OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
V100R006C00
Product Description
Issue 01
Date 2016-01-15
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2016. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Related Versions
The following table lists the product versions related to this document.
Product Name Version
OptiX RTN 360 V100R006C00
iManager U2000–T V200R015C60
About This Document
About This Document
iManager U2000–M V200R015C10
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
l Network planning engineer
l Hardware installation engineer
l Installation and commissioning engineer
l Field maintenance engineer
l Data configuration engineer
l System maintenance engineer
Familiarity with the basic knowledge related to digital microwave communication technology
will help you apply the information in this document.
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol Description
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Symbol Description
About This Document
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in death
or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, may result in minor
or moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in
equipment damage, data loss, performance
deterioration, or unanticipated results.
NOTICE is used to address practices not
related to personal injury.
Calls attention to important information,
best practices and tips.
NOTE is used to address information not
related to personal injury, equipment
damage, and environment deterioration.
General Conventions
The general conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention Description
Times New Roman Normal paragraphs are in Times New Roman.
Boldface Names of files, directories, folders, and users are in
Italic Book titles are in italics.
Courier New
Change History
boldface. For example, log in as user root.
Examples of information displayed on the screen are in
Courier New.
Changes between document issues are cumulative. The latest document issue contains all the
changes made in earlier issues.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15)
This issue is the first release for the product version V100R006C00.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 Product Introduction.....................................................................................................................1
1.1 Network Application...................................................................................................................................................... 2
1.2 Product Specifications.................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Site Configurations......................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.3.1 Sites Providing One-Direction Microwave Links....................................................................................................... 4
1.3.2 Sites Providing Two-Direction Microwave Links.......................................................................................................5
1.3.3 Sites Providing Multi-direction Microwave Links......................................................................................................6
2 Functions and Features.................................................................................................................8
2.1 Integration.....................................................................................................................................................................10
2.2 TDD.............................................................................................................................................................................. 10
2.3 Automatic Frequency Selection....................................................................................................................................11
2.4 Adaptive Modulation....................................................................................................................................................12
2.5 Power over Ethernet..................................................................................................................................................... 14
2.6 Ethernet Service Processing Capability........................................................................................................................15
2.7 QoS............................................................................................................................................................................... 17
2.8 Clock Features.............................................................................................................................................................. 19
2.9 Network Management.................................................................................................................................................. 20
2.10 Rapid Deployment......................................................................................................................................................21
2.11 Easy Maintenance.......................................................................................................................................................22
2.11.1 Contact-Free Maintenance.......................................................................................................................................22
2.11.2 Equipment-Level OAM...........................................................................................................................................23
2.11.3 Packet OAM (TP-Assist).........................................................................................................................................25
2.12 Security Management................................................................................................................................................. 27
2.13 Energy Saving.............................................................................................................................................................30
2.14 Environmental Protection........................................................................................................................................... 30
3 Product Structure......................................................................................................................... 31
3.1 System Architecture..................................................................................................................................................... 32
3.2 Service Signal Processing Flow................................................................................................................................... 34
3.3 Ports.............................................................................................................................................................................. 36
3.4 Indicators...................................................................................................................................................................... 41
3.5 Labels............................................................................................................................................................................43
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description Contents
4 Network Management System..................................................................................................46
4.1 Network Management Solutions.................................................................................................................................. 47
4.2 Web LCT...................................................................................................................................................................... 48
4.3 Mobile LCT.................................................................................................................................................................. 48
4.4 U2000-T........................................................................................................................................................................49
4.5 U2000-M...................................................................................................................................................................... 51
5 Technical Specifications.............................................................................................................52
5.1 Ethernet Service Specifications.................................................................................................................................... 53
5.2 RF Performance............................................................................................................................................................54
5.3 Antenna Performance................................................................................................................................................... 55
