Page 1

Munchkin
When installing models manufactured after July 7, 2008, you will notice additional selections on the control installer menu that will not
apply to this unit. DO NOT CHANGE THESE FACTORY SETTINGS. Refer to the Control Program Reference Chart within this manual
for selections that apply to this model.
This manual must be used by a qualified installer/service technician. Read all instructions in this manual before installing. Perform steps
in the given order. Failure to comply could result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
NOTE TO CONSUMER: PLEASE KEEP ALL INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
LP-185 Rev. 2.7.14
Gas-Fired Boiler
INSTALLATION
START-UP
MAINTENANCE
PARTS
Models
T50M / T80M
80M / 140M / 199M / 399M
NOTICE: HTP reserves the right to make product changes or updates without notice and will not be held liable for typographical errors
in literature.
120 Braley Rd. P.O. Box 429 East Freetown, MA 02717-0429 www.htproducts.com
Page 2

2
IF THE INFORMATION IN THIS MANUAL IS NOT FOLLOWED EXACTLY, A FIRE OR EXPLOSION MAY RESULT, CAUSING
PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY, OR LOSS OF LIFE. DO NOT STORE GASOLINE OR OTHER FLAMMABLE VAPORS
AND LIQUIDS IN THE VICINITY OF THIS OR ANY OTHER BOILER.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
Do not try to light any appliance.
Do not touch any electrical switch.
Do not use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas supplier’s instructions.
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire department. Installation and service must be provided by a qualified installer,
service agency, or the gas supplier.
Page 3
The following defined terms are used throughout this manual to bring attention to the presence of hazards of various risk
levels, or to important product information.
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
CAUTION used without the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in property
damage.
This manual must only be used by a qualified heating installer/service technician. Read all instructions in this manual before installing.
Perform steps in the order given. Failure to comply could result in severe personal injury, death or substantial property damage.
FOREWORD
This manual is intended to be used in conjunction with other literature provided with the MC Series Gas-Fired Boiler. This includes all
related control information. It is important that this manual, all other documents included with this system, and additional publications
including the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-2002, be reviewed in their entirety before beginning any work.
Installation should be made in accordance with the regulations of the Authority Having Jurisdiction, local code authorities, and utility
companies which pertain to this type of water heating equipment.
Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) – The Authority Having Jurisdiction may be a federal, state, local government, or individual such
as a fire chief, fire marshal, chief of a fire prevention bureau, labor department or health department, building official or electrical
inspector, or others having statutory authority. In some circumstances, the property owner or his/her agent assumes the role, and at
government installations, the commanding officer or departmental official may be the AHJ.
NOTE: HTP, Inc. reserves the right to modify product technical specifications and components without prior notice.
3
FOR THE INSTALLER
This boiler must be installed by qualified and licensed personnel. The installer should be guided by the instructions furnished with the
boiler, and with local codes and utility company requirements. In the absence of local codes, preference should be given to the National
Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 – latest edition.
INSTALLATIONS MUST COMPLY WITH:
Local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws, regulations and ordinances.
The latest version of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1, from American Gas Association Laboratories, 8501 East Pleasant
Valley Road, Cleveland, OH 44131.
In Canada – CGA No. B149 (latest version), from Canadian Gas Association Laboratories, 55 Scarsdale Road, Don Mills, Ontario,
Canada M3B 2R3. Also, Canadian Electrical Code C 22.1, from Canadian Standards Association, 5060 Spectrum Way, Suite 100,
Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L4W 5N6.
Code for the installation of Heat Producing Appliances (latest version), from American Insurance Association, 85 John Street, New
York, NY 11038.
The latest version of the National Electrical Code, NFPA No. 70.
The hydronic supply and return connections of these products are for installation in closed loop systems ONLY! Use of this
product in any manner other than described in this manual may result in premature product failure, substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death. Damage or failure of this product (or the system in which it is installed) due to unauthorized use IS NOT
Page 4

COVERED BY WARRANTY.
IMPORTANT
In accordance with Section 325 (f) (3) of the Energy Policy and Conservation Act, HTP, Inc. has provided this boiler with
multiple features designed to save energy by reducing the boiler water temperature as heating load decreases.
These features include:
A modulating combustion system that adjusts firing rate based on heat demand.
Adjustment of boiler set point based on inferred heat load as determined by an outdoor sensor. The outdoor sensor
is supplied by HTP, Inc. with this boiler.
This boiler does not include a standing pilot.
This boiler is designed and shipped to assure the highest efficiency operation possible. Such high efficiency is
achieved by limiting heating circuit water temperature to 140°F when there is no anticipated heat load, based upon
the outdoor sensor and the Outdoor Reset Curve (sensor response curve) in the boiler software.
This feature may be over-ridden as described below in specific installations:
The boiler control is equipped with an outdoor sensor override for use with building management systems or in
cascaded systems (for systems with total input of 300,000 BTU/hr or greater).
See statement below for an important notice on the use of the override.
IMPORTANT
In accordance with Section 325 (f) (3) of the Energy Policy and Conservation Act, this boiler is equipped with a feature that
saves energy by reducing the boiler water temperature as the heating load decreases. This feature is equipped with an
override which is provided primarily to permit the use of an external energy management system that serves the same
function. THIS OVERRIDE MUST NOT BE USED UNLESS AT LEAST ONE OF THE FOLLOWING CONDITIONS IS TRUE:
An external energy management system is installed that reduces the boiler water temperature as the heating load
decreases.
This boiler is not used for space heating.
This boiler is part of a modular or multiple boiler system having a total input of 300,000 BTU/hr or greater.
This boiler is equipped with a tankless coil.
NOTE: The gas manifold and controls met safe lighting and other performance criteria when undergoing tests specified in ANSI
Z21.10.3 – latest edition.
4
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART 1 – GENERAL SAFETY INFORMATION .......................................................................................................................... 7
A. PRECAUTIONS .......................................................................................................................................................................... 7
B. IMPROPER COMBUSTION ........................................................................................................................................................ 7
C. GAS ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 7
D. WHEN SERVICING THE BOILER .............................................................................................................................................. 7
E. BOILER SYSTEM ....................................................................................................................................................................... 7
F. WATER CHEMISTRY* ................................................................................................................................................................ 8
G. WINTERIZING ............................................................................................................................................................................ 8
PART 2 – BEFORE YOU START ................................................................................................................................................ 8
A. WHAT’S IN THE BOX ................................................................................................................................................................. 8
B. HOW THE BOILER OPERATES................................................................................................................................................. 9
C. OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT ......................................................................................................................................................... 10
PART 3 – PREPARE BOILER LOCATION ............................................................................................................................... 10
A. BEFORE LOCATING THE BOILER .......................................................................................................................................... 10
B. LEVELING ................................................................................................................................................................................ 14
C. CLEARANCES FOR SERVICE ACCESS ................................................................................................................................. 15
Page 5

D. RESIDENTIAL GARAGE, CLOSET, AND ALCOVE INSTALLATIONS .................................................................................... 15
E. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE ....................................................................................................................................... 15
F. PREVENT COMBUSTION AIR CONTAMINATION .................................................................................................................. 16
G. REMOVING AN EXISTING BOILER FROM AN EXISTING COMMON VENT SYSTEM ......................................................... 16
PART 4 – PREPARE BOILER ................................................................................................................................................... 17
A. REMOVE BOILER FROM PACKAGING ................................................................................................................................... 17
B. WALL MOUNTING CONSIDERATIONS ................................................................................................................................... 17
C. WALL MOUNTING INSTRUCTIONS ........................................................................................................................................ 17
PART 5 – BOILER PIPING ........................................................................................................................................................ 18
A. GENERAL PIPING INFORMATION .......................................................................................................................................... 18
B. RELIEF VALVE ......................................................................................................................................................................... 19
C. SEPARATE LOW WATER CUTOFF ........................................................................................................................................ 20
D. BACKFLOW PREVENTER ....................................................................................................................................................... 20
E. SYSTEM WATER PIPING METHODS ..................................................................................................................................... 20
F. CIRCULATORS......................................................................................................................................................................... 20
G. HYDRONIC PIPING WITH CIRCULATORS, ZONE VALVES, AND MULTIPLE BOILERS ..................................................... 21
H. CIRCULATOR SIZING .............................................................................................................................................................. 21
I. ZONING WITH ZONE VALVES.................................................................................................................................................. 22
J. ZONING WITH CIRCULATORS ................................................................................................................................................ 23
K. MULTIPLE BOILERS ................................................................................................................................................................ 23
L. FILL AND PURGE HEATING SYSTEM .................................................................................................................................... 23
M. PIPING DETAILS ..................................................................................................................................................................... 24
PART 6 – PIPING WITH OPTIONAL VISION 1 SYSTEM ......................................................................................................... 31
5
A. VISION 1 SYSTEM PIPING ...................................................................................................................................................... 31
B. ZONING WITH ZONE VALVES USING VISION 1 .................................................................................................................... 31
C. ZONING WITH CIRCULATORS USING VISION 1 ................................................................................................................... 31
D. PIPING DETAILS WITH THE VISION 1 SYSTEM .................................................................................................................... 32
PART 7 – VENTING, COMBUSTION AIR, AND CONDENSATE REMOVAL ........................................................................... 42
A. GENERAL ................................................................................................................................................................................. 42
B. APPROVED MATERIALS FOR EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE .................................................................................... 42
C. REQUIREMENTS FOR INSTALLATION IN CANADA .............................................................................................................. 43
D. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE LOCATION.................................................................................................................... 43
1. DETERMINE EXHAUST VENT LOCATION ........................................................................................................................................................ 43
2. DETERMINE INTAKE PIPE LOCATION ............................................................................................................................................................. 44
E. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE SIZING .......................................................................................................................... 45
G. LONGER VENT RUNS ............................................................................................................................................................. 45
H. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................ 46
I. DIAGRAMS FOR SIDEWALL VENTING .................................................................................................................................... 48
J. DIAGRAMS FOR VERTICAL VENTING .................................................................................................................................... 50
PART 8 – GAS PIPING .............................................................................................................................................................. 51
A. GAS CONNECTION ................................................................................................................................................................. 51
Page 6

B. GAS PIPING ............................................................................................................................................................................. 51
C. CHECK INLET GAS PRESSURE ............................................................................................................................................. 52
D. GAS VALVE .............................................................................................................................................................................. 53
PART 9 – FIELD WIRING .......................................................................................................................................................... 54
A. INSTALLATION MUST COMPLY WITH: .................................................................................................................................. 54
B. FIELD WIRING.......................................................................................................................................................................... 54
C. LINE VOLTAGE WIRING .......................................................................................................................................................... 54
D. THERMOSTAT ......................................................................................................................................................................... 54
PART 10 – FIELD WIRING – VISION 1 OPTION ...................................................................................................................... 57
PART 11 – START-UP PREPARATION.................................................................................................................................... 58
A. CHECK/CONTROL WATER CHEMISTRY ............................................................................................................................... 58
B. FREEZE PROTECTION (WHEN USED) .................................................................................................................................. 59
C. FILL AND TEST WATER SYSTEM .......................................................................................................................................... 59
D. PURGE AIR FROM WATER SYSTEM ..................................................................................................................................... 59
E. CHECK FOR GAS LEAKS ........................................................................................................................................................ 60
F. CHECK THERMOSTAT CIRCUIT(S) ........................................................................................................................................ 60
G. CHECK CONDENSATE REMOVAL ......................................................................................................................................... 60
H. FINAL CHECKS BEFORE STARTING BOILER ....................................................................................................................... 60
PART 12 – START-UP PROCEDURE ....................................................................................................................................... 61
6
A. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS ................................ ................................ ................................................................................. 61
B. ADJUSTING THE SET POINT .................................................................................................................................................. 61
C. STATUS MENU ........................................................................................................................................................................ 62
D. TEST MODE ............................................................................................................................................................................. 62
PART 13 – START-UP PROCEDURES WITH VISION 1 OPTION ........................................................................................... 63
A. PROGRAMMING THE VISION I OPTION ................................................................................................................................ 63
B. VISION 1 PROGRAM ACCESS ................................................................................................................................................ 63
C. VISION 1 PROGRAM NAVIGATION ........................................................................................................................................ 63
PART 14 – TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................................................................ 65
A. ERROR CODE .......................................................................................................................................................................... 65
B. BOILER ERROR ....................................................................................................................................................................... 65
C. BOILER FAULT ........................................................................................................................................................................ 65
PART 15 – MAINTENANCE ...................................................................................................................................................... 68
A. MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES .............................................................................................................................................. 68
B. MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE FOR THE SERVICE TECHNICIAN ........................................................................................... 68
C. COMBUSTION CHAMBER COIL CLEANING INSTRUCTIONS .............................................................................................. 69
BOILER START-UP REPORT ................................................................................................................................................... 76
MAINTENANCE REPORT ......................................................................................................................................................... 76
MAINTENANCE NOTES ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 80
HTP CUSTOMER INSTALLATION RECORD FORM ............................................................................................................................................. 81
Page 7

INSTALLER – Read all instructions in this manual before installing. Perform steps in the order given.
USER – This manual is for use only by a qualified heating installer/service technician. Refer to user’s information manual for your
reference. Have this boiler serviced/inspected by a qualified service technician annually.
FAILURE TO ADHERE TO THE GUIDELINES ON THIS PAGE AND HAVE THIS BOILER SERVICED/INSPECTED ANNUALLY
CAN RESULT IN SUBSTANTIAL PROPERTY DAMAGE, SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH.
DO NOT USE THIS BOILER IF ANY PART HAS BEEN SUBMERGED IN WATER. Immediately call a qualified service technician. The
boiler MUST BE replaced if it has been submerged. Attempting to operate a boiler that has been submerged could create numerous
harmful conditions, such as a potential gas leakage causing a fire and/or explosion, or the release of mold, bacteria, or other harmful
particulates into the air. Operating a previously submerged boiler could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
NOTE: Boiler damage due to flood or submersion is considered an Act of God, and IS NOT covered under product warranty.
Be sure to disconnect electrical power before opening boiler cabinet or performing service. Failure to do so could result in an electrical
shock that could result in property damage, serious personal injury, or death.
NOTE: If the boiler is exposed to the following, do not operate until all corrective steps have been made by a qualified serviceman:
1. FIRE
2. DAMAGE
3. WATER
Any claims for damage or shortage in shipment must be filed immediately against the transportation company by the consignee.
Due to the low water content of the boiler, improper sizing of the boiler with regard to heating system load will result in excessive cycling
and accelerated component failure. HTP DOES NOT warrant failures caused by improperly sized boiler applications. DO NOT oversize
the boiler to the system. Modular boiler installations greatly reduce the likelihood of boiler oversizing.
Do not obstruct combustion and ventilating air flow. Adequate air must be provided for safe operation. Failure to keep the exhaust vent
and intake pipe clear of ice, snow, or other debris could result in property damage, serious personal injury, or death.
PART 1 – GENERAL SAFETY INFORMATION
A. PRECAUTIONS
This boiler is for indoor installations only. Clearance to combustible materials: 0” top, bottom, sides and back. Front must have room for
service, 24” recommended. (A combustible door or removable panel is acceptable front clearance.) This boiler has been approved for
closet installation. Do not install this boiler directly on carpeting. Category IV vent systems only.
NOTE: When inquiring about service or troubleshooting, reference the model and serial numbers from the boiler rating label.
7
B. IMPROPER COMBUSTION
C. GAS
Should overheating or gas supply fail to shut off, do not turn off or disconnect electrical supply to circulator. Instead, shut off the gas
supply at a location external to the boiler.
D. WHEN SERVICING THE BOILER
To avoid electric shock, disconnect electrical supply before performing maintenance.
To avoid severe burns, allow boiler to cool.
E. BOILER SYSTEM
Do not use petroleum-based cleaning or sealing compounds in a boiler system. Gaskets and seals in the system may be
damaged. This can result in substantial property damage.
Do not use “homemade cures” or “patent medicines”. Substantial property damage, damage to boiler, and/or serious personal
injury may result.
Page 8
NEVER use any toxic chemical, including automotive, standard glycol antifreeze, or ethylene glycol made for hydronic (non-potable)
systems. These chemicals can attack gaskets and seals in boilers, are poisonous if consumed, and can cause injury or death.
Consider piping and installation when determining boiler location.
Continual fresh make-up water will reduce boiler life. Mineral buildup reduces heat transfer, overheats the stainless steel heat
exchanger, and causes failure. Addition of oxygen by make-up water can cause internal corrosion in system components.
Leaks in the boiler or piping must be repaired at once.
If you have an old system with cast iron radiators, thoroughly flush the system (without boiler connected) to remove sediment.
The high-efficiency heat exchanger can be damaged by build-up or corrosion due to sediment.
NOTE: Damages resulting from incorrect installation or from use of products not approved by HTP, Inc. ARE NOT covered by warranty.
F. WATER CHEMISTRY*
Sodium less than 20mGL.
Water pH between 6.0 and 8.0
o Maintain water pH between 6.0 and 8.0. Check with litmus paper or have it chemically analyzed by water treatment
company.
o If the pH differs from above, consult local water treatment company for treatment needed.
Hardness less than 7 grains
o Consult local water treatment companies for unusually hard water areas (above 7 grains hardness).
Chlorine concentration less than 100 ppm
o Using chlorinated fresh water should be acceptable as levels are typically less than 5 ppm.
o Do not connect the boiler to directly heat swimming pool or spa water.
o Do not fill boiler or operate with water containing chlorine in excess of 100 ppm.
*NOTE: It is recommended to clean heat exchanger at least once a year to prevent lime scale buildup. To clean the heat
exchanger, follow the maintenance procedure in Part 15, Section B of this manual.
Hardness: 7 grains
Chloride levels: 100 ppm
pH levels: 6-8
TDS: 2000 ppm
Sodium: 20 mGL
8
G. WINTERIZING
To winterize the boiler, drain the entire system. Then apply air pressure to the drain valve and allow air and water to escape from the
purge valve (see piping instructions).
Once you have evacuated as much water as possible, pump non-toxic, NSF food grade propylene glycol, FDA rated as GRAS
(Generally Recognized As Safe), into the system. Consult the glycol manufacturer for specific instructions on concentration percentage
as well as freeze and burst protection methods. Check the volume and concentration of antifreeze to assure protection is adequate to
protect the entire system from freezing. When pumping, allow air and remaining water to escape from purge valve. When the stream
coming out of the purge valve matches the color of the non-toxic glycol, the system is adequately filled.
Finally, it is recommended to start the circulation pump and allow the system to circulate for at 30 minutes to completely blend any
trapped water that might be in the system with the glycol.
PART 2 – BEFORE YOU START
A. WHAT’S IN THE BOX
Also included with the boiler:
Temperature and Pressure Relief Valve
Pressure and Temperature Gauge
Intake PVC Tee with Screens
Exhaust PVC Coupling with Screens
Installation Manual
Warranty
Page 9

