Page 1

HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack User Guide
Abstract
This document describes the management of the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
System. This document is intended for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots
servers and is skilled in network configuration and virtual environments.
Part Number: 876840-007
Published: June 2019
Edition: 7
Page 2

©
Copyright 2017-2019 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
Notices
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for Hewlett
Packard Enterprise products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Hewlett Packard Enterprise required for possession,
use, or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer
Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government
under vendor's standard commercial license.
Links to third-party websites take you outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website. Hewlett Packard
Enterprise has no control over and is not responsible for information outside the Hewlett Packard
Enterprise website.
Acknowledgments
Intel®, Itanium®, Pentium®, Intel Inside®, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in
the U.S. and other countries.
Microsoft, Azure, Azure Stack, Windows, and Windows Server are either registered trademarks or
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
CISCO® is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. in the U.S. or certain other countries.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Page 3

Contents
Product introduction...............................................................................6
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview............... 8
Current version..............................................................................................................................6
Hardware overview....................................................................................................................... 8
Hardware Lifecycle Host Management node.............................................................................. 11
Azure Stack compute nodes....................................................................................................... 12
Solution switches........................................................................................................................ 12
Network cabling...........................................................................................................................14
Optional components.................................................................................................................. 14
HPE G3 KVM analog switches.........................................................................................14
HPE Intelligent PDUs....................................................................................................... 14
HPE G2 Metered PDUs....................................................................................................14
HPE Update Service for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack................................... 15
Expansion and scaling................................................................................................................ 15
Adding nodes to an existing scale unit.............................................................................15
Adding scale units or regions to an existing deployment................................................. 15
Expanding storage capacity............................................................................................. 16
Adding memory................................................................................................................ 16
HPE OneView............................................................................................................................. 16
Using HPE OneView with HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack.................................16
HPE OneView Remote Support....................................................................................... 17
Solution management...........................................................................19
Recommended administrative activities......................................................................................19
System administration guidelines............................................................................................... 19
Accessing the HPE management portions of the solution.......................................................... 20
Solution component IP Addresses................................................................................... 20
Solution component access............................................................................................. 20
Accessing Hardware Lifecycle Host with Microsoft RDP.......................................21
Accessing HPE OneView...................................................................................... 21
Accessing Switches...............................................................................................21
Hardware monitoring...................................................................................................................21
Monitoring health with HPE OneView.............................................................................. 22
Updates.......................................................................................................................................27
HPE Solution Update Bundle........................................................................................... 28
Management node updates............................................................................................. 28
Overview of Hardware Lifecycle Host update process..........................................28
Hardware Lifecycle Host node firmware update....................................................29
Hardware Lifecycle Host Microsoft Windows updates.......................................... 29
HPE OneView updates..........................................................................................30
Azure Stack node updates............................................................................................... 30
Azure Stack node firmware update....................................................................... 30
Azure Stack node software update....................................................................... 30
Hardware Lifecycle Host backup and recovery process............................................................. 31
Hardware Lifecycle Host Windows OS backup................................................................31
HPE OneView backup and restore...................................................................................32
Validate user privileges..........................................................................................33
3
Page 4

Configuring automatic backups............................................................................. 33
Creating and saving an HPE OneView backup file............................................... 34
Restoring the appliance.........................................................................................34
HPE OneView reference documentation...............................................................36
Disaster recovery............................................................................................................. 36
Hardware Lifecycle Host power down.........................................................................................37
Managing passwords, certificates, and keys.............................................................................. 37
Managing passwords and credentials..............................................................................37
HPE OneView password....................................................................................... 38
HPE iLO credentials.............................................................................................. 38
Hardware Lifecycle Host password....................................................................... 39
ToR and BMC switch passwords...........................................................................40
HPE iPDU password............................................................................................. 40
HPE G2 Metered PDU password.......................................................................... 41
Additional resources for managing passwords......................................................41
Managing certificates....................................................................................................... 41
Managing BitLocker recovery keys.................................................................................. 44
Managing Device Guard............................................................................................................. 44
Modifying Device Guard policy.........................................................................................45
Temporarily disabling Device Guard................................................................................ 46
System expansion.......................................................................................................................46
Preparing for Add Node................................................................................................... 46
Troubleshooting.................................................................................... 51
Components and items not included in original solution.............................................................51
Troubleshooting preparation....................................................................................................... 51
Get-HPEMASSupportDump........................................................................................................51
Troubleshooting HPE OneView.................................................................................................. 52
HPE OneView web UI or REST API not accessible.........................................................53
HPE OneView only accessible from HLH.........................................................................54
Attempting to connect to Azure Stack node iLO or console from HPE OneView fails..... 55
Troubleshooting ProLiant servers............................................................................................... 55
Troubleshooting solution switches.............................................................................................. 55
Attempts to modify the solution switch configurations have resulted in failures...............55
Troubleshooting HPE iPDUs.......................................................................................................56
Lost iPDU connectivity..................................................................................................... 56
Troubleshooting Azure Stack nodes........................................................................................... 57
Unplanned Azure Stack node shutdown or outage..........................................................57
Troubleshooting the Hardware Lifecycle Host node................................................................... 57
Unable to access Hardware Lifecycle Host......................................................................58
Unable to run scripts or applications on the Hardware Lifecycle Host............................. 59
Resources for troubleshooting.................................................................................................... 59
Updating HPE OneView with the UI.....................................................61
Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support...................................... 62
Configuring HPE OneView appliance host name and DNS........................................................62
Enabling HPE OneView Remote Support...................................................................................63
Enabling remote support on server hardware.............................................................................65
Validate OVRS functionality........................................................................................................ 65
Support and other resources...............................................................67
4
Page 5

Websites for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution...................................................67
Accessing Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support......................................................................... 67
Information to collect........................................................................................................ 67
Accessing updates......................................................................................................................68
Customer Self Repair..................................................................................................................68
Requesting support for HPE Azure Stack solution products.......................................................69
Requesting support electronically through the HPE Support Center............................... 69
Requesting support by phone.......................................................................................... 70
Remote support.......................................................................................................................... 71
Support process with HPE OneView Remote Support.....................................................71
Support for products not branded Hewlett Packard Enterprise...................................................71
Warranty information...................................................................................................................72
Regulatory information................................................................................................................73
Documentation feedback............................................................................................................ 73
Acronyms and abbreviations...............................................................74
5
Page 6

Product introduction
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack is a hybrid cloud solution that transforms on-premises data center
resources into flexible hybrid cloud services. These services provide a simplified development,
management, and security experience consistent with Azure public cloud services.
The HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack hybrid cloud solution is co-engineered by Hewlett Packard
Enterprise and Microsoft. This collaboration allows businesses to:
• maintain data sovereignty
• run high performance analytics
• run big data and low-latency applications
• support edge and disconnected applications
• deploy applications to either the public or private cloud
Current version
About this document
This document provides user information about the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution.
Important changes included in this updated HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack User Guide are:
• HPE Insight Remote Support information has been removed from this guide. HPE Insight RS is no
longer supported for any version of HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack.
• The "Updates" section has been reorganized for a more logical flow and the role of HPE Solution
Update Bundle has been clarified.
• Information about managing HPE iLO credentials has been expanded and clarified.
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solutions
Because the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack can consist of two distinct solutions, the following is
used to identify each solution in this document:
Table 1: HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solutions
Shipped before June 4, 2018 Shipped after June 4, 2018
Solution recipe 1.0.xxxx.x 2.0.xxxx.x
Remote Support HPE Insight Remote Support HPE OneView Remote Support
Compute nodes HPE ProLiant Gen9 HPE ProLiant Gen9 or Gen10
Management node HPE ProLiant Gen9 HPE ProLiant Gen9 or Gen10
NOTE: The term "recipe" refers to the defined combination of hardware, firmware, and software
components that make up the complete HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. The recipe is
updated regularly when new components are available and is identified by a unique coded
“series.yearmonth.release” tag.
For the latest supported hardware, firmware, and software versions, see:
6 Product introduction
Page 7

• HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix
• HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix
For information on enhancements and fixes, see the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Release
Notes.
Revision history
Revision Date Description Part number
1 November
2017
2 April 2018 Add support for Cisco switches. 876840-002
3 June 2018 • Add Gen10 servers.
4 July 2018 • Clarify text concerning availability of 16-node support.
5 October 2018 • Add support for Gen10 management node.
6 March 2019 • Add support for All-Flash solutions
Initial release of HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
User Guide
• Add HPE OneView RS support.
• Move legacy IRS content to separate chapter
• Add HPE OneView 4.0 support.
• Add content about soon to be supported add node
feature.
• Add instructions to find system information required to
add nodes.
• Add support for Arista switches.
876840-001
876840-003
876840-004
876840-005
876840-006
• Correct HLH updates from SPP to HPE solution
update bundle
• Reorganize the Updates section
• Enhance and correct information about managing iLO
credentials
• Remove Insight Remote Support information
7 June 2019 • Update locations of existing tools
• Add Cisco switch support for Gen10 systems
876840-007
Product introduction 7
Page 8

HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack is a solution that uses a combination of:
• Hewlett Packard Enterprise hardware
• Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Microsoft software
• Hewlett Packard Enterprise services
• Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Microsoft support
This hybrid cloud solution is co-engineered by Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Microsoft to enable the
easy movement and deployment of applications. These features combine to meet security, compliance,
cost, and performance needs:
• Scaling from 4 to 12 Gen9 nodes, 4 to 16 Gen10 Hybrid nodes, or 4 to 8 Gen10 All-Flash nodes
• Based on industry-leading HPE ProLiant servers with core, memory, and storage configuration
flexibility
• Factory integrated for quality and faster time-to-value with onsite deployment to address your specific
data center needs.
Hardware overview
Your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution is engineered and factory-built in an HPE rack.
Standard rack options are available for this solution. The rack and power infrastructure choices include
basic and standard HPE PDUs and HPE iPDUs, and an optional 8 or 16-port KVM switch.
For Gen9 solutions, see HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 Software and Firmware
Compatibility Matrix.
For Gen10 solutions, see HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware
Compatibility Matrix.
8 HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
Page 9
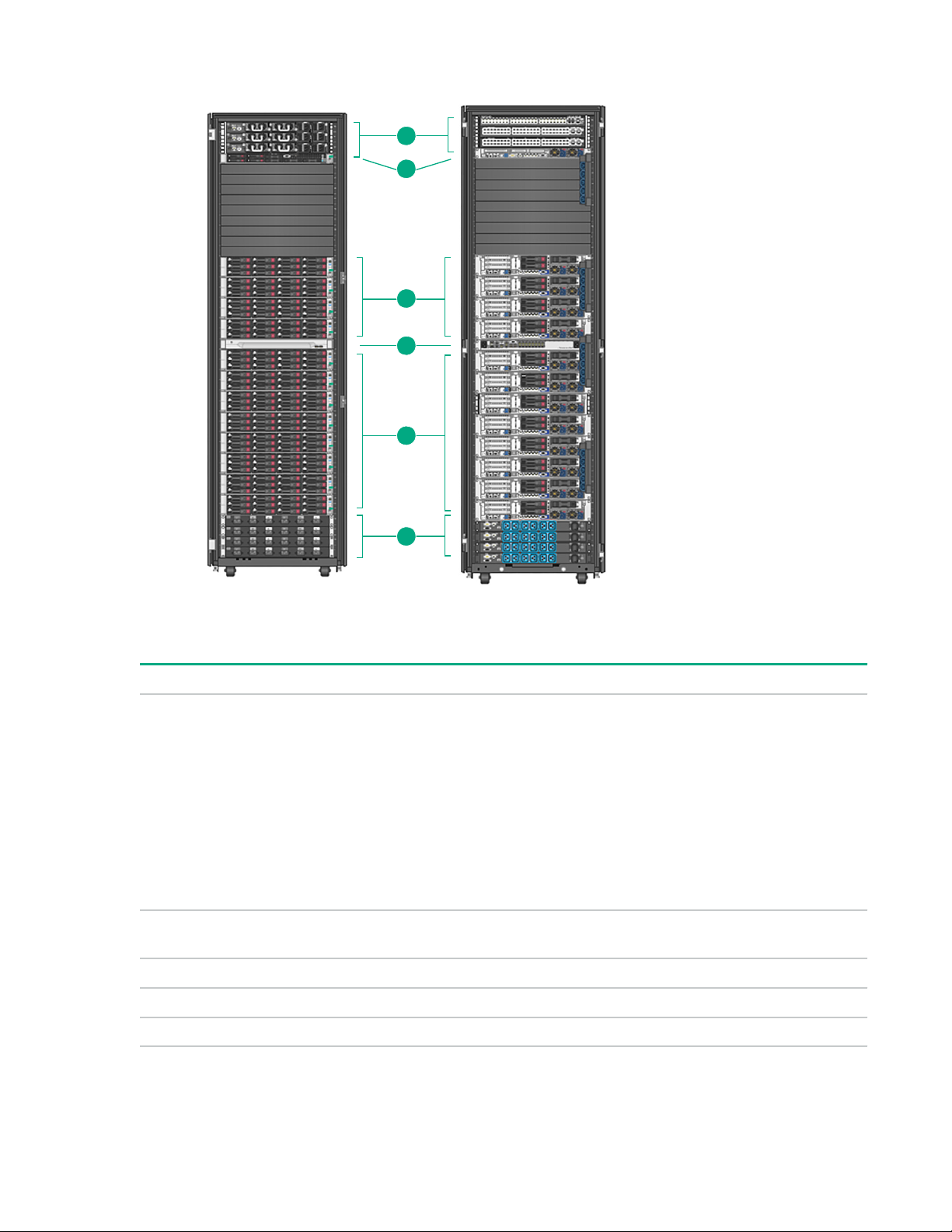
Gen9 solutions
Front Rear
1
3
4
3
5
2
Figure 1: HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 rack view
Item Description
1 Solution switch defaults (illustrated):
• (2) HPE Ethernet Switch 5900-48XG-2QSFP+ (ToR)
• (1) HPE Ethernet Switch 5900AF-48G -4XG-2QSFP+ (BMC)
Solution switch options (not illustrated):
• (2) Cisco Ethernet Switch Nexus N3K-C3172PQ-XL (ToR)
• (1) Cisco Ethernet Switch Nexus N3K-C3048-FA-L3 (BMC)
2 (1) HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 with Microsoft Azure Stack Hardware Lifecycle Host
management node
3 (4-12) HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen9 with Microsoft Azure Stack compute nodes
4 (1) Optional 8 or 16-port KVM switch and optional LCD8500 Rackmount console
5 (2 or 4) power distribution units
1
Depending on option you chose, the count and color may vary from this illustration.
1
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview 9
Page 10
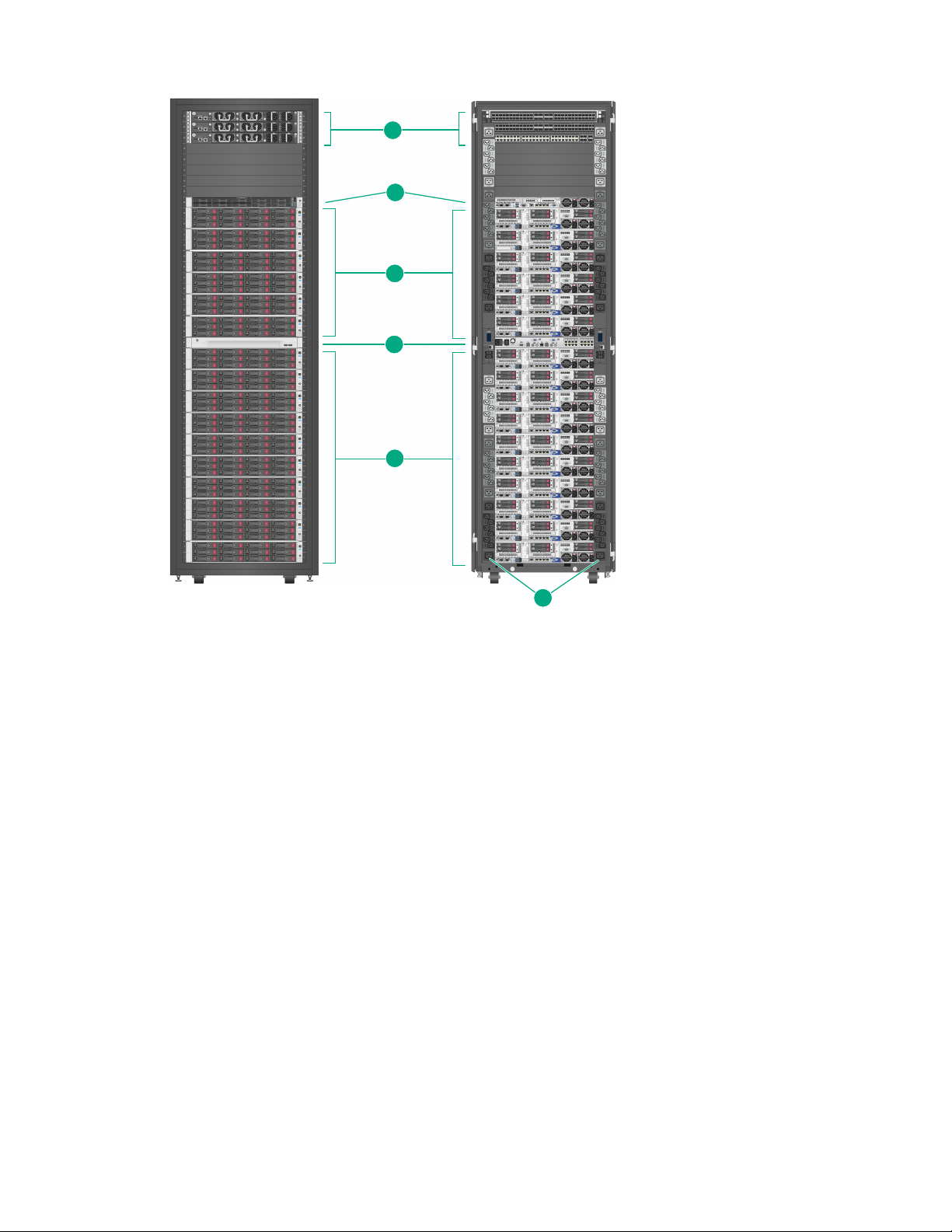
Gen10 solutions
1
3
3
4
2
5
Figure 2: HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 rack view
10 HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
Page 11

