Huawei Quidway S2700 Configuration Manual
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
V100R006C00
Configuration Guide - Network
Management
Issue 01
Date 2011-07-15
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2011. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or representations
of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
TIP
NOTE
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management About This Document
About This Document
Intended Audience
This document provides the basic concepts, configuration procedures, and configuration
examples in different application scenarios of the Network Management feature supported by
the S2700.
This document describes how to configure the Network Management feature.
This document is intended for:
l Data configuration engineers
l Commissioning engineers
l Network monitoring engineers
l System maintenance engineers
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol
Description
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk, which if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a medium or low level of risk, which
if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which if not
avoided, could result in equipment damage, data loss,
performance degradation, or unexpected results.
Indicates a tip that may help you solve a problem or save
time.
Provides additional information to emphasize or supplement
important points of the main text.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management About This Document
Command Conventions
The command conventions that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Convention Description
Boldface The keywords of a command line are in boldface.
Italic Command arguments are in italics.
[ ] Items (keywords or arguments) in brackets [ ] are optional.
{ x | y | ... } Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected.
[ x | y | ... ] Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. One item is selected or no item is selected.
{ x | y | ... }
[ x | y | ... ]
&<1-n> The parameter before the & sign can be repeated 1 to n times.
# A line starting with the # sign is comments.
*
*
Change History
Updates between document issues are cumulative. Therefore, the latest document issue contains
all updates made in previous issues.
Changes in Issue 01 (2011-07-15)
Initial commercial release.
Optional items are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars. A minimum of one item or a maximum of all
items can be selected.
Optional items are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars. Several items or no item can be selected.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management Contents
Contents
About This Document.....................................................................................................................ii
1 SNMP Configuration....................................................................................................................1
1.1 Introduction to SNMP........................................................................................................................................2
1.1.1 SNMP Overview........................................................................................................................................2
1.1.2 SNMP Features Supported by the S2700..................................................................................................4
1.2 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv1..........................................7
1.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.........................................................................................................7
1.2.2 Configuring Basic SNMPv1 Functions.....................................................................................................8
1.2.3 (Optional) Controlling the NM Station's Access to the Device...............................................................11
1.2.4 (Optional) Enabling the SNMP Extended Error Code Function.............................................................12
1.2.5 (Optional) Configuring the Trap Function..............................................................................................13
1.2.6 (Optional) Configuring the Constant Interface Index Feature.................................................................14
1.2.7 Checking the Configuration.....................................................................................................................15
1.3 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv2c......................................15
1.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.......................................................................................................16
1.3.2 Configuring Basic SNMPv2c Functions.................................................................................................17
1.3.3 (Optional) Controlling the NM Station's Access to the Device...............................................................19
1.3.4 (Optional) Enabling the SNMP Extended Error Code Function.............................................................21
1.3.5 (Optional) Configuring the Trap Function..............................................................................................21
1.3.6 (Optional) Configuring the Constant Interface Index Feature.................................................................24
1.3.7 Checking the Configuration.....................................................................................................................25
1.4 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv3........................................25
1.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.......................................................................................................26
1.4.2 Configuring Basic SNMPv3 Functions...................................................................................................27
1.4.3 (Optional) Controlling the NM Station's Access to the Device...............................................................29
1.4.4 (Optional) Enabling the SNMP Extended Error Code Function.............................................................31
1.4.5 (Optional) Configuring the Trap Function..............................................................................................32
1.4.6 (Optional) Configuring the Constant Interface Index Feature.................................................................33
1.4.7 Checking the Configuration.....................................................................................................................34
1.5 SNMP Configuration Examples.......................................................................................................................34
1.5.1 Example for Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Using SNMPv1..............35
1.5.2 Example for Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Using SNMPv2c............38
1.5.3 Example for Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Using SNMPv3..............42
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management Contents
2 LLDP Configuration...................................................................................................................46
2.1 Introduction to LLDP.......................................................................................................................................47
2.2 LLDP Feature Supported by the S2700............................................................................................................50
2.3 Configuring LLDP............................................................................................................................................53
2.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.......................................................................................................53
2.3.2 Enabling Global LLDP............................................................................................................................54
2.3.3 (Optional) Disabling LLDP on an Interface............................................................................................54
2.3.4 (Optional) Configuring an LLDP Management Address........................................................................55
2.3.5 (Optional) Configuring the TLV in the LLDPDU...................................................................................56
2.3.6 (Optional) Configuring LLDP Timers.....................................................................................................57
2.3.7 (Optional) Enabling the LLDP Trap Function........................................................................................60
2.3.8 Checking the Configuration.....................................................................................................................61
2.4 Maintaining LLDP............................................................................................................................................61
2.4.1 Clearing LLDP Statistics.........................................................................................................................62
2.4.2 Monitoring LLDP Status.........................................................................................................................62
2.5 Configuration Examples...................................................................................................................................62
2.5.1 Example for Configuring LLDP on the Device That Has a Single Neighbor.........................................62
2.5.2 Example for Configuring LLDP on the Device That Has Multiple Neighbors.......................................67
2.5.3 Example for Configuring LLDP on the Network Where Link Aggregation Is Configured....................72
3 HGMP Configuration.................................................................................................................79
3.1 Introduction to HGMP......................................................................................................................................80
3.2 HGMP Features Supported by the S2700.........................................................................................................82
3.3 Configuring Basic HGMP Functions...............................................................................................................86
3.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.......................................................................................................86
3.3.2 Configuring NDP.....................................................................................................................................86
3.3.3 Configuring NTDP..................................................................................................................................88
3.3.4 Creating a Cluster....................................................................................................................................89
3.3.5 Adding a Member Switch........................................................................................................................92
3.3.6 (Optional) Deleting or Quitting a Cluster................................................................................................93
3.3.7 (Optional) Deleting a Member Switch....................................................................................................94
3.3.8 Checking the Configuration.....................................................................................................................95
3.4 Configuring Advanced HGMP Functions........................................................................................................97
3.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.......................................................................................................97
3.4.2 Adjusting Parameters of the Cluster........................................................................................................98
3.4.3 Managing Switches in a Cluster Through HGMP.................................................................................101
3.4.4 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................105
3.5 Maintaining HGMP........................................................................................................................................108
3.5.1 Clearing the NDP Statistics...................................................................................................................108
3.5.2 Monitoring the Operation Status of the HGMP Cluster........................................................................108
3.5.3 Debugging HGMP.................................................................................................................................109
3.6 HGMP Configuration Examples....................................................................................................................109
3.6.1 Example for Configuring Basic HGMP Functions for a Cluster...........................................................109
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
v

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management Contents
3.6.2 Example for Configuring the Interconnection of FTP Servers and Devices in and out of the HGMP Cluster
(in NAT Mode)...............................................................................................................................................119
3.6.3 Example for Configuring the Interconnection of FTP Servers and Devices in and out of the HGMP Cluster
(in Non-NAT Mode).......................................................................................................................................129
3.6.4 Example for Configuring Devices in the HGMP Cluster to Access the Outside SNMP Host (in NAT
Mode)..............................................................................................................................................................138
3.6.5 Example for Configuring Devices in the HGMP Cluster to Access the Outside SNMP Host (in non-NAT
Mode)..............................................................................................................................................................148
3.6.6 Example for Configuring the Batch Distribution Function for an HGMP Cluster...............................159
3.6.7 Example for Configuring the Batch Restart Function for an HGMP Cluster.......................................169
3.6.8 Example for Configuring the Incremental Configuration Function for an HGMP Cluster...................178
3.6.9 Example for Configuring the Configuration Synchronization Function for an HGMP Cluster............188
3.6.10 Example for Configuring Security Features for an HGMP Cluster....................................................198
4 NTP Configuration....................................................................................................................209
4.1 Introduction to NTP........................................................................................................................................210
4.2 NTP Supported by the S2700.........................................................................................................................212
4.3 Configuring Basic NTP Functions.................................................................................................................213
4.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................213
4.3.2 Configuring the NTP Primary Clock.....................................................................................................214
4.3.3 Configuring the Unicast Server/Client Mode........................................................................................215
4.3.4 Configuring the Peer Mode...................................................................................................................216
4.3.5 Configuring the Broadcast Mode..........................................................................................................217
4.3.6 Configuring the Multicast Mode...........................................................................................................218
4.3.7 Disabling the Interface From Receiving NTP Packets..........................................................................219
