Page 1

HUAWEI
1. Getting Started
2. Port
3. VLAN
4. Multicast
5. QoS/ACL
6. Integrated Management
7. STP
8. Security
9. Network Protocol
10. System Management
11. Appendix
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches
Command Manual
VRP3.10
Page 2

Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches
Command Manual
Manual Version
T2-081996-20040712-C-1.04
Product Version
VRP3.10
BOM
31190196
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support
and service. If you purchase the products from the sales agent of Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd., please contact our sales agent. If you purchase the products from Huawei
Technologies Co., Ltd. dir ectly, Please feel free to c ontact our local off ice, customer care
center or company headquarters.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Administration Building, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.,
Bantian, Longgang District, Shenzhen, P. R. China
Postal Code: 518129
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Page 3

Copyright © 2004 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
No part of this manual m ay be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means without prior written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks
, HUAWEI, C&C08, EAST8000, HONET, , ViewPoint, INtess, ETS, DMC,
TELLIN, InfoLink, Netkey, Quidway, SYNLOCK, Radium,
M900/M1800,
TELESIGHT, Quidview, Musa, Airbridge, Tellwin, Inmedia, VRP, DOPRA, iTELLIN,
HUAWEI OptiX, C&C08
iNET, NETENGINE , OptiX, iS ite, U-SY S, iMUSE, Ope nEye,
Lansway, SmartAX , infoX, TopEng are tradem arks of Huawei Technologies C o.,
Ltd.
All other tradem arks menti oned in this m anual are the pro perty of t heir respecti ve
holders.
Notice
The information in this manual is subj ec t to cha nge without not ic e. Ev er y eff or t has
been made in the preparation of this manual to ensure accuracy of the contents, but
all statements, inf orm ation, and r ecom m endations in t his m anual do not c onstitut e
the warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Page 4
About This Manual
Release Notes
The product version that corresponds to the manual is VRP3.10.
Related Manuals
The following manuals provide more information about the Quidway S2000 Series
Ethernet Switches.
Manual Content
Quidway S2403H Ethernet Switch
Installation Manual
It provides information for the system installation.
Quidway S2008/S2016 Ethernet
Switch Installation Manual
It provides information for the system installation.
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet
Switches Operation Manual
It is used for assisting the users in data configurations and
typical applications.
Organization
Quidway S2000 Series Et her net Switc hes Co mmand Manual c onsis ts of the following
parts:
z
Getting Started
This module introduces the commands used for accessing the Ethernet Switch.
z
Port
This module introduces the commands used for configuring Ethernet port, link
aggregation and port mirroring.
z
VLAN
This module introduces the commands used for configuring VLAN.
z
Multicast
This module introduces the commands used for configuring multicast protocols.
z
QoS/ACL
This module introduces the commands used for configuring QoS/ACL.
Page 5

z
Integrated Management
This module introduces the commands used for integrated management.
z
STP
This module introduces the commands used for configuring STP.
z
Security
This module introduces the commands used for configuring 802.1X, AAA &
RADIUS, and HABP.
z
Network Protocol
This module introduces the commands used for configuring network protocols.
z
System Management
This module introduces the commands used for system management and
maintenance.
z
Appendix
This module includes all the commands in this command manual, which are
arranged alphabetically.
Intended Audience
The manual is intended for the following readers:
z
Network engineers
z
Network administrators
z
Customers who are familiar with network fundamentals
Conventions
The manual uses the following conventions:
I. General conventions
Convention Description
Arial
Normal paragraphs are in Arial.
Arial Narrow Warnings, Cautions, Notes and Tips are in Arial Narrow.
Boldface Headings are in Boldface.
Courier New
Terminal Display is in Courier New.
Page 6
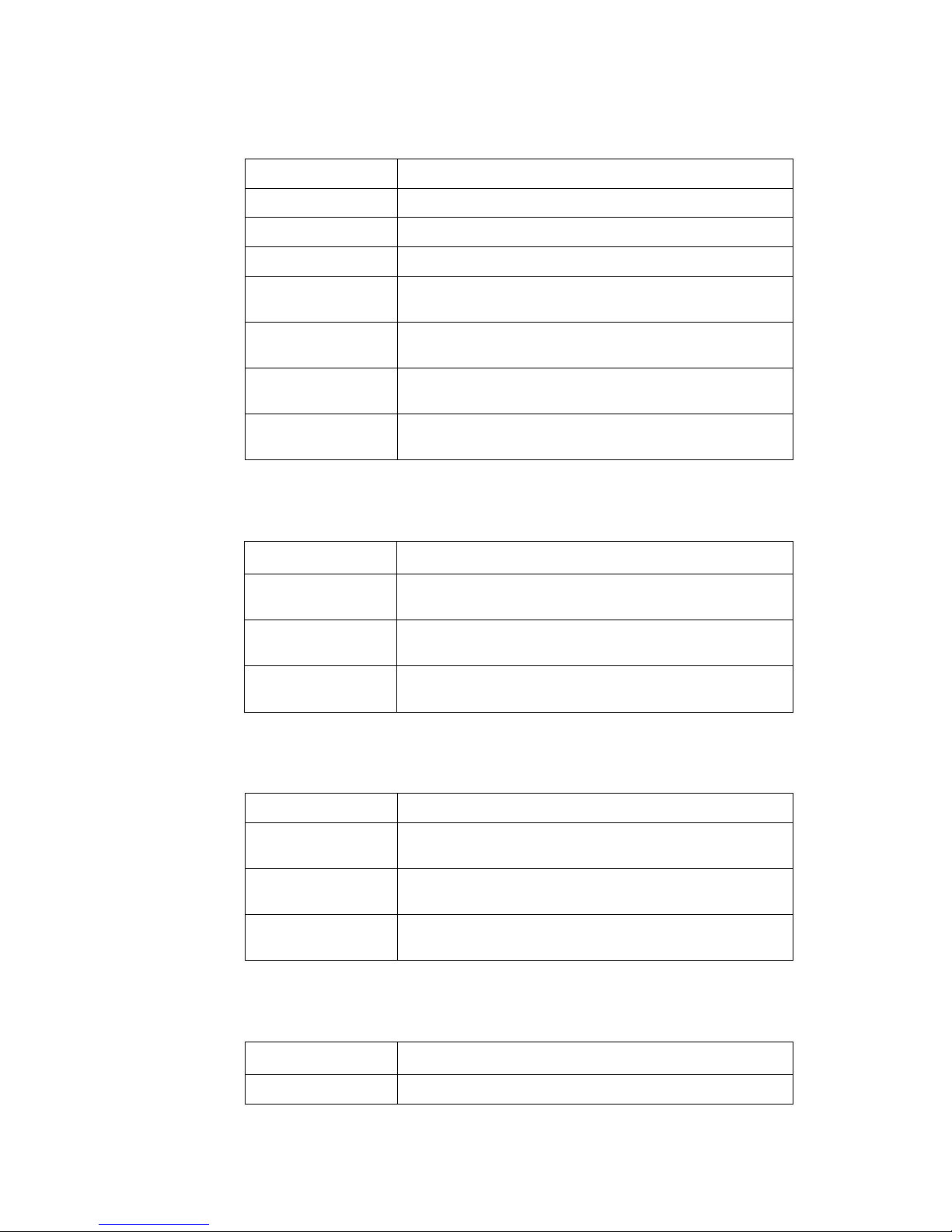
II. Command conventions
Convention Description
Boldface The keywords of a command line are in Boldface.
italic Command arguments are in italic.
[ ] Items (keywords or arguments) in square brackets [ ] are optional.
{ x | y | ... }
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars.
One is selected.
[ x | y | ... ]
Optional alternative items are grouped in square brackets and separated
by vertical bars. One or none is selected.
{ x | y | ... } *
Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars. A
minimum of one or a maximum of all can be selected.
[ x | y | ... ] *
Optional alternative items are grouped in square brackets and separated
by vertical bars. Many or none can be selected.
III. GUI conventions
Convention Description
< >
Button names are inside angle brackets. For example, click the <OK>
button.
[ ]
Window names, menu items, data table and field names are inside
square brackets. For example, pop up the [New User] window.
/
Multi-level menus are separated by forward slashes. For example,
[File/Create/Folder].
IV. Keyboard oper at i on
Format Description
<Key>
Press the key with the key name inside angle brackets. For example,
<Enter>, <Tab>, <Backspace>, or <A>.
<Key1+Key2>
Press the keys concurrently. For example, <Ctrl+Alt+A> means the three
keys should be pressed concurrently.
<Key1, Key2>
Press the keys in turn. For example, <Alt, A> means the two keys should
be pressed in turn.
V. Mouse operation
Action Description
Click Press the left button or right button quickly (left button by default).
Page 7

Action Description
Double Click Press the left button twice continuously and quickly.
Drag Press and hold the left button and drag it to a certain position.
VI. Symbols
Eye-catching s ymbols are also used in the manual t o highlight the points wort hy of
special attention during the operation. They are defined as follows:
Caution, Warning: Means reader be extremely careful during the operation.
Note: Means a complementary description.
Page 8

HUAWEI
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches
Command Manual
1. Getting Started
Page 9

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
i
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands ................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands ............................................................................ 1-1
1.1.1 authentication-mode................................................................................................ 1-1
1.1.2 auto-execute command........................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.3 command-privilege level ......................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.4 databits.................................................................................................................... 1-3
1.1.5 display history-command ........................................................................................ 1-4
1.1.6 display user-interface..............................................................................................1-5
1.1.7 display users ........................................................................................................... 1-6
1.1.8 flow-control..............................................................................................................1-7
1.1.9 free user-interface................................................................................................... 1-7
1.1.10 header ...................................................................................................................1-8
1.1.11 history-command max-size................................................................................... 1-9
1.1.12 idle-timeout............................................................................................................ 1-9
1.1.13 language-mode ................................................................................................... 1-10
1.1.14 lock......................................................................................................................1-11
1.1.15 parity.................................................................................................................... 1-11
1.1.16 quit....................................................................................................................... 1-12
1.1.17 return...................................................................................................................1-12
1.1.18 screen-length ...................................................................................................... 1-13
1.1.19 send.....................................................................................................................1-14
1.1.20 service-type telnet............................................................................................... 1-14
1.1.21 set authentication password................................................................................ 1-15
1.1.22 shell.....................................................................................................................1-16
1.1.23 speed................................................................................................................... 1-17
1.1.24 stopbits................................................................................................................ 1-18
1.1.25 super ................................................................................................................... 1-18
1.1.26 super password................................................................................................... 1-19
1.1.27 sysname.............................................................................................................. 1-20
1.1.28 system-view......................................................................................................... 1-20
1.1.29 telnet.................................................................................................................... 1-21
1.1.30 user-interface ...................................................................................................... 1-22
1.1.31 user privilege level .............................................................................................. 1-22
Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands ........................................................................ 2-1
2.1 System IP Configuration Commands ................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 description...............................................................................................................2-1
2.1.2 display interface vlan-interfac e ............................................................................... 2-1
Page 10

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
ii
2.1.3 display ip host ......................................................................................................... 2-2
2.1.4 display ip interface vlan-interfac e............................................................................ 2-3
2.1.5 display ip routing-table............................................................................................ 2-4
2.1.6 display ip routing-table ip_address ......................................................................... 2-5
2.1.7 display ip routing-table ip_address1 ip_address2................................................... 2-8
2.1.8 display ip routing-table verbose .............................................................................. 2-9
2.1.9 interface vlan-interface.......................................................................................... 2-10
2.1.10 ip address............................................................................................................ 2-11
2.1.11 ip host..................................................................................................................2-12
2.1.12 ip route-static....................................................................................................... 2-12
2.1.13 shutdown............................................................................................................. 2-13
Page 11

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-1
Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1.1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1.1.1 authentication-mode
Syntax
authentication-mode { password
|
scheme }
authentication-mode none
View
User interface view
Parameter
password: Perform local password authentication.
scheme: Perform local or remote authentication of username and password.
Description
Using authentication-mode com mand, you can configure t he authentic ation m ethod
for login user. Using authentication-mode none command, you can configure no
authentication.
This command with the password parameter indicates to perform local password
authentication, that is, you need to configure a login password using the set
authentication password { cipher | simple }
password
command.
This command with the scheme parameter indicates to perform authentication of local
or remote usernam e and password. The type of the authentication depe nds on your
configuration. For detailed information, see “Security” section.
By default, users lo gging in via the Console port do not need to pass any terminal
authentication, where as the password is required for authenticating the Telnet users
when they log in.
Example
# Configure local password authentication.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] authentication-mode password
Page 12
Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-2
1.1.2 auto-execute command
Syntax
auto-execute command text
undo auto-execute command
View
User interface view
Parameter
text: Specifies the command to be run automatically.
Description
Using auto- execute command comm and, you can configure to automaticall y run a
specified command. W hen a user logs in, the command configured will be execute d
automatically. The user will be disconnected after that. Using undo auto-execute
command command, you can configure not to run the command automatically.
This command is usually used to configure the telnet command on the terminal, which
will connect the user to a designated device automatically.
By default, auto run is disabled.
Caution:
1) If you execute this command, the user-interface can no longer be used to perform routine
configurations on the local system. Therefore use caution when using this command.
2) Ensure that you will be able to log into the system in some o ther way to cancel the configuration,
before you configure the auto-execute command command and save the configuration.
Example
# Configure to automatically telnet 10.110.100.1 after the user logs in via VTY 0.
[Quidway-ui-vty0] auto-execute command telnet 10.110.100.1
1.1.3 command-privilege level
Syntax
command-privilege level
level
view
view command
undo command-privilege view
view command
Page 13

