Huawei UPS5000-A-300KTTL, UPS5000-A-200K-FT, UPS5000-A-200K-ST, UPS5000-A Series, UPS5000-A-300K-FT User Manual
...Page 1
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
Issue
03
Date
2019-02-15
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2019. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
http://e.huawei.com
Page 3
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
About This Document
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
Purpose
Symbol
Description
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
This document describes the UPS5000-A-(200 kVA–800 kVA) in terms of its features,
performance specifications, working principles, appearance as well as instructions for
installation, and operation and maintenance (O&M). UPS is short for uninterruptible power
system.
Intended Audience
About This Document
This document is intended for:
Sales engineers
Technical support engineers
System engineers
Hardware installation engineers
Commissioning engineers
Data configuration engineers
Maintenance engineers
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Page 4

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
About This Document
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Symbol
Description
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, could result in equipment damage, data
loss, performance deterioration, or unanticipated
results.
NOTICE is used to address practices not related to
personal injury.
Calls attention to important information, best
practices and tips.
NOTE is used to address information not related to
personal injury, equipment damage, and
environment deterioration.
Change History
Changes between document issues are cumulative. The latest document issue contains all the
changes made in earlier issues.
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Added the isolation protection model.
Issue 02 (2018-11-30)
Update some MDU screenshots.
Issue 01 (2018-03-05)
This issue is the first official release.
Page 5

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
Contents
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
Contents
About This Document .................................................................................................................... ii
1 Safety Precautions ......................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 General Safety .............................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Electrical Safety ............................................................................................................................................................ 3
1.3 Operating Environment................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.4 Battery Safety ............................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.5 Mechanical Safety ........................................................................................................................................................ 8
1.6 Laying Out Cables ........................................................................................................................................................ 9
1.7 Information About Foreign Objects near UPS Equipment Installation ....................................................................... 10
2 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 12
2.1 Model Description ...................................................................................................................................................... 12
2.2 Working Principles...................................................................................................................................................... 14
2.2.1 Conceptual Diagram ................................................................................................................................................ 14
2.2.2 Working Modes ........................................................................................................................................................ 15
2.2.2.1 Normal Mode ........................................................................................................................................................ 15
2.2.2.2 Bypass Mode ........................................................................................................................................................ 16
2.2.2.3 Battery Mode ........................................................................................................................................................ 16
2.2.2.4 Maintenance Bypass Mode ................................................................................................................................... 17
2.2.2.5 ECO Mode ............................................................................................................................................................ 17
2.3 Product Introduction ................................................................................................................................................... 19
2.3.1 Product Appearance (200K, 300K) ................................................................................................ .......................... 19
2.3.2 Product Appearance (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) .................................................................................... 20
2.3.3 Product Structure (200K, 300K) .............................................................................................................................. 23
2.3.4 Product Structure (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ........................................................................................ 26
2.4 Control Unit ................................................................................................................................................................ 32
2.4.1 Overview ................................................................................................................................................................. 32
2.4.2 ECM......................................................................................................................................................................... 32
2.4.3 Dry contact card ....................................................................................................................................................... 33
2.4.4 Monitoring interface card ........................................................................................................................................ 35
2.5 MDU ........................................................................................................................................................................... 40
2.6 Typical configurations ................................................................................................................................................ 43
2.6.1 Single UPS ............................................................................................................................................................... 43
Page 6

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
Contents
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v
2.6.2 Parallel System ........................................................................................................................................................ 43
2.6.3 Dual-Bus System ..................................................................................................................................................... 44
2.7 Optional Components (200K, 300K) ................................................................................................ .......................... 45
2.8 Optional Components (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) .................................................................................... 48
3 Installation.................................................................................................................................... 51
3.1 Installation Preparations ............................................................................................................................................. 51
3.1.1 Site ........................................................................................................................................................................... 51
3.1.1.1 UPS Weight and Dimensions (200K, 300K) ......................................................................................................... 51
3.1.1.2 UPS Weight and Dimensions (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ................................................................... 52
3.1.1.3 Installation Environment ....................................................................................................................................... 56
3.1.1.4 Installation Clearances .......................................................................................................................................... 56
3.1.2 Tools and Instruments .............................................................................................................................................. 57
3.1.3 Preparing Power Cables (200K, 300K) ................................................................................................................... 59
3.1.4 Preparing Power Cables (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ............................................................................. 62
3.1.5 Unpacking (200K, 300K) ........................................................................................................................................ 66
3.1.6 Unpacking (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) .................................................................................................. 67
3.1.7 (Optional) Splitting the Power Cabinet and Bypass Cabinet (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K) ................................. 68
3.1.8 (Optional) Combining the Power Cabinet and Bypass Cabinet (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K) ............................ 75
3.2 Single UPS Installation ............................................................................................................................................... 76
3.2.1 Installing UPS Cabinets (200K, 300K) .................................................................................................................... 76
3.2.2 Installing UPS Cabinets (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) .............................................................................. 81
3.2.2.1 Installing the UPS on the Floor ............................................................................................................................. 81
3.2.2.2 Installing the UPS on Channel Steel ..................................................................................................................... 84
3.2.3 Installing UPS Cabinets (800K)................................................................ ............................................................... 85
3.2.3.1 Installing the UPS on the Floor ............................................................................................................................. 85
3.2.3.2 Installing the UPS on Channel Steel ..................................................................................................................... 95
3.2.4 Installing Batteries ................................................................................................................................................... 96
3.2.5 Installing Optional Components .............................................................................................................................. 97
3.2.5.1 Installing Antiseismic Kits (200K, 300K) ............................................................................................................. 97
3.2.5.2 Installing an IP21 Component ............................................................................................................................ 100
3.2.5.3 Connecting an Ambient T/H Sensor ................................................................................................................... 101
3.2.5.4 Connecting the BCB Box ................................................................................................................................... 101
3.2.5.5 Installing a Battery Grounding Failure Detector (200K, 300K) ......................................................................... 101
3.2.5.6 Installing a Battery Grounding Failure Detector (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ................................... 105
3.2.5.7 Connecting the iBAT .......................................................................................................................................... 106
3.2.6 UPS Cable Connection Reference ......................................................................................................................... 107
3.2.7 Routing Cables (UPS5000-A-200K-ST) ............................................................................................................... 108
3.2.7.1 Routing Cables from the Top .............................................................................................................................. 108
3.2.7.2 Routing Cables from the Bottom ........................................................................................................................ 115
3.2.8 Routing Cables (UPS5000-A-200K-FT) ............................................................................................................... 121
3.2.8.1 Routing Cables from the Top .............................................................................................................................. 121
Page 7

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
Contents
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vi
3.2.8.2 Routing Cables from the Bottom ........................................................................................................................ 128
3.2.9 Routing Cables (UPS5000-A-200K-FT, Isolation Protection)............................................................................... 137
3.2.10 Routing Cables (UPS5000-A-300KTTL) ............................................................................................................ 142
3.2.11 Routing Cables (UPS5000-A-300K-STT) ........................................................................................................... 149
3.2.12 Routing Cables (UPS5000-A-300K-STT, Isolation Protection) .......................................................................... 155
3.2.13 Routing Cables (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K) .................................................................................................. 159
3.2.13.1 Top Cable Routing ............................................................................................................................................ 160
3.2.13.2 Bottom Cable Routing ...................................................................................................................................... 173
3.2.14 Routing Cables (800K) ........................................................................................................................................ 181
3.2.14.1 Top Cable Routing ............................................................................................................................................ 181
3.2.14.2 Bottom Cable Routing ...................................................................................................................................... 189
3.2.15 Remote EPO ........................................................................................................................................................ 197
3.2.16 Connecting Communications Cables ................................................................................................................... 198
3.3 Parallel System Installation ...................................................................................................................................... 198
3.3.1 Installing the UPSs ................................................................................................................................................ 198
3.3.2 Connecting Power Cables (200K, 300K) ............................................................................................................... 201
3.3.3 Connecting Signal Cables (200K, 300K) ............................................................................................................... 204
3.3.4 Connecting Power Cables (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ......................................................................... 206
3.3.5 Connecting Signal Cables (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ......................................................................... 212
3.4 Installing a Lock ....................................................................................................................................................... 214
3.5 Installation Verification ............................................................................................................................................. 215
4 User Interface ............................................................................................................................. 220
4.1 LCD Interface ........................................................................................................................................................... 220
4.1.1 Main Menu ............................................................................................................................................................ 220
4.1.2 System Info Screen ................................................................................................................................ ................ 221
4.1.2.1 Running .............................................................................................................................................................. 222
4.1.2.2 Alarms Screen ..................................................................................................................................................... 225
4.1.2.3 Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 227
4.1.2.4 Maintenance ........................................................................................................................................................ 247
4.1.2.5 About Screen ....................................................................................................................................................... 251
4.1.3 System Status ................................ ................................................................ ......................................................... 251
4.1.4 Common Functions ................................ ................................................................ ................................ ................ 252
4.2 WebUI ....................................................................................................................................................................... 252
4.2.1 Login ...................................................................................................................................................................... 252
4.2.2 Monitoring ............................................................................................................................................................. 254
4.2.2.1 Parameter Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 255
4.2.2.2 Communication Settings ..................................................................................................................................... 263
4.2.2.3 Control ................................................................................................................................................................ 263
4.2.3 Query ..................................................................................................................................................................... 263
4.2.3.1 Historical Alarms ................................................................................................................................................ 263
4.2.3.2 Logs .................................................................................................................................................................... 264
Page 8

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
Contents
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii
4.2.4 Config. Page .......................................................................................................................................................... 264
4.2.4.1 User Management ............................................................................................................................................... 264
4.2.4.2 Site Config. ......................................................................................................................................................... 265
4.2.4.3 RCCMD .............................................................................................................................................................. 267
4.2.4.4 Managing the UPS by Using the NMS Complying with RFC1628 Standard ..................................................... 276
4.2.5 Protecting the Server by Using the RCCMD Software .......................................................................................... 277
4.2.5.1 Introduction to the Software ............................................................................................................................... 277
4.2.5.2 RCCMD Event Shutdown and Message Sending ............................................................................................... 278
4.2.5.3 UPS Alive Check Function ................................................................................................................................. 279
5 Operations .................................................................................................................................. 282
5.1 Powering On and Starting the UPS ........................................................................................................................... 282
5.1.1 Powering On the UPS ............................................................................................................................................ 282
5.1.2 Starting the Inverter ............................................................................................................................................... 282
5.1.2.1 Initial Startup ...................................................................................................................................................... 283
5.1.2.2 Non-initial Startup .............................................................................................................................................. 289
5.1.3 Powering On Loads ............................................................................................................................................... 291
5.1.4 (Optional) Setting Parameters for the BCB Box .................................................................................................... 292
5.2 Shutting Down and Powering Off the UPS .............................................................................................................. 292
5.3 Starting the UPS in Battery Mode ............................................................................................................................ 294
5.4 Transferring to Bypass Mode .................................................................................................................................... 294
5.5 Setting ECO Mode .................................................................................................................................................... 295
5.6 Testing Batteries ....................................................................................................................................................... 296
5.6.1 Forced Equalized Charging Test ............................................................................................................................ 296
5.6.2 Shallow Discharge Test .......................................................................................................................................... 297
5.6.3 Capacity Test.......................................................................................................................................................... 298
5.6.4 Test Data Download ............................................................................................................................................... 299
5.7 Transferring to Maintenance Bypass Mode (200K, 300K) ....................................................................................... 300
5.8 Transferring to Maintenance Bypass (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K) ........................................................... 304
5.9 Transferring from Maintenance Bypass Mode to Normal Mode .............................................................................. 306
5.10 Performing EPO...................................................................................................................................................... 306
5.11 Clearing the EPO State ........................................................................................................................................... 307
5.12 Exporting Data ........................................................................................................................................................ 307
6 Routine Maintenance ............................................................................................................... 309
6.1 UPS Maintenance ..................................................................................................................................................... 309
6.1.1 Monthly Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................ 309
6.1.2 Quarterly Maintenance .......................................................................................................................................... 310
6.1.3 Annual Maintenance .............................................................................................................................................. 310
6.2 Battery Maintenance ................................................................................................................................................. 311
6.2.1 Precautions for Battery Maintenance ..................................................................................................................... 312
6.2.2 Monthly Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................ 312
6.2.3 Quarterly Maintenance .......................................................................................................................................... 313
Page 9

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
Contents
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
viii
6.2.4 Annual Maintenance .............................................................................................................................................. 314
7 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................ 315
8 Technical Specifications .......................................................................................................... 318
8.1 Physical Parameters .................................................................................................................................................. 318
8.2 Internal Switch Parameters ....................................................................................................................................... 318
8.3 Environment Parameters ........................................................................................................................................... 319
8.4 Safety Regulations and EMC .................................................................................................................................... 319
8.5 Mains Input Electrical Specifications ....................................................................................................................... 320
8.6 Bypass Input Electrical Specifications ................................................................ ................................ ...................... 320
8.7 Battery Specifications ............................................................................................................................................... 321
8.8 Output Electrical Specifications ............................................................................................................................... 321
8.9 System Electrical Specifications ............................................................................................................................... 322
9 Menu Hierarchy......................................................................................................................... 323
9.1 Menus on the LCD .................................................................................................................................................... 323
9.2 Menus on the WebUI ................................ ................................................................ ................................ ................ 325
10 Alarm List ................................................................................................................................. 328
A Acronyms and Abbreviations ................................................................................................ 342
Page 10
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1
1.1 General Safety
This section describes safety precautions to consider before installing, maintaining, and
operating the UPS.
1 Safety Precautions
Declaration
To minimize the risk of personal injury and damage to equipment, read and follow all the
precautions in this document before performing any operation. The "DANGER",
"WARNING", "CAUTION", and "NOTICE" statements in this document are only
supplemental and do not represent all the safety instructions.
Only trained and qualified personnel are allowed to install, operate, and maintain Huawei
equipment.
Follow the precautions and special safety instructions provided by Huawei when operating
Huawei products. Huawei will not be liable for any consequences that are caused due to
violations regarding general safety regulations and equipment design, production, and usage
safety standards.
Huawei does not take responsibilities for the following situations:
Operation under severe environments that are not specified in this document.
Installation or use in environments that are not specified in related international
standards.
Unauthorized product changes and software code modification.
Operations not complying with the operation instructions and safety precautions in this
document.
Damage caused by extreme natural environments.
Damage caused by using batteries provided by Huawei for non-Huawei UPSs.
Damage caused by using batteries not provided by Huawei.
Page 11

