Huawei Quidway S5600 Operation Manual

HUAWEI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches
Operation Manual
Release 1510
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches
Operation Manual
Manual Version
Product Version
BOM
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support
and service. If you purchase the products from the sales agent of Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd., please contact our sales agent. If you purchase the products from Huawei
Technologies Co., Ltd. directly, Please feel free to contact our local office, customer care
center or company headquarters.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Administration Building, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.,
Bantian, Longgang District, Shenzhen, P. R. China
T2-081651-20060628-C-1.00
Release 1510
3116A051
Postal Code: 518129
Website:
http://www.huawei.com
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Copyright © 2006 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means without prior written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks
, HUAWEI, C&C08, EAST8000, HONET, , ViewPoint, INtess, ETS, DMC,
TELLIN, InfoLink, Netkey, Quidway, SYNLOCK, Radium,
M900/M1800,
TELESIGHT, Quidview, Musa, Airbridge, Tellwin, Inmedia, VRP, DOPRA,
iTELLIN, HUAWEI OptiX, C&C08
iNET, NETENGINE, OptiX, iSite, U-SYS, iMUSE,
OpenEye, Lansway, SmartAX, infoX, and TopEng are trademarks of Huawei
Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this manual a re the property of
their respective holders.
Notice
The information in this manual is subject to change without notice. Every effort has
been made in the preparation of this manual to ensure accuracy of the contents,
but all statements, information, and recommendations in this manual do not
constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
About This Manual
Release Notes
The product version that corresponds to the manual is Release 1510.
Related Manuals
The related manuals are listed in the following table.
Manual Content
Organization
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual consists of the following
parts:
z 0 Product Overview
z 1 CLI
z 2 Login
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet
Switches Installation Manual
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet
Switches Command Manual
It provides information for the system installation.
It is used for assisting the users in using various
commands.
Introduces the characteristics and implementation s of the Ethernet switch.
Introduces the command hierarchy, command view and CLI features of the
Ethernet switch.
Introduces the ways to log into an Ethernet switch.
z 3 Configuration File Management
Introduces the ways to manage configuration files.
z 4 VLAN
Introduces VLAN fundamental and the related configuration.
z 5 IP Address and Performance Configuration
Introduces IP address and IP performance fundamental and the related
configuration.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

z 6 Management VLAN
Introduces the management VLAN configuration and DHCP/BOOTP client
configuration.
z 7 Voice VLAN
Introduces voice VLAN fundamental and the related configuration.
z 8 GVRP
Introduces GVRP and the related configuration.
z 9 Port Basic Configuration
Introduces basic port configuration.
z 10 Link Aggregation
Introduces link aggregation and the related configuration.
z 11 Port Isolation
Introduces port isolation and the related configuration.
z 12 Port Security&Port Binding
Introduces port security, port binding, and the related configuration.
z 13 DLDP
Introduces DLDP and the related configuration.
z 14 MAC Address Table
Introduces MAC address forwarding table and the related configuration.
z 15 Auto Detect
Introduces auto detect and the related configuration.
z 16 MSTP
Introduces STP and the related configuration.
z 17 Routing Protocol
Introduces the routing protocol-related configurations, including static route
configuration, RIP configuration, OSPF configuration, IS-IS configuration, BGP
configuration, and routing policy configuration.
z 18 Multicast
Introduces the configuration of GMRP, IGMP Snooping, IGMP, PIM-DM, PIM-SM,
and MSDP.
z 19 802.1x
Introduces 802.1x and the related configuration.
z 20 AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS&EAD
Introduces AAA, RADIUS, HWTACACS, EAD, and the related configurations.
z 21 VRRP
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Introduces VRRP and the related configuration.
z 22 Centralized MAC Address Authentication
Introduces centralized MAC address authentication and the related configuration.
z 23 ARP
Introduces ARP and the related configuration.
z 24 DHCP
Introduces DHCP server, DHCP relay, DHCP-Snooping, and the related
configurations.
z 25 ACL
Introduces ACL and the related configuration.
z 26 QoS&QoS Profile
Introduces QoS, QoS profile and the related configuration.
z 27 Mirroring
Introduces port mirroring and the related configuration.
z 28 IRF Fabric
Introduces IRF fabric-related configuration.
z 29 Cluster
Introduces the configuration to form clusters using HGMP V2.
z 30 PoE&PoE Profile
Introduces PoE, PoE profile and the related configuration.
z 31 UDP Helper
Introduces UDP Helper and the related configuration.
z 32 SNMP&RMON
Introduces the configuration to manage network devices through SNMP and
RMON.
z 33 NTP
Introduces NTP and the related configuration.
z 34 SSH Terminal Service
Introduces SSH2.0 and the related configuration.
z 35 File System Management
Introduces basic configuration for file system management.
z 36 FTP and TFTP
Introduces basic configuration for FTP and TFTP, and the applications.
z 37 Information Center
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
Introduces the configuration to analyze and diagnose networks using the
information center.
z 38 System Maintenance and Debugging
Introduces daily system maintenance and debugging.
z 39 VLAN VPN
Introduces VLAN VPN and the related configuration.
z 40 HWPing
Introduces HWPing and the related configuration.
z 41 DNS
Introduces DNS and the related configuration.
z 42 Appendix A Acronyms
Lists the acronyms used in this manual.