B. HOW THE BOILER OPERATES
Modulation Condensing Technology is an intelligent system that delivers highly efficient hydronic heating, while maximizing
efficiency by measuring the data parameters of your system.
Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger
The highly efficient and durable stainless steel heat exchanger is designed to extract the last bit of energy from flue gas before it is
exhausted.
Modulating Combustion System
Modulation during operation is based on supply temperature and desired temperature set point. The set point used for the control
depends upon the programmed central heating curve. The heating curve slope can be changed by the installer to better fit system
needs. The control monitors the system to regulate burner output during operation to match system demand. This increase in efficiency
allows for substantial fuel savings.
Gas Valve
The gas valve senses suction from the blower, allowing gas to flow only if the gas valve is energized and combustion air is flowing.
Supply Water Temperature Sensor
This sensor monitors boiler output water temperature (system outlet/supply). The control module adjusts the boiler firing rate so the
outlet/supply temperature is correct.
Return Water Temperature Sensor
This sensor monitors the return water temperature (system inlet/return). The control module reduces or increases boiler input,
depending on how close the inlet/return water temperature is to the outlet water temperature.
Temperature and Pressure Gauge
Allows the user to monitor system temperature and pressure.
Control
The integrated control system monitors inlet/return and outlet/supply water temperature and regulates fan speed to regulate the unit’s
BTU output. This allows the unit to deliver the required amount of heated energy and nothing more.
Burner
Constructed of high grade stainless steel, the burner uses pre-mixed air and gas and provides a wide range of firing rates.
Electrical Field Connections with Terminal Strips
The electrical cover plate allows access to the line voltage and low voltage terminal strips. Attach line voltage conduits to the three
holes at the right of the line voltage terminal strip for power, CH pump and DHW pump. Route low voltage wires through the opening to
the left of the low voltage terminal strip (see Field Wiring Instructions, Part 9).
Condensate Drain Connection
As this is a condensing high efficiency appliance, the unit has a condensate removal system. Condensate is nothing more than water
vapor, derived from combustion products and similar to an automobile when it is initially started. It is very important that the condensate
line slopes away from the boiler and down to a suitable inside drain.
If the condensate outlet on the boiler is lower than the drain, you must use a condensate removal pump (kit p/n 554200 available from
HTP.) In addition, local authorities may require a condensate neutralizer to neutralize the condensate. Condensate neutralizers are
made up of lime crystals, marble or phosphate chips. Neutralizers can be purchased from HTP (p/n 7450P-218).
It is also very important not to expose the condensate line to freezing temperatures or any type of blockage. Plastic tubing must be the
only material used for the condensate line. Steel, brass, copper or other materials will be subject to corrosion or deterioration. A second
vent may be necessary to prevent condensate line vacuum lock on a long horizontal run. Also, an increase in pipe size may be
necessary to allow condensate to drain properly. Support of the condensation line may be necessary to avoid blockage of the
condensate flow.
Spark Ignition
The burner flame is ignited by applying a high voltage to the system spark electrode. This causes a spark from electrode to ground.
The Vision 1 Optional System
By controlling the temperature delivered to the central heating circuits based on outside temperature, the Vision 1 System allows the
installer to take this highly efficient boiler and make it even more efficient. The Vision 1 System is a two temperature system, using one
temperature for central heating and the other for use with an indirect water heater. This allows the user to increase the temperature
supplied to the indirect water heater to get a faster recovery by prioritizing the flow at a higher temperature than may be needed for the
central heating circuits (this requires two separate circulators). You must follow the piping, wiring, and programming instructions located
in the Vision One section of this manual.
9
Page 10
Carefully consider installation when determining boiler location. Please read the entire manual before attempting installation. Failure to
properly take factors such as boiler venting, piping, condensate removal, and wiring into account before installation could result in
wasted time, money, and possible property damage and personal injury.
Incorrect ambient conditions can lead to damage to the heating system and put safe operation at risk. Ensure that the boiler installation
location adheres to the information included in this manual. Failure to do so could result in property damage, serious personal injury, or
death.
Failure of boiler or components due to incorrect operating conditions IS NOT covered by product warranty.
The service life of the boiler’s exposed metallic surfaces, such as the casing, as well as internal surfaces, such as the heat exchanger,
are directly influenced by proximity to damp and salty marine environments. In such areas, higher concentration levels of chlorides from
sea spray coupled with relative humidity can lead to degradation of the heat exchanger and other boiler components. In these
environments, boilers must not be installed using direct vent systems which draw outdoor air for combustion. Such boilers must be
installed using room air for combustion. Indoor air will have a much lower relative humidity and, hence, potential corrosion will be
minimized.
This boiler is certified for indoor installations only. Do not install the boiler outdoors. Failure to install this boiler indoors could result in
substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
C. OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT
Below is a list of optional equipment available from HTP:
Indirect Tank Sensor (Part # 7250P-325)
Outdoor sensor (Part # 7250P-319)
2” Stainless Steel Outside Termination Vent Kit (V500)
3” Stainless Steel Outside Termination Vent Kit (V1000)
2” PVC Concentric Vent Kit (Part # KGAVT0501CVT)
3" PVC Concentric Vent Kit (Part # KGAVT0601CVT)
3” Polypro Vent Kit (Part # 8400P-001)
3” Polypro Pipe (33’ length Part # 8400P-002, 49.5’ length Part # 8400P-003)
U.L. 353 Compliant Low Water Cut-Off Interface Kit with Manual Reset (Part # 7450P-225)
Alarm System (Part # 7350P-602) (to monitor any failure)
Condensate Pump (Part # 554200)
Condensate Neutralizer (Part # 7450P-218)
Vision 1 Outdoor Sensing System (Part # 7250P-622)
These additional options may be purchased through your HTP distributor.
PART 3 – PREPARE BOILER LOCATION
10
A. BEFORE LOCATING THE BOILER
1. Installation Area (Mechanical Room) Operating Conditions
Ensure ambient temperatures are higher than 32oF/0oC and lower than 104oF/40oC.
Prevent the air from becoming contaminated by the products, places, and conditions listed in this manual, Part 3, Section F.
Avoid continuously high levels of humidity
Never close existing ventilation openings
2. Check for nearby connections to:
System water piping
Venting connections
Gas supply piping
Electrical power
Page 11

11
Failure to keep boiler area clear and free of combustible materials, liquids, and vapors can result in substantial property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
Condensate drain
3. Check area around boiler. Remove any combustible materials, gasoline, and other flammable liquids.
4. Gas control system components must be protected from dripping water during operation and service.
5. If the boiler is to replace an existing boiler, check for and correct any existing system problems, such as:
System leaks
Location that could cause the system and boiler to freeze and leak.
Incorrectly-sized expansion tank
6. Clean and flush system when reinstalling a boiler.
NOTE: When installing in a zero clearance location, it may not be possible to read or view some product labeling. It is recommended to
make note of the boiler model and serial number.
Page 12
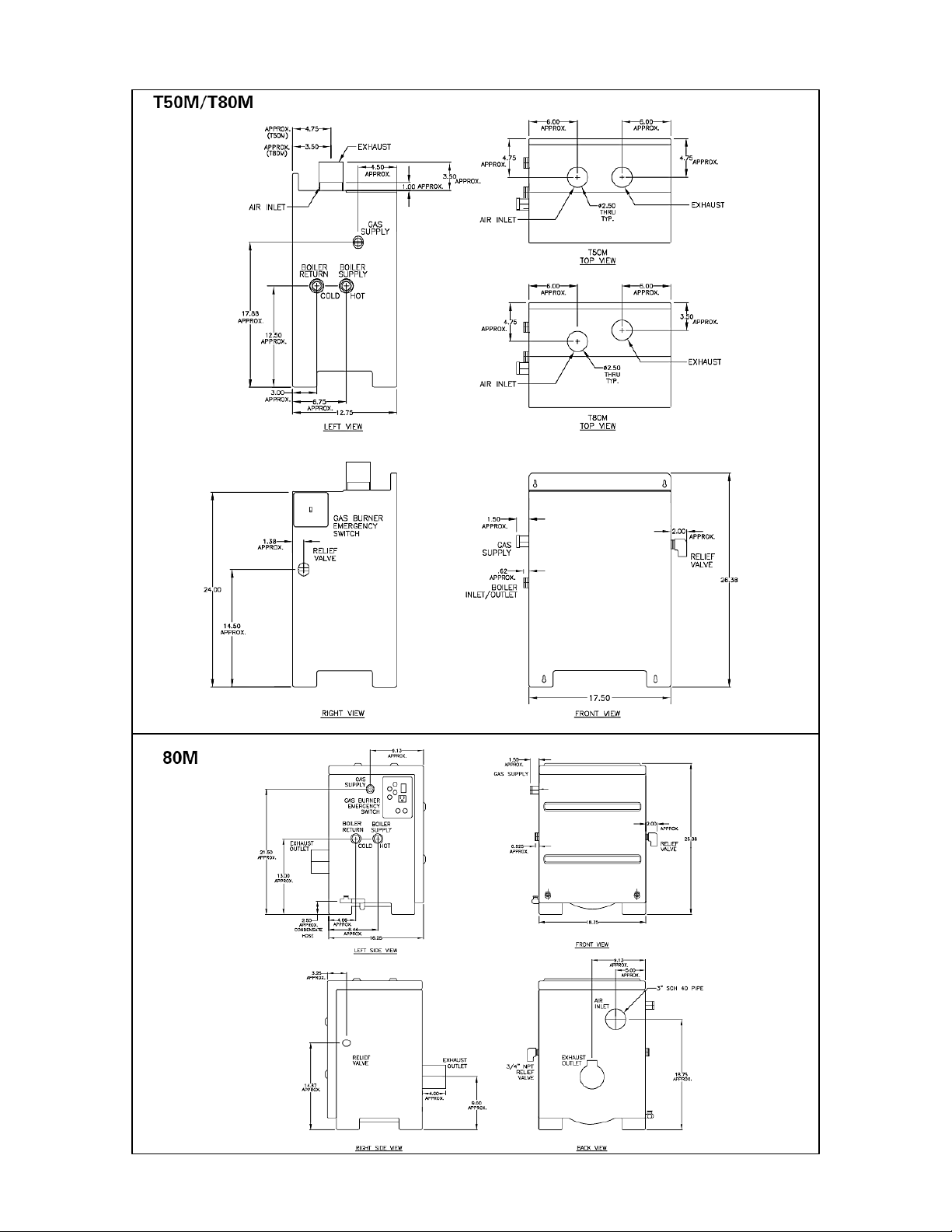
12
Figure 1 – Dimensions – T-50M / T-80M / 80M
Page 13
13
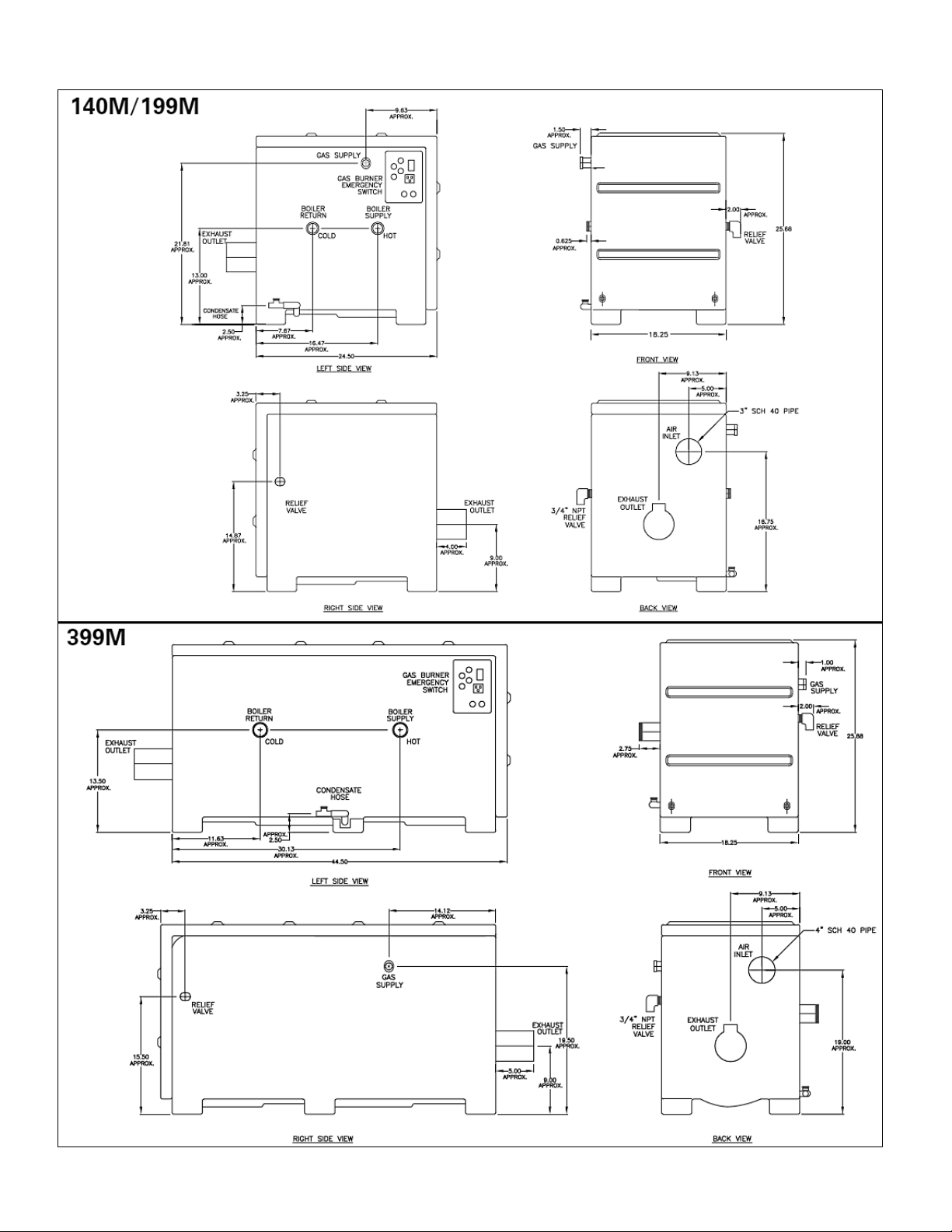
Figure 2 – Dimensions - 140M / 199M / 399M
Page 14
14
In order for the condensate to properly flow out of the collection system, the boiler must be installed with 1/8” per foot pitch toward the
back. The location must also support the boiler when it is full of water. The boiler comes equipped with leveling feet. Should the floor
beneath the boiler be uneven, use a wrench to adjust the feet so the boiler is pitched back at 1/8” per foot.
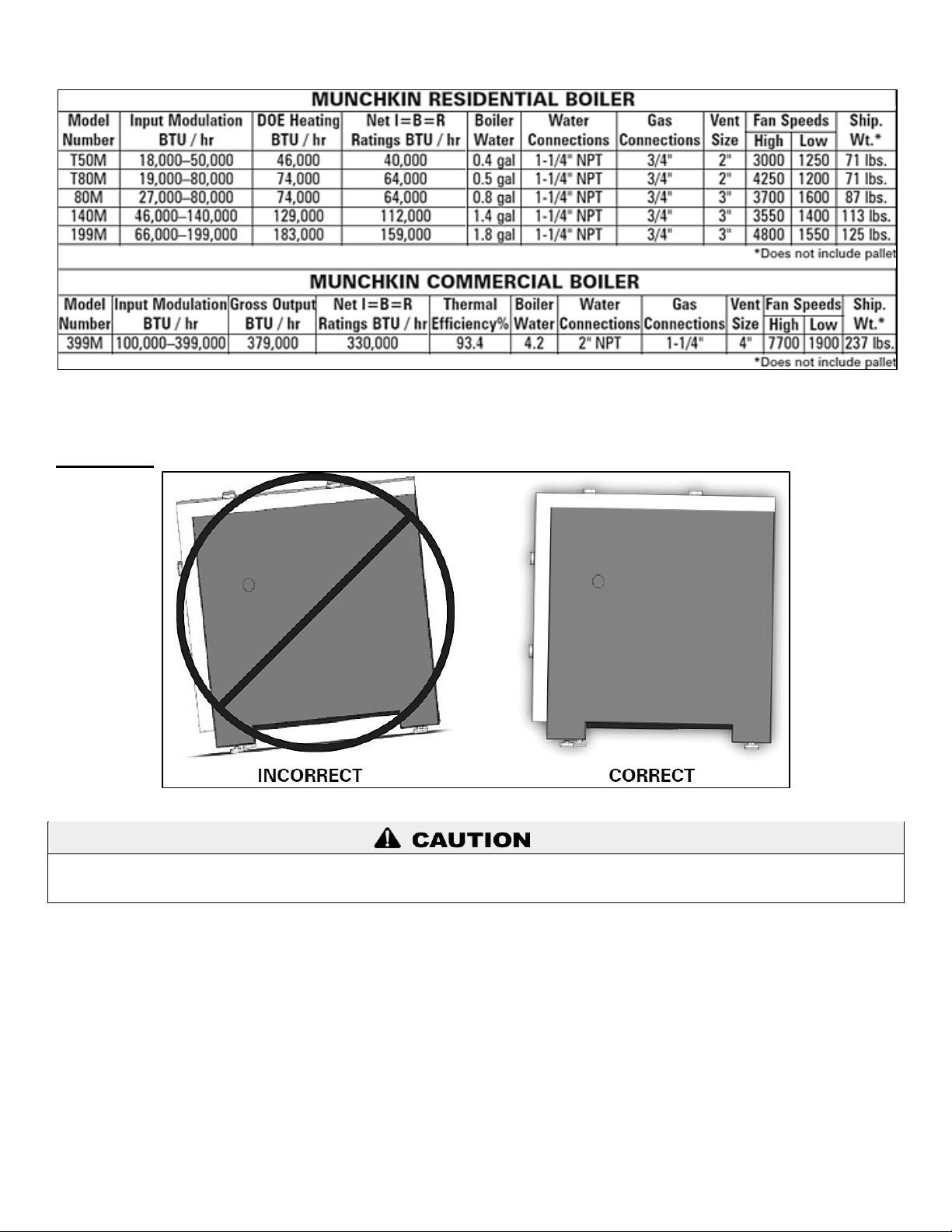
Table 1 – Specifications
Before considering location, many factors need to be addressed. Piping, Venting, and Condensation Removal are just a few of the
issues that need attention prior to the installation of the boiler. Please read the entire manual, as it could save time and money.
B. LEVELING
Figure 3 – Boiler Leveling
Page 15
Check with your local Authority Having Jurisdiction for
requirements when installing boiler in a garage, closet, or
alcove. Please read the entire manual before attempting
installation. Failure to properly take factors such as boiler
venting, piping, condensate removal, and wiring into
account before installation could result in wasted time,
money, and possible property damage and personal
injury.
For closet or alcove installations, a two pipe venting system must be used. Failure to follow this warning could result in substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
The space must be provided with correctly sized combustion/ventilation air openings for all other appliances located in the space with
the boiler. Do not install the boiler in an attic. Failure to comply with these warnings could result in substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
Vents must be properly supported. Boiler exhaust and intake connections are not designed to carry heavy weight. Vent support
brackets must be within 1’ of the boiler and the balance at 4’ intervals. Boiler must be readily accessible for visual inspection for the first
3’ from the boiler.
Space must be provided with combustion/ventilation air
openings correctly sized for all other appliances located in
the same space as the boiler. The boiler cover must be
securely fastened to prevent the boiler from drawing air
form the boiler room. This is particularly important if the
boiler is in a room with other appliances. Failure to comply
with the above warnings could result in substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
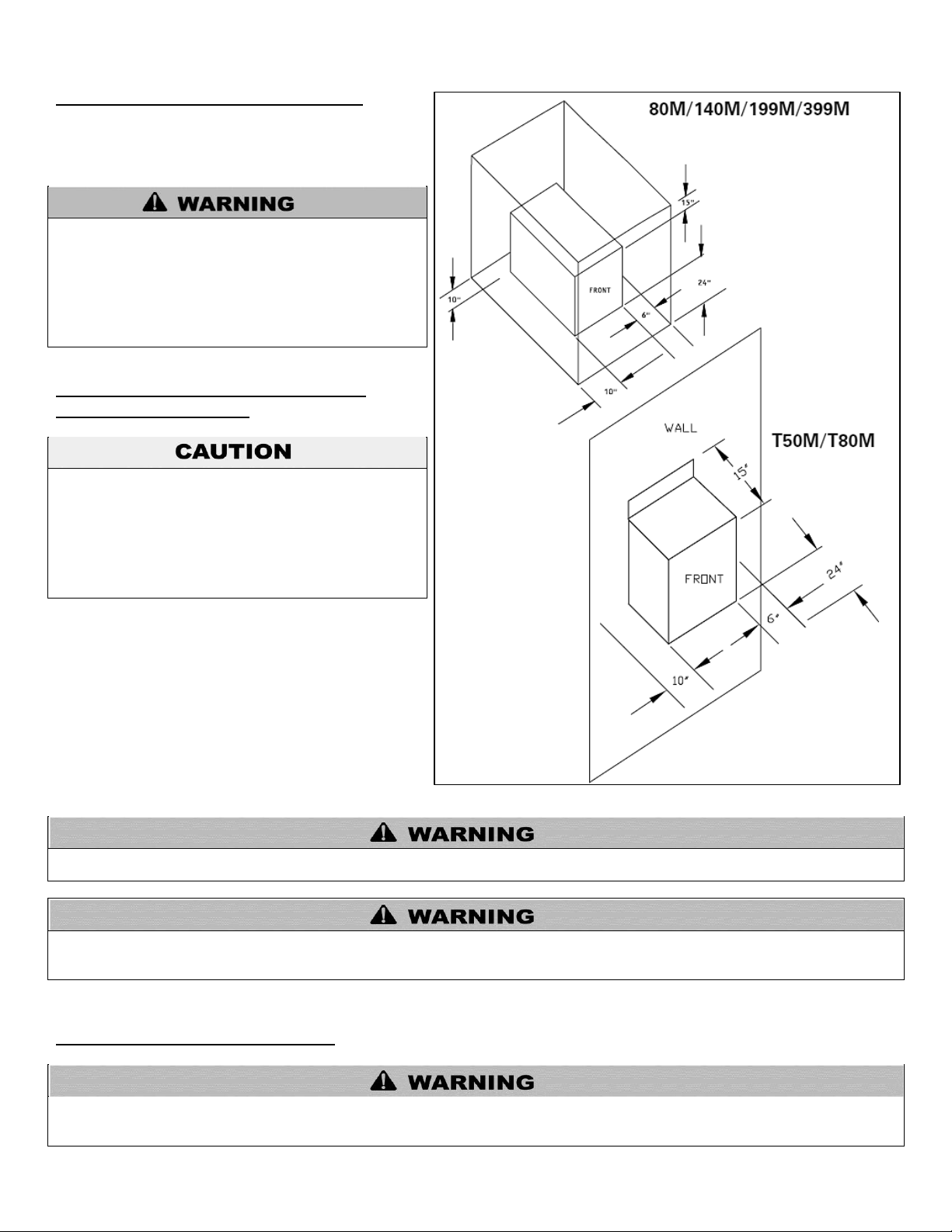
C. CLEARANCES FOR SERVICE ACCESS
See Figure 4 for recommended service clearances. If you
do not provide the minimum clearances shown, it may not
be possible to service the boiler without removing it from
the space.
D. RESIDENTIAL GARAGE, CLOSET, AND
ALCOVE INSTALLATIONS
15
PRECAUTIONS
If the boiler is located in a residential garage, per ANSI
Z223.1:
Mount the bottom of the boiler a minimum of 18”
above the floor of the garage, to ensure the
burner and ignition devices are well off the floor.
Locate or protect the boiler so it cannot be
damaged by a moving vehicle.
Figure 4 – Required Clearances
NOTE: For installations using room air for combustion, refer to the boiler venting section, Part 6 in this manual.
E. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE
Page 16

