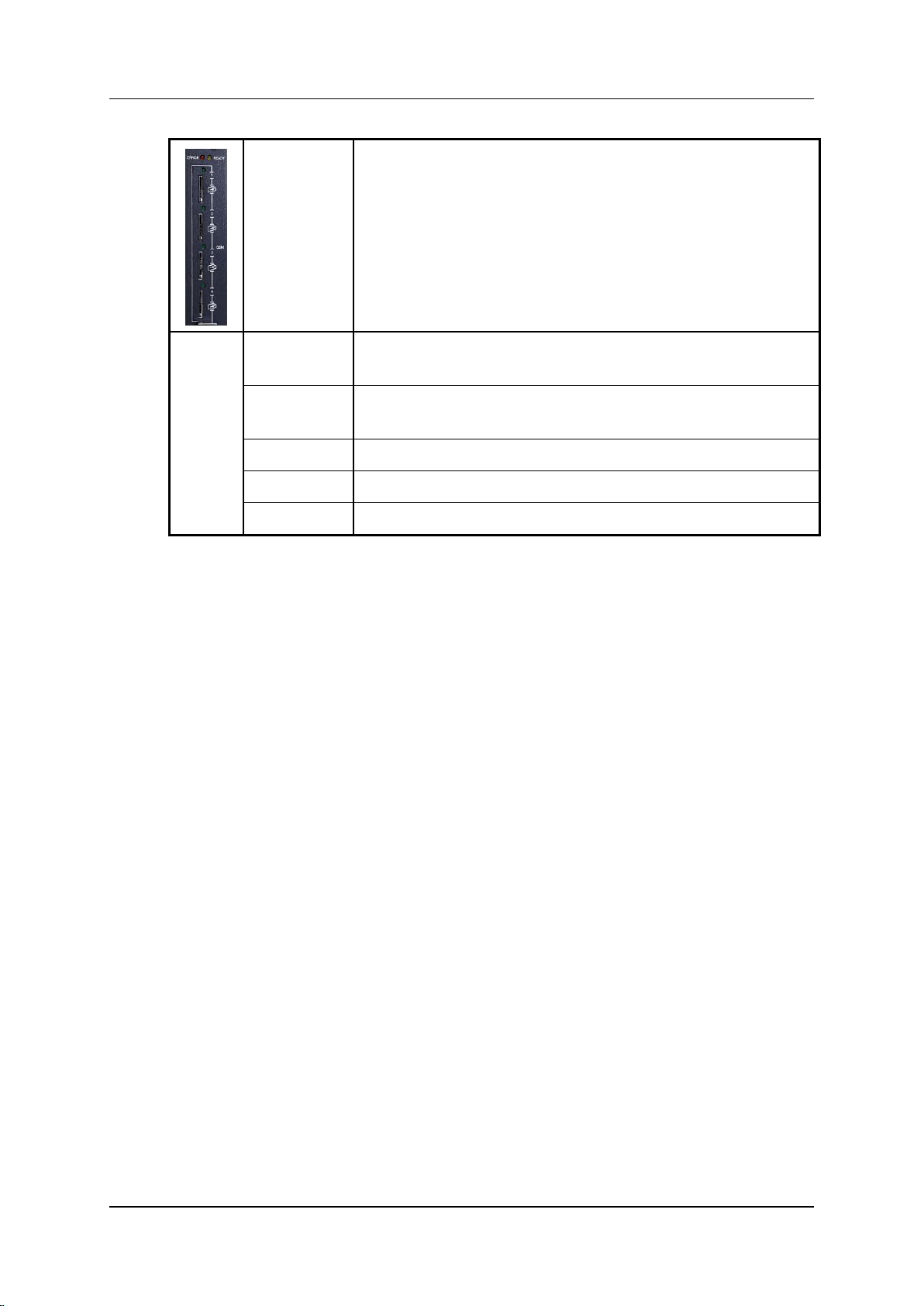
Hardware and Installation
State
Explanation
Flashing
A SIM card is not installed in this channel or the port is still
being initialized.
LED is off
No reception; the channel is not registered to a cellular
network.
Short blink
Stand by; the channel is registered but no call is in progress.
Long blink
User is either dialing out or receiving a call on this channel.
Steady on
In use. A call is in progress.
Powering Up and LEDs
Table 6. Cellular Card Green SIM LEDs
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
14