4.3.8 (Optional) Setting the Maximum Number of Dynamic NTP Sessions.................................................220
4.3.9 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................220
4.4 Configuring NTP Security Mechanisms.........................................................................................................221
4.4.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................221
4.4.2 Setting NTP Access Authorities............................................................................................................223
4.4.3 Enabling NTP Authentication...............................................................................................................224
4.4.4 Configuring NTP Authentication in Unicast Server/Client Mode........................................................225
4.4.5 Configuring NTP Authentication in Peer Mode....................................................................................225
4.4.6 Configuring NTP Authentication in Broadcast Mode...........................................................................226
4.4.7 Configuring NTP Authentication in Multicast Mode............................................................................226
4.4.8 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................227
4.5 Maintaining NTP............................................................................................................................................227
4.6 Configuration Examples.................................................................................................................................228
4.6.1 Example for Configuring NTP Authentication in Unicast Client/Server Mode....................................228
4.6.2 Example for Configuring the Common NTP Peer Mode......................................................................233
4.6.3 Example for Configuring NTP Authentication in Broadcast Mode......................................................236
4.6.4 Example for Configuring the Common NTP Multicast Mode..............................................................240
5 Ping and Tracert.........................................................................................................................245
5.1 Ping.................................................................................................................................................................246
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vi

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management Contents
5.2 Tracert.............................................................................................................................................................246
5.3 Performing Ping and Tracert Operations........................................................................................................247
5.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................248
5.3.2 Checking Network Connectivity Through the Ping Operation.............................................................248
5.3.3 Locating Faults on the Network Through the Tracert Operation..........................................................249
5.4 Debugging Ping and Tracert...........................................................................................................................250
5.5 Configuration Examples.................................................................................................................................250
5.5.1 Example for Performing Ping and Tracert Operations..........................................................................250
6 NQA Configuration..................................................................................................................253
6.1 Introduction to NQA.......................................................................................................................................255
6.2 Comparisons Between NQA and Ping...........................................................................................................255
6.3 NQA Server and NQA Clients.......................................................................................................................256
6.4 NQA Supported by the S2700........................................................................................................................257
6.5 Configuring the ICMP Test............................................................................................................................258
6.5.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................258
6.5.2 Configuring ICMP Test Parameters......................................................................................................259
6.5.3 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................260
6.6 Configuring the FTP Download Test.............................................................................................................261
6.6.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................261
6.6.2 Configuring the FTP Download Test Parameters..................................................................................262
6.6.3 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................263
6.7 Configuring the FTP Upload Test..................................................................................................................264
6.7.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................264
6.7.2 Configuring the FTP Upload Test Parameters......................................................................................265
6.7.3 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................267
6.8 Configuring the HTTP Test............................................................................................................................268
6.8.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................268
6.8.2 Configuring HTTP Test Parameters......................................................................................................269
6.8.3 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................270
6.9 Configuring the DNS Test..............................................................................................................................271
6.9.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................271
6.9.2 Configuring the DNS Test Parameters..................................................................................................271
6.9.3 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................273
6.10 Configuring the Traceroute Test...................................................................................................................273
6.10.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................273
6.10.2 Configuring Parameters for a Traceroute Test....................................................................................274
6.10.3 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................275
6.11 Configuring the SNMP Query Test..............................................................................................................276
6.11.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................276
6.11.2 Configuring the SNMP Query Test Parameters..................................................................................277
6.11.3 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................278
6.12 Configuring the TCP Test.............................................................................................................................279
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
vii

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management Contents
6.12.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................279
6.12.2 Configuring the TCP Server................................................................................................................279
6.12.3 Configuring the TCP Client.................................................................................................................280
6.12.4 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................281
6.13 Configuring the UDP Test............................................................................................................................282
6.13.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................282
6.13.2 Configuring the UDP Server...............................................................................................................283
6.13.3 Configuring the UDP Client................................................................................................................283
6.13.4 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................285
6.14 Configuring the Jitter Test............................................................................................................................285
6.14.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................286
6.14.2 Configuring the Jitter Server...............................................................................................................287
6.14.3 Configuring the Jitter Client................................................................................................................287
6.14.4 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................289
6.15 Configuring Universal NQA Test Parameters..............................................................................................290
6.15.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................290
6.15.2 Configuring Universal Parameters for the NQA Test Instance...........................................................290
6.15.3 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................294
6.16 Configuring Round-Trip Delay Thresholds.................................................................................................295
6.16.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................295
6.16.2 Configuring Round-Trip Delay Thresholds........................................................................................296
6.16.3 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................297
6.17 Configuring the Trap Function.....................................................................................................................297
6.17.1 Establishing the Configuration Task...................................................................................................297
6.17.2 Sending Trap Messages When Test Failed..........................................................................................298
6.17.3 Sending Trap Messages When Probes Failed......................................................................................299
6.17.4 Sending Trap Messages When Probes Are Complete.........................................................................300
6.17.5 Sending Trap Messages When the Transmission Delay Exceeds Thresholds....................................301
6.17.6 Checking the Configuration.................................................................................................................301
6.18 Maintaining NQA.........................................................................................................................................302
6.18.1 Restarting NQA Test Instances...........................................................................................................302
6.18.2 Clearing NQA Statistics......................................................................................................................303
6.18.3 Debugging NQA..................................................................................................................................303
6.19 Configuration Examples...............................................................................................................................304
6.19.1 Example for Configuring the ICMP Test............................................................................................304
6.19.2 Example for Configuring the FTP Download Test.............................................................................306
6.19.3 Example for Configuring the FTP Upload Test..................................................................................308
6.19.4 Example for Configuring the HTTP Test............................................................................................311
6.19.5 Example for Configuring the DNS Test..............................................................................................312
6.19.6 Example for Configuring the Traceroute Test.....................................................................................314
6.19.7 Example for Configuring the SNMP Query Test................................................................................317
6.19.8 Example for Configuring the TCP Test...............................................................................................319
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
viii

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management Contents
6.19.9 Example for Configuring the UDP Test..............................................................................................321
6.19.10 Example for Configuring the Jitter Test............................................................................................323
6.19.11 Example for Configuring the Test of Sending NQA Threshold Traps to the NMS..........................326
7 RMON Configuration...............................................................................................................330
7.1 Introduction to RMON...................................................................................................................................331
7.2 RMON Suported by the S2700.......................................................................................................................331
7.3 Configuring RMON........................................................................................................................................333
7.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task.....................................................................................................333
7.3.2 Enabling the RMON Statistics Function on the Interface.....................................................................334
7.3.3 Configuring the ethernetStatsTable.......................................................................................................335
7.3.4 Configuring the HistoryControlTable...................................................................................................335
7.3.5 Configuring the EventTable..................................................................................................................336
7.3.6 Configuring the AlarmTable.................................................................................................................337
7.3.7 Configuring the PrialarmTable..............................................................................................................337
7.3.8 Checking the Configuration...................................................................................................................338
7.4 Maintaining RMON........................................................................................................................................340
7.5 Configuration Examples.................................................................................................................................340
7.5.1 Examples for Configuring RMON........................................................................................................340
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ix

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
1 SNMP Configuration
About This Chapter
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a standard network management protocol
widely used on TCP/IP networks. It uses a central computer (a network management station)
that runs network management software to manage network elements. There are three SNMP
versions, SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. Users can choose to configure one or more
versions if needed.