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2
Power Grid Requirements
A standard UPS can connect to a three-phase, five-wire (L1, L2, L3, N, PE) TT, TN-C, TN-S,
and TN-C-S AC power distribution system (IEC60364-1).
Local Laws and Regulations
Equipment operations must comply with local laws and regulations. The safety instructions in
this document are only supplemental to local safety regulations.
Personal Requirements
Only Huawei engineers or engineers certified by Huawei are allowed to perform UPS
commissioning and maintenance. Otherwise, human injury or equipment damage may occur,
and any resulting UPS faults will be beyond warranty scope.
Personnel who plan to install or maintain Huawei equipment must receive thorough training,
understand all necessary safety precautions, and master the correct operation methods.
Trained and qualified personnel, or personnel certified or authorized by Huawei are:
Allowed to install, operate, and maintain the equipment.
Allowed to remove safety facilities and inspect the equipment.
Allowed to replace or change the devices or components (including software).
Operation personnel must report faults or errors that might cause serious safety issues to
related owners.
This product should be installed and used according to the installation and technical,
specification requirements found in this manual. Otherwise, the product may be damaged,
and the resulting product exceptions or component damage will be beyond the warranty
scope.
Grounding Requirements
Devices to be grounded (excluding the energy storage unit) must meet the following
requirements:
When installing a device, install the ground cable first. When removing a device, remove
the ground cable at the very end.
Do not damage the ground conductor.
Do not operate devices if the ground conductor is not installed. Before operating a device,
check the electrical connection of the device to ensure that it is securely grounded.
Personal Safety
Do not operate the product, or handle cables, during thunderstorms.
To avoid electric shocks, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to
telecommunication network voltage (TNV) circuits.
Page 12

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3
Device Safety
Before operating a device, wear electrostatic discharge (ESD) clothes, ESD gloves, and
an ESD wrist strap. Remove any conductors (such as jewelry or watches) before the
operation to avoid electric shocks or burns.
In the case of fire, leave the building or the equipment room immediately, and turn on the
fire alarm bell or make an emergency call. Never enter the building on fire in any case.
If the cabinet provides an ESD jack, wear an ESD wrist strap and insert the ground
terminal of the ESD wrist strap into the jack.
Ensure all switches are turned to OFF during device installation.
Power on the UPS only after authorized engineers arrive at the site.
If a C2 UPS is used in residential areas, additional measures must be taken to prevent
radio frequency interferences.
If the UPS is used for life-supporting medical apparatus and facilities such as lifts where
adequate care has to be taken to ensure personal safety, discuss with the manufacturer in
advance about the applicability, settings, management, and maintenance of the UPS,
which require special considerations during design.
Before operation, ensure that the device is firmly anchored to the floor or other solid
objects, such as a wall or an installation rack.
Ensure ventilation vents are unblocked while the system is operating.
Before powering on the device, ensure that all the screws inside it are securely tightened
and will not fall off during operation.
After the installation, remove packing materials from the equipment area.
Replace danger signs that have worn out or are unreadable.
A UPS can be used to serve resistive-capacitive loads, resistive loads, and
micro-inductive loads. It is recommended that a UPS not be used for pure capacitive
loads, pure inductive loads, and half-wave rectification loads. It does not apply to energy
feedback loads.
Do not alter the UPS internal structure or installation procedure unless consent from the
manufacturer is given.
Never use water to clean electrical components inside or outside the UPS.
Do not drill holes into a cabinet.
1.2 Electrical Safety
High Voltage
The high voltage power supply provides power for the device operation. Direct or indirect
contact with high voltage power sources may result in fatal injury.
Non-standard or incorrect high voltage operations may result in fire and electric shocks.
The personnel who install the AC facility must be qualified to perform high voltage and
AC operations.
Page 13

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4
When selecting, connecting, and routing power cables, ensure compliance with local
laws and regulations.
When operating the AC power supply facility, ensure compliance with local laws and
regulations.
Before connecting cables to the UPS, ensure that the input power and mains power
distribution switches and output power distribution switch are turned off.
Use only dedicated tools during high voltage and AC operations.
If the operation is performed in a damp environment, ensure that the device is dry. When
water is found in the rack or the rack is damp, switch off the power supply immediately.
High Leakage Current
Ground a device before powering it on. Otherwise, personal injury or device damage may
occur.
If a "high leakage current" tag is attached to the panel of the device, ground the protective
ground terminal on the device enclosure before connecting the AC power supply to
prevent electric shocks.
The UPS can generate high leakage currents. Using a circuit breaker that has the leakage
current protection function is not recommended.
Power Cable
Fuse
Do not install or remove power cables when the device is on. Transient contact between the
core of the power cable and the conductor may generate electric arcs or sparks, which may
cause fire or damage eyesight.
Before moving or reconnecting the UPS, disconnect the mains and batteries, open the
output power distribution switch, and wait a period of at least 5 minutes after the UPS
completely powers off. Otherwise, electric shocks may occur.
Before installing or removing the power cable, open the power switch.
Before connecting a power cable, check that its label is correct.
If a fuse needs replacing, ensure the new fuse is of the same type and specifications so that the
system runs safely.
Page 14

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5
Backfeed Protection Dry Contact
The UPS can be configured with a backfeed protection dry contact to work with an external
automatic circuit breaker, preventing the voltage from flowing back to input terminals over
static bypass circuits. If device installation and maintenance personnel do not need to use
backfeed protection, paste labels on the external bypass input circuit breakers informing that
the circuit is connected to the UPS. Disconnect the device from the UPS before performing
operations on the circuit.
Electrostatic Discharge
Static electricity generated by human bodies may damage the electrostatic-sensitive
components on boards, for example, the large-scale integrated (LSI) circuits.
Wear a pair of ESD gloves or a well-grounded ESD wrist strap when touching the device
or handling boards or application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
When holding a board, hold its edge without touching any components, especially chips.
Package boards with ESD packaging materials before storing or transporting them.
Figure 1-1 shows how to wear an ESD wrist strap.
Figure 1-1 Wearing an ESD wrist strap
Liquid Prevention
Do not place the product under areas prone to water leakage, such as near air conditioner
vents, ventilation vents, or feeder windows of the equipment room. Ensure that there is
no condensation inside the product or equipment room. Ensure that no liquid enters the
product. Otherwise, short circuits will occur and may result in serious injury or death.
If any liquid is detected inside the product, immediately disconnect the power supply and
contact the administrator.
Page 15
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
6
1.3 Operating Environment
The UPS is used for commercial and industrial purposes only. It cannot be used as a power
supply for life support devices.
The TIER4 or TIER3 power supply architecture specified in TIA942, that is, dual power
supply routes, must be used in the power supply systems that are crucial to major economic
interests or order of public places, such as the national computing center, military command
system, emergency command center, railway signal system and control center, civil aviation
air traffic control center, airport command center, financial clearing center, and transaction
center.
The UPS operating environment must meet the requirements for the climate indicator,
mechanically active substance indicator, and chemically active substance indicator in ETSI
EN 300 019-1 class 3.6.
Do not expose the equipment or perform any operations in an environment with flammable or
explosive gas, or smoke.
Any operation on any electrical device in an environment that has flammable air can cause
extreme danger. Strictly obey the operating environmental requirements specified in related
use manuals when using or storing the device.
Do not use the UPS in the following environments:
Environment containing flammable gases, corrosive gases, abnormal vibrations, and
impacts.
Non-confined environment near the ocean (0–3.7 km) and indoor or semi-indoor
environment where the temperature and humidity are not controllable, such as a simple
equipment room near the ocean, citizen house, garage, corridor, direct ventilation cabinet,
house with only the roof, railway station platform, gymnasium, aquarium, and so on.
1.4 Battery Safety
This section describes precautions for operating batteries.
Before operating batteries, carefully read the safety precautions to ensure correct battery
handling and connection is performed, and personal safety is managed.
Page 16

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
7
To ensure battery safety and efficient battery management, use the batteries delivered with
the UPS. Huawei shall not be responsible for battery damage caused by using non-Huawei
batteries for Huawei UPSs.
Ensure lead-acid battery handling is in accordance with local regulations.
Incorrect handling of batteries may cause hazards. When operating batteries, avoid
battery short circuits and electrolyte overflow or leakage.
Electrolyte overflow may damage the device by corroding metal parts and circuit boards,
and ultimately damaging the circuit boards.
Short circuits caused by incorrect operations may cause serious injuries due to high
power of batteries.
Do not reversely connect positive and negative battery terminals.
Use batteries of the specified type. Otherwise, the batteries may be damaged.
Check battery connections periodically to ensure that all screws are securely tightened.
Install or store batteries in clean, cool, and dry environments.
Do not decompose, transform, or damage batteries. Otherwise, battery short circuit,
electrolyte leakage, and even personal injury may occur.
Preventative Measures
When installing and maintaining batteries, pay attention to the following points:
Use dedicated insulated tools.
Take measures to protect eyes, such as using eye protection devices.
Avoid skin contact with electrolyte overflow. Wear rubber gloves and protective
clothing.
When handling a battery, ensure that its electrodes always point upward. Do not tilt or
overturn batteries.
Switch off the power supply during installation and maintenance.
Short Circuit
Battery short circuits may cause personal injury. The high transient current generated by a
short circuit may release a surge of power and cause a fire.
To avoid battery short circuits, do not maintain batteries while they are in use.
Harmful Gas
Page 17

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8
Do not use unsealed lead-acid batteries. Lead-acid batteries emit flammable gas. Therefore,
place and secure lead-acid batteries horizontally to prevent fire or corrosion.
Store lead-acid batteries in a place with good ventilation, and take fire safety precautions.
Battery Temperature
High temperature may result in battery distortion, damage, and electrolyte overflow.
Install or store batteries far away from fire sources and heating devices such as
transformers. Never burn batteries.
If the battery temperature exceeds 60°C, check the battery for electrolyte overflow. If
electrolyte overflows, handle the leakage immediately.
Electrolyte Leakage
In the case of electrolyte leakage, counteract and absorb the leaking electrolyte immediately.
When moving or handling a battery whose electrolyte leaks, note that the leaking electrolyte
may harm human bodies. If the electrolyte leaks, use the following substances to counteract
and absorb the leaking electrolyte:
Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda): NaHCO3
Sodium carbonate (soda): Na2CO3
When using substances to counteract and absorb electrolytes, strictly follow the guidelines
provided by the battery manufacturer.
If any personnel are exposed to battery electrolyte, wash the exposed area with clean water
immediately and seek medical advice if the situation is serious.
1.5 Mechanical Safety
Moving Sharp Objects
Wear protective gloves when moving sharp objects.
Page 18
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
9
Moving Heavy Objects
Perform operations in accordance with all instructional symbols on the device.
Take caution to avoid injury when moving heavy objects.
When moving or lifting a device, hold the handle or bottom of the device.
When transporting a device using a pallet truck, the forks must be properly positioned to
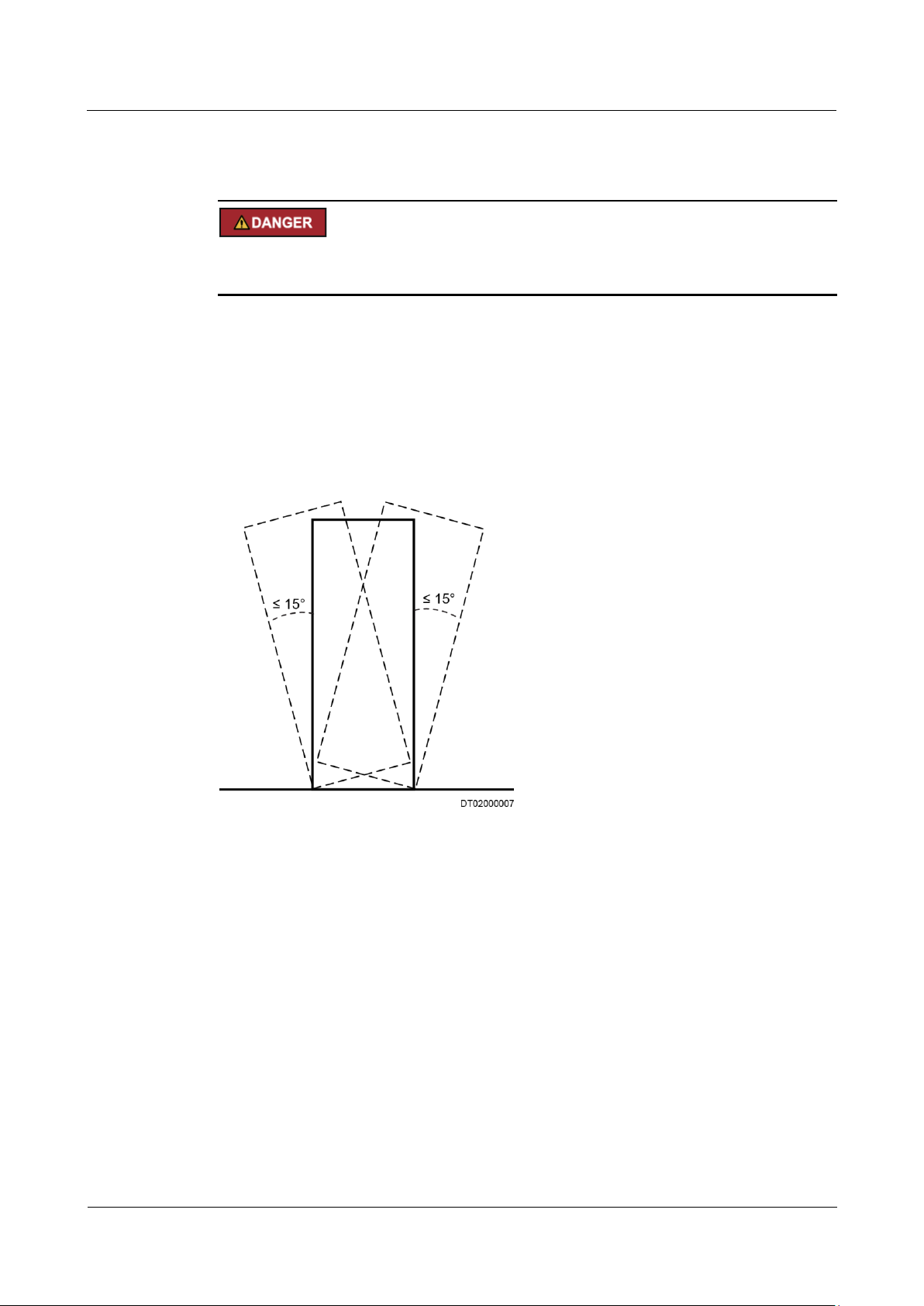
ensure that the device does not topple. No excessive tilt or jolt is allowed during the
transportation, and the maximum tolerance of the tilting angle during loading and
unloading is 15°. To avoid toppling, secure the device to the pallet truck by using ropes
before moving, and assign persons to watch out the device during movement.
Move the cabinet with caution. Any bumping or falling may damage the device.
Figure 1-2 Tilting angle of a cabinet
Handling Fans
Do not insert fingers or boards into the operating fans until the fans are switched off, and have
stopped running.
1.6 Laying Out Cables
Binding Signal Cables
Page 19

