Page 1

Scalable File Service
FAQs
Issue 01
Date 2019-05-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
Page 3

Scalable File Service
FAQs Contents
Contents
1 Concepts.................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 What Is SFS?............................................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 What Is SFS Turbo?................................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.3 What Are the Dierences Between SFS, OBS, and EVS?........................................................................................... 2
2 Specications............................................................................................................................4
2.1 What Is the Maximum Size of a File That Can Be Stored in a File System?...................................................... 4
2.2 What Access Protocols Are Supported by SFS?.............................................................................................................4
2.3 How Many File Systems Can Be Created by Each Account?.................................................................................... 4
2.4 How Many ECSs Can a File System Be Mounted To?................................................................................................. 4
3 Restrictions................................................................................................................................5
3.1 Can the Capacity of a File System Be Expanded?........................................................................................................ 5
3.2 Can Data in a File System Be Migrated Across Regions?..........................................................................................5
3.3 Can a File System Be Mounted to Multiple Accounts?.............................................................................................. 5
4 Networks................................................................................................................................... 6
4.1 Can a File System Be Accessed Across VPCs?................................................................................................................6
4.2 Does SFS Support Cross-Region Mounting?.................................................................................................................. 6
4.3 Does the Security Group of a VPC
4.4 What Can I Do If the Data of the File System That Is Mounted to Two Servers Is Not Synchronized?
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 8
Aect SFS?............................................................................................................. 6
5 Billing......................................................................................................................................... 9
5.1 How Do I Purchase SFS?....................................................................................................................................................... 9
5.2 How Do I Renew the Service?.......................................................................................................................................... 11
5.3 How Do I Check Whether the Subscriber Is in Arrears?..........................................................................................11
5.4 Can I Purchase SFS Capacity-Oriented Resource Packages When I Still Have Valid Ones in Use?......... 12
5.5 How Do I Check the Usage of an SFS Capacity-Oriented Resource Package?................................................12
5.6 Do SFS Capacity-Oriented and SFS Turbo Share One Resource Package?....................................................... 14
6 Others...................................................................................................................................... 15
6.1 How Do I Access a File System from an ECS?............................................................................................................ 15
6.2 How Do I Check Whether a File System on an ECS Running Linux Is Available?.......................................... 15
6.3 What Resources Does SFS Occupy?................................................................................................................................15
6.4 Why Is the Capacity Displayed as 10P After the File System Is Mounted?...................................................... 16
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
Page 4

Scalable File Service
FAQs Contents
6.5 How Can I Migrate Data Between SFS and OBS?..................................................................................................... 16
6.6 Can a File System Be Accessed Across Multiple AZs?.............................................................................................. 17
6.7 Can I Upgrade an SFS Capacity-Oriented File System to an SFS Turbo File System?.................................. 17
6.8 How Can I Migrate Data Between SFS and EVS?......................................................................................................17
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
Page 5

