Page 1
RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
Overview
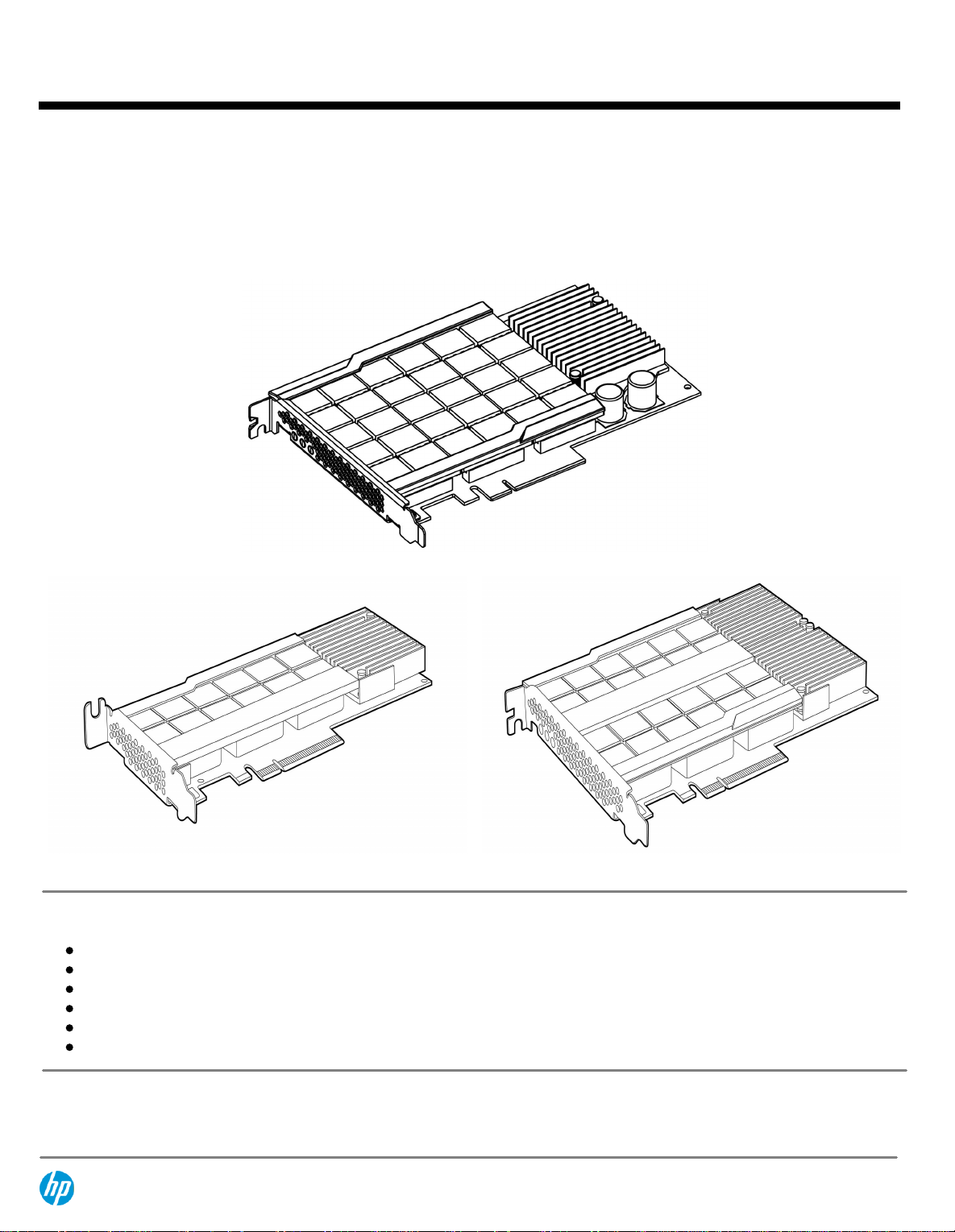
HP IO Accelerator for ProLiant Servers is a PCIe card-based direct-attach solid state storage technology solution for application
performance enhancement. Based on Multi-Level Cell (MLC) and Single Level Cell (SLC) NAND Flash technology, these devices are ideal
for low latency workloads requiring high transaction rates and real-time data access.