Hypermedia Systems
Hardware and Installation
1.6 Cable Connections
There are two types of connections:
For Hybrid Cards (HBS/HBD)
For PC
1.6.1 Hybrid Cards (HBS/HBD)
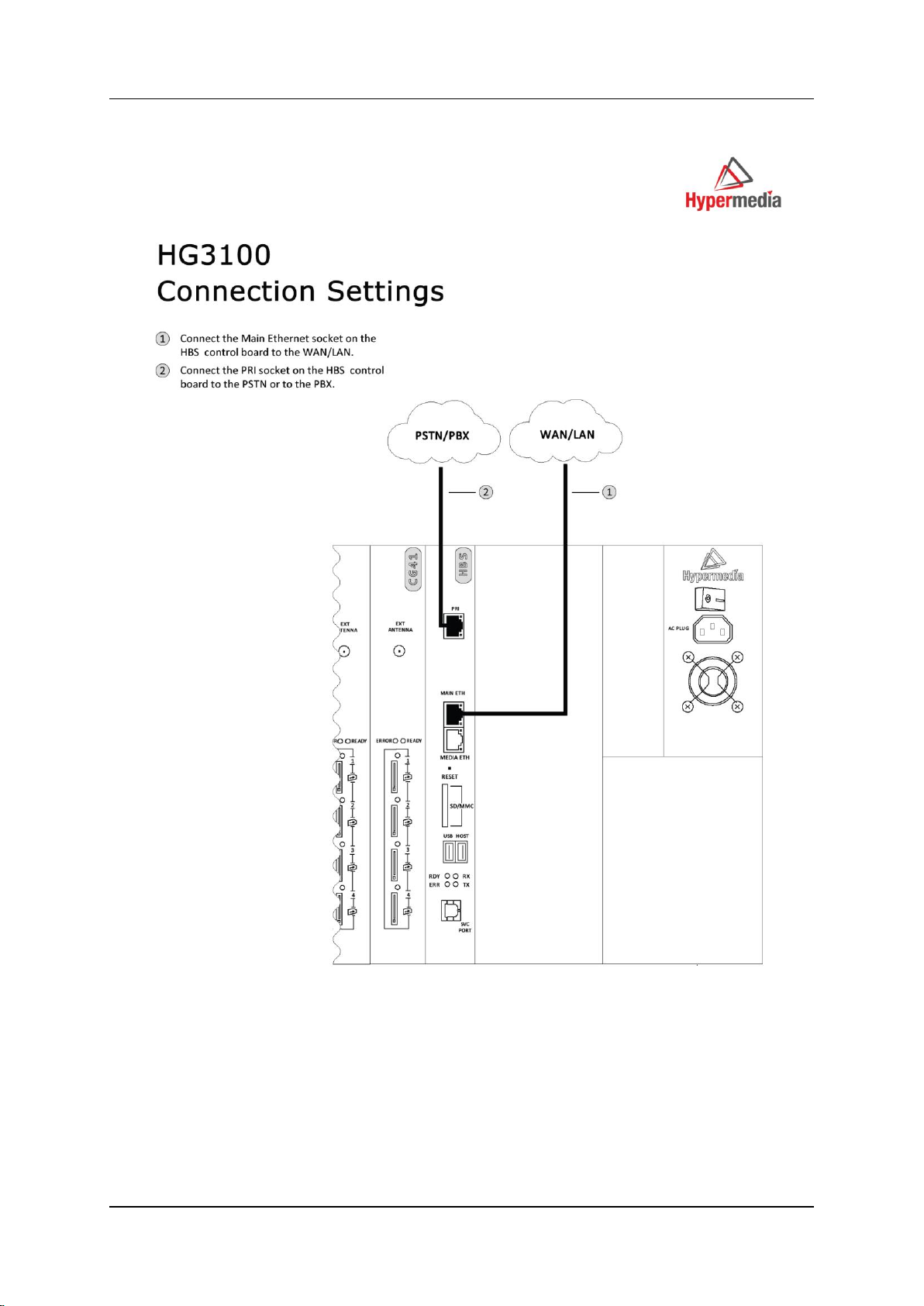
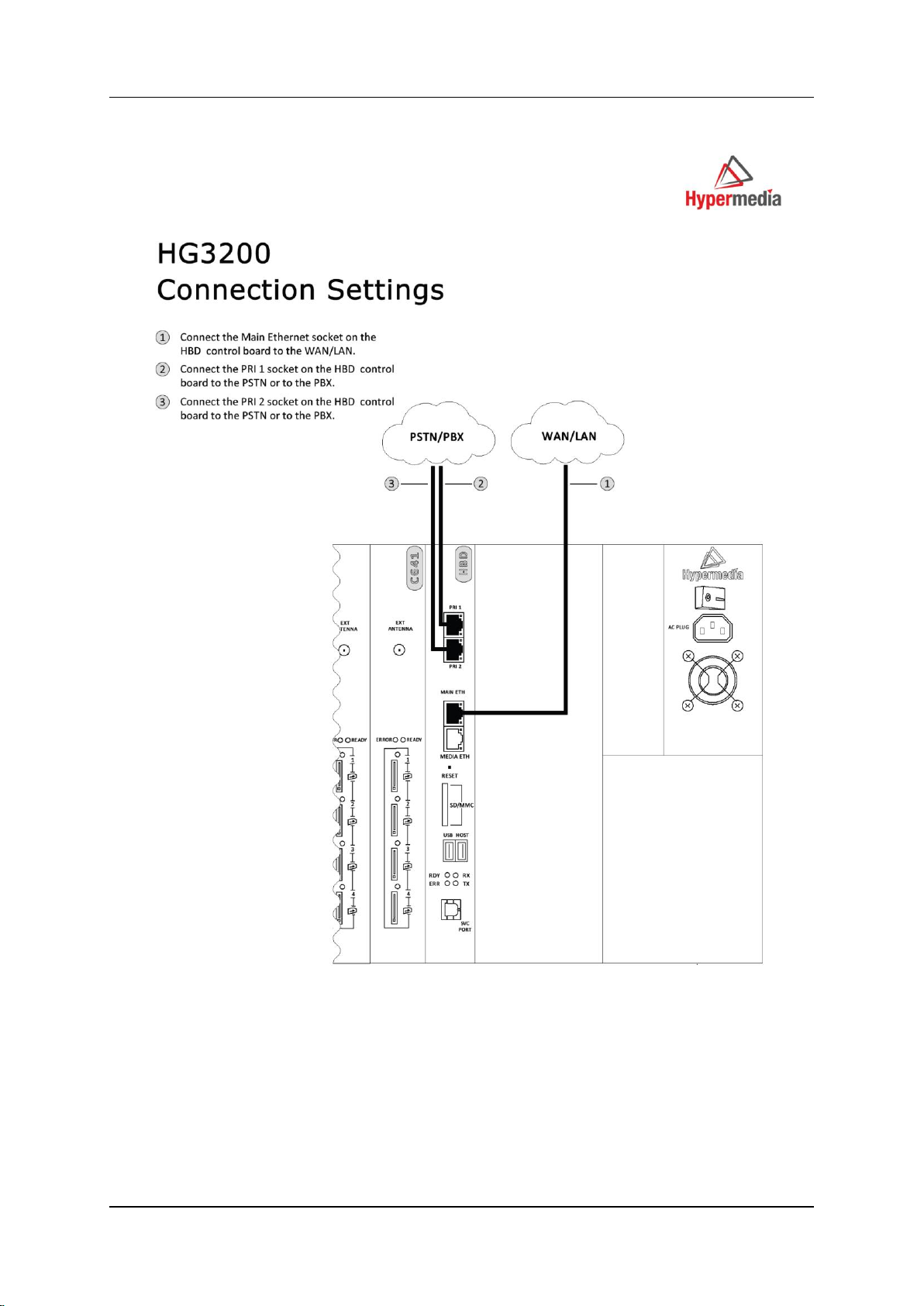
To install the HG3000 with an HBS or HBD card (see Figure 8 and Figure 9):
1. Install the Hypermedia Software (included in the CD).
2. Connect a PC or Laptop with a straight Ethernet cable to the Main ETH port at
the HBX card.
3. Ping the HG default IP address, 192.168.9.2, to test the connection.
4. Check and verify your PC/Laptop IP is configured as follows:
IP: 192.168.9.5
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
5. Open the Server list application and add 192.168.9.2 as a server (the default
password is admin).
6. Use the HGS setup parameters application (first from the left):
a. Login with the password admin.
b. Change the IP address with the desired IP address of the client’s subnet.
7. Connect the Main ETH port to the client’s network.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
15
Hardware and Installation
Cable Connections
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
16
Figure 8. HG3100 Connection Settings
Hypermedia Systems
Hardware and Installation
Figure 9. HG3200 Connection Settings
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
17

Hardware and Installation
Cable Connections
1.6.2 PC
To install the HG3000 with a PC:
1. Install the Hypermedia Software (included in the CD).
2. Connect a PC or Laptop with a straight Ethernet cable to the LAN1 port at the
PC1 card.
3. Ping the HG default IP address, 192.168.0.2, to test the connection.
4. Check and verify your PC/Laptop IP is configured as follows:
IP: 192.168.0.5
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
5. Open the Server list application and add 192.168.0.2 as a server (the default
password is admin).
6. Use the HGS setup parameters application (first from the left):
a. Login with the password admin.
b. Change the IP address with the desired IP address of the client’s subnet.
7. Connect the LAN1 port to the client’s network.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
18

Hypermedia Systems
HMC Quick Start
2 HMC Quick Start
Use the Hypermedia Management Console (HMC) to configure and monitor a
Hypermedia Gateway. Access to the Gateway is over TCP/IP using a standard
version of Internet Explorer.
This section includes:
Installation (section 2.1)
Setting the IP Address (section 2.2)
Start-up and Initial Connection (section 2.3)
Save, Backup and Restore (section 2.4)
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
19

HMC Quick Start
Installation
2.1 Installation
To install the Hypermedia Management Console program:
1. Ensure that the computer matches the following minimum system requirements:
Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7 or 8
Internet Explorer 7 or above
2. Ensure that you have access to the installation file. It is included with the
Hypermedia Gateway CD-ROM.
Figure 10. Hypermedia Gateway CD-ROM
The installation file name begins with the letter HMC and ends with the
extension .exe. The specific name depends upon the type of installation.
3. Double-click the file HMCxxx-xxx.exe file. The Setup program starts.
Figure 11. Setup Welcome Screen
4. Click Next. The License Agreement is displayed.
5. To continue, you must accept the terms of the agreement. Click I accept the
agreement and click Next. The Select Destination Location window is
displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
20

Hypermedia Systems
HMC Quick Start
6. Define the location where the program files will be installed. The default
location is "C:\ProgramFiles\Hypermedia". Click Next. The Select Start Menu
Folder is displayed.
7. Define the name of the program group that will be added to the Start Menu. The
default name is Hypermedia. Click Next. The Additional Tasks window is
displayed.
8. Optionally, select the checkbox to create a Desktop shortcut. Click Next. The
Ready to Install window is displayed.
Figure 12. Setup Ready to Install Screen
9. Click Install. The installation process begins. A progress bar reports on the
progress of the installation.
10. After installation is complete, click Finish. The installation program creates a
program group in the Start menu and, optionally, a Desktop shortcut.
Figure 13. Setup Finish Screen
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
21

HMC Quick Start
Setting the IP Address
2.2 Setting the IP Address
To change or set the IP address:
1. From the Hypermedia program group, select Server List. The Hyper-Gateway
Servers Address List screen opens in the default browser.
2. When required, click the warning bar at the top of the screen and, from the
dropdown menu, click Allow Blocked Content. Confirm your choice by
clicking Yes at the confirmation message.
Figure 14. Hypermedia Gateway Server List
Note: To avoid recurring displays of the warning bar, from the menu bar click Tools >
Internet Options > Advanced > Allow active content to run in files on My Computer.
Your Gateway appears in the Server List with its default address.
3. Click (Change Server Settings). The Login screen is displayed.
Figure 15. The Login Screen
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
22