Intended Audience
The manual is intended for the following readers:
z Network engineers
z Network administrators
z Customers who are familiar with network fundamentals
Conventions
The manual uses the following conventions:
I. General conventions
II. Command conventions
Convention Description
Arial Normal paragraphs are in Arial.
Boldface
Courier New
Headings are in Boldface.
Terminal Display is in Courier New.
Convention Description
Boldface
italic
The keywords of a command line are in Boldface.
Command arguments are in italic.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
Convention Description
[ ]
{ x | y | ... }
[ x | y | ... ]
{ x | y | ... } *
[ x | y | ... ] *
# A line starting with the # sign is comments.
III. GUI conventions
Convention Description
Boldface
Items (keywords or arguments) in square brackets [ ] are
optional.
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. One is selected.
Optional alternative items are grouped in square brackets
and separated by vertical bars. One or none is selected.
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. A minimum of one or a maximum of all can be
selected.
Optional alternative items are grouped in square brackets
and separated by vertical bars. Many or none can be
selected.
Button names and menu items are in Boldface. For
example, click OK.
/
IV. Keyboard operation
Format Description
<Key>
<Key1+Key2>
<Key1, Key2>
V. Mouse operation
Action Description
Select
Multi-level menus are in bold and separated by forward
slashes. For example, select the File/Create/Folder menu.
Press the key with the key name inside angle brackets. For
example, <Enter>, <Tab>, <Backspace>, or <A >.
Press the keys concurrently. For example, <Ctrl+Alt+A>
means the three keys should be pressed concurrently.
Press the keys in turn. For example, <Alt, A> means the
two keys should be pressed in turn.
Press and hold the primary mouse button (left mouse
button by default).
Click
Select and release the primary mouse button without
moving the pointer.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Action Description
Double-Click
Drag
Press the primary mouse button twice continuously and
quickly without moving the pointer.
Press and hold the primary mouse button and move the
pointer to a certain position.
VI. Symbols
Eye-catching symbols are also used in the manual to highlight the points worthy of
special attention during the operation. They are defined as follows:
Caution, Warning, Danger: Means reader be extremely careful during the
operation.
Note, Comment, Tip, Knowhow, Thought: Means a complementary
description.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Obtaining the Documentation .................................................................................... 1-1
1.1 CD-ROM............................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.2 Huawei-3Com Website......................................................................................................1-1
1.3 Software Release Notes.................................................................................................... 1-2
Chapter 2 Documentation and Software Version....................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Software Version for the Manual .......................................................................................2-1
2.2 Document List.................................................................................................................... 2-2
Chapter 3 Product Overview........................................................................................................ 3-1
3.1 Preface...............................................................................................................................3-1
3.2 Switch Models.................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.3 Software Features .............................................................................................................3-2
Chapter 4 Networking Applications.............................................................................................4-1
4.1 Application in Small/Middle-Scaled Enterprise Networks.................................................. 4-1
4.2 Application in Large-Scaled/Campus Networks ................................................................4-1
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
i

Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1 Obtaining the Documentation
Chapter 1 Obtaining the Documentation
Huawei-3Com Technologies Co., Ltd. provides various ways for you to obtain
documentation, through which you can obtain the product documentations and those
concerning newly added new features. The document ations are av ailable in one of the
following ways:
z CD-ROMs shipped with the devices
z Huawei-3Com website
z Software release notes
1.1 CD-ROM
Huawei-3Com delivers a CD-ROM together with each device. The CD-ROM contains a
complete product document set, including the operation manual, command manual,
installation manual, and compatibility manual. After installing the reader program
provided by the CD-ROM, you can search for the desired contents in a co nvenient way
through the reader interface.
The contents in the manual are subject to update on an irregular basis due to product
version upgrade or some other reasons. Therefore, the contents in the CD-ROM may
not be the latest version. This manual serves the purpose of user guide only. Unless
otherwise noted, all the information in the document set does not claim or imply any
warranty. For the latest software documentation, go to the Huawei-3Com website.
1.2 Huawei-3Com Website
Perform the following steps to query and download th e product documentation from the
Huawei-3Com website.
Table 1-1 Acquire product documentation from the Huawei-3Co m website
Log into http:// www.huawei-3com.com. Click
Registering
Acquire product
documentation
[Login/Register] in the home page. Enter your username
and password and click Register.
Click Documentation Center on the home page to query
the documentation by product category.
Select a product to display a detailed description of the
product.