Scalable File Service
FAQs 1 Concepts
1 Concepts
1.1 What Is SFS?
Scalable File Service (SFS) provides high-performance le storage that can be
expanded and shrunk on demand. With SFS, you can enjoy shared
spanning multiple ECSs. SFS supports the Network File System (NFS) protocol. You
can seamlessly integrate existing applications and tools with the service.
le access
SFS provides an easy-to-use graphical user interface (GUI). On the GUI, users can
create and
optimizing
In addition, SFS features high reliability and availability. It can be elastically
expanded, and it performs better as its capacity grows. The service is suitable for a
wide range of scenarios, including media processing,
management and web services, big data, and analytic applications.
congure le systems, saving eort in deploying, resizing, and
le systems.
1.2 What Is SFS Turbo?
SFS Turbo enables high-performance le storage that can be expanded and
shrunk on demand. It provides
SFS Turbo supports the Network File System (NFS) protocol (only NFSv3). You can
seamlessly integrate existing applications and tools with the service.
SFS Turbo provides an easy-to-use graphical user interface (GUI). On the GUI,
users can create and
and optimizing le systems.
In addition, SFS Turbo features high reliability and availability. It can be elastically
expanded, and it performs better as its capacity grows. The service is suitable for a
wide range of scenarios, including enterprise
and software development. For details about the
System Types.
congure le systems, saving eort in deploying, resizing,
le sharing, content
le sharing services for Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs).
oce, high-performance websites,
le system types, see File
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
Page 6
Scalable File Service
FAQs 1 Concepts
1.3 What Are the Dierences Between SFS, OBS, and
EVS?
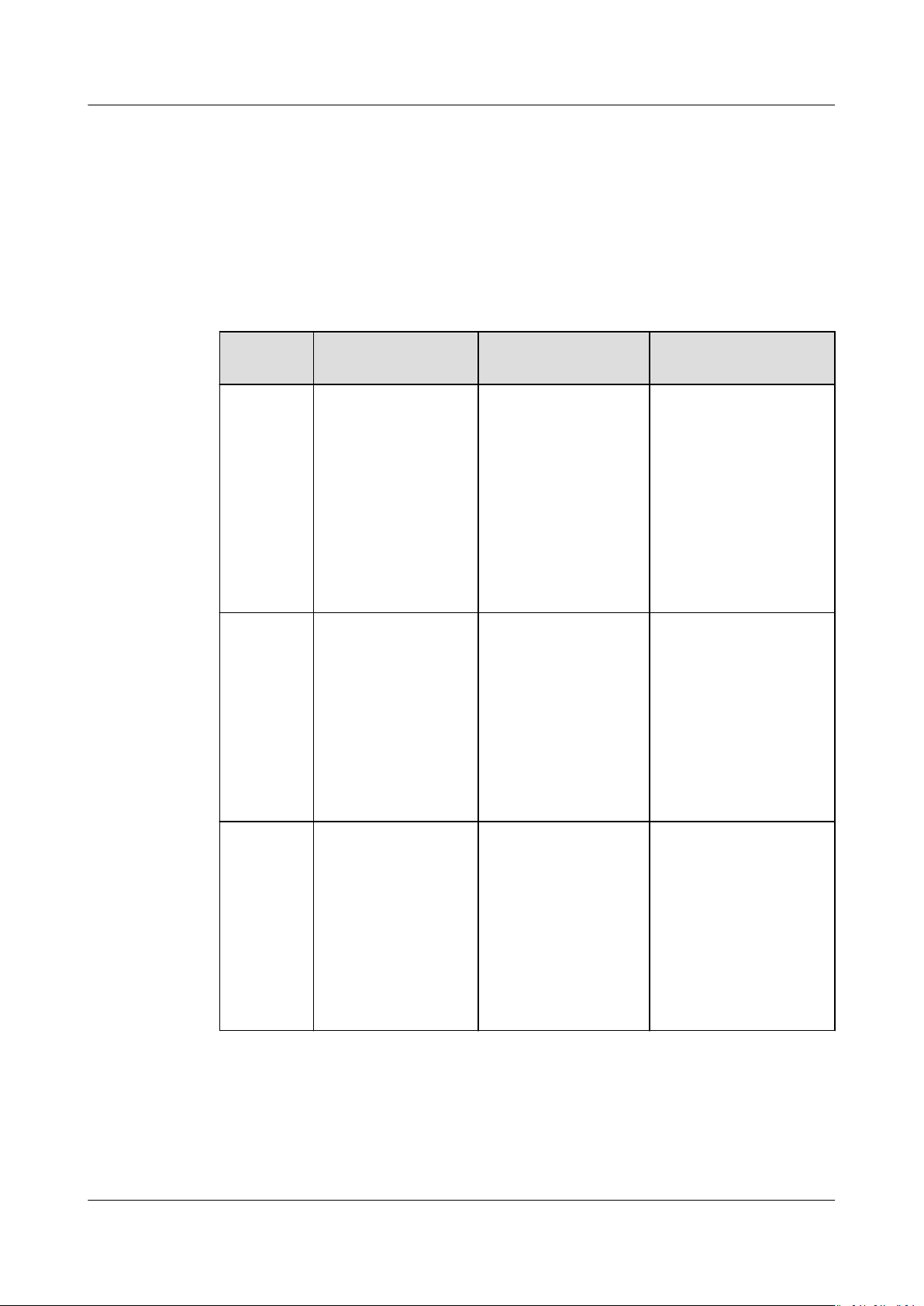
Table 1-1 shows the comparison between SFS, Object Storage Service (OBS), and
Elastic Volume Service (EVS).
Table 1-1 Comparison between SFS, OBS, and EVS
DimensionSFS OBS EVS
Concept SFS provides on-
demand highperformance le
storage, which can
be shared by
multiple ECSs. SFS
is similar to a
remote directory
for Windows or
Linux OSs.
Data
storage
logic