PRODUCTS TO AVOID
AREAS LIKELY TO HAVE CONTAMINANTS
Spray cans containing fluorocarbons
Dry cleaning/laundry areas and establishments
Permanent wave solutions
Swimming pools
Chlorinated waxes/cleaners
Metal fabrication plants
Chlorine-based swimming pool chemicals
Beauty shops
Calcium chloride used for thawing
Refrigeration repair shops
Sodium chloride used for water softening
Photo processing plants
Refrigerant leaks
Auto body shops
Paint or varnish removers
Plastic manufacturing plants
Hydrochloric or Muriatic acid
Furniture refinishing areas and establishments
Cements and glues
New building construction
Antistatic fabric softeners used in clothes dryers
Remodeling areas
Chlorine-type bleaches, laundry detergents, and cleaning solvents
Garages and workshops
Adhesives used to fasten building products
You must pipe outside air to the boiler air intake. Ensure that the intake air will not contain any of the contaminants listed in Table 2. For
example, do not pipe intake air near a swimming pool. Also, avoid areas subject to exhaust fumes from laundry facilities. These areas
always contain contaminants. Contaminated air will damage the boiler, resulting in possible substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
Do not install the boiler into a common vent with any other
appliance. This will cause flue gas spillage or appliance
malfunction, resulting in possible substantial property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
Failure to follow all instructions can result in flue gas spillage and
carbon monoxide emissions, causing severe personal injury or
death.
NOTE: DAMAGE TO THE BOILER CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO CORROSIVE VAPORS IS NOT COVERED BY WARRANTY.
(Refer to the limited warranty for complete terms and conditions).
Figure 5
The boiler is rated ANSI Z21.13 Category IV (pressurized vent, likely to form condensate in the vent) and requires a special vent
system designed for pressurized venting.
You must also install intake piping from outdoors to the boiler flue adaptor. The resultant installation is categorized as direct vent
(sealed combustion). NOTE: To prevent combustion air contamination, see Table 2.
Exhaust and intake must terminate near each other and may be vented vertically through the roof or out a side wall. Exhaust vent and
intake piping methods are detailed in the Venting Section. Do not attempt to install the boiler using any other means. Be sure to locate
the boiler such that the exhaust vent and intake piping can be routed through the building and properly terminated. The exhaust vent
and intake piping lengths, routing and termination method must all comply with the methods and limits given in the venting section.
F. PREVENT COMBUSTION AIR CONTAMINATION
Install intake air piping for the boiler as described in the Venting section. Do not terminate exhaust in locations that can allow
contamination of intake air.
16
Table 2 - Contaminant Table
G. REMOVING AN EXISTING BOILER FROM AN EXISTING COMMON VENT SYSTEM
When removing an existing boiler, follow the steps below with each
appliance remaining connected to the common venting system in
operation, while other appliances remaining connected to common
venting system are not operating.
1. Seal any unused openings in the common venting system.
2. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and horizontal
pitch to determine if there is blockage, leakage, corrosion or other
Page 17

17
UNCRATING BOILER – Any claims for damage or shortage in shipment must be filed immediately against the transportation company
by the consignee.
COLD WEATHER HANDLING – If the boiler has been stored in a very cold location (BELOW 0oF) before installation, handle with care
until the plastic components come to room temperature.
The wall must be capable of carrying the weight of the boiler and its related components. The weights of the boilers are approximately:
T50M – 71 lbs.
T80M – 74 lbs.
Failure to comply with above could result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
It is recommended and safer to wall mount the boiler with two people. Use caution as to not drop the boiler, which could damage it and
cause property damage and/or personal injury. Verify that the boiler is securely mounted before leaving unsupervised. Failure to comply
with the above and properly mount the boiler could result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
deficiencies that could cause an unsafe condition.
3. If practical, close all building doors, windows and all doors between the space in which the appliance remains connected to the
common venting system located and other spaces in the building. Turn on clothes dryers and any appliances not connected to the
common venting system. Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range hoods and bathroom exhausts, at maximum speed. Do not operate
a summer exhaust fan. Close all fireplace dampers.
4. Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow the lighting instructions. Adjust the thermostat so the appliance will operate
continuously.
5. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening after 5 minutes of main burner operation. Use the flame of a match or candle or
smoke from a cigarette.
6. After it has been determined that each appliance remaining connected to common venting system properly vents when tested as
outlined, return doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and any other gas burning appliance to their previous condition of use.
7. Any improper operation of the common venting system should be corrected to conform to the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1.
When resizing any portion of the common venting system, the system should approach the minimum size as determined using the
appropriate tables in Appendix G in the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z 223.1.
PART 4 – PREPARE BOILER
A. REMOVE BOILER FROM PACKAGING
The boiler is easy to handle. Care must be taken to place it in a safe location prior to installation to prevent damage to the mechanical
connections.
B. WALL MOUNTING CONSIDERATIONS
T50M and T80M boilers may be wall mounted. Use only the wall mounting instructions included in installation envelope.
C. WALL MOUNTING INSTRUCTIONS
1. The wall must be vertically plumb and capable of carrying the weight of the boiler and its related components.
2. The building frame (studs) must be 16" on center. If not, you must use 1/2" minimum plywood 24" x 48", fastened with at least (14)
#12 x 3" (3/16" x 3") round head tapping screws to the frame of the building to provide proper support for the boiler. Alternate methods
of mounting must not be used. (ex. toggle bolts, hollow wall anchors) or any other fastener other than #12 x 3" (3/16" x 3") round head
tapping screws.
Page 18
18
If the boiler is not vertically plumb, improper and unsatisfactory operation may occur, causing excessive condensation build-up,
nuisance fault codes, and unnecessary maintenance.
Failure to follow the instructions in this section WILL VOID the warranty and may result in property damage, serious injury, or death.
The building piping system must meet or exceed the piping requirements in this manual.
Use two wrenches when tightening water piping at boiler. Use one wrench to prevent the boiler return or supply line from turning.
Failure to prevent piping connections from turning could cause damage to boiler components.
Never use dielectric unions or galvanized steel fittings when connecting to a stainless steel storage tank or boiler. Use only copper or
brass fittings. Teflon thread sealant must be used on all connections. All piping and components connected to the boiler must be
approved for potable water systems.
The National Standard Plumbing Code, the National Plumbing Code of Canada, and the Uniform Plumbing Code limit the pressure of
the heat transfer fluid to less than the minimum working pressure of the potable water system up to 30 psi maximum. The heat transfer
fluid must be water or other non-toxic fluid having a toxicity of Class 1, as listed in Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products, 5th
Edition.
3. Prior to lifting the boiler onto the wall, use the enclosed template to level and locate the 2 primary (#12 x 3" [3/16" x 3"]) round head
tapping screws, leaving about 1/4" between the screw head and the wall surface to allow for access to the keyway slot located in the
back of the boiler panel. It is extremely important that the line on the template is level when locating the first 2 screws. Failure to do so
will result in an uneven or out of level installation.
4. Remove the boiler cover. Locate the 2 keyway slots over the screws. Then lower the boiler onto the smallest part of the keyway slot.
5. Once the boiler is mounted on the first 2 screws, finish tightening the screws to the back panel. Then install the 6 additional screws of
the same size to the back panel holes. This will provide additional strength and support to the boiler.
PART 5 – BOILER PIPING
Plumbing of this product should only be done by a qualified, licensed plumber in accordance with all local plumbing codes. The boiler
may be connected to a storage tank to supply domestic hot water. HTP offers 60/80/119/175 gallon size storage tanks in either
stainless steel or glass-lined construction. These storage tanks can be directly connected to the boiler supply and return connection.
A. GENERAL PIPING INFORMATION
1. The water supply should be shut off while connecting the boiler. A manual control valve must be placed on the inlet connection to the
boiler. Unions can be used on both the hot and cold water lines for future servicing and disconnection of the unit.
2. Purge the water line to remove all debris and air. Debris will damage the water boiler.
3. If the boiler is to be used as a potable water source, it must not be connected to a system that was previously used for non-potable
purposes.
4. Ensure that the water filter on the boiler is clean and installed.
5. New plumbing typically has contamination in the lines. Please flush the system before connection.
Page 19

