Huawei Quidway S3100 Operation Manual

HUAWEI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
Operation Manual
VRP3.10
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
Operation Manual
Manual Version
Product Version
BOM
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support
and service. If you purchase the products from the sales agent of Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd., please contact our sales agent. If you purchase the products from Huawei
Technologies Co., Ltd. directly, Please feel free to contact our local office, customer care
center or company headquarters.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Administration Building, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.,
Bantian, Longgang District, Shenzhen, P. R. China
T2-08160Y-20060317-C-1.01
VRP3.10
3116A00Y
Postal Code: 518129
Website:
http://www.huawei.com
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Copyright © 2006 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means without prior written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks
, HUAWEI, C&C08, EAST8000, HONET, , ViewPoint, INtess, ETS, DMC,
TELLIN, InfoLink, Netkey, Quidway, SYNLOCK, Radium,
M900/M1800,
TELESIGHT, Quidview, Musa, Airbridge, Tellwin, Inmedia, VRP, DOPRA,
iTELLIN, HUAWEI OptiX, C&C08
iNET, NETENGINE, OptiX, iSite, U-SYS, iMUSE,
OpenEye, Lansway, SmartAX, infoX, and TopEng are trademarks of Huawei
Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this manual a re the property of
their respective holders.
Notice
The information in this manual is subject to change without notice. Every effort has
been made in the preparation of this manual to ensure accuracy of the contents,
but all statements, information, and recommendations in this manual do not
constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
About This Manual
Release Notes
The product version that corresponds to the manual is VRP3.10.
Related Manuals
The following manuals provide more information about the Quidway S3100 Series
Ethernet Switches.
Manual Content
Organization
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Operation Manual consists of the following
parts:
z Product Overvi ew
z CLI
z Login
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet
Switches Installation Manual
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet
Switches Command Manual
It provides information for the system
installation.
It is used for assisting the users in using
various commands.
Introduces the technical specifications, service features, and network design of
the Ethernet Switch.
Introduces the command hierarchy, command view and CLI features of the
Ethernet Switch.
Introduces several ways to log onto an Ethernet Switch.
z VLAN
Introduces VLAN and Voice VLAN related configuration.
z Management VLAN
Introduces the management VLAN configuration and DHCP/BOOTP client
configuration.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

z GVRP
Introduces GVRP and the related configuration.
z Port
Introduces basic port configuration.
z Link Aggregation
Introduces link aggregation and the related configuration.
z Port Isolation
Introduces port isolation and the related configuration.
z MAC Address Forwarding Table
Introduces MAC address forwarding management.
z MSTP
Introduces STP and the related configuration.
z 802.1x
Introduces 802.1x and the related configuration.
z AAA&RADIUS
Introduces AAA, RADIUS and their related configurations.
z Centralized MAC Address Authen tication
Introduces centralized MAC address authentication and the related configuration.
z ARP
Introduces ARP and the related configuration.
z DHCP-Snooping
Introduces DHCP snooping and the related configuration.
z ACL
Introduces ACL and the related configuration.
z QoS
Introduces QoS and the related configuration.
z IGMP Snooping
Introduces IGMP snooping and the related configuration.
z Stack&Cluster
Introduces the related configuration for cluster management by using HGMP V2.
z SNMP
Introduces the configuration for network management through SNMP.
z RMON
Introduces the configuration for remote network management through RMON.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

z NTP
Introduces NTP and the related configuration.
z SSH2.0
Introduces SSH2.0 and the related configuration.
z File System Management
Introduces basic configuration for file system management.
z FTP and TFTP
Introduces basic configuration for FTP and TFTP, and the applications.
z Information Center
Introduces information center configuration.
z System Maintenance and Debugging
Introduces daily maintenance and debugging to the system.
z Appendix
Lists the acronyms in this manual
Intended Audience
The manual is intended for the following readers:
z Network engineers
z Network administrators
z Customers who are familiar with network fundamentals
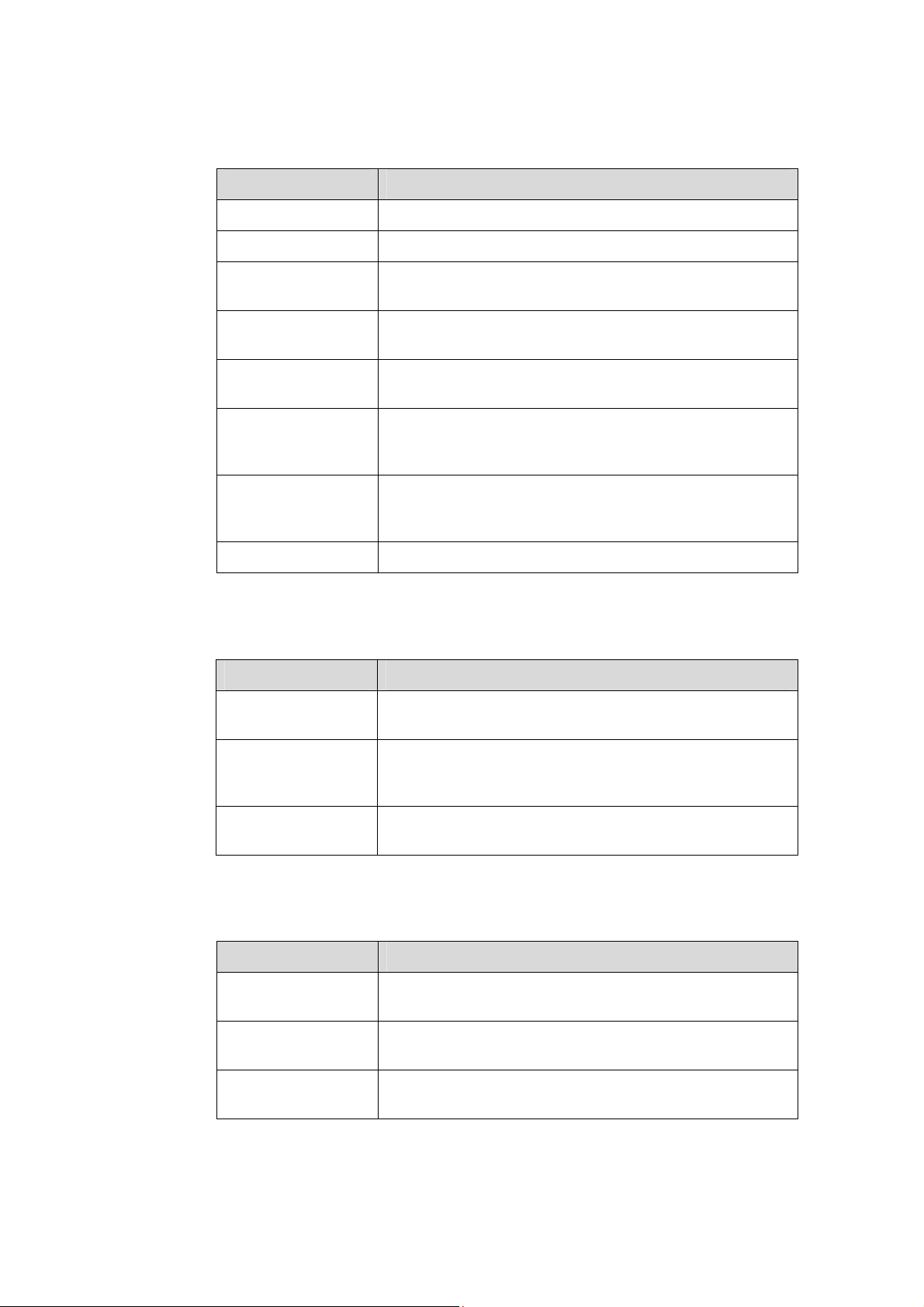
Conventions
The manual uses the following conventions:
I. General conventions
Convention Description
Arial Normal paragraphs are in Arial.
Boldface
Courier New
Headings are in Boldface.
Terminal Display is in Courier New.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
II. Command conventions
Convention Description
Boldface
italic
[ ]
{ x | y | ... }
[ x | y | ... ]
{ x | y | ... } *
[ x | y | ... ] *
# A line starting with the # sign is comments.
III. GUI conventions
The keywords of a command line are in Boldface.
Command arguments are in italic.
Items (keywords or arguments) in square brackets [ ] are
optional.
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. One is selected.
Optional alternative items are grouped in square brackets
and separated by vertical bars. One or none is selected.
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. A minimum of one or a maximum of all can be
selected.
Optional alternative items are grouped in square brackets
and separated by vertical bars. Many or none can be
selected.
Convention Description
< >
[ ]
/
IV. Keyboard operation
Format Description
<Key>
<Key1+Key2>
<Key1, Key2>
Button names are inside angle brackets. For example, click
the <OK> button.
Window names, menu items, data table and field names
are inside square brackets. For example, pop up the [New
User] window.
Multi-level menus are separated by forward slashes. For
example, [File/Create/Folder].
Press the key with the key name inside angle brackets. For
example, <Enter>, <Tab>, <Backspace>, or <A >.
Press the keys concurrently. For example, <Ctrl+Alt+A>
means the three keys should be pressed concurrently.
Press the keys in turn. For example, <Alt, A> means the
two keys should be pressed in turn.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
V. Mouse operation
Action Description
Select
Click
Double-Click
Drag
Press and hold the primary mouse button (left mouse
button by default).
Select and release the primary mouse button without
moving the pointer.
Press the primary mouse button twice continuously and
quickly without moving the pointer.