ioDrive (Generation2) FH/HL
ioDrive (Generation2) HH/HL
ioDrive Duo (Generation2) FH/HL
What's New
Introducing the Gen2 HP IO Accelerators for ProLiant ML/DL/SL server platforms
As low as 17 microsecond WRITE latency
Performance: Up to 935,000 WRITE IOPS, up to 892,000 READ IOPS, up to 3GB/s Bandwidth
Industry-Leading Capacity: Up to 3TB
Enterprise Endurance: Wear leveling, predictive monitoring and management, and warranty forecasting
Enterprise Reliability: Adaptive flashback technology provides on-card redundancy with no downtime on multichip failures
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 1
Page 2

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Overview
Models
HP I/O Accelerator
Options
Second Generation Accelerators
HP 365GB Multi Level Cell G2 PCIe ioDrive2 for ProLiant Servers
HP 785GB Multi Level Cell G2 PCIe ioDrive2 for ProLiant Servers
HP 1205GB Multi Level Cell G2 PCIe ioDrive2 for ProLiant Servers
HP 2410GB Multi Level Cell G2 PCIe ioDrive2 Duo for ProLiant Servers
HP 3TB G2 FH/HL PCIe ioDrive2 IO Accelerator for ProLiant Servers
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
673642-B21
673644-B21
673646-B21
673648-B21
721458-B21
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 2
Page 3
RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Compatibility
Compatibility
Second Generation
Accelerators Support
ProLiant DL (rack-optimized):
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
HP ProLiant DL160 G6
HP ProLiant DL160 Gen8
HP ProLiant DL180 G6
HP ProLiant DL360 G7
NOTE: Support for 673648-B21 only in x16 slot.
HP ProLiant DL360 G7
NOTE:
Support for 673648-B21 only in x16 slot.
HP ProLiant DL360e Gen8
HP ProLiant DL360p Gen8
NOTE:
Support for 673648-B21 only in x16 slot.
HP ProLiant DL370 G6
HP ProLiant DL380 G7
HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8
HP ProLiant DL385 G7
HP ProLiant DL385p Gen8
HP ProLiant DL560 Gen8
HP ProLiant DL580 G7
HP ProLiant DL585 G6
HP ProLiant DL585 G7
HP ProLiant DL980 G7
ProLiant ML (expansion-optimized):
HP ProLiant ML350 G6
HP ProLiant ML350p Gen8
HP ProLiant ML370 G6
ProLiant SL (Scalable System)
HP ProLiant SL230s Gen8
HP ProLiant SL250s Gen8
HP ProLiant SL4540 Gen8
HP ProLiant SL4545 G7
NOTE:
For the list of supported skus per server, please see each server QuickSpecs.
NOTE:
This is a list of supported servers. Some may be discontinued.
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 3
Page 4

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Standard Features
What is an IO Accelerator?
Single Level Cell and
Multilevel Cell
IO and Read/Write
Performance
Latency
The IO Accelerator is an PCIe card-based, advanced storage device that uses solid state storage technology
directly on the PCI bus, assuring high read and write data rates and accelerated application performance.
The associated application performance improvements will have a positive impact on business results and
the ability to accelerate IO-bound workloads like databases, virtualization and data analytics, resulting in
significant cost and time savings.
NAND technology uses flash memory cells to store data. Single level Cell (SLC) stores one bit per cell, while
Multi-level Cell (MLC) uses two bits per cell. While MLC can store more data within each device, it has lower
endurance characteristics than SLC.