1.1 Introduction to SNMP
SNMP provides a set of standard protocols for the communication between the network
management station (NM station) and devices, allowing the NM station to normally manage
devices and receive alarms reported by the devices.
1.2 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv1
After SNMPv1 is configured, a managed device and an NM station can run SNMPv1 to
communicate with each other. To ensure normal communication, you need to configure both
sides. This section describes only the configurations on a managed device (the agent side). For
details about configurations on an NM station, see the pertaining NM station operation guide.
1.3 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv2c
After SNMPv2c is configured, a managed device and an NM station can run SNMPv2c to
communicate with each other. To ensure normal communication, you need to configure both
sides. This section describes only the configurations on a managed device (the agent side). For
details about configurations on an NM station, see the pertaining NM station operation guide.
1.4 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv3
After SNMPv3 is configured, a managed device and an NM station can run SNMPv3 to
communicate with each other. To ensure normal communication, you need to configure both
sides. This section describes only the configurations on a managed device (the agent side). For
details about configurations on an NM station, see the pertaining NM station operation guide.
1.5 SNMP Configuration Examples
This section provides several configuration examples of SNMP. The configuration roadmap in
the examples will help you understand the configuration procedures. Each configuration
example provides information about the networking requirements, configuration notes, and
configuration roadmap.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
1.1 Introduction to SNMP
SNMP provides a set of standard protocols for the communication between the network
management station (NM station) and devices, allowing the NM station to normally manage
devices and receive alarms reported by the devices.
1.1.1 SNMP Overview
Get and Set operations can be performed on a managed device that runs the SNMP agent to
manage device objects by NM stations These objects are uniquely identified in the Management
Information Base (MIB).
As network services develop, more and more devices are deployed on existing networks. It is
some distance from the devices to the central equipment room where a network administrator
works. Once faults occur on the remote devices, it is impossible for the network administrator
to detect, locate and rectify faults immediately because the faults will not be reported by the
devices. This affects maintenance efficiency and greatly increases maintenance workload.
To solve this problem, equipment vendors have provided network management functions in
some products. The NM station then can query the status of remote devices, and devices can
send alarms to the NM station in the case of particular events.
SNMP operates at the application layer of the IP suite and defines how to transmit management
information between the NM station and devices. SNMP defines several device management
operations that can be performed by the NM station and allows devices to notify the NM station
of device faults by sending alarms.
An SNMP-managed network consists of three components: NM station, agent, and managed
device. The NM station uses the MIB to identify and manage device objects. The operations
used for device management include GetRequest, GetNextRequest, GetResponse, GetBulk,
SetRequest, and notification from the agent to the NM station. The following sections give details
on the components, MIB, and operations.
SNMP Components
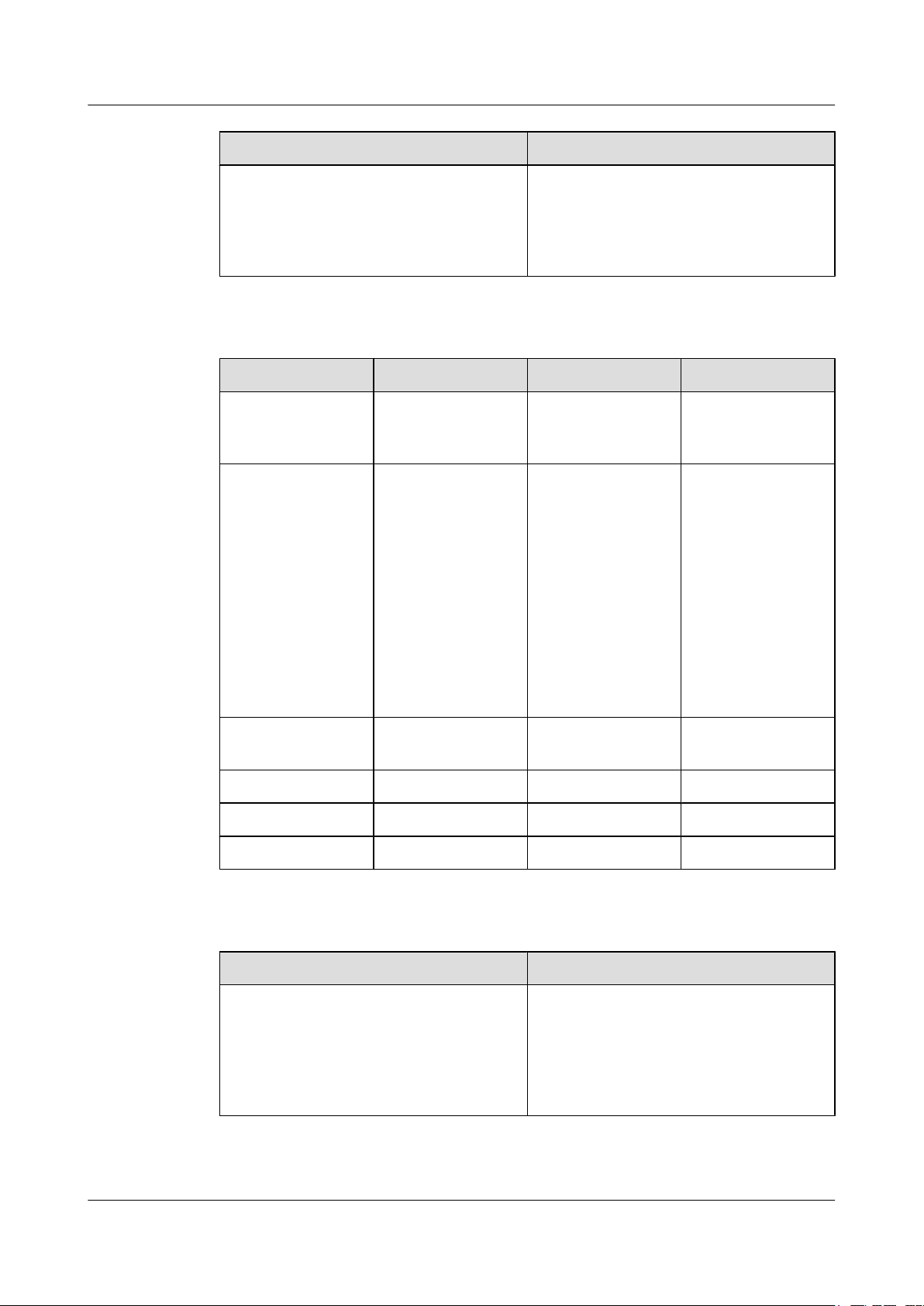
Three components are used in SNMP device management:
l NM station: sends various query packets to query managed devices and receives alarms
from these devices.
l Agent: is a network-management process on a managed device. An agent has the following
functions:
– Receives and parses query packets sent from the NM station.