Access
method
Stores les and
sorts and displays
data in the
hierarchy of les
and folders.
Attach le systems
to ECSs. You need
to specify a
network address for
access or change
the network
address to a local
directory for access.
The NFS and CIFS
protocols are used.
OBS provides
massive, secure,
reliable, and cost-
eective data
storage capabilities
for users to store
data of any type
and size.
Stores objects. Files
can be directly
stored. The les
automatically
generate
corresponding
system metadata.
Users can also
customize the
metadata of
You can access OBS
through the Internet
or Direct Connect.
You need to specify
the bucket address
for access. The
transmission
protocols such as
HTTP and HTTPS
are used.
les.
EVS provides scalable
block storage that
features high
reliability, high
performance, and rich
specications for ECSs
to meet service
requirements in
dierent scenarios. An
EVS disk is similar to a
hard disk on a PC.
Stores binary data and
cannot directly store
les. To store les, you
need to format the
le system rst.
An EVS disk can only
be used by mounting
to an ECS or BMS and
cannot be directly
accessed by OS
applications. It must
be formatted into a
le system for access.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
Page 7
Scalable File Service
FAQs 1 Concepts
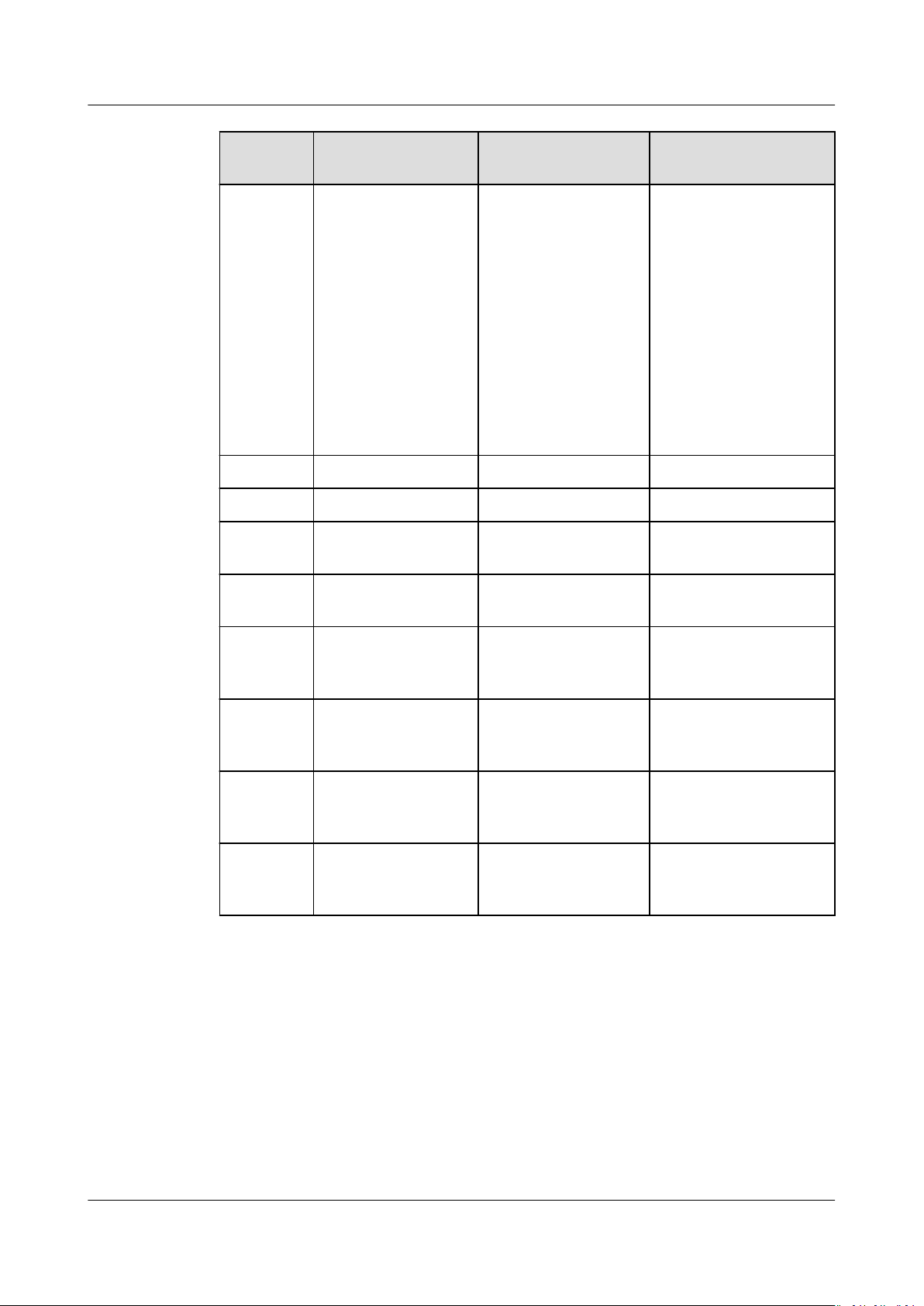
DimensionSFS OBS EVS
Applicatio
n
Scenario
High-performance
computing (HPC),
media processing,
le sharing, content
management, and
web services
NOTE
HPC: High
bandwidth is
required for shared
le storage, such as
gene sequencing
and image
rendering.
Big data analysis,
static website
hosting, online video
on demand (VoD),
gene sequencing,
and intelligent video
surveillance
HPC, enterprise core
cluster applications,
enterprise application
systems, and
development and
testing
NOTE
HPC: High-speed and
high-IOPS storage is
required, such as
industrial design and
energy exploration.
Capacity PB-scale EB-scale TB-scale
Latency 3–10 ms 10 ms 1–2 ms
IOPS/TPS 10,000 for a single
le system
Quadrillion 33,000 for a single
disk
BandwidthGB/s TB/s MB/s
Data
Yes Yes Yes
sharing
supported
Remote
access
supported
Online
editing
supported
Used
independe
ntly
Yes Yes No
Yes No Yes
Yes Yes No
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
Page 8