HP PCIe IO Accelerators offer superior IO performance up to 892,000 READ IOPS and 935,000 WRITE IOPS,
and high throughput up to 3.0 GB/s READ and up to 2.5 GB/s WRITE.
HP PCIe IO Accelerators offer very low latency access to data, as low as 17 microseconds to write a 4K
block and as low as 68 microseconds to read a 4K block. In other words, a virtually zero seek time
compared to rotating magnetic media.
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
RAM Requirements
Manageability
PCI IDs
Upgradeability
The amount of free RAM required by the driver depends on the size of the blocks used when writing to the
drive. The smaller the blocks, the more RAM required. Here are the guidelines for each 100GB of storage:
Average
Block Size (bytes)
8,192
4,096 (most common)
2,048
1,024
512
Command Line (CLI) tools for both Linux and Windows to configure, monitor, and upgrade firmware
SNMP Agent and System Management Homepage provided for Linux and Windows.
ioManager GUI for Windows and Linux.
Vendor & Device ID 1AED:1005; Subsystem Vendor & Device ID 103C:324E for Generation1 products. The
Device ID for Generation2 is 2001. In Gen2 the Subsystem Vendor ID has changed to 1590. Each capacity
has its own Subsystem Device ID.
The controller for the HP IO Accelerators can be upgraded in the future with new firmware. Online firmware
update tools are available for all supported operating systems.
System RAM usage (Megabytes) per 100GB of storage for Driver
version 2.x and 3.x
280MB
530MB
1030MB
2,000MB
3,970MB
Wear-leveling
NAND Flash devices use semiconductor technology that has a finite number of data that can be written to
the device, defined as the Maximum Lifetime. Projected lifetime of the NAND storage due to wear-out
varies with type of NAND and amount of writes to the device.
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 4
Page 5

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Standard Features
Maximum usage
NOTE:
supported lifetime and/or the maximum usage limitations. Maximum supported lifetime-the period in
years set to equal the warranty for the device. Maximum usage limit-This is the maximum amount of data
that can be written to the device before write burn-out. Drive writes per day (DWPD) is the maximum
number of 4K host writes to the
entire drive capacity per day over a five year period.
NOTE:
Data Integrity
Using advanced ECC techniques, the HP IO Accelerators can correct up to 11 bits out of every 240 bytes,
with a design target of a 1 in 10 to the 20th Power probability of uncorrectable data and a 1 in 10 to the
30th Power probability of undetected bad data.
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
ioDrive2 (4 SKUs)
365GB 785GB
2 Drive Writes/Day 2 Drive Writes/Day 2 Drive Writes/Day 2 Drive Writes/Day
4 PB written
Subject to maximum usage limitations. Parts and components that have exceeded their maximum
PB written listed is writes to Flash, not host writes.
11 PB written 17 PB written 37 PB written
ioDrive2 Duo (1 SKU)
2410GB
2 Drive Writes/Day
34 PB written
1205GB 3000GB
OS Support
Configurations
Warranty
RHEL 4,5,6 (64-bit support only)
SLES 10, 11 (64-bit support only)
Windows Server x86-64 2003, 2008 (64-bit support only), 2008 R2, 2012
Oracle Enterprise Linux 5 (OEL 5)
CentOS 5, 6
VMware ESX 4.0 Update 1, ESXi 5.0/5.1
Oracle Enterprise Linux 6
Solaris x86 10, 11
VMWare ESXi 4.1
NOTE:
The HP IO Accelerators are currently not supported as boot devices.
Mixing of capacities is allowed, OS RAID
3/0/0 warranty; Customer Self Repair (CSR) Subject to maximum usage limitations (Please see note under
Additional Services Information).
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 5
Page 6

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Service and Support
Service and Support
HP Technology Services
HP Technology Services offers you technical consultants and support expertise to solve your most
complex infrastructure problems. We help keep your business running, boost availability, and avoid
downtime.