Press and hold the primary mouse button and move the
pointer to a certain position.
VI. Symbols
Eye-catching symbols are also used in the manual to highlight the points worthy of
special attention during the operation. They are defined as follows:
Caution, Warning, Danger: Means reader be extremely careful during the
operation.
Note, Comment, Tip, Knowhow, Thought: Means a complementary
description.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

HUAWEI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
Operation Manual
Product Overview
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Product Overview........................................................................................................ 1-1
1.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.2 Technical Specifications .................................................................................................... 1-2
1.2.1 S3126T/S3116T/S3108T ........................................................................................ 1-2
1.2.2 S3126C/S3116C/S3108C ....................................................................................... 1-2
1.3 Service Features................................................................................................................ 1-3
1.3.1 S3126T/S3116T/S3108T ........................................................................................ 1-4
1.3.2 S3126C/S3116C/S3108C ....................................................................................... 1-6
Chapter 2 Network Design............................................................................................................ 2-1
2.1 MAN Access Solution ........................................................................................................ 2-1
2.2 Education Network Solution............................................................................................... 2-1
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
i

Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Note:
For the convenience of users, units of Mega bps/1000 Mega bps in the following
chapters are simplified as M/G.
1.1 Introduction
Huawei Technologies' Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches (hereinafter referred
to as S3100 series) are wire-speed Layer 2 Ethernet switching products. They are
intelligent network manageable switches designed for the network environments that
require high performance, high port density and easy installation.
Product Overview
The S3100 series provide 10/100 Mbps downlink and 1000 Mbps uplink Ethernet ports.
In enterprise networks, they can serve as access devices for 100 Mbps-to-desktop
applications. In metropolitan area networks (MANs) or various industry networks, they
connect end users or aggregate low end switches through 100 Mbps electrical
interfaces in the downlink direction, and converge at an IP switching center or a large
capacity Layer 3 switch in the uplink direction through GE interface or link aggregation.
Currently, the S3100 series include the following models:
z S3126T
z S3116T
z S3108T
z S3126C
z S3116C
z S3108C
S3100 series switches feature the following advantages:
1) Fan-free mute design, suitable for some quiet environment such as corridors and
offices.
2) Virtual cable test (VCT) supported, convenient for troubleshooting.
3) Bidirectional port rate-limiting with the granularity of 64 Kbps, supporting finer
bandwidth allocation.
4) Up to 4 K IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLANs, convenient for networking.
5) Remote switched port analyzer (RSPAN), enhancing the monitoring of the
network.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-1
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
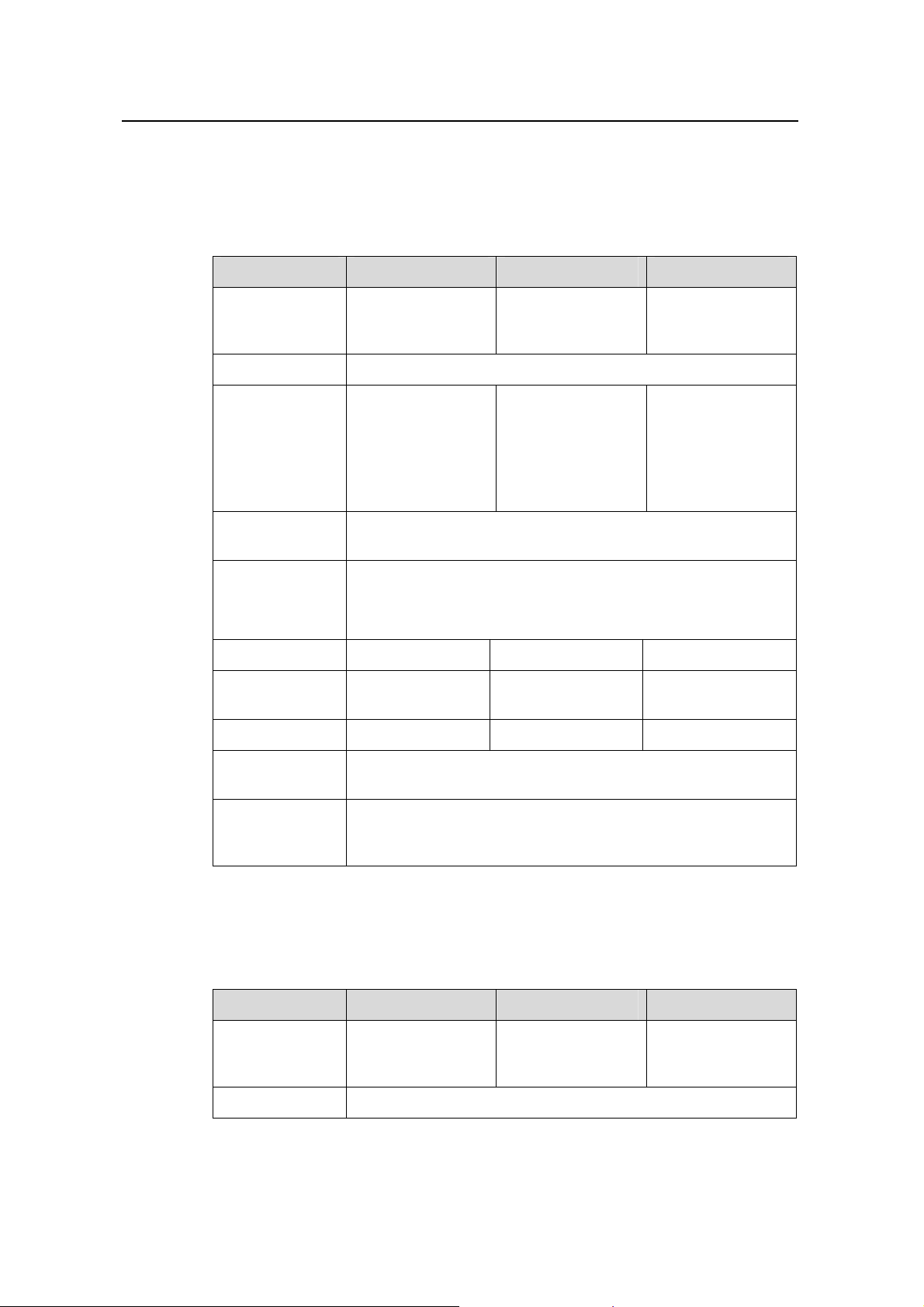
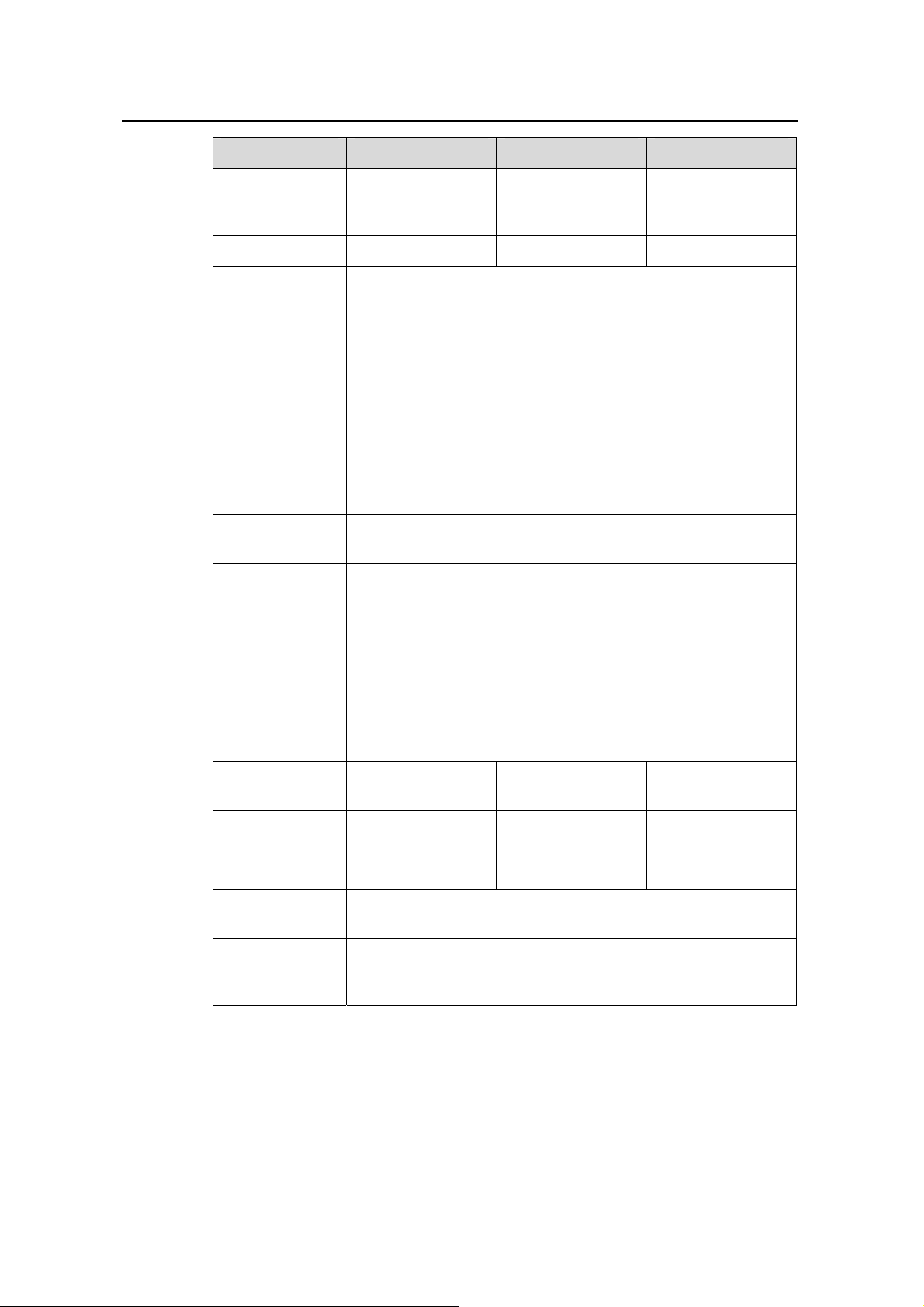
1.2 Technical Specifications
1.2.1 S3126T/S3116T/S3108T
Table 1-1 Technical specifications for S3126T/S3116T/S3108T Ethernet switches
Item S3126T S3116T S3108T
Product Overview
Physical
dimensions (H x
W x D)
Weight ≤ 3.2 kg (7.1 lb)
Service port
Management
port
Power supply
PoE Not supported Not supported Not supported
Max power
consumption
Fan None None None
42 × 436 × 240 mm
(1.7 x 17.2 x 9.5 in.)