5.4 Predicted Reliability..................................................................................................................................................... 55
5.5 Integrated System Performance....................................................................................................................................56
6 Accessories.................................................................................................................................... 58
6.1 Power Injector...............................................................................................................................................................59
6.2 USB Flash Drives......................................................................................................................................................... 59
6.3 Wi-Fi Module............................................................................................................................................................... 62
7 Cables.............................................................................................................................................64
7.1 Outdoor Network Cables.............................................................................................................................................. 65
7.2 Outdoor Optical Fiber...................................................................................................................................................66
7.3 RSSI Cables..................................................................................................................................................................67
7.4 RTN 360 PGND Cables................................................................................................................................................68
A Appendix......................................................................................................................................69
A.1 Port Loopbacks............................................................................................................................................................ 70
A.2 Component Photos.......................................................................................................................................................70
A.3 Compliance Standards................................................................................................................................................. 71
A.3.1 ITU-R Standards.......................................................................................................................................................71
A.3.2 ITU-T Standards....................................................................................................................................................... 73
A.3.3 ETSI Standards......................................................................................................................................................... 74
A.3.4 CEPT Standards........................................................................................................................................................76
A.3.5 IEC Standards........................................................................................................................................................... 77
A.3.6 IETF Standards......................................................................................................................................................... 78
A.3.7 IEEE Standards.........................................................................................................................................................79
A.3.8 Other Standards........................................................................................................................................................ 80
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
About This Chapter
The OptiX RTN 360 radio transmission system (RTN 360 for short) is a full-outdoor radio
transmission product that operates at the V-band (a frequency band ranging from 59 GHz to
64 GHz).
1 Product Introduction
1 Product Introduction
1.1 Network Application
RTN 360 is tailored for service backhaul for small cell base stations that are deployed on
buildings or at the street level. RTN 360 plays an important role in the Huawei radio backhaul
solution for small cell base stations.
1.2 Product Specifications
RTN 360's specifications meet the requirements of service backhaul for small cell base
stations. In addition, RTN 360 features excellent immunity to interference, and is easy to
install and maintain.
1.3 Site Configurations
RTN 360s are usually powered by power injector (PI) or other standard power sourcing
equipment (PSE). RTN 360s can form sites providing one-direction, two-direction, or multidirection microwave links.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1
V-Band
V-Band
V-Band
V-Band
V-Band
V-Band
Macro cell RTN 360
Small cell
V-Band
V-Band
V-Band
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
1.1 Network Application
RTN 360 is tailored for service backhaul for small cell base stations that are deployed on
buildings or at the street level. RTN 360 plays an important role in the Huawei radio backhaul
solution for small cell base stations.
As V-band full-outdoor radio equipment, RTN 360 has the following characteristics:
l RTN 360 operates at the frequency band ranging from 59 GH to 64 GHz. It requires
unobstructed line of sight (LOS) and features low inter-site interference and rich idle
frequency spectrum resources. A V-band link can span a maximum distance of 300 m,
meeting the requirements of service backhaul for small cell base stations. RTN 360 can
provide large-capacity microwave links for small cell base stations densely deployed in
downtown areas.
l RTN 360 is a highly integrated full-outdoor radio transmission product. Its antenna, RF
unit, and baseband unit are integrated into an outdoor unit that supports zero-footprint
installation, providing carriers with cost-effective full-outdoor radio solutions.
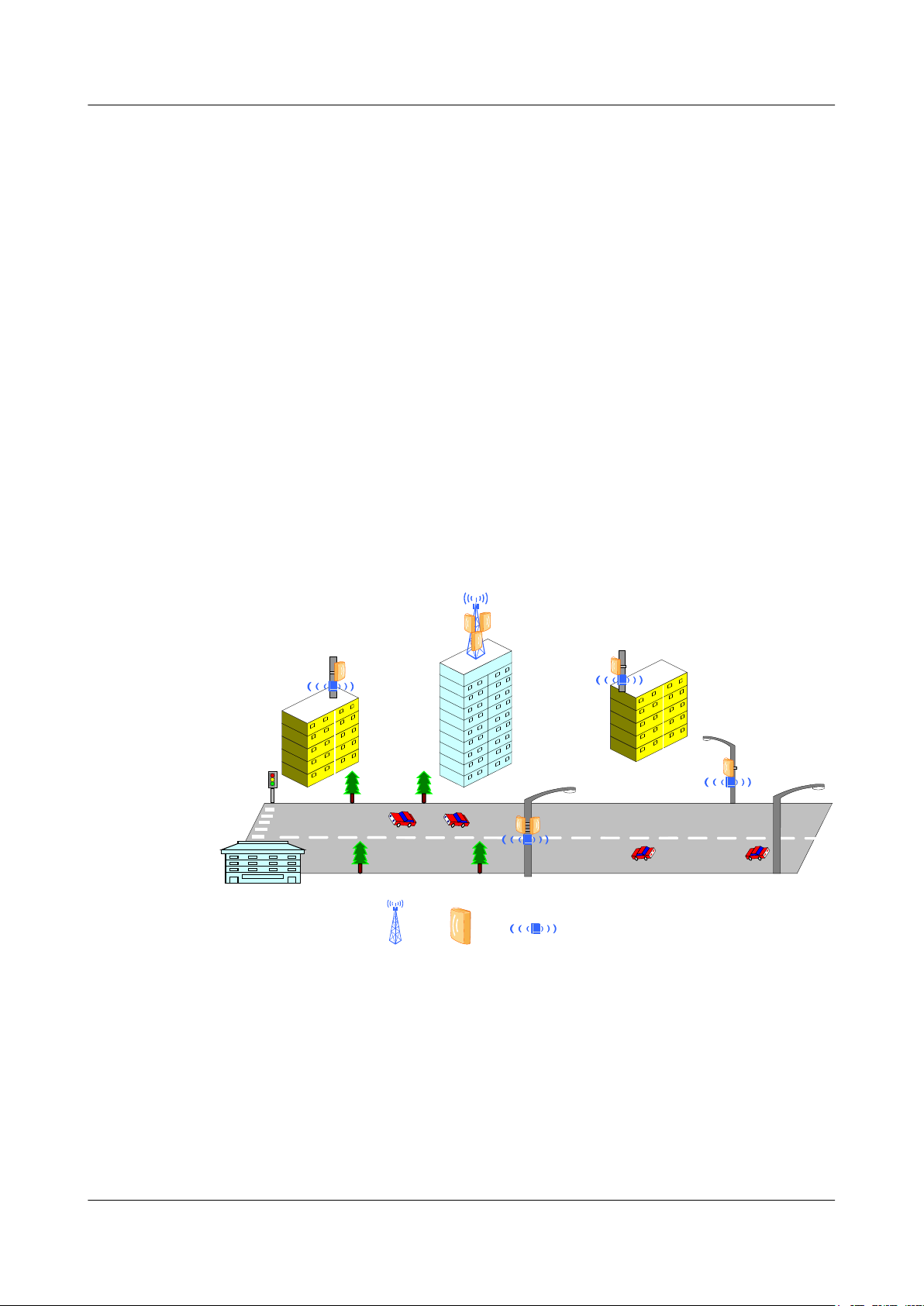
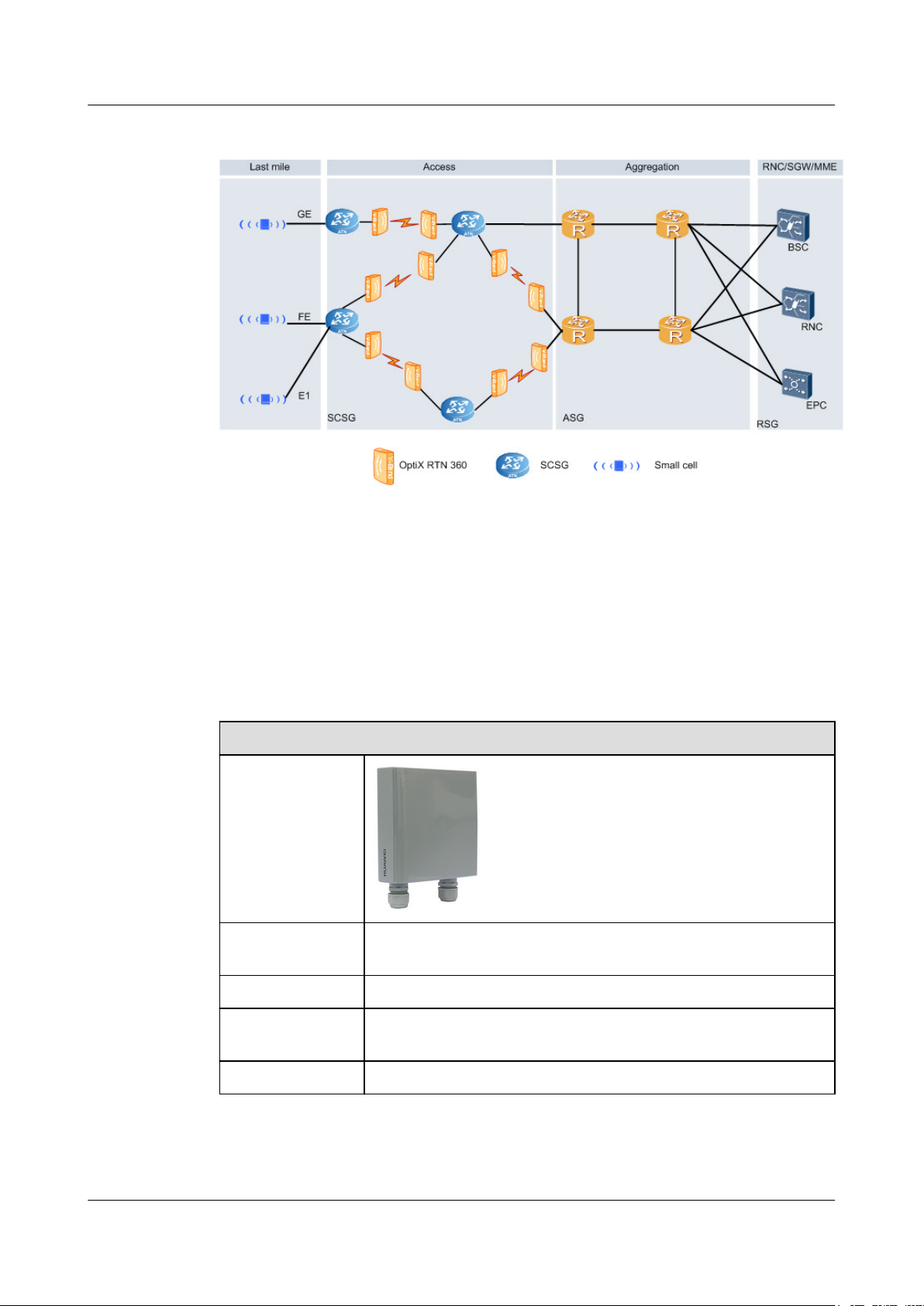
RTN 360 provides backhaul links for small cell base stations on buildings or at the street level
in downtown areas. See
Figure 1-1.
1 Product Introduction
Figure 1-1 RTN 360 backhaul link solution for small cell base stations
RTN 360 can work with the small cell site gateway (SCSG) to provide a microwave channel
solution for transparent transmission for small cells on the IP RAN. See Figure 1-2.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Figure 1-2 RTN 360 working with the SCSG
1 Product Introduction
1.2 Product Specifications
RTN 360's specifications meet the requirements of service backhaul for small cell base
stations. In addition, RTN 360 features excellent immunity to interference, and is easy to
install and maintain.
Table 1-1 Product Specifications
Appearance
Dimensions (H x
W x D)/Weight
Antenna Built-in panel antenna
Operating
frequency band
192.5 mm x 192.5 mm x 70 mm/2.5 kg
59 GHz to 64 GHz
Product Specifications
Duplex mode TDD
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
1 Product Introduction
Product Specifications
Radio working
mode (modulation
scheme/channel
spacing)
AM Supported
Air-interface
throughput
Maximum
transmission
distance
Service port Two GE electrical service ports
RF configuration
mode
Power supply
mode
Basic Ethernet
features
Modulation scheme: QPSK, 16QAM, 32QAM
Channel spacing: 200 MHz
≥ 800 Mbit/s
300 m
1+0 configuration
Power over Ethernet (PoE), supplied by the AC power injector (PI),
DC power injector (PI), and other standard power sourcing
equipment (PSE)
l E-Line/E-LAN
l QinQ
l QoS
l HQoS
l Synchronous Ethernet
1.3 Site Configurations
RTN 360s are usually powered by power injector (PI) or other standard power sourcing
equipment (PSE). RTN 360s can form sites providing one-direction, two-direction, or multidirection microwave links.
1.3.1 Sites Providing One-Direction Microwave Links
If a small cell base station is located at the end of a transmission link, an RTN 360 is required
to provide a 1+0 unprotected microwave link. The RTN 360 receives power signals and
service signals from power infector (PI).
Figure 1-3 illustrates configurations of a site providing a one-direction microwave link.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4
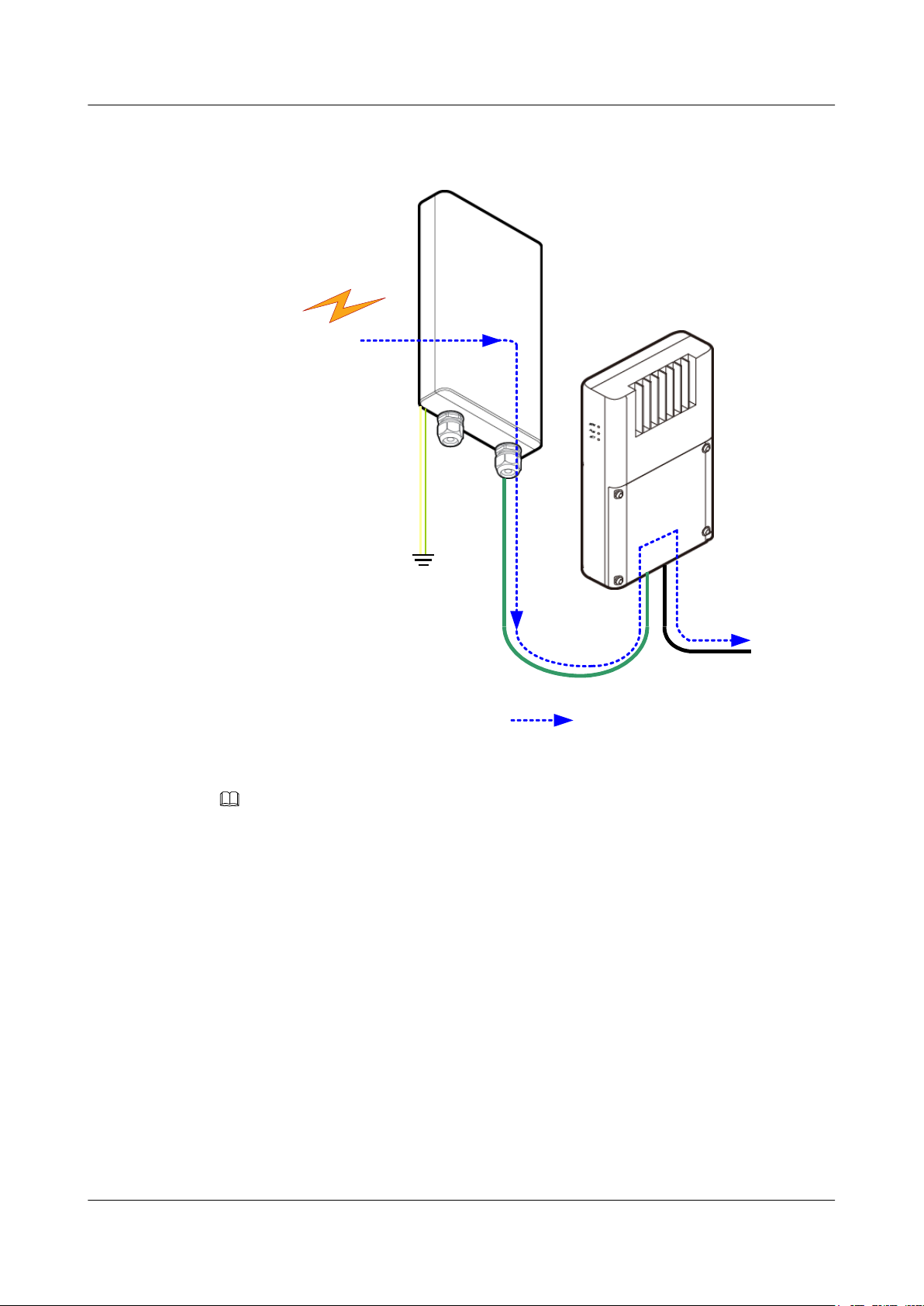
P&E
GE
To Small
cell
P&E
RTN 360
Power
Injector
Down link Service
From a
remote
RTN 360
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Figure 1-3 Site providing a one-direction microwave link
1 Product Introduction
NOTE
If a small cell base station can serve as standard PSE, RTN 360s can directly receive power signals and
service signals from the small cell base station.
1.3.2 Sites Providing Two-Direction Microwave Links
If a small cell base station is an intermediate node on a transmission link, two RTN 360s are
required to provide two 1+0 unprotected microwave links in different directions. RTN 360s
receive power signals and service signals from the Dock of the small cell base station.
