HYNIX HMS81C4308, HMS81C4316, HMS81C4324, HMS81C4332, HMS87C4060 Datasheet
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
1
November 2001 ver 1.2
HMS81C43xx/GMS87C 4060
CMOS SINGLE-CHIP 8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
FOR TELEVI SI ON
1. OVERVIEW
1.1 Description
The HMS81C43xx/GMS87C4060 is a n a dvanced CMOS 8- bit mi crocon trolle r wit h 8~32K(60 K) byt es of ROM. The devic e
is one of GMS800 family. The HYNIX’s HMS81C43xx/GMS 87C4060 is a powerful mic rocontrolle r which provides a highly flexible and cost effective solution to many TV applications. The HMS81C43xx/GMS87C4060 provides the following
standard features: 8~32K(60K) bytes of ROM, 256~512/1, 536 bytes of RAM, 8-bit timer/counter .
1.2 GMS 87C4060 (OTP) Features
• 60K Bytes On-chip Program Memory
• 1,536 Bytes of On-chip Data RAM
(Included 256 bytes stack memory)
• Instruction Cycle Time (ex:NOP)
- 0.5us at 8MHz
• 40 Programmable I/O pins
- 33 Input/Ooutput and 7 Output pins
• Serial I/O : 8bit x 1ch
•I
2
C Bus interface
- Multimaster (2 Pairs interface pins)
• A/D Converter : 8bit x 6ch (TBD LSB)
• Pulse Width Modulation
- 14bit x 1ch
- 8bit x 6ch
•Timer
- Timer/Counter : 8bit x 4ch (16bit x 2ch)
- Basic interval timer : 8bit x 1ch
- Watch Dog Timer
• Number of Interrupt sources : 18
• On Screen Display
- Number of characters : 512 (6 characters are
reserved for IC test)
- Character size : 12 dots(X) x 16 dots(Y)
- Character display size : Large, Medium, Small
- DIsplay capability : 24Characters x 16 Lines
- Character, Back ground color : 16kinds
- Special functions : Rounding, Outline, Sprite,
Shadow, Half Tone Background,...
• Buzze r D riv in g port
- 500Hz ~ 250kHz @8MHz (Duty 50%)
• Operating Range : 4.5V to 5.5V
1.3 HMS81C43xx Family Features
• On-chip Program Memry and Data memry
HMS81C4332 ( 32K ROM, 512 RAM)
HMS81C4324 ( 24K ROM, 256 RAM)
HMS81C4316 ( 16K ROM, 256 RAM)
HMS81C4308 ( 8K ROM, 256 RAM)
(Included 64/256 bytes stack memory)
• Instruc ti on Cycle Time (e x: NOP)
- 1.0us at 4MHz
• 21 Programmable I/O pins
- 19 Input/Out put and 3 Out put pins
•I
2
C Bus interface
- Multimaster (2 Pairs interface pins)
Device name ROM Size RAM Size Package
HMS81C43xx
8~32 K bytes
Mask ROM
256~512
bytes
32 PDI P
GMS87C4060
60K bytes
EPROM
1,536 bytes 52 SDIP
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
2
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
• A/D Converter : 8bit x 6ch (TBD LSB)
• Pulse Width Modulation
- 14bit x 1ch
- 8bit x 2ch
•Timer
- Timer/Counter : 8bit x 4ch (16bit x 2ch)
- Basic interval timer : 8bit x 1ch
- Watch Dog Timer
• Number of Interrupt sour ces : 18
• On Screen Display
- Number of characters : 256
- Character size : 12 dots(X) x 16 dots(Y)
- Character display size : Large, Medium, Small
- DIsplay capability : 24Characters x 16 Lines
- Character, Back ground color : 8 kinds
- Special functions : Rounding, Outline,
Shadow, Half tone Background...
• Buzze r D riv in g port
- 250Hz ~ 125kHz @4MHz (Duty 50%)
• Operating Range : 4.5V to 5.5V
•
1.4 Development Tools
The HMS81C43xx/GMS87C4060 is supported by a fullfeatured macro as sem bler / linker , OSD font editor, an incircuit emulator CHOICE-Dr
TM
.
In Circuit Emulators
CHOICE-Dr.
(with EVA81C4xxx board)
Assembler / Linker
HYNIX’s Macro Assembler /
Linker
Font Editor
MS-Windows GUI version
Debugger
MS-Windows GUI version
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
3
November 2001 ver 1.2
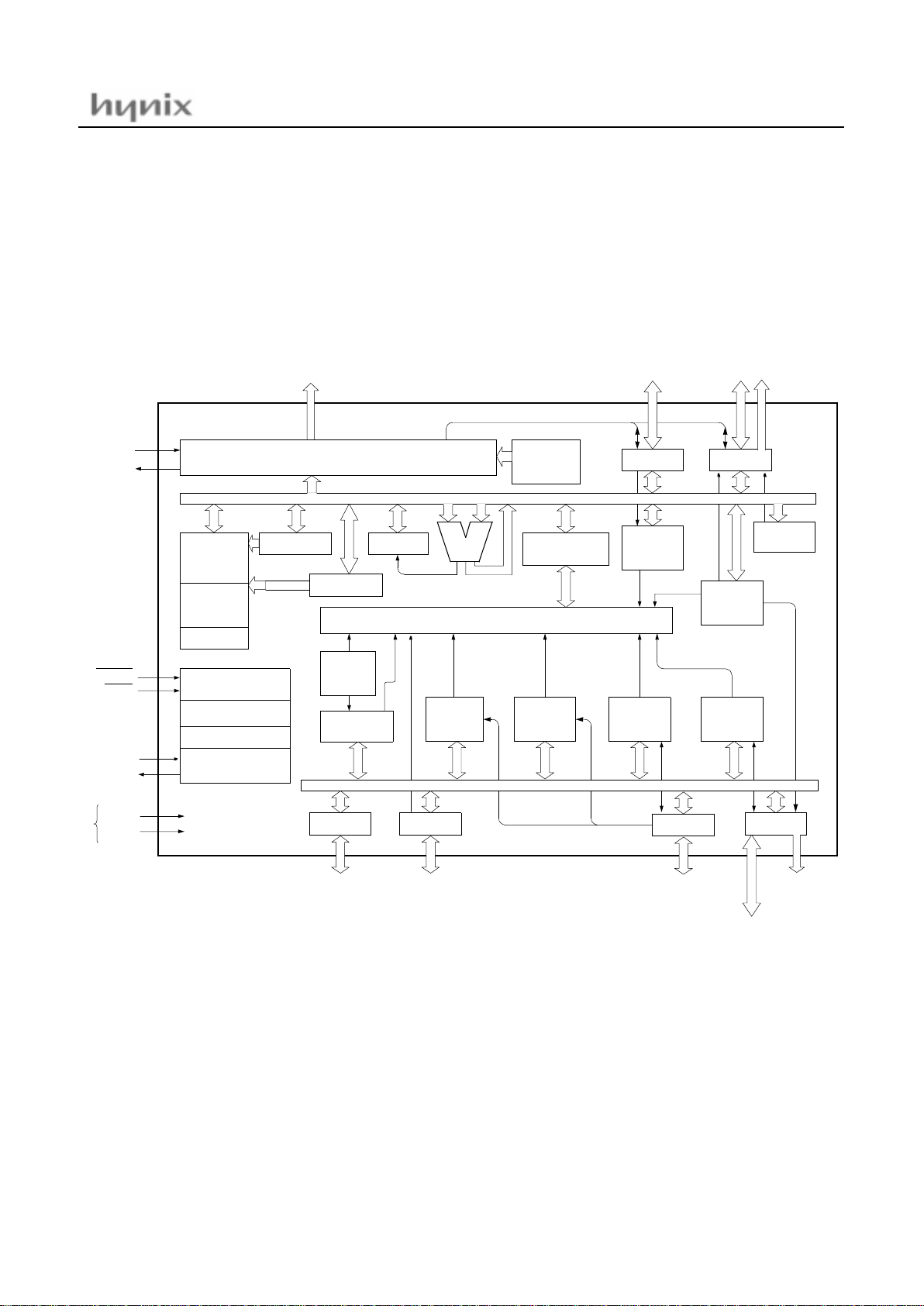
2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
ALU
OSD (On Screen Display) Controller
Accumulator
Interrupt Controller
Data
Memory
OSD
Memory
Display
8-bit x 4
Counter
Timer/
Program
Memory
Vector Table
8-bit Basic
Timer
Interval
Watchdog
Timer
PSW
System controller
Timing generator
System
Clock Controller
RESET
TEST
XIN
XOUT
OSC1
OSC2
R,G,B
VDD
VSS
Power
Supply
R1
Clock generator
& Index X,Y
8bit A/D
Convertor
Buzze r
R5
PWM
14bit x 1
8bit x 6
Da ta b u s
I2C
Interfa c e
R4
Da ta b u s
Serial I/O
Inte rface
Interrupt
Interval
Measure
R2
R0 R6
Stack pointer
PC
R00
R01
R02
R03
R04
R05
R06
R07
R67 / INT1
R20 / INT2
R21 / Sclk
R22 / Sout
R23 / Sin
R24 / INT3
R25 / EC2
R26 / INT4
R27 / EC3
R40 / PWM0
R41 / PWM1
R42 / PWM2
R43 / PWM3
R44 / SCL0
R45 / SCL1 / PWM4
R46 / SDA0
R47 / SDA1 / PWM5
R10 / AN0
R11 / AN1
R12 / AN2
R13 / AN3
R14 / AN4
R15 / AN5
R16 / VD
R17 / HD
R50 / BUZZ
R51 / PWM8
R52 / INT0
R53
R54 / YM
R55 / YS
R56 / I
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
4
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
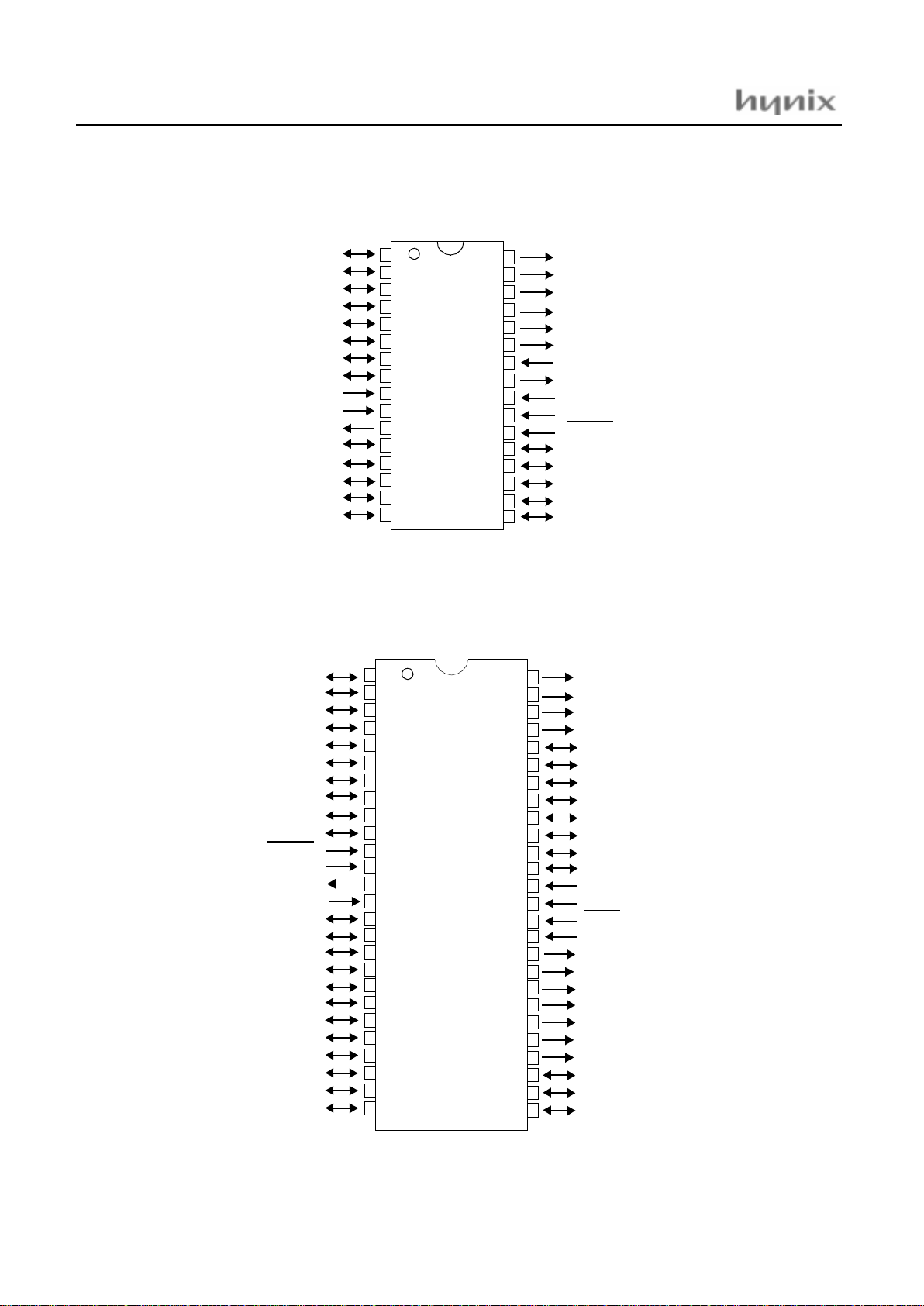
3. PIN ASSIGNMENT
R
G
B
R56
R55/YS
R54/YM
OSC1
OSC2
TEST
Vdd
RESET
R53
R52/INT0
R51/PWM8
R50/BUZZ
R26/INT4
R17/HD
R16/VD
R15/AN5
R14/AN4
R13/AN3
R12/AN2
R11/AN1
R10/AN0
Vss
Xin
Xout
R47/SDA1/PWM5
R46/SDA0
R45/SCL1/PWM4
R44/SCL0
R27/EC3
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
HYNIX
HMS81C4332
R40/PWM0
R41/PWM1
R42/PWM2
R43/PWM3
R44/SCL0
R45/SCL1/PWM4
R46/SDA0
R47/SDA1/PWM5
R50/BUZZ
R51/PWM8
R52/INT0
R53
Vss
Vdd
TEST
OSC1
OSC2
R54/YM
R55/YS
R56/I
B
G
R
R00
R01
R02
R27/EC3
R26/INT4
R25/EC2
R24/INT3
R23/Sin
R22/Sout
R21/Sclk
R20/INT2
R17/HD
R16/VD
RESET
Vss
Xout
Xin
R15/AN5
R14/AN4
R13/AN3
R12/AN2
R11/AN1
R10/AN0
R07
R06
R05
R04
R03
R67/INT1
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
HYNIX
GMS87C4060
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
5
November 2001 ver 1.2
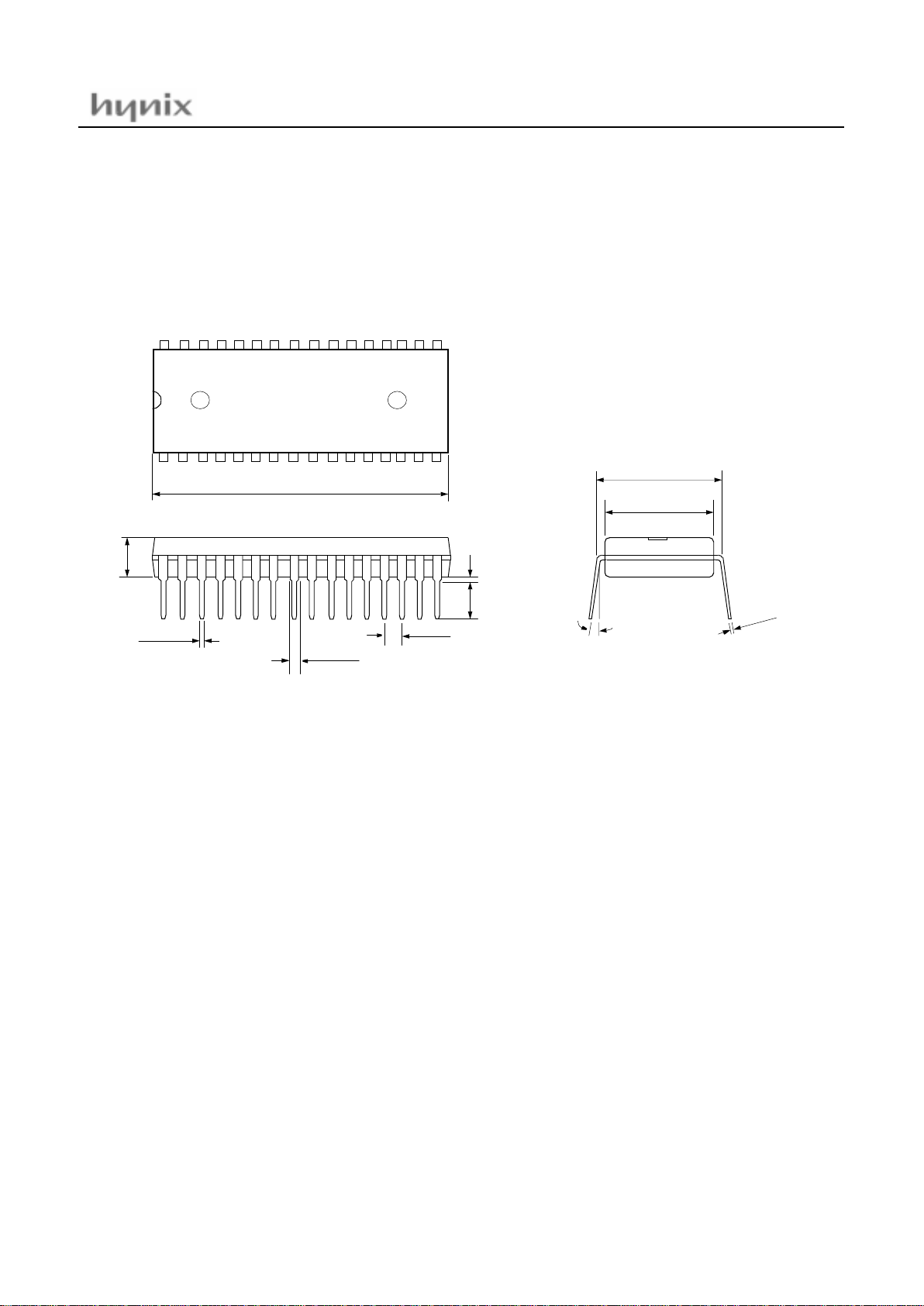
4. PACKAGE DIAGRAM
1.665
0.015
0.065
0.1 BSC
TYP 0.600 BSC
0.550
0
.