The boiler control module uses temperature sensors to provide both high limit protection and modulating temperature control. The
control module also provides low water protection by sensing the water pressure. Some codes/jurisdictions may require additional
external controls.
To avoid water damage or scalding due to relief valve operation:
Discharge line must be connected to relief valve outlet and run to a safe place of disposal. Terminate the discharge line in a
manner that will prevent possibility of severe burns or property damage should the relief valve discharge.
Discharge line must be as short as possible and the same size as the valve discharge connection throughout its entire length.
Discharge line must pitch downward from the valve and terminate at least 6” above the floor drain, making discharge clearly
visible.
The discharge line shall terminate plain, not threaded, with a material serviceable for temperatures of 375oF or greater.
Do not pipe discharge to any location where freezing could occur.
No shutoff valve may be installed between the relief valve and boiler or in the discharge line. Do not plug or place any
obstruction in the discharge line.
Test the operation of the relief valve after filling and pressurizing the system by lifting the lever. Make sure the valve
discharges freely. If the valve fails to operate correctly, immediately replace with a new properly rated relief valve.
Test relief valve at least once annually to ensure the waterway is clear. If valve does not operate, turn the boiler “off” and call
a plumber immediately.
Take care whenever operating relief valve to avoid scalding injury or property damage.
For boilers installed with only a pressure relief valve, the separate storage vessel must have a temperature and pressure relief
valve installed. This relief valve shall comply with Relief Valves for Hot Water Supply Systems, ANSI Z21.22 / CSA4.4.
FAILURE TO COMPLY WITH THE ABOVE GUIDELINES COULD RESULT IN FAILURE OF RELIEF VALVE OPERATION,
RESULTING IN POSSIBILITY OF SUBSTANTIAL PROPERTY DAMAGE, SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH.
Hot water outlet pipes can be hot to touch. Insulation must be used for hot water pipes below 36” to protect children against injuries due
to scalds.
APPROXIMATE TIME / TEMPERATURE RELATIONSHIPS IN SCALDS
120oF
More than 5 minutes
125oF
1 ½ to 2 minutes
130oF
About 30 seconds
135oF
About 10 seconds
140oF
Less than 5 seconds
145oF
Less than 3 seconds
150oF
About 1 ½ seconds
155oF
About 1 second
Table 3
B. RELIEF VALVE
The relief valve must comply with the standard for Relief Valves and Automatic Gas Shutoff Devices for Hot Water Supply Systems
(ANSI Z21.22) and/or the standard Temperature, Pressure, Temperature and Pressure Relief Valves and Vacuum Relief Valves,
CAN1-4.4, as well as all local codes. In addition, the relief valve must be rated to the maximum BTU/hr rating of the boiler.
The American National Standard (ANSI Z21.10.3) / Canadian Standard (CSA 4.3) do not require a combination temperature and
pressure relief valve for this boiler. However, a combination temperature and pressure relief valve may be required by local codes.
Connect discharge piping to safe disposal location. See the following guidelines.
19
NOTE: If a relief valve discharges periodically, this may
be due to thermal expansion in a closed water supply
system. DO NOT PLUG THE RELIEF VALVE. An
expansion tank may be required.
Page 20
20
All piping methods shown in this manual use primary/secondary connection to the boiler loop. This is to avoid the possibility of noise or
actuator problems in zone valves because of the high-head boiler circulator. For other piping methods, consult your local HTP
representative or refer to separate piping details in this manual.
Expansion tanks must be sized according to total system volume. This includes all length of pipe, all fixtures, appliances, etc. Failure to
properly size system expansion could result in wasted time, money, and possible property damage, personal injury, or death.
Undersized expansion tanks cause system water to be lost from relief valve and make-up water to be added through fill valve. Eventual
failure can result due to excessive make-up water addition. SUCH FAILURE IS NOT COVERED BY WARRANTY.
DO NOT install automatic air vents on closed-type expansion tank systems. Air must remain in the system and return to the tank to
provide its air cushion. An automatic air vent would cause air to leave the system, resulting in water-logging the expansion tank.
DO NOT use the boiler circulator in any location other than the ones shown in this manual. The boiler circulator is selected to ensure
adequate flow through the boiler. Failure to comply could result in unreliable performance and nuisance shut downs from insufficient
flow.
C. SEPARATE LOW WATER CUTOFF
A low water cutoff may be required by state and local codes, or by some insurance companies. A low water cutoff is also required if the
boiler is installed above the piping level. Check code requirements before installing the boiler.
If required:
Use an electrode probe type low water cutoff designed for hydronic installations.
Install in a tee on the supply piping above the boiler.
Follow low water cutoff manufacturer’s instructions.
D. BACKFLOW PREVENTER
Use a backflow preventer specifically designed for hydronic boiler installations. This valve should be installed on the cold water fill
supply line per local codes. (See piping details at the end of this section.)
E. SYSTEM WATER PIPING METHODS
EXPANSION TANK AND MAKE-UP WATER
1. Ensure expansion tank size will handle boiler and system water volume and temperature. Allow 3 gallons for the boiler and its piping;
4 gallons for 399 models and piping.
2. Expansion tank must be located as shown in Piping diagrams, or following recognized design methods. See tank manufacturer’s
instructions for details.
3. Connect the expansion tank to the air separator only if the separator is on the suction side of the circulator. Always install the system
fill connection at the same point as the expansion tank connection to the system.
4. Most chilled water systems are piped using a closed type expansion tank.
DIAPHRAGM (OR BLADDER) EXPANSION TANK
Always install an automatic air vent on top of the air separator to remove residual air from the system.
F. CIRCULATORS
SIZING SPACE HEAT SYSTEM PIPING
1. See Piping Details in this section. In all diagrams, the space heating system is isolated from the heating loop by the
primary/secondary connection.
2. Size the piping and components in the space heating system using recognized design methods.
Page 21
21
The boiler should not be operated as a potable hot water boiler. Operating this boiler as a potable water boiler will VOID warranty.
G. HYDRONIC PIPING WITH CIRCULATORS, ZONE VALVES, AND MULTIPLE BOILERS
This boiler may function in a closed loop 15 psi system. A factory installed water pressure switch ensures adequate pressure in the
system. The boiler will not operate without a minimum of 10 psi water pressure. This assures you that if the system does have a leak,
the boiler will lock out (PRO on the display) before it damages the heat exchanger.
The included temperature and pressure gauge allows the user to monitor the system pressure and outlet temperature from the boiler. It
is important to note that the boiler has a minimal amount of pressure drop that must be calculated when sizing the circulators. Each
installation must also have an air elimination device that will remove air from the system.
Install the boiler so the gas ignition components are protected from water (dripping, spraying, etc.), and allow clearance for basic
service of the circulator, valves, and other components. Observe minimum 1” clearance around all un-insulated hot water pipes when
openings around pipes are not protected by noncombustible materials. On a boiler installed above radiation level, some states and local
codes require a low water cut off device (See Part C this section). If the boiler supplies hot water to heating coils in air handler units,
flow control valves or other devices must be installed to prevent gravity circulation of boiler water in the coils during the cooling cycle.
Chilled water medium must be piped in parallel with the boiler.
Freeze protection for new or existing systems must use glycol specifically formulated for hydronic systems that includes inhibitors to
prevent the glycol from attacking the metallic system components. The system should be check annually, and as recommended by the
glycol producer, to ensure that the system is operating with the correct glycol concentration and inhibitor level. Allowances should be
made for the expansion of glycol solution in the system, as 50% by volume glycol solution expands 4.8% in volume when increasing in
temperature from 32oF to 180oF, while water expands 3% over the same temperature rise.
The basic steps listed below provide a basic installation guide for the boiler.
1. Connect the system return marked “Boiler In”.
2. Connect the system supply marked “Boiler Out”.
3. Install purge and balance valve or shut off valve and drain on system return to purge air out of each zone.
4. Install a back flow preventer on the cold feed make-up water line.
5. Install a pressure reducing valve on the cold feed make-up water line, (15 psi nominal on the system return). Check temperature and
pressure gauge, which should read minimum pressure of 12 psi.
6. Install a circulator as shown in piping details (this section). Make sure the circulator is properly sized for the system and friction loss.
7. Install an expansion tank on the system supply. Consult the tank manufacturer’s instruction for specific information relating to
expansion tank installation. Size the expansion tank for the required system volume and capacity.
8. Install an air elimination device on the system supply.
9. Install a drain valve at the lowest point of the system. NOTE: The boiler cannot be drained completely of water without purging the
unit with an air pressure 15 psi.
10. The safety relief valve is installed at the factory. Pipe the discharge of the safety relief valve to prevent injury in the event of
pressure relief. Pipe the discharge 6” above the drain to a drain. Provide piping that is the same size as the safety relief valve outlet.
Never block the outlet of safety relief valve.
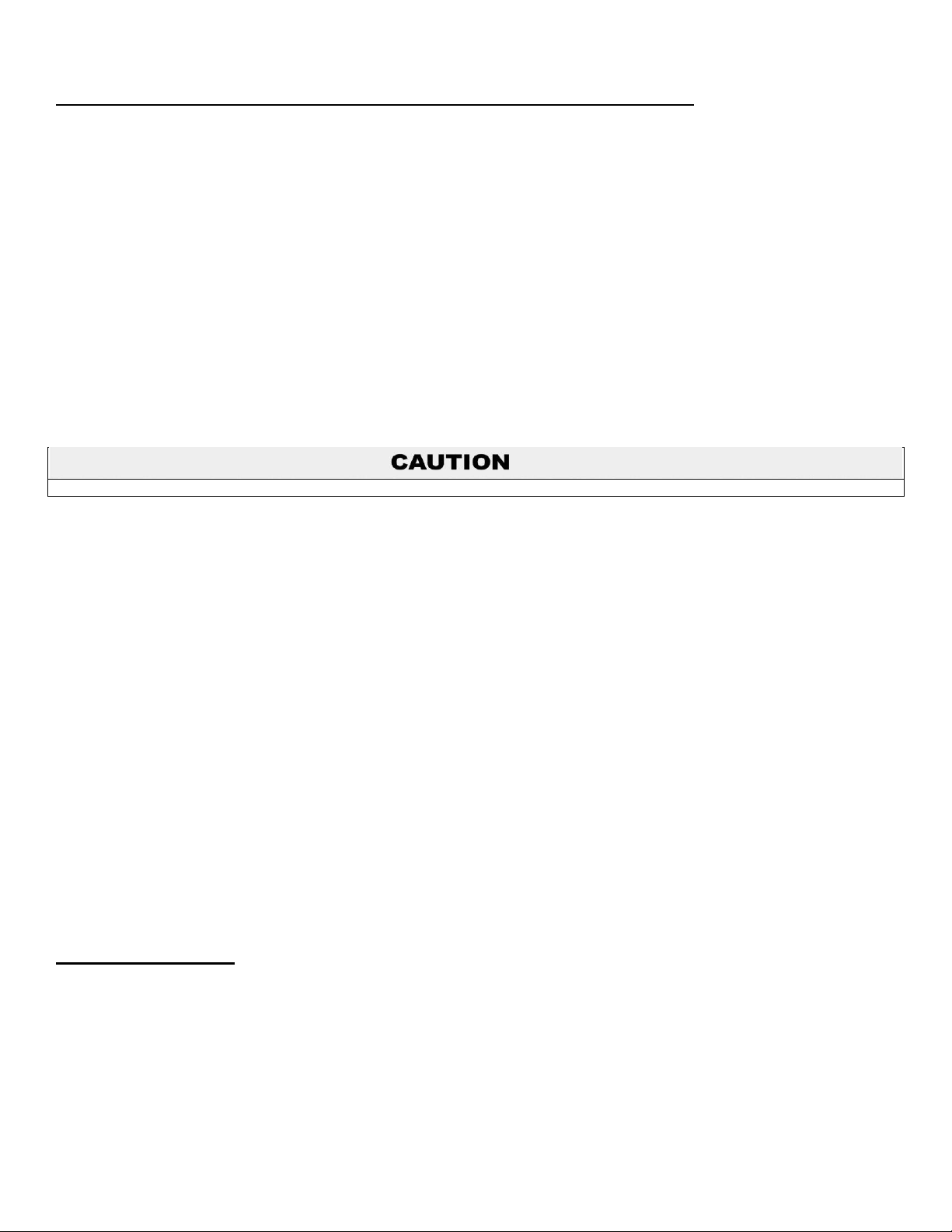
H. CIRCULATOR SIZING
The heat exchanger has pressure drop which must be considered in your system design. Refer to the graph in Figure 6 for pressure
drop through the heat exchanger for recommended pump selection at a 20∆t design.
The chart below represents various system temperatures and their respective flows and friction loss through the boiler, which will aid
circulator selection.
Page 22
22
Figure 6 – Pressure Drop Graph and Temperature Rise Chart – LP-171-F NOTE: The recommended circulators are based on 1 gpm per 10,000
btu/hr with 20∆t.
The chart below represents various system temperatures, respective flows and friction loss through the boiler to aid in circulator
selection.
I. ZONING WITH ZONE VALVES
1. Connect boiler to system as shown in 2A and 2B in Piping Details when zoning with zone valves. The primary/secondary piping
shown ensures the boiler loop will have sufficient flow. It also avoids applying the high head of the boiler circulator to the zone valves.
Page 23
For installations that incorporate standing iron radiation and systems with manual vents at the highest points: Follow the
above section and, starting with the nearest manual vent, open until water flows out. Then close vent. Repeat procedure, working your
way toward furthest air vent. It may be necessary to install a basket strainer in an older system where larger amounts of sediment may
be present. Annual cleaning of the strainer may be necessary.
Use only inhibited propylene glycol solutions, specially formulated for hydronic systems. Ethylene glycol is toxic and can attack gaskets
and seals used in hydronic systems. Glycol mixtures should not exceed 50%.
It is highly recommended that you carefully follow the glycol manufacturer’s concentrations, expansion requirements, and maintenance
recommendations (pH additive breakdown, inhibitor reduction, etc.) You must carefully figure the additional system friction loss, as well
as the reduction in heat transfer coefficients.
2. Connect DHW (domestic hot water) piping to indirect storage water heater as shown.
J. ZONING WITH CIRCULATORS
1. Connect boiler to system when circulator zoning as shown in 2C and 2D in Piping Details when zoning with circulators. The boiler
circulator cannot be used for a zone. It must supply only the boiler loop.
2. Install a separate circulator for each zone.
3. Connect DHW (domestic hot water) piping to indirect storage water boiler as shown.
K. MULTIPLE BOILERS
1. Connect multiple boilers as shown in 2E and 2F in Piping Details.
2. All piping shown is reverse return to assure balanced flow through the connected boilers.
3. Each connected boiler must have its own circulator pump to assure adequate flow.
4. Connect DHW (domestic hot water) piping to indirect storage water heater as shown.
L. FILL AND PURGE HEATING SYSTEM
Attach the hose to balance and purge hose connector or drain valve and run hose to nearest drain.
Close the other side of the balance and purge valve or the shut off valve after the drain.
Open first zone balance and purge or drain valve to let water flow out the hose. If zone valves are used, open the valves one
at a time manually. (NOTE: You should check valve manufacturer’s instruction prior to opening valves manually, so as not to
damage the valve.)
Manually operate fill valve regulator. When water runs out of the hose, while it’s connected to the balance and purge valve or
drain you will see a steady stream of water (without bubbles). Close balance and purge valve or drain to stop the water from
flowing. Disconnect the hose and connect it to next zone to be purged.
Repeat this procedure for additional zones (one at time).
23
Upon completion, make sure that the fill valve is in automatic position and each zone balance and purge or shut off is in an open
position and zone valves are positioned for automatic operation.
1. Glycol for hydronic applications includes inhibitors that prevent it from attacking metallic system components. Make certain that the
system fluid is checked for the correct glycol concentration and inhibitor level.
2. The glycol solution should be tested at least once a year and as recommended by the glycol manufacturer.
3. Anti-freeze solutions expand more than water. For example a 50% by volume solution expands 4.8% in volume for a temperature
increase from 32° F to 180° F, while water expands 3% with the same temperature rise. Allowances must be made for this expansion in
the system design.
4. A 30% mixture of glycol will result in 15% BTU output loss and a 5% increase in head against system circulator.
5. A 50% mixture of glycol will result in 30% BTU output loss and a 50% increase in head against system circulator.
Page 24
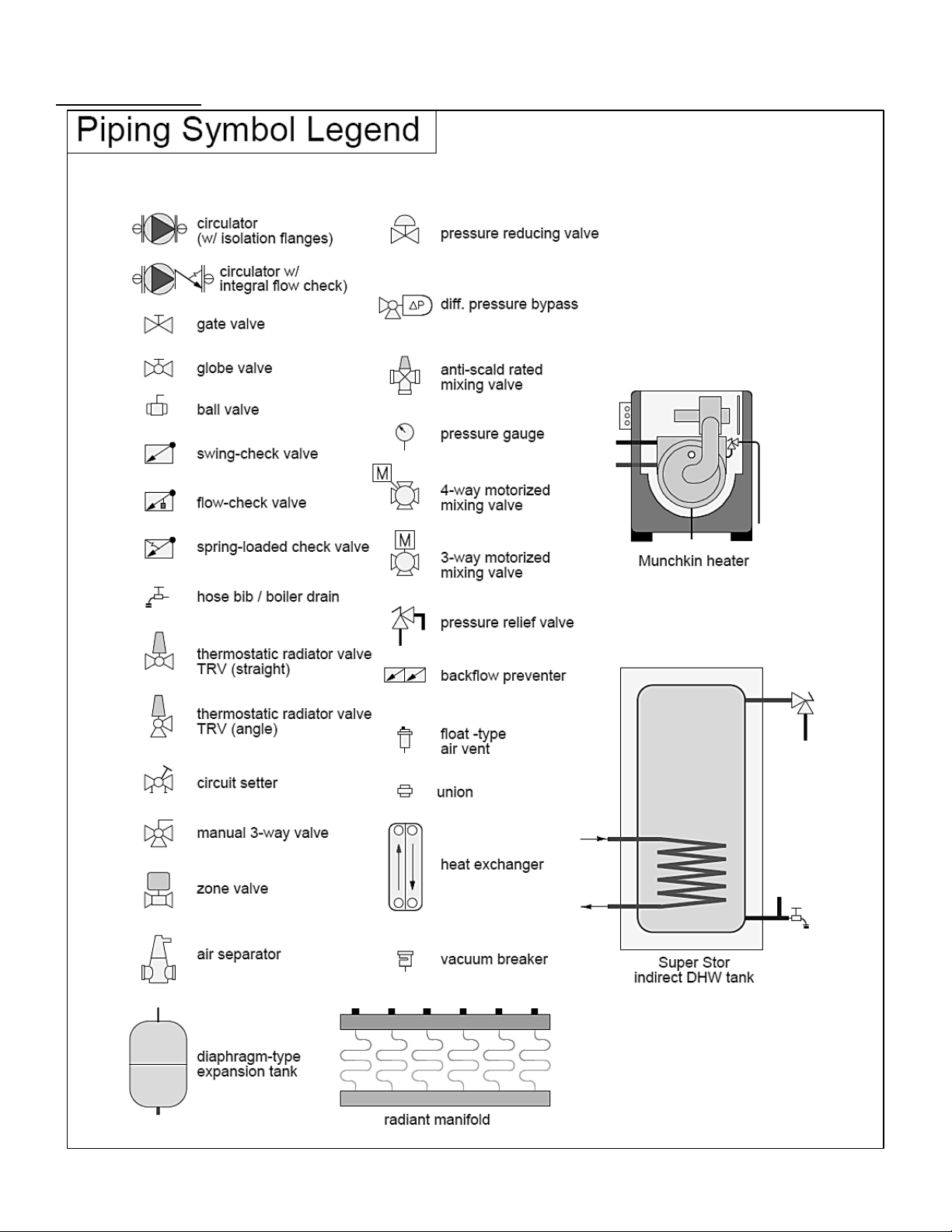
M. PIPING DETAILS
24
Figure 7
Page 25
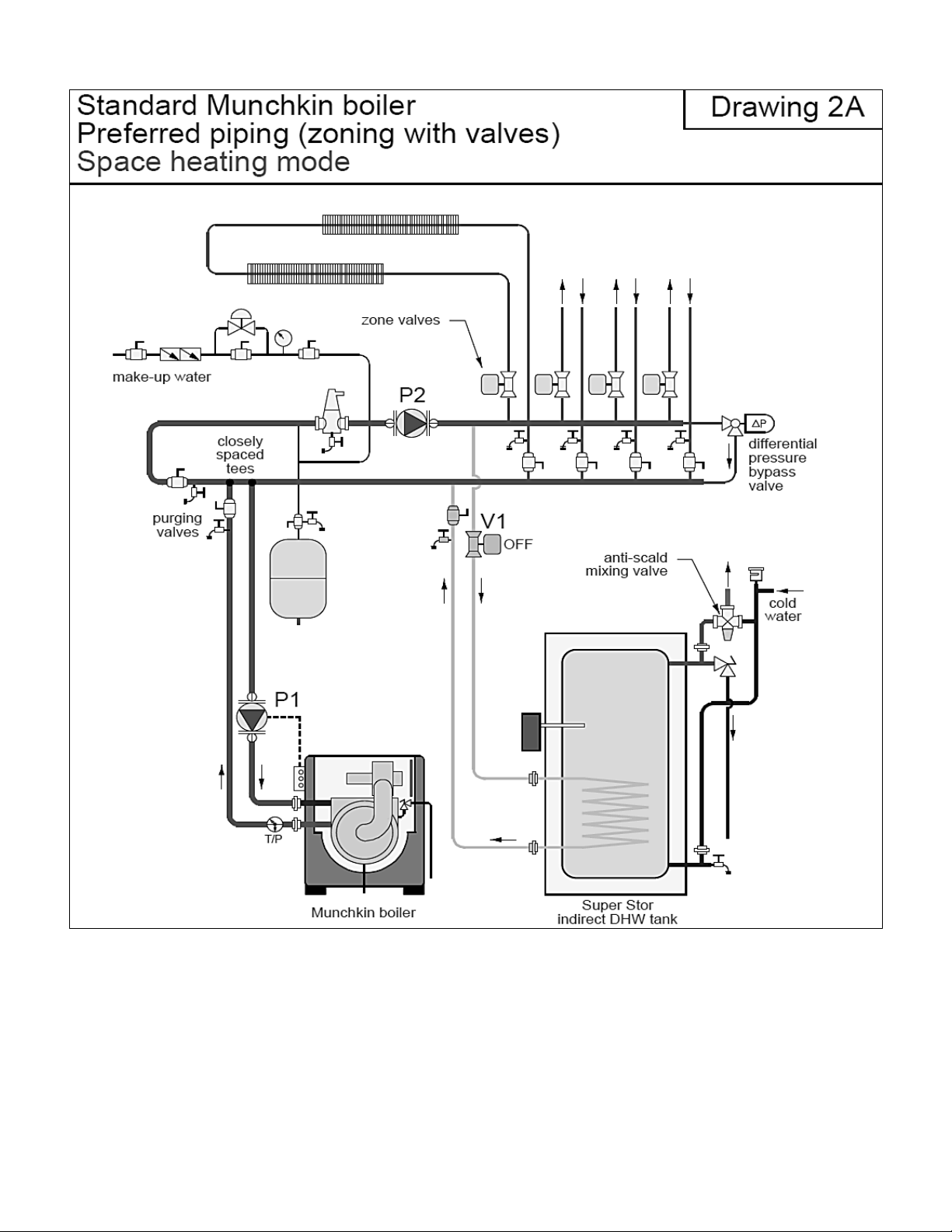
25
Figure 8
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water boiler is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
NOTE: For Vision piping applications, refer to the Vision Installation Piping Diagrams.
Page 26