Specify a device type and select a manual for that product.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-1

Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1 Obtaining the Documentation
1.3 Software Release Notes
With software upgrade, new software features may be added. You can acquire the
information about the newly added software features through software release notes.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-2
Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 2 Documentation and Software Version
Chapter 2 Documentation and Software Version
2.1 Software Version for the Manual
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual Release1510 and
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches Command Manual Release1510
correspond to the following three software versions of the S5600 series switches:
Release0035, ESS1508, and Release1510. The three software versions have dif ferent
features:
z Compared with Release0035, Release1510 and ESS1508 have six new
features, as shown in
z Compared with ESS1508 and Release0035, Release1510 has seven new
features additionally, as shown in
Table 2-1 Newly added features in Release1510 and ESS1508
Table 2-1.
Table 2-2.
New features supported in both
Release1510 and ESS1508
Configuring the interval to generate port
statistics
Newly added port security mode: autolearn
Standard MSTP (STP Compliance)
Unknown Multicast Drop
HUAWEI Terminal Access Controller Access
Control System (HWTACACS)
Domain Name System (DNS)
Table 2-2 Features unique to Release1510
Giant packet statistics (you can
enable/disable the feature)
Active/standby switchover supported by
DLDP
New features unique to Release1510 Related part
09 Port Basic Configuration
12 Port Security&Port Binding
16 MSTP
18 Multicast
20
AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS&EAD
41 Domain Name System
09 Basic Configuration
13 DLDP
Related part
BPDU drop 16 MSTP
RPT-to-SPT switch inhibition 18 Multicast
BPDU Tunnel 39-VLAN VPN
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
2-1
Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 2 Documentation and Software Version
New features unique to Release1510 Related part
Opening/
closing a
TCP/UD
P port
Opening/closing Telnet TCP port
23 and SSH TCP port 22
Opening/closing HTTP TCP port
80
Opening/closing RAW socket for
multicast routing
02 Login Operation
02 Login Operation
18 Multicast
Opening/closing UDP port 1812
for RADIUS authentication and
UDP port 1813 for RADIUS
20
AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS&EAD
accounting
Opening/closing UDP port 1645
for LOCALSERVER
authentication and UDP port
