SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
Issue
01
Date
2020-07-02
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.

Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
i
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2020. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties,
guarantees or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
https://e.huawei.com

Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
ii

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
About This Document
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
iii
Purpose
Symbol
Description
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk which, if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a medium level of risk which, if
not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a low level of risk which, if not
avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
About This Document
This document describes the SUN2000-8KTL-M2, SUN2000-10KTL-M2,
SUN2000-12KTL-M2, SUN2000-15KTL-M2, SUN2000-17KTL-M2, and
SUN2000-20KTL-M2 (SUN2000 for short) in terms of installation, electrical
connections, commissioning, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Read this
document through, understand the safety information, and get familiar with the
functions and features of the SUN2000 before installing and operating it.
The SUN2000-8KTL-M2 and SUN2000-10KTL-M2 inverters are applicable only to Australia.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
Installers
Users
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
About This Document
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
iv
Symbol
Description
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in equipment damage, data loss,
performance deterioration, or unanticipated results.
NOTICE is used to address practices not related to
personal injury.
Supplements the important information in the main text.
NOTE is used to address information not related to
personal injury, equipment damage, and environment
deterioration.
Change History
Changes between document issues are cumulative. The latest document issue
contains all updates made in previous issues.
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
This issue is used for first office application (FOA).

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
Contents
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
v
Contents
About This Document .............................................................................................................. iii
1 Safety Information ................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 General Safety ........................................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Personnel Requirements ........................................................................................................................................................ 2
1.3 Electrical Safety ......................................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.4 Installation Environment Requirements........................................................................................................................... 4
1.5 Mechanical Safety .................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.6 Commissioning .......................................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.7 Maintenance and Replacement .......................................................................................................................................... 6
2 Overview .................................................................................................................................. 7
2.1 Product Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Appearance ............................................................................................................................................................................... 11
2.3 Label Description .................................................................................................................................................................... 13
2.3.1 Enclosure Labels .................................................................................................................................................................. 13
2.3.2 Product Nameplate ............................................................................................................................................................ 14
2.4 Working Principles ................................................................................................................................................................. 15
2.4.1 Circuit Diagram .................................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.4.2 Working Modes ................................................................................................................................................................... 15
3 Storage .................................................................................................................................... 18
4 Installation ............................................................................................................................. 19
4.1 Checking Before Installation .............................................................................................................................................. 19
4.2 Tools ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 20
4.3 Determining the Installation Position ............................................................................................................................. 21
4.3.1 Environment Requirements ............................................................................................................................................. 21
4.3.2 Space Requirements........................................................................................................................................................... 22
4.4 Moving an Inverter ................................................................................................................................................................ 25
4.5 Installing the Mounting Bracket ....................................................................................................................................... 26
4.5.1 Wall-mounted Installation .............................................................................................................................................. 27
4.5.2 Support-mounted Installation ........................................................................................................................................ 30

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
Contents
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
vi
5 Electrical Connections ......................................................................................................... 33
5.1 Preparing for Installation .................................................................................................................................................... 34
5.2 Connecting the PE cable ...................................................................................................................................................... 37
5.3 Connecting the AC Output Power Cable ....................................................................................................................... 39
5.4 Connecting the DC input power cable............................................................................................................................ 43
5.5 (Optional) Installing the Smart Dongle ......................................................................................................................... 48
5.6 (Optional) Installing the Signal Cable ............................................................................................................................ 49
5.6.1 Connecting the RS485 Communications Cable (Inverter Cascading) .............................................................. 52
5.6.2 Connecting the RS485 Communications Cable (Smart Power Sensor) .......................................................... 53
5.6.3 Connecting the Rapid shutdown signal cable .......................................................................................................... 56
5.6.4 Connecting the Power Grid Scheduling Signal Cable ............................................................................................ 58
6 Commissioning ...................................................................................................................... 60
6.1 Check Before Power-On ....................................................................................................................................................... 60
6.2 Powering On the System ..................................................................................................................................................... 61
7 Man-Machine Interaction ................................................................................................... 66
7.1 App Commissioning ............................................................................................................................................................... 66
7.1.1 Downloading the FusionSolar App ............................................................................................................................... 66
7.1.2 (Optional) Registering an Installer Account ............................................................................................................. 67
7.1.3 Creating a PV Plant and a User ..................................................................................................................................... 68
7.1.4 (Optional) Setting the Physical Layout of the Smart PV Optimizers .............................................................. 69
7.1.5 Detect optimizer disconnection ..................................................................................................................................... 71
7.2 Parameters Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 72
7.2.1 Energy Control ..................................................................................................................................................................... 72
7.2.1.1 Grid-tied Point Control .................................................................................................................................................. 73
7.2.2 AFCI .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 76
7.2.3 IPS Check (for Italy CEI0-21 Grid Code Only) .......................................................................................................... 77
7.3 SmartLogger Networking Scenario .................................................................................................................................. 79
8 Maintenance .......................................................................................................................... 80
8.1 System Power-Off .................................................................................................................................................................. 80
8.2 Routine Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................................ 81
8.3 Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................................................................................... 82
9 Handling the Inverter .......................................................................................................... 94
9.1 Removing a SUN2000 ........................................................................................................................................................... 94
9.2 Packing the SUN2000 ........................................................................................................................................................... 94
9.3 Disposing of the SUN2000 .................................................................................................................................................. 94
10 Technical Data .................................................................................................................... 95
10.1 SUN2000 Technical Specifications ................................................................................................................................. 95

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
Contents
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
vii
10.2 Optimizer Technical Specifications ............................................................................................................................. 100
A Grid Codes ........................................................................................................................... 103
B Device Commissioning ..................................................................................................... 107
C Resetting Password ........................................................................................................... 111
D Rapid Shutdown ................................................................................................................ 114
E Locating Insulation Resistance Faults .......................................................................... 116
F Acronyms and Abbreviations .......................................................................................... 120

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
1 Safety Information
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
1
1.1 General Safety
Statement
Before installing, operating, and maintaining the equipment, read this document
and observe all the safety instructions on the equipment and in this document.
1 Safety Information
The "NOTICE", "CAUTION", "WARNING", and "DANGER" statements in this
document do not cover all the safety instructions. They are only supplements to the
safety instructions. Huawei will not be liable for any consequence caused by the
violation of general safety requirements or design, production, and usage safety
standards.
Ensure that the equipment is used in environments that meet its design
specifications. Otherwise, the equipment may become faulty, and the resulting
equipment malfunction, component damage, personal injuries, or property damage
are not covered under the warranty.
Follow local laws and regulations when installing, operating, or maintaining the
equipment. The safety instructions in this document are only supplements to local
laws and regulations.
Huawei will not be liable for any consequences of the following circumstances:
Operation beyond the conditions specified in this document
Installation or use in environments which are not specified in relevant
international or national standards
Unauthorized modifications to the product or software code or removal of the
product
Failure to follow the operation instructions and safety precautions on the
product and in this document
Equipment damage due to force majeure, such as earthquakes, fire, and storms
Damage caused during transportation by the customer

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
1 Safety Information
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
2
Storage conditions that do not meet the requirements specified in this
document
General Requirements
Do not work with power on during installation.
Do not install, use, or operate outdoor equipment and cables (including but not
limited to moving equipment, operating equipment and cables, inserting
connectors to or removing connectors from signal ports connected to outdoor
facilities, working at heights, and performing outdoor installation) in harsh
weather conditions such as lightning, rain, snow, and level 6 or stronger wind.
After installing the equipment, remove idle packing materials such as cartons,
foam, plastics, and cable ties from the equipment area.
In the case of a fire, immediately leave the building or the equipment area, and
turn on the fire alarm bell or make an emergency call. Do not enter the
building on fire in any case.
Do not scrawl, damage, or block any warning label on the equipment.
Tighten the screws using tools when installing the equipment.
Understand the components and functioning of a grid-tied PV power system
and relevant local standards.
Repaint any paint scratches caused during equipment transportation or
installation in a timely manner. Equipment with scratches cannot be exposed to
an outdoor environment for a long period of time.
Do not open the host panel of the equipment.
Personal Safety
If there is a probability of personal injury or equipment damage during
operations on the equipment, immediately stop the operations, report the case
to the supervisor, and take feasible protective measures.
Use tools correctly to avoid hurting people or damaging the equipment.
Do not touch the energized equipment, as the enclosure is hot.
1.2 Personnel Requirements
Personnel who plan to install or maintain Huawei equipment must receive
thorough training, understand all necessary safety precautions, and be able to
correctly perform all operations.
Only qualified professionals or trained personnel are allowed to install, operate,
and maintain the equipment.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
1 Safety Information
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
3
Only qualified professionals are allowed to remove safety facilities and inspect
the equipment.
Personnel who will operate the equipment, including operators, trained
personnel, and professionals, should possess the local national required
qualifications in special operations such as high-voltage operations, working at
heights, and operations of special equipment.
Only professionals or authorized personnel are allowed to replace the
equipment or components (including software).
Professionals: personnel who are trained or experienced in equipment operations and are
clear of the sources and degree of various potential hazards in equipment installation,
operation, and maintenance
Trained personnel: personnel who are technically trained, have required experience, are
aware of possible hazards on themselves in certain operations, and are able to take
protective measures to minimize the hazards on themselves and other people
Operators: operation personnel who may come in contact with the equipment, except
trained personnel and professionals
1.3 Electrical Safety
Grounding
For the equipment that needs to be grounded, install the ground cable first
when installing the equipment and remove the ground cable last when
removing the equipment.
Do not damage the ground conductor.
Do not operate the equipment in the absence of a properly installed ground
conductor.
Ensure that the equipment is connected permanently to the protective ground.
Before operating the equipment, check its electrical connection to ensure that it
is securely grounded.
General Requirements
Before connecting cables, ensure that the equipment is intact. Otherwise, electric
shocks or fire may occur.
Ensure that all electrical connections comply with local electrical standards.
Obtain approval from the local electric utility company before using the
equipment in grid-tied mode.
Ensure that the cables you prepared meet local regulations.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
1 Safety Information
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
4
AC and DC Power
Do not connect or disconnect power cables with power on. Transient contact
between the core of the power cable and the conductor will generate electric arcs or
sparks, which may cause fire or personal injury.
Use dedicated insulated tools when performing high-voltage operations.
Before making electrical connections, switch off the disconnector on the
upstream device to cut off the power supply if people may contact energized
components.
Before connecting a power cable, check that the label on the power cable is
correct.
If the equipment has multiple inputs, disconnect all the inputs before operating
the equipment.
Cabling
When routing cables, ensure that a distance of at least 30 mm exists between
the cables and heat-generating components or areas. This prevents damage to
the insulation layer of the cables.
Bind cables of the same type together. When routing cables of different types,
ensure that they are at least 30 mm away from each other.
Ensure that the cables used in a grid-tied PV power system are properly
connected and insulated and meet specifications.
1.4 Installation Environment Requirements
Ensure that the equipment is installed in a well ventilated environment.
To prevent fire due to high temperature, ensure that the ventilation vents or
heat dissipation system are not blocked when the equipment is running.
Do not expose the equipment to flammable or explosive gas or smoke. Do not
perform any operation on the equipment in such environments.
1.5 Mechanical Safety
Using Ladders
Use wooden or fiberglass ladders when you need to perform live working at
heights.
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
1 Safety Information
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
5
When a step ladder is used, ensure that the pull ropes are secured and the
ladder is held firm.
Before using a ladder, check that it is intact and confirm its load bearing
capacity. Do not overload it.
Ensure that the wider end of the ladder is at the bottom, or protective
measures have been taken at the bottom to prevent the ladder from sliding.
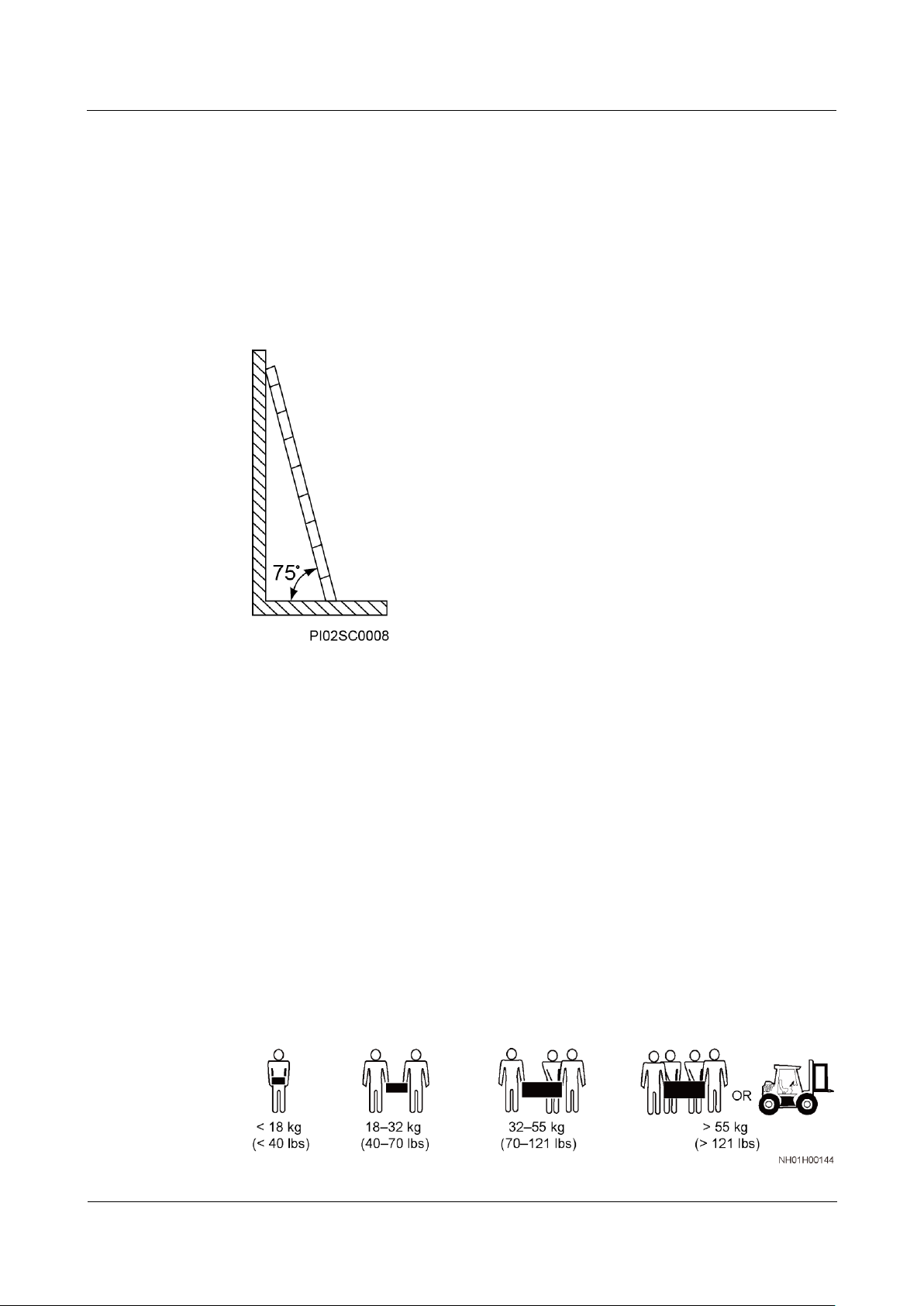
Ensure that the ladder is securely positioned. The recommended angle for a
ladder against the floor is 75 degrees, as shown in the following figure. An
angle rule can be used to measure the angle.
When climbing a ladder, take the following precautions to reduce risks and
ensure safety:
− Keep your body steady.
− Do not climb higher than the fourth rung of the ladder from the top.
− Ensure that your body's center of gravity does not shift outside the legs of
the ladder.
Drilling Holes
When drilling holes into a wall or floor, observe the following safety precautions:
Wear goggles and protective gloves when drilling holes.
When drilling holes, protect the equipment from shavings. After drilling, clean
up any shavings that have accumulated inside or outside the equipment.
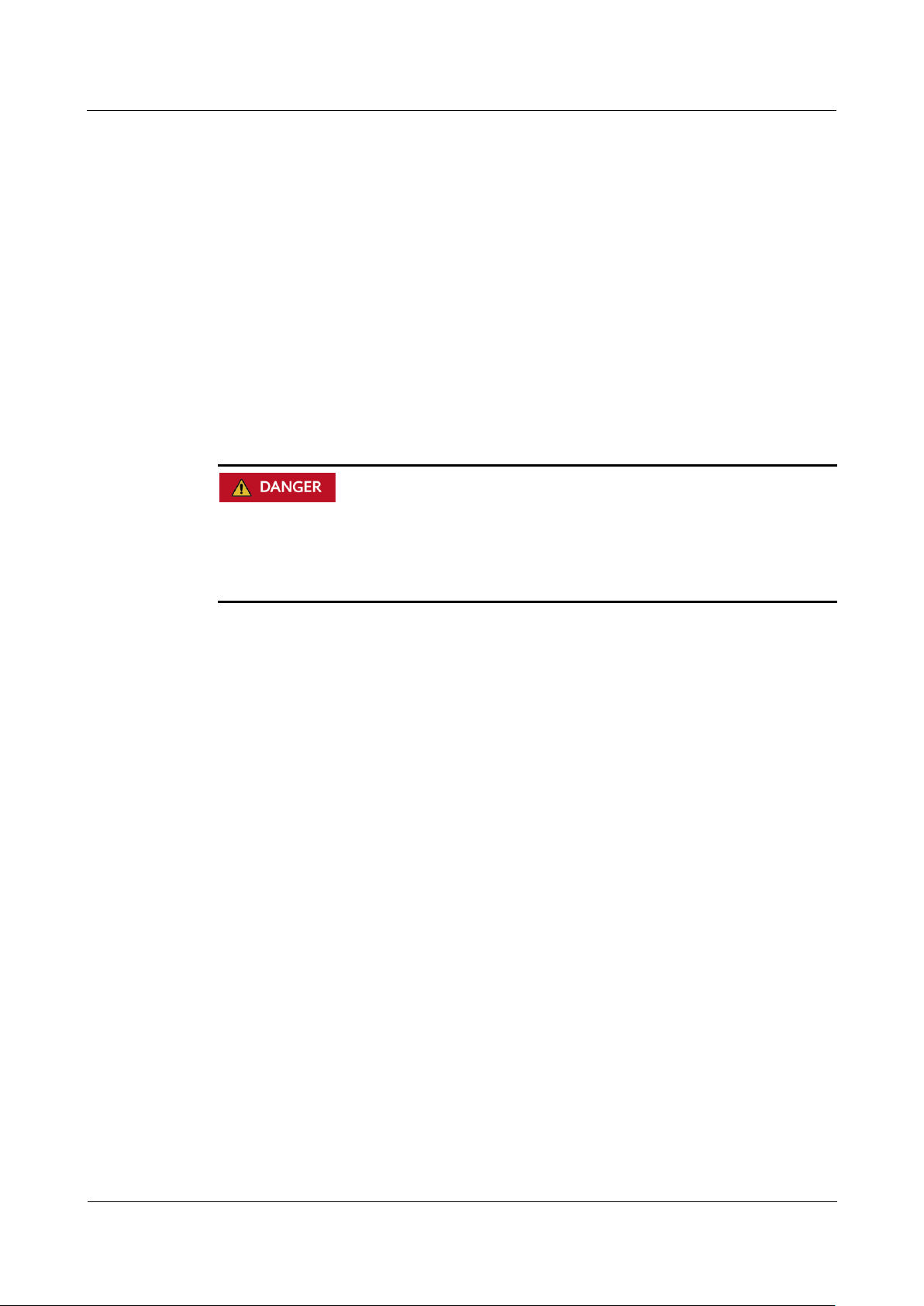
Moving Heavy Objects
Be cautious to avoid injury when moving heavy objects.
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
1 Safety Information
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
6
When moving the equipment by hand, wear protective gloves to prevent
injuries.
1.6 Commissioning
When the equipment is powered on for the first time, ensure that professional
personnel set parameters correctly. Incorrect settings may result in inconsistency
with local certification and affect the normal operation of the equipment.
1.7 Maintenance and Replacement
High voltage generated by the equipment during operation may cause an electric
shock, which could result in death, serious injury, or serious property damage. Prior
to maintenance, power off the equipment and strictly comply with the safety
precautions in this document and relevant documents.
Maintain the equipment with sufficient knowledge of this document and using
proper tools and testing equipment.
Before maintaining the equipment, power it off and follow the instructions on
the delayed discharge label to ensure that the equipment is powered off.
Place temporary warning signs or erect fences to prevent unauthorized access
to the maintenance site.
If the equipment is faulty, contact your dealer.
The equipment can be powered on only after all faults are rectified. Failing to
do so may escalate faults or damage the equipment.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
7
2.1 Product Introduction
Function
The SUN2000 is a three-phase grid-tied PV string inverter that converts the DC
power generated by PV strings into AC power and feeds the power into the power
grid.
2 Overview
Models
This document involves the following product models:
SUN2000-8KTL-M2
SUN2000-10KTL-M2
SUN2000-12KTL-M2
SUN2000-15KTL-M2
SUN2000-17KTL-M2
SUN2000-20KTL-M2
The SUN2000-8KTL-M2 and SUN2000-10KTL-M2 inverters are applicable only to Australia.
Figure 2-1 Model description (SUN2000-20KTL-M2 is used as an example)

