Page 1

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs
Issue 30
Date 2021-03-24
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
Page 3

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs Contents
Contents
1 General Questions................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 What Is a Quota?.................................................................................................................................................................... 1
2 Billing and Payments..............................................................................................................3
2.1 Will I Be Charged for Using the VPC Service?............................................................................................................... 3
2.2 How Is an EIP Billed? ............................................................................................................................................................ 3
2.3 How Do I Change the Billing Mode?................................................................................................................................ 4
2.4 How Do I Change the Bandwidth Billing Option from Bandwidth to
Bandwidth?..................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Trac or from Trac to
3 VPC and Subnet....................................................................................................................... 7
3.1 What Is Virtual Private Cloud?............................................................................................................................................7
3.2 Which CIDR Blocks Are Available for the VPC Service?............................................................................................. 9
3.3 How Many VPCs Can I Create?...........................................................................................................................................9
3.4 Can Subnets Communicate with Each Other?.............................................................................................................. 9
3.5 What Subnet CIDR Blocks Are Available?.......................................................................................................................9
3.6 Can I Modify the CIDR Block of a Subnet?.....................................................................................................................9
3.7 How Many Subnets Can I Create?.................................................................................................................................. 10
3.8 How Can I Delete a Subnet That Is Being Used by Other Resources?...............................................................10
3.9 How Do I Switch to a Private DNS Server?..................................................................................................................10
4 EIP............................................................................................................................................. 12
4.1 How Do I Assign or Retrieve a
4.2 What Are the Dierences Between EIP, Private IP Address, Floating IP Address, and Virtual IP Address?
............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
4.3 How Do I Access the Internet Using an EIP Bound to an Extension NIC?........................................................ 13
4.4 What Are the
4.5 Can an EIP That Uses Dedicated Bandwidth Be Changed to Use Shared Bandwidth?................................ 14
4.6 Can I Bind an EIP to Multiple ECSs?............................................................................................................................... 14
4.7 How Do I Access an ECS from the Internet After an EIP Is Bound to the ECS?.............................................. 14
4.8 What Is the EIP Assignment Policy?............................................................................................................................... 15
4.9 Can I Bind an EIP to an ECS, to Another ECS?............................................................................................................15
4.10 Does an EIP Change Over Time?.................................................................................................................................. 15
4.11 Can I Assign a
4.12 How Do I Query the Region of My EIPs?................................................................................................................... 16
4.13 Can a Bandwidth Be Used by Multiple Accounts?.................................................................................................. 16
Dierences Between the Primary and Extension NICs of ECSs?...............................................14
Specic EIP?.............................................................................................................................................16
Specic EIP?................................................................................................................12
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
Page 4

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs Contents
4.14 How Do I Change an EIP for an Instance?................................................................................................................ 16
4.15 Can I Bind an EIP to a Cloud Resource in Another Region?................................................................................ 19
5 Bandwidth............................................................................................................................... 20
5.1 What Are Inbound Bandwidth and Outbound Bandwidth?...................................................................................20
5.2 How Do I Know If My Used Bandwidth Exceeds the Limit?.................................................................................. 21
5.3 What Is the Bandwidth Size Range?.............................................................................................................................. 23
5.4 What Bandwidth Types Are Available?.......................................................................................................................... 23
5.5 What Are the
Bandwidth Be Changed to a Shared Bandwidth or the Other Way Around?.........................................................23
5.6 How Do I Buy a Shared Bandwidth?..............................................................................................................................23
5.7 Is There a Limit to the Number of EIPs That Can Be Added to Each Shared Bandwidth?..........................24
5.8 Can I Increase My Bandwidth Billed on Yearly/Monthly Basis and Then Decrease It?.................................24
5.9 What Is the Relationship Between Bandwidth and Upload/Download Rate?.................................................24
5.10 What Are the Dierences Between Static BGP and Dynamic BGP?................................................................. 24
Dierences Between a Dedicated Bandwidth and a Shared Bandwidth? Can a Dedicated
6 Connectivity............................................................................................................................ 26
6.1 Does a VPN Allow Communication Between Two VPCs?.......................................................................................26
6.2 Why Is Internet or Internal Domain Names in the Cloud Inaccessible Through Domain Names When
My ECS Has Multiple NICs?...................................................................................................................................................... 26
6.3 What Are the Constraints Related to VPC Peering?..................................................................................................27
6.4 Why Does Communication Fail Between VPCs That Are Connected by a VPC Peering Connection?.....28
6.5 How Many VPC Peering Connections Can I Create?................................................................................................ 32
6.6 What Are the Priorities of the Custom Route and EIP If Both Are
ECS to Access the Internet?...................................................................................................................................................... 32
6.7 Why Does Intermittent Interruption Occur When a Local Host Accesses a Website Built on an ECS?
............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 32
6.8 Why Do ECSs Using Private IP Addresses in the Same Subnet Only Support One-Way Communication?
............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 33
6.9 Why Does Communication Fail Between Two ECSs in the Same VPC or Packet Loss Occur When They
Communicate?.............................................................................................................................................................................. 34
6.10 Why Cannot the Virtual IP Address Be Pinged After It Is Bound to an ECS NIC?........................................37
6.11 Why Does My ECS Fail to Use Cloud-init?.................................................................................................................42
6.12 Why Does Internet Access Fail Even If My ECS Is Bound with an EIP?............................................................46
6.13 How Do I Handle the IB Network Failure?................................................................................................................50
6.14 Why Does My ECS Fail to Communicate at a Layer 2 or Layer 3 Network?.................................................52
6.15 How Do I Handle the BMS Network Failure?...........................................................................................................54
6.16 Why Does My ECS Fail to Obtain an IP Address?................................................................................................... 55
6.17 How Do I Handle the VPN or Direct Connect Connection Network Failure?................................................57
6.18 Why Does My Server Can Be Accessed from the Internet But Cannot Access the Internet?...................59
6.19 Can I Use a VPC Peering Connection to Connect VPCs in Dierent Regions?.............................................. 61
6.20 Will I Be Billed for Using a VPC Peering Connection?........................................................................................... 61
6.21 What Switches Can Connect to a L2CG on HUAWEI CLOUD?...........................................................................62
6.22 Why Is the Layer 2 Connection in the Not Connected State Even After Its Conguration Is Complete?
............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 62
Congured for an ECS to Enable the
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
Page 5

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs Contents
6.23 Why Is Communication Between the Cloud and On-premises Servers Unavailable Even When the
Layer 2 Connection Status Is Connected?........................................................................................................................... 62
6.24 Why Can't I Access Websites Using IPv6 Addresses After IPv4/IPv6 Dual Stack Is Congured?............ 62
7 Routing.................................................................................................................................... 64
7.1 How Do I
7.2 Why Can't I Ping an ECS with Two NICs Congured?.............................................................................................. 68
7.3 Can a Route Table Span Multiple VPCs?...................................................................................................................... 69
7.4 How Many Routes Can a Route Table Contain?........................................................................................................ 69
7.5 Are There Any Restrictions on Using a Route Table?............................................................................................... 69
7.6 Will a Route Table Be Billed?............................................................................................................................................ 70
7.7 Do the Same Routing Priorities Apply to Direct Connect Connections and Custom Routes in the Same
VPC?.................................................................................................................................................................................................. 70
7.8 Are There Dierent Routing Priorities of the VPN and Custom Routes in the Same VPC?........................70
Congure Policy-Based Routing for ECSs with Multiple NICs?.........................................................64
8 Security.................................................................................................................................... 71
8.1 Are the Security Group Rules Considered the Same If All Parameters Except Their Description Are the
Same?............................................................................................................................................................................................... 71
8.2 What Are the Requirements for Deleting a Security Group?................................................................................ 71
8.3 Why Is Outbound Access Through TCP Port 25 Restricted?.................................................................................. 72
8.4 Can I Change the Security Group of an ECS?..............................................................................................................73
8.5 How Many Security Groups Can I Have?......................................................................................................................73
8.6 Will a Security Group Be Billed?...................................................................................................................................... 73
8.7 How Do I
8.8 How Many Network ACLs Can I Create?...................................................................................................................... 73
8.9 Does a Security Group Rule or a Network ACL Rule Immediately Take Eect for Its Original Trac
After It Is Modied?.................................................................................................................................................................... 74
8.10 Why Are Some Ports in the Public Cloud System Inaccessible?.........................................................................74
8.11 Why Is Access from a Specic IP Address Still Allowed After a Network ACL Rule That Denies the
Access from the IP Address Has Been Added?...................................................................................................................75
8.12 What Do My Security Group Rules Not Take Eect?............................................................................................. 75
Congure a Security Group for Multi-Channel Protocols?.................................................................73
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iv
Page 6

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 1 General Questions
1 General Questions
1.1 What Is a Quota?
What Is a Quota?
A quota limits the quantity of a resource available to users, thereby preventing
spikes in the usage of the resource. For example, a VPC quota limits the number
of VPCs that can be created.
You can also request for an increase in quota if an existing quota cannot meet
your service requirements.
How Do I View My Quotas?
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. In the upper right corner of the page, choose Resources > My Quotas.
The Service Quota page is displayed.
Figure 1-1 My Quotas
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
4. View the used and total quota of each type of resources on the displayed
page.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
Page 7

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 1 General Questions
If a quota cannot meet service requirements, apply for a higher quota.
How Do I Apply for a Higher Quota?
1. Log in to the management console.
2. In the upper right corner of the page, choose Resources > My Quotas.
The Service Quota page is displayed.
Figure 1-2 My Quotas
3. Click Increase Quota.
4. On the Create Service Ticket page, congure parameters as required.
In Problem Description area,
5. After all necessary parameters are congured, select I have read and agree
to the Tenant Authorization Letter and Privacy Statement and click
Submit.
ll in the content and reason for adjustment.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
Page 8

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 2 Billing and Payments
2 Billing and Payments
2.1 Will I Be Charged for Using the VPC Service?
The VPC service is free of charge. However, EIP and bandwidth used together with
a VPC will be billed based on standard pricing.
2.2 How Is an EIP Billed?
EIPs can be billed on a yearly/monthly or pay-per-use basis.
Table 2-1 EIP billing details
Billing
Mode
Yearly/
Monthly
Pay-per-use Bandwidth EIP retention fee is not
Billed By EIP Retention Fee Bandwidth
Bandwidth - Included Not
Trac Not
included if the EIP is
bound to an ECS, BMS,
or load balancer.
EIP retention fee is
included if the EIP is
unbound but not
released.
Public
Price
Included Not
included
Network
Trac
Price
included
included
Included
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
Page 9

NO TE
NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 2 Billing and Payments
● "Not included" indicates that the fee will not be included in the bill. "Included" indicates
that the fee will be included in the bill.
● For details about the EIP pricing, see Product Pricing Details.
2.3 How Do I Change the Billing Mode?
Changing the Billing Mode from Pay-per-Use to Yearly/Monthly
You can change the billing mode of pay-per-use EIPs and shared bandwidth billed
by bandwidth to yearly/monthly. After the change is successful, the new billing
mode will take eect immediately.
You can change the billing mode on the EIP console. Do as follows to change the
billing mode of an EIP from pay-per-use to yearly/monthly.
The billing mode of an EIP that is billed by trac on a pay-per-use basis cannot be directly
changed to yearly/monthly. Change the EIP to be billed by bandwidth and then change its
billing mode to yearly/monthly.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Under Network, click Elastic IP.
3. On the displayed page, search for the pay-per-use EIP whose billing mode is
to be changed.
4. Locate the row that contains the target EIP and click Change Billing Mode in
the Operation column.
Figure 2-1 Changing the billing mode on the EIP console
5. Click Yes.
6. Set specications.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
Page 10

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 2 Billing and Payments
Figure 2-2 Setting specications
7. Click Submit and Pay.
You can also select multiple EIPs and click Change Billing Mode above the EIP list
to change the billing mode of all selected EIPs at the same time.
Changing the Billing Mode from Yearly/Monthly to Pay-per-Use
The billing mode of yearly/monthly EIPs and shared bandwidths can be changed
to pay-per-use. The new billing mode takes
the EIPs or bandwidths expires.
The billing mode of an EIP can be changed from yearly/monthly to pay-per-use in
the billing center. Do as follows to change the billing mode of an EIP from yearly/
monthly to pay-per-use:
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Choose Billing > Renewal.
Figure 2-3 Renewal
eect only after the validity period of
3. In the search box on the right, search for the EIP whose billing mode you
want to change.
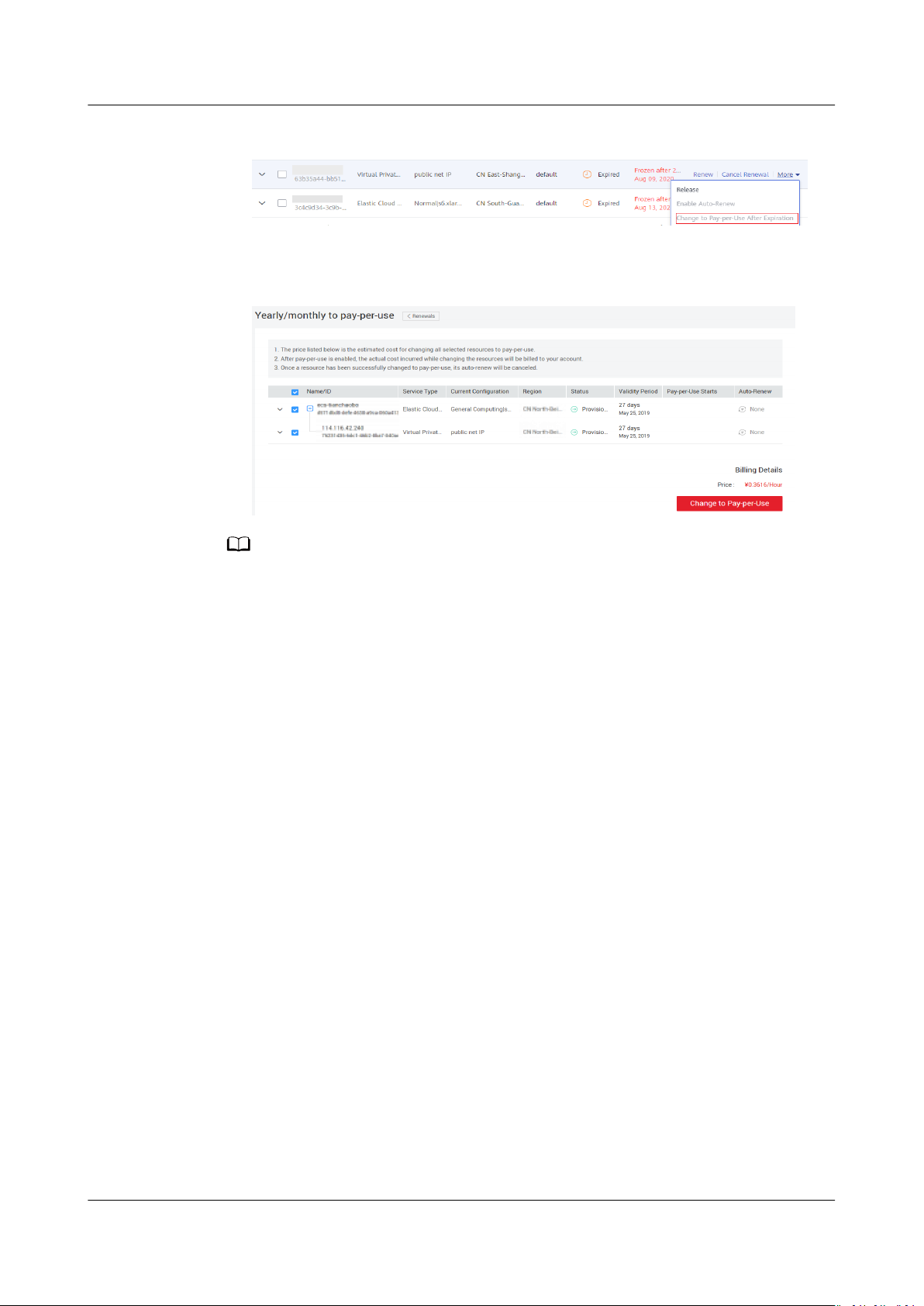
4. Locate the row that contains the target EIP and click Change to Pay-per-Use
After Expiration in the Operation column.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
Page 11
NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 2 Billing and Payments
Figure 2-4 Changing the billing mode to pay-per-use
5. In the page that is displayed, click the Change to Pay-per-Use button.
Figure 2-5 Conrming the change
The EIP remains the same after the billing mode is changed.
2.4 How Do I Change the Bandwidth Billing Option
from Bandwidth to Trac or from Trac to
Bandwidth?
● The billing option can be changed only when the billing mode is Pay-per-use.
For details, see Modifying EIP Bandwidth.
● A yearly/monthly resource can only be billed by bandwidth.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
Page 12