1646 for LOCALSERVER
20
AAA&RADIUS&HWTACACS&EAD
accounting
Opening/closing DHCP TCP port
67 and 68 for DHCP server/
24 DHCP
client/ relay
Opening/closing cluster UDP port
40000
30 Cluster
Opening/closing UDP port 161 for
SNMP-agent and UDP port 1024
32 SNMP&RMON
for SNMP-trap Client
Opening/closing UDP port 123 for
NTP
2.2 Document List
Table 2-3 Document list
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches Installation
Manual
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches Operation
Manual – Release1510
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches Command
Manual – Release1510
33 NTP
Name Version
(V1.04)
(V1.00)
(V1.00)
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
2-2
Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 3 Product Overview
Chapter 3 Product Overview
3.1 Preface
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches (hereinafter referred to as the S5600 se ries)
provide multi-layer switching capabilities, and support rich Layer 3 features and
enhanced growth capability. They are intelligent network-manageable switches
designed for network environments that require high performance, high port density
and easy-to-install characteristics.
3.2 Switch Models
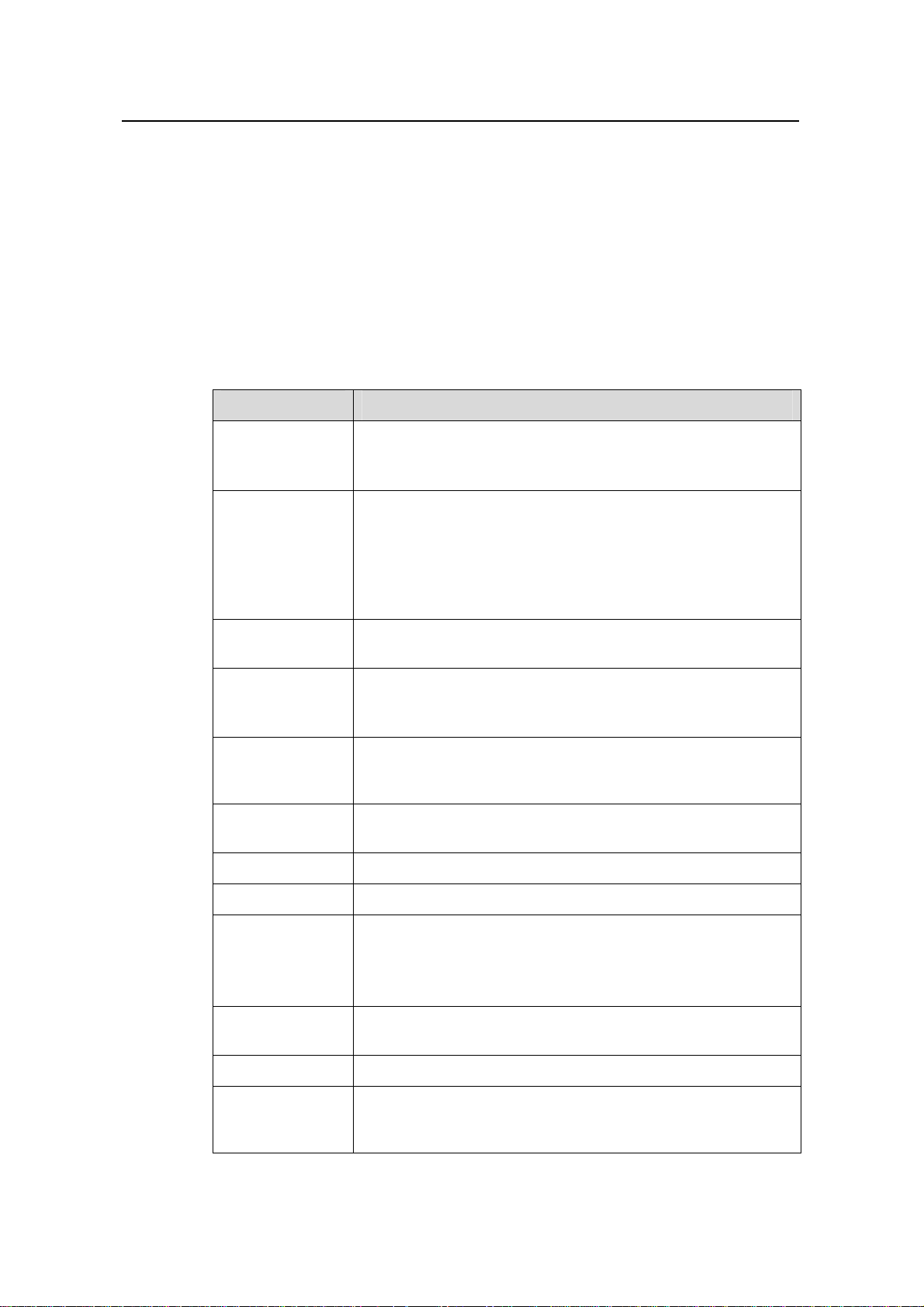
Table 3-1 lists the available models in the S5600 series.
Table 3-1 Models in the S5600 series
Model
Quidway
S5624P
Quidway
S5624P-PWR
Quidway
S5624F
Quidway
S5648P
Power
supply
AC and DC
dual input
power supply
(PSL130-AD)
AC/DC input
external PoE
power supply
(PSL480-AD2
4P)
AC and DC
dual input
power supply
(PSL130-AD)
AC and DC
dual input
power supply
(PSL180-AD)
Available
24
24
24
48
service
port
Service
port
24 x
10/100/100
0Base-T
electrical
ports
24 x
10/100/100
0Base-T
electrical
ports
24 x 1000
Mbps SFP
optical
ports
48 x
10/100/100
0Base-T
electrical
ports
Combo
port
4 x 1000
Mbps SFP
Combo
ports
4 x 1000
Mbps SFP
Combo
ports
4 x 1000
Mbps
RJ45
Combo
ports
4 x 1000
Mbps SFP
Combo
ports
Console
port
1
1
1
1
Quidway
S5648P-PWR
AC/DC input
external PoE
power supply
(PSL480-AD4
8P)
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
48
3-1
48 x
10/100/100
0Base-T
electrical
ports
4 x 1000
Mbps SFP
Combo
ports
1
Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 3 Product Overview
An S5600 series switch provides one 2-port Fabric interface and one expansion
module slot on its rear panel. The available exp ansion module s you can select includ e:
8-port 1000 Mbps SFP module, 1-port 10G XENPAK module and 2-port 10G XFP
module.
3.3 Software Features
The S5600 series have abundant software features and can meet the requirements of
different applications.