26
Figure 9
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
NOTE: For Vision piping applications, refer to the Vision Installation Piping Diagrams.
Page 27

27
Figure 10
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
NOTE: For Vision piping applications, refer to the Vision Installation Piping Diagrams.
Page 28

28
Figure 11
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
NOTE: For Vision piping applications, refer to the Vision Installation Piping Diagrams.
Page 29

29
Figure 12
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
NOTE: For Vision piping applications, refer to the Vision Installation Piping Diagrams.
Page 30

30
Figure 13
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
NOTE: For Vision piping applications, refer to the Vision Installation Piping Diagrams.
Page 31

31
PART 6 – PIPING WITH OPTIONAL VISION 1 SYSTEM
(DHW PRIORITY WITH OUTDOOR RESET)
A. VISION 1 SYSTEM PIPING
It is important that the system piping is done correctly when using the Vision 1 System. Follow the piping diagrams 3A through 4H when
piping your boiler. All general piping practices should still be maintained.
B. ZONING WITH ZONE VALVES USING VISION 1
1. Connect the boiler to the system as shown in piping details 3A through 3C.
2. Connect the DHW circulator (P2) directly to the boiler as shown in the piping details. The boiler circulator (P1) will shut down when
there is a DHW demand.
C. ZONING WITH CIRCULATORS USING VISION 1
1. Connect the boiler to the system as shown in piping details 4A through 4H.
2. Connect the DHW circulator (P2) directly to the boiler as shown in the piping details. The boiler circulator (P1) will shut down when
there is a DHW demand.
Page 32

D. PIPING DETAILS WITH THE VISION 1 SYSTEM
32
Figure 14
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 33

33
Figure 15
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 34

34
Figure 16
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
10. Adjust 3-way manually set mixing valve to yield proper supply temperature to lower temperature load.
Page 35

35
Figure 17
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 36

36
Figure 18
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 37

37
Figure 19
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 38

38
Figure 20
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 39

39
Figure 21
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
Page 40

40
Figure 22
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
10. High temperature loads cannot operate simultaneously with low temperature loads.
11. Supply water temperature to high temperature loads is not reset based on outdoor temperature.
12. Domestic water heating is highest priority load, and controlled through priority zone of multi-zone relay center.
Page 41

41
Figure 23
NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to demonstrate system piping concept only. Installer is responsible for all equipment and detailing required by local codes.
2. Adjust differential pressure bypass valve to eliminate any flow velocity noise when zone with highest pressure drop operates by itself.
3. The minimum pipe size for connecting an indirect water heater is 1”.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting the unit is 1.25” and 2” for the 399.
5. Circulators are shown with isolation flanges. The alternative is standard flanges with full port ball valves. Purge valves can be used with the circulator
flanges as an alternative.
6. The anti-scald mixing valve is recommended if the DHW temperature is set above the factory setting of 119oF.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators.
8. A minimum of 6 pipe diameters of straight pipe shall be installed upstream and downstream of all closely spaced tees.
9. All closely spaced tees shall be within 4 pipe diameters center to center spacing.
10. High temperature loads cannot operate simultaneously with low temperature loads.
11. Supply water temperature to high temperature loads is not reset based on outdoor temperature.
12. Domestic water heating is highest priority load, and controlled through priority zone of multi-zone relay center.
Page 42

The boiler must be vented as detailed in this Venting Section. Ensure exhaust vent and intake piping complies with these instructions
regarding vent system. Inspect finished exhaust vent and intake piping thoroughly to ensure all joints are well secured, airtight, and
comply with all applicable code requirements, as well as with the instructions provided in this manual. Failure to properly install the vent
system will result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
This boiler is certified as a “Category IV” appliance, and requires a special venting system. The vent system will operate with a positive
pressure in the pipe. Exhaust gases must be piped directly outdoors using the vent materials and rules outlined in these instructions.
Do not connect vent connectors serving appliances vented by natural draft into any portion of mechanical draft systems operating under
positive pressure. Follow the venting instructions below carefully. Failure to do so will result in substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
Exhaust vent and intake pipes are to be piped separately, and MUST exit from the same side of the building to ensure safe, correct
boiler operation. This boiler cannot share a common exhaust or intake with multiple appliances. Failure to follow this instruction will
result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Improper seating of vent pipe gaskets can cause eventual gasket failure and exhaust gas leakage. Ensure the exhaust vent pipe is
properly beveled and seated before insertion into the flue adapter. Failure to do so could result in property damage, severe personal
injury, or death.
Due to the extreme flammability of most glues, cements, solvents, and primers used to join plastic exhaust vent and intake pipes,
explosive solvent vapors must be cleared from all vent piping before start-up. Avoid using excess cement or primer, as this may pool in
the vent pipes. Vent assemblies should be allowed to cure for a period of at least 8 hours before powering a connected appliance.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death. It is the installers’
responsibility to understand the hazards associated with explosive solvents and take the necessary precautions to avoid these risks.
APPROVED EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE MATERIAL
Item
Material
Standards for Installation in:
United States
Canada*
Exhaust vent or Intake pipe
and fittings
PVC schedule 40/80
ANSI/ASTM D1785
PP, CPVC, and PVC venting
must be ULC-S636 Certified.
IPEX is an approved
manufacturer in Canada,
supplying vent material listed
to ULC-S636.
PVC-DWV*
ANSI/ASTM D2665*
CPVC schedule 40/80
ANSI/ASTM F441
Polypropylene
ULCS636
Stainless Steel AL29-4C
Certified for Category IV and
direct vent appliance venting
Certified for Category IV and
direct vent appliance venting
Pipe cement/primer
PVC
ANSI/ASTM D2564
IPEX System 636 Cements &
Primers
CPVC
ANSI/ASTM F493
PART 7 – VENTING, COMBUSTION AIR, AND CONDENSATE REMOVAL
A. GENERAL
1. Installation should be made in accordance with the regulations of the Authority Having Jurisdiction, local code authorities, and utility
companies which pertain to this type of water heating equipment.
2. Install the venting system in accordance with these instructions and with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54,
CAN/CGA B149, and/or applicable provisions of local building codes.
3. This boiler must be vented with materials, components, and systems listed and approved for Category IV appliances.
42
NOTE: To avoid contamination often contained in indoor air, it is best to pipe all intake combustion air directly to the outdoors.
B. APPROVED MATERIALS FOR EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE
Table 4
Page 43

The exhaust and intake components installed with this boiler must be used for near boiler piping BEFORE transitioning to the
approved materials listed above. DO NOT REMOVE these installed components. Doing so WILL VOID appliance warranty.
PVC/CPVC pipe and fittings of the same diameter are considered interchangeable.
Do NOT use Foam Core Pipe in any portion of the exhaust piping from this boiler.
DO NOT connect PVC/CPVC to PP without an approved vent connector.
When installing AL29-4C vent piping, install a PVC-to-stainless adapter at the boiler vent connection, and at the termination
when using an HTP PVC termination kit. DO NOT mix AL-29-4C piping from different manufacturers unless using adapters
specifically designed for the purpose by the manufacturer.
*PVC-DWV for air intake applications ONLY.
Failure to follow these directions will result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
DO NOT mix components from different venting systems. The vent system could fail, causing leakage of flue products into the living
space. Use only the approved pipe and fitting materials, and primer and cement specifically designed for the material used, as listed in
Table 4. Failure to do so could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Exhaust vent adaptors are not designed as load-bearing devices, and must not be used to support exhaust vent piping. All vent pipes
must be glued, properly supported, and the exhaust must be pitched a minimum of ¼” per foot back to the boiler to allow drainage of
condensate. Failure to properly support vent piping and follow the information in this statement could result in product damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
You must not use “B” vent in an exhaust application. “B” vent is for intake applications ONLY. Using “B” vent in an exhaust application
will result in serious injury or death.
NOTE: The use of double-wall vent or insulated material for the combustion air inlet pipe is recommended in cold climates to prevent
the condensation of airborne moisture in the incoming combustion air.
43
C. REQUIREMENTS FOR INSTALLATION IN CANADA
1. Installations must be made with a vent pipe system certified to ULC-S636. IPEX is an approved vent manufacturer in Canada
supplying vent material listed to ULC-S636. Additionally you may use AL29-4C stainless steel venting to comply with Canadian
requirements.
2. The first three (3) feet of vent pipe from the boiler flue outlet must be readily accessible for visual inspection.
3. The components of the certified vent system must not be interchanged with other vent systems or unlisted pipe / fittings.
Cellular foam core piping may be used on air inlet piping only.
D. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE LOCATION
NOTE: SEE ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR MASSACHUSETTS IN THE BACK OF THIS MANUAL.
1. DETERMINE EXHAUST VENT LOCATION
a. The vent piping for this boiler is approved for zero clearance to combustible construction.
b. See illustration within this section of clearances for location of exit terminals of direct-vent venting systems.
c. This boiler vent system shall terminate at least 3 feet (0.9 m) above any forced air intake located within 10 ft (3 m). Note:
this does not apply to the combustion air intake of a direct-vent appliance.
d. Provide a minimum of 1 foot distance from any door, operable window, or gravity intake into any building.
e. Provide a minimum of 1 foot clearance from the bottom of the exhaust above the expected snow accumulation level. Snow
removal may be necessary to maintain clearance.
f. Provide 4 feet horizontal clearance from electrical meters, gas meters, gas regulators, relief equipment, exhaust fans and
inlets. In no case shall the exit terminal be above or below the aforementioned equipment unless the 4 foot horizontal distance
is maintained.
g. Do not locate exhaust over public walkways where condensate could drip and / or freeze and create a nuisance or hazard.
h. When adjacent to a public walkway, locate exit terminal at least 7 feet above grade.
i. Do not locate the exhaust directly under roof overhangs to prevent icicles from forming.
j. Provide 4 feet clearance from the inside corner of vertical walls, chimneys, etc., as well as horizontal corners created by roof
overhangs.
Page 44

44
The building owner is responsible for keeping the exhaust and intake terminations free of snow, ice, or other potential blockages, as
well as scheduling routine maintenance. Failure to keep the vent piping terminations clear and properly maintain the boiler could result
in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
For each floor containing bedroom(s), a carbon monoxide detector and alarm shall be placed in the living area outside the bedrooms,
as well as in the room that houses the boiler. Detectors and alarms shall comply with NFPA 720 (latest edition). Failure to comply with
requirements for detectors and alarms could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
If using a condensate pump, select one approved for use with condensing boilers and furnaces. The pump should have an overflow
switch to prevent property damage from condensate spillage.
It is very important that the condensate piping be no smaller than ¾”. To prevent sagging and maintain pitch, condensate piping should
be supported with pipe supports, and pitched ¼” per foot to allow for proper drainage.
The condensate line must remain unobstructed, allowing free flow of condensate. If condensate freezes in the line, or if line is
obstructed in any other manner, condensate can exit from the tee, resulting in potential water damage to property.
2. DETERMINE INTAKE PIPE LOCATION
a. Provide 1 foot clearance from the bottom of the intake pipe and the level of maximum snow accumulation. Snow removal
may be necessary to maintain clearances.
b. Do not locate intake pipe in a parking area where machinery may damage the pipe.
c. When venting with a two pipe system, maximum distance between exhaust vent and intake pipe is 6 feet (1.8 m). Minimum
distance between exhaust vent and intake pipe on single boiler is 10” (0.255 m) center-to-center. Minimum distance between
exhaust vents and intake pipes on multiple boilers is 10” (0.255 m) center-to-center.
NOTE: Due to potential moisture build-up, sidewall venting may not be the preferred venting option. To save time and cost, carefully
consider venting installation and location.
3. Determine location of condensate piping:
This is a high efficiency boiler, and therefore produces condensate: a by-product of the combustion process. Condensate is nothing
more than water vapor derived from combustion products, and is similar to that of an automobile when it is initially started.
It is very important that the condensate line is sloped away from the boiler to a suitable drain. If the boiler condensate outlet is lower
than the drain, a condensate pump (kit p/n 554200 available from HTP) must be used.
NOTE: The use of ½” PVC or CPVC pipe are acceptable materials for condensate piping. Steel, brass, copper or other materials will be
subject to corrosion or deterioration. However, use materials approved by the authority having jurisdiction.
In the absence of other authority, PVC and CPVC pipe must comply with ASTM D1785 or D2845. Cement and primer must comply with
ASME D2564 or F493. For Canada, use CSA or ULC certified PVC or CPVC pipe, fittings, and cement. If pipe is used, deburr and
chamfer pipe to allow proper mating to the drainage assembly.
NOTE: To allow for proper drainage on long horizontal runs, a second line vent may be required and tubing size may need to increase
to 1”. Support of the condensate line may be necessary to avoid blockage of the condensate flow. Failure to add a second vacuum
break could result in condensate backup, improper boiler operation, and nuisance shutdowns.
NOTE: Check with your local gas company to determine if combustion condensate disposal is permitted in your area. In the state of
Massachusetts, condensate must be neutralized before entering a drain.
4. Condensate neutralization
Condensate from the boiler is slightly acidic with a pH of 3.2 - 4.5. To avoid long term damage to the drainage system and to meet local
code requirements, HTP recommends neutralizing the condensate with a Condensate Neutralizer Kit (p/n 7450P-218). The neutralizer
kit connects to the drain system and contains limestone chips that neutralize the pH level of the water vapor. The neutralizer kit should
be checked annually and the limestone chips replenished if necessary. When replacing the limestone chips, take care to ensure chips
are no smaller than ½” to avoid blockage in condensate piping (for piping details, refer to condensate neutralizer installation instruction.)
Page 45

FRICTION LOSS EQUIVALENT IN PIPING AND FITTINGS
FITTINGS OR PIPING
EQUIVALENT FEET
2”
3”
4”
6”
90 DEGREE ELBOW*
5’
5’
3’
3’
45 DEGREE ELBOW
3’
3’
1’
1’
COUPLING
0’
0’
0’
0’
AIR INLET TEE
0’
0’
0’
0’
STRAIGHT PIPE
1’
1’
1’
1’
CONCENTRIC VENT KIT
3’
3’
N/A
N/A
V500 2” VENT KIT
1’
N/A
N/A
N/A
V1000 3” VENT KIT
N/A
1’
1’
1’
V2000 4” VENT KIT
N/A
1’
1’
1’
VENT CONNECTION
REDUCING COUPLING
VENT TRANSITION
2”
3” X 2”
3”
3”
4” X 3”
4”
4”
6” X 4”
6”
TRANSITION POINT (FT.
FROM BOILER)
TEL OF STANDARD 2”
VENT PIPE (FT.)
TEL OF OVERSIZED 2”, 3”, OR
4” VENT PIPE (FT.)
MAXIMUM TEL OF ALL VENT
PIPE (FT.)
15
30
95
125
20
40
77-1/2
117-1/2
25
50
60-1/2
110-1/2
30
60
43
103
35
70
26
96
40
80
8-1/2
88-1/2
NONE
85 0 85
E. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE SIZING
1. The exhaust vent and intake pipe size is 2" for the T50/80, 3” for the 80/140/199M, and 4” for the 399M.
2. The total equivalent length of exhaust vent and intake pipe should not exceed 85’.
a. The equivalent length of elbows, tees, and other fittings are listed in the Friction Loss Table below:
Table 5 - *Friction loss for long radius elbow is 1 foot less. NOTE: Consult Polypropylene venting instructions for friction loss and pressure
drop equivalents.
b. For example: If the exhaust vent has two 90° elbows and 10 feet of PVC pipe we will calculate:
Exhaust Vent Equivalent Length = (2 x 5) + 10 = 20 feet.
Further, if the intake pipe has two 90° elbows, one 45° elbow and 10 feet of PVC pipe, the following calculation applies:
Intake Pipe Equivalent Length = (2 x 5) + 3 + 10 = 23 feet.
Finally, if a concentric vent kit is used we find:
Total Equivalent Length = 20 + 23 + 3 = 46 feet.
The total equivalent length is 46 feet, which is well below the maximum of 85 feet.
c. The exhaust vent and intake pipe are intended to penetrate the same wall or roof of the building.
d. Effort should be made to keep a minimum difference in equivalent length between the exhaust vent and intake pipe.
3. The minimum total equivalent length is 32 equivalent feet.
45
G. LONGER VENT RUNS
The maximum total equivalent length can be extended by increasing the diameter of both exhaust vent and intake pipe equally.
However, the transitions should begin a minimum of 15 equivalent feet from the boiler.
a. Transitions should always be made in vertical sections of pipe to prevent the condensate from pooling in the vent pipe.
b. The maximum equivalent length for increased diameter vent pipes is 125 feet.
Table 6 – Reducing Couplings
c. If the transition occurs at a distance greater than 15 equivalent feet from the boiler, the maximum equivalent length will be
reduced. See Table 7. The standard vent pipe is 2”.
Table 7
Page 46

46
All joints of positive pressure vent systems must be sealed completely to prevent leakage of flue products into living space.
Figure 24
H. EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE INSTALLATION
1. Use only solid PVC or CPVC pipe, AL29-4C Stainless Steel, or a Polypropylene vent system approved for use with Category IV
appliances. FOAM CORE PIPING IS NOT APPROVED.
2. Remove all burrs and debris from joints and fittings.
3. When using PVC or CPVC pipe, all joints must be properly cleaned, primed, and cemented. Use only cement and primer approved
for use with the pipe material. Cement must conform to ASTM D2564 for PVC and ASTM F493 for CPVC pipe. NOTE: DO NOT
CEMENT POLYPROPYLENE PIPE.
4. Ensure the vent is located where it will not be exposed to prevailing winds.
5. In all roof venting applications, exhaust discharge must point away from the pitch of the roof.
6. To prevent water leakage, install adequate roof flashing where the pipe enters the roof.
7. Do not locate vent over public walkways, driveways, or parking lots. Condensate could drip and freeze, resulting in a slip hazard or
damage to vehicles and machinery.
8. Due to potential moisture build-up, sidewall venting may not be the preferred venting option. To save time and cost, carefully
consider venting installation and location.
9. Horizontal lengths of exhaust vent must slope back towards the boiler not less than ¼" per foot to allow condensate to drain from the
vent pipe.
Page 47