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
Signal cables must be bound separately from strong-current cables and high-voltage cables.
Laying Out Cables
When the temperature is low, a violent strike or vibrations may damage the cable sheathing.
To ensure cable safety, comply with the following requirements:
Cables can be laid, or installed, only when the temperature is higher than 0°C (32°F).
Handle cables with caution, especially at lower temperatures.
Before laying out cables that have been stored in temperatures lower than 0°C (32°F),
move the cables to an environment that is at the requisite ambient temperature. Store
them in this environment for at least 24 hours.
Do not drop the cables directly from the vehicle.
As the insulation layer of a cable may age, or be damaged from high temperatures,
ensure a sufficient distance between cables and the DC busbars, shunts, and fuses.
Cables prepared by the customer should be flame resistant. Cables must not be routed
behind the air exhaust vent of the cabinet. The air exhaust vent should not be blocked by
any object.
Before connecting a cable, ensure that the cable and cable label to be used meet the actual
installation requirements.
1.7 Information About Foreign Objects near UPS Equipment Installation
The purpose of this note is to provide information and warnings about the potential risks of
the operational integrity of an installed UPS. These risks are caused by foreign objects in or
near the UPS modules and relevant auxiliary equipment/components.
These risks are particularly high if conductive materials have entered the UPS modules/units
or the channels in the relevant auxiliary equipment/components.
Potential risks include damage to installed UPS equipment and subsequent power derating
and power failure of loads at critical positions.
Huawei UPS uses the highest safety standard in equipment design to ensure that live parts are
not in contact with the exterior and that no foreign object will enter the equipment during
operation.
However, when the UPS baffle plate and cover are open and the electrical wiring terminals
are exposed by the electrical contractor/installation personnel who are setting up a power line
connection, it is almost impossible to ensure that no foreign object will enter Huawei UPS
during onsite installation.
It is common to have someone working in the same room as the UPS during onsite
installation. Sometimes some people may be working above the UPS and relevant auxiliary
equipment/components.
To avoid serious damage to the onsite operation, property hazards, and personal injury
including fatal injury, it is the responsibility of each equipment manager or construction
Page 20

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
1 Safety Precautions
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
manager to ensure that no foreign object enters the UPS modules/units or relevant auxiliary
equipment/components.
Page 21