Hypermedia Systems
HMC Quick Start
4. Enter the password and click Submit. The default password is admin. The HGS
Setup Parameters screen is displayed.
Figure 16. HGS Setup Parameters Screen
5. From the HGS Server system function line, click Stop. A confirmation message
indicates that the service was stopped successfully.
6. On the IP Configuration line, click Change. The IP Address screen is displayed.
Figure 17. IP Address Screen
7. Enter the new IP Address parameters.
Note: Setting the IP address through this page will permanently affect the gateway IP
address settings once rebooted.
8. Click Update. Focus is returned to the HGS Setup Parameters Screen.
9. From the HGS Server line, click Start. A confirmation message indicates that
the service was started successfully.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
23

HMC Quick Start
Start-up and Initial Connection
2.3 Start-up and Initial Connection
To run the Hypermedia Management Console:
1. Click the Windows Start button > Programs > Hypermedia. The Hypermedia
program group expands.
2. Click Hypermedia Management Console. The program opens in the default
browser.
Figure 18. HMC Connection Screen
3. Click the warning bar at the top of the screen and, from the dropdown menu,
click Allow Blocked Content. Confirm your choice by clicking Yes at the
confirmation message.
Figure 19. HMC Connection Screen
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
24

Hypermedia Systems
HMC Quick Start
Note: To avoid recurring displays of the warning bar, from the menu bar click Tools >
Internet Options > Advanced > Allow active content to run in files on My Computer.
4. Enter the IP address:
a. Expand the Configure branch.
b. Expand the Server Settings branch.
c. Select IP address. The Server Address screen is displayed.
Figure 20. HMC Server Address Screen
d. Enter the IP address and click Apply Settings.
Note: If the Gateway is located behind a firewall, enable traffic on TCP ports 8878, 8879
and 80. Contact the network administrator for details.
Note: The IP address setting above does not affect the gateway’s address but only defines
the IP address to which HMC will attempt to connect.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
25

HMC Quick Start
Start-up and Initial Connection
5. Either press F5 or click the browser’s Refresh button. The authorization screen
is displayed.
Figure 21. HMC Login Authorization Request
Note: The default password is admin.
6. Enter the password and click Submit. A confirmation message is displayed
which indicates that you have successfully connected to the Hypermedia
Gateway. The Connection State screen is displayed.
Figure 22. HMC Connection State Display
A list of all services will be displayed, including their versions and current
activation/installation state.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
26

Hypermedia Systems
HMC Quick Start
2.4 Save, Backup and Restore
2.4.1 Save All
Use the configuration branch to permanently save all the configuration settings in
the HyperGateway.
Figure 23. Save All Settings configuration branch
2.4.2 Save All Settings on Cards
Use this option to permanently save all the configuration settings in the Hypermedia
Gateway. This process might take up to 60 seconds.
2.4.3 Backup/Restore
Use this option to download the entire configuration of the gateway to your PC. The
downloaded backup file can then be uploaded by preforming a system restore.
Figure 24. Backup and Restore
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
27

HMC Quick Start
Save, Backup and Restore
This page is intentionally blank
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
28

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3 Configuring a Cellular Card
This section includes:
Cellular Card and System Terminology (section 3.1)
Volume Settings (section 3.2)
Media Connections (section 3.3)
PIN Codes (section 3.4)
MSN Values (section 3.5)
Reset (section 3.6)
Information Screens (section 3.7)
Locks (section 3.8)
SIM Select (section 3.9)
SIM Counters (section 3.10)
SIM Auto Manage (section )
Call Counter Steps (section 3.12)
CLI Blocking (section 3.13)
Call Limits (section 3.14)
Cell Selection (section 3.15)
Settings (section 3.16)
Network Parameters (section 3.17)
USSD SIM Balance (section 3.18)
Monitoring Cellular Cards (section 3.19)
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
29

Configuring a Cellular Card
Spring-loaded
SIM ports
Additional
SIM cards
Cellular Card and System Terminology
3.1 Cellular Card and System Terminology
A cellular card has 4 modules, each of which can have 1 to 4 SIM holders.
Therefore, each card can hold up to 16 SIM cards. The Hypermedia Gateway can
include several cards.
The first SIM cards of each module are loaded into the spring-loaded SIM port from
the front of the Cellular Card.
Some parameters can be applied either to specific SIM cards, or to specific modules,
or to the entire cellular card, or to all the cards in the system.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
30

Hypermedia Systems
Hypermedia recommends
not adjusting these.
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.2 Volume Settings
Use Volume Settings to adjust a cellular module’s audio level. This can be done for
each of the cellular modules on a Hypermedia Gateway. To adjust the audio level:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Volume
Settings sub-branch. The Volume Settings screen is displayed.
Figure 25. HMC Volume Settings Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Volume
Settings screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. To increase the volume, move the slider to the right. Each module includes two
sliders:
In
“In” adjusts the volume heard by the party on the PBX (or local network) side of
the conversation.
Out
“Out” adjusts the volume heard by the remote party.
Note: Changes to volume are saved automatically. The message “New volumes set
successfully” is displayed.
4. Select or clear the Echo Canceller checkbox. There are several different causes
of the echo effect. Selecting Echo Canceller minimizes or cancels the echo
effect.
5. After enabling Echo Canceller, from the HMC navigation pane, click the
Save/Load branch and then click Save All Settings.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
31

Configuring a Cellular Card
Media Connections
3.3 Media Connections
Use the Media Connection screen to configure the connections from the channels of
a Cellular card to other cards and channels in the system, including PRI and VoIP.
Connections can be either static or dynamic, as in the case of LCR.
For example, you can assign each cellular channel to a specific PRI channel. In this
case, every time there is an incoming call from a specific PRI channel, it will be
routed to the configured channel on the cellular card and vice versa.
Note: The media matrix can be configured in any combination. Routing can be assigned
between any cellular channel and any other channel in the system, including other cellular
channels.
3.3.1 Associating/Linking Cellular Channels
To associate a cellular channel with another media channel:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Media
Connections sub-branch. The Media Matrix is displayed.
Figure 26. Cellular Media Matrix screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific cellular card. The Media
Matrix of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Click within a channel row. The row turns yellow.
4. Click Edit. The row becomes configurable.
Figure 27. Media Matrix Row when Configurable
5. From the first dropdown list, allocate this channel to a card by selecting the card.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
32

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
Note: If all of the card’s channels are already allocated, the message “Fully allocated”
appears.
6. From the second dropdown list, assign this channel to a specific channel on the
target card.
Figure 28. Assigning a Target Link
7. Click Save. The configuration dropdown boxes are hidden.
8. Optionally, repeat the process for additional channels and other media types.
9. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
3.3.2 Auto Linking
Enables associating all channels of one media card to another media card.
To create an auto-link:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Media
Connections sub-branch. The Media Matrix is displayed.
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific cellular card. The Media
Matrix of that cellular card is displayed.
Figure 29. Auto Media connecting
3. Click within a channel row. The row turns yellow.
4. Click Auto Link.
5. All channels can be associated of one media card to another media card: Card X
channel 1 to Card Y channel 1, Card X channel 2 to Card Y channel 2 etc.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
33

Configuring a Cellular Card
Media Connections
3.3.3 Unlinking Cellular Allocations
To break an allocation:
1. From the Cellular Card branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Media
Connections sub-branch. The Media Matrix is displayed.
2. Click within a channel row. The row turns yellow.
Figure 30. Breaking a Target Link
3. Click Unlink.
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
34

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.4 PIN Codes
Use the PIN Codes screen to configure the PIN code that the gateway uses when a
SIM card with an active PIN is inserted. Consult your cellular provider for more
information regarding the PIN code.
To enter a SIM card’s PIN code:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the PIN
Codes sub-branch. The PIN Codes screen is displayed.
Figure 31. HMC Cellular PIN Codes Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The PIN
Codes screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Enter the PIN code into the associated Module’s field.
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
35