Item Description
1 Solution switch defaults (illustrated):
• (2) HPE Ethernet Switch 5950 48SFP28 8QSFP28 (ToR)
• (1) HPE Ethernet Switch 5900AF 48G -4XG-2QSFP+ (BMC)
Solution switch options (not illustrated):
Arista switches
• (2) Arista Ethernet Switch DCS-7160-48YC6-R (ToR)
• (1) Arista Ethernet Switch DCS-7020TRA-48-R (BMC)
Cisco switches
• (2) Cisco Ethernet Switch Nexus N9K-C93180YC-EX (ToR)
• (1) Cisco Ethernet Switch Nexus N9K-C9348GC-FXP (BMC)
2 (1) HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 or Gen10 with Microsoft Azure Stack Hardware Lifecycle Host
management node.
3 (4-16) HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 Microsoft Azure Stack Hybrid nodes.
(4-8) HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 Microsoft Azure Stack All-Flash nodes.
4 (1) Optional 8 or 16-port KVM switch and optional LCD8500 Rackmount console
5 (2 or 4) Vertical HPE G2 Standard or Metered power distribution units
Hardware Lifecycle Host Management node
The Hardware Lifecycle Host (HLH) is an HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 or Gen10 Server. The HLH is used
for solution deployment, monitoring, and management. The HLH is a Hyper-V host for HPE OneView
software management components.
NOTE: HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solutions ordered before June 4, 2018, are configured
with recipe 1.x and include Gen9 based Azure Stack compute nodes and upgraded with HPE OneView
Remote Support. HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solutions ordered after June 4, 2018, ship from
the factory with an updated solution recipe 2.x that includes Gen9 or Gen10 based Azure Stack compute
nodes and HPE OneView Remote Support. Therefore, HPE Insight Remote Support is no longer
available or used in HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solutions.
Management node hardware
The HLH Management node is composed of the following hardware components:
Server HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen10
Processors
Max RAM
(2) Intel E5-2620v4 (2) Intel E5-2620v4
64GB 96GB
Table Continued
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview 11
Page 12

Server HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen10
Storage capacity
Ethernet network
adapter
iLO
Management node software
The Management node hosts the components for the installed recipe version as specified in the HPE
ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix and HPE
ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix.
The Management node acts as a Hyper-V host and hosts the HPE OneView instances that manage and
monitor the solution. During deployment and upgrade the HPE Solution Update Bundle and solution
custom SPP will typically be loaded onto the management node. Scripts residing on the Management
node orchestrate the delivery of those components to the rest of the solution. A typical recipe upgrade
scenario will extract an HPE Solution Update Bundle on the Management node and initiate an upgrade
script. The HPE Solution Update Bundle contains all the HPE components of the solution recipe.
(4) 600GB disks configured in a RAID
6 array
546FLR-SFP+ 10Gb 640FLR-SFP+ 25Gb
Dedicated iLO 4 with the iLO
Advanced License
Azure Stack compute nodes
The Azure Stack compute nodes consist of HPE DL380 servers configured with the following:
(4) 960GB SSDs configured in a RAID
6 array
iLO 5
Azure Stack compute node Gen9 solutions Gen10 solutions
Server HPE DL380 Gen9 HPE DL380 Gen10
Processors 2 - selectable 2 - selectable
Max RAM 768GB 1.5TB
Storage capacity
Ethernet network adapter 546FLR-SFP+ 10Gb 640FLR-SFP+ 25Gb
iLO iLO 4 iLO 5
Supported compute nodes per solution 4-12
1
Reflects capacity of (HDD) drives for Hybrid solutions. Hybrid solutions will additionally include cache (WI or MU
SSD) drives.
2
Advanced Premium Security edition.
1
40TB, 60TB, or 80TB
(Hybrid storage)
48TB, 72TB, 96TB, or 120TB
(Hybrid solutions)
12.8TB, 19.2TB, 25.6TB,
38.4TB, 51.2TB, 76.8TB, or
102.4TB (All-Flash solutions)
2
4-16 for Hybrid solutions
4-8 for All-Flash solutions
Solution switches
The HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution supports the following Hewlett Packard Enterprise,
Cisco, or Arista switches.
12 HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
Page 13

The Top of Rack (ToR) switch pair is used by the Azure Stack nodes for solution production and storage
traffic. If used, the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) switch is used primarily for management
connections—iLO, iPDU's. The ToR and BMC switches must be from the same switch family.
NOTE: For the latest supported firmware and software versions, see the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft
Azure Stack Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix.
HPE switches
The HPE FlexFabric 5900 and 5950 switch series is a family of high performance and low-latency data
center switches. These switches can handle virtual environments and convergence of Ethernet and
storage traffic.
Component Solution Description Quantity
Gen9 Gen10
HPE 5900AF 48XG 4QSFP+ X ToR switch 2
HPE 5950AF 48SFP28 8QSFP28 X ToR switch 2
HPE 5900AF 48G-4XG 2QSFP+ X X BMC Switch 1
Cisco switches
These high performance, low-latency Cisco switches are available as an optional alternative to the
standard Hewlett Packard Enterprise data center switches in Gen9 and Gen10 solutions.
Component Solution Description Quantity
Gen9 Gen10
Nexus N3K-C3172PQ-XL X ToR switch 2
Nexus N3K-C3048-FA-L3 X BMC Switch 1
Nexus N9K-C93180YC-EX X ToR switch 2
Nexus N9K-C9348GC-FXP X BMC switch 1
NOTE: Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends purchasing a Cisco support agreement with a similar
level of support to the rest of the solution. At minimum, a support agreement allowing the ability to
download firmware is required for the specific models listed and FW version specified in the HPE
ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix are
supported. See Support for products not branded Hewlett Packard Enterprise on page 71 for
information about support for Cisco switches.
Arista switches
These high performance, low-latency Arista switches are available as an optional alternative to the
standard Hewlett Packard Enterprise data center switches in Gen10 solutions. See the HPE ProLiant for
Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix for the latest firmware
required for these switches.
Component Solution Description Quantity
Gen9 Gen10
Arista DCS-7160-48YC6-R X ToR switch 2
Arista DCS-7020TRA-48-R X BMC Switch 1
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview 13
Page 14
Network cabling
The solution is either shipped from the factory already cabled or is cabled by Hewlett Packard Enterprise
personnel. Do not remove, reroute, or otherwise change network cables. If a network cable fails, do not
replace the cable until a replacement is available.
Optional components
HPE G3 KVM analog switches
HPE KVM Analog Console Switches allow you to view and manage up to 256 rackmount servers across
your data center through a single user interface. This console utilizes a local On-Screen Display (OSD)
interface accessed through a rack console, such as the HPE LCD8500. The console provides intuitive
menus for accessing each attached server or serial managed device.
HPE G3 KVM Analog Console Switches support an optional USB Remote Access Key that allows you to
upgrade to KVM-over-IP functionality, providing remote access and management through the On-Board
Web Interface (OBWI). The new G3 models also support HPE Power Discovery Services and Location
Discovery Services when connected to the appropriate power distribution unit and KVM rack console.
HPE KVM Analog Console Switches are available in 8 and 16-port versions. Standard rack mounting of
the KVM Analog Console Switch shares 1U of front panel rack space with the HPE LCD8500 display
console.
For additional usage information, refer to the HPE G3 KVM Console Switch User Guide.
HPE Intelligent PDUs
The HPE Intelligent PDU brings state-of-the-art management and control to rack-mounted PDUs. This
management feature can be used to prevent over-provisioning of power that might restrict growth in your
data center. Using core and stick architecture, the HPE Intelligent PDU provides monitoring of power
consumption at the core, load segment, stick, and outlet level with unmatched precision and accuracy.
Remote management is built in and provides power cycle ability of individual outlets on the Intelligent
Extension Bars. Hewlett Packard Enterprise is the first to incorporate Power Discovery Services. When
combined with the HPE line of Platinum or Platinum Plus high efficiency power supplies, Power Discovery
Services communicates with the attached servers to collect asset information for the automatic mapping
of the power topology inside a rack. This speeds implementation time and greatly reduces the risk of
human errors that can cause power outages.
NOTE: iPDUs are only supported in Gen9 (recipe 1.x) solutions. iPDUs are not supported in Gen10
(recipe 2.x) solutions.
For additional usage information, refer to the HPE Intelligent Power Distribution Unit User Guide.
HPE G2 Metered PDUs
HPE G2 Metered Power Distribution Units (PDU) provide both local and remote rack power management
to meter or restrict outlet usage. Each PDU can be accessed and configured remotely through secure
Web, SNMP or SSH interfaces and supports multiple access levels for enhanced security. An LCD screen
provides local monitoring and alert indications.
The HPE G2 Metered PDUs are a low-profile design with multiple mounting options and offer complete
compatibility with HPE Advanced and Enterprise series racks. Up to four units can be daisy-chained to
share the network connection and IP address. The HPE G2 Metered PDU network management card can
be removed and replaced (hot swap) without affecting power distribution for zero downtime for network
connection issues.
14 HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
Page 15

For more information see the HPE G2 Series Metered, Switched, and Metered & Switched Power
Distribution Units User Guide and HPE G2 Metered Power Distribution Units QuickSpecs.
HPE Update Service for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
You have an optional update service available called the "HPE Update Service for HPE ProLiant for
Microsoft Azure Stack." This update service allows you to engage HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
experts to implement HPE software and firmware updates quickly and efficiently, and reduce the
disruption to your environment.
Expansion and scaling
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack is designed to be upgraded and expanded in a controlled
environment. Refer to the table below for current information on availability of certain features.
For more information about each of these features, select the link in the table.
Expansion feature Supported Not supported
Adding nodes to an existing scale unit X
Adding scale units or regions to an existing deployment X
Expanding storage capacity X
Adding memory X
Adding nodes to an existing scale unit
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends that you consider the CPU, memory, and storage growth rates
of your workload when performing solution sizing. Then purchase sufficient capacity in each scale unit to
meet future workload demands.
Adding nodes to an existing scale unit is supported subject to the following limitations:
• The existing scale unit has been updated to Microsoft Azure Stack 1807 or newer that supports the
"Add Node" capability. See the Microsoft release notes at https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/
azure-stack/azure-stack-update-1807.
• The maximum number of Azure Stack compute nodes is limited to the current maximum for your
system: 8 (Gen10 All-Flash), 12 (Gen9), or 16 (Gen10 Hybrid).
• All Azure Stack nodes must be configured identically, including CPUs, memory, and storage
resources. For instructions on how to find the required information about existing Azure Stack nodes,
see Preparing for Add Node.
• The mandatory Add Node service from HPE Pointnext Operational Services must be used to provide
onsite node hardware installation into the rack and requisite updates to HPE Management tools and
switch configurations.
• The customer is responsible for the logical addition of the new Azure Stack nodes through the Azure
Stack user interface.
Adding scale units or regions to an existing deployment
Adding scale units or regions is not currently supported.
Based on the constraints of Microsoft Azure Stack software, at initial release, a single region is supported
and within that region a single scale unit is allowed.
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview 15
Page 16

At initial release, it is possible to increase capacity through the addition of new scale units. Each new
scale unit must be deployed as a separate instance of Microsoft Azure Stack with its own unique external
DNS domain.
Expanding storage capacity
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack does not directly support expansion of storage such as adding
drives or replacing lower capacity drives with higher capacity drives.
The Microsoft Azure Stack architecture currently requires all nodes in a scale unit to be configured using
an identical homogeneous configuration. For storage, consistent capacity cache drive sizes and
quantities must be consistent across the entire scale unit. This requirement prevents incrementally adding
or replacing disks in the solution with the exception of replacing drives that have failed with identically
sized replacements.
The solution is designed to support expanding storage capacity following a hyperconverged model of
creating additional nodes or scale units. However, neither is available at initial release. See Adding
nodes to an existing scale unit or Adding scale units or regions to an existing deployment for
details.
Adding memory
Adding memory to an already deployed HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack system is supported. This
feature will allow expansion of memory capacity without the need to redeploy.
The Microsoft Azure Stack architecture currently requires all nodes in a Scale Unit to have the same
physical amount of memory.
NOTE: When expanding, only options listed in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9
Quickspecs or HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Quickspecs are supported.
Depending on the original configuration, this may require removing previously installed memory to
prevent expanding to an unsupported configuration.
The minimum supported version of Microsoft Azure Stack for memory expansion is 1802.
For additional information on how to implement memory expansion, contact your Hewlett Packard
Enterprise account team or HPE Pointnext representative.
HPE OneView
Using HPE OneView with HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
HPE OneView is used as an infrastructure automation engine serving as the core element of the
hardware monitoring and life cycle management solution.
HPE OneView unified infrastructure management capabilities enable you to closely monitor the health of
your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution hardware, including iPDUs. The dashboards of HPE
OneView provide real-time status information and alerts, which are useful for tracking and maintaining the
health of your solution. Additionally, the HPE OneView API and broad composable environment, including
language bindings and expanding environment of third-party integrations, provide the opportunity to
integrate HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution monitoring into your tool of choice. For more
information, see: https://www.hpe.com/us/en/solutions/developers/composable.html.
HPE OneView is used to increase reliability by integrating HPE OneView template-based management
capabilities to simplify life cycle management tasks. Each solution is deployed with an HPE OneView
server profile template designed and validated for use with Microsoft Azure Stack nodes.
16 HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
Page 17