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-3
View
System view
Parameter
level: Specifies the command level, ranging from 0 to 3.
view: Specifies the comm and view, which can be an y of the views sup ported by the
switch.
command: Specifies the command to be configured.
Description
Using command-privilege level command, you can configure the priority of the
specifically comm and of the specific ally view. Using undo command-privilege view
command, you can restore the default command priority.
The command leve ls inclu de visit, monitor ing, conf iguratio n, and m anagem ent, which
are identified as 0 through 3 res pectively. An administrator assigns auth orities as per
user requirements and a llows them to operate in corr esponding views. W hen a user
logs in the switch, the command level that it can access depends on two points. One is
the command level that the user its elf can ac cess , the other is the s et c omm and level
of this user interface. If the two levels are different, the former will be taken. For
example, the comm and le vel of VT Y 0 user i nterf ace i s 1, h owever, user Tom has the
right to access com m ands of lev el 3; if Tom logs in from VTY 0 us er i nterf ace, h e can
access commands of level 3 and lower.
By default, ping, tracert, and telnet are at vis it le vel (0 ); display and debugging are
at monitoring level (1); all the config uration commands are at configuration l evel (2);
and FTP, XMODEM, TFTP and commands for file system operations are at
management level (3).
Example
# Configure the precedence of the command "interface" as 0.
[Quidway] command-privilege level 0 view system interface
1.1.4 databits
Syntax
databits { 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 }
undo databits
View
User interface view
Page 14

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-4
Parameter
5: The data bits are 5.
6: The data bits are 6.
7: The data bits are 7.
8: The data bits are 8.
Description
Using databits command, you can configure the data bits for AUX ( Console) port.
Using undo databits command, you can restore the default bits of the AUX (Console).
This command can only be performed in AUX user interface view.
By default, the value is 8.
Example
# Configure the data bits of AUX (Console) port to 7 bits.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] databits 7
1.1.5 display history-command
Syntax
display history-command
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display history-command command, you can view the saved history
commands.
For the related command, see history-command max-size.
Example
# Display history commands.
<Quidway> display history-command
sys
quit
display his
Page 15

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-5
1.1.6 display user-interface
Syntax
display user-interface [ type number ] [ number ]
View
Any view
Parameter
type: Specifies the type of a user interface.
number: Specifies the number of a user interface.
Description
Using display user-interface command, you can view the relational information of the
user interface. The displayed information includes user interface type,
absolute/relative index, transmission speed, priority, and authentication methods.
Example
# Display the relational information of user interface 0.
<Quidway> display user-interface 0
Idx Type Tx/Rx Modem Privi Auth
F 0 A UX 0 9600 3 N
+ : Current user-interface is active.
F : Current user-interface is active and work in async mode.
Idx : Absolute index of user-interface.
Type : Type and relative index of user-interface.
P rivi: The privile ge of user-interface.
Auth : The authentication mode of user-interface.
A: Authenticate use AAA.
L: Authenticate use local users table.
N: Current user-interface need not authentication.
P: Authenticate use current UI's password.
Page 16
Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-6
Table 1-1 Output description of the display user-interface command
Field Description
+ Current user interface is in use.
F Current user interface is in use and work in asynchronous mode.
Idx Absolute index of user interface
Type Type and relative index of user interface
Tx/Rx User interface speed
Modem Modem operation mode
Privi Which levels of commands can be used after logging in from the user interface.
Auth User interface authentication method
1.1.7 display users
Syntax
display users
[ all ]
View
Any view
Parameter
all: Display the information of all user inter f ac es.
Description
Using display users command, you can view the information of the user interface.
Example
# Display the information of the current user interface.
[Quidway] display users
UI Delay IPaddress Username
F 0 AUX 0 00:00:00
Table 1-2 Output description of the display users command
Field Description
F Current user interface is in use and work in asynchronous mode.
UI
Number of the first list is the absolute number of user interface. Number of the second list is the
relative number of user interface.
Delay Indicates the interval from the latest input till now in seconds.
IPaddress Displays initial connection location, namely the host IP address of the incoming connection.
Username Display the name of the user using this user interface, namely the login username of the user.
Page 17

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-7
1.1.8 flow-control
Syntax
flow-control { hardware | none | software }
undo flow-control
View
User interface view
Parameter
hardware: Configures to perform hardware flow control.
none: Configures no flow control.
software: Configures to perform software flow control.
Description
Using flow-control command, you can configure the flow control mode on AUX
(Console) port. Using undo flow-control command, you can r estore the default flo w
control mode.
This command can only be performed in AUX user interface view.
By default, the value is none. That is, no flow control will be performed.
Example
# Configure software flow control on AUX (Console) port.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] flow-control software
1.1.9 free user-interface
Syntax
free user-interface [ type ] number
View
User view
Parameter
type
: Specifies the user interface type.
number
: Specifies the absolute/relative number of the user interface. Configured
together with the
type
, it will specify the us er interface number of the corresponding
type. If the type is not specified, number will specify an absolute user interface
number.
Page 18

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-8
Description
Using free user-interface command, you can reset a specified user interface. The
user interface will be disconnected after the command is executed.
Note that the current user interface cannot be cleared.
Example
# Reset user interface 1 after logged in to the Ethernet switch via user interface 0.
<Quidway> free user-interface 1
After the command is executed, user interface 1 will be disconnected. It will not be
connected to the Ether net switch until you l og in via the user i nterface 1 for the next
time.
1.1.10 header
Syntax
header [ shell | incoming | login ] text
undo header [ shell | incoming | login ]
View
System view
Parameter
login: Configures to display login infor mation.
shell: Configures to display the header of setting up a session for the user.
incoming: Configures to display the login header.
text
: Specifies the header content.
Description
Using header command, you can configur e to d isplay hea der when user log in. Us ing
undo header command, you can configure not to display the header.
When the users log in the Ethernet switch, if a connection is activated, the login
header will be displayed. After the user successfully logs in the switch, the shell
header will be displayed.
The first English character in the text is reg arded as the start and stop char acters.
After the stop character is input, the system will exit interactive process automatically.
If you do not want to enter the interact ive process, input the text with same En glish
characters at the beginning and end of the text and press <Enter> directly.
Page 19

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-9
Example
# Configure the header of setting up a session.
[Quidway] header shell %
Enter TEXT messag e. End with the characte r '%'.
SHELL : Hello! Welcome %
The header of setting up a session displays on terminal when a user logs on again.
[Quidway] quit
<Quidway> quit
Press ENTER to get started
SHELL : Hello! Welcome
<Quidway>
1.1.11 history-command max-size
Syntax
history-command max-size value
undo history-command max-size
View
User interface view
Parameter
value
: Defines the size of the history buffer, ranging from 0 to 256. By default, the size
is 10, that is, 10 history commands can be saved.
Description
Using history-command max-size command, you can configure the size of the
history command buffer. Using undo history -command max-si ze command, you can
restore default size of the history command buffer.
Example
# Set the history buffer to 20, namely saving 20 history commands.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] history-command max-size 20
1.1.12 idle-timeout
Syntax
idle-timeout minutes [ seconds ]
undo idle-timeout
Page 20

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-10
View
User interface view
Parameter
minutes: Specifies the minute, ranging from 0 to 35791.
seconds: Specifies the second, ranging from 0 to 59.
Description
Using idle-timeout comm and, you can configure the tim eout function. If there is no
user operation performed before idle-timeout expires, the user interface will be
disconnected. Using undo idle-timeout command, you can restore the default
idle-timeout.
idle-timeout 0 means disabling idle-timeout.
By default, idle-timeout is set to 10 minutes.
Example
# Configure the timeout value to 1 minute on the AUX user interface.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] idle-timeout 1 0
1.1.13 language-mode
Syntax
language-mode { chinese | english }
View
User view
Parameter
chinese: Configures the language environment of command line interface as Chinese.
english: Configures the language environment of command line interface as English.
Description
Using language-mode command, you can switch between different language
environments of command line interface for convenience of different users.
By default, the value is English.
Example
# Switch from English mode to Chinese mode.
<Quidway> language-mode chinese
Page 21

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-11
1.1.14 lock
Syntax
lock
View
User view
Parameter
none
Description
Using lock command, you can lock the user interface to prevent unauthorized user
from operating it.
Example
# Lock the current user interface.
<Quidway> lock
Password: xxxx
Again: xxxx
1.1.15 parity
Syntax
parity { even | mark | none | odd | space }
undo parity
View
User interface view
Parameter
even: Configures to perform even parity.
mark: Configures to perform mark parity.
none: Configures not to perform parity.
odd: Configures to perform odd parit y.
space: Configures to perform space parity.
Description
Using parity com mand, you can configure the parity mode on AUX (Console) port.
Using undo parity command, you can restore the default parity mode.
Page 22

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-12
This command can only be performed in AUX user interface view.
By default, the mode is set to none.
Example
# Set mark parity on the AUX (Console) port.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] parity mark
1.1.16 quit
Syntax
quit
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using quit comm and, you can retur n to the lo wer level view from the c urrent vie w. If
the current view is user view, you can quit the system.
There are three levels of views, which are listed from low to high as follows:
z
User view
z
System view
z
VLAN view, Ethernet port view, and so on.
For the related commands, see return, system-view.
Example
# Return to user view from system view.
[Quidway] quit
<Quidway>
1.1.17 return
Syntax
return
View
System view
Page 23

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-13
Parameter
none
Description
Using return command, you can return to user view from a view other than user view.
Combination key <Ctrl+Z> performs the same function with the return command.
For the related command, see quit.
Example
# Return to user view from system view.
[Quidway] return
<Quidway>
1.1.18 screen-length
Syntax
screen-length screen-length
undo screen-length
View
User interface view
Parameter
screen-length: Specifies how many lines can be displayed on a screen, ranging from 0
to 512. The default value is 24.
Description
Using screen-length command, you can configure how many lines that can be
displayed on a screen of the term inal. Usin g undo screen-length command, you can
restore the default number of terminal information lines displayed on the terminal
screen.
The screen-length 0 command is used to disable this function.
Example
# Configure the lines that can be displayed on a screen as 20 lines.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] screen-length 20
Page 24

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-14
1.1.19 send
Syntax
send { all | number | type number }
View
User view
Parameter
all: Configures to send message to all user interfaces.
type: Specifies the user interface type, which can be aux or vty.
number: Specifies the absolute/relative number of the user interface.
Description
Using send command, you can send messages between different user interfaces.
Example
# Send message to all the user interfaces.
<Quidway> send all
1.1.20 service-type telnet
Syntax
service-type telnet [ level level ]
undo service-type telnet [ level ]
View
Local-user view
Parameter
level: Specifies which level of command a user can use after logon, ranging from 0 to 3
and defaults to level 1.
Description
Using service-type telnet command, you can conf igure which level of comm and a
user can use after logon. U sing undo service-type telnet command, you can res tor e
the default level of command a user can use after logon.
Commands are classified into four levels, namely visit level, monitoring level,
configuration level and management level. They are introduced as follows:
Page 25

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-15
z
Visit level: Comm ands of this level involve c ommand of network diagnos is tool
(such as ping and tracert), command of switch between different language
environments of user interfac e (language-mode), and telnet command etc. T he
operation of saving configuration file is not allowed on this level of commands.
z
Monitoring level: Commands of this level, including the display command and the
debugging command, are used for system maintenance, service f ault d iag nos is ,
etc. The operation of savi ng the configuration file is not allowed on this level of
commands.
z
Configuration level: Service configuration commands, including routing command
and commands on each network layer, are used to provide direct network service
to the user.
z
Management level: These are commands that influence the basic operation of the
system and system s upport module, which plays a supporting role on service.
Commands of this le vel involve file system commands, FTP comm ands, TFTP
commands, XModem downloading commands, user management commands,
and level setting commands.
Example
# Configure the user zbr to use commands at level 0 after logon.
[Quidway] local-user zbr
[Quidway-luser- zbr] serv ic e - t ype telnet le ve l 0
# Quit the system and logs on with us ernam e “zbr” again. No w onl y the comm ands at
level 0 are listed on the terminal.
[Quidway] quit
<Quidway> ?
User view command s:
language-mode Specify the language environment
ping Ping function
q uit Exit from current command view
super Privilege specified user priority level
telnet Establish one TELNET connection
tracert Trace route function
1.1.21 set authentication password
Syntax
set authentication password { cipher | simple } password
undo set authentication password
View
User interface view
Page 26
Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-16
Parameter
cipher: Configure encrypted text password.
simple: Configure plain text password.
password: If the authen tication is i n the simple mode, the password m ust be in plai n
text. If the authentication is in the cipher mode, the password can be either in
encrypted text or in plain text. The result is determined by the input. A plain text
password is a sequential character string of no more than 16 digits, for example,
huawei918. The length of an encrypted password m ust be 24 dig its and in enc rypted
text, for example, _(TT8F]Y\5SQ=^Q`MAF4<1!!.
Description
Using set authenticatio n password command, you c an configure the pass word for
local authentication. Usin g undo set authentication password command, you can
cancel local authenticat io n pass wor d.
The password in plain text is required when performing authentication, regardless
whether the configuration is plain text or encrypted text.
Note:
By default, password is required to be set for authenticating the users connecting via Telnet. If no
password has been set, the following prompt will be displayed “password required, but none set.”
Example
# Configure the local authentication password on VTY 0 to huawei.
[Quidway-ui-vty0] set authentication password simple huawei
1.1.22 shell
Syntax
shell
undo shell
View
User interface view
Parameter
none
Page 27