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 3 VPC and Subnet
3 VPC and Subnet
3.1 What Is Virtual Private Cloud?
The Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) service enables you to provision logically isolated,
congurable, and manageable virtual networks for cloud servers, cloud containers,
and cloud databases, improving cloud service security and simplifying network
deployment.
Within your own VPC, you can create security groups and VPNs,
address ranges, specify bandwidth sizes, manage the networks in the VPC, and
make changes to these networks as needed, quickly and securely. You can also
dene rules for communication between ECSs in the same security group or in
dierent security groups.
Product Architecture
The product architecture consists of the VPC components, security features, and
VPC connectivity options.
congure IP
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
Page 13

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 3 VPC and Subnet
Figure 3-1 Architecture
VPC Components
Each VPC consists of a private CIDR block, route tables, and at least one subnet.
● Private CIDR block: When creating a VPC, you need to specify the private CIDR
block used by the VPC. The VPC service supports the following CIDR blocks:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255, 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255, and 192.168.0.0 –
192.168.255.255
● Subnet: Cloud resources, such as ECSs and databases, must be deployed in
subnets. After you create a VPC, divide the VPC into one or more subnets.
Each subnet must be within the VPC. For more information, see Subnet.
● Route table: When you create a VPC, the system automatically generates a
default route table. The route table ensures that all subnets in the VPC can
communicate with each other. If the routes in the default route table cannot
meet application requirements (for example, an ECS without an elastic IP
address (EIP) bound needs to access the Internet), you can create a custom
route table. For more information, see Example Custom Route in a VPC and
Example Custom Route Outside a VPC.
Security Features
Security groups and network ACLs ensure the security of cloud resources deployed
in a VPC. A security group acts as a virtual
rewall to provide access rules for
instances that have the same security requirements and are mutually trusted in a
VPC. For more information, see Security Group Overview. A network ACL can be
associated with subnets that have the same access control requirements. You can
add inbound and outbound rules to precisely control inbound and outbound
trac
at the subnet level. For more information, see Network ACL Overview.
VPC Connectivity
HUAWEI CLOUD provides multiple VPC connectivity options to meet diverse
requirements. For details, see Application Scenarios.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
Page 14

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 3 VPC and Subnet
● VPC Peering allows two VPCs in the same region to communicate with each
other using private IP addresses.
● Elastic IP or NAT Gateway allows ECSs in a VPC to communicate with the
Internet.
● Virtual Private Network (VPN), Cloud Connect, or Direct Connect can connect
a VPC to your data center.
3.2 Which CIDR Blocks Are Available for the VPC Service?
The VPC service supports the following CIDR blocks:
● 10.0.0.0/8-24
● 172.16.0.0/12-24
● 192.168.0.0/16-24
3.3 How Many VPCs Can I Create?
By default, you can create a maximum of
of VPCs cannot meet your service requirements, submit a service ticket to
request a quota increase.
ve VPCs in your account. If the number
3.4 Can Subnets Communicate with Each Other?
Subnets in the same VPC can communicate with each other while subnets in
dierent VPCs cannot communicate with each other by default. However, you can
create VPC peering connections to enable subnets in
communicate with each other.
If a subnet is associated with a network ACL, congure network ACL rules to allow
communication between subnets.
dierent VPCs to
3.5 What Subnet CIDR Blocks Are Available?
A subnet CIDR block must be included in its VPC CIDR block. Supported VPC CIDR
blocks are 10.0.0.0/8–24, 172.16.0.0/12–24, and 192.168.0.0/16–24. The allowed
block size of a subnet is between the netmask of its VPC CIDR block and the /28
netmask.
3.6 Can I Modify the CIDR Block of a Subnet?
You can modify the CIDR block of a subnet only when you are creating the subnet.
After the subnet is created, you cannot modify its CIDR block.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
Page 15

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 3 VPC and Subnet
3.7 How Many Subnets Can I Create?
By default, you can create a maximum of 100 subnets in your cloud account. If the
number of subnets cannot meet your service requirements, submit a service
ticket to request a quota increase.
3.8 How Can I Delete a Subnet That Is Being Used by Other Resources?
The VPC service allows you to create private, isolated virtual networks. In a VPC,
you can manage private IP address ranges, subnets, and gateways. ECSs, BMSs,
databases, and some other applications can use subnets created in VPCs.
A subnet cannot be deleted if it is being used by other resources. You must delete
all resources in the subnet before you can delete the subnet.
You can view all resources of your account on the console homepage and check
the resources that are in the subnet you want to delete.
The resources may include:
● ECS
● CCI instance
● Load balancer
● VPN
● Private IP address
● Custom route
● NAT gateway
● VPC endpoint and VPC endpoint service
If you cannot delete a subnet even after deleting all the resources it contains,
submit a service ticket.
3.9 How Do I Switch to a Private DNS Server?
ECSs use private DNS servers for domain name resolution in VPCs. ECSs in a VPC
can access the Internet using public domain names and other cloud services like
OBS and SMN through private DNS servers, with no need to connect to the
Internet.
For VPCs created earlier before private domain names are available, a public DNS
server (114.114.114.114) is
private domain names, you can change the public DNS server to the private DNS
servers
private DNS server address, see What Are the Private DNS Server Addresses
Provided by the DNS Service?
Perform the operations provided in this section to change the public DNS servers
to private DNS servers.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
congured for the VPC subnets. For instructions about how to obtain a
congured. To allow ECSs in these VPCs to access
Page 16
NO TICE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 3 VPC and Subnet
Checking the DNS Server Addresses of an ECS
1. Log in to the management console.
2. In the Computing category, click Elastic Cloud Server.
The Elastic Cloud Server page is displayed.
3. In the ECS list, click the ECS name.
4. On the ECS details page, click the VPC name.
The Virtual Private Cloud page is displayed.
5. Locate the target VPC and click the number in the Subnets column.
The Subnets page is displayed.
6. Click the name of the target subnet.
In the Gateway and DNS Information area, view the DNS server addresses
used by the ECS.
Changing the DNS Servers for a VPC Subnet
If the ECS uses default public DNS servers, change them to private DNS servers
provided by the DNS service.
1. In the Gateway and DNS Information area, click
Address.
2. Change the DNS server addresses to private DNS server addresses.
For example, in the CN North-Beijing1 region, change the DNS server
addresses of a VPC subnet to 100.125.1.250 and 100.125.21.250.
Updating the DNS Server Addresses for the ECS
New DNS server addresses will not take
The DNS server addresses needs to be updated rst. There are two ways to do
this:
● Restart the OS. The ECS will then obtain the new DNS server addresses from
the DHCP server.
Restarting the OS will interrupt services on the ECS. Perform this operation
during o-peak hours.
Alternatively, wait for the DHCP lease to expire, which takes 24 hours by
default. After the lease time expires, the DHCP server allocates another IP
address and updates the DNS server addresses to the ECS.
eect immediately on the ECS.
next to DNS Server
● Manually change the DNS congurations on the ECS.
If DHCP is disabled on the ECS, manually update DNS congurations.
For example, if the ECS is running Linux, change the DNS congurations by
editing the /etc/resolv.conf
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
le.
Page 17

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
4 EIP
4.1 How Do I Assign or Retrieve a Specic EIP?
If you want to retrieve an EIP that you have released or assign a specic EIP, you
can use APIs. When assigning an EIP, set the value of ip_address to the IP address
that you want to assign. For details, see Elastic IP API Reference.
● If the EIP has been assigned to another user, you will fail to assign your required EIP.
● You cannot use the management console to assign a specic EIP.
4.2 What Are the Dierences Between EIP, Private IP
Address, Floating IP Address, and Virtual IP Address?
An EIP is an IP address that can be accessed over the Internet. Each EIP can be
used by only one ECS at a time.
A private IP address is used on the private network of the public cloud for private
communications. It cannot be reached from the Internet.
oating IP address is similar to an EIP. They are both public IP addresses that are
A
used to connect to the Internet, but a oating IP address API cannot be used to
congure bandwidth parameters. For details, see Floating IP Address.
A virtual IP address can be shared among multiple ECSs. A virtual IP address is
used for active/standby switchover of ECSs for higher availability. If the active ECS
becomes faulty and cannot provide services, the virtual IP address is dynamically
re-assigned to the standby ECS so services can continue uninterrupted. For details,
see Virtual IP Address Overview.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Page 18
NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
4.3 How Do I Access the Internet Using an EIP Bound to an Extension NIC?
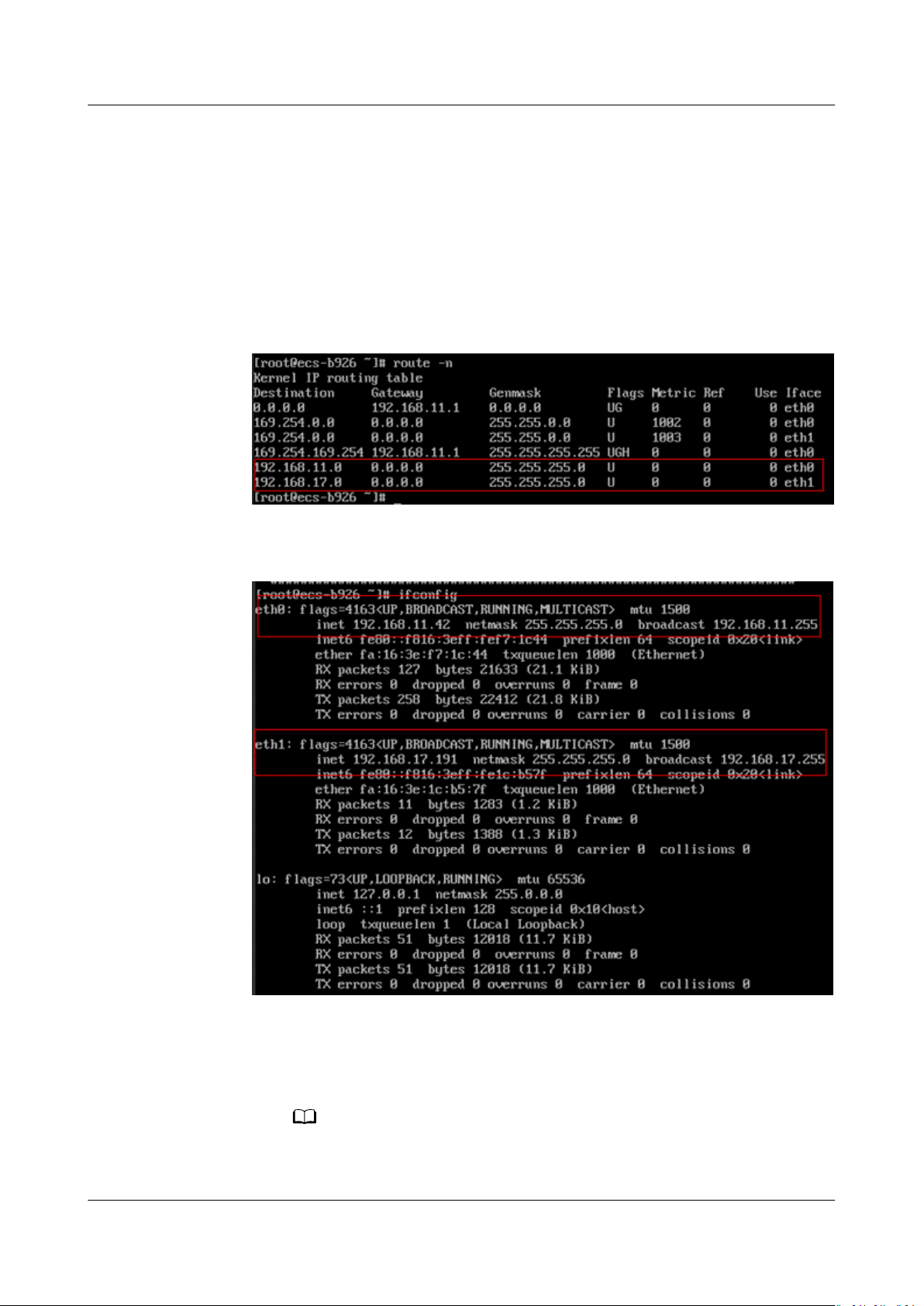
1. After an EIP is bound to an extension NIC, log in to the ECS and run the route
command to query the route.
You can run route --help to learn more about the route command.
Figure 4-1 Viewing route information
2. Run the ifcong command to view NIC information.
Figure 4-2 Viewing NIC information
3. Enable access to the Internet through the extension NIC by default.
a. Run the following command to delete the default route of the primary
NIC:
route del 0.0.0.0 192.168.11.1 dev eth0
This operation will interrupt ECS communication. It is recommended that you
perform the conguration by following step 4.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Page 19

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
b. Run the following command to congure the default route for the
extension NIC:
route add default gw 192.168.17.1
4.
Congure Internet access from the extension NIC based on your destination
address.
Run the following command to congure access to a specied CIDR block (for
example,
You can
route add -net xx.xx.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 gw 192.168.17.1
xx.xx
.0.0/16) through the extension NIC:
congure the CIDR block as required.
4.4 What Are the Dierences Between the Primary and
Extension NICs of ECSs?
The dierences are as follows:
● Generally, the OS default routes preferentially use the primary NICs. If the OS
default routes use the extension NICs, network communication will be
interrupted. Then, you can check the route
network communication error.
● Primary NICs can communicate with the public service zone (zone where PaaS
and DNS services are deployed). Extension NICs cannot communicate this
zone.
conguration to rectify the
4.5 Can an EIP That Uses Dedicated Bandwidth Be Changed to Use Shared Bandwidth?
No. An EIP that uses a dedicated bandwidth cannot be changed to use a shared
bandwidth.
In addition, an EIP that uses a shared bandwidth cannot be changed to use a
dedicated bandwidth.
4.6 Can I Bind an EIP to Multiple ECSs?
Each EIP can be bound to only one ECS at a time.
Multiple ECSs cannot share the same EIP. An ECS and its bound EIP must be in the
same region. If you want multiple ECSs in the same VPC to share an EIP, you have
to use a NAT gateway. For more information, see NAT Gateway User Guide.
4.7 How Do I Access an ECS from the Internet After an EIP Is Bound to the ECS?
Each ECS is automatically added to a security group after being created to ensure
its security. The security group denies access
(except TCP trac from port 22 through SSH to the Linux OS and TCP trac from
trac from the Internet by default
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Page 20

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
port 3389 through RDP to the Windows OS). To allow external access to ECSs in
the security group, add an inbound rule to the security group.
You can set Protocol to TCP, UDP, ICMP, or All as required on the page for
creating a security group rule.
● If the ECS needs to be accessible over the Internet and the IP address used to
access the ECS over the Internet has been
does not need to be accessible over the Internet, set Source to the IP address
range containing the IP address that is allowed to access the ECS over the
Internet.
● If the ECS needs to be accessible over the Internet and the IP address used to
access the ECS over the Internet has not been
recommended that you retain the default setting 0.0.0.0/0 for Source, and
then set Port Range to improve network security.
● Allocate ECSs that have dierent Internet access policies to dierent security
groups.
The default source IP address 0.0.0.0/0 indicates that all IP addresses can access ECSs
in the security group.
congured on the ECS, or the ECS
congured on the ECS, it is
4.8 What Is the EIP Assignment Policy?
By default, EIPs are assigned randomly.
In case that an EIP is released by mistake, the system will assign you the EIP that
you have released in the last 24 hours preferentially.
If you want an EIP that you released 24 hours ago, see How Do I Assign or
Retrieve a Specic EIP?
If you do not want an EIP that you have released, it is recommended that you buy
another EIP
rst and then release the one that you do not want.
4.9 Can I Bind an EIP to an ECS, to Another ECS?
Yes.
Unbind the EIP from the current ECS. For details, see Unbinding or Releasing an
EIP.
Then, bind the EIP to another ECS. For details, see Binding an EIP to Cloud
Resources.
Another related operation is to change the EIP associated with an ECS.
For details, see Changing an EIP.
4.10 Does an EIP Change Over Time?
EIPs will not be changed after they are assigned.
Stopping and starting an ECS does not aect its EIP.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
Page 21

