Page 1

Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series Routers
V200R005
Configuration Guide - Basic
Configurations
Issue
05
Date
2010-01-30
Part Number
31501234
Page 2

Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. For
any assistance, please contact our local office or company headquarters.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Lt d. 2010. Al l right s reserved .
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Page 3

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
About This Document..................................................................................................................... 1
1 Product Overview ......................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.1 NE20/20E..........................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.2 Architecture.......................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.3 VRP...................................................................................................................................................1-3
1.2 Functional Features.....................................................................................................................................1-4
1.3 Functions.....................................................................................................................................................1-9
1.3.1 File System......................................................................................................................................1-10
1.3.2 SNMP Configuration.......................................................................................................................1-10
1.3.3 T erm inal Services............................................................................................................................1-11
1.3.4 High Reliability...............................................................................................................................1-11
1.3.5 Interfaces.........................................................................................................................................1-12
1.3.6 Link Layer Protocols.......................................................................................................................1-12
1.3.7 IP Services.......................................................................................................................................1-13
1.3.8 Unicast Routing Protocols...............................................................................................................1-13
1.3.9 Multicast Routing Protocols............................................................................................................1-14
1.3.10 MPLS Features..............................................................................................................................1-14
1.3.11 VPN Services.................................................................................................................................1-15
1.3.12 QoS................................................................................................................................................1-15
1.3.13 Security Features...........................................................................................................................1-17
2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment..............................................................2-1
2.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.1 Establishing the Configuration Environment by the Console Port....................................................2-2
2.1.2 Configuring the Router Through Telnet............................................................................................2-2
2.1.3 Establishing the Configuration Environm ent Through the AUX Port...............................................2-3
2.2 Establishing the Local Configuration Environment Through the Console Port..........................................2-3
2.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................2-3
2.2.2 Establishing the Physical Connection ...............................................................................................2-4
2.2.3 Configuring Terminals.......................................................................................................................2-4
2.2.4 Logging In to the Router...................................................................................................................2-4
Page 4

Contents
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
ii
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
2.3 Establishing the Configuration Environment Thro ugh Telnet.....................................................................2-4
2.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................2-4
2.3.2 Establishing the Physical Connection ...............................................................................................2-5
2.3.3 Configuring Login User Parameters..................................................................................................2-5
2.3.4 Logging In from the Telnet Client.....................................................................................................2-5
2.4 Establishing the Configuration Environment Thro ugh the AUX Port.........................................................2-6
2.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................2-6
2.4.2 Establishing the Physical Connection ...............................................................................................2-6
2.4.3 Initializing and Configuring the Modem on the Interface.................................................................2-7
2.4.4 Configuring the Connection Between Remote Terminal and the Router..........................................2-7
2.4.5 Logging In to the Router...................................................................................................................2-7
2.5 Configuration Examples..............................................................................................................................2-7
2.5.1 Example for Login Through the Console Port ..................................................................................2-7
2.5.2 Example for Login Through Telnet................................................................................................. 2-10
2.5.3 Example for Login Through the AUX Port.....................................................................................2-11
3 CLI Overview..............................................................................................................................3-1
3.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.1 Characteristics of the CLI..................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.2 Command Levels...............................................................................................................................3-3
3.1.3 Command Line Views.......................................................................................................................3-3
3.1.4 Regular Expressions..........................................................................................................................3-3
3.2 Configuring the Command Line View ........................................................................................................3-4
3.3 Online Help of the Command Line.............................................................................................................3-7
3.4 Error Messages of the Command Line........................................................................................................3-8
3.5 History Commands......................................................................................................................................3-8
3.6 Editing Characteristics.................................................................................................................................3-9
3.7 Displaying Characteristics.........................................................................................................................3-10
3.8 Outputting the Display ..............................................................................................................................3-11
3.8.1 Vi ewing the Display........................................................................................................................3-11
3.8.2 Filtering the Display........................................................................................................................3-11
3.9 Filtering the Information Through Regular Expressions...........................................................................3-11
3.10 Shortcut Keys..........................................................................................................................................3-12
3.10.1 Classifying Shortcut Keys.............................................................................................................3-12
3.10.2 Defining Shortcut Keys.................................................................................................................3-14
3.10.3 Use of Shortcut Keys.....................................................................................................................3-14
3.11 Configuration Examples..........................................................................................................................3-14
3.11.1 Example for Using Shortcut Keys.................................................................................................3-14
4 Basic Configuration ...................................................................................................................4-1
4.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................4-2
4.1.1 Extension of Command Levels.........................................................................................................4-2
4.1.2 Extension of User Levels..................................................................................................................4-2
Page 5

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
4.2 Configuring Basic System Environment.....................................................................................................4-2
4.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................4-2
4.2.2 Switching Language Mode................................................................................................................4-3
4.2.3 Configuring the Device Name...........................................................................................................4-4
4.2.4 Configuring the System Clock..........................................................................................................4-4
4.2.5 Configuring the Header Text.............................................................................................................4-4
4.2.6 Configuring the Password for Switching User Levels ......................................................................4-5
4.2.7 Switching User Levels ......................................................................................................................4-5
4.2.8 Locking the User Interface................................................................................................................4-6
4.2.9 Configuring Command Privilege Levels...........................................................................................4-6
4.2.10 Displaying System Status Messages................................................................................................4-7
5 User Management ......................................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.1 User Interface View...........................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.2 User Management .............................................................................................................................5-3
5.2 Configuring a User Interface.......................................................................................................................5-5
5.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................5-5
5.2.2 Transmitting Messages Between User Interfaces..............................................................................5-6
5.2.3 Configuring Asynchronous Interface Attributes................................................................................5-6
5.2.4 Setting Terminal Attributes................................................................................................................5-7
5.2.5 Configuring the User Interface Priority............................................................................................. 5-8
5.2.6 Configuring Modem Attributes.........................................................................................................5-8
5.2.7 Configuring an Auto-executed Command.........................................................................................5-9
5.2.8 Configuring the Redirection Function...............................................................................................5-9
5.2.9 Configuring the Call-in or Call-out Restrictions of the VTY User Interface...................................5-10
5.2.10 Configuring the Maximum Number of VTY User Interfaces........................................................ 5-10
5.2.11 Configuring the Authentication T im eout Time for VTY Users.....................................................5-11
5.2.12 Disconnecting a Specified User Interface.....................................................................................5-11
5.2.13 Checking the Configuration..........................................................................................................5-11
5.3 Configuring User Management.................................................................................................................5-12
5.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................5-12
5.3.2 Configuring Authentication Mode...................................................................................................5-13
5.3.3 Configuring the Authentication Password.......................................................................................5-13
5.3.4 Setting Username and Password for AAA Local Authentication ....................................................5-14
5.3.5 Configuring the User Priority..........................................................................................................5-14
5.3.6 Checking the Configuration............................................................................................................5-14
5.4 Configuring the Local User Management .................................................................................................5-15
5.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................5-15
5.4.2 Creating the Local User Account ....................................................................................................5-16
5.4.3 Configuring the Service Type of the Local User.............................................................................5-16
5.4.4 Configuring FTP Directory Authority of the Local U ser.................................................................5-17
Page 6

Contents
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
iv
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
5.4.5 Configuring the Local User Status..................................................................................................5-17
5.4.6 Configuring the Local User Priority................................................................................................5-17
5.4.7 Configuring the Access Restriction of the Local User ....................................................................5-18
5.4.8 Checking the Configuration............................................................................................................5-18
5.5 Configuration Examples............................................................................................................................5-18
5.5.1 Example for Logging In to the Router Through Password Authentication.....................................5-19
5.5.2 Example for Logging In to the Router Through AAA.....................................................................5-20
6 File System ..................................................................................................................................6-1
6.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.1 File System........................................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.2 Storage Devices.................................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.3 Files...................................................................................................................................................6-2
6.1.4 Directories.........................................................................................................................................6-2
6.2 Managing Directories..................................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................6-2
6.2.2 Viewing the Current Directory..........................................................................................................6-3
6.2.3 Switching the Directory.....................................................................................................................6-3
6.2.4 Displaying the Directory of File........................................................................................................6-4
6.2.5 Creating a Directory.......................................................................................................................... 6-4
6.2.6 Deleting a Directory..........................................................................................................................6-4
6.3 Managing Files............................................................................................................................................6-5
6.3.1 Displaying Contents of a File............................................................................................................6-6
6.3.2 Copying a File...................................................................................................................................6-6
6.3.3 Moving a File....................................................................................................................................6-6
6.3.4 Renaming a File ................................................................................................................................6-7
6.3.5 Deleting a File...................................................................................................................................6-7
6.3.6 Deleting Files in the Recycle Bin......................................................................................................6-7
6.3.7 Undeleting Files ................................................................................................................................6-7
6.4 Configuring Batch Configuration................................................................................................................6-8
6.5 Managing Storage Devices..........................................................................................................................6-9
6.6 Configuring Prompt Modes.........................................................................................................................6-9
6.7 Example for Configuring Directory Management.....................................................................................6-10
7 Management of Configuration Files ......................................................................................7-1
7.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................7-2
7.1.1 Definitions.........................................................................................................................................7-2
7.1.2 Configuration Files and Current Configurations...............................................................................7-2
7.2 Displaying the Configuration of the Router................................................................................................7-2
7.2.1 Vi ewing the Intial Configuration.......................................................................................................7-2
7.2.2 Vi ewing the Current Configuration...................................................................................................7-3
7.2.3 Viewing the Running Configuration in the Current View.................................................................7-3
7.3 Saving the Current Configuration................................................................................................................7-3
Page 7

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v
7.4 Clearing the Running Information...............................................................................................................7-3
7.5 Comparing Configuration Files...................................................................................................................7-4
8 FTP, TFTP and XModem ..........................................................................................................8-1
8.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.1 FTP....................................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.2 TFTP .................................................................................................................................................8-2
8.1.3 XModem ...........................................................................................................................................8-2
8.2 Configuring the Router to be the FTP Server..............................................................................................8-3
8.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................8-3
8.2.2 Enabling the FTP Server ...................................................................................................................8-4
8.2.3 Configuring the Timeout Period........................................................................................................8-4
8.2.4 Configuring the Local Username and the Password..........................................................................8-4
8.2.5 Configuring Service Types and Authorization Information...............................................................8-5
8.2.6 Checking the Configuration..............................................................................................................8-5
8.3 Configuring FTP ACL.................................................................................................................................8-6
8.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................8-6
8.3.2 Enabling the FTP Server ...................................................................................................................8-6
8.3.3 Configuring the Basic ACL...............................................................................................................8-7
8.3.4 Configuring the Basic FTP ACL.......................................................................................................8-7
8.4 Configuring the Router to Be the FTP Client..............................................................................................8-8
8.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................8-8
8.4.2 Logging In to the FTP Server............................................................................................................8-8
8.4.3 Configuring File Transmission Mode................................................................................................8-9
8.4.4 Viewing Online Help of the FTP Command.....................................................................................8-9
8.4.5 Uploading or Downloading Files......................................................................................................8-9
8.4.6 Managing Directories......................................................................................................................8-10
8.4.7 Managing Files................................................................................................................................8-11
8.4.8 Changing Login Users.....................................................................................................................8-11
8.4.9 Disconnecting with FTP..................................................................................................................8-11
8.5 Configuring TFTP.....................................................................................................................................8-12
8.5.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................8-12
8.5.2 Downloading Files Through TFTP..................................................................................................8-12
8.5.3 Uploading Files Through TFTP ......................................................................................................8-13
8.6 Limiting the Access to the TFTP Server....................................................................................................8-13
8.6.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................8-13
8.6.2 Configuring the Basic ACL.............................................................................................................8-14
8.6.3 Configuring the Basic TFTP ACL...................................................................................................8-14
8.7 Configuring XModem...............................................................................................................................8-15
8.7.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................8-15
8.7.2 Getting a File Through XModem....................................................................................................8-15
8.8 Configuration Examples............................................................................................................................8-16
Page 8

Contents
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
vi
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
8.8.1 Example for Configuring the FTP Server........................................................................................8-16
8.8.2 Example for Configuring FTP ACL................................................................................................8-18
8.8.3 Example for Configuring the FTP Client........................................................................................8-20
8.8.4 Example for Configuring TFTP ......................................................................................................8-21
8.8.5 Example for Configuring XModem................................................................................................8-23
9 Telnet and SSH...........................................................................................................................9-1
9.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................9-1
9.1.1 Overview of User Login....................................................................................................................9-2
9.1.2 T elnet Te rm inal Services...................................................................................................................9-2
9.1.3 SSH Terminal Services......................................................................................................................9-3
9.2 Configuring T elnet Te rminal Services.........................................................................................................9-6
9.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................9-6
9.2.2 Establishing a Telnet Connection......................................................................................................9-7
9.2.3 Scheduled Telnet Disconnection.......................................................................................................9-7
9.2.4 Checking the Configuration..............................................................................................................9-7
9.3 Configuring SSH Users...............................................................................................................................9-8
9.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..................................................................................................9-8
9.3.2 Creating an SSH User .......................................................................................................................9-9
9.3.3 Configuring SSH for the VTY User Interface.................................................................................9-10
9.3.4 Generating a Local RSA Key Pair...................................................................................................9-10
9.3.5 Configuring the Authentication Mode for SSH Users.....................................................................9-11
9.3.6 Configuring the Basic Authentication Information for SSH Users.................................................9-12
9.3.7 Authorizing SSH Users Through the Command Line.....................................................................9-12
9.3.8 Configuring the Service Type of SSH Users................................................................................... 9-13
9.3.9 Configuring the Authorized Directory of SFTP Service for SSH Users..........................................9-13
9.3.10 Checking the Configuration..........................................................................................................9-13
9.4 Configuring the SSH Server......................................................................................................................9-14
9.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................9-14
9.4.2 Enabling the STelnet Service...........................................................................................................9-15
9.4.3 Enabling the SFTP Service..............................................................................................................9-15
9.4.4 Enabling the Earlier Version-Compatible Function.........................................................................9-15
9.4.5 Configuring the Number of the Port Monitored by the SSH Server................................................9-16
9.4.6 Enabling the Tra p Function.............................................................................................................9-16
9.4.7 Configuring the Interval for Updating the Key Pair on the SSH Server .........................................9-17
9.4.8 Checking the Configuration............................................................................................................9-17
9.5 Configuring the STelnet Client Function...................................................................................................9-17
9.5.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................9-17
9.5.2 Enabling the First-Time Authentication on the SSH Client.............................................................9-18
9.5.3 Configuring the SSH Client to Assign the RSA Public Key to the SSH Server..............................9-19
9.5.4 Enabling the STelnet Client.............................................................................................................9-19
9.5.5 Checking the Configuration............................................................................................................9-20
Page 9