Figure 1-4 illustrates configurations of a site providing two microwave links in different
directions.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5
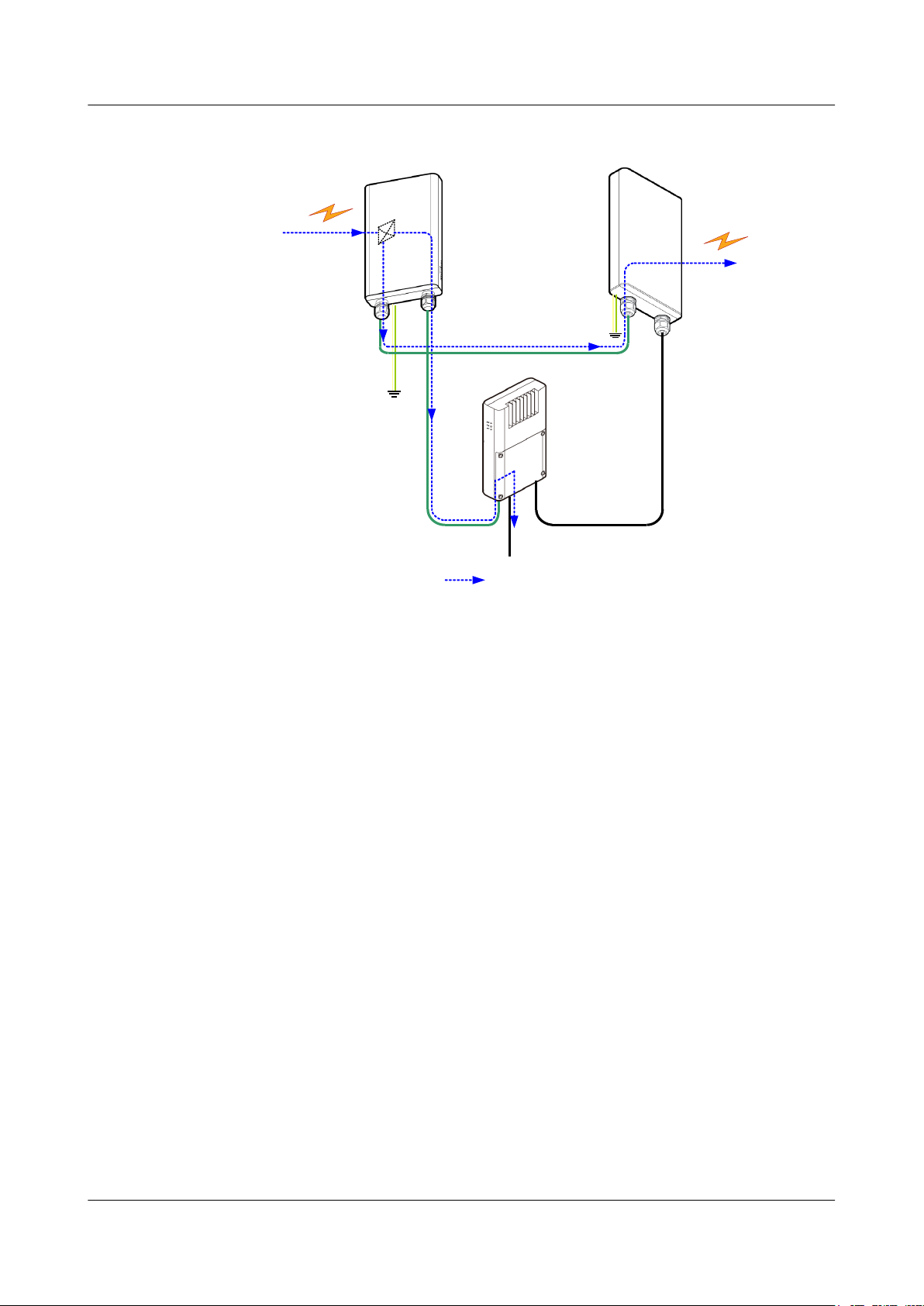
P&E1
To Small cell
P&E
RTN 360
Power
Injector
Down link Service
RTN 360
From a remote
RTN 360
To a remote
RTN 360
GE1
P&E2
LAN Switch
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Figure 1-4 Site providing two microwave links in different directions
1 Product Introduction
A site providing two-direction microwave links can work together with RTN B20 PIs to
receive service signals from small cell base stations and power signals. Two RTN 360s are
cascaded through GE(e) ports for service aggregation.
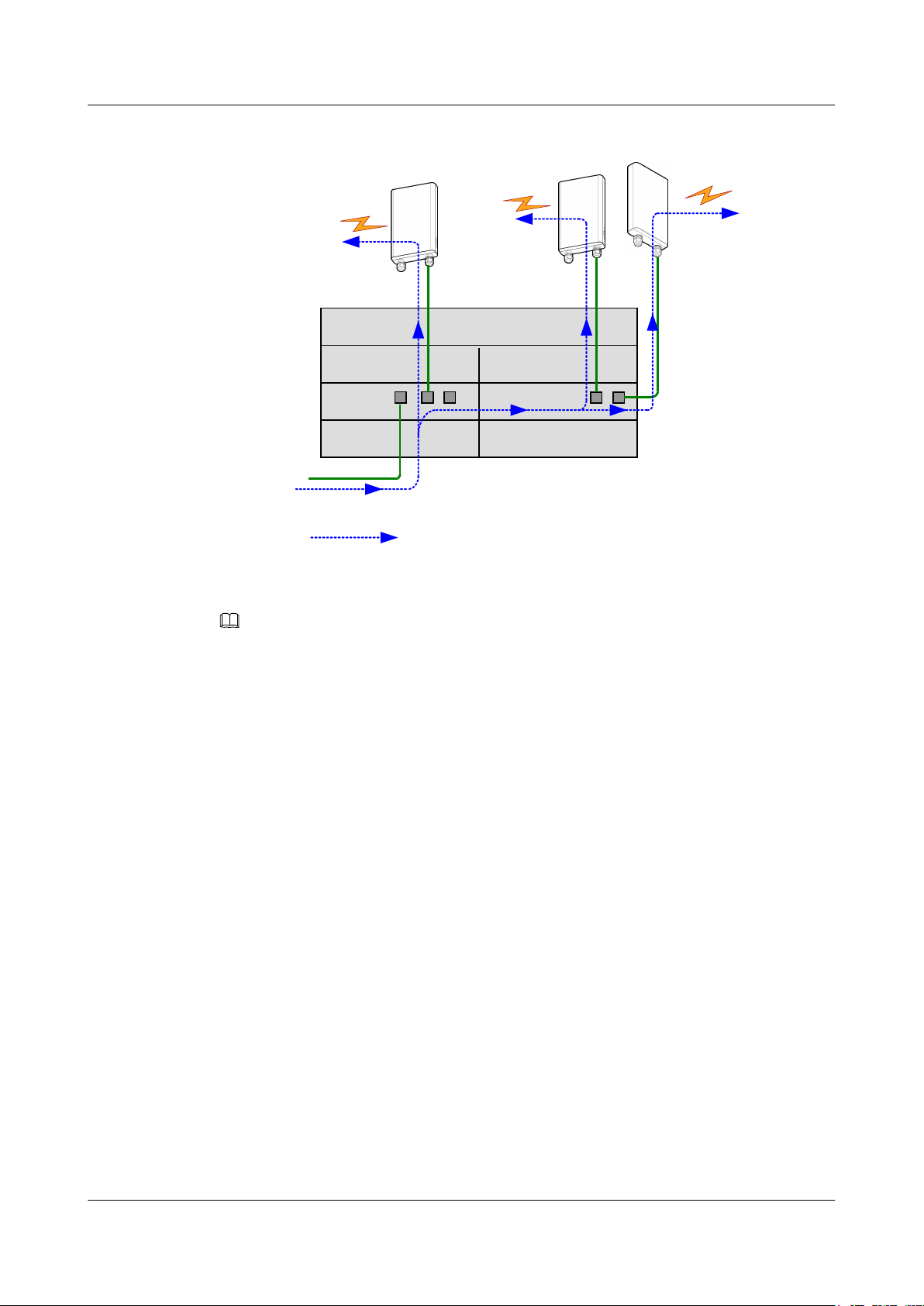
1.3.3 Sites Providing Multi-direction Microwave Links
If a macro base station connects to multiple small cell base stations in a star topology, in
addition to multiple RTN 360s, an OptiX RTN 900 (IDU) (for example, an IDU 950A) or
other power sourcing equipment (PSE) is required. The IDU supplies power to the RTN 360s
through a PoE board (for example, an EG4P board) and aggregates services.
Figure 1-5 illustrates configurations of a site providing multi-direction microwave links.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
6
EG4P
ISV3
ISV3
EG4P
P&E
P&E
IDU 950A
To a remote
RTN 360
To a remote
RTN 360
To a remote
RTN 360
From EPC
P&E
CSHO
Downlink service
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Figure 1-5 Site providing multi-direction microwave links
1 Product Introduction
NOTE
In addition to RTN 360s, the OptiX RTN 900 IDU may connect to FOs or ODUs operating at other
frequency bands to implement backhaul.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
7

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
About This Chapter
RTN 360 provides a variety of functions and features.
2 Functions and Features
2 Functions and Features
2.1 Integration
RTN 360 integrates a built-in antenna and uses a wide frequency band design, which allows a
single chassis to cover the entire V-band.
2.2 TDD
Time division duplex (TDD) has unique advantages over frequency division duplex (FDD) in
asymmetric transmission and high frequency spectrum resource utilization.
2.3 Automatic Frequency Selection
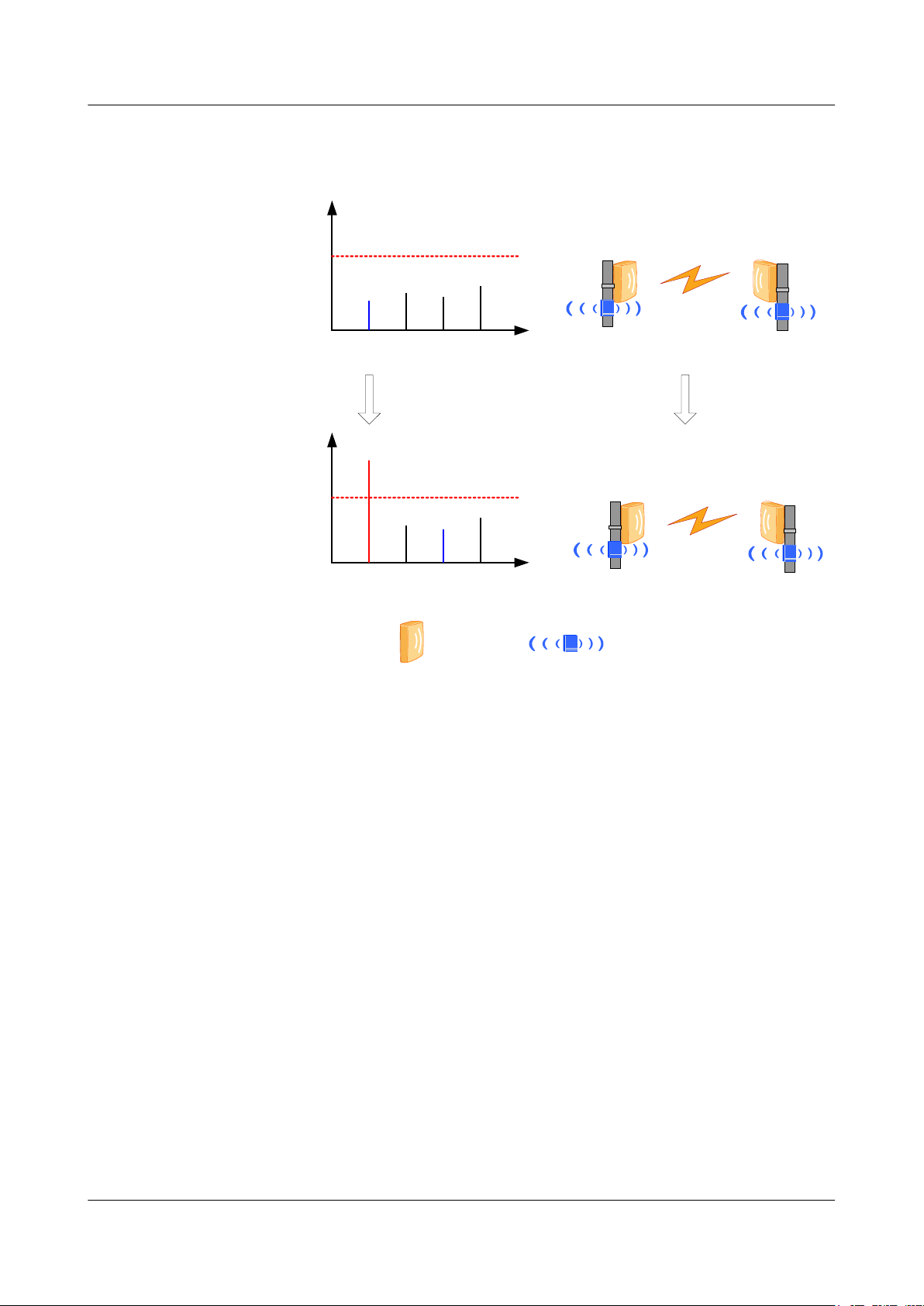
RTN 360 supports automatic frequency selection, which enables it to automatically select an
interference-free channel as the working channel.