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
An EIP will be released if it expires or if the EIP owner's account is in arrears.
4.11 Can I Assign a Specic EIP?
By default, EIPs are assigned randomly. If you have released EIPs before, the
system preferentially assigns an EIP from what you released.
Certain APIs need to be called to assign
EIP.
specic EIPs. For details, see Assigning an
4.12 How Do I Query the Region of My EIPs?
You can visit https://en.ipip.net/?origin=CN to query the region of your EIPs.
● The region of an EIP identied using a third-party website may be dierent
from the region that the EIP belongs to.
● If the region identied using another third-party website is dierent from the
one identied using https://en.ipip.net/?origin=CN, use the region identied
using https://en.ipip.net/?origin=CN.
● If the region identied using https://en.ipip.net/?origin=CN is dierent from
the one you selected when purchasing the EIP, use the region you had
selected during EIP purchase.
● If your service is adversely
determined, submit a service ticket.
To know more about the region of EIPs, submit a service ticket.
aected because the region of your EIP cannot be
4.13 Can a Bandwidth Be Used by Multiple Accounts?
A bandwidth cannot be shared between dierent accounts. Each account can use
and manage only its own EIP bandwidths.
4.14 How Do I Change an EIP for an Instance?
Scenario 1: Changing an EIP for an ECS
1. Unbind an EIP.
a. Log in to the management console.
b. On the console homepage, under Network, click Elastic IP.
c. On the displayed page, locate the row that contains the target EIP, and
click Unbind.
d. Click Yes.
2. Assign an EIP.
a. Log in to the management console.
b. On the console homepage, under Network, click Elastic IP.
c. On the displayed page, click Buy EIP.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
Page 22

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
d. Set the parameters as prompted.
e. Click Next.
3. Bind the new EIP to the ECS.
a. On the EIPs page, locate the row that contains the target EIP, and click
Bind.
b. Select the desired ECS.
c. Click OK.
4. Release the EIP that has been replaced.
a. Release a single EIP.
i. Log in to the management console.
ii. On the console homepage, under Network, click Elastic IP.
iii. In the EIP list, locate the row that contains the target EIP, and click
Release.
iv. Click Yes.
b. Unbind multiple EIPs at a time.
i. Log in to the management console.
ii. On the console homepage, under Network, click Elastic IP.
iii. In the EIP list, select the EIPs to be unbound.
iv. Click Unbind above the EIP list.
v. Click Yes.
Scenario 2: Changing an EIP for a Load Balancer
1. Unbind an EIP.
a. Log in to the management console.
b. Click Service List. Under Network, click Elastic Load Balance.
c. In the load balancer list, locate the target load balancer and choose More
> Unbind EIP in the Operation column.
d. Click Yes.
2. Assign an EIP. For details, see 2.
3. Bind the new EIP to the load balancer.
a. Log in to the management console.
b. Click Service List. Under Network, click Elastic Load Balance.
c. In the load balancer list, locate the target load balancer and choose More
> Bind EIP in the Operation column.
d. In the Bind EIP dialog box, select the EIP to be bound and click OK.
4. Release the EIP that has been replaced. For details, see 4.
Scenario 3: Changing an EIP for a NAT Gateway
1. Assign an EIP. For details, see 2.
2. Modify an SNAT rule.
For details about how to modify an SNAT rule, see Modifying an SNAT Rule.
In the EIP area, select the newly assigned EIP and deselect the original EIP
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
Page 23

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
(ensure that the deselected EIP belongs to the IP address range on Telefonica
Open Cloud).
Figure 4-3 Selecting the newly assigned EIP
3. Modify a DNAT rule.
For details about how to modify a DNAT rule, see Modifying a DNAT Rule.
In the EIP area, select the newly assigned EIP (ensure that the original EIP
belongs to the IP address range on Telefonica Open Cloud).
Figure 4-4 Selecting the newly assigned EIP
4. Release the EIP that has been replaced. For details, see 4.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
Page 24

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 4 EIP
4.15 Can I Bind an EIP to a Cloud Resource in Another Region?
No. EIPs and their associated cloud resources must be in the same region. For
example, an EIP in the CN North-Beijing1 region cannot be bound to a resource
in the CN North-Beijing4 region.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
Page 25

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 5 Bandwidth
5 Bandwidth
5.1 What Are Inbound Bandwidth and Outbound Bandwidth?
Inbound bandwidth: refers to the bandwidth consumed when data is transferred
from the Internet to HUAWEI CLOUD. For example, resources are downloaded
from the Internet to ECSs in the cloud.
Outbound bandwidth: refers to the bandwidth consumed when data is transferred
from HUAWEI CLOUD to the Internet. For example, the ECSs in the cloud provide
services accessible from the Internet and external users download resources from
the ECSs.
Figure 5-1 Inbound bandwidth and outbound bandwidth
HUAWEI CLOUD only bills for the outbound bandwidth.
Inbound and outbound bandwidths have been adjusted as follows since July 31, 2020
00:00:00 GMT+08:00:
● If your purchased or
inbound bandwidth will be 10 Mbit/s, and the outbound bandwidth will be the same
as the purchased or modied bandwidth.
● If your purchased or modied bandwidth is greater than 10 Mbit/s, both the inbound
and the outbound bandwidth will be the same as the purchased or modied
bandwidth.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
modied bandwidth is less than or equal to 10 Mbit/s, the
Page 26

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 5 Bandwidth
5.2 How Do I Know If My Used Bandwidth Exceeds the Limit?
Symptom
The bandwidth size congured when you buy a dedicated or shared bandwidth is
the upper limit of the outbound bandwidth. If the
bound for the Internet is not transferred smoothly, check whether the outbound
bandwidth of the EIP bound to the ECS is greater than the congured bandwidth
size.
If the outbound bandwidth exceeds the congured bandwidth size, packet loss may occur.
To prevent data loss, it is recommended that you monitor the bandwidth.
Troubleshooting
trac of your web application
The following fault causes are sequenced based on their occurrence probability.
If the fault persists after you have ruled out a cause, check other causes.
Figure 5-2 Troubleshooting
Table 5-1 Troubleshooting
Possible Cause
System processes
leading to high
bandwidth
Solution
See System Processes Leading to High Bandwidth
Usage
Improper Cloud Eye
alarm rules
EIP connection failure See Why Does Internet Access Fail Even If My ECS Is
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
See Improper Cloud Eye Alarm Rules
Bound with an EIP?
Page 27
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 5 Bandwidth
System Processes Leading to High Bandwidth Usage
If some heavy-duty system processes or applications running on your ECS are
causing the high bandwidth or CPU usage, your ECS will run slowly or become
inaccessible unexpectedly.
You can visit the following links to locate the processes that have led to
excessively high bandwidth or CPU usage, and optimize or stop the processes.
● Troubleshooting High Bandwidth or CPU Usage of a Windows ECS
● Troubleshooting High Bandwidth or CPU Usage of a Linux ECS
Improper Cloud Eye Alarm Rules
In the case that you have created alarm rules for bandwidth usage on the Cloud
Eye console, if the outbound bandwidth limit or the alarm period is set too small,
the system may generate alarms frequently.
You need to set an appropriate alarm rule based on your purchased bandwidth.
For example, if your purchased bandwidth is 5 Mbit/s, you can create an alarm
rule to report an alarm when the maximum outbound bandwidth is greater than
or equal to 4.8 Mbit/s in three consecutive periods. You can also increase your
bandwidth.
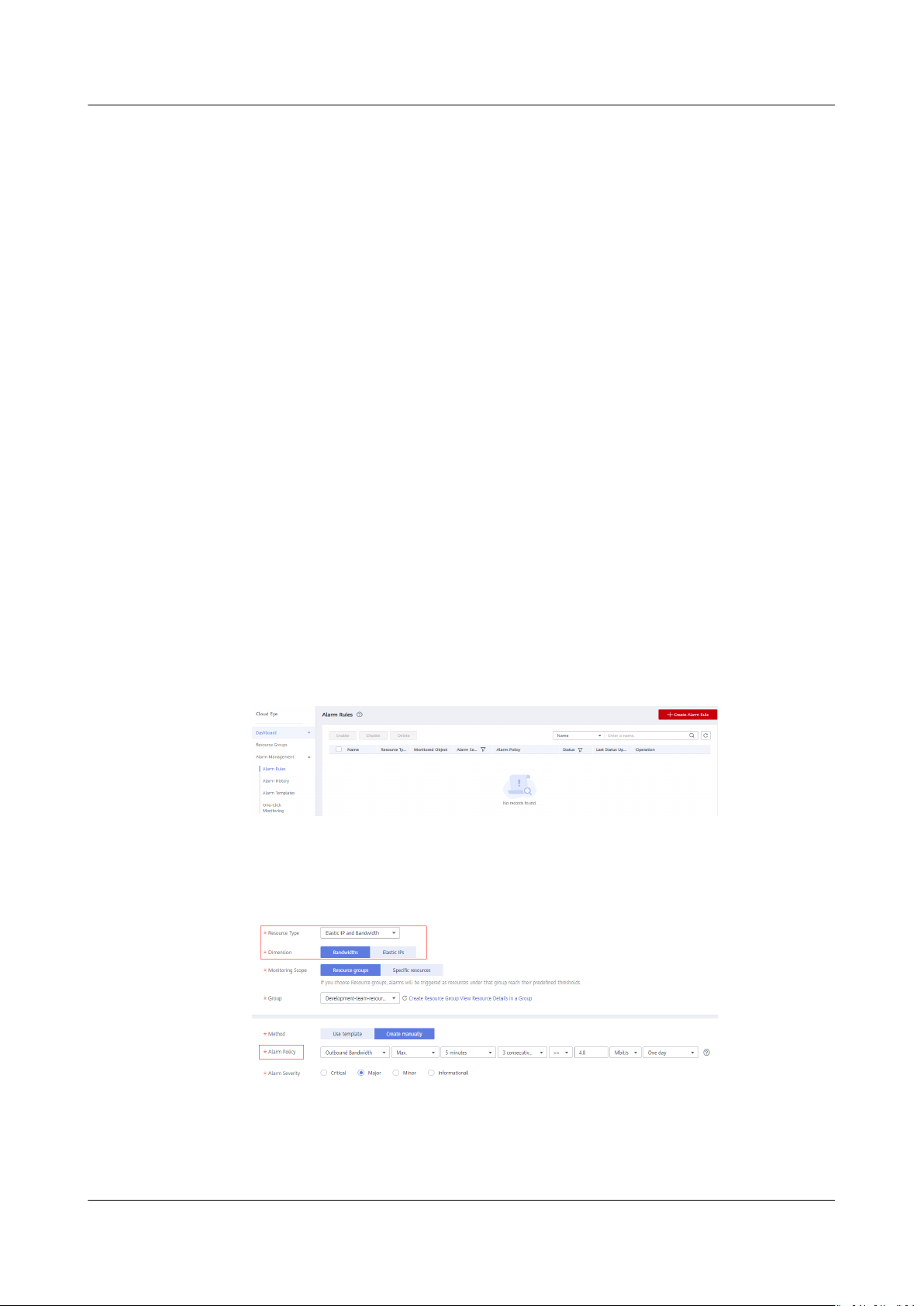
1. Log in to the management console, under Management & Deployment, click
Cloud Eye. On the Cloud Eye console, choose Alarm Management > Alarm
Rules.
Figure 5-3 Alarm Rules
2. Click Create Alarm Rule and congure an alarm rule to generate alarms
when the bandwidth exceeds the limit.
Figure 5-4 Creating an alarm rule
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
Page 28

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 5 Bandwidth
5.3 What Is the Bandwidth Size Range?
The bandwidth ranges from 1 Mbit/s to 2000 Mbit/s.
The bandwidth in regions LA-Mexico City1 and LA-Sao Paulo1 ranges from 1
Mbit/s to 1000 Mbit/s.
5.4 What Bandwidth Types Are Available?
There are dedicated bandwidth and shared bandwidth. A dedicated bandwidth can
only be used by one EIP, whereas a shared bandwidth can be used by multiple
EIPs.
5.5 What Are the Dierences Between a Dedicated
Bandwidth and a Shared Bandwidth? Can a Dedicated
Bandwidth Be Changed to a Shared Bandwidth or the
Other Way Around?
Dedicated bandwidth: The bandwidth can only be used by one EIP and the EIP can
only be used by one cloud resource, such as an ECS, a NAT gateway, or a load
balancer.
Shared bandwidth: The bandwidth can be shared by multiple pay-per-use EIPs.
Adding an EIP to or removing an EIP from a shared bandwidth does not
your workloads.
A dedicated bandwidth cannot be changed to a shared bandwidth or the other
way around. You can purchase a shared bandwidth for your pay-per-use EIPs.
● After you add an EIP to a shared bandwidth, the EIP will use the shared
bandwidth.
● After you remove an EIP from a shared bandwidth, the EIP will use the
dedicated bandwidth.
aect
5.6 How Do I Buy a Shared Bandwidth?
1. Log in to the management console.
2. On the console homepage, under Network, click Virtual Private Cloud.
3. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Elastic IP and Bandwidth >
Shared Bandwidths.
4. In the upper right corner, click Buy Shared Bandwidth. On the displayed
congure parameters as prompted to buy a shared bandwidth.
page,
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
Page 29

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 5 Bandwidth
5.7 Is There a Limit to the Number of EIPs That Can Be Added to Each Shared Bandwidth?
A maximum of 20 EIPs can be added to each shared bandwidth. If you want to
add more EIPs to each shared bandwidth, submit a service ticket to request a
quota increase.
5.8 Can I Increase My Bandwidth Billed on Yearly/ Monthly Basis and Then Decrease It?
You can increase bandwidth for a yearly/monthly EIP any time you want to, and
the change takes
the EIP subscription, and the decreased bandwidth will take
billing cycle. For details, see Modifying EIP Bandwidth.
eect immediately. But you can only decrease it when you renew
eect in the new
5.9 What Is the Relationship Between Bandwidth and Upload/Download Rate?
The bandwidth unit is bit/s, which is the number of binary bits transmitted per
second. The unit of the download rate is byte/s, which is the number of bytes
transmitted per second.
1 byte = 8 bits, that is, download rate = bandwidth/8
If the bandwidth is 1 Mbit/s, the actual upload or download rate is generally lower
than 125 kByte/s (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 Kbit/s, upload or download rate = 1,000/8 =
125 kByte/s) in consideration of losses, such as computer performance, network
device quality, resource usage, and network peak hours.
5.10 What Are the
Dierences Between Static BGP and
Dynamic BGP?
dierences between static BGP and dynamic BGP are as follows:
The
Table 5-2 Dierences between static BGP and dynamic BGP
Aspect
Static BGP Dynamic BGP
Denition Static routes are manually
congured and must be
manually recongured any time
the network topology or link
status changes.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
Dynamic BGP provides automatic
failover and chooses the optimal
path based on the real-time
network conditions as well as
preset policies.
Page 30

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 5 Bandwidth
Aspect Static BGP Dynamic BGP
AssuranceWhen changes occur on a
network that uses static BGP,
the manual conguration takes
some time and high availability
cannot be guaranteed.
NOTE
If you select static BGP, your
application system must have
disaster recovery setups in place.
When a fault occurs on a carrier's
link, dynamic BGP will quickly
select another optimal path to
take over services, ensuring
service availability.
Currently, carriers in China that
support dynamic BGP routing
include China Telecom, China
Mobile, China Unicom, China
Education and Research Network
(CERNET), National Radio and
Television Administration, and Dr.
Peng Group.
Service
99% 99.95%
availabilit
y
Billing Their price from least to most expensive: static BGP, dynamic BGP.
For details, see EIP Pricing Details.
For more information about service availability, see Huawei Cloud Service Level
Agreement.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
Page 31