0
1
2
0 ~ 15°
MIN 0.015
0.140
0.530
0
.
0
0
8
0.2 max
0.045
0.022
0.120
HYNIX
HMS81C4332
1.645
UNIT: inch
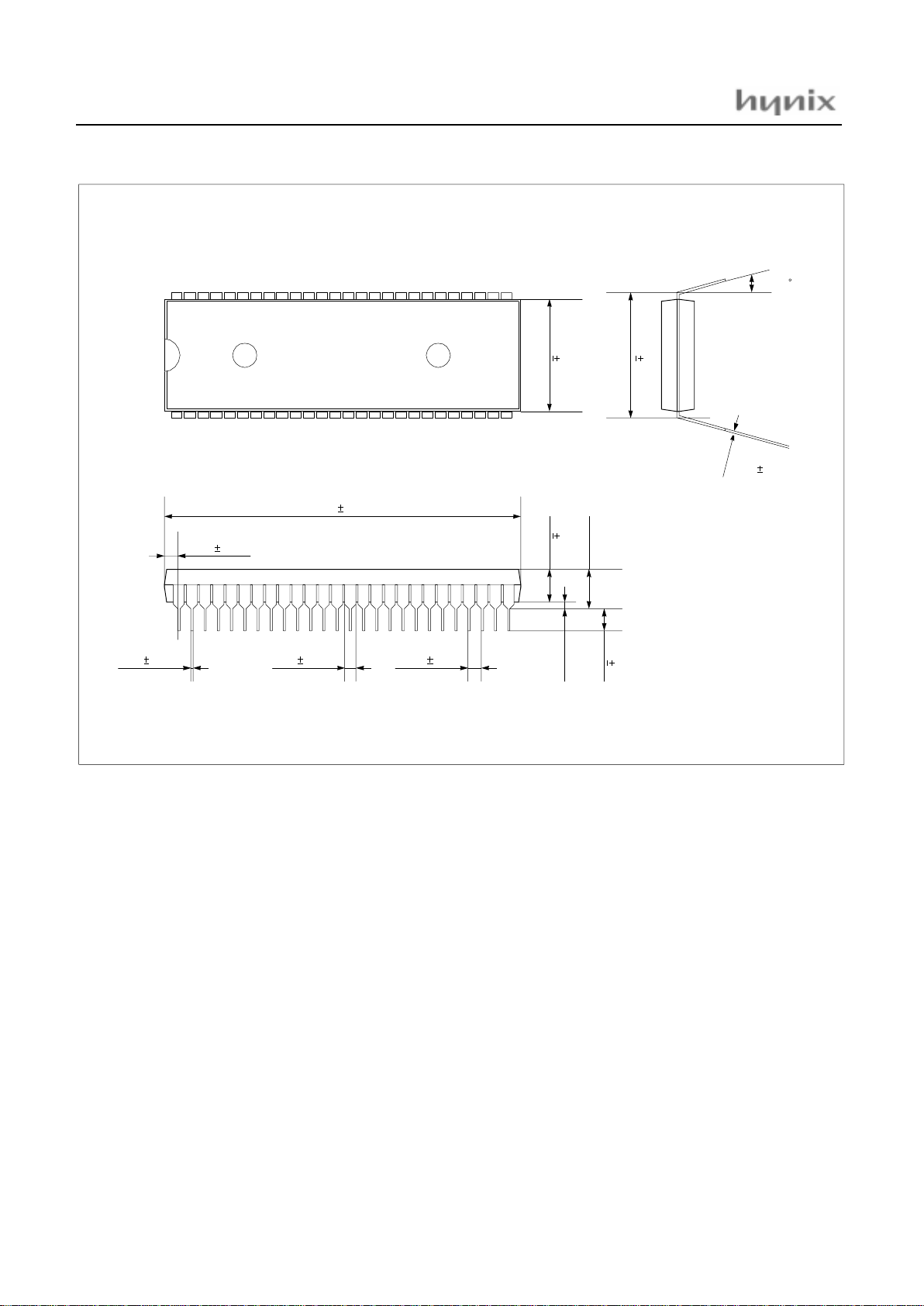
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
6
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
Figure 4-1 52pin Shrink DIP Package Diagram
UNIT: mm
HYNIX
GMS87C4060
1
26
2752
45.97
0.13
0.76
0.13
1.778
0.25
4.38 Max.
13.97
0.25
15.24
0.25
0.47 0.13 1.02 0.25
3.81 0.13
3.24
0.20
0.50 Min.
0.25 0.05
0 ~ 15
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
7
November 2001 ver 1.2
5. PIN FUNCTION
V
DD
: Supply voltage.
V
SS
: Circuit ground.
TEST
: Used for shipping inspect ion of the IC. F or normal
operation, it should not be connected .
RESET
: Rese t th e MCU.
X
IN
: Input to the inver tin g oscil lator ampli fie r and i nput to
the internal main clock operating circui t.
X
OUT
: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
OSC1
: Input to the internal On Screen Display operating
circuit.
OSC2
: Output from the inverting OSC1 amplifier.
R00~R07
: R0 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/ O port. R0
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as outputs or inpu ts.
R10~R17
: R1 is an 8-bit CMOS bidirectional I/ O port. R1
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as outputs or inpu ts.
In addition, R1 serves the functions of the various following special features.
R20~R27
: R2 is a 8-bit CMOS bidi rectional I/O por t. Each
pins 1 or 0 written to the their Port Direction Register can
be used as outputs or inputs.
In addition, R2 serves the functions of the various following special features.
R40~R47
: R40~R43 are 8-bit NM OS open drain output
and R45~R47 are bidirec tional CMOS Input / NMOS open
drain output port. R4 pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Registe r can be used as outputs or inpu ts.
In addition, R4 serves the functions of the various following sp ec ial featur es.
R50~R56
: R50~R53 are 4-bi t CMOS bidire ctional I/ O and
R54~R56 are CMOS output port. R5 pins 1 or 0 writ ten to
the Port Direction Register can be used as outputs or inputs.
In addition, R5 serves the functions of the various following sp ec ial featur es.
R67
: R67 is an 1- bit CMOS bidirection al I/O port. R67
pins 1 or 0 written to the Port Direction Register can be
used as outputs or inputs.
In addition, R67 serves the functions of the vario us following sp ec ial featur es.
R,G,B
: R,G,B CMOS outpu t port. E ach pin s cont rols Re d,
Green,. Blue color co ntrol.
Port pin Alternate funct ion
R10
R11
R12
R13
R14
R15
R16
R17
AN0 (A/D converter input 0)
AN1 (A/D converter input 1)
AN2 (A/D converter input 2)
AN3 (A/D converter input 3)
AN4 (A/D converter input 4)
AN5 (A/D converter input 5)
VD (Vertical Sync. input)
HD (Horisontal Sync. input)
Port pin Alternate funct ion
R20
R21
R22
R23
R24
R25
R26
R27
INT2 (External interrupt input 2)
Sclk (Serial communication clock)
Sout (Serial communication data out)
Sin (Serial communi cation data in)
INT3 (External interrupt input 3)
EC2 (Event counter in put 2)
INT4 (External interrupt input 4)
EC3 (Event counter in put 3)
Port pin Alternate function
R40
R41
R42
R43
R44
R45
R46
R47
PWM0 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 0)
PWM1 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 1)
PWM2 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 2)
PWM3 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 3)
SCL0 (I
2
C Clock 0)
SCL1 (I
2
C Clock 1)
PWM4 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 4)
SDA0 (I
2
C Data 0)
SDA1 (I
2
C Data 1)
PWM5 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 5)
Port pin Alternate function
R50
R51
R52
R54
R55
R56
BUZZ (Buzzer output)
PWM8 (Pulse Width Modul ation output 8)
INT0 (External int errupt input 0)
YM (Back ground)
YS (Edge)
I (Intencity)
Port pin Alternate function
R67 INT1 (External int errupt input 1)
