Page 1
IMPORTANT: Read this Owner’s Manual Completely before attempting to use this
equipment. Save this manual and keep it handy for quick reference. Pay particular
attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection. Contact your
distributor if you do not fully understand this manual.
M250 DOUBLE-PULSE SYNERGIC
MULTI-MIG WELDING SYSTEM
OPERATORS’ MANUAL
Page 2

CONTENT
I
CONTENT
§1 Safety ......................................................................................................... 1
§1.1 Symbols Explanation ................................................................................... 1
§1.2 Machine Operating warnings! ..................................................................... 1
§1.3 EMC device classification ........................................................................... 8
§1.4 EMC measure ............................................................................................... 9
§1.5 Warning label ............................................................................................. 10
§2 Overview .................................................................................................. 11
§2.1 Features ....................................................................................................... 11
§2.2 Technical Data ............................................................................................ 12
§2.3 Brief Introduction ....................................................................................... 12
§2.4 Duty Cycle and Over-heat.......................................................................... 13
§2.5 Working Principle....................................................................................... 14
§2.6 Volt-Ampere Characteristic ....................................................................... 14
§3 Panel Functions & Descriptions ............................................................ 15
§3.1 Machine Layout Description ..................................................................... 15
§3.2 Control panel of welding machine ............................................................ 16
§4 Installation & Operation ......................................................................... 25
§4.1 Installation & Operation for MMA/Stick Electrode Welding..................... 25
§4.1.1 Set-Up Installation .............................................................................................. 25
§4.1.2 MMA/Stick Electrode Welding ........................................................................... 26
§4.1.3 MMA Welding Fundamentals ............................................................................. 27
§4.2 Installation & Operation for TIG Welding.................................................. 29
§4.2.1 Set-Up for TIG Welding ....................................................................................... 29
§4.2.2 DCTIG Welding .................................................................................................... 32
§4.2.3 TIG Welding Fusion Technique ......................................................................... 33
§4.2.4 Tungsten Electrodes ........................................................................................... 35
§4.2.5 Tungsten Preparation ......................................................................................... 37
§4.2.6 TIG Torch Switch Controls ................................................................................. 39
§4.3 Installation & Operation for MIG Welding ................................................. 40
§4.3.1 Set up installation for MIG Welding (Gas shielded wire) ................................ 40
§4.3.2 Wire Feed Roller Selection ................................................................................. 42
Page 3

CONTENT
II
§4.3.3 Wire Installation and Set-Up Guide ................................................................... 44
§4.3.4 Set up for MIG Welding- Aluminum or Silicone Bronze Wire ......................... 46
§4.3.5 MIG Torch Liner Installation ............................................................................... 46
§4.3.6 MIG Torch Liner Types and Information ........................................................... 48
§4.3.7 Torch & Wire Feed Set-Up for Aluminum Wire ................................................. 49
§4.3.8 Set-Up Installation for Spool Gun ..................................................................... 50
§4.3.9 MIG Welding ........................................................................................................ 51
§4.3.10 Spool Gun Control NEED NEW TORCH INFO!! ......................................... 58
§4.4 Standard Welding Programs & Settings Chart......................................... 59
§4.5 Welding Parameters ................................................................................... 61
§4.6 Operation Environment ............................................................................. 63
§4.7 Operation Notices ...................................................................................... 63
§5Diagram for Guns ..................................................................................... 64
§5.1 MIG Torches AK15 (Cu/Si), AK25 (Fe) & AK26 (Al) ................................... 64
§5.2 TIG Torch .................................................................................................... 67
§5.3 Spool Gun (Optional) ................................................................................. 68
§6 Welding Trouble Shooting ..................................................................... 69
§6.1 MIG Welding - Trouble Shooting ............................................................... 69
§6.2 MIG Wire Feed - Trouble Shooting ............................................................ 71
§6.3 DC TIG Welding - Trouble Shooting .......................................................... 73
§6.4 MMA Welding - Trouble Shooting ............................................................. 75
§7 Maintenance & Troubleshooting ........................................................... 77
§7.1 Maintenance ............................................................................................... 77
§7.2 Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 78
§7.3 List of Error Codes..................................................................................... 80
§7.4 Electrical Schematic Drawing ................................................................... 81
§7.5 Replacement Parts Drawing ................................................................ ...... 82
Page 4

SAFETY
-1-
§1 Safety
Welding and cutting equipment can be dangerous to both the operator and
people in or near the surrounding working area, if the equipment is not
correctly operated. Equipment must only be used under the strict and
comprehensive observance of all relevant safety regulations. Read and
understand this instruction manual carefully before the installation and
operation of this equipment.
§1.1 Symbols Explanation
The above symbols mean warning!
Notice! Running parts, getting an electric shock or making contacts with
thermal parts will cause damage to your body and others. The underline
message is as follows:
Welding is quite a safe operation after taking several necessary
protection measures!
§1.2 Machine Operating warnings!
The following symbols and words explanations are for some damages to
your body or others, which could happen during the welding operation. While
seeing these symbols, please remind yourself and others to be careful.
Only people who are trained professionally can install, debug, operate,
maintain and repair the welding equipment covered with this Operator’s
Manual!
During the welding operation, non-concerned people should NOT be
around, especially children!
After shutting off the machine power, please maintain and examine the
Page 5

SAFETY
-2-
equipment according to §7 because of the DC voltage existing in the
electrolytic capacitors at the output of the power supply!
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks or severe burns. The
electrode and work circuit is electrically live whenever the output is on. The
input power circuit and internal machine circuits are also live when power is
on. In Mig/Mag welding, the wire, drive rollers, wire feed housing, and all
metal parts touching the welding wire are electrically live. Incorrectly installed
or improperly grounded equipment is dangerous.
Never touch live electrical parts.
Wear dry, hole-free gloves and clothes to insulate your body.
Be sure to install the equipment correctly and ground the work or metal to
be welded to a good electrical (earth) ground according to the operation
manual.
The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are electrically “hot” when the
machine is ON. Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin or wet
clothing. Wear dry, hole-free gloves to insulate hands.
In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode, electrode reel,
welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation. Make certain
the insulation is large enough to cover your full area of physical contact with
work and ground.
Be Careful when using the equipment in small places, falling-off and wet
circumstance.
Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical connection with the
metal being welded. The connection should be as close as possible to the
area being welded.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and welding
Page 6

SAFETY
-3-
machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace damaged insulation.
Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode holders
connected to two welders because voltage between the two can be the total
of the open circuit voltage of both welders.
When working above the floor level, use a safety belt to protect yourself
from a fall should you get an electric shock!
FUMES AND GASES CAN BE DANGEROUS.
Smoke and gas generated whilst welding or cutting can be harmful to
people’s health. Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing these fumes
and gases can be hazardous to your health.
Do not breathe the smoke and gas generated whilst welding or cutting, keep
your head out of the fumes. Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc
to keep fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding with
electrodes which require special ventilation such as stainless or hard facing
or on lead or cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings which
produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low as possible and below the
Threshold Limit Values using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In
confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may be
required. Additional precautions are also required when welding on
galvanized steel.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors coming from
degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the arc can
react with solvent vapors to form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other
irritating products.
Shielded gases used for arc welding can displace air and cause injury or
death. Always use enough ventilation, especially in confined areas, to insure
breathing air is safe.
Page 7

SAFETY
-4-
Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this equipment
and the consumables to be used, including the material safety data sheet and
follow your employer’s safety practices.
ARCRAYS: Harmful to people’s eyes and
skin.
Arc rays from the welding process produce intense visible and invisible
ultraviolet and infrared rays that can burn eyes and skin.
Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your eyes from
sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or observing open arc welding.
Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material to protect
your skin and that of your coworkers from the arc rays.
Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable screening and
/or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose themselves to the arc rays or to
hot spatter or metal.
SELF-PROTECTION
Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in position and in
good repair. Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools away from V-belts, gears,
fans and all other moving parts when starting, operating or repairing
equipment.
Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to override the
governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control rods while the engine is
running.
DO NOT add any fuel near an open-flame welding arc or
when the engine is running. Stop the engine and allow it to cool before
refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporizing on contact with hot engine
parts and igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If fuel is spilled, wipe it up
Page 8

SAFETY
-5-
and do not start engine until fumes have been eliminated.
WELDING SPARKS can cause fire or
explosion.
Welding on closed containers, such as tanks, drums, or pipes, can cause
them to explode. Flying sparks from the welding arc, hot work piece, and hot
equipment can cause fires and burns. Accidental contact of electrode to metal
objects can cause sparks, explosion, overheating, or fire. Check and be sure
the area is safe before doing any welding
Remove fire hazards material from the welding area. If this is not possible,
cover them to prevent the welding sparks from starting a fire. Remember that
welding sparks and hot materials from welding can easily go through small
cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid welding near hydraulic lines.
Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special precautions
should be used to prevent hazardous situation.
When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is touching
the work or ground. Accidental contact can cause overheating and create a
fire hazard.
Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the proper steps
have been taken to insure that such procedures will not cause flammable or
toxic vapors from substances inside. They can cause an explosion even
though they have been “cleaned”.
Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or welding. They
may explode.
Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free protective
garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuff less trousers, high shoes
and a cap over your hair. Wear earplugs when welding out of position or in
confined places. Always wear safety glasses with side shields when in a
Page 9
SAFETY
-6-
welding area.
Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area as practical.
Work cables connected to the building framework or other locations away
from the welding area increase the possibility of the welding current passing
through lifting chains, crane cables or other alternate circuits. This can create
fire hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they fail.
Rotating parts may be dangerous.
Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct shielding gas for
the process used and properly operating regulators designed for the gas and
pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be suitable for the application
and maintained in good condition.
Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to an
undercarriage or fixed support.
Cylinders should be located:
- Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to physical
damage.
- At a safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and any other
source of heat, sparks, or flame.
Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other electrically “hot”
parts to touch a gas cylinder.
Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet when opening
the cylinder valve.
Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand tight except
when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.
Gas Cylinders.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure. If damaged, a
Page 10
SAFETY
-7-
cylinder can explode. Because gas cylinders are normally part of the welding
process, be sure to treat them carefully. CYLINDERS can explode if
damaged.
Protect gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechanical shocks, physical
damage, slag, open flames sparks, and arcs.
Insure cylinders are held secure and upright to prevent tipping or falling over.
Never allow the welding electrode or earth clamp to touch the gas cylinder,
do not drape welding cables over the cylinder.
Never weld on a pressurised gas cylinder, it will explode and kill you.
Open the cylinder valve slowly and turn your face away from the cylinder
outlet valve and gas regulator.
Gas build up.
The buildup of gas can cause a toxic environment, deplete the oxygen
content in the air resulting in death or injury. Many gases use in welding are
invisible and odourless.
Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
Always ventilate confine spaces or use approved air-supplied respirator.
Electric and Magnetic Fields.
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized Electric and
Magnetic Fields (EMF). The discussion on the effect of EMF is ongoing in the
entire world. Up to now, no material evidences show that EMF may have
effects on health. However, the research on the effect of EMF is still ongoing.
Before any conclusion, we should minimize exposure to EMF as few as
possible.
In order to minimize EMF, we should use the following procedures:
Route the electrode and work cables together – Secure them with tape
when possible.
Page 11

SAFETY
-8-
All cables should be put away and far from the operator.
Never coil the power cable around your body.
Make sure welding machine and power cable to be far away from the
operator as far as possible according to the actual circumstance.
Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close as possible to the area
being welded.
The people with heart-pacemaker should be away from the welding area.
Noise can damage hearing.
Noise from some processes or equipment can damage hearing. You must
protect your ears from loud noise to prevent permanent loss of hearing.
To protect your hearing from loud noise, wear protective ear plugs and/or ear
muffs. Protect others in the workplace.
Noise levels should be measured to be sure the decibels (sound) do not
exceed safe levels.
Hot parts.
Items being welded generate and hold high heat and can cause severe
burns. Do not touch hot parts with bare hands. Allow a cooling period before
working on the welding gun. Use insulated welding gloves and clothing to
handle hot parts and prevent burns.
§1.3 EMC device classification
Radiation Class A Device.
Only can be used in the industrial area
If it is used in other area, it may cause connection
and radiation problems of circuit.
Page 12

SAFETY
-9-
Radiation Class B device.
It can meet the radiation requirements of residential area and industrial area.
It also can be used in residential area which power is supplied by public low
voltage circuit.
EMC device can be classified by power nameplate or technical data.
Hi-zone welding machines belong to Class A.
§1.4 EMC measure
In the special situation, the specified area may be affected,
the standard of radiation limit value has been complied with
(eg: The device, which is easy effected by electromagnetism,
is used at the installation location, or there is radio or TV near the installation
location). In this condition, the operator should adopt some appropriate
measures to remove interference.
According to the domestic and international standards, the ambient devices’
electromagnetism situation and anti-interference ability must be checked:
Safety device
Power line, Signal transmission line and Date transmission line
Date processing equipment and telecommunication equipment
Inspection and calibration device
The effective measures avoid the problem of EMC:
a) Power source
Even though the power source connection meet rules, we still need to take
additional measure to remove the electromagnetic interference. (eg: Use
the right power filter. )
b) The welding line
Try to shorten the length of cable
Put the cable together
Be Far away from other cable
Page 13