24x
10/100BASE-TX
autosensing ports
2x
10/100/1000BASET ports
One console port
AC input
Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50 Hz or 60 Hz
Max voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC, 47 Hz to 63 Hz
20 W 12 W 10 W
42 × 436 × 200 mm
(1.7 x 17.2 x 7.9 in.)
16x
10/100BASE-TX
autosensing ports
1x
10/100/1000BASET port
42 × 326 × 200 mm
(1.7 x 12.8 x 7.9 in.)
8x
10/100BASE-TX
autosensing ports
1x
10/100/1000BASET port
Operating
temperature
Relative
humidity
(noncondensing)
0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F)
10% to 90%
1.2.2 S3126C/S3116C/S3108C
Table 1-2 Technical specifications for S3126C/S3116C/S3108C Ethernet switches
Item S3126C S3116C S3108C
Physical
dimensions (H x
W x D)
Weight ≤ 3.2 kg (7.1 lb)
42 × 436 × 240 mm
(1.7 x 17.2 x 9.5 in.)
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
42 × 436 × 200 mm
(1.7 x 17.2 x 7.9 in.)
42 × 326 × 200 mm
(1.7 x 12.8 x 7.9 in.)
1-2
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
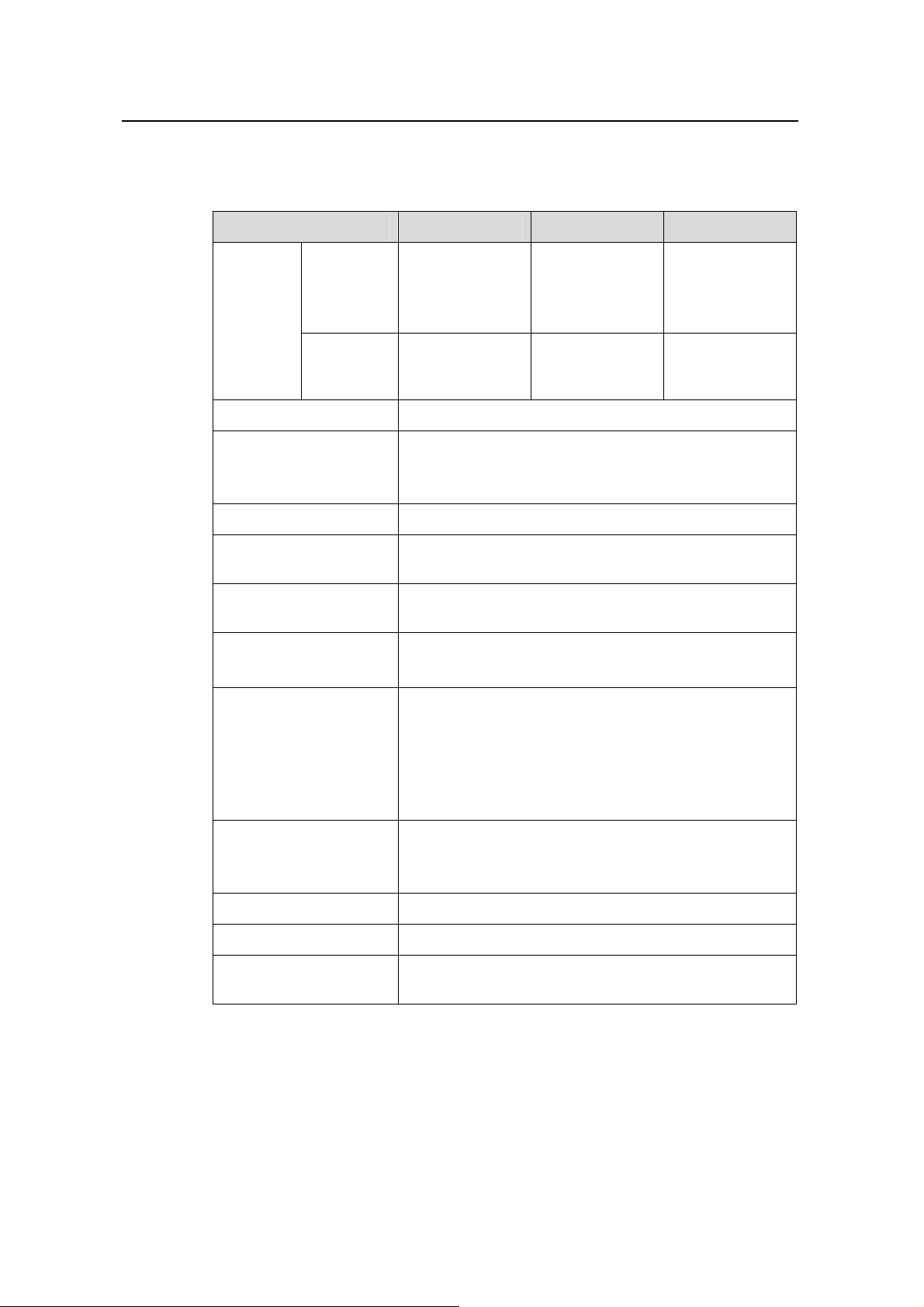
Item S3126C S3116C S3108C
Product Overview
Service port
24x
10/100BASE-TX
autosensing ports
16x
10/100BASE-TX
autosensing ports
8x
10/100BASE-TX
autosensing ports
Expanded slot Two Two One
10/100/1000BASE-T: max transmission distance: 100 m (328 ft)
100BASE-SX: SC connector, 2 km (1.24 mi)
100BASE-LX: SC connector, 15 km (9.32 mi)
Supported
interface type of
expansion
module
100BASE-LH40: SC connector, 40 km (24.86 mi)
1000BASE-SX: SC connector, 0.5km (0.31 mi)
1000BASE-LX: SC connector, 10 km (6.21 mi)
1000BASE-LH40: LC connector, 40 km (24.86 mi)
1000BASE-LH70: LC connector, 70 km (43.50 mi)
1000BASE-STACK (not supported by S3108C)
100BASE-TX PD (Powered Device) (not supported by S3126C)
Management
port
One console port
Two models of switches are available, one supports AC input
and the other supports DC input.
AC input:
Rated voltage range: 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50 Hz or 60 Hz
Power supply
Max voltage range: 90 VAC to 264 VAC, 47 Hz to 63 Hz
DC input:
Rated voltage range: –48 VDC to –60V DC
Max voltage range: –36 VDC to –72 VDC
PoE (Powered
Device )
Max power
consumption
Fan None None None
Operating
temperature
Relative
humidity
(noncondensing)
1.3 Service Features
The software for S3100 series is developed based on Huawei Technologies' versatile
routing platform (VRP). It has the following service features.