Scalable File Service
FAQs 2 Specications
2 Specications
2.1 What Is the Maximum Size of a File That Can Be Stored in a File System?
For SFS Capacity-Oriented
240 TB.
For SFS Turbo le systems, the supported maximum size of a le is 16 TB.
le systems, the supported maximum size of a le is
2.2 What Access Protocols Are Supported by SFS?
SFS supports the standard network le protocol NFSv3.
2.3 How Many File Systems Can Be Created by Each Account?
Currently, a maximum of 10 SFS Capacity-Oriented
le systems can be created by each cloud account.
● SFS Capacity-Oriented
than 10 SFS Capacity-Oriented le systems, click Increase quota on the page
for creating a le system.
● Only one SFS Turbo
10 SFS Turbo le systems, click Service Tickets in the upper right corner of
the console to submit a service ticket.
le systems can be created in batches. To create more
le system can be created at a time. To create more than
le systems and 10 SFS Turbo
2.4 How Many ECSs Can a File System Be Mounted To?
You can mount an SFS Capacity-Oriented
ECSs.
You can mount an SFS Turbo le system to a maximum of 500 ECSs.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
le system to a maximum of 10,000
Page 9

Scalable File Service
FAQs 3 Restrictions
3 Restrictions
3.1 Can the Capacity of a File System Be Expanded?
SFS Capacity-Oriented le systems: If automatic capacity expansion is disabled,
online capacity expansion is supported. For details, see Resizing a File System. If
automatic capacity expansion is enabled, manual capacity expansion is not
needed.
SFS Turbo
expansion, the le system will be unavailable for two to three minutes. Online
capacity expansion may not be available for some instances of earlier versions. If
capacity expansion is required, click Service Tickets in the upper right corner of
the console to submit a service ticket.
le systems: support online capacity expansion. During the capacity
3.2 Can Data in a File System Be Migrated Across Regions?
Currently, cross-region
determine the region properly when purchasing a le system. Alternatively, you
can copy the data to a local device and then transfer the data to another region.
le system data migration is not supported. You need to
3.3 Can a File System Be Mounted to Multiple Accounts?
Currently, a
le system cannot be mounted to multiple accounts.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
Page 10

Scalable File Service
FAQs 4 Networks
4 Networks
4.1 Can a File System Be Accessed Across VPCs?
Yes.
● Multiple VPCs can be
that ECSs belonging to dierent VPCs can share the same le system, as long
as the VPCs that the ECSs belong to are added to the VPC list of the le
system or the ECSs are added to the authorized addresses of the VPCs. For
details, see Conguring Multiple VPCs.
● An SFS Turbo
interconnect with each other through VPC peering connection. In this case,
dierent VPCs are in the same network, and ECSs under these VPCs can share
the same le system. For details about VPC peering connection, see VPC
Peering Connection.
le system allows two or more VPCs in the same region to
congured for an SFS Capacity-Oriented le system so
4.2 Does SFS Support Cross-Region Mounting?
Currently, SFS does not support cross-region mounting. A le system can be
mounted only to ECSs in the same region.
For example, the
CN North-Beijing4 only.
le systems in CN North-Beijing4 can be mounted to the ECSs in
4.3 Does the Security Group of a VPC Aect SFS?
A security group is a collection of access control rules for ECSs that have the same
security protection requirements and are mutually trusted in a VPC. After a
security group is created, you can create
group to protect the ECSs that are added to this security group. The default
security group rule allows all outgoing data packets. ECSs in a security group can
access each other without the need to add rules. The system creates a security
group for each cloud account by default. Users can also create custom security
groups by themselves.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
dierent access rules for the security
Page 11