SAFETY
-10-
c) Equipotential connection
d) Ground connection of work-piece
When necessary, use appropriate capacitance to connect the ground.
e) Shielding, when necessary
Shield the ambient devices
Shield the whole welding machine
§1.5 Warning label
The device with a warning label. Do not remove, destroy or cover this
label. These warnings are intended to avoid incorrect device operations that
could result in serious personal injury or property damage.
Page 14
OVERVIEW
-11-
§2 Overview
§2.1 Features
⚫ New PWM technology and IGBT inverter technology for high efficiency operation.
⚫ Three dedicated wire feed systems for high productivity and no cross contamination.
⚫ MIG/MAG with Pulse Synergic / Dual Pulse Synergic, Manual and Synergic function
-Synergic programs for aluminum,
mild steel, stainless steel and silicone bronze
-JOB mode (Save and call 100 job records)
- 2T /4T/S4T/ & Spot Weld welding mode
- Function parameter adjustment
⚫ MMA function (Stick electrode)
- Hot start (improves electrode starting)
- Adjustable Arc Force
⚫ DC TIG
- Lift Arc ignition (No high frequency)
- 2T /4T Trigger Control
- Adjustable Up/Downslope
-Adjustable pre and post gas
⚫ Three internal 4-roll, gear drive wire feeders
with 4” (100mm) and 8” (300mm) spool holders.
⚫ Three euro-connect outputs for steel, aluminum, silicone bronze and spool gun
torches.
⚫ Dual cylinder supports and shield gas lines with four gas solenoid valves.
⚫ IP23 rating for environmental/safety protection
⚫ Spool gun connection (Allows controlled feeding of smallest diameter wire for thin
panels.
⚫ TIG torch connection (Independent of MIG gun connects for increased productivity.
⚫ MMA stick electrode connection with hot-start and arc-force adjustment.
Page 15
OVERVIEW
-12-
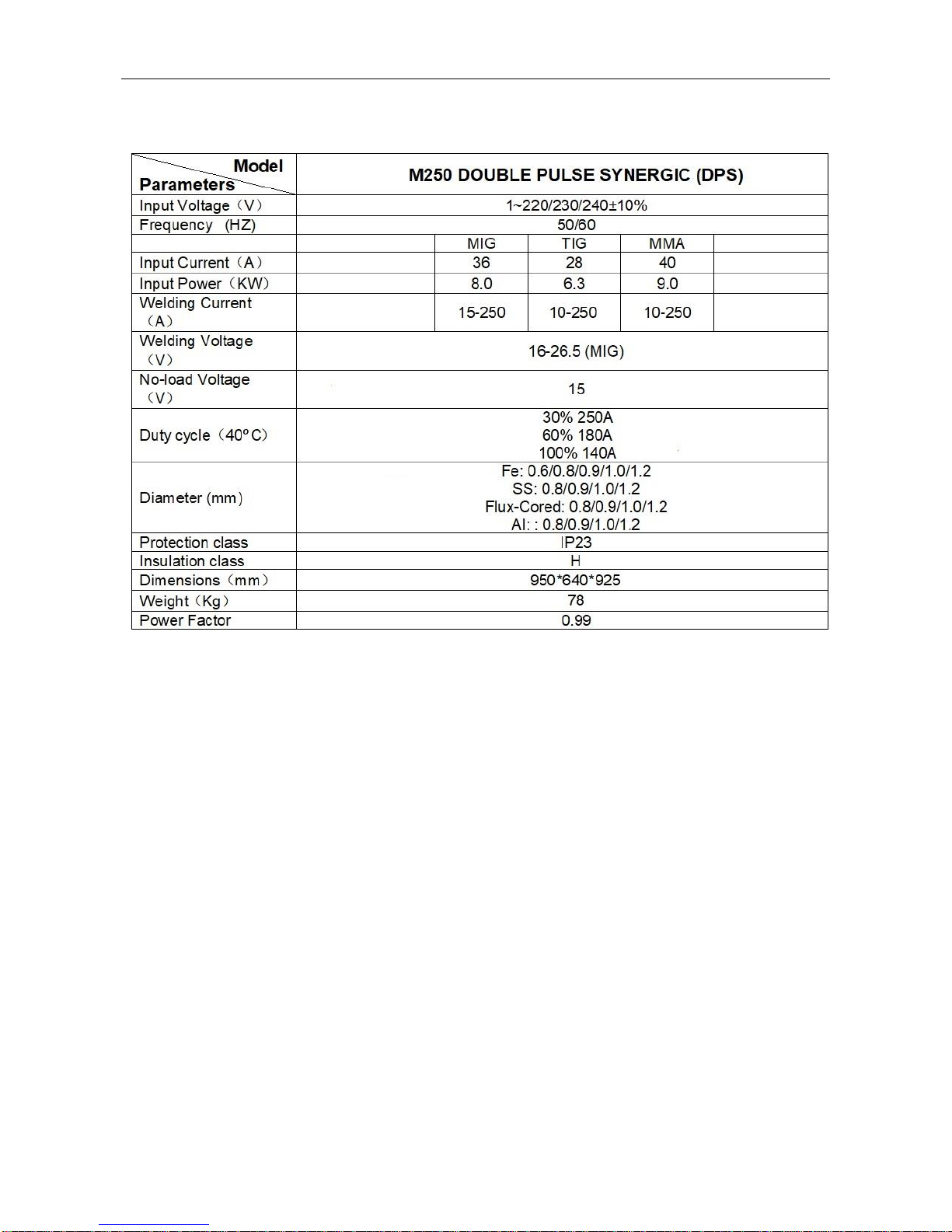
§2.2 Technical Data
Note: The above parameters are subject to change.
§2.3 Brief Introduction
The DOUBLE PULSE SYNERGIC (DPS) series of welding machines is a new
inverter-based MIG/MMA/TIG Welding machine with Synergic Programs and Dual pulse
functions. The MIG function allows you to weld with Gas Shielded wire applications giving
excellent, professional welding results. Easy step-less adjustment of voltage and wire
feed coupled with integrated digital meters allows easy setting of welding parameters.
Synergic setting of welding machines features MIG welding with Synergic welding
programs designed for ease of use with your selected gas mixture. The operator selects
the gas mixture and wire diameter they are using then simply start welding. Once this is
done the operator can make fine adjustments to the voltage for even greater control of the
weld pool. The added Lift-Arc DC TIG capability delivers perfect arc ignition every time
and a remarkably smooth stable arc produces high quality TIG welds. TIG functionality
Page 16
OVERVIEW
-13-
includes adjustable up/down slope & pre/post gas control. The stick welding (MMA)
capability delivers easy electrode welding with high quality results, including cast Iron,
stainless and low hydrogen with hot-start and arc-force adjustment. An additional feature
is the spool gun function that allows the simple connection of Spool Gun for the use of
thin or softer wires that don’t have the column strength to feed through MIG torches, such
as some aluminum and silicone bronze wires. In the JOB mode, 100 different JOB
records can be stored and recalled, improve the quality of welding process.
The DPS series of arc welding machine is an industrial quality machine that is suitable
for all positions welding for various plates made of stainless steel, carbon steel, alloyed
steel etc. Applications applied to automotive, petrochemical, architecture, industrial and
common steel fabrication.
The DPS series of welding machines has built-in automatic protection functions to
protect the machines from over-voltage, over-current and over-heat. If any one of the
above problems happens, the alarm lamp on the front panel will illuminate and output
current will be shut off automatically to protect machine and operator.
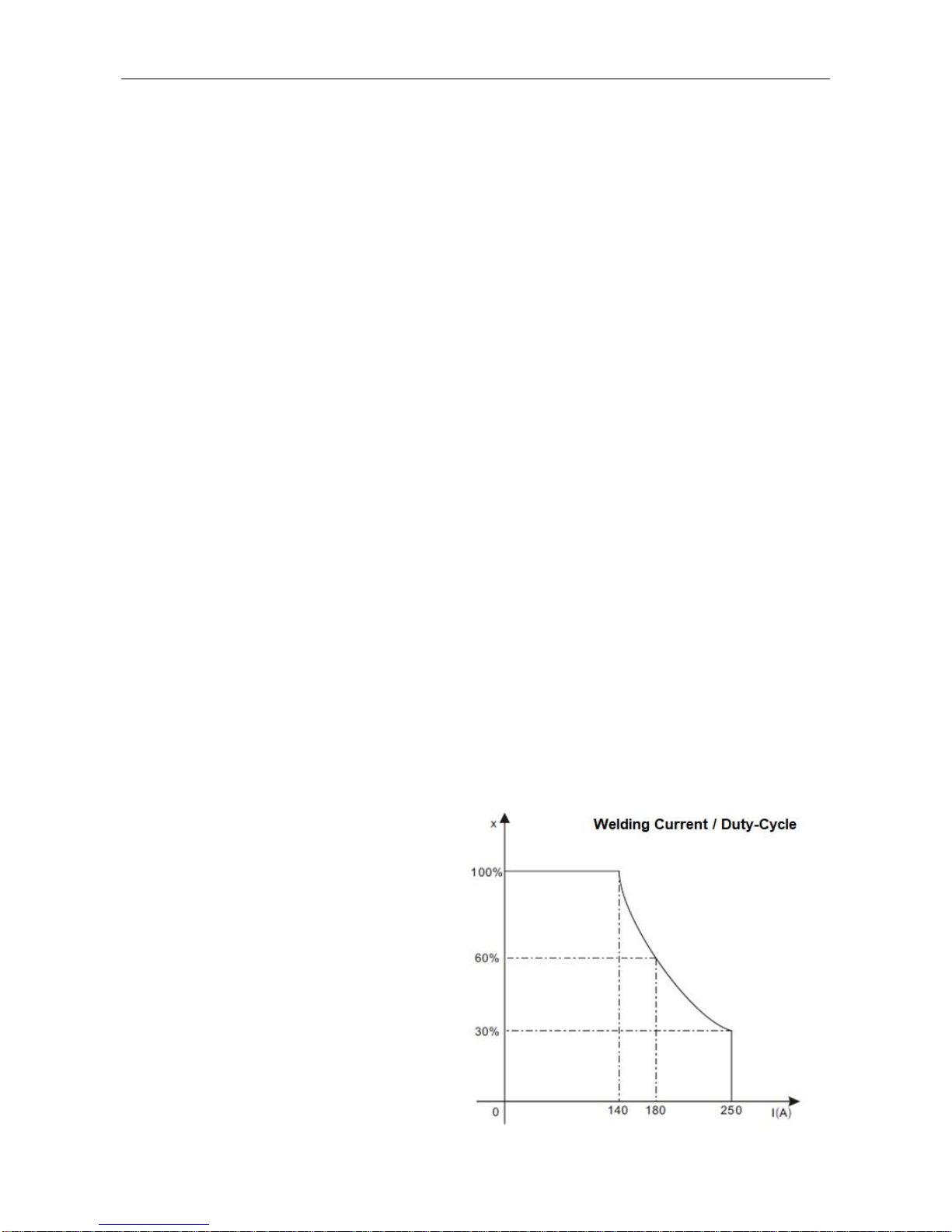
§2.4 Duty Cycle and Over-heat
The letter “X” stands for Duty Cycle, which is defined as the portion of the time a
welding machine can weld at maximum rated output current within a 10-minute cycle.
If the welding machine is operated beyond the rated duty-cycle, the IGBT heat sensor
will send a signal to the welding
machine control unit to switch the
output welding current OFF and light
the over-heat. The machine should not
be operated for 10-15 minutes to allow
cool down. When operating the
machine again, the welding output
current should be reduced to match the
duty cycle.
Page 17
OVERVIEW
-14-
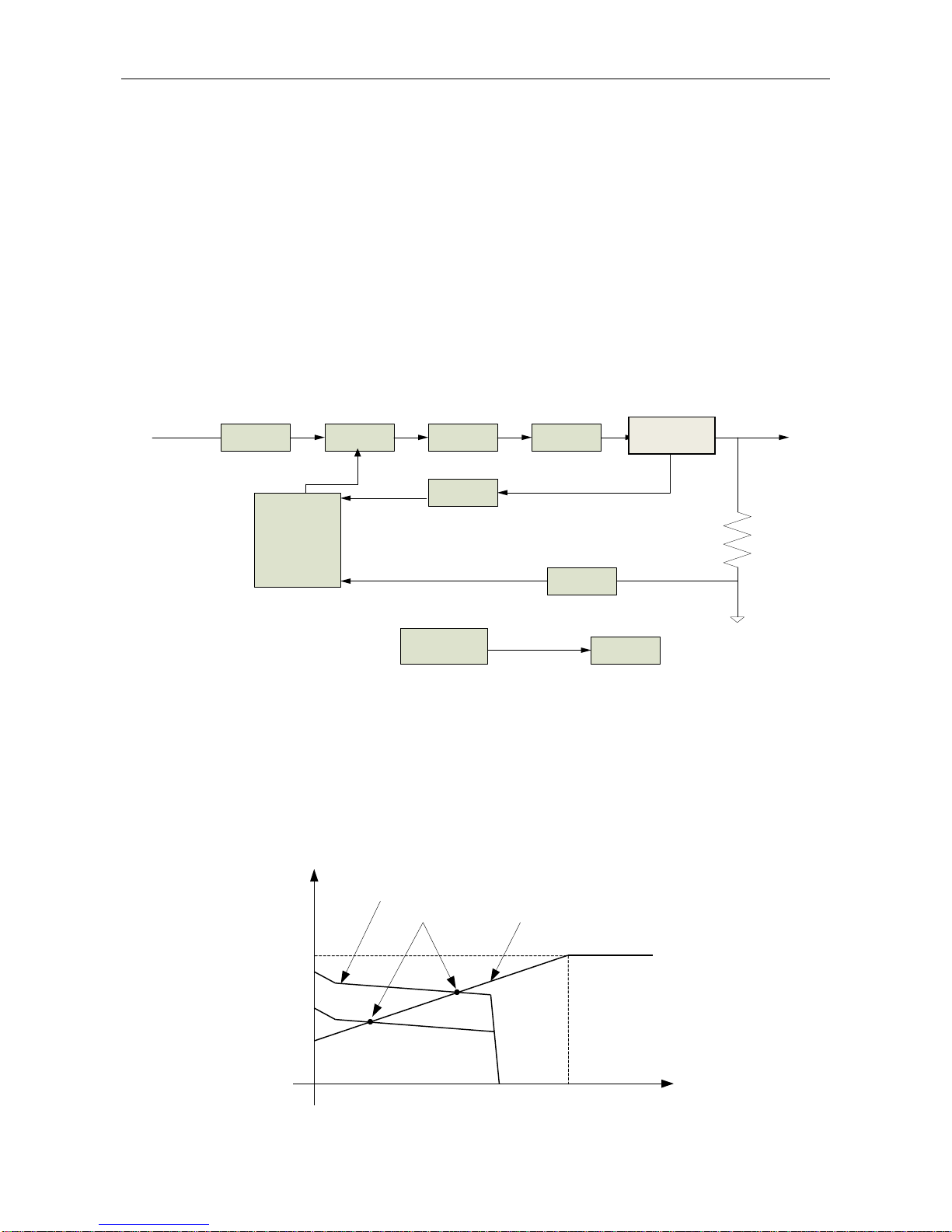
§2.5 Working Principle
The working principle of DPS series welding machine is shown as the following figure.
Single-phase 208-240VAC is rectified into DC, then is converted to medium frequency AC
(about 20KHz) by inverter device (IGBT), after reducing voltage by medium transformer
(the main transformer) and rectifying by medium frequency rectifier (fast recovery diodes),
and fine-tuned by inductance filtering. The circuit utilizes current feedback control
technology to insure current output stability when MMA or TIG and adopts to voltage
feedback control technology to insure voltage output stability when operating in MIG
mode.
Rectifier Inverter Transformer Rectifier Hall
Current
Feedback
control
Single-phase AC
DC
AC DC
220V 50Hz
AC DC
Welding current
regulate
(Wire feed speed)
Wire feeder
motor
PWM signal
CPU control
Voltage
Feedback
control
§2.6 Volt-Ampere Characteristic
DPS series of welding machines have an excellent volt-ampere characteristic as shown
in the following figure. The relation between the rated loading voltage (U2) and welding
current (I2) is defined as follows: U2=14+0.05I
2
(V)
44
14
0 600
Io(A)
Uo(V)
Working point
Volt-ampere characteristic
The relation between the rated loading
voltage and welding current
208-240V 60HZ
Current sensor
Page 18
OPERATION
-15-
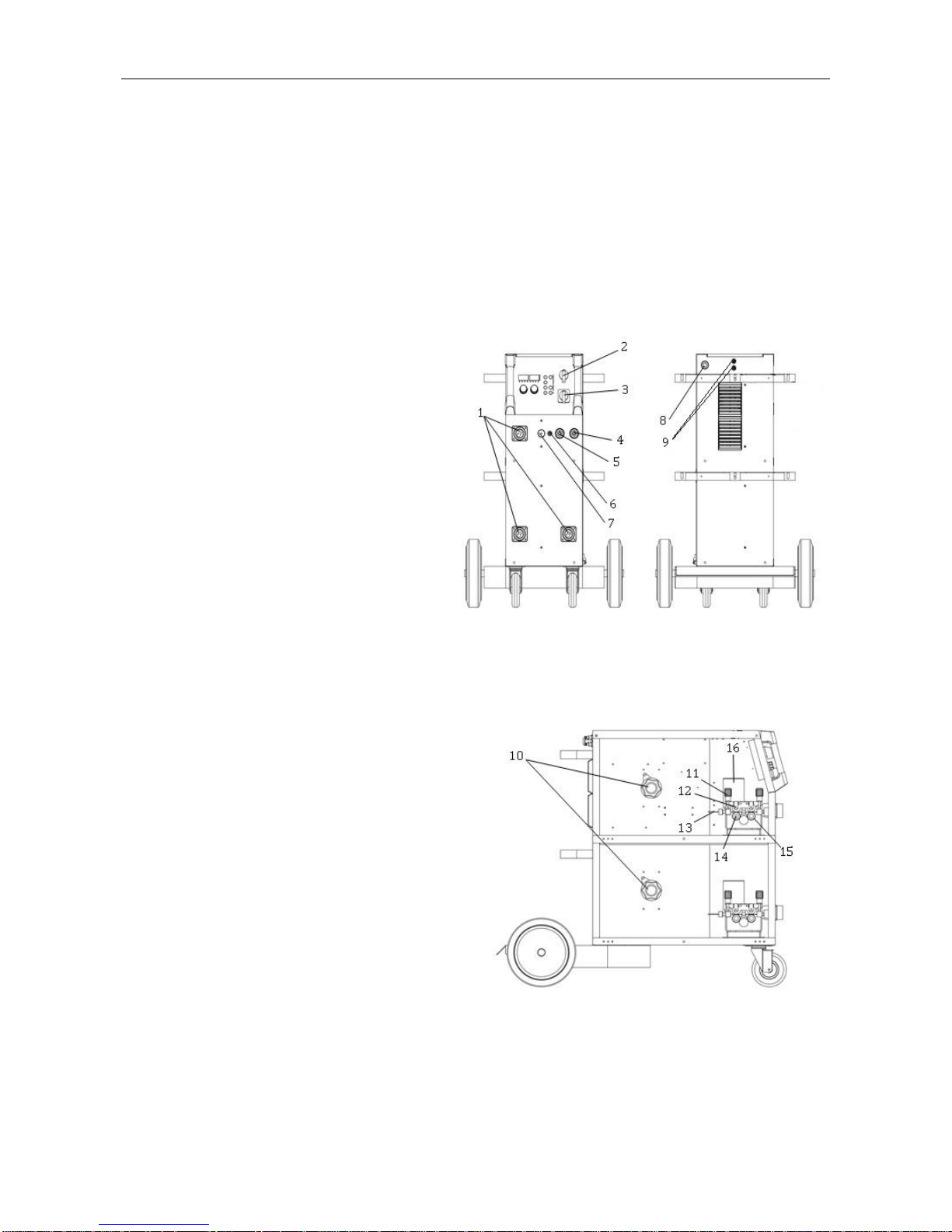
§3 Panel Functions & Descriptions
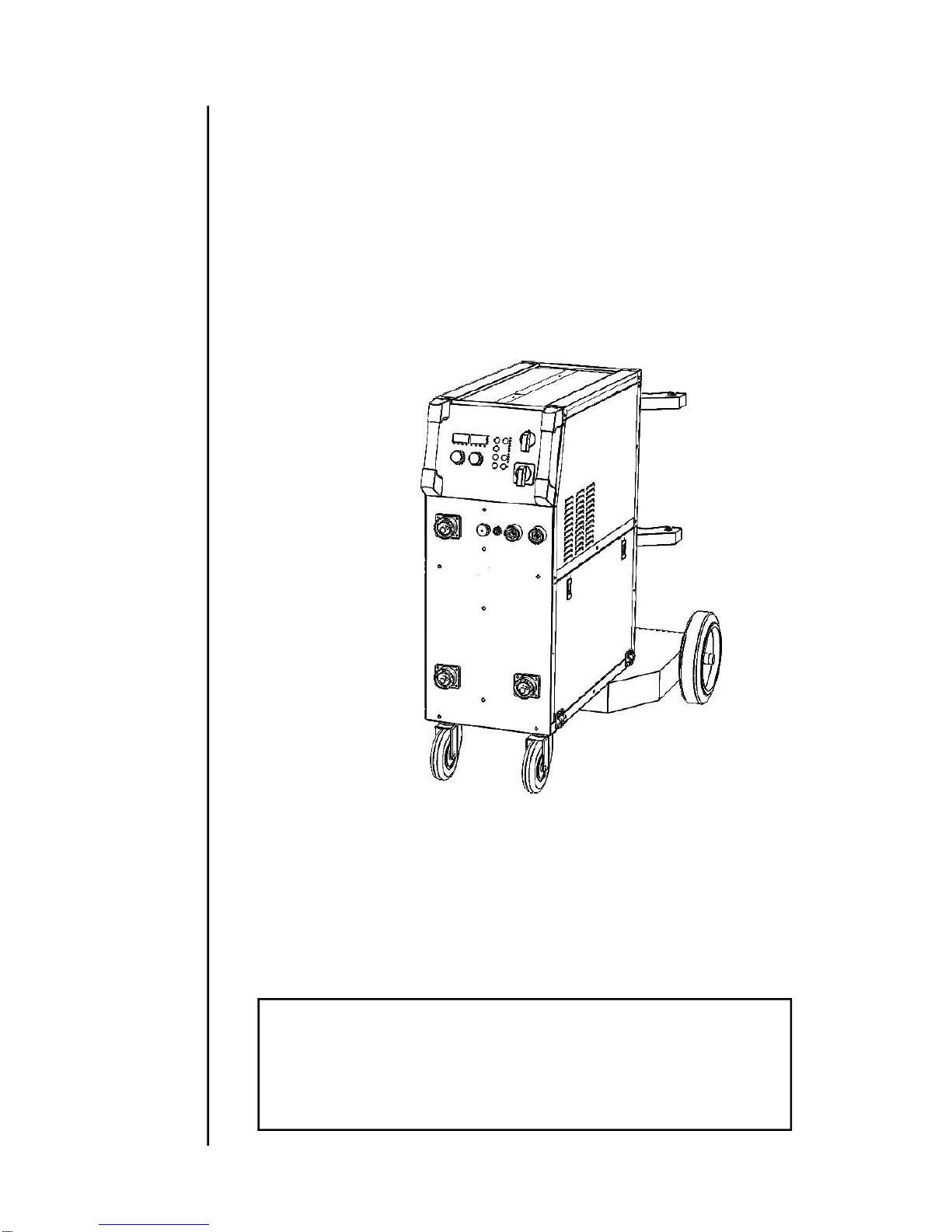
§3.1 Machine Layout Description
Front and rear panel layout of welding machine
1. MIG torch euro-connectors (3)
2. Main power ON/OFF Switch
3. Torch output “SELECT” switch (0-3)
4. Positive(+) welding power output
5. Negative(-) welding power output
6. TIG torch gas connector (5/8-18F).
7. Control circuit 9-pin connect plug.
8. Input power cord NEMA6-50P
(230VAC @ 50A Max.).
9. TIG Gas input connectors(above).
MIG Gas input connectors(below).
Wire feed cabinet (3) on welding
machine
10. Spool holder.
11. Wire feed tension adjustment (2x).
12. Wire feed tension arm (2x).
13. Wire feeder inlet guide.
14. Drive roller retainer (2x).
15. Wire drive roller (2x).
16. Wire feed motor.
Page 19
OPERATION
-16-
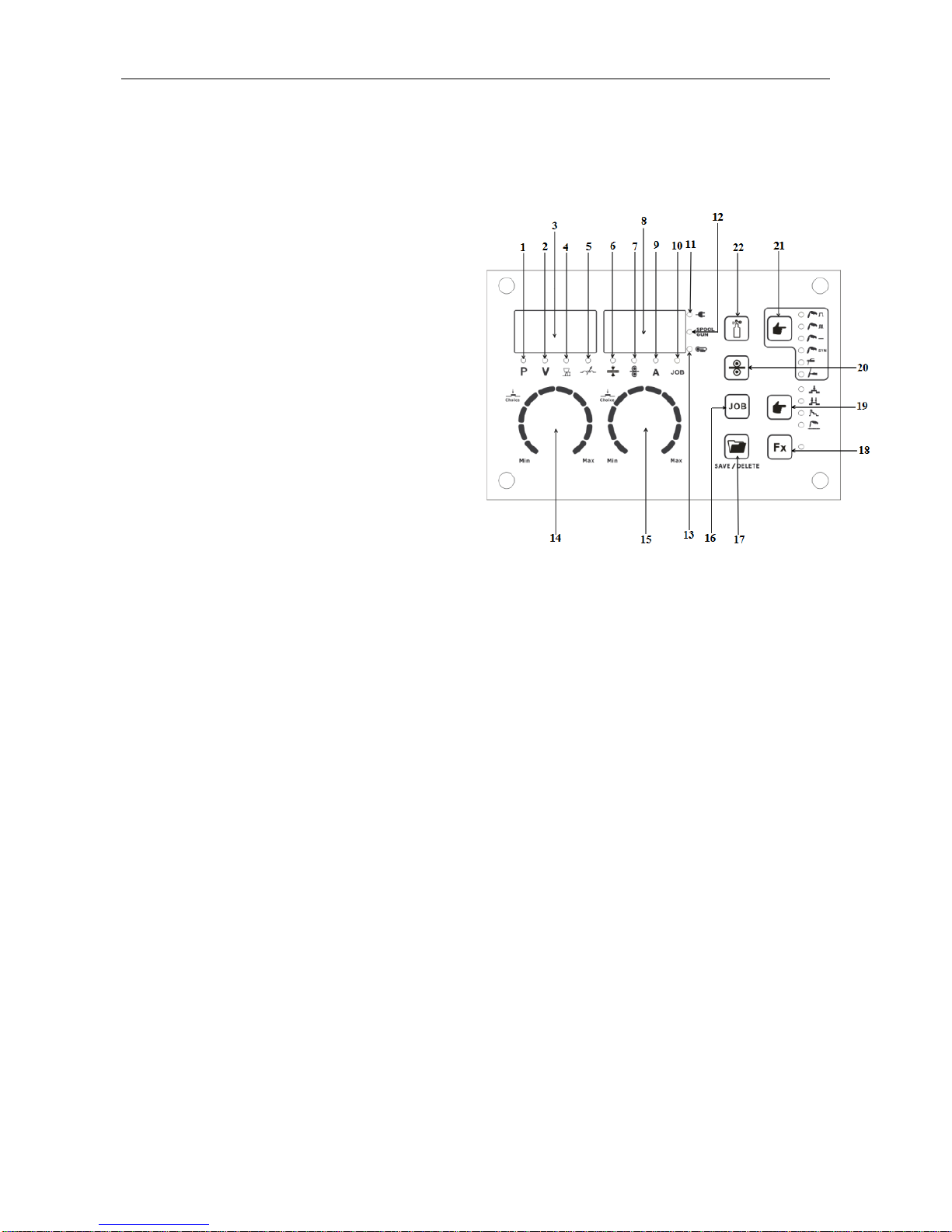
§3.2 Control panel of welding machine
1. Synergic program indicator.
2. Welding voltage indicator.
3. RH digital multifunction display.
4. Arc length indicator.
5. Inductance indicator.
6. Material thickness indicator.
7. Wire feed indicator.
8. LH digital multifunction display.
9. Welding current indicator.
10. JOB indicator.
11. Power “ON” indicator.
12. Spool gun mode indicator.
13. Over-temp alarm indicator.
14. LH parameter select/adjust knob.
15. RH parameter select/adjust knob.
16. JOB button.
17. Program save/delete button.
18. Function button.
19. Trigger mode select button: Select 2T/4T/S4T/Spot Weld
20. Manual wire feed button.
21. Welding process select button.
22. Manual shield gas check button.
Arc Length (4)
If arc length is decreased, the arc cone becomes narrower and the arc more focused
resulting in a weld bead that is narrow with slightly decreased penetration. Conversely, if
arc length is increased, the arc cone and the arc are wider resulting in a weld bead that is
wider and flatter with slightly increased penetration. Wire speed must be constant (preset
synergic) for arc length adjustment to have the desired effect on the weld.
Inductance / Wave Form (5)
Inductance slows the rate of current rise. A high inductance setting (+10) increases the
time of each arc cycle creating more penetration. A low inductance setting (-10)
decreases the time of each individual arc cycle creating a narrow bead or less
blow-through on thin material.
Page 20