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
2.1 Model Description
Product Model
Abbreviation in
This Document
Description
UPS5000-A-200K-ST
200K
Top or bottom cable routing
UPS5000-A-200K-FT
Top cable routing, or bottom cable
routing if a cable entry cabinet is
installed
UPS5000-A-300K-STT
300K
Top cable routing
UPS5000-A-300KTTL
Bottom cable routing
UPS5000-A-300K-FT
300K-FT
Top or bottom cable routing
UPS5000-A-400K-SC
400K
UPS5000-A-400K-FC
UPS5000-A-400K-FT
UPS5000-A-500K-SC
500K
UPS5000-A-500K-FC
UPS5000-A-500K-FT
UPS5000-A-600K-F600-SC
600K
UPS5000-A-600K-F600-FC
UPS5000-A-800K-F800-SC
800K
UPS5000-A-800K-F800-FC
Table 2-1 Product model description
2 Overview
Page 22
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
Figure 2-1 UPS model number 1
No.
Item
Description
1
Product
category
UPS, short for uninterruptible power system
2
UPS family
5000
3
UPS
subcategory
A
4
Output capacity
200K: The output capacity is 200 kVA.
300K: The output capacity is 300 kVA.
400K: The output capacity is 400 kVA.
500K: The output capacity is 500 kVA.
5
Configuration
type
ST, SC: standard configuration
FT, FC: full configuration
TT: tower-mounted
6
Others T: top cable routing
L: external large-capacity battery pack
Table 2-2 UPS model number description 1
Figure 2-2 UPS model number 2
Page 23
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
Table 2-3 UPS model number description 2
No.
Item
Description
1
Product
category
UPS, short for uninterruptible power system
2
UPS family
5000
3
UPS
subcategory
A
4
Output capacity
600K: The output capacity is 600 kVA.
800K: The output capacity is 800 kVA.
5
Rack F600: 600 kVA rack
F800: 800 kVA rack
6
Configuration
type
SC: standard configuration
FC: full configuration
2.2 Working Principles
indicates an input mode.
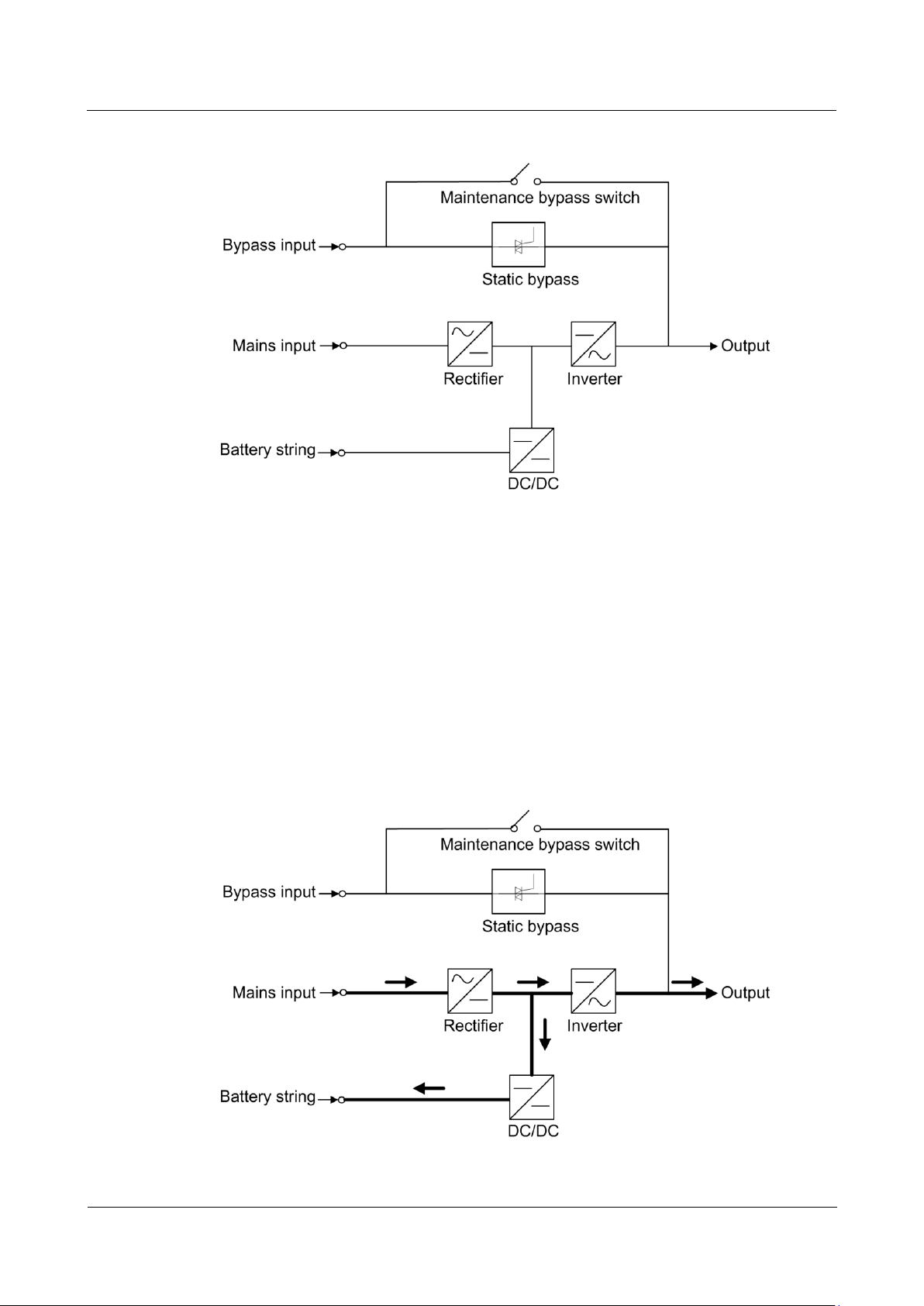
2.2.1 Conceptual Diagram
The UPS5000-A is an online double-conversion UPS that uses digital signal processing (DSP)
technology and features high efficiency and high power density. Figure 2-3 shows a
conceptual diagram for the UPS.
indicates the energy flow direction.
Page 24
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
Figure 2-3 UPS conceptual diagram
2.2.2 Working Modes
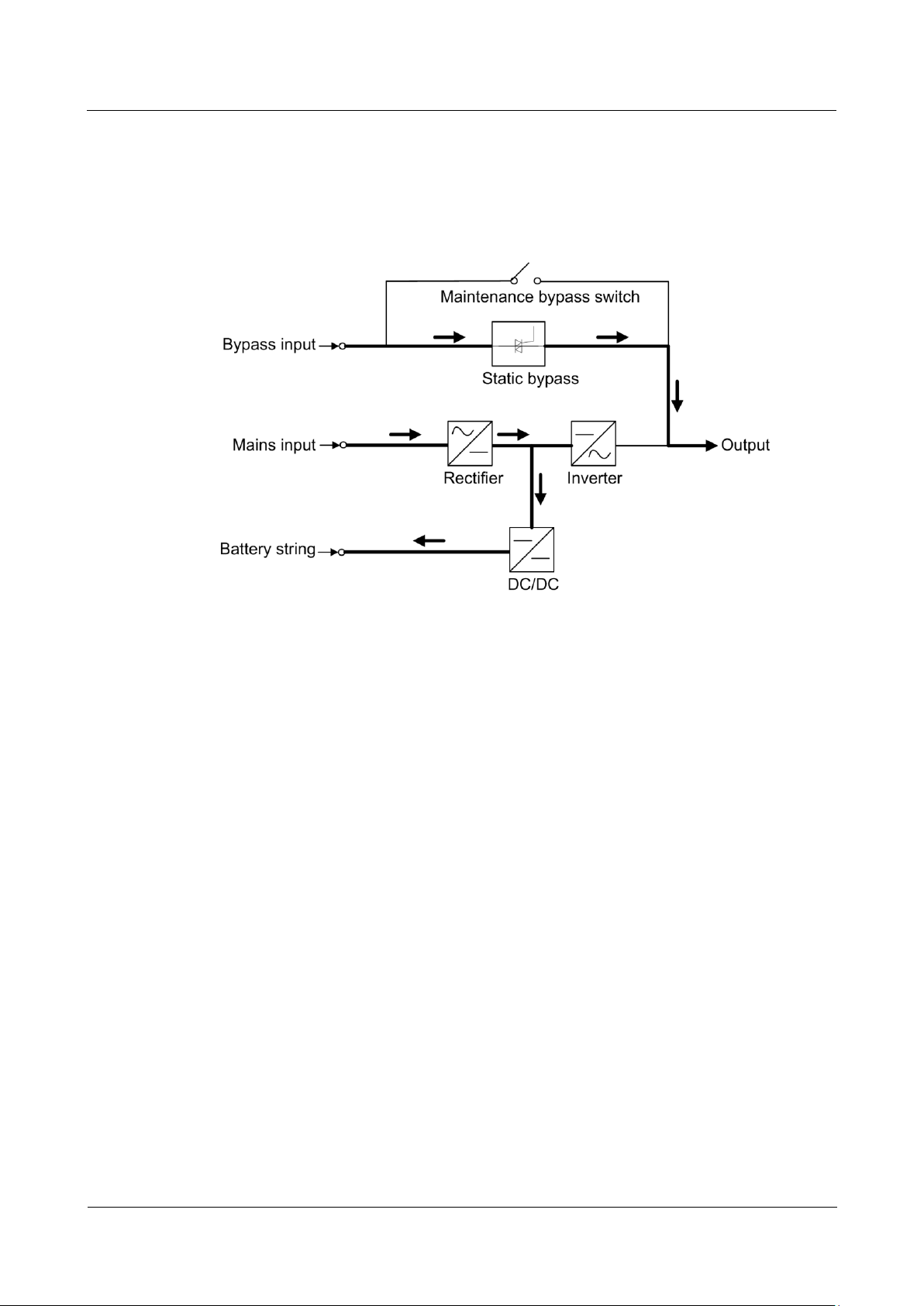
2.2.2.1 Normal Mode
When the UPS works in normal mode, the rectifier converts the AC input voltage into the DC
voltage, which is then raised to the bus voltage by the power factor correction (PFC) circuit.
Then one part of the voltage passes through the DC-DC circuit to charge the battery string,
and the other part is converted by the inverter into AC voltage outputs. The two conversions
ensure high-precision and high-quality output voltages, protecting loads from interferences
such as input harmonics, burrs, and voltage transients. Figure 2-4 shows the conceptual
diagram of the UPS working in normal mode.
Figure 2-4 UPS conceptual diagram in normal mode
Page 25
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
2.2.2.2 Bypass Mode
If the inverter does not start or is manually shut down after the UPS is powered on, the bypass
supplies power to loads. The UPS automatically transfers from normal mode to bypass mode
if it detects power unit overtemperature, overload, or other faults that may cause the inverter
to shut down. The bypass power supply is not protected by the UPS which means it may be
affected by mains outage, and incorrect AC voltage or frequency. Figure 2-5 shows a
conceptual diagram of the UPS working in bypass mode.
Figure 2-5 UPS conceptual diagram in bypass mode
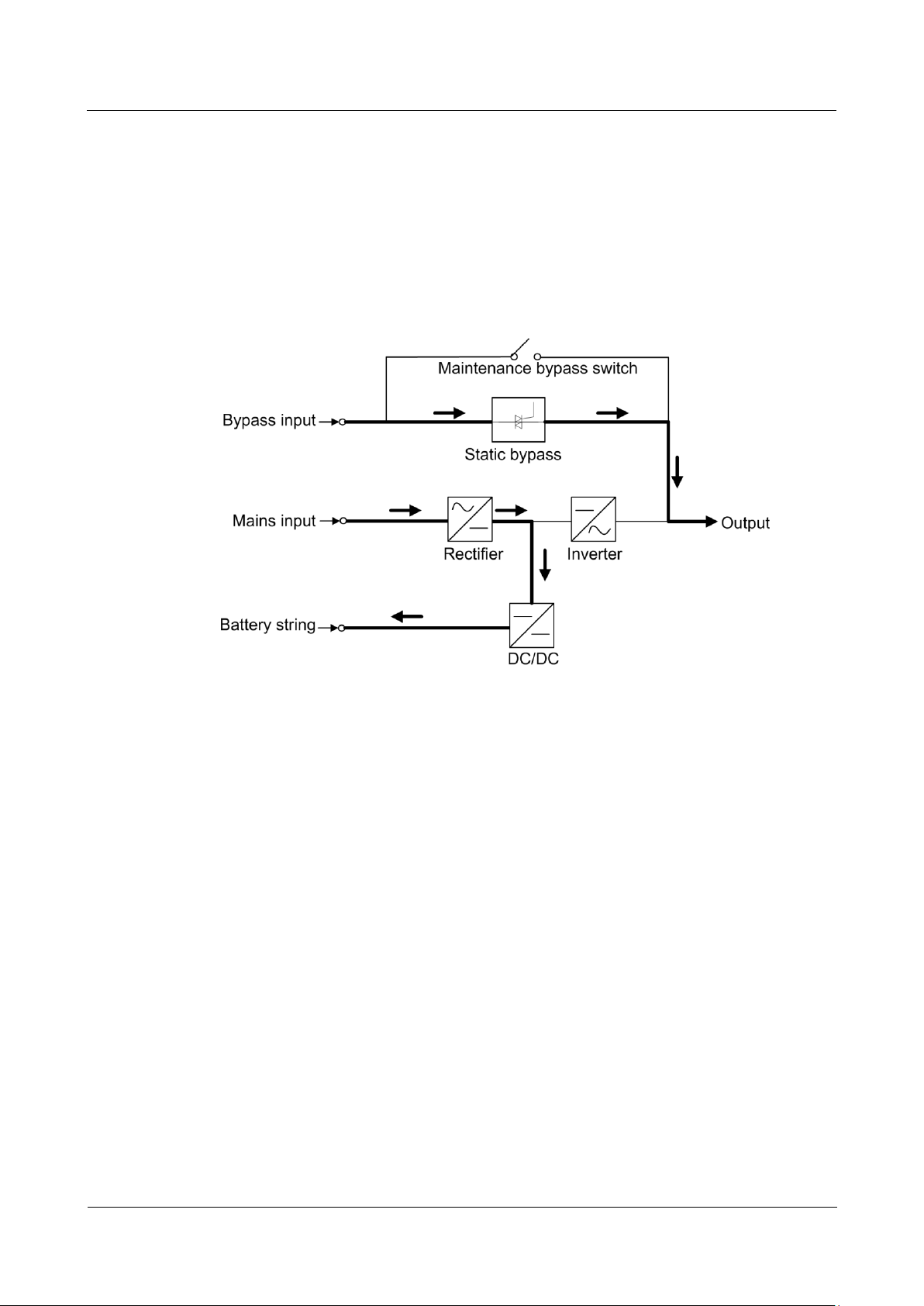
2.2.2.3 Battery Mode
If the AC input voltage is not normal, the UPS transfers to battery mode to obtain power from
batteries. The inverter then converts the power into AC outputs. Figure 2-6 shows a
conceptual diagram of the UPS working in battery mode.
Page 26
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
Figure 2-6 UPS conceptual diagram in battery mode
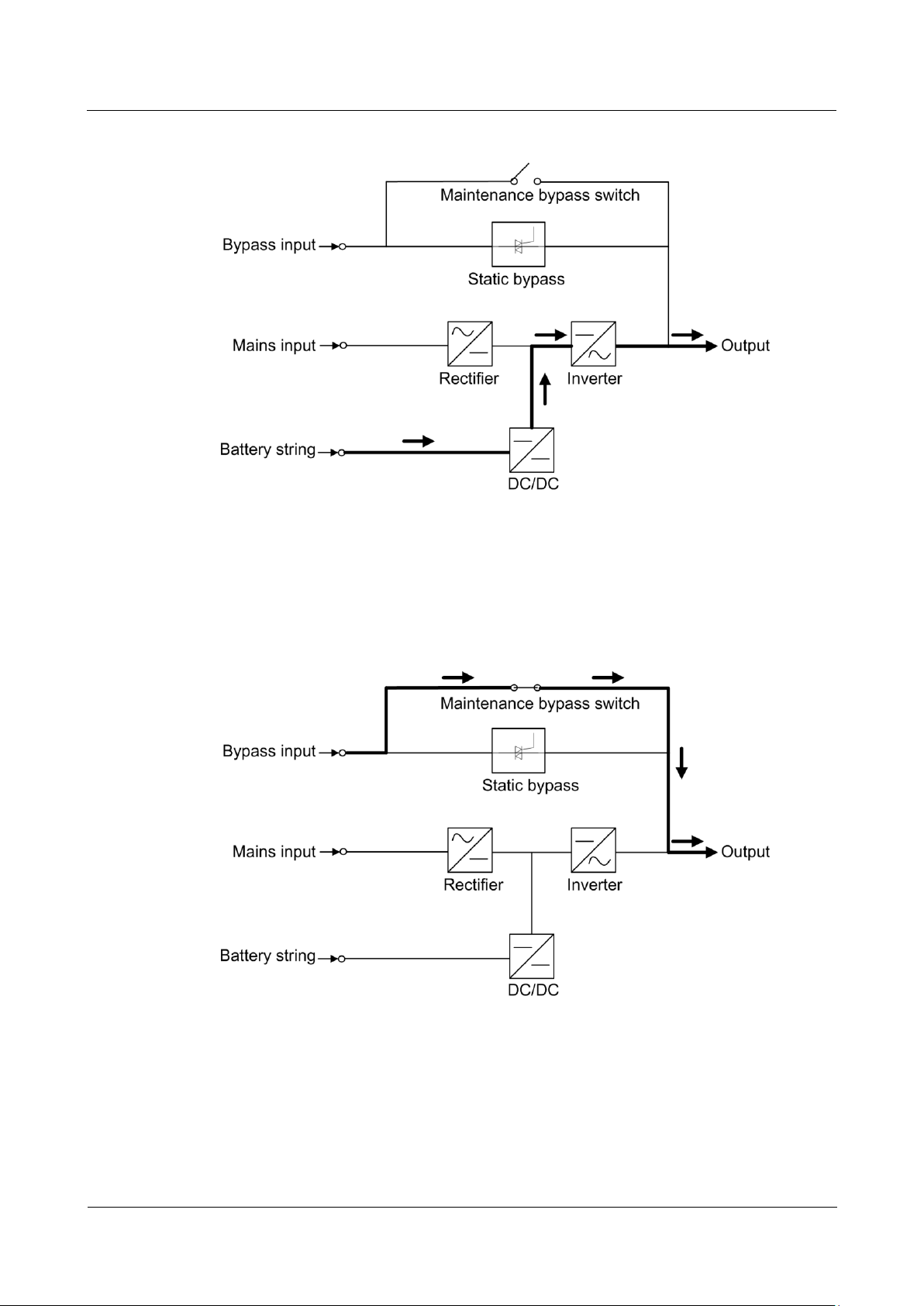
2.2.2.4 Maintenance Bypass Mode
The current flows through the maintenance bypass, instead of the power unit or bypass unit.
UPS maintenance can be performed in this mode.
Figure 2-7 UPS conceptual diagram in maintenance bypass mode
2.2.2.5 ECO Mode
The economy control operation (ECO) mode is an energy-saving mode, which you can
configure on the liquid crystal display (LCD) or web user interface (WebUI). In ECO mode,
when the bypass input voltage is within the ECO voltage range, the bypass combined switch
turns on, and the bypass supplies power. When the bypass input voltage is beyond the ECO
Page 27
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
voltage range, the UPS transfers from bypass mode to normal mode. In bypass mode or
normal mode, the rectifier keeps working and charges batteries using a charger. The ECO
mode delivers a higher efficiency. Figure 2-8 shows a conceptual diagram of the UPS working
in ECO mode.
Figure 2-8 UPS conceptual diagram in ECO mode
Page 28
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19
2.3 Product Introduction
(1) Monitor display unit (MDU)
(2) Rack
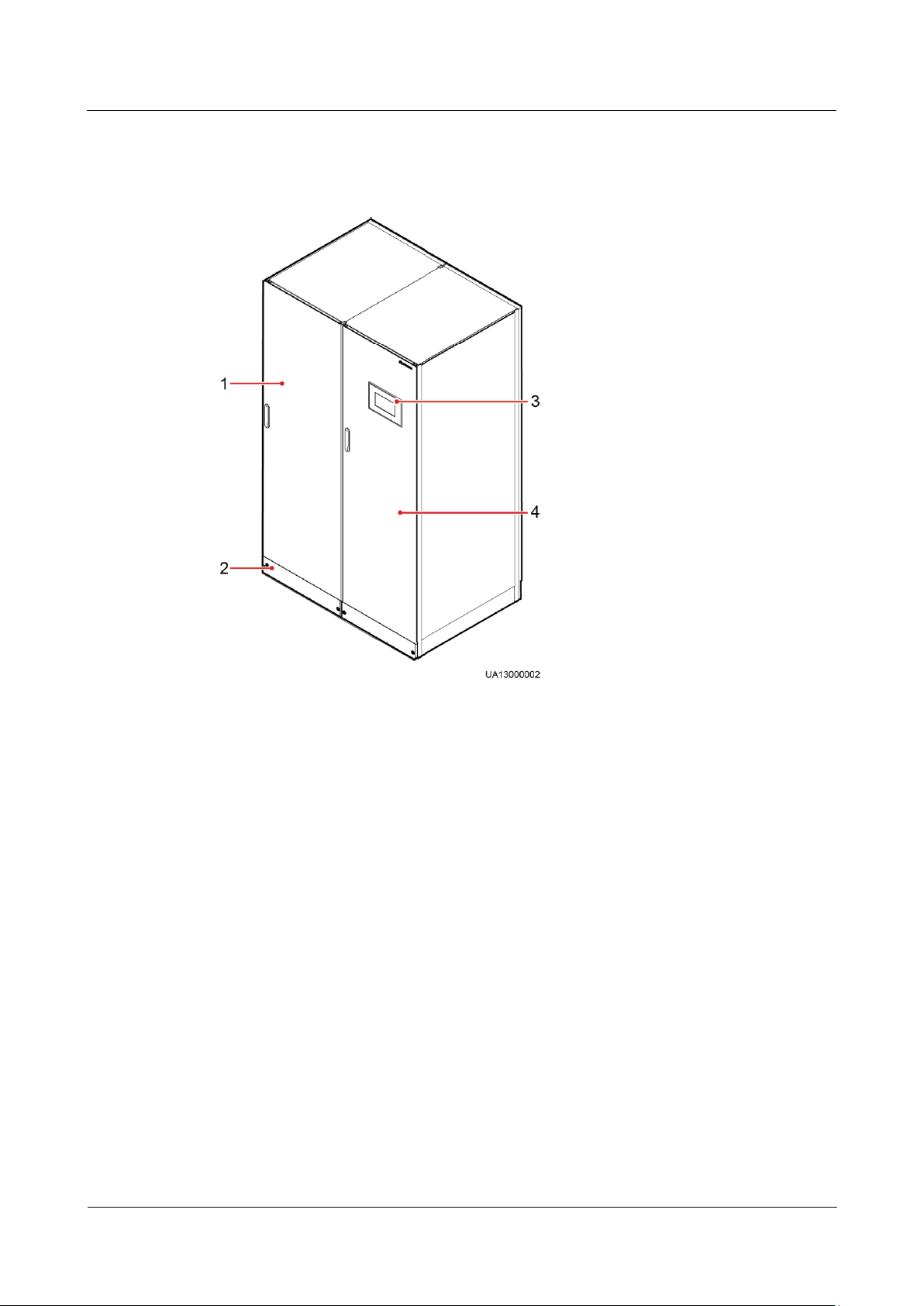
2.3.1 Product Appearance (200K, 300K)
Figure 2-9 UPS appearance (200K, 300K)
Page 29
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
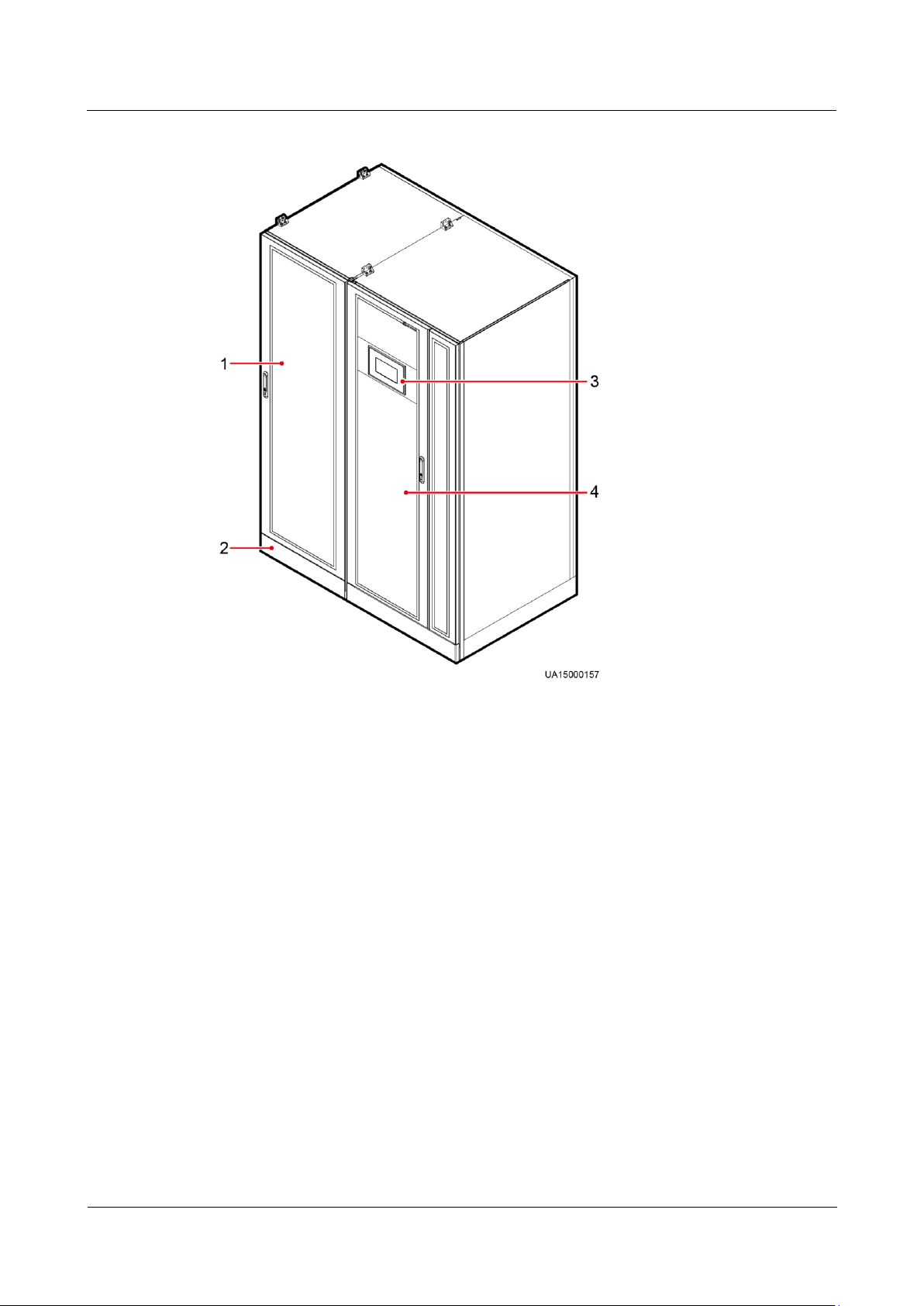
2.3.2 Product Appearance (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
(1) Power cabinet
(2) Anchor baffle plates
(3) MDU
(4) Bypass cabinet
Figure 2-10 UPS appearance (300K-FT, 400K, 500K)
Page 30
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
Figure 2-11 UPS appearance (600K)
(1) Power cabinet
(2) Anchor baffle plates
(3) MDU
(4) Bypass cabinet
Page 31