Configuring a Cellular Card
MSN Values
3.5 MSN Values
Use Multiple Subscriber Number (MSN) values to route incoming calls to a specific
extension on the PBX. You can assign a different extension for each channel or
route all channels to the same extension.
Note: Hypermedia’s use of MSN differs from the traditional ISDN use. MSN is an incoming
call routing method in which a group of phone numbers is assigned to a particular PRI ISDN
line by the telephone company.
To route incoming calls to a specific extension on the PBX:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the MSN
Values sub-branch. The MSN Values screen is displayed.
Figure 32. Cellular MSN Values
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The MSN
Values screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Enter a PBX extension number.
4. Select or clear the Auto MSN checkbox. When selected, if a local user “A”
called a remote user “B” through a cellular module and later “B” calls the
cellular module’s number, the system will automatically route the incoming call
to “A”. The system remembers that “A” was the last local user to call “B”
through that cellular module.
5. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
36

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.6 Reset
Use the Cellular Card Reset screen to reset either the entire cellular card or a specific
cellular module.
To reset a cellular card or module:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Reset
sub-branch. The Reset screen is displayed.
Figure 33. Cellular Card Reset screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Reset
screen of that cellular card is displayed.
Caution: There is no confirmation message. The Reset command is sent as soon as the
reset button is clicked.
3. Click Reset. The screen confirms that the Reset command has been sent.
Figure 34. Reset Screen After Sending the Reset Command
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
37

Configuring a Cellular Card
Information Screens
3.7 Information Screens
Several of the HMC screens display information.
3.7.1 Module Info
Use the Module Info screen to review information about the modules of a cellular
card.
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Module
Info sub-branch. The Module Info screen is displayed.
Figure 35. HMC Module Info Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Module
Info screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3.7.2 Serial Numbers
Use the Serial Numbers screen to view the GSM Modules International Mobile
Equipment Identity (IMEI) and the SIMs International Mobile Subscriber Identity
(IMSI) and Integrated Circuit Card Identifier (ICCID) values.
From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click
the Serial Numbers sub-branch. The Serial Numbers screen is
displayed.
3. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
38
Figure 36. HMC Serial Numbers Screen

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.8 Locks
Use Locks to restrict access to specific GSM operators and/or a specific SIM card.
When a lock is defined, the Gateway will only register to an operator network or
allow a SIM card that matches the Lock number.
In addition, use Locks to prevent roaming handover in cases where the Gateway is
located close to county or country borders.
To define a Lock number:
1. Ensure that:
you have obtained the codes from the cellular operator
the cellular modules support SIM locks
2. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Locks
sub-branch. The Locks screen is displayed.
Figure 37. HMC Cellular Locks Screen
3. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Locks
screen of that cellular card is displayed.
4. Enter:
SIM Lock
Use SIM Locks to avoid using SIM cards other than those whose Mobile
Network Code (MNC) and Mobile Country Code (MCC) values have been
entered.
Operator Lock
Use Operator Locks to avoid registration to any network other than the one
whose MNC and MCC values have been entered.
5. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
39

Configuring a Cellular Card
SIM Select
3.9 SIM Select
Use the SIM Select screen to manually select and activate a SIM card for current
use. SIM Select should not be used when SIM Auto-Manage is active (see
section 3.11, SIM Auto Manage). The definition can be applied just to the module,
to all 4 modules on the card, or to all the cellular cards in the system (see section 3.1,
Cellular Card and System Terminology.
To define which of a module’s SIM cards are associated with the SIM Auto Manage
feature:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the SIM
Select sub-branch. The SIM Select screen is displayed.
Figure 38. HMC SIM Select Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The SIM
Select screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Select an application option:
Module Settings
Applies the SIM configuration to the specific module.
Entire Card
Applies the SIM configuration to all the modules on the card.
Entire System
Applies the SIM configuration to all the cards in the system.
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
40

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.10 SIM Counters
Use the SIM Counter screen to review the actual usage time of each SIM card and to
set counter steps per module.
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the SIM
Counters sub-branch. The SIM Counters screen is displayed.
Figure 39. HMC SIM Counters Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The SIM
Counters screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Optionally, select from the following controls:
Reset
Resets the counter for the specific step.
Reset All
Resets all the counters in that module.
Refresh
Updates the information.
4. Optionally, click Set Counter Steps per Module to set the exact period of time
per counting step. The Cellular Card Call Counters Steps screen is displayed
(see section 3.12, Call Counter Steps).
Note: Setting Counter Steps is important when using the SIM Auto Manage with prepaid
SIM cards.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
41

Configuring a Cellular Card
SIM Auto Manage
3.11 SIM Auto Manage
Use the SIM Auto Manage screen to configure the Gateway to automatically
alternate and/or discontinue use of SIM cards. This enables load-balancing between
a GSM module’s SIM cards based on preconfigured switched time cycle.
To enable automatic management of SIM cards:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the SIM
Auto Manage sub-branch. The SIM Auto Manage screen is displayed.
Figure 40. HMC SIM Auto Manage Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The SIM Auto
Manage screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Select the checkbox beside a module number in the Enable Auto Switch column.
The SIM column checkboxes and Minutes column fields are displayed.
4. To assign a SIM card to a module, select the checkboxes in the SIM column.
Note: In Figure 40, each module has two SIM cards assigned to it. The Gateway will allow
a SIM card to function for 1000 minutes and then switch to the second SIM card. Once a
SIM card has functioned for 4000 minutes—that is, 4 cycles—it is blocked. It can only be
unblocked manually.
5. In the Minutes until SIM is switched field, enter an amount of time measured
in minutes. This is the how long each SIM card will be used until the Gateway
automatically switches to the next SIM card assigned to that module.
6. In the Minutes until SIM is blocked field, enter an amount of time measured in
minutes. This is the total amount of time a SIM card is used before the Gateway
discontinues using it.
7. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
42

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.12 Call Counter Steps
Steps, Time Periods and Repetitions work as follows: If Time Period = 60 seconds
and the Repetition = 3, and the caller speaks for 10 seconds, he will be charged for
the Time Period = 60 seconds. If the caller speaks for 110 seconds, he will be
charged for the Time Period = 120 seconds. This charging policy—that is, step—
expires after 180 seconds that being the Time Period (= 60 seconds) times the
Repetition (= 3). Then, the next step is applied. The final step will always have
unlimited repetitions.
Figure 41. HMC Cellular Call Counter Steps Screen
To configure Counter Steps:
1. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The SIM
Counters screen of that cellular card is displayed.
2. Select a checkbox to enable the step. When enabled, the area is displayed in the
color green.
3. From the upper dropdown menu, select either Seconds or Minutes. This
determines the duration of time indicated by the numbers in the Time Period
column.
4. Increase the number of steps by clicking the plus sign beside the module
number.
5. For each step, define the Time Period—that is, how long—the step is applied.
6. For each step, define the number of repetitions.
7. Repeat the procedure for additional modules.
8. Click Save Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
43

Configuring a Cellular Card
CLI Blocking
3.13 CLI Blocking
Use the Calling Line Identification (CLI) Blocking screen to hide the caller’s phone
number from the person receiving the call.
Note: Some operators do not allow CLI Blocking. In some cases, if the CLI is blocked, the
call does not go through. Check the operator’s policy.
To block CLI:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the CLI
Blocking sub-branch. The CLI Blocking screen is displayed.
Figure 42. HMC Cellular CLI Blocking Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The CLI
Blocking screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Use one of the two options:
Card
Block
Click Block to block CLI for all 4 of a card’s modules.
Unblock
Click Unblock to allow CLI for all 4 of a card’s modules.
Module
Block enforced
Select Block enforced to block CLI for a specific module.
Block not enforced
Select Block not enforced to allow CLI for a specific module.
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
44

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.14 Call Limits
Use the Call Limits screen to configure various call-related timing parameters.
To set Call Limits:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Call
Limits sub-branch. The Call Limits the screen is displayed.
Figure 43. HMC Cellular Call Limits Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Call
Limits screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Select or clear the following limits:
Set the limit for an outgoing cellular call to be answered
When enabled, enter a time duration (measured in seconds) that the gateway will
wait for the call to be answered before ending the call.
Set the maximum length of an outgoing call
When enabled, enter a time duration (measured in seconds) that is the maximum
permitted length of an outgoing phone call through any of the card’s cellular
channels. Calls are disconnected at the beginning of the last minute, rather than
its end.
Round the call length up to the maximum length
When enabled, a call counter for a specific cellular channel will be rounded up
to reflect the maximum length of an outgoing call through that channel (defined
above) when such a call ends, even when the conversation is shorter than the
maximum length.
Note: Round the call up to the maximum length cannot be used with SIM Counters steps
(see section 3.12, Call Counter Steps).
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
45