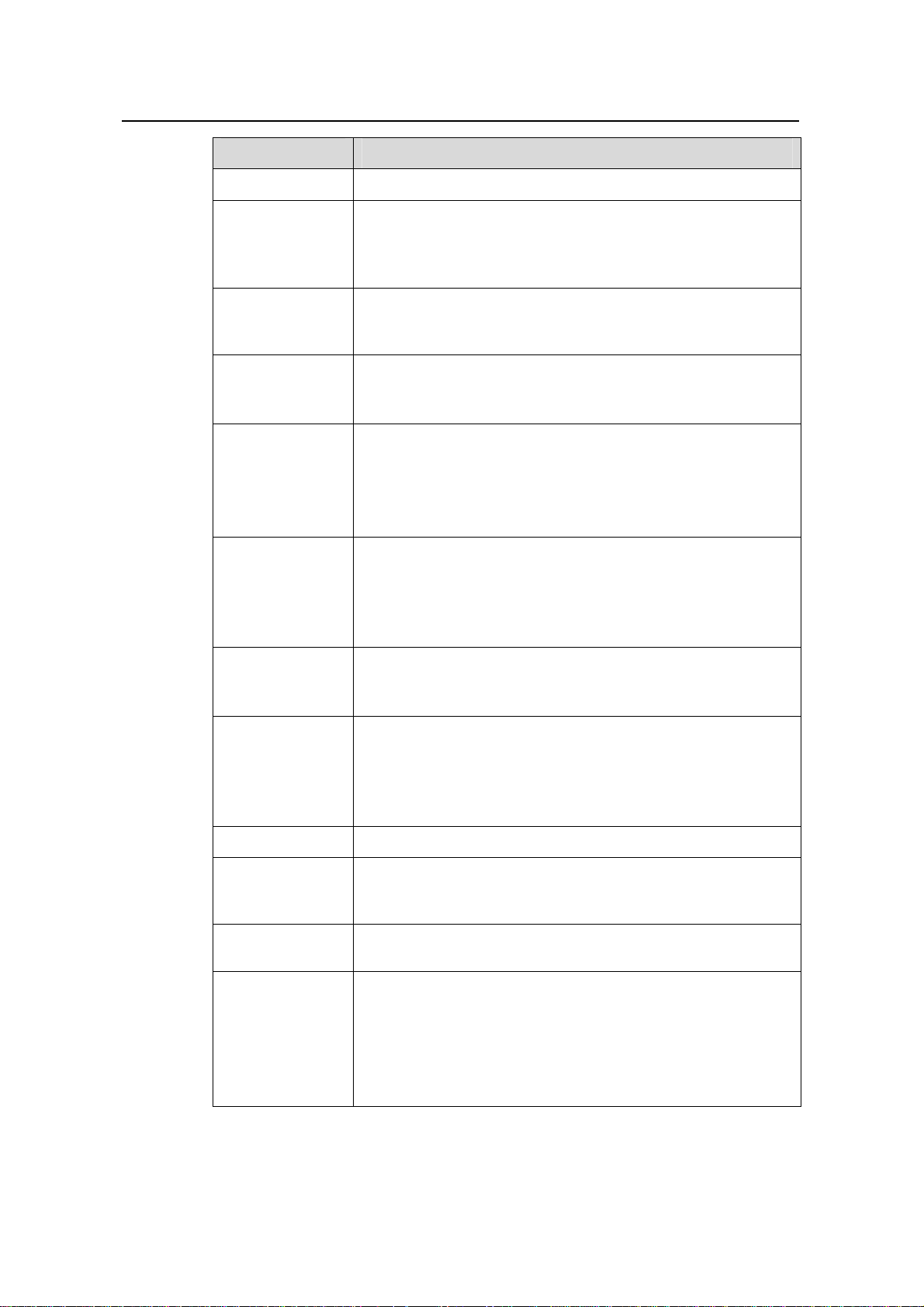
Table 3-2 Service features of the S5600 series
Part Features
1 CLI
2 Login
Table 3-2 summarizes the features provided by each module.
z CLI
z Hierarchically grouped commands
z CLI online help
z Logging into a switch through the Console port
z Logging into a switch through an Ethernet port by using
Telnet or SSH
z Logging into a switch through the Console port by using
modem
z Logging into a switch through Web or NMS
3 Configuration
File Management
4 VLAN
5 IP Address and
Performance
Configuration
6 Management
VLAN
7 Voice VLAN
8 GVRP
9 Port Basic
Configuration
10 Link
Aggregation
11 Port Isolation
z Saving, restoring, and deleting the configuration file
z IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLAN
z Port-based VLAN
z Protocol-based VLAN
z Configuring an IP address for a switch
z Configuring the TCP attributes for a switch
z Management VLAN configuration
z Management VLAN interface configuration
z Voice VLAN
z GARP VLAN registration protocol (GVRP)
z Three port states supported: Access, Trunk, and Hybrid
z Setting broadcast storm suppression globally
z Loopback detection supported
z Cable test
z Link aggregation control protocol (LACP)
z Port isolation group
12 Port
Security&Port
Binding
z Multiple security modes
z MAC address-to-port binding
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
3-2
Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 3 Product Overview
Part Features
13 DLDP
14 MAC Address
Table
15 Auto Detect
z Device link detection protocol (DLDP)
z Manually configuring dynamic, static, and black hole
MAC addresses
z Configuring the aging time for MAC addresses
z MAC address learning limit
z Auto detect
z Auto detect applications in static routing, VRRP, and
VLAN interface backup
z STP/RSTP/MSTP
16 MSTP
17 Routing
Protocols.