NO TE
Scalable File Service
FAQs 4 Networks
After an SFS Turbo le system is created, the system automatically enables the
security group port required by the NFS protocol in the SFS Turbo le system. This
ensures that the SFS Turbo le system can be accessed by your ECS and prevents
le system mounting failures. The inbound ports required by the NFS protocol are
ports 111, 2049, 2051, 2052, and 20048. If you need to change the enabled ports,
choose Access Control > Security Groups of the VPC console and locate the
target security group.
You are advised to use an independent security group for an SFS Turbo instance to
isolate it from service nodes.
You need to add inbound and outbound rules for the security group of an SFS
Capacity-Oriented
le system. For details, see Adding a Security Group Rule. In
an SFS Capacity-Oriented le system, the inbound ports required by the NFS
protocol are ports 111, 2049, 2051, and 2052. The inbound port required by the
DNS server is port 53.
Example Value
● Inbound rule
DirectionProtocol Port
Inbound TCP and
UDP
● Outbound rule
Direction
Protocol Port
Outbound TCP and
UDP
Source IP
Range
Address
111 IP
Addr
ess
Range
111 IP
0.0.0
.0/0
(conf
igur
able
)
Source IP
Address
0.0.
Addr
ess
0.0/
0
(co
ng
ura
ble)
Description
One port corresponds to
one access rule. You need
to add information to the
ports one by one.
Description
One port corresponds to
one access rule. You need
to add information to the
ports one by one.
The bidirectional access rule must be congured for port 111. The inbound rule can be
set to the front-end service IP range of SFS. You can obtain it by running the following
command: ping
name or IP address
For ports 2049, 2050, 2051, and 2052, only the outbound rule needs to be added,
which is the same as the outbound rule of port 111.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
File system domain name or IP address
.
or dig
File system domain
Page 12

Scalable File Service
FAQs 4 Networks
4.4 What Can I Do If the Data of the File System That Is Mounted to Two Servers Is Not Synchronized?
Symptom
When le system C is mounted to both server A and server B, there is a delay in
synchronizing the
no delay when the le is uploaded to server B separately.
Fault Diagnosis
Add noac to the mount parameters of the two servers. noac indicates that cache
is disabled and synchronous write is forcibly performed. To improve performance,
the NFS client caches
le properties periodically and updates them if the properties are changed. Within
the cache validity period, the client does not check whether the le properties on
the server are changed. The default value is ac. Set this parameter to noac.
le to server B after it is uploaded to server A. However, there is
le properties (the default value is ac), and then checks the
Solution
Step 1 If the
Step 2 Prepare for the mount by referring to Mounting an NFS File System to ECSs
Step 3 Run the following command to mount the
le system has been mounted, unmount it by referring to Unmounting a
File System.
le system:
mount -t nfs -o vers=3,timeo=600,noac,noresvport,nolock
----End
Shared path Local path
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
Page 13

NO TE
Scalable File Service
FAQs 5 Billing
5 Billing
5.1 How Do I Purchase SFS?
Pay-per-use
Step 1 Register an account.
Step 2 Top up your account.
By default, SFS is billed in pay-per-use mode. That is, the service is billed by the
storage capacity you select during purchase and the duration of use. You can
purchase a yearly or monthly package based on your resource usage and duration
plan. In case of arrears, you need to renew the service within 15 days. Otherwise,
le system resources will be cleaned up.
your
The size of a resource package is irrelevant to the computing throughput of the le system.
1. Visit the HUAWEI CLOUD website at www.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/.
2. In the upper right corner of the page, click Register.
3. Complete the registration as instructed.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click Top Up and the top-up page is displayed.
3. Top up the account as prompted.
4. After the top-up is complete, close the dialog box and go back to the
management console homepage.
Step 3 Use SFS.
1. Choose Storage > Scalable File Service to go to SFS Console.
2. Click Create File System. You do not need to select a billing mode for the SFS
Capacity-Oriented
created.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
le system. The resource use starts once the le system is
Page 14