DESCRIPTION
STOCK CODE
2” PVC CONCENTRIC VENT TERMINATION KIT
KGAVT0501CVT
3” PVC CONCENTRIC VENT TERMINATION KIT
KGAVT0601CVT
2” STAINLESS STEEL VENT TERMINATION KIT
V500
3” STAINLESS STEEL VENT TERMINATION KIT
V1000
4” STAINLESS STEEL VENT TERMINATION KIT
V2000
3” POLYPRO VENT KIT
8400P-001
10. The exhaust vent must terminate where vapors cannot make accidental contact with people or pets, or damage shrubs or plants.
11. In vacant chimney applications, install and seal a rain cap over existing chimney openings.
12. All piping must be fully supported. Use pipe hangers at a minimum of 4 foot intervals to prevent sagging of the pipe where
condensate may form.
13. Do not use the boiler to support any piping.
14. A screened straight coupling is provided with the boiler for use as an outside exhaust termination.
15. A screened inlet air tee is provided with the boiler to be used as an outside intake termination.
The following information on Table 8 lists optional exhaust/intake terminations available from HTP.
Table 8
47
Page 48

I. DIAGRAMS FOR SIDEWALL VENTING
48
Figure 25 – Venting
Page 49

49
Figure 26 – Sidewall Venting
Page 50

J. DIAGRAMS FOR VERTICAL VENTING
50
Figure 27 – Vertical Venting
Page 51

51
Failure to follow all precautions in this section could result in fire, explosion, severe injury or death!
It is very important that you are connected to the type of gas noted on the rating plate. “LP” for liquefied petroleum, propane gas, or
“NAT” for natural or city gas. Prior to turning the gas on, all gas connections must be approved by the local gas supplier or utility, in
addition to the governing authority.
Do not attempt to support the weight of gas piping with the boiler or its accessories. The gas valve and blower will not support the
weight of the piping. Failure to follow this warning could result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Nominal Iron
Pipe Size
(Inches)
Internal
Diameter
(Inches)
Length of Pipe (Feet)
BTU’s
Per Hour
x
1,000
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
125
150
175
200
¾
.824
278
190
152
130
115
105
96
90
84
79
72
64
59
55
1
1.049
520
350
285
245
215
195
180
170
160
150
130
120
110
100
1 ¼
1.380
1,050
730
590
500
440
400
370
350
320
305
275
250
225
210
1 ½
1.610
1,600
1,100
890
760
670
610
560
530
490
460
410
380
350
320
PART 8 – GAS PIPING
A. GAS CONNECTION
Connect the gas supply to the system following state and local plumbing codes.
The gas supply shall have a maximum inlet pressure of less than 14" water column (350 mm), ½ pound pressure (3.5 kPa), and a
minimum of 3.5" water column. The entire piping system, gas meter and regulator must be sized properly to prevent pressure drop
greater than 0.5" WC as stated in the National Fuel Gas Code. This information is listed on the rating plate.
NOTE: Maximum inlet gas pressure must not exceed 14” w.c. (3.5 kPa).
*NOTE: Installer must supply trap to meet local code requirements.
The nipple provided is ½” with a factory installed ¾” bell reducer. DO NOT REMOVE this ¾” by ½” bell reducer! It is mandatory that this
fitting is used for connection to a field fabricated drip leg per the National Fuel Gas Code. Ensure that the entire gas line to the
connection is no smaller than ¾”.
Once all inspections have been performed, the piping must be leak tested. If the leak test requirement is a higher test pressure than the
maximum gas inlet pressure, you must isolate the boiler from the gas line to continue leak testing. To do this, turn off the factory and
field-installed gas cocks. This will minimize the possibility of damaging the gas valve. Failure to do so may damage the gas valve. In the
event the gas valve is exposed to a pressure greater than ½ PSI, 14" water column, the gas valve must be replaced. Never use an
open flame (match, lighter, etc.) to check gas connections.
Refer to the table below to size the supply piping to minimize pressure drop between meter or regulator and unit.
Maximum capacity of pipe in cubic feet of gas per hour for gas pressures of .5 psi or less and a pressure drop of .3 inch water column:
Table 9
It is recommended that a soapy solution be used to detect leaks. Bubbles will appear on the pipe to indicate a leak is present. The gas
piping must be sized for proper flow and length of pipe to avoid excessive pressure drop. Both the gas meter and the gas regulator
must be properly sized for the total gas load. If you experience a pressure drop greater than 1" WC, the meter, regulator or gas line is
undersized or in need of service. You can attach a manometer to the incoming gas drip leg by removing the cap. The gas pressure
must remain between 3.5" WC and 14" WC during stand-by (static) mode and while in operating (dynamic) mode at full output.
If an in-line regulator is used, it must be a minimum of 10 feet from the boiler. It is very important that the gas line is properly
purged by the gas supplier or utility. Failure to properly purge the lines or improper line sizing will result in ignition failure.
This problem is especially noticeable in NEW LP installations and also in empty tank situations. This can also occur when a utility
company shuts off service to an area to provide maintenance to their lines. The gas valve must not be replaced with a conventional gas
valve under any circumstances. As an additional safety feature, the gas valve in this boiler has a flanged connection to the swirl plate
and blower.
B. GAS PIPING
1. Run the gas supply line in accordance with all applicable codes.
Page 52

52
Failure to apply pipe sealing compound as detailed above could result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
CSA / UL listed flexible gas connections can be used when installing the boiler. Flexible gas connections have different capacities and
must be sized correctly for the connected boiler firing rates. Consult with the flex line supplier to assure the line size is adequate for the
job. Follow local codes for proper installation and service requirements.
Never use an open flame (match or lighter) to check for gas leaks. Use a soapy solution to test connection. Failure to use a soapy
solution test or check gas connection for leaks could result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Use a two-wrench method when tightening gas piping near the boiler and its piping connection: One wrench to prevent the boiler gas
line connection from turning; the second to tighten the adjacent piping. Failure to support the boiler gas piping connection could
damage the boiler beyond repair. Such damage IS NOT covered by warranty.
Ensure the pressure tap screw is properly tightened to prevent gas leaks. Failure to do so could cause substantial property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
2. Locate and install manual shutoff valves in accordance with state and local requirements.
3. In Canada, the Manual Shutoff must be identified by the installing contractor.
4. It is important to support gas piping as the boiler is not designed to structurally support a large amount of weight.
5. Purge all gas lines thoroughly to avoid start up issues with air in the lines.
6. Sealing compound (pipe dope) must be used and approved for gas connections. Apply sparingly, and only to the male threads. Care
must be taken when applying compound to prevent blockage or obstruction of gas flow which may affect the operation of the boiler.
C. CHECK INLET GAS PRESSURE
The gas valve is equipped with an inlet gas pressure tap that can be used to measure the gas pressure to the boiler. To check gas
pressure, perform the steps listed below:
1. IMPORTANT! Before you connect to the inlet pressure, shut off the gas and electrical power to boiler.
2. Loosen the pressure tap with a small screwdriver. Refer to Figure 28 for location.
3. Each boiler is equipped with a needle valve that will accept a 5/16 ID hose to connect to a digital manometer or liquid gauge
designed to measure incoming pressure from 0-35” w.c. See Figure 28.
4. Turn on the gas and power up the boiler.
5. Put the boiler into manual test mode (details on test mode are in Part 12 Section D). In service mode, monitor pressure to assure it
does not drop below 1 inch from its idle reading. If gas pressure is out of range or pressure drop is excessive, contact the gas utility,
gas supplier, qualified installer, or service agency to determine correct action that is needed to provide proper gas pressure to the
boiler. If Gas Pressure is within normal range proceed to Step 6.
6. Exit test mode, then turn power off and shut off gas supply at the manual gas valve before disconnecting the hose from the gas
monitoring device. Tighten screw on the pressure tap and turn gas on. Check for leaks with soapy solution. Bubbles will appear on the
pipe to indicate a leak is present.
The gas piping must be sized for the proper flow and length of pipe to avoid pressure drop. The gas meter and regulator must be
properly sized for the total gas load. If you experience a pressure drop greater than 1" w.c. (.87 kPa), the meter, regulator or gas line
may be undersized or in need of service. You can attach a manometer to the incoming gas drip leg after removing the cap. The gas
pressure must remain between 3.5" (.87 kPa) and 14" (3.5 kPa) during stand-by (static) mode and while in operating (dynamic) mode.
Page 53

DO NOT adjust or attempt to measure gas valve outlet pressure. The gas valve is factory-set for the correct outlet pressure and
requires no field adjustment. Attempts by the installer to adjust or measure the gas valve outlet pressure could result in damage to the
valve and cause substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Do not do a gas conversion on this boiler without an officially approved conversion kit and instructions supplied by HTP. Failure to use a
conversion kit when converting the boiler to fire on Natural or LP gas will result in extremely dangerous burner operation, leading to fire,
explosion, severe injury or death.
Strain on the gas valve and fittings may result in vibration, premature component failure and gas leakage, and result in fire, explosion,
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Adjustments to the throttle screw or offset may only be made by a qualified gas technician using a calibrated combustion analyzer
capable of measuring CO2 and CO. Failure to follow this instruction could result in fire, explosion, property damage, severe personal
injury, or death.
If an in-line high gas pressure regulator is used, it must be installed a minimum of 10 feet from the boiler. It is very important
that the gas line is properly purged by the gas supplier or utility. Failure to properly purge the lines, or improper line sizing,
will result in ignition failure. This problem is especially noticeable in NEW LP installations and empty tank situations. This situation
can also occur when a utility company shuts off service to an area to provide maintenance to their lines. This gas valve must not be
replaced with a conventional gas valve under any circumstances.
D. GAS VALVE
53
Figure 28 – LP-171-N
Page 54

ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD – Turn off electrical power supply at service entrance panel before making any electrical connections.
Failure to do so can cause severe personal injury or death.
Wiring must be N.E.C. Class 1. If original wiring supplied with the boiler must be replaced, use only UL Listed TEW 105o C wire or
equivalent. Boiler must be electrically grounded as required by National Electrical Code ANSI/NFPA 70 – Latest Edition.
In order to ease future servicing and maintenance, it is advised to label all wires. Wiring errors can cause improper and dangerous
operation. Failure to follow these instructions could result in property damage or personal injury.
To avoid electrical shock, turn off all power to the boiler prior to opening an electrical box within the unit. Ensure the power remains off
while any wiring connections are being made. Failure to follow these instructions could result in component or product failure, serious
injury, or death. Such product failure IS NOT covered by warranty.
PART 9 – FIELD WIRING
A. INSTALLATION MUST COMPLY WITH:
National Electrical Code and any other national, state, provincial or local codes or regulations.
In Canada, CSA C22.1 Canadian Electrical Code Part 1, and any local codes.
54
B. FIELD WIRING
The boiler box has a 24 volt terminal strip on the boiler cabinet and a 120 volt terminal strip enclosed in the electrical box. Each terminal
connection is clearly marked to assure correct installation.
C. LINE VOLTAGE WIRING
1. Connect 120 VAC power wiring to the line voltage terminal strip located inside the electric junction box, as shown in Figure 30.
2. Wire the Boiler Primary Circulator (P1) to the terminal strip. See wiring diagram in this section.
D. THERMOSTAT
1. Connect room thermostat or end switch.
2. Install thermostat on inside wall away from influences of drafts, hot or cold water pipes, lighting fixtures, television, sunrays or
fireplaces.
3. Thermostat anticipator (if applicable):
a. If connected directly to boiler, set for 0.1 amps.
b. If connected to relays or other devices, set to match total electrical power requirements of connected devices. See
specifications of the device and thermostat instructions for details.
Page 55

55
Figure 29
Page 56

56
Figure 30– NOTE: A resistor is provided between Bus Lines A and B. DO NOT REMOVE THIS RESISTOR! DOING SO WILL
EFFECT HEATER OPERATION AND VOID WARRANTY!
Page 57

The wire to outdoor sensor must not be laid closer than 6’ to line voltage wiring (120/240 V) and must never be in the same conduit.
Caution should be used to ensure neither of these terminals becomes connected to ground.
Failure to use the correct sensor may result in tank temperature being either above or below set point, and could result in decreased
performance, substantial property damage, or heightened risk of injuries due to scalds.
PART 10 – FIELD WIRING – VISION 1 OPTION
Outdoor Sensor Function
The user can program the desired supply temperature based on the heat transmitter (baseboard, radiant floor, air handler) that will be
used in the installation. Once the outdoor sensor (light green wires) is connected to the control board, the water temperature of the
boiler will adjust to run the boiler more efficiently and provide greater comfort to the living space.
Connection Specification – Wire 22 AWG maximum to 100 feet or 18 AWG up to 150 feet. Length of wire run cannot exceed 150 feet.
Outdoor Sensor
NOTE: If the system requires a fixed operating temperature, the outdoor sensor is not required and should not be installed.
Connected in the boiler junction box, the Outdoor Sensor allows the control to automatically change the temperature going to the
central heating loop. Route wires from the boiler terminal strip to your outdoor sensor. Place the sensor preferably to the north or
northwest or to the side which will be affected by changing weather conditions outside. NOTE: Do not locate the sensor in direct
sunlight.
NOTE: For correct mounting procedures, follow instructions provided with the sensor.
NOTE: If sensor wires are located in an area with sources of potential electromagnetic interference (EMI), the sensor wires should be
shielded, or the wires routed in a grounded metal conduit. If using shielded cable, the shielding should be connected to the common
ground of the boiler.
Indirect Sensor Function
The maximum run time on priority function for the SuperStor Ultra Indirect Fired Water Heater is from 1-60 minutes. The water
temperature can only be adjusted when using a sensor (not a mechanical control). Temperature adjustments are from 95 to 185
degrees, plus a differential 1-18 degrees (Note: It is recommended that you do not exceed 5 minutes on the DHW pump post purge
cycle to avoid cooling down your DHW tank).
Indirect Sensor
The Indirect Sensor connects to the boiler main control. Route wires from the terminal strip to the sensor or the mechanical control,
Honeywell part # L4080b1395 (not included in Vision I Package), into the control well located in the front of the water heater. This will
allow the installer to control the temperature of the indirect from the boiler and give the indirect priority over the central heating circuit.
Once the indirect is satisfied, the boiler will then switch back to central heating if there is a call for heat. If not, the boiler will then shut
down.
57
NOTE: If sensor wires are located in an area with sources of potential electromagnetic interference (EMI), the sensor wires should be
shielded, or the wires routed in a grounded metal conduit. If using shielded cable, the shielding should be connected to the common
ground of the boiler.
Indirect Circulator (P2) Program Function
The Indirect Circulator Program Function will automatically start when the water heater sensor reads a call for heat. The installer can
also program the post purge function on the circulator. The post purge circulator function ranges from 1-30 minutes.
Indirect Circulator (P2)
The Indirect Circulator connects to the boiler terminal strip. Run wire to the SuperStor Ultra Indirect circulating pump. The purple wire is
the neutral lead and the pink wire is the hot. This will supply 120 volts directly to the water boiler circulator.
Fault Code Alarm Output
If there is a lockout fault present in the boiler control, a 120 volt output is activated. This is useful when you have a remote display that
will notify you of a fault condition, or if you have auxiliary equipment that needs to shut down in the event of a lockout.
Page 58

58
Do not tie neutrals or hot wire leads to any other wires. Go directly from the boiler controller to the circulator.
Thoroughly clean and flush any system that has used glycol before installing the boiler. Provide the customer with a material safety
data sheet (MSDS) on the fluid used.
Chemical imbalance of your water can cause severe damage to your boiler and associated equipment, and may also affect efficiency.
You may have to have your water quality professionally analyzed to determine whether you need to install a water softener. It is
important that the water chemistry on both the domestic hot water and central heating sides are checked before installing the boiler, as
water quality will affect the reliability of the system. Outlined below are those water quality parameters which need to be met in order for
the system to operate efficiently for many years. Failure of a heat exchanger due to lime scale build-up on the heating surface,
low pH or other imbalance IS NOT covered by the warranty.
Do not use petroleum-based cleaning or sealing compounds in boiler system. Damage to elastomer seals and gaskets in system could
occur, resulting in substantial property damage.
Fault Code Alarm Function
Connect the fault annunciator or lights to the alarm output on the boiler terminal strip and the incoming neutral line in the junction box.
NOTE: The annunciator or light must be rated for 120 volt AC. A relay may be employed to use devices with ratings other than 120 volt
AC.
Connection Specification – Wire 18 AWG maximum. Length of wire run cannot exceed 100 feet.
PART 11 – START-UP PREPARATION
A. CHECK/CONTROL WATER CHEMISTRY
To assure extended service life, it is recommended to test water quality prior to installation. Listed below are some guidelines.
Sodium less than 20 mGL
Water pH between 6.0 and 8.0
1. Maintain boiler water pH between 6.0 and 8.0. Check with litmus paper or have chemically analyzed by water treatment company.
2. If pH differs from above, consult local water treatment company for treatment needed.
Hardness less than 7 grains
Consult local water treatment companies for unusually hard water areas (above 7 grains hardness).
Chlorine concentration less than 100 ppm
1. Filling with chlorinated fresh water should be acceptable since drinking water chlorine levels are typically less than 5 ppm.
2. Do not use the boiler to directly heat swimming pool or spa water.
3. Do not fill boiler or operate with water containing chlorine in excess of 100 ppm.
Clean system to remove sediment
1. You must thoroughly flush the system (without boiler connected) to remove sediment. The high-efficiency heat exchanger can be
damaged by buildup or corrosion due to sediment.
2. For zoned systems, flush each zone separately through a purge valve. (If purge valves and isolation valves are not already installed,
install them to properly clean the system.)
3. Flush system until water runs clean and you are sure piping is free of sediment.
Test/replace freeze protection fluid
1. For systems using freeze protection fluids, follow fluid manufacturer’s instructions to verify inhibitor level and that other fluid
characteristics are satisfactory.
Page 59