Not supported Supported Supported
20 W 12 W 10 W
0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F)
10% to 90%
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-3
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
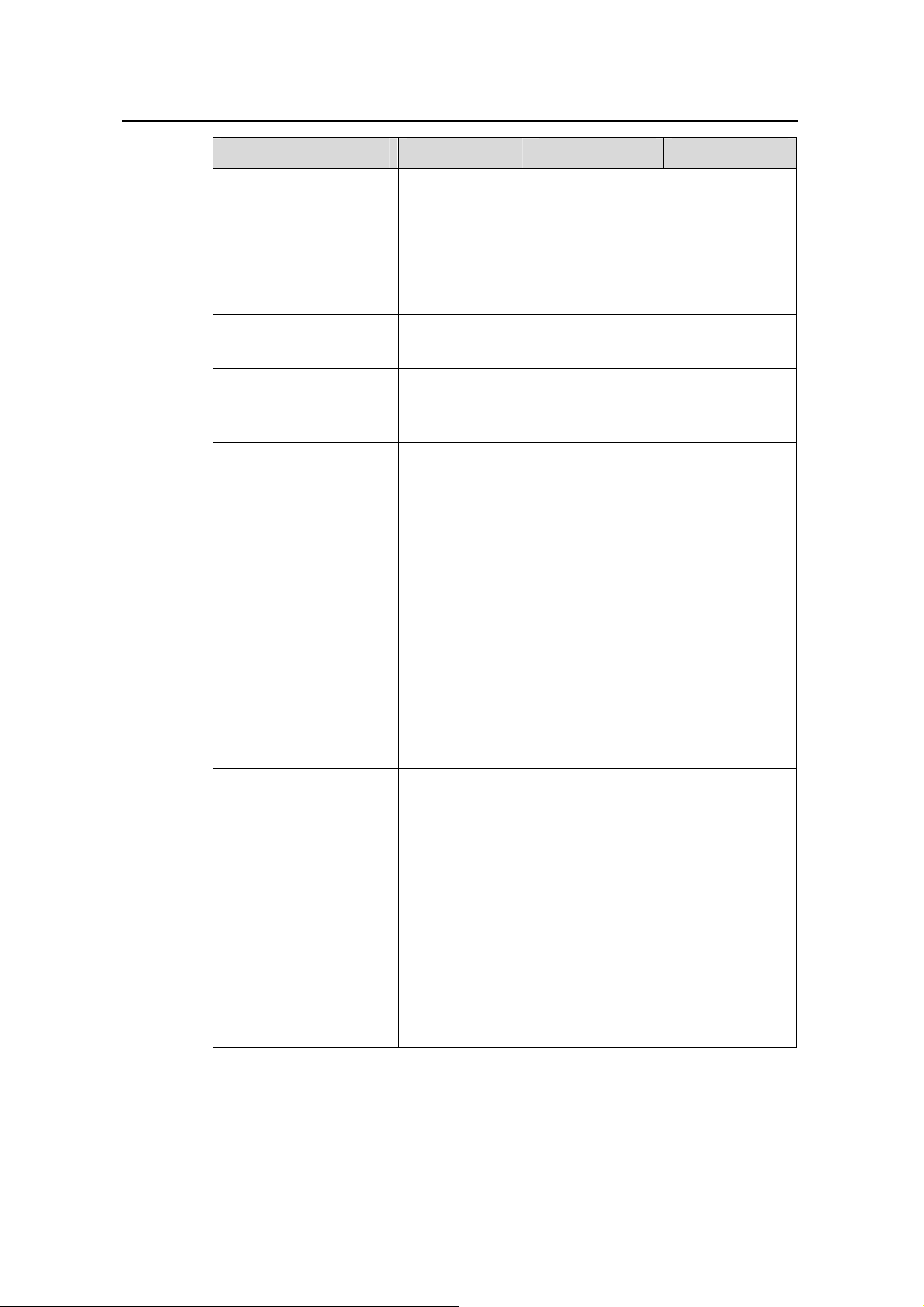
1.3.1 S3126T/S3116T/S3108T
Table 1-3 Service features for S3126T/S3116T/S3108T Ethernet switches
Item S3126T S3116T S3108T
Product Overview
Wire-spee
d Layer 2
switching
Switching
capacity
Packet
forwarding
All ports support
wire-speed
forwarding
8.8 Gbps
6.55 Mpps 3.87 Mpps 2.68 Mpps
All ports support
wire-speed
forwarding
5.2 Gbps
rate
Switching mode Store and forward
Up to 4K IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLANs (virtual local
VLAN
area networks)
GVRP (GARP VLAN registration protocol)
VLAN interface One VLAN virtual interface
Broadcast storm
suppression
Multicast
Spanning tree protocol
Port bandwidth percentage-based suppression
IGMP Snooping (Internet group management protocol
snooping)
STP, RSTP (rapid STP), MSTP (multiple STP)
Up to 16 spanning tree instances
Manual link aggregation through command line
FE/GE (Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet) link aggregation
Port aggregation
Up to three link aggregation groups; up to eight ports for
one FE aggregation group, and up to two ports for one
GE aggregation group (the ports in the same group must
be of the same type)
All ports support
wire-speed
forwarding
3.6 Gbps
Many-to-one port mirroring (that is, multiple mirroring
Port mirroring
ports, and one monitor port)
Remote switched port analyzer (RSPAN)
Port isolation Supported
Port self-loop detection Supported
Port loopback
(internal/external test)
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
Supported
1-4
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
Item S3126T S3116T S3108T
Address self-learning
IEEE 802.1D standard-compliant
MAC address table
Up to 8 K MAC addresses
1 K static MAC addresses
Adding of dynamic/static unicast MAC address,
multicast MAC address, and blackhole MAC address
Product Overview
Flow control
Loading and upgrade
Management
Maintenance
IEEE 802.3x flow control (full duplex)
Back-pressure based flow control (half duplex)
XModem
FTP (file transfer protocol), TFTP (trivial file transfer
protocol)
Configuration through CLI (command line interface)
Remote configuration through Telnet
Configuration through console port
SNMP (simple network management protocol)
1/2/3/9 group MIBs of RMON (Remote Monitoring)
Huawei Quidview NMS
Web-based network management
System log
Hierarchical alarm
Debug information output
Ping, traceroute, multicast traceroute
Telnet
VCT (virtual cable test)
QoS/ACL
Four output queues on each port
802.1p, DSCP (differentiated services codepoint
priority), and IP-precedence priorities
WRR (weighted round robin), and HQ+WRR
(high-priority queuing + WRR) queue scheduling
algorithm
Bidirectional port rate-limiting with the granularity of 64
Kbps:
z 100 Mbps port: the rate limit ranges from 64 Kbps to
99,968 Kbps
z Gigabit port: the rate limit ranges from 64 Kbps to
1,000,000 Kbps
Drop of unknown multicast packets
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-5
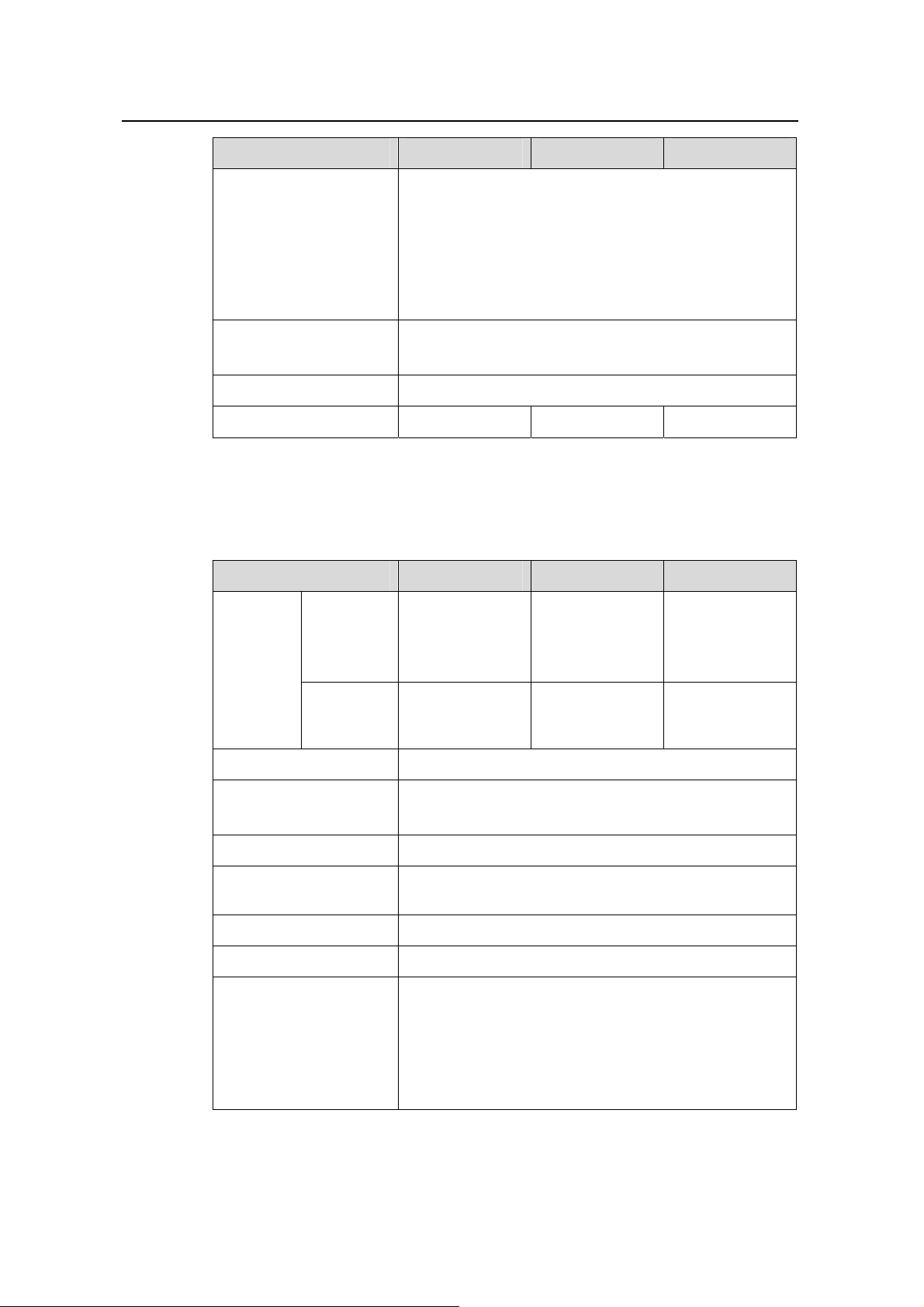
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
Item S3126T S3116T S3108T
Hierarchical user management and password protection
Guest VLAN
Security
IEEE 802.1x authentication
MAC address-based authentication
Centralized MAC address authentication
SSH2.0
Product Overview
DHCP (dynamical host
configuration protocol)
NTP Supported
HGMP V2 Supported Not supported Not supported
1.3.2 S3126C/S3116C/S3108C