– Reads or writes management variables based on the query type, and generates and sends
– Sends an alarm to the NM station when triggering conditions defined on each protocol
response packets to the NM station.
module corresponding to the alarm are met. For example, the system view is displayed
or closed, or the device is restarted.
l Managed device: is managed by an NM station and generates and reports alarms to the NM
station.
Figure 1-1 shows the relationship between the NM station and agent.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2

UDP Port161
Request
Response
NM Station
Agent
NM Station
Agent
UDP Port162
A
2
6
1
5
2
1
1
2
1
B
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
Figure 1-1 SNMP structure
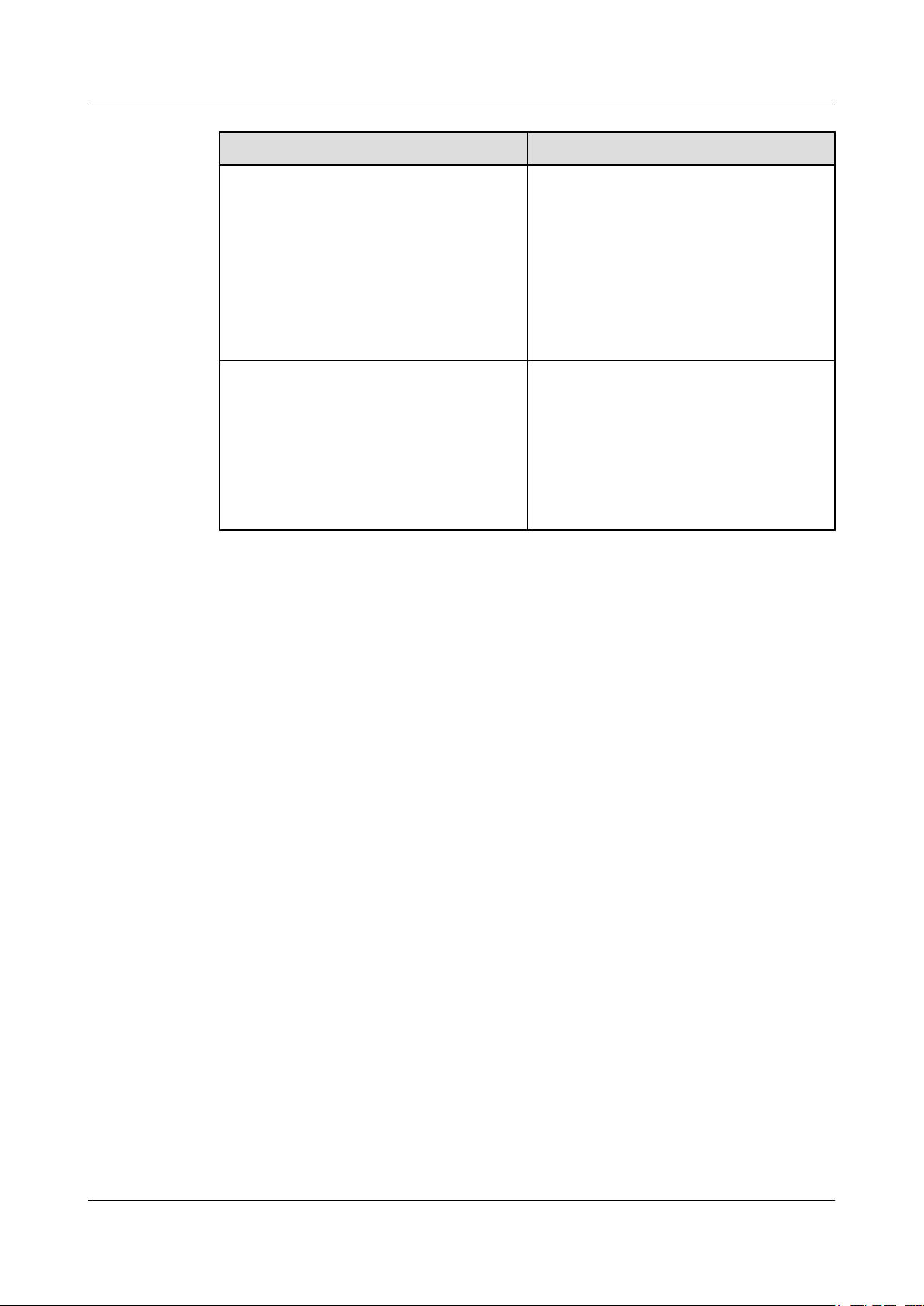
MIB
SNMP uses a hierarchical naming convention to identify managed objects and to distinguish
between managed objects. This hierarchical structure is similar to a tree with the nodes
representing managed objects, Figure 1-2 shows a managed object that can be identified by the
path from the root to the node representing it.
Figure 1-2 Structure of a MIB tree
As shown in Figure 1-2, object B is uniquely identified by a string of numbers, {1.2.1.1}. Such
a number string is called an Object Identifier (OID). A MIB tree is used to describe the hierarchy
of data in a MIB that collects the definitions of variables on the managed devices.
A user can use a standard MIB or define a MIB based on certain standards. Using a standard
MIB can reduce the costs on proxy deployment and therefore reduce the costs on the entire
network management system.
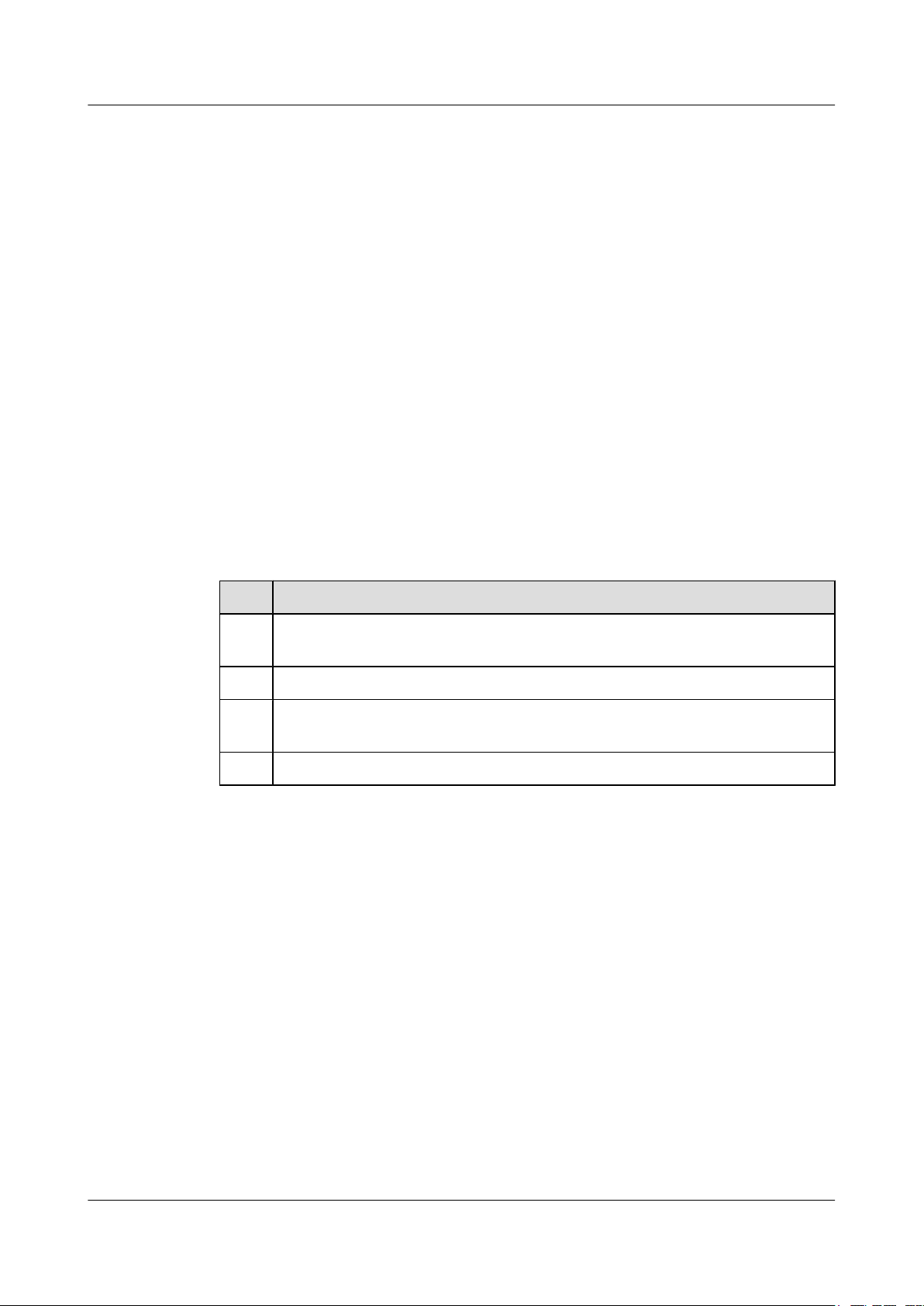
SNMP Operations
SNMP uses Get and Set operations to replace a complex command set. The operations described
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
in Figure 1-3 can implement all functions.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3

UDP Port161
NM Station
Agent
UDP Port162
get-request
get-response
get-next-request
get-response
set-request
get-response
trap
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
Figure 1-3 Schematic diagram of SNMP operations
Table 1-1 gives details on the SNMP operations.