Configuring a Cellular Card
Cell Selection
3.15 Cell Selection
Use the Cell Selection screen to manually camp on a cellular site. Most often, a user
selects the strongest cell site. However, if the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) or
tower is locked, this service cannot be applied.
To camp on a site:
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Cell
Selection sub-branch. The Cell Selection screen is displayed.
Figure 44. HMC Cellular Cell Selection Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Cell
Selection screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. From the Select module dropdown box, select a module. This is the module that
the Camp selection will be applied to.
4. In one of the CellID boxes, click Camp. The screen indicates Camp Cell and
new controls are displayed at the top of the screen.
5. Optionally, to camp all the card’s modules on the same cell, click Camp all
modules on.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
46

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.16 Settings
Use the Settings screen to enable and disable advanced parameters. For assistance
with these, contact Technical Support.
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Settings
sub-branch. The Cellular Card Settings screen is displayed.
Figure 45. HMC Cellular Card Settings Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Cellular
Card Settings screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
47

Configuring a Cellular Card
Network Parameters
3.17 Network Parameters
Use the Network Parameters screen to define the bandwidth used by a carrier.
1. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Network
Parameters sub-branch. The Cellular Card Network Parameters screen is
displayed.
Figure 46. HMC Cellular Card Network Parameters Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific Cellular Card. The Network
Parameters screen of that cellular card is displayed.
3. From the dropdown menu, select the required GSM bands for the cellular
network to which you wish to connect. For a table of GSM bands per mobile
carrier and per country, see en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_country_code.
4. From the HMC navigation pane, click the Save/Load branch and then click
Save All Settings.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
48

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.18 USSD SIM Balance
Use the USSD SIM Balance screen to check the balance remaining on a prepaid SIM
card and to add value to (recharge/top-up) a SIM card.
1. Ensure that your Service Provider has given you a USSD string for checking
balance and a second string for adding value (recharging) the SIM card.
2. From the Cellular Cards branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the USSD
SIM Balance sub-branch.
Figure 47. HMC Cellular USSD SIM Balance Screen
3. Enter the Balance checking USSD string.
4. Enter the Recharging USSD string.
5. Select or clear the Check All checkbox. When selected, the Hypermedia
Management Console will check the balance of all the SIM cards.
6. Click (Check Balance). The balance is displayed in the USSD Reply
column.
7. Optionally, recharge the SIM card:
a. Ensure that you have a recharge string. Often, the string is displayed on
recharge cards after a removing a layer of ink that hides the string.
b. Enter the string into the Recharge Balance field.
c. Click the (Recharge Balance) button.
8. Optionally, click the (Excel) icon to save the results as an Excel file.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
49

Configuring a Cellular Card
Monitoring Cellular Cards
3.19 Monitoring Cellular Cards
To monitor the status of cellular cards, open the Monitor > Cellular branch of the
Hypermedia Management Console. There are three views.
3.19.1 All Cells
To view information about all the cellular modules on all cards, expand the Monitor
> Cellular Cards sub-branch and select All Cells. The Cellular Cards Reception
screen is displayed.
Figure 48. Cellular Cards Reception Screen
The screen displays the following information:
Module
This indicates the card and the SIM slot number.
Type
The module can support GSM, CDMA or UMTS.
Operator
This is the cellular network associated with the SIM card and the Cell ID.
RX Level
This indicates the received power level in dBm. The value can be between –51 dBm
and –110 dBm
RX BER
Bit Error Rate (BER) is a calculated figure for the quality of the signal received from
the base. It is an indication of the number of errors detected in the signal received by
the cellular channel, graded into quality ratings according to the percentage of errors
in the data. Typical values for BER are between less than 0.2% and 6.4%.
BER of more than 6.4 will result in calls being disconnected as well as “noisy” calls.
If this occurs, find a better location for the antenna or check the connections to the
antenna.
Status
This displays the status of the specific module.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
50

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring a Cellular Card
3.19.2 Reception
To view information about the SIM slots on a specific cellular module, especially
the reception level and the BER level:
1. Expand the Monitor > Cellular Cards sub-branch and select Reception.
2. Select a specific slot. The Cellular Cards Reception screen for that card is
displayed.
Figure 49. Specific Card’s Cellular Reception Screen
The screen displays the following information:
Operator
This is the cellular network associated with the SIM card and the Cell ID.
RX Level
This indicates the received power level in dBm. The value can be between –51 dBm
and –110 dBm.
RX BER
Bit Error Rate (BER) is a calculated figure for the quality of the signal received from
the cellular base-station.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
51

Configuring a Cellular Card
Monitoring Cellular Cards
3.19.3 Status
To view information about the status of cellular modules on a specific card:
1. Expand the Monitor > Cellular Cards sub-branch and select Status.
2. Select a specific slot. The Cellular Cards Status screen for that card is displayed.
Figure 50. Cellular Cards Status Screen
3. Review the status. Common possibilities include:
Module doesn’t exist or is faulty
Idle
Incoming call from cellular network
Remote side ringing
Call connected
Call cleared
Dialing out through cellular network
No Signal
Missing SIM card
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
52

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4 Configuring LCR
This section includes:
Overview (section 4.1)
Linking to LCR (section 4.2)
Groups (section 4.3)
Resource Map (section 4.4)
Rules (section 4.5)
Filters (section 4.6)
Advanced Call Routing (ACR) (section 4.7)
Number Filters (section 4.8)
CDR (section 4.9)
Activating LCR (section 4.10)
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
53

Configuring LCR
Overview
4.1 Overview
Gateways with Least Cost Routing (LCR) route calls based on rules created by the
administrator. This results in per-call routing. In contrast, when using gateways
without LCR, all call routes are fixed.
LCR enables greater customizing and, potentially, saves money. The best-practice
order of building the LCR plan is:
Note: A best-practice is a technique or methodology that, through experience and research,
has been proven to efficiently and reliably lead to the desired result.
1. Link media to the LCR module
2. Create Groups
3. Assign the LCR Resources to Groups
4. Create Rules
The following are optional:
Create IN or OUT filters, to manipulate over dialed numbers
Create Time Frames, to determine the time of day each of the Rules is active
Configure the ACR, to analyze source and destination numbers and to enable
rout/block/manipulate actions
This section follows the best-practice order.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
54

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.2 Linking to LCR
Each media type must be configured to refer calls to the LCR module. This can be
done either from the specific media branch or from the LCR branch.
Note: Each of the media type branches (such as Cellular, BRI, PRI, and VoIP) includes a
sub-branch named Media Connections.
4.2.1 Linking from a Media Branch
To link a media to LCR:
1. From the HMC navigation pane, click a Media Connections sub-branch. The
Media Matrix is displayed.
Figure 51. Media Matrix before LCR
2. Click within a channel row. The row turns yellow.
3. Click Edit. The row becomes configurable.
Figure 52. Channel Row when Configurable
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
55

Configuring LCR
Linking to LCR
4. From the dropdown lists, select LCR and the Resource number.
5. Click Save. The configuration dropdown boxes are hidden.
Figure 53. Channel Row Dropdown Lists
Figure 54. Channel Row Configured
6. Optionally, repeat the process for additional channels and other media types.
7. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
8. When finished, from the LCR branch, select Media Connections. The LCR
Media Matrix displays the links.
Figure 55. Two Views of the LCR Media Matrix Display
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
56

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.2.2 Linking from the LCR Branch
To link a media to LCR:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Media Connections
sub-branch. The LCR Media Matrix is displayed.
Figure 56. LCR Media Matrix
2. Click within a Resource row. The row turns yellow.
3. Click Edit. The row becomes configurable.
Figure 57. LCR Row when Configurable
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
57