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-17
Description
Using shell command, you can enable terminal service of a user interface. Using
undo shell command, you can disable the terminal service of a user interface.
By default, terminal service is enabled.
When using the undo shell command, note the following points.
z
For the sake of security, the undo shell command can only be used on the user
interfaces other than the AUX user interface.
z
You cannot use this command on the user interface via which you log in.
z
You will be asked to confir m before executing this comm and on any legal user
interface.
Example
# Disable terminal service on the vty user interface 0 to 4 after logging in to the
Ethernet switch via user interface 0.
[Quidway] user-interface vty 0 4
[Quidway-ui-vty0-4] undo shell
# The following message will be displayed on the Telnet terminal after logon.
Connection to hos t lo st.
1.1.23 speed
Syntax
speed speed-value
undo speed
View
User interface view
Parameter
speed-value: Specifies the transmission rate on the AU X (Cons ole) port i n bit/s , whic h
can be 300, 600, 1200, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 5760 0 115200 or 4096000. The
default rate is 9600bit/s.
Description
Using speed command, you can configure the transmission rate on the AUX (Console)
port. Using undo speed command, you can restore the default rate.
This command can only be performed in AUX user interface view.
Page 28

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-18
Example
# Configure the transmission speed on the AUX (Console) port as 9600bit/s.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] speed 9600
1.1.24 stopbits
Syntax
stopbits { 1 | 1.5 | 2 }
undo stopbits
View
User interface view
Parameter
1: Sets 1 stop bit.
1.5: Sets 1.5 stop bits.
2: Sets 2 stop bits.
Description
Using stopbits command, you can c o nf igur e the s top bits o n t he AUX ( Co ns ole) por t.
Using undo stopbits command, you can restore the default stop bits.
This command can only be performed in AUX user interface view.
By default, the value is 1.
Example
# Configure 2 stop bits on the AUX (Console) port.
[Quidway-ui-aux0] stopbits 2
1.1.25 super
Syntax
super [ level ]
View
User view
Parameter
level
: User level, ranging 0 to 3. The default value is 3.
Page 29

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-19
Description
Using super command, you can enable the user to change to user level from the
current user level. If the user has set the super p assword [ level level ] { simple |
cipher } password, t hen user password of the higher level is needed, or the form er
user level will not change.
Login users are class ified into f our lev els that cor respond t o the four comm and levels
respectively. After users of different levels log in, t hey can only use com mands at th e
levels that are equal to or lower than its own level.
For the related commands, see super password, quit.
Example
# change to user level 3 from the current user level.
<Quidway> super 3
Password:
1.1.26 super password
Syntax
super password [ level level ] { simple | cipher }
password
undo super password [ level level ]
View
System view
Parameter
level
: User level, ranging fr om 1 to 3. The default value is 3, i. e. do not specify user
level. It means the password to be set is used for entering level 3.
simple: Configure plain text password.
cipher: Configure encrypted text password.
password: If the authen tication is i n the simple mode, the password m ust be in plai n
text. If the authentication is in the cipher mode, the password can either be in
encrypted text or in plain text. The result is determined by the input. A plain text
password is a sequential character string of no more than 16 digits, for example,
huawei918. The length of an encrypted password m ust be 24 dig its and in enc rypted
text, for example, _(TT8F]Y\5SQ=^Q`MAF4<1!!.
Description
Using super password command, you can configur e the pass word for changing th e
user from a lower level to a higher level. I n order to prevent unauthorized users fr om
illegal intrusion , user ID authentication is performed when users switch from a lower
Page 30

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-20
level to a higher level. For the sak e of confidentialit y, on the screen t he user cannot
see the passw o rd t ha t he en t e re d . Only when correct pa ssword is input fo r t h re e t imes,
can the user switch to the higher level. O therwise, the origin al user level will re main
unchanged. Using undo super password command, you can cancel the current
settings.
The password in plain text is required when performing authentication, regardless
whether the configuration is plain text or encrypted text.
Example
# Configure the password to zbr for changing the user from the current level to level 3.
[Quidway] super password level 3 simple zbr
1.1.27 sysname
Syntax
sysname text
undo sysname
View
System view
Parameter
text: Specifies the h ostname with a character s tring, rang ing from 1 to 30 c haracter s.
The default name is Quidway.
Description
Using sysname c ommand, you can configure the hostname of the Eth ernet switch.
Using undo sysname command, you can restore the default hostname.
Changing the hostnam e of the Ethern et switch will affect the prom pt of c ommand line
interface. For exam ple, if the hos tnam e of the Ethernet switc h is Qu id way, the prompt
in user view will be <Quidway>.
Example
# Configure the hostname of Ethernet switch to Huawei.
[Quidway] sysname Huawei
[Huawei]
1.1.28 system-view
Syntax
system-view
Page 31

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-21
View
User view
Parameter
none
Description
Using system-view command, you can enter system view from user view.
For the related commands, see quit, return.
Example
# Enter system view from user view.
<Quidway> system-view
Enter system view , return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Quidway]
1.1.29 telnet
Syntax
telnet host-ip-address [ service-port ]
View
User view
Parameter
host-ip-address: Specifies the IP address or the hostname of the remote Ethernet
switch. If it is the hostname, the Ethernet switch must have the function of static
resolution.
service-port: Designa tes the T CP port on t he rem ote Ether net switch pr ovid ing Telnet
service, ranging from 0 to 65535.
Description
Using telnet command, you can log in to another Ethernet switch from the current one
via telnet for remote management. To terminate the Telnet logon, press <Ctrl+]>.
By default, when the service-port is not sp ecif ied, the default telnet port number is 23.
For the related command, see display tcp status.
Example
# Log in to Ethernet switch Quidway2 at 129.102.0.1 from the current Quidway1
switch.
Page 32

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-22
<Quidway1> telnet 129.102.0.1
Trying 129.102. 0. 1
Connected to 129.102.0.1
<Quidway2>
1.1.30 user-interface
Syntax
user-interface [ type ] first-number [ last-number ]
View
System view
Parameter
type: Specifies the user interface type, which can be aux or vty.
first-number: Specifies the number of the first user interface to be configured.
last-number: Specifies the number of the last user interface to be configured.
Description
Using user-interface command, you can enter single user interface vie w or multipl e
user interface views to configure the corresponding user interfaces.
Example
# Enter user interface vi ew 0 through 5, that is, 1 AUX ( Console) port user interf ace
view and 5 VTY user interface views.
[Quidway] user-interface 0 5
[Quidway-ui0-5]
1.1.31 user privilege level
Syntax
user privilege level level
undo user privilege level
View
User interface view
Parameter
level: Specifies which level of command a user can use after logon from the
specifically user interface, ranging from 0 to 3.
Page 33

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Logging in Ethernet Switch Commands
1-23
Description
Using user privilege lev el command, you can configure whic h level of command a
user can use after log on f r om the specifically user i nter face, so that a user can us e all
the available commands at this level. Using undo user privilege level command, you
can restore the default level of command a user can use after logon from the
specifically user interface.
By default, a user ca n access the comm ands at Level 3 after l ogging in throug h the
AUX user interface, an d the commands at Level 0 af ter logging in through the VTY
user interface.
Example
# Configure to use commands level 0 after logging in from VTY 0 user interface.
[Quidway-ui-vty0] user privilege level 0
# After you telnet from VTY 0 user interface to the switc h, you will view the ter minal
only displays commands at level 0.
<Quidway> ?
User view command s:
language-mode Specify the language environment
ping Ping function
q uit Exit from current command view
super Privilege specified user priority level
telnet Establish one TELNET connection
tracert Trace route function
Page 34

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-1
Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2.1 System IP Configuration Commands
2.1.1 description
Syntax
description string
undo description
View
VLAN interface view
Parameter
string: Descript ion character string of management VLAN interf ace, ranges from 1 to
32 characters. The default character string is HUAWEI, Quidway Series,
Vlan-interface1 Interface. Vlan-interface1 is the management VLAN interface name.
Description
Using description command, you can configure the description character string of
management VLAN interface. Using undo description command, you can restore the
default description character string of management VLAN interface.
For the related command, see display interface vlan-interface.
Example
# Configure the description character string of management VLAN interface as
RESEARCH.
[Quidway-Vlan-interface1] description RE SE ARCH
2.1.2 display interface vlan-interface
Syntax
display interface vlan-interface [ vlan_id ]
View
Any view
Parameter
vlan_id: ID of management VLAN interface, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Page 35

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-2
Description
Using display interface vlan-interface command, you can view the related
information about management VLAN interface such as physical status and link status
of management VLAN interface, Ethernet frame format, MAC address, IP address and
sub-net mask, description character string and MTU, etc.
For the related command, see interface vlan-interface.
Example
# Display related information about management VLAN interface.
<Quidway> display interface vlan-interface 1
Vlan-interface1 current state : DOWN
Line protocol current state : DOWN
IP Sending Frames' Format is PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware address is 00e0-fc07-4101
Internet Addres s is 10.1.1.1/24 Prima ry
Descriptio n : HUAWEI, Quidway Se ries, Vlan-interface1 Interfac e
The Maximum Tr ansmit Unit is 1500
Table 2-1 Output description of display interface vlan-interface command
Field Description
Vlan-interface1 current state The current state of management VLAN interface
Line protocol current state The current state of Line protocol
IP Sending Frames' Format Ethernet frame format
Hardware address MAC address corresponding management VLAN interface
Internet Address IP address
Description management VLAN interface description character string
The Maximum Transmit Unit The Maximum Transmit Unit
2.1.3 display ip host
Syntax
display ip host
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display ip host command, you can view all the host names and their IP
addresses.
Page 36

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-3
Example
# Display all the host names and their IP addresses.
<Quidway> displa y ip host
Host Age Flags Address(es)
My 0 static 1.1.1.1
Aa 0 static 2.2.2.4
Table 2-2 Output description of display ip host command
Field Description
Host Host name
Age term of validity
Flags Flags
Address(es) IP address of the host
2.1.4 display ip interface vlan-interface
Syntax
display ip interface vlan-interface vlan-id
View
Any view
Parameter
vlan-id: Specifies the management VLAN interface ID.
Description
Using display ip interfac e vlan-interface command, you can view the inf ormation
about the management VLAN interface.
Example
# Display the information about the management VLAN interface 1.
<Quidway> display ip interface vlan-interface 1
Vlan-interface1 current state : DOWN ,
Line protocol current state : DOWN
Internet Addres s is 1.1.1.1/8 Primary
Broadcast address : 1.255.255.255
The Maximum Tr ansmit Unit : 1500 byt es
input packet s : 0, bytes : 0, multicas ts : 0
output packets : 0, bytes : 0, multicasts : 0
Page 37

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-4
Table 2-3 Output description of display ip interface vlan-interface command
Field Description
Vlan-interface1 current state The current state of management VLAN interface
Line protocol current state The current state of Line protocol
Internet Address IP address
Broadcast address Broadcast address
The Maximum Transmit Unit The Maximum Transmit Unit
2.1.5 display ip routing-table
Syntax
display ip routing-table
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display ip routing-table command, you can view the routing table summary.
This command displays routing table information in summary form. Each line
represents one route. The contents include destination address/mask length, protocol,
preference, metric, next hop and output interface.
Only current used route, i.e., best route, is disp layed using displa y ip routing-table
command.
Example
# View the summary of routing table.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table
Routing Table: public net
Destination/M ask Proto Pre Cost Nexthop Interface
1.1.1.0/24 DIRECT 0 0 1.1.1.1 Vlan-interface1
1.1.1.1/32 DIRECT 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
2.2.2.0/24 DIRECT 0 0 2.2.2.1 Vlan-interface2
2.2.2.1/32 DIRECT 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
3.3.3.0/24 DIRECT 0 0 3.3.3.1 Vlan-interface3
3.3.3.1/32 DIRECT 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
4.4.4.0/24 DIRECT 0 0 4.4.4.1 Vlan-interface4
4.4.4.1/32 DIRECT 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.0/8 DIRECT 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Page 38

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-5
127.0.0.1/32 DIREC T 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Table 2-4 Description of information generated by the command display ip routing-table
Field Description
Destination/Mask Destination address/Mask length
Proto Routing protocol
Pre Routing preference
Cost Cost
Nexthop Next hop address
Interface
Output interface, through which the data packet destined for the destination
network segment is sent
2.1.6 display ip routing-table ip_address
Syntax
display ip routing-table ip_address [ mask ] [ longer-match ] [ verbose ]
View
Any view
Parameter
ip_address: Destination IP address.
mask: IP address m ask, length in dotte d decimal not ation or int eger. It ranges from 0
to 32 when it is expressed with integer.
verbose: With the verbose parameter, this command displays the verbose
information of both the active and inactive routes. Without the parameter, this
command only displays the summary of active routes.
longer-match: Address route matching the destination address in natural mask range.
Description
Using display ip routing-table ip_address command, you can view the routing
information of the specified destination address.
With different parameters, the output of command is different. The following is the
output description for different forms of this command:
z
display ip routing-table ip_address
If destination address, ip_address, has corresponding route in natural mask range,
this command will display all subnet routes or only the route best matching the
destination address, ip_address, is displayed. And onl y the active matching route i s
displayed.
z
display ip routing-table ip_address mask,
Page 39