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
8
Table 2-1 Model description
Icon
Meaning
Description
1
Product
SUN2000: three-phase grid-tied PV string inverter
2
Power level
8K: The rated power is 8 kW.
10K: The rated power is 10 kW.
12K: The rated power is 12 kW.
15K: The rated power is 15 kW.
17K: The rated power is 17 kW.
20K: The rated power is 20 kW.
3
Topology
TL: transformerless
4
Product code
M2: the product series with the 1080 V DC input voltage
Network Application
The SUN2000 applies to grid-tied PV systems for residential rooftops and small
ground plants. Typically, a grid-tied system consists of the PV string, SUN2000, AC
switch, and alternating current distribution unit (ACDU).
Figure 2-2 Networking application - Single inverter scenario (optional in dashed boxes)

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
9
Figure 2-3 Networking application - Inverter cascading scenario (optional in dashed
(A) PV string
(B) DC switch
(C) SUN2000
(D) AC switch
(E) ACDU
(F) Smart Power Sensor
(G) Power grid
(H) 4G Smart Dongle
(I) WLAN-FE Smart
Dongle
(J) Router
(K) FusionSolar
management system
(L) FusionSolar APP
(M) Load
(N) Ripple Control Device
(O) Rapid shutdown
switch
boxes)
indicates a power cable, indicates a signal cable, indicates wireless
communication.
If the inverter is connected to the FusionSolar app over its built-in WiFi network, only local
commissioning can be performed.
In the RS485 cascading communication networking, the master inverter model is
SUN2000-(3KTL-20KTL)-M2 and SUN2000-(3KTL-20KTL)-M0, and the slave inverter
model can be SUN2000-(3KTL-20KTL)-M2, SUN2000-(3KTL-20KTL)-M0,
SUN2000-50KTL/60KTL/65KTL-M0, SUN2000-29.9KTL/36KTL, or SUN2000-33KTL-A.
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
10
(P) Smart PV optimizer
Supported Power Grids
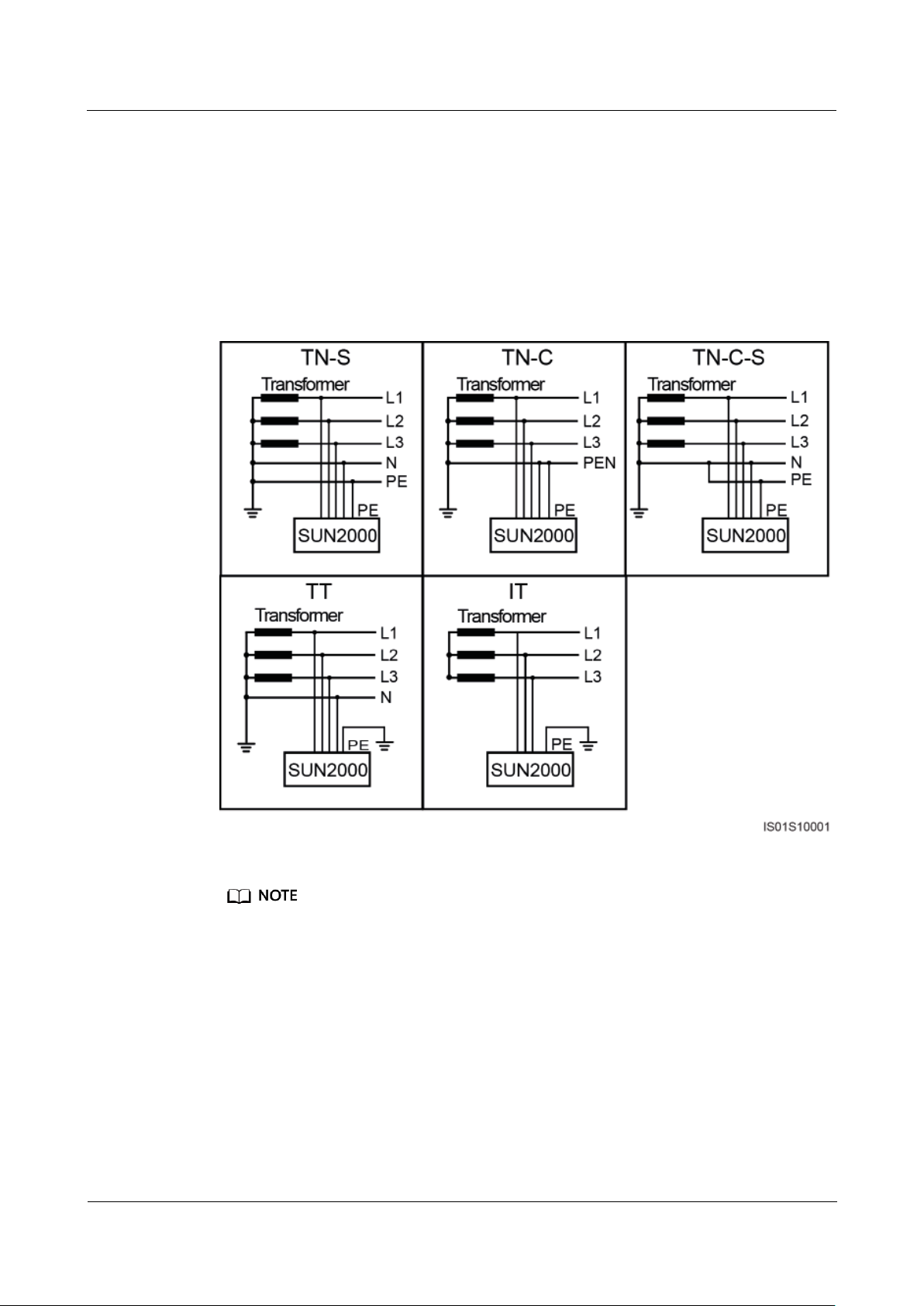
Power grid types supported by the SUN2000 include TN-S, TN-C, TN-C-S, TT, and IT.
Figure 2-4 Supported power grids
In a TT power grid, the N-PE voltage should be lower than 30 V.
In an IT power grid, you need to set isolation settings to input not grounded, with a
transformer.
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
11
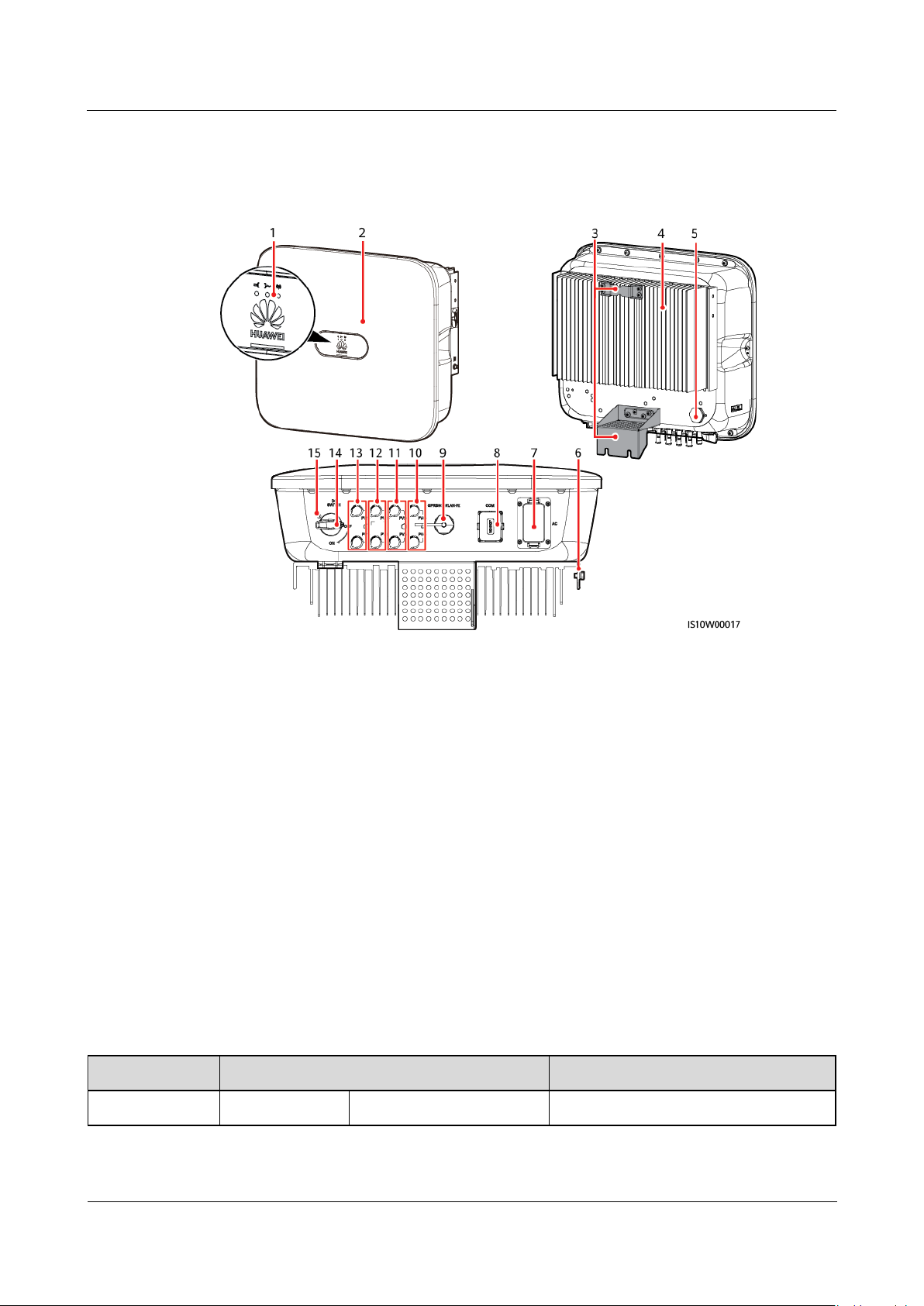
2.2 Appearance
(1) LED indicator
(2) Front panel
(3) Mounting plate
(4) Heat sink
(5) Ventilation valve
(6) Ground screw
(7) AC output port (AC)
(8) Communication port (COM)
(9) Smart Dongle port
(GPRS/4G/WLAN-FE)
(10) DC input terminals (PV4+/PV4–)
(11) DC input terminals (PV3+/PV3–)
(12) DC input terminals (PV2+/PV2–)
(13) DC input terminals (PV1+/PV1–)
(14) DC switch (DC SWITCH)
(15) Screw hole for the DC switch (for Australia only)
Category
Status
Meaning
Running
LED1
LED2
N/A
Figure 2-5 Appearance
Table 2-2 LED indicator description
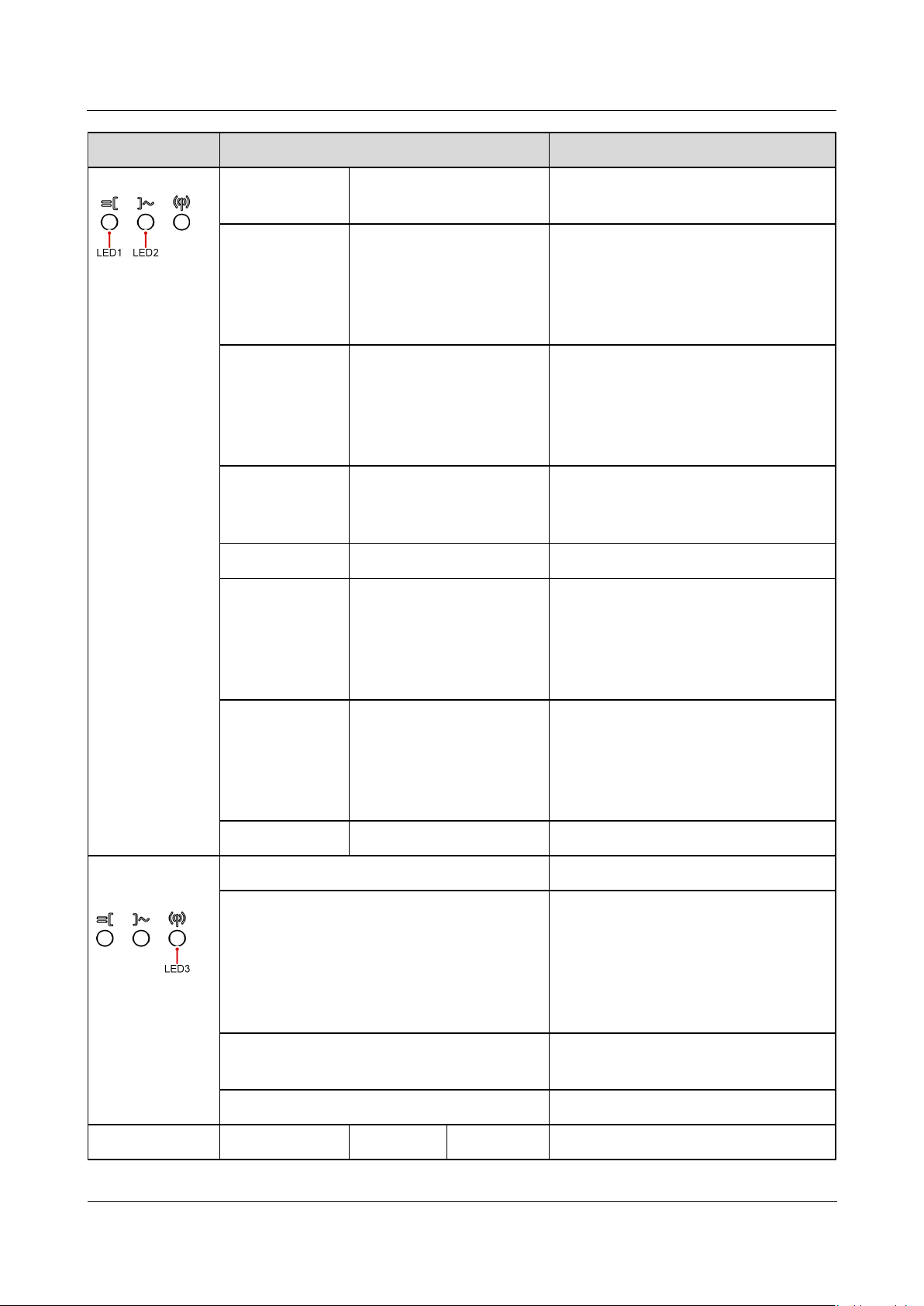
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
12
Category
Status
Meaning
indication
Steady green
Steady green
The SUN2000 is operating in
grid-tied mode.
Blinking green
at long
intervals (on
for 1s and then
off for 1s)
Off
The DC is on and the AC is off.
Blinking green
at long
intervals (on
for 1s and then
off for 1s)
Blinking green at long
intervals (on for 1s and
then off for 1s)
The DC is on, the AC is on, and the
SUN2000 is not exporting power to
the power grid.
Off
Blinking green at long
intervals (on for 1s and
then off for 1s)
The DC is off and the AC is on.
Off
Off
Both the DC and AC are off.
Blinking red at
short intervals
(on for 0.2s
and then off
for 0.2s)
N/A
There is a DC environmental alarm,
such as an alarm indicating that
High String Input Voltage, String
Reverse Connection, or Low
Insulation Resistance.
N/A
Blinking red at short
intervals (on for 0.2s and
then off for 0.2s)
There is an AC environmental alarm,
such as an alarm indicating Grid
Undervoltage, Grid Overvoltage,
Grid Overfrequency, or Grid
Underfrequency.
Steady red
Steady red
Fault
Communicatio
n indication
LED3
N/A
Blinking green at short intervals (on for
0.2s and then off for 0.2s)
Communication is in progress.
(When a mobile phone is connected
to the SUN2000, the indicator first
indicates that the phone is
connected to the SUN2000): blinks
green at long intervals.)
Blinking green at long intervals (on for 1s
and then off for 1s)
The mobile phone is connected to
the SUN2000.
Off
There is no communication.
Device
LED1
LED2
LED3
N/A
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
13
Category
Status
Meaning
replacement
indication
Steady red
Steady red
Steady red
The SUN2000 hardware is faulty.
The SUN2000 needs to be replaced.
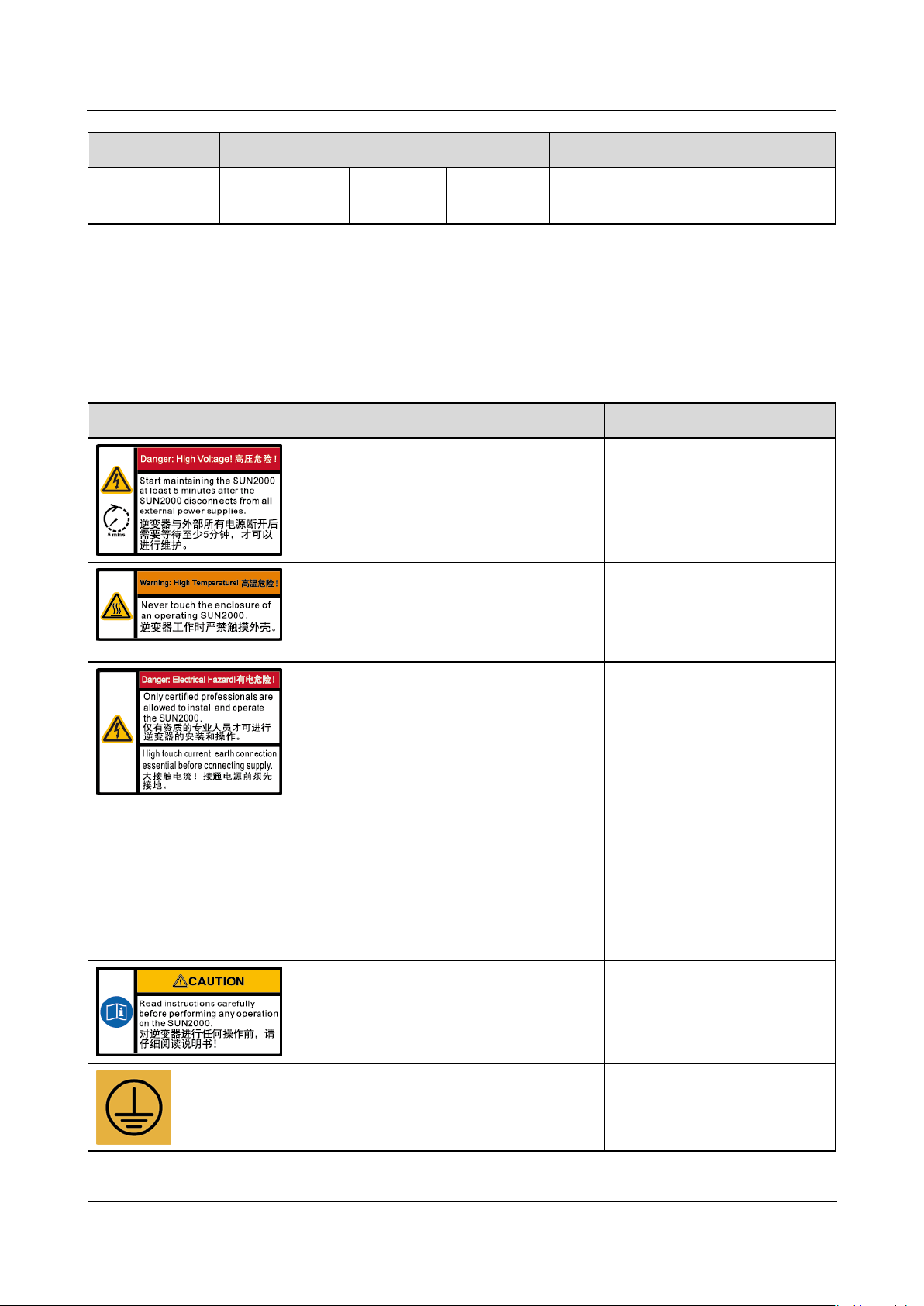
Symbol
Name
Meaning
Delayed discharge
Residual voltage exists after
the SUN2000 is powered off.
It takes 5 minutes for the
SUN2000 to discharge to the
safe voltage.
Burn warning
Do not touch an operating
SUN2000 because it
generates high temperatures
on the shell.
Electric shock warning label
High voltage exists after
the SUN2000 is powered
on. Only qualified and
trained electrical
technicians are allowed to
perform operations on
the SUN2000.
High touch current exists