NO TE
NO TE
Scalable File Service
FAQs 5 Billing
– The SFS Capacity-Oriented le system is billed by the used storage capacity and
duration of use.
– The SFS Turbo
purchase and the duration of use.
le system is billed by the storage capacity you select during
----End
Yearly/Monthly Subscription
You can purchase the resource package of an SFS Capacity-Oriented
clicking Buy Storage Package. Resource packages cannot be used across regions.
Check your region before purchasing a resource package.
For an SFS Turbo
le system, you can purchase a resource package when creating
the le system and change the billing mode from pay-per-use to yearly/monthly.
Procedure for SFS Capacity-Oriented
Step 1 Purchase resource packages.
1. On SFS Console, click Buy Storage Package.
2. On the page that is displayed, set the parameters as instructed.
You can click Product Pricing Details to view the detailed prices.
3. Click Next.
4.
Conrm the order information and click Submit.
If the order information is incorrect, click Previous to modify it and then
continue purchasing.
5. Complete the payment as instructed.
6. Return to SFS Console to use SFS.
The purchased SFS resource packages cannot be viewed on SFS Console. For
details about how to view the resource packages, see How Do I View the
Usage of a Resource Package?
le system by
The SFS Capacity-Oriented resource package takes eect immediately after being
purchased. If the capacity of the resource package is greater than the le system usage, the
pay-per-use billing mode stops immediately. The capacity of the resource packages is
preferentially used when you use the le systems.
SFS resource packages cannot be expanded, but can be purchased multiple times. For
details, see Can I Purchase SFS Capacity-Oriented Resource Packages When I Still Have
Valid Ones in Use?.
For example, if a user purchases a 1 TB SFS Capacity-Oriented resource package for one
year and creates a 500 GB SFS Capacity-Oriented le system (le system A) on SFS
Console, the used capacity of the resource package is 500 GB. For details about how to view
the usage of the resource package, see How Do I View the Usage of a Resource Package?
One month later, the user creates another 600 GB SFS Capacity-Oriented le system (le
system B). Now the purchased 1 TB capacity is used up, and 100 GB beyond the capacity is
billed in pay-per-use mode. If you do not want to be billed in pay-per-use mode, you can
purchase more resource packages. For details, see Yearly/Monthly Subscription.
Step 2 Use SFS.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
Page 15

NO TE
Scalable File Service
FAQs 5 Billing
1. Choose Storage > Scalable File Service to go to SFS Console.
2. Click Create File System to start using resources.
----End
Procedure for SFS Turbo
Method 1: Purchase a yearly/monthly le system. Create a le system by following
the instructions in Creating a File System and set the billing mode to Yearly/
Monthly.
Method 2: In the Operation column of the pay-per-use
to Yearly/Monthly to change the billing mode to yearly/monthly.
5.2 How Do I Renew the Service?
If the arrears are not paid in time, your account may be frozen and your order
may be canceled.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 In the upper right corner of the page, choose Billing > Renewals. The renewal
management page is displayed.
Step 3 On the Renewals page, click Renew in the Operation column for the desired
resource.
Step 4 Pay for the order as prompted.
● After the payment, the system automatically pays the arrears.
● For more information about renewal, including auto-renewal, exporting the renewal list,
and changing subscriptions, see Renewal Management.
● For more information about orders, unsubscription, coupons, and consumption details,
see the Billing Center User Guide.
le system, click Change
----End
5.3 How Do I Check Whether the Subscriber Is in Arrears?
You can view the outstanding amount on the Billing Center page. The retention
periods vary based on the customer level and subscription mode. When an
account is in arrears, the system processes resources and fees in SFS according to
the retention period. For details, see Service Suspension and Resource Release.
To prevent service suspension and resource release, repay arrears or top up in
time.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
Page 16

NO TE
Scalable File Service
FAQs 5 Billing
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 Click Billing in the upper right corner of the page to switch to the Billing Center
page.
Step 3 On the Overview page, you can view the outstanding amount of the current
account.
Step 4 Top up your account to pay arrears if any.
----End
● For details about how to repay the outstanding amount, see Repaying Arrears.
● For more information about orders, unsubscription, coupons, and consumption details,
see the Billing Center User Guide.
5.4 Can I Purchase SFS Capacity-Oriented Resource Packages When I Still Have Valid Ones in Use?
You can still purchase resource packages on top of the valid packages. The
capacity of the resource package purchased
For example: A subscriber has le data of 1.2 TB. The subscriber purchases the
resource package A with the capacity of 1 TB on August 15 and the resource
package B with the capacity of 1 TB on August 20. Then, from August 20 to
September 15, the capacity of the resource package A (1 TB) is used up, and the
capacity used in the resource package B is 0.2 TB. The resource package A expires
on September 15. If the resource package A is not renewed, the capacity of the
resource package B (1 TB) is used up from September 15 to September 20.
rst is used up rst.
5.5 How Do I Check the Usage of an SFS CapacityOriented Resource Package?
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to SFS Console.
Step 2 Choose Resources > My Packages in the upper right corner. See Figure 5-1.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Page 17