z QinQ BPDU tunnel
z Huawei-3Com-proprietary MSTP path cost standard
z Static route
z Routing information protocol (RIP) v1/v2
z Open shortest path first (OSPF)
z Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
z Routing policy
z Internet group management protocol snooping (IGMP
Snooping)
18 Multicast
19 802.1x
20
AAA&RADIUS&H
WTACACS&EAD
z Internet group management protocol (IGMP)
z Protocol-independent multicast-dense mode (PIM-DM)
z Protocol-independent multicast-sparse mode (PIM-SM)
z 802.1X authentication
z Guest VLAN
z Huawei authentication bypass protocol (HABP)
z Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA)
z Remote authentication dial-In user service (RADIUS)
z Huawei terminal access controller access control system
(HWTACACS)
z Endpoint admission defense (EAD)
21 VRRP
z Virtual router redundancy protocol (VRRP)
22 Centralized
MAC Address
Authentication
23 ARP
24 DHCP
z Centralized MAC address authentication
z Gratuitous ARP
z Manually configuring ARP entries
z DHCP server
z DHCP relay
z DHCP Snooping
z DHCP accounting
z Using Option184 in DHCP server
z Using Option82 in DHCP relay
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
3-3
Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 3 Product Overview
Part Features
z Basic ACLs
25 ACL
26 QoS&QoS
Profile
27 Mirroring
28 IRF Fabric
29 Cluster
30 PoE&PoE
Profile
z Advanced ACLs
z Layer 2 ACLs
z User-defined ACLs
z Quality of Service (QoS)
z QoS profile
z Traffic mirroring
z Port mirroring
z Remote port mirroring
z IRF Fabric
z Stack port optional
z Peer end detection for stack ports
z Huawei group management protocol (HGMP) v2
z Neighbor discovery protocol (NDP)
z Neighbor topology discovery protocol (NTDP)
z Power over Ethernet (PoE)
z PoE profile
31 UDP Helper
32 SNMP&RMON
33 NTP
34 SSH Terminal
Service
35 File System
Management
36 FTP and TFTP
37 Information
Center
38 System
Maintenance and
Debugging
39 VLAN VPN
z Forwarding UDP broadcast packets by using UDP Helper
z Simple network management protocol (SNMP) v3,
compatible with SNMP v1/v2
z Remote monitoring (RMON)
z Network time protocol (NTP)
z Secure shell (SSH)
z Secure FTP (SFTP)
z File system management
z Configuration file backup and restoration
z FTP/TFTP lighting
z Operating as an FTP server/FTP client
z Operating as a TFTP client
z System logs
z Hierarchical alarms
z Debugging information output
z Configuring system time
z Language (Chinese/English) selecting
z Displaying and configuring system device state
z VLAN VPN (QinQ)
z Configuring VLAN VPN interior-layer priority replication
z Configuring TPID value
z Configuring BPDU Tunnel
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
3-4

Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 3 Product Overview
Part Features
40 HWPing
41 DNS
z HWPing
z Domain Name System (DNS)
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
3-5

Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 4 Networking Applications
Chapter 4 Networking Applications
The S5600 series support flexible networking. They can be used as broadband access
devices, as well as networking devices in enterprise networks. The following describes
several typical networking methods for the S5600 series.
4.1 Application in Small/Middle-Scaled Enterprise Networks
The S5600 series can be used as backbone switches in the branches of
small/middle-scaled enterprises, where they can be connected (by routers) to the
networks of other branches or the headquarters. When the branches or enterprises
grow in scale, the S5600 series also provide seamless growth through IRF.
Core/Aggreg ation
Access
5600
3900
Figure 4-1 Application in small/middle-scaled enterprise branches
4.2 Application in Large-Scaled/Campus Networks
The S5600 series can also be used as aggregation devices in large-scaled enterprise
networks and campus networks, where each of them can be connect with multiple
Layer 2/3 downstream Ethernet switches (for example, S3900 series switches), and
connected to Layer 3 core upstream switches through the GE expansion module slot,
to provide a full solution for building enterprise networks in various size (from Gigabit
backbone network, 100 Mbps network to desktop netwo rk).
4-1

Operation Manual – Overview
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 4 Networking Applications
Core
6500
6500
5600
5600
3900
3900
Core
Aggregation
Aggregation
Access
Access
Figure 4-2 Application in large-scaled/campus networks
4-2

Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 CLI Overview................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Introduction to the CLI .......................................................................................................1-1
1.2 Command Level/Command View......................................................................................1-1
1.2.1 Switching between User Levels.............................................................................. 1-2
1.2.2 Configuring the Level of a Specific Command in a Specific View..........................1-3
1.2.3 CLI Views................................................................................................................ 1-3
1.3 CLI Features...................................................................................................................... 1-9
1.3.1 Online Help..............................................................................................................1-9
1.3.2 Terminal Display....................................................................................................1-10
1.3.3 Command History..................................................................................................1-11
1.3.4 Error Messages..................................................................................................... 1-12
1.3.5 Command Edit.......................................................................................................1-12
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
i

Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
Chapter 1 CLI Overview
1.1 Introduction to the CLI
A Quidway series Ethernet switch provides a command line interface (CLI) and
commands for you to configure and manage the Ethernet switch. The CLI is featured by
the following:
z Commands are grouped by levels. This prevents unauthorized users from
operating the switch with relevant commands.
z Users can gain online help at any time by entering the question mark "?".
z Commonly used diagnosing utilities (such as Tracert and Ping) are available.
z Debugging information of various kinds is available.
z The command history is available. You can recall and execute a history command
easily.
z You can execute a command by only entering part of the command in the CLI, as
long as the keywords you input uniquely identify the corresponding ones.