NOTE: Do not create or modify the server profiles or server profile templates directly. To manage the
solution properly when performing daily monitoring, users are encouraged to use only user accounts with
read-only roles to avoid accidentally modifying server profiles or templates.
HPE OneView 4.0 provides enhanced remote support functionality as well as fully integrated hardware
monitoring, management, and remote support functions. This simplifies and streamlines basic system
maintenance functions, such as updates and backups. See HPE OneView Remote Support for more
information about HPE OneView Remote Support.
HPE OneView user guides, other manuals, and white papers are available on the Hewlett Packard
Enterprise Information Library: http://www.hpe.com/info/oneview/docs.
HPE OneView Remote Support
HPE OneView RS is a software solution that enables reactive and proactive remote support to improve
the availability of your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution.
HPE OneView RS enables enhanced delivery of your warranty or support services contract. To ensure
maximum system availability, HPE OneView RS supplements continuous system monitoring by providing
intelligent event diagnosis and automatic, secure submission of hardware event notifications to Hewlett
Packard Enterprise. This continuous monitoring initiates a fast and accurate resolution, based on your
product service level. If configured and available in your country/region, notifications may be sent to your
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Authorized Channel Partner for onsite service.
HPE OneView RS is included with your Proactive Care support agreement and is used as an automatic
service request submission for detected solution issues. Through the use of remote real-time hardware
event monitoring, HPE OneView RS can identify when a failure has happened or is about to occur. In
some cases, it proactively initiates a secure Internet event submission for a support experience and
automatically sends the replacement part to you. HPE OneView RS provides proactive care for each of
the solution hardware components, including:
• Hardware Lifecycle Host Management node
• Azure Stack Compute nodes
HPE OneView RS does not support PDUs or network switches.
Features and benefits
HPE OneView Remote Support supports HPE servers, providing you with the following features and
benefits:
• Preintegrated into the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution and easily configured to
monitor your environment.
• 24x7 real-time hardware event monitoring and secure Internet event submission help you identify and
prevent potentially critical problems for your environment.
• Automatic service request submission saves time monitoring and reporting issues.
• Intelligent analysis of issues provides faster restoration of your monitored devices to operational
status.
• Support for Scope Based Access Control (SBAC) allows remote access control of subsets of
resources (Scope).
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview 17
Page 18

• HPE OneView RS can easily be configured to forward service events to a supported version of
Systems Insight Manager and offers integration into Insight Online.
• Collection of configuration information from your devices to help Hewlett Packard Enterprise resolve
problems more quickly and accurately.
NOTE: No business information is collected and the data is managed according to the Hewlett
Packard Enterprise Data Privacy policy.
HPE OneView RS checks every device to make sure it has a valid Hewlett Packard Enterprise warranty
or contract.
If a device does not have a Hewlett Packard Enterprise warranty or contract, the monitoring health
indicator in the HPE OneView RS console is red. When the indicator is red, no service events are
analyzed or sent to Hewlett Packard Enterprise.
Using HPE OneView RS with HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
HPE OneView RS is initially configured as part of the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Deployment
Accelerator Service. If a monitored device requires replacement, the network configuration changes, or
the credentials of a monitored device are modified, the devices may need to be rediscovered to re-enable
monitoring. For more information about HPE OneView Remote Support, see the HPE OneView 4.0 User
Guide and the Settings: Remote support topics in HPE OneView 4.0 Help.
HPE OneView configuration and installation guides, user guides, other manuals, and white papers are
available at http://www.hpe.com/info/oneview/docs or in the Hewlett Packard Enterprise Information
Library.
18 HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution overview
Page 19

Solution management
Monitoring and maintaining the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution hardware is an important
part of maintaining a healthy Microsoft Azure Stack deployment. The following sections outline the best
practices for hardware life cycle actions for the solution.
NOTE: See the Microsoft Azure Stack User Guide for Microsoft Azure Stack software life cycle
management details.
Recommended administrative activities
Adhere to the following guidelines to:
• simplify life cycle management tasks
• follow security best practices
• prevent data loss
• avoid solution administrator activities from causing a misconfiguration of the solution
Monitoring
• To prevent unintended interruptions in service, monitor the health of the system on a regular basis.
See Hardware monitoring on page 21 for details.
• For regular monitoring activities, use only accounts with minimal privileges, such as a read-only role
account when accessing HPE OneView or a Microsoft Windows user other than Administrator when
accessing the Hardware Lifecycle Host. See Monitoring health with HPE OneView on page 22 for
additional information.
Backup
Perform a backup prior to any maintenance such as updates. Transfer backup files to a location outside
of the solution. See Hardware Lifecycle Host backup and recovery process on page 31 for details.
Security
• Regularly rotate passwords. See Managing passwords for details.
• Regularly check the status of certificates. See Managing certificates for details.
• Regularly update encrypted data recovery keys: See Managing BitLocker recovery keys for details.
• Keep Microsoft Windows security features such as Device Guard and Windows Defender enabled and
up to date. See Managing Device Guard for details.
System administration guidelines
Administrators must take care to adhere to the following guidelines:
Solution management 19
Page 20

Avoid these actions Explanation
Do not directly search for and download individual
firmware, drivers, or software updates for
components of the solution. This directive includes
Hardware Lifecycle Host Management node, Azure
Stack Compute nodes, switches, HPE OneView,
HPE iLO, iPDU or G2 Metered PDU.
Do not attempt to directly modify HPE OneView
server profiles or server profile templates unless
explicitly guided to do so.
Do not directly power-down the Azure Stack nodes. Before powering down, Azure Stack nodes must
Software, firmware, and drivers are pretested to be
compatible with all components in the HPE
ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. When
updating the solution, use only the solution-specific
update bundles from Hewlett Packard Enterprise or
the Microsoft software update bundle from
Microsoft. These bundles contain the correct
software, firmware, and driver versions as specified
in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
Gen10 Software and Firmware Compatibility
Matrix.
Use read-only role accounts to avoid accidentally
changing server profiles. Use HPE OneView
integrations to accumulate health information from
multiple HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
deployments or to enable other automated
monitoring use cases. See https://
www.hpe.com/us/en/solutions/developers/
composable.html for more information on the
environment of HPE OneView Integrations.
first be put into maintenance mode and verified that
they are drained of active workloads (moved to
different nodes).
Do not modify system BIOS or boot order settings. BIOS settings have been tested and verified for
each HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
solution recipe release.
Do not modify the switch configuration. The switch configuration has been preconfigured in
the factory and refined as needed as part of the
initial setup and delivery. Necessary updates are
provided as part of solution update bundles for the
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution.
Accessing the HPE management portions of the solution
Solution component IP Addresses
User access to individual solution software applications is by static IP addresses. These IP addresses
have been provided to you at the conclusion of the deployment service. If these materials are lost,
c:\cdw\untagged\ip-iaddresses.csv
can be consulted for a listing of component IP addresses.
In some cases, an icon is also included on the Administrator desktop of the HLH as a direct link to the
application UI.
Solution component access
20 Solution management
Page 21

Accessing Hardware Lifecycle Host with Microsoft RDP
Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) can be used to access the HLH Management node. Using
RDP requires the remote desktop to have an RDP client installed. Necessary access information such as
the IP address, user name, and password, is included in materials provided during the deployment
service.
Accessing HPE OneView
NOTE: Due to firewall restrictions, the HPE OneView dashboard can only be accessed from the HLH
Management node.
Access to the HPE OneView dashboard can be made through:
• A bookmark to the HPE OneView dashboard on the desktop of the HLH (requires network connection)
• Browse to https://<OneView VM IP address> (requires network connection)
• Using the Hyper-V console
Use this method if the network connection is not available.
1. Open the Hyper-V management console, right-click the HPE OneView VM, and select Connect.
2. Log on using your HPE OneView VM credentials.
Accessing Switches
NOTE: You can install an SSH client of your choice on the Hardware Lifecycle Host that allows you to
administer the switch from the HLH Management node. Putty is also available on the HLH and can be
used for switch administration access. If you encounter difficulty in establishing connectivity, you may
need to use console connectivity. Contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise support or your Hewlett Packard
Enterprise consultant for further assistance.
For detailed information about accessing and managing HPE switches in HPE ProLiant for Microsoft
Azure Stack systems, refer to the HPE FlexFabric 5900 or 5950 switch documentation.
For information about accessing and managing Cisco switches in HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
systems, refer to the Cisco Nexus 3000 Series NX-OS Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release
6.x for Gen9 solutions or Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Fundamentals Configuration Guide,
Release 7.x for Gen10 solutions.
For information about accessing and managing Arista switches in HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
systems, refer to the EOS System Configuration Guide.
Hardware monitoring
The Microsoft Azure Stack Health Resource Provider (HRP) performs basic hardware health monitoring
for the servers:
• Heartbeat monitoring of each node
• Per disk error reporting of SSD and HDD failures
To supplement the HRP, Hewlett Packard Enterprise has included HPE OneView integrated into the
solution to provide a complete hardware monitoring solution. See Monitoring health with HPE OneView
for guidance on configuring and using HPE OneView to monitor the solution hardware.
Solution management 21
Page 22

Monitoring health with HPE OneView
User roles and accounts for Monitoring
User roles allow the administrator to define the role of a user account by restricting permissions and
privileges based on the user's job responsibilities. Refer to About User roles in the HPE OneView 4.0
Help for full detailed descriptions of each role and its permissions or privileges.
To monitor the Azure Stack node resources with HPE OneView, Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends
only using a read-only account, which decreases the chance of making unwanted changes. To create and
check user account privileges in HPE OneView used for monitoring, follow these steps.
1. Navigate to Users and Groups page from the HPE OneView drop-down menu.
2. Click the +Add User button to the left side of the page.
3. Type in the user data and select the Read Only radio button.
4. Click Add when complete.
5. To test, log out and log in with the newly created user. Then navigate to a server-hardware page, click
Action, and notice "No authorization" text.
Accessing the HPE OneView help sidebar
At the top right corner of each page, there is a question mark in the banner. To open the Help sidebar,
click the question mark. The help sidebar provides:
• hyperlinks to the help system
• open-source code used in the product
• partner programs
• initial configuration procedures
• license agreement
• written offer
• online user forum
Useful help sidebar links:
1. Help on this page: Opens context-sensitive help for the current screen in a new browser window or
tab. This context-sensitive help is useful to browse through a page with items on the current screen
without referring to the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide.
2. Browser help: Opens the top of the help contents in a new browser window. The new window enables
you to navigate to the entire table of contents for the UI help.
Dashboard page
The Dashboard is the first page displayed every time a user logs in. The Dashboard provides a visual
overview of managed resources including server hardware, server profile, and power devices. These
devices can be customized by adding custom or predefined panels that interest you. The panels can also
be rearranged in the order of your prioritization. The Dashboard page provides alerts and warnings to
help get the infrastructure attention of the manager. The user can go directly to the resource page that
needs attention by clicking the name of resource.
1. The dashboard chart colors indicate the following.
22 Solution management
Page 23

Color Indication
Green Healthy status.
Yellow An event has occurred that might require your attention.
Red A critical condition requires your immediate attention.
Blue For a status graph, the resource instances that match the data being measured.
A solid blue chart indicates 100%.
Light gray Resource instances do not match the data being measured. This indicator is
used in combination with blue to total 100%.
Dark gray Indicates that resource instances are Disabled or Unknown and also indicates
any status other than OK, Warning, or Critical.
2. Recommended resources are included in Dashboard view:
a. Server profiles
b. Server profiles templates
c. Server hardware
d. Appliance alerts
e. Activity
f. Power delivery devices
g. All resources
NOTE: For full details on how to customize the Dashboard page and interpret data, refer to the help page
within HPE OneView. To add or remove items from the Dashboard, see Dashboard in HPE OneView 4.0
Help.
Server profile page
A server profile is the configuration for a server instance when it gets added to the HPE OneView
appliance as a managed server. The Azure Stack Compute and Management nodes will be a part of rack
mount server hardware type. Only certain server profile features are applicable with this hardware type.
Supported features for rack mount server profile:
• Basic server identification information: server type, serial, power.
• Firmware versions: Specify the Service Pack for ProLiant version to apply.
• Local storage settings: Configure the disk drives directly connected to the integrated Smart Array
Controller.
• Boot settings: Specify boot order.
• BIOS settings: Specify the BIOS settings to apply.
Monitoring a server profile resource:
1. Navigate to the server hardware page from the main menu.
2. To the left side, there will be a list of server profiles by name, select one to monitor.
Solution management 23
Page 24

3. The middle panel, will display the data for the resources depending on what view is selected, by the
default "Overview" is displayed. See the following for supported server profile views and descriptions.
4. To the top right side, there is a drop-down action button where authorized user roles are allowed to
Create, Edit, Copy, and Launch a console.
Supported server profile views for the solution:
• Overview: Includes short description of general, firmware, local storage, and BIOS settings.
• General: Expanded details.
• Boot settings: Managed boot mode (UEFI, legacy), and boot order.
• BIOS settings: Display all settings or only the modified.
• Activity: View that provides notifications including user initiated tasks and alerts about the selected
profile.
Actions supported in server profile page for the solution:
The following is a partial list of all operations that can be performed with the server profile. For a full list,
review the Server profiles section in the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide.
• Power on and off the server hardware to which the server profile is assigned.
• Manage the BIOS and boot settings of a server.
• Update firmware with a server profile.
• Manage local storage of a server.
IMPORTANT: Settings changes to the server profile must be done only by the administrator and
only when instructed to do so by Hewlett Packard Enterprise support team. Use only a read-only
account to monitor the server profiles.
Server profile template page
Server profile templates help to monitor, alert, and update server profiles in HPE OneView. A server
profile template serves as a structural reference when creating a server profile. All of the configuration
constructs of a server profile are present in the server profile template.
A server profile continues to maintain an association to its server profile template after being created from
the template. Any drift in configuration consistency is made visible on both the server profile template and
the associated server profiles.
A server profile template allows you to do the following tasks:
• Easily reapply the configuration to the server hardware if the server hardware is serviced or replaced.
• Capture significant portions of the server configuration in one place, greatly simplifying and hastening
server configuration.
• Manage many server profiles with the same configuration.
• Control configuration changes for multiple servers at once. HPE OneView checks compliance for all
the server profiles that are referenced to the template.
• Automatically resolve the compliance issues using the Update from Template action. The server profile
configuration is adjusted to match the server profile template.
24 Solution management
Page 25