OPERATION
-17-
Alarm Indicator (13)
Illuminates when the power supply has exceeded duty-cycle and entered an
over-temperature condition. The unit will automatically reset once cooled and lamp will go
off.
JOB program save (16)
In the JOB mode, 100 different JOB records can be stored and recalled. When leaving
the factory, has no saved JOB programs; therefore, operator must first save a program.
Saving the JOB program
⚫ Set JOB mode parameters (welding function, welding mode, welding parameters,
etc).
⚫ Press the JOB button (16) and LED will illuminate.
⚫ Select JOB number by the adjustment Knob (15) shown on the digital meter (8).
⚫ Press the Save/Delete button (17) to save the JOB under the selected number.
Recall the JOB program
⚫ Press the JOB button (16) and the JOB LED will illuminate.
⚫ Selectthe required JOB number by the adjustment Knob (15) as shown on the meter
(8).
⚫ Press the JOB button (16) again and the JOB LED is off that signals exit of JOB
mode.
Function button (18)
• Implicit parameter menu and parameter adjustment method for import and
export
a) Press the function button (18) indicator light “ON” indicates in parameter adjusting
mode.
b) Scroll through parameter codes turning knob (14). Codes are shown on meter (3).
Once parameter is selected, adjust the knob (15) with selection shown on the meter
(8).
c) Press the function button(18)again, light “OFF” signals exit parameter adjusting
mode.
Page 21
OPERATION
-18-
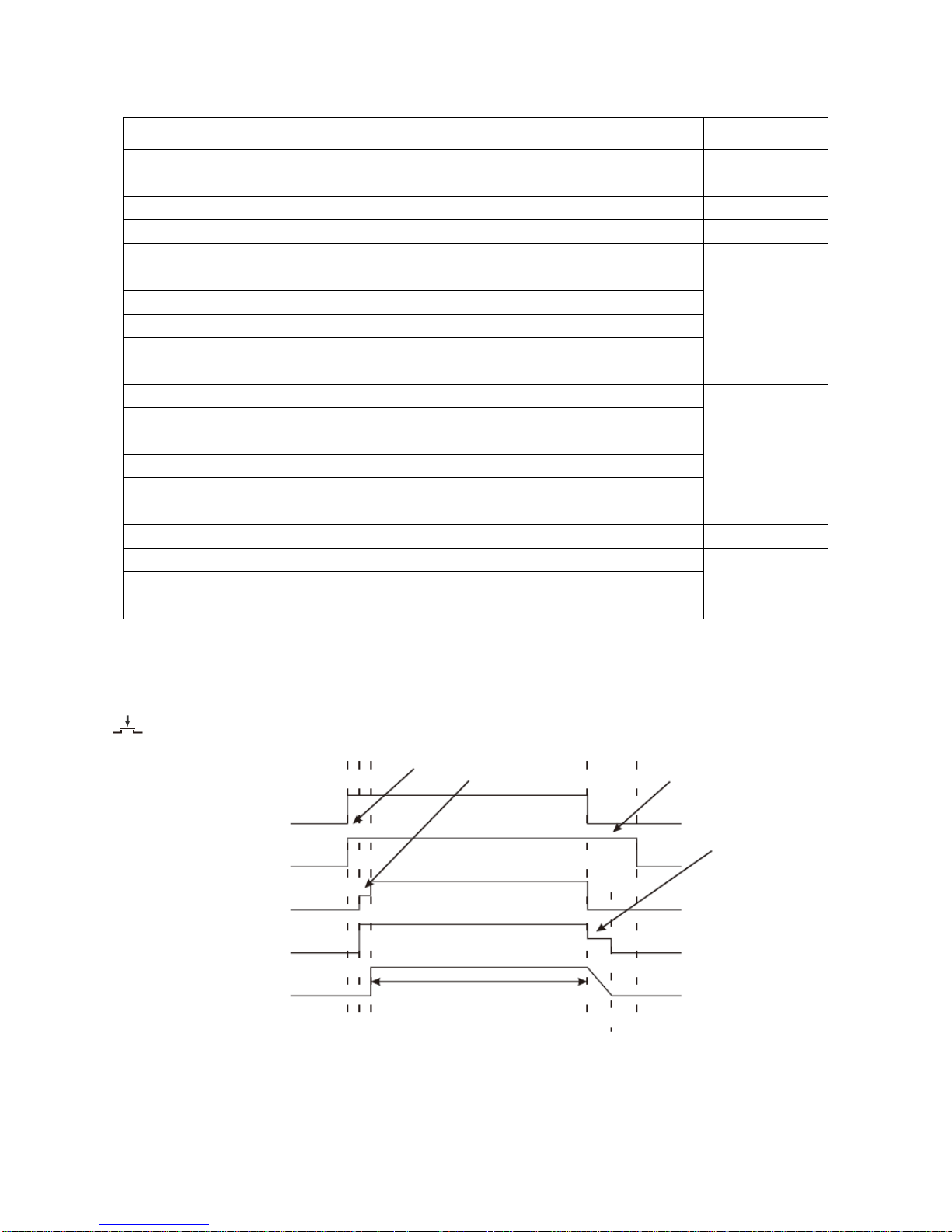
DISPLAY
FUNCTION
ADJUSTABLE RANGE
MODE
PrG
PRE GAS
0-5S
PoG
POST GAS
0-10S
SFt
SLOW FEED TIME
0-10S
bub
BURN BACK
0-10
SPt
SPOT WELD TIME
0-10S
dPC
DELTA PULSE CURRENT
0-200A
DUAL PULSE
FdP
DUAL PULSE FREQUENCY
0.5-3.0Hz
dut
DUAL PULSE DUTY
10-90%
bAL
DUAL PULSE BASE CURRENT
ARC LENGTH
+10 / -10
SCP
START CURRENT PERCENT
1-200%
S4T
SAL
START CURRENT
ARC LENGTH
+10 / -10
ECP
END CURRENT PERCENT
1-200%
EAL
END CURRENT ARC LENGTH
+10 / -10
HdC
HYDROCOOLING
ON/OFF
SPG
SPOOL GUN
ON/OFF
HSt
HOT START
0-10
MMA
ACF
ARC FORCE
0-10
dSL
DOWN SLOPE
0-10S
TIG
Trigger mode select button (19)
2T mode (ON/OFF)
Pre Gas Time
Slow Feed Time
Post Gas Time
Welding conditions
Gun Switch
Gas Supply
Wire Feed
Output Voltage
Output Current
Burn back Time
Page 22
OPERATION
-19-
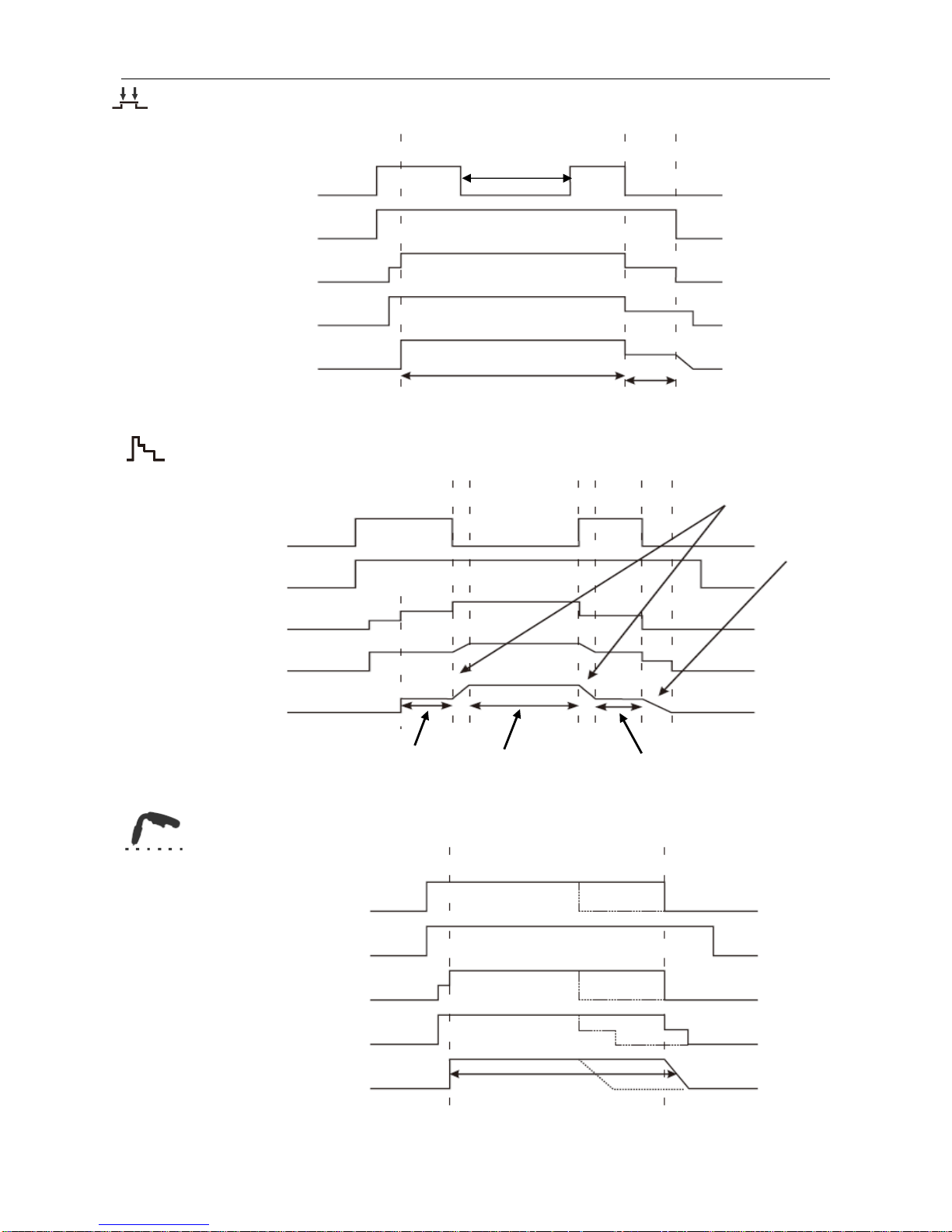
4T mode (Latching)
S4T mode
Spot weld
Welding conditions
Gun Switch
Gas Supply
Wire
Output Voltage
Output Current
End Current conditions
Self-Locking
Gun Switch
Gas Supply
Wire Feed
Output Voltage
Output Current
Welding condition
Initial condition
End Current condition
Transition Time
Burnback Time
Gun Switch
Gas Supply
Wire Feed
Output Voltage
Output Current
Spot Weld Time
Page 23