59
NEVER use automotive or standard glycol antifreeze, or ethylene glycol made for hydronic systems. System water, including additives,
must be non-toxic, having a toxicity rating or Class of 1, as listed in Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. Use only freezeprevention fluids certified by fluid manufacturer as suitable for use with stainless steel boilers, verified in fluid manufacturer literature.
Thoroughly clean and flush any system that has used glycol before installing the new boiler. Provide boiler owner with a material safety
data sheet (MSDS) on the fluid used.
Ensure the boiler is full of water before firing the burner. Failure to do so will damage the boiler. Such damage IS NOT covered by
warranty, and could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Eliminate all system leaks. Continual fresh make-up water will reduce boiler life. Minerals can build up in the heat exchanger, reducing
heat transfer, overheating heat exchanger, causing heat exchanger failure, and possibly resulting in property damage, severe personal
injury, or death.
It is important that you purge the system of air to avoid damage to the boiler. Make sure that this procedure is followed before firing the
boiler.
2. Freeze protection fluid must be replaced periodically due to degradation of inhibitors over time. Follow all fluid manufacturer
instructions.
NOTE: Boiler failure due to improper water chemistry is not covered by warranty.
B. FREEZE PROTECTION (WHEN USED)
1. Determine freeze protection fluid quantity using total system water content, following fluid manufacturer’s instructions. Remember to
include expansion tank water content.
2. NOTE: Local codes may require back flow preventer or actual disconnect from city water supply.
3. When using freeze protection fluid with automatic fill, install a water meter to monitor water makeup. Freeze protection fluid may leak
before the water begins to leak, causing concentration to drop, reducing the freeze protection level.
C. FILL AND TEST WATER SYSTEM
1. Fill system only after ensuring the water meets the requirements of this manual.
2. Close manual and automatic air vents and boiler drain valve.
3. Fill to correct system pressure. Correct pressure will vary with each application.
a. Typical cold water fill pressure for a residential system is 12 psi.
b. Pressure will rise when boiler is turned on and system water temperature increases. Operating pressure must never exceed
25 psig.
4. At initial fill and during boiler startup and testing, check system thoroughly for any leaks. Repair all leaks before proceeding further.
5. The system may have residual substances that could affect water chemistry. After the system has been filled and leak tested, verify
water pH and chlorine concentrations are acceptable.
D. PURGE AIR FROM WATER SYSTEM
To purge air from system:
a. Connect a hose to the purge valve and route hose to an area where water can drain and be seen.
b. Close the boiler or system isolation valve between the purge valve and fill connection to the system.
c. Close zone isolation valves.
d. Open quick-fill valve on cold water makeup line.
e. Open purge valve.
Page 60

Before starting the boiler, and during initial operation, smell near the floor and around the boiler for gas odorant or any unusual odor.
Remove boiler front door and smell interior of boiler enclosure. Do not proceed with startup if there is any indication of a gas leak.
Repair any leak at once.
Propane boiler only – Your propane supplier mixes an odorant with the propane to make its presence detectable. In some instances,
the odorant can face, and the gas may no longer have an odor. Before startup (and periodically thereafter), have the propane supplier
verify the correct odorant level in the gas.
f. One zone at a time, open the isolation valves. Allow water to run through the zone, pushing out the air. Run until no
noticeable air flow is present. Close the zone isolation valves and proceed with the next zone. Follow this procedure until all
zones are purged.
g. Close the quick-fill water valve and purge valve and remove the hose. Open all isolation valves. Watch that system pressure
rises to correct cold-fill pressure.
h. After the system has operated for a while, eliminate any residual air by using the manual air vents located throughout the
system.
i. If purge valves are not installed in system, open manual air vents in system one at a time, beginning with lowest floor. Close
vent when water squirts out. Repeat with remaining vents.
j. Refill to correct pressure.
E. CHECK FOR GAS LEAKS
F. CHECK THERMOSTAT CIRCUIT(S)
1. Disconnect the two external wires connected to the boiler thermostat terminals (low voltage terminal strip terminals 5 and 6).
2. Connect a voltmeter across these two incoming wires. Close each thermostat, zone valve and relay in the external circuit one at a
time and check the voltmeter reading across the incoming wires.
3. There should NEVER be a voltage reading.
4. If a voltage does occur under any condition, check and correct the external wiring. (This is a common problem when using 3-wire
zone valves.)
5. Once the external thermostat circuit wiring is checked and corrected if necessary, reconnect the external thermostat circuit wires to
boiler low voltage terminal strip. Allow the boiler to cycle.
60
G. CHECK CONDENSATE REMOVAL
1. This a high efficiency condensing boiler, therefore, the unit has a condensation drain. Condensate is nothing more than water vapor,
derived from combustion products, similar to an automobile when it is initially started. The condensation is slightly acidic (typically with
pH of 3 to 5) and must be piped with the correct materials. Never pipe the condensate using steel, copper, brass or other materials that
will be subject to corrosion. Plastic PVC or CPVC pipe are the only approved materials. A condensate filter, if required by local
authorities, can be made up of lime crystals marble or phosphate chips that will neutralize the condensate. This may be done by the
installer or you may purchase a condensate neutralizer from HTP (p/n 7450P-218).
2. The boiler is equipped with a ¾” pipe connection that runs the condensation line to a local drain. It is very important that the
condensate line is sloped away from the boiler and down to a suitable inside drain. If the condensate outlet is lower than the drain, you
must use a condensate removal pump, available at HTP (#554200). This pump is equipped with two leads that can be connected to an
alarm or another type of warning device to alert residents of a condensate overflow, which, if not corrected, could cause property
damage.
3. The boiler is equipped with an internal vent on the top plug connection to assure adequate flow of condensate. This vent should
never be blocked.
4. If a long horizontal run is used, it may be necessary to create a second vent to prevent a vacuum lock in the condensate line. Do not
expose the condensate to freezing temperatures.
5. Do not expose the condensate to freezing temperatures.
6. It is very important you support the condensation line to assure proper drainage.
H. FINAL CHECKS BEFORE STARTING BOILER
1. Read Startup Procedures within this manual for proper steps to start boiler. (See Startup Report to record steps for future reference.)
Page 61

FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY READ BEFORE OPERATING
1. This boiler does not have pilot. It is equipped with an ignition device which automatically lights the burner. Do not try to light the
burner by hand.
2. BEFORE OPERATING: smell all around the boiler area for gas. Be sure to smell next to the floor because some gas is heavier than
air and will settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
Do not try to light any boiler.
Do not touch any electric switch; do not use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor's phone. Follow the gas suppliers' instructions.
If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire department.
Turn off gas shutoff valve (located outside of the boiler) so that the handle is crosswise to the gas pipe. If the handle will not
turn by hand, don't try to force or repair it, call a qualified service technician. Force or attempted repair may result in a fire or
explosion.
4. Do not use this boiler if any part has been under water. Immediately call a qualified service technician to inspect the boiler and to
replace any part of the control system and any gas control that has been damaged.
5. The boiler shall be installed so the gas ignition system components are protected from water (dripping, spraying, rain, etc.) during
boiler operation and service (circulator replacement, condensate trap, control replacement, etc.)
Failure to follow these instructions could result in property damage, serious personal injury, or death.
2. Verify the boiler and system are full of water and all system components are correctly set for operation.
3. Fill condensate trap with water.
4. Verify electrical connections are correct and securely attached.
5. Inspect exhaust vent and intake pipe for signs of deterioration from corrosion, physical damage or sagging.
PART 12 – START-UP PROCEDURE
61
A. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Remove boiler cover. If you smell gas, STOP. Follow listed safety instructions. If you do not smell gas, follow the next steps.
1. Turn on all electric power to boiler.
2. If desired, adjust the temperature set point of the boiler. The factory default
setting is 180oF. If changes are necessary follow “Adjusting the Set point” in
this section.
3. Set the thermostat to the desired setting.
4. If the boiler fails to start, refer to the “Troubleshooting” section in the back of
this manual.
B. ADJUSTING THE SET POINT
Before changing the temperature from the factory setting of 180 degrees, you must make sure that none of the thermostats are calling
for heat. The controller will not memorize a program setting while in a heating cycle.
To adjust the boiler temperature simply press in the {S3} key for three seconds until you see a flashing (C) then an alternate value of
(180). This number is the factory set point of the unit, which is 180 degrees. To change the temperature, simply push either {S1} to
decrease or {S2} to increase the boiler temperature. The temperature of the boiler can be set as low as 50 Degrees or as high 180
Degrees. These ranges are your minimum and maximum boiler temperature ranges.
In addition to changing the temperature, you may also change three more settings in this model: 1. Boiler differential, 2. Indirect setting
(with Vision System option), and 3. Celsius to Fahrenheit measurement. Press {S3} to get to next value. The boiler differential setting
will appear in the display ch and alternating value of 30. This allows the installer to adjust the activation of the burner based on the
Page 62

62
COMBUSTION SETTINGS
HIGH FIRING RATES and LOW FIRING RATES ON ALL MODELS
NATURAL GAS
PROPANE LP
Low
High
Low
High
Carbon Monoxide (CO%)
0 – 20 ppm
70 – 135 ppm
0 – 20 ppm
80 – 150 ppm
Carbon Dioxide (CO2%)
8 ½% - 9 ½%
8 ½% - 9 ½%
9 ½% - 10 ½%
9 ½% - 10 ½%
FAN SPEEDS
BOILER
HIGH
LOW
IGNITION
T50M
3000
1250
3000
T80M
4250
1200
3000
80M
3700
1600
3220
140M
3550
1400
2765
199M
4800
1500
2765
399M
7700
1900
3000
differential temperature setting of the boiler. The burner will not start until the outlet water temperature reaches a temperature equal to
the setting for the boiler, minus the differential EX: The boiler is set to heat at 180°F degrees and the differential is set at 30°F. The
burner will not start until the outlet temperature of the system reaches 149°F degrees (180° – 30°F = 150°F). To adjust, press either
{S1} (Decrease Value) or {S2} (Increase Value) Ranges 5°F to 30°F.
Press {S3} again and you will see the Indirect Setting de and an alternative value of 119 (with Vision Systems option). To adjust,
press either {S1} (Decrease Value) or {S2} (Increase Value).
The final adjustment in this mode is the Fahrenheit to Celsius measurement. Press {S3} again and you will see t and alternating value
of F. To change value, press {S1} or {S2} to choose the correct measurement.
C. STATUS MENU
Installers are also able to check the current status of boiler parameters by pressing {S4} for 3 seconds. Once activated, the display will
show |d1| alternating value of the actual outlet temperature. Actual values are displayed for each function. To view the next value, press
{S4}. Listed below are the values which can be displayed. These values cannot be changed. To exit this menu, press {S3} to resume
normal operation.
Function Value
d1 — Actual Temperature from outlet sensor
d2 — Actual Temperature from inlet sensor
d3 — If using a standard mechanical control, the control will display |1| for closed |0| for open. If the sensor is connected to the
SuperStor Indirect Fired Water Heater it will measure the actual temperature (Vision option).
d4 — Not used
d5 — Actual Temperature from the outdoor sensor (Vision option).
d6 — Actual Fan speed multiplied by 10 (Example: If fan speed displayed is |410| RPM x 10 = 4100 actual fan speed)
d7 — Actual Ionization current read from Flame Rectification probe
d8 — Actual Status of the Central Heating Circulator Off = |0|, On = |1|. (Vision option.)
d9 — Actual Status of the Indirect Fired Circulator Off = |0|, On = |1|. (Vision option.)
d10 — Actual Status bus communication |co| = connected, |no| = not connected
d11 — Central Heating Set Point
d12 — Power On Hours in units
d13 — Total Central Heat Hours
d14 — Total Indirect/dhw Hours
d15 — Passed Ignition Attempts
D. TEST MODE
This function is intended to simplify the gas valve adjustment if needed. Listed below are the recommended limits on each boiler and
the combustion settings. Automatic modulation does not take place when the controller is in Test mode, only temperature limitation
based on the boiler central heating set point. The user will be allowed to increase or decrease the fan speed by pressing in either {S1}
or {S2}.
To activate Test mode, press {S2} and {S3} together for 1 second. Once activated, you will see {Ser} in the display and the fan speed
(shown in a multiple of 10). The measurement of the combustion levels should always be taken at the highest and lowest fan speed.
After 10 minutes, the Test mode stops automatically. To exit Test mode, press {S1} and {S2} together for 1 second.
Table 10
Table 11
Page 63

63
START-UP PROCEDURES WITH VISION 1 OPTION
DEFAULT
FUNCTION
FUNCTION
VALUE
DESCRIPTION
1
de
Not Applicable
2
149oF
Not Applicable
3
160oF
Maximum domestic delivery water temperature set point the installer will program for indirect water
heater. (NOTE: Does not apply if used with mechanical control).
Range: 95oF to 160oF
4
36oF
Not Applicable
5
7oF
Allows the installer to change the differential in the indirect water heater. (Does not apply if used with
mechanical control.)
Range: 1oF to 18oF
6
0 Min.
Allows the installer to change the indirect circulator post purge time once the sensor is satisfied. (NOTE: It is
recommended that circulator post purge time be set no greater than 5 minutes.
Range: 0 to 60 minutes
7
68oF
Outdoor temperature that you wish the central heating should be disabled – (warm weather shutoff).
Range: 41oF to 122oF
*8
5oF
Changes the minimum outside design temperature.
Range: -49oF to 32oF (See Table 14 to set outdoor reset curve.)
*9
180oF
Changes the design supply water temperature based on the minimum outside design temperature.
Range: 77oF to 180oF
*10
68oF
Changes the maximum outside design temperature for central heating.
Range: 95oF to 32oF
*11
95oF
Changes the design supply water temperature from the boiler based on the maximum outside design
temperature.
Range: 32oF to 180oF
12
68oF
Sets the lowest temperature on boiler for central heating.
Range: 32oF to 180oF
13
0 Min.
Changes the central heating circulator post purge time once the thermostat is satisfied.
Range: 0 to 10 minutes
14
30 Min.
Sets the maximum run time for the indirect water heater and the minimum run time for central heating.
Range: 0 to 60 minutes
15
0
Bus address (0=zone master 1-8=cascade slave). (Not currently used.)
16
0
Interface Board Activation
0 = not active, 1 = active
WARNING: Never change the default setting without the boiler interface board installed.
PART 13 – START-UP PROCEDURES WITH VISION 1 OPTION
The Vision I option allows the user to have one temperature for central heating and another temperature for the SuperStor Ultra Indirect
Fired Water Heater. This enables the user to increase the temperature supplied to the indirect water heater by prioritizing flow at a
higher temperature than may be needed for the central heating circuits (this will require two separate circulators). Once the indirect
water heater is satisfied, the Vision I system will switch back to the central heating circuit to continue to heat the living space at a
temperature based on outside temperature. This gives you a higher comfort level and further increases boiler efficiency.
A. PROGRAMMING THE VISION I OPTION
The Vision I option allows the installer to set the system limits and heat curve for the boiler. These system limits should not be changed
by the user. For future reference, it is important to document your settings within this manual after you program the system parameters.
B. VISION 1 PROGRAM ACCESS
Press and hold {S3} and {S4} simultaneously for three seconds to begin. You will notice that the display will change to |000|. Then,
press down {S1} until you see |925| on the display. This is the pass code. Press and hold {S3} for 1 second to confirm the pass code. If
the pass code is entered incorrectly, the controller program function will be cancelled and the control returns to normal operation. If the
code is entered correctly, the control will switch off the gas valve and purge fan while showing a solid |---| in the display. The display will
then show a |1| alternating to |de|. This first function verifies that the control will address the requirements of the indirect water heater.
C. VISION 1 PROGRAM NAVIGATION
Next you will have to press {S3} to move through each function. To increase or decrease a value, you will need to press either {S1} or
{S2} to change the default values. If there is no key action for 1 minute, the display returns to normal operation. Changes are effective
immediately but not directly stored until the {S4} key is pressed down for 3 seconds then the new values are stored. Listed below are
the varieties of functions the installer can program into the Vision I System.
NOTE: The boiler cannot be programmed when there is a call for heat. See Table 14 to set outdoor reset curve.
Page 64

DEFAULT
FUNCTION
FUNCTION
VALUE
DESCRIPTION
17
0
Interface Board Function
0 = Building Management, 1 = Enables Tekmar Modulating Control
(Consult with Tekmar to assure the Tekmar Control is compatible.)
18
1
Step Modulation – Regulates the burner output in 6 steps in one-minute intervals. This reduces short cycling.
1 = on, 0 = off
19
180o
Indirect boiler set point (flow)
Temperature default = 119o to 180o
20
1
Not applicable
NOTE: The maximum water temperature leaving the boiler is limited to 185oF.
CONTROL PROGRAM REFERENCE CHART
FUNCTION
DEFAULT
SETTING
PROGRAMMED
SETTING
1
de
No change allowed
2
149oF
No change allowed
3
160oF
4
36oF
No change allowed
5
7oF 6
0 Min.
7
68oF 8
5oF
9
180oF 10
68oF
11
95oF
12
68oF 13
0 Min.
14
30 Min. 15 0
16 0
17 0
18 1
19
180oF
Table 13 – Reference Chart
Table 12 - *Central Heating Curve Function
Central heating demand is detected when the room thermostat closes. When an
outside sensor is also connected, the supply temperature will depend on the factory
default central heating curve.
To set your heat curve, you will have to set the following parameters:
1. Minimum outside design temperature: Function 8.
2. Design supply water temperature at the minimum design outside temperature:
Function 9.
3. Maximum outside design temperature: Function 10.
4. Design supply water temperature at the maximum outside temperature: Function
11.
NOTE: The homeowner can adjust the heat curve down by adjusting the central
heating temperature to a lower setting.
64
Page 65

65
When servicing or replacing any components of this boiler be certain that:
The gas is off.
All electrical power is disconnected.
Table 14 – Central Heating Curve – Factory Default
PART 14 – TROUBLESHOOTING
A. ERROR CODE
An error code may occur in the installation of the boiler. This condition may lead to a lock out condition of the controller, which will need
to be manually reset through the {S4}. These temporary codes will help the installer correct the problem before going into a lock out
condition, which will require a manual reset.
B. BOILER ERROR
1. When an error condition occurs the controller will display an error code on the display module.
2. These error codes and several suggested corrective actions are included in Table 15.
3. In the case of E00, E13, and E14 this error, if uncorrected, will go into a fault condition as described is Paragraph C (Boiler Fault).
C. BOILER FAULT
1. When a fault condition occurs the controller will illuminate the red “fault” indication light and display a fault code in the format
(Example: |F00|) on the display module.
2. Note the fault code and refer to Table 16 for an explanation of the fault code along with several suggestions for corrective actions.
3. Press the reset key to clear the fault and resume operation. Be sure to observe the operation of the unit to prevent a recurrence of
the fault.
Page 66