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
22
Figure 2-12 UPS appearance (800K)
(1) Power cabinet 1
(2) Power cabinet 2
(3) Anchor baffle plates
(4) MDU
(5) Bypass cabinet 2
(6) Bypass cabinet 1
Page 32

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
23
2.3.3 Product Structure (200K, 300K)
(1) Power units
(2) Bypass unit
(3) Control unit
(4) Power distribution subrack cover
(5) Maintenance bypass switch
(6) MDU
(7) Folder
(1) Power units
(2) Bypass unit
(3) Control unit
Figure 2-13 UPS5000-A-200K-ST structure
Figure 2-14 UPS5000-A-200K-FT structure
Page 33

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
24
(4) Power distribution subrack
cover
(5) Maintenance bypass
switch
(6) MDU
(7) Folder
(8) Bypass input switch
(9) Mains input
switch
(10) Output switch
(1) Cover
(2) Mains input
switch
(3) Bypass input
switch
(4) Maintenance bypass
switch
(5) Output switch
(6) Control unit
(7) Bypass unit
(8) Power units
(9) Monitor display
unit
(10) Folder
Figure 2-15 UPS5000-A-200K-FT (isolation protection) structure
Page 34

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
25
Figure 2-16 UPS5000-A-300K-STT structure
(1) Power units
(2) Bypass unit
(3) Control unit
(4) Power distribution subrack cover
(5) Maintenance bypass switch
(6) MDU
(1) Power units
(2) Bypass unit
(3) Control unit
(4) Power distribution subrack cover
(5) Maintenance bypass switch
(6) MDU
(7) Folder
Figure 2-17 UPS5000-A-300KTTL structure
Page 35

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
26
(1) Cover
(2) Maintenance bypass switch
(3) Control unit
(4) Bypass unit
(5) Power units
(6) Monitor display unit
Figure 2-18 UPS5000-A-300K-STT (isolation protection) structure
2.3.4 Product Structure (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
The following figures show a UPS with its front door open.
Page 36

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
27
Figure 2-19 UPS5000-A-300K-FT structure
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Mains input switch
(4) Output switch
(5) Power distribution unit
cover
(6) Maintenance bypass
switch
(7) Bypass input
switch
(8) Bypass unit
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Power distribution unit cover
(4) Maintenance bypass switch
(5) Bypass unit
Figure 2-20 UPS5000-A-400K-SC structure
Page 37

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
28
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Mains input switch
(4) Output switch
(5) Power distribution unit
cover
(6) Maintenance bypass
switch
(7) Bypass input
switch
(8) Bypass unit
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Power distribution unit cover
Figure 2-21 UPS5000-A-400K-FC structure
Figure 2-22 UPS5000-A-500K-SC structure
Page 38

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
29
(4) Maintenance bypass switch
(5) Bypass unit
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Mains input switch
(4) Output switch
(5) Power distribution unit
cover
(6) Maintenance bypass
switch
(7) Bypass input
switch
(8) Bypass unit
Figure 2-23 UPS5000-A-500K-FC structure
Page 39

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
30
Figure 2-24 UPS5000-A-600K-F600-SC structure
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Power distribution unit cover
(4) Maintenance bypass switch
(5) Bypass unit
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Mains input switch
(4) Output switch
(5) Power distribution unit
cover
(6) Maintenance bypass
switch
(7) Bypass input
switch
(8) Bypass unit
Figure 2-25 UPS5000-A-600K-F600-FC structure
Page 40

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
31
Figure 2-26 UPS5000-A-800K-F800-SC structure
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Maintenance bypass switch
(4) Power distribution unit cover
(5) Bypass unit
(1) Power units
(2) Control unit
(3) Maintenance bypass
switch
(4) Power distribution unit
cover
(5) Bypass unit
(6) Mains input switch
(7) Output switch
(8) Bypass input
switch
Figure 2-27 UPS5000-A-800K-F800-FC structure
Page 41

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
32
2.4 Control Unit
(1) Ground terminal
(2) Parallel port 1
(3) BSC port 1
(4) ECM 1 ready
switch
(5) Indicators for ECM 1
(6) Parallel port 2
(7) BSC port 2
(8) ECM 2 ready switch
(9) Indicators for ECM 2
(10) Dry contact card
(11) Dry contacts
(12) MDU port
(13) RS485 port
(14) Fast Ethernet (FE) port
(15) COM2 port
(16) COM1 port
(17) Battery temperature sensor
port
(18) Optional card subrack
cover
2.4.1 Overview
In a standard configuration, the control unit consists of two energy control modules (ECMs),
one dry contact card, and one monitoring interface card. The four cards are hot swappable.
One subrack is reserved above the dry contact card. A backfeed protection card or dry contact
extended card can be inserted into this subrack.
Figure 2-28 Signal panel on the control unit
2.4.2 ECM
The control unit consists of two ECMs in active/standby mode. Each ECM provides one bus
synchronization controller (BSC) port and one parallel port, as shown in Figure 2-29.
Figure 2-29 ECM
Page 42

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
33
Table 2-4 Ports on the ECM
Silk Screen
Description
PARALLEL
The PARALLEL port transmits parallel signals.
BSC
This port is used in a dual-bus system to balance output frequencies and
phases between UPS systems, ensuring that two buses can switch with
each other.
BSC cables are hot-swappable.
Indicator
Color
Status
Description
NORMAL
Green
Steady on
This ECM is the active ECM.
Blinking at 0.5
Hz
This ECM is the standby ECM and it is
ready.
Off
This ECM is not ready or the CPLD of
this ECM is being upgraded.
Blinking at 4 Hz
The DSP of the ECM is being upgraded or
not configured.
ALM
Yellow
Steady on
The ECM has a minor alarm, but it does
not need to be replaced.
Off
The ECM has no minor alarm or the DSP
of the ECM is being upgraded.
FAULT
Red
Steady on
The ECM has a critical alarm.
Off
The ECM has no critical alarm or the DSP
of the ECM is being upgraded.
For a single UPS, the parallel cable is not needed.
Table 2-5 Indicator description
2.4.3 Dry contact card
Appearance
Figure 2-30 Dry contact card
Page 43

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
34
Table 2-6 Ports on the dry contact card
Silk
Screen
Description
Status
Initial Status
BTG
Port for detecting battery
grounding faults
Connected: battery
grounding fault
Disconnected: no
battery grounding
fault
Disconnected
0V
Port for signal ground
GEN
Port for detecting diesel
generator (D.G.) mode
Connected: D.G.
mode
Disconnected:
non-D.G. mode
Disconnected
0V
Port for signal ground
BCB_OL
Port for detecting the BCB
box
Grounded: BCB
box connected
Disconnected:
BCB box not
connected
Grounded
BCB_STA
Port for monitoring the
battery switch
Connected: battery
switch ON
Disconnected:
battery switch
OFF
Disconnected
BCB_DR
V
Controls battery circuit
breaker trip. When the
voltage is +12 V, the circuit
breaker trips.
0 V: battery
switch not tripped
12 V: battery
switch tripped
0 V
BCB_0V
Port for signal ground
EPO_NO
Emergency power-off
(EPO) port
If the normally open
(NO) port is
connected to the
EPO_12V port, EPO
is triggered.
Disconnected
EPO_12V
+12 V
EPO_NC
EPO port
If the normally closed
(NC) port is
disconnected from the
EPO_12V port, EPO
is triggered.
Connected
EPO_12V
+12 V
SWITCH
STATUS_
OUT
Port for monitoring the UPS
output circuit breaker
Connected: circuit
breaker ON
Disconnected:
circuit breaker
OFF
Connected
SWITCH
STATUS_
0V
Port for signal ground
Page 44

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
35
Silk
Screen
Description
Status
Initial Status
SWITCH
STATUS_
MT
Port for monitoring the
maintenance circuit breaker
Disconnected:
circuit breaker ON
Connected: circuit
breaker OFF
Disconnected
SWITCH
STATUS_
0V
Port for signal ground
SWITCH
STATUS_
BP
Port for monitoring the
bypass input circuit breaker
Connected: circuit
breaker ON
Disconnected:
circuit breaker
OFF
Connected
SWITCH
STATUS_
0V
Port for signal ground
SPD
Port for monitoring the
input AC surge protective
device (SPD)
Connected: SPD
enabled
Disconnected:
SPD disabled
Connected
0V
Port for signal ground
The dry contact interface card takes effect only after it is set on the monitoring system. Set the
unused dry contact signal to the unused status.
Set the EPO port to NO or NC as required.
When multiple UPSs are paralleled, all dry contact signals to be used need to connect to each UPS.
Single cables require dual-insulated twisted cables. If the length of a power cable is within 25–50 m,
its cross-sectional area must be 0.5 mm2 to 1.5 mm2.
Functions
The dry contact card allows the UPS to detect and manage the switch status of the battery
system (including the external battery switch) and implement remote emergency power-off
(EPO).
Specifications
Hot-swappable
0.5 U high
2.4.4 Monitoring interface card
Page 45

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
36
Port
Silk
Screen
Description
DO_1
NO
DO_1 is used to output alarms and indicates critical alarms by
default. It can be set to indicate minor alarms, bypass mode,
battery mode, or low battery voltage.
COM
DO_2
NO
DO_2 is used to output alarms and indicates minor alarms by
default. It can be set to indicate critical alarms, bypass mode,
battery mode, or low battery voltage.
COM
DO_3
NO
DO_3 is used to output alarms and indicates bypass mode by
default. It can be set to indicate critical alarms, minor alarms,
battery mode, or low battery voltage.
COM
DO_4
NO
DO_4 is used to output alarms and indicates battery mode by
default. It can be set to indicate critical alarms, minor alarms,
bypass mode, or low battery voltage.
COM
The FE port resembles the RS485 port. Therefore, follow the silk screen when you connect
communications cables. If you mistake the RS485 port as the FE port during cable
connection, the WebUI and MDU communication fails. If you mistake the FE port as the
RS485 port during cable connection, RS485 communication fails.
Dry contact signals take effect after you set them. Set unused dry contact signals to the
unused state on the WebUI or LCD.
In a parallel system, ensure that used dry contacts properly connect to each UPS.
The monitoring interface card provides external ports as well as monitoring and control
functions for the MDU. The ports include the ambient temperature and humidity sensor port,
FE port, battery temperature monitoring port, and network management port. The MDU
monitors the UPS, allows users to set parameters, delivers commands, reports information,
and displays the UPS key information and parameters on the LCD.
Figure 2-31 Monitoring interface card
DO_1 to DO_4 meet the maximum voltage and current requirements of 30 V DC/1 A or 60 V DC/0.5 A.
Table 2-7 Ports on the monitoring interface card
Page 46

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
37
Port
Silk
Screen
Description
DB26
MDU
Provides FE, RS485, Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C), and control
area network (CAN) signals.
Battery
temper
ature
sensor
port
B_TEMP
Connects to an indoor battery temperature sensor.
Southb
ound
port 1
COM1
Connects to an ambient temperature and humidity sensor over two
wires.
Southb
ound
port 2
COM2
Connects to a southbound device.
Networ
k port
FE
Connects to the network port on a PC.
Northb
ound
commu
nications
port
RS485
Connects to a northbound network management device or
third-party network management device over two wires.
Signal cables must be double-insulated twisted cables. If the cable length is 25–50 m, the
cross-sectional area must be 0.5–1.5 mm2.
RS485 cables and FE cables must be shielded cables.
Figure 2-32 and Figure 2-33 are recommended wiring methods for DO ports.
Figure 2-32 Wiring method 1
Page 47