Supported server profile template views are similar to the preceding server profile views.
Server hardware page
The server hardware page displays all the physical servers that are added to the HPE OneView appliance
as managed or monitored.
Actions supported from the server hardware page:
• Obtain information about the server hardware.
• Collect remote support data for server hardware.
• To manage servers remotely, launch the HPE iLO remote console.
• View activities
NOTE: The online appliance help provides full information on performing these tasks.
Supported server profile views:
• Overview: Includes a short description of general, firmware, local storage, and BIOS settings.
• Hardware: Includes the state, model, product ID, server profile, iLO IP address.
• Firmware: iLO firmware, ROM, and Intelligent Provisioning version
• Utilization: Displays metrics including CPU usage, power consumption, storage space capacity, and
temperature.
• Activity: Provides notifications including user initiated tasks, and alerts about the selected hardware.
Activity page
The activity page lists alerts and other notifications about appliance activity and events occurring in your
data center. You can filter, sort, and expand areas of the screen to refine how information is displayed.
Links within activity details also enable you to view additional information about specific resources,
especially when the notification is reporting an event that requires immediate attention.
Alert types:
• Alerts: Messages used by the appliance to report issues or a change that occurred with the resources
under management. It includes, severity, state, description, and urgency.
IMPORTANT: There is a limit of 75,000 alerts and 50,000 tasks. During typical operation of this
solution, it is not expected to reach these limits. See the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide for
details.
• Tasks: Activities initiated by the user or system. User-initiated tasks include creating, editing, or
removing a server profile. An appliance initiated task includes updating utilization data.
Alert states and statuses:
• States: Depending on the type of activity, for example alert or task, the states vary. Alert states are
Active, Locked, and Cleared. Task states are Completed, Running, Pending, Error, and Warning. For a
list of all states with descriptions, see the HPE OneView 4.0 Help or HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide.
• Statuses: The activity statuses are Critical, Warning, OK, Unknown, and Disabled. Investigate Critical
and Warning statuses immediately.
Solution management 25
Page 26

NOTE: For more information, see the Activity states and Activity statuses topics in HPE OneView 4.0
Help.
Setting up email alerts
Users can configure the appliance to send email messages regarding notifications when an alert gets
generated. It can include as many as 50 recipients in one single email message.
When configured and enabled, the appliance performs these actions:
• The appliance compares the alert to configured search criteria.
• If the alert matches, it creates an email message containing the text of the alert.
• The appliance sends the email message to designated recipients in both plain text and HTML MIME.
Configuring the appliance for email notification of critical and warning alerts:
1. Login using the infrastructure administrator role.
2. From the main drop-down menu, click the Settings link and navigate to the Settings page.
3. Hover the mouse over the Notification section and click Edit.
4. Enter the email information for sending emails.
5. In the alert email section, select Enabled.
6. Click Add Alert Email Filter and wait for the Add Alert page to appear.
7. Enter in the required information and click Add. Click Add+ to create more than one filter notification.
Monitor power utilization and powering down server
The appliance gathers and reports power consumption, temperature, and capacity data for certain
resources for server hardware and power delivery devices. These data are displayed using graphs and
meters in the Utilization panel for the managed resources.
The minimum data collection interval is an averaged 5 minutes. The maximum is an averaged 60
minutes.
Viewing server hardware utilization including CPU, power, and temperature:
1. Navigate to the Server Hardware Page, select your server hardware on the left side panel.
2. Click the drop-down View menu next to the server hardware name and select Utilization.
3. There are four categories: CPU, Power, Temperature, and Custom. To expand the details, click the
arrow.
NOTE: The same data can be accessed through the REST API. For more information, see the "REST
API power and temperature monitoring" section of the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide.
4. Repeat steps 1-3 for the remaining server hardware.
Shutting down the HLH Management node gracefully:
26 Solution management
Page 27

1. Log in to the Microsoft Windows Server.
2. Follow the instructions in the user guide for each running application for properly shutting down the
application. For example, see the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide to shut down HPE OneView
properly.
3. Use the Microsoft Windows Server settings to perform a shutdown.
WARNING: Only perform a shutdown when instructed or guided by Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Support Team. If an unexpected shutdown occurs, contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support to
troubleshoot the root cause.
Viewing power delivery device/iPDU utilization:
1. Navigate to the Power Delivery Devices from the HPE OneView main menu.
2. Select the iPDU from the left side.
3. Click the View drop-down menu next to the name of device and select Utilization.
4. Click the arrow in the Power category to expand the details.
Creating a Report
HPE OneView offers predefined reports to help you manage your appliance and its environment. You can
view the reports in the UI. The reports can be saved as a Microsoft Excel workbook (*.xlsx) or CSV
MS-DOS (*.csv). These reports provide an inventory of the resources managed by HPE OneView
including server model, serial number, and part number.
Creating a predefined report from the UI:
1. Logon using the Infrastructure Administrator Role.
2. Navigate to the Reports page from the main menu.
3. Select the desired report name on the left side.
4. Click the Actions button to the right side and select Save-as.
5. Select the file format and click OK.
Updates
Perform all updates to Microsoft Azure Stack as documented in Manage updates in Azure Stack
overview and Apply updates in Azure Stack sections in the Microsoft Azure Stack Operator Guide.
Updates to the Microsoft software components are available monthly. To keep your system current, be
sure to apply these updates regularly. The Microsoft updates are not cumulative and require the previous
update package as a prerequisite. For more information about Microsoft update policies, see the "Azure
Stack servicing policy" in the Microsoft Azure Stack Operator Guide.
Firmware and software updates and instructions for HPE components are explicitly provided by Hewlett
Packard Enterprise for the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. These updates are included
in the HPE Solution Update Bundle which can be downloaded from http://www.hpe.com/info/
MASupdates.
For the latest supported firmware and software versions, see the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure
Stack Gen9 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix or the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure
Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix.
Solution management 27
Page 28

HPE Solution Update Bundle
The HPE Solution Update Bundle is an accumulation of software and firmware updates for all major
components of the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. The HPE Solution Update Bundle is
used as a delivery mechanism to periodically update Azure Stack and Hardware Lifecycle Host nodes as
well as HPE OneView.
Download the HPE Solution Update Bundle from HPE Software Depot at http://www.hpe.com/info/
MASupdates.
To extract the files for updating the Hewlett Packard Enterprise components of the solution, perform these
steps.
1. Transfer the bundle zip file to the Hardware Lifecycle Host.
For connected environments, simply download the bundle using Internet Explorer on the HLH. For
disconnected environments, the transfer can be accomplished by one of the following:
• Mount an SMBv3 file share containing the file (recommended).
• Insert USB storage device into the HLH and transfer the file.
• Using HPE iLO virtual media to mount and transfer the file.
2. Extract all files from the bundle zip file to your choice of staging location.
Example: c:\update\2.0.1810.1
3. To perform the update steps, follow the instructions in the Release Notes associated with the update
bundle. In general, most update steps will be performed by executing a single script.
For detailed update instructions, see the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Solution Update Bundle
Installation Guide available from the HPE Support Center at http://www.hpe.com/support/hpesc.
Management node updates
Overview of Hardware Lifecycle Host update process
All HPE software, firmware, and driver updates for the Hardware Lifecycle Host are delivered and staged
with the HPE Solution Update Bundle. In most cases, the HPE Solution Update Bundle will perform online
updates of these components. However, sometimes a reboot or a graceful shutdown of the Hardware
Lifecycle Host is required. To verify the requirements of the update you are applying, refer to the release
notes of the HPE Solution Update Bundle. See HPE solution update bundle.
In addition to installing HPE Solution Update Bundle, regular Microsoft Windows OS updates must be
installed on the Hardware Lifecycle Host. See Hardware Lifecycle Host Microsoft Windows updates.
NOTE: Before initiating any updates on the Hardware Lifecycle Host, make a backup of the HPE
OneView. See Hardware Lifecycle Host backup and recovery process.
If installation of an HPE Solution Update Bundle or Microsoft Windows OS update requires a reboot, you
can use the HPE iLO Remote Console from the iLO web page to monitor the HLH throughout the update
process. For more information, see "Using the iLO Remote Consoles" in the HPE iLO 4 User Guide or
"Using the Remote Console features" in the HPE iLO 5 User Guide.
28 Solution management
Page 29

Hardware Lifecycle Host node firmware update
To update the Hardware Lifecycle Host, use the HPE Solution Update Bundle and follow the instructions
in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Solution Update Bundle Installation Guide included with the
bundle. See HPE solution update bundle.
Hardware Lifecycle Host Microsoft Windows updates
Microsoft Windows updates are provided by Microsoft as part of their monthly Azure Stack update
package.
1. Get the Azure Stack update package from Microsoft. See Download the update package for
instructions on how to download the update package.
2. Transfer the update to the HLH using one of these methods:
• Transfer the complete update package to the HLH, or
• Transfer individual files to the HLH
a. To transfer individual files:
I. Extract Windows update files from the update package. There will be one .xml file,
one .exe file, and one or more .bin files.
II. Execute the *.exe file.
III. On the Welcome to Azure Stack Update window, click Next.
IV. Specify a location to extract the update files into and click Next.
V. After the files have been extracted, locate any LCU or SSU files. These files contain the
necessary Microsoft Windows updates to be applied to the HLH.
NOTE: SSU files contain the latest Microsoft Windows updates, if any. LCU files contain
the latest cumulative Microsoft Windows update rollup.
VI. Locate the .cab file. This file contains the Windows update that you will be installing.
b. Review the associated documentation for the included .cab file.
3. Back up the HLH. See
4. Install the updates on the HLH with one of these options:
• DISM from cmd prompt window (as administrator)
Dism /Online /Add-package /PackagePath:<path to cab>
IMPORTANT: When prompted to reboot, select No. This selection will allow a graceful
shutdown of HPE OneView and the HLH when ready to restart.
Hardware Lifecycle Host backup and recovery process.
• Add-WindowsPackage from PowerShell window (as administrator)
Add-WindowsPackage -Online -NoRestart -PackagePath:<path to cab>
5. Reboot the HLH (if required).
Solution management 29
Page 30

HPE OneView updates
Update HPE OneView during normal solution updates
HPE OneView updates are included in the HPE Solution Update Bundle. HPE OneView is automatically
updated as needed whenever the solution is updated.
See HPE solution update bundle for more information about the HPE Solution Update Bundle.
Backing up HPE OneView before and after an update
Before changing the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution, it is a best practice to make a
backup of the HPE OneView appliance. See Creating and saving an HPE OneView backup file for
steps to manually create an HPE OneView backup.
After updating HPE OneView, make another backup using the same procedure.
NOTE: Be sure to save the backup file to a remote location. Do not store the backup file on the appliance.
For information about the backup and restore features and processes of HPE OneView, see the Backup
and restore features section of the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide. Refer to Back up an appliance
manually in the HPE OneView 4.0 Help for steps to run a manual backup.
HPE OneView reference documentation
For more information see the following guides:
• HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide
• HPE OneView Deployment and Management Guide (v4.0)
• HPE OneView 4.0 Release Notes
• HPE OneView 4.0 Help
• HPE OneView Global Dashboard 1.40 User Guide
Azure Stack node updates
Azure Stack node firmware update
To update the Azure Stack compute nodes, use the HPE Solution Update Bundle and follow the
instructions in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Solution Update Bundle Installation Guide
included with the bundle. See HPE solution update bundle.
Azure Stack node software update
For updates to the software on the Azure Stack nodes, see Manage updates in Azure Stack overview
and Apply updates in Azure Stack sections in the Microsoft Azure Stack Operator Guide.
Monitoring updates through Privileged Endpoint (PEP)
The Privileged Endpoint (PEP) tool included in the Microsoft update bundle can be used to monitor the
update process. To use this tool, follow the instructions in Monitoring updates through Privileged
Endpoint (PEP).
Validating Azure Stack updates
If you suspect there may be a problem after an update, you can validate the Microsoft Azure Stack
solution. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-stack/azure-stack-diagnostic-test for
the Microsoft validation procedure.
30 Solution management
Page 31

Hardware Lifecycle Host backup and recovery process
Rather than having a single Hardware Lifecycle Host backup solution, backup and recovery is performed
individually for the products running on the Hardware Lifecycle Host. These products include HPE
OneView and the Microsoft Windows OS instances running on Hardware Lifecycle Host.
Hardware Lifecycle Host Windows OS backup
During the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Solution delivery, a backup policy can be enabled for
daily backups of the Windows environment on the Hardware Lifecycle Host. These backup policies are
enabled with tools which use the standard Windows Server Backup Tools. These tools allow for easy
recovery using the Windows Server Manager.
The EnableHLHBackup.ps1 tool is designed to be used to configure the Windows Backup facility to
back up the desired files on the C: drive. The daily backups are performed with the target output written
either to the local V: drive or a remote share that is specified when enabled. When the script runs, the
new policy is set and a backup will be run.
There are a number of configurable items which can be modified for the backup policy:
• Backup location.
• Backup schedule time
• Backup Log file
• Volumes to be backed up
Default is C:
• Use the Volume Snapshot Service
Default is YES
• System State Restore
Default is ON
The limitations are:
The Windows Backup facility will only keep one copy of the backups on the specified media. If more
archived backup instances are required, use a remote network share and manually manipulate the files
outside of the HLH.
How to implement the backups
The Backup Policy can be initialized or changed using the EnableHLHBackup.ps1 tool. The tool can be
run at any time and will create a full backup.
Solution management 31
Page 32

Table 2: C:/HPE/Admin-tools/backup/EnableHLHBackup.ps1
Parameter Definition
LogfilePath <log file>
BackupTarget <Local drive|
Network Share>
ScheduledTime ”HH:MM”
File <BackupExcludeList>
TranscriptFileName
<transcript>
Recovery of Hardware Lifecycle Host files
Files will be recovered using the Recovery Wizard in the Windows Server Manager. Individual files and
folders can be restored as well as the complete C: volume and the System State.
Backup log file path. Default Log file is c:\HPE\Logs
\EnableHLHBackup.log
Backup location. Volumes will be backed up to either the FRU
drive at V: or a network share. Local drive is a valid drive
letter followed by a colon ":". A network share is the form \
\Share. Default is V:.
The schedule time in 24-hour format when the backup process
will start. Default is 3:00 AM local time.
A CSV file with 2 fields, Action and Filename or path to be
excluded from backups. The only valid action currently is
"Exclude".
The file containing the complete transcript of the backup policy
enablement and backup.
HPE OneView backup and restore
An HPE OneView backup file is a snapshot of the appliance configuration and management data. This
backup file can be used to restore a corrupted HPE OneView appliance if there is a catastrophic failure.
The backup process involves creating a backup file and then downloading that file so that you can store it
to a safe and secure (off-appliance) location for future use. Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends
configuring automatic backup operations and designate a remote location for the backup file.
IMPORTANT: In the unlikely event you must restore the appliance, Hewlett Packard Enterprise
recommends backing up your appliance configuration on a regular basis, preferably daily and
especially:
• After adding hardware
• After changing the appliance configuration
• Before and after updating the appliance firmware
To prevent a backup file from being overwritten or deleted, download it and save it to an off-appliance
location before running the next backup process. The appliance stores one backup file or one support
dump file on the appliance at a time.
To set up HPE OneView backups on the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution, see:
32 Solution management
Page 33