Table 1-1 SNMP operations
Operation Function
GetRequest Retrieves the value of a variable. The NM station sends the
request to a managed device to obtain the value of an object
on the device.
GetNextRequest Retrieves the value of the next variable. The NM station
sends the request to a managed device to obtain the status
of the next object on the device.
GetResponse Responds to GetRequest, GetNextRequest, and
SetRequest operations. It is sent from the managed device
to the NM station.
GetBulk Is an NMS-to-agent request, equaling continuous GetNext
operations.
SetRequest Sets the value of a variable. The NM station sends the
request to a managed device to adjust the status of an object
on the device.
Trap Reports an event to the NM station.
1.1.2 SNMP Features Supported by the S2700
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
This section compares SNMP versions in terms of their support for features and usage scenarios
to provide a reference for your SNMP version selection during network deployment.
The S2700 supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3. Table 1-2 lists the features supported
by SNMP, and Table 1-3 shows the support of different SNMP versions for the features. Table
1-4 describes the usage scenarios of SNMP versions, which will help you choose a proper version
for the communication between an NM station and managed devices based on the network
operation conditions.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
NOTE
When multiple NM stations using different SNMP versions manage the same device in a network,
SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 can all be configured on the device for its communication with all the
NM stations.
Table 1-2 Description of features supported by SNMP
Feature Description
Access control This function is used to restrict a user's device
administration rights. It gives specific users
the rights to manage specified objects on
devices and therefore provides fine
management.
Authentication and encryption Packets transmitted between the NM station
and managed devices are authenticated and
encrypted. This prevents data packets from
being intercepted or modified, improving
data sending security.
Error code Error codes are used to identify particular
faults. They help an administrator quickly
locate and rectify faults. The larger the variety
of error codes, the more greatly they help an
administrator in device management.
Trap Traps are sent from managed devices to the
NM station. These traps allow an
administrator to discover device faults
immediately.
The managed devices do not require the
acknowledgement from the NM station after
sending traps.
Inform
Informs are sent from managed devices to the
NM station.
The managed devices require the
acknowledgement from the NM station after
sending informs. If a managed device does
not receive an acknowledgement after
sending an inform, it will resend the inform
to the NM station and generate alarm logs.
Even if the NM station restarts, it can still
synchronize the informs sent during the
restart process.
If the device does not receive an
acknowledgement from the NM station after
sending an inform, it will store the inform in
its memory. In this regard, using informs may
consume lots of system resources.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
Feature Description
GetBulk GetBulk allows an administrator to perform
Get-next operation in batches. In a large-scale
network, GetBulk reduces the administrator's
workload and improves management
efficiency.
Table 1-3 Different SNMP versions' support for the features
Feature SNMPv1 SNMPv2c SNMPv3
Access control Community-name-
based access control
supported
Authentication and
Not supported Not supported Supported, and the
encryption
Community-namebased access control
supported
User or user-groupbased access control
supported
supported
authentication and
encryption modes are
as follows:
Authentication
mode:
l MD5
l SHA
Encryption mode:
DES56
Error code
6 error codes
supported
16 error codes
supported
16 error codes
supported
Trap Supported Supported Supported
Inform Not supported Supported Not supported
GetBulk Not supported Supported Supported
Table 1-4 Usage scenarios of different SNMP versions
Version
Usage Scenario
SNMPv1 This version is applicable to small-scale
networks whose networking is simple and
security requirements are low or whose
security and stability are good, such as
campus networks and small enterprise
networks.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
6
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
Version Usage Scenario
SNMPv2c This version is applicable to medium and
large-scale networks whose security
requirements are not strict or whose security
is good (for example, VPNs) but whose
services are so busy that traffic congestion
may occur.
Using informs can ensure that the messages
sent from managed devices are received by
the NM station.
SNMPv3
If you plan to build a new network, choose an SNMP version based on your usage scenario. If
you plan to expand or upgrade an existing network, choose an SNMP version to match the SNMP
version running on the NM station to ensure the normal communication between managed
devices and the NM station.
This version is applicable to networks of
various scales, especially the networks that
have strict requirements on security and can
be managed only by authorized
administrators, such as the scenario where
data between the NM station and managed
devices needs to be transmitted over a public
network.
1.2 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv1
After SNMPv1 is configured, a managed device and an NM station can run SNMPv1 to
communicate with each other. To ensure normal communication, you need to configure both
sides. This section describes only the configurations on a managed device (the agent side). For
details about configurations on an NM station, see the pertaining NM station operation guide.
The NM station manages a device in the following manners:
l Sends requests to the managed device to perform the GetRequest, GetNextRequest,
GetResponse, GetBulk, or SetRequest operation, obtaining data and setting values.
l Receives alarms from the managed device and locates and rectify device faults based on
the alarm information.
In the following configuration, after basic SNMP functions are configured, the NM station can
manage the device in these manners. For details on how to configure finer management such as
accurate access control or alarm module specification, see the following configuration
procedures.
1.2.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Before configuring a device to communicate with an NM station by running SNMPv1,
familiarize yourself with the applicable environment, complete the pre-configuration tasks, and
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
7
Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
obtain the data required for the configuration. This will help you complete the configuration task
quickly and accurately.
Applicable Environment
SNMP needs to be deployed in a network to allow the NM station to manage network devices.
If the network has a few devices and its security is good, such as a campus network or a small
enterprise network, SNMPv1 can be deployed to ensure the normal communication between the
NM station and managed devices.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring a device to communicate with an NM station by running SNMPv1, complete
the following task:
l Configuring a routing protocol to ensure that the switch and NM station are routable
Data Preparation
Before configuring a device to communicate with an NM station by running SNMPv1, you need
the following data.