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
6 Connectivity
6.1 Does a VPN Allow Communication Between Two VPCs?
If the two VPCs are in the same region, you can use a VPC peering connection to
enable communication between them.
If the two VPCs are in dierent regions, you can use a VPN to enable
communication between the VPCs. The CIDR blocks of the two VPCs are the local
and remote subnets, respectively.
6.2 Why Is Internet or Internal Domain Names in the Cloud Inaccessible Through Domain Names When My ECS Has Multiple NICs?
When an ECS has more than one NIC, if
congured for the subnets used by the NICs, the ECS cannot access the Internet or
internal domain names in the cloud.
You can resolve this issue by
subnets used by the same ECS. You can perform the following steps to modify
DNS server addresses of subnets in a VPC:
1. Log in to the management console.
conguring the same DNS server address for the
dierent DNS server addresses are
2. On the console homepage, under Network, click Virtual Private Cloud.
3. In the navigation pane on the left, click Virtual Private Cloud.
4. On the Virtual Private Cloud page, locate the VPC for which a subnet is to
be modied and click the VPC name.
5. In the subnet list, locate the row that contains the subnet to be modied, click
Modify. On the displayed page, change the DNS server address as prompted.
6. Click OK.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
Page 32

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
6.3 What Are the Constraints Related to VPC Peering?
● VPC peering connections created between VPCs that have overlapping subnet
CIDR blocks may not take eect.
● You cannot have more than one VPC peering connection between any two
VPCs at the same time.
● You cannot create a VPC peering connection between VPCs in
regions.
● Even if VPC 1 and VPC 2 are connected using a VPC peering connection, ECSs
in VPC 2 cannot access the Internet through the EIP of VPC 1. If you want to
allow the ECSs in VPC 2 to access the Internet through the EIP of VPC 1, you
can use a NAT gateway service or
Having an ECS Without a Public IP Address Access the Internet.
● If you request a VPC peering connection with a VPC of another account, the
peer account must accept the request to activate the connection. If you
request a VPC peering connection with a VPC of your own, the system
automatically accepts the request and activates the connection.
● After a VPC peering connection is established, the local and peer tenants must
add routes in the local and peer VPCs to enable communication between the
two VPCs.
● VPC A is peered with both VPC B and VPC C. If VPC B and VPC C have
overlapping CIDR blocks, you cannot
destinations for VPC A.
● To ensure security, do not accept VPC peering connections from unknown
accounts.
● Either owner of a VPC in a peering connection can delete the VPC peering
connection at any time. If a VPC peering connection is deleted by one of its
owners, all information about this connection will also be deleted
immediately, including routes added for the VPC peering connection.
● If VPCs connected by a VPC peering connection have overlapping CIDR blocks,
the connection can only enable communication between
overlapping) subnets in the VPCs. If subnets in the two VPCs of a VPC peering
connection have overlapping CIDR blocks, the peering connection will not
eect. When you create a VPC peering connection, ensure that the VPCs
take
involved do not contain overlapping subnets.
● You cannot delete a VPC that has VPC peering connection routes
● A VPC peering connection can be created between VPCs in same region even
if one is created on the HUAWEI CLOUD Chinese Mainland console and
another on the HUAWEI CLOUD international console.
congure an SNAT server. For details, see
congure routes with the same
dierent
specic (non-
congured.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
Page 33

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
6.4 Why Does Communication Fail Between VPCs That Are Connected by a VPC Peering Connection?
Symptom
Two VPCs cannot communicate with each other after you create a VPC peering
connection between them.
Troubleshooting
The following fault causes are sequenced based on their occurrence probability.
If the fault persists after you have ruled out a cause, check other causes.
Figure 6-1 Troubleshooting
Table 6-1 Troubleshooting
Possible Cause
Incorrect VPC Peering
Connection
Conguration
Incorrect Network
Conguration
ECS Communication
Failure
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
Solution
See Incorrect VPC Peering Connection
Conguration
See Incorrect Network Conguration
See ECS Communication Failure
Page 34
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Possible Cause Solution
Route Conicts
Between VPC Peering
and Direct Connect or
Between VPC Peering
and VPN
Route Already Exists Replan the network connection scheme.
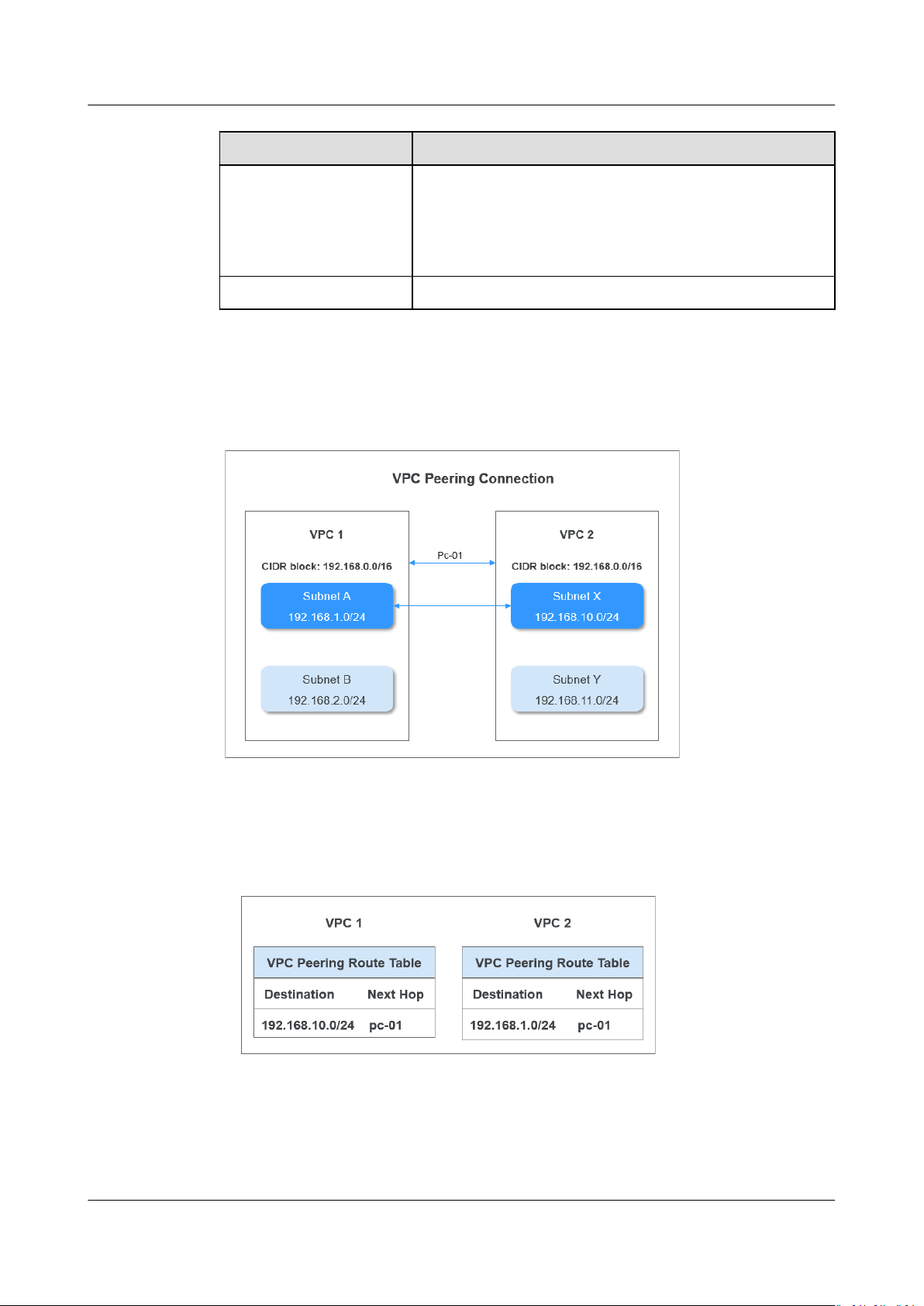
Incorrect VPC Peering Connection
Figure 6-2 VPC peering connection network diagram
Replan the network connection scheme.
Conguration
Add routes to enable communication between Subnet A in VPC 1 and Subnet X in
VPC 2. Figure 6-3 shows the route table
Figure 6-3 VPC peering connection route table
Figure 6-2 is used as an example. Perform the following operations:
1. Check whether a VPC peering connection has been successfully created for
the two VPCs, especially, whether the VPC IDs are correctly
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
congurations.
congured.
Page 35

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
If the VPC peering connection is not correctly congured, create it again.
2. Check whether routes have been congured for the VPC peering connection.
For example, the destination of the route for VPC 1 must be the subnet CIDR
block in VPC 2.
If the routes of the VPC peering connection are incorrect, add local and peer
routes on the VPC peering connection details page. The VPC peering
connection works properly only after the routes are correctly
3. Check whether VPC 1 and VPC 2 have overlapping subnets. For example, if
VPC 1 and VPC 2 each has a subnet with the same CIDR block, such as
192.168.11.0/24, the VPC peering connection will become invalid.
Figure 6-4 Invalid VPC peering connection example
congured.
Incorrect Network Conguration
1. Check whether the security group of the ECS NIC is correctly congured.
You can view the security group on the ECS details page. Check whether a
security group rule that allows the ECS to communicate with the peer VPC
subnet has been
Figure 6-5 has to be congured for the NICs of all ECSs in VPC 1.
Figure 6-5 Security group
2. Check whether trac ltering has been congured on the rewall associated
with the subnet to which the ECS NIC belongs. If the required trac is
blocked,
3. Check whether the trac between the subnets involved in the VPC peering
connection is blocked by the network ACLs. If the required
congure network ACL rules to allow the trac.
4. If the ECS has more than one NIC, ensure that correct policy-based routing
has been
addresses match their own rules.
For example, if the IP address of eth0 is 192.168.1.10/24, and that of eth1 is
192.168.2.10/24, run the following commands:
congure rewall rules to allow the trac.
congured for the ECS and that packets with dierent source IP
congured. For example, a security group rule described in
conguration
trac is blocked,
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
Page 36

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
ping -I 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.1
ping -I 192.168.2.10 192.168.2.1
If the two IP addresses can be pinged, the policy-based routing congured for
the two NICs is correct.
Otherwise, you need to congure policy-based routing for the ECS with
multiple NICs. For details, see How Do I
ECSs with Multiple NICs?
Congure Policy-Based Routing for
ECS Communication Failure
1. Check whether the ECS NIC has an IP address assigned.
2. Ping the gateway address of the subnet to which the ECS belongs to check
Route
Conicts Between VPC Peering and Direct Connect or Between VPC
Peering and VPN
Check whether any of the VPC connected by the VPC peering connection have a
VPN or Direct Connect connection connected. If yes, check the next hop
destination of their routes.
If the route destination of the VPC peering connection overlaps with that of a
Direct Connect or VPN connection, the route may be invalid.
Log in to the ECS, and run the
ECS NIC IP address.
If an ECS runs the Window OS, run the
If the ECS NIC has no IP address assigned, see Why Does My ECS Fail to
Obtain an IP Address?
the ECS communication.
Obtain the gateway address from the VPC details page on the console. In
most cases, the gateway address is in the format
gateway address to check the communication. If the ping operation for the
gateway address fails, see Why Does My ECS Fail to Communicate at a
Layer 2 or Layer 3 Network?
ifcong or ip address command to check the
ipcong command.
xxx. xxx. xxx. 1
. Ping the
Route Already Exists
If a message indicating that this route already exists is displayed when you add a
route for a VPC peering connection, check whether the destination of a VPN,
Direct Connect, or VPC peering connection route already exists. If the destination
already exists, the VPC peering connection cannot take
eect.
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
You need to ping the ECS at one side of the VPC peering connection from another
ECS at the other side of the VPC peering connection to send ICMP packets and
provide the technical support engineer with the following information:
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
Page 37

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Item Description Value
VPC1 ID ID of VPC 1 -
VPC2 ID ID of VPC 2 -
VM1 ID ID of the ECS in VPC1-
VM2 ID ID of the ECS in VPC2-
Subnet1 ID ID of the subnet used
by ECS 1
Subnet2 ID ID of the subnet used
by ECS 2
IP1 ECS 1 IP address -
IP2 ECS 2 IP address -
You can add - t to the end of the ping command to enable the Windows ECS to
continuously send ICMP packets.
-
-
6.5 How Many VPC Peering Connections Can I Create?
You can create a maximum of 50 VPC peering connections in one region. Accepted
VPC peering connections consume the quota of both the owners of a VPC peering
connection. A VPC peering connection in the pending approval state consumes the
quota of only the requester.
6.6 What Are the Priorities of the Custom Route and
EIP If Both Are
Congured for an ECS to Enable the ECS
to Access the Internet?
The priority of an EIP is higher than that of a custom route. That is, if both are
congured for an ECS to enable Internet access, the EIP will be used preferentially.
6.7 Why Does Intermittent Interruption Occur When a Local Host Accesses a Website Built on an ECS?
Symptom
After you build a website on an ECS, some users occasionally fail to access the
website through the local network.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
Page 38

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Troubleshooting
1. Check the local network of the user.
If the local host communicates with the ECS using NAT, this problem may
occur.
2. Run the following command to check whether tcp_tw_recycle is enabled on
the ECS:
sysctl -a|grep tcp_tw_recycle
If the value of tcp_tw_recycle is 1, the function is enabled.
3. Run the following command to check the number of lost packets of the ECS:
cat /proc/net/netstat | awk '/TcpExt/ { print $21,$22 }'
If the value of ListenDrops is not 0, packet loss occurs, that is, the network is
faulty.
Procedure
This problem can be solved by modifying the kernel parameters of the ECS.
● Run the following command to temporarily modifying the parameters (the
modication becomes invalid after the ECS is restarted):
sysctl -w net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle=0
● Perform the following operations to permanently modify the parameters:
a. Run the following command and modify the /etc/sysctl.conf le:
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
Add the following content to the le:
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle=0
b. Press Esc, enter :wq!, and save the le and exit.
c. Run the following command to make the
sysctl -p
modication take eect:
6.8 Why Do ECSs Using Private IP Addresses in the Same Subnet Only Support One-Way Communication?
Symptom
Two ECSs (ecs01 and ecs02) are in the same subnet in a VPC. Their IP addresses
are 192.168.1.141 and 192.168.1.40, respectively.
ECS ecs01 can ping ECS ecs02 through a private IP address successfully, but ECS
ecs02 cannot ping ECS ecs01 through a private IP address.
Troubleshooting
1. Ping ECS ecs01 from ECS ecs02 through the EIP. If ECS ecs01 can be pinged,
the NIC of ECS ecs01 is working properly.
2. Run the arp -n command on ECS ecs02 to check whether the command
output contains the MAC address of ECS ecs01. If the command output does
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
Page 39

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
not contain the MAC address of ECS ecs01, ECS ecs02 fails to learn the MAC
address of ECS ecs01 when using the private IP address to ping ECS ecs01.
3. Run the ip a command on ecs01 to check the NIC conguration of ECS ecs01.
The following gure shows an example.
Figure 6-6 Viewing ECS ecs01 NIC conguration
The IP address 192.168.1.40/32 should not be congured based on the
command output. As a result, ECS ecs01 fails to send packets to ECS ecs02.
Procedure
Modify the NIC
the redundant IP address, for example, 192.168.1.40/32, congured on the NIC
eth0:
ip a del 192.168.1.40/32 dev eth0
conguration of ECS ecs01. Run the following command to delete
6.9 Why Does Communication Fail Between Two ECSs in the Same VPC or Packet Loss Occur When They Communicate?
Symptom
Two ECSs in the same VPC cannot communicate with each other or packet loss
occurs when they communicate.
Troubleshooting
The following fault causes are sequenced based on their occurrence probability.
If the fault persists after you have ruled out a cause, check other causes.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
Page 40
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-7 Troubleshooting
Table 6-2 Troubleshooting
Possible Cause Solution
Security group rules See Security Group Rules
Network ACL rules See Network ACL Rules
ECS NIC conguration See ECS NIC Conguration
Port unreachable See Port Unreachable
Security Group Rules
Check whether the ECS NIC security group allows the outbound and inbound
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) trac.
Take the inbound direction as an example. The security group rules must contain
at least one of the following rules.
Figure 6-8 Inbound security group rule
If packets of other protocols are tested, congure the security group rules to allow
the corresponding protocol
whether the security group allows the inbound UDP trac.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
trac. For example, if UDP packets are tested, check
Page 41