66
When servicing or replacing parts that are in direct contact with boiler water, be certain that:
There is no pressure in the boiler. (Pull the release on the relief valve. Do not rely on the pressure gauge reading.)
The boiler water is not hot.
The electrical power is off.
DO NOT USE THIS BOILER IF ANY PART HAS BEEN SUBMERGED IN WATER. Immediately call a qualified service technician. The
boiler MUST BE replaced if it has been submerged. Attempting to operate an boiler that has been submerged could create numerous
harmful conditions, such as a potential gas leakage causing a fire and/or explosion, or the release of mold, bacteria, or other harmful
particulates into the air. Operating a previously submerged boiler could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
NOTE: Boiler damage due to flood or submersion is considered an Act of God, and IS NOT covered under product warranty.
This boiler has wire function labels on all internal wiring. Observe the position of each wire before removing it. Wiring errors may cause
improper and dangerous operation. Verify proper operation after servicing.
925 Control Board FAULT
Code
Description
Remedy
F00
High temperature switch limit
exceeded 194oF
1. Check circulation pump operation.
2. Assure that there is adequate flow through the boiler by accessing the status menu and assuring that
there is less than a 50oF rise from the return thermister to the supply thermister.
3. Check thermister reading on supply thermister. Replace switch if faulty.
4. If this is a new installation, disconnect the two light grey wires from the zone control, and twist the wires
together. Press S4. If the fault clears, the problem is outside the boiler.
5. If this is an existing installation with glycol, check the condition of the water pressure switch. It may be
necessary to jump out the water pressure switch (temporarily only, as a troubleshooting aid). The 24 VAC
signal may have grounded through the glycol if the water pressure switch is leaking.
F01
Vent temperature limit
exceeded
1. Push the red reset button on the vent temperature limit switch.
2. Check the flue temperature during operation using a combustion analyzer.
3. Replace the vent limit switch if faulty.
4. Verify the combustion drain is clear and draining properly.
5. Visually inspect the target wall and ensure it is intact. If not intact, replace the target wall.
If overheating occurs or the gas supply fails to shut off, do not turn off electrical power to the circulating pump. This may aggravate the
problem and increase the likelihood of boiler damage. Instead, shut off the gas supply to the boiler at the gas service valve.
925 CONTROL BOARD ERROR CODES
CODE
DESCRIPTION
DURATION
CORRECTIVE ACTION
E001
High Limit Exceeded
50 Sec.
1. Check circulation pump operation.
2. Assure there is adequate flow through the boiler by accessing the status menu
and assuring there is less than a 50oF rise from the return thermistor to the supply
thermistor.
3. Replace switch if faulty.
E131
Combustion Fan Speed Low.
The boiler combustion air fan
speed less than 70% of
expected.
60 Sec.
1. Check the combustion air fan wiring.
2. Replace the combustion air fan.
3. Replace the control board.
E14
Combustion Fan Speed High.
The boiler combustion air fan
speed is more than 130% of
expected.
60 Sec.
1. Check the combustion air fan wiring.
2. Replace the combustion air fan.
3. Replace the control board.
PRO
Water Pressure Switch is
Open
Until Corrected
1. Assure that the system pressure is above 10 psig.
2. Check for leaks in the system piping.
FLU
Blocked Vent Pressure Switch
open
Until Corrected
1. Check the flue vent to be sure it is not blocked or damaged.
2. Check the blocked vent pressure switch operation by applying a jumper.
(If the switch is not functioning properly, replace it.
Do not “Jump Out” any of the devices in this circuit. These devices
ensure product safety and must be in place and connected at all times
of normal operation.
Table 15
Page 67

67
Code
Description
Remedy
F02
Interrupted or shorted supply
(outlet) thermister.
1. Check the electrical connection to the thermister on the outlet manifold. Verify 5 VDC by checking in
Molex connector. Verify thermistor values by referencing the chart in this manual.
2. If connection is okay, replace thermister.
F03
Interrupted or shorted return
(inlet) thermister.
1. Check the electrical connection to the thermister on the outlet manifold. Verify 5 VDC by checking in
Molex connector. Verify thermistor values by referencing the chart in this manual.
2. If connection is okay, replace thermister.
F05
Supply (outlet) temperature
exceeds 230oF.
1. Check circulation pump operation.
2. Assure that there is adequate flow through the boiler by accessing the status menu and assuring that
there is less than a 50oF rise from the return thermister to the supply thermister.
F06
Return (inlet) temperature
exceeds 230oF.
1. Check circulation pump operation.
2. Assure that there is adequate flow through the boiler by accessing the status menu and assuring that
there is less than a 50oF rise from the return thermister to the supply thermister.
3. Check direction of flow on boiler circulator.
F09
No flame detected – The boiler
will make three attempts at
ignition before the control goes
into this lockout condition. *See
spark electrode detail.
1. Watch the igniter through the observation window provided.
2. If there is no spark, check the spark electrode for the proper ¼” gap by holding two quarters together and
sliding them through the gap.
3. Remove any corrosion from the spark electrode and flame rectifier probe.
4. If there is a spark but no flame, check the gas supply to the boiler.
5. If there is a flame, check the flame sensor.
6. Check any flue blockage or condensate blocks.
F10
Loss of flame signal – The
boiler will relight 4 times before
the control goes into this lockout
condition. Will reset in 1 hour.
1. Monitor the gas pressure to the unit while in operation.
2. Assure that the flame is stable when lit.
3. Check to see if the green light on the display module is out while the boiler is running.
4. If the green light doesn’t come on or goes off during operation check the flame signal on the status
menu.
5. If the signal reads less than 1 microampere, clean the flame rectifier probe.
6. If the flame rectifier probe continues to read low, replace it.
7. Check the stability of the flame rectification signal. If the signal is unstable, you may need to replace the
burner gasket.
F11F
False flame signal – The boiler
will lock out if it senses a flame
signal when there should be
none present.
1. Turn the gas off to the unit at the service valve.
2. If the flame signal is still present replace the igniter.
3. If the flame signal is not present after turning off the gas supply, check the gas valve electrical
connection.
4. If there is no power to the gas valve, remove the valve and check for obstruction in the valve seat or
replace the gas valve.
5. Turn the gas on at the service valve after corrective action is taken.
6. Check for condensate back up. Condensate back up can damage the refractory wall. If the wall falls
against the rectifier probe, it may conduct the signal to ground, giving a false signal.
F13
Combustion fan speed low –
The boiler will lock out if it
senses that the fan speed is
less than 70% of expected rate
for more than 60 seconds.
1. Check the combustion air fan wiring.
2. Check the quality of the 24 VAC signal by measuring from any connected safety to ground. A low voltage
situation may cause a “false” error code.
3. Replace the combustion air fan.
4. Replace the control board.
F14
Combustion fan speed high –
The boiler will lock out if it
senses that the fan speed is
less than 130% of expected rate
for more than 60 seconds.
1. Check the combustion air fan wiring.
2. Replace the combustion air fan.
3. Replace the control board.
F18
Gas Valve Error
1. Make sure the connector is correctly connected to the gas valve.
2. Check the electrical wiring from the valve to the control board.
3. Voltage readings will be from 18-22 VDC on the outlet of the gas valve plug from any pin to ground. The
connector must remain in contact with the pins.
ON THE 399M only, check the 24 VAC relay block.
4. Replace the low voltage wiring harness assembly.
5. Replace control board.
F19
Supply voltage frequency out of range. (92-132 VAC 60 Hz)
F30
Watchdog
Call factory for further assistance.
F31
Parameter Memory
Call factory for further assistance.
F32
Parameter Memory Write Error
Call factory for further assistance.
F33
Programming Error
Call factory for further assistance.
PP
Parameters Programmed
Press S4 to reset.
Nc
Internal processor error, due to incoming voltage problems. (92-132 VAC 60 Hz) May also occur if neutral wire is broken or damaged.
F
Internal Error
Table 16
Page 68

BEFORE EACH HEATING SEASON a trained and qualified service technician should perform the inspections and maintenance
procedures as identified in this manual. In addition, the maintenance and care of the boiler outlined in this manual must be performed to
assure maximum efficiency and reliability. Failure to do so could result in substantial property damage, serious personal injury, or
death.
The combustion chamber insulation in this product contains ceramic fiber material. Ceramic fibers can be converted to cristobalite in
very high temperature applications. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has concluded, “Crystalline silica inhaled
in the form of quartz or cristobalite from occupational sources is carcinogenic to humans (Group 1).”
Avoid breathing dust and contact with skin and eyes.
Use NIOSH certified dust respirator (N95). This type of respirator is based on the OSHA requirements for cristobalite at the
time this document was written. Other types of respirators may be needed depending on job site conditions. Current NIOSH
recommendations can be found on the NIOSH website at http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/homepage.html. NIOSH approved
respirators, manufacturers, and phone numbers are also listed on this website.
Wear long-sleeved, loose fitting clothing, gloves, and eye protection.
Apply enough water to the combustion chamber to prevent dust.
Wash potentially contaminated clothes separately from other clothing. Rinse clothes washer thoroughly.
NIOSH stated First Aid.
Eye: Irrigate immediately.
Breathing: Fresh Air.
BOILER SENSOR (7250P-059)
INDIRECT SENSOR (7250P-325)
NOTE: If receiving an F09 fault
code, check the gap spacing by
holding two quarters together and
sliding them through the gap. There
should be a slight resistance.
BOILER AND INDIRECT
TEMPERATURE (oF)
RESISTANCE (ohms)
32
32550
41
25340
50
19870
59
15700
68
12490
77
10000
86
8059
95
6535
104
5330
113
4372
122
3605
131
2989
140
2490
149
2084
158
1753
167
1481
176
1256
185
1070
194
915
203
786
212
667
OUTDOOR SENSOR
(7250P-319)
OUTSIDE TEMP.
(oF)
RESISTANCE
(ohms)
-22
171800
-13
129800
-4
98930
5
76020
14
58880
23
45950
32
36130
41
28600
50
22800
59
18300
68
14770
77
12000
86
9804
95
8054
104
6652
113
5522
Table 17
Table 18
Resistance Tables
68
PART 15 – MAINTENANCE
A. MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Periodic maintenance should be performed once a year by a qualified service technician to assure that all the equipment is in safe
efficient operation. The owner can make necessary arrangements with a qualified heating contractor for periodic maintenance of the
boiler. Installer must also inform the owner that the lack of proper care and maintenance of the boiler may result in a hazardous
condition. The installer should discuss the contents of the User's Information Manual with the owner.
B. MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE FOR THE SERVICE TECHNICIAN
The following maintenance should be performed annually by a qualified service technician:
General
Attend to any reported problems.
Page 69

69
Do not use solvents to clean any of the burner components. The components could be damaged, resulting in unreliable or unsafe
operation. Failure to do so could result in death or serious injury.
Inspect the interior of the boiler jacket area; clean and vacuum if necessary.
Clean the condensate trap and fill with fresh water.
Check for water, gas, flue and condensate leaks.
Verify flue vent piping and air inlet piping are in good condition, properly supported, and tightly sealed.
Check boiler water pressure, piping and expansion tank.
Check control settings.
Check ignition electrode. Sand off any white oxide. Clean and reposition.
Check ignition and ground wiring.
Check all control wiring and connections.
Check burner flame pattern (stable and uniform).
Additional Items if Combustion or Performance is Poor
Clean heat exchanger and flue ways.
Remove burner assembly and clean burner head using compressed air only.
Once the maintenance items are completed, review service with the owner.
C. COMBUSTION CHAMBER COIL CLEANING INSTRUCTIONS
*Before beginning this procedure, you must have on hand the following items:
A nylon, stainless or brass brush (not steel)
A liquid calcium and lime deposit remover
Gloves, eye protection
1. Shut down the boiler by using the following steps:
a. Close the gas valve, shut down the unit and wait for the unit to be cool to the touch.
b. Disconnect the condensate hose from the outside connection, (not from the boiler side), so flow can be observed.
c. Disconnect connections from the gas valve, spark electrode and flame rectification probe and combustion blower.
d. Remove the (4) screws on the aluminum ½” NPT connector on the gas valve.
e. Disconnect the wiring connected to the combustion blower motor.
f. Remove the (6) 10MM nuts from the burner plate assembly to access the coils.
g. Pull the entire burner plate assembly with blower still attached towards you, while removing or pushing aside any wiring to
allow the removal of the assembly.
2. Using a spray bottle filled with calcium and lime deposit remover, spray liberally on the coils, making sure the solution penetrates and
funnels down through the condensate hose. If the condensate hose is blocked, let the chemical penetrate for at least 15 minutes or until
it drains.
3. Use the nylon, stainless or brass brush (do not use steel) and scrub coils to remove any buildup. Then vacuum the debris from the
coils. WARNING: Follow above precautions.
4. Spray the coils with clear water, making sure to confine the spray to the area being cleaned (try to avoid getting the back ceramic
wall of the unit wet). Flush the combustion chamber with fresh water. At this point, the boiler should be ready to power back up.
Before powering up the boiler follow the steps below:
a. Re-install the burner assembly.
b. Replace the (6) 10MM nuts to the burner plate.
c. Re-connect all wiring connections.
e. Replace the (4) screws on the aluminum ½” NPT connector on the gas valve. Turn the gas back on. (IMPORTANT: CHECK
FOR GAS LEAKS.)
f. Re-set thermostats (IMPORTANT: MAKE SURE EXHAUST VENT IS NO LONGER BLOCKED!)
g. Turn the boiler back on and observe condensate flow.
h. Re-connect the condensate hose to the outside connection.
Page 70

70
Figure 31
Page 71

71
Figure 32
Page 72

72
Figure 33
Page 73

73
Figure 34
Page 74

74
Figure 35
Page 75

75
Figure 36
Page 76

LIGHT OFF ACTIVITIES
DATE COMPLETED ________________
1) Fill the
heating system
Check all piping and gas connections, verify all
are tight
Pressurize system (12-15 PSI)
____ PSI
Add water to prime condensate hose
What percentage of propylene glycol is
installed in the system (0-50%)
____ %
Verify near boiler piping is properly supported
2) Check gas
pipe
Leak test using locally approved methods
(consult jurisdictional code book)
Check incoming gas pressure (3.5” to 14”
W.C.)
____ in w.c.
Static
What is the “drop” on light off (No more than 1”
W.C.)
____ in w.c.
Dynamic
3) Check
combustion
Check and adjust (if necessary) carbon
dioxide content
____% CO2
High Fire
____% CO2
Low Fire
Check and adjust (if necessary) carbon
monoxide content
____ppm CO
High Fire
____ ppm CO
Low Fire
4) Verify
system
operation
Turn up thermostat to verify wiring connections
5) Record
ionization
current
Check uA reading at d7 on the status menu
(see start-up section)
____ uA
High Fire
____ uA
Low Fire
6) Record
system settings
Record heating curve (with optional Vision
One kit, record steps)
____*8
____*9
____*10
____*11
7) Indirect
water boiler
Verify safety and operation of the indirect
water heater, record settings
____de
____dh
8) Convert the
boiler
If necessary, convert the boiler to the proper
gas type
Locate the stickers in the appropriate locations
on the boiler
Verify combustion settings after gas
conversion, Carbon Dioxide
____% CO2
High Fire
____% CO2
Low Fire
Verify combustion settings after gas
conversion, Carbon Monoxide
____ppm CO
High Fire
____ppm CO
Low Fire
Mail in the conversion registration
Notes:
In unusually dirty or dusty conditions, care must be taken to keep boiler cabinet door in place at all times. Failure to do so VOIDS
WARRANTY!
Allowing the boiler to operate with a dirty combustion chamber will hurt operation. Failure to clean the heat exchanger as needed by the
installation location could result in boiler failure, property damage, personal injury, or death. Such product failures ARE NOT covered
under warranty.
BOILER START-UP REPORT
76
Table 19
MAINTENANCE REPORT
The boiler requires minimal periodic maintenance under normal conditions. However, in unusually dirty or dusty conditions, periodic
vacuuming of the cover to maintain visibility of the display and indicators is recommended.
Periodic maintenance should be performed once a year by a qualified service technician to assure that all the equipment is operating
safely and efficiently. The owner should make necessary arrangements with a qualified heating contractor for periodic maintenance of
Page 77

INSPECTION ACTIVITIES
DATE LAST COMPLETED
PIPING
1st YEAR
2nd YEAR
3rd YEAR
4th YEAR*
Near boiler piping
Check boiler and system piping for any sign of leakage, make
sure they are properly supported.
Vent
Check condition of all vent pipes and joints.
Gas
Check Gas piping, test for leaks and signs of aging. Make sure
all pipes are properly supported.
SYSTEM
Visual
Do a full visual inspection of all system components.
Functional
Test all functions of the system (Heat, Safeties)
Temperatures
Verify safe settings on heater or Anti-Scald Valve
Temperatures
Verify programmed temperature settings
ELECTRICAL
Switch and Plug
Verify ON/OFF switch and convenience plug are functional.
Connections
Check wire connections. Make sure they are tight.
Smoke and CO
detector
Verify devices are installed and working properly. Change
batteries if necessary.
Circuit Breakers
Check to see that the circuit breaker is clearly labeled. Exercise
circuit breaker.
CHAMBER/BURNER
Combustion Chamber
Check burner tube and combustion chamber coils. Clean
according to maintenance section of manual. Vacuum
combustion chamber.
Spark Electrode
Clean. Set gap at ¼”.
Flame Probe
Clean. Check ionization in uA (d7 on status menu in Start-up
Procedures). Record high fire and low fire.
CONDENSATE
Neutralizer
Check condensate neutralizer. Replace if necessary.
Condensate hose
Disconnect condensate hose. Clean out dirt. Fill with water to
level of outlet and re-install. (NOTE: Verify the flow of
condensate, making sure that the hose is properly connected
during final inspection.)
GAS
Pressure
Measure incoming gas pressure (3.5” to 14” W.C.)
Pressure Drop
Measure drop in pressure on light off (no more than 1” W.C.)
Check gas pipe for
leaks
Check piping for leaks. Verify that all are properly supported.
COMBUSTION
CO/CO2 Levels
Check CO and CO2 levels in Exhaust (See Start-up Procedures
for ranges). Record at high and low fire.
SAFETIES
ECO (Energy Cut Off)
Check continuity on Flue and Water ECO. Replace if corroded.
Water Pressure Switch
Check operation and for signs of leakage. Replace if corroded.
Thermistors
Check wiring. Verify through ohms reading.
FINAL INSPECTION
Check list
Verify that you have completed entire check list. WARNING:
FAILURE TO DO SO COULD RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY
OR DEATH.
Homeowner
Review what you have done with the homeowner.
the boiler. Installer must also inform the owner that the lack of proper care and maintenance of the boiler may result in a hazardous
condition.
77
Table 20 - *Continue annual maintenance beyond the 4th year as required.
Page 78

78
Page 79

79
Page 80

80
MAINTENANCE NOTES
Page 81

Customer’s Name:
Installation Address:
Date of Installation:
Installer’s Code/Name:
Product Serial Number(s):
Comments:
Installer’s Phone Number:
Signed by Installer:
Signed by Customer:
LP-185 Rev. 2.7.14
HTP CUSTOMER INSTALLATION RECORD FORM
The following form should be completed by the installer for you to keep as a record of the installation in case of a warranty claim. After
reading the important notes at the bottom of the page, please also sign this document.
81
IMPORTANT NOTES:
Customer: Please only sign after the installer has reviewed the installation, safety, proper operation and maintenance of the
system. In the case that the system has any problems, please call the installer. If you are unable to make contact, please
contact your HTP Sales Representative.
Distributor/Dealer: Please insert contact details.
 Loading...
Loading...