• Configuring automatic remote backups
• Creating and saving an HPE OneView backup file
• Restoring HPE OneView from a backup file
For more information about HPE OneView backups, see:
• HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide, Backup and restore features.
• HPE OneView 4.0 Help
◦ Best practices for backing up an appliance for advice on creating and archiving a backup file.
◦ Configure automatic remote backups for steps to set up automatic backups.
◦ Back up an appliance manually for steps to manually initiate a backup before and after making
hardware or firmware updates.
Validate user privileges
Infrastructure or Backup roles are required to perform a backup and restore.
To perform backups, Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends the creation of a user account assigned to
the specialized "Backup Administrator" role. This role would be used with the account specifically for
backing up the appliance by permitting access to other resource read-only views without permitting
actions on those resources or other tasks.
Configuring automatic backups
Automatic HPE OneView backups are controlled from a remote (to the HPE OneView VM host) computer.
Prerequisites
• Minimum required privileges: Infrastructure administrator, Backup administrator
• User account on a remote computer and the credentials for that account.
Procedure
1. From the HPE OneView main menu, select Settings.
2. Click Backup, and then select Actions > Edit backup.
3. Supply the data requested in the Edit Backup screen.
For detailed information about using the Edit Backup screen, see Edit Backup screen details in the
HPE OneView 4.0 Help.
NOTE: Some fields are hidden or revealed according to selections. When scheduling an automatic
remote backup, enter the Time as two numeric values separated by a colon.
4. Click OK.
5. Verify the success of the configuration by monitoring the progress of the test backup file that is
generated and transmitted.
Solution management 33
Page 34

Creating and saving an HPE OneView backup file
A backup file saves the configuration settings and management data for your appliance. You can recover
from a catastrophic failure by restoring your appliance from the backup file.
NOTE: To reduce the size of the backup file and the time it takes to create it, the firmware bundles you
have uploaded to the appliance are not included in the backup file.
Prerequisites
Minimum required privileges: Infrastructure administrator or Backup administrator.
Procedure
1. At the top of the HPE OneView window, next to OneView, click the drop-down arrow to access the
main menu and select Settings.
2. On the Settings screen, click Backup and then select Actions > Create Backup.
The backup file will be created. You can watch the progress bar in the Overview pane.
3. To verify that the backup file was created correctly, click the Create backup notification banner. The
backup file name will reflect the current date and time.
The backup file name has the format:
appliance-host-name_backup_yyy-mm-dd_hhmmss.bkp
Once the backup is complete, an optional backup file is available for download from the appliance.
4. To download the backup file, select Actions > Download backup.
5. To save the backup file for safekeeping, select the appropriate option in the dialog box.
• To store the backup file in the specified remote backup location, select Transfer backup to remote
backup location.
• To store the backup file on the local computer, select Download the backup to my computer. Do
not store the backup file on the appliance.
NOTE: If you choose not to download the backup, one is stored on the HPE OneView VM local disk.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends that you store the backup in a secure and remote location for
disaster and recovery, as well as on the Hardware Lifecycle Host management node in the following
directory: C:/OneView_backups
Restoring the appliance
Following are the basic steps to restore the HPE OneView appliance from a backup.
Procedure
1. Make note of the logon credentials.
2. Create an unencrypted support dump.
3. Download and store the existing logs in an easily accessed location.
4. Stop all automatically scheduled backups.
5. On the appliance, place the backup file in an easily accessed location.
34 Solution management
Page 35

6. Log out all currently logged on users.
7. Perform the restoration using the backup file you stored in step 5.
See Restoring HPE OneView from a backup file.
8. Complete the restoration by resolving discrepancies identified in Tasks to complete after appliance
restoration.
For a complete list of restoration best practices, see the Best practices for restoring an appliance
section in the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide.
Restoring HPE OneView from a backup file
Once you have uploaded a backup file and want to restore HPE OneView, perform the following steps.
NOTE: See the Restore an appliance from a backup file using the HPE OneView GUI section in the HPE
OneView 4.0 User Guide for additional information on restoring an appliance from backup.
Prerequisites
• Minimum required privileges: Infrastructure administrator
• You have completed the steps in Restoring the appliance.
• You have the original network configuration information available to enter.
Procedure
1. From the main menu, select Settings > Backup.
2. Select Actions > Restore from backup
A dialog box opens.
3. Select Select a backup file.
4. Click Browse, then locate and select the saved backup file.
5. Click Upload and Restore.
The upload process starts. The restore process starts when the upload has completed. When the
restore process is complete, you are returned to the login page.
6. Once restore is complete, logon to the appliance and resolve and discrepancies that the restore
operation did not resolve automatically.
Tasks to complete after appliance restoration
During a restore operation, the appliance reconciles the data in the backup file with the current state of
the managed environment. There are some discrepancies that a restore operation cannot resolve
automatically; for example, if servers were added after the backup file was created.
To eliminate the risk of duplicate IDs, you must manually resolve any remaining alerts and add these
servers back into the appliance. If server profiles are forcibly unassigned, or if the hardware is forcibly
removed without first being unconfigured, you must perform manual clean-up of hardware including
servers, interconnects, and enclosures.
1. After a restore operation is complete, re-add any server hardware added since the selected backup.
2. For any server profile alerts about the profile not matching the server hardware:
Solution management 35
Page 36

a. Identify all server profiles with a mismatch-type of error message. Make a list of these server
profiles and the assigned server hardware.
b. Gracefully drain the node that requires servicing to prepare it for maintenance using the Azure
Stack portal or CLI. Refer to Azure Stack Node Actions for specific instructions on how to drain
the node.
c. Power off the server, and then unassign all the server profiles individually. From the Server Profiles
screen, select Actions > Edit, and then select Unassign from the server hardware drop-down
selector. Click OK.
d. Select Actions > Edit again, and then reassign all the documented profiles to the documented
server hardware.
3. Do a virtual disk health check and resume node action after healthy in HPE OneView again.
a. Ensure the server is healthy in HPE OneView.
b. Refer to Azure Stack Node Actions to power on and resume the node in Azure Stack.
c. Wait until the virtual disk is healthy before to moving to the next node. See Check the status of
virtual disk repair for instructions on how to monitor the virtual disk health of Azure Stack.
4. Recreate any profiles for the servers that were added in step 1 by creating a new server profile for
such servers using the Actions menu on the appropriate Server Profile Template page.
a. Gracefully drain and power down the server.
b. Recreate the profiles.
c. Power up the server and resume node action.
To address any issues after restoring the appliance, follow the post-restoration tasks in the Postrestoration tasks section of the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide. If powering down a server, be sure to
gracefully drain and resume the node.
HPE OneView reference documentation
For more information see the following guides:
• HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide
• HPE OneView Deployment and Management Guide (v4.0)
• HPE OneView 4.0 Release Notes
• HPE OneView 4.0 Help
• HPE OneView Global Dashboard 1.40 User Guide
Disaster recovery
If a major system disaster cannot be resolved by restoring customer-serviceable components, contact
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support for assistance in bringing the system back online.
36 Solution management
Page 37

Hardware Lifecycle Host power down
Precautions
The Hardware Lifecycle Host node is used as the Hyper-V host for the HPE OneView virtual machine.
Before shutting down the Hardware Lifecycle Host Management node, the HPE OneView virtual machine
must be gracefully powered down. Follow the outlined procedures.
CAUTION: Do not force the Hardware Lifecycle Host to power down by removing system power
directly. Doing so may cause failures of both the Hardware Lifecycle Host and the underlying virtual
machines.
IMPORTANT: Do not use the "Turn Off" option within Hyper-V unless directed to do so by Hewlett
Packard Enterprise Support, or is absolutely necessary. This option forces an immediate power off
which could result in appliance failures.
HPE OneView power down
To power off the HPE OneView appliance, first ensure that a backup is completed. See HPE OneView
backup and restore for instructions on how to perform a backup.
After a backup has been completed, you may start an appliance shutdown by opening the HPE OneView
portal. From there, navigate to Settings > Appliance. On the drop-down Actions menu, choose the
option Shut down to begin the process of shutting down HPE OneView.
During the HPE OneView shut-down, you can monitor the progress through the appliance portal or by
opening the HPE OneView virtual machine within the Hyper-V manager of the Hardware Lifecycle Host.
After HPE OneView has completed its shut-down process, the HPE OneView virtual machine will now be
in a powered off state.
Hardware Lifecycle Host power down
NOTE: Before powering off the Hardware Lifecycle Host, it is recommended that a Windows backup be
created. If one has not yet been created, do so before proceeding. See Hardware Lifecycle Host
Windows OS backup.
After the HPE OneView virtual machine has been gracefully powered down, the Hardware Lifecycle Host
OS may be shut down safely through the Microsoft Windows Start menu.
Managing passwords, certificates, and keys
Follow your security policies and best practices to manage data and network security with password or
certificate rotation.
Managing passwords and credentials
As a best practice, rotate passwords and other credentials regularly. Use the information in this section to
change all passwords in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution.
You can use password rotation according to your security policies and best practices. See the following
sections for changing your passwords and related guidance:
• HPE OneView password on page 38
• HPE iLO credentials on page 38
• Hardware Lifecycle Host password on page 39
Solution management 37
Page 38

• ToR and BMC switch passwords on page 40
• HPE iPDU password on page 40 (Gen9 solutions)
• HPE G2 Metered PDU password on page 41 (Gen10 solutions)
• Additional resources for managing passwords on page 41
When managing passwords as part of a secrets rotation process or policy, use your corporate standard
method to handle OS password rotation for the HLH according to the standard process in Microsoft
Windows Server 2016. For example, changing the password with the ctrl-alt-del method, or through
local users and groups settings.
HPE OneView password
To change the HPE OneView password:
1. To reset a user password, edit a local user account as Infrastructure administrator.
2. From the HPE OneView User Interface main menu, select Users and Groups.
3. Select the user account you want to edit.
4. To change the user account settings, select Actions > Edit.
5. Enter User password.
6. Click OK.
HPE iLO credentials
Overview of HPE iLO credentials used by Microsoft Azure Stack
Microsoft Azure Stack (MAS) software uses a registered HPE iLO account to communicate with the
individual HPE iLO of each of the Azure Stack nodes. The Microsoft Azure Stack software securely stores
the credentials for that account at time of deployment and those credentials can be updated at any time
using the Set-BMCCredential cmdlet. This account is used by the software to:
• Reboot and reimage nodes as appropriate as part of the Microsoft Patch and Update (PnU) process
when updating Microsoft Azure Stack software.
• Basic node monitoring (heartbeat)
• Power down nodes (node actions)
For the purposes of rotating the HPE iLO credentials used by Microsoft Azure Stack, we will refer to the
account that is being used for these purposes as the "MAS Integration Account" as a generalized name
for convenience in this guide. The actual name account will be set by the customer. The expectation is
that this account is set up at time of deployment as part of the first credential rotation and maintained
according to the best practices of your organization for secrets rotation.
38 Solution management
Page 39

IMPORTANT:
• The user name and credentials used for the MAS Integration Account are expected to be
managed by the administrators of the solution.
• Do NOT modify the default HPE iLO "Administrator" account or any built-in HPE OneView
account, such as "_HPEOneView" or similar account. The account used as the MAS Integration
Account must be a separate account with administrator permissions.
• The MAS Integration Account credentials used must ALWAYS be identical for the HPE iLO on all
nodes, both the Hardware Lifecycle Host and Azure Stack nodes.
• The User Name and Login Name of the MAS Integration Account must NOT be "admin" or
"administrator" or any variation of those values with different capitalization, such as "ADMIN".
Updating credentials in HPE iLO
Use the following procedure to change the MAS Integrated Account user credentials on the Hardware
Lifecycle Host and Azure Stack nodes:
1. Log in to HPE iLO using your current User Operator credentials.
2. In the left pane, under Administration select User Administration.
3. Place a check mark in the right pane for the MAS Integration Account and click Edit.
4. If the User Name and Login Name is still set to the default "admin" user, update them with a new
name.
5. Select the Change password checkbox.
6. Enter the New Password and Confirm Password.
7. Click Update User to save the new password.
8. Repeat this procedure for the HPE iLO on each physical server in the solution.
Updating Microsoft Azure Stack with the new HPE iLO password
After updating all HPE iLO passwords, use the Microsoft-supplied "Set-BMCCredential" cmdlet to notify
Microsoft Azure Stack of the new username (if applicable) and password credentials. Instructions to
complete this process can be found at:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-stack/azure-stack-rotate-secrets#update-thebaseboard-management-controller-bmc-credential
NOTE: The Microsoft documentation uses generalized language and refers the HPE iLO as the
"Baseboard Management Controller (BMC)" throughout. Anytime you see the terms "Baseboard
Management Controller" or "BMC" it is talking about the HPE iLO. For example, the document says
"Update the BMC on the Azure Stack physical servers by following your OEM instructions" this statement
refers to the instructions for rotating HPE iLO credentials.
Hardware Lifecycle Host password
The Microsoft Windows administrator password is a key element to keeping your environment secure. By
default, the Microsoft Windows password expiration period is set to 60 days. Failure to reset your
password before this expiration period will require you to reset your password the next time you attempt
to login.
To change the local administrator password of the HLH Management node:
Solution management 39
Page 40

1. While logged in as the administrator, select Ctrl Alt Del and choose Change Password.
2. Enter Current Password, New Password, Confirm Password, and click arrow to change the
password.
3. In the left pane, under Administration, select User Administration.
ToR and BMC switch passwords
To change a network switch password, log in to the switch and execute the following commands in
system view.
<snetsw> system-view
<snetsw> local-user admin
<snetsw-luser-manage-admin>password simple <new password>
Replace <new password> with a new password.
[snetsw-luser-manage-admin]quit
[snetsw]quit
<snetsw> save force
Validating file. Please wait...
Saved the current configuration to mainboard device successfully.
<snetsw>
For more information about changing HPE switch passwords, see Password control commands in the
HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Security Command Reference and the HPE FlexFabric 5950 Switch
Series Security Command Reference.
For information about Cisco switch passwords, see User Password Requirements in Cisco Nexus 3000
Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide for Gen9 solutions or Cisco Nexus 9000
Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide for Gen10 solutions.
For information about Arista switch passwords, see AAA Configuration in the EOS System
Configuration Guide.
HPE iPDU password
IMPORTANT: Changing the iPDU password will cause HPE OneView to lose connectivity to the
iPDU. To resolve the issue, see Lost iPDU connectivity.
To change the iPDU password:
1. Sign in to the iPDU web interface and click My Account in the left navigation frame.
2. Enter the new password in the Password field.
3. Enter the password again in the Verify Password field.
4. Do one of the following:
• To save the new password, click Save Settings.
• To undo the changes, click Undo Changes.
• To view online help, click Help.
40 Solution management
Page 41