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Network ACL Rules
1. Check whether the subnet of ECS NIC has an associated network ACL.
2. Check the network ACL status in the network ACL list.
– If Disabled is displayed in the Status column, the network ACL has been
disabled. Go to 3.
– If Enabled is displayed in the Status column, the network ACL has been
enabled. Go to 4.
3. Click the network ACL name and
Outbound Rules tabs to allow the ICMP trac.
4. If the network ACL is disabled, all packets in the inbound and outbound
directions are discarded by default. In this case, delete the network ACL or
enable the network ACL and allow the ICMP
congure rules on the Inbound Rules and
trac.
ECS NIC Conguration
The following procedure uses a Linux ECS as an example. For a Windows ECS,
check the
rewall restrictions.
1. Check whether multiple NICs are congured for the ECS. If the ECS has
multiple NICs and the EIP is bound to an extension NIC, congure policybased routing for the ECS. For details, see How Do I Congure Policy-Based
Routing for ECSs with Multiple NICs?
2. Log in to the ECS and run the following command to check whether the NIC
has been created and obtained a private IP address. If there is no NIC
information or the private IP address cannot be obtained, contact technical
support.
ifcong
Figure 6-9 NIC IP address
3. Run the following command to check whether the CPU usage of the ECS is
too high. If the CPU usage exceeds 80%, the ECS communication may be
adversely
top
4. Run the following command to check whether the ECS has any restrictions on
security group rules:
iptables-save
5. Run the following command to check whether the /etc/hosts.deny
contains the IP addresses that limit communication:
vi /etc/hosts.deny
If the hosts.deny
address from the hosts.deny le and save the le.
aected.
le
le contains the IP address of another ECS, delete the IP
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 36
Page 42

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Port Unreachable
1. If a port of the ECS cannot be reached, check whether the security group rules
and network ACL rules enable the port.
2. On the Linux ECS, run the following command to check whether the ECS
listens on the port: If the ECS does not listen on the port, the ECS
communication may be adversely aected.
netstat -na | grep <
Port number
>
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
6.10 Why Cannot the Virtual IP Address Be Pinged After It Is Bound to an ECS NIC?
Symptom
After you bind a virtual IP address to an ECS NIC, you cannot ping the virtual IP
address.
Troubleshooting
The following fault causes are sequenced based on their occurrence probability.
If the fault persists after you have ruled out a cause, check other causes.
Figure 6-10 Troubleshooting
Table 6-3 Troubleshooting
Possible Cause
Virtual IP address of the ECS
NIC
ECS NIC conguration See ECS NIC Conguration
Security group or network ACL
conguration
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 37
Solution
See Virtual IP Address of the ECS NIC
See Security Group or Network ACL
Conguration
Page 43

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Virtual IP Address of the ECS NIC
Check whether the source/destination check of the NIC is disabled and whether
the virtual IP address is bound to the NIC.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click Service List and click Elastic Cloud Server under Computing.
3. In the ECS list, click the name of the ECS.
4. On the displayed ECS details page, click the NICs tab.
5. Ensure that Source/Destination Check is disabled.
6. Ensure that an IP address is displayed for Virtual IP Address on the NIC
details page. If no IP address is displayed for Virtual IP Address, click
Manage Virtual IP Address and
To check whether the virtual IP address has been congured, you can only run the ip
address command. For details, see Binding a Virtual IP Address to an EIP or ECS.
congure an IP address.
ECS NIC
Conguration
The following uses Linux and Windows ECSs as examples to describe how to check
whether an ECS NIC has been correctly
For a Linux ECS:
1. Run the following command on the ECS to check whether NIC eth
ifcong
Figure 6-11 Checking for NIC eth
congured.
X:X
X:X
exists:
The command output in the preceding gure contains the NIC eth
192.168.1.137 is the virtual IP address of the ECS NIC.
X:X
– If NIC eth
– If NIC eth
2. If the command output does not contain the NIC eth
command to switch to the
cd /etc/syscong/network-scripts
3. Run the following command to create and then modify the ifcfg-eth0:1 le:
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 38
exists, the ECS NIC is correctly congured.
X:X
does not exist, perform the following operations:
X:X
, run the following
/etc/syscong/network-scripts directory:
X:X
.
Page 44

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
vi ifcfg-eth0:1
Add the following NIC information to the le:
BOOTPROTO=static
DEVICE=eth0:1
HWADDR=fa:16:3e:4d:5b:98
IPADDR=192.168.1.137
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
NETMADK=255.255.255.0
ONBOOT=yes
ONPARENT=yes
4. Press Esc, enter :wq!, and save the
le and exit.
5. Restart the ECS and run the ifcong command to check whether the virtual
IP address has been
congured for the ECS.
For a Windows ECS:
1. In the Start menu, open the Windows command line window and run the
following command to check whether the virtual IP address has been
congured:
ipcong /all
Figure 6-12 Checking whether the virtual IP address has been congured
In the preceding command output, check whether the value of IPv4 Address
is the virtual IP address 192.168.10.137 of the ECS NIC.
– If yes, the virtual IP address has been congured for the ECS NIC.
– If no, perform the following operations:
2. Choose Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network Connections.
Right-click the corresponding local connection and then click Properties.
3. On the Network tab page, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
4. Click Properties.
5. Select Use the following IP address, and set IP address to the private IP
address displayed in Figure 6-12. For example, 192.168.10.41.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 39
Page 45

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-13 Conguring a private IP address
6. Click Advanced.
7. On the IP Settings tab, click Add in the IP addresses area.
Add the virtual IP address
congured in Figure 6-12. For example,
192.168.10.137.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 40
Page 46

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-14 Conguring virtual IP address
Security Group or Network ACL Conguration
Check whether the ECS security groups and the network ACLs associated with the
subnet used by the ECS NIC are blocking trac.
1. On the ECS details page, click the Security Groups tab and conrm that
required security group rules have been congured for the virtual IP address.
If the required security group rules have not been
Security Group or Modify Security Group Rule to change the security group
or modify the security group rules.
2. Click Service List. Under Network, click Virtual Private Cloud. In the
navigation pane on the left of the network console, click Network ACLs and
check whether the network ACL rules associated with the subnet used by the
ECS NIC are blocking access to the virtual IP address.
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
congured, click Change
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 41
Page 47

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
6.11 Why Does My ECS Fail to Use Cloud-init?
Symptom
An ECS fails to use cloud-init.
Troubleshooting
Figure 6-15 shows the process for an ECS to obtain metadata using the cloud-init.
Figure 6-15 Process for obtaining metadata
Check the following possible causes.
Figure 6-16 Possible causes
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 42
Page 48
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Table 6-4 Possible causes
Possible Cause Solution
The ECS has no IP
address obtained.
Incorrect route for
169.254.169.254
Fail to obtain the ECS
metadata.
Fail to log in to the ECS
or create a non-root
user after cloud-init is
congured.
Fail to use an obtained
private key to log in to
an ECS after the ECS
starts (Fail to obtain
the ECS login
password).
See The ECS Has No IP Address Obtained
See Incorrect Route for 169.254.169.254
See Failing to Obtain the ECS Metadata
Check the format of the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
conguration le. For details, see Failing to Log in to
the ECS or Create a Non-root User After Cloud-init
Is Congured.
Restart the ECS and try again.
The ECS Has No IP Address Obtained
Check whether the ECS has obtained an IP address.
If no IP address is obtained, run the dhclient command to obtain the IP address
(this command varies depending on the ECS OSs). Alternatively, you can run the
ethx
ifdown
command to enable it to allow the ECS NIC to automatically obtain an IP address
again.
command to disable the network port and then run the ifup
ethx
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 43
Page 49

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-17 ECS IP address
Incorrect Route for 169.254.169.254
Ping IP address 169.254.169.254/32 from the ECS. If the IP address cannot be
pinged, perform the following steps:
1. Check the exact route
169.254.169.254/32.
In most cases, the next hop of the exact route for IP address
169.254.169.254/32 is the same as that of the default route for the IP
address.
Figure 6-18 Route for IP address 169.254.169.254/32
2. If there is no exact route for IP address 169.254.169.254/32, the cause is as
follows:
Images with CentOS 5 OSs do not support the cloud-init function. To use this
function, change the ECS OS.
3. If the next hop of the exact route for IP address 169.254.169.254/32 is
dierent from that of the default route for the IP address, handle the issue
based on the following information:
– If the ECS was created before cloud-init is enabled, run the service
network restart command to obtain the correct route.
congured on the ECS for IP address
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 44
Page 50

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
– If the ECS is newly created, submit a service ticket or contact technical
support.
Failing to Obtain the ECS Metadata
Run the following command on the ECS to obtain the metadata:
curl http://169.254.169.254/openstack/latest/meta_data.json
If information similar to that shown in Figure 6-19 is displayed, the ECS
successfully obtains the metadata.
Figure 6-19 Command output
Failing to Log in to the ECS or Create a Non-root User After Cloud-init Is
Congured
Check whether the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg conguration le format is correct. For
details, see the
following gure shows the example /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg conguration le for the
Ubuntu OSs.
Figure 6-20
le format requirements posed by Linux OS providers. The
Conguration le
Failing to Use an Obtained Private Key to Log in to an ECS After the ECS
Starts (Failing to Obtain the ECS Login Password)
Restart the ECS to rectify the fault.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 45
Page 51

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the EIP still fails to use cloud-init after performing the preceding steps, submit a
service ticket.
Provide the following information to the technical support engineer.
Item Description Example Value
VPC CIDR block Required for
customer
gateway
conguration
VPC ID N/A Example:
CIDR block of subnet
1 (can be the same
as the VPC CIDR
block)
ECS ID N/A N/A N/A
ECS IP address N/A Example: 192.168.1.192/24 N/A
ECS route
information
N/A Example: 10.0.1.0/24 N/A
N/A N/A -
Example: 10.0.0.0/16 N/A
N/A
120b71c7-94ac-45b8-8ed6-30
aafc8fbdba
6.12 Why Does Internet Access Fail Even If My ECS Is Bound with an EIP?
Symptom
You have an ECS that has an EIP bound, but the ECS cannot access the Internet.
Troubleshooting
Figure 6-21 shows the process for an ECS to access the Internet using an EIP.
Figure 6-21 EIP network diagram
Locate the fault based on the following procedure.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 46
Page 52
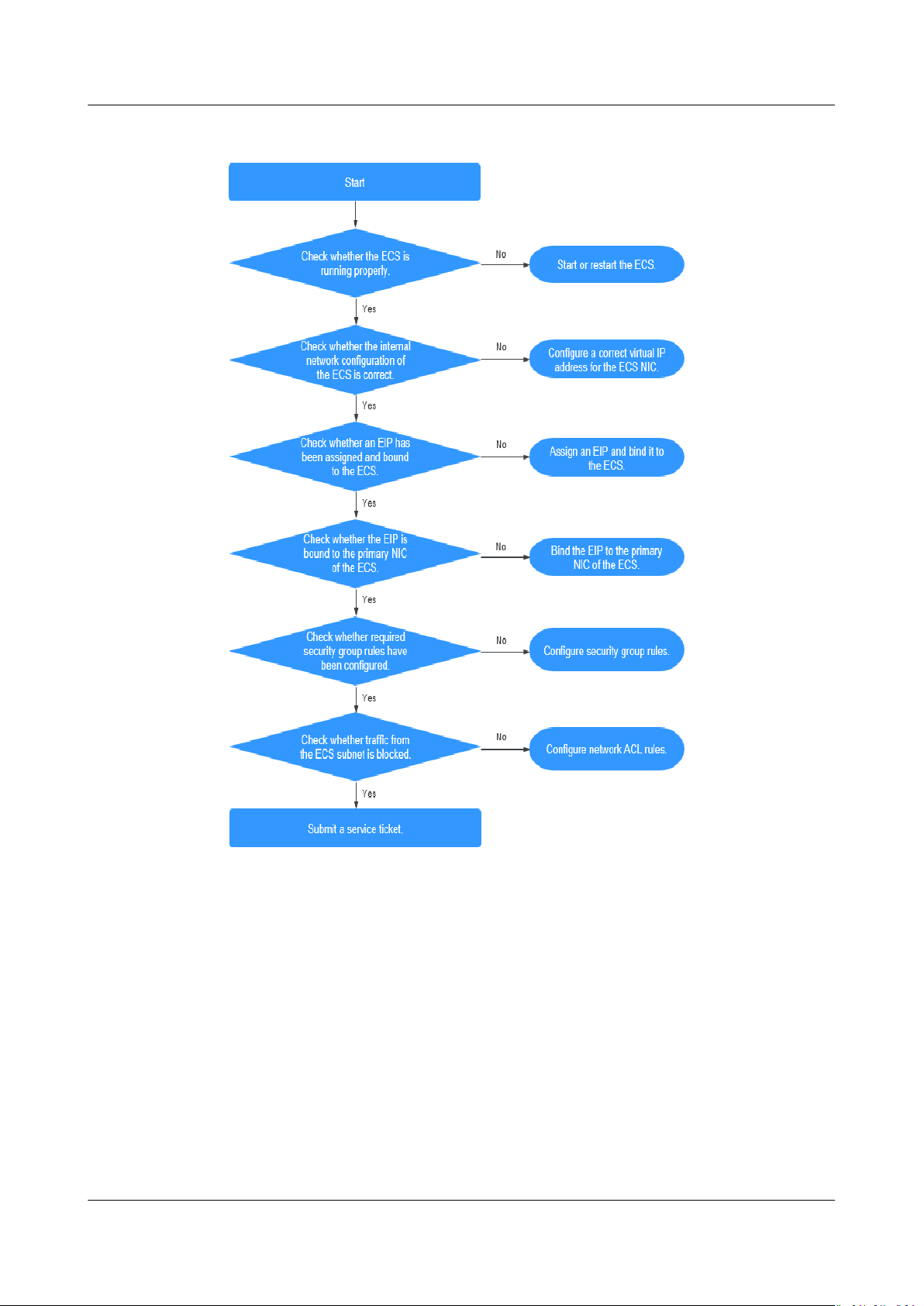
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-22 Troubleshooting procedure
1. Step 1: Check Whether the ECS Is Running Properly
2. Step 2: Check Whether the Network Conguration of the ECS Is Correct
3. Step 3: Check Whether an EIP Has Been Assigned and Bound to the ECS
4. Step 4: Check Whether the EIP Is Bound to the Primary NIC of the ECS
5. Step 5: Check Whether Required Security Group Rules Have Been
Congured.
6. Step 6: Check Whether Trac from the ECS Subnet Is Blocked
Step 1: Check Whether the ECS Is Running Properly
Check whether the ECS is running properly.
If the ECS state is not Running, start or restart the ECS.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 47
Page 53

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-23 ECS status
Step 2: Check Whether the Network Conguration of the ECS Is Correct
1. Check whether the ECS NIC has an IP address assigned.
Log in to the ECS, and run the ifcong or ip address command to check the
ECS NIC IP address.
If an ECS runs the Window OS, run the ipcong command.
2. Check whether the virtual IP address is correctly congured on the ECS NIC.
Log in to the ECS, and run the ifcong or ip address command to check the
ECS NIC IP address. If the ECS NIC does not have an IP address congured,
run a command to congure an IP address for the ECS NIC. For example, run
the ip addr add
192.168.1.192/24 for the NIC.
Figure 6-24 Virtual IP address of a NIC
virtual IP address
eth0 command to congure IP address
Check whether the ECS NIC has a default route. If no default route exists, run
the ip route add command to add the default route.
Figure 6-25 Default route
Step 3: Check Whether an EIP Has Been Assigned and Bound to the ECS
Check whether an EIP has been assigned and bound to the ECS. (If no EIP has
been assigned, assign an EIP and bind it to the ECS.)
The ECS shown in Figure 6-26 has no EIP bound and only has a private IP address
bound.
Figure 6-26 EIP status
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 48
Page 54