No.
1 SNMP version, SNMP community name, destination address of alarm messages,
2 (Optional) ACL number, IP address of the NM station, and MIB object
3 (Optional) Name of the alarm-sending module, source address of trap messages,
4 (Optional) Number of interfaces indexed by fixed numbers
Data
administrator's contact information and location, and SNMP packet size
queue length for trap messages, and lifetime of trap messages
1.2.2 Configuring Basic SNMPv1 Functions
After basic SNMP functions are configured, an NM station can perform basic operations such
as Get and Set operations on a managed device, and the managed device can send alarms to the
NM station.
Context
Steps 3, 4, and 5 are mandatory for the configuration of basic SNMP functions. After the
configurations are complete, basic SNMP communication can be conducted between the NM
station and managed device.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
system-view
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 (Optional) Run:
snmp-agent
The SNMP agent function is enabled.
By default, the SNMP agent function is disabled. Running any command with the parameter
snmp-agent can enable the SNMP agent function, so this step is optional.
Step 3 Run:
snmp-agent sys-info version v1
The SNMP version is set.
By default, SNMPv3 is enabled.
After SNMPv1 is enabled on the managed device, the device supports both SNMPv1 and
SNMPv3. This means that the device can be monitored and managed by NM stations running
SNMPv1 or SNMPv3.
Step 4 Run:
snmp-agent community { read | write } community-name
The community name is set.
After the community name is set, if no MIB view is configured, the NM station that uses the
community name has rights to access objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1).
l read needs to be configured in the command if the NM station administrator needs the read
permission in a specified view in some cases. For example, a low-level administrator needs
to read certain data.
l write needs to be configured in the command if the NM station administrator needs the read
and write permissions in a specified view in some cases. For example, a high-level
administrator needs to read and write certain data.
Step 5 Choose either of the following commands as needed to configure a destination IP address for
the alarms and error codes sent from the device.
l To configure a destination IPv4 address for the alarms and error codes sent from the device,
run:
snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain ip-address [ udp-port portnumber ] [ public-net | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] params securityname
security-string [ v1 ] [ private-netmanager ]
The descriptions of the command parameters are as follows:
l The default destination UDP port number is 162. In some special cases (for example, port
mirroring is configured to prevent a well-known port from being attacked), the parameter
udp-port can be used to specify a non-well-known UDP port number. This ensures normal
communication between the NM station and managed device.
l If the alarms sent from the managed device to the NM station need to be transmitted over a
public network, the parameter public-net needs to be configured. If the alarms sent from the
managed device to the NM station need to be transmitted over a private network, the
parameter vpn-instance vpn-instance-name needs to be used to specify a VPN that will take
over the sending task.
l The parameter securityname identifies the alarm sender, which will help you learn the alarm
source.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
9

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
l If the NM station and managed device are both Huawei products, the parameter private-
netmanager can be configured to add more information to alarms, such as the alarm type,
alarm sequence number, and alarm sending time. The information will help you locate and
rectify faults more quickly.
Step 6 (Optional) Run:
snmp-agent sys-info { contact contact | location location }
The equipment administrator's contact information or location is configured.
This step is needed if the NM station administrator needs to know equipment administrators'
contact information and locations when the NM station manages many devices. This will allow
the NM station administrator to quickly contact the equipment administrators for fault location
and rectification.
To configure both the equipment administrator's contact information and location, you need to
run the command twice to configure them separately.
Step 7 (Optional) Run:
snmp-agent packet max-size byte-count
The maximum size of an SNMP packet that the device can receive or send is set.
By default, the maximum size of an SNMP packet that the device can receive or send is 12000
bytes.
After the maximum size is set, the device will discard any SNMP packet that is larger than the
set size. The allowable maximum size of an SNMP packet for a device depends on the size of a
packet that the NM station can process; otherwise, the NM station cannot process the SNMP
packets sent from the device.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
After the configurations are complete, basic communication can be conducted between the NM
station and managed device.
l Access control allows any NM station that uses the community name to monitor and manage
all the objects on the managed device.
l The managed device sends alarms generated by the modules that are enabled by default to
the NM station.
If finer device management is required, follow directions below to configure a managed device:
l To allow a specified NM station that uses the community name to manage specified objects
on the device, follow the procedure described in Controlling the NM Station's Access to
the Device.
l To allow a specified module on the managed device to report alarms to the NM station,
follow the procedure described in Configuring the Trap Function.
l If the NM station and managed device are both Huawei products, follow the procedure
described in Enabling the SNMP Extended Error Code Function to allow the device to
send more types of error codes. This allows more specific error identification and facilitates
your fault location and rectification.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
l If the functions such as accounting and fault location need to be bound to specified
interfaces to prevent changes in interface indexes during device or interface restart, follow
the procedure described in Configuring the Constant Interface Index Feature.
1.2.3 (Optional) Controlling the NM Station's Access to the Device
This section describes how to specify an NM station and manageable MIB objects for SNMPbased communication between the NM station and managed device to improve communication
security.
Context
If a device is managed by multiple NM stations that use the same community name, note the
following points:
l If all the NM stations that use the community name need to have rights to access the objects
in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1), skip the following steps.
l If some of the NM stations that use the community name need to have rights to access the
objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1), skip Step 5.
l If all the NM stations need to manage specified objects on the device, skip Steps 2, 3, and
4.
l If some of the NM stations that use the community name need to manage specified objects
on the device, perform all the following steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
Step 2 Run:
Step 3 Run:
Step 4 Run:
Step 5 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
acl acl-number
A basic ACL is created to filter the NM station users that can manage the device.
rule [ rule-id ] { deny | permit } source { source-ip-address source-wildcard |
any }
A rule is added to the ACL.
quit
Return to the system view.
snmp-agent mib-view { excluded | included } view-name oid-tree
A MIB view is created, and manageable MIB objects are specified.
By default, an NM station has rights to access the objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1).
l If a few MIB objects on a device or some objects in the current MIB view do not or no longer
need to be managed by the NM station, excluded needs to be specified in the related command
to exclude these MIB objects.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
l If a few MIB objects on the device or some objects in the current MIB view need to be
managed by the NM station, included needs to be specified in the related command to include
these MIB objects.
Step 6 Run:
snmp-agent community { read | write } { community-name | cipher community-name } [
mib-view view-name | acl acl-number ]
*
The NM station's access rights are specified.
l read needs to be configured in the command if the NM station administrator needs the read
permission in the specified view in some cases. For example, a low-level administrator needs
to read certain data. write needs to be configured in the command if the NM station
administrator needs the read and write permissions in the specified view in some cases. For
example, a high-level administrator needs to read and write certain data.
l cipher is used to display the community name in cipher text. It can be configured in the
command to improve security. If the parameter is configured, the administrator needs to
remember the community name. If the community name is forgotten, it cannot be obtained
by querying the device.
l If some of the NM stations that use the community name need to have rights to access the
objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1), mib-view view-name does not need to be
configured in the command.
l If all the NM stations that use the community name need to manage specified objects on the
device, acl acl-number does not need to be configured in the command.
l If some of the NM stations that use the community name need to manage specified objects
on the device, both mib-view and acl need to be configured in the command.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
After the access rights are configured, especially after the IP address of the NM station is
specified, if the IP address changes (for example, the NM station changes its location, or IP
addresses are reallocated due to network adjustment), you need to change the IP address of the
NM station in the ACL. Otherwise, the NM station cannot access the device.