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii
9.6 Configuring the SFTP Client Function......................................................................................................9-20
9.6.1 Establishing the Configuration Task................................................................................................9-20
9.6.2 Configuring the First-Time Aut hentication on the SSH Client .......................................................9-21
9.6.3 Configuring the SSH Client to Assign the RSA Public Key to the SSH Server..............................9-21
9.6.4 Enabling the SFTP Client................................................................................................................9-21
9.6.5 Managing the Directory...................................................................................................................9-22
9.6.6 Managing the File............................................................................................................................9-23
9.6.7 Displaying the SFTP Client Command Help...................................................................................9-23
9.6.8 Checking the Configuration............................................................................................................9-24
9.7 Maintaining Telnet and SSH......................................................................................................................9-24
9.7.1 Debugging Telnet Terminal Services...............................................................................................9-24
9.7.2 Debugging SSH Terminal Services.................................................................................................9-25
9.8 Configuration Examples............................................................................................................................9-26
9.8.1 Example for Configuring Te lnet Term inal Services........................................................................9-26
9.8.2 Example for Connecting the STelnet Client to the SSH Server.......................................................9-27
9.8.3 Example for Connecting the SFTP Client to the SSH Server..........................................................9-33
9.8.4 Example for Accessing the SSH Server Through Other Port Numbers...........................................9-37
9.8.5 Example for Authenticating SSH Through RADIUS......................................................................9-43
10 Router Maintenance ..............................................................................................................10-1
10.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................10-2
10.1.1 Device Operation Management.....................................................................................................10-2
10.1.2 Electronic Label ............................................................................................................................10-2
10.2 Powering off the FIC/HIC.......................................................................................................................10-2
10.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................10-2
10.2.2 Powering off the FIC/HIC.............................................................................................................10-3
10.2.3 Checking the Configuration ..........................................................................................................10-3
10.3 Managing the Device Operation..............................................................................................................10-4
10.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................10-4
10.3.2 Specifying the Slave RPU.............................................................................................................10-5
10.3.3 Restarting the Router.....................................................................................................................10-5
10.3.4 Performing the Master/Slave Switchover......................................................................................10-6
10.4 Monitoring the Router Status ..................................................................................................................10-7
10.4.1 Displaying the Basic Device Information .....................................................................................10-7
10.4.2 Displaying the System Version Information..................................................................................10-7
10.4.3 Displaying the Restart Information of RPU..................................................................................10-8
10.5 Configuring the Electronic Label............................................................................................................10-9
10.5.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................10-9
10.5.2 Querying the Electronic Label.......................................................................................................10-9
10.5.3 Backing Up the Electronic Label ..................................................................................................10-9
11 System Software Upgrade ....................................................................................................11-1
11.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................11-2
Page 10

Contents
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
viii
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
11.1.1 System Software Upgrade.............................................................................................................11-2
11.1.2 License ..........................................................................................................................................11-2
11.2 Uploading the System Software and License Files..................................................................................11-3
11.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................11-3
11.2.2 Uploading the System Software and License to the Master RPU...............................................11-3
11.2.3 Copying the System Software and License to the Slave RPU....................................................11-4
11.2.4 Checking the Configuration...........................................................................................................11-4
11.3 Specifying the System Software for the Next Startup of the Router.......................................................11-5
11.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................11-5
11.3.2 Specifying the System Software for the Next Startup of the Master RPU .................................11-5
11.3.3 Specifying the System Software for the Next Startup of the Slave RPU....................................11-6
11.3.4 Checking the Configuration...........................................................................................................11-6
12 Patch Management.................................................................................................................12-1
12.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................12-2
12.2 Checking the Running of Patch in the System........................................................................................12-3
12.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................12-3
12.2.2 Checking the Running of Patch on the RPU.................................................................................12-3
12.3 Loading a Patch.......................................................................................................................................12-4
12.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................12-4
12.3.2 Uploading a Patch to the Root Directory of the Flash of the Master RPU.................................12-4
12.3.3 Copying a Patch to the Root Directory of the Flash of the Slave RPU ......................................12-5
12.4 Installing a Patch on the RPU...............................................................................................................12-5
12.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................12-5
12.4.2 Uploading the RPU Patch..............................................................................................................12-6
12.4.3 Activating the RPU Patch...........................................................................................................12-6
12.4.4 Running the RPU Patch.................................................................................................................12-6
12.5 Stop Running the RPU Patch...................................................................................................................12-7
12.5.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................12-7
12.5.2 Deactivating the RPU Patch.......................................................................................................12-7
12.6 Unloading the RPU Patch........................................................................................................................12-7
12.6.1 Establishing the Configuration Task..............................................................................................12-7
12.6.2 Deleting the RPU Patch.................................................................................................................12-8
A Glossary .................................................................................................................................... A-1
B Acronyms and Abbreviations ................................................................................................ B-1
Index ................................................................................................................................................ i-1
Page 11

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Figures
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ix
Figures
Figure 1-1 architecture......................................................................................................................................1-3
Figure 2-1 Networking diagram of logging in through the console port..........................................................2-7
Figure 2-2 New connection..............................................................................................................................2-8
Figure 2-3 Setting the port................................................................................................................................2-9
Figure 2-4 Setting the port communication param e ters....................................................................................2-9
Figure 2-5 Establishing the configuration environment through WAN..........................................................2-10
Figure 2-6 Running the Telnet program on the PC.........................................................................................2-11
Figure 2-7 Establishing the remote configuration environment.....................................................................2-11
Figure 8-1 Using FTP to download files.........................................................................................................8-16
Figure 8-2 FTP ACL.......................................................................................................................................8-18
Figure 8-3 Configuring the FTP client............................................................................................................8-20
Figure 8-4 Using TFTP to download files......................................................................................................8-21
Figure 8-5 Setting the Base Directory of the TFTP server.............................................................................8-22
Figure 8-6 Specifying the file to be sent.........................................................................................................8-23
Figure 9-1 Telnet client services .......................................................................................................................9-2
Figure 9-2 Usage of Telnet shortcut keys.........................................................................................................9-3
Figure 9-3 Establishing an SSH channel in a LAN..........................................................................................9-4
Figure 9-4 Establishing an SSH channel in a WAN..........................................................................................9-4
Figure 9-5 Networking diagram of the Telnet terminal services mode...........................................................9-26
Figure 9-6 Networking diagram of connecting the STelnet client to the SSH server.....................................9-28
Figure 9-7 Networking diagram of connecting the SFTP client to the SSH server........................................9-34
Figure 9-8 Networking diagram of accessing the SSH server through other port numbers............................9-38
Figure 9-9 Networking diagram of authenticating the SSH through RADIUS..............................................9-43
Figure 12-1 Conversion between the statuses of a patch................................................................................12-2
Page 12

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations T ables
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
xi
Tables
Table 1-1 System service features.....................................................................................................................1-4
Table 3-1 Command line views ........................................................................................................................3-5
Table 3-2 Common error messages of the command line.................................................................................3-8
Table 3-3 Access the history commands...........................................................................................................3-9
Table 3-4 Editing functions...............................................................................................................................3-9
Table 3-5 Displaying functions.......................................................................................................................3-10
Table 3-6 Metacharacter description...............................................................................................................3-11
Table 3-7 System-defined shortcut keys .........................................................................................................3-12
Table 5-1 Example for the absolute numbering................................................................................................5-3
Page 13

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
About This Document..................................................................................................................... 1
Page 14
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations About This Document
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1
About This Document
Purpose
This part describes the organization of this document, product version, intended audience,
conventions, and update history.
Related Versions
The following table lists the product versions related to this document.
Product Name Version
Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series Routers V200R005
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
z
Commissioning engineer
z
Data configuration engineer
z
Network monitoring engineer
z
System maintenance engineer
Organization
This document consists of six chapters and is organized as follows.
Chapter Content
1 Product Overview This chapter describes the architecture, functional features
and main functions of the NE20/20E.
2 Establishment of the
Configuration Environment
This chapter describes the procedures to set up the
configuration environments through CON, Telnet, and
AUX.
Page 15
About This Document
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Chapter Content
3 CLI Overview This chapter describes the command line interface,
command levels, command views and hot keys.
4 Basic Configurtion This chapter describes how to configure the basic system
environment on the router
5 User Management This chapter describes the basic concepts of the user
interface and the user management
6 File System This chapter describes the file system and its configuration,
uploading and downloading files through FTP, TFTP and
XModem, and the management of configuration file.
7 Management of
Configuration Files
This chapter describes how to configure the file
management.
8 FTP,TFTP and XModem This chapter describes how to configure the basic functions
of the FTP server.
9 Telnet and SSH This chapter describes how to log in to the router through
Telnet and configure the router.
10 Router Maintenance This chapter describes the principle and concepts of the
router maintenance.
11 System Software
Upgrade
This chapter describes the pr inciple and concepts of th e
system software upgrade.
12 Patch Management This chapter describes the principle and concepts of patch
management.
Appendix A Glossary & B
Acronyms and
Abbreviations
This chapter collates glossary and frequently used
acronyms and abbreviations in this manual.
Index This chapter collates important keywords used in this
manual to help the reader to access the required information
quickly.
Conventions
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol Description
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk, which if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Page 16
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations About This Document
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3
Symbol Description
Indicates a hazard with a medium or low level of risk, which if
not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which if not
avoided, could result in equipment damage, data loss,
performance degradation, or unexpected results.
Indicates a tip that may help you solve a problem or save time.
Provides additional information to emphasize or supplement
important points of the main text.
General Conventions
The general conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention Description
Times New Roman Normal paragraphs are in Times New Roman.
Boldface
Names of files, directories, folders, and users are in
boldface. For example, log in as user root.
Italic Book titles are in italics.
Courier New
Examples of information displayed on the screen are in
Courier New.
Command Conventions
The command conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention Description
Boldface
The keywords of a command line are in boldface.
Italic Command arguments are in italics.
[ ] Items (keywords or arguments) in square brackets [ ] are
optional.
{ x | y | ... } Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected.
[ x | y | ... ] Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected or no item is selected.
{ x | y | ... } * Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. A minimum of one item or a maximum of all
items can be selected.
Page 17
About This Document
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
4
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Convention Description
[ x | y | ... ] * Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. Several items or no item can be selected.
&<1-n>
The parameter before the & sign can be repeated 1 to n
times.
# A line starting with the # sign is comments.
GUI Conventions
The GUI conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention Description
Boldface
Buttons, menus, parameters, tabs, windows, and dialog titles
are in boldface. For example, click OK.
> Multi-le ve l m enus are in boldface and separated by the ">"
signs. For example, choose File > Create > Folder.
Keyboard Operations
The keyboard operations that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Format Description
Key
Press the key. For example, press Enter and press Tab.
Key 1+Key 2 Press the keys concurrently. For example, pressing
Ctrl+Alt+A means the three keys should be pressed
concurrently.
Key 1, Key 2 Press the keys in turn. For example, pressing Alt, A means
the two keys should be pressed in turn.
Mouse Operations
The mouse operations that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Action Description
Click Select and release the primary mouse button without
moving the pointer.
Double-click Press the primary mouse button twice continuously and
quickly without moving the pointer.
Page 18
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations About This Document
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5
Action Description
Drag Press and hold the primary mouse button and move the
pointer to a certain position.
Update History
Updates between document issues are cumulative. Therefore, the latest document issue
contains all updates made in previous issues.
Updates in Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
For fifth commercial release.
Updates in Issue 04 (2008-07-24)
For fourth commercial release.
Updates in Issue 03 (2007-07-20)
For third commercial release.
Updates in Issue 02 (2007-06-15)
For second commercial release.
Modified the naming method of the manual version.
Updates in Issue 01(2007-03-18)
The commercial release has the following updates:
Initial field trial release.
Page 19

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
1 Product Overview ......................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.1 NE20/20E.............................................................................................................................................1-2
1.1.2 Architecture.......................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.3 VRP......................................................................................................................................................1-3
1.2 Functional Features.......................................................................................................................................1-4
1.3 Functions.......................................................................................................................................................1-9
1.3.1 File System ........................................................................................................................................1-10
1.3.2 SNMP Configuration.........................................................................................................................1-10
1.3.3 T erm inal Services...............................................................................................................................1-11
1.3.4 High Reliability..................................................................................................................................1-11
1.3.5 Interfaces............................................................................................................................................1-12
1.3.6 Link Layer Protocols..........................................................................................................................1-12
1.3.7 IP Services..........................................................................................................................................1-13
1.3.8 Unicast Routing Protocols .................................................................................................................1-13
1.3.9 Multicast Routing Protocols...............................................................................................................1-14
1.3.10 MPLS Features.................................................................................................................................1-14
1.3.11 VPN Services...................................................................................................................................1-15
1.3.12 QoS..................................................................................................................................................1-15
1.3.13 Security Features..............................................................................................................................1-17
Page 20

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Figures
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Figures
Figure 1-1 architecture.......................................................................................................................................1-3
Page 21

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations T ables
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v
Tables
Table 1-1 System service features ......................................................................................................................1-4
Page 22
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-1
1 Product Overview
About This Chapter
The following table shows the contents of this chapter.
Section Description
1.1 Introduction This section describes the characteristics of the
NE20/20E.
1.2 Functional Features This section describes the functional features of the
NE20/20E.
1.3 Functions This section describes the main functions of the
NE20/20E.
Page 23