OPERATION
-20-
Program SELECT Indicator (21)
Synergic Function
The operator simply sets the welding current like MMA or TIG welding and the machine
calculates the optimal voltage and wire speed for the material type, wire type and size
and shielding gas being used. Obviously other variables such as welding joint type and
thickness, air temperature affect the optimal voltage and wire feed setting, so the program
provides a voltage fine tuning function for the synergic program selected. Once the
voltage is adjusted in a synergic program, it will stay fixed at this variation when the
current setting is changed. To reset the voltage for a synergic program back to factory
default, change to another program and back again
The synergic programs are given a number from 1-17, this is accessed on the L display
(3) using the L knob (14), indicator 'P'. To select the relevant program for the welding
application, check the chart printed on the inside door of the welding machine or further
on in this manual.
Single Pulse Function
Pulse allows the arc to enter spray transfer at lower currents and feed speeds than
manual allowing faster welding with high deposition and smaller heat effected zones due
to the extra arc energy provided at peak of pulse. Used for stainless or aluminum edge or
seam welds.
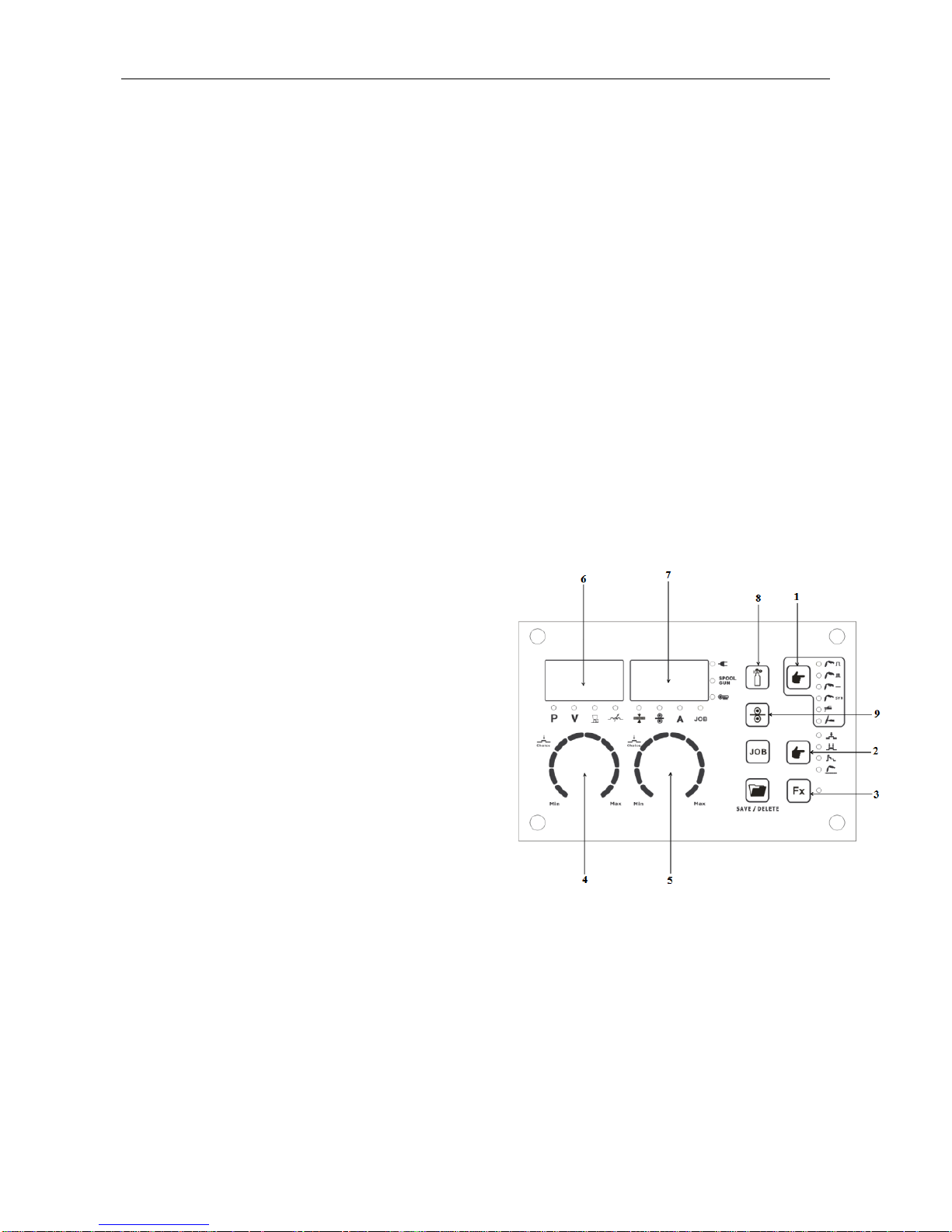
Double-Pulse Function
Double pulse allows more precise control of heat input as “peak” is offset by “base”
allowing puddle stability. It is mainly used in aluminum alloy welding for strong penetration
with narrow bead and smooth surface. It can produce the ripple effect of a TIG weld
without torch modulation. Dual pulse reference waveform as shown below:
Wire
Current
Page 24
OPERATION
-21-
◼ DUAL PULSE FREQUENCY
Set pulse frequency, as shown in Figure regulating the value of time T, namely, ripple
pattern of density regulation. Higher Hz produces many short ripples with slightly lower
penetration.
◼ DUAL PULSE DUTY
Set strong pulse time T1 (peak) for penetration and low-frequency cycle T2 ratio
(cooling), namely the regulation of the proportion of the ripple pattern on weld puddle
surface and resulting depth in groove.
MIG Single-Pulse Synergic Function- Front Panel Description
1. Function Select: MIG Single-Pulse Synergic
2. Trigger Select: 2T/4T/S4T/Spot
3. Function Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Synergic Program Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Set: Voltage / Arc Length / Inductance
5. Set: Material Thickness / Current / Wire
Speed
6. Display: Program / Voltage / Arc Length /
Inductance
7. Display: Current / Wire Speed / Material
Thickness
8. Shield Gas Purge
9. Manual Wire Feed
Page 25
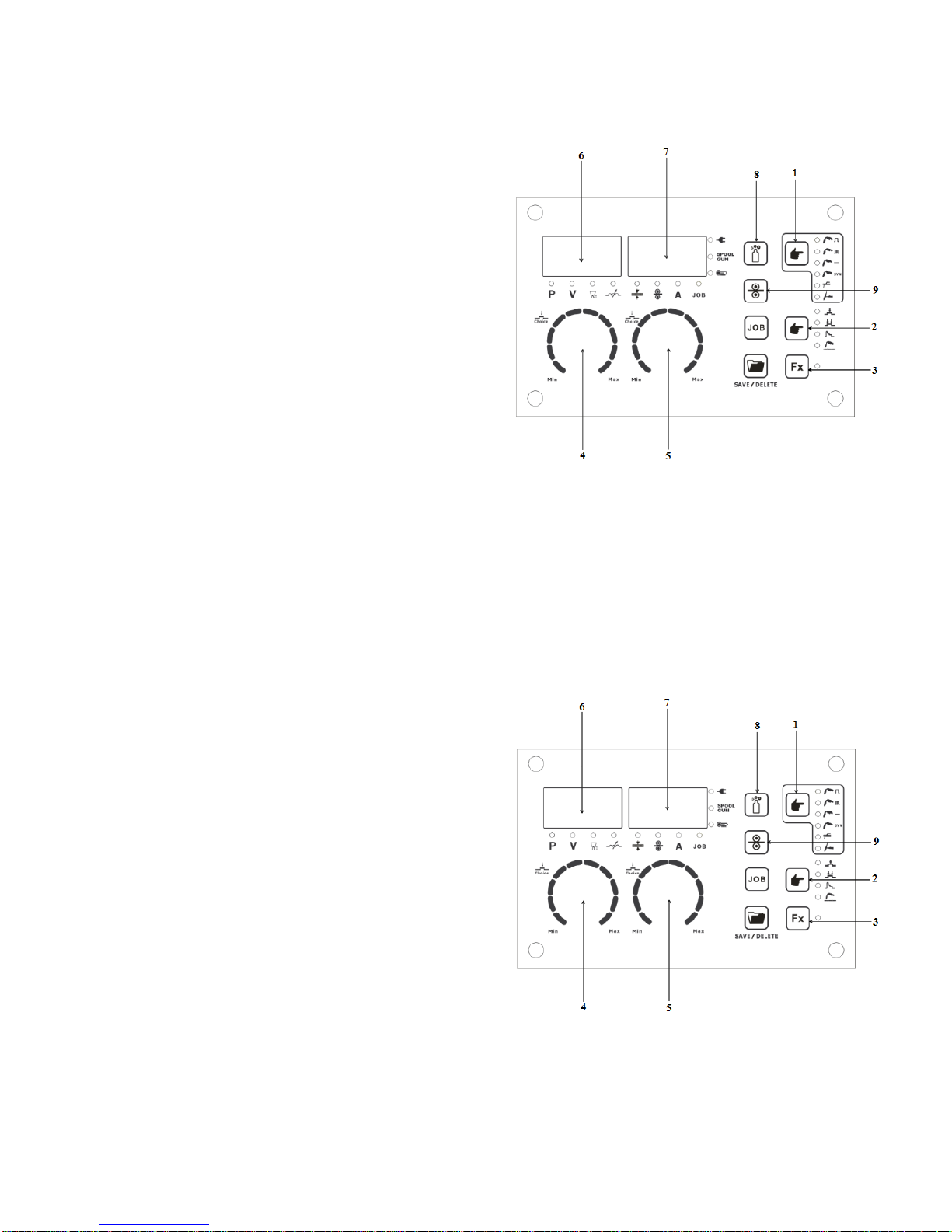
OPERATION
-22-
MIG Double-Pulse Synergic Function- Front Panel Description
1. Function Select: MIG Double-Pulse Synergic
2. Trigger Select: 2T/4T/S4T/Spot
3. Function Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Synergic Program Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Set: Voltage / Arc Length / Inductance
5. Set: Material Thickness / Current / Wire
Speed
6. Display: Program / Voltage / Arc Length /
Inductance
7. Display: Current / Wire Speed / Material
Thickness
8. Shield Gas Purge
9. Manual Wire Feed
MIG Manual Function- Front Panel Description
1. Function Select: MIG Manual
2. Trigger Select: 2T/4T/S4T/Spot
3. Function Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Set: Voltage / Inductance
5. Set: Thickness /Current / Wire Speed
6. Display: Voltage / Inductance
7. Display: Thickness / Current / Wire Speed
8. Shield Gas Purge
9. Manual Wire Feed
Page 26
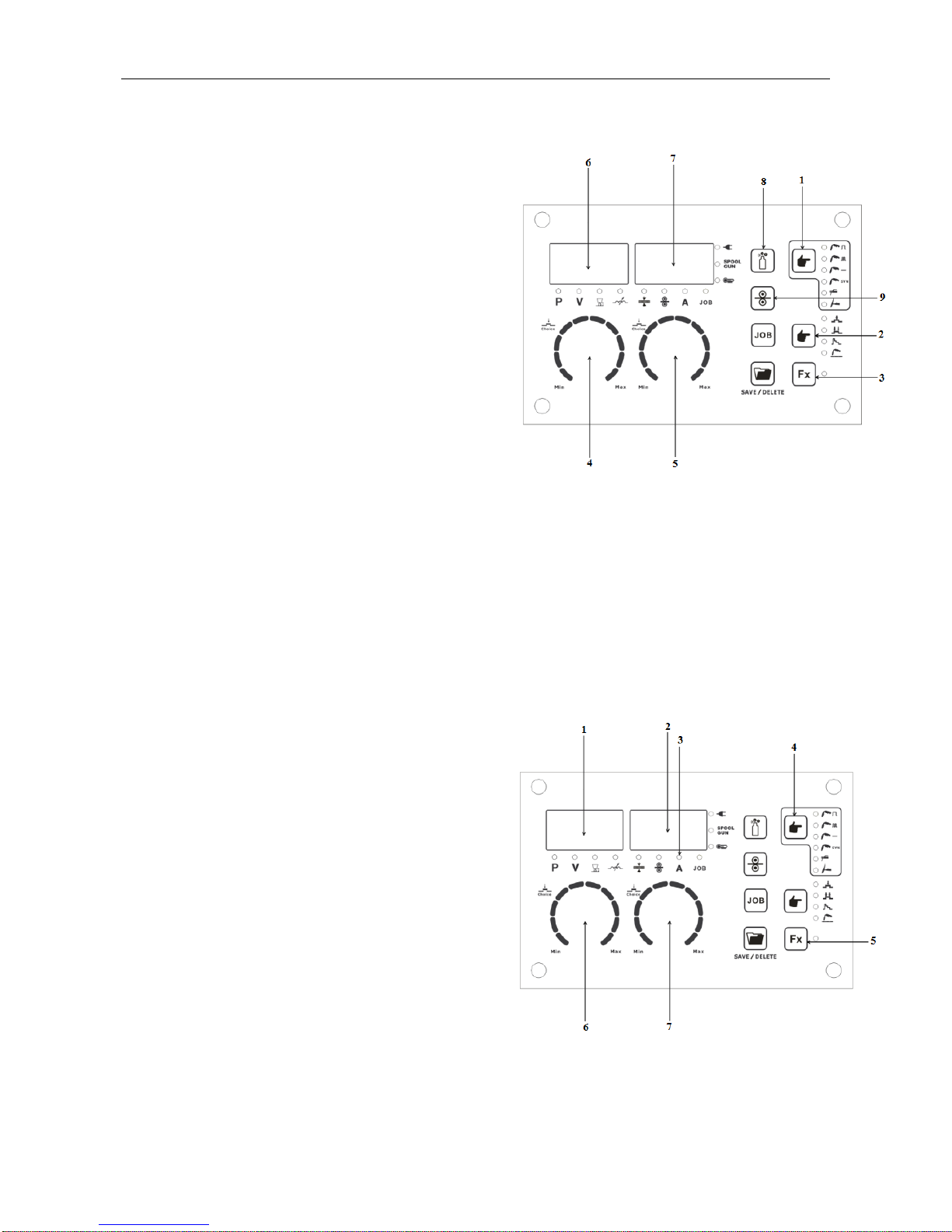
OPERATION
-23-
MIG Synergic Function-Front Panel
Description
1. Function Select: MIG Synergic
2. Trigger Select: 2T/4T/S4T/Spot
3. Function Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Synergic Program Select: refer to§ 4.4
4. Set: Voltage / Arc Length / Inductance
5. Set: Material Thickness / Current / Wire
Speed
6. Display: Program / Voltage / Arc Length /
Inductance
7. Display: Current / Wire Speed / Material Thickness
8. Shield Gas Purge
9. Manual Wire Feed
MMA Mode - Front Panel Description
1. Display Code Parameter: Hot Start / Arc
Force
2. Display Welding Current: Hot Start / Arc
Force
3. Welding Current Indicator (Amps)
4. Function Select: MMA / Stick Electrode
5. Parameter Select: Hot Start / Arc Force
6. Code Parameter Select: Hot Start / Arc Force
7. Welding Current Set: Hot Start / Arc Force
Page 27