Protect your business beyond warranty with HP Care Pack Services
When you buy HP Options, it's also a good time to think about what level of service you may need. HP Care
Pack services provide total technical support and expertise with committed response choices designed to
meet your specific IT and business need.
HP Foundation Care services deliver scalable reactive support-packages for HP industry-standard servers
and software. You can choose the type and level of service that is most suitable for your business needs.
New to this portfolio is HP Collaborative Support. If you are running business critical environments, HP
offers Proactive Care or Critical Advantage. These services help you deliver high levels of application
availability through a single point of contact, proactive service management and advanced technical
response.
Here is the support service recommendation from the Foundation Care and Proactive Care portfolio. For
customized support service solution, HP can work with you to tailor a service solution for your unique
support requirements using broader services portfolio of Foundation Care and Proactive Care.
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
Recommended Services
Recommended HP Care Pack Services for optimal satisfaction with your HP product
3-Year HP 24x7 4 hour Response, Proactive Care
Helps optimize your systems and delivers high levels of application availability through proactive service
management and advanced technical response. You will work with a single point of contact, aTechnical
Manager who will own your logged call and issue from end to end until resolved, accessing the resources
that you need to resolve all issues and help minimize downtime.
OR
3-Year HP 24x7 4 hour Response, HP Collaborative Support
Provides problem resolution support across the stack of HW, firmware, and HP and 3rd party SW. In case
the issue is with 3rd party SW, HP does known issue resolution. If HP cannot solve the issue, it will contact
the third-party vendor and create a problem incident on your behalf
http://h20195.www2.p.com/V2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA3-8232ENW.pdf
HP Installation of ProLiant Add On Options Service
This easy-to-buy, easy-to-use HP Care Pack service helps ensure that your new HP hardware or software is
installed smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal disruption of your IT and business operations
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 6
Page 7

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Service and Support
Related Services
Related HP Care Pack Services to enhance your HP product experience
3-Year HP 24x7 4 hour Response, Proactive Care
Helps optimize your systems and delivers high levels of application availability through proactive service
management and advanced technical response. A Technical Account Manager will be assigned to you and
work all problems from end to end until resolved, plus work with you to help minimize downtime and
mitigate risk.
OR
3-Year HP 24x7 4 hour Response, Hardware Support Onsite Service
Provides you with rapid remote support and if required an HP technical representative will be on site 24X7
any day of the year to begin hardware maintenance service within 4 hours of the service request being
logged.
http://h20195.www2.hp.com/V2/GetPDF.aspx/5982-6547EEE.pdf
3-Year HP 6-hour Onsite Call-to-Repair, HP Collaborative Support
Offers customers a single point of contact for server problem diagnosis, hardware problem resolution to
return the hardware in operating condition within 6 hours of the initial service request to the HP Global
Solution Center, and basic software problem diagnosis, fault isolation, and resolution if available to HP.
http://h20195.www2.hp.com/V2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA3-8232ENW.pdf
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
Insight Remote Support
HP Support Center
HP Proactive Select Service
Provides a flexible way to purchase HP best-in-class consultancy and technical services. You can buy
Proactive Select Service Credits when you purchase your hardware and then use the credits over the next
12 months.
http://h20195.www2.hp.com/V2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA2-3842ENN.pdf
Provides 24 X 7 remote monitoring, proactive notifications, and problem resolution. Learn more
http://www.hp.com/go/insightremotesupport
Personalized online support portal with access to information, tools and experts to support HP business
products. Submit support cases online, chat with HP experts, access support resources or collaborate with
peers. Learn more
HP's Support Center Mobile App* allows you to resolve issues yourself or quickly connect to an agent for
live support. Now, you can get access to personalized IT support anywhere, anytime.
HP Insight Remote Support and HP Support Center are available at no additional cost with a HP warranty,
HP Care Pack or HP contractual support agreement.