1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-2 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
1.1 Introduction
This section covers what you need to learn about the NE20/20E:
z
NE20/20E
z
Architecture
z
VRP
1.1.1 NE20/20E
The NE20/20E router is grouped into NE20-2, NE2 0-4 a nd NE2 0-8 in terms of the number of
slots. The NE20E series router has only one type, the NE20E-8. The equipment structure and
the system of the NE20E are almost the same as the NE20. All of them adopt modular
architecture, providing many kinds of optional multifunctional interface modules such as
High-speed Interface Card (HIC) and Flexible Interface Card (FIC).
The NE20/20E series routers provide coherent network interface, user interface and
management interface as well as strong flexibility and configurability. The routers integrate
many emerging technologies, such as Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS), Virtual Private
Network (VPN), Quality of Service (QoS), traffic engineering, multicast, and user
management. The routers also support abundant link layer protocols. In networking
applications, as high-performance convergence devices, the routers can provide overall
service processing capacity and flexible network solutions, and thus effectively add the
network value and save the construction cost.
1.1.2 Architecture
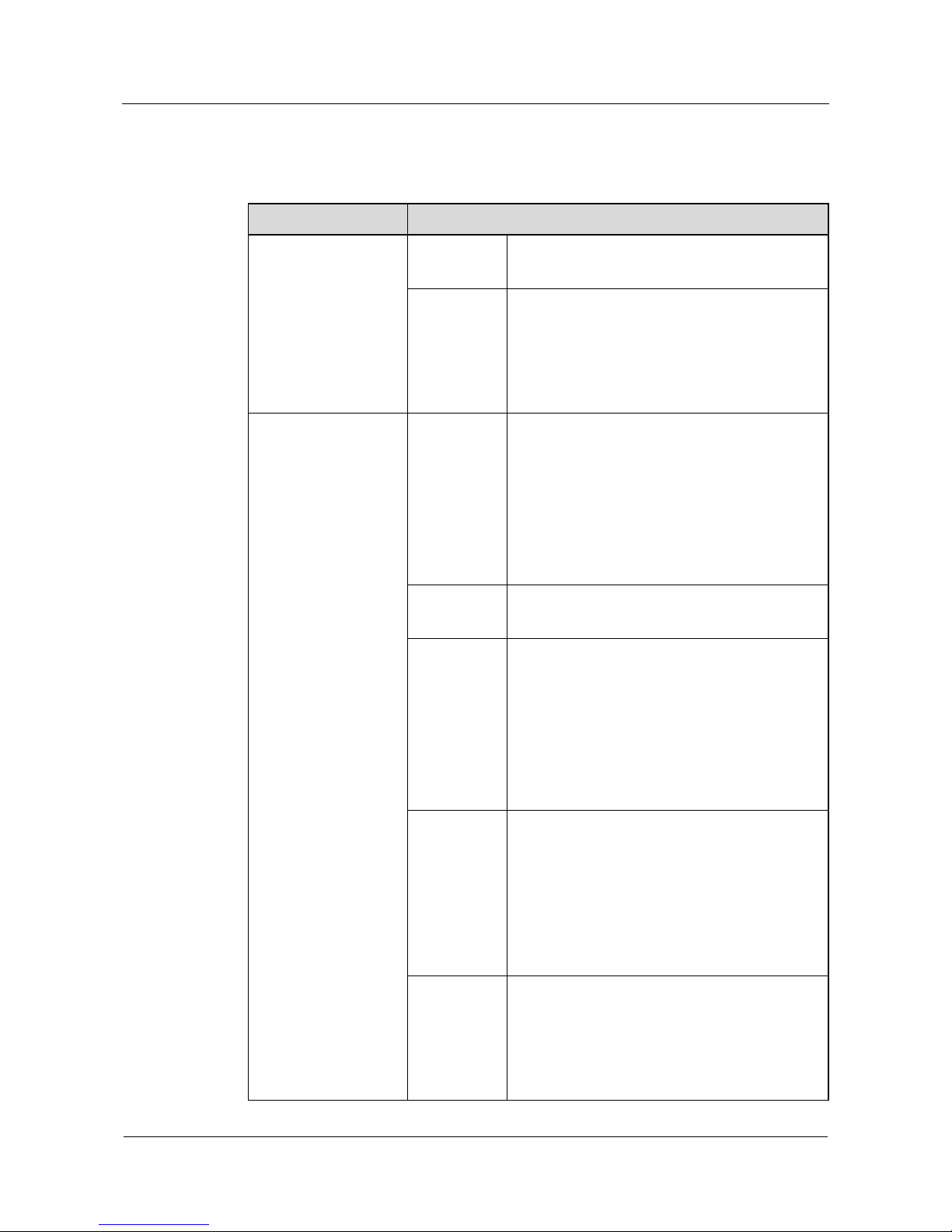
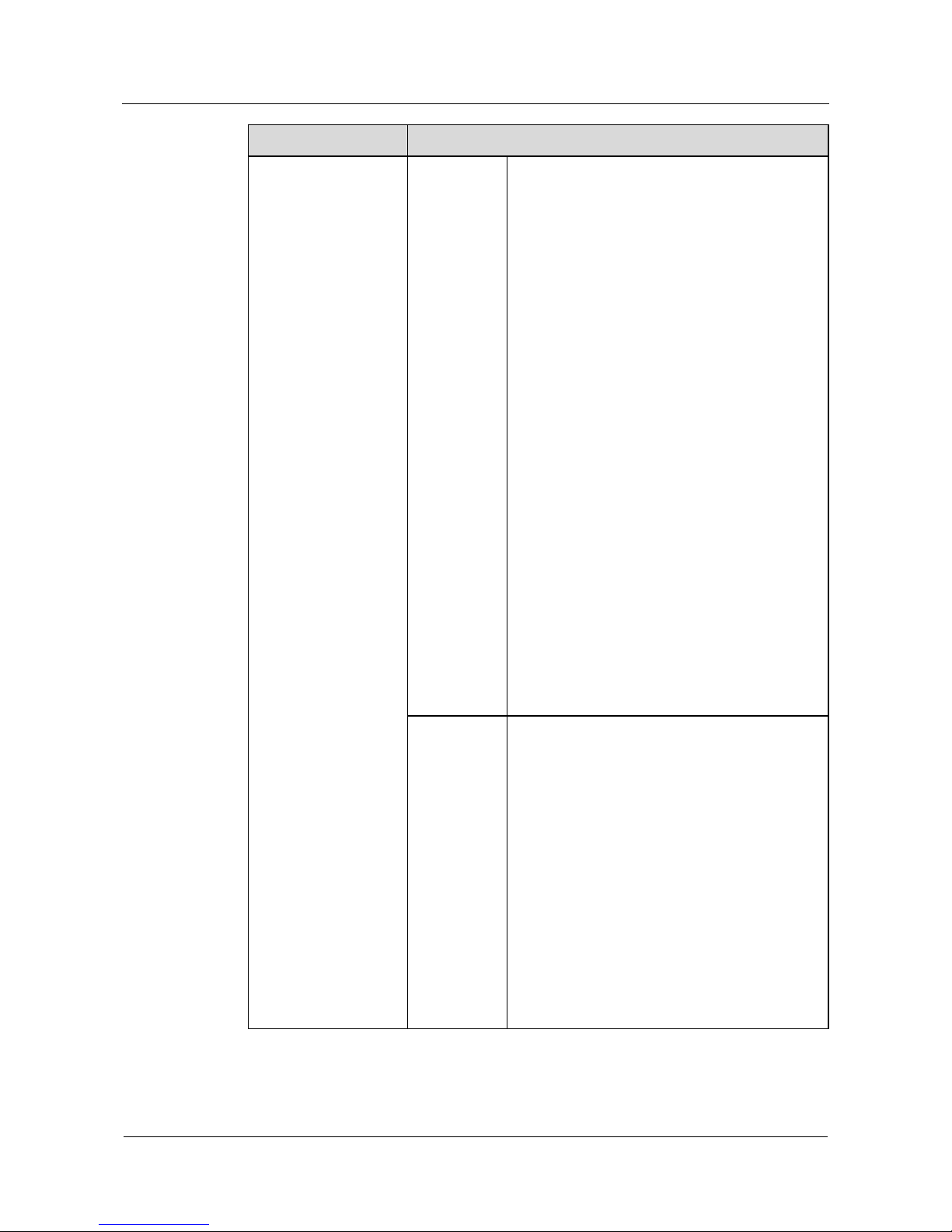
Based on the TCP/IP structure model, the NE20/20E supports multiple data link layer
protocols, network layer protocols and application layer protocols, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Page 24

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-3
Figure 1-1 architecture
Service Control Plane(SCP)
Protocol Client
AAA/Local-MCM
Data Forwarding Plane(DFP)
FE API
FEC
FE DRV
FE
General Control Plane(GCP)
Routing
URP4/6 MRP4/6
VPN_ExTE_Ex
RM4/6
VPN
L2VPN/L3VPN
IP Stack
Application Layer
Socket Layer
TCP4/6 UDP4/6
IP4/6 ICMP4/6
MPLS
CSPF/CR-LDP/
RSVP-TE
Net Interface
IFNET/PPP/ETH/
ATM/Tunnel
Security
FireWall/ACL/
NAT
QoS
BW-M/QoSM/
RSVP
System Manage
Plane(SMP)
Config Management
CLI/SNMP/WebUI
CMO
Information
Management
Trace/State Multi
Languages
Device
Management
Hot Plug
Switch Over
System Servic e Plane(SSP)
RPC
IPC
OSAL
Operating System
1.1.3 VRP
The Versatile Routing Platform (VRP) is a versatile operating system platform. It is developed
for the data communication products of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred
to as Huawei). VRP takes the IP service as its core service, and has a modular architecture. It
can provide rich functional features and scalability based on applications.
With TCP/IP as its core protocol suite, VRP is Huawei's proprietary network operating system
and it can do the following:
z
Integrates routing, QoS, VPN, security and IP voice in the operating system.
z
Provides excellent data forwarding capabilities for routing equipment by using the IP
TurboEngine technology.
z
Provides various hardware platforms with consistent network interface, user interface
and management interface.
z
Provides users with flexible application solutions.
At the same time, the VRP is a sustainable platform. It protects users' investments to the
maximum extent.
Page 25
1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-4 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
1.2 Functional Features
Table 1-1 System service features
Service Features Description
LAN
protocol
Ethernet
VLAN
Network
interconnection
Link Layer
protocol
PPP and MP
HDLC (High-level Data Link Control)
Frame Relay
ATM
PPPoE, IPoA, PPPoA and PPPoEoA
IP service ARP
Domain name resolution
NAT
IP unnumbered address
DHCP relay and DHCP server
IP policy-based routing
IP packet filtering
Protocol
stacks
IPv4 and IPv6 dual protocol stacks
IPv6 forwarding through the hardware
IPv4 routing Static route management
Dynamic unicast routing protocols:
RIP-1/RIP-2
OSPF
IS-IS
BGP-4/MBGP/BGP VPN V4
Routing policies
IPv6 routing IPv4-to-IPv6 transition technologies: manual
configuration of the tunnel, automatic
configuration of the Tunnel, 6to4 tunnel,
NAT-PT on the hardware
IPv6 static route, BGP4/BGP4+, RIPng,
OSPFv3, and ISISv6 dynamic routing protocol
IPv6 MIB: ICMPv6 MIB, UDP6 MIB, TCP6
MIB, and IPv6 MIB
Network protocol
IP Multicast
protocols
IGMP
PIM-DM, PIM-SM
PIM-SSM
MBGP
MSDP
Page 26
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-5
Service Features Description
MPLS MPLS Basic MPLS forwarding
MPLS LDP
MPLS TE
MPLS QoS
Hierarchy of PE (HoPE)
L2VPN MPLS L2VPN (Martini, Kompella, CCC and
SVC)
VPLS
L2TP
PWE3 Single- and multi-hop PWs in LDP mode
Static PW, dynamic PW, and RSVP-PW
LSP, GRE and TE tunnels
Pseudo wire templates
Interconnection with different media
PW QoS
Many encapsulation modes: Ethernet, VLAN,
FR, PPP, HDLC, ATM-n-to-1, ATM-1-to-1, and
ATM-SDU
Multi-hop LDP-PW loop detection
PWE3 inter-AS
Interworking between PWE3 and VPLS
ATM QoS class, CLP, DSCP, 801.1p, and MPLS
EXP mapping
ATM OAM transparent transmission
VPN
L3VPN MPLS/BGP VPN, serving as PE/ P
Inter-AS VPN
Hierarchy of VPN (HoVPN)
GRE
AAA service CHAP authentication
PAP authentication
RADIUS
HWTACACS
Local user management
Network security
IPSec
encryption
IKE and IPSec through hardware, including IKE
negotiation, IPSec packet process and SA
management
Page 27
1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-6 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Service Features Description
NetStream Making a NetStream flow with a septet,
including the source IP address, destination IP
address, source port number, destination port
number, IP protocol type, IP TOS, and ingress
information
Recording and measuring information of traffic
The routing and peer entity information: the next
hop address, source AS number, destination AS
number, source address mask, destination
address mask
Exporting statistics packets in format V5, V8 and
V9
Convergence according to AS, protocol-port,
source-prefix, destination-prefix, prefix and ToS
Connecting normal ageing and compelled ageing
configured by users
Monitoring TCP link state
Making a flow with fragments (the first
fragment)
NAT NetStream
Inbound/Outbound NetStream of MPLS
Collecting packet information either in definite
proportion or random proportion
Multicast data flow
ATM, POS, ETH (including high speed and low
speed card FE/GE), VLAN sub-interface, E1,
HSSI and CE1 statistics
NAT Pure IP address translation, and simultaneous
translation of IP address and port number
Load balancing between multiple public network
egresses
Internal servers
Hybrid addressing of internal networks
Various NAT ALGs
One public network to multiple private networks,
and one private network to multiple public
networks
Traffic limit and rate limit to specific users
Traffic limit to BT
NAT statistics
NAT log
Page 28
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-7
Service Features Description
Other
security
features
Terminal access security
IP Packet filtering (interface based ACL and
time-range based ACL)
Firewall (packet filtering firewall and state
firewall)
Port mirroring
Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (URPF)
Hierarchical protection of commands to ensure that the
unauthorized users have no access to the router
Redundancy
hot backup
1:1 backup of RPU and NPU
Power 1+1 redundancy backup
Power, fan and service interface module hot
plugging as well as automatic adjustment of fan
rotate speed
GR Protocol-level GR: IS-IS, OSPF, BGP and LDP
FRR IP FRR
MPLS TE FRR
VPN FRR
LDP FRR
BFD Creating, deleting and modifying a BFD session
Bi-directional fault detection for links
Deleting faults in asynchronous and query modes
BFD detection of single- and multi-hop links
Providing information of link state for the
application layer by BFD
Automatic switchover for protection
Device reliability
Other
features
backup center
VRRP
NextHop Backup
Maintainability Automatic fault diagnosis function
remote configuration and maintenance through AUX
Page 29
1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-8 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Service Features Description
Traffic
classification
Simple traffic classification
Complex traffic classification, based on the port
number, layer 2, layer 3 and layer 4 packet
information
Traffic
policing and
shaping
Traffic policing and shaping based on srTCM
and trTCM
Services such as EF and AF based on Diff-Serv
GTS
Congestion
management
LLS, LLQ, NLS, PQ, CQ, WFQ, and CBWFQ
Congestion
avoidance
RED, WRED and SARED
Policy-based
routing
Route re-direction, and distribution of LSP
explicit route of MPLS
MPLS QoS Mapping between DSCP and EXP at the domain
boundary
L2 QoS 802.1p mark and DSCP/IP Precedence mark
QoS
HQoS Hierarchical QoS
Page 30
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-9
Service Features Description
Command
line interface
Local configuration through the console port
Local configuration or remote configuration
through the Aux port
Local configuration or remote configuration
through Telnet
Local configuration or remote configuration
through SSH login
Command hierarchical protection to prevent
unauthorized users from accessing the router
Detailed debugging information that help
diagnose network faults
Network test tools such as tracert and ping
commands to quickly diagnose the network
The Telnet command to log in to and manage
other routers
FTP Server/Client: to download and upload
configuration files and application programs
through FTP
TFTP Client: to download and upload
configuration files and application programs
through TFTP
To download configuration file s and application
programs locally by using the Xmodem protocol
Log function
Virtual file system
User-interface configuration: multiple modes of
authentication and authorization for login users
Time service Time zone
NTP Server and NTP Client
Online
service
Online loading
Online upgrade
Information
processing
center
Outputting alarm information and log
information to the log host and login user
terminal through SNMP Agent and cache buffer
Configuration
management
Network
management
SNMP V1/V2c/VC3
RMON and RMON2
1.3 Functions
This section covers the following contents:
Page 31