OPERATION
-24-
TIG Mode - Front Panel Description
1. Display Code Parameter: Down Slope
2. Display Welding Current: Down Slope
3. Welding Current Indicator (Amps)
4. Function Select: TIG (Lift-Arc)
5. Trigger Select: 2T or 4T
6. Parameter Select: Down Slope
7. Code Select: Down Slope
8. Welding Current or Down Slope Time
Page 28

OPERATION
-25-
§4 Installation & Operation
§4.1 Installation & Operation for MMA/Stick Electrode Welding
§4.1.1 Set-Up Installation
(1) Connection of Output Cables: Two sockets are available on this welding machine,
One Positive(+) and one Negative (-) polarity, to connect MMA/Electrode holder cable and
earth clamp cable. Various electrodes require different polarity for optimum results and
careful attention should be paid to the polarity, refer to the electrode manufacturers
information for the correct polarity.
DCEP: Electrode connected to Positive (+) output socket.
DCEN: Electrode connected to Negative (-) output socket.
(2) Turn the power source on and press the Function Select button (#1) to
MMA/Electrode.
(3) Set the welding current relevant to the electrode type and size being used as
recommended by the electrode manufacturer.
(2) Set the welding current
using the knob
(4) Connect the earth lead to
NEGATIVE (-) terminal
(3) Connect the electrode lead
to POSITIVE (+) terminal
(1) Press the MMA/Stick
Electrode Button
Page 29

OPERATION
-26-
(4) Set the Hot Start and Arc Force as required using the Fx select and setting knobs.
(5) Place the electrode into the electrode holder and clamp tight.
(6) Strike the electrode against the work piece to create and arc and hold the electrode
steady to maintain the arc.
§4.1.2 MMA/Stick Electrode Welding
One of the most common types of arc welding is manual metal arc welding (MMA) or
stick welding. An electric current is used to strike an arc between the base material and a
consumable electrode rod or ‘stick’. The electrode rod is made of a material that is
compatible with the base material being welded and is covered with a flux that releases a
gaseous vapor that serve as a shielding gas and providing a layer of slag, both of which
protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. The electrode core itself acts as
filler material the residue from the flux that forms slag covering over the weld metal must
be chipped away after welding.
3
2
Page 30

OPERATION
-27-
MMA / Stick Electrode
•The arc is initiated by momentarily touching the electrode to the base metal.
• The melted electrode metal is transferred across the arc into the molten pool and
becomes weld metal.
• The deposit is covered and protected by slag from the electrode flux coating.
Flux Properties
● producing a protective gas around the weld area
● providing fluxing elements and deoxidizer
● creating a protective slag coating over the weld
● establishing arc characteristics
● adding alloying elements
Stick electrodes serve many purposes in addition to filler metal to the molten pool. These
additional functions are provided mainly by the various coverings on the electrode.
§4.1.3 MMA Welding Fundamentals
Electrode Selection
As a general rule, the selection of an electrode is straight forward, in that it is only a
matter of selecting an electrode of similar composition to the parent metal. However, for
some metals there is a choice of several electrodes, each of which has particular
properties to suit specific classes of work. It is recommend to consult your welding
supplier.
Page 31

OPERATION
-28-
The size of the electrode generally
depends on the thickness of the section
being welded, and the thicker the section
the larger the electrode required. The
maximum size of electrodes that may be
used for various thicknesses based on a
general purpose type 6013 electrode.
Welding Current (Amperage)
Correct current selection for a particular
job is an important factor in arc welding.
With the current set too low, difficulty is
experienced in striking and maintaining a
stable arc. The electrode tends to stick to
the work, penetration is poor and beads
with a distinct rounded profile will be
deposited. Too high current is accompanied
by overheating of the electrode resulting undercut and burning through of the base metal
and producing excessive spatter. Normal current for a particular job may be considered
as the maximum, which can be used without burning through the work, over-heating the
electrode or producing a rough spattered surface. The table shows current ranges
generally recommended for a general purpose type 6013 electrode.
Arc Length
To strike the arc, the electrode should be gently scraped on the work until the arc is
established. There is a simple rule for the proper arc length; it should be the shortest arc
that gives a good surface to the weld. An arc too long reduces penetration, produces
spatter and gives a rough surface finish to the weld. An excessively short arc will cause
sticking of the electrode and result in poor quality welds. General rule of thumb for down
hand welding is to have an arc length no greater than the diameter of the core wire.
Average Thickness
of Material
Max. Recommended
Electrode Diameter
1.0-2.0 mm
2.5 mm
2.0-5.0 mm
3.2 mm
5.0-8.0 mm
4.0 mm
>8.0mm
5.0 mm
Electrode Size
ø mm
Current Range
(Amps)
2.5 mm
60-95
3.2 mm
100-130
4.0 mm
130-165
5.0 mm
165-260
Page 32

OPERATION
-29-
Electrode Angle
The angle that the electrode makes with the work is important to ensure a smooth, even
transfer of metal. When welding in down hand, fillet, horizontal or overhead the angle of
the electrode is generally between 5 and 15 degrees towards the direction of travel. When
vertical up welding the angle of the electrode should be between 80 and 90 degrees to
the work piece.
Travel Speed
The electrode should be moved along in the direction of the joint being welded at a
speed that will give the size of run required. At the same time, the electrode is fed
downwards to keep the correct arc length at all times. Excessive travel speeds lead to
poor fusion, lack of penetration etc, while too slow a rate of travel will frequently lead to
arc instability, slag inclusions and poor mechanical properties.
Material and Joint Preparation
The material to be welded should be clean and free of any moisture, paint, oil, grease,
mill scale, rust or any other material that will hinder the arc and contaminate the weld
material. Joint preparation will depend on the method used include sawing, punching,
shearing, machining, flame cutting and others. In all cases edges should be clean and
free of any contaminates. The type of joint will be determined by the chosen application.
§4.2 Installation & Operation for TIG Welding
§4.2.1 Set-Up for TIG Welding
(1) Insert the earth cable plug into the positive socket on the front of the machine and
twist to lock in place
(2) Plug the welding torch into the negative socket on the front panel and twist to lock.
(3) Connect the gas line of TIG torch to outlet gas connector on the front of the machine.
(4) Connect the control cable of torch switch to 9-pin socket on the front of the machine.
(5) Connect the gas regulator to the gas cylinder and the gas line to the gas regulator.
(6) Connect the gas line to the machine inlet gas connector located on the rear panel.
Page 33

OPERATION
-30-
(7) Connect the power cable of welding machine to the electrical outlet. (230VAC, 1Ph)
(8) Carefully open the valve of the gas cylinder, set the required gas flow rate.
(9) Select TIG function on the front panel.
(10) Set torch operation for 2T or 4T:
• When 2T operation is selected, pressing trigger starts gas, touch and lift arc to start.
Release trigger to stop gas and arc.
• When 4T operation is selected, press and release trigger to start gas, touch and lift
arc to start. Press and release trigger again to stop gas and arc.
(8) Carefully open the valve of the gas cylinder (9) Select TIG function using the button.
and set the required gas flow rate.
(10) Select 2T or 4T trigger as required. (11) Select welding current and down slope.
(12) Select welding current as required. The selected welding current will show on
display.Set down slope time as required. The down slope time will show on the digital
display.
1
3
2
Page 34

OPERATION
-31-
(13) Assemble front end parts of the TIG (14) Lay the outside edge of the cup
torch, fitting a sharpened tungsten suitable on work piece with the tungsten 1- 2mm
for the material to be welded. from the work piece.
(15) With a small movement rotate the gas (16) Now rotate the gas cup in the reverse
cup forward so that the tungsten electrode direction to lift the tungsten electrode from
touches the work piece. the work piece to create the arc. (Lift Arc)
(17) Weld the material by placing the filler rod into the arc.
(18) Release the trigger to stop the welding.
IMPORTANT! – It is recommended that you check for gas leaks prior to operation and
that the operator close the cylinder valve when the machine is not in use.
Page 35

OPERATION
-32-
§4.2.2 DCTIG Welding
The DC power source uses what is known as DC (direct current)
in which the main electrical component, known as electrons, flow
in only one direction from the negative terminal (-) to the positive
terminal (+). In the DC electrical circuit there is an electrical
principle at work which provides that, in a DC circuit, 70% of the
energy (heat) is always on the positive side. This is important
because it determines what terminal to connect the TIG torch.
DC TIG welding is a process in which an arc is struck
between a TUNGSTEN electrode and the metal work
piece. The weld area is shielded by an inert gas flow to
prevent contamination of the tungsten, molten pool and
weld area. When the TIG arc is struck the inert gas is
ionized and superheated changing its’ molecular
structure which converts it into a plasma stream. This
plasma stream that flows between the tungsten and the work piece is the TIG arc and can
be as hot as 19,000°C. It is a very pure and concentrated arc which provides the
controlled melting of most metals into a weld pool. TIG welding offers the user the
greatest amount of flexibility to weld the widest range of materials, thickness and profiles.
DC TIG welding is also the cleanest weld with no sparks or spatter.
The intensity of the arc is proportional to
the current that flows from the tungsten.
The welder regulates the welding current
to adjust the power of the arc. Typically
thin material requires a less powerful arc
with less heat to melt the material so less
current (amps) is required, thicker material requires a more powerful arc with more heat
so more current (amps) are necessary to melt the material.
Page 36

OPERATION
-33-
LIFT ARC IGNITION for TIG Welding
Lift Arc is a form of arc ignition where the machine has voltage on the electrode to only a
few volts, with a current limit of one or two amps (well below the limit that causes metal to
transfer and contamination of the weld or electrode). When the machine detects that the
tungsten has left the surface and a spark is present, it immediately (within microseconds)
increases power, converting the spark to a full arc. It is a simple, safe lower cost
alternative arc ignition process to HF (high frequency) and a superior arc start process to
scratch start.
§4.2.3 TIG Welding Fusion Technique
Manual TIG welding is often considered the most difficult of all
the welding processes. Because the welder must maintain a
short arc length, great care and skill are required to prevent
contact between the electrode and the workpiece. Similar to
Oxygen / Acetylene torch welding, TIG welding normally
requires two hands and in most instances requires the welder
to manually feed a filler wire into the weld pool with one hand while manipulating the
welding torch in the other. However, some welds combining thin materials can be
accomplished without filler metal like edge, corner, and butt joints. This is known as
Fusion welding where the edges of the metal pieces are melted together using only the
heat and arc force.
gas flow
tungsten off
the work
Lay the nozzle on the
job without the tungsten
touching the work.
Rock the torch sideways
so that the tungsten
touches the work & hold
momentarily.
tungsten touches
the work
Rock the torch back in
the opposite direction,
the arc will ignite as
the tungsten lifts off.
arc ignition
Lift the torch to
maintain the arc.
established
TIG arc
Page 37

OPERATION
-34-
TIG Welding with Filler Wire Technique
It is necessary in many situations with TIG welding to
add a filler wire into the weld pool to build up weld
reinforcement and create a strong weld. Once the arc is
started the torch tungsten is held in place until a weld pool
is created, a circular movement of the tungsten will assist
is creating a weld pool of the desired size. Once the weld
pool is established tilt the torch at about a 75° angle and
move smoothly and evenly along the joint. The filler metal is introduced to the leading
edge of the weld pool. The filler wire is usually held at about a 15° angle and fed into the
leading edge of the molten pool, the arc will melt the filler wire into the weld pool as the
torch is moved forward. A “dabbing” technique can be used to control the amount of filler
wire added. The wire is fed into the molten pool and retracted in a repeating sequence as
the torch is moved slowly and evenly forward. It is important during the welding to keep
the molten end of the filler wire inside the gas shield as this protects the end of the wire
from being oxidized and contaminating the weld pool.
Page 38

OPERATION
-35-
§4.2.4 Tungsten Electrodes
Tungsten is a rare metallic element used for manufacturing TIG welding electrodes. The
TIG process relies on tungsten’s hardness and high-temperature resistance to carry the
welding current to the arc. Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal, 3,410
degrees Celsius. Tungsten electrodes are a consumable and come in a variety of sizes,
they are made from pure tungsten or an alloy of tungsten and other rare earth elements.
Choosing the correct tungsten depends on the material being welded, amps required and
whether you are using AC or DC welding current. Tungsten electrodes are color-coded at
the end for easy identification.
Thoriated (RED)
Thoriated tungsten electrodes (AWS classification EWTh-2) contain a minimum of 97.30
percent tungsten and 1.70 to 2.20 percent thorium and are called 2% thoriated. They are
the most commonly used DC electrodes today and are preferred for their longevity and
ease of use. Thorium however is a low-level radioactive hazard and many users have
switched to other alternatives. Regarding the radioactivity, thorium is an alpha emitter but
when it is enclosed in a tungsten matrix the risks are negligible. Thoriated tungsten
should not get in contact with open cuts or wounds. The more significant danger to welder
can occur when thorium oxide gets into the lungs. This can happen from the exposure to
vapors during welding or from ingestion of material/dust in the grinding of the tungsten.
Follow the manufacturer’s warnings, instructions, and the Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS).
Pure (Green)
Pure tungsten electrodes (AWS classification EWP/WP) contain a minimum of 99.5%
percent tungsten. Pure Tungsten Electrodes provide conductivity similar to zirconiated
electrodes. Pure Tungsten Electrodes work well on AC constant current power sources,
such as transformer, for aluminum and magnesium alloys in low to medium temperature
applications. They can be used DC electrode negative with a pointed end, or balled for
use with AC power sources, they tend to split at higher amperages and should be used
for non-critical welds only.
Page 39