2.4 Adaptive Modulation
Adaptive modulation (AM) technology automatically adjusts the modulation scheme based on
channel quality.
2.5 Power over Ethernet
The RTN 360 provides a P&E port through which the RTN 360 supports power over Ethernet
(PoE) as a powered device (PD).
2.6 Ethernet Service Processing Capability
RTN 360 can process native Ethernet services.
2.7 QoS
RTN 360 supports quality of service (QoS) functions, including traffic classification, traffic
policing, congestion avoidance, queue scheduling, and traffic shaping.
2.8 Clock Features
RTN 360's clock features meet clock transmission requirements of mobile communications
networks and offer a wide selection of clock protection mechanisms.
2.9 Network Management
RTN 360 supports multiple network management modes and provides comprehensive
management information exchange solutions.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
2.10 Rapid Deployment
A variety of technologies are used to simplify RTN 360 installation so that wireless
installation personnel can deploy an RTN 360 within 30 minutes.
2.11 Easy Maintenance
RTN 360 supports contact-free maintenance, powerful equipment-level OAM functions, and
end-to-end TP-Assist.
2.12 Security Management
RTN 360 works with its network management system (NMS) to prevent unauthorized logins
and operations, ensuring equipment management security.
2.13 Energy Saving
RTN 360 consumes less energy by using:
2.14 Environmental Protection
RTN 360 is designed to meet environmental protection requirements. The product complies
with restriction of hazardous substances (RoHS) directives.
2 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
9
Panel
antenna
Baseband
board
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
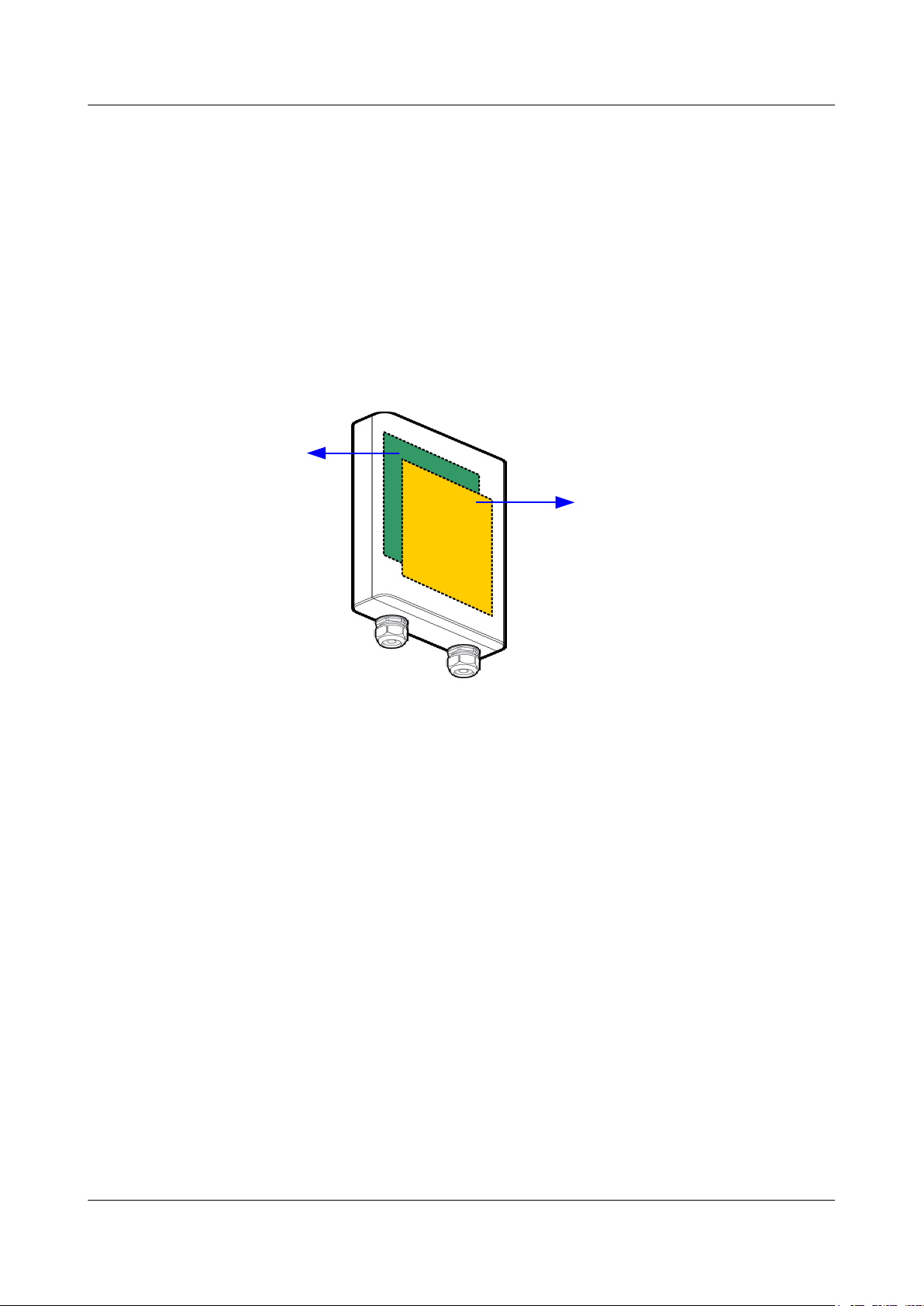
2.1 Integration
RTN 360 integrates a built-in antenna and uses a wide frequency band design, which allows a
single chassis to cover the entire V-band.
Built-in Antenna
RTN 360 integrates its system control unit, clock unit, power unit, baseband unit, RF unit, and
antenna into a single chassis. See
Figure 2-1 Integrated chassis with a built-in antenna
2 Functions and Features
Figure 2-1.
Such a highly integrated design facilitates quick and flexible installation of RTN 360s in fulloutdoor scenarios.
Wide Frequency Band
RTN 360 uses a wide frequency band design, which enables a single chassis to cover the
entire V-band from 59 GHz to 64 GHz. This eliminates the need to distinguish TX high and
low sites, which means that spare parts need to be prepared for only one equipment model.
Both RTN 360 and Huawei small cell base stations can be installed on walls and poles. They
are similar in appearance and look harmonious when installed together.
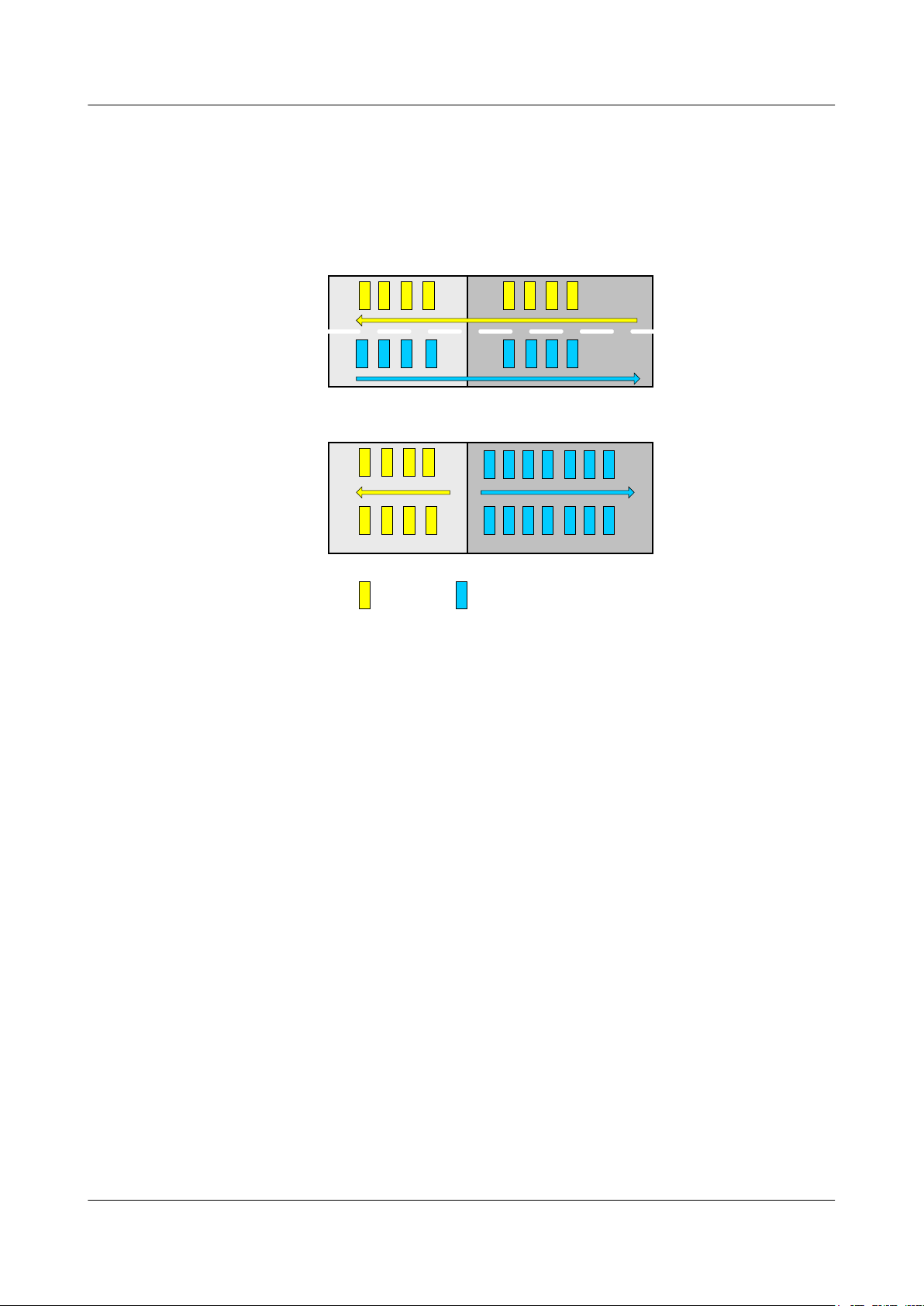
2.2 TDD
Time division duplex (TDD) has unique advantages over frequency division duplex (FDD) in
asymmetric transmission and high frequency spectrum resource utilization.
In FDD mode, symmetric frequencies are required to function as the uplink and downlink
channels. The V-band is license-free in most areas and may be used by multiple users, and it
is difficult to obtain interference-free symmetric frequencies. Therefore, RTN 360 uses TDD
mode.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
t0
t1
FDD
f1
f2
t0
t1
TDD
f1 or f2
Downlink
data
Uplink
data
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
In TDD mode, asymmetric frequencies are used. Uplink and downlink data is transmitted in
different time periods. The ratio of timeslots for uplink data to those for downlink data can be
configured based on service requirements, flexibly using frequency resources.