Table 1-4 Service features for S3126C/S3116C/S3108C Ethernet switches
Item S3126C S3116C S3108C
Wire
speed
Layer 2
switching
Switching mode Store and forward
Switching
capacity
Packet
forwarding
rate
DHCP Client
DHCP snooping
All ports support
wire-speed
forwarding
8.8 Gbps
All ports support
wire-speed
forwarding
7.2 Gbps
All ports support
wire-speed
forwarding
3.6 Gbps
6.55 Mpps 5.36 Mpps 2.68 Mpps
VLAN
Up to 4 K IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLAN
GVRP
VLAN interface One VLAN virtual interface
Broadcast storm
suppression
Port bandwidth percentage-based suppression
Multicast IGMP Snooping
Spanning tree protocol STP/RSTP/MSTP, up to 16 spanning tree instances
Manual link aggregation through command line
FE/GE link aggregation
Port aggregation
Up to three link aggregation groups; up to eight ports for
one FE aggregation group, and up to two ports for one
GE aggregation group (the ports in the same group must
be of the same type)
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-6
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
Item S3126C S3116C S3108C
Many-to-one port mirroring (that is, multiple mirroring
Port mirroring
ports, and one monitor port)
RSPAN
Port isolation Supported
Port self-loop detection Supported
Product Overview
Port loopback
(internal/external test)
Supported
Address self-learning
IEEE 802.1D standard-compliant
MAC address table
Up to 8 K MAC addresses
1 K static MAC addresses
Adding of dynamic/static unicast MAC address,
multicast MAC address, and blackhole MAC address
Flow control
Loading and upgrade
IEEE 802.3x flow control (full duplex)
Back-pressure based flow control (half duplex)
XModem
FTP, TFTP
Configuration through CLI
Remote configuration through Telnet
Configuration through console port
SNMP
Management
1/2/3/9 group MIBs of RMON
Huawei Quidview NMS
Web-based network management
System log
Hierarchical alarm
Maintenance
QoS/ACL
Debug information output
Ping, traceroute, multicast traceroute
Telnet
VCT (Virtual Cable Test)
Four output queues on each port
802.1p, DSCP, and IP-precedence priority
WRR and HQ+WRR queue scheduling algorithm
Bidirectional port rate-limiting with the granularity of 64
Kbps:
z 100 Mbps port: the rate limit ranges from 64 Kbps to
99,968 Kbps
z Gigabit port: the rate limit ranges from 64 Kbps to
1,000,000 Kbps
Drop of unknown multicast packets
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-7
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1
Item S3126C S3116C S3108C
Hierarchical user management and password protection
Guest VLAN
Security
IEEE 802.1x authentication
MAC address-based authentication
Centralized MAC address authentication
SSH2.0
Product Overview
DHCP (dynamic host
configuration protocol)
DHCP Client
DHCP snooping
NTP Supported
HGMP V2 Supported Supported Not supported
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-8
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2
Chapter 2 Network Design
The S3100 series can be flexibly deployed in networks. They can be used in enterprise
networks, or serve as broadband access points. The following examples are two typical
networks using the S3100 series.
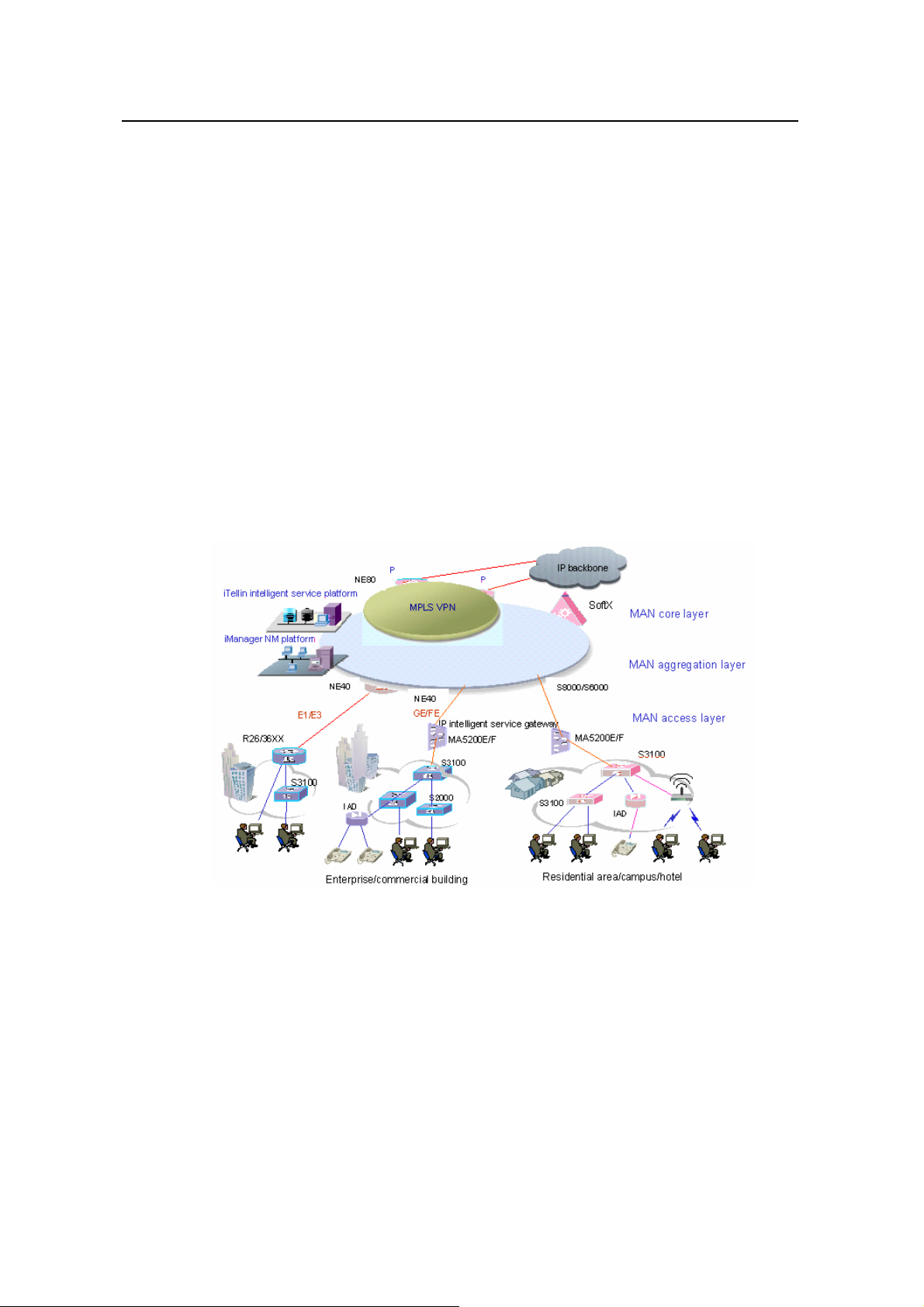
2.1 MAN Access Solution
In a metropolitan area network (MAN), the S3100 series can serve as access devices.
In the downlink direction, they directly connect to users through 100 Mbps interfaces;
and in the uplink direction, they connect to an aggregation layer (Layer 3) switches or
Quidway MA5200 intelligent service gateways, which further connect to the core of the
MAN through routers. This provides you a comprehensive gigabit-to-backbone
100-Mbps-to-desktop MAN solution.