Scalable File Service
FAQs 5 Billing
Figure 5-1 Selecting My Packages
Step 3 Information of the purchased resource packages is displayed in the list. Click the
target resource package. Then click View Details in the Operation column to
view the usage of the resource package. See Figure 5-2.
Figure 5-2 Viewing resource package usage
Step 4 View the resource package usage. See Figure 5-3.
Figure 5-3 Usage of a resource package
----End
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Page 18

Scalable File Service
FAQs 5 Billing
5.6 Do SFS Capacity-Oriented and SFS Turbo Share One Resource Package?
No. You need to purchase and use SFS and SFS Turbo resource packages
separately.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Page 19

Scalable File Service
FAQs 6 Others
6 Others
6.1 How Do I Access a File System from an ECS?
To access a le system, run the mount command on a Linux-based ECS to mount
le system. Then, you can share the les and directories of the le system.
the
6.2 How Do I Check Whether a File System on an ECS Running Linux Is Available?
Log in to the ECS as the root user. Run the following command, and the command
output displays all available le systems with the same domain name or IP
address.
showmount -e
File system domain name or IP address
6.3 What Resources Does SFS Occupy?
To ensure that le systems can be used properly, the service occupies the following
resources:
● For SFS Turbo
– When an SFS Turbo le system is created, two private IP addresses and
one virtual IP address are created in the subnet entered by the user.
– When an SFS Turbo
445, 2049, 2051, 2052, and 20048 are enabled in the security group
entered by the user. The default source IP address is 0.0.0.0/0. You can
change the IP address as required.
When data is written to the folders of a
server is occupied, but the storage space of the server disk is not occupied. The le
system uses independent space.
le systems:
le system is created, the inbound rules of ports 111,
le system, the running memory of the
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
Page 20