Configuring LCR
Linking to LCR
4. From the dropdown menus, select the media and the Resource number.
5. Click Save. The configuration dropdown boxes are hidden.
Figure 58. LCR Row Dropdown Lists
Figure 59. LCR Row Configured
6. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
58

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.2.3 Editing a Target Link
To edit a link:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Media Connections
sub-branch. The LCR Media Matrix is displayed.
Figure 60. LCR Media Matrix
2. Click within a Resource row. The row turns yellow.
3. Click Edit. The row becomes configurable.
4. From the dropdown menus, edit the settings.
5. Click Save. The configuration dropdown boxes are hidden.
6. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
4.2.4 Breaking a Link (Unlink)
To break a link:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Media Connections
sub-branch. The LCR Media Matrix is displayed.
2. Click within a Resource row. The row turns yellow.
3. Click Unlink. The settings disappear.
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
59

Configuring LCR
Groups
4.3 Groups
Creating Groups simplifies consistent application of LCR strategies.
4.3.1 Creating a Group
To create a group:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Groups sub-branch.
The Groups screen is displayed.
Figure 61. LCR Groups Screen
2. Name the Group. Since the Group name appears in other places, we recommend
using an identifiable name.
3. In the Cyclic column dropdown menu, define whether or not the Group will be
cyclic:
Yes
The LCR module begins searching for an available channel from the last used
channel.
No
The LCR module begins searching for an available channel from the first
channel in that group.
4. Optionally, and if already defined, from the In Filter dropdown menu, select an
In Filter. See 4.6, Filters.
5. Optionally, and if already defined, from the Out Filter dropdown menu, select
an Out Filter. See 4.6, Filters.
6. From the Route to Group dropdown menu, define whether or not calls arriving
to that Group will be rerouted to a specific Group, or dynamically routed
according to the LCR rules:
none
The LCR Rules are applied and the call is routed to a specific channel
accordingly.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
60

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
< Specific Group Name >
All calls coming from Resources assigned to this Group are rerouted to the
selected Group. The LCR rules are not analyzed for calls entering the LCR
module from this group.
7. Select or clear the Int. Routing checkbox. When selected, all outgoing calls
through the group are logged. The logs are then checked to determine the
destination number for incoming calls. If a match is found, the original
destination number is ignored.
8. Select or clear the Report Calls checkbox. When selected, calls are sent to an
external Hypermedia application for billing.
9. Click Save Settings.
4.3.2 Using the Default Group Settings
The HMC includes pre-defined Group settings. These can be used instead of
customized settings.
To apply the default Group settings:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Groups sub-branch.
The Groups screen is displayed.
2. Scroll to the bottom of the screen. The Create Default Groups button appears
within the Default Groups prompt.
Figure 62. Create Default Groups Button
3. Click Create Default Groups.
4. Scroll to the top of the page.
5. Click Save Settings.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
61

Configuring LCR
Resource Map
4.4 Resource Map
Use the LCR Resource Map to assign Resources to Groups.
4.4.1 Sample Assignment
The picture below illustrates Resource assignment. The first 30 Resources are
assigned to the PBX, the second 30 are assigned to the PSTN, and the final 4 are
assigned to Cellular.
Figure 63. Sample Resource Assignment
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
62

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.4.2 Assigning LCR Resources
To assign LCR Resources to Groups:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Resource Map sub-
branch. The Resource Map screen is displayed.
Figure 64. LCR Resource Map Before Assignments
2. Click a cell to select it. To select many cells, hold down the Shift key and click a
cell elsewhere on the map. The selected cells are shaded blue and the Set Group
and Set Resource Type dropdown lists appear near the top of the screen.
Figure 65. Selecting LCR Resources
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
63

Configuring LCR
Resource Map
3. From the Select Group dropdown list, select a Group. This is the Group the
shaded cells will be associated with.
4. Click Set. The assignment is applied and saved.
Figure 66. Group Dropdown List
5. From the Resource Type dropdown list, select either:
Bi Directional
This Resource can be used for both incoming calls and for outbound calls.
Outbound Only
This Resource can only be used for outbound calls.
6. Click Set. This completes the procedure.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
64

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.5 Rules
Rules determine to which Group a call is routed.
4.5.1 Creating a Rule
To create a Rule:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Rules sub-branch. The
Rules screen is displayed.
Figure 67. LCR Rules Screen
2. Place the cursor in an empty Rule # Prefix cell.
3. Enter the Prefix, that is, the first numbers of the destination number. The Prefix
is often the first numbers of a mobile phone service provider.
4. Configure the following:
1st Group
From the dropdown list, select the Group to which the LCR module will first
route calls with this prefix.
2nd / 3rd Group
Optionally, enter a second and third choice for where the call should be routed.
These choices are used when the 1st Group’s Resources are busy.
ACR
When this checkbox is selected, the gateway redirects the call to a database
containing Advanced Call Routing lists. The call is routed according to rules on
an external application with advanced routing options.
5. Optionally, repeats steps 2 until 4 for additional rules.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
65

Configuring LCR
Rules
6. Ensure that the Rules are in the correct order. Rules are applied from top to
bottom. Therefore, place a Rule with a prefix identical to but shorter than
another Rule’s prefix after the longer Rule.
For example, if Rule 1’s prefix is 082 and Rule 2’s prefix is 08, calls beginning
with 082 will be routed according to Rule 1 and all other calls beginning with 08
will be routed according to Rule 2. If Rule 2 is placed above, the 082 calls will
also be routed according to it and the 082 Rule will be rendered ineffective.
7. Optionally, select a Default Rule.
This rule is applied when a call’s prefix does not match one of the defined
prefixes. Time Frames are not applied to the Default Rule.
a. From the dropdown list, select a rule.
b. Select or clear the ACR checkbox. When selected, the gateway redirects the
8. Disregard the Default Text Rule. For more information, contact Technical
Support.
call to a database containing Advanced Call Routing lists. The call is routed
according to rules on an external application with advanced routing options.
9. Click Save Settings.
4.5.2 Deleting a Rule
To delete a Rule:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Rules sub-branch. The
Rules screen is displayed.
2. Place the cursor in the Prefix cell on the Rule’s row.
3. Delete the entry.
4. Click Save Settings.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
66

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.6 Filters
Filters enable consistent, automatic management of phone numbers before they are
routed.
An IN filter changes the destination number before the list of rules is processed.
An OUT filter changes the destination number after the list of rules has been
processed and the destination group has been chosen. The process is identical for
both.
To create a Filter:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click either the IN or OUT
Filters sub-branch. The Filters screen is displayed.
Figure 68. LCR Filters Screen
2. Configure the following for up to eight filters:
Trim Left
From the dropdown menu, select the amount of digits that will be deleted from
the beginning of the destination number.
Add Left
Optionally enter the numeric prefix that will be added to the beginning of the
destination number.
Match Condition
Optionally enter the exact expected numeric prefix with which the dialed
number should begin, for this filter to be applied.
3. Click Save Settings.
4. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Groups sub-branch.
The Groups screen is displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
67

Configuring LCR
Filters
5. Optionally, from a Group’s In Filter dropdown menu, select an In Filter. The IN
filter will be applied to calls entering the LCR module from one of the system’s
interfaces.
6. Optionally, from a Group’s Out Filter dropdown menu, select an Out Filter.
The OUT filter will be applied to calls exiting the LCR module to one of the
system's interfaces.
7. Click Save Settings.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
68

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.7 Advanced Call Routing (ACR)
Use ACR to define, for example, white lists and black lists. ACR supplements the
LCR rules created on the Rules screen.
Note: A white list includes the phone numbers that are authorized as dialed destinations
whereas a black list includes the phone numbers that are prevented from being dialed.
Enabling ACR requires the following steps:
a. Prepare and upload the Number List (optional)
b. Define the ACR rules.
c. Prioritize the rules by re-arranging them. The list of rules is scanned and
applied from top to bottom.
d. Set the default action to be carried out when none of the rules above it were
a match, or no rule provided an LCR group selection.
4.7.1 Modifying the Existing ACR Number List
To modify the existing ACR Number List:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the ACR Numbers Lists
sub-branch. The ACR Number Lists screen is displayed.
Figure 69. ACR Number Lists Screen
2. Click Export. The standard Windows browse dialog box is displayed.
3. Save the .csv file.
4. Open the file in a text-editor, such as Notepad.
5. Modify the file. Preserve the format; that is, the words tag,number must appear
as the first row of the list.
6. Save and close the file.
7. On the ACR Number Lists Screen, click Browse. The standard Windows
browse dialog box is displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
69