OPERATION
-36-
Ceriated (Orange)
Ceriated tungsten electrodes (AWS classification EWCe-2) contain a minimum of 97.30
percent tungsten and 1.80 to 2.20 percent cerium and are referred to as 2% ceriated.
Ceriated tungsten performs best in DC welding at low current settings. They have
excellent arc starts at low amperages and become popular in such applications as orbital
tube welding, thin sheet metal work. They are best used to weld carbon steel, stainless
steel, nickel alloys, and titanium, and in some cases it can replace 2% Thoriated
electrodes. Ceriated tungsten is best suited for lower amperages it should last longer than
Thoriated tungsten higher amperage applications are best left to Thoriated or
Lanthanated tungsten.
Lanthanated (Gold)
Lanthanated tungsten electrodes (AWS classification EWLa-1.5) contain a minimum of
97.80 percent tungsten and 1.30 percent to 1.70 percent lanthanum and are known as 1.5%
lanthanated. These electrodes have excellent arc starting, a low burn off rate, good arc
stability, and excellent re-ignition characteristics. Lanthanated tungsten also share the
conductivity characteristics of 2% Thoriated tungsten. Lanthanated tungsten electrodes
are ideal if you want to optimize your welding capabilities. They work well on AC or DC
electrode negative with a pointed end, or they can be balled for use with AC sine wave
power sources. Lanthanated tungsten maintains a sharpened point well, which is an
advantage for welding steel and stainless steel on DC or AC from square wave power
sources.
Zirconiated (White)
Zirconiated tungsten electrodes (AWS classification EWZr-1) contain a minimum of
99.10 percent tungsten and 0.15 to 0.40 percent zirconium oxide. Most commonly used
for AC welding, Zirconiated tungsten produces a very stable arc and is resistant to
tungsten spitting. It is ideal for AC welding because it retains a balled tip and has a high
resistance to contamination. Its current-carrying capacity is equal to or greater than that
of thoriated tungsten. Zirconiated tungsten is not recommended for DC welding.
Page 40

OPERATION
-37-
Tungsten Electrodes Rating for Welding Currents
Tungsten
Diameter
mm
DC Current Amps
Torch Negative
2% Thoriated
AC Current Amps
Un-Balanced Wave
0.8% Zirconiated
AC Current Amps
Balanced Wave
0.8% Zirconiated
1.0mm
15-80
15-80
20-60
1.6mm
70-150
70-150
60-120
2.4mm
150-250
140-235
100-180
3.2mm
250-400
225-325
160-250
4.0mm
400-500
300-400
200-320
§4.2.5 Tungsten Preparation
Always use DIAMOND wheels when grinding and cutting. While tungsten is a very hard
material, the surface of a diamond wheel is harder, and this makes for smooth grinding.
Grinding without diamond wheels, such as aluminium oxide wheels, can lead to jagged
edges, imperfections, or poor surface finishes not visible to the eye that will contribute to
weld inconsistency and weld defects.
Always ensure to grind the tungsten in a longitudinal direction on the grinding wheel.
Tungsten electrodes are manufactured with the molecular structure of the grain running
lengthwise and thus grinding crosswise is “grinding against the grain”. If electrodes are
ground crosswise, the electrons have to jump across the grinding marks and the arc can
start before the tip and wander. Grinding longitudinally with the grain, the electrons flow
steadily and easily to the end of the tungsten tip. The arc starts straight and remains
narrow, concentrated and stable.
Page 41

OPERATION
-38-
Electrode Shape & Angle
The shape of the tungsten electrode tip is an important process variable in precision arc
welding. A good selection of tip/flat size will balance the need for several advantages. The
bigger the flat, the more likely arc wander will occur and the more difficult it will be to arc
start. However, increasing the flat to the maximum level that still allows arc start and
eliminates arc wonder will improve the weld penetration and increase the electrode life.
The included angle determines weld bead shape and size. Generally, as the included
angle increases, penetration increases and bead width decreases.
Some welders still grind electrodes to a sharp point, which makes arc starting easier.
However, they risk decreased welding performance from melting at the tip.
Electrode Included Angle/Taper - DC Welding
Tungsten electrodes for DC welding should be ground longitudinally and concentrically
with diamond wheels to a specific included angle in conjunction with the tip/flat
preparation. Different angles produce different arc shapes and offer different weld
penetration capabilities.
Blunter electrodes with larger included angle provide:
• Last Longer
• Have better weld penetration
• Have a narrower arc shape
• Can handle more amperage without eroding.
Sharper electrodes with smaller included angle provide:
• Offer less arc weld
• Have a wider arc
• Have a more consistent arc
Page 42

OPERATION
-39-
Tungsten
Diameter
Diameter at
the Tip - mm
Constant
Included Angle -
Degrees
Current Range
Amps
Current Range
Pulsed Amps
1.0mm
.250
20
05 - 30
05 - 60
1.6mm
.500
25
08 - 50
05 - 100
1.6mm
.800
30
10 - 70
10 - 140
2.4mm
.800
35
12 - 90
12 - 180
2.4mm
1.100
45
15 - 150
15 - 250
3.2mm
1.100
60
20 - 200
20 - 300
3.2mm
1.500
90
25 - 250
25 - 350
§4.2.6 TIG Torch Switch Controls
Adjust current roller wheel,
when it’s roll upwards, the
current increase, when
downwards, the current
decrease.
Gun switch
Remote Control Socket
Page 43

OPERATION
-40-
§4.3 Installation & Operation for MIG Welding
§4.3.1 Set up installation for MIG Welding (Gas shielded wire)
(1) Insert the earth cable plug
into the Negative (-) socket and
twist to tighten.
(2) Plug the MIG welding gun
into one of the THREE
euro-connect sockets on the front
panel and tighten locking nut
securely.
(3) Connect the gas regulator to
the gas cylinder and connect the
gas line to the regulator.
(4) Connect the gas line to gas
connector on the rear panel.
(5) Open the gas cylinder valve,
set regulator. Check for Leaks!
(6) Connect the power cord of
welding machine with the outlet
on electrical box.
(7) Place the wire spool onto the spool holder. Snip the wire from the spool being sure to
hold the wire to prevent rapid uncoiling. Feed the wire into the wire feeder inlet guide tube
through to the drive roller. (SEE Section 4.3.3 for more information)
(7) Place wire onto spool holder - (spool retaining
nut is left hand thread) Feed wire through the
inlet guide tube on to the drive roller.
Page 44

OPERATION
-41-
(8) Carefully feed the wire over the drive roller into the outlet guide tube, feed through
about ½” (150mm) into the torch receptacle.
(9) Check that the drive roller size is compatible with the wire diameter, replace the roller if
necessary. (SEE Section 4.3.2 for more information)
(10) Align the wire into the groove of the drive roller and close the top roller tension arms
making sure the wire is in the groove of
the bottom drive roller, lock the tension
arms into place with pressure knobs
and tighten by turning clockwise.
(9) Tension arms
(11) Remove the gas nozzle and contact tip from the torch neck.
(12) Press and hold the manual wire button to feed the wire through to the torch neck,
release the manual wire key when the wire exits the torch neck.
Page 45

OPERATION
-42-
(11) Remove Tip (12) Feed wire manually
(WARNING: Be sure to keep torch neck away from your eyes, face or hands as the
wire exits the swan neck!)
(13) Fit the correct sized contact tip and feed the wire through
it, screw the contact tip into the tip holder of the torch neck
and nip it up tightly.
(14) Fit the gas nozzle to the torch head.
(15) Carefully open the gas cylinder valve Set the required gas flow rate on the regulator.
(16) Select torch switch mode 2T/ 4T/S4T
(17) Select the desired MIG function, Select program number to suit the wire diameter
and gas type being used as shown on the digital meter.
(18) Set the required welding parameters to suit the material thickness being welded as
shown on the digital meter.
§4.3.2 Wire Feed Roller Selection
The importance of smooth consistent wire feeding during MIG welding cannot be
emphasized enough. Simply put the smoother the wire feed then the better the weld.
Feed rollers or drive rollers are used to feed the wire mechanically through the length of
the welding gun cable. Feed rollers are designed to be used for certain types of welding
wire and they have different types of grooves machined in them to accommodate the
different types of wire. The wire is held in the groove by the top roller of the wire drive unit
and is referred to as the pressure roller, pressure is applied by a tension arm that can be
adjusted to increase or decrease the pressure as required. The type of wire will determine
how much pressure can be applied and what type of drive roller is best suited to obtain
Page 46

OPERATION
-43-
optimum wire feed.
Solid Hard Wire - like Steel, Stainless Steel require a drive roller with a “V” shape groove
for optimum grip and drive capability. Solid wires can have more tension applied to the
wire from the top pressure roller that holds the wire in the groove and the “V” shape
groove is more suited for this. Solid wires are more forgiving to feed due to their higher
cross-sectional column strength, they are stiffer and don’t deflect so easily.
Soft Wire – Such as Aluminum, require a “U” shape groove. Aluminum wire has a lot less
column strength, can bend easily and is therefore more difficult to feed. Soft wires can
easily buckle at the wire feeder where the wire is fed into inlet guide tube of the torch. The
U-shaped roller offers more surface area grip and traction to help feed the softer wire.
Softer wires also require less tension from the top pressure roller to avoid deforming the
shape of the wire, too much tension will push the wire out of shape and cause it to catch
in the contact tip.
Flux Core / Gasless Wire - These wires are made up of a thin metal sheath that has flux
and metal compounds layered onto the surface and then rolled into a cylinder to form the
finished wire. The wire cannot take too much pressure from the top roller as it can be
crushed and deformed if too much pressure is applied. A knurled-V drive roller has been
developed and it has small serrations in the groove, the serrations grip the wire and assist
to drive it without too much pressure from the top roller. The down side to the knurled wire
feed roller on flux cored wire is it will slowly over time bit by bit eat away at the surface of
the welding wire, and these small pieces will eventually go down into the liner. This will
cause clogging in the liner and added friction that will lead to welding wire feed problems.
A U groove wire can also be used for flux core wire without the wire particles coming off
the wire surface. However, it is considered that the knurled roller will give a more
positive feed of flux core wire without any deformation of the wire shape.
Page 47

OPERATION
-44-
§4.3.3 Wire Installation and Set-Up Guide
The importance of smooth consistent wire feeding during MIG welding cannot be
emphasized enough. The correct installation of the wire spool and the wire into the wire
feed unit is critical to achieving an even and consistent wire feed. A high percentage of
faults with MIG welders emanate from poor set up of the wire into the wire feeder. The
guide below will assist in the correct setup of your wire feeder.
(1) Remove the spool retaining nut. (2) Note the tension spring adjuster and
spool locating pin.
(3) Fit the wire spool onto the spool holder (4) Snip the wire carefully, be sure to hold
fitting the locating pin into the location hole wire to prevent the spool uncoiling.
on the spool. Replace the retaining nut. Carefully feed the wire into the inlet guide
tube of the wire feed unit.
Page 48

OPERATION
-45-
(5) Feed the wire through the drive rollers (6) Lock down the top pressure roller and
and into the outlet guide tube of the wire tighten using the tension adjustment knob.
(7) Check that the wire passes through the center
of the outlet guide tube without touching the sides.
Loosen the locking screw and then loosen the
outlet guide tube retaining nut too make adjustment
if required. Carefully retighten the locking nut and
screw to hold the new position.
(8) A simple check for the correct drive tension is to
bend the end of the wire over hold it about 100mm
from your hand and let it run into your hand, it
should coil round in your hand without stopping and
slipping at the drive rollers, increase the tension if it
slips.
WARNING: Must wear gloves
Page 49

OPERATION
-46-
(9) The weight and speed of the wire spool turning
creates an inertia that can cause the spool to run on
and the wire loop over the side of the spool and
tangle. If this happens increase the pressure on the
tension spring inside the spool holder assembly
using the tension adjustment screw.
§4.3.4 Set up for MIG Welding- Aluminum or Silicone Bronze Wire
(1) REPEAT all steps as listed in 4.3.1
(2) Fit the correct size U-groove drive
roller for soft wires.
(3)Change shield gas to 100% Argon.
§4.3.5 MIG Torch Liner Installation
(1) Remove MIG torch front end parts. (2) Remove the liner retaining nut.
Page 50

OPERATION
-47-
(3) Carefully pull out and completely remove (4) Carefully unravel the new liner.
(5) Carefully feed in the new liner down the torch (6) Fit the liner retaining nut and screw
lead all the way to exit the torch neck. only 1/2 way down.
(7) Snip the liner off 3mm past the end of the (8) Replace the front end parts.
torch neck. (Remove any burrs)
(9) Fully screw down the liner retaining
nut and tighten.
Page 51

OPERATION
-48-
§4.3.6 MIG Torch Liner Types and Information
MIG Torch Liners
The liner is both one of the simplest and most important components of a MIG gun. Its
sole purpose is to guide the welding wire from the wire feeder, through the gun cable and
up to the contact tip.
Steel Liners
Most MIG gun liners are made from coiled steel wire also known as piano wire, which
provides the liner with good rigidity and flexibility and allows it to guide the welding wire
smoothly through the welding cable as it bends and flex during operational use. Steel
liners are primarily used for feeding of solid steel wires, other wires such as Aluminum,
Silicon Bronze, Etc. will perform better using a Teflon or Polyamide line. The internal
diameter of the liner is important and relative to the wire diameter being used. The correct
inside diameter and will assist in smooth feeding and prevention of the wire kinking and
bird-nesting at the drive rollers. Also bending the cable too tightly during welding
increases the friction between the liner and the welding wire making it more difficult to
push the wire through the liner resulting in poor wire feeding, premature liner wear and
bird-nesting. Dust, grime and metal particles can accumulate inside the liner over time
and cause friction and blockages, it is recommended to periodically blow out the liner with
compressed air. Small diameter welding wires, 0.6mm through 1.0mm have relatively low
columnar strength, and if matched with an oversized liner, can cause the wire to wander
or drift within the liner. This in turn leads to poor wire feeding and premature liner failure
due to excessive wear. By contrast, larger diameter welding wires, 1.2mm through 2.4mm
have much higher columnar strength but it is important to make sure the liner has enough
internal diameter clearance. Most manufacturers will produce liners sized to match wire
diameters and length of welding torch cable and most are color coded to suit.
Blue-0.6mm-0.8mm
Red - 0.9mm - 1.2mm
Yellow - 1.6mm
Green - 2.0mm - 2.4mm
Steel Liners
Page 52

OPERATION
-49-
Teflon and Polyamide (PA) Liners
Teflon liners are well suited for feeding soft wires with poor column strength like
aluminum wires. The interiors of these liners are smooth and provide stable feeding,
especially on small diameter welding wire Teflon can be good for higher heat applications
that utilize water-cooled torches and brass neck liners. Teflon has good abrasion
resistance characteristics and can be used with a variety of wire types such as silicon
bronze, stainless steel as well as aluminum. A note of caution to careful inspect the end of
the welding wire prior to feeding it down the liner. Sharp edges and burrs can score the
inside of the liner and lead to blockages and accelerated wear. Polyamide Liners (PA) are
made of carbon infused nylon and are ideal for softer aluminum, copper alloy welding
wires and push pull torch applications. These liners are generally fitted with a floating
collet to allow the liner to be inserted all the way to the feed rollers.
Copper - Brass Neck Liners
For high heat applications fitting brass or copper wound jumper or neck liner on the end
of the liner at the neck end will increase the working temperature of the liner as well as
improve the electrical conductivity of the welding power transfer to the wire. It is
recommended for all Aluminum and Silicone Bronze welding applications.
§4.3.7 Torch & Wire Feed Set-Up for Aluminum Wire
The same method is used for Teflon and/or Polyamide Liners (PA).
Blue-0.6mm-0.8mm
Red - 0.9mm - 1.2mm
Yellow - 1.6mm
Teflon Liners
PA Liner
Black-1.0mm-1.6mm
Copper Neck Liner
Page 53

OPERATION
-50-
§4.3.8 Set-Up Installation for Spool Gun
(1) Insert the earth cable plug into the negative (-) socket on the front of the machine
and twist to tighten.
(2) Plug the Spool Gun into the euro-connect socket on the front panel and tighten.
IMPORTANT: When connecting the torch be sure to tighten the adaptor nut
completely tight. A loose connection can result in arcing between the gun and
machine connector and that causes serious damage to both the torch and
machine connections.
(3) Connect the Spool Gun control cable to the 9-pin receptacle on the front panel.
(4) Connect the gas regulator to the gas cylinder and connect the gas line to the
regulator.
(5) Connect the gas line to gas connector on the rear panel.
(6) Open the gas cylinder valve, set regulator. Check for Leaks!
(7) Connect the power cord of welding machine with the outlet on electrical box.
(9) Remove the spool cover by pressing (10) Place a spool of wire inside the
button and lifting off the cover. spool holder on post.
(8) Select Spool Gun using the
Function key and Adjustment
knobs
Page 54