NO TE
Scalable File Service
FAQs 6 Others
6.4 Why Is the Capacity Displayed as 10P After the File System Is Mounted?
If you select automatic capacity expansion when creating a le system, the
capacity of the le system is unlimited. When you run the df -h command on the
client, the system returns 10P for display purposes.
6.5 How Can I Migrate Data Between SFS and OBS?
Background
HUAWEI CLOUD Object Storage Service (OBS) is a stable, secure,
easy-to-use cloud storage service. With the Representational State Transfer (REST)
application programming interfaces (APIs), OBS is able to store any amount and
form of unstructured data.
HUAWEI CLOUD Scalable File Service (SFS) is a network attached storage (NAS)
service that provides scalable high-performance
access can be achieved among multiple Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs), Bare Metal
Servers (BMSs), and containers created on Cloud Container Engine (CCE) and
Cloud Container Instance (CCI).
How to Migrate
SFS
between SFS and OBS is actually the data migration between servers/containers
and OBS. Data in servers or containers is stored in the mounted SFS
Therefore, after an SFS le system is mounted to a server or container, you can log
in to the server or container and use OBS tools, APIs, or SDKs to migrate data. For
example, if you want to migrate data from SFS to OBS, use the OBS upload
function on the server or container to upload data to OBS. If you want to migrate
data from OBS to SFS, use the OBS download function on the server or container
to download data to the SFS
and write permissions are required.
ecient, and
le storage. With SFS, shared
le systems need to be mounted to ECSs, containers, or BMSs. Data migration
le systems.
le system mounted on the server or container. Read
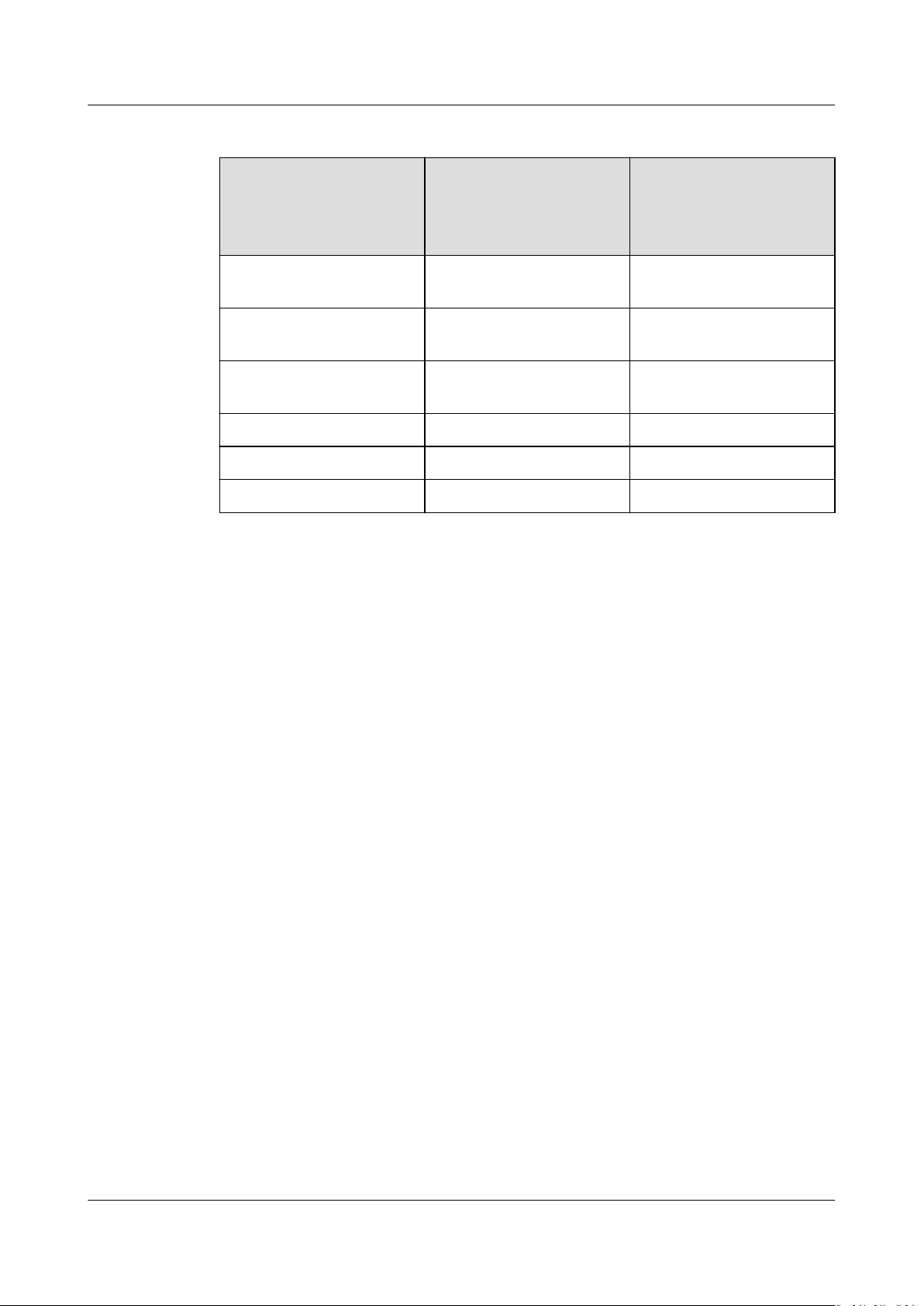
As listed in Table 6-1, OBS provides various methods for data migration. Select a
suitable migration method according to your operating system and actual needs,
and migrate data by referring to the upload and download sections in the guide
manual.
The supported operating systems, data volume, and operation complexity vary according to
the migration methods. obsutil is recommended.
To reduce costs, it is recommended that you congure the intranet DNS and migrate data
over the HUAWEI CLOUD intranet. For details, see Accessing OBS over Intranet.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
Page 21
Scalable File Service
FAQs 6 Others
Table 6-1 Data migration tools provided by OBS
Tool Supported OS
(Refer to each tool
guide for supported
versions.)
OBS Console Windows Console Operation
OBS Browser Windows OBS Browser Tool
OBS Browser+ Windows OBS Browser+ Tool
obsutil (Recommended) Windows/Linux obsutil Tool Guide
SDK All SDK Reference
API All API Reference
Document
Guide
Guide
Guide
6.6 Can a File System Be Accessed Across Multiple AZs?
1. A single le system can be created only in one AZ, for example, AZ 1, but can
be mounted to and accessed from any AZ.
2. A le system does not support data redundancy across AZs. If the AZ where a
le system resides is unavailable, the le system is unavailable.
6.7 Can I Upgrade an SFS Capacity-Oriented File System to an SFS Turbo File System?
No. If you want an SFS Turbo le system, you need to delete or unsubscribe from
the SFS Capacity-Oriented
le system and purchase an SFS Turbo le system.
6.8 How Can I Migrate Data Between SFS and EVS?
Mount a le system and an EVS disk to the same ECS, and then manually replicate
data between the le system and EVS disk.
Issue 01 (2019-05-30) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
 Loading...
Loading...