1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-10 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
z
File System
z
SNMP Configuration
z
Terminal Services
z
High
z
Link Layer Protocols
z
IP
z
Unicast Routing Protocols
z
Multicast Routing Protocols
z
VPN Services
z
QoS
z
Security Features
1.3.1 File System
The NE20/20E provides rich file system functionality that can:
z
Facilitate your management over the files and directories in a storage device.
z
Support such operations as deleting a file, recovering a deleted file, clearing the files in
the recycle bin, displaying the contents of a file, renaming a file, copying a file, moving a
file, running batch processing files and displaying the information of a specified/private
file.
The NE20/20E supports file transmission service between remote hosts through FTP:
z
FTP Server service: You can log in to NE20/20E for file access by running the FTP client
program.
z
FTP Client service: You can log in to a router with a terminal emulation program or
Telnet and run certain FTP command to establish a connection with the remote FTP
Server to access the files on the remote host.
The NE20/20E can:
z
Support the TFTP-based file transmission to fit into the environments with simple
client-server interworking.
z
Support Xmodem-based file transmission that can be applied to the AUX port to support
128-byte packets and Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC).
The HyperTerminal has the function to send files.
1.3.2 SNMP Configuration
The NE20/20E supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), one of most
widely applied protocol on data communications networks, to do the following:
z
Transmit management information between any two points.
z
Makes it possible for an administrator to conduct information retrieval, information
modification, fault location, fault diagnosis, capacity planning and report generation on
any node of the network.
The SNMP Agent of the NE20/20E supports public MIBs prescribed by a series of RFCs and
those defined by Huawei so as to implement real-time monitoring over a great amount of
network devices. It has been widely applied and accepted by more and more customers.
Page 32

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-11
1.3.3 Terminal Services
Telnet Service
The NE20/20E supports the versatile Telnet Server and the Telnet Client services. They enable
you to log in to a specified port of a router from your PC by running Telnet client and then to
initiate communication with the device connecting to the asynchronous serial port of the
router. In this way, you realize remote configuration and maintenance for the device.
SSH Terminal Service
Network attacks are usually triggered by the Telnet service that is provided by the server. As
the Telnet protocol does not provide a secure authentication mode and the data transmitted
over the TCP is in plain text, this challenges the security of the network.
The NE20/20E provides Secure Shell (SSH) service and supports PASSWORD, RSA
authentication, DES and 3DES encryption:
z
The user name and password used for the communication between the SSH client and
server are encrypted, which effectively prevents the password from being intercepted.
z
Meanwhile, the SSH service encrypts the data in transmission to ensure the security and
reliability of the data.
z
All of these make it possible for secure remote access to be implemented over insecure
networks.
z
The RSA authentication, in particular, realizes secure key exchange and final secure
session by generating a public key and a private key according to the encryption
principal for asymmetric encryption system.
1.3.4 High Reliability
The NE20/20E effectively ensures the network availability through redundancy of key
modules, high availability of Line Processing Units (LPUs), Fast Reroute (FRR) and Graceful
Restart (GR).
Redundancy of Key Modules
The NE20/20E can work with a single Routing Process Unit (RPU) or two RPUs in
redundancy. The RPU of the NE20/20E supports hot backup.
The NE20/20E supports the following two switchover methods:
z
Automatic switchover
z
Forcible switchover
The NE20/20E supports backup of management bus and 1+1 backup for the power module.
The LPU, the power module and the fan modules are hot swappable.
IP/MPLS Fast Reroute
The Fast Reroute (FRR) can minimize data loss due to network faults. The switch time can
achieve less than 50 ms
The NE20/20E provides the following FR functions:
z
IP fast reroute
Page 33

1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-12 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
z
LDP FRR
z
TE FRR
z
VPN FRR
GR
The Graceful Restart (GR) is a key technology for providing HA. Network administrators or
faults may trigger GR. GR upon network faults does not delete the routing information in the
routing or forwarding table or reset the LPU so that services are not interrupted.
The NE20/20E supports system-based GR and protocol-based GE. The protocol-based GR are
as follows:
z
BGP GR
z
OSPF GR
z
ISIS GR
z
MPLS LDP GR
z
L3 VPN GR
1.3.5 Interfaces
The NE20/20E supports rich interface types:
z
Physical interface that falls into the LAN interface and the WAN interface
z
Logical interfaces that is not physical but configured to carry out data exchange
The NE20/20E supports the following physical interfaces:
z
Ethernet interface
z
POS interface
z
CPOS interface
z
ATM interface
z
E1/CE1/CT1/CE3
The NE20/20E supports the following logical interfaces: sub-interface, virtual Ethernet
interface, Loopback interface, Null interface and Tunnel interface.
1.3.6 Link Layer Protocols
The NE20/20E supports abundant protocols that are related to the link layer, including PPP,
HDLC, ATM, IP over ATM, 1483B, RPR, RRPP and FR.
The NE20/20E can:
z
Support VLAN and realizes the VLAN function under the IEEE 802.1Q specification.
z
Support IP packet forwarding between different VLANs.
z
Intercommunicate with the devices of other vendors in the industry.
z
Carry out data forwarding between several VLANs on a single physical Ethernet
interface, by creating several sub-interfaces (each of which acts as an independent
Ethernet interface) for each Ethernet interface, which saves the interface resource
effectively.
Page 34

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-13
1.3.7 IP Services
Configuring Interface IP Address Flexibly
The NE20/20E provides rich applications based on IP address.
z
Support for multiple secondary IP addresses: Each interface can be configured with a
primary IP address and several subordinate IP addresses to be connected to different
subnets. This improves the efficiency of networking.
z
IP address negotiable: Users who access the Internet through an ISP are usually allocated
with addresses by a remote server. This requires the interface to be encapsulated with the
PPP and configured as IP address negotiable so that it can accept the IP addresses
allocated by the peer end through PPP negotiation.
z
IP unnumbered: To enable an interface not configured with an address to operate
normally, you can borrow the IP address of another interface to spare the IP address.
ARP Functions
The NE20/20E supports dynamic and static ARP functions.
Under special circumstance (such as some fixed IP addresses available on the LAN gateway),
you can use the static ARP function to bind these IP addresses to a specified network interface
card. This is to ensure that the packets heading for these addresses must be forwarded by the
gateway. When you desire to filter some illegal IP addresses, you can configure the static ARP
table manually.
DHCP Relay
The standard DHCP only applies to the cases where the DHCP client and server lie on the
same subnet. It is necessary to set a DHCP server for every subnet in order to provide
dynamic host configuration for clients on different subnets. This is absolutely not economical.
The NE20/20E uses DHCP relay function to:
z
Provide relay service for the DHCP clients and servers across different subnets.
z
transmit DHCP packets to the destination DHCP server (or client) crossing the subnet
relay. So the DHCP clients of different subnets can share one DHCP server, and therefore,
centralized management of clients' information.
Policy-based Routing
Policy-based routing is a route selection mechanism that is based on customized policy. The
policy-based routing provided by the NE20/20E supports flexible route assignment based on
such information of the input packets as source address and address length.
Multicast packets are usually forwarded according to the routing table. By customizing the
routing policy for multicast traffic, however, you can have multicast packets forwarded
according to a specific policy.
1.3.8 Unicast Routing Protocols
In terms of routing protocols, the NE20/20E can:
z
Support both static routing and dynamic routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF, IS-IS and
BGP.
Page 35

1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-14 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
z
Perform centralized management over the routes discovered by these protocols.
z
Provide varying routing policies, implementing sharing of routes discovered by both
static and dynamic routing protocols.
In networking practice, the routing table is always large, while the memory of the router is
limited. To ease this contradiction, the NE20/20E provides a size control mechanism for
routing tables. It monitors the current free memory of the system, based on which it decides
whether to add routes to the routing table and whether to keep the connection of the routing
protocol.
Besides, the NE20/20E supports load sharing and route backup functions.
1.3.9 Multicast Routing Protocols
IGMP
The NE20/20E supports the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) that is used to
establish and maintain the multicast members between the IP host and the directly connected
multicast routers.
Various Multicast Routing Protocols
The NE20/20E supports various multicast routing protocols as follows:
z
Protocol Independent Multicast-Dense Mode (PIM-DM) and Protocol Independent
Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) that are used in the same area
z
Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) and Multi-protocol Border Gateway
Protocol (MBGP) that are used between areas
1.3.10 MPLS Features
The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) uses short labels with fixed length to encapsulate
network layer packets, and it can:
z
Act as an intermediate layer between the network and link layers.
z
Provide connection-oriented network services through the services obtained from the
link layer protocols such as PPP and FR.
The NE20/20E forms forwarding equivalence classes (FECs) based on such information as IP
address prefix, and perform the role as below:
z
Generates label forwarding table.
z
Forwards information traffics of different FECs (with different label fields in the headers)
through the different label switch paths (LSPs).
The MPLS supports the following:
z
Policy-and-constraint-based routing (such as limitations formed in accordance with the
VPN and Diff-Serv) on LSPs, which enables you to freely select a router from the MPLS
network to establish an LSP.
z
LSP tunneling technology and maintains a label stack at both the ingress and egress of a
tunnel to carry out tunnel nesting and to fit into different application requirements.
The MPLS functions of the NE20/20E are:
z
Accelerate packet forwarding to a great extent.
Page 36

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-15
z
Carry out MPLS VPN applications, interworking between various types of VPNs, and
such networking applications as traffic engineering, QoS and Diff-Serv.
The MPLS of the NE20/20E supports Layer 3 and Layer 2 protocols such as IP, FR, ATM and
Ethernet. The MPLS provides an OAM mechanism without dependence on the upper or lower
layers in the TCP-IP protocol suite.
The IP Telecommunication Network (IPTN)IPTN network supported by the NE20/20E is
constructed on the basis of IP network technologies. IPTN can meet the end-to-end QoS,
reduce the investment of carriers and create value-added telecommunication network
solutions.
1.3.11 VPN Services
IP VPN
The Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) protocol is used to encapsulate pac ke ts of certain
network layer protocols (such as IP and IPX packets) so that these encapsulated packets can
be transmitted in the network running another network layer protocol (such as IP). As a tunnel
protocol, GRE uses the tunnel technology in the protocol layer.
GRE can be used to:
z
Transmit data of local multi-protocol network through the single-protocol backbone
network.
z
Extend the network that is limited by hops such as IPX network.
z
Connect the separated subnets for a VPN.
z
Access MPLS VPN through GRE tunnels.
L2VPN
The NE20/20E provides Layer 2 VPN services based on MPLS. It supports VPLS, Martini
MPLS L2VPN, Kompella MPLS L2VPN, CCC MPLS L2VPN, and SVC MPLS L2VPN to
carry VLL services, and supports PWE3.
MPLS/BGP L3VPN
The NE20/20E implements MPLS/BGP L3VPN and provides carriers with end-to-end V PN
solutions as follows:
z
Carrier's carrier
z
Inter-AS VPN
z
HoVPN
z
RRVPN
1.3.12 QoS
Traffic Policing
The NE20/20E supports such parameters as the committed rate, the peak rate, the committed
burst size, and maximum burst size for every kind of flow according to the Service Level
Agreements (SLA). To the traffic beyond the SLA, the router can pass or drop the flow.
Page 37

1 Product Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
1-16 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Traffic policing does not influence the forwarding performance of the device because a
hardware coprocessor is used internally to implement the Committed Access Rate (CAR).
Congestion Management
The NE20/20E adopts the Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) congestion control
mechanism.
The NE20/20E can configure individual congestion control algorithm for each priority queue
on the port.
Traffic Shaping
The NE20/20E adopts the Generic Traffic Shaping (GTS) algorithm to buffer packets, to
avoid the congestion of downstream devices and to reduce the drop of packets. The NE20/20E
supports the shaping for services like Expedited Forwarding (EF) and Assured Forwarding
(AF) to smooth the transmission rate of Diff-Serv services to the downstream traffic.
Traffic Classification
The NE20/20E supports simple and complex traffic classification.
If no QoS guarantee or traffic classification is required, or there are no rules to match packets
after traffic classification, the device processes the packets with the Best-Effort (BE) service.
VPN QoS
As a QoS Policy Propagation through the Border Gateway Protocol (QPPB) policy, VPN QoS
can transmit private network routes through BGP, which extends QPPB application in L3VPN
environment. It can be applied to VPN instances and VPNv4.
When VPN QoS is applied to the private network route of a specific VPN instance, the
inbound and outbound route policy should be applied to the VPN instance. If VPN QoS is
applied to the private network route of all VPN instances, the inbound and outbound route
policy should be applied to VPNv4 neighbors of BGP.
FR QoS
FR has its own QoS that can be configured with Permanent Virtual Paths (PVCs) to provide
flexible services for customers.
The NE20/20E supports multiple QoS technologies like FRTS, FRTP, FR congestion
management, FR queue management and FR fragmentation.
HQoS
Hierarchical Qos (HQoS) is a kind of QoS technology that can control traffic and carry out
queue scheduling on the basis of the user's priority at the same time. HQoS uses a two-level
scheduling mode and supports the following two scheduling modes:
z
Priority Queue (PQ)
z
Confirmed Bandwidth Priority Queue (CBPQ)
HQoS supports complete traffic statistics. You can view the bandwidth usage of all services
and distribute bandwidth properly according to traffic analysis.
Page 38

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 1 Product Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1-17
1.3.13 Security Features
The NE20/20E can do the following to ensure security:
z
Carry out Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) functions.
z
Build up distributed client/server secure access applications based on the ITU-T
RADIUS protocol specifications.
z
Provide AAA services for local, login and dialup users to prevent unauthorized access
based on the PAP and CHAP specification.
The NE20/20E supports protocol security authentication as follows:
z
PPP supports PAP and CHAP authentication modes.
z
Routing protocols including RIPv2, OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP support plain text
authentication and MD5 encrypted text authentication.
z
SNMP supports SNMPv3 encryption and authentication.
The NE20/20E supports the mirroring function. Mirroring indicates that the system sends a
copy of the packet on the current node to one specific packet analysis device from an
observing port without interrupting services. You can define the mirroring port number and
connect the port with the packet analysis device to monitor the traffic.
In compliance with the command levels, users are divided into four levels. A login user can
only use the commands with the levels no higher than the user's level.
Supporting the Network Address Translation (NAT) function, the NE20/20E relays the access
between private and public networks. It converts a private IP address to a public IP address or
changes the mix of internal IP address and port to the mix of external IP address and port.
This enables the hosts of internal network to access the Internet resources flexibly without
hazarding the "privacy" of the internal network.
Page 39

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment..............................................................2-1
2.1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................................2-2
2.1.1 Establishing the Configuration Environment by the Console Port ......................................................2-2
2.1.2 Configuring the Router Through Telnet...............................................................................................2-2
2.1.3 Establishing the Configuration Environm ent Through the AUX Port..................................................2-3
2.2 Establishing the Local Configuration Environment Through the Console Port............................................2-3
2.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ....................................................................................................2-3
2.2.2 Establishing the Physical Connection..................................................................................................2-4
2.2.3 Configuring Terminals .........................................................................................................................2-4
2.2.4 Logging In to the Router......................................................................................................................2-4
2.3 Establishing the Configuration Environment Thro ugh Telnet.......................................................................2-4
2.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ....................................................................................................2-4
2.3.2 Establishing the Physical Connection..................................................................................................2-5
2.3.3 Configuring Login User Parameters ....................................................................................................2-5
2.3.4 Logging In from the Telnet Client........................................................................................................2-5
2.4 Establishing the Configuration Environment Thr o ugh the AUX Port...........................................................2-6
2.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ....................................................................................................2-6
2.4.2 Establishing the Physical Connection..................................................................................................2-6
2.4.3 Initializing and Configuring the Modem on the Interface....................................................................2-7
2.4.4 Configuring the Connection Between Remote Terminal and the Router.............................................2-7
2.4.5 Logging In to the Router......................................................................................................................2-7
2.5 Configuration Examples................................................................................................................................2-7
2.5.1 Example for Login Through the Console Port.....................................................................................2-7
2.5.2 Example for Login Through Telnet....................................................................................................2-10
2.5.3 Example for Login Through the AUX Port........................................................................................2-11
Page 40