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Step 4: Check Whether the EIP Is Bound to the Primary NIC of the ECS
Check whether the EIP is bound to the primary NIC of the ECS. If the EIP is not
bound to the primary NIC of the ECS, bind it.
You can view the NIC details by clicking the NICs tab on the ECS details page. By
default, the
primary NIC as shown in the following gure.
Figure 6-27 Checking whether the EIP is bound to the primary NIC of the ECS
rst record in the list is the primary NIC and the EIP is bound to the
Step 5: Check Whether Required Security Group Rules Have Been
Congured.
For details about how to add security group rules, see Adding a Security Group
Rule.
If security group rules have not been congured, congure them based on your
service requirements. (The remote IP address indicates the allowed IP address, and
0.0.0.0/0 indicates that all IP addresses are allowed.)
Step 6: Check Whether
Check whether trac ltering by network ACL has been congured to block
certain trac from the subnet used by the ECS NIC.
You can congure the network ACL on the VPC console. Make sure that the
network ACL rules allow the
Trac from the ECS Subnet Is Blocked
trac from the ECS subnet.
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the EIP still fails to communicate with the Internet after you perform all the
steps above, submit a service ticket.
Provide the following information to technical support.
Item
VPC CIDR
block
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 49
Description Example Value
Required for
gateway
conguration
Example: 10.0.0.0/16 N/A
Page 55
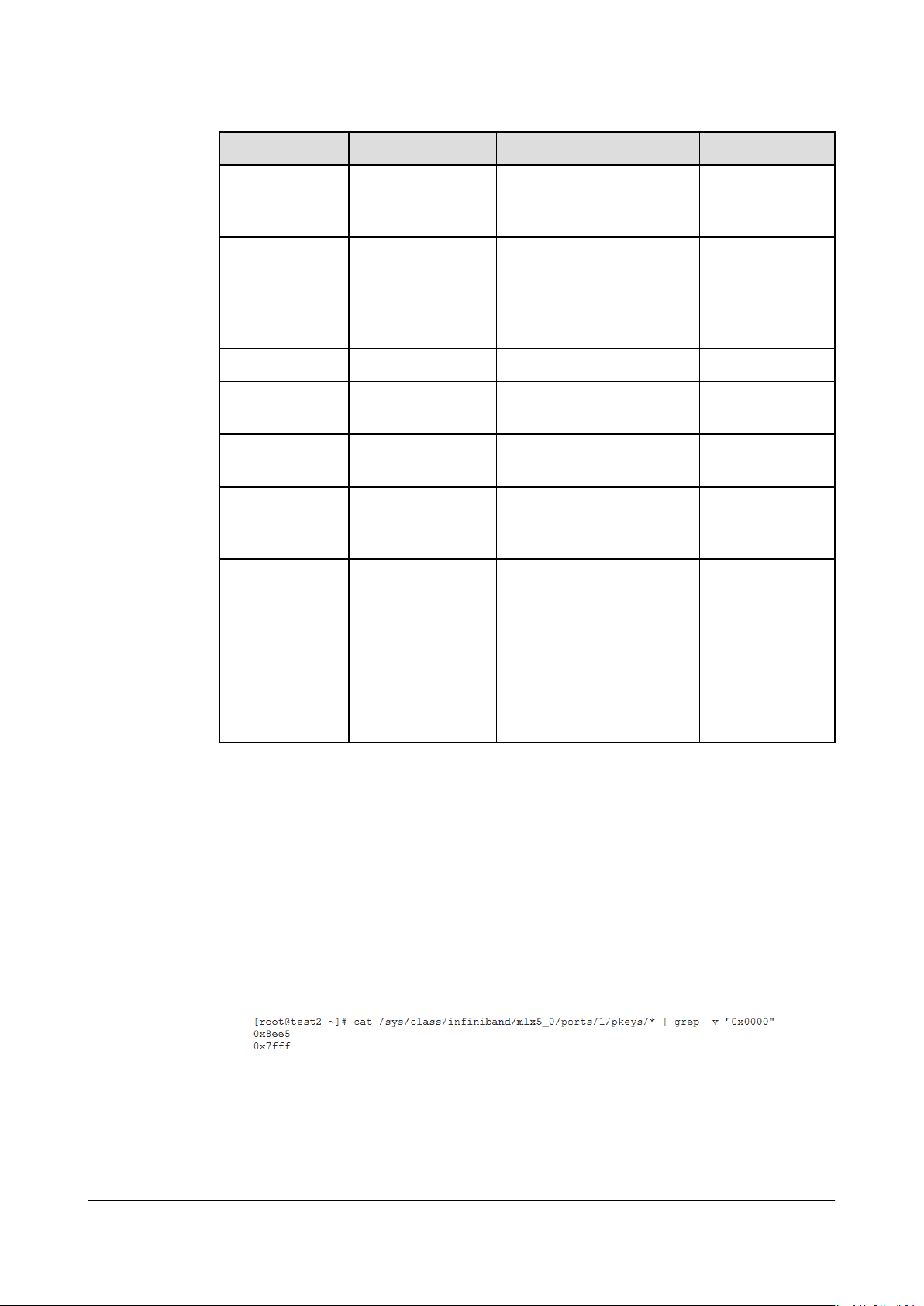
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Item Description Example Value
VPC ID N/A Example:
120b71c7-94ac-45b8-8e
d6-30aafc8fbdba
CIDR block of
subnet 1 (can
be the same as
the VPC CIDR
block)
ECS ID N/A N/A N/A
ECS IP address N/A Example:
ECS route
information
EIP Required for the
EIP bandwidth Maximum
N/A Example: 10.0.1.0/24 N/A
192.168.1.192/24
N/A N/A N/A
Example: 10.154.55.175 N/A
ECS to access the
Internet
Example: 1 Mbit/s N/A
bandwidth size
used by the ECS
to access the
Internet
N/A
N/A
EIP ID N/A Example:
b556c80e-6345-4003-
b512-4e6086abbd48
6.13 How Do I Handle the IB Network Failure?
RDMA Communication Failure Between Two IB ECSs
1. Check whether the Pkeys on the two ECSs are consistent.
Run the following command to check for the Pkeys allocated to the ECSs:
cat /sys/class/inniband/mlx5_0/ports/1/pkeys/* | grep -v "0x0000"
Figure 6-28 Checking Pkey consistency
– If only one Pkey is obtained, contact technical support.
– If two Pkeys are obtained, ensure that the two Pkeys on the two ECSs are
the same.
2. Run the following command to check whether the
rewall is disabled:
N/A
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 50
Page 56

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
service rewalld status
Figure 6-29 Checking the rewall
If the rewall is not disabled, run the following command to disable it:
service rewalld stop
3. Check whether the RDMA communication command is correct.
Run the following command on ECS 1 (client):
ib_write_lat -x 0 --pkey_index 0 192.168.0.218
Run the following command on ECS 2 (server):
ib_write_lat -x 0 --pkey_index 0
No IP Address for the ECS IB Port
After you run the ifcong command, the command output shows that no IP
address has been assigned to the ECS InniBand (IB) port.
1. Run the following command to check for the Pkey:
/sys/class/inniband/mlx5_0/ports/1/pkeys/* | grep -v "0x0000"
cat
Figure 6-30 Checking Pkey
If only one Pkey is obtained, contact technical support.
2. Run the following command to assign an IP address to the ECS IB port:
dhclient ib0
If no command output is displayed, the IP address cannot be obtained using
DHCP.
3. Contact technical support.
After you have performed the preceding steps, if the IB network still cannot
be used for communication or the IB port still cannot obtain an IP address,
contact technical support for assistance and provide the technical support
engineer with the following information.
Ite
DescriptionExample Value
m
VP
VPC 1 ID Example: fef65559C1
ID
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 51
c154-4229afc4-9ad0314437ea
N/A
Page 57

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
ItemDescriptionExample Value
VM
1
ID
VM
2
ID
ID of ECS
1 in VPC
1
ID of ECS
2 in VPC
1
Example:
f7619b12-3683-4203-9
271-f34f283cd740
Example:
f75df766-68aa-4ef3a493-06cdc26ac37a
N/A
N/A
6.14 Why Does My ECS Fail to Communicate at a Layer 2 or Layer 3 Network?
Symptom
An ECS fails to ping the gateway of the subnet where the ECS resides.
Troubleshooting
Locate the fault based on the following procedure.
Figure 6-31 Troubleshooting procedure
1. Checking Whether the ECS Has Obtained an IP Address
2. Checking Whether the Security Group Allows Communication Between
Subnets Involved in the VPC Peering Connection
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 52
Page 58

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
3. Checking Whether the Network ACL Allows Communication Between
Subnets Involved in the VPC Peering Connection
Checking Whether the ECS Has Obtained an IP Address
Log in to the ECS, and run the ifcong or ip address command to check the ECS
NIC IP address. If an ECS runs the Window OS, run the ipcong command.
If the ECS does not have an IP address, check whether DHCP has been enabled for
the required subnet.
Switch to the subnet details page and check whether the DHCP function has been
enabled.
For details, see Why Does My ECS Fail to Obtain an IP Address?
Checking Whether the Security Group Allows Communication Between
Subnets Involved in the VPC Peering Connection
You can view the security group on the ECS details page. Check whether a security
group rule that allows the ECS to communicate with the peer VPC subnet has
congured.
been
Figure 6-32 Security group rule
Checking Whether the Network ACL Allows Communication Between
Subnets Involved in the VPC Peering Connection
In the navigation pane on the left of the VPC console, choose Network ACLs. On
the displayed page, select the network ACL associated with the subnets of the VPC
peering connection. On the network ACL details page, check whether network ACL
rules allow the communication between the subnets involved in the VPC peering
connection.
Figure 6-33 Network ACL rule
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 53
Page 59

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
6.15 How Do I Handle the BMS Network Failure?
1. Run the following command to check whether the BMS network ports have
been bonded:
ifcong
Figure 6-34 Checking for bond
If no bonding information is obtained, the BMS network ports are not bonded.
Contact technical support.
2. Run the following command to check whether the BMS route information is
correct:
route –n
Figure 6-35 Checking BMS route information
Check whether the default route (with a destination of 0.0.0.0/0) exists.
Figure 6-36 Checking the default route
Check whether a route to 169.254.169.254 exists.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 54
Page 60

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-37 Checking the route for IP address range 169.254.169.254
If required routes do not exist, contact technical support engineers.
3. If BMSs in a VPC cannot communicate with each other or a BMS with an EIP
bound cannot access the Internet, rectify the failure based on the related FAQ.
4. If the failure cannot be
contact technical support.
Obtain the VPC and BMS information on the management console and
provide the technical support engineer with the following information.
rectied after you perform the preceding operations,
Ite
m
VPC
1 ID
BMS
1 ID
BMS
2 ID
Descript
ion
VPC 1
ID
ID of
BMS 1
in VPC 1
ID of
BMS 2
in VPC 1
Example Value
Example: fef65559c154-4229afc4-9ad0314437ea
Example:
f7619b12-3683-4203-92
71-f34f283cd740
Example:
f75df766-68aa-4ef3a493-06cdc26ac37a
N/A
N/A
N/A
6.16 Why Does My ECS Fail to Obtain an IP Address?
Symptom
The private IP address of the ECS fails to be obtained.
Troubleshooting
Locate the fault based on the following procedure.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 55
Page 61

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-38 Troubleshooting process
1. Checking Whether DHCP Is Enabled
2. Checking Whether the dhclient Process Exist
3. Checking ECS Logs
Checking Whether DHCP Is Enabled
Check whether the DHCP function of the subnet is enabled (enabled by default).
Switch to the subnet details page. If DHCP is disabled, you must manually
congure a static IP address for the ECS by referring to step 3.
Checking Whether the dhclient Process Exist
1. Run the following command to check whether the dhclient process exists:
ps -ef | grep dhclient
2. If the dhclient process does not exist, log in to the ECS and restart the ECS
NIC or send a DHCP request.
– Linux OS:
Run the dhclient ethx command. If dhclient commands are supported,
run the ifdown ethx;ifup ethx command. In the command,
indicates the ECS NIC, for example, eth0 and eth1.
ethx
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 56
Page 62

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
– Windows OS:
Disconnect the network connection and connect it.
3. If the DHCP client does not send requests for a long time, for example, the
fault occurs again after the NIC restarts, you can use the following method to
congure the static IP address.
– Linux OS:
– Windows OS:
Checking ECS Logs
i. Run the following command to open the
scripts/ifcfg-eth0 le:
vi /etc/syscong/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
ii. Modify the following conguration items in the /etc/syscong/
network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=192.168.1.100 #IP address
NETMASK=255.255.255.0 #Subnet mask
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 #Gateway address
iii. Run the following command to restart the network service:
service network restart
On the Local Area Connection Status tab, click Properties. In the
displayed area, Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click
Properties. In the displayed area, enter the IP address, subnet mask, and
the default gateway address.
le.
/etc/syscong/network-
Check the ECS messages log in the /var/log/messages directory.
Search for the NIC MAC address and check whether any processes that cause
failures in obtaining IP addresses over DHCP exist.
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
Provide the customer service with the ECS ID, the ID of the subnet used by the
ECS, and the ID of the VPC used by the ECS.
6.17 How Do I Handle the VPN or Direct Connect Connection Network Failure?
VPN Network
Figure 6-39 shows your network, the customer gateway, the VPN, and the VPC.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 57
Page 63
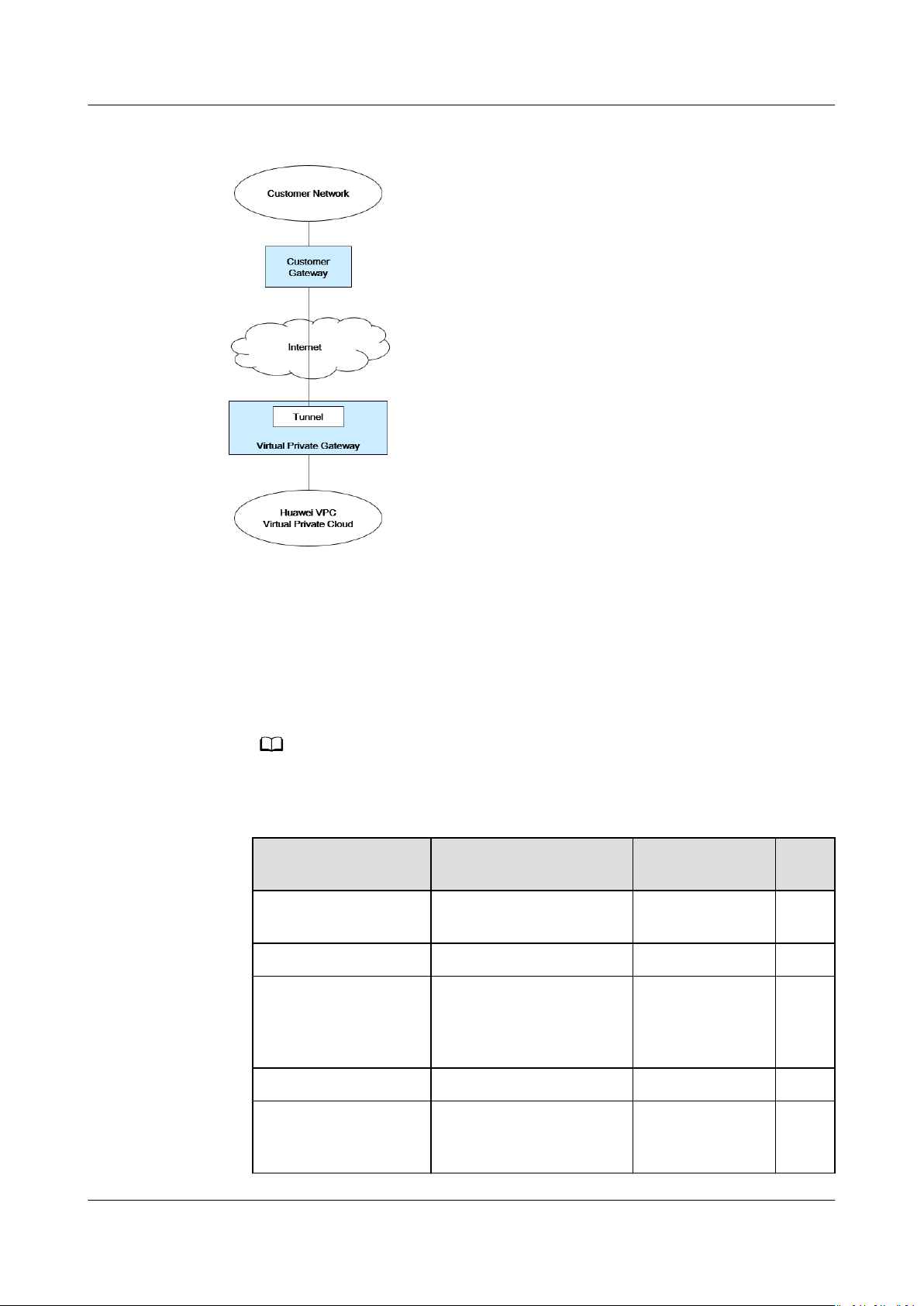
NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-39 VPN network
Customer Self-Check Guidance
1. Provide your network information.
Obtain information listed in Table 6-5. This table lists example values. You
can determine the actual values based on the example values. You must
obtain all actual values of your project.
You can print this table and ll in your values.
Table 6-5 Network information
Item
VPC CIDR block Required for customer
VPC ID N/A N/A N/A
CIDR block of subnet
1 (can be the same
as the VPC CIDR
block)
Description Example Valu
e
Example:
gateway conguration
10.0.0.0/16
N/A Example:
N/A
N/A
10.0.1.0/24
ECS ID N/A N/A N/A
Customer gateway
N/A N/A N/A
type (for example,
Cisco)
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 58
Page 64
NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Item Description Example Valu
e
Public IP address
used by the customer
gateway
2. Provide your gateway conguration information.
You can check the gateway connectivity issues based on the following steps:
You must take the IKE, IPsec, ACL rules, and route selection into consideration.
You can rectify the failure in any desired sequence. However, it is
recommended that you check for the failure in the following sequence: IKE,
IPsec, ACL rules, and route selection.
a. Obtain the IKE policy used by your gateway device.
b. Obtain the IPsec policy used by your gateway device.
c. Obtain the ACL rule used by your gateway device.
d. Check whether your gateway device can communicate with the gateway
devices in the public cloud system.
The commands used on dierent gateway devices are dierent. You can run the
commands based on your gateway device (such as Cisco, H3C, AR, or Fortinet device)
to obtain the preceding required information.
N/A The value must
be static.
N/A
O&M Operations That Require Assistance
You must send communication requests from the ECSs to the remote device.
Method:
Log in to an ECS and ping an IP address in your on-premises data center.
6.18 Why Does My Server Can Be Accessed from the Internet But Cannot Access the Internet?
Symptom
The server can be accessed from, but cannot access the Internet.
Troubleshooting
Check the following possible causes.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 59
Page 65