Figure 2-2 Comparison between FDD and TDD modes
2 Functions and Features
Using TDD mode, RTN 360 has the following advantages:
l One RTN 360 can cover the operating frequency band (59 GHz to 64 GHz), eliminating
the need to distinguish TX high and low sites.
l Timeslots for uplink and downlink data can be flexibly adjusted based on actual traffic.
The ratio of timeslots for uplink data to those for downlink data can be configured to 5:1,
4:1, 3:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, or 1:5.
2.3 Automatic Frequency Selection
RTN 360 supports automatic frequency selection, which enables it to automatically select an
interference-free channel as the working channel.
RTN 360 scans frequencies within a specified range to select interference-free channels. See
Figure 2-3.
Automatic frequency selection applies to the following two scenarios:
l During commissioning in site deployment, this function is used to obtain interference-
free channels, releasing engineers from planning microwave link frequencies.
l For an in-service RTN 360, this function is used to reselect and switch to an interference-
free channel if the current microwave link is interrupted or fails due to interference on
the working channel, improving microwave links' immunity to interference.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
f0 f1 f2 f3
V-Band
V-Band
f0
Interference
signal strength
f0 f1 f2 f3
V-Band
V-Band
f2
f0 interference signal
becoming stronger
Automatically
selecting f2
V-Band
RTN 360
Small cell
base station
Interference
signal threshold
Interference
signal threshold
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Figure 2-3 Automatic frequency selection diagram
2 Functions and Features
2.4 Adaptive Modulation
Modulation Scheme and Air-interface Capacity
Adaptive modulation (AM) technology automatically adjusts the modulation scheme based on
channel quality.
When AM technology is enabled and the same channel spacing is used, the available radio
service bandwidth varies according to the modulation scheme: the higher the modulation
efficiency, the higher the bandwidth of the transmitted services.
l When channel conditions are favorable (such as on sunny days), the equipment uses a
higher-order modulation scheme to transmit more user services. This improves
transmission efficiency and spectrum utilization of the system.
l When channel conditions are unfavorable (such as on stormy or foggy days), the
equipment uses a lower-order modulation scheme to ensure that higher-priority services
are transmitted first. If some lower-priority queues become congested due to a lack of
available bandwidth, some or all interfaces in these queues are discarded. This method
improves the anti-interference capabilities of a microwave link and ensures link
availability for high-priority services.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
QPSK
16QAM
32QAM
16 QAM
QPSK
32 QAM
99.999%
Receive Signal
99.995%
99.99%
High-priority service
Low-priority
service
16QAM
32QAM
Low-priority
service
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Modulation Scheme Shift and Service Priorities
For Ethernet services transmitted through IP microwave, priorities can be set based on the
service bandwidth and QoS policies corresponding to the current modulation scheme, to
control service transmission. The transmission of services with the highest priority is ensured.
With the QoS technology, ethernet services are scheduled to queues with different priorities.
The services in different queues are transmitted to the microwave port after running the queue
scheduling algorithm. When modulation scheme switching occurs, certain queues may be
congested due to insufficient capacity at the air interface. As a result, certain services or all
the services in these queues are discarded.
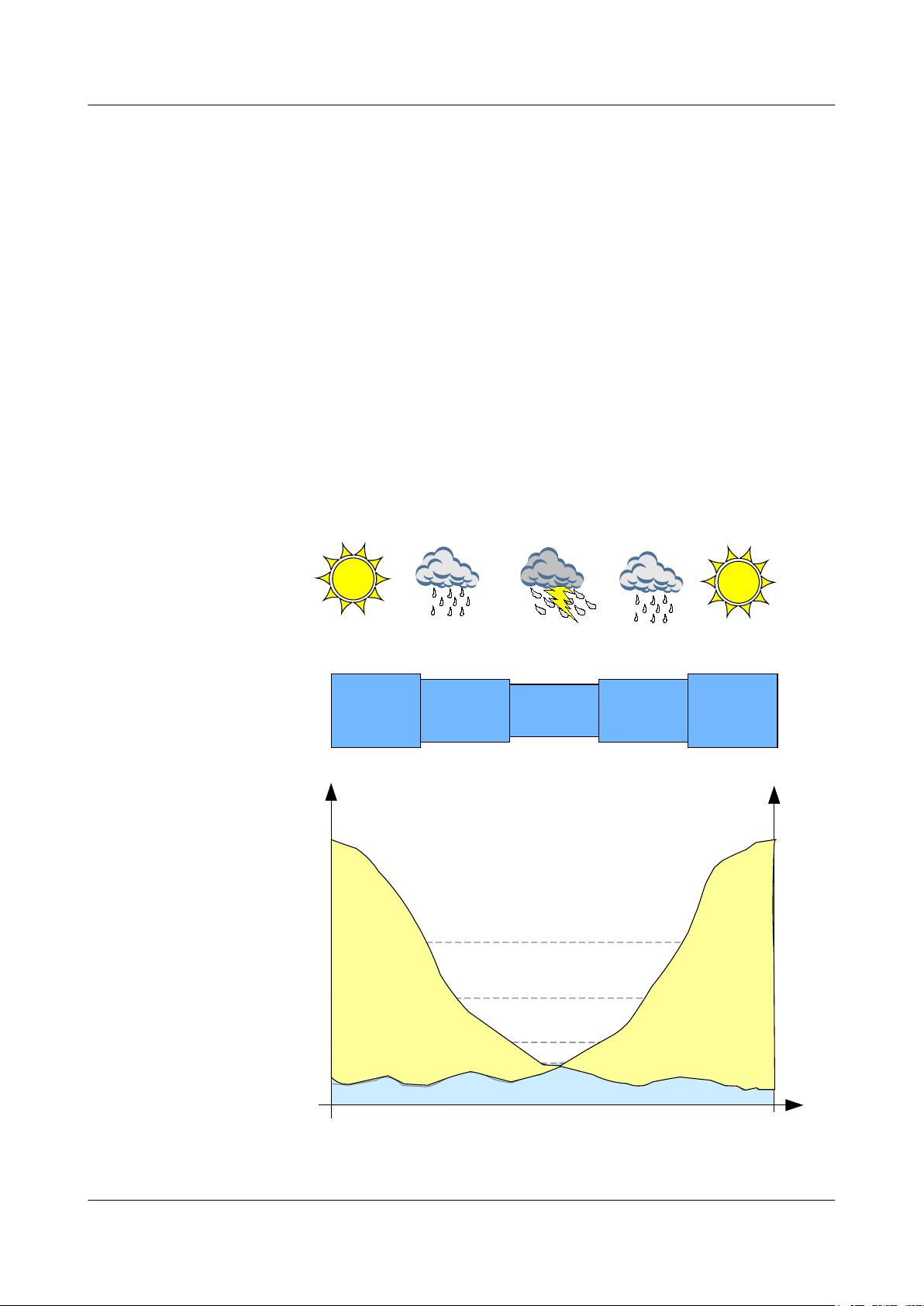
Adaptive Modulation
Figure 2-4 shows how the modulation scheme shifts step by step according to weather
changes and how modulation schemes affect service throughput and reliability. In this
example, the modulation scheme of guaranteed AM capacity is QPSK and the modulation
scheme of full AM capacity is 32QAM.
Figure 2-4 Adaptive modulation
2 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
Power
injector
P&E port
GE signal
Power
signal
P&E port
Injecting
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Characteristics
The AM technology used by RTN 360 has the following characteristics:
l Supports the QPSK, 16QAM, and 32QAM modulation schemes.
l Can configure both the lowest-order modulation scheme (also called reference scheme or
modulation scheme of guaranteed AM capacity) and the highest-order modulation
scheme (also called nominal scheme or modulation scheme of full AM capacity).
l Can switch modulation schemes without changing the transmit frequency, receive
frequency, or channel spacing.
l Switches modulation schemes step-by-step.
l Features hitless switching. When the modulation scheme is downshifted, high-priority
services are not affected while low-priority services are discarded. Switching is
successful even when 100 dB/s channel fast fading occurs.
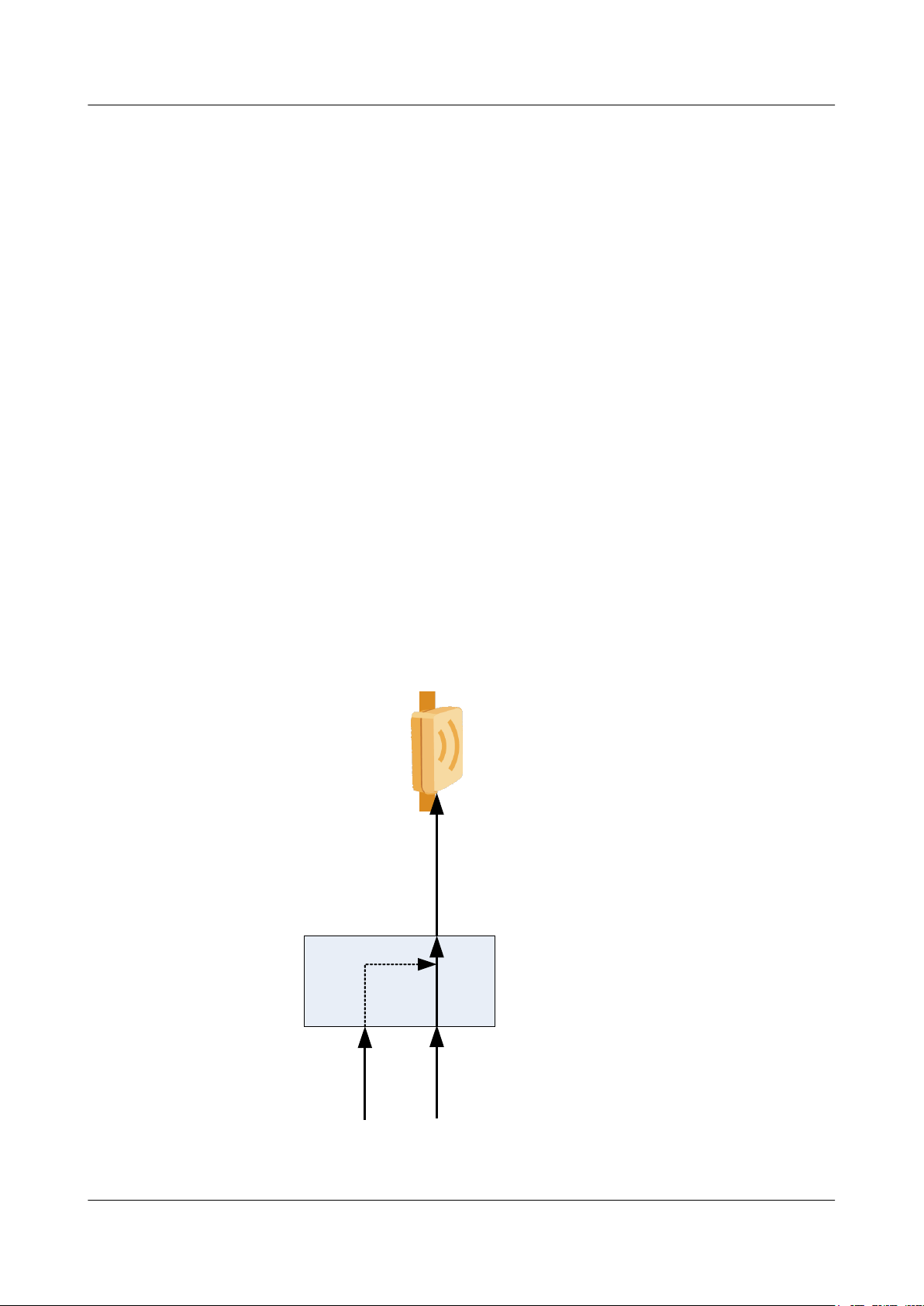
2.5 Power over Ethernet
The RTN 360 provides a P&E port through which the RTN 360 supports power over Ethernet
(PoE) as a powered device (PD).