1.2.4 (Optional) Enabling the SNMP Extended Error Code Function
This section describes how to enable the extended SNMP error code function when both the NM
station and managed device are Huawei products. After this function is enabled, more types of
error codes are provided to help you locate and rectify faults more quickly and accurately.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
snmp-agent extend error-code enable
The SNMP extended error code function is enabled.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
By default, SNMP standard error codes are used. After the extended error code function is
enabled, extended error codes can be sent to the NM station.
----End
1.2.5 (Optional) Configuring the Trap Function
This section describes how to specify the alarms to be sent to the NM station, which will help
you to locate important problems. After relevant parameters are set, the security of alarm sending
can be improved.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
snmp-agent trap enable
Alarm sending is enabled.
Step 3 Run:
snmp-agent trap enable feature-name feature-name trap-name trap-name
A trap function of a feature module is enabled. This means that an alarm of a specified feature
can be sent to the NM station.
The undo snmp-agent trap enable feature-name command can be used to disable a trap
function of a module.
Step 4 Run:
snmp-agent trap source interface-type interface-number
The source interface for trap messages is specified.
NOTE
If the snmp-agent trap enable command is run to enable the trap functions of all modules, or the snmpagent trap enable feature-name command is run to enable three or more trap functions of a module, note
the following points:
l To disable the trap functions of all modules, you need to run the snmp-agent trap disable command.
l To restore the trap functions of all modules to the default status, you need to run the undo snmp-agent
trap enable or undo snmp-agent trap disable command.
l To disable one trap function of a module, you need to run the undo snmp-agent trap enable feature-
name command.
After the source interface is specified, its IP address becomes the source IP address of trap
messages. Configuring the IP address of the local loopback interface as the source interface is
recommended, which can ensure device security.
The source interface specified on the switch for trap messages must be consistent with that
specified on the NM station; otherwise, the NM station will not accept the trap messages sent
from the switch.
Step 5 Run:
snmp-agent trap queue-size size
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
The length of the queue storing trap messages to be sent to the destination host is set.
The queue length depends on the number of generated trap messages. If the switch frequently
generates trap messages, a longer queue length can be set to prevent trap messages from being
lost.
Step 6 Run:
snmp-agent trap life seconds
The lifetime of every trap message is set.
The lifetime of every trap message depends on the number of generated trap messages. If the
switch frequently generates trap messages, a longer lifetime can be set for every trap message
to prevent trap messages from being lost.
----End
1.2.6 (Optional) Configuring the Constant Interface Index Feature
This section describes how to configure the constant interface index feature. This feature allows
some interface indexes remain unchanged in the case of interface deletion or addition, system
restart, or hardware or software configuration change to meet the need of some functions such
as accounting and fault diagnosis that require fixed interfaces.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
Step 2 Run:
Step 3 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
ifindex constant
The constant interface index feature is enabled.
After the feature is enabled, the indexes for all the existing interfaces and newly created interfaces
are fixed. If the system needs to restart, the save command must be run to save interface
configurations; otherwise, the interface indexes will change after the system is restarted.
set constant-ifindex max-number number
The maximum number of interfaces indexed by fixed numbers is set.
If interfaces are frequently added or deleted during system operation, the interface index file
stored in the device may have a great size and consume too many system resources. Setting the
maximum number of interfaces indexed by fixed numbers can prevent the interface index file
from exceeding an expected size.
After the maximum number of interfaces indexed by fixed numbers is set, the system will allocate
fixed indexes to interfaces within the specified value range. If the specified value is smaller than
the number of interfaces configured on the device, the system allocates fixed interface indexes
to the interfaces enabled earlier. The interfaces enabled later are not indexed by fixed numbers.
By default, a maximum of 131070 interfaces can be indexed by fixed numbers. If the value is
set to 0, no interfaces will be indexed by fixed numbers.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
Step 4 Run:
set constant-ifindex subinterface { dense-mode | sparse-mode }
The memory distribution mode for the sub-interface index is set.
When a sub-interface is created, the system generates an index image file for the sub-interface
in the memory in a specified mode. You may use various sub-interface numbering modes, such
as the continuous mode or the discontinuous mode. In real-world situations, one of the following
distribution modes can be used as needed:
l Sparse mode: applies to discontinuous sub-interface numbering.
l Dense mode: applies to continuous sub-interface numbering.
----End
1.2.7 Checking the Configuration
After SNMPv1 functions are configured, you can view the SNMPv1 configurations.
Prerequisite
Procedure
The configurations of basic SNMPv1 functions are complete.
l Run the display snmp-agent community command to check the configured community
name.
l Run the display snmp-agent sys-info version command to check the enabled SNMP
version.
l Run the display acl acl-number command to check the rules in the specified ACL.
l Run the display snmp-agent mib-view command to check the MIB view.
l Run the display snmp-agent sys-info contact command to check the equipment
administrator's contact information.
l Run the display snmp-agent sys-info location command to check the location of the
device.
l Run the display snmp-agent extend error-code status command to check whether the
SNMP extended error code feature is enabled.
l Run the display constant-ifindex configuration command to check the constant interface
index function and relevant configuration information.
----End
1.3 Configuring a Device to Communicate with an NM Station by Running SNMPv2c
After SNMPv2c is configured, a managed device and an NM station can run SNMPv2c to
communicate with each other. To ensure normal communication, you need to configure both
sides. This section describes only the configurations on a managed device (the agent side). For
details about configurations on an NM station, see the pertaining NM station operation guide.
The NM station manages a device in the following manners:
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
l Sends requests to the managed device to perform the GetRequest, GetNextRequest,
GetResponse, GetBulk, or SetRequest operation, obtaining data and setting values.
l Receives alarms from the managed device and locates and rectify device faults based on
the alarm information.
In the following configuration, after basic SNMP functions are configured, the NM station can
manage the device in these manners. For details on how to configure finer management such as
accurate access control or alarm module specification, see the following configuration
procedures.
1.3.1 Establishing the Configuration Task
Before configuring a device to communicate with an NM station by running SNMPv2c,
familiarize yourself with the applicable environment, complete the pre-configuration tasks, and
obtain the data required for the configuration. This will help you complete the configuration task
quickly and accurately.
Applicable Environment
SNMP needs to be deployed in a network to allow the NM station to manage network devices.
If your network is a large scale with many devices and its security requirements are not strict or
its security is good (for example, a VPN network) but services on the network are so busy that
traffic congestion may occur, SNMPv2c can be deployed to ensure communication between the
NM station and managed devices.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring a device to communicate with an NM station by running SNMPv2c, complete
the following task:
l Configuring a routing protocol to ensure that the switch and NM station are routable
Data Preparation
Before configuring a device to communicate with an NM station by running SNMPv2c, you
need the following data.
No.
1 SNMP version, SNMP community name, address of the alarm destination host,
2 (Optional) ACL number, IP address of the NM station, MIB object
Data
administrator's contact information and location, and SNMP packet size
3 (Optional) Name of the alarm-sending module, source address of trap messages,
queue length for trap messages, lifetime of trap messages, expiry time of informs,
allowable number of inform retransmissions, allowable maximum number of informs
to be acknowledged, aging time of log messages, and allowable maximum number
of log messages about the trap and inform events in the log buffer
4 (Optional) Number of interfaces indexed by fixed numbers
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
1.3.2 Configuring Basic SNMPv2c Functions
After basic SNMP functions are configured, an NM station can perform basic operations such
as Get and Set operations on a managed device, and the managed device can send alarms to the
NM station.