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Figures
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Figures
Figure 2-1 Networking diagram of logging in through the console port............................................................2-7
Figure 2-2 New connection................................................................................................................................2-8
Figure 2-3 Setting the port..................................................................................................................................2-9
Figure 2-4 Setting the port communication parameters......................................................................................2-9
Figure 2-5 Establishing the configuration environment through WAN............................................................2-10
Figure 2-6 Running the Telnet program on the PC...........................................................................................2-11
Figure 2-7 Establishing the remote configuration environment.......................................................................2-11
Page 41

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2-1
2 Establishment of the Configuration
Environment
About This Chapter
The following table shows the contents of this chapter.
Section Description
2.1 Introduction This section describes the working modes of establishing
configuration environments.
2.2 Establishing the Local
Configuration Environment
Through the Console
This section describes how to establish configuration
environments through the console port.
See Example for Login Through the Console Port.
2.3 Establishing the
Configuration Environment
Through Telnet
This section describes how to establish configuration
environments through Telnet.
See Example for Login Through Telnet.
2.4 Establishing the
Configuration Environment
Through the AUX Port
This section describes how to establish configuration
environments through the AUX port.
See Example for Login Through the AUX.
2.5 Configuration Examples This section provides several examples of establishing
configuration environments.
Page 42

2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2-2 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
2.1 Introduction
This section describes the following three methods of establishing configuration
environments:
z
Establishing the Configuration Environment by the Console Port
z
Configuring the Router Through Telnet
z
Establishing the Configuration Environment Through the AUX Port
2.1.1 Establishing the Configuration Environment by the Console
Port
Applicable Environment
You can configure the router by local login.
Applications
In the following cases, use only the console port to configure the router:
z
The router is powered on for the first time.
z
The configuration environment cannot be established through Telnet or the AUX port.
2.1.2 Configuring the Router Through Telnet
Applicable Environment
You can configure the router by local or remote login.
Applications
Pre-configure the IP addresses of interfaces on the router, the user account, the login
authentication and the incoming and outgoing call restriction. Also, ensure that there are
directly-connected or reachable routes between terminals and the router.
The destination router authenticates the user based on the configured parameters in three
modes:
z
Password authentication: indicates the login user should enter the correct password.
z
AAA local authentication: indicates the login user should enter the correct user name and
password.
z
Non-authentication: indicates the login user need not enter the user name or password.
If the login succeeds, a command line prompt such as
Quidway appears on the Telnet client
interface.
Enter the command to check the running status of the router or to configure the router.
Enter "?" for help.
Page 43

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2-3
Do not modify the IP address of the router when you configure the router through Telnet because the
modification may disconnect Telnet. If necessary, set up the connection again after entering a new IP
address.
2.1.3 Establishing the Configuration Environment Through the
AUX Port
Applicable Environment
You can configure the router by remote login.
Applications
If you cannot configure the router by local login and there is no reachable route to other
routers, connect the PC and the router through PSTN network.
Pre-enable the Modem dialup of the AUX port through the console port and configure the
username and password.
2.2 Establishing the Local Configuration Environment
Through the Console Port
2.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
You can connect the serial port of the PC to the console port of the router using the standard
RS-232 cable.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring the router through the console port, complete the following tasks:
z
Preparing the PC/terminal (including serial port and RS-232 cable)
z
Installing terminal emulation program on the PC (such as Windows XP hyper terminal)
Data Preparation
To configure the router, you need the following data.
No. Data
1 Terminal communication parameters (including baud rate, data bit, parity, stop
bit and flow control)
Page 44

2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2-4 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Establishing the Physical Connection
2 Configuring Terminals
3 Logging In to the Router
2.2.2 Establishing the Physical Connection
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Connect the COM port on the PC and the console port on the router by cable.
Step 2 Power on all devices to perform a self-check.
----End
2.2.3 Configuring Terminals
Do as follows on the PC:
Run the terminal emulation program on the PC, setting the communication parameter of the
terminal to 9600 bps, data bit to 8, stop bit to 1. Specify no parity and no flow control.
2.2.4 Logging In to the Router
Do as follows on the PC:
Press "Enter"until a command line prompt such as Quidway appears. Now enter the
configuration environment in the user view.
2.3 Establishing the Configuration Environment Through
Telnet
2.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
Configure the router by local login or remote login through Telnet.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring the router through Telnet, complete the following tasks:
z
Powering on devices and performing a self-check
z
Preparing the PC (including the serial port and Ethernet crossover/direct network cable
Page 45

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2-5
Data Preparation
To configure the router through Telnet, you need the following data.
No. Data
1 IP address of the PC
2 IP address of the Ethernet interface on the router
3 User information accessed through Telnet (including user name, password and
authentication mode)
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Establishing the Physical Connection
2 Configuring Login User Parameters
3 Logging In from the Telnet Client
2.3.2 Establishing the Physical Connection
Connect the router and the PC directly or connect the router and the PC respectively to the
network through the network cable.
2.3.3 Configuring Login User Parameters
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Configure the authentication mode of login users.
Step 2 Configure the authority limitation of login user.
For details, refer to the Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series Routers User Management.
----End
2.3.4 Logging In from the Telnet Client
Do as follows on the PC:
Step 1 Run the Telnet client program on the PC, and input the IP address of the interface on the
destination router that provides the Telnet service.
Step 2 Enter the user name and password in the login window. After authentication, a command line
prompt such as
Quidway appears. Now enter the configuration environment in the user view.
----End
Page 46

2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2-6 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
2.4 Establishing the Configuration Environment Through
the AUX Port
2.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
If you cannot configure the router by local login and there is no reachable route to other
routers, connect the serial port of the PC and the AUX port of the router through the Modem.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring the router through the AUX port dialup, complete the following tasks:
z
Preparing the PC/terminal (including the serial port and RS-232 cable)
z
Preparing the PC terminal emulation program (such as Windows XP hyper terminal)
z
Preparing two Modems
Data Preparation
To configure the router, you need the following data.
No. Data
1 Type of terminals
2 Terminal communication parameters
3 Modem communication parameters
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Establishing the Physical Connection
2 Initializing and Configuring the Modem on the Interface
3 Configuring the Connection Between Remote Terminal and the Router
4 Logging In to the Router
2.4.2 Establishing the Physical Connection
Step 1 Connect the Modem with the PC and the network.
Step 2 Connect the Modem with the router through the AUX port and the network.
----End
Page 47

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2-7
2.4.3 Initializing and Configuring the Modem on the Interface
Do as follows on the router:
z
Configure the authentication mode of login user
z
Configure the authority limitation of login user
For details, refer to the Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series Routers Configuration Guide -
Security.
2.4.4 Configuring the Connection Between Remote Terminal and
the Router
Do as follows on the terminal PC:
Step 1 Run the terminal emulation program on the PC (such as Windows XP HyperTerminal) to
enter the Connection Description window.
Step 2 Enter the connection name of the PC and the router, such as Dial.
Step 3 Click OK to enter the Connect To window.
Step 4 Enter the parameters and select options.
Step 5 Click OK to enter the Connect window.
Step 6 Click Dial.
----End
2.4.5 Logging In to the Router
Enter the user name and password in the login window.
After configuration, a command line prompt such as Quidway appears. Now enter the
configuration environment in the user view.
2.5 Configuration Examples
2.5.1 Example for Login Through the Console Port
Networking Requirements
Initialize the configuration of the router when the router is powered on for the first time.
Figure 2-1 Networking diagram of logging in through the console port
Router
PC
Page 48

2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2-8 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Configuration Roadmap
1. Connect the PC and the router through the console port
2. Configure the parameters on the PC end
3. Log in to the router
Data Preparation
Terminal communication parameters (including baud bit, data bit, parity, stop bit and flow
control).
Configuration Procedure
Step 1 Connect the serial port of the PC (or terminal) to th e con sole port of the router throu gh
standard RS-232 configuration cable. The local configuration environment is established.
Step 2 Run the terminal emulation program on the PC. Set the terminal communication parameters to
be 9600 bps, data bit to be 8, stop bit to be 1. Specify no parity and no flow control as shown
from Figure 2-2 to Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-2 New connection
Page 49

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2-9
Figure 2-3 Setting the port
Figure 2-4 Setting the port communication parameters
Power on the router to perform a self-check and the system performs automatic configuration.
When the self-check ends, you are prompted to press Enter until a command line prompt
such as
Quidway appears.
Enter the command to check the running status of the router or configure the router.
Enter "?" for help.
Page 50

2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2-10 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
For details, refer to the following chapters.
----End
2.5.2 Example for Login Through Telnet
Networking Requirements
You can log in to the router on other network segments through the PC or other terminals to
perform remote maintenance.
Figure 2-5 Establishing the configuration environment through WAN
PC Router
Target
Router
WAN
GE1/0/0
202.38.160.92/16
Configuration Roadmap
1. Establishing the physical connection
2. Configuring user login parameters
3. Logging in to the router from the client side
Data Preparation
z
IP address of the PC
z
IP address of the Ethernet interface on the router
z
User information accessed through Telnet (including the user name, password and
authentication mode)
Configuration Procedure
Step 1 Connect the PC and the router respectively to the network.
Step 2 Configure login user parameters.
# Configure the login address
<Quidway> system-view
[Quidway] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/0
[Quidway-GigabitEthernet1/0/0] ip address 202.38.160.92 255.255.0.0
[Quidway-GigabitEthernet1/0/0] quit
# Configure login authentication mode
[Quidway] aaa
[Quidway-aaa] local-user huawei password cipher test2
[Quidway-aaa] local-user huawei service-type telnet
[Quidway-aaa] local-user huawei level 3
Page 51

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2-11
[Quidway-aaa] quit
[Quidway] user-interface vty 0 4
[Quidway-ui-vty0-14] authentication-mode aaa
Step 3 Configure client login.
Run the Telnet on the PC, as shown in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6 Running the Telnet program on the PC
Click OK.
Enter the user name and password in the login window. After authentication, a command line
prompt such as
Quidway appears. Now enter the configuration environment in the user view.
----End
2.5.3 Example for Login Through the AUX Port
Networking Requirements
If you cannot configure the router by local login and there is no reachable route to other
routers, connect the serial port of the PC and the AUX port of the router through the Modem.
The detailed configuration environment is shown as Figure 2-7.
Figure 2-7 Establishing the remote configuration environment
Modem
Router
PC
COM
AUX
Modem
PSTN
Page 52

2 Establishment of the Configuration Environment
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
2-12 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Configuration Roadmap
1. Establishing the physical connection
2. Configuring Modem parameters
3. Configuring the AUX port to support the Modem dialup
Data Preparation
z
Type of terminals
z
Terminal communication parameters
z
Modem communication parameters
Configuration Procedure
Step 1 Establish the physical connection as shown in Figure 2-7.
Step 2 Configure the AUX port to support the Modem dialup.
<Quidway> system-view
[Quidway] aaa
[Quidway-local-aaa-server] local-user huawei password cipher test1
[Quidway-local-aaa-server] local-user huawei service-type terminal
[Quidway-local-aaa-server] local-user huawei level 3
[Quidway-local-aaa-server] quit
[Quidway] user-interface aux 0
[Quidway-ui-aux0] authentication-mode aaa
[Quidway-ui-aux0] modem both
Step 3 Configure Modem parameters.
# Run the PC emulation terminal, refer to Establishing the Configuration Environment by the
Console Port.
Press Enter on the PC emulation terminal/ terminal until a command line prompt of the
Modem such as
> appears.
Configure the Modem to meet the requirements of AUX communication.
For details, refer to Modem descriptions.
Step 4 Log in to the router.
Enter the user name and password in the remote terminal emulation program.
After authentication, a command line prompt such as
Quidway appears.
Enter the command to check the running status of the router or configure the router.
Enter "?" for help.
For detailed operations, refer to the following chapters.
----End
Page 53

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
3 CLI Overview..............................................................................................................................3-1
3.1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.1 Characteristics of the CLI .................................................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.2 Command Levels .................................................................................................................................3-3
3.1.3 Command Line Views..........................................................................................................................3-3
3.1.4 Regular Expressions.............................................................................................................................3-3
3.2 Configuring the Command Line View ..........................................................................................................3-4
3.3 Online Help of the Command Line...............................................................................................................3-7
3.4 Error Messages of the Command Line..........................................................................................................3-8
3.5 History Commands........................................................................................................................................3-8
3.6 Editing Characteristics ..................................................................................................................................3-9
3.7 Displaying Characteristics...........................................................................................................................3-10
3.8 Outputting the Display ................................................................................................................................3-11
3.8.1 Viewing the Display........................................................................................................................... 3-11
3.8.2 Filtering the Display ..........................................................................................................................3-11
3.9 Filtering the Information Through Regular Expressions............................................................................. 3-11
3.10 Shortcut Keys............................................................................................................................................3-12
3.10.1 Classifying Shortcut Keys................................................................................................................3-12
3.10.2 Defining Shortcut Keys....................................................................................................................3-14
3.10.3 Use of Shortcut Keys .......................................................................................................................3-14
3.11 Configuration Examples............................................................................................................................3-14
3.11.1 Example for Using Shortcut Keys....................................................................................................3-14
Page 54

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Tables
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Tables
Tab l e 3- 1 Command line views ..........................................................................................................................3-5
Tab l e 3- 2 Common error messages of the command line...................................................................................3-8
Tab l e 3- 3 Access the history commands.............................................................................................................3-9
Tab l e 3- 4 Editing functions ................................................................................................................................3-9
Tab l e 3- 5 Displaying functions.........................................................................................................................3-10
Tab l e 3- 6 Metacharacter description................................................................................................................. 3-11
Tab l e 3- 7 System-defined shortcut keys ...........................................................................................................3-12
Page 55

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-1
3 CLI Overview
About This Chapter
The following table shows the contents of this chapter.
Section Description
3.1 Introduction This section describes the basic concepts of the command
line.
3.2 Configuring the Command
Line View
This section describes the concepts and use of the
command view.
3.3 Online Help of the
Command Line
This section describes how to use the online help of the
command line.
3.4 Error Messages of the
Command Line
This section describes the error messages of the command
line.
3.5 History Commands This section describes the concepts and use of the history
command.
3.6 Editing Characteristics This section describes how to use the editing functions.
3.7 Displaying Characteristics This section describes how to use the displaying
functions.
3.8 Outputting the Display This section describes how to output the display.
3.9 Filtering the Information
Through Regular Expressions
This section describes how to use regular expressions.
3.10 Shortcut Keys This section describes how to use shortcut keys.
3.11 Configuration Examples This section provides examples for using shortcut keys.
Page 56