after the SUN2000 is
powered on. Ensure that
the SUN2000 has been
grounded before
powering on it.
Refer to documentation
Reminds operators to refer
to the documents shipped
with the SUN2000.
Grounding
Indicates the position for
connecting the protective
earthing (PE) cable.
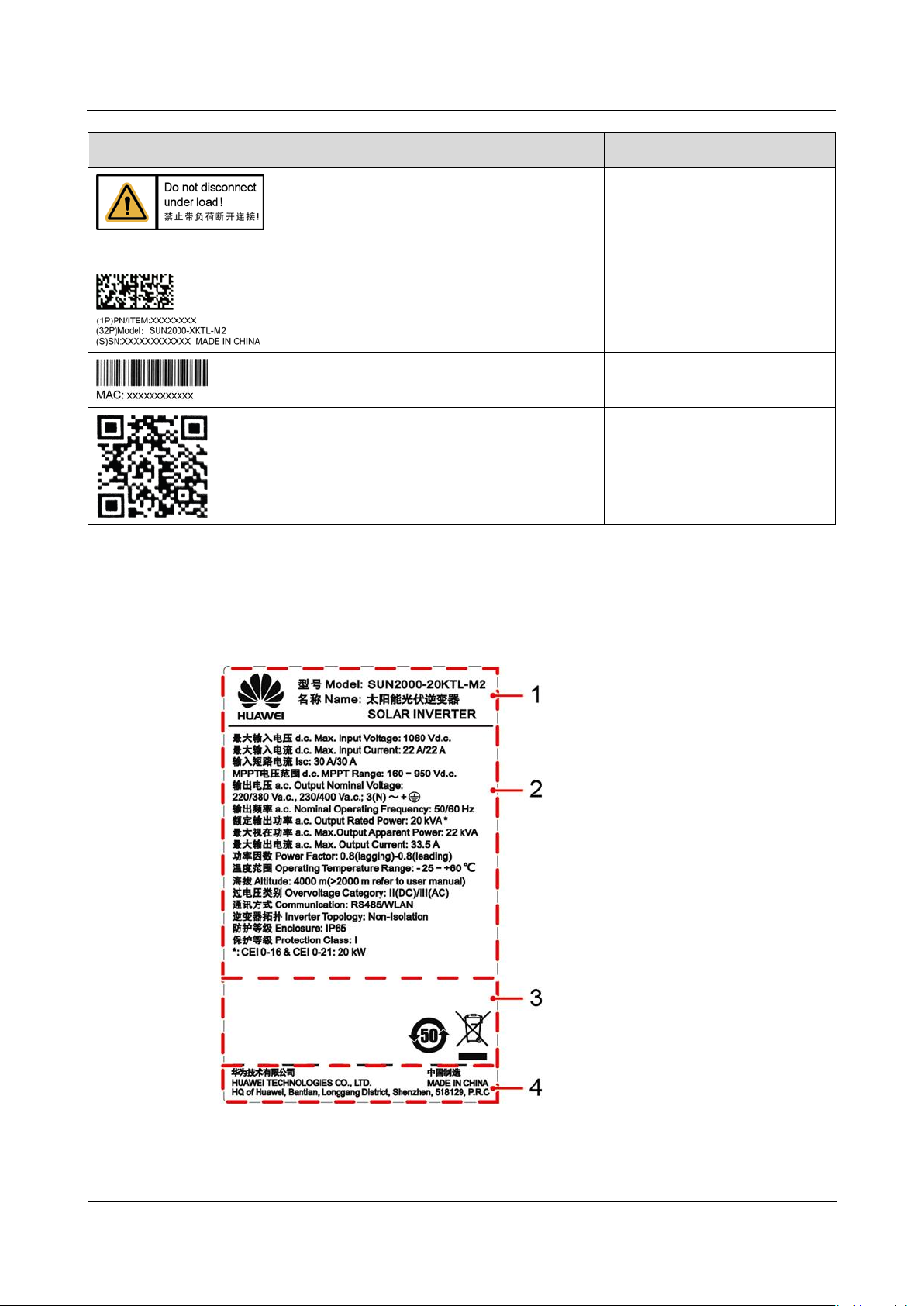
2.3 Label Description
2.3.1 Enclosure Labels
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
14
Symbol
Name
Meaning
Operation warning
Do not remove the DC input
connector or the AC output
connector when the
SUN2000 is running.
SUN2000 serial number (SN)
label
Indicates the SUN2000 SN.
SUN2000 MAC address label
Indicates the MAC address.
QR code label for SUN2000
WiFi connection
Scan the QR code to connect
to Huawei SUN2000 WiFi
network.
2.3.2 Product Nameplate
Figure 2-6 Nameplate (SUN2000-20KTL-M2 as an example)
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
15
(1) Trademark and product model
(2) Important technical specifications
(3) Compliance symbols
(4) Company name and country of
manufacture
The nameplate figure is for reference only.
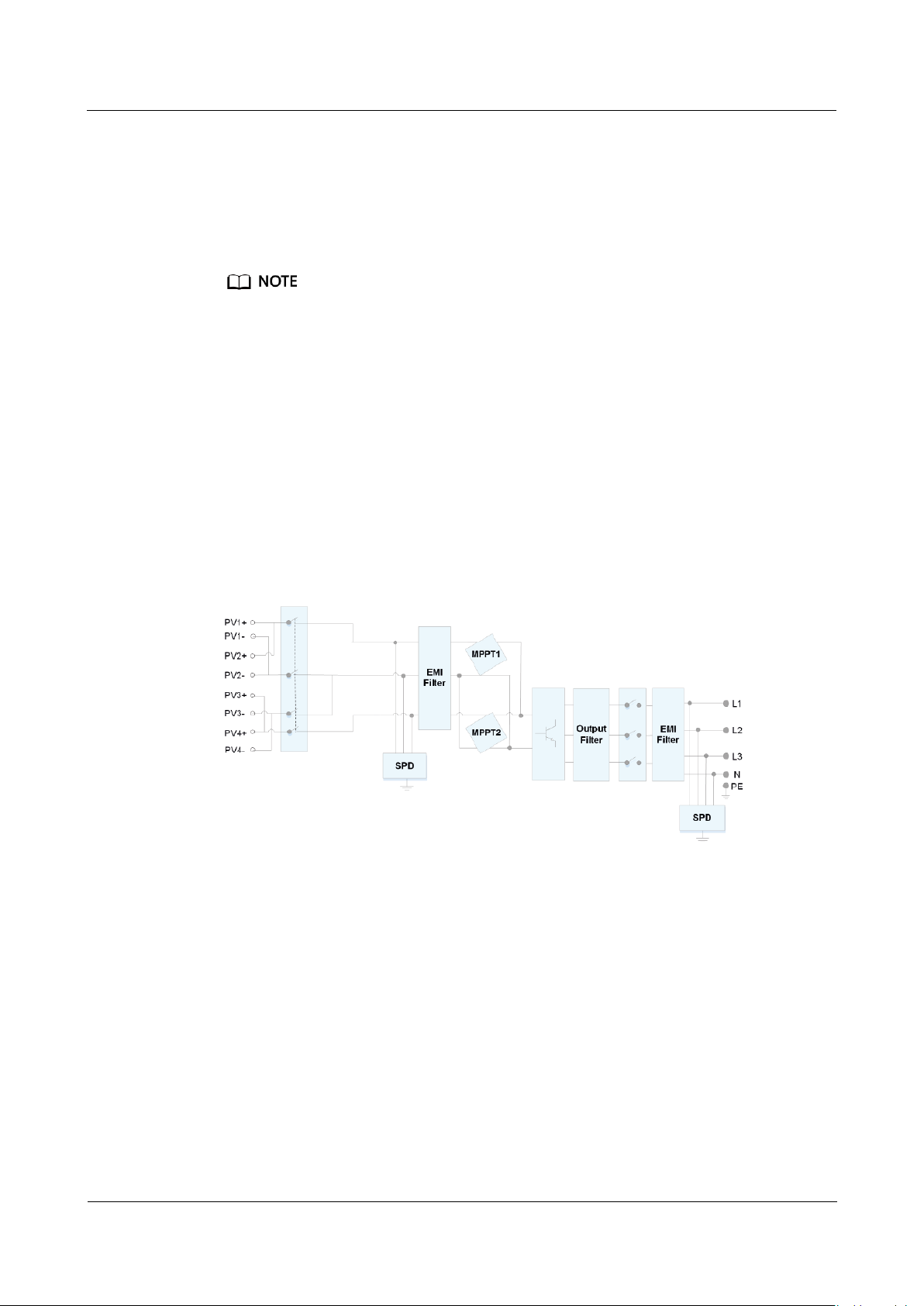
2.4 Working Principles
2.4.1 Circuit Diagram
Four PV strings connect to the SUN2000, and their maximum power points are
tracked by two maximum power point tracking (MPPT) circuits. The SUN2000
converts DC power into three-phase AC power through an inverter circuit. Surge
protection is supported on both the DC and AC sides.
Figure 2-7 SUN2000 conceptual diagram
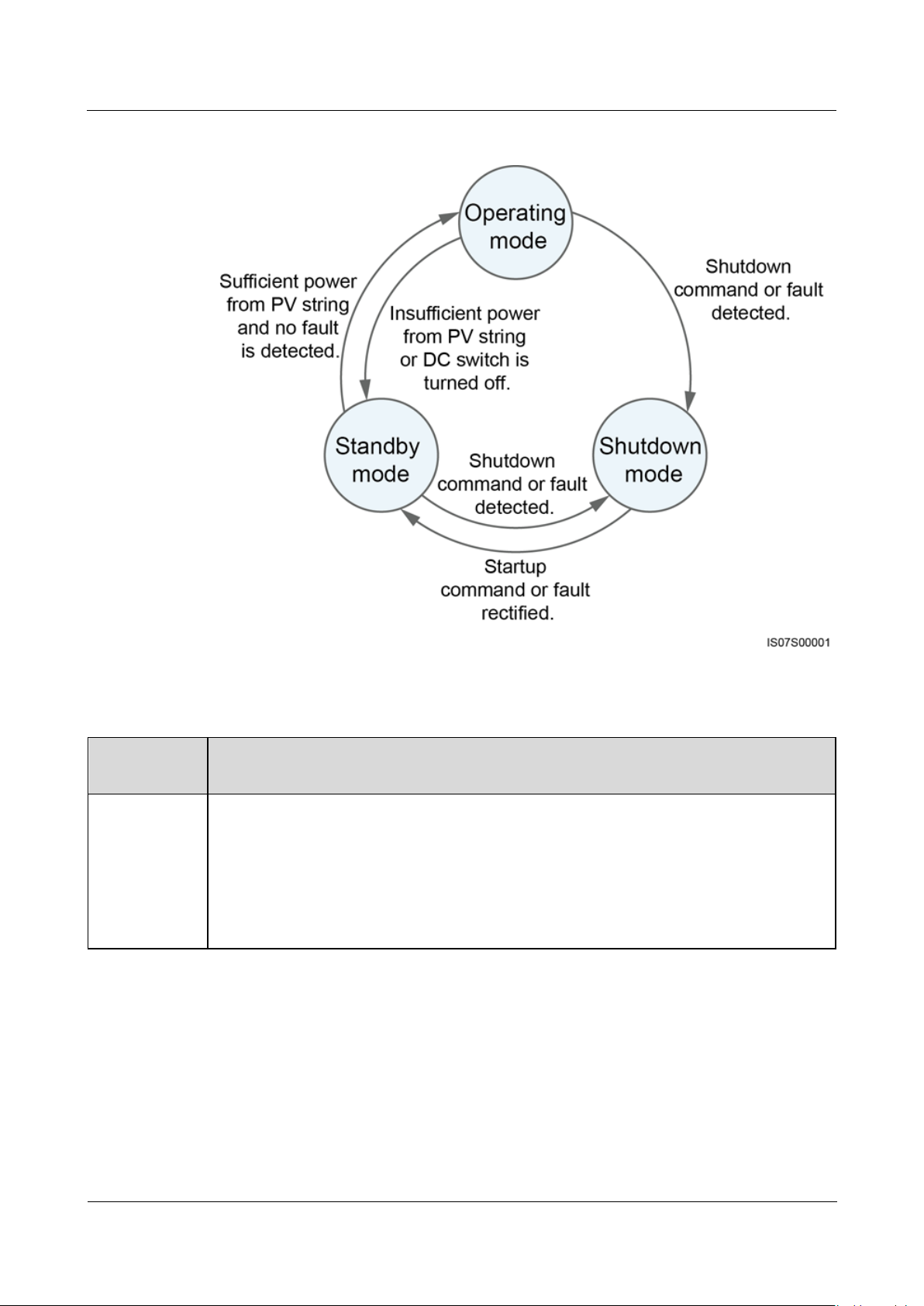
2.4.2 Working Modes
The SUN2000 can work in Standby, Operating, or Shutdown mode.
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
16
Figure 2-8 Working modes
Working
Mode
Description
Standby
The SUN2000 enters Standby mode when the external environment does not meet
the operating requirements. In Standby mode:
The SUN2000 continuously performs status check and enters the Operating
mode once the operating requirements are met.
The SUN2000 enters Shutdown mode after detecting a shutdown command or a
fault after startup.
Table 2-3 Working mode description
SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
2 Overview
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
17
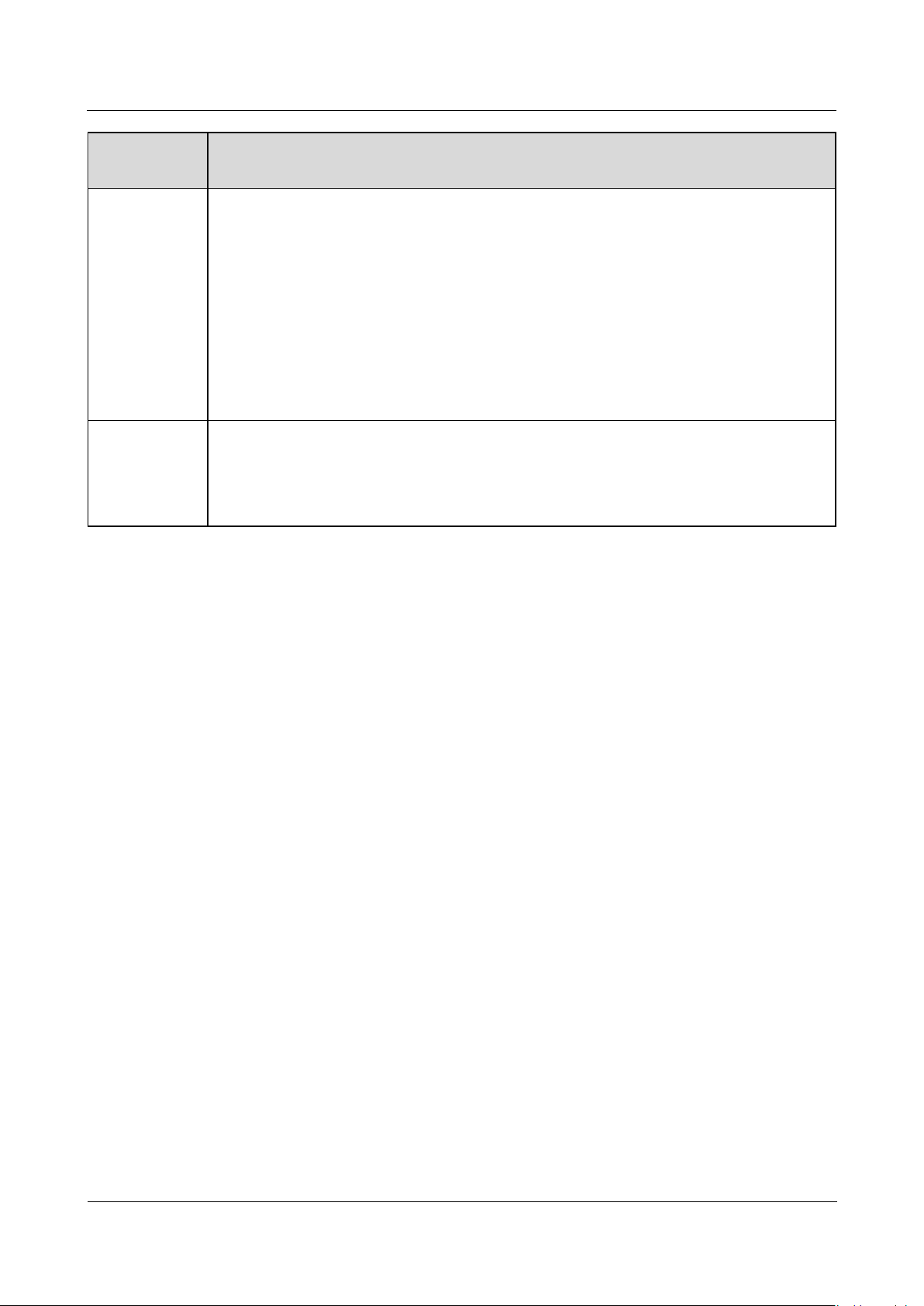
Working
Mode
Description
Operating
In Operating mode:
The SUN2000 converts DC power from PV strings into AC power and feeds the
power to the power grid.
The SUN2000 tracks the maximum power point to maximize the PV string
output.
If the SUN2000 detects a fault or a shutdown command, it enters the Shutdown
mode.
The SUN2000 enters Standby mode after detecting that the PV string output
power is not suitable for connecting to the power grid for generating power.
Shutdown
In Standby or Operating mode, the SUN2000 enters Shutdown mode after
detecting a fault or shutdown command.
In Shutdown mode, the SUN2000 enters Standby mode after detecting a startup
command or that the fault is rectified.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
3 Storage
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
18
3 Storage
The following requirements should be met if the SUN2000 is not put into use
directly:
Do not unpack the SUN2000.
Keep the storage temperature at –40°C to +70°C and the humidity at 5%–95%
RH (non-condensing).
The SUN2000 should be stored in a clean and dry place and be protected from
dust and water vapor corrosion.
A maximum of six SUN2000s can be stacked. To avoid personal injury or device
damage, stack SUN2000s with caution to prevent them from falling over.
Periodic inspections are required during the storage. Replace the packing
materials if necessary.
If the SUN2000 has been long-term stored, inspections and tests should be
conducted by qualified personnel before it is put into use.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
19
4.1 Checking Before Installation
Outer Packing Materials
Before unpacking the inverter, check the outer packing materials for damage, such
as holes and cracks, and check the inverter model. If any damage is found or the
inverter model is not what you requested, do not unpack the package and contact
your supplier as soon as possible.
4 Installation
You are advised to remove the packing materials within 24 hours before installing the
inverter.
Package Contents
After unpacking the inverter, check that the contents are intact and complete. If any
damage is found or any component is missing, contact your supplier.
For details about the number of contents, see the
Packing List
in the packing case.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
20
Type
Tool
Installa
tion
Tools
Hammer drill
Drill bit: Φ8 mm and
Φ6 mm
Socket wrench set
Torque screwdriver
Phillips head: M3
Diagonal pliers
Wire stripper
Removal wrench
Model: PV-MS-HZ
Open-end Wrench;
manufacturer:
Staubli
Rubber mallet
Utility knife
Cable cutter
Crimping tool
Model:
PV-CZM-22100;
manufacturer:
Staubli
Multimeter
DC voltage
measurement range
≥ 1100 V DC
Vacuum cleaner
Marker
Measuring tape
Bubble or digital
level
Cord end terminal
crimper
4.2 Tools