2 Functions and Features
In PoE mode, an outdoor network cable carries Ethernet service signals along with DC power
signals. PoE has the following advantages:
l Reduces the number of power cables and simplifies installation.
An RTN 360 can work with a power injector (PI) to implement power over Ethernet through
its P&E port. See
Figure 2-5 Working with a PI
Figure 2-5.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
GE and -48V signal
P&E port
RTN 905 2E
P&E port
GE1/P1 GE2/P2
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
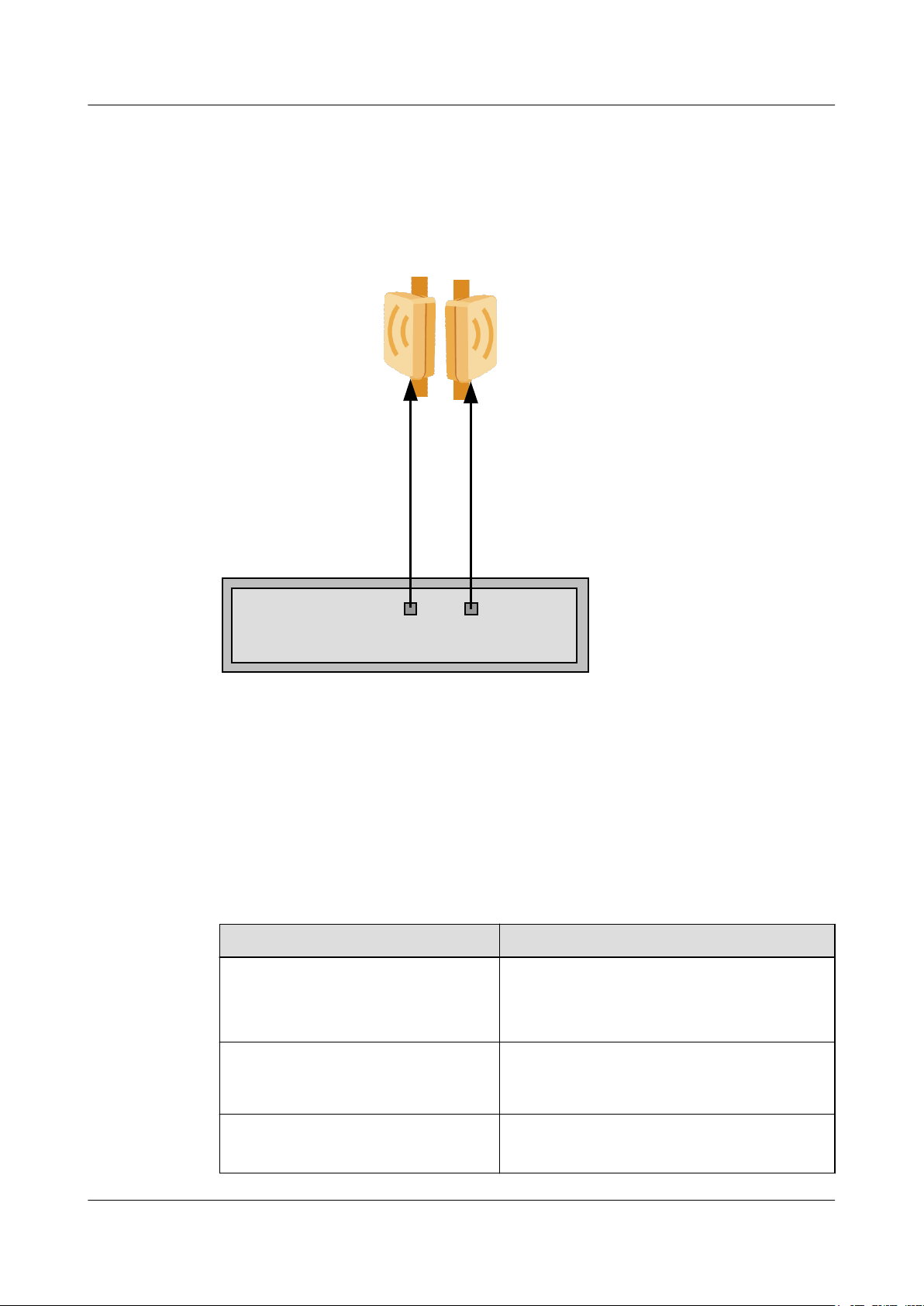
An RTN 360 can also work with other power sourcing equipment (PSE), such as an RTN 900
IDU, to implement power over Ethernet through its P&E port. For example, when an OptiX
RTN 905 2E IDU is used, it provides two PoE ports, as shown in
Figure 2-6 Working with an OptiX RTN 900
2 Functions and Features
Figure 2-6.
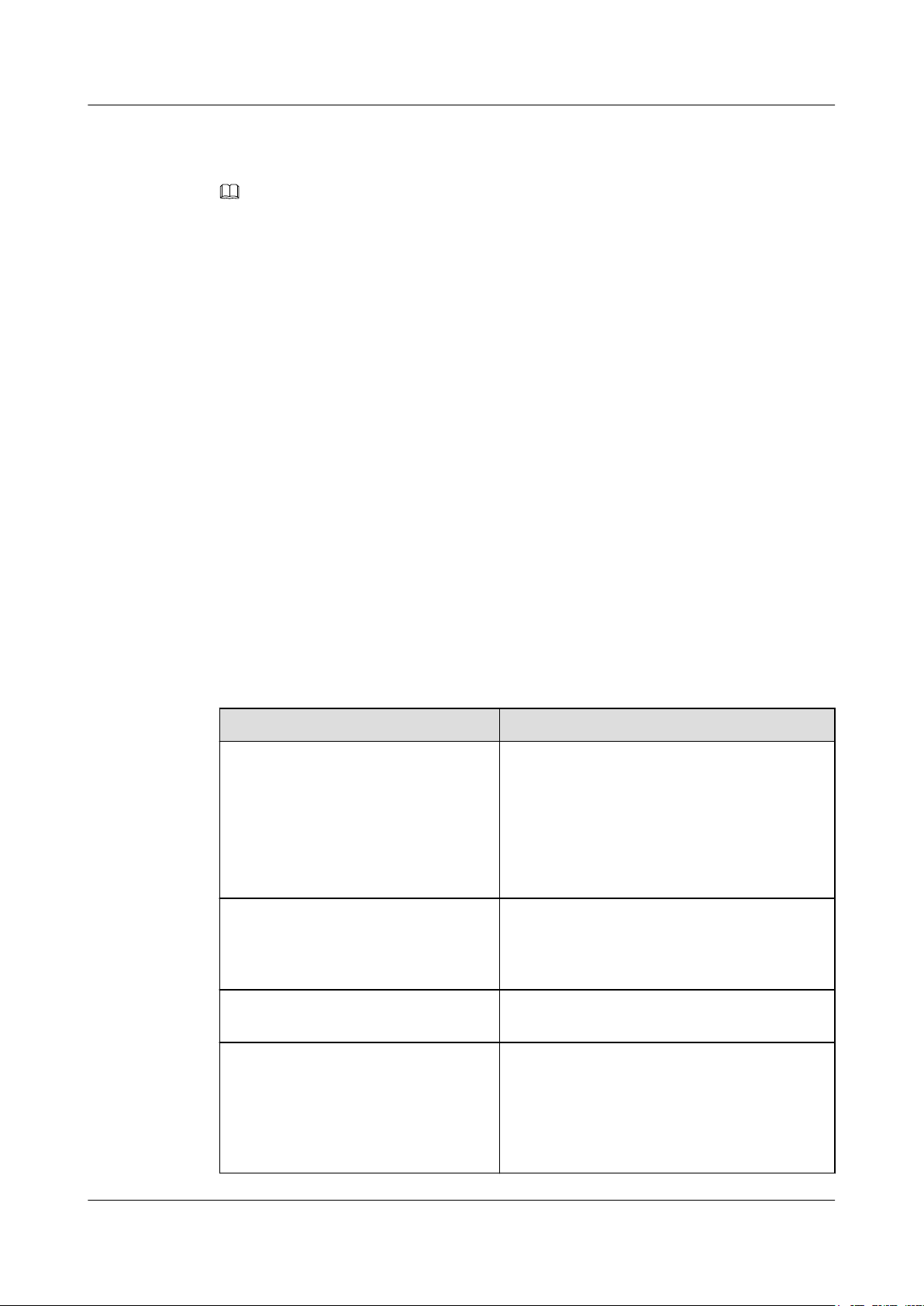
2.6 Ethernet Service Processing Capability
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
RTN 360 can process native Ethernet services.
Table 2-1 Ethernet service processing capability
Item Description
Service ports Two GE service ports
Port attributes The GE electrical port supports 10M full-
Ethernet service types
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
l The first GE port is a P&E port.
l The second GE port is a fixed electrical port.
duplex, 100M full-duplex, 1000M full-duplex,
and auto-negotiation.