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-2 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
3.1 Introduction
This section covers the following topics that you need to know before you configure the
command line.
z
Characteristics of the CLI
z
Command Levels
z
Command Line Views
z
Regular Expressions
3.1.1 Characteristics of the CLI
The appearance of the command line prompt means the entry to the command line interface
(CLI). Users often use the CLI to interact with routers.
The system provides a series of configuration commands. Users can configure and manage
the router by entering the command in the CLI.
The CLI has the following characteristics:
z
Local or remote configuration through the AUX port.
z
Local configuration through the console port.
z
Local or remote configuration through Telnet or Secure Shell (SSH).
z
Allows logging in to the asynchronous serial interface of a router through Modem dialup
to perform the remote configuration.
z
Provides the user interface view for the terminal users to perform specific configuration.
z
Hierarchical command protection for the users of different levels, that is, supports
running the commands based on the corresponding level.
z
Provides local authentication, password authentication and Authentication, Authorization
and Accounting (AAA) to prevent the unauthorized user from accessing the router.
z
Supports the user to enter ? for online help at any time.
z
Provides the network testing commands such as tracert and ping for rapidly diagnosing
the fault in a network.
z
Provides abundant debugging information to help in diagnosing the network fault.
z
Uses the telnet command to directly log in to and manage other routers.
z
Provides the FTP service for the convenience of file uploading and downloading.
z
Provides the function that is similar to DOS-Key for running a history command.
z
The command line interpreter provides intelligent command resolution methods such as
key word fuzzy match and context conjunction. These methods make it easy for users to
enter their commands.
Page 57

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-3
z
The system supports the command with 256 characters at most. The command can be in an
incomplete form.
z
The system saves the incomplete command to the configuration files in the complete form; therefore,
the command may have more than 256 characters. However, when the system is restarted, the
incomplete command cannot be restored. So, pay attention to the length of the incomplete command.
3.1.2 Command Levels
The system adopts a hierarchical protection mode that has 16 command levels in an
increasing order.
By default, the commands are registered as one of the following four levels:
z
Visit level: Commands of this level include commands of network diagnosis tool (such
as ping and tracert) and commands that start from the local device and visit external
device (including Telnet client side, SSH client side and Rlogin) and so on.
z
Monitoring level: Commands of this level, including the display command and the
debugging command, are used for system maintenance, service fault diagnosis, and so
on.
z
Configuration level: Commands of this level are service configuration commands that
provide direct network service to the user, including routing and network layer
commands.
z
Management level: Commands of this level are commands that influence basis operation
of the system and provide support to the service. They include file system command,
FTP command, TFTP command, XModem downloading command, configuration file
switching command, power supply control command, backup board control command,
user management command, level setting command, system internal parameter setting
command, and so on.
z
The default command level may be higher than the command level defined according to the
command rules in application.
z
Login users have the same four levels as the command levels. The login users can use only the
command of the levels that are equal to or lower than their own levels. For details of login user
levels, refer to section 5.1.3 "User Management" in Chapter 5 "User Login."
3.1.3 Command Line Views
System specifies the command line views to describe corresponding command interfaces.
Each command is registered and run only in a certain command view.
3.1.4 Regular Expressions
When a lot of information is output, you can filter the unnecessary contents out with regular
expressions and display the necessary contents.
Specify the filtering mode in the commands:
Three kinds of filtering modes are used to filter the output. In the commands that support
regular expressions, these three modes are | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression:
z
begin: displays the information that begins with the line that matches regular expression.
z
exclude: displays the information that excludes lines that match regular expression.
z
include: displays the information that includes lines that match regular expression.
Page 58

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-4 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Specify the filtering mode when the information is displayed in screens:
When a lot of information is output and displayed in screens, you can specify the filtering
mode in the prompt "---- More ----".
z
/regular-expression: displays the information that begins with the line that matches
regular expression.
z
-regular-expression: displays the information that excludes lines that match regular
expression.
z
+regular-expression: displays the information that includes lines that match regular
expression.
Regular expressions are used to filter the output. When using the metacharacter {}, If the
number of matching times exceeds the scope specified in {}, It will cause the matching time
out and the information cannot be displayed normally.
The system provides many display commands for displaying the system status. When
displaying the information, add regular expressions | { begin | exclude | include }
regular-expression to the specified commands to filter the information.
Three options are as follows:
z
begin regular-expression: displays the information that begins with the line that matches
regular-expression.
z
exclude text: displays the information that excludes lines that match regular-expression.
z
include text: displays the information that includes lines that match regular-expression.
3.2 Configuring the Command Line View
# Establish connection with the router. If the router adopts the default configuration, you can
enter the user view with the prompt of
<Quidway>.
# Type system-view, and you can enter the system view.
<Quidway> system-view
[Quidway]
# Type aaa in the system view, and you can enter the AAA view.
[Quidway] aaa
[Quidway-aaa]
The prompt Quidway indicates the default router name. The prompt <> indicates the user view and the
prompt [] indicates other views.
Some commands that are implemented in the system view can also be implemented in the
other views. But the function implemented associate with the command view. For example,
the mpls command (for starting MPLS) can be run in the system view to enable the MPLS
Page 59

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-5
capability globally. It can also be run in the interface view to enable the MPLS capability on
this interface.
The command line views are shown in Ta b l e 3 - 1 .
Table 3-1 Command line views
View Description
aaa AAA view
aaa-accounting AAA accounting view
aaa-authen AAA authentication view
aaa-author AAA authorization view
aaa-domain AAA domain view
aaa-recording AAA recording view
acl-adv Advanced ACL view
acl-basic Basic ACL view
acl-if ACL view based on interface
aspf-policy ASPF policy view
Atm ATM interface view
Atm-class ATM view
Atm-pvc ATM PVC view
aux AUX interface view
bgp BGP view
bgp-af-l2vpn BGP AF L2VPN view
bgp-af-vpnv4 BGP AF VPNV4 view
bgp-af-vpn-instance BGP AF VPN instance view
vpls-family VPLS address family view
cpos CPOS interface view
dhcp DHCP address pool view
e1 E1 interface view
e3 E3 interface view
ethernet Ethernet interface view
explicit-path Explicit path view
fr-class Frame relay view
ftp-client FTP client view
Page 60

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-6 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
View Description
GigabitEthernet GE interface view
hwtacacs HWTACACS view
ike-proposal IKE view
ipsec-policy-isakmp IPSEC policy Isakmp view
ipsec-policy-manual IPSEC policy manual view
ipsec-policy-template IPSEC policy template view
ipsec-proposal IPSEC view
isis IS-IS view
l2tp L2TP view
loopback Loopback interface view
mp-group Mp-group interface view
mpls MPLS view
mpls-l2vpn MPLS-L2VPN view
mpls-ldp MPLS-LDP view
null Null interface view
ospf OSPF view
ospf-area OSPF area view
policy-based-route Policy-based route view
pos POS interface view
radius RADIUS view
rip RIP view
rip-af-vpn-instance RIP AF VPN instance view
ripng RIPng view
route-policy Route policy view
rsa-key-code RSA key code view
rsa-public-key RSA public key view
serial Serial interface view
shell Shell view
system System view
t1 T1 interface view
t3 T3 interface view
Page 61

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-7
View Description
tunnel Tunnel interface view
tunnel-policy Tunnel policy view
user-interface User interface view
virtual-ethernet Virtual Ethernet interface view
virtual-template Virtual template interface view
vpn-instance VPN instance view
3.3 Online Help of the Command Line
The command line interface provides the two online helps:
z
Full help
z
Partial help
You can obtain the help in these two ways described as follows:
z
Full help
# Enter ? in any command line view to display all the commands and their simple
descriptions.
<Quidway> ?
# Enter a command and ? separated by a space. If the key word is at this position, all key
words and their simple descriptions are displayed. For example:
<Quidway> language-mode ?
chinese Chinese environment
English English environment
Chinese and English are keywords; Chinese environment and English environment describe
the keywords respectively.
# Enter a command and ? separated by a space, and if a parameter is at this position, the
related parameter names and parameter descriptions are displayed. For example:
[Quidway] display aaa ?
configuration AAA configuration
[Quidway] display aaa configuration?
<cr>
Here configuration is parameter name, and AAA configuration is the description of the
parameter; <cr> indicates that no parameter is at this position. The command is repeated in
the next command line. You can press Enter to run the command.
z
Partial help
# Enter a character string and ? a space to display all commands that begin with this character
string.
Page 62

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-8 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
<Quidway> d?
debugging delete dir display
# Enter a command with ? closely following it to display all the key words that begin with
this character string.
<Quidway> display v?
version virtual-access vlan vpls vrrp vsi
3.4 Error Messages of the Command Line
All the commands entered by the user are run correctly, if the grammar check has been passed.
Otherwise, error messages are reported to the user. Refer to Table 3-2 for the common error
messages.
Table 3-2 Common error messages of the command line
Error messages Cause of the error
The command cannot be found. Unrecognized command
The key word cannot be found.
Parameter type error Wrong parameter
The parameter value exceeds the boundary.
Incomplete command Incomplete command inputted
Too many parameters Too many parameters inputted
Ambiguous command Indefinite parameters inputted
3.5 History Commands
The command line interface automatically saves the history command entered by the user.
This function is similar to the DOS-Key. The user can invoke and run the saved history
command at any time.
By default, the command line interface saves 10 history commands at most for each user . The
operations are as shown in Table 3-3.
Table 3-3 Access the history commands
Action Key or Command Result
Display the
history
commands.
display
history-command
Display the history commands entered by users.
Page 63

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-9
Action Key or Command Result
Access the last
history
command.
Up cursor key
↑ or Ctrl+P
Display the last history command if there is an
earlier history command
Otherwise, the alarm bell rings.
Access the
next history
command.
Down cursor key ↓
or Ctrl+N
Display the next history command if there is a
later history command.
Otherwise, the command is cleared and the alarm
bell rings.
On the HyperTerminal of Windows 9X, the cursor key ↑ is invalid. Because the HyperTerminals of
Windows 9X define the keys differently. In this case, you can replace the cursor key ↑ with Ctrl+P.
When you use the history command, note the following:
z
The saved history commands are the same as that those input by users. For example, if
the user inputs an incomplete command, the saved command also is incomplete.
z
If the user runs the same command for several times, the earliest command is saved. If
the command is input in different forms, they are considered as different commands.
z
For example, if the display ip routing-table command is run for several times, only one
history command is saved. If the display ip routing command and the display ip
routing-table command are run, two history commands are saved.
3.6 Editing Characteristics
The command line interface provides the basic command editing function and supports
multi-line edition. The maximum length of each command is 256 characters as shown in
Tabl e 3 -4 .
Table 3-4 Editing functions
Key Function
Common key Inserts a character in the current position of the cursor if the
editing buffer is not full and the cursor moves rightward.
Otherwise the alarm bell rings.
Backspace Deletes the character on the left of the cursor and the cursor
moves leftward.
When the cursor reaches the head of the command, the alarm
bell rings.
Left cursor key ← or
Ctrl+B
Moves the cursor leftward by the space of a character. When
the cursor reaches the head of the command, the alarm bell
rings.
Right cursor key → or
Ctrl+F
Moves the cursor rightward by the space of a character.
When the cursor reaches the end of the command, the alarm
bell rings.
Page 64

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-10 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Key Function
Tab Press Tab after typing the incomplete key word and the
system runs the partial help:
z
If the matching key word is unique, the system replaces the
typed one with the complete key word and displays it in a
new line with the cursor a space behind.
z
If there are several matches or no match at all, the system
displays the prefix first. Then you can press Tab to view
the matching key word one by one. In this case, the cursor
is closely following the word end and you can type a space
to enter the next word.
z
If a wrong key word is typed in, press Tab and your input
is displayed in a new line.
3.7 Displaying Characteristics
The command line interface provides the following displaying characteristics:
z
To facilitate users, the prompt and help information can be displayed in both Chinese and
English.
z
When the information displayed exceeds a full screen, it can provide the pause function.
In this case, the user has three choices as shown in Table 3-5.
Table 3-5 Displaying functions
Key Function
Ctrl+C Stops the display and running of the command.
Space Continues to display the information on next screen.
Enter Continues to display the information on next line.
3.8 Outputting the Display
3.8.1 Viewing the Display
Do as follows on the router:
Run:
display current-configuration
The current configuration is displayed.
Page 65

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-11
3.8.2 Filtering the Display
Do as follows on the router:
Run:
display current-configuration | include ip
The commands that include "ip" are displayed.
3.9 Filtering the Information Through Regular Expressions
When a lot of information is output, you can filter the display information through regular
expressions.
The regular expression is a tool for matching and replacing modes. Users should construct the
matching mode based on certain rules, and then match the mode with the target object.
To help users construct the matching mode flexibly, regular expressions provide some special
characters that are called metacharacters. Metacharacters are used to define the matching
modes of other characters in the regular expressionMetacharacters are described in Table 3-6.
Table 3-6 Metacharacter description
Metacharacter Connotation
\ Escape character
. Matches any single character including the space except for \n.
* Characters on the left of it appear for 0 or many times continuously
in the target object.
+ Characters on the left of it appear for 1 or many times continuously
in the target object.
| The 'or' relationship exists between characters on the left and right
sides of it.
^ Characters on the right of it must appear at the beginning of the
target object.
$ Characters on the left of it must appear at the end of the target
object.
[xyz] Matches the character listed in the square character.
[^xyz] Matches any character that is not listed in the square bracket (^ is on
the left of the character).
[a-z] Matches any character within the specified range.
[^a-z] Matches any character that is not within the specified range.
{n} The matches appear for n times (n is a non-negative integer).
{n,} The matches appear for at least n times (n is a non-negative integer).
Page 66

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-12 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Metacharacter Connotation
{n,m} The matches appear for n-m times (m and n are non-negative
integer and n is smaller than or equal to m).
Note that there is no space between n and m.
For example:
^ip: matches the target object that begins with the character string "ip".
ip$: matches the target object that ends with the character string "ip".
The simplest regular expressions do not contain any metacharacter. For example, when a
regular expression is defined as "hello", it matches only the character string "hello".
3.10 Shortcut Keys
3.10.1 Classifying Shortcut Keys
The shortcut keys in the system are classified into the following types:
z
User-oriented and user-defined shortcut keys: CTRL_G, CTRL_L, and CTRL_O. The
user can correlate these shortcut keys with any commands. When the shortcut keys are
pressed, the system automatically runs the corresponding command. For the details of
defining the shortcut keys, see Defining Shortcut Keys.
z
System-defined shortcut keys: These shortcut keys with fixed functions are defined by
the system. Table 3-7 lists the system-defined shortcut keys.
Different terminal software defines these keys differently. Therefore, the shortcut keys on the terminal
may be different from those listed in this section.
Table 3-7 System-defined shortcut keys
Key Function
CTRL_A The cursor moves to the beginning of the current
line.
CTRL_B The cursor moves leftward by the space of a
character.
CTRL_C Terminates the running function.
CTRL_D Deletes the character where the cursor lies.
CTRL_E The cursor moves to the end of the current line.
CTRL_F The cursor moves rightward by the space of a
character.
CTRL_H Deletes one character on the left of the cursor.
CTRL_K Terminates the outbound connection.
Page 67