Context
Steps 3, 4, and 5 are mandatory for the configuration of basic SNMP functions. After the
configurations, basic SNMP communication can be conducted between the NM station and
managed device.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 (Optional) Run:
snmp-agent
The SNMP agent function is enabled.
By default, the SNMP agent function is disabled. Running any command with the parameter
snmp-agent can enable the SNMP agent function, so this step is optional.
Step 3 Run:
snmp-agent sys-info version v2c
The SNMP version is set.
By default, SNMPv3 is enabled.
After SNMPv2c is enabled on the managed device, the device supports both SNMPv2c and
SNMPv3. This means that the device can be monitored and managed by NM stations running
SNMPv2c and SNMPv3.
Step 4 Run:
snmp-agent community { read | write } community-name
The community name is set.
After the community name is set, if no MIB view is configured, the NM station that uses the
community name has rights to access objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1).
l read needs to be configured in the command if the NM station administrator needs the read
l write needs to be configured in the command if the NM station administrator needs the read
permission in a specified view in some cases. For example, a low-level administrator needs
to read certain data.
and write permissions in a specified view in some cases. For example, a high-level
administrator needs to read and write certain data.
Step 5 Choose one of the following commands as needed to configure the destination IP address for
the alarms and error codes sent from the device.
l If the network is an IPv4 network, configure the device to send either traps or informs to the
NM station.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
NOTE
The differences between traps and informs are as follows:
l The traps sent by the managed device do not need to be acknowledged by the NM station.
l The informs sent by the managed device need to be acknowledged by the NM station. If no
acknowledgement message from the NM station is received within a specified time period, the
managed device will resend the inform until the number of retransmissions reaches the maximum.
When the managed device sends an inform, it records the inform in the log. If the NM station and
link between the NM station and managed device recovers from a fault, the NM station can still
learn the inform sent during the fault occurrence and rectification.
In this regard, informs are more reliable than traps, but the device may need to buffer a lot of informs
because of the inform retransmission mechanism and this may consume many memory resources.
If the network is stable, using traps is recommended. If the network is unstable and the device's memory
capacity is sufficient, using informs is recommended.
– To configure a destination IP address for the traps and error codes sent from the device,
run:
snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain ip-address [ udp-port portnumber ] [ public-net | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] params securityname
security-string [ v2c ] [ private-netmanager ]
– To configure a destination IP address for the informs and error codes sent from the device,
run:
snmp-agent target-host inform address udp-domain ip-address [ udp-port portnumber ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] params securityname securitystring v2c
The descriptions of the command parameters are as follows:
l The default destination UDP port number is 162. In some special cases (for example, port
mirroring is configured to prevent a well-known port from being attacked), the parameter
udp-port can be used to specify a non-well-known UDP port number. This ensures normal
communication between the NM station and managed device.
l If the alarms sent from the managed device to the NM station need to be transmitted over a
public network, the parameter public-net needs to be configured. If the alarms sent from the
managed device to the NM station need to be transmitted over a private network, the
parameter vpn-instance vpn-instance-name needs to be used to specify a VPN that will take
over the sending task.
l The parameter securityname identifies the alarm sender, which will help you learn the alarm
source.
l If the NM station and managed device are both Huawei products, the parameter private-
netmanager can be configured to add more information to alarms, such as the alarm type,
alarm sequence number, and alarm sending time. The information will help you locate and
rectify faults more quickly.
NOTE
An IPv6 network supports only traps, not informs.
Step 6 (Optional) Run:
snmp-agent sys-info { contact contact | location location }
The equipment administrator's contact information or location is configured.
This step is needed if the NM station administrator needs to know equipment administrators'
contact information and locations when the NM station manages many devices. This will allow
the NM station administrator to quickly contact the equipment administrators for fault location
and rectification.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
To configure both the equipment administrator's contact information and location, you need to
run the command twice to configure them separately.
Step 7 (Optional) Run:
snmp-agent packet max-size byte-count
The maximum size of an SNMP packet that the device can receive or send is set.
By default, the maximum size of an SNMP packet that the device can receive or send is 12000
bytes.
After the maximum size is set, the device will discard any SNMP packet that is larger than the
set size. The allowable maximum size of an SNMP packet for a device depends on the size of a
packet that the NM station can process; otherwise, the NM station cannot process the SNMP
packets sent from the device.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
After the configurations are complete, basic communication can be conducted between the NM
station and managed device.
l Access control allows any NM station that uses the community name to monitor and manage
all the objects on the managed device.
l The managed device sends alarms generated by the modules that are open by default to the
NM station.
If finer device management is required, follow directions below to configure the managed
device:
l To allow a specified NM station that uses the community name to manage specified objects
of the device, follow the procedure described in Controlling the NM Station's Access to
the Device.
l To allow a specified module on the managed device to report alarms to the NM station,
follow the procedure described in Configuring the Trap FunctionConfiguring the Trap
Function.
l If the NM station and managed device are both Huawei products, follow the procedure
described in Enabling the SNMP Extended Error Code Function to allow the device to
send more types of error codes. This allows more specific error identification and facilitates
your fault location and rectification.
l If the functions such as accounting and fault location need to be bound to specified
interfaces to prevent changes in interface indexes during device or interface restart, follow
the procedure described in Configuring the Constant Interface Index Feature.
1.3.3 (Optional) Controlling the NM Station's Access to the Device
This section describes how to specify an NM station and manageable MIB objects for SNMPbased communication between the NM station and managed device to improve communication
security.
Context
If a device is managed by multiple NM stations that use the same community name, note the
following points:
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19

Quidway S2700 Series Ethernet Switches
Configuration Guide - Network Management 1 SNMP Configuration
l If all the NM stations that use the community name need to have rights to access the objects
in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1), skip the following steps.
l If some of the NM stations that use the community name need to have rights to access the
objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1), skip Step 5.
l If all the NM stations need to manage specified objects on the device, skip Steps 2, 3, and
4.
l If some of the NM stations that use the community name need to manage specified objects
on the device, perform all the following steps.
Procedure
Step 1 Run:
system-view
The system view is displayed.
Step 2 Run:
acl acl-number
A basic ACL is created to filter the NM station users that can manage the device.
Step 3 Run:
rule [ rule-id ] { deny | permit } source { source-ip-address source-wildcard |
any }
A rule is added to the ACL.
Step 4 Run:
quit
Return to the system view.
Step 5 Run:
snmp-agent mib-view { excluded | included } view-name oid-tree
A MIB view is created, and manageable MIB objects are specified.
By default, an NM station has rights to access the objects in the Viewdefault view (1.3.6.1).
l If a few MIB objects on a device or some objects in the current MIB view do not or no longer
l If a few MIB objects on the device or some objects in the current MIB view need to be
Step 6 Run:
snmp-agent community { read | write } { community-name | cipher community-name } [
mib-view view-name | acl acl-number ]
need to be managed by the NM station, excluded needs to be specified in the related command
to exclude these MIB objects.
managed by the NM station, included needs to be specified in the related command to include
these MIB objects.
*
The NM station's access rights are specified.
l read needs to be configured in the command if the NM station administrator needs the read
permission in the specified view in some cases. For example, a low-level administrator needs
to read certain data. write needs to be configured in the command if the NM station
administrator needs the read and write permissions in the specified view in some cases. For
example, a high-level administrator needs to read and write certain data.
Issue 01 (2011-07-15) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
 Loading...
Loading...