CLI Overview
1.2 Command Level/Command View
To prevent unauthorized accesses, commands are grouped by command levels.
Commands fall into four levels: visit, monitor , system, and manage:
z Visit level: Commands at this level are mainly used to diagnose network and
change the language mode of user interface, and cannot be saved i n configuration
files. For example, the ping, tracert, and language-mode commands are at this
level.
z Monitor level: Commands at this level are mainly used to maintain the system and
diagnose service problems, and cannot be saved to configuration files. For
example, the display and debugging commands are at this level.
z System level: Commands at this level are mainly used to configure services.
Commands concerning routing and network layers are at this level. Y ou can utilize
network services by using these commands.
z Manage level: Commands at this level are associated with the basic operation of
the system, and the system supporting modules. These commands provide
supports to services. Commands concerning file system, FTP/TFTP/XModem
downloading, user management, and level setting are at this level.
Users logging into a switch also fall into four levels, each of which corresponding to one
of the above command levels. Users at a specific level can only use the commands of
the same level and those of the lower levels.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-1
Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
1.2.1 Switching between User Levels
A user can switch the user level from one to another by executing a related command
after logging into a switch. The administrator can also set user level switching
passwords as required.
I. Setting a user level switching password
Table 1-1 lists the operations to set a user level switching password.
Table 1-1 Set a user level switching password
Operation Command Description
CLI Overview
Enter system view
Set a password for
switching from a lower
user level to the user level
identified by the level
argument
system-view
super password
[ level level ]
{ simple | cipher }
password
II. Switching to another user level
Table 1-2 lists operations to switch to another user level.
Table 1-2 Switch to another user level
Operation Command Description
Required
Execute this command in user view.
Switch to the user
level identified by
the level argument
super [ level ]
If a password for switching to the user
level identified by the level argument is
set and you want to switch to a lower
user level, you will remain at the lower
user level unless you provide the correct
password after executing this command.
Optional
A password is necessary only
when a user switch es from a
lower user level to a higher
user level.
Note:
z If the user level is not specified when user level switching and the switching
password are set, the user level is 3 by default.
z For security purpose, the password a user enters when switching to a higher user
level is not displayed. A user will remain at the original user level if the user has tried
three times to enter the correct password but fails to do this.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-2

Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
CLI Overview
1.2.2 Configuring the Level of a Specific Command in a Specific View
You can configure the level of a specific command in a specific view. Commands fall
into four command levels: visit, monitor , system, and manage, which are i dentified as 0,
1, 2, and 3 respectively. The administrator can change the command level a command
belongs to.
Table 1-3 lists the operations to configure the level of a specific command.
Table 1-3 Configure the level of a specific command in a specific view
Operation Command Description
Enter system view
Configure the level
of a specific
command in a
specific view
1.2.3 CLI Views
CLI views are designed for different configuration tasks. They are interrelated. You will
enter user view once you log into a switch successfully, where you can perform
operations such as displaying operation status and statistical information. And by
executing the system-view command, you can enter system view, where you can
enter other views by executing the corresponding commands.
The following CLI views are provided:
z User view
z System view
z Ethernet port view
z VLAN view
z VLAN interface view
z Loopback interface view
z Cascade interface view
z Local user view
z User interface view
z FTP client view
z SFTP client view
z MST region view
z Cluster view
z Public key view
z Public key editing view
z DHCP address pool view
z PIM view
system-view
command-privilege
level level view view
command
Required
Use this command with caution to
prevent inconvenience on
maintenance and operation.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-3
Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
z RIP view
z OSPF view
z OSPF area view
z Routing policy view
z Basic ACL view
z Advanced ACL view
z Layer 2 ACL view
z User-defined ACL view
z QoS profile view
z RADIUS scheme view
z ISP domain view
z HWPING view
z HWTACACS view
z MSDP view
z PoE profile view
Table 1-4 lists information about CLI views (including the operations you can performed
in these views, how to enter these views, and so on).
CLI Overview
Table 1-4 CLI views
View
Available
operation
Display
operation
User view
status and
statistical
information
System
view
Configure
system
parameters
Configure
Ethernet
port view
Ethernet
port
parameters
VLAN
view
Configure
VLAN
parameters
Prompt
example
<Quidway>
[Quidway]
[Quidway-Gi
gabitEtherne
t1/1/1]
[Quidway-vla
n1]
Enter method Quit method
Enter user view
once logging
into the switch.
Execute the
system-view
command in
user view.
Execute the
interface
gigabitetherne
t 1/1/1
command in
system view.
Execute the quit
command in user
view to log out of the
switch.
Execute the quit or
return command to
return to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
Execute the
vlan 1
command in
system view.
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-4
Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
CLI Overview
VLAN
interface
view
Loopback
interface
view
Cascade
interface
view
Local
user view
Configure IP
interface
parameters
for VLANs
and
aggregated
VLANs
Configure
Loopback
interface
parameters
Configure
Cascade
interface
parameters
Configure
local user
parameters
[Quidway-Vl
an-interface1
]
[Quidway-Lo
opBack0]
[Quidway-Ca
scade1/2/1]
[Quidway-lus
er-user1]
Execute the
interface
vlan-interface
1 command in
system view.