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-13
Key Function
CTRL_N Displays the next command in the history command
buffer.
CTRL_P Displays the previous command in history command
buffer.
CTRL_R Redisplays the information of the current line.
CTRL_SHIFT_V Pastes the contents on the clipboard.
CTRL_T Kill outgoing connection when connecting.
CTRL_U Delete all characters up to the cursor.
CTRL_W Deletes a character string or character on the left of
the cursor.
CTRL_X Deletes all the characters on the left of the cursor.
CTRL_Y Deletes all the characters on the right of the cursor.
CTRL_Z Returns to the user view.
CTRL_] Terminates the inbound or redirection connections.
ESC_B The cursor moves leftward by the space of a word.
ESC_D Deletes a word on the right of the cursor.
ESC_F The cursor moves rightward to the next word end.
ESC_N The cursor moves downward to the next line.
ESC_P The cursor moves upward to the previous line.
ESC_SHIFT_< Sets the position of the cursor to the beginning of the
clipboard.
ESC_SHIFT_< Sets the position of the cursor to the end of the
clipboard.
3.10.2 Defining Shortcut Keys
When defining the shortcut keys, use double quotation marks to define the command if this command
contains several commands words. That is, spaces exist in the command.
Configure as follows in the system view.
Action Command
Define shortcut
keys.
hotkey { CTRL_G | CTRL_L | CTRL_O } command-text
Page 68

3 CLI Overview
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
3-14 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
3.10.3 Use of Shortcut Keys
z
You can press the shortcut keys wherever you can type a command. Then the system
displays the full corresponding command.
z
If you have typed part of a command and have not pressed Enter, you can press the
shortcut keys to clear the input and display the full corresponding command. This
operation has the same effect with that deleting all commands and then re-entering the
complete command.
z
The shortcut keys are run as the commands, the syntax is recorded to the command
buffer and log for fault location and querying.
The terminal in use may affect the functions of the shortcut keys. For example, if the customized
shortcut keys of the terminal conflict with those of the router, the input shortcut keys are captured by the
terminal program and hence the shortcut keys do not function.
Run the following command in any view to display the use of shortcut keys.
Action Command
View the use of shortcut keys.
display hotkey
3.11 Configuration Examples
3.11.1 Example for Using Shortcut Keys
Defining Shortcut Keys
Step 1 Correlate Ctrl_Gwith the display ip routing-table command and run the shortcut keys.
<Quidway> system-view
[Quidway] hotkey ctrl_u display ip routing-table
Step 2 Press Ctrl+G when the prompt Quidway appears.
[Quidway] display ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 5 Routes : 5
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
51.51.51.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
100.2.0.0/16 Direct 0 0 D 100.2.150.51 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
100.2.150.51/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
100.2.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Page 69

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 3 CLI Overview
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3-15
----End
Copying Commands Using Shortcut Keys
Step 1 Enter the command in any view.
# Move the cursor to the beginning of the command and press ESC_SHIFT_<. Move the
cursor to the end and press ESC_SHIFT_>. Then, press CTRL_Cf for copying.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table
Step 2 Run the display clipboard command to view the contents on the clipboard.
<Quidway> display clipboard
---------------- CLIPBOARD----------------display ip routing-table
Step 3 Press Ctrl+Shift+V to paste the contents of clipboard.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table
----End
Page 70

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
4 Basic Configuration ...................................................................................................................4-1
4.1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................................4-2
4.1.1 Extension of Command Levels............................................................................................................4-2
4.1.2 Extension of User Levels.....................................................................................................................4-2
4.2 Configuring Basic System Environment.......................................................................................................4-2
4.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ....................................................................................................4-2
4.2.2 Switching Language Mode..................................................................................................................4-3
4.2.3 Configuring the Device Name.............................................................................................................4-4
4.2.4 Configuring the System Clock............................................................................................................. 4-4
4.2.5 Configuring the Header Text................................................................................................................4-4
4.2.6 Configuring the Password for Switching User Levels.........................................................................4-5
4.2.7 Switching User Levels.........................................................................................................................4-5
4.2.8 Locking the User Interface...................................................................................................................4-6
4.2.9 Configuring Command Privilege Levels..............................................................................................4-6
4.2.10 Displaying System Status Messages..................................................................................................4-7
Page 71

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 4 Basic Configuration
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4-1
4 Basic Configuration
About This Chapter
The following table shows the contents of this chapter.
Section Description
4.1 Introduction This section describes the basic configurations.
4.2 Configuring Basic System
Environment
This section describes how to configure the basic system
environment on the router.
Page 72

4 Basic Configuration
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
4-2 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
4.1 Introduction
Before configuring the services, you need to configure the basic system environments to meet
the requirements of the practical environments, such as the system name and system time.
4.1.1 Extension of Command Levels
By default, the product supports command levels at 0 to 3, which correspond to visit,
monitoring, configuration, and management respectively. This limited number of command
levels cannot meet the requirements to implement fine management on authorization of users
at the device end. In the networking environment, the product cannot interwork with devices
that support command levels at 0 to 15.
By using the extension of command levels, you can advance in batches the command levels at
0 to 3 to levels at 0 to 15.
If the levels of commands are not modified separately, all the command levels are adjusted
after advanced in batches:
z
Commands at levels 0 and 1 remain unchanged.
z
Commands at level 2 are advanced to level 10.
z
Commands at level 3 are advanced to level 15.
z
No command exists at levels 2 to 9 and 11 to 14.
Command levels at 2 to 9 and 11 to 14 do not correspond to the visit, monitoring,
configuration, and management levels. You can adjust commands to levels at 2 to 9 and 11 to
14 to implement fine management on authorization of users.
The advancement of commands levels at 2 and 3 to levels at 10 and 15 respectively is performed in
batches at one time.
4.1.2 Extension of User Levels
The command levels are advanced to 0 and 15, and the user levels also should be advanced to
0 and 15 from the previous levels at 0 to 3.
4.2 Configuring Basic System Environment
4.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
Before configuring the services, you need to configure the basic system environments to meet
the requirements of the practical environments.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring basic system environment, power on the router.
Page 73

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 4 Basic Configuration
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4-3
Data Preparation
To configure basic system environment, you need the following data.
No. Data
1 Language mode
2 System time
3 Host name
4 Password for switching user levels
5 Command level
6 Login information
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Switching Language Mode
2 Configuring the Device Name
3 Configuring the System Clock
4 Configuring the Header Text
5 Configuring the Password for Switching User Levels
6 Switching User Levels
7 Locking the User Interface
8 Configuring Command Privilege Levels
9 Displaying System Status Messages
4.2.2 Switching Language Mode
Do as follows on the router:
Run:
language-mode { chinese | english }
The language mode is switched.
By default, the English mode is used. The help information on the router can be in English
and in Chinese. When you need the help information in Chinese, run this command to switch
the language mode.
Page 74

4 Basic Configuration
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
4-4 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
4.2.3 Configuring the Device Name
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
sysname host-name
The device name is set.
----End
You can change the name of the router that appears in the command prompt.
4.2.4 Configuring the System Clock
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Run:
clock datetime HH:MM:SS YYYY-MM-DD
The UTC standard time is set.
Step 2 Run:
clock timezone time-zone-name { add | minus } offset
The time zone is set.
Step 3 Run:
clock daylight-saving-time time-zone-name one-year start-time start-data end-time
end-data offset
Or:
second | third | fourth | fifth | last } weekday | start-date } end-time { end-year month
{ first | second | third | fourth | fifth | last } weekday | end-date } offset
The daylight time is set.
----End
To guarantee cooperation with other devices, you need to accurately set the system time. The
product supports setting the time zone and daylight time.
4.2.5 Configuring the Header Text
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
Page 75

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 4 Basic Configuration
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4-5
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
header login { information text | file file-name }
The header text is set during login.
Step 3 Run:
header shell { information text | file file-name }
The header text is set after the login.
----End
Header text is the prompt displayed by the system when users connect to the router, log in or
start interactive configuration. Configure the header text to provide detailed indication.
4.2.6 Configuring the Password for Switching User Levels
z
When simple is used, the password is saved in the configuration files in simple text. Login
users with lower level can get the password by viewing the configuration. This may cause
security problems. Therefore, cipher is used to save the password in encrypted text.
z
When cipher is used to set a password, the password cannot be taken back from the
system. You must keep well the password from being forgotten or lost.
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
super password [ level user-level ] { simple | cipher } password
The password for switching user levels is configured.
----End
When users log in to the router with a lower user level, they switch to a super user level to
perform advanced operations by entering the corresponding password. The password needs to
be configured beforehand.
4.2.7 Switching User Levels
Do as follows on the router:
Run:
Page 76

4 Basic Configuration
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
4-6 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
super [ level ]
User levels are switched.
An accurate password must be entered when the user is switched from a lower level to a
higher level.
When configuring the switchover of user levels on the router, users can perform HWTACACS
Authentication. For detailed configurations, refer to Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series
RoutersConfiguration Guide - Security.
When the login user of lower levels is switched to the user of higher level through super, the system
automatically sends trap messages records the switchover in the log. When the switched level is lower
than that of the current level, the system only records the switchover in the log.
4.2.8 Locking the User Interface
Do as follows on the router:
Run:
lock
The user interface is locked.
When you leave the operation terminals for the moment, you can lock the user interface in
case unauthorized users operate the interface. You must enter the correct password to unlock
the user interface.
4.2.9 Configuring Command Privilege Levels
Do as follows on the router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
command-privilege level rearrange
The command levels are advanced in batches.
Step 3 Run:
command-privilege level level view view-name command-key
The command level is set.
----End
Page 77

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 4 Basic Configuration
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4-7
z
All commands have default views and privileges and need not be configured again.
z
When you run the command-privilege level rearrange command, the system prompts that a super
password that corresponds to level 15 users should be set, if the password that corresponds to the
level 15 users is not set. If N is selected, you need to set a password. If Y is selected, the command
levels are advanced in batches. In the latter case, the user levels cannot be advanced when you log in
to the router through methods other than the Console port.
4.2.10 Displaying System Status Messages
Using the display commands to get the following status messages:
z
System configuration message
z
System working status message
z
System statistics message
z
Restart message on Activ e Mai n Board (AMB)
See the related sections for display commands about protocols and interfaces. The following
only shows the system display commands.
Run the following commands in all views.
Commands Displaying System Configuration
Run the following commands as required:
z
Run the display version command to display the system edition.
z
Run the display clock command to display the system time.
z
Run the display users [ all ] command to display the terminal user.
z
Run the display saved-configuration command to display the original configuration.
z
Run the display current-configuration command to display the current configuration.
Commands Displaying System Status
Run the following commands as required:
z
Run the display debugging [ interface interface-type interface-numb er ]
[ module-name ] command to display the debugging status.
z
Run the display this command to display the configuration of the current view.
Commands Displaying System Statistics
Run the following commands as required:
Run :
display diagnostic-information [ file-name ]
The zystem diagnosis information is displayed.
When the system fails or performs the routine maintenance, you need collect a lot of
information to locate the fault. But you cannot collect enough information, because there are
many display commands. You can use the display diagnostic-information command to
collect the running information of the current modules in the system.
Page 78

4 Basic Configuration
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
4-8 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
The display diagnostic-information command collects all display inf ormation of the
following commands, including display clock, display version, display cpu, display
interface, display current-configuration, display saved-configuration, display
history-command.
Displaying the Restarting Information of the RPU
Perform one or both of the following commands as required:
z
Run the display system restart command to display the restarting information about the
AMB for the last 10 times.
z
Run the display system slave-restart command to display the restarting information of
the Slave Main Board (SMB) for the last 10 times.
The restarting time and possible causes are recorded.
Page 79

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Contents
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Contents
5 User Management ......................................................................................................................5-1
5.1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.1 User Interface View .............................................................................................................................5-2
5.1.2 User Management ................................................................................................................................5-3
5.2 Configuring a User Interface.........................................................................................................................5-5
5.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ....................................................................................................5-5
5.2.2 Transmitting Messages Between User Interfaces.................................................................................5-6
5.2.3 Configuring Asynchronous Interface Attributes ..................................................................................5-6
5.2.4 Setting Terminal Attributes ..................................................................................................................5-7
5.2.5 Configuring the User Interface Priority ...............................................................................................5-8
5.2.6 Configuring Modem Attributes............................................................................................................5-8
5.2.7 Configuring an Auto-executed Command............................................................................................5-9
5.2.8 Configuring the Redirection Function .................................................................................................5-9
5.2.9 Configuring the Call-in or Call-out Restrictions of the VTY User Interface ..................................... 5-10
5.2.10 Configuring the Maximum Number of VTY User Interfaces ..........................................................5-10
5.2.11 Configuring the Authentication Timeout Time for VTY Users........................................................5-11
5.2.12 Disconnecting a Specified User Interface........................................................................................5-11
5.2.13 Checking the Configuration............................................................................................................. 5-11
5.3 Configuring User Management...................................................................................................................5-12
5.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ..................................................................................................5-12
5.3.2 Configuring Authentication Mode .....................................................................................................5-13
5.3.3 Configuring the Authentication Password..........................................................................................5-13
5.3.4 Setting Username and Password for AAA Local Authentication ....................................................... 5-14
5.3.5 Configuring the User Priority ............................................................................................................5-14
5.3.6 Checking the Configuration...............................................................................................................5-14
5.4 Configuring the Local User Management ...................................................................................................5-15
5.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task ..................................................................................................5-15
5.4.2 Creating the Local User Account .......................................................................................................5-16
5.4.3 Configuring the Service Type of the Local User................................................................................ 5-16
5.4.4 Configuring FTP Directory Authority of the Local User ...................................................................5-17
5.4.5 Configuring the Local User Status.....................................................................................................5-17
5.4.6 Configuring the Local User Priority ..................................................................................................5-17
Page 80

Contents
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
ii Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
5.4.7 Configuring the Access Restriction of the Local User.......................................................................5-18
5.4.8 Checking the Configuration...............................................................................................................5-18
5.5 Configuration Examples..............................................................................................................................5-18
5.5.1 Example for Logging In to the Router Through Password Authentication........................................ 5-19
5.5.2 Example for Logging In to the Router Through AAA .......................................................................5-20
Page 81

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations Tables
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Tables
Table 5-1 Example for the absolute numbering..................................................................................................5-3
Page 82

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-1
5 User Management
About This Chapter
The following table shows the contents of this chapter.
Section Description
5.1 Introduction This section describes the basic concepts of the user
interface and the user management.
5.2 Configuring a User
Interface
This section describes how to configure and manage the
physical and logical interfaces in the asynchronous
interactive mode.
5.3 Configuring User
Management
This section describes how to manage and authenticate
the user that logs in to the router.
5.4 Configuring the Local
User Management
This section describes how to configure the local user
management.
5.5 Configuration Examples This section provides examples for logging in to the
router in different ways.
Page 83