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
38
Figure 2-33 Wiring method 2
Pin
Description
1
GND
2
N/A
3
RS485-
4
RS485+
5
N/A
6
12V_PORT
Figure 2-34 and Table 2-8 describe the COM1 pin definitions.
Figure 2-34 COM1 pins
Table 2-8 COM1 pin definition
Figure 2-35 and Table 2-9 describe the COM2 pin definitions.
Page 48

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
39
Figure 2-35 COM2 pins
Pin
Description
1
RS485+
2
RS485-
3
N/A
4
RS485+
5
RS485-
6
GND
7
CANH0
8
CANL0
Table 2-9 COM2 pin definition
Figure 2-36 and Table 2-10 describe the RS485 pin definitions.
Figure 2-36 RS485 pins
Page 49

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
40
Table 2-10 RS485 pin definition
Pin
Description
1
RS485_T+
2
RS485_T–
3
N/A
4
RS485_R+
5
RS485_R–
6
GND
7
N/A
8
N/A
(1) Status indicator
(2) LCD touchscreen
If cables are prepared onsite, follow the three methods below:
Connect pin 1 and pin 2. Pin 1 connects to RS485+ and pin 2 connects to RS485–.
Connect pin 4 and pin 5. Pin 4 connects to RS485+ and pin 5 connects to RS485–.
Connect pins 1, 2, 4, and 5. Twist cables to pin 1 and pin 4 into one cable and then connect it to
RS485+. Twist cables to pin 2 and pin 5 into one cable and then connect it to RS485–.
2.5 MDU
Appearance
Figure 2-37 MDU
Page 50

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
41
Status
Color
Meaning
On
Red
A critical alarm has been
generated, and the buzzer
sounds continuously.
Yellow
A minor alarm has been
generated, and the buzzer
buzzes at 2 Hz.
Green
The UPS is running properly
or a warning has been
generated.
Off
N/A
The MDU is powered off.
Touch the LCD screen firmly because it is an industrial resistive touchscreen. It is recommended that
you use your fingernails for accurate selection and quick response.
Figure 2-38 Touching the LCD
Table 2-11 Status indicator
The indicator on the LCD panel is yellow when the bypass supplies power in non-ECO mode.
The ports of the LCD screen are located at the side of the LCD screen.
Page 51

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
42
Figure 2-39 LCD screen ports
No.
Port Name
Description
1
MUS05A (DB26)
Connects to the MDU and
monitoring interface card
2
FE
Network port for connecting to the
web service and for SNMP
networking
3
CAN
Reserved
4
RS485_1
Reserved
5
USB Host
After installing the WiFi
module, connect the WiFi
module to the UPS using the app
on the mobile phone to obtain
the initial startup password.
Insert the USB flash drive,
import and export the
configuration file, export run
logs, and upgrade software.
6
RST
Restart switch for the MDU
7
SD
Reserved
8
DIP switch
Implements specific functions by
using the DIP switch and specific
buttons; controls the CAN
communication build-out resistor in
a parallel system
Table 2-12 Description of LCD screen ports
Page 52

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
43
Functions
Configuration
Application Scenario
Single UPS
Supplies power to common loads.
Parallel system
Supplies power to important loads in small- and medium-sized data
centers. It features high availability and strong transient overload
capability.
Dual-bus system
The dual-bus system is suitable for scenarios where high availability
requirements are posed for power supply. The dual-bus system
supplies power to important loads in large- and medium-sized
equipment rooms and data centers.
In addition to common parallel system advantages, the dual-bus
system also provides outstanding availability and eliminates
bottleneck failures. However, configuration of the dual-bus system is
complex.
The monitor display unit (MDU) allows for general UPS operations, parameter setting,
viewing of running status and alarms, and so on.
Specifications
Dimensions (H x W x D): 175 mm x 264 mm x 40 mm
2.6 Typical configurations
Table 2-13 Typical UPS configurations
A 1+1 parallel system is a typical configuration. You can set the number of requisite UPSs and
redundant ones on the LCD or WebUI.
2.6.1 Single UPS
The UPS5000-A is a high frequency tower-mounted UPS. It uses a unit-level design to handle
power functionality, and provides an embedded maintenance bypass switch to ensure
maintenance with power on. Figure 2-3 shows the conceptual diagram of a single UPS.
2.6.2 Parallel System
In a parallel system, the mains input, bypass input, and AC output terminals between cabinets
are connected in parallel. Energy control modules (ECMs) on each UPS are connected over
parallel cables. The parallel connections synchronize the UPS outputs to supply power to
loads. If one UPS fails, the other UPSs continue supplying power to loads.
Page 53

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
44
Figure 2-40 Conceptual diagram of an N+X parallel system
2.6.3 Dual-Bus System
A dual-bus system consists of two independent UPS systems. Each of these UPS systems in
turn consists of one or more UPSs connected in parallel. Of the two UPS systems, one is a
master system, and the other is a slave system. This design makes the dual-bus system highly
reliable and suitable for loads with multiple input terminals. An optional static transfer switch
(STS) can be installed to start the bus synchronization controller (BSC). The UPS systems
work in normal mode or bypass mode.
Page 54

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
45
Figure 2-41 Conceptual diagram of a dual-bus system
Optional
Component
Model
Function
Reference Document
BCB box
PDC-0250DC
0384BXA
PDC-0400DC
0384BXA
PDC-0630DC
0384BXA
PDU8000-012
5DCV8-BXA
001
PDU8000-025
0DCV8-BXA
001
PDU8000-040
0DCV8-BXA
001
PDU8000-063
0DCV8-BXA
001
PDU8000-080
0DCV8-BXA
001
Controls the connection
between battery strings
and the UPS, and
supports overload
protection, short-circuit
protection, and remote
trip control.
PDU8000-(0125, 0250,
0400, 0630, 0800)
DCV8-BXA001 BCB
Box User Manual
PDC-(0250,0400,0630)
DC0384BXA BCB Box
User Manual
2.7 Optional Components (200K, 300K)
Page 55

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
46
Optional
Component
Model
Function
Reference Document
BBB box
PDU8000-063
0DCV8-BGA
001
PDU8000-125
0DCV8-BGA
001
PDU8000-200
0DCV8-BGA
001
Converges the current of
multiple battery strings.
PDU8000-(0630, 1250,
2000) DCV8-BGA001
BBB Box User Manual
Surge
protection box
N/A
Improves the UPS surge
protection capability.
UPS Surge Protection
Box Quick Installation
Guide (02311DJH)
Surge
protection box
subrack
N/A
Install this subrack when
the surge protection box
is used. The position for
installing the surge
protection box subrack
and ECM expansion
subrack is the same, and
therefore the two types
of subracks cannot be
used simultaneously.
N/A
ECM
expansion
subrack
N/A
Install this subrack when
the UPS is equipped
with a backfeed
protection card and dry
contact expansion card.
The position for
installing the surge
protection box subrack
and ECM expansion
subrack is the same, and
therefore the two types
of subracks cannot be
used simultaneously.
N/A
Antiseismic kit
N/A
Reinforces the cabinet
so that the cabinet can
resist magnitude 9
earthquakes.
N/A
IP21
component
N/A
Prevents water from
dropping into the
cabinet, protecting the
cabinet to IP21.
N/A
Dry contact
expansion card
N/A
Provides monitoring
expansion ports: five
relay output ports and
five input ports.
UPS5000 Dry Contact
Extended Card User
Manual (03021RKN)
Page 56

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
47
Optional
Component
Model
Function
Reference Document
Backfeed
protection card
N/A
Provides mains and
bypass backfeed
detection and protection.
UPS5000 Backfeed
Protection Card User
Manual (03021KQQ)
Battery
grounding
failure detector
N/A
Detects current leakage
and generates alarms.
When equipped with a
remote trip switch, the
detector protects devices
and prevents fire
disasters. Detects battery
grounding failures and
sends alarm signals
when the ground leakage
current exceeds the
specified value.
UPS Battery Grounding
Failure Detector User
Manual
Ambient
temperature
and humidity
sensor
N/A
The ambient
temperature and
humidity sampling
board is applicable to
batteries.
UPS Ambient
Temperature and
Humidity Sensor User
Manual
iBAT
N/A
Collects battery
information. It collects
battery status data from
the downstream BIM
groups through wireless
communication, and
sends the data to the
ECC and the third-party
NMS through COM or
PoE ports.
iBAT 2.0-CIM01C2
Quick Guide
Parallel cable
5 m/10 m/15 m
Connects UPSs in
parallel.
N/A
BSC cable
5 m/10 m/15
m/60 m
Transmits bus
synchronization signals
in a dual-bus system.
N/A
Top air-flow
cabinet
N/A
Used to ensure heat
dissipation.
UPS5000-(200 kVA-800
kVA) Top Air-flow
Cabinet User Manual
Cable entry
cabinet
N/A
If a cable entry cabinet
is installed, cables can
be routed from the
bottom of cabinets.
N/A
Page 57

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
48
Optional
Component
Model
Function
Reference
Document
BCB box
300K-F
T,
400K,
500K,
600K
PDU800
0-0400D
CV8-BX
A001
PDU800
0-0630D
CV8-BX
A001
PDU800
0-0800D
CV8-BX
A001
Controls the
connection between
battery strings and the
UPS, and supports
overload protection,
short-circuit
protection, and
remote trip control.
PDU8000-(0125,
0250, 0400, 0630,
0800) DCV8-BXA001
BCB Box User
Manual
800K
PDU800
0-0630D
CV8-BX
A001
PDU800
0-0800D
CV8-BX
A001
BBB box
300K-F
T,
400K,
500K,
600K
PDU800
0-1250D
CV8-BG
A001
PDU800
0-2000D
CV8-BG
A001
Converges the current
of multiple battery
strings.
PDU8000-(0630,
1250, 2000)
DCV8-BGA001 BBB
Box User Manual
800K
PDU8000-2
000DCV8-B
GA001
The ECM expansion subrack does not support onsite installation. If you require this optional
component, inform Huawei when you purchase the UPS so that Huawei can install the subrack
before delivery.
IP21 components cannot be configured for the UPS5000-A-300K-STT or UPS5000-A-200K-FT.
IP21 components cannot be configured for the UPS5000-A-200K-ST when cables are routed from
the top of the cabinet. Only the UPS5000-A-200K-FT can be configured with a cable entry cabinet.
2.8 Optional Components (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
Page 58

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
49
Optional
Component
Model
Function
Reference
Document
Top air-flow
cabinet
N/A
Used to ensure heat
dissipation.
UPS5000-(200
kVA-800 kVA) Top
Air-flow Cabinet User
Manual
iBAT
N/A
Collects battery
information. It
collects battery status
data from the
downstream BIM
groups through
wireless
communication, and
sends the data to the
ECC and the
third-party NMS
through COM or PoE
ports.
iBAT 2.0-CIM01C2
Quick Guide
Air filter
N/A
Prevents the UPS
from dust and ensure
normal operations.
N/A
IP21
component
N/A
Prevents water from
dropping into the
cabinet, protecting the
cabinet to IP21.
N/A
ECM
expansion
subrack
N/A
Install this subrack
when the UPS is
equipped with a
backfeed protection
card and dry contact
expansion card. The
position for installing
the surge protection
box subrack and
ECM expansion
subrack is the same,
and therefore the two
types of subracks
cannot be used
simultaneously.
N/A
Dry contact
expansion card
N/A
Provides monitoring
expansion ports: five
relay output ports and
five input ports.
UPS5000 Dry
Contact Extended
Card User Manual
(03021RKN)
Backfeed
protection card
N/A
Provides mains and
bypass backfeed
detection and
protection.
UPS5000 Backfeed
Protection Card User
Manual (03021KQQ)
Page 59

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
50
Optional
Component
Model
Function
Reference
Document
Battery
grounding
failure detector
N/A
Detects current
leakage and generates
alarms. When
equipped with a
remote trip switch,
the detector protects
devices and prevents
fire disasters. Detects
battery grounding
failures and sends
alarm signals when
the ground leakage
current exceeds the
specified value.
UPS Battery
Grounding Failure
Detector User
Manual
Parallel cable
10 m/15 m
Connects UPSs in
parallel.
N/A
BSC cable
15 m/60 m
Transmits bus
synchronization
signals in a dual-bus
system.
N/A
If an IP21 component is installed, cables cannot be routed from the top of the cabinet.
The ECM expansion subrack does not support onsite installation. If this component is required,
inform Huawei before purchasing the UPS to receive pre-installation services.
Page 60

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
51
3.1 Installation Preparations
Model
Weight
Dimensions (H x W x D)
UPS5000-A-200K-S
T
340 kg
2000 mm x 600 mm x 850 mm
UPS5000-A-200K-F
T
370 kg
UPS5000-A-200K-F
T (isolation
protection)
380 kg
UPS5000-A-300K-S
TT
460 kg
UPS5000-A-300K-S
TT (isolation
protection)
470 kg
UPS5000-A-300KTT
L
450 kg
3.1.1 Site
3.1.1.1 UPS Weight and Dimensions (200K, 300K)
Ensure that the floor or installation support can bear the weight of the UPS, batteries, and
battery racks. The weight of batteries and battery racks varies depending on the site
requirements.
3 Installation
Table 3-1 UPS weight
Page 61

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
52
Figure 3-1 Dimensions (200K, 300K, unit: mm)
Model
Weight
Dimensions (H x W x D)
UPS5000A-300K-F
T
650 kg
2000 mm x 1200 mm x 850
mm
UPS5000A-400K-S
C
680 kg
3.1.1.2 UPS Weight and Dimensions (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
Ensure that the floor or installation support can bear the weight of the UPS, batteries, and
battery racks. The weight of batteries and battery racks depends on the site requirements.
Table 3-2 UPS weight
Page 62

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
53
Model
Weight
Dimensions (H x W x D)
UPS5000A-400K-F
C
UPS5000A-400K-F
T
710 kg
UPS5000A-500K-S
C
810 kg
UPS5000A-500K-F
C
UPS5000A-500K-F
T
850 kg
UPS5000A-600K-F
600-SC
1060 kg
2000 mm x 1400 mm x 850
mm
UPS5000A-600K-F
600-FC
1100 kg
UPS5000A-800K-F
800-SC
1530 kg
2000 mm x 2400 mm x 850
mm
UPS5000A-800K-F
800-FC
1610 kg
Page 63

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
54
Figure 3-2 Dimensions (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, unit: mm)
Page 64

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
55
Figure 3-3 Dimensions (600K, unit: mm)
Page 65