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
8
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
PIN NAME Pin No. In/Out Function
V
DD
39 - Supply voltage
V
SS
12, 40 - Circuit ground
TEST
38 I For test purposes. Should not be connected. (N.C.)
RESET
11 I Reset signal input
X
IN
14 I Main oscillation input
X
OUT
13 O Main oscillation output
OSC1 37 I
On screen display functions
On screen display oscillation input
OSC2 36 O On screen display osc. output
R17/HD 9 I/O Horisontal Sync. input
R16/VD 10 I/O Vertical Sync. input
R 30 O Red signal output
G 31 O Green signal output
B 32 O Blue signal output
R56/I 33 O Intencity sign al output
R55/YS 34 O Edge signal output
R54/YM 35 O Background signal output
R40/PWM0 52 O
PWM functions
8bit PWM
R41/PWM1 51 O 8bit PWM
R42/PWM2 50 O 8bit PWM
R43/PWM3 49 O 8bit PWM
R45/SCL1/
PWM4
47 I/O
Include I
2
C Serial clock 1 (SCL1)
R47/SDA1/
PWM5
45 I/O
Include I
2
C Serial data 1 (SDA1)
R51/PWM8 43 I/O 14bit PWM
R44/SCL0 48 I/O
I
2
C functions
I
2
C Serial clock 0
R46/SDA0 46 I/O
I
2
C Serial data 0
R23/Sin 5 I/O
SCI functions
Serial data input
R22/Sout 6 I/ O Ser ial data output
R21/Sclk 7 I/O Serial communication clock
R27/EC3 1 I/O
Timer event functions
Event counter input 3
R25/EC2 3 I/O Event counter input 2
R50/Buzzer 44 I /O Buzzer function 500Hz ~ 250KHz @8MHz
Table 5-1 Port Function Description
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
9
November 2001 ver 1.2
R52/INT0 42 I/O
External interrupt functions
External interrupt input 0
R67/INT1 26 I/O External interrupt input 1
R20/INT2 8 I/O External interrupt input 2
R24/INT3 4 I/O External interrupt input 3
R26/INT4 2 I/O External interrupt input 4
R10/AN0 20 I/O
A/D conversion functions
Analog input 0
R11/AN1 19 I/O Analog input 1
R12/AN2 18 I/O Analog input 2
R13/AN3 17 I/O Analog input 3
R14/AN4 16 I/O Analog input 4
R15/AN5 15 I/O Analog input 5
R00 29 I/O
Digital I/O functions
R01 28 I/O
R02 27 I/O
R03 25 I/O
R04 24 I/O
R05 23 I/O
R06 22 I/O
R07 21 I/O
R53 41 I/O
PIN NAME Pin No. In/Out Function
Table 5-1 Port Function Description
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
10
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
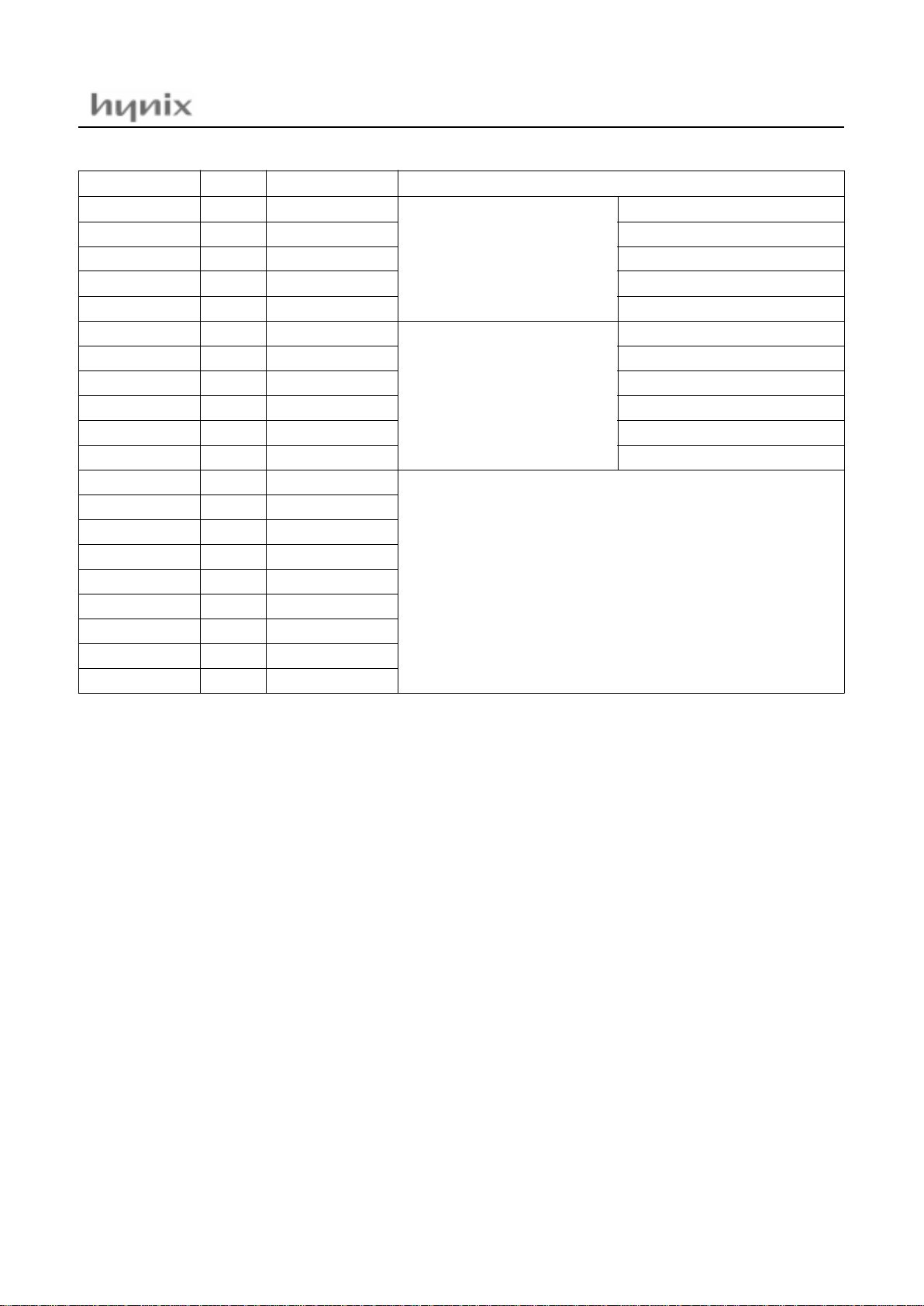
6. PORT STRUCTURES
RESET
TEST
XIN, X
OUT
OSC1, OSC2
R00~07, R53
R10~15 (AN0~5)
RESET
V
DD
V
SS
Noise
Canceler
V
DD
V
SS
X
IN
X
OUT
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
Main frequency
clock
V
SS
OSDON
OSC1
OSC2
V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
Main frequency
clock
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
DD
V
SS
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
DD
V
SS
AN0~5
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
11
November 2001 ver 1.2
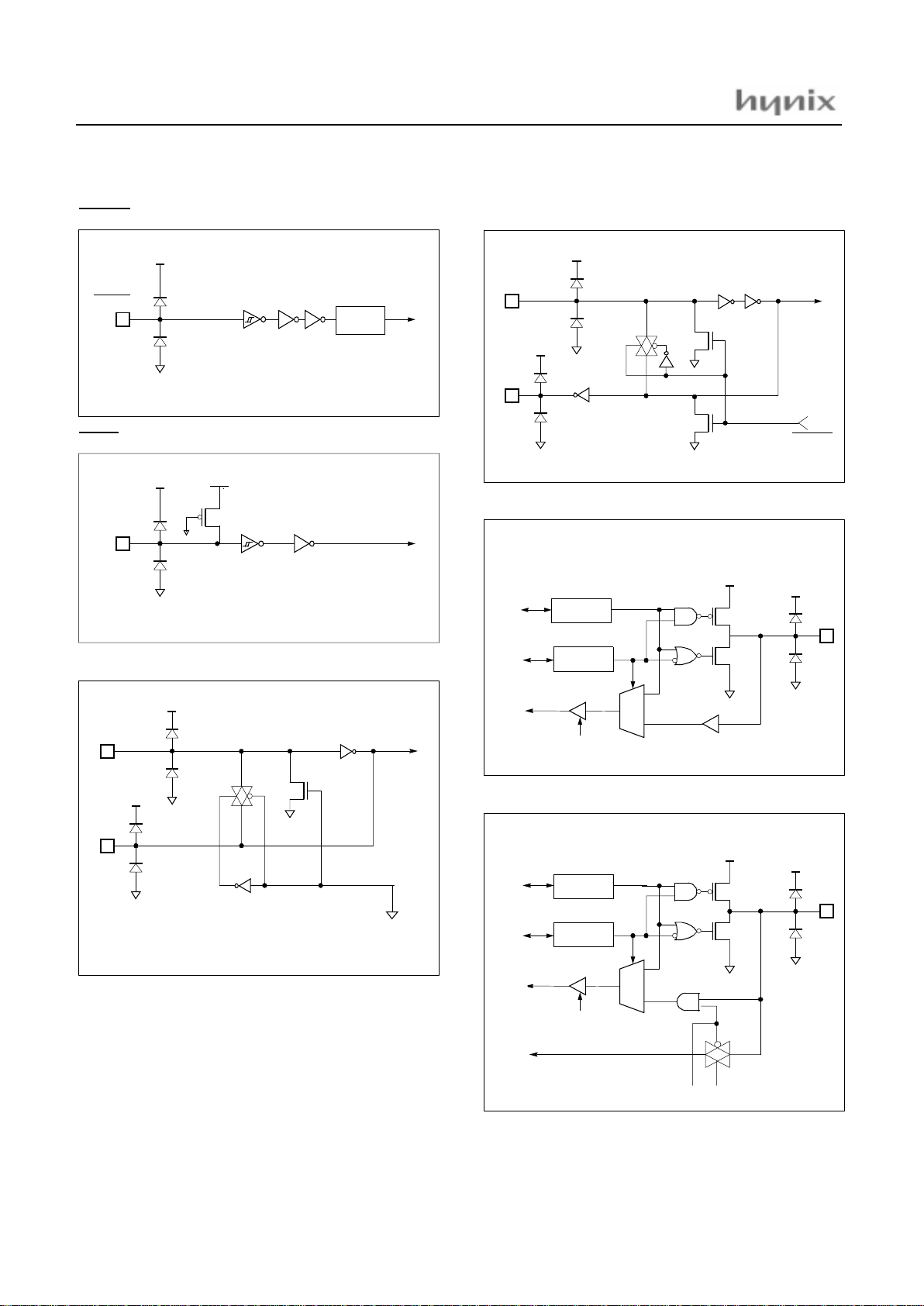
R16, 17, 20, 24, 25, 26, 27, 52, 67
R21/Sclk, R22/So ut
R23/Sin
R40~43 (PWM0~3)
R44, 45, 46, 47 (SCL, SDA, PWM)
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
DD
V
SS
HD,VD,
EC2~3
INT0~INT4
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
DD
V
SS
Sclk
MUX
Sout, Sclk
Selection
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
DD
V
SS
Sin
Selection
Pin
Data Reg.
DB
V
SS
MUX
PWM0~3
Selection
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
SS
SCL, SDA
MUX
PWM4,PWM5
Selection
SCL,SDA
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
12
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
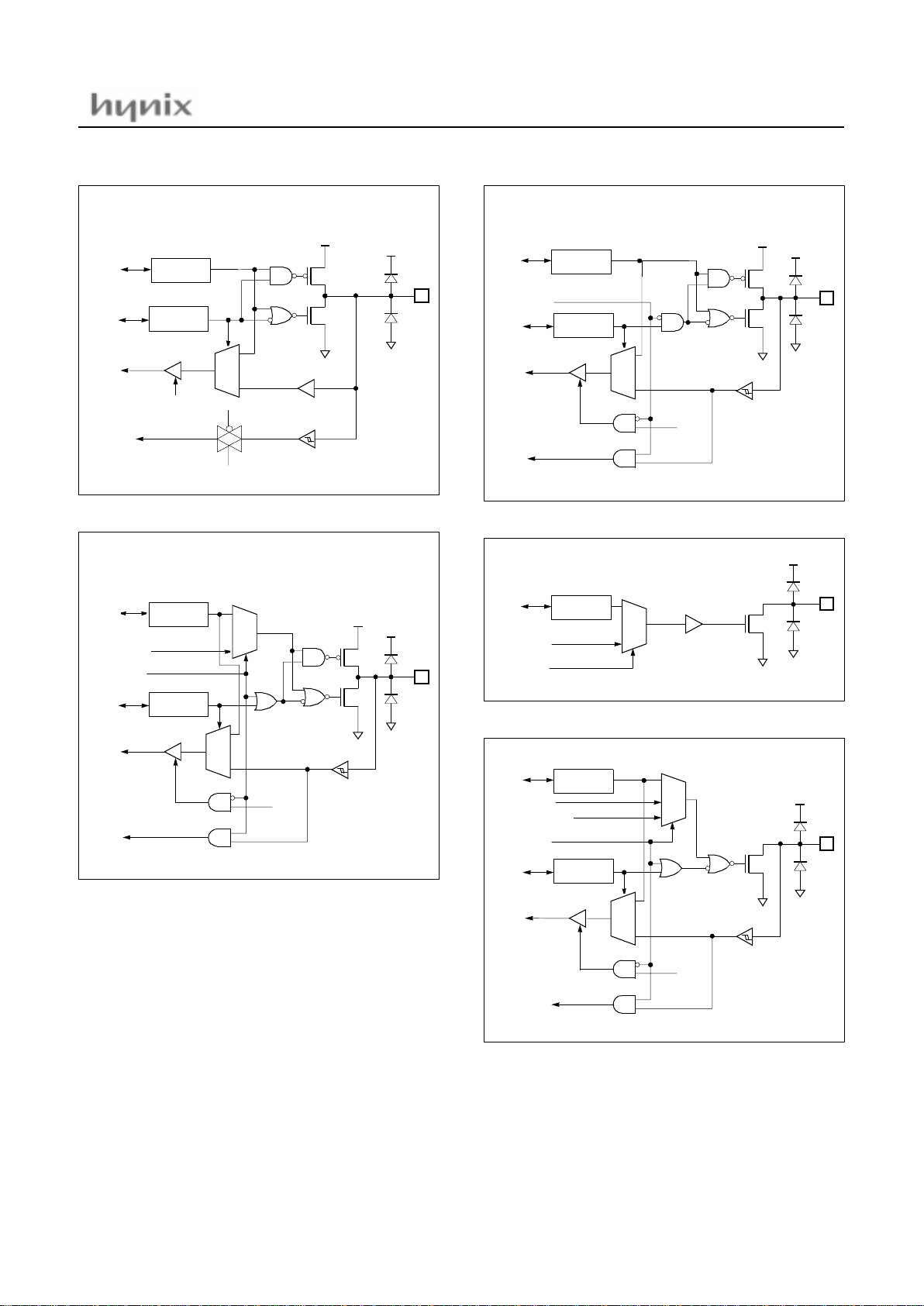
R50/BUZZ, R51/PWM8
R54/YM, R55/YS, R56/I
R, G, B
Pin
Data Reg.
Dir. Reg.
DB
DB
DB
MUX
RD
V
DD
V
SS
MUX
Buzz, PWM8
Selection
Pin
Data Reg.
DB
V
DD
V
SS
MUX
YM, YS, I
Selection
OSD ON or Data Reg Write.
Pin
R, G, B
V
DD
V
SS
i
OSD_ON
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
13
November 2001 ver 1.2
7. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Supply voltage...........................................-0.3 to +6.0 V
Storage Temperature ................................-40 to +125 °C
Voltage on any pin with respect to Ground (V
SS
)
............................................................... -0.3 to V
DD
+0.3
Maximum current ou t of V
SS
pin ........................100 mA
Maximum current into V
DD
pin ............................80 mA
Maximum current sunk by (I
OL
per I/O Pin) ........20 mA
Maximum output current sourced by (I
OH
per I/O Pin)
...... .. .. .......... ... .. .......... .. ... ......... ... .. .................... .. ... ..8 mA
Maximum current (ΣI
OL
)...................................... 80 mA
Maximum current (ΣI
OH
)......................................50 mA
Note:
Stresses above those listed under "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause pe rmanent dam age to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of
the device at a ny other condit ions above those indicated in
the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
Exposure to abso lute maximum rati ng conditions for extended periods may aff ect device reliability.
7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
7.3 DC Electrical Characteristics - HMS81C43xx
(TA=-10~70°C, VDD=4.5~5.5V)
,
Parameter Symbol Condition
Specifications
Unit
Min. Max.
Supply Voltage
V
DD
f
XIN
=8MHz
f
OSC
=16MHz
4.5 5.5 V
Operating Frequency
f
XIN
VDD=4.5~5.5V
48MHz
On Screen Display Operating Frequency
f
OSC
VDD=4.5~5.5V
816MHz
Operating Temperature
T
OPR
-10 70
°
C
Parameter Symbol Condition
Specifications
Unit
Min. Typ. Max.