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
21
Type
Tool
Heat shrink tubing
Heat gun
Cable tie
Hydraulic pliers
PPE
Safety gloves
Safety goggles
Anti-dust respirator
Safety shoes
4.3 Determining the Installation Position
4.3.1 Environment Requirements
Basic Requirements
The SUN2000 is protected to IP65 and can be installed indoors or outdoors.
Do not install the SUN2000 in a place where personnel are easy to come into
contact with its enclosure and heat sinks, because these parts are extremely hot
during operation.
Do not install the SUN2000 in areas with flammable or explosive materials.
Do not install the SUN2000 at a place within children's reach.
Do not install the SUN2000 outdoors in salt areas because it will be corroded
there and may cause fire. A salt area refers to the region within 500 meters
from the coast or prone to sea breeze. The regions prone to sea breeze vary
depending on weather conditions (such as typhoons and monsoons) or terrains
(such as dams and hills).
The SUN2000 must be installed in a well-ventilated environment to ensure
good heat dissipation.
Recommended: Install the SUN2000 in a sheltered place or a place with an
awning.
Mounting Structure Requirements
The mounting structure where the SUN2000 is installed must be fireproof.
Do not install the SUN2000 on flammable building materials.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
22
The SUN2000 is heavy. Ensure that the installation surface is solid enough to
bear the weight load.
In residential areas, do not install the SUN2000 on drywalls or walls made of
similar materials which have a weak sound insulation performance because the
noise generated by the SUN2000 is noticeable.
4.3.2 Space Requirements
Installation Angle Requirements
The SUN2000 can be wall-mounted or pole-mounted. The installation angle
requirements are as follows:
Install the SUN2000 vertically or at a maximum back tilt of 15 degrees to
facilitate heat dissipation.
Do not install the SUN2000 at forward tilted, excessive back tilted, side tilted,
horizontal, or upside down positions.
Figure 4-1 Installation tilts
Installation Space Requirements
Reserve enough space around the SUN2000 to ensure sufficient space for
installation and heat dissipation.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
23
Figure 4-2 Installation space
When installing multiple SUN2000s, install them in horizontal mode if
sufficient space is available and install them in triangle mode if no sufficient
space is available. Stacked installation is not recommended.
Figure 4-3 Horizontal installation (recommended)