OPERATION
-51-
(11) Feed the wire through the drive (12) Pull the trigger to drive the wire
rolls and into the inlet guide tube. down the neck until it exits the contact
Tighten the wire tension swing arm. tip.
(13) Carefully open the gas cylinder valve and set the required gas flow rate.
(14) Set welding parameters using the knobs as shown on digital displays.
§4.3.9 MIG Welding
Definition of MIG Welding
MIG (metal inert gas) welding also known as GMAW (gas metal arc welding) or MAG
(metal active gas welding), is a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process in which
a continuous and consumable wire electrode and a shielding gas are fed through a
welding gun. A constant voltage, direct current power source is most commonly used with
MIG welding. There are four primary methods of metal transfer in MIG welding, called
short circuit (also known as dip transfer) globular transfer, spray transfer and pulsed-spray,
each of which has distinct properties and corresponding advantages and limitations.
Short Circuit Transfer - Short circuit transfer is the most common used method whereby
the wire electrode is fed continuously down the welding torch through to and exiting the
contact tip. The wire touches the work piece and causes a short circuit the wire heats up
and begins to form a molten bead, the bead separates from the end of the wire and forms
a droplet that is transferred into the weld pool. This process is repeated about 100 times
per second, making the arc appear constant to the human eye.
Page 55

OPERATION
-52-
The pinch causes the
forming droplet to
separate and falls towards
the now creating weld
pool.
An arc is created at the
separation of the droplet
and the heat and force of
the arc flattens-out the
droplet into the weld pool.
The wire feed speed
overcomes the heat of
the arc and the wire
again approaches the
work to short circuit
and repeat the cycle.
Basic MIG Welding
Good weld quality and weld profile depends on gun angle, direction of travel, electrode
extension (stick out), travel speed, thickness of base metal, wire feed speed and arc
voltage. To follow are some basic guides to assist with your setup.
Gun Position - Travel Direction, Work Angle: Gun position or technique usually refers
to how the wire is directed at the base metal, the angle and travel direction chosen. Travel
speed and work angle will determine the characteristic of the weld bead profile and
The wire touches the
work creating a short
circuit. Because there is
no space between the
wire and the base metal
there is no arc.
The wire cannot
support all the current
flow so resistance
builds up and the wire
The current flow
creates a magnetic
field that begins to
pinch the melting wire
forming it into droplet.
Page 56

OPERATION
-53-
degree of weld penetration
Push Technique - The wire is located at the leading edge of the weld pool and pushed
towards the un-melted work surface. This technique offers a better view of the weld joint
and direction of the wire into the weld joint. Push technique directs the heat away from the
weld puddle allowing faster travel speeds providing a flatter weld profile with light
penetration - useful for welding thin materials. The welds are wider and flatter allowing for
minimal clean-up and grinding time.
Perpendicular Technique - The wire is fed directly into the weld, this technique is used
primarly for automated situations or when conditions make it necessary. The weld profile
is generally taller and a deeper penetration is achieved.
Drag Technique - The gun and wire are dragged away from the weld bead. The arc and
heat is concentrated on the weld pool, the base metal receives more heat, deeper melting,
more penetration and the weld profile is higher with more build up.
Flat even weld
profile light
Narrower weld
profile even
Narrow higher
weld profile more
penetration
Page 57

OPERATION
-54-
Travel Angle - Travel angle is the right to left angle relative to the direction of welding. A
travel angle of 5°- 15° is ideal and produces a good level of control over the weld pool. A
travel angle greater that 20° will give an unstable arc condition with poor weld metal
transfer, less penetration, high levels of spatter, poor gas shield and poor quality finished
weld.
Angle to Work - The work angle is the forward back angle of the gun relative to the work
piece. The correct work angle provides good bead shape, prevents undercut, uneven
penetration, poor gas shield and poor quality finished weld.
Angle 5°- 15°
Not enough
Angle more than 20°
Good level of
control over the
weld pool, even flat
weld.
less control over the
weld pool more
spatter.
poor control, unstable
arc, less penetration,
lots of spatter.
Good level of
control over the
weld pool, even flat
weld.
Less control over the
weld pool equals more
spatter.
Poor control, unstable
arc, less penetration,
lots of spatter.
Correct
Too much angle
Not enough angle
Page 58

OPERATION
-55-
Stick Out- Stick out is the length of the un-melted wire protruding from the end of the
contact tip. A constant even stick out of 5-10mm will produce a stable arc, and an even
current flow providing good penetration and even fusion. Too short stick out will cause an
unstable weld pool, produce spatter and over heat the contact tip. Too long stick out will
cause an unstable arc, lack of penetration, lack of fusion and increase spatter.
Travel Speed - Travel speed is the rate that the gun is moved along the weld joint and is
usually measured in inches per minute (IPM). Travel speeds can vary depending on
conditions and the welder’s skill and is limited to the welders ability to control the weld
pool. Push technique allows faster travel speeds than drag technique. Gas flow must also
correspond with the travel speed, increasing with faster travel speed and decreasing with
slower speed. Travel speed needs to match the amperage and will decrease as the
material thickness and amperage increase.
Too Fast Travel Speed - A too fast travel speed produces too little heat per mm of travel
resulting in less penetration and reduced weld fusion, the weld bead solidifies very quickly
trapping gases inside the weld metal causing porosity. Undercutting of the base metal can
also occur and an unfilled groove in the base metal is created when the travel speed is
too fast to allow molten metal to flow into the weld crater created by the arc heat.
Normal stick out
Too short
Too long
Even arc, good
penetration even
fusion, good
finish.
Unstable arc,
spatter, over heat
contact tip.
Unstable arc,
spatter, poor
penetration and
fusion.
Too Fast Travel Speed
high narrow bead
undercut
lack of fusion
lack of joint penetration
spatter
porosity
Page 59

OPERATION
-56-
Too Slow Travel Speed
large wide bead
lack of fusion
porosity
cold lap
lack of joint penetration
Too Slow Travel Speed - A too slow travel speed produces a large weld with lack of
penetration and fusion. The energy from the arc dwells on top of the weld pool rather than
penetrating the base metal. This produces a wider weld bead with more deposited weld
metal per mm than is required resulting in a weld deposit of poor quality.
Correct Travel Speed - The correct travel speed keeps the arc at the leading edge of the
weld pool allowing the base metal to melt sufficiently to create good penetration, fusion
and wetting out of the weld pool producing a weld deposit of good quality.
Gas selection - The purpose of the gas in the MIG process is to protect / shield the wire,
the arc and the molten weld metal from the atmosphere. Most metals when heated to a
molten state will react with the air in the atmosphere, without the protection of the
shielding gas the weld produced would contain defects like porosity, lack of fusion and
slag inclusions.
The correct gas flow is also very important in protecting the welding zone from the
atmosphere.
Use the correct shielding gas. CO2 is good for steel and offers good penetration, the
weld profile is narrower and slightly more raised than the weld profile obtained from
Argon/CO2 mixed gas. Argon CO2 (Argon 80% & CO2 20%) mix gas offers better weld
Correct Travel Speed
even shaped bead
good side wall fusion
good toe fusion
good penetration
Page 60

OPERATION
-57-
ability for thin metals and has a wider range of setting tolerance on the machine.
Argon gas at 100% mixture is good for aluminum and silicone bronze applications. It
offers good penetration and weld control. CO2 is not recommended for these metal alloys.
Wire types and sizes - Use the correct wire type for the base metal being welded. Use
stainless steel wire for stainless steel, aluminum for aluminum and steel wires for steel.
Use a smaller diameter wire for thin base metals. For thicker materials use a larger wire
diameter and larger machine, check the recommended welding capability of your
machine. As a guide refer to the “Welding Wire Thickness Chart” below.
WELDING WIRE DIAMETER CHART
MATERIALTHICKNESS
RECOMMENDED WIRE DIAMETERS
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.2
1.6
0.8mm
0.9mm
1.0mm
1.2mm
1.6mm
2.0mm
2.5mm
3.0mm
4.0mm
5.0mm
6.0mm
8.0mm
10mm
14mm
18mm
22mm
For material thickness of 5.0mm and greater, multi-pass runs or a beveled joint design may
be required depending on the amperage capability of your machine.
Argon/CO2 CO2
Penetration Pattern for Steel
Page 61

OPERATION
-58-
§4.3.10 Spool Gun Control NEED NEW TORCH INFO!!
226 Spool Gun NEED PHOTO OF QLBF200 w/ #26 NECK
Socket Pin
Function
1
Spool gun motor
2
Not connected
3
Not connected
4
Spool gun motor
5
10k ohm (maximum) connection to 10k ohm remote control potentiometer.
6
Zero ohm (minimum) connection to 10k ohm remote control potentiometer.
7
Wiper arm connection to 10k ohm remote control potentiometer.
8
Not connected
9
Not connected
Gun switch
Spool cover switch
Adjust current button
Remote Control Socket
Page 62

OPERATION
-59-
§4.4 Standard Welding Programs & Settings Chart
Page 63

OPERATION
-60-
Welding Programs & Settings Chart
Page 64

OPERATION
-61-
§4.5 Welding Parameters
Process reference for CO2 butt welding of low carbon steel solid welding wire
Process reference for CO2 corner welding of low carbon steel solid welding wire
Page 65

OPERATION
-62-
Low carbon steel, stainless steel pulse MAG welding process reference
Welding process of aluminum alloy pulse MIG
Welding
position
Material
thicknes
s
(MM)
Wire
diamete
r
(MM)
Weldin
g
current
(A)
Weldin
g
voltage
(V)
Welding
speed
(CM/MIN
)
Nozzle and
workpiece
spacing(MM
)
Gas-flo
w rate
(L/MIN)
Butt-joint
1.5
1.0
60-80
16-18
60-80
12-15
15-20
2.0
1.0
70-80
17-18
40-50
15
15-20
3.0
1.2
80-100
17-20
40-50
14-17
15-20
4.0
1.2
90-120
18-21
40-50
14-17
15-20
6.0
1.2
150-18
0
20-23
40-50
17-22
18-22
4.0
1.2
160-21
0
22-25
60-90
15-20
19-20
4.0
1.6
170-20
0
20-21
60-90
15-20
19-20
6.0
1.2
200-23
0
24-27
40-50
17-22
20-24
6.0
1.6
200-24
0
21-23
40-50
17-22
20-24
8.0
1.6
240-27
0
24-27
45-55
17-22
20-24
12.0
1.6
270-33
0
27-35
55-60
17-22
20-24
16.0
1.6
330-40
0
27-35
55-60
17-22
20-24
Corner
joint
1.5
1.0
60-80
16-18
60-80
13-16
15-20
2.0
1.0
100-15
0
22-26
35-45
13-16
15-20
Page 66

OPERATION
-63-
3.0
1.2
100-12
0
19-21
40-60
13-17
15-20
4.0
1.2
120-15
0
20-22
50-70
15-20
15-20
6.0
1.2
150-18
0
20-23
50-70
18-22
18-22
4.0
1.2
180-21
0
21-24
35-50
18-22
16-18
4.0
1.6
180-21
0
18-20
35-45
18-22
18-22
6.0
1.2
220-25
0
24-25
50-60
18-22
16-24
6.0
1.6
220-24
0
20-24
37-50
18-22
16-24
8.0
1.6
250-30
0
25-26
60-65
18-22
16-24
12.0
1.6
300-40
0
26-28
65-75
18-22
16-24
§4.6 Operation Environment
▲ Height above sea level ≤1000 M
▲ Operation temperature range 14 - 104°F (-10~+40°C)
▲ Air relative humidity is below 90%
▲ Preferable site the machine some angles above the floor level does not exceed 15°.
▲ Protect the machine against high moisture, water AND against direct sunshine.
▲ Take care that there is sufficient ventilation during welding. There must be at least
1-1/2” (38cm) free distance between the machine and wall.
§4.7 Operation Notices
▲ Read Section §1 carefully before starting to use this equipment.
▲ Ensure that the input is 208-240VAC, single-phase: 50/60Hz.
▲ Before operation, clear the working area. Do not watch the arc in unprotected eyes.
▲ Ensure good ventilation of the machine to improve duty cycle and life.
▲ Turn off power supply when the operation finished for energy consumption efficiency.
▲ When power switch shuts off protectively because of failure. Don’t restart it until
problem has been resolved. Otherwise, permanent damage could occur.
▲ In case of problems, contact your local dealer.
Page 67

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-64-
§5Diagram for Guns
§5.1 MIG Torches AK15 (Cu/Si), AK25 (Fe) & AK26 (Al)
§5.1.1 MIG Torch #1 / AK15 with RED Handle for Silicone Bronze Wire
Page 68

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-65-
§5.1.2 MIG Torch #2 / AK26 with BLUE Handle for Aluminum Wire
Page 69

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-66-
§5.1.3 MIG Torch #3 / AK25 with GREEN Handle for Steel Wire
Page 70

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-67-
§5.2 TIG Torch
§5.2.1 TIG Torch #17 with Thumb-Wheel Control & Trigger in Handle
Page 71

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-68-
§5.3 Spool Gun (Optional)
§5.3.1 NSG226 Spool Gun with Speed Potentiometer & 9-Pin Plug (20’)
Page 72

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-69-
§6 Welding Trouble Shooting
§6.1 MIG Welding - Trouble Shooting
The following chart addresses some of the common problems of MIG welding. In all
cases of equipment malfunction, the manufacturer’s recommendations should be strictly
adhered to and followed.
NO.
Trouble
Possible Reason
Suggested Remedy
1
Excessive
Spatter
Wire feed speed set too high
Select lower wire feed speed
Voltage too high
Select a lower voltage setting
Wrong polarity set
select the correct polarity for
the wire being used - see
machine setup guide
Stick out too long
Bring the torch closer to the
work
Contaminated base metal
Remove materials like paint,
grease, oil, and dirt, including
mill scale from base metal
Contaminated mig wire
Use clean, dry, rust free wire.
Do not lubricate the wire with
oil, grease etc.
Inadequate gas flow or too much
gas flow
Check the gas is connected,
check hoses, gas valve and
torch are not restricted. Set the
gas flow between 20-40 CFH
(6-12 l/min) flow rate. Check
hoses and fittings for leaks.
Protect the welding zone from
wind and drafts
Page 73

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-70-
2
Porosity -
small cavities
or holes
resulting from
gas pockets in
weld metal.
Wrong gas
Check that the correct gas is
being used
Inadequate gas flow or too much
gas flow
Check the gas is connected,
check hoses, gas valve and
torch are not restricted. Set the
gas flow between 20-40 CFh
(6-12 l/min) flow rate. Check
hoses and fittings for leaks.
Protect the welding zone from
wind and drafts
Moisture on the base metal
Remove all moisture from
base metal before welding
Contaminated base metal
Remove materials like paint,
grease, oil, and dirt, including
mill scale from base metal
Contaminated MIG wire
Use clean, dry, rust free wire.
Do not lubricate the wire.
Gas nozzle clogged with spatter,
worn or out of shape
Clean or replace the gas
nozzle
Missing or damaged gas diffuser
Replace the gas diffuser
MIG torch euro connect o-ring
missing or damaged
Check and replace the o-ring
3
Wire stubbing
during welding
Holding the torch too far away
Bring the torch closer to the
work and maintain stick out of
5-10mm
Welding voltage set too low
Increase the voltage
Wire Speed set too high
Decrease the wire feed speed
4
Lack of Fusion
− failure of
weld metal to
fuse
completely.
Lack of Fusion
− failure of
weld metal to
fuse
completely.
Contaminated base metal
Remove materials like paint,
grease, oil, and dirt, including
mill scale from base metal
Not enough heat input
Select a higher voltage range
and /or adjust the wire speed
to suit
Improper welding technique
Keep the arc at the leading
edge of the weld pool.
Gun angle to work should be
between 5 & 15°. Direct the arc
at the weld joint
Adjust work angle or widen
groove to access bottom
during welding
Momentarily hold arc on side
walls if using weaving
technique
Page 74

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-71-
5
Excessive
Penetration −
weld metal
melting
through base
metal
Too much heat
Select a lower voltage range
and /or adjust the wire speed
to suit Increase travel speed
6
Lack of
Penetration −
shallow fusion
between weld
metal and base
metal
Poor in incorrect joint
preparation
Material too thick. Joint
preparation and design needs
to allow access to bottom of
groove while maintaining
proper welding wire extension
and arc characteristics. Keep
the arc at the leading edge of
the weld pool and maintain the
gun angle at 5 & 15° keeping
the stick out between 5-10mm
Not enough heat input
Select a higher voltage range
and /or adjust the wire speed
to suit reduce travel speed.
Contaminated base metal
Remove materials like paint,
grease, oil, and dirt, including
mill scale from base metal
§6.2 MIG Wire Feed - Trouble Shooting
The following chart addresses some of the common WIRE FEED problems during MIG
welding. In all cases of equipment malfunction, the manufacturer’s recommendations
should be strictly adhered to and followed.
NO.
Trouble
Possible Reason
Suggested Remedy
1
No wire
feed
Wrong mode selected
Check that the TIG/MMA/MIG
selector switch set to MIG position
Page 75