l E-Line
l E-LAN
15
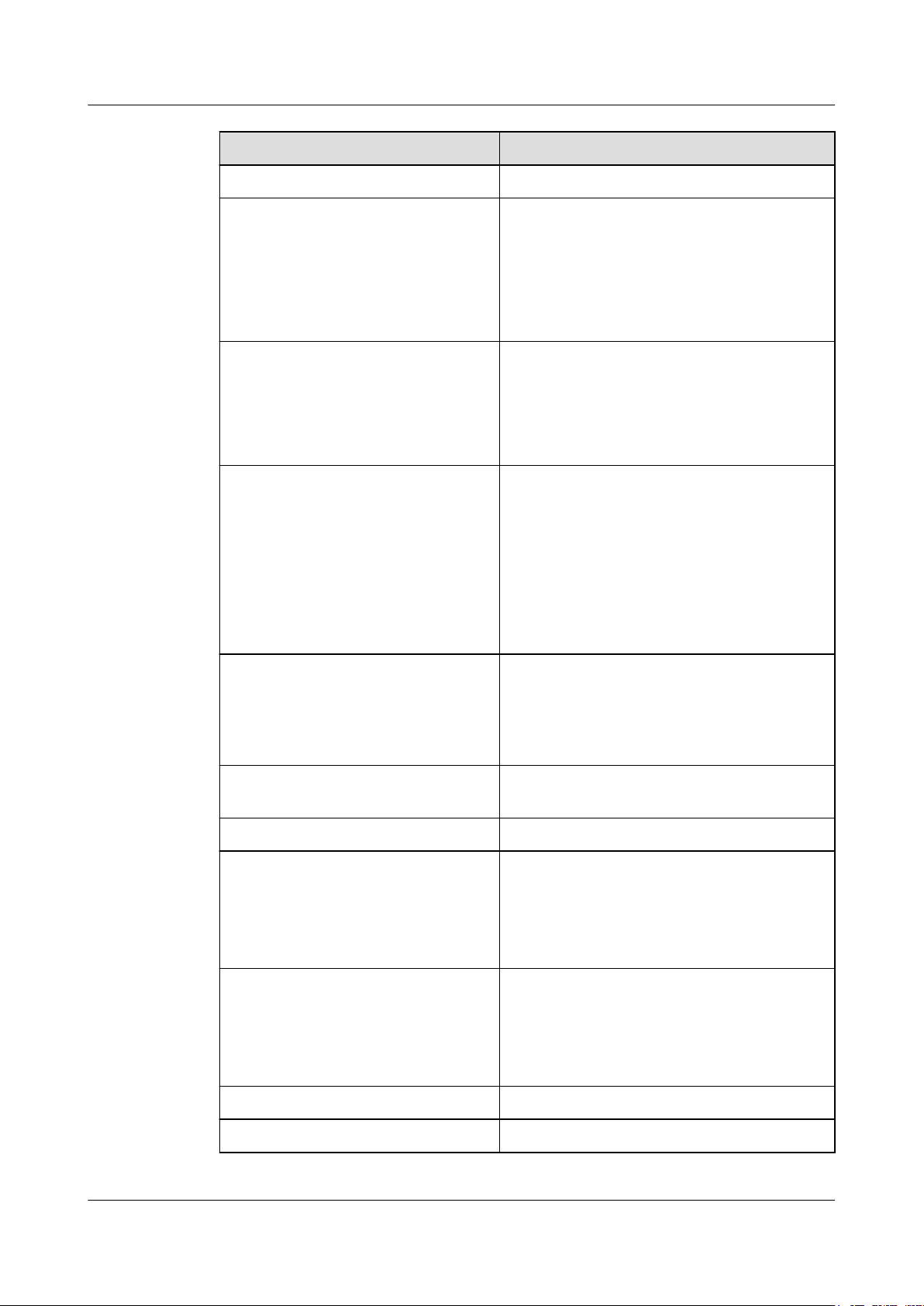
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Item Description
Range of maximum frame length 1518 bytes to 9600 bytes
2 Functions and Features
VLAN
QinQ
MAC address management
l Adds, deletes, and swaps VLAN tags that
comply with IEEE 802.1Q/P, and forwards
packets based on VLAN tags.
l Processes packets based on the port tag
attribute (Tag/Hybrid/Access).
l The VLAN ID ranges from 1 to 4094.
l Adds, deletes, and swaps S-TAG tags, and
forwards packets based on S-VLAN tags.
l The S-VLAN ID ranges from 1 to 4094.
l The QinQ type domain is configurable. The
default value is 88A8.
l Supports MAC address self-learning for E-
LAN services in two learning modes: SVL
and IVL.
l Filters blacklisted MAC addresses.
l Sets static MAC address entries.
l Supports a MAC address table with a
maximum of 16K capacity (including static
and blacklist entries).
Link-state pass through (LPT) Supports simple LPT. When a microwave link is
faulty, the related RTN 360 automatically
disables the remote Ethernet port that is
connected to a user-to-network interface (UNI)
device.
QoS/HQoS Supports QoS and HQoS. For details, see
2.7
QoS.
Traffic control Supports IEEE 802.3x-compliant traffic control.
ETH OAM
l Supports IEEE 802.1ag- and IEEE 802.3ah-
compliant ETH OAM.
l Supports ITU-T Y.1731-compliant packet
loss measurement, delay measurement, and
delay variation measurement.
Ethernet performance monitoring
l Supports IETF RFC 2819-compliant remote
network monitoring (RMON).
l Supports measurement of real-time and
historical traffic, bandwidth utilization, and
packet loss for ports.
Synchronous Ethernet Supported
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Supported
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
NOTE
l RTN 360 supports a maximum of 64 E-Line services. The supported E-Line services fall into the
following types:
l Port-based E-Line services
l Port+VLAN-based E-Line services
l Port+QinQ-based E-Line services
l RTN 360 supports only one E-LAN service. The supported E-LAN services fall into the following types:
l IEEE 802.1d bridge-based E-LAN services
l IEEE 802.1Q bridge-based E-LAN services
l IEEE 802.1ad bridge-based E-LAN services
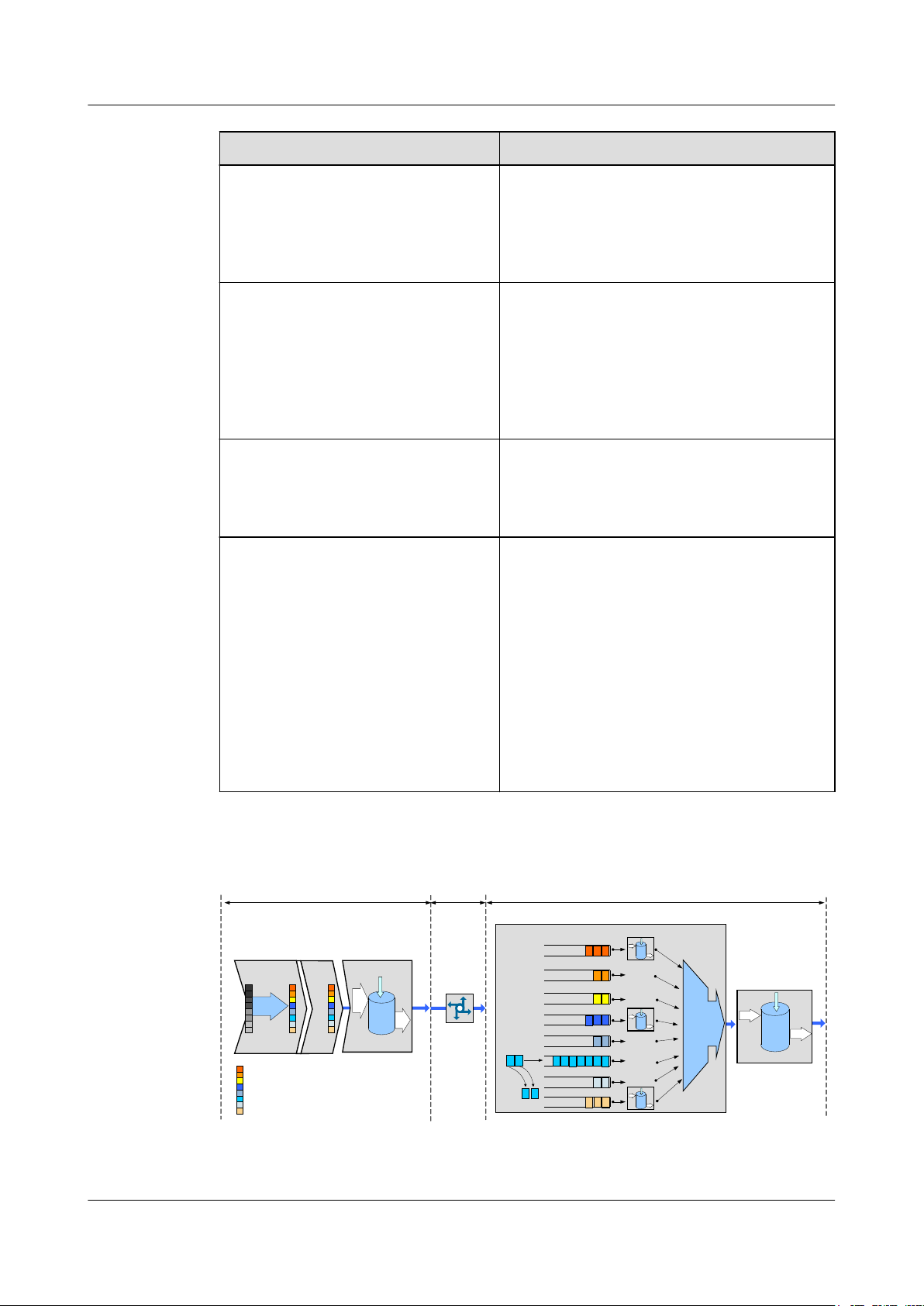
2.7 QoS
RTN 360 supports quality of service (QoS) functions, including traffic classification, traffic
policing, congestion avoidance, queue scheduling, and traffic shaping.
2 Functions and Features
QoS Functions
QoS provides different levels of service quality in certain aspects of services as required, such
as bandwidth, delay, jitter, and packet loss ratio. This ensures that the request and response of
a user or application reaches an expected quality level.
Table 2-2 QoS functions
Function Description
Simple traffic classification (DiffServ)
l Supports one DiffServ (DS) domain.
l Maps Ethernet services into different per-hop
behaviors (PHBs) based on C-VLAN
priorities, S-VLAN priorities, IP
differentiated services code point (DSCP)
values, or MPLS experimental bits (EXP)
values.
Complex traffic classification Supports traffic classification by MAC address,
VLAN ID, VLAN priority, IP address, DSCP
value, protocol type, port ID, or Internet Control
Message Protocol (ICMP) type at ports.
ACL Supports ACL based on complex traffic
classification.
Traffic policing Supports committed access rate (CAR) based on
complex traffic classification at ports and
supports the setting of the committed
information rate (CIR), peak information rate
(PIR), committed burst size (CBS), and peak
burst size (PBS).
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
Forwarding
Queue scheduling
Ingress Egress
Packet switching
Congestion
avoidance
Buffer queue
Threshold
Queue traffic
shaping
Scheduling
Drop
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Port shaping
Token
bucket
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Simple traffic
classification
Mapping
DiffServ
CoS x
.
.
.