Network Design
Figure 2-1 Network diagram for a MAN using S3100 series
2.2 Education Network Solution
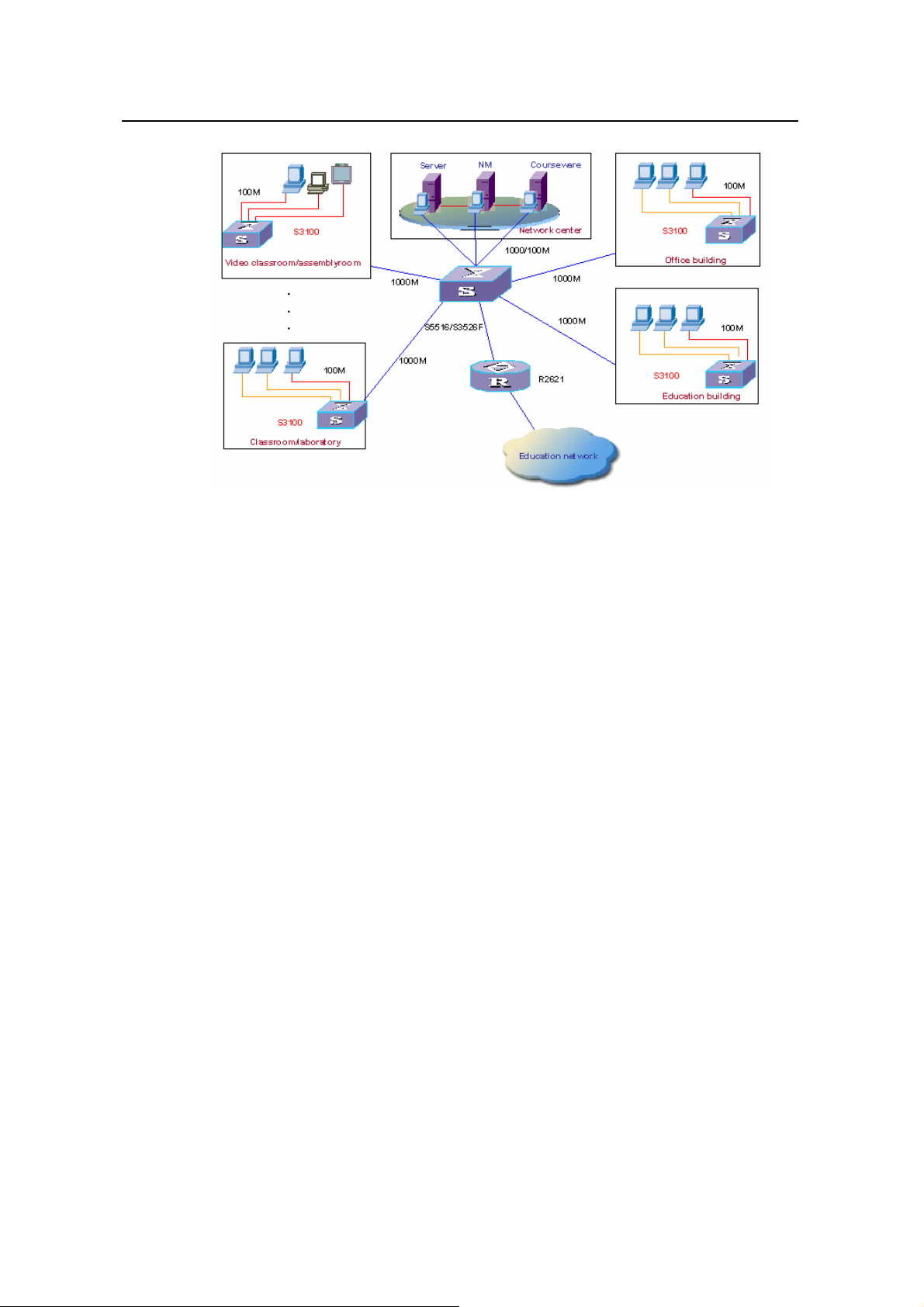
In a campus network, the S3100 series can serve as desktop switching devices at the
access layer. They directly connect to users in education buildings through 100 Mbps
downlink interfaces; and connect to the core switch in the campus through a 1000 Mbps
uplink interface; the core switch further connects to the education network through a
router. This enables the users in the campus to exchange information and share
resources in the scope of the education network.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
2-1
Operation Manual – Product Overview
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2
Figure 2-2 Network diagram for an education network using S3100 series
Network Design
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
2-2

HUAWEI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches
Operation Manual
CLI
Huawei Technologies Proprietary

Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 CLI Overview................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 Introduction to the CLI ....................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Command Protection/Command View .............................................................................. 1-1
1.2.1 Switching between User Levels.............................................................................. 1-2
1.2.2 Configuring the Level of a Specific Command in a Specific View..........................1-3
1.2.3 CLI Views................................................................................................................ 1-3
1.3 CLI Features...................................................................................................................... 1-7
1.3.1 Online Help..............................................................................................................1-7
1.3.2 Terminal Display......................................................................................................1-8
1.3.3 Command History....................................................................................................1-9
1.3.4 Error Messages....................................................................................................... 1-9
1.3.5 Command Edit.......................................................................................................1-10
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
i

Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
Chapter 1 CLI Overview
1.1 Introduction to the CLI
A Quidway series Ethernet switch provides a command line interface (CLI) and
commands for you to configure and manage the Ethernet switch. The CLI is featured by
the following:
z Commands are grouped by levels. This prevents unauthorized users from
operating the switch with relevant commands.
z Users can gain online help at any time by entering the question mark "?".
z Commonly used diagnosing utilities (such as Tracert and Ping) are available.
z Debugging information of various kinds is available.
z The command history is available. Y ou can recall a nd execute a hist ory command
easily.
z You can execute a command by only entering part of the command in the CLI, as
long as the keywords you input uniquely identify the corresponding ones.
1.2 Command Protection/Command View
To prevent unauthorized accesses, commands are protected at different levels.
Commands fall into four protection levels: visit, monitor, system, and manage:
z Visit level: Commands at this level are mainly used to diagnose network and
change the language mode of user interface, and cannot be saved i n configuration
files. For example, the ping, tracert, and language-mode commands are at this
level.
z Monitor level: Commands at this level are mainly used to maintain the system and
diagnose service problems, and cannot be saved to configuration files. For
example, the display and debugging commands are at this level.
z System level: Commands at this level are mainly used to configure services.
Commands concerning routing and network layers are at this level. Y ou can utilize
network services by using these commands.
z Manage level: Commands at this level are associated with the basic operation of
the system, and the system supporting modules. These commands provide
supports to services. Commands concerning file system, FTP/TFTP/XModem
downloading, user management, and level setting are at this level.
Users logging into a switch also fall into four levels, each of which corresponding to one
of the above command levels. Users at a specific level can only use the commands of
the same level and those of the lower levels.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-1
Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
1.2.1 Switching between User Levels
A user can switch the user level from one to another by executing a related command
after logging into a switch. The administrator can also set user level switching
passwords so that users can switch their levels from lower ones to higher ones only
when they input the correct passwords.
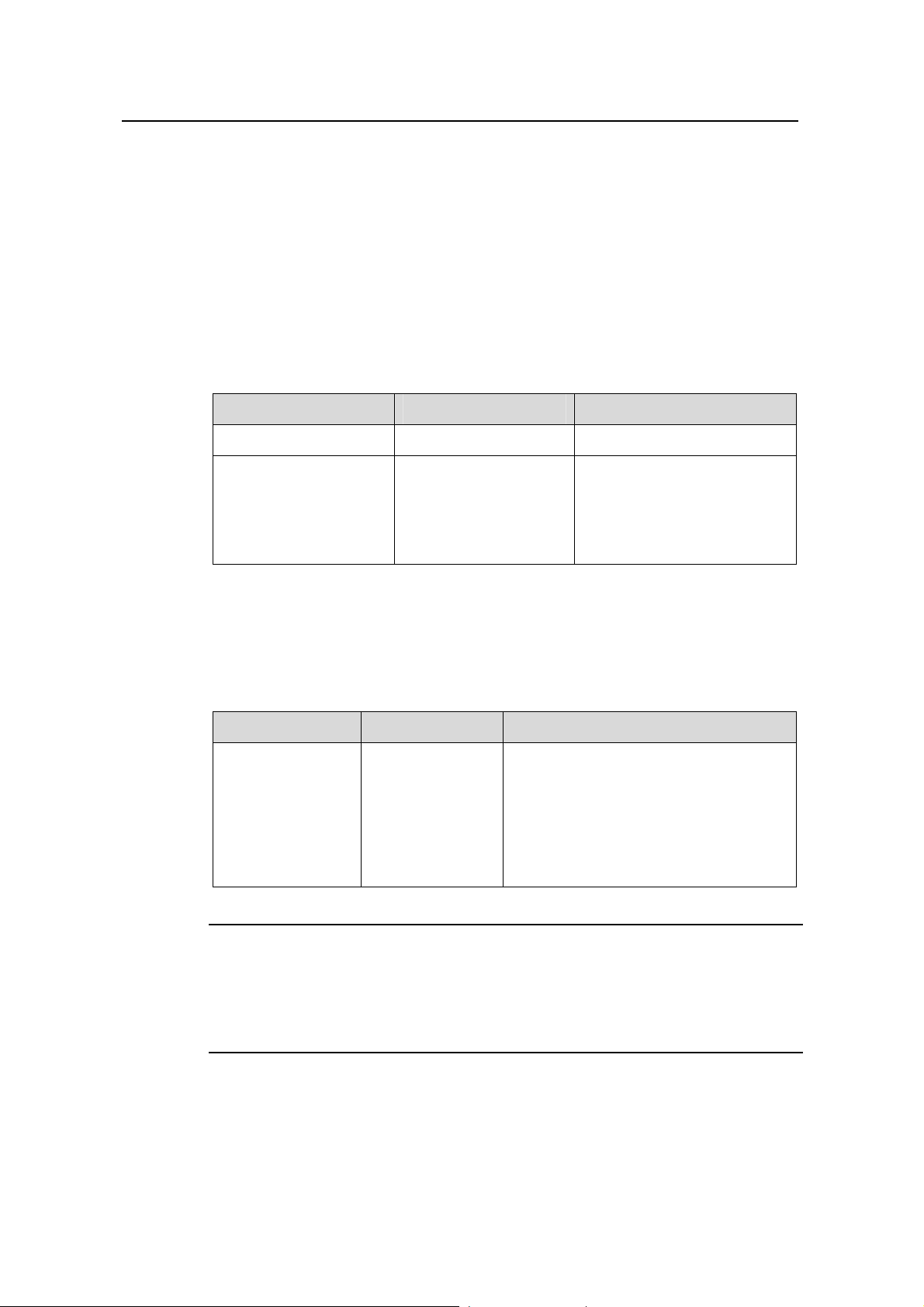
I. Setting a user level switching password
Table 1-1 lists the operations to set a user level switching password.
Table 1-1 Set a user level switching password
Operation Command Description
Enter system view
system-view
Set a password for
switching from a lower
user level to the user
level identified by the
super password
[ level level ] { simple |
cipher } password
level argument
II. Switching to another user level
Table 1-2 lists operations to switch to another user level.
Table 1-2 Switch to another user level
Operation Command Description
Required
If a password for switching to the user
Switch to the user
level identified by
the level argument
super [ level ]
level identified by the level argument is
set and you want to switch to a lower
user level, you will remain at the lower
user level unless you provide the correct
password after executing this command.