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-72-
Wrong torch selector switch
Check that the Wire Feeder / Spool
Gun selector switch is set to Wire
Feeder position for MIG welding and
Spool Gun when using the Spool
gun
2
Inconsistent
/ interrupted
wire feed
Adjusting wrong dial
Be sure to adjust the wire feed and
voltage dials for MIG welding. The
amperage dial is for MMA and TIG
welding mode
Wrong polarity selected
Select the correct polarity for the
wire being used. (see machine
setup guide)
Incorrect wire speed setting
Adjust the wire feed speed
Voltage setting incorrect
Adjust the voltage setting
MIG torch lead too long
Small diameter wires and soft wires
like aluminum don’t feed well
through long torch leads - replace
the torch with a lesser length torch
MIG torch lead kinked or too
sharp angle being held
Remove the kink, reduce the angle
or bend
Contact tip worn, wrong size,
wrong type
Replace the tip with correct size and
type
Liner worn or clogged (the
most common causes of bad
feeding)
Try to clear the liner by blowing out
with compressed air as a temporary
cure, it is recommended to replace
the liner
Wrong size liner
Install the correct size liner
Blocked or worn inlet guide
tube
Clear or replace the inlet guide tube
Wire misaligned in drive roller
groove
Locate the wire into the groove of
the drive roller
Incorrect drive roller size
Fit the correct size drive roller eg;
0.8mm wire requires 0.8mm roller.
Wrong type of drive roller
selected
Fit the correct type roller (e.g.
knurled rollers needed for flux cored
wires
Worn drive rollers
Replace the drive rollers
Drive roller pressure too high
Can flatten the wire electrode
causing it to lodge in the contact tip reduce the drive roller pressure
Page 76

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-73-
Too much tension on wire
spool hub
Reduce the spool hub brake tension
Wire crossed over on the spool
or tangled
Remove the spool untangle the wire
or replace the wire
Contaminated MIG wire
Use clean, dry, rust free wire. Do not
lubricate the wire.
§6.3 DC TIG Welding - Trouble Shooting
The following chart addresses some of the common problems of DC TIG welding. In all
cases of equipment malfunction, the manufacturer’s recommendations should be strictly
adhered to and followed.
NO.
Trouble
Possible Reason
Suggested Remedy
1
Tungsten burning
away quickly
Incorrect Gas or No Gas
Use pure Argon. Check cylinder
has gas, connected, turned on
and torch valve is open
Inadequate gas flow
Check the gas is connected,
check hoses, gas valve and torch
are not restricted.
Back cap not fitted
correctly
Make sure the torch back cap is
fitted so that the O-ring is inside
the torch body
Torch connected to DC +
Connect the torch to the DCoutput terminal
Incorrect tungsten being
used
Check and change the tungsten
type if necessary
Tungsten being oxidised
after weld is finished
Keep shielding gas flowing 10–15
seconds after arc stoppage. 1
second for each 10amps of weld
current.
2
Contaminated
tungsten
Touching tungsten into the
weld pool
Keep tungsten from contacting
weld puddle. Raise the torch so
that the tungsten is off the work
piece 2 - 5mm
Touching the filler wire to
the tungsten
Keep the filler wire from touching
the tungsten during welding, feed
the filler wire into the leading
edge of the weld pool in front of
the tungsten
Page 77

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-74-
3
Porosity - poor
weld appearance
and color
Wrong gas / poor gas flow
/gas leak
Gas is connected, valve ON,
check hoses, gas valve and torch
are not restricted. Set the gas
flow between 20-40 CFH (6-12
l/min). Check hoses and fittings
for leaks.
Contaminated base metal
Remove moisture and materials
like paint, grease, oil, and dirt
from base metal
Contaminated filler wire
Remove all grease, oil, or
moisture from filler metal
Incorrect filler wire
Check the filler wire and change if
necessary
4
Yellowish residue
/ smoke on the
alumina nozzle &
discolored
tungsten
Incorrect Gas
Use pure Argon gas
Inadequate gas flow
Set the gas flow between 20-40
CFH (10-20 l/min) flow rate
Alumina gas nozzle too
small
Increase the size of the alumina
gas nozzle
5
Unstable Arc
during DC
welding
Torch connected to DC +
Connect the torch to the DCoutput terminal
Contaminated base metal
Remove materials like paint,
grease, oil, and dirt, including mill
scale from base metal.
Tungsten is contaminated
Remove 10mm of contaminated
tungsten and re grind the
tungsten
Arc length too long
Lower torch so that the tungsten
is off of the work piece 2 - 5mm
6
Arc wanders
during DC
welding
Poor gas flow
Check and set the gas flow
between 20-40 CFH flow rate
Incorrect arc length
Lower torch so that the tungsten
is off the work piece 2 - 5mm
Tungsten incorrect or in
poor condition
Check that correct type of
tungsten is being used. Remove
10mm from the weld end of the
tungsten and re sharpen rod.
Poorly prepared tungsten
Grind marks should run
lengthwise with tungsten, not
circular. Use proper grinding
method and wheel.
Page 78

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-75-
Contaminated base metal
or filler wire
Remove contaminating materials
like paint, grease, oil, and dirt,
including mill scale from base
metal. Remove all grease and oil
from filler metal
7
Arc difficult to
start or will not
start DC welding
Incorrect machine set up
Check machine set up is correct
No gas, incorrect gas flow
Check the gas is connected and
cylinder valve open, check hoses,
gas valve and torch are not
restricted. Set the gas flow
between 20-40 CFH flow rate
Incorrect tungsten size or
type
Check and change the size and
or the tungsten if required
Loose connection
Check all connectors and tighten
Earth clamp not connected
to work
Connect the earth clamp directly
to the work piece wherever
possible
§6.4 MMA Welding - Trouble Shooting
The following chart addresses some of the common problems of MMA welding. In all
cases of equipment malfunction, the manufacturer’s recommendations should be strictly
adhered to and followed.
NO.
Trouble
Possible Reason
Suggested Remedy
1
No arc
Incomplete welding circuit
Check earth lead is connected.
Check all cable connections.
Wrong mode selected
Check the MMA selector switch is
selected
No power supply
Check that the machine is
switched ON and has a power
2
Porosity − small
cavities or holes
resulting from
gas pockets in
weld metal
Arc length too long
Shorten the arc length
Work piece dirty,
contaminated or moisture
Remove moisture and materials
like paint, grease, oil, and dirt,
including mill scale from metal
Damp electrodes
Use only dry electrodes
3
Excessive Spatter
Amperage too high
Decrease the amperage or
choose a larger electrode
Arc length too long
Shorten the arc length
Page 79

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-76-
4
Weld sits on top,
lack of fusion
Insufficient heat input
Increase the amperage or choose
a larger electrode
Work piece dirty,
contaminated or moisture
Remove moisture and materials
like paint, grease, oil, and dirt,
including mill scale from metal
Poor welding technique
Use the correct welding
technique or seek assistance for
the correct technique
5
Lack of
penetration
Insufficient heat input
Increase the amperage or choose
a larger electrode
Poor welding technique
Use the correct welding
technique or seek assistance for
the correct technique
Poor joint preparation
Check the joint design and fit up,
make sure the material is not too
thick for wire size.
6
Excessive
penetration - burn
through
Excessive heat input
Reduce the amperage or use a
smaller electrode
Incorrect travel speed
Try increasing the weld travel
speed
7
Uneven weld
appearance
Unsteady hand, wavering
hand
Use two hands where possible to
steady up, practice your
technique
8
Distortion −
movement of
base metal during
welding
Excessive heat input
Reduce the amperage or use a
smaller electrode
Poor welding technique
Use the correct welding
technique or seek assistance for
the correct technique
Poor joint preparation and
or joint design
Check the joint design and fit up,
make sure the material is not too
thick. Seek assistance for the
correct joint design and fit up
9
Electrode welds
with different or
unusual arc
characteristic
Incorrect polarity
Change the polarity, check the
electrode manufacturer for
correct polarity
Page 80

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-77-
§7 Maintenance & Troubleshooting
§7.1 Maintenance
The operator must understand the maintenance procedure of inverter welding machine
and carry on simple examinations, cleanings and inspections. Do your best to protect the
machine from contamination environment and leaving unit ON when not in use to
lengthen service life of inverter arc welding machine. Inverter machines have transistors
that are cooled by aluminum heat sinks. When the power supply is ON, the cooling fan
brings dirt & dust into the machine covering the heat sinks and reducing cooling capacity
over time.
● Warning: For safety while maintaining the machine, please shut off the main
input power and wait for 5 minutes, until capacitors voltage drops to safe voltage
36V!
Date
Maintenance items
Daily
examinati
on
Observe that the knobs and switches in the front and at the back of arc
welding machine are flexible and put correctly in place. If any knob has
not been put correctly in place, please correct. If you can't correct or fix
the knob, please replace immediately;
If any switch is not flexible or it can't be put correctly in place, please
replace immediately! Please get in touch with maintenance service
department if there are no accessories.
After turn-on power, watch/listen if the arc-welding machine has
shaking, whistle calling or peculiar smell. If there is one of the above
problems, find out the reason and clear it. If you can't find out the reason,
please contact your local service repair station or distributor/Agent.
Observe that the display value of LED is intact. If the display number is
not intact, please replace the damaged LED. If it still doesn’t work, please
maintain or replace the display PCB.
Observe that the min./max.Values on LED agree with the set value. If
there is any difference and it has affected the normal welding results,
please adjust it.
Check whether the fan is damaged and whether it is normal to rotate or
control. If the fan is damaged, please change immediately. If the fan does
not rotate but it starts when blades are rotated in direction of fan, the start
capacity should be replaced.
Observe whether the fast connector is loose or overheated. If the
arc-welding machine has the above problems, it should be fastened or
changed.
Observe whether the current output cable is damaged. If it is damaged,
it should be insulated or changed.
Page 81

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-78-
Monthly
examinati
on
Using the dry compressed air to clear the inside of arc welding
machine. Especially for clearing up the dusts on aluminium heat-sinks,
inductors, IGBT modules, fast recover diodes, PCB’s, etc.
Check the screws and bolts in the machine. If any are loose, please
tighten. Check all torch, earth clamp and hose connections to insure they
are securely in place. Loose connections can cause major failures.
Quarter-
yearly
examinati
on
Check whether the actual current accords with the displaying value. If
they did not accord, they should be regulated. The actual welding current
value can be measured by and adjusted by plier-type ampere meter.
Yearly
examinati
on
Measure the insulating impedance among the main circuit, PCB and
case, if it below 1MΩ, insulation is thought to be damaged and needs to
changed to strengthen insulation.
§7.2 Troubleshooting
⚫ Before the welding machines are dispatched from the factory, they have
already been tested and calibrated accurately. Do not change settings on the
equipment!
⚫ Maintenance course must be operated carefully. If any wire becomes flexible or is
misplaced, it maybe potential danger to user!
⚫ Only professional maintenance staff that is authorized by manufacturer should
service the machine!
⚫ Be sure to shut off the Main Input Power before doing any repair work on the
welding machine and wait 5 minutes for capacitor voltage to decrease!
⚫ If there is any problem and there is no authorized professional maintenance personal
on site, please contact local agent or the distributor!
If there are some simple troubles with the welding machine, you can consult the
following Chart:
NO.
Troubles
Reasons
Solution
1
Turn ON power but the
power light is not
illuminated.
Switch damaged
Change it
Fuse damaged
Change it
Power cord damaged
Change it
Page 82

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-79-
2
After welding machine
is over-heat, the fan
doesn’t work
Fan damaged
Change it
The cable is loose
Screw the cable tight
3
Press the
gun
switch,
no output
shielded
gas
No output
gas when
test gas
No gas in the gas
cylinder
Change it
Gas hose leaks gas
Change it
Electromagnetic valve
damaged
Change it
Output
gas when
test gas
Control switch damaged
Repair the switch
Control circuit damaged
Check the PCB
4
Wire-feed
er doesn’t
work
Wire reel
doesn’t
work
Motor damaged
Check and change it
Control circuit damaged
Check the PCB
Wire reel
works
The idler roll is loose or
weld wire skids
Adjust tension screws
The drive roll doesn’t fit
with the diameter of
weld wire
Change the roll
Wire reel damaged
Change it
Wire feed pipe is jammed
Repair or change it
Tip is jammed because
of splash
Repair or change it
5
No striking arc and no
output voltage
Output cable is
connected incorrectly or
loosen
Screw it down or change it
Control circuit damaged
Check the circuit
6
Welding stops, and
alarm light is on
Machine has
self-protection
Check over-voltage,
over-current,
over-temperature,
lower-voltage and
over-temperature, and solve it
7
Welding current is run
away and can be not
controlled
The potentiometer
damaged
Check or change it
The control circuit
damaged
Check the circuit
8
The crater current can
be not adjusted
The PCB damaged
Check it
9
No post-gas
The PCB damaged
Check it
Page 83

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-80-
§7.3 List of Error Codes
Error Type
Error
code
Description
Lamp status
Thermal relay
E01
Over-heating (1st thermal relay)
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E02
Over-heating (2nd thermal relay)
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E03
Over-heating (3rd thermal relay)
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E04
Over-heating (4th thermal relay)
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E09
Over-heating (Program default)
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
Welding
machine
E10
Phase loss
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E11
N/A
Yellow lamp(lack
water) always on
E12
No gas
Red lamp always on
E13
Under voltage
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E14
Over voltage
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E15
Over current
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E16
Wire feeder over load
Switch
E20
Button fault on operating panel
when switch on the machine
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E21
Other faults on operating panel
when switch on the machine
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E22
Torch fault when switch on the
machine
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
E23
Torch fault during normal
working process
Yellow lamp(thermal
protection) always on
Accessory
E30
Cutting torch disconnection
Red lamp blink
E31
N/A
Yellow lamp(lack
water) always on
Communication
E40
Connection problem between
wire feeder and power source
E41
Communication error
Page 84

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-81-
§7.4 Electrical Schematic Drawing
Page 85

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-82-
§7.5 Replacement Parts Drawing
Page 86

THANK YOU FOR USING OUR PRODUCTS
-83-
Parts Service Contact: 704-935-5242
Item No Part No Description Quantity
1 521.2516 Rubber Tool Pad 1
2 521.2522 Lifting Lug M8 4
3 521.2550 Cabinet - Top Cover 1
4 521.2551 Cabinet - LH Side Panel (Top) 1
5 521.2517 Latch - Wire Feed Door 6
6 521.2528 MIG Power PCB 1
7 521.2523 Gas Soleniod Valve 4
8 521.2529 Exchange PCB 1
9 521.2512 Wire Feed Drive PCB 1
10 521.2530 Front Control Panel PCB 1
11 521.2552 Mount Strip - LHT 1
12 521.2519 Hinge - Wire Feed Door 6
13 521.2553 Cabinet - LH Side Panel (Bottom) 2
14 521.2518 Handle - Machine M250 2
15 521.2520 Power Switch Rotary 7
16 521.2511 Knob M250 2
17 521.2521 Output Select Swtich (4 position) 1
18 521.2554 Cabinet - Front panel 1
19 521.0011 Control Socket (9-pin) 1
20 521.2526 Gas Output Fitting 5/8-18RHT 3
21 511N0014 Dinse connector 35/50 CX58 2
22 521.2510 Wire Feed Drive #1 1
23 521.2510 Wire Feed Drive #2 1
24 521.2510 Wire Feed Drive #3 1
25 501N0167 Euro connector M250 3
26 521.2527 Wheel Caster 2
27 521.2531 Double Pulse Control PCB 1
28 521.2555 Cabinet - Cylinder Plate 1
29 521.2513 Spool Holder 3
30 521.2561 Cabinet - Axle 1
31 521.2562 Cabinet - Rear Wheel 2
32 521.2556 Mount Strip (RHB) 2
33 521.2557 Cabinet - RH Side Panel (Bottom) 1
34 521.2514 Main Relay Contactor 3
35 521.2515 Transformer Inductor 1
36 521.2524 Cooling Fan 2
37 521.2525 Cooling Fan cover 2
38 521.2558 Cabinet - Back Panel 1
39 521.2559 Cylinder Holder Bracket 2
40 521.2563 Torch Hook 3
41 521.2560 Cabinet - RH Side Panel (Top) 1
42 521.2532 Digital MIG torch exchange board 1
43 707.0173 Strain Relief - Power Cord 1
44 520.0009 Gas Hose 3M Brass 5/8-18RHT Fittings 2
M250 Double-Pulse MultiMIG Parts List
 Loading...
Loading...