High level input vol tage
V
IH1
TEST, RESET, Xin, OSC1, R17~16,
R27~20, R47~44, R52, R67
0.8 V
DD
-
V
DD
V
V
IH2
R0, R15~10, R53~50
0.7 V
DD
-
V
DD
V
Low leve l in put vo lta g e
V
IL1
TEST, RESET, Xin, OSC1, R17~16,
R27~20, R47~44, R52, R67
0-
0.12 V
DD
V
V
IL2
R0, R15~10, R53~50 0 -
0.3 V
DD
V
High level output voltage
V
OH
I
OH
= -5mA
R0, R1, R2, R5, R67
V
DD
- 1
--V
I
OH
= -1.2mA
R,G,B
V
DD
- 1
--V
Low level output voltage
V
OL
I
OL
= 5mA
R0, R1, R2, R4, R5, R67, R, G, B
-
-1.0V
Supply current in
ACTIVE mode
I
DD
V
DD
--30mA
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
14
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
pull-up lekage current
I
RUP
VDD = 5.5v, V
PIN
= 0.4V
TEST
-1.5 -400
µ
A
High input leakage
current
I
IZH
V
DD
= 5.5V, V
PIN
= V
DD
All input, I/O pin s except XIN, OSC1,
R47~40
-5 - 5
µ
A
Low input leakage
current
I
IZL
V
DD
= 5.5V, V
PIN
= 0V
All input, I/O pin s except X
IN
, OSC1,
R47~44
-5 - 5
µ
A
Open drain leakage
current
I
LOZ
V
DD
= 5.5V, V
OH
= VDD, N-ch Tr. off
R47~40
--10µA
RAM data retention
voltage
V
RAMVDD
1.2 - - V
I
2
C port impedance
(I/O Tra n s is to r o ff)
R
BS
V
DD
= 4.5V
,
V
SCL0
= V
SCL1
= 2.25V
V
SDA0
= V
SDA1
= 2.25V
SCL0:SCl1 (R44:R45)
SDA0:SDA1 (R46:R47)
- - 120
Ω
Hysterisis
Vt+ ~
Vt-
TEST
, RESET, Xin, OSC1, R17~16,
R27~20, R47~44, R52, R67
1.0 - - V
Parameter Symbol Condition
Specifications
Unit
Min. Typ. Max.
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
15
November 2001 ver 1.2
7.4 A/D Comparator Characteristics
(TA=-10~70°C, VDD=5.0V)
7.5 AC Characteristics
(TA=-10~70°C, VDD=5V±10%, VSS=0V)
Parameter Symbol Pins
Specifications
Unit
Min. Typ. Max.
Analog Input Voltage Range
V
AIN
AN0~AN5
V
SS
-
V
DD
V
Accuracy
N
FS
---
ΤΒ∆
LSB
Parameter Symbol Pins
Specifications
Unit
Min. Typ. Max.
Operating Frequency
f
XIN
X
IN
4-8MHz
f
OSC
OSC 8 - 16 MHz
External Clock Pulse Width
t
MCPW
X
IN
62.5 - 125 nS
t
SCPW
S
CLK
0.5 -
µ
S
External Clock Transition Time
t
MRCP,tMFCP
X
IN
- - 20 nS
t
SRCP,tSFCP
S
CLK
- - 20 nS
Oscillation Stabilizing Time
t
ST
XIN, X
OUT
--20mS
Interrupt Pulse Width
t
IW
INT0~4 2 - -
t
SYS
1
RESET Inpu t Width
t
RST
RESET 8--
t
SYS
1
Event Counter Input Pulse
Width
t
ECW
EC2, EC3 2 - -
t
SYS
1
Event Counter Transition Time
t
REC,tFEC
EC2, EC3 - - 20 nS
1. t
SYS
is one of 2/f
XIN
main cloc k operation mode,
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
16
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
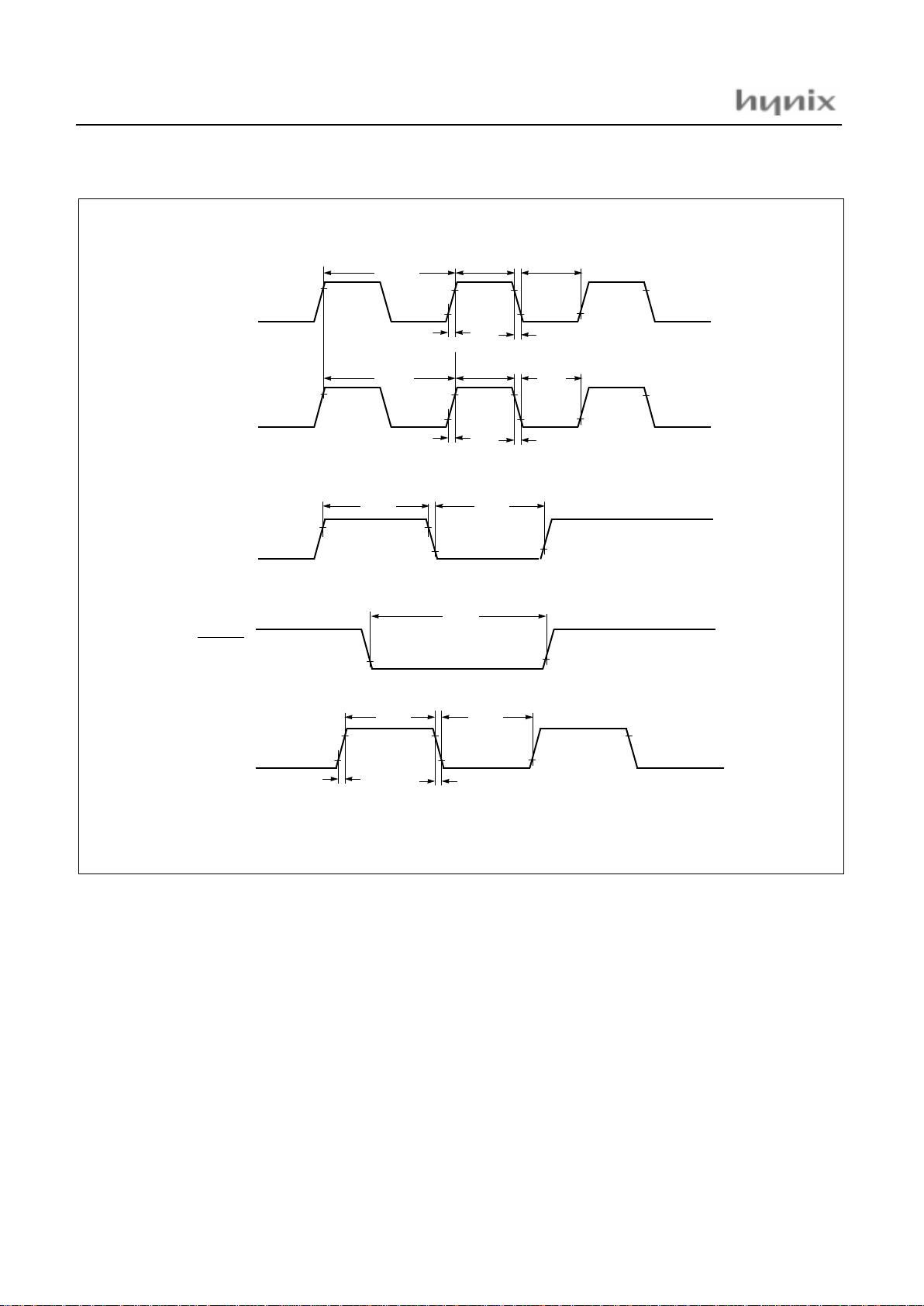
Figure 7-1 Timing Chart
t
MRCP
t
MFCP
X
IN
INT0 ~ 4
0.5V
V
DD
-0.5V
0.2V
DD
0.8V
DD
0.2V
DD
RESET
t
REC
t
FEC
0.2V
DD
0.8V
DD
EC2, EC3
t
IW
t
IW
t
RST
t
ECW
t
ECW
1/f
XIN
t
MCPW
t
MCPW
t
SRCP
t
SFCP
S
CLK
0.5V
V
DD
-0.5V
1/f
SCLK
t
SCPW
t
SCPW

HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
17
November 2001 ver 1.2
7.6 Typical Characteristics
This data will generate after evaluation.
Not available at this time.
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
18
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
8. MEMORY ORGANIZATION
The GMS81C43xx/GMS87C4060 has separate address
spaces for P rogram memo ry, Data M emory and D isplay
memory. Program memory can only be read, not written
to. It can be up to 32K/60K byte s of Program memo ry.
Data memory can be read and written to up to 256~512/
1,536 bytes includi ng the stack are a. Font memory has prepared 16K bytes for OSD.
8.1 Registers
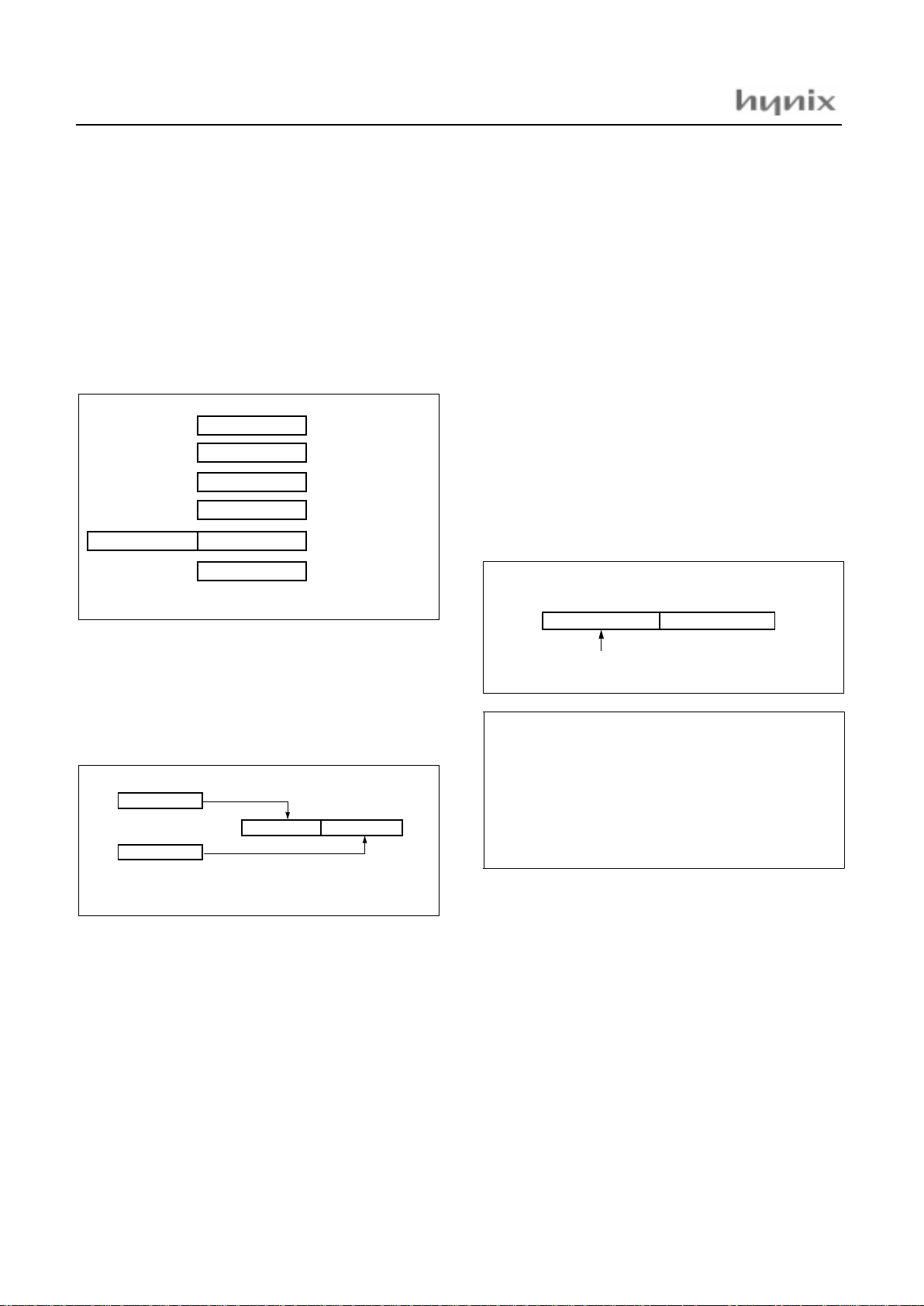
This device has six registers that are the Program Counter
(PC), a Accumulator (A), two index registers (X, Y), the
Stack Pointer (SP), and the Program Status Word (PSW).
The Program Counter consists of 16-bit register.
Figure 8-1 Configuration of Registers
Accumulator:
The Accumulator is the 8-bit general purpose register, use d for data opera tio n such as tr ansfer , temporary saving, an d conditional judg em ent, etc.
The Accumulator can be used as a 16-bit register with Y
Register as shown below.
Figure 8-2 Configurati on of YA 16-bit Register
X, Y Registers
: In the addressing mode which uses these
index registers , the register contents are added to the specified addr ess, which be comes the act ual address. The se
modes are extremely effective for referencing subroutine
tables and memory table s. The index re gisters al so have increment, decrement, comparison and data transfer functions, and they can be used as simple accumulators.
Stack Pointer
: The Sta ck Poi nte r is an 8-b it re gist er us ed
for occurrence inte rrupts and calling ou t subrouti nes. Stack
Pointer identifies the location in the stack to be accessed
(save or resto re).
Generally, SP is automatically updated when a subroutine
call is executed or an interrupt is accepted. However, if it
is used in excess of the stack area permitted by the data
memory allocating configuration, the user-processed data
may be lost.
The stack can be located at any position within 0100
H
to
01FF
H
of the internal data memory. The SP is not initialized by hardware, requiring to write the initial value (the
location wit h whi ch the use of the stac k st arts) by u sing t he
initialization routine. Normally, the initial value of "FF
H
"
is used.
Program Counter
: The Program Counter is a 16-bit wide
which consists of two 8-bit registers, PCH and PCL. This
counter indicates the address of the next instruction to be
executed. In r eset st ate, the program counter has reset routine address (PC
H
:0FFH, PCL:0FEH).