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
24
Figure 4-4 Staggered installation (recommended)

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
25
Figure 4-5 Stacked installation (not recommended)
4.4 Moving an Inverter
Procedure
Step 1 Two persons are required to move the inverter and one person on both sides. Lift
the inverter from the packing case and move it to the specified installation position.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
26
To prevent personal injury and damage to the device, take care to keep your
balance when moving the SUN2000.
Do not use the wiring terminals and ports at the bottom to support any weight
of the SUN2000.
When you need to temporally place the SUN2000 on the ground, use foam,
paper or other protective materials to prevent damage to its enclosure.
Figure 4-6 Moving an inverter
----End
4.5 Installing the Mounting Bracket
Installation Precautions
Figure 4-7 shows the dimensions of installation holes on the SUN2000.
Figure 4-7 Mounting bracket dimensions

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
27
(1) Bolt
(2) Nut
(3) Spring washer
(4) Flat washer
(5) Expansion tube
Two M6 screw holes are reserved on both left and right sides of the enclosure for installing
an awning.
4.5.1 Wall-mounted Installation
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the installation positions for drilling holes, and mark the positions using
a marker.
Step 2 Secure the mounting brackets.
M6x60 expansion bolts are delivered with the SUN2000. If the length and amount of the
bolts do not meet installation requirements, prepare M6 stainless steel expansion bolts by
yourself.
The expansion bolts delivered with the inverter are used for solid concrete walls. For other
types of walls, prepare bolts by yourself and ensure that the wall meets the load bearing
requirements of the inverter.
Figure 4-8 Expansion bolt composition
Avoid drilling holes in the utility pipes or cables attached to the back of the wall.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
28
To prevent dust inhalation or contact with eyes, wear safety goggles and an
anti-dust respirator when drilling holes.
Clean up any dust in and around the holes using a vacuum cleaner and measure
the distance between holes. If large hole tolerance exists, position and drill holes
again.
After removing the bolt, spring washer, and flat washer, level the front of the
expansion tube with the concrete wall. Otherwise, the mounting brackets will
not stay steady on the concrete wall.
Partially loosen the nut, flat washer and spring washer of the two expansion
bolts below.
Figure 4-9 Installing the Mounting Bracket
Step 3 (Optional) Install the locking screw for the DC switch.
The screws for DC switches are delivered with solar inverters. According to Australian
standards, the screws are used to secure DC switches (DC SWITCH) to prevent them from
being turned on by mistake.
For the model used in Australia, perform this step to meet the local standards.
Figure 4-10 Installing a locking screw for the DC switch
Step 4 Install the SUN2000 onto the mounting bracket.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
29
Step 5 Tighten nuts.
Figure 4-11 Installing the SUN2000
Step 6 (Optional) Install the anti-theft lock.
Prepare an anti-theft lock suitable for the lock hole diameter (Ф8 mm) by
yourself.
An outdoor waterproof lock is recommended.
Keep the key to the anti-theft lock safe.
Figure 4-12 Installing the anti-theft lock
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
30
4.5.2 Support-mounted Installation
Prerequisites
Prepare M6 stainless bolt assemblies (including flat washers, spring washers, and
M6 bolts) with appropriate lengths as well as matched flat washers and nuts based
on the support specifications.
Procedure
Step 1 Determine the hole positions based on the marking-off template, and then mark
the hole positions using a marker.
Figure 4-13 Determining hole positions
Step 2 Drill holes using a hammer drill.
You are advised to apply anti-rust paint on the hole positions for protection.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
31
Figure 4-14 Drilling holes
Step 3 Secure the mounting bracket.
Figure 4-15 Securing the mounting bracket
Step 4 Install the SUN2000 onto the mounting bracket.
Step 5 Tighten the bolt assembly.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
4 Installation
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
32
Figure 4-16 Installing the SUN2000
Step 6 (Optional) Install the anti-theft lock.
Prepare an anti-theft lock suitable for the lock hole diameter (Ф8 mm) by
yourself.
An outdoor waterproof lock is recommended.
Keep the key to the anti-theft lock safe.
Figure 4-17 Installing the anti-theft lock
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
33
Precautions
5 Electrical Connections
Before connecting cables, ensure that the DC switch on the SUN2000 and all the
switches connecting to the SUN2000 are OFF. Otherwise, the high voltage of the
SUN2000 may result in electric shocks.
The equipment damage caused by incorrect cable connections is beyond the
warranty scope.
Only certified electricians are allowed to connect cables.
Operation personnel must wear proper PPE when connecting cables.
The cable colors shown in the electrical connection diagrams provided in this chapter are for
reference only. Select cables in accordance with local cable specifications (green-and-yellow
cables are only used for PE).

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
34
5.1 Preparing for Installation
No.
Component
Description
Source
A
PV module
A PV string is composed of the PV
modules connected in series.
The SUN2000 supports the input
from four PV strings.
Prepared by the customer
B
Smart PV optimizer
The SUN2000-450W-P smart PV
optimizer is supported.
Purchased from Huawei
C
DC switch
Recommended: a PV circuit breaker with
a rated voltage greater than or equal to
1100 V DC and a rated current of 15 A.
Prepared by the customer
D
Smart Donglea
WLAN-FE Smart Dongle:
SDongleA-05.
4G Smart Dongle: SDongleA-03.
Purchased from Huawei
Figure 5-1 SUN2000 cable connections (optional in dashed boxes)
If the Smart Dongle is configured, you are advised to install the Smart Dongle
before connecting the signal cable.
Table 5-1 Component description

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
35
No.
Component
Description
Source
E
SUN2000
Select a proper model based on
requirements.
Purchased from Huawei
F
SmartLogger
Select a proper model based on
requirements.
Purchased from Huawei
G
Smart Power
Sensor
The recommended electricity meter
model is DTSU666-H.
Purchased from Huawei
H
Ripple Control
Device
Select the devices that meet the power
grid scheduling requirements.
Provided by local power
grid companies
I
Rapid shutdown
switch
Select a proper model based on
requirements.
Prepared by the customer
J
AC switchb
Recommended: a three-phase AC circuit
breaker with a rated voltage greater
than or equal to 415 V AC and a rated
current of:
25 A (SUN2000-8KTL-M2,
SUN2000-10KTL-M2,
SUN2000-12KTL-M2)
40 A (SUN2000-15KTL-M2,
SUN2000-17KTL-M2,
SUN2000-20KTL-M2)
Prepared by the customer
Note a: WLAN-FE Smart Dongle: For details about the SDongleA-05 operation, see
SDongleA-05
Quick Guide (WLAN-FE)
; 4G Smart Dongle: For details about the SDongleA-03 operation, see
SDongleA-03 Quick Guide (4G)
. You can obtain the quick guide at
https://support.huawei.com/enterprise by searching for the Smart Dongle model.
Note b: SUN2000-8KTL-M2 and SUN2000-10KTL-M2 inverters are applicable only to Australia.
No.
Name
Type
Recommended Specifications
1
DC input power cable
Standard PV cable in
the industry
Conductor cross-sectional area: 4–6
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 5.5–9 mm
2
(Optional) RS485
communications cable
(used to cascade
inverters or connect to
the RS485 signal port on
the SmartLogger)
Two-core outdoor
shielded twisted pair
cable
Conductor cross-sectional area: 0.2–1
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 4–11 mm
Table 5-2 Cable description

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
36
No.
Name
Type
Recommended Specifications
3
(Optional) RS485
communications cable
(used to connect to the
RS485 signal port on a
Smart Power Sensor for
export limitation)
Two-core outdoor
shielded twisted pair
cable
Conductor cross-sectional area: 0.2–1
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 4–11 mm
4
(Optional) Rapid
shutdown switch signal
cable
Two-core outdoor
shielded twisted pair
cable
Conductor cross-sectional area: 0.2–1
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 4–11 mm
5
(Optional) Grid
scheduling signal cable
Five-core outdoor
cable
Conductor cross-sectional area: 0.2–1
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 4–11 mm
6
AC output power cablea
Outdoor copper
cableb
SUN2000-8KTL-M2,
SUN2000-10KTL-M2,
SUN2000-12KTL-M2:
Conductor cross-sectional area: 6–16
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 11–26 mm
SUN2000-15KTL-M2,
SUN2000-17KTL-M2,
SUN2000-20KTL-M2:
Conductor cross-sectional area: 10–16
mm2
Cable outer diameter: 11–26 mm
7
PE cable
Single-core outdoor
copper cablec
SUN2000-8KTL-M2,
SUN2000-10KTL-M2,
SUN2000-12KTL-M2: Conductor
cross-sectional area ≥ 6 mm2
SUN2000-15KTL-M2,
SUN2000-17KTL-M2,
SUN2000-20KTL-M2: Conductor
cross-sectional area ≥ 10 mm2
Note a: The minimum cable diameter depends on the fuse rating on the AC side.
Note b: The SUN2000-8KTL-M2 and SUN2000-10KTL-M2 inverters are applicable only to
Australia.
Note c: The SUN2000-8KTL-M2 and SUN2000-10KTL-M2 inverters are applicable only to
Australia.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
37
The minimum cable diameter should comply with the local cable standard.
Factors influencing cable selection are as follows: nominal AC current, type of cable,
routing method, ambient temperature, and maximum desired line losses.
5.2 Connecting the PE cable
Precautions
Ensure that the PE cable is properly connected. If it is disconnected or loose,
electric shocks may occur.
Do not connect the neutral wire to the enclosure as a PE cable. Otherwise,
electric shocks may occur.
The PE point at the AC output port is used only as a PE equipotential point, and cannot
substitute for the PE point on the enclosure.
After the ground cable is installed, it is recommended that the silica gel or paint be
applied to the ground terminal for protection.
Additional Information
The SUN2000 has the grounding detection function. This function detects whether
the SUN2000 is grounded properly before its startup, or whether the ground cable is
disconnected when the SUN2000 is running. This function works under limited
conditions. To ensure the safe operation of the SUN2000, ground the SUN2000
properly according to the connection requirements of the PGND cable. For some
power grid types, if the output side of the inverter is connected to an isolation
transformer, ensure that the inverter is properly grounded and set isolation
settings to Input not grounded, with a transformer to enable the inverter to run
properly.
According to IEC62109, to ensure safe application in case of the ground cable is
damaged or disconnected, connect the PE cable properly before the grounding
detection function is disabled. Ensure that the PE cable meets at least one of
the following requirements.
− The PE cable is a single-core outdoor copper cable with a conductor
− Use cables that have the same diameter as the AC output cable, and
cross-sectional area of at least 10 mm 2.
ground the PE terminal on the AC connector and the ground screw on the
enclosure respectively.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
38
Procedure
(1) Cable
(2) Core wire
(3) Heat shrink tubing
(4) OT terminal
(5) Crimping tool
(6) Heat gun
Step 1 Crimp the OT terminal.
In some countries and regions, additional ground cables are required for the
SUN2000. In this case, use cables that have the same diameter as the AC
output cable, and ground the PE terminal on the AC connector and the ground
screw on the enclosure respectively.
Pay attention not to damage the core wire when stripping a cable.
The cavity formed after crimping the conductor strip of the OT terminal needs to
wrap the core wire completely. The core wire needs to contact the OT terminal
closely.
Wrap the wire crimping area with the heat shrink tubing or the PVC insulation
tape. The following figure uses the heat shrink tubing as an example.
When using the heat gun, protect devices from being scorched.
Figure 5-2 Crimping an OT terminal

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
39
Step 2 Connect the PE cable.
Figure 5-3 Connecting the PE cable
----End
5.3 Connecting the AC Output Power Cable
Precautions
A three-phase AC switch needs to be installed on the AC side of the SUN2000. To
ensure that the SUN2000 can safely disconnect itself from the power grid when an
exception occurs, select a proper overcurrent protection device in compliance with
local power distribution regulations.
Do not connect loads between the SUN2000 and the AC switch directly connected
to it.
The SUN2000 is integrated with a comprehensive residual current monitoring unit.
Once detecting that the residual current exceeds the threshold, the SUN2000
immediately disconnects itself from the power grid.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
40
If the external AC switch can perform earth leakage protection, the rated
leakage action current should be greater than or equal to 100 mA.
If multiple SUN2000s connect to the general residual current device (RCD)
through their respective external AC switches, the rated leakage action current of
the general RCD should be greater than or equal to the number of SUN2000s
multiplied by 100 mA.
A knife switch cannot be used as an AC switch.
The hex key is delivered with the inverter and bound to the hanging kit at the
bottom of the inverter.
Figure 5-4 Hex key
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the AC output power cable to the AC connector.
Figure 5-5 Stripping requirements

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
41
Ensure that the cable jacket is inside the connector.
Ensure that the exposed core wire is totally inserted into the cable hole.
Ensure that AC terminations provide firm and solid electrical connections. Failing
to do so may cause SUN2000 malfunction and damage to its AC connectors.
Ensure that the cable is not twisted.
Figure 5-6 Three-core cable (L1, L2, and L3)
Figure 5-7 Four-core cable (L1, L2, L3, and PE)