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-2 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
5.1 Introduction
This section covers the following topics that you need to know before you configure user
management:
z
User Interface View
z
User Management
5.1.1 User Interface View
The user interface view is a command line view provided by the system. It is used to
configure and manage all the physical and logical interfaces in the asynchronous mode.
User Interfaces Supported by the System
z
Console port (CON)
The console port is a serial port provided by the main control unit of the router provides the
console port.
The main control unit provides one EIA/TIA-232 DCE console port for local configuration by
directly connecting a terminal to a router.
z
Auxiliary port (AUX)
The main control unit of a router provides the auxiliary port that is a line device port. The
main control unit has one EIA/TIA-232 DTE AUX port, and is used by a terminal to access
the router through the Modem.
z
Virtual type line (VTY)
The virtual port is a logical terminal line. A virtual type line (VTY) is the Telnet connection
with the router through a terminal. It is used for local or remote access to the router.
User Interface Numbering
The following are user interface numbering methods:
z
Relative numbering
The format of the relative numbering is user interface type + number.
Relative numbering is used to uniquely identify a single interface or a group of user interfaces
of the same type.:
− Number of the console port: CON 0
− Number of the auxiliary port: AUX 0
− Number of the VTY: VTY 0 for the first line, VTY 1 for the second line and so on.
z
Absolute numbering
This specifies a user interface or a group of user interfaces.
The starting number is 0 and the rest is in the sequence of CON -> AUX -> VTY. There is
only a single console port and an AUX port and there are15 VTY interfaces. You can use the
user-interface maximum-vty command to set the maximum number of user interfaces. The
default number is five.
Page 84

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-3
By default, the system supports three types of user interfaces: CON, AUX, and VTY.
Tabl e 5 -1 shows the absolute numbers of the user interfaces in this system.
Table 5-1 Example for the absolute numbering
Absolute number User-interface
0 CON0
145 AUX0
146 The first virtual interface (VTY0)
147 The second virtual interface (VTY1)
148 The third virtual interface (VTY2)
149 The fourth virtual interface (VTY3)
150 The fifth virtual interface (VTY4)
For different types of devices, the absolute numbers of the AUX interface and the VTY interface may be
different.
Run the display user-interface command to view the absolute number of user interfaces.
5.1.2 User Management
The username and the password are not configured when a router is powered on for the first
time.
In such a condition, any user can configure the router by connecting a PC with it through the
console port.
The remote user accesses the router through Telnet if the router is configured with the IP
address of the Routing Process Unit
(RPU) or that of the interface board. The remote user
accesses the network by establishing a PPP connection with the router.
Configure the usernames and the user password for the router to ensure network security and
to ease user management.
User Classification
Based on the services obtained, users of a router are classified as follows:
z
HyperTerminal users: They access the router through the console port or the AUX port.
z
Telnet users: They access the router through Telnet.
z
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) users: They establish FTP connections with the router to
transfer files.
z
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) users: They establish PPP connections (such as dialing
and PPPoA) with the router to access the network.
z
Secure Shell (SSH) users: They establish SSH connections with the router to access the
network.
Page 85

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-4 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
User Level
The system provides hierarchical management to HyperTerminal users and Telnet users.
The login user has the same 16 levels like the command. They are marked from 0 to15. The
higher the mark is, the higher the priority is.
A user can access the commands with the level equal to or smaller than the user level. For
example, if the user level is 2, the user can access the commands with the level 0, 1, or 2. The
user with the level 3 can access all the commands.
For details of command levels, refer to the chapter on "Command Line Introduction."
User Authentication
After the user configuration, the system authenticates users when they access the router.
The four types of user authentication are as follows:
z
Non-authentication: In this type, a user accesses the router without the username and
password. This is not recommended due to security reasons
z
Password authentication: In this type, a user accesses the router only with the password
rather than the username. This is safer when compared to non-authentication.
z
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) authentication: It supports local
authentication and remote authentication A user requires both the user name and
password to access the router in local authentication. The remote authentication scheme
cooperates with the AAA server, which authenticates PPP users commonly.
AAA local authentication authenticates the Telnet and HyperTerminal users.
User Planning
The network administrator provides the user plan based on the actual requirements.
z
At least one HyperTerminal user is created on a router
z
A Telnet user is created for remote access.
z
An FTP user uploads or downloads files on a router from the remote.
z
A PPP user can access networks through PPP connections.
z
For the configuration of FTP user, refer to the Chapter "FTP, TFTP and XModem."
z
For the configuration of PPP user, refer to Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series Routers Configuration
Guide - Security.
5.2 Configuring a User Interface
5.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
To guarantee a smooth and secure login, do as follows:
Page 86

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-5
z
Confirm the user interface type and configure the login parameters of the user interface.
z
Classify the login user level and configure the authentication mode for the user.
z
Configure the terminal services.
The following shows only how to configure a user interface.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring a user interface, complete the following tasks:
z
Powering on the router
z
Connecting the PC with the router properly
Data Preparation
To configure a user-interface, you need the following data.
No. Data
1 Transmission rate (optional)
2 Flow control mode (optional)
3 Parity mode (optional)
4 Stop bits (optional)
5 Data bits (optional)
6 Terminal user timeout (optional)
7 One-screen length of the terminal screen (optional)
All the default values of the data are stored on the router and does not need additional configuration.
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Transmitting Messages Between User Interfaces
2 Configuring Asynchronous Interface Attributes
3 Setting Terminal Attributes
4 Configuring the User Interface
5 Configuring Modem Attributes
6 Configuring an Auto-executed Command
7 Configuring the Redirection Function
8 Configuring the Call-in or Call-out Restrictions of the VTY User Interface
Page 87

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-6 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
No. Procedure
9 Configuring the Maximum Number of VTY User Interfaces
10 Configuring the Authentication Timeout Time for VTY Users
11 Disconnecting a Specified User Interface
12 Checking the Configuration
You can configure one or more user interfaces simultaneously in any view.
5.2.2 Transmitting Messages Between User Interfaces
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Run:
send { all | ui-number | ui-type ui-number1 }
The message is transmitted between the user interfaces.
5.2.3 Configuring Asynchronous Interface Attributes
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
speed speed-value
The transmission rate is set.
Step 4 Run:
flow-control { hardware | none | software }
The flow control mode is set.
Step 5 Run:
parity { even | mark | none | odd | space }
The parity mode is set.
Step 6 Run:
stopbits { 1.5 | 1 | 2 }
Page 88

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-7
The stop bit is set.
Step 7 Run:
databits { 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 }
The data bit is set.
----End
5.2.4 Setting Terminal Attributes
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
Shell
The terminal service is started.
Step 4 Run:
idle-timeout minutes [ seconds ]
The timeout period is set.
Step 5 Run:
screen-length screen-length
One-screen length of the terminal screen is set.
Step 6 Run:
history-command max-size size-value
The buffer of the history command is set.
----End
5.2.5 Configuring the User Interface Priority
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Page 89

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-8 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
user privilege level level
The priority of the user interface is set.
----End
5.2.6 Configuring Modem Attributes
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface aux 0
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
modem timer answer seconds
The interval between the system receiving the Ring signal and waiting for CD_UP is set. The
time it takes from off-pick of the Modem to carrier detection is set
Step 4 Run:
modem auto-answer
The automatic answer is set.
Step 5 Run:
modem [ both | call-in ]
The incoming and outgoing calls are set.
----End
5.2.7 Configuring an Auto-executed Command
Page 90

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-9
z
The auto-execute command command should be used carefully because it may cause
failure of the system configuration through the user-interface.
z
Before configuring this command and saving the configuration, you should make sure that
this configuration can be removed by logging in to the system in other ways such as
logging on the router through the console port..
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface aux 0
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
auto-execute command command
The auto-executed command is set.
----End
5.2.8 Configuring the Redirection Function
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
redirect
The Telnet redirection is enabled.
----End
Page 91

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-10 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
5.2.9 Configuring the Call-in or Call-out Restrictions of the VTY
User Interface
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
acl acl-number { inbound | outbound }
The call-in and call-out restrictions of the VTY user interface are configured.
----End
5.2.10 Configuring the Maximum Number of VTY User Interfaces
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface maximum-vty number
The maximum number of the VTY user interface is configured.
----End
In Step 2, you can configure the maximum number of the user that log in to the router at the
same time.
If the maximum number of configured VTY user interfaces is smaller than that of the current
maximum number, you do not need other configurations.
If the maximum number of configured VTY user interfaces is greater than that of the current
maximum number, you need to configure the authentication mode and the password for the
newly added user interfaces. Because by default, the newly added user interfaces use the
password authentication. The prompt is as follows:
Warning:Login password has not been set!
For example, if the current maximum number of VTY users that are allowed to be online is
five and you need to configure the maximum number to be 15, run the authentication-mode
and the set authentication password commands to configure the authentication mode and the
password for 5-14 VTY user interfaces. The configuration is as follows:
Page 92

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-11
<Quidway> system-view
[Quidway] user-interface maximum-vty 15
[Quidway] user-interface vty 5 14
[Quidway-ui-vty5-14] authentication-mode password
[Quidway-ui-vty5-14] set authentication password cipher huawei
5.2.11 Configuring the Authentication Timeout Time for VTY
Users
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
authorization-cmd timeout timeout-value
The authorization and authentication timeout time of the command line is configured.
----End
The NE supports HWTACACS command line authentication based on the login user level or
the name of the SSH user.
When a user logs in to the router, every input command should be authorized by
HWTACACS server if the command line authorization is configured.
If the router receives no authorization result form HWTACACS server before timeout, it
processes the authorization as a failure and then the input command cannot be run.
5.2.12 Disconnecting a Specified User Interface
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Run:
free user-interface { ui-number | ui-type ui-number1 }
The specified user interface is disconnected.
5.2.13 Checking the Configuration
Run the following commands to check the previous configuration.
Action Command
Check the information about
the user interface use.
display users [ all ]
Page 93

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-12 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
Action Command
Check the maximum number
of VTY user interfaces.
display user-interface maximum-vty
Check the physical attributes
and configurations of the user
interface.
display user-interface [ ui-type ui-number ] [ summary ]
5.3 Configuring User Management
5.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
This section describes how to configure the user priority and the authentication.
To access the network, remote users can log in to the router to access networks through Telnet
or establish a PPP connection with the router. This can be done if the router is configured with
the IP address of the MCU or that of the interface board. Remote users access the network by
establishing PPP connection with the router. To ensure network security and ease user
management, configure a username and the user password for the router.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring user management, complete the following tasks:
z
Powering on the router
z
Connecting the PC with the router properly
Data Preparation
To configure user management, you need the following data.
No. Data
1 Authentication mode
2 Username and password
3 User priority
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Configuring Authentication Mode
2 Configuring the Authentication Password
Page 94

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-13
No. Procedure
3 Setting Username and Password for AAA Local Authentication
4 Configuring the User Priority
5 Checking the Configuration
5.3.2 Configuring Authentication Mode
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
authentication-mode { simple | cipher }
The user password authentication mode is configured.
----End
5.3.3 Configuring the Authentication Password
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
set authentication password { cipher | simple } password
The authentication password is configured.
----End
The default authentication mode is the password authentication.
Page 95

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-14 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
5.3.4 Setting Username and Password for AAA Local
Authentication
Do as follows on the router that the user logs in to:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
user-interface [ ui-type ] first-ui-number [ last-ui-number ]
The user interface view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
set authentication password { cipher | simple } password
The password of the local authentication is set.
Step 4 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 5 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 6 Run:
local-user user-name password { simple | cipher } password
The local username and the password are configured.
----End
5.3.5 Configuring the User Priority
Refer to the Quidway NetEngine20/20E Series RoutersConfiguration Guide - Security.
5.3.6 Checking the Configuration
Run the following commands to check the previous configuration.
Action Command
Check the user information. display users [ all ]
Check the information of local users.
display local-user
Check the information of the access users.
display access-user
Page 96

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-15
5.4 Configuring the Local User Management
5.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Applicable Environment
You can create and manage the separate local user on the broadband access server.
Pre-configuration Tasks
None
Data Preparation
To configure the local user management, you need the following data:
No. Data
1 Username and password
2 Service type of the local user
3 FTP directory of the local user
4 The status of the local user
5 The maximum number of accessing local users
Configuration Procedures
No. Procedure
1 Creating the Local User Account
2 Configuring the Service Type of the Local User
3 Configuring FTP Directory Authority of the Local User
4 Configuring the Local User Status
5 Configuring the Local User Priority
6 Configuring the Access Restriction of the Local User
7 Checking the Configuration
5.4.2 Creating the Local User Account
Do as follows on the broadband access router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
Page 97

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-16 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
local-user user-name password { simple | cipher } password
The local user account is created.
----End
5.4.3 Configuring the Service Type of the Local User
Do as follows on the broadband access router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
local-user user-name service-type { ftp | ppp | ssh | telnet | terminal } *
The service type of the local user is configured.
----End
By configuring the service type of the local user, you can manage the user based on service types.
5.4.4 Configuring FTP Directory Authority of the Local User
Do as follows on the broadband access router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
local-user user-name ftp-directory directory
Page 98

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-17
The FTP directory authority of the local user is configured.
----End
5.4.5 Configuring the Local User Status
Do as follows on the broadband access router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
local-user user-name state { active | block }
The local user status is configured.
----End
5.4.6 Configuring the Local User Priority
Do as follows on the broadband access router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
local-user user-name level level
The local user priority is configured.
----End
5.4.7 Configuring the Access Restriction of the Local User
Do as follows on the broadband access router:
Step 1 Run:
system-view
Page 99

5 User Management
Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations
5-18 Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Issue 05 (2010-01-30)
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
aaa
The AAA view is displayed.
Step 3 Run:
local-user user-name access-limit access-limit
The access restriction of the local user is configured.
----End
5.4.8 Checking the Configuration
Run the following command to check the previous configuration.
Action Command
Check the attribute of the local
user.
display local-user [ domain domain-name | user-name
user-name ]
5.5 Configuration Examples
After the following two configuration examples are completed, the current user VTY0 cannot
run commands at levels higher than two. Ensure that you can log in to the router through other
methods to delete the configuration.
This section provides the following examples:
z
Example for Logging In to the Router Through Password
z
Example for Logging In to the Router Through AAA
5.5.1 Example for Logging In to the Router Through Password
Authentication
Networking Requirements
The COM port of the PC is connected with the Console port. Set the priority of VTY0 to 2
and authenticate the passwords of users. Users need to input the password Huawei to log on
successfully.
After login, if the operations are not carried out in 30 minutes, it means that the user-interface
is disconnected from the router.
Page 100

Quidway NetEngine20/20E
Configuration Guide - Basic Configurations 5 User Management
Issue 05 (2010-01-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5-19
Configuration Roadmap
1. Enter the user interface.
2. Configure the priority of VTY0 as 2.
3. Configure the simple authentication and the disconnect time.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
z
The password of the authentication mode
z
The connection time
Configuration Procedure
<Quidway> system-view
[Quidway] user-interface vty 0
[Quidway-ui-vty0] user privilege level 2
[Quidway-ui-vty0] authentication-mode password
[Quidway-ui-vty0] set authentication password simple huawei
[Quidway-ui-vty0] idle-timeout 30
# Use the display this command to check all configurations.
[Quidway-ui-vty0] display this
#
user-interface con 0
user-interface aux 0
user-interface vty 0
user privilege level 2
set authentication password simple huawei
idle-timeout 30 0
user-interface vty 1 4
#
return
# Use the display current-configuration command to view the system files.
[Quidway] display current-configuration
#
sysname Quidway
#
user-interface con 0
user-interface aux 0
user-interface vty 0
user privilege level 2
set authentication password simple huawei
idle-timeout 30 0
user-interface vty 1 4
#
return
Configuration Files
#
sysname Quidway
 Loading...
Loading...