*HP' Support Center Mobile App is subject to local availability
http://www.hp.com/go/hpsc
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 7
Page 8

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Service and Support
Parts and materials
Warranty / Service
Coverage
HP will provide HP-supported replacement parts and materials necessary to maintain the covered
hardware product in operating condition, including parts and materials for available and recommended
engineering improvements. Supplies and consumable parts will not be provided as part of this service;
standard warranty terms and conditions apply. Parts and components that have exceeded their maximum
supported lifetime and/or the maximum usage limitations as set forth in the manufacturer's operating
manual or the technical product data sheet will not be provided, repaired or replaced as part of this service.
For ProLiant servers and storage systems, this service covers HP-branded hardware options qualified for
the server, purchased at the same time or afterward, internal to the enclosure, as well as external
monitors up to 22" and tower UPS products; these items will be covered at the same service level and for
the same coverage period as the server unless the maximum supported lifetime and/or the maximum
usage limitation has been exceeded. Coverage of the UPS battery is not included; standard warranty terms
and conditions apply.
The defective media retention service feature option applies only to Disk or eligible SSD/Flash Drives
replaced by HP due to malfunction. It does not apply to any exchange of Disk or SSD/Flash Drives that have
not failed. SSD/Flash Drives that are specified by HP as consumable parts and/or that have exceeded
maximum supported lifetime and/or the maximum usage limit as set forth in the manufacturer's operating
manual or the technical data sheet are not eligible for the defective media retention service feature option.
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
For more information
Subject to:
drive. After this period no further service coverage will be available for the drive. Maximum usage limit:
This is the maximum amount of data that can be written to the drive. Drives that have reached this limit will
not be eligible for services coverage
To learn more on services for HP ESSN Options, please contact your HP sales representative or HP
Authorized Channel Partner. Or visit:
www.hp.com/services/bladesystem
Maximum supported lifetime: This is a period in years set to equal the warranty for the specific
http://www.hp.com/services/proliant
or
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 8
Page 9

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Technical Specifications
HP 3TB G2 FH/HL PCIe
ioDrive2 IO Accelerator
for ProLiant Servers
721458-B21
HP 2410GB Multi Level
Cell G2 PCIe Solid State
Drive IO Accelerator
673648-B21
Usable Capacity
Technology
Max Sequential
Throughput
Average Access Latency
(4KiB,Q1)
IOPS (4KiB,Q16)
Form factor
Bus Interface
Power
Operating Temperature
Supported Driver Version
Usable Capacity
Technology
Max Sequential
Throughput
Average Access Latency
(4KiB,Q2)
IOPS (4KiB,Q16)
Form factor
Bus Interface
Power
Operating Temperature
Supported Driver Version
Auxillary Power
(for ioDrive2 Duo only)
(Nominal)
(Nominal)
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
3000GB
NAND Flash, MLC
Reads 1.4 GiB/s, Writes 1 GiB/s
Reads 495 microseconds, Writes 35 microseconds
Reads 98,000 IOPS, Writes 72,900 IOPS
Full Height/Half length-Low profile PCI Express x 8 slot (spec 2.0)
PCI Express x 4
PCI Express x 4 (power spec 2.0)
0-55°C (Operational)/-40-70°C (non-operational)
3.2.3 and higher
2410GB
NAND Flash, MLC
Reads 2.8 GiB/s, Writes 1.8 GiB/s
Reads 110 microseconds, Writes 30 microseconds
Reads 112,000 IOPS, Writes 88,700 IOPS
Full Height/Half length PCI Express x 8 slot (spec 2.0)
PCI Express 2.0 x 8
PCI Express 2.0 x 8
0-55°C (Operational)/-40-70°C (non-operational)
3.x and higher
NOTE:
This SKU may require auxiliary power to achieve maximum
performance. Included in the box is a power cable kit that will plug into the
Duo and into a GPU power cable kit for the server (which is not included with
the Duo). Please refer to the Quickspec of the applicable server to determine
which GPU power cable kit from HP is required.