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
42
Figure 5-8 Four-core cable (L1, L2, L3, and N)
Figure 5-9 Five-core cable (L1, L2, L3, N, and PE)
The cable colors shown in the figures are for reference only. Select an appropriate cable
according to local standards.
Step 2 Connect the AC connector to the AC output port.
Ensure that the AC connector is connected securely.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
43
Figure 5-10 Securing the AC connector
Step 3 Check the route of the AC output power cable.
Figure 5-11 Cable route
----End
Disconnection
Disconnection can be performed in reverse order.
5.4 Connecting the DC input power cable
Precautions

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
44
Before connecting the DC input power cable, ensure that the DC voltage is within
the safe range (lower than 60 V DC), and that the DC SWITCH is set to the OFF
position. Failure to do so could generate high voltage, which may cause electric
shocks.
When the SUN2000 is operating, it is not allowed to operate the DC input power
cable, such as connecting or disconnecting a PV string or a PV module in a PV
string. Failing to do so may cause electric shocks.
If no PV string is connected to a DC input terminal of the SUN2000, do not
remove the watertight cap from the terminal. Otherwise, the IP rating of the
SUN2000 will be affected.
Ensure that the following conditions are met. Otherwise, the SUN2000 may be
damaged, or even a fire could happen.
PV modules connected in series in each PV string are of the same specifications.
The open-circuit voltage of each PV string is always lower than or equal to 1080
V DC.
The maximum short-circuit current of each PV string must be lower than or
equal to 15 A.
The DC input power cable is correctly connected. The positive and negative
terminals of a PV module are connected to corresponding positive and negative
DC input terminals of the SUN2000.
If the DC input power cable is reversely connected, do not operate the DC switch
and positive and negative connectors. Wait until the solar irradiance declines at
night and the PV string current reduces to below 0.5 A, and then turn off the DC
switch. Remove the positive and negative connectors to correct the polarity.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
45
(1) Terminals of DC input 1
(2) Terminals of DC input 2
(3) Terminals of DC input 3
(4) Terminals of DC input 4
Because the output of the PV string connected to the SUN2000 cannot be
grounded, ensure that the PV module output is insulated to ground.
The PV strings connecting to the same MPPT route should contain the same
number and model of PV modules or Smart PV optimizers.
During the installation of PV strings and the SUN2000, the positive or negative
terminals of PV strings may be short-circuited to ground if power cables are not
properly installed or routed. An AC or DC short circuit may occur and damage the
device when the SUN2000 is operating. The caused device damage is not covered
under any warranty.
Terminal Description
Figure 5-12 Terminals
Procedure
Before inserting the positive and negative connectors into the positive and negative
DC input terminals of the SUN2000, check that the DC SWITCH is OFF.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
46
Cables with high rigidity, such as armored cables, are not recommended as DC
input power cables, because poor contact may be caused by the bending of the
cables.
Before assembling DC connectors, label the cable polarities correctly to ensure
correct cable connections.
After crimping the positive and negative metal contacts, pull the DC input power
cables back to ensure that they are connected securely.
Insert the crimped metal contacts of the positive and negative power cables into
the appropriate positive and negative connectors. Then pull back the DC input
power cables to ensure that they are connected securely.
If the DC input power cable is reversely connected and the DC SWITCH is set to
the ON position, do not operate the DC SWITCH and positive and negative
connectors. Otherwise, the device may be damaged. The caused device damage
is not covered under any warranty. Wait until the solar irradiance declines and
the PV string current drops to below 0.5 A. Then set the two DC SWITCH to the
OFF position, remove the positive and negative connectors, and rectify the
connection of the DC input power cable.
The DC voltage measurement range of the multimeter must be at least 1080 V. If the
voltage is a negative value, the DC input polarity is incorrect and needs correction. If the
voltage is greater than 1080 V, too many PV modules configured in the same string.
Remove some PV modules.
If the PV string is configured with an optimizer, check the cable polarity by referring to the
Smart PV optimizer quick guide.
Step 1 Connect the DC input power cable.
Use the Staubli MC4 positive and negative metal terminals and DC connectors
delivered with the SUN2000. Using incompatible positive and negative metal
terminals and DC connectors may result in serious consequences. The caused device
damage is not covered under any warranty or service agreement.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
47
Figure 5-13 Assembling a DC connector
----End
Removing a DC connector
Before removing the positive and negative connectors, ensure that the DC SWITCH
is OFF.
To remove the positive and negative connectors from the SUN2000, insert an
open-end wrench into the notch and press hard to remove the DC connector.
Figure 5-14 Removing a DC connector

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
48
5.5 (Optional) Installing the Smart Dongle
Procedure
If WLAN-FE communication is used, install a WLAN-FE Smart Dongle (SDongleA-05).
If 4G communication is used, install a 4G Smart Dongle (SDongleA-03).
You need to purchase the Smart Dongle by yourself.
WLAN-FE Smart DongleDongle (FE Communication)
You are advised to use a CAT 5E outdoor shielded network cable (outer
diameter < 9 mm; internal resistance ≤ 1.5 ohms/10 m) and shielded RJ45
connectors.
Figure 5-15 Installing a WLAN-FE Smart Dongle (FE communication)
4G Smart Dongle (4G Communication)
If you prepared a Smart Dongle without a SIM card, you need to prepare a standard SIM
card (size: 25 mm x 15 mm) with the capacity greater than or equal to 64 KB.
When installing the SIM card, determine its installation direction based on the silk screen
and arrow on the card slot.
When being pressed into place, the SIM card will be locked, which means that the card is
installed correctly.
To remove the SIM card, push it inwards. Then the SIM card springs out automatically.
When reinstalling the WLAN-FE Smart Dongle or 4G Smart Dongle, ensure that the
buckle springs back in place.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
49
Figure 5-16 Installing the 4G Smart Dongle
There are two types of Smart Dongle:
For details about how to use the WLAN-FE Smart Dongle SDongleA-05, see the
SDongleA-05 Quick Guide (WLAN-FE)
document.
. You can also scan the QR code to obtain the
For details about how to use the 4G Smart Dongle SDongleA-03, see the
Quick Guide (4G)
The quick guide is delivered with the Smart Dongle.
. You can also scan the QR code to obtain the document.
5.6 (Optional) Installing the Signal Cable
Communication port signal definitions
SDongleA-03

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
50
Pin
Defini
tion
Function
Description
Pin
Defini
tion
Function
Description
1
485A1
-1
RS485
differential
signal+
Used to
connect to the
RS485 signal
port on the
SUN2000 or
SmartLogger10
00
2
485A1
-2
RS485
differential
signal+
Used to
connect to the
RS485 signal
port on the
SUN2000 or
SmartLogger10
00A
3
485B1
-1
RS485
differential
signal–
4
485B1
-2
RS485
differential
signal–
5
PE
Shielding
ground
N/A
6
PE
Shielding
ground
N/A
7
485A2
RS485
differential
signal+
Used to
connect to an
RS485 signal
port on a Smart
Power Sensor
for export
limitation
8
DIN1
Dry contact
interface for
grid
scheduling
Connects to the
Ripple Control
Device.
9
485B2
RS485
differential
signal–
10
DIN2
Not all inverter models are delivered with the signal cable connector.
When routing the signal cable, ensure that it is separate from the power cable
and away from interfering sources to prevent communication from being
affected.
The protection layer of the cable is in the connector. Cut off surplus core wires
from the protection layer. Ensure that the core wires are completely inserted into
the cable holes, and that the cable is securely connected.
If the Smart Dongle is configured, you are advised to install the Smart Dongle
before connecting the signal cable.
Figure 5-17 Signal definitions
Table 5-3 Signal definitions

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
51
Pin
Defini
tion
Function
Description
Pin
Defini
tion
Function
Description
11
N/A
N/A
N/A
12
DIN3
13
GND
GND
Used to
connect to the
rapid shutdown
DI signal port
and served as a
reserved port
for the signal
cable of the NS
protection.
14
DIN4
15
DIN5
Rapid
shutdown
signal+
16
GND
Communication Networking
Smart Dongle Networking Scenario
Figure 5-18 Smart Dongle networking
In the Smart Dongle networking scenario, the SmartLogger cannot be connected.
The Smart Power Sensor is necessary for export limitation. Only the DTSU666-H Smart
Power Sensor (provided by Huawei) can be used.
The Smart Power Sensor and Smart Dongle need to be connected to the same inverter.
SmartLogger Networking Scenario

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
52
Figure 5-19 SmartLogger networking
In the SmartLogger networking scenario, the Smart Dongle cannot be connected.
A maximum of 80 devices can connect to a single SmartLogger, such as inverters, Smart
Power sensor, and EMI. You are advised to connect fewer than 30 devices to each RS485
route.
The Smart Power Sensor is necessary for export limitation. Select the Smart Power
Sensor according to the actual project.
To ensure the system response speed, the Smart Power Sensor is recommended to be
connected to a COM port separately from inverter COM port.
5.6.1 Connecting the RS485 Communications Cable (Inverter Cascading)
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the signal cable to the signal cable connector.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
53
Figure 5-20 Installing the cable
Step 2 Connect the signal cable connector to the COM port.
Figure 5-21 Securing the signal cable connector
----End
5.6.2 Connecting the RS485 Communications Cable (Smart Power Sensor)
Cable Connection
The following figure shows the cable connections between the inverter and the
Smart Power Sensor.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
54
Figure 5-22 Cable connection (Three Phase Three Wire)

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
55
Figure 5-23 Cable connection (Three Phase Four Wire)
(1) Shielding layer of the signal cable
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the signal cable to the signal cable connector.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
56
Figure 5-24 Installing the cable
Step 2 Connect the signal cable to the COM port.
Figure 5-25 Securing the signal cable connector
----End
5.6.3 Connecting the Rapid shutdown signal cable
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the signal cable to the signal cable connector.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
57
If optimizers are configured for some PV modules, the rapid shutdown function is
not supported.
To enable the rapid shutdown function, you need to connect the access switch to
pins 13 and 15. The switch is closed by default. The rapid shutdown is triggered
when the switch changes from closed to open.
Figure 5-26 Installing the cable
Step 2 Connect the signal cable connector to the COM port.
Figure 5-27 Securing the signal cable connector
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
58
5.6.4 Connecting the Power Grid Scheduling Signal Cable
Cable Connection
The following figure shows the cable connections between the inverter and the
Ripple Control Device.
Figure 5-28 Cable connection
Procedure
Step 1 Connect the signal cable to the signal cable connector.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
5 Electrical Connections
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
59
Figure 5-29 Installing the cable
Step 2 Connect the signal cable to the COM port.
Figure 5-30 Securing the signal cable connector
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
6 Commissioning
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
60
6.1 Check Before Power-On
No.
Check Item
Acceptance Criteria
1
SUN2000 installation
The SUN2000 is installed correctly, securely, and
reliably.
2
Smart Dongle
The Smart Dongle is installed correctly and
securely.
3
Cable layout
Cables are routed properly as required by the
customer.
4
Cable tie
Cable ties are secured evenly and no burr exists.
5
Grounding
The ground cable is connected correctly, securely,
and reliably.
6
Turn off the switches
The DC SWITCH and all the switches connected
to the SUN2000 are set to OFF.
7
Cable connections
The AC output power cable, DC input power
cable, and signal cable are connected correctly,
securely, and reliably.
8
Unused terminals and ports
Unused terminals and ports are locked by
watertight caps.
9
Installation environment
The installation space is proper, and the
installation environment is clean and tidy,
without foreign matter.
Table 6-1 Installation checklist
6 Commissioning

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
6 Commissioning
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
61
6.2 Powering On the System
Category
Status
Meaning
Running
indication
LED1
LED2
N/A
Steady green
Steady green
The SUN2000 is operating in
grid-tied mode.
Precautions
Before turning on the AC switch between the SUN2000 and the power grid, use a
multimeter set to the AC position to check that the AC voltage is within the
specified range.
If the DC is on and the AC is off, the SUN2000 reports a Grid Failure alarm. The
SUN2000 starts normally only after the fault is automatically rectified.
Procedure
Step 1 Turn on the AC switch between the SUN2000 and the power grid.
Step 2 (Optional) Remove the locking screw from the DC switch.
Figure 6-1 Removing the locking screw from a DC switch
Step 3 If there is a DC switch between the PV string and the inverter, turn on the DC switch.
Step 4 Set the DC SWITCH at the bottom of the SUN2000 to the ON position.
Step 5 Wait for about 1 minute, and then observe the LED indicators of the inverter to
check the running status.
Table 6-2 LED indicator description

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
6 Commissioning
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
62
Category
Status
Meaning
Blinking green
at long
intervals (on
for 1s and then
off for 1s)
Off
The DC is on and the AC is off.
Blinking green
at long
intervals (on
for 1s and then
off for 1s)
Blinking green at long
intervals (on for 1s and
then off for 1s)
The DC is on, the AC is on, and the
SUN2000 is not exporting power to
the power grid.
Off
Blinking green at long
intervals (on for 1s and
then off for 1s)
The DC is off and the AC is on.
Off
Off
Both the DC and AC are off.
Blinking red at
short intervals
(on for 0.2s
and then off
for 0.2s)
N/A
There is a DC environmental alarm,
such as an alarm indicating that
High String Input Voltage, String
Reverse Connection, or Low
Insulation Resistance.
N/A
Blinking red at short
intervals (on for 0.2s and
then off for 0.2s)
There is an AC environmental alarm,
such as an alarm indicating Grid
Undervoltage, Grid Overvoltage,
Grid Overfrequency, or Grid
Underfrequency.
Steady red
Steady red
Fault
Communicatio
n indication
LED3
N/A
Blinking green at short intervals (on for
0.2s and then off for 0.2s)
Communication is in progress.
(When a mobile phone is connected
to the SUN2000, the indicator first
indicates that the phone is
connected to the SUN2000): blinks
green at long intervals.)
Blinking green at long intervals (on for 1s
and then off for 1s)
The mobile phone is connected to
the SUN2000.
Off
There is no communication.
Device
replacement
indication
LED1
LED2
LED3
N/A
Steady red
Steady red
Steady red
The SUN2000 hardware is faulty.
The SUN2000 needs to be replaced.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
6 Commissioning
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
63
LED Color
Status
Remarks
Description
N/A
Off
Normal
The Dongle is not secured or
is not powered on.
Yellow (blinking
green and red
simultaneously)
Steady on
The Dongle is secured and
powered on.
Red
Blinking at short
intervals (on for 0.2s
and then off for 0.2s)
The parameters for
connecting to the router are
to be set.
Steady on
Abnormal
The Dongle is faulty. Replace
the Dongle.
Green
Blinking at long
intervals (on for 0.5s
and then off for 0.5s)
Normal
Connecting to the router.
Steady on
Successfully connected to
the management system.
Blinking at short
intervals (on for 0.2s
and then off for 0.2s)
The inverter is
communicating with the
management system
through the Dongle.
Step 6 (Optional) Observe the LED to check the operating status of the Smart Dongle.
WLAN-FE Smart Dongle
Figure 6-2 WLAN-FE Smart Dongle
Table 6-3 LED indicator description