Execute the
interface
loopback 0
command in
system view
Execute the
interface
cascade 1/2/1
command in
system view
Execute the
local-user
user1
command in
system view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
User
interface
view
FTP
client
view
SFTP
client
view
MST
region
view
Configure
user
interface
parameters
Configure
FTP client
parameters
Configure
SFTP client
parameters
Configure
MST region
parameters
[Quidway-ui0
]
[ftp]
<sftp-client>
[Quidway-ms
t-region]
Execute the quit
Execute the
user-interface
0 command in
system view.
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the ftp
command in
user view.
Execute the
sftp 10.1.1.1
command in
system view.
Execute the
stp
region-config
uration
command in
system view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-5
Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
Cluster
view
Configure
cluster
parameters
[Quidway-clu
ster]
Execute the
cluster
command in
system view.
to user view.
CLI Overview
Public
key view
DHCP
address
pool view
PIM view
Configure
RSA public
keys for
[Quidway-rsa
-public-key]
SSH users
Configure
DHCP
address
pool
[Quidway-dh
cp-pool-a123
]
parameters
Configure
PIM
parameters
[Quidway-pi
m]
Execute the
rsa
peer-public-ke
y a003
command in
system view.
Execute the
dhcp server
ip-pool a123
command in
system view
Execute the
peer-public-key
end command to
return to system
view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the
pim command
in system view
If multicast
routing is not
enabled, you
should use the
multicast
routing-enabl
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
e command
first.
RIP view
OSPF
view
OSPF
area view
Configure
RIP
parameters
Configure
OSPF
protocol
parameters
Configure
OSPF area
parameters
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
[Quidway-rip]
[Quidway-os
pf-1]
[Quidway-os
pf-1-area-0.0
.0.1]
1-6
Execute the quit
Execute the rip
command in
system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
Execute the
ospf command
in system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
Execute the
area 1
command in
OSPF view
command to return
to OSPF view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
BGP view
Configure
BGP
protocol
parameters
[Quidway-bg
p]
Execute the
bgp 100
command in
system view
to user view.
CLI Overview
BGP IPv4
address
multicast
view
Routing
policy
view
Public
key
editing
view
Basic
ACL view
Configure
BGP IPv4
address
multicast
[Quidway-bg
p-af-mul]
parameters
Configure
routing
policies
[Quidway-ro
ute-policy]
Edit RSA
public keys
of SSH
[Quidway-rsa
-key-code]
users
Define rules
for a basic
ACL (ACLs
with their
IDs ranging
[Quidway-acl
- basic-2000]
from 2000 to
2999 are
basic ACLs.)
Execute the
ipv4-family
multicast
command in
BGP view
Execute the
route-policy
policy1 permit
node 10
command in
system view
Execute the
public-key-co
de begin
command in
public key view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the
public-key-code
end command to
return to public key
view.
Execute the quit
Execute the acl
number 2000
command in
system view.
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Define rules
for an
advanced
Advance
d ACL
view
ACL (ACLs
with their
IDs ranging
from 3000 to
3999 are
advanced
ACLs.)
Define the
sub-rules of
Layer 2
ACL view
Layer 2
ACLs, which
is numbered
from 4000 to
4999.
Execute the acl
[Quidway-acl
- adv-3000]
number 3000
command in
system view.
[Quidway-acl
-ethernetfra
me-4000]
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-7
Execute the acl
number 4000
command in
system view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Operation Manual - CLI
Quidway S5600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
CLI Overview
User-defi
ned ACL
view
QoS
profile
view
RADIUS
scheme
view
ISP
domain
view
Define the
sub-rules of
user-defined
ACLs, which
are in the
[Quidway-acl
-user-5000]
range of
5000 to
5999
Define QoS
profile
Configure
RADIUS
parameters
Configure
parameters
for an ISP
domain
[Quidway-qo
s-profile-a12
3]
[Quidway-ra
dius-1]
[Quidway-isp
-huawei163.
net]
Execute the quit
Execute the acl
number 5000
command in
system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
Execute the
qos-profile
a123 command
in system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the
radius
scheme 1
command in
system view.
Execute the
domain
huawei163.net
command in
system view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
HWPING
view
HWTACA
CS view
MSDP
view
Configure
HWPing
parameters
Configure
HWTACACS
parameters
Configure
MSDP
parameters
[Quidway-hw
ping-a123-a1
23]
[Quidway-hw
tacacs-a123]
[Quidway-ms
dp]
Execute the quit
Execute the
hwping a123
a123 command
in system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
Execute the
hwtacacs a123
command in
system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Execute the quit
Execute the
msdp
command in
system view
command to return
to system view.
Execute the return
command to return
to user view.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-8
 Loading...
Loading...