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-40 Possible causes
Table 6-6 Possible causes
Network
Possible Cause Solution
Network congurations See Network Congurations
EIP connection See Why Does Internet Access Fail Even If My ECS Is
Security group rules See Security Group Rules
Network ACL rules See Network ACL Rules
Congurations
● Firewall
Disable rewall rules for the ECS and check whether the fault is rectied.
– For a Linux ECS, see Checking the Firewall Conguration.
– For a Windows ECS, see Checking the Firewall Conguration.
● NIC
Check whether the NIC and DNS
– For a Linux ECS, see Checking the NIC Conguration.
Bound with an EIP?
congurations.
– For a Windows ECS, see Checking the NIC
Conguration.
Security Group Rules
Check whether any security group rule of the server denies the outbound trac.
By default, a security group allows all outbound trac. If the outbound trac is
denied,
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 60
congure security group rules or click Allow Common Ports.
Page 66
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-41 Allow Common Ports
Network ACL Rules
Check whether the network ACL of the subnet that the server belongs to denies
the outbound
By default, a network ACL denies all outbound trac. You need to add an
outbound rule with Action set to Allow to the network ACL associated with the
server.
trac.
Figure 6-42 Allowing outbound
trac
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
6.19 Can I Use a VPC Peering Connection to Connect
VPCs in
Dierent Regions?
No. You can use a VPC peering connection to connect VPCs in dierent AZs, but in
the same region.
You can use Cloud Connect to enable communication between VPCs in
regions. For details, see Cloud Connect.
dierent
6.20 Will I Be Billed for Using a VPC Peering Connection?
No. Currently, VPC peering connections are free of charge.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 61
Page 67

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
6.21 What Switches Can Connect to a L2CG on HUAWEI CLOUD?
You can use switches, such as CE6850 and Cisco Nexus 9300, which support
VXLAN functions.
6.22 Why Is the Layer 2 Connection in the Not
Connected State Even After Its
Conguration Is
Complete?
Possible causes and solutions:
1. The VXLAN tunnel of your data center is not properly congured.
Log in to the switch of your data center and check its tunnel congurations.
For details, see Conguring a Tunnel Gateway in Your Data Center.
2. The Direct Connect connection used by the L2CG is not properly
Check the Direct Connect connection congurations. For details, see Network
and Connectivity.
congured.
6.23 Why Is Communication Between the Cloud and On-premises Servers Unavailable Even When the Layer 2 Connection Status Is Connected?
Possible cause: The VXLAN tunnel of your data center is not properly
Solution: Log in to the switch of your data center and check its tunnel
congurations. For details, see Conguring a Tunnel Gateway in Your Data
Center.
congured.
6.24 Why Can't I Access Websites Using IPv6 Addresses
After IPv4/IPv6 Dual Stack Is
Symptom
You have enabled IPv4/IPv6 dual stack for the ECS, but the ECS cannot access
websites using IPv6 addresses.
Troubleshooting
● Check whether the IPv4/IPv6 dual stack is correctly congured and whether
the dual-stack NIC of the ECS has obtained an IPv6 address.
● Check whether the obtained IPv6 address of the dual-stack NIC has been
added to a shared bandwidth.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 62
Congured?
Page 68

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 6 Connectivity
Figure 6-43 NIC details
Solution
● When you buy an ECS, select Automatically-assigned IPv6 address for
Network.
If an IPv6 address fails to be automatically assigned or the selected image
does not support the function of automatic IPv6 address allocation, manually
obtain the IPv6 address by referring to Dynamically Assigning IPv6
Addresses.
If an ECS is created from a public image:
● By default, dynamic IPv6 address assignment is enabled for Windows public
images.
● Before enabling dynamic IPv6 address assignment for a Linux public image, check
whether IPv6 is supported and then check whether dynamic IPv6 address
assignment has been enabled. Currently, all Linux public images support IPv6, and
dynamic IPv6 address assignment is enabled for the Ubuntu 16 OS by default. You
do not need to
For other Linux public images, you need to enable this function.
congure dynamic IPv6 address assignment for the Ubuntu 16 OS.
● By default, IPv6 addresses can only be used for private network
communication. If you want to use an IPv6 address to access the Internet or
want it to be accessed by IPv6 clients on the Internet, you need to add the
IPv6 address to a shared bandwidth. For details, see Buy a Shared Bandwidth
and Add the IPv6 Address to It.
If you already have a shared bandwidth, add the IPv6 address to it.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 63
Page 69

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
7 Routing
7.1 How Do I Congure Policy-Based Routing for ECSs
with Multiple NICs?
Scenarios
Procedure
If an ECS has multiple NICs, you can perform the following procedure to
policy-based routing for the ECS and enable network communication using
extension NICs.
For a Linux ECS:
1. Run the following command to add the priority value and name of the route
table for each NIC to the /etc/iproute2/rt_tables
represents a higher priority. In this example, 250 and net0 indicate the route
table priority value and name of eth0, respectively. 251 and net1 indicate the
route table priority value and name of eth1, respectively. If there are multiple
NICs, add the route table priority value and name of each NIC one by one.
vi /etc/iproute2/rt_tables
# added for dual net
250 net0
251 net1
2. Run the following command to add routing information of each NIC to
the /etc/rc.local
vi /etc/rc.local
eth0 is used as an example here. If an IPv4 NIC is used, obtain the following
information:
IPv4 address (192.168.0.129), subnet (192.168.0.0/24), gateway address
(192.168.0.1), and route table added in step 1 (net0)
# wait for nics up
sleep 5
# Add v4 routes for eth0
ip route
ush table net0
le:
le. A smaller priority value
congure
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 64
Page 70

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
ip route add default via 192.168.0.1 dev eth0 table net0
ip route add 192.168.0.0/24 dev eth0 table net0
ip rule add from 192.168.0.129 table net0
# Add v4 routes for eth1
ip route ush table net1
ip route add default via 192.168.1.1 dev eth1 table net1
ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth1 table net1
ip rule add from 192.168.1.138 table net1
Before
that IPv6-related
conguring policy-based routing for NICs using IPv6 addresses, ensure
congurations have been performed. For details, see "Linux
(Automatic Conguration of IPv6)" in Dynamically Assigning IPv6
Addresses.
eth0 is used as an example here. If an IPv6 NIC is used, obtain the following
information:
IPv6 address (2407:c080:802:1be:2233:64bf:b095:54bf), subnet
(2407:c080:802:1be::/64), gateway address
(fe80::f816:3e:fef3:20dc), and
route table added in step1 is net0
Run the command ip -6 route show| grep default to view the IPv6 gateway
address of a NIC.
If there are multiple NICs, add their routing information one by one.
# Add v6 routes for eth0
ip -6 route
ip -6 route add default via fe80::f816:3e:fef3:20dc dev eth0 table net0
ip -6 route add 2407:c080:802:1be::/64 dev eth0 table net0
ip -6 rule add from 2407:c080:802:1be:2233:64bf:b095:54bf table net0
# Add v6 routes for eth1
ip -6 route
ip -6 route add default via fe80::f816:3e:fe10:5447 dev eth1 table net1
ip -6 route add 2407:c080:802:1bf::/64 dev eth1 table net1
ip -6 rule add from
ush table net0
ush table net1
2407:c080:802:1bf:39ea:be:13a2:7a1f table net1
3. Run the following command to add the execute permission for the rc.local
le:
# chmod +x /etc/rc.local
4. Run the reboot command to restart the ECS.
5. After the restart, run the following command to check whether the
congured
routes and route tables take eect.
For IPv4 NICs:
ip rule
ip route show table net0
ip route show table net1
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 65
Page 71
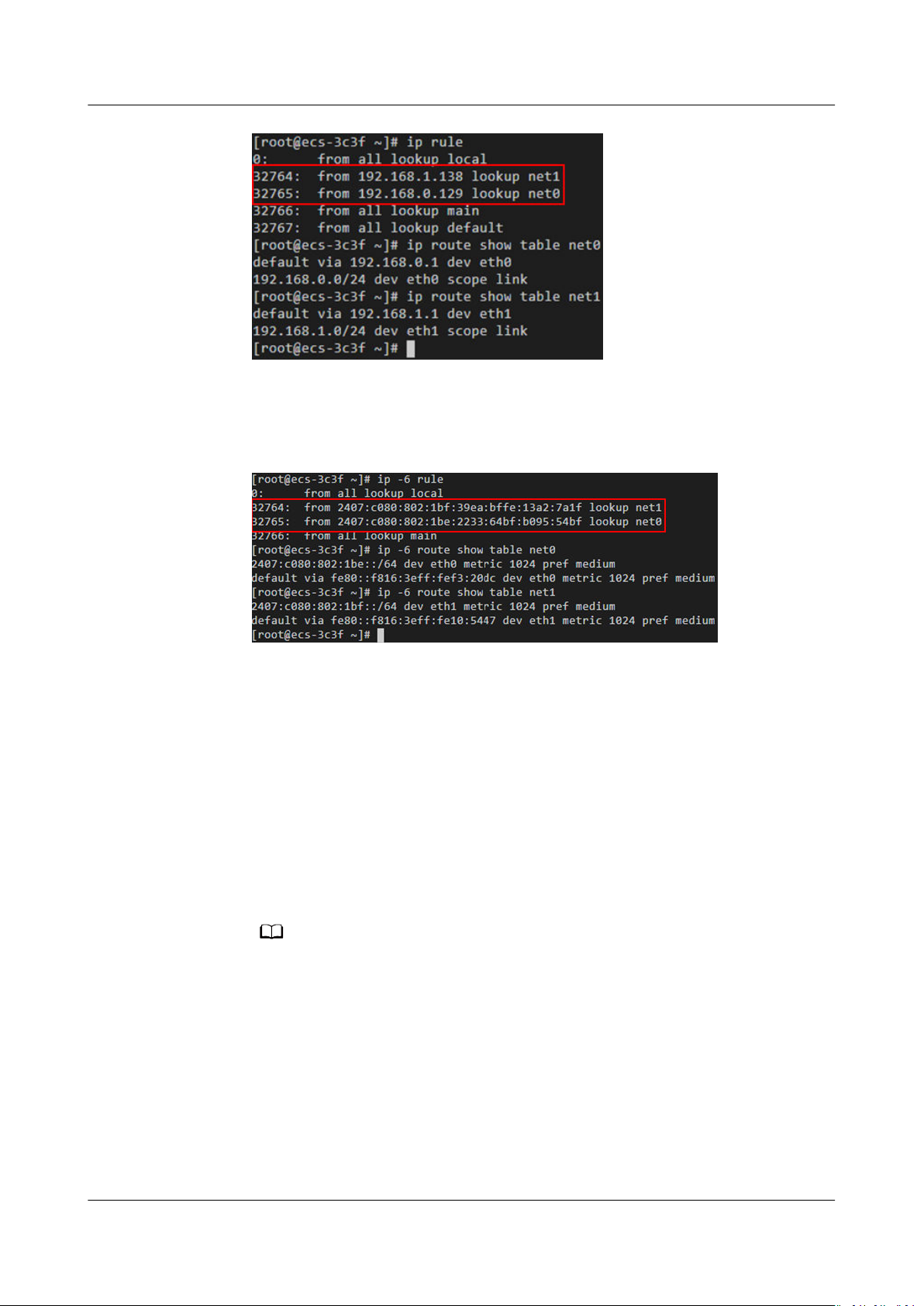
NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
For IPv6 NICs:
ip -6 rule
ip -6 route show table net0
ip -6 route show table net1
6. Specify the source addresses for the test.
For IPv4 addresses:
ping -I 192.168.0.129 xxx
ping -I 192.168.1.138 xxx
For IPv6 addresses:
ping -I 2407:c080:802:1be:2233:64bf:b095:54bf xxx
ping -I
2407:c080:802:1bf:39ea:be:13a2:7a1f xxx
For a Windows ECS:
1. Choose Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network Connections.
Right-click Local Area Connection 2 and then click Properties.
Right-click to add NICs based on the site requirements. If there are multiple NICs,
there will be multiple local area connections. Congure them one by one.
2. On the Network tab page, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
3. Click Properties.
4. On the General tab page, click Advanced.
5. On the IP Settings tab, click Add in the Default gateways area.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 66
Page 72
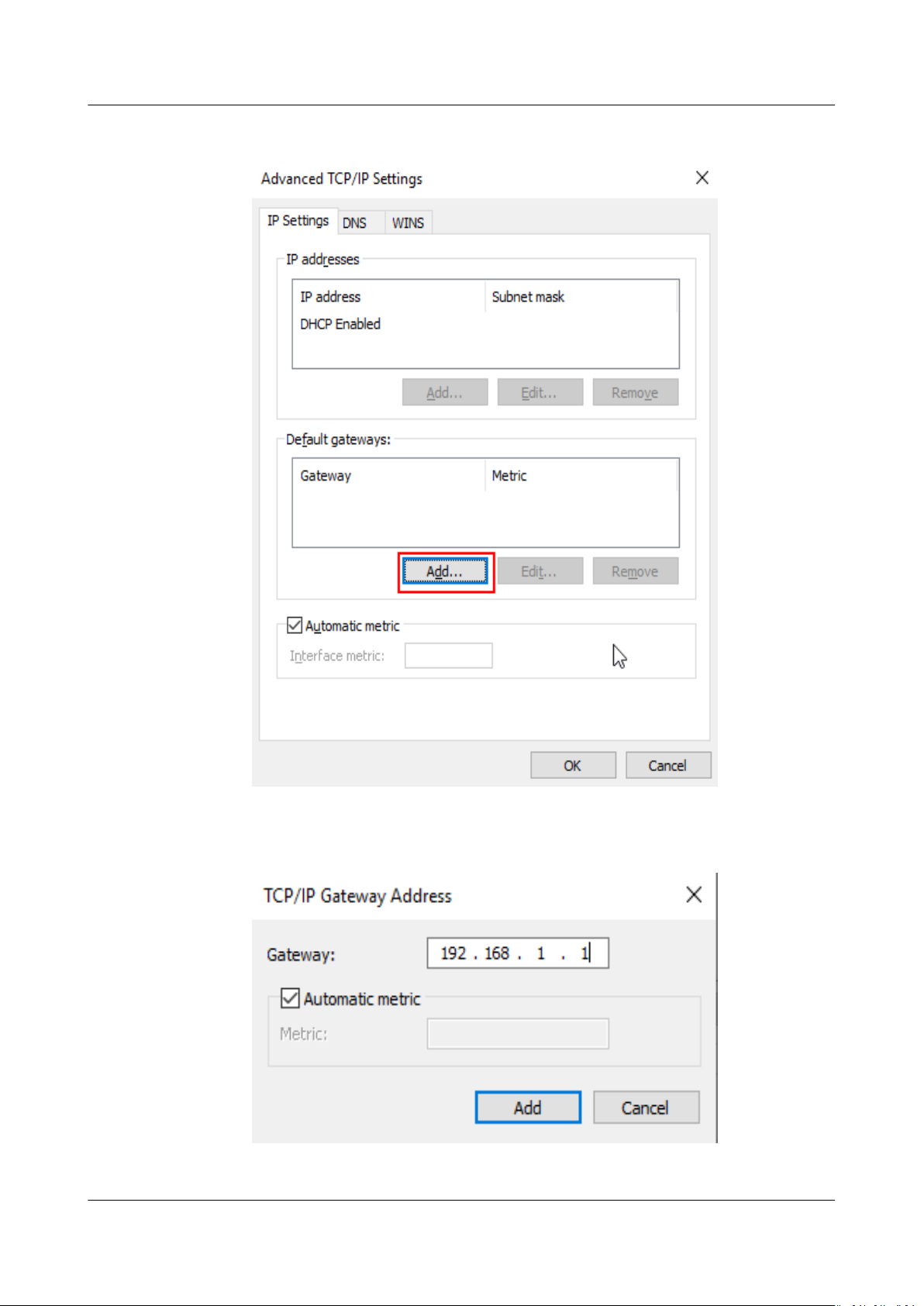
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
Figure 7-1 Advanced TCP/IP settings
6. Enter the gateway address of the secondary NIC and click Add.
Figure 7-2 TCP/IP Gateway Address
7. Click OK.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 67
Page 73