For more information about changing iPDU passwords, see the My Account menu and User Accounts
menu sections in the HPE Intelligent Power Distribution Unit User Guide.
HPE G2 Metered PDU password
To change the password for HPE G2 Metered PDUs:
1. Log into the PDU remotely:
a. Open a browser and enter the IP address of the PDU.
b. Enter the user name and password and press Enter.
2. Go the User Administration > Change Password.
3. In the Change User Password window, enter the old password and then the new password twice to
confirm.
Passwords must be between 8 and 32 characters.
4. To complete the password change, click Change Password.
5. Log out of the PDU.
a. Click the user name icon in the top right corner of the screen.
b. Select Log Out in the drop-down menu.
For more information about changing the HPE G2 Metered PDU password, see Changing the password
in the HPE G2 Series Metered, Switched, and Metered & Switched Power Distribution Units User
Guide.
Additional resources for managing passwords
For additional information, see the following resources:
• HPE OneView: HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide
Search for "Managing user passwords".
• HPE iPDUs: HPE Intelligent Power Distribution Unit User Guide
Search for "My Account menu".
• HPE 5900AF Series Switch: HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Security Configuration Guide
Search for "Configuring password control".
• HPE 5950 Series Switch: HPE FlexFabric 5950 Switch Series Security Command Reference
Search for "Configuring password control".
• Cisco switch: Cisco Nexus 3000 Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide.
Search for "User Password Requirements".
Managing certificates
All certificates must be externally generated and therefore imported into your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft
Azure Stack solution.
Each of the following can import certificates:
Solution management 41
Page 42
• HPE OneView
• HPE iLO
• HPE iPDU
• HPE 5900 and 5950 switches
• Cisco switches
When managing certificates as part of a secrets rotation process or policy, note the following:
HPE OneView
• To import an HPE OneView certificate, see Import an appliance certificate in the HPE OneView 4.0
User Guide.
• The Understanding the security features of HPE OneView chapter in the HPE OneView 4.0 User
Guide has definitive information about maintaining a secure system and best practice
recommendations for:
◦ User accounts, roles, and access
◦ Importing and managing certificates
◦ Passwords and credentials
◦ Network access
◦ Updates
◦ Virtual environments
HPE iLO
• To import an HPE iLO certificate, refer to the instructions in Obtaining and importing an SSL certificate
in the HPE iLO 4 User Guide or Administering SSL certificates in the HPE iLO 5 User Guide.
• HPE iLO allows you to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) that you can send to a Certificate
Authority (CA) to obtain a trusted SSL certificate to import into HPE iLO.
The CSR contains a public and private key pair that validates communications between the client
browser and iLO. Key sizes up to 2,048 bits are supported. The generated CSR is held in memory
until a new CSR is generated, HPE iLO is reset to the factory default settings, or a certificate is
imported.
HPE iPDU
• To install an HPE iPDU certificate, see the instructions in the Security considerations chapter in the
HPE Intelligent Power Distribution Unit User Guide.
• The HPE iPDU implements strict security for two important reasons:
◦ The HPE iPDU manages devices that have the potential to perform sensitive and destructive
operations.
◦ The HPE iPDU has browser accessibility.
To better ensure the security of the HPE iPDU and the devices it manages, evaluate the following
considerations in accordance with your organization's security policies and the HPE iPDU operating
environment.
42 Solution management
Page 43

◦ Remote access to the HPE iPDU requires a secure user name and password.
◦ Each account can be given different access levels for different capabilities. Ensure that the
appropriate access levels are granted to users.
◦ The web interface is installed behind the firewall.
◦ Browsing to the HPE iPDU can be done using SSL, which encrypts the data between the browser
and HPE iPDU. The HPE iPDU is supported by a 1024-bit encryption level. SSL also provides
authentication of the HPE iPDU by means of a digital certificate. Securely import the certificate to
ensure the identification of the HPE iPDU.
◦ Use a custom SSL certificate that is certified by a third-party SSL authority.
◦ When a browser logs in to the web interface, other browsers on the system also login. Consider
limiting the time that a browser can be logged in to an account with administrative privileges.
◦ Use nonstandard ports for the HPE iPDU web interface.
◦ Disable Telnet if remote configuration is not used.
◦ Disable the web interface if the web interface is not preferred.
• For information about possible browser security issues, see Browser security alert in the HPE
Intelligent Power Distribution Unit User Guide.
Switches
HPE network switches
HPE 5900 and 5950 series switches use PKI to increase security with remote access.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is an asymmetric key infrastructure to encrypt and decrypt data for
securing network services. Data encrypted with the public key can be decrypted only with the private key.
Data encrypted with the private key can be decrypted only with the public key.
PKI uses digital certificates to distribute and employ public keys and to provide network communication
with security services, such as user authentication, data confidentiality, and data integrity.
For detailed information about creating and managing a secure PKI environment for HPE 5900 and 5950
series ToR and BMC switches, see Configuring PKI in the HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Security
Configuration Guide and PKI commands in the HPE FlexFabric 5950 Switch Series Security
Command Reference.
Cisco network switches
Cisco switches support the use of certificates to increase remote access security. It is the customer's
responsibility to configure and manage certificates for these switches.
For information about managing certificates for Cisco switches, see Configuring X.509v3 Certificate-
Based SSH Authentication in the Cisco Nexus 3000 Series NX-OS Security Configuration Guide for
Gen9 solutions or SSH Authentication Using Digital Certificates in the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS
Security Configuration Guide for Gen10 solutions.
Arista network switches
Arista switches support the use of certificates to increase remote access security. It is the customer's
responsibility to configure and manage certificates for these switches.
For information about managing certificates for Arista switches, see Transport Layer Security/
Configuration in the EOS System Configuration Guide.
Solution management 43
Page 44

Managing BitLocker recovery keys
To retrieve the current recovery key and create one for the encrypted drives, use the BitLocker Device
Encryption Configuration Tool: manage-bde.
Assuming C: is the BitLocker protected drive you want to change recovery password, do the following
within an elevated command prompt.
1. List the recovery passwords and copy the ID:
manage-bde C: -protectors –get –type RecoveryPassword
There will be only one protector key for the drive. Locate and copy the key ID field, including the curly
braces.
2. Delete the protector:
manage-bde -protectors -delete C: -id [ID you copied]
3. Create a protector:
manage-bde -protectors -add C: -rp
The output of this command is the recovery key.
NOTE: Specify a 48-digit password at the end of this command or a new password is randomly
generated for you. Computer generated passwords are more random, and therefore harder to break.
4. Repeat steps 1-3 for each of the encrypted data drives.
IMPORTANT: To prevent data loss, save this numerical recovery key in a secure location away from
the solution. This key helps ensure that you can unlock the encrypted volume.
Managing Device Guard
Windows Device Guard is a new feature in Microsoft Windows Server 2016 that locks down a computer
so that it only runs trusted applications. These trusted applications are defined in code integrity policies.
Device Guard is implemented on the Hardware Lifecycle Host of the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure
Stack solution. For more information on Device Guard, refer to the Microsoft documentation at https://
docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/device-security/device-guard/device-guard-deployment-guide.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recognizes that there might be a need to run an application that is blocked by
active Device Guard policy on the HLH. See the table following for information on the recommended
methods to modify Device Guard settings.
44 Solution management
Page 45

Action When to use
Permanently modify
Device Guard policy
Temporarily disable Device
Guard
Use to permanently add specific applications or scripts that you want to
execute to the existing Device Guard policy. See Modifying Device Guard
policy
RECOMENDED: Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends this approach.
Modifying Device Guard policy is faster and maintains the prior Device
Guard restrictions while adding the newly authorized applications. Always
use this alternative if possible.
Use to temporarily disable Device Guard, perform an action, and then reenable Device Guard. See Temporarily disabling Device Guard
IMPORTANT: Hewlett Packard Enterprise does not recommend
disabling Device Guard. However, if you have determined that
modifying the policy is not sufficient, temporarily disabling Device
Guard can be used with care. This alternative disables all
restrictions, leaving the system temporarily vulnerable.
Modifying Device Guard policy
Hewlett Packard Enterprise has developed a PowerShell utility that modifies an existing Device Guard
policy. The script is located in c:\hpe\common\Scripts\deviceguard\Modify-
DeviceGuardPolicy.ps1 and can modify an existing Device Guard Policy in two ways:
• If called with the -ScanPath parameter:
The utility will recursively scan all files in a given path and create policy entries that will be added to
the existing, running, policy.
• If called with the -ExistingPolicy parameter:
The utility will add the provided Device Guard policy XML file to the existing, running, policy. The
existing policy can be a policy that was created on the local computer, or was created on a different
computer and copied over to the target computer. The remotely created policy file must be a valid
Device Guard policy XML file.
Both parameters can be combined into a single call to the utility as shown in the example.
Example:
This example shows syntax that can be executed from the HLH from an elevated PowerShell command
prompt.
To scan all executables that are located in c:\tools and to add a Device Guard policy
myExecutable.xml created on different host:
1. Launch Microsoft PowerShell as an Administrator.
2. Navigate to c:\hpe\common\Scripts\deviceguard.
3. Run the following command:
Modify-DeviceGuardPolicy.ps1 -ScanPath c:\tools -AddPolicyFile c:\policies
\myExecutable.xml
Solution management 45
Page 46

4. Reboot the HLH (required). See Hardware Lifecycle Host power down.
5. Complete the administrative tasks by running the previously blocked application that is located in c:
\tools or is defined in the myExecutable.xml policy file.
Known issues:
At the start of script execution, an error may occur in the PowerShell window relating to the file log path
being empty or invalid. This error is a known issue and can be safely ignored.
Temporarily disabling Device Guard
Hewlett Packard Enterprise has developed a PowerShell utility to simplify the disabling and re-enabling
Device Guard policy restrictions. The script, located in c:\hpe\admin-tools\DeviceGuard
\Toggle-PolicyRestrictions.ps1, can be initiated to disable or enable restriction as shown in the
following example.
IMPORTANT: Disabling Microsoft Windows Device Guard is not recommended except for
administrative actions which require doing so. If disabled, Hewlett Packard Enterprise highly
recommends that Microsoft Windows Device Guard is re-enabled immediately after you have
completed the administrative tasks.
Example:
1. To disable Device Guard, launch Microsoft PowerShell as an Administrator.
2. Navigate to C:\hpe\admin-tools\DeviceGuard.
3. Run the following command:
Toggle-PolicyRestrictions -Action Disable
4. Reboot the HLH (required). See
5. Complete administrative tasks by running the previously blocked application.
6. To re-enable Device Guard, launch Microsoft PowerShell as an Administrator.
7. Navigate to C:\hpe\admin-tools\DeviceGuard.
8. Run the following command:
Toggle-PolicyRestrictions -Action Enable
9. Reboot the HLH (required). See Hardware Lifecycle Host power down.
10. Verify that previously blocked application is once again blocked.
System expansion
This section provides instructions for customers upgrading an existing HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure
Stack system.
Hardware Lifecycle Host power down.
Preparing for Add Node
Each new scale unit Azure Stack node must be homogenous in CPU type, memory, disk size, and disk
numbers that are already present in the existing nodes.
46 Solution management
Page 47

Obtain the hardware configuration by accessing the HPE iLO Web UI of one of the existing Azure Stack
compute nodes. Use the following procedures to locate and note the information necessary to duplicate
the configuration of additional Azure Stack node.
Find the node product information
1. Navigate to Information > Overview.
2. Note the Product Name (ProLiant model) and Product ID (SKU) information.
Find the processor information
1. Navigate to Information > System Information.
2. In the Processor tab, click the Processor Name field and note the processor model number.
Verify that all processors in the node are the same model.
Find the storage information
Storage is the HDD or SSD drives in the node.
Solution management 47
Page 48

1. Navigate to Information > System Information.
2. In the Storage tab, select the Physical View.
3. By scrolling down the page, count the number of HDD drives in Media Type and note the size of each
drive in Capacity.
Total HDD capacity = Number of HDD drives multiplied by the size of one drive.
4. By scrolling down the page, count the number of SSD drives in Media Type and note the size of each
drive in Capacity.
Total SSD capacity = Number of SSD drives multiplied by the size of one drive.
48 Solution management
Page 49

Find the system memory information
1. Navigate to Information > System Information.
2. In the Memory tab, in the Memory Summary section:
a. Calculate the total system memory by adding the Total Memory of all processors.
3. In the Memory tab, in the Memory Details section:
a. Note the value in the Technology column.
Verify that all DIMMs are identical.
b. Count the total number of DIMMs for all processors in the node.
NOTE: In most cases, the total memory is the only information required to order identical
expansion nodes. However, for Gen9 nodes with 768GB configured memory, the Technology must
be considered as well. If the Technology value is listed as "LRDIMM", then select the "High
Performance" memory option when ordering expansion nodes.
Solution management 49
Page 50

50 Solution management
Page 51

Troubleshooting
This guide provides troubleshooting information using multiple Hewlett Packard Enterprise server
products and software tools that support multiple Hewlett Packard Enterprise server products. Some
information contained in the individual component documentation referenced in this guide may not
specifically apply to the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. To assure that solution-specific
guidance is followed, refer first to the instructions in this guide before consulting other referenced
materials.
Components and items not included in original solution
One of the first steps in troubleshooting is to assure that the integrity of the solution has not been
compromised by adding unsupported components or applying unsupported product updates to the
solution.
1. Software for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack products must be kept in compliance with the
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware Compatibility Matrix.
See Azure Stack node software update.
2. Do not connect additional devices to the unused ports of the solution switches.
3. Do not add servers or components to fill blank spaces in the rack.
4. Do not use the HPE OneView instance running on the solution Management node to manage or
monitor items that are not part of the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution.
Troubleshooting preparation
WARNING: To avoid potential issues, always read the warnings and cautionary information in the
product documentation before removing, replacing, reseating, or modifying system components.
1. Review the important safety information.
2. Gather and record symptom information.
3. Run the Get-HPEMASSupportDump system information gathering tool.
4. Gather all error information, such as the full POST error message displayed.
5. If necessary to contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise, download the Active Health System log.
6. Prepare the server for diagnosis.
Important safety information
For important safety, environmental, and regulatory information, see Safety and Compliance
Information for Server, Power, Networking, and Rack Products.
Get-HPEMASSupportDump
Get-HPEMASSupportDump is a troubleshooting tool used to gather a set of information to aid in
diagnosing problems or determining the status of the Microsoft Azure Stack HLH. This information
includes all HLH log files and the solution configuration data. A zip file will be created which can be sent
back to HPE Support and Factory to aid in troubleshooting if necessary. No customer information is
included in the zip file. The output zip file is created in C:\HPE.
Troubleshooting 51
Page 52