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
6 Commissioning
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
64
LED Color
Status
Remarks
Description
N/A
Off
Normal
The Dongle is not secured or
is not powered on.
Yellow (blinking
green and red
simultaneously)
Steady on
Normal
The Dongle is secured and
powered on.
Green
Blinking in a 2-second
cycle (on for 0.1s and
then off for 1.9s)
Normal
Dialing (duration < 1 min).
Abnormal
If the duration is longer than
1 min, the 4G parameter
settings are incorrect. Reset
theparameters.
Blinking at long intervals
(on for 1s and then off
for 1s)
Normal
The dial-up connection is set
up successfully (duration <
30s).
Abnormal
If the duration is longer than
30s, the settings of the
management system
parameters are incorrect.
Reset the parameters.
Steady on
Normal
Successfully connected to
the management system.
Blinking at short
intervals (on for 0.2s and
then off for 0.2s)
The inverter is
communicating with the
management system
through the Dongle.
Red
Steady on
Abnormal
The Dongle is faulty. Replace
Dongle.
Blinking at short
intervals (on for 0.2s and
then off for 0.2s)
The Dongle has no SIM card
or the SIM card is in poor
contact. Check whether the
SIM card has been installed
or is in good contact. If not,
install the SIM card or
remove and insert the SIM
card.
4G Smart Dongle
Table 6-4 LED indicator description

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
6 Commissioning
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
65
LED Color
Status
Remarks
Description
Blinking at long intervals
(on for 1s and then off
for 1s)
The Dongle fails to connect
to the management system
because it has no signals,
weak signal, or no traffic. If
the Dongle is reliably
connected, check the SIM
card signal through the APP.
If no signal is received or the
signal strength is weak,
contact the carrier. Check
whether the tariff and traffic
of the SIM card are normal.
If not, recharge the SIM card
or buy traffic.
Blinking red and
green alternatively
Blinking at long intervals
(on for 1s and then off
for 1s)
No communication with the
inverter.
Remove and insert the
Dongle.
Check whether inverters
match the Dongle.
Connect the Dongle to
other inverters. Check
whether the Dongle or
the USB port of the
inverter is faulty.
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
66
7 Man-Machine Interaction
7.1 App Commissioning
7.1.1 Downloading the FusionSolar App
Search for FusionSolar in Google Play (Android) to download and install the app.
You can also scan one of the following QR codes to obtain the app.
Figure 7-1 QR code
The latest Android version must be used for device commissioning. The iOS version is not
updated and can be used only for viewing PV plant information. For iOS users, you can
search for FusionSolar in the App Store or scan the following QR code to download the
iOS version.
The screenshots are for reference only. The actual screens prevail.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
67
7.1.2 (Optional) Registering an Installer Account
If you have an installer account, skip this step.
You can register an account only using a mobile phone only in China.
The mobile number or email address used for registration is the user name for logging in
to the FusionSolar app.
Create the first installer account and create a domain named after the company
name.
Figure 7-2 Creating the first installer account
To create multiple installer accounts for a company, log in to the FusionSolar app
and tap New User to create an installer account.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
68
Figure 7-3 Creating multiple installer accounts for the same company
7.1.3 Creating a PV Plant and a User
Figure 7-4 Creating a PV plant and a user
For details about how to use the site deployment wizard, see
You can also scan the QR code to obtain the document.
FusionSolar App Quick Guide
.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
69
7.1.4 (Optional) Setting the Physical Layout of the Smart PV Optimizers
If smart PV optimizers are configured for PV strings, ensure that the smart PV optimizers
have been successfully connected to the SUN2000 before performing the operations in
this section.
Check that the SN labels of smart PV optimizers are correctly attached to the physical
layout template.
Take and save a photo of the physical layout template. Keep your phone parallel to the
template and take a photo in landscape mode. Ensure that the four positioning points in
the corners are in the frame. Ensure that each QR code is attached within the frame.
For details about the physical layout of smart PV optimizers, see
Guide
. You can also scan the QR code to obtain the document.
FusionSolar App Quick
Scenario 1: Setting on the FusionSolar Server Side (Solar Inverter Connected
to the Management System)
Step 1 Log in to the FusionSolar app and tap the plant name on the Home screen to access
the plant screen. Select Plant layout, tap , and upload the physical layout
template photo as prompted.
Figure 7-5 Uploading the physical layout template photo (App)
You can also upload the physical layout template photo on the WebUI as follows: Log in to
https://intl.fusionsolar.huawei.com to access the WebUI of the FusionSolar Smart PV
Management System. On the home page, click the plant name to go to the plant page.
Choose Plant layout, click Add Physical Layout > , and upload the physical layout
template photo.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
70
Figure 7-6 Uploading the physical layout template photo (WebUI)
Step 2 Log in to https://intl.fusionsolar.huawei.com to access the WebUI of the FusionSolar
Smart PV Management System. On the Homepage page, click the plant name to go
to the plant page. Select Plant layout. Choose > Generate with AI, and create
a physical layout as prompted. You can also manually create a physical location
layout.
Figure 7-7 Physical layout design of PV modules
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
71
Scenario 2: Setting on the Solar Inverter Side (Solar Inverter Not Connected
to the Management System)
Step 1 Access the Device Commissioning screen on the FusionSolar app to set the physical
layout of Smart PV Optimizers.
1. Log in to the FusionSolar app. On the Device Commissioning screen, choose
Maintenance > Physical layout design of PV modules. The Physical layout
design of PV modules screen is displayed.
2. Tap the blank area. The Identify image and Add PV modules buttons are
displayed. You can use either of the following methods to perform operations
as prompted:
− Method 1: Tap Identify image and upload the physical layout template
photo to complete the optimizer layout. (The optimizers that fail to be
identified need to be manually bound.)
− Method 2: Tap Add PV modules to manually add PV modules and bind the
optimizers to the PV modules.
Figure 7-8 Physical layout design of PV modules
----End
7.1.5 Detect optimizer disconnection
On the SUN2000 screen, choose Maintenance > Optimizer disconnection
detection, tap the detection button to detect the optimizer disconnection, and
rectify the fault based on the detection result.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
72
Figure 7-9 Detect optimizer disconnection
7.2 Parameters Settings
Go to the Device Commissioning screen and set SUN2000 parameters. For details
about entering the Device Commissioning screen, see B Device Commissioning.
To set more parameters, tap Settings. For details about the parameters, see the
FusionSolar APP and SUN2000 App User Manual
obtain the document.
7.2.1 Energy Control
On the home screen, tap Power adjustment to perform the corresponding
operation.
Figure 7-10 Energy control
. You can also scan the QR code to

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
73
7.2.1.1 Grid-tied Point Control
Parameter Name
Description
Active
power
Unlimited
-
If this parameter is set to Unlimited, the output power of the
SUN2000 is not limited and the SUN2000 can connect to the
power grid at the rated power.
Grid
connectio
n with
zero
power
Closed-loop
controller
If multiple SUN2000s are cascaded, set this parameter to
SDongle/SmartLogger.
If there is only one SUN2000, set this parameter to
Inverter.
Limitation
mode
Total power indicates export limitation of the total power at
the grid-tied point.
Power
adjustment
period
Specifies the shortest interval for a single anti-backfeeding
adjustment.
Power control
hysteresis
Specifies the dead zone for adjusting the SUN2000 output
power. If the power fluctuation is within the power control
hysteresis, the power is not adjusted.
Active power
output limit
for fail-safe
Specifies the derating value of the SUN2000 active power by
percentage. If the Smart Dongle does not detect any meter
data or the communication between the Smart Dongle and
the SUN2000 is disconnected, the Smart Dongle delivers the
derating value of the SUN2000 active power by percentage.
Function
Limits or reduces the output power of the PV power system to ensure that the
output power is within the power deviation limit.
Procedure
Step 1 On the home screen, choose Power adjustment > Grid-tied point control.
Figure 7-11 Grid-tied point control
Table 7-1 Grid-tied point control

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
74
Parameter Name
Description
Communicatio
n
disconnection
fail-safe
In the SUN2000 anti-backfeeding scenario, if this parameter
is set to Enable, the SUN2000 will derate according to the
active power derating percentage when the communication
between the SUN2000 and the Smart Dongle is disconnected
for a period longer than Communication disconnection
detection time.
Communicatio
n
disconnection
detection time
Specifies the time for determining the communication
disconnection between the SUN2000 and the Dongle.
This parameter is displayed when Communication
disconnection fail-safe is set to Enable.
Grid
connectio
n with
limited
power
(kW)
Closed-loop
controller
If multiple SUN2000s are cascaded, set this parameter to
SDongle/SmartLogger.
If there is only one SUN2000, set this parameter to
Inverter.
Limitation
mode
Total power indicates export limitation of the total power at
the grid-tied point.
Maximum grid
feed-in power
Specifies the maximum active power transmitted from the
grid-tied point to the power grid.
Power
adjustment
period
Specifies the shortest interval for a single anti-backfeeding
adjustment.
Power control
hysteresis
Specifies the dead zone for adjusting the SUN2000 output
power. If the power fluctuation is within the power control
hysteresis, the power is not adjusted.
Active power
output limit
for fail-safe
Specifies the derating value of the SUN2000 active power by
percentage. If the Smart Dongle does not detect any meter
data or the communication between the Smart Dongle and
the SUN2000 is disconnected, the Smart Dongle delivers the
derating value of the SUN2000 active power by percentage.
Communicatio
n
disconnection
fail-safe
In the SUN2000 anti-backfeeding scenario, if this parameter
is set to Enable, the SUN2000 will derate according to the
active power derating percentage when the communication
between the SUN2000 and the Smart Dongle is disconnected
for a period longer than Communication disconnection
detection time.
Communicatio
n
disconnection
detection time
Specifies the time for determining the communication
disconnection between the SUN2000 and the Dongle.
This parameter is displayed when Communication
disconnection fail-safe is set to Enable.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
75
Parameter Name
Description
Grid
connectio
n with
limited
power
(%)
Closed-loop
controller
If multiple SUN2000s are cascaded, set this parameter to
SDongle/SmartLogger.
If there is only one SUN2000, set this parameter to
Inverter.
Limitation
mode
Total power indicates export limitation of the total power at
the grid-tied point.
PV plant
capacity
Specifies the total maximum active power in the SUN2000
cascading scenario.
Maximum grid
feed-in power
Specifies the percentage of the maximum active power of
the grid-tied point to the PV plant capacity.
Power
adjustment
period
Specifies the shortest interval for a single anti-backfeeding
adjustment.
Power control
hysteresis
Specifies the dead zone for adjusting the SUN2000 output
power. If the power fluctuation is within the power control
hysteresis, the power is not adjusted.
Active power
output limit
for fail-safe
Specifies the derating value of the SUN2000 active power by
percentage. If the Smart Dongle does not detect any meter
data or the communication between the Smart Dongle and
the SUN2000 is disconnected, the Smart Dongle delivers the
derating value of the SUN2000 active power by percentage.
Communicatio
n
disconnection
fail-safe
In the SUN2000 anti-backfeeding scenario, if this parameter
is set to Enable, the SUN2000 will derate according to the
active power derating percentage when the communication
between the SUN2000 and the Smart Dongle is disconnected
for a period longer than Communication disconnection
detection time.
Communicatio
n
disconnection
detection time
Specifies the time for determining the communication
disconnection between the SUN2000 and the Dongle.
This parameter is displayed when Communication
disconnection fail-safe is set to Enable.
----End

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
76
7.2.2 AFCI
Function
If PV modules or cables are incorrectly connected or damaged, electric arcs may be
generated, which may cause fire. Huawei solar inverters provide arc detection
meets the requirement of UL 1699B-2018, ensuring the user safety and property.
This function is enabled by default. The solar inverter automatically detects arc
faults. To disable this function, log in to the FusionSolar app, enter the Device
Commissioning screen, choose Settings > Feature parameters, and disable AFCI.
For details about entering the Device Commissioning screen, see B Device
Commissioning.
Clearing Alarms
The AFCI function involves the DC arc fault alarm.
The SUN2000 has the AFCI alarm automatic clearance mechanism. If an alarm is
triggered for less than five times within 24 hours, the SUN2000 automatically clears
the alarm. If the alarm is triggered for more than five times within 24 hours, the
SUN2000 locks for protection. You need to manually clear the alarm on the
SUN2000 so that it can work properly.
You can manually clear the alarm as follows:
Log in to the FusionSolar app and choose My > Device Commissioning. On the
Device commissioning screen, connect and log in to the SUN2000 that generates
the AFCI alarm, tap Alarm management, and tap Clear on the right of the DC arc
fault alarm to clear the alarm.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
77
Figure 7-12 Alarm management
7.2.3 IPS Check (for Italy CEI0-21 Grid Code Only)
Function
The Italy CEI0-21 grid code requires an IPS check for the SUN2000. During the
self-check, the SUN2000 checks the protection threshold and protection time of the
maximum voltage over 10 min (59.S1), maximum overvoltage (59.S2), minimum
undervoltage (27.S1), minimum undervoltage (27.S2), maximum overfrequency
(81.S1), maximum overfrequency (81.S2), minimum underfrequency (81.S), and
minimum underfrequency (81.S2).
Procedure
Step 1 On the home screen, choose Maintenance > IPS test to access the IPS test screen.
Step 2 Tap Start to start an IPS test. The SUN2000 detects maximum voltage over 10 min
(59.S1), maximum overvoltage (59.S2), minimum undervoltage (27.S1), minimum
undervoltage (27.S2), maximum overfrequency (81.S1), maximum overfrequency
(81.S2), and minimum underfrequency (81.S1), and minimum underfrequency
(81.S2).