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
8. Open the command line interface (CLI) of the Windows OS and enter route
print to view the policy-based routes.
9. Specify the source addresses for the test.
ping -S 192.168.0.129 xxx
ping -S 192.168.1.138 xxx
Related Operations
If you want to access the Internet using an extension NIC, see How Do I Access
the Internet Using an EIP Bound to an Extension NIC?
7.2 Why Can't I Ping an ECS with Two NICs
Symptom
Your ECS has one primary NIC and one extension NIC in the same subnet. Both
the NICs have an EIP bound to access the Internet. The EIP bound to the primary
NIC can access the Internet, but that bound to the extension NIC cannot.
Possible Causes
By default, ECSs running CentOS have the reverse path
enabled. The default route of the ECSs is to forward outgoing trac through the
extension NIC to eth0. However, the system considers that the response data
packets should be forwarded from eth1. The system determines that the
received from a wrong NIC and then discards the response packets.
Solution
ltering (RP-Filter)
Congured?
trac is
Congure a policy-based routing rule so that the extension NIC trac is
forwarded from the extension NIC.
1. Run the following command to edit the rt_tables
vi /etc/iproute2/rt_tables
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 68
le:
Page 74
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
Add an alias for the routing table, such as test.
2. Save the modication and exit.
3. Run the following command to add a route to the test table:
ip route add default via
table
Name of the routing table
For example, run the following command:
ip route add default via 192.168.166.1 dev eth1 table test
4. Run the following command to add a policy-based routing rule:
ip rule add from
prio
table
For example, run the following command:
ip rule add from 192.168.166.22 lookup test prio 32000
5. Check whether the EIP bound to the extension NIC can access the Internet. If
you want to make this rule take eect permanently, add the preceding
command to the startup script /etc/rc.local.
lower than 32766 but higher than the main table
IP address of the extension NIC
Gateway IP address of the extension NIC
lookup
Name of the routing
dev eth1
7.3 Can a Route Table Span Multiple VPCs?
No.
7.4 How Many Routes Can a Route Table Contain?
Each route table can contain a maximum of 200 routes by default, including
routes added for Direct Connect and VPC peering connections.
7.5 Are There Any Restrictions on Using a Route Table?
● The ECS providing SNAT must have the Unbind IP from MAC function
enabled.
● The destination of each route in a route table must be unique. The next hop
must be a private IP address or a virtual IP address in the VPC. Otherwise, the
route table will not take eect.
● If a virtual IP address is set to be the next hop in a route, EIPs bound with the
virtual IP address in the VPC will become invalid.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 69
Page 75

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 7 Routing
7.6 Will a Route Table Be Billed?
The route table function itself is free of charge. However, you are charged for the
ECSs and bandwidth that you use together with the route table function.
7.7 Do the Same Routing Priorities Apply to Direct Connect Connections and Custom Routes in the Same VPC?
No. Direct Connect connections and custom routes are used in dierent scenarios.
Therefore, there are
dierent routing priorities for them.
7.8 Are There
Dierent Routing Priorities of the VPN
and Custom Routes in the Same VPC?
No. The routing priority of custom routes and that of VPNs are the same.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 70
Page 76

NO TE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
8 Security
8.1 Are the Security Group Rules Considered the Same If All Parameters Except Their Description Are the Same?
Yes. You cannot add or import a security group rule that has the same parameters
dierent description than an existing rule in the security group.
but a
8.2 What Are the Requirements for Deleting a Security Group?
● Before deleting a security group, ensure that the security group is not used by
any cloud resource, such as ECS, Relational Database Service (RDS), and
Distributed Cache Service (DCS). If the security group is used by a cloud
resource, release the cloud resource or change the security group used by the
cloud resource, and then delete the security group.
● If the security group you want to delete is associated with rules of another
security group (Source), delete or modify the associated security group rules,
and then delete the security group.
● The default security group cannot be deleted.
● If a security group is associated with resources other than servers and extension NICs,
the security group cannot be deleted.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 71
Page 77

NO TICE
Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
8.3 Why Is Outbound Access Through TCP Port 25 Restricted?
Symptom
You cannot access an external address using TCP port 25. For example, you cannot
run the Telnet smtp.***.com 25 command.
Cause
By default, TCP port 25 is disabled in the outbound direction for security purposes.
You do not need to enable TCP port 25, unless you want to deploy an email
service on the cloud.
This section applies only to the AP-Hong-Kong region.
Solution
● Use port 465 supported by the third-party email service provider.
● Apply for enabling TCP port 25 in the outbound direction.
If you must enable TCP port 25 on the ECS for external communications,
submit an application.
Before sending the application, you must agree and guarantee that TCP port 25 is
only used to connect to third-party Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) servers
and that emails are sent using the third-party SMTP servers. If you use the EIP
specied in the service ticket to directly send emails over SMTP, we will
permanently disable TCP port 25 and you will no longer be able to use it or
request for it to be enabled.
1. On the Create Service Ticket page, choose Products > Elastic Cloud Server.
For details about how to submit a service ticket, see Submitting a Service
Ticket.
2. Click Open Port 25 under Select Subtype and click Create Service Ticket.
Figure 8-1 Creating a service ticket
3. On the displayed page, enter the required information.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 72
Page 78

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
8.4 Can I Change the Security Group of an ECS?
Yes. Log in to the ECS console, switch to the page showing ECS details, and change
the security group of the ECS.
8.5 How Many Security Groups Can I Have?
Each account can have a maximum of 100 security groups and 5000 security
group rules.
When you create an ECS, you can select multiple security groups. It is
recommended that you select no more than ve security groups.
8.6 Will a Security Group Be Billed?
Security groups are free of charge.
8.7 How Do I
Congure a Security Group for Multi-
Channel Protocols?
Conguration
ECS
The TFTP daemon determines whether the conguration le species the port
range. If you use the TFTP conguration le that allows the data channel ports to
congurable, it is a good practice to congure a small range of ports that are
be
not listened on.
Security Group Conguration
You can congure port 69 and congure the data channel ports used by TFTP for
the security group. In RFC1350, the TFTP protocol species that ports available to
data channels range from 0 to 65535. However, not all these ports are used by the
TFTP daemon processes of
small range of ports for the TFTP daemon.
The following
if the ports used by data channels range from 60001 to 60100.
Figure 8-2 Security group rules
gure provides an example of the security group rule conguration
dierent applications. Therefore, you can congure a
8.8 How Many Network ACLs Can I Create?
You can create a maximum of 200 network ACLs. It is recommended that you
congure a maximum of 20 inbound or outbound rules for each network ACL. If
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 73
Page 79

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
you congure more than 20 inbound or outbound rules for a network ACL, the
forwarding performance will deteriorate.
8.9 Does a Security Group Rule or a Network ACL Rule
Immediately Take Eect for Its Original Trac After It
Modied?
Is
● Security groups are stateful. Responses to outbound trac are allowed to go
in to the instance regardless of inbound security group rules, and vice versa.
Security groups use connection tracking to track
trac to and from instances. If a security group rule is added, deleted, or
modied, or an instance in the security group is created or deleted, the
connection tracking of all instances in the security group will be automatically
cleared. In this case, the inbound or outbound trac of the instance will be
considered as new connections, which need to match the inbound or
outbound security group rules to ensure that the rules take
immediately and the security of incoming trac.
● A modied network ACL rule will not immediately take eect for its original
trac. It takes about 120 seconds for the new rule to take eect, and trac
will be interrupted during this period. To ensure that the trac is immediately
interrupted after the rule is changed, it is recommended that you congure
security group rules.
trac information about
eect
8.10 Why Are Some Ports in the Public Cloud System Inaccessible?
Symptom: Users in certain areas cannot access some ports in the public cloud
system.
Analysis: Ports listed in the following table are high-risk ports and are blocked by
default.
Table 8-1 High-risk ports
Protocol
TCP 42, 135, 137, 138, 139, 444, 445, 593, 1025, 1068, 1434, 3127, 3128,
UDP 135 to 139, 1026, 1027, 1028, 1068, 1433, 1434, 4789, 5554, and
Solution: It is recommended that you use ports that are not listed in the table for
your services.
Port
3129, 3130, 4444, 4789, 5554, 5800, 5900, and 9996
9996
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 74
Page 80

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
8.11 Why Is Access from a Specic IP Address Still
Allowed After a Network ACL Rule That Denies the
Access from the IP Address Has Been Added?
Network ACL rules have priorities. A smaller priority value represents a higher
priority. Each network ACL includes a default rule whose priority value is an
asterisk (*). Default rules have the lowest priority.
If rules
If you need a rule to take eect before or after a specic rule, you can insert that
rule before or after the
the priority of rule B is higher than that of rule A, insert rule B before rule A. In
this case, the priority of rule B is 1 and that of rule A is 2. Similarly, if the priority
of rule B is lower than that of rule A, insert rule B after rule A.
When a rule that denies access from a
rules that allow access from all IP addresses at the end. Then, the rule that denies
access from the specied IP address will take priority over the other rules and will
be
conict, the rule with the highest priority takes eect.
specic rule. For example, if the priority of rule A is 1 and
specied IP address is added, insert the
eective. For details, see Changing the Sequence of a Network ACL Rule.
8.12 What Do My Security Group Rules Not Take
Eect?
Symptom
The security group rules you have congured for an ECS have not taken eect.
Troubleshooting
The following fault causes are sequenced based on their occurrence probability.
If the fault persists after you have ruled out a cause, check other causes.
Figure 8-3 Troubleshooting
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 75
Page 81

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
Table 8-2 Troubleshooting
Possible Cause Solution
Incorrect Security
See Incorrect Security Group Rule Conguration
Group Rule
Congurations
Conicts Between
Network ACL Rules and
See Conicts Between Network ACL Rules and
Security Group Rules
Security Group Rules
Incorrect ECS Firewall
See Incorrect ECS Firewall Congurations
Congurations
Incorrect Security Group Rule Conguration
If security group rules are incorrectly congured, ECSs cannot be protected. Check
the security group rules based on the following causes:
1. The direction of a rule is incorrect.
2. The protocol of a rule is incorrect.
3. The port used in a rule is risky and cannot be accessed. For details about
common ports and risky ports, see Common Ports Used by ECSs.
4. The port used in a rule is not opened. You can perform the following steps to
check whether a port is being listened on the server.
For example, you have deployed a website on ECSs. Users need to access your
website over TCP (port 80), and you have added the security group rule
shown in Table 8-3.
Table 8-3 Security group rule
Directio
Protocol Port Source
n
Inbound TCP 80 0.0.0.0/0
Linux ECS
To verify the security group rule on a Linux ECS:
a. Log in to the ECS.
b. Run the following command to check whether TCP port 80 is being
listened on:
netstat -an | grep 80
If command output shown in Figure 8-4 is displayed, TCP port 80 is being
listened on.
Figure 8-4 Command output for the Linux ECS
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 76
Page 82

Virtual Private Cloud
FAQs 8 Security
c. Enter http://
If the requested page can be accessed, the security group rule has taken
eect.
Windows ECS
To verify the security group rule on a Windows ECS:
a. Log in to the ECS.
b. Choose Start > Accessories > Command Prompt.
c. Run the following command to check whether TCP port 80 is being
listened on:
netstat -an | ndstr 80
If command output shown in Figure 8-5 is displayed, TCP port 80 is being
listened on.
Figure 8-5 Command output for the Windows ECS
d. Enter http://
If the requested page can be accessed, the security group rule has taken
eect.
5. ECSs belong to dierent VPCs. If two ECSs are in the same security group but
in dierent VPCs, the ECSs cannot communicate with each other. To enable
communications between the ECSs, use a VPC peering connection to connect
the two VPCs. For details about VPC connectivity, see Application Scenarios.
ECS EIP
ECS EIP
in the address box of the browser and press Enter.
in the address box of the browser and press Enter.
You can add a security group rule or modify a security group rule to select the
correct direction, protocol, and open the ports.
Conicts Between Network ACL Rules and Security Group Rules
Security groups operate at the ECS level, whereas network ACLs operate at the
subnet level.
For example, if you
port 80 and a network ACL rule to deny access over port 80, the security group
rule will not take
You can add a network ACL rule or modify a network ACL rule to allow trac
from the corresponding protocol port.
congure an inbound security group rule to allow access over
eect.
Incorrect ECS Firewall Congurations
Check whether the rewall of the ECS opens the required ports.
For details, see Disabling a Windows ECS Firewall and Adding a Port Exception
on a Windows ECS Firewall or Disabling a Linux ECS Firewall and Adding a
Port Exception on a Linux ECS Firewall.
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the problem persists, submit a service ticket.
Issue 30 (2021-03-24) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 77
 Loading...
Loading...