—
Optional
A password is necessary only
when a user switch es from a
lower user level to a higher
user level.
Note:
For security purpose, the password a user enters when switching to a higher user level
is not displayed. A user will remain at the original user level if the user has tried three
times to enter the correct password but fails to do this.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-2

Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
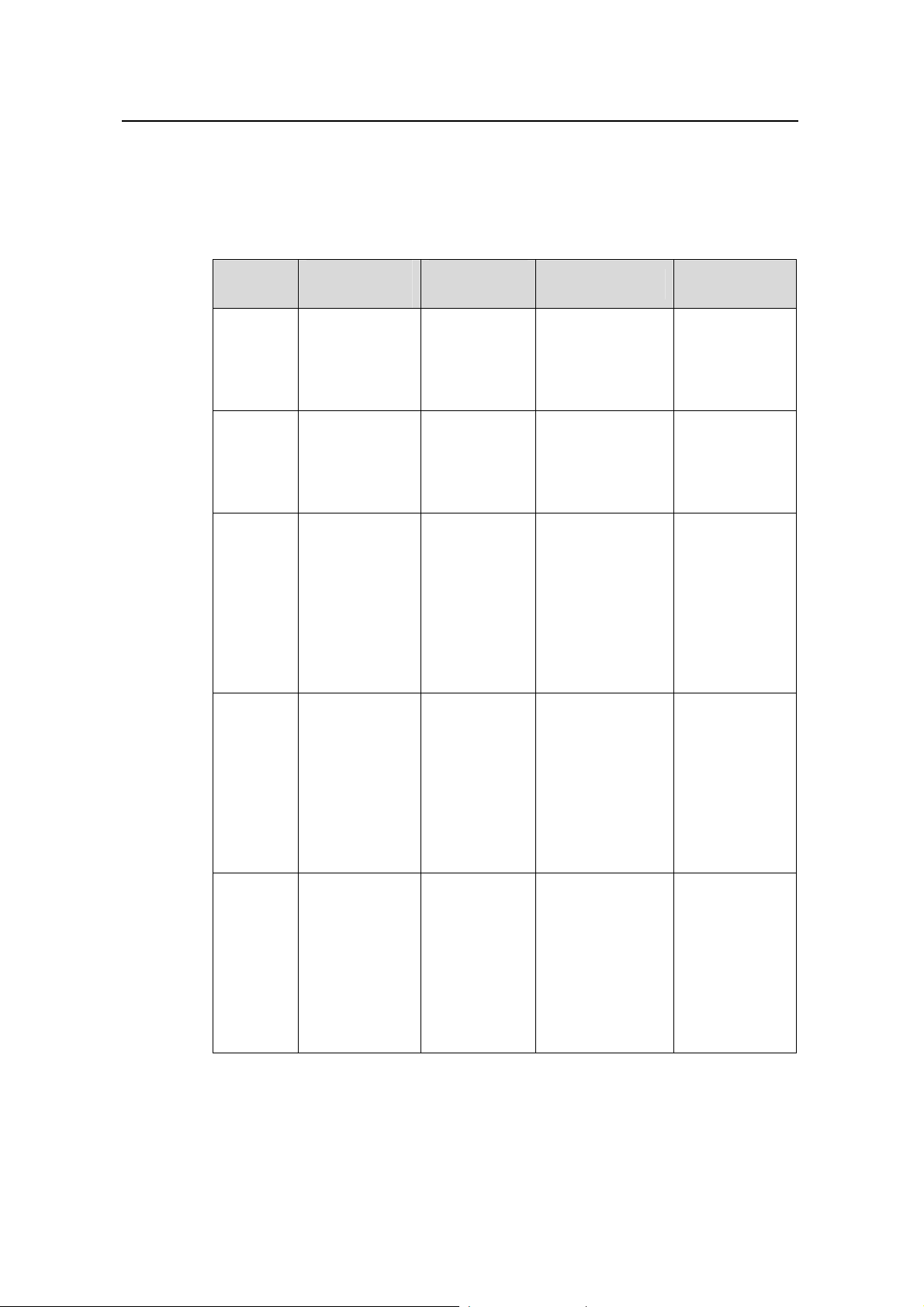
1.2.2 Configuring the Level of a Specific Command in a Specific View
You can configure the level of a specific command in a specific view. Commands fall
into four command levels: visit, monitor , system, and manage, which are i dentified as 0,
1, 2, and 3 respectively. The administrator can change the command level a command
belongs to.
Table 1-3 lists the operations to configure the level of a specific command.
Table 1-3 Configure the level of a specific command in a specific view
Operation Command Description
Enter system view
Configure the level of
a specific command
in a specific view
1.2.3 CLI Views
CLI views are designed for different configuration tasks. They are interrelated. You will
enter user view once you log into a switch successfully, where you can perform
operations such as displaying operation status and statistical information. And by
executing the system-view command, you can enter system view, where you can
enter other views by executing the corresponding commands.
The following CLI views are provided:
z User view
z System view
z Ethernet port view
z VLAN view
z VLAN interface view
z LoopBack interface view
z Local user view
z User interface view
z FTP client view
z SFTP client view
z MST region view
z Cluster view
z Public key view
z Public key editing view
z Basic ACL view
z Advanced ACL view
z RADIUS scheme view
system-view
command-privilege
level level view view
command
—
Required
Use this command with caution to
prevent inconvenience on
maintenance and operation.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-3
Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
z ISP domain view
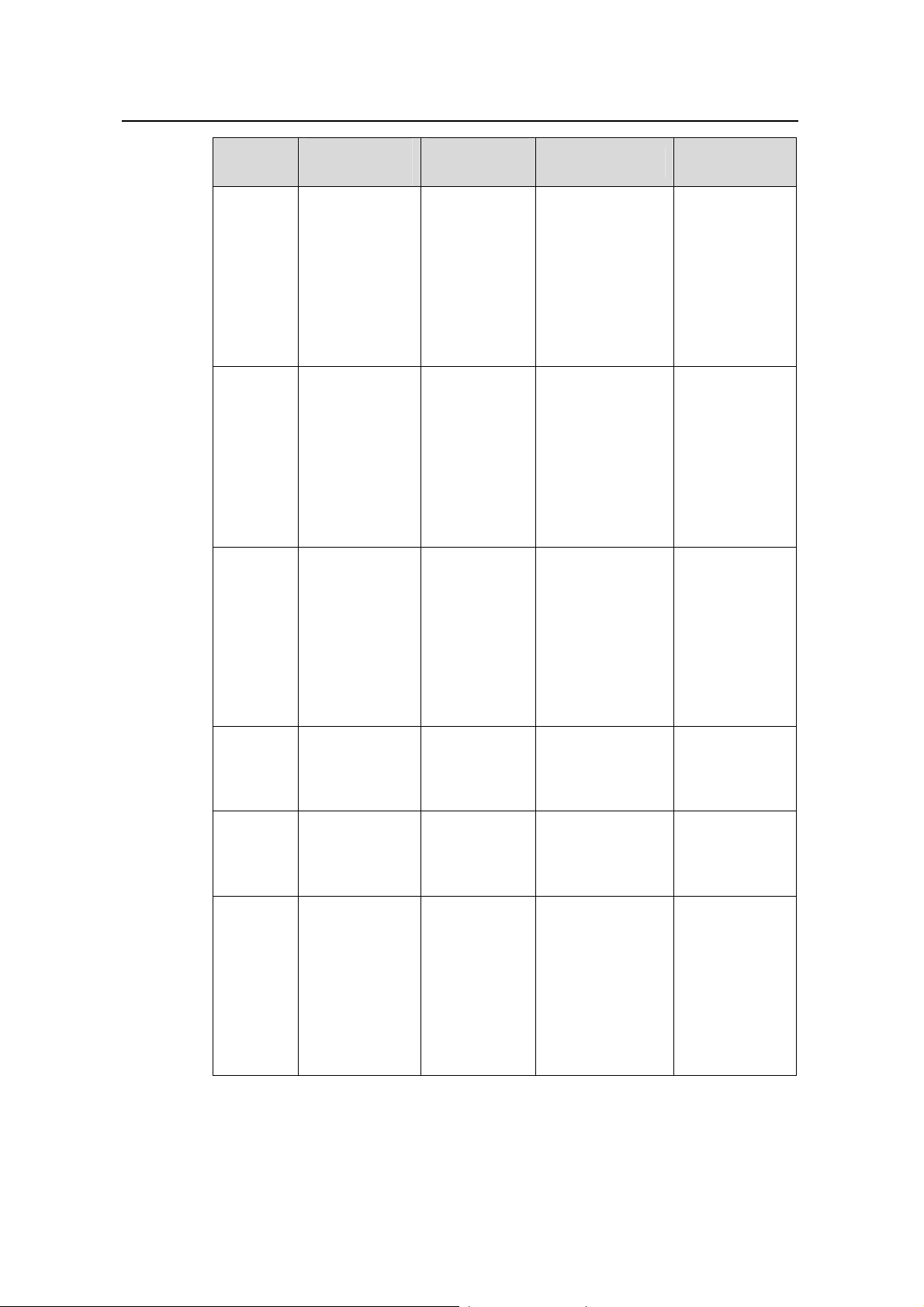
Table 1-4 lists information about CLI views (including the operations you can performed
in these views, how to enter these views, and so on).