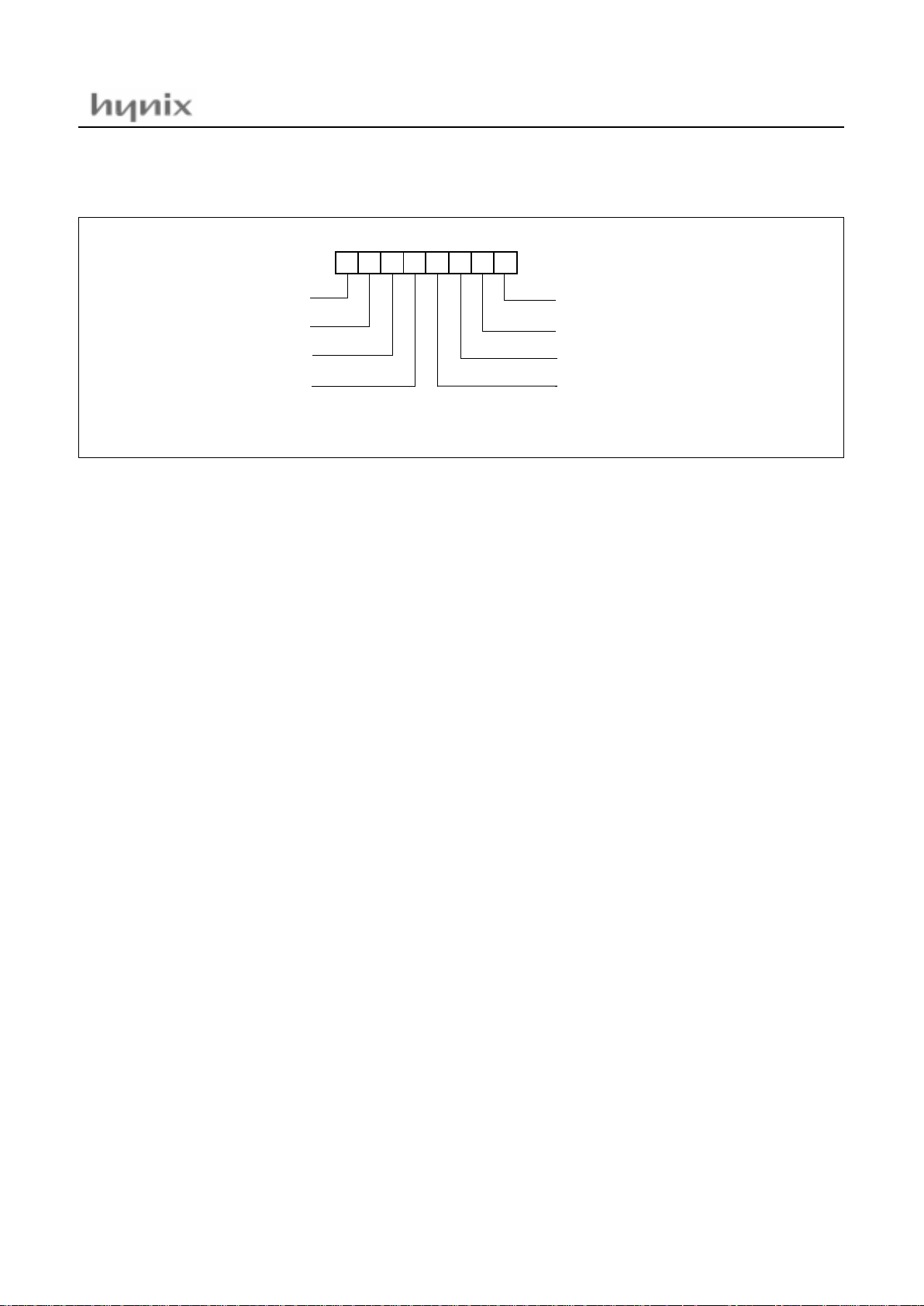
Program Status Word
: The Program Status Word (PSW)
contains several bits that reflect the current state of the
CPU. The PSW is described in Figure 8-3 . It contains the
Negative flag, the Overflow flag, the Break flag the Half
Carry (for BCD operation), the Interrupt enable flag, the
Zero flag, and the Carry flag.
[Carry flag C]
This flag stores a ny carry o r borro w from the ALU of CPU
A
ACCUMULATOR
X REGISTER
Y REGISTER
STACK PO INT ER
PROGRAM COUNTER
PROGRAM STATUS
WORD
X
Y
SP
PCLPCH
PSW
Two 8-bit Registers can be used as a "YA" 16-bit Register
Y
A
Y A
Caution:
The Stack Pointer must be initialized by software be-
cause its value is u ndefined after RESET .
Example: To initialize the SP for 81C4324 (256 RAM)
LDX #03FH
TXSP ; SP ← 3F
H
SP
01
Stack Address ( 0100
H
~ 013F or 01FFH )
15 087
Hardware fixed
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
19
November 2001 ver 1.2
after an arithmetic operation and is also changed by the
Shift Instruction or Rotate Instruction.
Figure 8-3 PSW (Program Status Wo rd) Register
[Zero flag Z]
This fl ag is set when the re sult of an arith metic op erat ion
or data transfer is "0" and is cleared by any other result.
[Interrupt disable flag I]
This flag enables/disables all interrupts except interrupt
caused by Reset o r software BRK in struction. All interrupts are disabled when cleared to "0". This flag immediately becomes "0" when an interrupt is served. It is set by
the EI instruction and cleared by the DI instruc tion.
[Half carry flag H]
After operation, this is set when there is a carry from bit 3
of ALU or there is borrow from bit 4 of ALU. This bit can
not be set or cleared except CLRV instruction with Overflow flag (V).
[Break flag B]
This flag is set by softwar e BRK instruction to distinguish
BRK from TCA LL instruction with the s ame vector address.
[Direct page flag G]
This flag a ssigns RAM pa ge for dire ct a ddres sing mode. In
the direct addressing mode, addressing area is from zero
page 00
H
to 0FFH when this flag is "0". If it is set to "1",
addressing area is assigned by DPGR register (address
0F8
H
). It is set by SETG i nstru ction a nd clear ed by CL RG.
[Overflow flag V]
This flag is set to "1" when an overflow occurs as the result
of an arithmetic operation involving signs. An overflow
occurs when the r esult of an add ition or s ubtraction exceeds + 127(7F
H
) or -128(80H). The CLRV instruction
clears the overflow flag. There is no set instruc tion. When
the BIT instruction is executed, bit 6 of memory is copied
to this flag.
[Nega tiv e f la g N ]
This flag is set to match the sign bit (bit 7) status of the re-
sult of a data or arithmetic operation. When the BIT instruction is execu ted, bit 7 of memor y is copied to this fla g.
N
NEGATIVE FLAG
V G B H I Z C
MSB LSB
RESET VALUE : 00
H
PSW
OVERFLOW FLAG
BRK FLAG
CARRY FLAG RECEIVES
ZERO FLAG
INTERRUPT ENABLE FLAG
CARRY OUT
HALF CARRY FLAG RECEIVES
CARRY OUT FROM BIT 1 OF
ADDITION OPERLANDS
SELECT DIRECT PAGE
when G=1, page is addressed by RPR
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
20
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
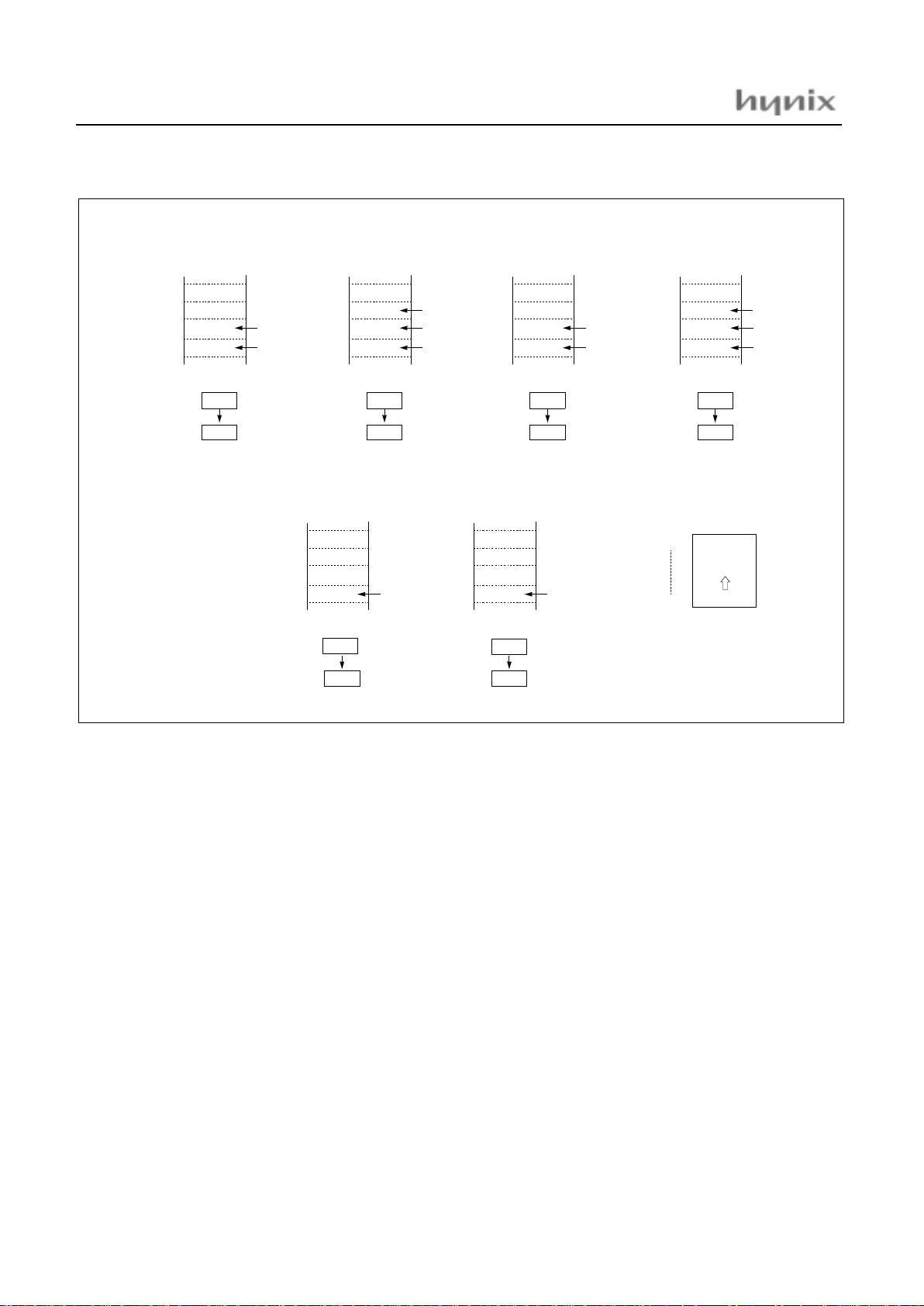
Figure 8-4 Stack Operation
At execution of
a CALL/TCALL/PCALL
PCL
PCH
01FF
SP after
execution
SP before
execution
01FD
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FF
Push
down
At acceptance
of interrupt
PCL
PCH
01FF
01FC
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FF
Push
down
PSW
At execution
of RET instruction
PCL
PCH
01FF
01FF
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FD
Pop
up
At execution
of RETI instruction
PCL
PCH
01FF
01FF
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FC
Pop
up
PSW
0100H
01FFH
Stack
depth
At execution
of PUSH in struction
A
01FF
01FE
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FF
Push
down
SP after
execution
SP before
execution
PUSH A (X,Y,PSW)
At execution
of POP instruction
A
01FF
01FF
01FE
01FD
01FC
01FE
Pop
up
POP A (X,Y,PSW)
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
21
November 2001 ver 1.2
8.2 Program Memory
A 16-bit program counter is capable of addressing up to
64K bytes, but HMS81C43xx/GMS87C4060 has 8~32K/
60K bytes program memory space only physically implemented. Accessing a location above FFFF
H
will cause a
wrap-around to 0000
H
.
Figure 8-5 , shows a map of Pro gram Memory. Aft er reset,
the CPU begins e xecution from reset vect or which is stored
in address FFFE
H
and FFFFH as shown in Figure 8-6 .
As shown in Figure 8-5 , each area is assigned a fixed location in Program Memory. Progr am Memory area c ontains the user program.
Figure 8-5 Program Memory Map
Page Call (PCALL) area contains subroutine program to
reduce program byte length by using 2 bytes PCALL instead of 3 bytes CALL instr uction. If it is frequent ly called ,
it is more useful to save program byte lengt h.
Table Call (TCALL) causes the CPU to jump to each
TCALL address, where it commences the execution of the
serv ic e r ou t in e. The Tab l e Call s er v ic e area s pa ce s 2 - b y te
for every TCALL: 0FFC0
H
for TCALL15, 0FFC2H for
TCALL14, etc., as shown in Figure 8-7 .
Example: Usage of TCALL
The in terrupt cau s es the CP U to ju m p to specific l oc a t i on ,
where it comm ence s the ex ecuti on of th e serv ice ro utine.
The External interrupt 0, for example, is assigned to location 0FFFC
H
. The in terr up t se rvic e lo catio ns spa ces 2-by te
interval: 0FFF8
H
and 0FFF9H for Ex terna l Interr upt 1,
0FFFC
H
and 0FFFDH for External Interrupt 0, etc.
Any area from 0FF00
H
to 0FF FFH, if it is not going to be
used, its service location is available as general purpose
Program Memory.
Figure 8-6 Interr upt Vector Area
PROGRAM
MEMORY
TCALL
AREA
INTERRUPT
VECTOR AREA
87C4060:1000H
FEFFH
FF00H
FFC0H
FFDFH
FFE0H
FFFFH
PCALL
AREA
81C4332:8000H
FFBFH
81C4324:A000H
81C4316:C000H
81C4308:E000H
LDA #5
TCALL 0FH ;
1BYTE INSTRUCTION
:;
INSTEAD OF 2 BYTES
:;
NORMAL CALL
;
;TABLE CALL ROUTINE
;
FUNC_A: LDA LRG0
RET
;
FUNC_B: LDA LRG1
RET
;
;TABLE CALL ADD. AREA
;
ORG 0FFC0H ;
TCALL ADDRESS AREA
DW FUNC_A
DW FUNC_B
1
2
0FFE0
H
E2
Address Vector Area Memory
E4
E6
E8
EA
EC
EE
F0
F2
F4
F6
F8
FA
FC
FE
I
2
C Bus Interface Interrupt Vector Area
Serial I/O Interrupt Vector Area
Basic Interval Timer Interrupt Vector Area
Watchdog Timer Interrupt Vector Area
Timer/Counter 3 Interrupt Vector Area
Timer/Counter 1 Interrupt Vector Area
V-Sync Interrupt Vector Area
Timer/Counter 2 Interrupt Vector Area
Timer/Counter 0 Interrupt Vector Area
External Interrupt 2 Vector Area
On Screen Display Interrupt Vector Area
External Interrupt 0 Vector Area
RESET Vector Area
External Interrupt 1 Vector Area
1 Frame Timer Interrupt Vector Area
External Interrupt 3/4 Vector Area
"-" means reserved area.