Configuring LCR
Advanced Call Routing (ACR)
8. Locate the .csv file containing the lists. Select it and click Open. The path to the
.csv file is displayed on the Number Lists Screen.
9. Select either:
Overwrite
When selected, the old .csv file is deleted and the new file replaces it.
Append
When selected, the entries on the new .csv file are added to the entries on the old
.csv file.
10. Click Import. The report of total lists and total numbers is automatically
updated.
4.7.2 Creating a New ACR Number List File
To define a number list:
1. Create a new file whose file-name ends with the extension .csv.
2. Open the file in a text-editor, such as Notepad.
3. Enter the words tag,number as the first row of the list.
Note: In step 4, the term “list” indicates all entries that are share the same tag.
4. Add the tag and number of each entry. Ensure that a comma separates the tag
and number.
The following example includes 5 lists:
tag,number
XYZ,0774445004
XYZ,0509080704
XYZ,0523030303
ABC,0509380137
ABC,0509380136
CLCOM,052
PHONE,054
CELLC,050
Caution: A comma must separate the tag and the number or the list will not register
properly.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
70

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
5. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the ACR Numbers Lists
sub-branch. The ACR Number Lists screen is displayed.
Figure 70. ACR Number Lists Screen
6. Click Browse. The standard Windows browse dialog box is displayed.
7. Locate the .csv file containing the lists. Select it and click Open. The path to the
.csv file is displayed on the Number Lists Screen.
8. Select either:
Overwrite
When selected, the old .csv file is deleted and the new file replaces it.
Append
When selected, the entries on the new .csv file are added to the entries on the old
.csv file.
9. Click Import. The report of total lists and total numbers is automatically
updated.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
71

Configuring LCR
Advanced Call Routing (ACR)
4.7.3 ACR Rules
To create an ACR Rule:
1. Ensure that an up-to-date ACR Number Lists .csv file has been uploaded to the
Gateway.
2. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the ACR Rules sub-
branch. The ACR Rules screen is displayed.
Figure 71. ACR Rules Screen
3. Click Add new rule. The Add New Rule screen is displayed.
Figure 72. Add New Rule Screen
4. In the Rule Name field, enter the name of the rule.
5. In the Check area, from either or both the On Source and the On Destination
dropdown menu, define the indication the rule will evaluate.
Note: On Source checks the origination phone number, that is, the phone number from
which the call was placed. On Destination checks the target phone number, that is, the
phone number of the called party.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
72

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
If an indication is selected, a dialog box similar to the following is displayed:
Figure 73. Sample Check Dialog Box
No Check
The rule does not check the Source number.
Begins With
The rule checks if the On Source begins with either specific digits or a tag that
appears on the list.
Ends With
The rule checks if the On Source ends with either specific digits or a tag that
appears on the list.
In Range
The rule checks if the On Source range is within a specific range.
Identical to
The rule checks if the On Source is exactly the specific digits or tag that appears
on the list.
6. Complete the dialog box and click Save.
7. In the Actions area, define what ACR does when it identifies a number matching
the indications defined in the Check area.
No Actions are Defined
If no actions are defined, the call is allowed as is.
Block
Calls matching the indications are not allowed.
Change Group
Calls matching the indications are routed through the LCR Group defined here.
On Source
Phone numbers of calls matching the indications are altered as defined here.
On Destination
Phone numbers of calls matching the indications are altered as defined here.
8. Click Save. The new rule is added to the ACR Rules screen.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
73

Configuring LCR
Advanced Call Routing (ACR)
9. Prioritize the rule. Use the arrows in the Priority column to increase or decrease
a rules prioritization.
10. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Rules sub-branch. The
Rules screen is displayed.
11. From the ACR column, select the checkbox in the LCR rule row that the ACR
rules will be applied to and click Save Settings.
Figure 74. Rule Prioritization Arrows
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
74

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.8 Number Filters
Use Number Filters to manipulate numbers that are sent to, or received by, the
Gateway. All numbers are compared to the configured set of rules. If the number
matches a rule, the rule is applied and a new number is dialed.
Note: Number Filters belong to the HyperConnect Package and require a separate license.
4.8.1 Creating a Number Filter
To create a Number Filter:
1. From the HMC navigation pane, expand the Manage branch.
2. Click the Number Filters sub-branch. The Number Filters screen is displayed.
Figure 75. Number Filters Screen
3. In the Add New Filter Name field, enter a name for the new filter.
4. Click Submit. The Number Filters screen is displayed; the new filter appears in
the list of Filter Names.
5. Click the Edit button beside the new filter’s name. The Rules for Filter
<name> screen is displayed.
Figure 76. Edit Number Filters Screen
6. Select a Rule Direction.
In
Use In filters to apply the filters to incoming calls.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
75

Configuring LCR
Number Filters
Out
Use Out filters to apply the filters to outgoing calls. For example, if a number
begins with the Country Code 44 and is followed by seven or more digits, this
filter— ^44(d\d\d\d\d\d\d+) $1 —removes the country code and dials only the
digits following the Country Code.
This second example is an Out filter that adds the suffix ‘9’ to all outgoing calls
which have five or more digits (for getting an outside line)—(\d\d\d\d\d+) 9$1
7. Using standard Regular Expressions, enter the Match Pattern and the Action that
will occur when the pattern is matched.
Note: For more information about Regular Expressions, see: http://www.regular-
expressions.info
8. Click Submit. The Rule is listed in either the Out Filter Rules or the In Filter
Rules list.
Figure 77. New Filter is Displayed
9. Click the Number Filters sub-branch.
10. Click Update Filters.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
76

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
4.9 CDR
Use the LCR Settings branch to enable the collection of Call Detail Records (CDR)
and to access CDR files.
On systems equipped with an HBS/HBD card, an external storage device (an SD
card) must be used. The active file is located within the internal system memory
while completed files are moved onto the external storage device during the night.
Caution: Failure to plug in an external storage device will result in loss of CDR data. The
memory device should not be removed.
On PC-based systems, the CDR files are stored on the hard-drive.
On all systems (HBS/HBD based as well as PC based) the user is responsible for
deleting old CDR files. This is required both in order to prevent memory overflow as
well as to be able to easily locate a file.
4.9.1 Enabling Collection of CDR
To enable collection of CDR files:
1. From the HMC navigation pane’s LCR branch, click the Settings sub-branch.
The Feature list is displayed.
2. Select or clear the checkbox. When selected, the HMC collects Call Detail
Records.
Note: Unless its size exceeds a predefined limit, only one CDR file is created each day.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
77

Configuring LCR
CDR
4.9.2 Downloading a CDR File
To download a CDR file:
1. From the HMC navigation pane, expand the Monitor branch.
2. Expand the LCR Card sub-branch and select LCR CDRs. The list of CDR files
is displayed.
3. Click a file name. The standard Windows Open dialog box is displayed.
4. Define the location where the file will be saved and click OK. The file is
downloaded to that location.
4.9.3 Deciphering the CDR File
A CDR line is created in the file each time a LCR call ends. All CDR fields appear
on a single line. For example:
12364,5003,0546858576,0546858576,1,2,2008-09-05 13:48:13,2008-09-05
13:48:14,2008-09-05 13:48:24,2008-09-05 13:50:42,31,23,1,0,10,138
The entries are explained in Table 7. The format of the line is:
Call Index Number, Source Number, Original Destination Number, Filtered
Destination Number, Source Group Number, Destination Group Number, Dial Date
& Time, Alert Date & Time, Answer Date & Time, Hangup Date & Time, From
Resource, To Resource, Source Hangup Direction, Destination Hangup Direction,
Hangup Reason, Call Duration
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
78