Table 1-4 CLI views
View
User view
System
view
Ethernet
port view
VLAN
view
Available
operation
Display
operation
status and
<Quidway>
statistical
information
Configure
system
[Quidway]
parameters
Configure
Ethernet port
parameters
Configure
VLAN
parameters
[Quidway-Eth
ernet1/0/1]
[Quidway-Vla
n1]
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
Execute the
Enter user view
once logging into
the switch.
quit command
in user view to
log out of the
switch.
Execute the
system-view
command in user
view.
Execute the
quit or return
command to
return to user
view.
Execute the
quit command
Execute the
interface
ethernet 1/0/1
command in
system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Execute the
quit command
to return to
Execute the vlan
1 command in
system view.
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
VLAN
interface
view
Configure IP
interface
parameters for
VLANs and
[Quidway-Vla
n-interface1]
aggregated
VLANs
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-4
Execute the
quit command
Execute the
interface
vlan-interface 1
command in
system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
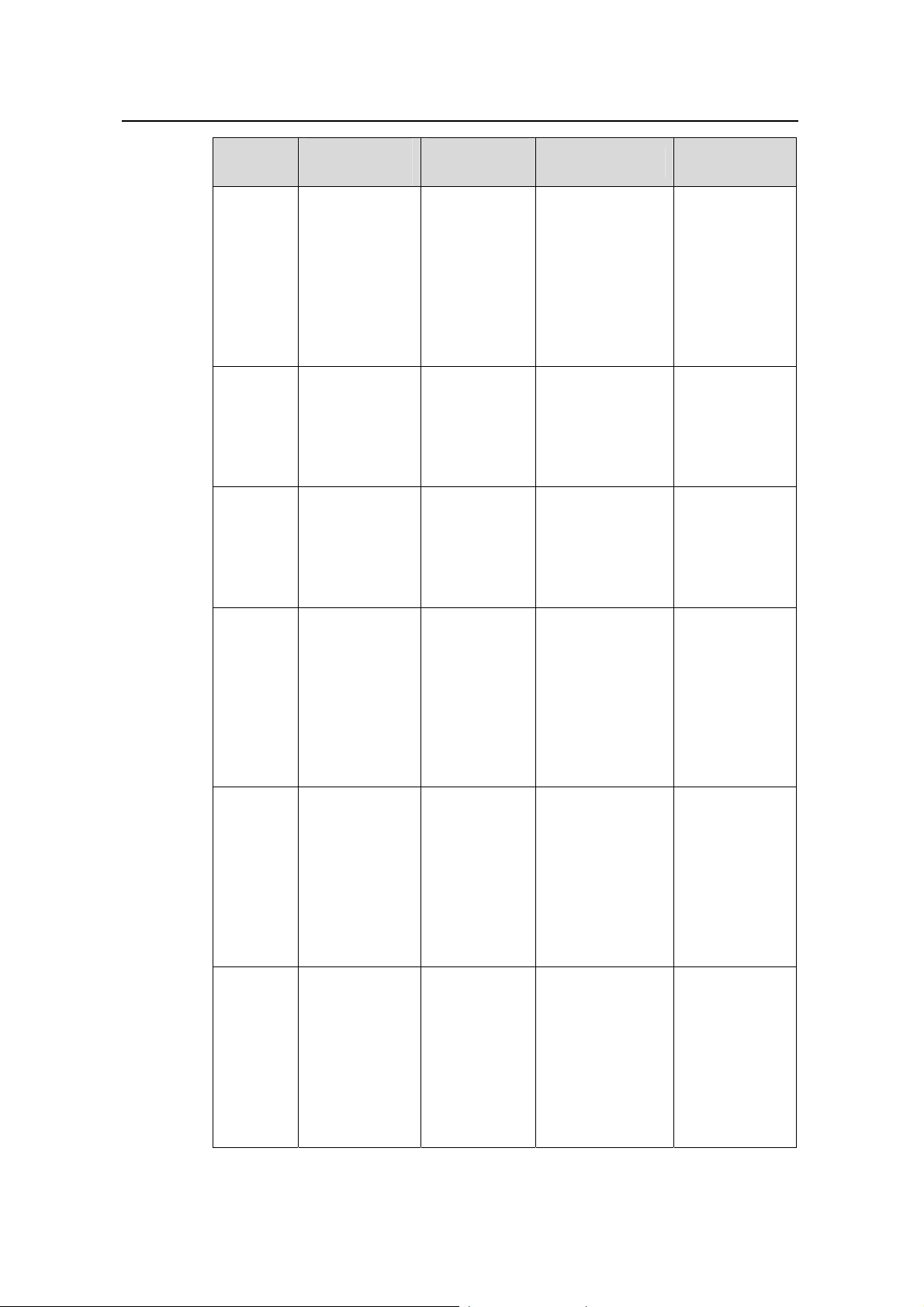
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
Execute the
quit command
LoopBac
k
interface
view
Configure
LoopBack
interface
parameters
[Quidway-Loo
pBack0]
Execute the
interface
loopback 0
command in
system view
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Execute the
quit command
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
Local
user view
Configure local
user
parameters
[Quidway-lus
er-user1]
Execute the
local-user user1
command in
system view.
return to user
view.
User
interface
view
FTP
client
view
SFTP
client
view
MST
region
view
Configure user
interface
[Quidway-ui0]
parameters
Configure FTP
client
[ftp]
parameters
Configure
SFTP client
sftp-client>
parameters
Configure MST
region
parameters
[Quidway-mst
-region]
Execute the
quit command
Execute the
user-interface 0
command in
system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Execute the ftp
command in user
view.
Execute the sftp
10.1.1.1
command in
system view.
Execute the
quit command
to return to
user view.
Execute the
quit command
to return to
user view.
Execute the
quit command
Execute the stp
region-configur
ation command
in system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-5
Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
Execute the
quit command
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
Cluster
view
Configure
cluster
parameters
[Quidway-clus
ter]
Execute the
cluster
command in
system view.
return to user
view.
Public
key view
Public
key
editing
view
Configure RSA
public keys for
SSH users
Edit RSA public
keys of SSH
users
Define rules for
a basic ACL
(ACLs with
Basic
ACL view
their IDs
ranging from
2000 to 2999
are basic
ACLs.)
Define rules for
an advanced
Advance
d ACL
view
ACL (ACLs
with their IDs
ranging from
3000 to 3999
are advanced
ACLs.)
[Quidway-rsa-
public-key]
[Quidway-rsa-
key-code]
[Quidway-acl-
basic-2000]
[Quidway-acl-
adv-3000]
Execute the rsa
peer-public-key
quidway003
command in
system view.
Execute the
public-key-code
begin command
in public key
view.
Execute the
peer-public-ke
y end
command to
return to
system view.
Execute the
public-key-co
de end
command to
return to public
key view.
Execute the
quit command
Execute the acl
number 2000
command in
system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Execute the
quit command
Execute the acl
number 3000
command in
system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
RADIUS
scheme
view
Configure
RADIUS
parameters
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
[Quidway-radi
us-1]
1-6
Execute the
quit command
Execute the
radius scheme 1
command in
system view.
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
return to user
view.
Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
View
Available
operation
Prompt
example
Enter method Quit method
Execute the
quit command
to return to
system view.
Execute the
return
command to
ISP
domain
view
Configure
parameters for
an ISP domain
[Quidway-isp-
huawei163.ne
t]
Execute the
domain
huawei163.net
command in
system view.
return to user
view.
1.3 CLI Features
1.3.1 Online Help
CLI provides two types of online help: complete online help and partial online help.
They assist you with your configuration.
I. Complete online help
Enter a "?" character in any view on your terminal to display all the commands available
in the view and their brief descriptions. The following t ake s user view as an example.
<Quidway> ?
User view commands:
boot Set boot option
cd Change the current path
clock Specify the system clock
cluster Run cluster command
copy Copy the file
debugging Enable system debugging functions
delete Delete the file
dir Display the file list in system
display Display current system information
<omitted>
Enter a command, a space, and a "?" character (instead of a keyword available in this
position of the command) on your terminal to display all the available keywords and
their brief descriptions. The following takes the clock command as an example.
<Quidway> clock ?
datetime Specify the time and date
summer-time Configure summer time
timezone Configure time zone
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-7

Operation Manual – CLI
Quidway S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 CLI Overview
Enter a command, a space, and a "?" character (instead of an argument available in
this position of the command) on your terminal to display all the available arguments
and their brief descriptions. The following takes the interface vlan command as an
example.
[Quidway] interface vlan ?
<1-4094> VLAN interface number
[Quidway] interface vlan 1 ?
<cr>
The string <cr> means no argument is available in the position occupied by the "?"
character. You can execute the command without providing any other information.
II. Partial online help
Enter a string followed directly by a "?" character on your terminal to display all the
commands beginning with the string. For example:
<Quidway> pi?
ping
Enter a command, a space, and a string followed by a "?" character on your terminal to
display all the keywords that belong to the command and begin with the string (if
available). For example:
<Quidway> display ver?
version
Enter a command, the first several characters of an available keyword which uniquely
identifies the keyword, and press <Tab>, to complete the keyword will be automatically
completed.
1.3.2 Terminal Display
CLI provides the following display feature:
z Display suspending. That is, the displaying of output information can be paused
when the screen is full and you can then perform the three operations listed in
Table 1-5 as needed.
Table 1-5 Displaying-related operations
Operation Function
Press <Ctrl+C> Suspend displaying and executing.
Press the space key Scroll the output information up by one page.
Press <Enter> Scroll the output information up by one line.
Huawei Technologies Proprietary
1-8
 Loading...
Loading...