NOTE:
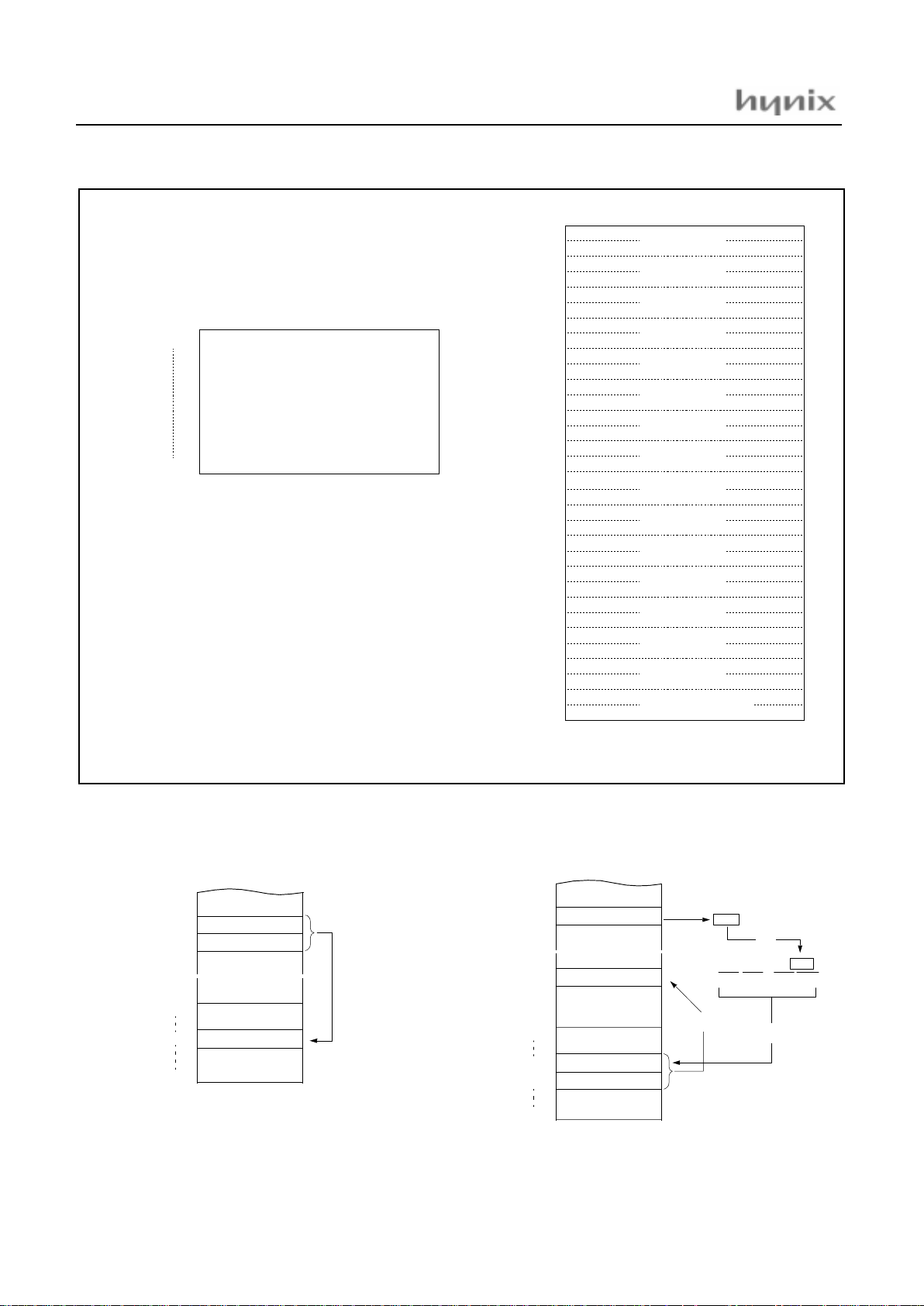
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
22
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
Figure 8-7 PCALL and TCALL Memory Area
PCALL
→
→ →
→
rel
4F35 PCALL 35H
TCALL
→
→ →
→
n
4A TCALL 4
0FFC0
H
C1
Address Program Memory
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
0FF00
H
Address PCALL Area Memory
0FFBF
H
PCALL Area
(192 Bytes)
* means that the BRK software interrupt is using
same address with TCALL0.
NOTE:
TCALL 15
TCALL 14
TCALL 13
TCALL 12
TCALL 11
TCALL 10
TCALL 9
TCALL 8
TCALL 7
TCALL 6
TCALL 5
TCALL 4
TCALL 3
TCALL 2
TCALL 1
TCALL 0 / BRK *
C9
CA
CB
CC
CD
CE
CF
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
DA
DB
DC
DD
DE
DF
4F
~
~
~
~
Sub-routine
35
0FF35H
0FF00H
0FFFFH
Upper address is
assumed 0FF
H.
11111111
11010110
01001010
PC:
FHFHDH6
H
4A
~
~
~
~
25
0FFD6H
0FF00H
0FFFFH
D1
Sub-routine
0FFD7H
þ
À
Ã
0D125H
Reverse

HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
23
November 2001 ver 1.2
Example: The usage software example of Vector address and the initialize part in HMS81C4324.
ORG 0FFE0H
DW I2C ; I2C
DW SERIAL ; Serial I/ O
DW BIT ; Basic interval timer
DW WATCHDOG ; Watch dog timer
DW INT3_4 ; Interrupt 3/4
DW TIMER3 ; Timer 3
DW TIMER1 ; Timer 1
DW VSYNC ; Vertica l Sy nc .
DW One_Frame ; 1 Frame interrupt
DW TIMER2 ; Timer 2
DW TIMER0 ; Timer 0
DW INT2 ; Interrupt 2
DW INT1 ; Interrupt 1
DW OSD ; On Screen Display
DW INT0 ; Interrupt 0
DW RESET ; Reset
ORG 0A000H ; Start Address of 24 kbytes Program Memory
;********************************************
; MAIN PROGRAM *
;********************************************
;
RESET: DI ; Disable All Interrupts
LDX #0
LDA #0 ; RAM Page0 Clear(!0000H->!00BFH)
RAM_CLR: STA {X}+
CMPX #0C0H
BNE RAM_CLR
;
CALL OSD_Stop ; Stop OSD displa y
;
LDX #03FH ; Stack Pointer Initialize
TXSP
LDM R0, #0 ; Normal Port 0
LDM R0DD,#1000_0010B ; Normal Port Direction
:
:
:
:
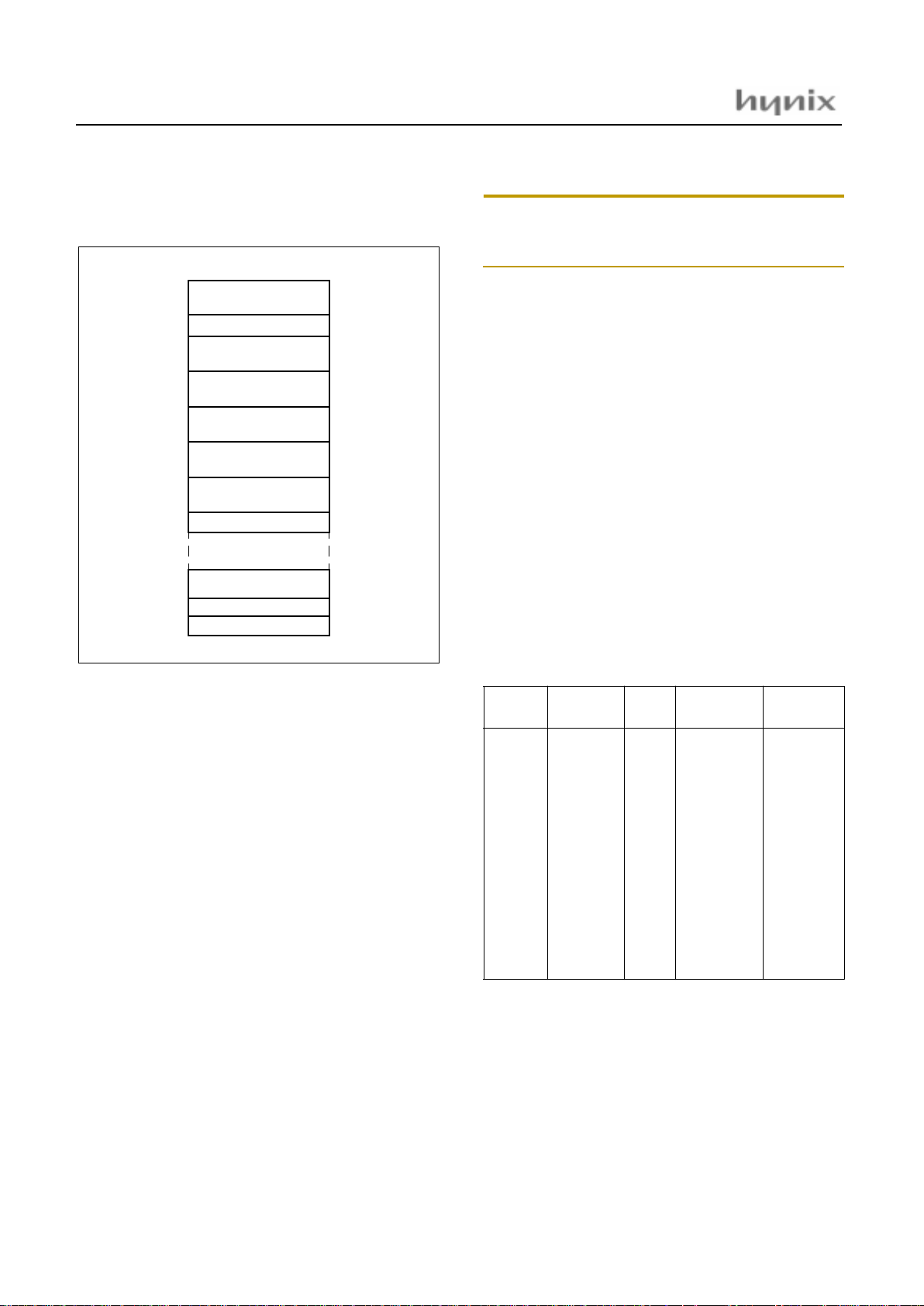
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
24
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
8.3 Data Memory
Figur e 8- 8 sho w s th e i nt er n a l D at a M emory spac e av ai lable. Data Memory is di vided into four groups, a user RAM,
control registers, Stack, and OSD memory.
Figure 8-8 Data Memory Map
User Memory
The GMS87C4060 has 1,536 × 8 bits for the user memory
(RAM). HMS81C4332 has 512 x 8 bit for the user memory (RAM) address ed 00 0H ~ 23F H exc ept
Peripheral Reg. (64
bytes)
. HMS81C4308 /16/24 has 256 x 8 bit RAM addressed 000H ~ 13FH except periph eral register
(0C0h~0FFh)
Control Registers
The control registers are used by the CPU and Peripheral
function blocks for controlling the desired operation of the
device. Theref ore these regis ters contai n contr ol a nd sta tus
bits for the interrupt system , the timer / counters, analo g to
digital conv ert ers and I /O po rts. The ba sic co ntro l regis t ers
are in address range of 00C0
H
to 00FFH. And OSD control
registers are assigned within 0AE0
H
~ 0AFFH.
Note that unoccupied addresses may not be implemented
on the chip . Re ad ac ce sse s to t hese add ress es w ill in g eneral return random data, and write accesses will have an indeterminate effect.
More detailed informations of each register are explained
in each periphera l sectio n .
Note:
Write only registers can not be accessed by bit manipulatio n instruct ion. Do no t us e read-modi fy-wr ite i nstru ction. Use byte manip ulation instruc ti on.
Example; To write at CKCTLR
LDM CLCTLR,#09H ;Divide ratio ÷8
Stack Area
The stack pro vides the area where the return address is
saved before a jump is performed du ring the pro cessing
routine at the execution of a subroutine call instruction or
the acceptance o f an in terru p t .
When returning from the processing routine, executing the
subroutine re turn inst ruction [RET ] restores t he contents of
the program counter fro m the stack; executing the int errupt
return instruction [RETI] restores the contents of the program counter and flags.
The save/restore locations in the stack are determined by
the stack pointed (SP). The SP is automatically decreased
after the saving, and increased before the restoring. This
means the value of the SP indicates the stack location
number for the next save. Refer to Figure 8-4 on page 20.
Page0
RAM (192 bytes)
Peripheral Reg. (64 bytes)
0100H
00C0H
0000H
RAM (256 bytes)
0200H
RAM (256 bytes)
0300H
RAM (256 bytes)
0400H
RAM (256 bytes)
0500H
RAM (256 bytes)
0600H
RAM (64 bytes)
0A00H
OSD RAM (192 bytes)
0AE0H
Peripheral Reg. (32 bytes)
0C00H
Sprite RAM (96 bytes)
Empty area
Page1
Page2
Page3
Page4
Page5
Page6
PageA
PageC
063FH
Stack area
0C5FH
Address Symbol R/W Reset Value
Addressing
mode
00C0H
00C1H
00C2H
00C3H
00C4H
00C5H
00C8H
00C9H
00CAH
00CBH
00CCH
00CDH
00CEH
00CFH
R0
R0DD
R1
R1DD
R2
R2DD
R4
R4DD
R5
R5DD
R6
R6DD
FUNC1
FUNC2
R/W
W
R/W
W
R/W
W
R/W
W
R/W
W
R/W
W
W
W
????????
00000000
????????
00000000
????????
00000000
????????
0000---????????