Hypermedia Systems
Entry
Explanation
Call Index Number
Counts from 0, does not reset when a new
file is created (i.e. when the date changes).
Source Number, Original Destination
Number
Dialing and dialed numbers respectively.
Filtered Destination Number
Dialed number after a filter was applied to
it (where relevant). Otherwise identical to
the Original Destination Number.
Source Group Number, Destination
Group Number
Group of LCR resources from which the
call had arrived to the LCR, as well as the
group through which the call is sent out
from the LCR.
Dial Date & Time
The moment the gateway received the call
request (format = YYYY-MM-DD
HH:MM:SS).
Alert Date & Time
The moment the remote party had begun
ringing (if reported by the remote party,
and supported by the outgoing resource).
Answer Date & Time
The moment the call had been connected
(i.e. answered by the remote party).
Hangup Date & Time
The moment any of the parties had
terminated the call.
From Resource
The resource through which the call
entered the LCR entity.
To Resource
The resource through which the call was
placed (after being routed according to the
LCR rules).
Source Hangup Direction
0 = source party had terminated the call, 1
= call was terminated by LCR (due to
termination by the destination party, no
route to destination, unavailable
destination resource, etc.)
Destination Hangup Direction
0 = destination party had terminated the
call, 1 = call was terminated by LCR (due
to termination by the source party etc.)
Hangup Reason
Cause code as reported by the party that
had first terminated the call.
Call Duration
In seconds, measured between AnswerTime and Hangup-Time.
Configuring LCR
Table 7. CDR Line Entries Explained
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
79

Configuring LCR
Activating LCR
4.10 Activating LCR
On some systems (mainly VoIP-enabled ones) the LCR service must be manually
activated.
To manually activate LCR:
1. Click the Windows Start button > All Programs.
2. From the Hypermedia program group, select HGS Setup Parameters. The HGS
Setup Parameters logon screen is displayed.
3. Enter your password and click Submit. The HGS Setup Parameters screen is
displayed.
Figure 78. HGS Setup Parameters Screen
4. From the HGS Server system function line, click Stop. A confirmation message
indicates that the service was stopped successfully.
5. Refresh the browser page, reenter your password and click Submit. The HGS
Setup Parameters screen is displayed in Edit mode.
Figure 79. HGS Setup Parameters Screen in Edit Mode
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
80

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring LCR
6. On the Disable LCR line, click Edit. The Value field becomes editable.
Figure 80. Editable Disable LCR Value Field
7. Enter 0 (zero). Zero indicates that LCR is enabled.
8. Click Save.
9. Click Submit.
10. From the HGS Server system function line, click Start. A confirmation message
indicates that the service was started successfully.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
81

Configuring LCR
Activating LCR
This page is intentionally blank
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
82

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring the PRI Card
5 Configuring the PRI Card
Note: For information on Callback and Callthrough, see the Business Applications Users
Guide.
This section includes:
PRI Media Connections (section 5.1)
Connection Settings (section 5.2)
PRI Card Dial Plan (section 5.3)
Monitoring PRI Card Status (section 5.4)
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
83

Configuring the PRI Card
PRI Media Connections
5.1 PRI Media Connections
Use the Media Connection screen to configure the connections from a PRI card to
other cards and channels in the system, including Cellular cards channels and VoIP
ones. The media matrix can be configured in any combination.
5.1.1 Associating/Linking PRI Channels
To associate a PRI channel with another media channel:
1. From the PRI Card branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Media
Connections sub-branch. The Media Matrix is displayed.
Figure 81. HMC PRI Media Matrix
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific PRI card. The Media Matrix
of that PRI card is displayed.
3. Click within a channel row. The row turns yellow.
4. Click Edit. The row becomes configurable.
Figure 82. Media Matrix Row when Configurable
5. From the first dropdown list, allocate this channel to a card by selecting the card.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
84

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring the PRI Card
Note: If all of the card’s channels are already allocated, the message “Fully allocated”
appears.
6. From the second dropdown list, assign this channel to a specific channel on the
target card.
Figure 83. Assigning a PRI Target Link
7. Click Save. The configuration dropdown boxes are hidden.
8. Optionally, repeat the process for additional channels and other media types.
9. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
85

Configuring the PRI Card
PRI Media Connections
5.1.2 Unlinking PRI Allocations
To break an allocation:
1. From the PRI Card branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Media
Connections sub-branch. The Media Matrix is displayed.
2. Click within a channel row. The row turns yellow.
Figure 84. Breaking a PRI Target Link
3. Click Unlink.
4. Click Apply Settings and wait for Configuration Saved to be displayed.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
86

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring the PRI Card
5.2 Connection Settings
The PRI card typically connects between the Hypermedia Gateway and a PBX. It
can also be assigned to connect directly to the landline operator's network.
To configure the PRI parameters:
1. 1. From the PRI Card branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Connection
Settings sub-branch. The PRI General Settings screen is displayed.
Figure 85. PRI Connection Settings
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific PRI card. The General
Settings of that PRI card is displayed.
3. Configure the settings:
PLL Clock Sync
ISDN device clocks must be synchronized. Some PBXs are Masters, that is, they
deliver the clock signal. In this case, the Gateway should be set to Slave.
Otherwise, the Gateway should be set to Master.
Remote Device
Define if the Gateway is connected to a PBX or to an operator’s network.
Line Coding
A line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for
transmission purposes. Select the line coding that is used by the remote device.
Framing Type
ISDN transmissions are framed using one of several existing framing methods,
for example, Cyclic Redundancy Check 4 (CRC-4). Select the framing type that
is used by the remote device. CRC-4 support is required for all network switches
in Europe. However, some older switches including private branch exchanges
(PBXs) do not support CRC-4.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
87

Configuring the PRI Card
Connection Settings
Long Haul
If the Gateway is connected to a PBX, select Short. Short Haul connections are
connections between user-owned devices. If the Gateway connects to the
telephone company’s network, optionally select Long Haul.
Inbound Dialing
ISDN supports two dialing methods – enblock (all digits dialed within one
message) and overlap (each message includes one or more dialed digits). Select
the dialing method required for calls from the PBX to the gateway.
Country Code
ISDN varies from one country to the next. Select the ISDN country code being
used.
ISDN Version
There are several versions of ISDN. Select the ISDN version being used.
4. Click Apply Settings.
5. From the HMC navigation pane, click Save Configuration Initialization takes
about 15 seconds.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
88

Hypermedia Systems
Configuring the PRI Card
5.3 PRI Card Dial Plan
A dial plan establishes the expected number and pattern of digits for a telephone
number. This includes country codes, access codes, area codes and all combinations
of digits dialed. Most PBXs support variable-length dial plans that use 3 to 11 digits.
Dial plans must comply with the telephone networks to which they connect. Use the
PRI Card Dial Plan screen to configure the local dial plan:
Note: This feature is only available in OVERLAP mode and will possible shorten the delay
after a destination number is dialed and until the remote party phone starts ringing.
OVERLAP mode is set on the Connection Settings branch (see section 5.2, Connection
Settings).
1. From the PRI Card branch of the HMC navigation pane, click the Dial Plan sub-
branch. The PRI Dial Plan screen is displayed.
Figure 86. HMC PRI Card Dial Plan Screen
2. If more than one slot is displayed, select a specific PRI card. The Dial Plan of
that PRI card is displayed.
3. Enter the prefix to which the specific dial plan entry will be applied.
4. Click Edit. A dropdown list of Number Lengths is displayed.
5. Expand the list and select a Number Length value corresponding to the expected
dialed number length (for a number beginning with the prefix entered above).
6. Click Save.
7. Click Apply Settings and wait for Saved successfully to be displayed.
Release 5.3 (June 2013)
89

Configuring the PRI Card
Monitoring PRI Card Status
5.4 Monitoring PRI Card Status
To view information about the status of PRI channels on a specific PRI cards:
1. Expand the Monitor > PRI Cards sub-branch and select PRI Status.
2. Select a specific slot. The PRI Card Status screen for that card is displayed.
Figure 87. PRI Card Status Screen
3. Review the PRI Status. Errors and other PRI Status information are displayed
above the channel status table.
4. Review the status of channels. Common messages include:
Idle
Incoming call from PRI network
Remote side ringing
Call connected
Call cleared
Dialing out through PRI network
5. Review the totals. The total number of connected, dialing, and incoming calls
are displayed below the channel status table.
Hypermedia Systems Ltd.
90
 Loading...
Loading...