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-6
This command only displays the route fully matching with specified destination
address and mask.
z
display ip routing-table ip_address longer-match
This command displays all destination address route matching with destination
address in natural mask range.
Example
# There is corresponding route in natural mask range. Display the summary.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table 169.0.0.0
Routing Tables:
Summary count:1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Nexthop Interface
169.0.0.0/16 Static 60 0 2.1.1.1 LoopBack1
For detailed description of the output information, see Table 2-4.
# There is no corres ponding route (only the longest matching route is displayed) in
natural mask range and summary is displayed.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table 169.253.0.0
Routing Tables:
Summary count:1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Nexthop Interface
169.0.0.0/8 Static 60 0 2.1.1.1 LoopBack1
# There are corresponding routes in the natural mask range. Display the detailed
information.
<Quidway> display ip routing- tab le 169 .0.0 .0 verbose
Routing Tables:
Generate Defaul t: no
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, # = Both * = Next hop in use
Summary count:2
**Destination : 16 9.0.0.0 Mask: 255.0.0.0
Protocol: #Static Preference: 60
*NextHop: 2.1.1.1 Interface: 2.1.1.1(LoopBack1)
Vlinkindex: 0
State: <Int ActiveU Static Unicast>
Age: 3:47 Cost: 0/0
**Destination : 16 9.0.0.0 Mask: 255.254.0.0
Protocol: #Static Preference: 60
*NextHop: 2.1.1.1 Interface: 2.1.1.1(LoopBack1)
Vlinkindex: 0
State: <Int ActiveU Static Unicast>
Age: 3:47 Cost: 0/0
Page 40

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-7
# There are no correspond ing routes in the natural mask r ange (only displaying the
longest matched route). Display the detailed information.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table 169.253.0.0 verbose
Routing Tables:
Generate Defaul t: no
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, # = Both * = Next hop in use
Summary count:1
**Destination : 16 9.0.0.0 Mask: 255.0.0.0
Protocol: #Static Preference: -60
*NextHop: 2.1.1.1
Vlinkindex: 0
State: <Int ActiveU Static Unicast>
Age: 3:47 Cost: 0/0
Table 2-5 Description of information generated by the command display ip routing-table ip_address
Field Description
Destination Destination address
Mask Mask
Proto Routing protocol
Preference Routing preference
Nexthop Next hop address
Interface
Output interface, through which the data pac ket destined for the des tination network s egment
is sent
Vlinkindex Virtual link index
Page 41

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-8
Field Description
Route state description:
ActiveU The route is selected and is optimum
Blackhole
Blackhole route is similar to Reject route, but it will not send the ICMP
unreachable message to the source end
Delete The route is deleted
Gateway Identifies that the route is not an interface route
Hidden
The route exists, but it is unavailable temporarily for some reasons (e.g.,
configured policy or interface is Down). Mor eover, you do not wish to delete it.
Therefore, you need to hide it, so as to restore it again later
Holddown
Holddown is one kind of route redistribution policy adopted by some
distance-vector (D-V) routi ng protocols, through whi ch these routing prot ocols
can avoid the flooding of error routes and deliver the routing unreachable
message accurately. For example, the RIP redistributes a certai n route ev ery a
period of time regardless of wh ether the actuall y found routes desti ned for the
same destination change. For more details, refer to the specific routing
protocols.
Int The route is discovered by interior gateway protocol (IGP).
NoAdvise
The routing protocol does not redistribute NoAdvi se route when it redistri butes
routes based on the policy.
NotInstall
The routing protocol general ly selects the route with the highes t precedence
from its routing table, then places it i n its c ore routi ng table and re dis tributes it.
Although the NotInstall rout e cannot be placed in the cor e routing table, it is
possibly that it is selected and redistributed.
Reject
Unlike the normal routes, the Reject route will discard the packets that select it
as their route, and the router will send ICMP unreachable message to the
source end. Reject route is usually used for the network test
Retain
When the routes from the routing tab le are delete d, the routes wi th Retain flag
will not be deleted. Using this function you can set Retain flag for some static
routes, so that they can exist in the core routing table.
Static
The route with Static flag will not be cleared from the routing table after you
save it and reboot the r outer. Generally, the static route configu red ma nuall y in
the router belongs to a Static route.
State
Unicast Unicast route
Age Time to live
Cost Cost
2.1.7 display ip routing-table ip_address1 ip_address2
Syntax
display ip routing-table
ip_address1 mask1 ip_address2 mask2
[ verbose ]
View
Any view
Parameter
ip_address1, ip_address2: Destination IP address in dotted decimal notation.
ip_address1
and
ip_address2
determine one address range together to display the
route in this address range.
mask1, mask2
: IP address mask, length in dotte d decim al notation or integer f orm. It
ranges from 0 to 32 when it is presented in integer.
Page 42

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-9
verbose: With the verbose parameter, this command displays the verbose
information of both the active and inactive routes. Without the parameter, this
command only displays the summary of active routes.
Description
Using display ip routin g-table ip_address1 ip_address2 command, you can view
the route information in the specified address range.
Example
# Display the routing information of destination addresses ranging from 1.1.1.0 to
2.2.2.0.
<Quidway>display ip routing-table 1.1.1.0 24 2.2.2.0 24
Routing tables:
Summary count: 3
Destination/M ask Proto Pre Cost Nexthop Interface
1.1.1.0/24 DIRECT 0 0 1.1.1.1 Vlan-interfa ce1
1.1.1.1/32 DIRECT 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
2.2.2.0/24 DIRECT 0 0 2.2.2.1 Vlan-interfa ce2
For detailed description of the output information, see Table 2-4.
2.1.8 display ip routing-table verbose
Syntax
display ip routing-table verbose
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display ip routing-table verbose command, you ca n vi e w the ve rbos e r o utin g
table information.
With the verbose parameter, this command displays the verbose routing table
information. T he descriptor describing the rou te state will be displa yed first, then the
statistics of the ent ire r o uti n g tab le will be out put and finally the verbose des c ript io n of
each route will be output.
All current rout es, including inactive r oute and invalid rout e, can be displayed us ing
display ip routing-table verbose command.
Page 43

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-10
Example
# Display the verbose routing table information.
<Quidway> display ip routing-table verbose
Routing Tables:
Generate Default: no
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, # = Both * = Next hop in use
Destinations: 3 Routes: 3
Holddown: 0 Delete: 62 Hidden: 0
**Destination : 1.1.1.0 Mask: 255.255.255.0
Protocol: #DIRECT Preference: 0
*NextHop: 1.1.1.1 Interface: 1.1.1.1(Vlan-interfa ce1)
State: <Int ActiveU Retain Unicast>
Age: 20:17:41 Cost: 0/0
**Destination : 1.1.1.1 Mask: 255.255.255.255
Protocol: #DIRECT Preference: 0
*NextHop: 127.0.0.1 Interface: 127.0.0.1(InLoopBa ck0)
State: <NoAdvise Int ActiveU Retain Gateway Unicast>
Age: 20:17:42 Cost: 0/0
**Destination : 2.2.2.0 Mask: 255.255.255.0
Protocol: #DIRECT Preference: 0
*NextHop: 2.2.2.1 Interface: 2.2.2.1(Vlan-interface 2)
State: <Int ActiveU Retain Unicast>
Age: 20:08:05 Cost: 0/0
First, display statis tics of th e whole routing t able and then output deta iled inform ation
of every route entry in turn. The meaning of route status is shown in T able 2-5, and the
statistics of routing table is shown in the following table.
Table 2-6 Description of information generated by the command display ip routing-table verbose
Field Description
Holddown Number of held-down routes
Delete Number of deleted routes
Hidden Number of hidden routes
2.1.9 interface vlan-interface
Syntax
interface vlan-interface vlan-id
undo interface vlan-interface
vlan-id
Page 44

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-11
View
System view
Parameter
vlan-id: Specifies the ide ntification of managem ent VLAN int erface, rang ing from 1 to
4094.
Description
Using interface vlan-interface command, you can create and enter management
VLAN interface view. Using undo interface vlan-interface com mand, you can cancel
management VLAN interface.
Before creating and entering the management VLAN interface view, the corresponding
VLAN specified by
vlan-id
must be created.
Example
# Enter the view of management VLAN interface 1.
[Quidway] interface vlan-interface 1
2.1.10 ip address
Syntax
ip address ip-address net-mask
undo ip address [ ip-address net-mask ]
View
VLAN interface view
Parameter
ip-address
: Configures the IP address of the management VLAN interface.
net-mask
: Configures the mask of the management VLAN interface.
Description
Using ip address command, you can configure the IP address and mask of the
management VLAN interfac e. Using undo ip address command, you can c ancel the
IP address and mask of the management VLAN interface.
For the related command, see display interface vlan-interface.
Example
# Configure the IP address and mask for management VLAN interface 20.
[Quidway-Vlan-interface20] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0
Page 45

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-12
2.1.11 ip host
Syntax
ip host hostname ip-address
undo ip host hostname [ ip-address ]
View
System view
Parameter
hostname: Name of the host, a character string consisting of 1 to 20 characters,
including letters, numbers, "_", or ",", and it must contain at least one letter.
ip-address: Specifies the host IP a ddress corresponding to t he host name in dotte d
decimal notation.
Description
Using ip host command, you can configure the host name and corresponding IP
address. Using undo ip host command, you can cancel the host name and
corresponding IP address.
By default, the host name and corresponding IP address are none.
For the related command, see display ip host.
Example
# Configure the IP address of the host named Lanswtich2 at 10.110.0.2.
[Quidway] ip host Lanswtich2 10.110.0.2
2.1.12 ip route-static
Syntax
ip route-static ip-address
{
mask
|
mask-length
} { null
null-interface-number
|
gateway-address
} [ preference
value
] [ reject | blackhole ]
undo ip route-static ip-address { mask | mask-length } [ null null-interface-number |
gateway-address ] [ preference value ]
View
System view
Parameter
ip-address
: Specifies the destination IP address in dotted decimal notation.
mask: Mask.
Page 46

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-13
mask-length: Mask length. Since "1" s in the 32-bit mask are required to be
consecutive, the mask in dotted decimal format can be replaced by mask-length,
which is the number of the consecutive "1" s in the mask.
null null-interface-number: Specif y the NULL interface of the route. The pack ets sent
to NULL interface, a kind of virtual in terface, wil l be disc arded at once. Thus this can
decrease the system load.
gateway-address: Specifies the next hop IP address (in dotted decimal notation) of the
route.
value
: Specifies the preference of the route, ranging from 1 to 255.
reject: Specifies an unreachable route.
blackhole: Specifies a blackhole route.
Description
Using ip route-static command, you can configure a static route. Using undo ip
route-static command, you can cancel the configured static route.
By default, the system c an obtain the sub- net route dir ectl y connecte d with the r outer.
When configuring a static route, the default preference is 60 if it is not specified.
Precautions: when the d estination IP a ddress and the mask are both 0.0. 0.0, it is th e
configured default route. If it fails to detect the routing table, a packet will be forwarded
along the default route.
For the related command, see display ip routing-table.
Example
# Configure the next hop of the default route as 129.102.0.2.
[Quidway] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 129.102.0.2
2.1.13 shutdown
Syntax
shutdown
undo shutdown
View
VLAN interface view
Parameter
none
Page 47

Command Manual - Getting Started
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 System IP Configuration Commands
2-14
Description
Using shutdown comm and, you can dis able the m anagem ent VLAN interfac e. Using
undo shutdown command, you can enable the management VLAN interface.
By default, when all the Ethernet ports be longing to the management VLAN are i n
down status, the management VLAN interface is also down, i.e. the management
VLAN interface is disabled. When there is one or more Ethernet ports in up status, the
management VLAN interface is also up, i.e. the management VLAN interface is
enabled.
Example
# Enable the management VLAN interface.
[Quidway-Vlan-interf ace1] undo shutd o wn
Page 48

HUAWEI
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches
Command Manual
2. Port
Page 49

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
i
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands............................................................................ 1-1
1.1.1 broadcast-suppression............................................................................................ 1-1
1.1.2 description...............................................................................................................1-1
1.1.3 display interface ...................................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.4 display lock-port-mac-aging-time............................................................................ 1-4
1.1.5 display loopback-detection...................................................................................... 1-5
1.1.6 display port..............................................................................................................1-6
1.1.7 duplex...................................................................................................................... 1-6
1.1.8 flow-control..............................................................................................................1-7
1.1.9 interface................................................................................................................... 1-8
1.1.10 lock-port mac-aging............................................................................................... 1-8
1.1.11 loopback................................................................................................................ 1-9
1.1.12 loopback-detection control enable ...................................................................... 1-10
1.1.13 loopback-detec tion enab le .................................................................................. 1-10
1.1.14 loopback-detection interval-time ......................................................................... 1-11
1.1.15 loopback-detection per-vlan ena bl e.................................................................... 1-12
1.1.16 mdi....................................................................................................................... 1-12
1.1.17 port access vlan .................................................................................................. 1-13
1.1.18 port hybrid pvid vlan............................................................................................ 1-13
1.1.19 port hybrid vlan.................................................................................................... 1-14
1.1.20 port link-type........................................................................................................ 1-15
1.1.21 port trunk permit vlan .......................................................................................... 1-16
1.1.22 port trunk pvid vlan.............................................................................................. 1-16
1.1.23 port vlan filter disable.......................................................................................... 1-17
1.1.24 reset counters interface....................................................................................... 1-18
1.1.25 shutdown............................................................................................................. 1-18
1.1.26 speed................................................................................................................... 1-19
Chapter 2 Ethernet Port Link Aggregation Commands............................................................. 2-1
2.1 Ethernet Port Link Aggregation Commands...................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 display link-aggregation .......................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 link-aggregation....................................................................................................... 2-2
Chapter 3 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Commands ....................................................... 3-1
3.1 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Com mands................................................................. 3-1
3.1.1 display mirror........................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.2 monitor-port.............................................................................................................3-1
3.1.3 port mirror................................................................................................................3-2
Page 50

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
ii
3.1.4 port mirror observing-port........................................................................................ 3-3
Page 51