CoS z
Traffic
monitoring
CAR
Token
bucket
Flow
Complex traffic
classification
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Function Description
2 Functions and Features
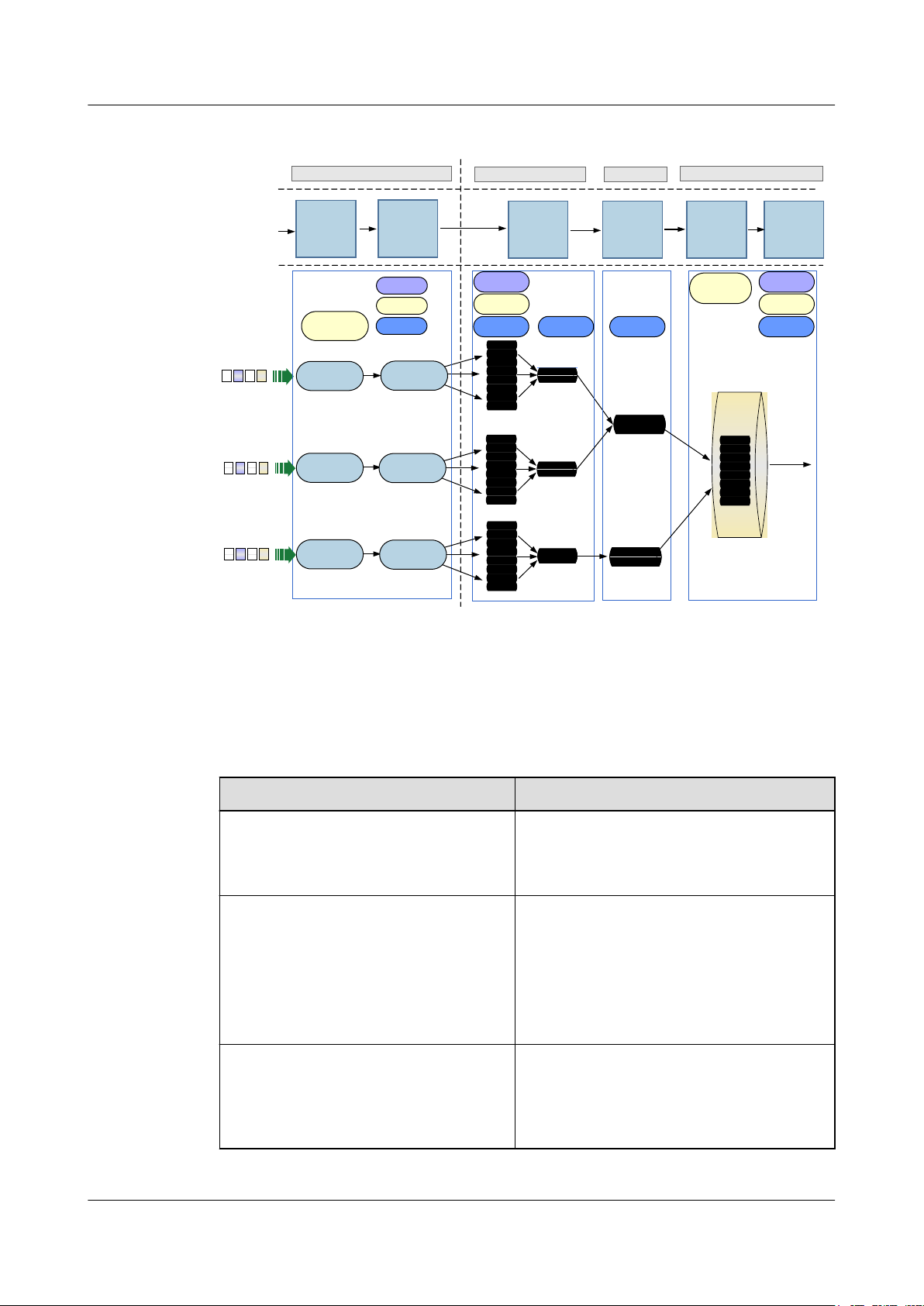
Congestion avoidance
Queue scheduling
Traffic shaping
HQoS
l Supports tail drop at both microwave ports
and Ethernet ports.
l Supports weighted random early detection
(WRED) at both microwave ports and
Ethernet ports.
l Supports eight levels of priority scheduling
at both Ethernet ports and microwave ports.
l Flexibly sets the queue scheduling scheme
for each Ethernet port and microwave port.
The queue scheduling schemes include strict
priority (SP), weighted round robin (WRR),
and SP+WRR.
l Supports traffic shaping for egress queues
and egress ports.
l Supports the setting of PIR in increments of
64 kbit/s and the setting of PBS.
l For QinQ NNI ports, supports two levels of
queue scheduling for QinQ queues and
egress queues, and supports four levels of
rate limiting for QinQ queues, QinQ, egress
queues, and egress ports.
l For UNI ports, supports three levels of queue
scheduling for V-UNI egress queues, V-UNI
egress groups, and egress queues, and
supports five levels of rate limiting for VUNI egress queues, V-UNI egress, VUNI
egress groups, egress queues, and egress
ports.
Figure 2-7 Typical QoS application
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
HQoS
application point
HQoS
technologies
Ingress port Egress port
Apply the
DS domain
HQoS
configuration
Apply the
port policy
Ethernet
packets of
user A
V-UNI
Port
Traffic
shaping
Traffic
shaping
CS7
CS6
EF
AF4
AF3
AF2
AF1
BE
Complex
traffic
classification
V-UNI
CS7
CS6
EF
AF4
AF3
AF2
AF1
BE
Complex
traffic
classification
V-UNI
CS7
CS6
EF
AF4
AF3
AF2
AF1
BE
Complex
traffic
classification
Queue
scheduling
Congestion
Avoidance
Traffic
shaping
ACL
CAR
CoS
DS mapping
in the egress
direction
DS mapping
in the ingress
direction
CS7
CS6
EF
AF4
AF3
AF2
AF1
BE
Queue
scheduling
Congestion
Avoidance
Traffic
shaping
Ethernet
packets of
user B
Ethernet
packets of
user C
Limit the
bandwidth
for the V-
UNI group
Apply the V-
UNI egress
policy
Apply the DS
domain
Apply the port
policy
V-UNI V-UNI group
V-UNI
group
V-UNI
group
Ethernet
packets
Simple
traffic
classification
Simple
traffic
classification
Simple
traffic
classification
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
Figure 2-8 Typical HQoS application
2 Functions and Features
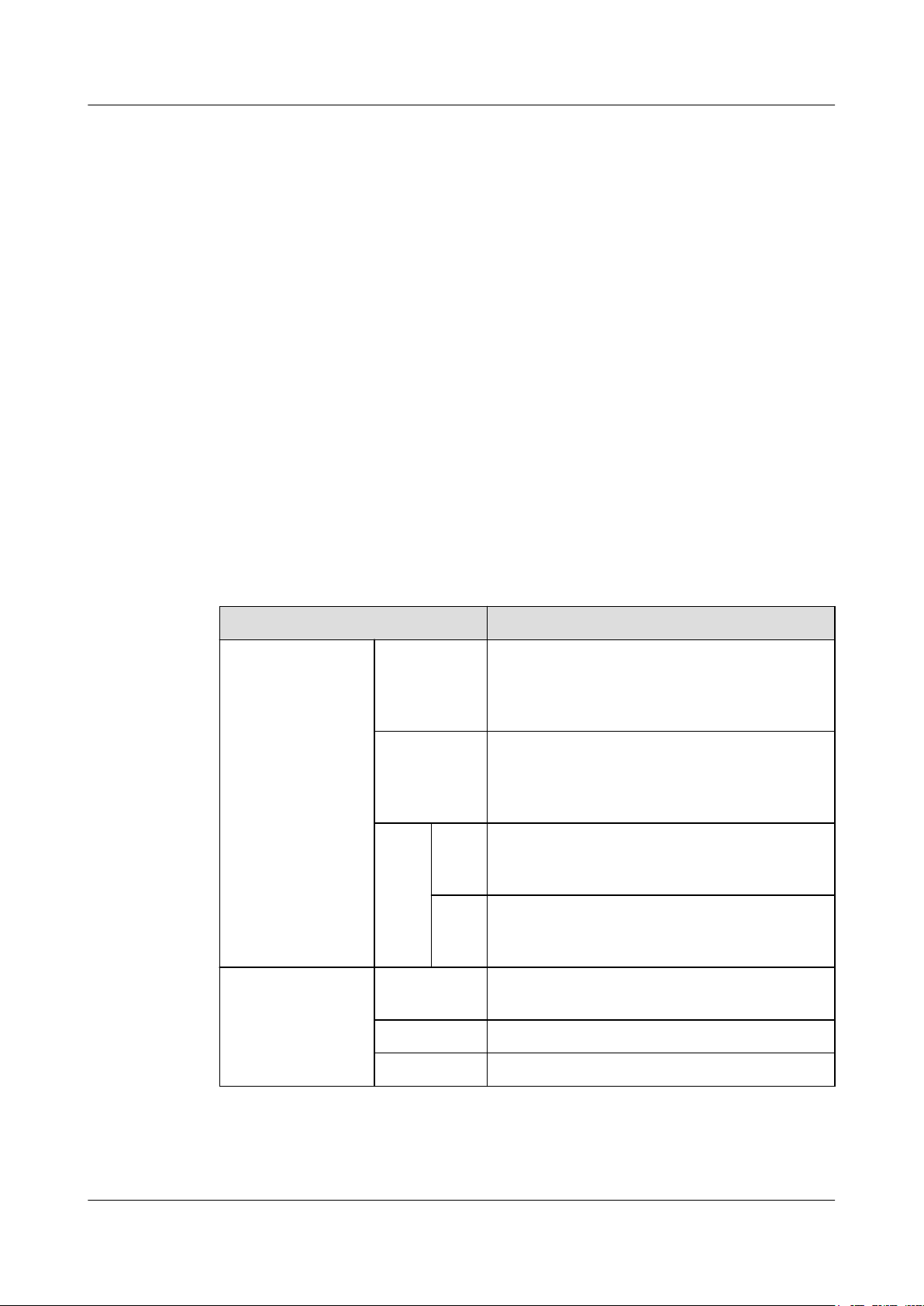
2.8 Clock Features
RTN 360's clock features meet clock transmission requirements of mobile communications
networks and offer a wide selection of clock protection mechanisms.
Item Description
Clock working mode
Clock source
Synchronization Status Message (SSM)
protocol or extended SSM protocol
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
l Tracing
l Holdover
l Free-run
l Microwave link clock
l Synchronous Ethernet clock
NOTE
When two RTN 360s form a hop of microwave
link, one is the master NE tracing the Synchronous
Ethernet clock, and the other is the slave NE
tracing the microwave link clock.
Supported. SSM information can be
transmitted in the following modes:
l Microwave link
l Synchronous Ethernet
19
OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
2.9 Network Management
RTN 360 supports multiple network management modes and provides comprehensive
management information exchange solutions.
Network Management Modes
RTN 360 supports the following network management modes:
l Uses the iManager U2000 Web LCT to manage local and remote NEs on a per-NE basis.
l Uses the Mobile LCT to manage local NEs on a per-NE basis through Wi-Fi.
l Uses the iManager U2000-T to manage Huawei OptiX RTN NEs and Huawei optical
transmission products in a unified manner. The iManager U2000-T is also able to
manage transport networks in a unified manner.
l Uses the iManager U2000-M, which manages Huawei mobile communications network
products in a unified manner, to manage RTN 360 using its NE Explore.
l Uses SNMP Get to query alarms, performance events, and RMON performance.
2 Functions and Features
Network Management Information Exchange Solutions
Table 2-3 DCN information exchange solutions
Item Specifications
DCN channel Data
communicatio
ns channel
(DCC) bytes
Network
management
system (NMS)
port
Inband
DCN
Network
management
protocol
HWECC
protocol
IP protocol Supported
Micr
owav
e link
GE
port
Three Huawei-defined DCC bytes in a microwave
frame
One NMS port
All in-band DCN channels are marked by one
VLAN ID. The bandwidth of an in-band DCN
channel is configurable.
All in-band DCN channels are marked by one
VLAN ID. The bandwidth of an in-band DCN
channel is configurable.
Supported
L2DCN Supported
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20

OptiX RTN 360 Radio Transmission System
Product Description
2.10 Rapid Deployment
A variety of technologies are used to simplify RTN 360 installation so that wireless
installation personnel can deploy an RTN 360 within 30 minutes.
So that it can be deployed rapidly, RTN 360:
l Uses TDD mode, in which signals are transmitted and received over the same frequency,
eliminating the need to distinguish TX high and low sites and requiring spare parts for
only one equipment model.
l Supports automatic frequency selection, simplifying microwave link frequency planning.
l Integrates panel antennas, simplifying installation.
l Uses an alignment scope to facilitate antenna alignment, improving installation
efficiency.
Figure 2-9 Aligning antennas using an alignment scope
2 Functions and Features
l Supports power over Ethernet. RTN 360 can work with power injector (PI), or other
power sourcing equipment (PSE) to receive service signals and power signals,
facilitating deployment.
l Supports configuration-free commissioning using a USB flash drive.
l Manages NEs on a per-NE basis using a Wi-Fi module.
Issue 01 (2016-01-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
 Loading...
Loading...