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
56
Figure 3-4 Dimensions (800K, unit: mm)
3.1.1.3 Installation Environment
Do not install the UPS in high temperature, low temperature, or damp environments.
Install the UPS away from water sources, heat sources, and flammable or explosive
materials. Keep the UPS away from direct sunlight, dust, volatile gases, corrosive
materials, and air dense with salt particles.
Do not install the UPS in environments with conductive metal scraps in the air.
The optimal operating temperatures for valve-regulated lead-acid batteries (VRLA
batteries) are 20–30°C. Operating temperatures higher than 30°C shorten the battery
lifespan and operating temperatures lower than 20°C reduce the battery backup time.
3.1.1.4 Installation Clearances
Reserve sufficient clearances around the cabinet to facilitate operations and ventilation:
Reserve a clearance of at least 800 mm from the front of the cabinet.
Reserve a clearance of at least 500 mm from the top of the cabinet.
If a top air-flow cabinet is deployed, the UPS can be installed against a wall and no space
needs to be reserved at the rear (except the 800 kVA UPS). If no top air-flow cabinet is
Page 66

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
57
deployed, at least 500 mm space should be reserved at the rear for ventilation. If the UPS
Tools and Meters
Electric pallet truck
Manual pallet truck
Ladder
Rubber mallet
will be operated from the rear, at least 800 mm space should be reserved for operations.
Figure 3-5 shows the clearances reserved for a 400 kVA cabinet.
Figure 3-5 Reserved clearances (unit: mm)
3.1.2 Tools and Instruments
Insulate installation tools to prevent electric shocks.
Prepare the following tools and meters indicated in Table 3-3 for installation.
Table 3-3 Tools and meters
Page 67

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
58
Tools and Meters
Hammer drill and
drill bit Φ16
Hand-held electric
drill
Alloy hole saw
Heat gun
Diagonal pliers
Crimping tools
Wire stripper
Electric hydraulic
pliers
Clamp meter
Multimeter
Cable tie
Level instrument
Polyvinyl chloride
(PVC) insulation
tape
Cotton cloth
Label
Electrician's knife
Electrostatic
discharge (ESD)
gloves
Protective gloves
Insulated gloves
Insulation protective
shoes
Torque screwdriver
Cable cutter
Brush
Flat-head
screwdriver
(2–5 mm)
Page 68

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
59
Tools and Meters
Phillips screwdriver
(M3/M4/M5/M6/M
8)
Insulated torque
wrench
(M6/M8/M12/M16)
Heat shrink tubing
Insulated adjustable
wrench
Item
200K
300K
Mains
input
Mains input current (A)
355
533
Recommended
cross-sectional area
(mm2)
L1
2 x (4 x 95)
2 x (4 x 150)
L2
L3 N PE
95
150
Bypass
input
Bypass input current (A)
304
456
Recommended
cross-sectional area
L1
2 x (4 x 95)
2 x (4 x 150)
L2
Table 3-3 lists only the common tools for installation and cable connection. For more dedicated tools
required, see the corresponding component manuals. Prepare tools based on site requirements.
3.1.3 Preparing Power Cables (200K, 300K)
The UPS can generate large leakage currents. A circuit breaker equipped with an RCD is
not recommended.
If multiple UPSs are connected in parallel, input and output power cables for each UPS
should have the same length and specifications.
The currents listed in the following table are measured at the rated voltage of 380 V.
Table 3-4 Recommended cross-sectional areas for power cables
Page 69

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
60
Item
200K
300K
(mm2)
L3 N PE
95
150
Output
Output current (A)
304
456
Recommended
cross-sectional area
(mm2)
U
2 x (4 x 95)
2 x (4 x 150)
V
W N PE
95
150
Battery
input
Nominal battery discharge current (A)
439
658
Maximum battery discharge current (A)
525
788
Recommended
cross-sectional area
(mm2)
+
2 x (3 x 120)
2 x (3 x 185)
N - PE
120
185
When selecting, connecting, and routing power cables, follow local safety laws and
regulations.
If the cable layout, ambient temperature, or other conditions are different from those
described in this document, perform verification in accordance with the IEC-60364-5-52
or the local regulations.
If the rated voltage is 400 V, multiply the currents by 0.95. If the rated voltage is 415 V,
multiply the currents by 0.92.
When the primary loads are non-linear loads, increase the cross-sectional areas of the
neutral wires by 1.5–1.7 times.
The nominal battery discharge current refers to the current of forty 12 V batteries at 480
V in standard configuration.
The maximum battery discharge current refers to the current when forty 12 V batteries in
standard configuration, that is, two hundred and forty 2 V battery cells (1.67 V/cell), stop
discharging.
The battery cable specifications are selected based on 40 batteries by default and
compatible with application scenarios with 30–44 batteries.
When the mains input and bypass input share a power source, configure mains input
power cables as input power cables. The recommended cables are used only when the
following requirements are met:
− 200 kVA: The cables are installed along the wall or on the floor (IEC-60364-5-52 C
standards). 300 kVA: The cables are routed over a ladder or bracket in a single layer
(IEC60364-5-52 F standards).
Page 70

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
61
− The ambient temperature is 30°C.
Port
Descript
ion
Connection
Method
Bolt
Specificat
ions
Bolt Hole
Diameter
Bolt Length
Torque
Mains
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
30 mm
26 N·m
Bypass
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
30 mm
26 N·m
Battery
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
45 mm
46 N·m
Output
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
30 mm
26 N·m
PE
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
30 mm
26 N·m
Port
Descript
ion
Connection
Method
Bolt
Specificat
ions
Bolt Hole
Diameter
Bolt Length
Torque
Mains
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
40 mm
26 N·m
Bypass
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
40 mm
26 N·m
Battery
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
60 mm
46 N·m
Output
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
40 mm
26 N·m
PE
Crimped OT
terminal
M10
10.5 mm
30 mm
26 N·m
− The AC voltage loss is less than 3%, and the DC voltage loss is less than 1%.
− 200 kVA: single- or multi-core 90°C flexible power cable with a copper conductor;
300 kVA: single-core 90°C flexible power cable with a copper conductor.
− Recommended cable lengths: for a 200 kVA UPS, AC power cable ≤ 30 m, DC
power cable ≤ 40 m; for a 300 kVA UPS, AC power cable ≤ 30 m, DC power cable
≤ 50 m.
Table 3-5 Power cable terminal requirements for the UPS5000-A-200K-ST
Table 3-6 Power cable terminal requirements for the UPS5000-A-200K-FT
Page 71

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
62
Table 3-7 Power cable terminal requirements for the UPS5000-A-300KTTL and
Port
Descript
ion
Recommende
d Connection
Method
Bolt
Specificat
ions
Bolt Hole
Diameter
Bolt Length
Torque
Mains
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
45 mm
46 N·m
Bypass
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
45 mm
46 N·m
Battery
input
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
45 mm
46 N·m
Output
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
45 mm
46 N·m
PE
Crimped OT
terminal
M12
13.5 mm
30 mm
46 N·m
UPS Capacity
Circuit Breaker Name
Specificationsa
200K
Mains input circuit breaker
400 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
400 A/3P
Downstream output circuit breaker
400 A/3P
300K
Mains input circuit breaker
630 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
630 A/3P
Downstream output circuit breaker
630 A/3P
a: Recommended specifications when the short-circuit current going through the circuit
breaker is less than 36 kA.
UPS5000-A-300K-STT
Table 3-8 Recommended upstream input and downstream output circuit breakers
If multiple loads are connected, specifications for branch circuit breakers must not exceed the
recommended specifications.
The circuit breaker selection principle is to protect loads and cables, and the cascading principle is to
achieve specific protection.
3.1.4 Preparing Power Cables (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
Page 72

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
63
Item
300K-FT
400K
500K
600K
800K
Main
s
input
Input current (A)
533
711
889
1066
1422
Recomme
nded
cross-secti
onal area
(mm2)
L1
2 x (4 x 150)
2 x (4 x 240)
3 x (4 x 185)
4 x (4 x 185)
4 x (4 x 240)
L2
L3 N PE
150
240
240
240
240
Bypa
ss
input
Input current (A)
456
608
760
912
1215
Recomme
nded
cross-secti
onal area
(mm2)
L1
2 x (4 x 150)
2 x (4 x 240)
3 x (4 x 185)
4 x (4 x 185)
4 x (4 x 240)
L2
L3 N PE
150
240
240
240
240
Outp
ut
Output current (A)
456
608
760
912
1215
Recomme
nded
cross-secti
onal area
(mm2)
U
2 x (4 x 150)
2 x (4 x 240)
3 x (4 x 185)
4 x (4 x 185)
4 x (4 x 240)
V W N
PE
150
240
240
240
240
Batte
ry
input
Nominal battery
discharge current
(A)
658
877
1096
1316
1754
Maximum battery
discharge current
(A)
788
1051
1313
1576
2101
Recomme
nded
cross-secti
+
2 x (3 x 185)
2 x (3 x 240)
3 x (3 x 185)
3 x (3 x 240)
4 x (3 x 240)
N
The UPS can generate large leakage currents. A circuit breaker equipped with an RCD is
not recommended.
If multiple UPSs are connected in parallel, input and output power cables for each UPS
should have the same length and specifications.
The currents listed in the following table are measured at the rated voltage of 380 V.
Table 3-9 Recommended cross-sectional areas for power cables
Page 73

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
64
Item
300K-FT
400K
500K
600K
800K
onal area
(mm2)
-
PE
185
240
240
240
240
Port
Descript
ion
Connection
Method
Bolt
Specificat
ions
Bolt Hole
Diameter
Bolt Length
Torque
Mains
input
Crimped DT
terminal
M16
18 mm
50 mm
120 N·m
Bypass
input
Crimped DT
terminal
M16
18 mm
50 mm
120 N·m
When selecting, connecting, and routing power cables, follow local safety regulations
and rules.
When the external conditions change, for example, cable layout or ambient temperatures,
perform verification in accordance with the IEC-60364-5-52 or the local regulations.
If the rated voltage is 400 V, multiply the currents by 0.95; if the rated voltage is 415 V,
multiply the currents by 0.92.
When the primary loads are non-linear loads, increase the cross-sectional areas of the
neutral wires by 1.5–1.7 times.
The nominal battery discharge current refers to the current of forty 12 V batteries at 480
V in standard configuration.
The maximum battery discharge current refers to the current when forty 12 V batteries in
standard configuration, that is, two hundred and forty 2 V battery cells (1.67 V/cell), stop
discharging.
The battery cable specifications are selected based on 40 batteries by default and
compatible with application scenarios with 30–44 batteries.
When the mains input and bypass input share a power source, configure mains input
power cables as input power cables. The recommended cables are used only when the
following requirements are met:
− The cables are routed over a ladder or bracket in a single layer (IEC60364-5-52 E
standards).
− The ambient temperature is 30°C.
− The AC voltage loss is less than 3%, and the DC voltage loss is less than 1%.
− The 90°C flexible power cable with a copper conductor is used.
− Recommended cable lengths: AC power cable ≤ 30 m, DC power cable ≤ 50 m.
When you connect power cables, comply with the tightening torque listed in the following
table to ensure secure connections and prevent safety risks.
Table 3-10 Power cable terminal requirements
Page 74

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
65
Port
Descript
ion
Connection
Method
Bolt
Specificat
ions
Bolt Hole
Diameter
Bolt Length
Torque
Battery
input
Crimped DT
terminal
M16
18 mm
50 mm
120 N·m
Output
Crimped DT
terminal
M16
18 mm
50 mm
120 N·m
PE
Crimped DT
terminal
M12
/
35 mm
47 N·m
UPS Capacity
Circuit Breaker Name
Specificationsa
300K-FT
Mains input circuit breaker
630 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
630 A/3P
Downstream output circuit
breaker
630 A/3P
400K
Mains input circuit breaker
800 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
630 A/3P
Downstream output circuit
breaker
630 A/3P
500K
Mains input circuit breaker
1000 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
800 A/3P
Downstream output circuit
breaker
800 A/3P
600K
Mains input circuit breaker
1250 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
1000 A/3P
Downstream output circuit
breaker
1000 A/3P
800K
Mains input circuit breaker
1600 A/3P
Bypass input circuit breaker
1250 A/3P
Downstream output circuit
breaker
1250 A/3P
a: Recommended specifications when the short-circuit current going through the circuit
breaker is less than 50 kA.
Table 3-11 Recommended upstream input and downstream output circuit breakers
Page 75

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
66
If multiple loads are connected, specifications for branch circuit breakers must not exceed the
recommended specifications.
The circuit breaker selection principle is to protect loads and cables, and the cascading principle is to
achieve specific protection.
3.1.5 Unpacking (200K, 300K)
Context
To prevent the UPS from falling over, secure it to a pallet truck using ropes before moving
it.
Move the UPS with caution to avoid bumping or toppling, which may damage the UPS.
After placing the UPS in the installation position, unpack it with care to prevent scratches.
Keep the UPS steady during unpacking.
If the UPS installation environment is in poor condition and the UPS needs to be stored for
a long time after it is unpacked, take measures to prevent dust. It is recommended that the
UPS be wrapped with the original plastic coat.
Procedure
Step 1 Use a pallet truck to transport the UPS to the installation position.
Step 2 Remove the UPS outer packing.
Step 3 After confirming that the UPS is intact, remove the L-shaped bracket that secures the UPS
and the pallet, and secure the sliding plate to the pallet using the two M12 bolts that you have
removed.
Figure 3-6 Removing an L-shaped bracket and securing the sliding plate
Page 76
UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
67
The figure is for reference only. The actual structure and screw quantity prevail.
Step 4 Raise the four leveling feet to the highest position using an adjustable wrench.
Figure 3-7 Raising the leveling feet
Step 5 Move the UPS over its castors near the installation position.
----End
3.1.6 Unpacking (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
Context
Page 77