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-1
Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1.1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1.1.1 broadcast-suppression
Syntax
broadcast-suppression pct
undo broadcast-suppression
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
pct: Specifies the m aximum wire speed ratio of the broadc ast traffic allowed on the
port. The value rang es fr om 5 to 100. The step is 5. By defau lt, the va lue is 100. T he
smaller the ratio is, the smaller the broadcast traffic is allowed.
Description
Using broadcast-suppression command, you can configure the broadcast traffic size
enabled on port. Once the broadcast traffic exceeds the value set by the user, the
system will discard s ome broadcast to ensure n etwork service s o that the traffic ratio
of broadcast is m aintained in a proper range. Using undo broadcast-suppression
command, you can res tore the default broadcast traffic enabled on port as 100. i.e.,
100% broadcast traffic is allowed to pass through.
Example
# Enable 20% broadcast cast to pas s, i.e. 80% broa dcas t storm suppres sion is m ade
on broadcast traffic of port.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] broa dc as t-s uppres s ion 20
1.1.2 description
Syntax
description text
undo description
View
Ethernet port view
Page 52

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-2
Parameter
text: Port description character string, with 80 characters at most.
Description
Using description comm and, you can configure the des cription character string for
Ethernet port. Using undo description command, you can cancel the port description
character string.
By default, the port description character string is null.
Example
# Configure the description character string of Ethernet port Ethernet0/1 as
lanswitch-interface.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] description lanswitch-int er f ace
1.1.3 display interface
Syntax
display interface [ interface_type | interface_type interface_num | interface_name ]
View
Any view
Parameter
interface_type: Specifies the port type.
interface_num: Specifies the port number.
interface_name: Specifies the port name in the interface_name= interface_type
interface_num format.
For parameter description, refer to the interface command.
Description
Using display in terf ace co m mand, you can view th e c onfigur atio n inf orm ation on the
port.
If the port type and num ber are not s pecified when displa ying th e port inf or mation, the
information of a ll the ports will be displayed. If o nly the port t ype is specified, al l the
information of the ports of this type will be displayed. If both port type and port number
are specified, the information of the designated port will be displayed.
Example
# Display configuration information of Ethernet0/1.
<Quidway> display interface ethernet0/1
Page 53

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-3
Ethernet0/ 1 current state : UP
IP Sending Frames' Format is PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware address is 00e0-fc00-0010
Description : aaa
The Maximum Tr ansmit Unit is 1500
Media type is tw isted pair, loopba ck not set
Port hardware typ e is 100_BASE_TX
100Mbps-speed mode, full-duplex mode
Link speed type is au to negotiation, lin k duplex type is autonegotiation
Flow-control is not supported
The Maximum Fr ame Length is 1522
Broadcast MA X-ratio: 100%
PVID: 1
Mdi type: auto
Port link-type: acc ess
Tagged VLAN ID : none
Untagged VLAN ID : 1
Last 5 minutes inpu t: 0 pack ets/sec 0 bytes/se c
Last 5 minutes outp ut : 0 pac kets/sec 0 bytes/s ec
input(total): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts
input(normal) : - packets, - bytes
- broadcasts, - multicasts
input: 0 input error s, 0 runts, 0 giants, - th rottles, 0 CRC
0 frame, - overruns, 0 aborts, 0 ignored, - parity errors
Output(total) : 0 pa ckets, 0 bytes
0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, 0 pauses
Output(normal): - packets, - bytes
- broadcasts, - multicasts, - pauses
Output: 0 output errors, 0 underruns, - buffer failures
- aborts, 0 deferred, 0 collisions, 0 late collisions
- lost carrier, - no carrier
Page 54

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-4
Table 1-1 Output description of the display interface command
Field Description
Ethernet0/1 current state
The current state of Ethernet port (enabled or disabled)
IP Sending Frames' Format Ethernet frame format
Hardware address Port hardware address
Description Port description character string
The Maximum Transmit Unit Maximum transmit unit
Media type Type of media
loopback not set Port loopback test state
Port hardware type Port hardware type
100Mbps-speed mode, full-duplex mode
Link speed type is autonegotiation, link
duplex type is autonegotiation
Both the duplex mode and the rat e are set to auto-negotiation.
The rate of 100Mbps and the m ode of full-duplex are adopted
after negotiating with its peer
Flow-control is not supported Port flow control state
The Maximum Frame Length
Maximum length of the Ethernet frames that can pass through
the port
Broadcast MAX-ratio Port broadcast storm suppression ratio
PVID Port default VLAN ID
Mdi type Cable type
Port link-type Port link type
Tagged VLAN ID The VLANs with packets tagged
Untagged VLAN ID The VLANs with packets untagged
Last 5 minutes output: 0 packets/sec 0
bytes/sec
Last 5 minutes input: 0 packets/sec 0
bytes/sec
The input/output rate and the passing packet number on this
port in the last 5 minutes.
input(total): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts
input(normal): - packets, - bytes
- broadcasts, - multicasts
input: 0 input errors, 0 runts, 0 giants , throttles, 0 CRC
0 frame, - overruns, 0 aborts,
0 ignored, - parity errors
Output(total): 0 packets, 0 bytes
0 broadcasts, 0 multicasts, 0
pauses
Output(normal): - packets, - bytes
- broadcasts, - multicasts, pauses
Output: 0 output errors, 0 underruns, buffer failures
- aborts, 0 deferred, 0
collisions, 0 late collisions
- lost carrier, - no carrier
The statistics information of input /output packets and errors on
this port
1.1.4 display lock-port-mac-aging-time
Syntax
display lock-port-mac-aging-time
View
Any view
Page 55

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-5
Parameter
none
Description
Using display lock-port- mac-aging-time comm and, you can view the aging time of
MAC address table corresponding to the lock port.
Example
# Display the MAC aging time of the lock port.
<Quidway> display lock-port-mac-aging-time
The mac aging time of lock-port: 1 hour(s)
Table 1-2 Output description of the display lock-port-mac-aging-time command
Field Description
The mac aging time of lock-port: 1 hour(s) The lock-port-mac-aging-time is 1 hour
1.1.5 display loopback-detection
Syntax
display loopback-detection
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display loopback-detection command, you can view whether the port
loopback detection has bee n enabl ed. If it has been e nabled, t hen the tim e int erval of
the detection and the current port loopbac k information will also be displayed.
Example
# Display if the port loopback detection is enabled.
<Quidway> display loopback-detection
Loopback-det ection is running
Detection interval time is 30 seconds
There is no port existing loopback link
Page 56

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-6
Table 1-3 Output description of the display loopback-detection command
Field Description
Loopback-detection is running The loopback detection is enabled
Detection interval time is 30 seconds The detection interval is 30 seconds
There is no port existing loopback link No port is in the loopback state
1.1.6 display port
Syntax
display port { hybrid | trunk }
View
Any view
Parameter
hybrid: Display Hybrid port.
Trunk: Display Trunk port.
Description
Using display po rt command, you can vi ew the ports in the cur rent system, whose
link type is Hybrid or Trunk. If there is any such port, display the c orresponding port
name.
Example
# Display the Hybrid ports in the current system.
<Quidway> display port hybrid
Now, the followin g hy brid ports exist:
Ethernet0/1 Ethernet0/2
The above information displays that the current system has two Hybrid ports,
Ethernet0/1 and Ethernet0/2.
1.1.7 duplex
Syntax
duplex { auto | full | half }
undo duplex
View
Ethernet port view
Page 57

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-7
Parameter
auto: Port auto-negotiation attrib ute.
full: Port full-duplex attribute.
half: Port half-duplex attribute.
Description
Using duplex com mand, you can conf igure the f ull-duplex /half-dup lex attribut e of the
Ethernet port. Using undo duplex comm and, you can restore the duplex attribute of
the port to default auto-negotiation mode.
By default, the duplex attribute is auto.
For the related command, see speed.
Example
# Configure the Ethernet port Ethernet0/1 as auto-negotiation attribute.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] dup l ex auto
1.1.8 flow-control
Syntax
flow-control
undo flow-control
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Description
Using flow-control command, you can enable flow control feat ure on the Ethernet
port to avoid discarding data packets due to congestion. Using undo flow-control
command, you can disable f low contro l featur e.
By default, flow control on the Ethernet port is disabled.
Example
# Enable flow control on Ethernet0/1.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] flow-control
Page 58

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-8
1.1.9 interface
Syntax
interface { interface_type interface_num | interface_name }
View
System view
Parameter
interface_type: Spec ifies the port type. For S2000 Series Ethernet S witches, it can
only be Ethernet.
interface_num: Spec ifies the port number. It adopts slot number/port num ber format.
For S2008/S2016 Eth ernet Switch es, Ethern et slot nu mber ranges from 0 to 1. Slot 0
contains the fixed 100M Ethernet ports provided by the switch. S2008 Ethernet Switch
port number ranges from 1 to 10, while S2016 Ethernet Switch port n umber ranges
from 1 to 18. Slot 1 contains the extended 100M o ptical Ethernet port and the por t
number can be 1 only.
For S2403H Ethernet Switch, Ethernet slot number ranges from 0 to 1. Slot 0 contains
the fixed 100M Ethernet ports provided by the switch and the port number ranges from
1 to 25. Slot 1 co ntains t he extended 100M optic al por t. The p ort n um ber can o nly b e
1.
interface_name: Specifies the port name in the interface_name= interface_type
interface_num format.
Description
Using interface command, you can enter the Ethernet port view.
If the user wants to configure the related parameters of the Ethernet port, he must first
use this command to enter the Ethernet port view.
Example
# Enter the Ethernet0/1 port view.
[Quidway] interface ethernet0/1
1.1.10 lock-port mac-aging
Syntax
lock-port mac-aging { age-time | no-age }
undo lock-port mac-aging
Page 59

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-9
View
System view
Parameter
age-time: Specifies the MAC agi ng tim e of a port. It ranges from 1 to 24, m easur ed in
hour. The default aging time is 1 hour.
no-age: No aging for address.
Description
Using lock-po rt mac-aging com mand, you c an configur e the agin g time of the MAC
address table corresponding to the lock port. Using undo lock-port mac-aging
command, you can restore the default ag ing time.
For the related command, see display lock-port-mac-aging-time.
Example
# Configure the MAC a ddress table corresponding to the loc k port to be aged in 2
hours.
[Quidway] lock-port mac-aging 2
1.1.11 loopback
Syntax
loopback { external | internal }
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
external: External loop test.
internal: Internal loop test.
Description
Using loopback command, you can configure the Ethernet port to perform the
loopback test to check whether the Ethernet port works nor mally and the loop tes t will
finish automatically after being performed for a while.
By default, the port will not perform the loopback test.
Example
# Perform the internal loop test for Ethernet0/1.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] lo op bac k internal
Page 60

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-10
1.1.12 loopback-detection control enable
Syntax
loopback-detection control enable
undo loopback-detection control enable
View
System view/Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Description
Using the command, you can enable loo pback detec tion controlled f unction on T runk
and Hybrid port, th at is, when the system f inds out that ports on a c ertain VLAN on
Trunk or Hybrid port is loop ed back , it the n mak es the Trunk and Hybrid port o perate
under control, meantim e, deletes the port corresponding M AC address entry. Using
the undo loopback-detection control enable command, you can disable this
function, that is, when the system finds out that port on a certain VLAN on Trunk or
Hybrid port is loope d back, it only reports the Trap inform ation. The Trunk or Hybri d
port is still operates in the normal state.
By default, loopback detection controlled function on Trunk or Hybrid port is enabled.
Note that, this command has no effect on Access ports.
Example
# Enable the port loopback detection controlled function.
[Quidway] loopback-detection control enable
1.1.13 loopback-detection enable
Syntax
loopback-detection enable
undo loopback-detection enable
View
System view/Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Page 61

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-11
Description
Using loopback-detection enable command, you can enable the port loopback
detection. If there is a loop back port found, the switc h will put it under contro l. Using
undo loopback-detection enable command, you can disable the port loopback
detection.
Using this command in the system, you can enable/disable the port loopback detection
function of the entire device; using this command in Ethernet port view, you can
enable/disable the port loopback detection function of the current port.
By default, port loopback detection is enabled.
For the related command, see display loopback-detection.
Example
# Enable the port loopback detection.
[Quidway] loopback-detection enable
1.1.14 loopback-detection interval-time
Syntax
loopback-detection interval-time time
undo loopback-detection interval-time
View
System view
Parameter
time: Specifies the interval of monitoring externa l loopback conditions of the port. It
ranges from 5 to 300, measured in seconds. By default, the interval is 30 seconds.
Description
Using loopback-detection interval-time command, you can configure detection
interval for the external loopback condition of each port. Using undo
loopback-detection interval-time command, you can restore the default interval.
For the related command, see display loopback-detection.
Example
# Configure the detection interval for the external loopback condition of each port to 10
seconds.
[Quidway] loopback-detection interval-time 10
Page 62

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-12
1.1.15 loopback-detection per-vlan enable
Syntax
loopback-detection per-vlan enable
undo loopback-detection per-vlan enable
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Description
Using the loopback-detection per-vlan enable command, you can configure that the
system performs loopb ack detection to all VLANs on T runk and Hybrid ports. Using
the undo loopback-detection per-vlan enable command, you can configure that the
system only performs loopback detection to the default VLANs on the port.
By default, the s ystem performs loopback detection to all VL ANs on T r unk and Hybrid
ports.
Example
# Configure the detection interval for the external loopback condition of each port to 10
seconds.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] lo op bac k-detection per-vlan enable
1.1.16 mdi
Syntax
mdi { across | auto | normal }
undo mdi
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
across: The network cable type is cross-over cable.
auto: The network cable will be recognized whether it is straight-through cable or
cross-over cable.
normal: The network cable of the port is straight-through cable.
Page 63