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
78
Figure 7-13 IPS test
IPS Test Type
Description
Maximum voltage
over 10 min
(59.S1)
The default maximum voltage over 10 min protection
threshold is 253 V (1.10 Vn), and the default protection time
threshold is 3s.
Maximum
overvoltage
(59.S2)
The default overvoltage protection threshold is 264.5 V (1.15
Vn), and the default protection time threshold is 0.2s.
Minimum
undervoltage
(27.S1)
The default undervoltage protection threshold is 195.5 V
(0.85 Vn), and the default protection time threshold is 1.5s.
Minimum
undervoltage
(27.S2)
The default undervoltage protection threshold is 34.5 V
(0.15 Vn), and the default protection time threshold is 0.2s.
Maximum
overfrequency
(81.S1)
The default overfrequency protection threshold is 50.2 Hz,
and the default protection time threshold is 0.1s.
Table 7-2 IPS test type

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
7 Man-Machine Interaction
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
79
IPS Test Type
Description
Maximum
overfrequency
(81.S2)
The default overfrequency protection threshold is 51.5 Hz,
and the default protection time threshold is 0.1s.
Minimum
underfrequency
(81.S1)
The default underfrequency protection threshold is 49.8 Hz,
and the default protection time threshold is 0.1s.
Minimum
underfrequency
(81.S2)
The default underfrequency protection threshold is 47.5 Hz,
and the default protection time threshold is 0.1s.
Step 3 After the IPS test is complete, IPS State is displayed as IPS state success. Tap
Historical report in the upper right corner of the screen to view the IPS check
report.
----End
7.3 SmartLogger Networking Scenario
See the
(Distributed Inverters + SmartLogger1000A + RS485 Networking)
Connecting to Huawei Hosting Cloud Quick Guide (Inverters + SmartLogger3000 +
RS485 Networking). You can scan the QR code to obtain it.
Figure 7-14 SmartLogger1000A
Figure 7-15 SmartLogger3000
Distributed PV Plants Connecting to Huawei Hosting Cloud Quick Guide
and PV Plants

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
80
8.1 System Power-Off
Precautions
8 Maintenance
Procedure
Step 1 Send a shutdown command on the app.
Step 2 Turn off the AC switch between the SUN2000 and the power grid.
Step 3 Turn off the DC switch at the bottom of the SUN2000.
Step 4 (Optional) Install the locking screw for the DC switch.
After the SUN2000 powers off, the remaining electricity and heat may still cause
electric shocks and body burns. Therefore, put on protective gloves and begin
operating the SUN2000 five minutes after the power-off.
Before maintaining the optimizers and PV strings, power off the system by
performing the following steps. Otherwise, the PV strings may be energized,
resulting in electric shocks.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
81
Figure 8-1 Installing a locking screw for the DC switch
Check Detail
Check Method
Maintenance Interval
System cleanliness
Check the heat sink for foreign matter or the
overall health of the SUN2000.
Annual or every time an
abnormality is detected
System running
status
Check the SUN2000 for damage or deformation.
Annual
Electrical
connections
Cables are securely connected.
Cables are intact, in particular, the parts
touching the metallic surface are not
scratched.
The first inspection is 6
months after the initial
commissioning. From then
on, the interval can be 6 to
12 months.
Grounding
reliability
Check whether the ground terminal and ground
cable are securely connected.
Annual
Sealing
Check whether all terminals and ports are
properly sealed.
Annual
Step 5 Turn off the DC switch between the SUN2000 and PV strings.
----End
8.2 Routine Maintenance
To ensure that the SUN2000 can operate properly for a long term, you are advised
to perform routine maintenance on it as described in this chapter.
Before cleaning the system, connecting cables, and maintaining the grounding
reliability, power off the system.
Table 8-1 Maintenance list

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
82
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2001
High String
Input Voltage
Major
The PV array is not
properly
configured.
Excessive PV
modules are
connected in series
to the PV string,
and therefore the
open-circuit voltage
exceeds the
maximum inverter
operating voltage.
Cause ID 1 = PV1
and PV2
Cause ID 2 = PV3
and PV4
Reduce the number of PV modules
connected in series to the PV string
until the PV string open-circuit
voltage is less than or equal to the
maximum inverter operating
voltage. After the PV array is
correctly configured, the inverter
alarm disappears.
2002
DC Arc Fault
Major
The PV string power
cable arcs or is in
poor contact.
Cause ID 1 = PV1
and PV2
Cause ID 2 = PV3
and PV4
Check that the PV string power
cable does not arc and is in good
contact.
8.3 Troubleshooting
Contact your dealer or Huawei technical support if the measures listed in the
Troubleshooting Suggestion column have been taken but the fault persists.
Alarm severities are defined as follows:
Major: The inverter is faulty. As a result, the output power decreases or the
grid-tied power generation is stopped.
Minor: Some components are faulty without affecting the grid-tied power
generation.
Warning: The inverter works properly. The output power decreases or some
authorization functions fail due to external factors.
Table 8-2 Common alarms and troubleshooting measures

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
83
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2011
String Reverse
Connection
Major
The PV string
polarity is reversed.
Cause ID 1 = PV1
Cause ID 2 = PV2
Cause ID 3 = PV3
Cause ID 4 = PV4
Check whether the PV string is
reversely connected to the
SUN2000. If yes, wait until the PV
string current decreases below 0.5
A, set DC SWITCH to OFF, and
adjust the PV string polarity.
2012
String Current
Backfeed
Warning
The number of PV
modules connected
in series to this PV
string is insufficient.
As a result, the end
voltage is lower
than that of other
strings.
Cause ID 1 = PV1
Cause ID 2 = PV2
Cause ID 3 = PV3
Cause ID 4 = PV4
1. Check whether the number of PV
modules connected in series to
this PV string is less than the
number of PV modules
connected in series to the other
PV strings connected in parallel
with this PV string. If yes, wait
until the PV string current
decreases below 0.5 A, set DC
SWITCH to OFF, and adjust the
number of PV modules in the PV
string.
2. Check whether the PV string is
shaded.
3. Check whether the open-circuit
voltage of the PV string is
normal.
2021
AFCI Self-Check
Failure
Major
Cause ID = 1, 2
AFCI check fails.
Turn off the AC output switch and
DC input switch, and then turn them
on after 5 minutes. If the fault
persists, contact your dealer or
Huawei technical support.
2031
Phase Wire
Short-Circuited
to PE
Major
Cause ID = 1
The impedance of
the output phase
wire to PE is low or
the output phase
wire is
short-circuited to
PE.
Check the impedance of the output
phase wire to PE, locate the position
with lower impedance, and rectify
the fault.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
84
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2032
Grid Loss
Major
Cause ID = 1
The power grid
experiences an
outage.
The AC power
cable is
disconnected or
the AC circuit
breaker is OFF.
1. Check that the AC voltage is
normal.
2. Check that the AC power cable is
connected and that the AC
switch is ON.
2033
Grid
Undervoltage
Major
Cause ID = 1
The grid voltage is
below the lower
threshold or the
low voltage
duration has lasted
for more than the
value specified by
LVRT.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the power grid may be abnormal
temporarily. The inverter
automatically recovers after
detecting that the power grid
becomes normal.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
check whether the grid voltage is
within the acceptable range. If
no, contact the local power
operator. If yes, login to the
mobile phone app, SmartLogger,
or NMS to modify the grid
undervoltage protection
threshold with the consent of the
local power operator.
3. If the fault persists, check the
connection between the AC
switch and the output power
cable.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
85
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2034
Grid
Overvoltage
Major
Cause ID = 1
The grid voltage
exceeds the higher
threshold or the
high voltage
duration has lasted
for more than the
value specified by
HVRT.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the power grid may be abnormal
temporarily. The inverter
automatically recovers after
detecting that the power grid
becomes normal.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
check whether the power grid
voltage is within the acceptable
range. If no, contact the local
power operator. If yes, log in to
the mobile app, SmartLogger, or
network management system
(NMS) to modify the grid
overvoltage protection threshold
with the consent of the local
power operator.
3. Check whether the peak voltage
of the power grid is too high. If
the fault persists and cannot be
rectified for a long time, contact
the power grid operator.
2035
Grid Voltage
Imbalance
Major
Cause ID = 1
The difference
between grid phase
voltages exceeds
the upper
threshold.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the power grid may be abnormal
temporarily. The inverter
automatically recovers after
detecting that the power grid
becomes normal.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
check whether the power grid
voltage is within the acceptable
range. If no, contact the local
power operator.
3. If the fault persists for a long
time, check the connection of the
AC output power cables.
4. If the AC output power cables are
correctly connected, but the
alarm persists and affects the
energy yield of the PV plant,
contact the local power operator.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
86
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2036
Grid
Overfrequency
Major
Cause ID = 1
Power grid
exception: The
actual grid
frequency is higher
than the
requirement of the
local power grid
standard.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the power grid may be abnormal
temporarily. The inverter
automatically recovers after
detecting that the power grid
becomes normal.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
check whether the grid frequency
is within the acceptable range. If
no, contact the local power
operator. If yes, log in to the
mobile phone app, SmartLogger,
or NMS to modify the grid
underfrequency protection
threshold with the consent of the
local power operator.
2037
Grid
Underfrequency
Major
Cause ID = 1
Power grid
exception: The
actual grid
frequency is lower
than the
requirement of the
local power grid
standard.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the power grid may be abnormal
temporarily. The inverter
automatically recovers after
detecting that the power grid
becomes normal.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
check whether the grid frequency
is within the acceptable range. If
no, contact the local power
operator. If yes, log in to the
mobile phone app, SmartLogger,
or NMS to modify the grid
underfrequency protection
threshold with the consent of the
local power operator.
2038
Unstable Grid
Frequency
Major
Cause ID = 1
Power grid
exception: The
actual grid
frequency change
rate does not
comply with the
local power grid
standard.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the power grid may be abnormal
temporarily. The inverter
automatically recovers after
detecting that the power grid
becomes normal.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
check whether the grid frequency
is within the acceptable range. If
no, contact the local power
operator.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
87
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2039
Output
Overcurrent
Major
Cause ID = 1
The grid voltage
drops dramatically
or the power grid is
short-circuited. As a
result, the inverter
transient output
current exceeds the
upper threshold,
and inverter
protection is
triggered.
1. The inverter monitors its external
working conditions in real time.
The inverter automatically
recovers after the fault is
rectified.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently
and affects the power production
of the PV plant, check whether
the output is short-circuited. If
the fault persists, contact your
dealer or Huawei technical
support.
2040
Output DC
Component
Overhigh
Major
Cause ID = 1
The DC component
in the grid current
exceeds the upper
threshold.
1. The inverter monitors its external
working conditions in real time.
The inverter automatically
recovers after the fault is
rectified.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently,
contact your dealer or Huawei
technical support.
2051
Abnormal
Residual Current
Major
Cause ID = 1
The
input-to-ground
insulation
impedance has
decreased during
the inverter
operation.
1. If the alarm occurs accidentally,
the external power cable may be
abnormal temporarily. The
inverter automatically recovers
after the fault is rectified.
2. If the alarm occurs frequently or
persists, check that the
impedance between the PV
string and ground is not below
the lower threshold.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
88
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2061
Abnormal
Grounding
Major
Cause ID = 1
The neutral wire
or ground cable
is not connected.
The PV array is
grounded, but
the inverter
output does not
connect to an
isolation
transformer.
Power off the inverter (turn off the
AC output switch and DC input
switch, and wait for 5 minutes), and
then perform the following
operations:
1. Check that the PE cable for the
inverter is connected properly.
2. If the inverter is connected to the
TN power grid, check whether
the N cable is properly connected
and whether the voltage to
ground is normal.
3. Check whether the AC output
connects to an isolation
transformer. If yes, after
powering on the inverter, log in
to the mobile phone app,
SmartLogger, or NMS and
disable Grounding inspection.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
89
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2062
Low Insulation
Resistance
Major
Cause ID = 1
The PV array is
short-circuited
to ground.
The PV array is
in a moist
environment
and the power
cable is not well
insulated to
ground.
1. Check the impedance between
the PV array output and PE, and
eliminate short circuits and poor
insulation points.
2. Check that the PE cable for the
inverter is connected correctly.
3. If you are sure that the
impedance is less than the preset
protection threshold in a cloudy
or rainy environment, log in to
the mobile phone app,
SmartLogger, or NMS and reset
the insulation impedance
protection threshold.
Current insulation resistance: x
MΩ, possible short circuit
position: x%. The short circuit
position is valid for a single PV
string. If there are multiple PV
strings, check the PV strings one
by one. For details, see
F Locating Insulation Resistance
Faults.
For details about how to query
the low insulation resistance
alarm, the
HUAWEI
SUN2000-8-20KTL-M2 Inverter
Low Insulation Resistance Fault
Indication Guide.
2063
Cabinet
Overtemperatur
e
Minor
Cause ID = 1
The inverter is
installed in a
place with poor
ventilation.
The ambient
temperature
exceeds the
upper threshold.
The inverter is
not working
properly.
Check the ventilation and
ambient temperature at the
inverter installation position.
If the ventilation is poor or the
ambient temperature exceeds
the upper threshold, improve the
ventilation and heat dissipation.
If the ventilation and ambient
temperature both meet
requirements, contact your
dealer or Huawei technical
support.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
90
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2064
Device Fault
Major
Cause ID = 1–12
An unrecoverable
fault has occurred
on a circuit inside
the inverter.
Turn off the AC output switch and
DC input switch, and then turn them
on after 5 minutes. If the fault
persists, contact your dealer or
Huawei technical support.
Note: If the cause ID is ID 1, perform
the preceding operation when the
PV string current is less than 1 A.
2065
Upgrade Failed
or Version
Mismatch
Minor
Cause ID = 1, 2 and
4
The upgrade ends
abnormally.
NOTE
Upgrade the inverter
again if it is stuck in
initialization state
without generating
any alarms and
cannot be restored
to the normal state
during the upgrade
when the PV inputs
are disconnected and
reconnected next
time.
1. Upgrade again.
2. If the upgrade fails several times,
contact your dealer or Huawei
technical support.
2066
License Expired
Warning
Cause ID = 1
The privilege
certificate has
entered the
grace period.
The privilege
feature will be
invalid soon.
1. Apply for a new certificate.
2. Load the new certificate.
61440
Faulty
Monitoring Unit
Minor
Cause ID = 1
The flash
memory is
insufficient.
The flash
memory has bad
sectors.
Turn off the AC output switch and
DC input switch, and then turn them
on after 5 minutes. If the fault
persists, replace the monitoring
board or contact your dealer
Huawei technical support.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
91
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2067
Faulty Power
Collector
Major
Cause ID = 1
Power meter
disconnection.
1. Check that the preset power
meter model is the same as the
actual model.
2. Check that the preset
communications parameters for
the power meter are the same as
the actual configurations.
3. Check that the power meter is
powered on and the RS485
communications cable is
connected.
2072
Transient AC
Overvoltage
Major
Cause ID = 1
The inverter detects
that the phase
voltage exceeds the
transient AC
overvoltage
protection
threshold.
1. Check whether the grid
connection voltage exceeds the
upper threshold. If yes, contact
the local power operator.
2. If you have confirmed that the
grid connection voltage exceeds
the upper threshold and
obtained the consent of the local
power operator, modify the
overvoltage protection threshold.
3. Check that the peak grid voltage
does not exceed the upper
threshold.

SUN2000-(8KTL-20KTL)-M2
User Manual
8 Maintenance
Issue 01 (2020-07-02)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
92
Alarm
ID
Alarm Name
Alarm
Severity
Possible Cause
Troubleshooting Suggestion
2080
Abnormal PV
Module
Configuration
Major
PV module
configuration does
not meet
requirements, or
the PV module
output is reversely
connected or
short-circuited.
Cause ID = 2, 3, 6, 7,
8, 9
2: The PV string
power or the
number of PV
modules
connected in
series exceeds
the upper
threshold.
3: The PV string
voltage is low or
the number of
PV modules
connected in
series is less than
the lower
threshold.
6: The PV string
or parallel
connection is
abnormal.
7: The string
configuration is
changed.
8: The sunlight is
abnormal.
9: The PV string
voltage exceeds
the upper
threshold.
Check whether the total number of
PV modules, number of PV modules
in a string, and number of PV strings
meet requirements and whether the
PV module output is reversely
connected.
ID2: Check whether the PV string
power or the number of PV
modules connected in series in
the PV string exceeds the upper
threshold.
ID3:
1. Check whether the number of
optimizers connected in series in
the PV string is below the lower
threshold.
2. Check whether the PV string
output is reversely connected.
3. Check whether the PV string
output is disconnected.
4. Check whether the optimizer
output extension cable is correct
(positive connector at one end
and negative connector at the
other).
ID6:
1. Check whether the number of
optimizers connected in series in
the PV strings connected in
parallel under the same MPPT is
the same.
2. Check whether the optimizer
output extension cable is correct
(positive connector at one end
and negative connector at the
other).
ID7: When the sunlight is normal,
perform the optimizer search
function again.
ID8: When the sunlight is normal,
perform the optimizer search
function again.
ID9: Calculate the PV string
voltage based on the number of
PV modules in the PV string and
check whether the PV string
voltage exceeds the upper
threshold of the inverter input
 Loading...
Loading...