----0000
?------0-------
-0000000
---00000
byte, bit
1
byte
2
byte, b it
byte
byte, b it
byte
byte, b it
byte
byte, b it
byte
byte, b it
byte
byte
byte
Table 8-1Control reg isters
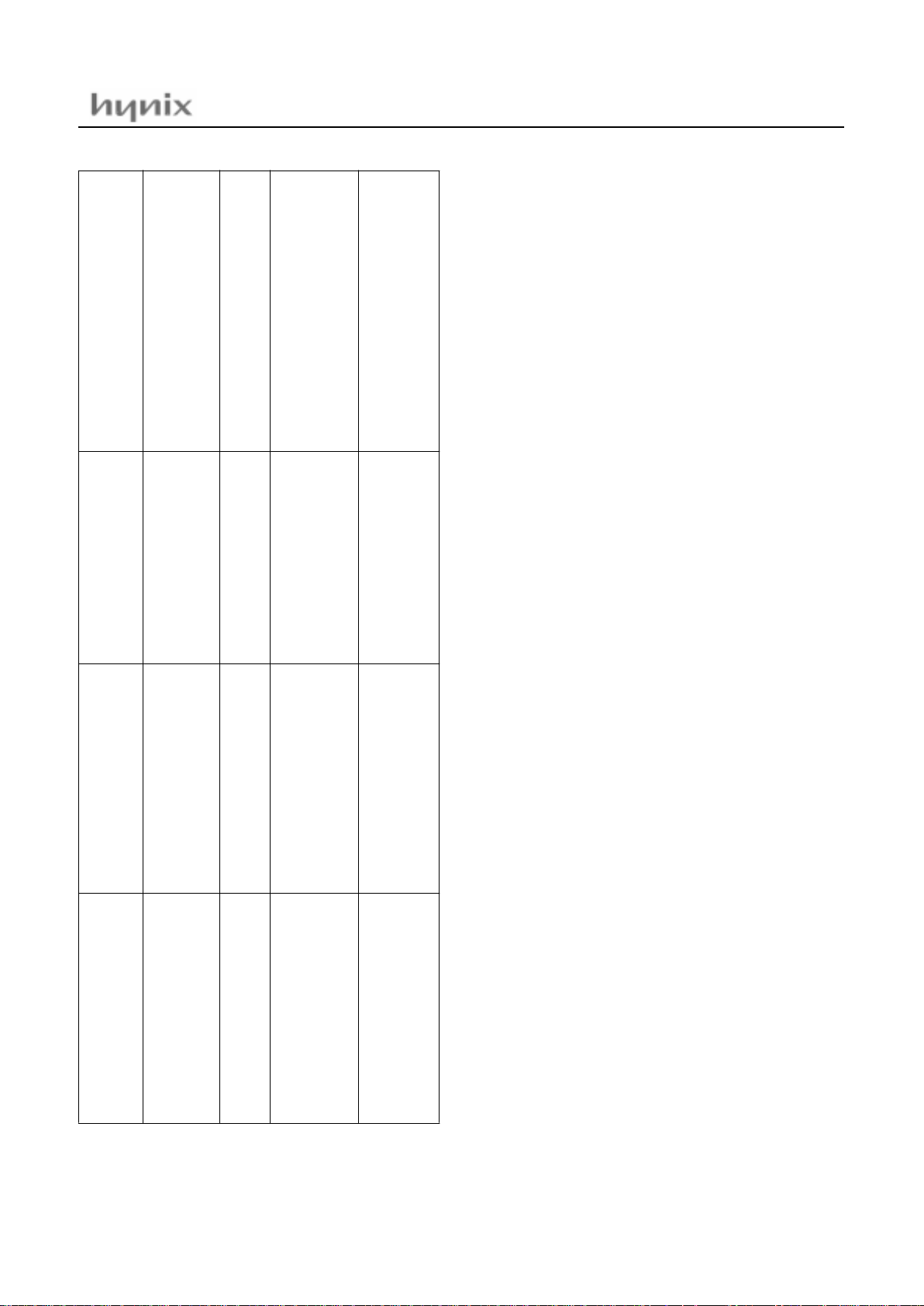
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
25
November 2001 ver 1.2
0D0H
0D1H
0D2H
0D3H
0D4H
0D5H
0D6H
0D7H
0D8H
0D9H
0DAH
0DBH
0DCH
0DEH
0DFH
TM0
TM2
TDR0
TDR1
TDR2
TDR3
BITR
CKCTLR
WDTR
ICAR
ICDR
ICSR
ICCR1
ICCR2
SIOM
SIOR
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R
W
W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
-0000000
-0000000
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
--010111
-0111111
00000000
11111111
000100000000000
00000000
-0000001
????????
byte
byte
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte
byte
byte
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
0E0H
0E1H
0E2H
0E3H
0E4H
0E5H
0E8H
0E9H
0EAH
0EBH
0EEH
0EFH
PWMR0
PWMR1
PWMR2
PWMR3
PWMR4
PWMR5
PWM8H
PWM8L
PWMCR1
PWMCR2
BUR
AIPS
W
W
W
W
W
W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
W
W
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
--??????
00000000
--0-0000
????????
--000000
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte
byte
0F0H
0F1H
0F2H
0F3H
0F4H
0F5H
0F6H
0F7H
0F9H
0FAH
0FBH
0FCH
0FDH
ADCM
ADR
IEDS
IMOD
IENL
IRQL
IENH
IRQH
IDCR
IDFS
IDR
DPGR
TMR
R/W
R
W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R
R
R/W
W
--011101
????????
--000000
--000000
0000000000000000000000
00000000
0000-000
1----001
????????
----0000
????????
byte, bi t
byte
byte
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte
byte
byte, bi t
byte
0AE0H
0AE1H
0AE2H
0AE3H
0AE4H
0AE5H
0AE6H
0AE8H
0AE9H
0AF0H
0AF1H
0AF3H
0AF4H
OSDcon1
OSDcon2
OSDPOL
FDWSET
EDGEcol
OSDLN
LHPOS
SPVPOS
SPHPOS
L1ATTR
L1VPOS
L2ATTR
L2VPOS
R/W
R/W
W
W
W
R
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
00000000
-0000000
????????
01111010
10000111
---00000
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
????????
byte, bi t
byte, bi t
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
byte
Table 8-1Control registers
1. "byte, bit" means that register can be addressed by not only bit
but byt e manipulation instruc tion.
2. "byte" means that register can be addressed by only byte
manipulation instruction. On the other hand, do not use any
read-modify-write instruction such as bit manipulation for clearing bit .
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
26
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
8.4 Addressing Mode
The GMS800 series uses six addressing modes;
• Register addressing
• Immediate addressing
• Direct page addressing
• Absolute addressing
• Indexed addressing
• Register-indirect addressing
(1) Register Addressing
Register addressin g accesses the A, X, Y, C and PSW.
(2) Immediate Addressing
→
→ →
→
#imm
In this mode, second byte (operand) is accessed as a data
immed iatel y.
Exam ple:
FE10: 0435 ADC #35H
When G-flag is 1, then RAM address is defined by 16-bit
address which is composed of 8-bit direct page accessable
register (DPGR) and 8-bit immediate data.
Example: G=1, DPGR=0CH
F100: E45535 LDM 35H,#55H
(3) Direct Page Addressing
→
→ →
→
dp
In this mode, a address is specified within di rect page.
Example; G=0
E551: C5 35 LDA 35H;A ←RAM[35H]
(4) Absolute Addressing
→
→ →
→
!abs
Absolute addr essing sets corr esponding memor y data to
Data , i.e. second byte(Operand I) of command becomes
lower level address and third byte (Operand II) becomes
upper level address.
With 3 bytes command, it is possible to access to whole
memory area.
ADC, AND, CMP, CMPX, CMPY, EOR, LDA, LDX,
LDY, OR, SBC, STA, STX, STY
Example;
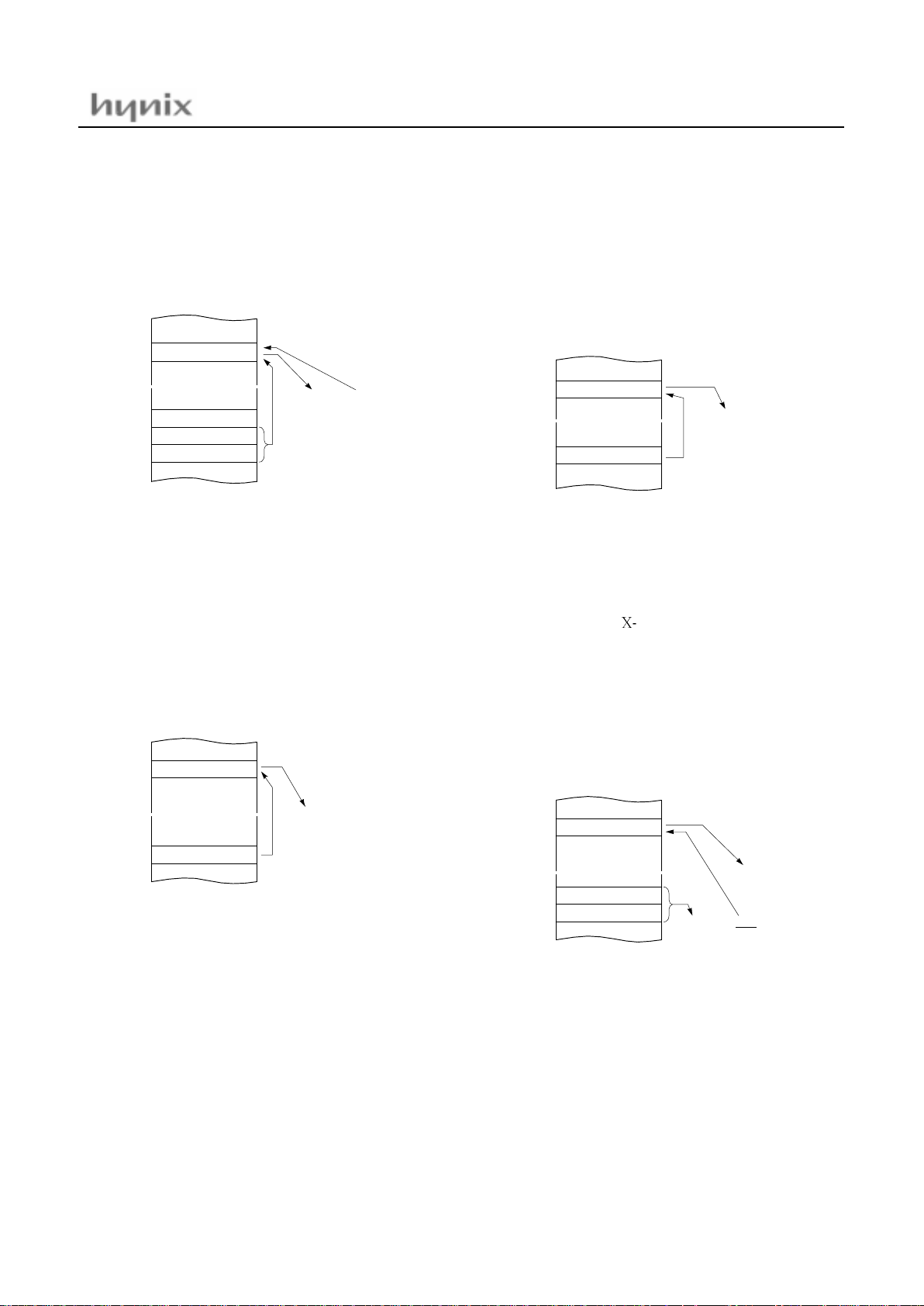
F100: 07 35 F0 ADC!0F 035H ;A ←ROM[0F035H]
35
A+35H+C → A
04
MEMORY
0FE10
H
E4
0F100
H
data
←
55H
~
~
~
~
data
0C35
H
þ
35
0F102
H
550F101
H
A
data
35
35
H
0E551
H
data → A
À
þ
~
~
~
~
C5
0E550
H
07
0F100
H
~
~
~
~
data0F035
H
P
F0
0F102
H
350F101
H
A
A+data+C → A
address: 0F035
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
27
November 2001 ver 1.2
The operation within data memory (RAM)
ASL, BIT, DEC, INC, LSR, ROL, ROR
Exam ple; A dd res sing ac cesses t he a ddre ss 0 135
H
regard-
less of G-flag and DPGR.
F100: 983501 INC!0135H ;A ←ROM[135H]
(5) Indexed Addressing
X indexe d di rec t pa g e (no of f set )
→
→ →
→
{X}
In this mode, a address is specified by the X register.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, OR, SBC, STA, XMA
Example; X=15
H
, G=1, DPGR=03
H
E550: D4 LDA {X};ACC←RAM[X].
X indexed direct page, auto increment
→
→ →
→
{X}+
In this mode, a address is specified within direct page by
the X register and the content of X is increased by 1.