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-13
Description
Using mdi comm and, you can c onfig ure the net work cable t ype of the Et hernet ports .
Using undo mdi command, you can restore the default type.
By default, the network cable type will be recognized automatically.
Note that this command only has effect 10/100Base-TX port.
Example
# Configure the network cable type of Ethernet port Ethernet0/1 as auto.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] mdi auto
1.1.17 port access vlan
Syntax
port access vlan vlan_id
undo port access vlan
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
vlan_id: VLAN ID defined in IEEE802.1Q, ranging from 2 to 4094.
Description
Using port ac cess v lan co mm and, you c an jo in the ac cess port to a sp ecif ied V LAN.
Using undo port access vlan comm and, you can cancel the access port from the
VLAN.
The use condition of this command is the VLAN indicated in vlan_id must exist.
Example
# Join Ethernet0/1 port to VLAN3 (VLAN3 has existed).
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] port ac c es s vlan 3
1.1.18 port hybrid pvid vlan
Syntax
port hybrid pvid vlan vlan_id
undo port hybrid pvid
View
Ethernet port view
Page 64

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-14
Parameter
vlan_id: VLAN ID defined in IEEE802.1Q, ranging from1 to 4094 and the default
vlan_id is 1.
Description
Using port hybrid pvid vlan command, you can c onf i gure the default VLAN ID of the
hybrid port. Using undo port hybrid pvid command, you can restore the default
VLAN ID of the hybrid port.
Hybrid port can be configured together with the isolate-user-vlan. But if the def ault
VLAN has set mapping in the isolate-user-vlan, the default VLAN ID cannot be
modified. If you want to modify it, cancel the mapping first.
The default VLAN ID of local h ybrid p ort shall be cons istent wit h that of the peer one ,
otherwise, the packet cannot be properly transmitted.
For the related command, see port link-type.
Example
# Configure the default VLAN of the hybrid port Ethernet0/1 to 100.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] por t h ybrid pv id vl an 100
1.1.19 port hybrid vlan
Syntax
port hybrid vlan vlan_id_list { tagged | untagged }
undo port hybrid vlan vlan_id_list
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
vlan_id_list: vlan_id_list = [ vlan_id1 [ to vlan_id2 ] ]&<1-10> specifies which VLAN the
hybrid port will be added to. It can be disc rete. The vlan_id ranges f rom 1 to 4094.
&<1-10> indicates that the former parameter can be input 10 times repeatedly at most.
tagged: The packet of specified VLAN will have tag.
untagged: The packet of specified VLAN will not have tag.
Description
Using port hybrid vlan command, you can join the hybrid port to specified ex isting
VLAN. Using undo port hybrid vlan comm and, you can canc el the h ybrid port f rom
the specified VLAN.
Page 65

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-15
Hybrid port can belong to multiple VLANs. If the port hybrid vlan vlan_id_list { tagged
| untagged } command is used for many times, the VLANs carried by the hybrid port is
the set of vlan_id_list.
This command can be use d on condition that the VLAN specif ied with vlan_id must
have been existed.
For the related command, see port link-type.
Example
# Join hybrid port Ether net0/1 to VL AN of 2, 4 and 50 -100, and thes e VLAN wil l have
tags.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] port hybrid vlan 2 4 50 to 100 tagged
1.1.20 port link-type
Syntax
port link-type { access | hybrid | trunk }
undo port link-type
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
access: Configure the port as access port.
hybrid: Configure the port as hybrid port.
trunk: Configure the port as trunk port
Description
Using port link-type command, you can configure the link type of Ethernet port. Using
undo port link-type command, you can restore the port as defaul t status, i.e. access
port.
You can configure three types of ports concurrently on the same switch, but you
cannot switch between trunk port and hybrid port. You must turn it first into access port
and then set it as other type. For example, you cannot configure a trunk port directly as
hybrid port, but first set it as access port and then as hybrid port.
By default, the port is access port.
Example
# Configure Ethernet port Ethernet 0/1 as trunk port.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] port link-type trunk
Page 66

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-16
1.1.21 port trunk permit vlan
Syntax
port trunk permit vlan { vlan_id_list | all }
undo port trunk permit vlan { vlan_id_list | all }
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
vlan_id_list: vlan_id_list = [ vlan_id1 [ to vlan_id2 ] ]&<1-10> is the VLAN range joined
by the trunk port. It can be discrete. The vlan_id ranges from 2 to 4094. &<1-10>
indicates that the former parameter can be input 10 times repeatedly at most.
all: Join the trunk port to all VLANs.
Description
Using port trunk permit vlan command, you can join trunk port to specif ied VLAN.
Using undo port trunk permit vlan command, you can cancel trunk port from
specified VLAN.
Trunk port can belong to multiple V LANs. If the port trunk permit vlan command is
used many times , then the VLAN enabled to pass on trunk port is th e set of these
vlan_id_list.
This command can be us ed on condition that the VL AN specified with vlan_id is not
the default one.
For the related command, see port link-type.
Example
# Join the trunk port Ethernet0/1 to VLAN 2, 4 and 50-100.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] port tr unk permit vlan 2 4 50 to 100
1.1.22 port trunk pvid vlan
Syntax
port trunk pvid vlan vlan_id
undo port trunk pvid
View
Ethernet port view
Page 67

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-17
Parameter
vlan_id: VLAN ID defined in IEEE802.1Q, ranging from1 to 4094 and the default
vlan_id is 1.
Description
Using port trunk pvid vlan command, you can configure the default VLAN ID of trunk
port. Using undo port trunk pvid command, you can restore the default VL AN ID of
the port.
Trunk port and isolate-user-vlan cannot be configured simultaneously.
The default VLAN ID of loc al tr u nk port should be consis tent with t hat of the peer one,
otherwise, the packet cannot be properly transmitted.
For the related command, see port link-type.
Example
# Configure the default VLAN of the trunk port Ethernet0/1 to 100.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] port tr unk pvid vlan 100
1.1.23 port vlan filter disable
Syntax
port vlan filter disable
undo port vlan filter disable
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Description
Using port vlan filter disable command, you can disable the VLA N filterin g function
of port. Using undo port vlan filter disable command, you can restore the VLAN
filtering function of the port.
By default, VLAN filtering function is enabled.
Example
# Disable the VLAN filtering function of Ethernet0/1.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] por t vl an filt er d isabl e
Page 68

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-18
1.1.24 reset counters interface
Syntax
reset counters interface [ interface_type | interface_type interface_num |
interface_name ]
View
User view
Parameter
interface_type: Specifies the port type.
interface_num: Specifies the port number.
interface_name: Specifies the port name in the interface_name= interface_type
interface_num format.
For parameter description, refer to the interface command.
Description
Using reset counters interface command, you can reset the statistical information on
the port. and count the related information again on the port for the user.
If the port type and number are not specified when clearing the port information,
information of all ports on the switch will be cleared. If only the port type is specified, all
the information on the ports of this type will be cleared. If both port type and port
number are specified, the information on the designated port will be cleared.
After 802.1X is enabled, the port information cannot be reset.
Example
# Reset statistical information on Ethernet port Ethernet0/1.
<Quidway> reset counters interface ethernet0/1
1.1.25 shutdown
Syntax
shutdown
undo shutdown
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Page 69

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 Ethernet Port Configuration Commands
1-19
Description
Using shutdown command, you can disable the Ethernet port. Using undo
shutdown command, you can enable the Ethernet port.
By default, the Ethernet port is enabled.
Example
# Enable Ethernet port Ethernet0/1.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] und o shutdown
1.1.26 speed
Syntax
speed { 10 | 100 | auto }
undo speed
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
10: The speed on the port is 10Mbps.
100: The speed on the port is 100Mbps.
auto: The port speed is in peer auto-negotiation status.
Description
Using speed command, you can configure the port speed. Using undo speed
command, you can restore the default speed.
By default, the speed is auto.
For the related command, see duplex.
Example
# Configure Ethernet port Ethernet 0/1 port sp eed as 10Mbps.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] speed 10
Page 70

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 Ethernet Port Link Aggregation Commands
2-1
Chapter 2 Ethernet Port Link Aggregation
Commands
2.1 Ethernet Port Link Aggregation Comma nds
2.1.1 display link-aggregation
Syntax
display link-aggregation [ master_port_num ]
View
Any view
Parameter
master_port_num: Master port num ber in an aggregation port group.
Description
Using display link-agg regation command, you can view the rel ated information on
aggregation port.
If the master port number of an aggregation is specified, information on this link
aggregation will be displayed. If the master port number is not specified, information of
all link aggregations will be displayed.
For the related command, see link-aggregation.
Example
# Display the related information of the aggregation group with the master port number
as Ethernet0/1.
<Quidway> display link-aggregation ethernet0/1
Master port: Ethe rn et0/1
Other sub-ports:
Ethern et0/2
Mode: both
Page 71

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 Ethernet Port Link Aggregation Commands
2-2
Table 2-1 The description of link aggregation
Field Description
Master port Master port
Other sub-ports Other member ports
Mode Aggregation mode
2.1.2 link-aggregation
Syntax
link-aggregation port_num1 to port_num2 { both | ingress }
undo link-aggregation { master_port_num | all }
View
System view
Parameter
port_num1: Starting range value of Ethernet port joined the Ethernet link aggregation.
port_num2: Last range value of Ethernet port joined the Ethernet link aggregation.
both: Configures that the s ub-por ts in t he li nk aggregation share out going load on the
port depending on the source address and destination MAC address.
ingress: Configures that the s ub-ports in the l ink aggr egation shar e outgo ing loa d on
the port depending on the source MAC addresses.
master_port_num: Master port number in link aggregation.
all: all aggregated ports.
Description
Using link-aggregation c o m m and, you c an co nfigure a series of ports to aggrega tion
port and the port with the smallest port number as master port. Using undo
link-aggregation command, you can cancel the Ethernet link aggregation.
Note that the Ethernet por ts to be aggre gated can no t work in auto- negotiation m ode
and must work in the same mode, which can be 10M_FULL (10Mbps speed, full
duplex) or 100M_FULL (100Mbps speed, full duplex), otherwise, they cannot be
aggregated.
For the related command, see display link-aggregation.
Example
# Configure outgoing load balance on the port depending on the source and
destination MAC addresses .
[Quidway] link-aggregatio n ether n et0/ 1 to ethernet0/2 both
Page 72

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Commands
3-1
Chapter 3 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration
Commands
3.1 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Commands
3.1.1 display mirror
Syntax
display mirror
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using
display mirror
command, you can view the information of monitor-mirror port.
For the related commands, see
monitor-port, port mirror
.
Example
# Display the information of monitor-mirror port.
[Quidway] display mirror
Informatio n about monitor port (s)
The observing port : Ethernet0/1
The monitored ports:
Ethernet0/ 2 Ethernet0/3 Ethernet0/4 Ethernet0/5 Ethernet0/6
Table 3-1 Description of port mirroring
Field Description
The observing port The observing port
The monitored ports The monitored ports list
3.1.2 monitor-port
Syntax
monitor-port
{ interface_type interface_num | interface_name }
Page 73

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Commands
3-2
undo monitor-port
{ interface_type interface_num | interface_name }
View
System view
Parameter
interface_name: Specified monitor port name, represented with interface_name=
interface_type interface_num. interface_type is port type and interface_num is port
number.
Description
Using
monitor-port
command, you can configure the monitor port. Using
undo
monitor-port
command, you can cancel the monitor port.
Note that:
z
The mirror port cann ot be conf igured un til the m onitor port config uration is done.
Moreover, the monitor port cannot be canceled, when there is corresponding
mirror port.
z
The specified monitor port cannot be aggregated port.
z
When new monitor port is set, the former monitor port will be cancelled
automatically, while the mirror port does not change.
For the related commands, see port mirror, display mirror.
Example
# Configure Ethernet0/1 as monitor port.
[Quidway] monitor-port ethernet0/1
3.1.3 port mirror
Syntax
port mirror { interface_ty pe interface_ num | interface_na me } [ to { interface_type
interface_ num | interface_name } ]
undo port mirror { interface_type interface_ num | interface_name } [ to
{ interface_type interface_ num | interface_name } ]
View
System view
Parameter
{ interface_type interface_ num | interface_name } [ to { interf ace _ty pe in ter fac e_ nu m
| interface_name } ]: Des ignate the mirror port. You can designate a p ort using the
command without to, or designate more than one mirror port with it. Here,
Page 74

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Commands
3-3
interface_name specifies the port name and it is expressed as
interface_name=interface_type interface_num. interface_type is the port type and
interface_num is the port number.
Description
Using port mirror command, you can configure the mirror port. Using undo port
mirror command, you can cancel the mirror port.
Note that the mirror por t cannot be configured until the m onitor port configuration is
done. Moreover, the monitor port cannot be cance led, when there is corresponding
mirror port.
For the related commands, see monitor-port, display mirror .
Example
# Configure Ethernet0/1 as mirror port.
[Quidway] port mirror ethernet0/1
3.1.4 port mirror observing-port
Syntax
port mirror interface_list1 observing-port
{ interface_type interface_ num |
interface_name }
undo port mirror interface_list1 observing-port { interface_type interface_ num |
interface_name }
View
System view
Parameter
interface_list1: Specified mirror port list. interface_list1 = { interface_type
interface_num | interface_name } [ to { interface_type interface_num |
interface_name } ].
interface_name: Specified monitor port name, represented with interface_name=
interface_type interface_num. interface_type is port type and interface_num is port
number.
Description
Using port mirror observing-port command, you can configure monitor port and
mirror port. Using undo port mirror observing-port command, you can cancel the
monitor port and mirror port.
This command equals to r unning two commands of monitor-port and port mirror.
When mirror por t is set, the monitor port is specif ied simultaneously. The specified
Page 75