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 9
Page 10

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
Technical Specifications
HP 1205GB Multi Level
Cell G2 PCIe Solid State
Drive IO Accelerator
673646-B21
HP 785GB Multi Level Cell
G2 PCIe Solid State Drive
IO Accelerator
673644-B21
Usable Capacity
Technology
Max Sequential
Throughput
Average Access Latency
(4KiB,Q1)
IOPS (4KiB,Q16)
Form factor
Bus Interface
Power
Operating Temperature
Supported Driver Version
Usable Capacity
Technology
Max Sequential
Throughput
Average Access Latency
(4KiB,Q1)
IOPS (4KiB,Q16)
Form factor
Bus Interface
Power
Operating Temperature
Supported Driver Version
(Nominal)
(Nominal)
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
1205GB
NAND Flash, MLC
Reads 1.4 GiB/s, Writes 1 GiB/s
Reads 410 microseconds, Writes 35 microseconds
Reads 96,000 IOPS, Writes 49,000 IOPS
Half Height/Half length-Low profile PCI Express x 8 slot (spec 2.0)
PCI Express x 4
PCI Express x 4 (power spec 2.0)
0-55°C (Operational)/-40-70°C (non-operational)
3.x and higher
785GB
NAND Flash, MLC
Reads 1.3 GiB/s, Writes 945 MiB/s
Reads 245 microseconds, Writes 35 microseconds
Reads 93,000 IOPS, Writes 42,000 IOPS
Half Height/Half length-Low profile PCI Express x 8 slot (spec 2.0)
PCI Express x 4
PCI Express x 4 (power spec 2.0)
0-55°C (Operational)/-40-70°C (non-operational)
3.x and higher
HP 365GB Multi Level Cell
G2 PCIe Solid State Drive
IO Accelerator
673642-B21
Usable Capacity
Technology
Max Sequential
Throughput
Average Access Latency
(4KiB,Q1)
IOPS (4KiB,Q16)
Form factor
Bus Interface
Power
(Nominal)
Operating Temperature
Supported Driver Version
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
365GB
NAND Flash, MLC
Reads 860 MiB/s, Writes 560 MiB/s
Reads 135 microseconds, Writes 35 microseconds
Reads 85,000 IOPS, Writes 26,000 IOPS
Half Height/Half length-Low profile PCI Express x 8 slot (spec 2.0)
PCI Express x 4
PCI Express x 4 (power spec 2.0)
0-55°C (Operational)/-40-70°C (non-operational)
3.x and higher
Page 10
Page 11

RETIRED: Retired products sold prior to the November 1, 2015 separation of Hewlett-Packard Company into Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company and HP Inc. may
have older product names and model numbers that differ from current models.
QuickSpecs
HP PCIe IO Accelerators for ProLiant Servers
Technical Specifications
Environment-friendly
Products and Approach
© Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Microsoft and Windows NT are US registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and
services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial
errors or omissions contained herein.
End-of-life Management
and Recycling
Hewlett-Packard offers end-of-life HP product return, trade-in, and recycling
programs in many geographic areas. For trade-in information, please go to:
http://www.hp.com/go/green
http://www.hp.com/go/green
Products returned to HP will be recycled, recovered or disposed of in a
responsible manner. The EU WEEE directive (2002/95/EC) requires
manufacturers to provide treatment information for each product type for use
by treatment facilities. This information (product disassembly instructions) is
posted on the Hewlett Packard web site at:
These instructions may be used by recyclers and other WEEE treatment
facilities as well as HP OEM customers who integrate and re-sell HP
equipment.
. To recycle your product, please go to:
or contact your nearest HP sales office.
http://www.hp.com/go/green
.
For hard drives, 1GB = 1 billion bytes. Actual formatted capacity is less.
DA - 13587 Worldwide — Version 27 — March 31, 2014
Page 11
 Loading...
Loading...