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
68
Procedure
Step 1 Use a pallet truck to transport the UPS to the installation position.
Step 2 Remove the UPS outer packing.
Step 3 Remove the bolts that secure the UPS to the pallet and remove the UPS from the pallet.
Only trained personnel are allowed to move the UPS. Use a pallet truck to transport the
UPS box secured to a wooden support to the installation position.
To prevent the UPS from falling over, secure it to an electric pallet truck using ropes
before moving it.
To prevent shocks or falls, move the UPS gently. After placing the UPS in the installation
position, unpack it with care to prevent scratches. Keep the UPS steady during unpacking.
If the UPS installation environment is in poor condition and the UPS will be stored for a
long time after it is unpacked, wrap the UPS with the original plastic coat to prevent dust.
Figure 3-8 Removing the pallet from the UPS
----End
3.1.7 (Optional) Splitting the Power Cabinet and Bypass Cabinet (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K)
Context
If the door of the power distribution equipment room is not wide enough to move the
UPS, you can split the power cabinet and bypass cabinet before the movement.
The splitting steps for the 300K-FT, 400K, 500K, and 600K UPS are similar. This
section describes how to split cabinets for the 400K UPS.
Page 78

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
69
Position
Screw Specifications
Quantity (PCS)
Soft copper bar
M12x35
26
Battery copper bar
component
M8x20
4
Top connecting kit
M6x30
8
Middle connecting kit
M6x30
8
Bottom connecting kit
M12x35
8
Position
Screw Specifications
Quantity (PCS)
Soft copper bar
M12x45 screw assembly
26
Battery copper bar
component
M6x30 screw assembly
4
Top connecting kit
M6x20 screw assembly
8
Middle connecting kit
M6x20 screw assembly
8
Bottom connecting kit
M12x35 screw assembly
8
Put away the removed screws and connecting kits and take photos to record removed
positions to facilitate later cabinet combination.
Table 3-12 Screw specifications and quantity (300K-FT, 400K, 500K)
Procedure
Step 1 Open the front door of the bypass cabinet and remove the covers of the power distribution
Table 3-13 Screw specifications and quantity (600K)
subrack.
The covers of the power distribution subrack can be removed from the bypass cabinet only when all
switches are OFF.
Page 79

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
70
Figure 3-9 Removing the covers of the power distribution subrack
Step 2 Remove the rear covers from the power cabinet and bypass cabinet.
Step 3 Record the cable connection positions, and remove the cable terminals that connect the
system signal interface board in the power cabinet to the bypass cabinet.
Figure 3-10 Silk screens on the system signal interface board in the power cabinet
Page 80

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
71
Table 3-14 Mapping between cables and ports on the system signal interface board
Bypass Cabinet
Cable Name
Label on the
Cable to be
Connected to the
System Signal
Interface Board
Port Silk Screen
on the System
Signal Interface
Board in the
Power Cabinet
Quantity (PCS)
Bypass unit DL37
cable
W301_J21
J21
1
W303_J24
J24
1
ECM 8-pin cable
W305_J22
J22
1
ECM system
monitoring bus
W307_J25
J25
1
CT cable
W309_J26
J26
1
Switch cable
SW1_J27
J27 1 SW2_J28
J28 1 SW4_J30
J30
1
Because the switch extension rod is sharp, exercise caution when removing the connecting
copper bars to prevent personal injury.
Each copper bar has a number on it. Put away the removed copper bars. When you combine
the power cabinet and bypass cabinet, strictly follow the numbers printed on the copper bars.
Step 4 Remove the soft copper bars numbered 43, 44, and 45.
Page 81

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
72
Figure 3-11 Removing soft copper bars numbered 43, 44, and 45
For a 500K or 600K UPS, remove the soft copper bars numbered 56, 58, and 60.
Step 5 Remove the battery copper bar component.
Page 82

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
73
Figure 3-12 Removing the battery copper bar component
Step 6 Remove the soft copper bars numbered 39–42.
Page 83

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
74
Figure 3-13 Removing soft copper bars numbered 39–42
For a 500K or 600K UPS, remove the soft copper bars numbered 48–54.
Step 7 Remove the top, middle, and bottom connecting kits in sequence from the power cabinet and
bypass cabinet.
Use a step ladder to remove the top connecting kits as the cabinet is high.
Page 84

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
75
Figure 3-14 Removing connecting kits
Step 8 Use a manual pallet truck to transport the power cabinet and bypass cabinet to the installation
position. Ensure that the two cabinets align with each other.
----End
3.1.8 (Optional) Combining the Power Cabinet and Bypass Cabinet (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K)
Procedure
Step 1 Reinstall the bottom, middle, and top connecting kits for the power cabinet and bypass cabinet
based on screw specifications, screw quantity, and recorded information.
Step 2 Reinstall the removed soft copper bars and battery copper bar components based on their
numbers, screw specifications, screw quantity, and recorded information.
Step 3 Reconnect the removed cables to the system signal interface board in the power cabinet, and
bind the cables based on the recorded information.
Step 4 Check that the power cabinet and bypass cabinet are combined completely and securely.
Step 5 After checking that cabinets are combined properly, reinstall the side covers and rear covers.
----End
Page 85

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
76
3.2 Single UPS Installation
The installation process and cable connection principle of UPSs in standard configuration and
UPSs in full configuration are the same. This section uses UPSs in full configuration as an
example.
When you install the UPS and connect cables, do not step on the front door baffle plate and
the door support at the bottom of the cabinet to prevent paint flake-off and deformation, as
shown in Figure 3-15. Otherwise, the front door will not be properly closed.
Figure 3-15 Front door baffle plate
3.2.1 Installing UPS Cabinets (200K, 300K)
Secured Installation
Step 1 Determine the position for installing the cabinet. Mark mounting holes for the UPS based on
the following figures:
Page 86

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
77
Figure 3-16 UPS mounting holes positioning (unit: mm)
(1) M12 bolt
(2) Spring washer
(3) Flat washer
(4) Expansion sleeve
Step 2 Use a hammer drill to drill four holes for installing expansion bolts and then install four
expansion bolts in the holes. Figure 3-17 shows the composition of an expansion bolt, and
Figure 3-18 shows how to install an expansion bolt.
Figure 3-17 Expansion bolt composition
Page 87

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
78
Ensure the expansion tube of the expansion bolts fits completely into the hole. The expansion
sleeves must be completely buried under the ground to properly facilitate subsequent
installation.
Figure 3-18 Installing expansion bolts (unit: mm)
1. Drill holes in the ground by using a hammer drill. The hole depth is 52 mm to 60 mm.
2. Partially tighten the expansion bolt and vertically insert it into the hole. Hit the
expansion bolt using a rubber mallet until the expansion sleeve is fully inserted into the
hole.
3. Partially tighten the expansion bolt.
4. Remove the bolt, spring washer, and flat washer.
Step 3 Move the cabinet over its castors to the installation position.
Step 4 (Optional) If the castors of the UPS need to be lifted from the ground, perform steps Step 1 to
Step 2 in Unsecured Installation.
Step 5 Remove the rear panel of the cabinet, and then open the front door.
Page 88

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
79
Figure 3-19 Removing the rear panel
Step 6 Remove the four plugs from the bottom of the cabinet (two at the front and two at the rear).
Figure 3-20 Removing plugs
Page 89

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
80
Step 7 Insert four M12x115 expansion bolts into the expansion bolt holes in the floor, and tighten the
expansion bolts in the direction.
Figure 3-21 Tightening expansion bolts
----End
Unsecured Installation
Step 1 Adjust the four anchor bolts at the bottom of the UPS cabinet until all the four castors at the
bottom hang in the air and the anchor bolts bear all of the cabinet weight, as shown in Figure
3-22.
Figure 3-22 Castors adjustment
Step 2 Check the cabinet levelness using a level. If the cabinet is not level, wrench the anchor bolts.
----End
Page 90

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
81
3.2.2 Installing UPS Cabinets (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, 600K, 800K)
3.2.2.1 Installing the UPS on the Floor
Context
Ensure that the installation floor is flat.
The marking-off template is delivered with the UPS.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the cabinet installation positions on the ground based on holes in the marking-off
template for ground installation.
A: mounting holes on the channel steel
B: mounting holes on the floor
Figure 3-23 Hole dimensions (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, unit: mm)
Page 91

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
82
Figure 3-24 Hole dimensions (600K, unit: mm)
(1) M12 bolt
(2) Spring washer
(3) Flat washer
(4) Expansion sleeve
(5) Expansion nut
(6) Concrete floor
Step 2 Drill holes and install expansion sleeves.
1. Drill a hole in the concrete floor using a hammer drill. The hole depth should range from
52 mm to 60 mm.
2. Slightly tighten the expansion bolt and vertically insert it into the hole. Knock the
expansion bolt using a rubber mallet until the expansion sleeve is fully inserted into the
hole.
3. Partially tighten the expansion bolt.
4. Remove the bolt, spring washer, and flat washer.
Figure 3-25 Drilling a hole and installing an expansion sleeve
Step 3 Use a pallet truck to move the cabinet to the installation position.
Page 92

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
83
Step 4 Secure the cabinet to the expansion bolt holes on the floor using M12x60 expansion bolts.
The installation methods for different UPS models are the same. The 400K UPS is used as an
example.
Figure 3-26 Tightening expansion bolts
Step 5 Install the front, rear, left, and right anchor baffle plates. The installation methods for different
UPS models are the same. The 400K UPS is used as an example.
Figure 3-27 Installing the front, rear, left, and right anchor baffle plates
Page 93

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
84
----End
3.2.2.2 Installing the UPS on Channel Steel
Context
Channel steel and expansion bolts for securing the channel steel should be purchased by
the customer. The recommended channel steel width is 50 mm or more.
Ensure that the spacing between external sides of a channel steel is 800 mm. Secure
channel steel to the ground by using expansion bolts.
Keep the channel steel surface flat.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the cabinet installation positions on the channel steel based on holes in the
marking-off template for channel steel installation.
A: mounting holes on the channel steel
B: mounting holes on the floor
Figure 3-28 Hole dimensions (300K-FT, 400K, 500K, unit: mm)
Page 94

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
85
Figure 3-29 Hole dimensions (600K, unit: mm)
Step 2 Drill cabinet mounting holes in channel steel by using a hammer drill.
Step 3 Use a pallet truck to move the cabinet to the installation position.
Step 4 Use common M12x45 bolts to secure the cabinets into the mounting holes in the channel steel
and tighten the bolts.
Step 5 Install the front, rear, left, and right anchor baffle plates.
----End
3.2.3 Installing UPS Cabinets (800K)
3.2.3.1 Installing the UPS on the Floor
Determining the UPS Installation Position
Ensure that the installation floor is flat.
The marking-off template is delivered with the UPS.
Step 1 Determine the cabinet installation positions on the ground based on holes in the marking-off
template for ground installation.
A: mounting holes on the channel steel
B: mounting holes on the floor
Page 95

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
86
Figure 3-30 Hole dimensions (unit: mm)
(1) M12 bolt
(2) Spring washer
(3) Flat washer
(4) Expansion sleeve
(5) Expansion nut
(6) Concrete floor
Step 2 Drill holes and install expansion sleeves.
1. Drill a hole in the concrete floor using a hammer drill. The hole depth should range from
52 mm to 60 mm.
2. Slightly tighten the expansion bolt and vertically insert it into the hole. Knock the
expansion bolt using a rubber mallet until the expansion sleeve is fully inserted into the
hole.
3. Partially tighten the expansion bolt.
4. Remove the bolt, spring washer, and flat washer.
Figure 3-31 Drilling a hole and installing an expansion sleeve
----End
Page 96

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
87
Combining Power Cabinets and Bypass Cabinets
Mounting
Fitting
Number of
Fittings
(PCS)
Screw
Specifications
Number of
Bolts (PCS)
Torque
(N•m)
Remarks
Bottom
connecting
kit
2
M12x25
8
47
Fittings are delivered
with the UPS. You can
see the fittings after
unpacking the bypass
cabinet.
The two soft copper bars
are numbered 52.
If holes are drilled for
routing cables at the top
of the cabinet, attach
grommet strips on the
hole edges to protect
cables.
Top
connecting
kit
2
M6x30
8
3
Soft
connecting
copper bar
2
M12x45
10
47
Grommet
strip
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Middle
connecting
kit
2
M6x30
4
3
Installed on the cabinet
before delivery.
The power cabinets and bypass cabinets are separately packed for delivery. Before installing
the UPS, combine the power cabinets and bypass cabinets. Before combining the cabinets,
ensure that the required fittings are complete. Table 3-15 lists the fittings.
Table 3-15 Fitting list
Step 1 Use a pallet truck to move the power cabinets and bypass cabinets to the mounting holes for
the cabinets with the power cabinets on the left and the bypass cabinets on the right. Align the
cabinets to ensure that their front doors are aligned.
Step 2 Open the front doors of the power cabinets and bypass cabinets.
Step 3 Install the connecting kits between the bypass cabinet and its adjacent power cabinet based on
the following sequence: bottom, top, and middle connecting kits.
Page 97

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
88
Figure 3-32 Installing connecting kits
Step 4 Use M12x60 expansion bolts to secure the cabinets to the expansion bolt holes on the floor.
Figure 3-33 shows how to secure the power cabinets.
Figure 3-33 Tightening expansion bolts
Page 98

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
89
Step 5 Install the front, rear, left, and right anchor baffle plates.
Figure 3-34 Installing the front, rear, left, and right anchor baffle plates
Step 6 Remove the front covers of the power distribution subrack from the bypass cabinets, as shown
in Figure 3-35.
The front covers of the power distribution subrack can be removed only when all the switches are OFF.
Page 99

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
90
Figure 3-35 Removing the front covers of the power distribution subrack
Step 7 Remove the rear covers from power cabinet 1 and its adjacent bypass cabinet.
Step 8 (Optional) Remove the extension rod of the maintenance bypass switch from the bypass
cabinet.
To facilitate cabinet combination, remove the switch extension rod from the left bypass cabinet. The
operation of removing the switch extension rod from the right bypass cabinet is optional.
Put away the removed screws, washers, and switch extension rod which need to be reinstalled after
cables are connected.
When reinstalling the switch extension rod, keep the dowel level, as shown in Figure 3-36. Insert the
switch extension rod to the blue mark, put washers, and tighten the slotted screw to reinstall the
switch extension rod.
Page 100

UPS5000-A-(200 kVA-800 kVA)
User Manual
3 Installation
Issue 03 (2019-02-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
91
Figure 3-36 Removing the switch extension rod
(1) Blue mark
Step 9 Install the soft copper bars between power cabinet 1 and its adjacent bypass cabinet.
1. Cut off the cable ties bound between holes in soft copper bars numbered 23, 24, 25, 26,
and 30.
2. Secure the soft copper bars numbered 23, 24, 25, 26, and 30 using M12x45 screws, as
shown in Figure 3-37.
 Loading...
Loading...