Command Manual - Port
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 Ethernet Port Mirror Configuration Commands
3-4
monitor port cannot be aggr egated p ort. W hen the n ew m onit or port is set, the fo rm er
monitor port will be cancelled automatically.
For the related commands, see monitor-port, port mirror, display mirror.
Example
# Configure Ethernet0/1 as monitor port and Ethernet0/2 as mirror port.
[Quidway] port mirror ethernet0/2 observing-port ethernet0/1
Page 76

HUAWEI
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches
Command Manual
3. VLAN
Page 77

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
i
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration Commands................................................................................ 1-1
1.1 VLAN Configuration Commands........................................................................................ 1-1
1.1.1 description...............................................................................................................1-1
1.1.2 display vlan..............................................................................................................1-1
1.1.3 port .......................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.4 vlan.......................................................................................................................... 1-3
1.1.5 vlan { enable | disable }........................................................................................... 1-4
Chapter 2 Isolate-User-Vlan Configuration Commands............................................................ 2-1
2.1 isolate-user-vlan Configuration Commands ...................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 display isolate-user-vlan.......................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 isolate-user-vlan...................................................................................................... 2-2
2.1.3 isolate-user-vlan enable .......................................................................................... 2-3
Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands.................................................................... 3-1
3.1 GARP Configuration Commands....................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 display garp statistics.............................................................................................. 3-1
3.1.2 display garp timer.................................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.3 garp timer ................................................................................................................3-2
3.1.4 garp timer leaveall................................................................................................... 3-3
3.1.5 reset garp statistics ................................................................................................. 3-4
3.2 GVRP Configuration Command......................................................................................... 3-5
3.2.1 display gvrp statistics.............................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.2 display gvrp status .................................................................................................. 3-6
3.2.3 gvrp ......................................................................................................................... 3-6
3.2.4 gvrp registration ......................................................................................................3-7
Page 78

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration Commands
1-1
Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration Commands
1.1 VLAN Configuration Commands
1.1.1 description
Syntax
description string
undo description
View
VLAN view
Parameter
string: description ch ar ac te r s tr ing of cur rent VLAN, with a length r ang in g f r om 1 to 32
characters. The default d es c riptio n c har acter s trin g of c ur rent VL AN is VL AN ID o f the
VLAN, e.g. VLAN 0001.
Description
Using description command, you can c onfigure a description f or the current VLAN.
Using undo description comm and, you can restore t he default des criptio n of curr ent
VLAN.
For the related command, see display vlan.
Example
# Specify a description character string “RESEARCH” for current VLAN.
[Quidway-vlan1] description RESEARCH
1.1.2 display vlan
Syntax
display vlan [ vlan_id | all | static | dynamic ]
View
Any view
Parameter
vlan_id: Display information of specified VLAN.
all: Display information of all VLANs.
Page 79

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration Commands
1-2
static: Display information of VLAN created statically by the system.
dynamic: Display information of VLAN created dynamically by the system.
Description
Using display vlan command, you can view related information about the specified or
all VLANs.
If vlan_id or all is specified, information of specified VLAN or all VLANs is displayed. It
includes: VLAN ID, VL AN state, whether the r outing f unction has been ena ble on this
VLAN (i.e. whether the route interface exists. If it exists, display IP address and mask),
VLAN description, and the ports VLAN conta ins.
If parameter is not specified, information of the VLAN that has been created and
information of whether VLAN feature has been enabled are displayed. If the parameter
dynamic or static is selec ted, inf orm ation of VLAN cr eated d ynam ic ally or s tatica lly b y
the system and information of whether VLAN feature has been enabled are displayed.
For the related command, see vlan.
Example
# Display the information about VLAN1.
[Quidway] displa y vlan 1
VLAN ID: 1
VLAN Type: static
Route interface: not configured
Description: HUAWEI
Tagged Por ts: none
Untagged Ports:
Ethernet0/1 Etherne t0/2 Ethernet0/3
1.1.3 port
Syntax
port interface_list
undo port interface_list
View
VLAN view
Parameter
interface_list: list of Ethernet ports to be added to or deleted from a certain VLAN,
expressed as interface_list= {{ inter face_type interface_num | interfac e_name } [ to
{ interface_type interface_num | interface_name } ] }&<1-10>. interface_type is
interface type, interface_numis interface number and interface_name is interface
Page 80

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration Commands
1-3
name. For their meanings and value range, read Parameter of “Port” in this document.
The interface number after keyword to must be larger than or equal to the port number
before to. &<1-10>: Representing the repeatable times of parameters, 1 is the minimal
and 10 is the maximal.
Description
Using port comm and, you can add one port or one group of ports to VLAN. Usin g
undo port command, you can cancel one port or one group of ports from VLAN.
Note that you can add/delete trunk port and hybrid port to/from VLAN by port and
undo port commands in Ethernet port view, but not in VLAN view.
For the related command, see display vlan.
Example
# Add Ethernet0/4 through Ethernet0/7, Ethernet0/9 and Ethernet0/11 through
Ethernet0/15 to VLAN 2. The repeated time of command parameter is 3 times.
[Quidway-vlan2] port ethernet0/4 to ethernet0/7 ethernet0/9 ethernet0/11 to
ethernet0/15
1.1.4 vlan
Syntax
vlan vlan_id
undo vlan { vlan_id [ to vlan_id ] | all }
View
System view
Parameter
vlan_id: Specifies the ID of a VL AN to be created and/or enter ed, ranging from 1 to
4094.
all: Delete all VLANs.
Description
Using vlan command, you can enter VLAN v iew. If the specified V LAN is not c rea ted,
create it first. Using undo vlan command, you can cancel the specified VLAN.
VLAN 1 is default VLAN and cannot be deleted.
For the related commands, see display vlan.
Example
# Enter the view of VLAN 1.
Page 81

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration Commands
1-4
[Quidway] vlan 1
1.1.5 vlan { enable | disable }
Syntax
vlan { enable | disable }
View
System view
Parameter
enable: Enable VLAN features of equipment.
disable: Disable the VLAN features of equipment.
Description
Using vlan { enable | disable } com m and, you ca n enab le/disab le t he VL AN fea tures
of equipment.
After the VLAN is disabled, the switch will not use VLAN ID during the packet
exchange, thereby losing the isolation function of VLAN domain.
For the related commands, see display vlan.
Example
# Enable the VLAN features of equipment.
[Quidway] vlan enable
Page 82

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 Isolate-User-Vlan Configuration Command s
2-1
Chapter 2 Isolate-User-Vlan Configuration
Commands
2.1 isolate-user-vlan Configuration Commands
2.1.1 display isolate-user-vlan
Syntax
display isolate-user-vlan [ isolate-user-vlan_num ]
View
Any view
Parameter
isolate-user-vlan_num: VLAN ID of isolate-user-vlan, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Description
Using display isolate-use r-vlan command, you can view the mapping relationship
and the ports identifying the mapping relationship between isolate-user-vlan and
Secondary VLAN.
For the related command, see isolate-user-vlan enable, isolate-user-vlan.
Example
# Display the mapping relationship between isolate-user-vlan and Secondary VLAN.
[Quidway] display isolate-user-vlan
Isolate-user-V LAN Vlan ID : 3
S econdary Vlan ID : 4-5
Vlan ID: 3
Vlan Type: static
I solate-user-VLAN Type : Isolate-u ser-VLAN
Route Interface: not configured
Description: VL AN 0003
Tagged Ports: none
Untagged Ports:
Ethernet0/4 Ethernet0/8 Ethernet0/18
Vlan ID: 4
Page 83

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 Isolate-User-Vlan Configuration Command s
2-2
Vlan Type: static
P rivate-vlan Type : Secondary
Route Interface: not configured
Description: VL AN 0004
Tagged Ports: none
Untagged Ports:
Ethernet0/4 Ethernet0/8
Vlan ID: 5
Vlan Type: static
P rivate-vlan Type : Secondary
Route Interface: not configured
Description: VL AN 0005
Tagged Ports: none
Untagged Ports:
Ethernet0/4 Ethernet0/18
2.1.2 isolate-user-vlan
Syntax
isolate-user-vlan isolate-user-vlan_num secondary secondary_vlan_numlist [ to
secondary_vlan_numlist ]
undo isolate-user-vlan isolate-user-vlan_num [ secondary secondary_vlan_numlist
[ to secondary_vlan_numlist
]
View
System view
Parameter
isolate-user-vlan_num
: VLAN ID of isolate-user-vlan, ranging from 1 to 4094.
secondary_vlan_numlist
: VLAN ID of Secondary vlan, ranging from 1 to 4094.
Description
Using isolate-user-vlan co mmand, you can assoc iate isolate- user-vlan to Sec ondar y
VLAN and establish the mapping relationship between isolate-user-vlan and
Secondary VLAN. Using undo isolate-user-vlan command, you can cancel the
mapping relationship between isolate-user-vlan and Secondary VLAN.
By default, there is no an y corresponding relations hip between isolate-us er-vlan and
Secondary VLAN created by the user.
Before the command is run, isolate-user-vlan and Secondary VLAN must include ports.
After the command is run, the mapping relationship between isolate-user-vlan and
Page 84

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 Isolate-User-Vlan Configuration Command s
2-3
Secondary VLAN is established. The actual operation include: add the ports of
isolate-user-vlan to every Secondary VLAN and add the ports of all Secondary VLANs
to isolate-user-vlan.
After undo command is run, the m apping relationship bet ween isolate-user-vl an and
Secondary VLAN will be canceled. The actual operation include: delete the ports
included in isolate- user-vlan from Secondar y VLAN and delete the ports included in
Secondary VLAN from isolate-user-vlan.
For the related command, see display isolate-user-vlan.
Example
# Associate isolate-user-vlan 10 with Secondary VLAN2, 3, 4, 5 and 9.
[Quidway] isolate-user-vlan 10 secondary 2 to 5 9
2.1.3 isolate-user-vlan enable
Syntax
isolate-user-vlan enable
undo isolate-user-vlan enable
View
VLAN view
Parameter
none
Description
Using isolate-user-vlan e nable command, you c an configure the type of one VLAN
as isolate-user-vlan. Using undo isolate-user-vlan enable command, you can cancel
the isolate-user-vlan type of one VLAN.
By default, the type of the VLAN created by the user has not been specified.
isolate-user-vlan can contain many ports, including the uplink ports connected to other
switches. isolate-user-vlan and Trunk ports cannot be conf igured s im ultaneo usly, i.e.,
if isolate-user-vlan is configured to the Ethernet switch, the Trunk port cannot be
configured. If the Trunk port is configured, then the isolate-user-vlan cannot be
configured.
For the related commands, see display isolate-user-vlan.
Example
# Configure VLAN 5 as isolate-user-vlan.
[Quidway-vlan5] isolate-user-vlan enable
Page 85

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-1
Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3.1 GARP Configuration Commands
3.1.1 display garp statistics
Syntax
display garp statistics [ interface
interface_list ]
View
Any view
Parameter
interface_list: List of Ethernet port to be displayed, expressed as interface _list =
{ { interface_type interface_num | interface_name } [ to { interface_type interface_num
| interface_name } ] }&<1-10>. interface_type is interface type, interface_numis
interface number and interface_name is interface name. For their meanings and value
range, read command parameters description of “Port” in this document.
&<1-10>: Representing the repeatable times of parameters, 1 is the minimal and 10 is
the maximal.
Description
Using
display garp statistics
command, you can view the GARP statistics
information, including the number of received/sent packet and the number of
discarded packet by GVRP/GMRP etc.
Example
# Display the GARP statistics information on Ethernet port Ethernet0/1.
<Quidway> display garp statistics interface ethernet0/1
G ARP statistics on port Ethernet0/1
Number Of GMRP Frames Received : 0
Number Of GVRP Frames Received : 0
Number Of GMRP Frames Transmitted : 0
Number Of GVRP Frames Transmitted : 0
Number Of Frames Discarded : 0
The above information indicates that the numbers of GVRP/GMRP packets
received/sent and discarded on Ethernet0/1 are 0.
Page 86

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-2
3.1.2 display garp timer
Syntax
display garp timer [ interface
interface_list ]
View
Any view
Parameter
interface_list: List of Ethernet port to be displayed, expressed as interface _list =
{ { interface_type interface_num | interface_name } [ to { interface_type interface_num
| interface_name } ] }&<1-10>. interface_type is interface type, interface_numis
interface number and interface_name is interface name. For their meanings and value
range, read command parameters description of “Port” in this document.
&<1-10>: Representing the repeatable times of parameters, 1 is the minimal and 10 is
the maximal.
Description
Using
display garp timer
command, you can view the value of GARP timer, including
Hold timer, Join timer, Leave timer and LeaveAll timer.
For the related command, see
garp timer, garp timer leaveall
.
Example
# Show GARP timer on Ethernet0/1.
<Quidway> display garp timer interface ethernet0/1
GARP timers on port Ethernet0/1
GARP JoinTime : 20 centiseconds
GARP Leave Time : 60 centisec onds
GARP LeaveAll Time : 1000 centiseconds
GARP Hold Time : 10 centiseconds
3.1.3 garp timer
Syntax
garp timer { hold | join | leave }
timer_value
undo garp timer { hold
|
join
|
leave
}
View
Ethernet port view
Page 87