This tool can be run at any time and will provide all data available at the time of execution. Therefore, at
different stages of the HLH life cycle, different sets of information will be contained in the zip file. The
individual output zip files will remain in c:/HPE/logs for onsite troubleshooting.
Optionally, an HPE OneView Support Dump can be created and included in the zip file. See the HPE
OneView documentation for details on the contents of the HPE OneView Support Dump.
Examples of the information retrieved
• HLH Registry, including the Uberinstaller entries.
• HLH Logs (C:\hpe and V:\factory) as c-hpe directory and v-factory respectively.
• Directory listing of the FRU drive showing all files and sizes sorted by name.
• Free and Used space for C: and V: drives.
• Unencrypted HPE OneView support dump (for OV support). If not needed, specify the SkipOvSupportDump option.
• Current Windows Firewall and Hyper-V VM ACL rules.
• List of Windows updates installed on the HLH.
Dependencies
These items are required to run Get-HPEMASSupportDump.
• The solution configuration file (all-info.xml) must be available.
• The HPEMAS\UtilityFunctions.psm1 has been installed to the default location:
C:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules
Running Get-HPEMASSupportDump
The tool is initiated with the Get-HPEMASSupportDump CLI command on the HLH and is controlled with
the following parameter options entered with the command. These options can be used together to create
the required output zip file.
-AllInfoPath PATH
Optional full path to the all-info.xml. Default location is C:\cdw\untagged\all-info.xml
-LogFolder PATH
Optional directory path of the location for creating the log files. Default location is c:\HPE\logs.
-SkipOVSupportDump
Do not create the HPE OneView Support Dump as part of the output.
-SupportId FILENAME
Optional name of the zip file. Default name is CUSTOMER.SERIALNUMBER.TIMESTAMP.
Troubleshooting HPE OneView
Basic troubleshooting techniques in HPE OneView
HPE OneView has a variety of troubleshooting tools you can use to resolve issues. By following a
combined approach of examining screens and logs, you can obtain a history of activity and the errors
encountered.
52 Troubleshooting
Page 53

• The Activity screen displays a log of all changes made on the appliance, whether user-initiated or
appliance-initiated. It is similar to an audit log, but with finer detail and it is easier to access from the
UI. The Activity screen also provides a log of health alerts and status notifications.
• Download an audit log to help you or an administrator understand what security relevant actions took
place on the system.
• Create a support dump file to gather logs and other information required for debugging into an
encrypted, compressed file that you can send to your authorized technical support for analysis.
• Review reports for server status. Reports can also provide inventory information and help you see the
types of server models and processors in your data center. They can also show you what firmware
must be updated.
HPE OneView troubleshooting
For detailed information on HPE OneView troubleshooting issues, see Troubleshooting the appliance in
the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide.
HPE OneView web UI or REST API not accessible
Symptom
Attempts to load the HPE OneView web UI, result in a "Page not Found" or similar not accessible error.
Solution 1
Action
Confirm that the Management node is running.
1. Log in to the HLH with RDP. See Accessing Hardware Lifecycle Host with Microsoft RDP.
2. If not successful, proceed to troubleshoot why the HLH is not accessible. See Troubleshooting the
Hardware Lifecycle Host node.
Solution 2
Action
Confirm the HPE OneView virtual machine is running.
1. Log in to the HLH with RDP. See Accessing Hardware Lifecycle Host with Microsoft RDP.
2. Once you are logged into the HLH node, check the status of the HPE OneView VM with Hyper-V
Manager.
a. Confirm that the VM status is "Running".
If it is not running, try to start the VM.
b. Use the Connect action to open the Hyper-V console to HPE OneView and check its status.
Troubleshooting 53
Page 54

HPE OneView only accessible from HLH
Symptom
HPE OneView can only be accessed from the Hardware Lifecycle Host management node, that is: you
can only open HPE OneView web UI from Internet Explorer on the HLH.
Cause
The BMC switch ACLs may have been adjusted from their default settings and are no longer allowing
access to HPE OneView from outside the solution.
Action
1. Compare your current BMC switch configuration to the default values for the ACL lines as shipped
from the factory. The original factory switch configuration is available at v:\factory\cdw
\untagged\<switch vendor>-BMC.*
a. Confirm that your running BMC switch configuration shows rules 970 and 980 in the BMCMgmt_IN
ACL. These rules are required to provide external access to HPE OneView.
b. If your configuration lacks rules 970 and 980, restore them from the original factory switch
configurations as in this example. (10.193.132.243 is IP address for HPE OneView in the example):
!!!
!!! ACL BMCMgmt_IN
!!!
acl number 3006 name BMCMgmt_IN
description "ACL for BMCMgmt_IN vlan id 6 Direction in"
rule 970 permit ip source 10.193.132.243 0.0.0.0 destination any
rule 970 comment "Permit ip ExternalAccessible-1 (10.193.132.243/32) to any"
rule 980 permit ip source any destination 10.193.132.243 0.0.0.0
c. Confirm your running BMC switch configuration shows rules 970 and 980 in the BMCMgmt_OUT
ACL. These rules are required to provide external access to HPE OneView.
d. If your configuration lacks rules 970 and 980, restore them from the original factory switch
configurations as in this example. (10.193.132.243 is IP address for HPE OneView in the example):
!!!
!!! ACL BMCMgmt_OUT
!!!
acl number 3206 name BMCMgmt_OUT
description "ACL for BMCMgmt_OUT vlan id 6 Direction out"
rule 970 permit ip source 10.193.132.243 0.0.0.0 destination any
rule 970 comment "Permit ip ExternalAccessible-1 (10.193.132.243/32) to any"
rule 980 permit ip source any destination 10.193.132.243 0.0.0.0
2. After adjusting the BMC switch configuration, attempt to access HPE OneView web UI from outside
the solution by browsing to https://OneViewIPAddress. See
Accessing HPE OneView.
54 Troubleshooting
Page 55

Attempting to connect to Azure Stack node iLO or console from HPE OneView fails
Symptom
Attempting to open the system console or use links to the iLO address of an HPE ProLiant DL380 Azure
Stack node node from HPE OneView fails.
Cause
If browsing to HPE OneView from outside the solution, this behavior is expected because the physical
switch ACL is blocking access to Azure Stack node node iLO.
Action
Connect to the HPE OneView UI or the HPE iLO webpage for the node you wish to access using Internet
Explorer on the HLH. See Accessing the HPE management portions of the solution.
Troubleshooting ProLiant servers
For detailed information about troubleshooting HPE ProLiant server issues:
• Gen9 servers - see the
• Gen10 servers - see the Troubleshooting Guide for HPE ProLiant Gen10 servers
HPE ProLiant Gen9 Troubleshooting Guide
Troubleshooting solution switches
HPE network switches
For detailed information about troubleshooting the HPE 5900 and 5950 Series ToR and BMC switches
installed as part of the solution, see the HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Troubleshooting Guide and
the HPE FlexFabric 5950 Switch Series Troubleshooting Page.
Cisco network switches
It is the customer's responsibility to be able to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with Cisco network
switches installed in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. Hewlett Packard Enterprise
strongly recommends that customers obtain and maintain a service agreement with Cisco or other vendor
to assist in troubleshooting any issues with these switches.
Arista network switches
It is the customer's responsibility to be able to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with Arista network
switches installed in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. Hewlett Packard Enterprise
strongly recommends that customers obtain and maintain a service agreement with Arista or other vendor
to assist in troubleshooting any issues with these switches.
Attempts to modify the solution switch configurations have resulted in failures
Symptom
Following an attempt to modify the solution TOR or BMC switch configuration has resulted in an error.
Troubleshooting 55
Page 56

Cause
The user has incorrectly modified the switch configuration and premodification backups are not available.
Action
1. Restore the original switch configurations from the factory.
The original factory switch configuration is available at v:\factory\cdw\untagged\<switch
vendor>-BMC.* and v:\factory\cdw\untagged\<switch vendor>-TOR.* respectively.
2. Repeat any valid modifications, such as password changes, that were applied after the original factory
deployment.
Troubleshooting HPE iPDUs
Following is a list of known troubleshooting issues that are applicable for the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft
Azure Stack solution.
Lost iPDU connectivity
For more HPE iPDU troubleshooting issues, see the Troubleshooting chapter in the HPE Intelligent
Power Distribution Unit User Guide.
Lost iPDU connectivity
Symptom
HPE OneView reports lost connectivity to one or more HPE iPDUs following a username or password
rotation on the iPDU.
Cause
HPE OneView is no longer able to access the iPDU using previous credentials because the password has
been changed.
Action
To re-establish the connection to HPE OneView, remove and then add the iPDU again in HPE OneView.
1. Log in to HPE OneView and navigate to the Power Delivery Devices page.
2. Select the iPDU that is reporting a connectivity failure and click Actions > Remove.
3. To remove the iPDU, click Yes, remove.
4. Wait for the iPDU to reset itself to fully reflect its removal and verify that it has been removed in the
master pane.
See Remove a power delivery device.
5. To add the iPDU again, click + Add power delivery device.
6. Select Actions > Add.
7. Enter the requested data and click Add.
You will need to provide a new password. See Add or edit a power delivery device.
8. Verify that the iPDU has been added to the master pane.
56 Troubleshooting
Page 57

Troubleshooting Azure Stack nodes
IMPORTANT: When troubleshooting and repair of the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
compute nodes, first take the instructions from Microsoft into consideration. This step will avoid
interruption of active workloads and let you know when planned maintenance windows must be
used. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-stack/azure-stack-node-actions
Unplanned Azure Stack node shutdown or outage
Symptom
The Azure Stack node administrator portal reports a node is Stopped or some other unexpected state
than Running. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-stack/azure-stack-node-
actions#view-the-status-of-a-scale-unit-and-its-nodes.
Cause
The server might have been powered off intentionally, might have experienced an unexpected power loss,
or might have experienced a component failure.
Action
Investigate if HPE OneView can provide details or alerts related to events occurring on the node.
1. Log in to HPE OneView and check the Server Hardware page for status or alerts for the node in
question.
See Monitoring health with HPE OneView.
2. To differentiate between the server simply being powered off and an unexpected failure or event, use
the information available on the Server Hardware page.
a. If the server is healthy, but off, the HPE iLO event logs may provide insight into what user or
mechanism powered down the server. This information is useful to determine if other administrators
must be consulted before powering on and resuming the node.
b. If the server has experienced an unexpected failure, take the appropriate action to recover, such
as:
• Follow instructions in Troubleshooting server hardware in the HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide
related to addressing your server hardware issues.
• Follow the instructions in Troubleshooting ProLiant servers to further address the issue.
• Contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise support. See Requesting support for HPE Azure Stack
solution products.
3. Once the server has either been repaired or confirmed OK to power back on, use normal procedures
to power on and resume the node. See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-stack/azurestack-node-actions.
Troubleshooting the Hardware Lifecycle Host node
Troubleshooting 57
Page 58

Unable to access Hardware Lifecycle Host
Symptom
Unable to access the HLH through Remote Desktop Protocol as documented in the Accessing
Hardware Lifecycle Host with Microsoft RDP.
Solution 1
Cause
The BMC switch ACLs rules have been changed from the Hewlett Packard Enterprise factory defaults to
no longer allow access to the HLH OS or the HLH iLO IP addresses from outside of the solution.
Action
1. Verify that the HLH is running and is not impacted by an issue preventing Windows Server from being
available.
2. Confirm with the solution administrator or your network security department, that they have not
modified the BMC switch configuration or blocked access to TCP port 3389 for the HLH IP address.
Solution 2
Cause
A physical server component failure or OS issue.
Action
1. Confirm that the HLH server is running by:
• accessing its HLH iLO, or
• physically checking the server, or
• accessing it through the optional KVM console
2. If the HLH appears to be off or Windows Server is not running (or is reporting an error), perform
troubleshooting documented in Troubleshooting ProLiant servers.
Solution 3
Cause
Network access to the HLH may have been lost due to a physical (NIC, cable, switch) issue or a
configuration change.
Action
1. Attempt to determine if only the RDP is not functioning and the HLH server can be reached over the
network with a ping.
If the system is reachable (responds to the ping), but is not accessible with RDP, proceed to step 2 to
investigate the reason for the RDP failure.
2. Attempt to access the HLH iLO for the HLH node by browsing to its secure web address and
specifying the current credentials (maintained by the solution administrator).
58 Troubleshooting
Page 59

https://<iLO address>
• If able to connect, open the Integrated Remote Console to the server and investigate if any network
configuration settings have been modified or failures are being reported.
• If not able to remotely connect to the HPE iLO webpage for the HLH, your organization might have
chosen not to make the HLH iLO available from outside of the solution switches.
In such cases, attempt to access the iLO through the normal procedures for your data center, such
as using the optional KVM and LCD console.
NOTE: Due to firewall restrictions, the Internet cannot be accessed directly from the HLH node.
Unable to run scripts or applications on the Hardware Lifecycle Host
Symptom
Invoking an application or a PowerShell script on the HLH fails with message similar to one of the
following:
• Your organization used Device Guard to block this app.
An error in a system binary was detected.
•
• The system administrator has set policies to prevent this installation.
Cannot invoke method. Method invocation is supported only on core types
•
in this language mode.
Cause
Microsoft Windows Device Guard has blocked the script or application from running on the HLH.
Action
To modify the Device Guard policy and allow the script or application to run on the HLH, follow the steps
outlined in Modifying Device Guard policy.
Resources for troubleshooting
To quickly access troubleshooting information for components used in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft
Azure Stack solution, use the following links.
• Hardware
◦ HPE ProLiant Gen9 servers
– HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 Server User Guide
– HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen9 Server User Guide
– HPE ProLiant Gen9 Troubleshooting Guide, Vol 1, Troubleshooting
– HPE ProLiant Gen9 Troubleshooting Guide, Vol 2, Error Messages
◦ HPE ProLiant Gen10 servers
Troubleshooting 59
Page 60

– HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen10 Server User Guide
– HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 Server User Guide
– Troubleshooting Guide for HPE ProLiant Gen10 servers
– Error Message Guide for HPE ProLiant Gen10 Servers and HPE Synergy
◦ HPE 5900 Switch Series Troubleshooting Guide
◦ HPE FlexFabric 5950 Switch Series Troubleshooting Page
◦ HPE iPDU User Guide
• Software
◦ HPE OneView 3.0 User Guide
◦ HPE OneView 4.0 User Guide
◦ HPE OneView 4.0 Help
◦ HPE iLO 4 User Guide
◦ HPE iLO 5 User Guide
◦ Microsoft Azure Stack User Guide
◦ Microsoft Azure Stack Operator Guide
• General information sources
◦ HPE Support Center
◦ HPE Information Library
◦ HPE UEFI System Utilities documentation
60 Troubleshooting
Page 61

Updating HPE OneView with the UI
HPE OneView is normally updated through automatic processes when updating the solution. See Update
HPE OneView during normal solution updates. However, if HPE OneView must be manually updated
off-cycle, follow these steps.
Prerequisites
• Minimum required privileges: Infrastructure administrator
• Ensure that no other users are logged in to the appliance and that no one logs in during the update.
• Create and download a backup file before updating the appliance.
• Create a VM snapshot of your system before you install an update file
Procedure
1. Log in to the HPE OneView appliance.
2. At the top of the screen, next to OneView, click the drop-down arrow to access the main menu and
select Settings.
3. On the Settings screen, click Appliance and select Actions > Update Appliance.
4. On the Update Appliance screen, choose Select an update image and click Upload and Install.
NOTE: The upload process contains two steps:
a. Uploading
b. Validating
5. Update the appliance.
a. Browse to select the uploaded image.
b. Select End User License Agreement and Written Offer. Review the terms and accept them by
clicking the check box.
c. Click Update.
6. View the status and progress of the update with the progress bar.
7. After the update completes, the appliance resumes activity. View any associated messages by
accessing the Activity screen, locating the Update appliance task, and clicking it.
8. Verify a successful update by examining the Firmware version and Date.
Updating HPE OneView with the UI 61
Page 62

Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support
If HPE OneView Remote Support must be reconfigured for any reason, follow these procedures to
manually configure and enable HPE OneView RS.
NOTE: Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support is not required if:
• The solution is disconnected from the Internet and has no ability to reach the support center.
• HPE OneView RS is already configured and is running normally.
For more information about HPE OneView Remote Support, see http://h17007.www1.hpe.com/docs/
enterprise/servers/oneview4.0/cic/en/index.html#c_settings-remote-support.html
Configuring HPE OneView RS workflow
To configure HPE OneView Remote Support, follow these steps:
1. Configuring HPE OneView appliance host name and DNS
2. Enabling HPE OneView Remote Support
3. Enabling remote support on server hardware
4. Validate OVRS functionality
Configuring HPE OneView appliance host name and DNS
If not configured previously, follow these steps to configure the HPE OneView network settings.
Procedure
1. Log into HPE OneView as administrator.
2. Go to Settings > Networking.
3. Select Edit.
62 Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support
Page 63

4. Complete the appliance hostname with the FQDN copied from the PRIVATE-DOMAIN-FQDN tag in
the C:\CDW\untagged\all-info.xml file on the HLH.
5. Enter the DNS IP copied from the MAS-UPSTREAM-DNS-SERVER tag in the C:\CDW\untagged
\all-info.xml file on the HLH in the preferred DNS server field.
6. Click OK.
The new network settings will be applied and user will see the following message:
NOTE: If there are any error/warning messages on network configuration, follow the resolution
provided in the respective messages.
Enabling HPE OneView Remote Support
Procedure
1. Log into HPE OneView as administrator.
2. Go to Settings > Remote Support.
Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support 63
Page 64

3. Select Edit.
4. Select the Enable Remote Support check box.
The Remote Support configuration page expands.
5. Select the Configure existing and automatically set up devices as they are discovered for
monitoring and service events check box.
IMPORTANT: Do NOT select the I consent to having HPE or my HPE authorized reseller
contact me to discuss optimizing my IT environment check box.
6. Complete the Registration Information, Initial Contact, and Data Center Address forms.
7. Select Register with Hewlett Packard Enterprise and click OK to complete the registration process.
64 Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support
Page 65

Enabling remote support on server hardware
Procedure
1. Log into HPE OneView as administrator.
2. Go to Settings > Server Hardware.
3. Select a server.
4. From the Actions menu, select the Edit Remote Support settings option.
5. From the General section, assure the Enable remote support check box is selected.
6. In the Warranty and Contract section, select the Manage contract type and support identifier
check box.
7. Select the Support agreement contract type and provide the 12-digit Support identifier of the server.
8. Click OK.
9. Repeat steps 2 - 8 for each server listed on the HPE OneView Server Hardware page.
Validate OVRS functionality
When finished configuring HPE OneView Remote Support, verify that it is functioning as intended with
these steps.
NOTE: For known issues on OVRS, see the HPE OneView 4.00.11 Update Release Notes at https://
support.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=a00054040en_us.
Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support 65
Page 66

Procedure
1. Log in to iLO of each node, navigate to the Remote Support > Registration page.
Check the registration status of the node with HPE OneView.
2. Navigate to the Remote Support > Service Events page and click Send Test Event.
Verify reception of the Test Event on the HPE OneView Reports page.
66 Configuring HPE OneView Remote Support
Page 67

Support and other resources
Websites for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution
Website Link
HPE Information Library www.hpe.com/info/enterprise/docs
HPE Support Center www.hpe.com/support/hpesc
Contact HPE Worldwide www.hpe.com/assistance
HPE Subscription Service/
Support Alerts
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft
Azure Stack documentation
HPE Software Depot www.hpe.com/support/softwaredepot
HPE OneView documentation www.hpe.com/info/oneview/docs
HPE iLO 5 documentation www.hpe.com/info/ilo-docs
HPE switch documentation www.hpe.com/info/networking-lookup
Cisco switch documentation https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/switches/nexus-3000-
Arista switch documentation https://www.arista.com/en/products
PDU documentation HPE G2 Series Metered and Switched Power Distribution Unit
www.hpe.com/support/e-updates
www.hpe.com/info/PL-MSFT-Azure-docs
series-switches/products-installation-and-configuration-guideslist.html
User Guide
Accessing Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support
• For live assistance, go to the Contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise Worldwide website.
• To access documentation and support services, go to the Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support
Center website.
Information to collect
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product name, model or version, and serial number
• Operating system name and version
• Firmware version
• Error messages
• Product-specific reports and logs
Support and other resources 67
Page 68

• Add-on products or components
• Third-party products or components
Accessing updates
• Some software products provide a mechanism for accessing software updates through the product
interface. Review your product documentation to identify the recommended software update method.
• To download product updates, go to either of the following:
◦ Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support Center Get connected with updates page
◦ Software Depot website
• To view and update your entitlements, and to link your contracts and warranties with your profile, go to
the Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support Center More Information on Access to Support
Materials page.
IMPORTANT: Access to some updates might require product entitlement when accessed
through the Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support Center. You must have an HPE Passport set up
with relevant entitlements.
Customer Self Repair
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends working with your HPE Pointnext representatives to maintain
your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack products, including proactive system monitoring, hardware
replacements, and system upgrades. For your convenience, you may choose to perform certain basic
maintenance activities without HPE Pointnext oversight. These maintenance activities include the
replacement of:
• System fans
• Power supplies
• Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
• Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
• Cisco ToR and BMC switches
Maintenance, troubleshooting, or replacement as appropriate based on your Cisco support agreement.
Systems with Gen9 servers
Refer to the HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen9 Server Maintenance and Service Guide for replacement
instructions on system nodes, and the HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 Server Maintenance and Service
Guide for replacement instructions on the management nodes. If at any time during the replacement you
have questions or issues, HPE Pointnext support is available to assist with completion of the
maintenance activity. Contact information can be found at the end of this manual.
Software for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack products must be kept in compliance with the
versions specified in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 Software and Firmware
Compatibility Matrix. The compatibility matrix represents combinations of firmware and software
versions that are qualified for use in this solution. Updating individual firmware or software components
may introduce incompatibilities or unknown behaviors to the solution. Not all component software
releases are necessary for the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. When the solution
requires component software updates, HPE will release a qualified solution update. As a best practice,
68 Support and other resources
Page 69

work with your HPE Pointnext representatives to keep your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
solution updated with the latest HPE software release.
Systems with Gen10 servers
Refer to the HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 Server Maintenance and Service Guide for replacement
instructions on compute nodes, and the HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen9 Server Maintenance and Service
Guide for replacement instructions on the management nodes. If at any time during the replacement you
have questions or issues, HPE Pointnext support is available to assist with completion of the
maintenance activity. Contact information can be found at the end of this manual.
Software for HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack products must be kept in compliance with the
versions specified in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and Firmware
Compatibility Matrix. The compatibility matrix represents combinations of firmware and software
versions that are qualified for use in this solution. Updating individual firmware or software components
may introduce incompatibilities or unknown behaviors to the solution. Not all component software
releases are necessary for the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. When the solution
requires component software updates, HPE will release a qualified solution update. As a best practice,
work with your HPE Pointnext representatives to keep your HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
solution updated with the latest HPE software release.
Requesting support for HPE Azure Stack solution products
HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack customers can contact HPE for support by Electronic Case
Logging through the Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support Center or by phone. Hewlett Packard
Enterprise recommends using the Electronic Case Logging process.
Before engaging HPE support, ensure that you have the following information available:
1. Passport account
2. Product name (HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack)
3. Product serial number
4. Support Agreement ID (SAID)
5. Support Account Reference (SAR)
6. Detailed description of your issue
7. Description of the severity of your issue (how it impacts your business).
8. Error information displayed.
9. Get-HPEMASSupportDump output file, if available.
To submit a new support case, see Requesting support electronically through the HPE Support
Center on page 69.
To contact HPE by phone, see Requesting support by phone on page 70.
NOTE: The level of support is based on your support service level and your location.
Requesting support electronically through the HPE Support Center
Prerequisites
To request HPE support through the HPE Support Center, be sure you have:
Support and other resources 69
Page 70

• An active HPE Passport account
• An active support contract and the contract Service Agreement ID (SAID)
• Your Support Case Manager (SCM) PIN, if used.
Procedure
1. Sign in to the My HPE Support Center with your HPE Passport credentials.
2. Under More support options column, select Submit or manage support cases.
The Support Case Manager screen is displayed.
3. Under Submit a case, enter your SAID and then click the Submit case button.
The Support Case Manager is displayed.
4. In the Action column, click Submit a case in the solution row.
The Case details page is displayed.
5. Enter detailed information about your request and then click Submit.
The Contact & equipment location information screen is displayed.
6. Verify, change, or enter the information in the Contact & equipment location information screen and
then click Submit.
NOTE: The PIN in the Support Case Manager PIN field, is the default PIN set in your SCM Settings.
If necessary, edit the PIN field to contain the correct Support Case Manager PIN. For a list of PINs,
see Support Case Manager PINs.
Requesting support by phone
The phone number and actions to contact HPE support are different depending on your geographic
location. The support phone number is provided in your welcome letter.
Prerequisites
Procedure
1. United States
a. In the USA you call the number provided in your support welcome package.
b. Once connected to the automated response system, select option 1 for “Hardware”.
c. Select option 3 for “Converged Systems and all other”.
NOTE: To ensure that you are correctly directed to the support team for your particular product, have
the following information ready to provide to the Customer Support Center.
• Product name: HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
• Support Agreement ID (SAID) HPE support
2. Outside of the United States
70 Support and other resources
Page 71

In other regions, you may speak directly to an HPE engineer who routes your call.
NOTE: To ensure that you are correctly directed to the support team for your particular product, have
the following information to provide to the Customer Support Center.
• Product name: HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
• Support Agreement ID (SAID) HPE support
IMPORTANT: Be sure that you identify your product as an HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure
Stack. Provide your Solution SAID to be routed to the correct support team. Indicating that you
have any other problem (a blade, or a 3PAR storage) may result in a misrouted call.
Remote support
Remote support is available with supported devices as part of your warranty or contractual support
agreement. It provides intelligent event diagnosis and automatic, secure submission of hardware event
notifications to Hewlett Packard Enterprise. These event notifications will initiate a fast and accurate
resolution based on your product service level. Hewlett Packard Enterprise strongly recommends that you
register your device for remote support.
For more information and device support details, see the HPE OneView website.
Support process with HPE OneView Remote Support
Requesting support for HPE OneView Remote Support issues
HPE recommends that you consult the HPE OneView RS documentation to resolve issues. However, if
you need further support for HPE OneView RS, help is available through HPE local Response Centers.
For contact details, go to:
http://www.hpe.com/services/getconnected
Contacting the HPE Support Center
If you have an HPE support agreement, you can submit a new Support Case request for problems that
are associated with devices monitored by HPE OneView Remote Support. See Submitting a support
case for an HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack.
For detailed information about contacting the HPE Support Center, see the HPE Support Center.
Support process when HPE OneView Remote Support has detected an event
HPE OneView Remote Support permits automatic notification to HPE of an "event" in one of the system
components that is monitored by HPE OneView RS. To enable this feature, the monitored devices must
be registered through HPE Insight Online. For information about enabling this feature, see the HPE
Insight Online User Guide.
When an event is automatically reported by HPE OneView Remote Support, an HPE or HPE Authorized
Channel Partner support agent will respond.
Support for products not branded Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Hewlett Packard Enterprise provides warranty and service support only for Hewlett Packard Enterprise
products. Customers are responsible for providing service support for products from other manufactures.
These products are required to have been tested and certified by Hewlett Packard Enterprise as operable
and compatible in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution. Currently these products include:
Support and other resources 71
Page 72

• PDUs
• ToR and BMC switches
For all products not branded Hewlett Packard Enterprise, customers are responsible for:
• Procuring the devices.
• Installing the recommended device firmware:
◦ PDUs must use the firmware recommended by the original device manufacturer.
◦ ToR and BMC switches must be installed with the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack solution
supported firmware versions. See the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen9 Software
and Firmware Support Matrix or HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack Gen10 Software and
Firmware Compatibility Matrix for firmware versions for supported switches.
NOTE: The standard solution deployment service will load the solution-specific configuration
settings for switches at the customer site. The customer is responsible for obtaining and installing
the firmware.
• Providing a service contract.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends a service agreement with a similar level of support as the
rest of the solution and with the ability to download firmware upgrades.
• Configuring and maintaining remote security access to these devices (if applicable), such as
passwords and certificates.
• Contacting the device manufacturer or service provider if there are hardware or firmware issues with
products not branded Hewlett Packard Enterprise.
• If a replacement component must be configured to work in the HPE ProLiant for Microsoft Azure Stack
solution, the HPE Pointnext support will advise the customer of the supported configuration settings
that have been certified to work with the solution. The customer is responsible for loading the
configuration settings to the replaced component.
Warranty information
To view the warranty for your product or to view the Safety and Compliance Information for Server,
Storage, Power, Networking, and Rack Products reference document, go to the Enterprise Safety and
Compliance website:
www.hpe.com/support/Safety-Compliance-EnterpriseProducts
Additional warranty information
HPE ProLiant and x86 Servers and Options
www.hpe.com/support/ProLiantServers-Warranties
HPE Enterprise Servers
www.hpe.com/support/EnterpriseServers-Warranties
HPE Storage Products
www.hpe.com/support/Storage-Warranties
HPE Networking Products
www.hpe.com/support/Networking-Warranties
72 Support and other resources
Page 73

Regulatory information
To view the regulatory information for your product, view the Safety and Compliance Information for
Server, Storage, Power, Networking, and Rack Products, available at the Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Support Center:
www.hpe.com/support/Safety-Compliance-EnterpriseProducts
Additional regulatory information
Hewlett Packard Enterprise is committed to providing our customers with information about the chemical
substances in our products as needed to comply with legal requirements such as REACH (Regulation EC
No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and the Council). A chemical information report for this product
can be found at:
www.hpe.com/info/reach
For Hewlett Packard Enterprise product environmental and safety information and compliance data,
including RoHS and REACH, see:
www.hpe.com/info/ecodata
For Hewlett Packard Enterprise environmental information, including company programs, product
recycling, and energy efficiency, see:
www.hpe.com/info/environment
Documentation feedback
Hewlett Packard Enterprise is committed to providing documentation that meets your needs. To help us
improve the documentation, send any errors, suggestions, or comments to Documentation Feedback
(docsfeedback@hpe.com). When submitting your feedback, include the document title, part number,
edition, and publication date located on the front cover of the document. For online help content, include
the product name, product version, help edition, and publication date located on the legal notices page.
Support and other resources 73
Page 74

Acronyms and abbreviations
BMC
Baseboard Management Controller
HLH
Hardware Lifecycle Host
HRP
Health Resource Provider
iLO
HPE integrated Lights Out
iPDU
HPE Intelligent Power Distribution Unit
KVM
Keyboard Video Mouse
MAS
Microsoft Azure Stack
OVRS
HPE OneView Remote Support
PDU
Power Distribution Unit
PEP
Privileged Endpoint
RDP
Remote Desktop Protocol
SAID
Support Agreement ID
SAR
Support Account Reference
SFP+
Enhanced Small Form-factor Pluggable
SSD
Solid-State Drive
SSH
Secure Shell
ToR
Top of Rack
74 Acronyms and abbreviations
Page 75

VM
Virtual Machine
Acronyms and abbreviations 75
 Loading...
Loading...