LDA, STA
Example; G=0, X=35
H
F100: DB LDA {X}+
X indexed direct page (8 bit offset)
→
→ →
→
dp+X
This address value is the second byte (Operand) of command plus the data of -register. And it assigns the memory in Direct page.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR , LDA, LDY, OR, SBC, STA
STY, XMA, ASL, D EC, INC, LSR, ROL, ROR
Example; G=0, X=0F5
H
E550: C6 45 LDA 45H+X
98
0F100
H
~
~
~
~
data135
H
þ
01
0F102
H
350F101
H
À
data+1 → data
Ã
address: 0135
data
D4
315
H
0E550
H
data → A
À
þ
~
~
~
~
data
DB
35
H
data → A
À
þ
~
~
~
~
36H → X
0F100
H
data
45
3A
H
0E551
H
data → A
À
þ
~
~
~
~
C6
0E550
H
45H+0F5H=13AH
Ã
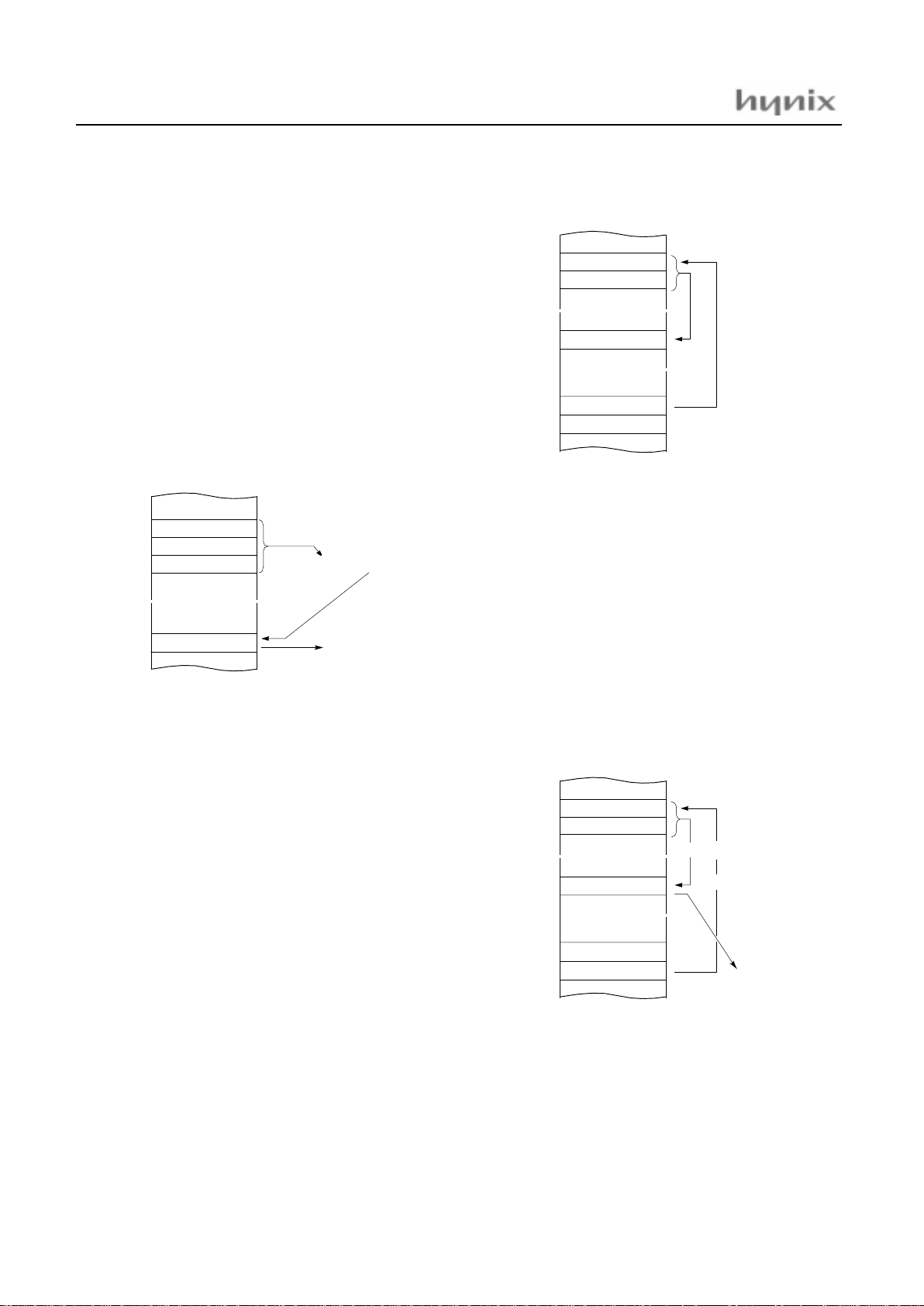
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
28
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
Y indexe d di rec t pa g e (8 bit off se t)
→
→ →
→
dp+Y
This address value is the second byte (Operand) of command plus the data of Y-register , which assign s Memory in
Direct page.
This is same with above (2). Use Y register instead of X.
Y indexed absolute
→
→ →
→
!abs+Y
Sets the value of 16 -bit absolute address plus Y-register
data as Memory. This addressing mode can specify memory in whole area.
Example; Y=55
H
F100: D500FA LDA !0FA00H+Y
(6) Indirect Addressing
Direct pa ge in di rec t
→
→ →
→
[dp]
Assigns data address to use for accomplishing command
which sets memory data(or pair memory) by Operand.
Also index can be used with Index register X,Y.
JMP, CALL
Example; G=0
FA00: 3F 35 JMP [35H]
X indexed indirect
→
→ →
→
[dp+X]
Processes memory data as Data, assigned by 16-bit pair
memory which is determined by pair data
[dp+X+1][dp+X] Operand plus X-register data in Direct
page.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, OR, SBC, STA
Example; G=0, X=10
H
FA00: 16 25 ADC [25H+X]
D5
0F100
H
data → A
þ
~
~
~
~
data
0FA55
H
0FA00H+55H=0FA55H
Ã
FA
0F102
H
00
0F101
H
À
0A
35
H
jump to address 0E30A
H
þ
~
~
~
~
35
0FA00
H
E3
36
H
À
3F
0E30A
H
NEXT
~
~
~
~
05
35
H
0E005
H
~
~
~
~
25
0FA00
H
E0
36
H
16
0E005
H
data
~
~
~
~
Ã
A + data + C → A
25 + X(10) = 35
H
þ
À
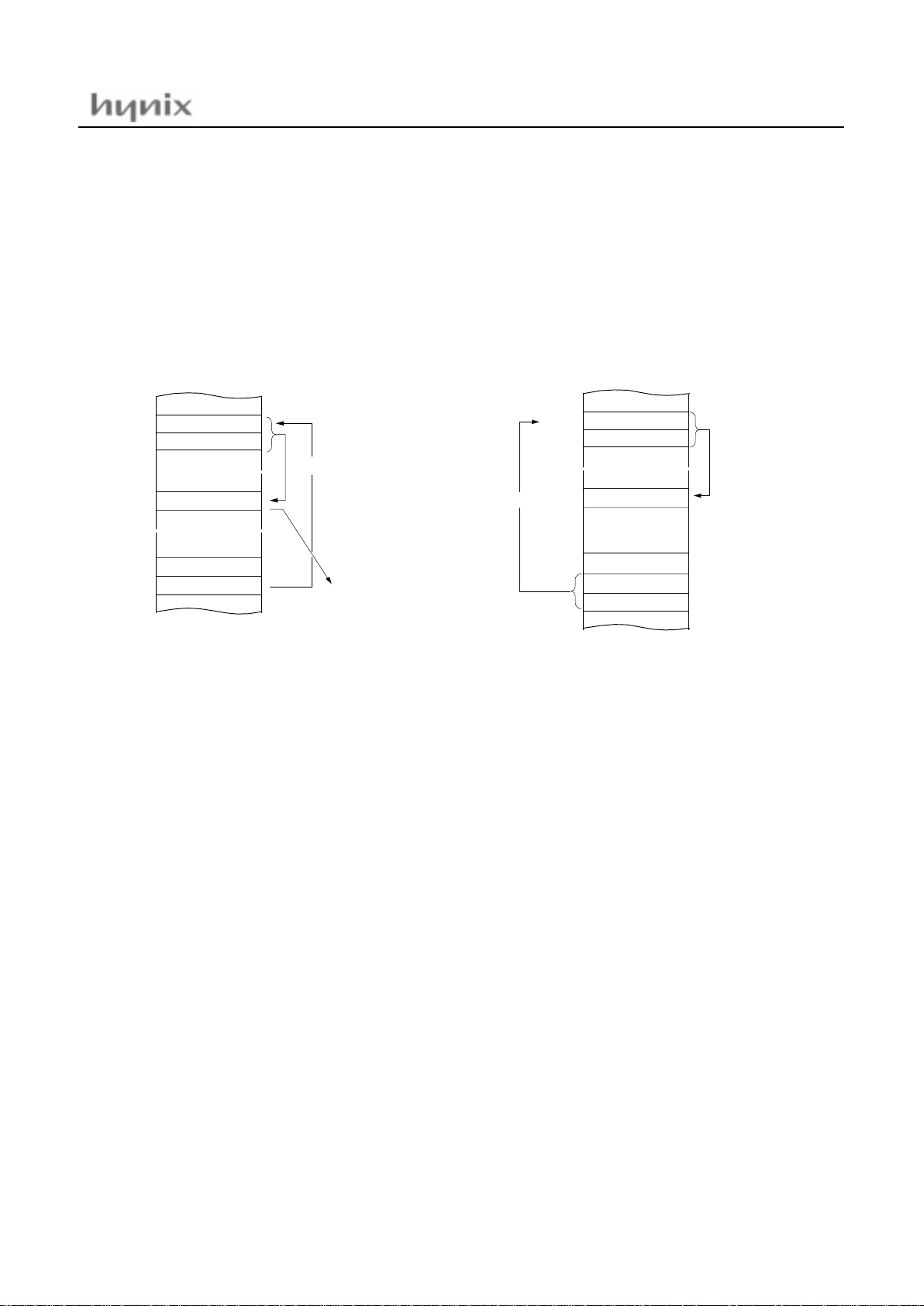
HMS81C43xx / GMS87C4060
29
November 2001 ver 1.2
Y indexed indirect
→
→ →
→
[dp]+Y
Processes momory data as Data, assigned by the data
[dp+1][dp] of 16-bit pair memory paired by Operand in Direct page plus Y-register data.
ADC, AND, CMP, EOR, LDA, OR, SBC, STA
Example; G=0, Y=10
H
FA00: 1725 ADC [25H]+Y
Absolute indirect
→
→ →
→
[!abs]
The program jumps to a ddres s speci fied by 16-b it a bsolu te
address .
JMP
Example; G=0
FA00: 1F 25 E0 JMP [!0C025 H]
05
25
H
0E005H + Y(10) = 0E015
H
þ
~
~
~
~
25
0FA00
H
E026
H
À
17
0E015
H
data
~
~
~
~
Ã
A + data + C → A
25
0E025
H
jump to
~
~
~
~
E0
0FA00
H
E70E026
H
À
25
0E725
H
NEXT
~
~
~
~
1F
PROGRAM MEMORY
þ
address 0E30A
H
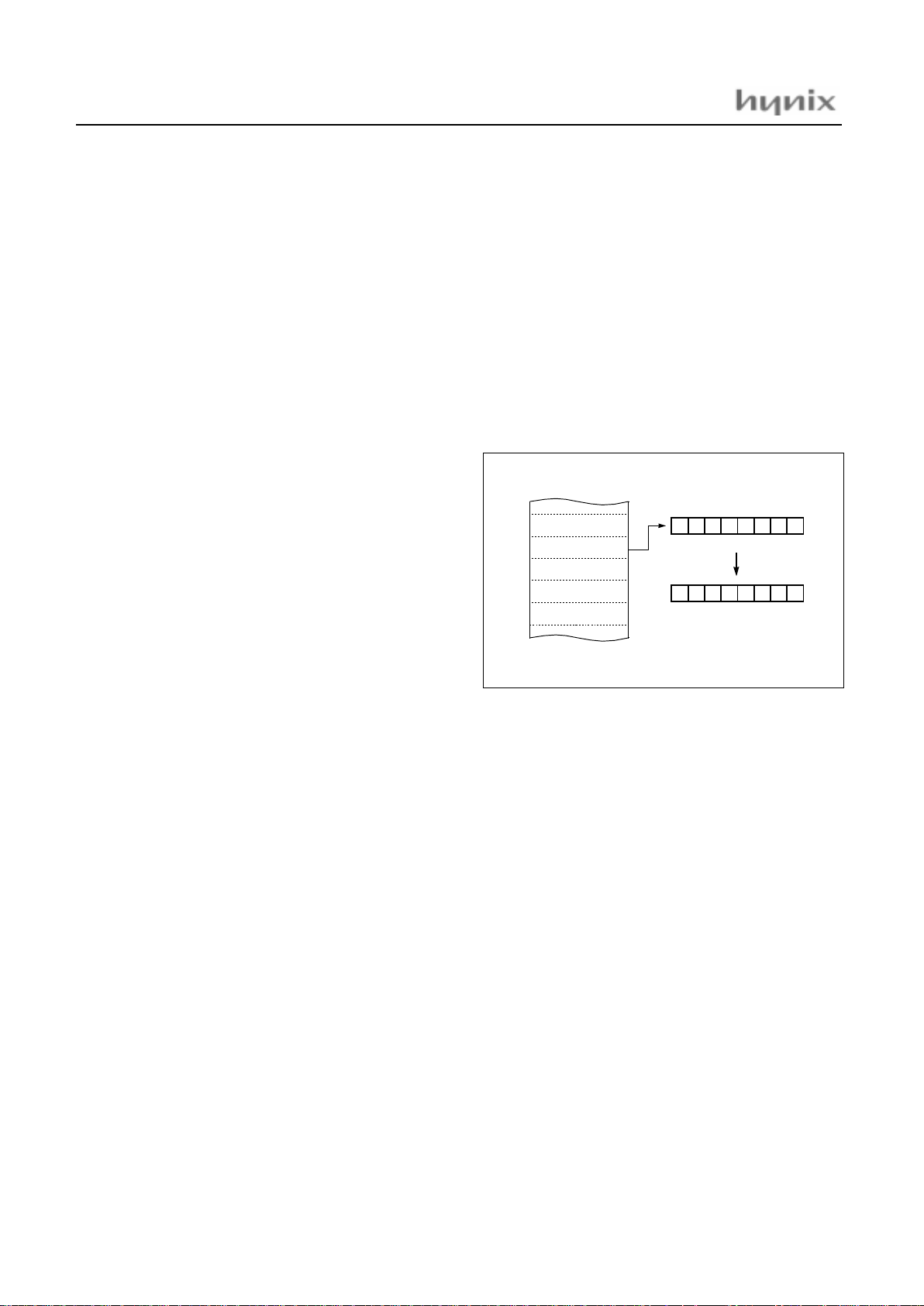
HMS8 1C 43xx / GMS87C 4060
30
Novem ber 2001 ver 1.2
9. I/O PORTS
The GMS87C4060 has digital ports (R0, R1, R2, R4, R5
and R6) and OSD ports (R,G,B), but HMS81C4 3xx has
R1, R2, R4, R5 and OSD ports (R,G,B)
These ports pins may be mul tiplexed with an alternate
function for the peripheral features on the device. In general, in a initial reset state, R ports are used as a general
purpose digital port.
9.1 Registers for Port
Port Data Registers
The Port Data Registers in I/O buffer in each R ports are
represented as a Type D fli p-flop, whic h will clo ck in a va lue from the internal bus in re spons e to a "write to data register" signa l from the CPU. T he Q outpu t of the fl ip-f lop is
placed on the internal bus in response to a "read data register" signal from the CPU. The level of the port pin itself
is placed on the internal bus in response to "read data register" signal from the CPU. Some instructions that read a
port activating the "read register" signal, and others activating the "read pin" signal
Port Direction Registers
All pi ns have data directio n registe rs which c an define
these ports as output or input. A "1" in the port direction
register c onfigure the corr esponding por t pin as output.
Conversely, write "0" to t he corresponding bit to s pecify it
as input pin. For example, to use the even numbered bit of
R0 as output ports and the odd numbered bits as input
ports, write "55
H
" to address 0C1H (R0 port direction reg-
ister) during ini tial setting as shown in F igure 9-1 .
All the port directio n registers in the HMS81C43x x/
GMS87C4060 have 0 wr itten to t hem by reset function. On
the other hand, its initial status is input.
Figure 9-1 Example of port I/O assignment
I : INPUT PORT
WRITE "55
H
" TO PORT R0 DIRECTION REGISTER
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
I O I O I O I O
R0 DATA
R4 DATA
R0 DIRECTION
R4 DIRECTION
0C0H
0C1H
0C8H
0C9H
76543210
BIT
76543210
PORT
O : OUTPUT PORT
~
~
~
~
 Loading...
Loading...