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-3
Parameter
hold
: GARP Hold timer. After received certain registration information, the GARP
application entit y will not se nd Join Mess age at onc e, instead, it starts the H old tim er.
All the registration information received within duration of the Hold timer will be
transmitted in the same frame after the Hold timer times out, thereby saving the
bandwidth resource.
join
: GARP Join tim er. GARP application entit y will send out Join message after th e
Join timer goes timeout to make other GARP application entity register its own
information.
leave
: GARP Leave timer . When a GARP application entity wants to deregister
certain attribute inf ormation, it sends Leave message. The G ARP application entity
received the mes sage will starts Leave tim er. If the entity receives no Join me ssage
before the timer goes timeout, it will deregister the attribute information.
timer_value: Value of GARP hold timer, join timer and lea ve tim er in c entisecon d. T he
step is 5 centisecon ds. The range is according to t he follo wing rule: the value of J oin
timer should be no les s than the double d value of Hol d timer, and the value of Leav e
timer should be greater than the doubled value of Join timer and sm aller than the
Leaveall timer value, and the minimal value of Join timer is 10 centiseconds. By
default, Hold timer is 10 centiseconds, Join timer is 20 centiseconds, Leave timer is 60
centiseconds.
Description
Using
garp timer
command, you ca n configure G ARP timer value. Usin g
undo garp
timer
command, you can restore the default value of GARP timer.
For the related command, see
display garp timer
.
Example
# Set Join timer of GARP as 300ms.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] garp timer join 30
3.1.4 garp timer leaveall
Syntax
garp timer leaveall
timer_value
undo garp timer leaveall
View
System view
Page 88

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-4
Parameter
timer_value: Value of GARP leaveall t imer in centisec ond, ranging fr om 65 to 32765.
The step is 5 centisecon ds. The value of Leaveall timer s hould be greater than the
value of Leave timer. By default, the value of Lea ve Al l timer is 1000 centis ec onds , i.e.
10s.
Description
Using
garp timer leaveall
command, you can c onfigure GARP leav eall timer. Using
undo garp timer leaveall
command, you can restore the default va lu e.
After every GARP application entity is started, the LeaveAll timer will be started
simultaneously. The GARP application entity will send LeaveAll message after the
timer times out to make other application entities re-register all attribute information on
themselves. Then, the LeaveAll timer is started and the new cycle begins.
For the related command, see
display garp timer
.
Example
# Set GARP LeaveAll timer as 1s.
[Quidway] garp timer leaveall 100
3.1.5 reset garp statistics
Syntax
reset garp statistics [ interface
interface_list ]
View
User view
Parameter
interface_list: Specifies a list of Ethernet ports, on which the GARP statistics
information will be cleared, expressed as interface_list = { { interface_type
interface_num | interface_name } [ to { interface_type interface_num |
interface_name } ] }&<1-10>. interface_type is interface type, interface_num is
interface number and interface_name is interface name. For their meanings and value
range, read Parameter Description of “Port” in this document.
&<1-10>: Representing the repeatable times of parameters, 1 is the minimal and 10 is
the maximal.
Description
Using
reset garp statisti cs
command, you can reset the G ARP statist ics inf ormation
(such as the received/sent packets or discarded packets by GVRP/GMRP). If the
Page 89

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-5
command has no parameter, it will clear the GARP statistics information of all the
ports.
For the related command, see
display garp statistics
.
Example
# Clear GARP statistics information.
<Quidway> reset garp statistics
3.2 GVRP Configuration Command
3.2.1 display gvrp statistics
Syntax
display gvrp statistics
[
interface
interface_list ]
View
Any view
Parameter
interface_list: List of Ethernet port to be displayed, expressed as interface _list =
{ { interface_type interface_num | interface_name } [ to { interface_type interface_num
| interface_name } ] }&<1-10>. interface_type is interface type, interface_num is
interface number and interface_name is interface name. For their meanings and value
range, read command parameters description of “Port” in this document.
&<1-10>: Representing the repeatable times of parameters, 1 is the minimal and 10 is
the maximal.
Description
Using
display gvrp statistics
command, you can view the GVRP statistics
information of all the Trunk ports, inc l ud ing t he lis t of p or ts enab led wit h G VR P, GVRP
status information, f ail ed GVRP registration en tr ies a n d the las t G V RP data un it o r igin
etc.
Example
# Display the GVRP statistics information about Ethernet0/1.
<Quidway> display gvrp statistics interface ethernet0/1
GVRP statistics on port Ethernet0/1
GVRP Status : Enabl ed
GVRP Failed Registrations : 0
GVRP Last Pdu Origin : 0000-0000-0000
GVRP Registration Type : Normal
Page 90

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-6
3.2.2 display gvrp status
Syntax
display gvrp status
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using
display gvrp status
command, you can view the global status information
about GVRP.
Example
# Display the global status information about GVRP.
<Quidway> display gvrp status
GVRP is enabled
3.2.3 gvrp
Syntax
gvrp
undo gvrp
View
System view/Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Description
Using
gvrp
command, you can enabl e GVRP. Using
undo gvrp
command, you can
restore the GVRP to default mode, i.e. disable GVRP.
By default, GVRP is disabled.
This command can be used to enable/disable global GVRP in System view or
enable/disable port GVRP in Ethernet port view.
Before enabling por t GVRP, the us er must enable global G VRP first and port GVRP
must be enabled/disabled on Trunk port.
Page 91

Command Manual - VLAN
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 3 GARP/GVRP Configuration Commands
3-7
For the related commands, see
display gvrp status
.
Example
# Enable global GVRP.
[Quidway] gvrp
3.2.4 gvrp registration
Syntax
gvrp registration
{
fixed
|
forbidden
|
normal
}
undo gvrp registration
View
Ethernet port view
Parameter
fixed
: Enable to create or register VL AN on the por t manuall y and disable t o register
or deregister VLAN dynamically.
forbidden
: Deregisters all VLANs except VLAN 1 and disables to creat e or register
any other VLAN on the port.
normal
: Enable to create, register and deregister VLAN on the port manually or
dynamically.
Description
Using
gvrp registration
command, you can config ure GVRP re gistration t ype. Using
undo gvrp registration
command, you can restore the default type.
By default, the registration type is
normal
.
This command can be only used on Trunk port.
For the related commands, see
display gvrp statistics
.
Example
# Set the GVRP registration type of Ethernet0/1 as fixed.
[Quidway-Ethernet0/1] gvrp registration fixed
Page 92

HUAWEI
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches
Command Manual
4. Multicast
Page 93

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
i
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 GMRP Configuration Commands............................................................................... 1-1
1.1 GMRP Configuration Commands...................................................................................... 1-1
1.1.1 debugging gmrp ...................................................................................................... 1-1
1.1.2 display gmrp statistics............................................................................................. 1-2
1.1.3 display gmrp status ................................................................................................. 1-2
1.1.4 gmrp ........................................................................................................................ 1-3
Chapter 2 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands............................................................... 2-1
2.1 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands ....................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 display igmp-snooping configuration....................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 display igmp-snooping group ..................................................................................2-2
2.1.3 display igmp-snooping statistics.............................................................................. 2-3
2.1.4 igmp-snooping......................................................................................................... 2-4
2.1.5 igmp-snooping host-aging-time............................................................................... 2-4
2.1.6 igmp-snooping max-response-time......................................................................... 2-5
2.1.7 igmp-snooping router-aging-time ............................................................................ 2-6
2.1.8 reset igmp-snooping s tatistic s................................................................................. 2-7
Chapter 3 Unknown Multicast Dropping Configuration Commands ....................................... 3-1
3.1 Unknown Multicast Dropping Configuration Commands................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 unknown-multicast drop enable .............................................................................. 3-1
Page 94

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 GMRP Configuration Commands
1-1
Chapter 1 GMRP Configuration Commands
1.1 GMRP Configuration Commands
1.1.1 debugging gmrp
Syntax
debugging gmrp { event | packet }
undo debugging gmrp { event | packet }
View
User view
Parameter
event: GMRP event.
packet: GMRP packet.
Description
Using debugging gmrp comm and, you can enable GMRP debugging. Us ing undo
debugging gmrp you can disable GMRP debugging.
Example
# Enable GMRP event debugging.
<Quidway> debugging gmrp event
GMRP: Max number of GMRP entries reached
Table 1-1 Description of information generated by the command debugging gmrp event
Field Description
GMRP: Max number of GMRP entries
reached
Maximum number of entries reached for GMRP local database
Page 95

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 GMRP Configuration Commands
1-2
1.1.2 display gmrp statistics
Syntax
display gmrp statistics [
interface interface- l ist ]
View
Any view
Parameter
interface interface-list: Specifies Ethernet port list, expressed as interface-list =
{ { interface_type interface_num | interface_name } [ to { interface_type
interface_num | interface_name } ]}&<1-10>. For meanings and value ranges of
interface-type, interface-number and interface-name, refer to the s yntax des c ript i on in
the Port Configuration of this manual.
Description
Using display gmrp statistics command, you can view the statistics information
about GMRP.
This command is used f or displa ying the stat istics inf orm ation about GMR P, including
the list of ports with GMRP enabled, GMRP status information, GMRP failed
registrations and last origin of GMRP packet data unit (PDU).
Example
# Display the statistics information about GMRP on Ethernet 0/1.
<Quidway> display gmrp statistics interface Ethernet 0/1
GMRP statistics on po rt Ethernet0/1
Gmrp Status : Enabled
Gmrp Failed Registrations : 0
Gmrp Last Pdu Origin : 0000-000 0-0000
1.1.3 display gmrp status
Syntax
display gmrp status
View
Any view
Page 96

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 GMRP Configuration Commands
1-3
Parameter
none
Description
Using display gmrp status command, you can view the status of global GMRP.
This command can be used for displaying the enabled/disabled status of global
GMRP.
Example
# Display the status of global GMRP.
<Quidway> display gmrp status
GMRP is enabled
Table 1-2 Global GMRP status information
Field Description
GMRP is enabled GMRP is enabled globally.
1.1.4 gmrp
Syntax
gmrp
undo gmrp
View
System view/Ethernet port view
Parameter
none
Description
Using gmrp command, you can enable global GMRP or enable GMRP on a port.
Using undo gmrp command, you ca n c onf ig ur e th e GMRP back to the def ault s e ttin g,
namely disabled.
By default, GMRP is disabled
Page 97

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 1 GMRP Configuration Commands
1-4
Executed in system view, this command will enable the global GMRP. After
performing this command in Ethernet port view, GMRP will be enabled on a port.
Before enabling GMRP on a port, you shall enable GMRP globally.
For the related command, see display gmrp status, display gmrp statistics.
Example
# Enable GMRP globally.
[Quidway] gmrp
Page 98

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands
2-1
Chapter 2 IGMP Snooping Configuration
Commands
2.1 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands
2.1.1 display igmp-snooping configuration
Syntax
display igmp-snooping configuration
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display igmp-snooping configuration command, you can view the IGMP
Snooping configuration information.
This command is us ed to dis play the IG MP Sn ooping configurati on infor mation of the
switch. The information displayed includes whether IGMP Snooping is enabled, router
port timeout, maximum response timeout of a query and the member port timeout.
For the related command, see igmp-snooping.
Example
# Display the IGMP Snooping configuration information of the switch.
<Quidway> display igmp-snooping configuration
Enable IGMP-Sno op ing.
The router port tim eo ut is 300 second (s ).
The max response timeout is 50 second(s).
The member port tim eo ut is 500 second(s).
Page 99

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands
2-2
The information above t ells us that: IGMP Snooping is enabled; the router port timer
is set to be 300 seconds; t he max respons e timer is set to be 50 s econds; the agin g
timer of multicast group member is set to be 500 seconds.
2.1.2 display igmp-snooping group
Syntax
display igmp-snooping group [ vlan vlanid ]
View
Any view
Parameter
vlan vlanid: Specifies the VLAN where the m ulticast group to be viewed is located .
When the parameter is om itted, the command will display the information about al l
the multicast groups on the VLAN.
Description
Using display igmp-snooping group command, you can view the IP multicast
groups and MAC multicast groups under VLAN.
This command displ ays the IP m ulticast group and MAC multicast gr oup information
of a VLAN or all the VLAN where the Ethernet switch is located. It displays the
information such as VLA N ID, router port, IP multic ast group address, m ember ports
in the IP multicas t group, MAC multicast gro up, MAC multicast group ad dress, and
the member ports in the MAC multicast group.
Example
# Display the multicast group information about VLAN2.
<Quidway> display igmp-snooping group vlan 2
***************Multicast group table***************
Vlan(id):2.
Router port(s): Et hernet0/1
IP group(s):the following ip group(s) match to one mac group.
IP group address: 23 0.45.45.1
Member port(s): Et hernet0/12
MAC group(s) :
MAC group addr ess:01-00-5e-2 d-2d-01
Member port(s): Et hernet0/12
Page 100

Command Manual - Multicast
Quidway S2000 Series Ethernet Switches Chapter 2 IGMP Snooping Configuration Commands
2-3
We can know from the information listed above that :
z
There is a multicast group in VLAN 2;
z
The router port is Ethernet 0/1;
z
The address of the multicast group is 230.45.45.1;
z
The member of the IP multicast group is Ethernet 0/12;
z
MAC multicast group is 0100-5e2d-2d01;
z
The member of the MAC multicast group is Ethernet 0/12.
2.1.3 display igmp-snooping statistics
Syntax
display igmp-snooping statistics
View
Any view
Parameter
none
Description
Using display igmp-snooping statistics command, you can view the statistics
information on IGMP Snooping.
This command displ ays the statistics inform ation about IGMP Snooping of Eth ernet
switch. It displays the information such as num ber of received general IGMP q uery
packets, received IGMP specific query packets, received IGMP Version 1 and Version
2 report packets, received IGMP leave packets and error packets, and sent IG MP
specific query packets.
For the related command, see igmp-snooping.
Example
# Display statistics information about IGMP Snooping.
<Quidway> display igmp-snooping stat is tic s
Received IGM P general query pack et(s) number:0.
Received IGMP spe ci fic query packet(s ) number:0.
Received IGMP V1 re po rt packet(s) numbe r:0.
Received IGMP V2 re po rt packet(s) numbe r:0.
Received IGMP leave packet(s) number:0.
 Loading...
Loading...