Page 1

HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide
Part number: T5214-96076
Seventh edition: August 2009
Page 2
Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2007, 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211
and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items
are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgments
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows XP are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Java is a US trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Hitachi and Universal Replicator are registered trademarks of Hitachi, Ltd.
ShadowImage and TrueCopy are registered trademarks of Hitachi, Ltd. and Hitachi Data Systems Corporation.
Export Requirements
You may not export or re-export this document or any copy or adaptation in violation of export laws or regulations.
Without limiting the foregoing, this document may not be exported, re-exported, transferred or downloaded to or within (or to
a national resident of) countries under U.S. economic embargo, including Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan, and Syria. This
list is subject to change.
This document may not be exported, re-exported, transferred, or downloaded to persons or entities listed on the U.S. Department
of Commerce Denied Persons List, Entity List of proliferation concern or on any U.S. Treasury Department Designated Nationals
exclusion list, or to parties directly or indirectly involved in the development or production of nuclear, chemical, biological
weapons, or in missile technology programs as specified in the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (15 CFR 744).
Revision History
DescriptionDateEdition
This edition applies to microcode version 60-04-04-00/00 or later.December 2008Fifth
This edition applies to microcode version 60-05-00-00/00 or later.June 2009Sixth
This edition applies to microcode version 60-05-00-00/00 or later.August 2009Seventh
Page 3

Contents
1 Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Disk/Cache Partition Software ............. 7
Introduction to Disk/Cache Partition .............................................................................................. 7
Benefits of Disk/Cache Partition .................................................................................................... 8
Improves Security ................................................................................................................. 8
Assures Quality of Service ..................................................................................................... 8
Enables Departmental View of Storage ................................................................................... 8
Feature Highlights ....................................................................................................................... 8
2 About Disk/Cache Partition ................................................................. 9
Storage Logical Partition (SLPR) ..................................................................................................... 9
Cache Logical Partition (CLPR) .................................................................................................... 10
3 Preparing for XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations ................................ 13
Storage Administrator and Storage Partition Administrator Privileges ................................................ 13
Possible Interacting and Conflicting Functions ............................................................................... 15
4 Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI ............................................... 17
Logical Partition Window ........................................................................................................... 17
Storage Management Logical Partition Window ........................................................................... 19
Cache Logical Partition Window ................................................................................................. 21
Select CU Dialog Box ................................................................................................................ 23
License Key Partition Definition Window ....................................................................................... 24
5 XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations ................................................... 29
Storage Logical Partition Operations ............................................................................................ 29
Creating a Storage Logical Partition ...................................................................................... 29
Partitioning and Allocating Licensed Capacity to Storage Logical Partitions ................................ 30
Migrating Resources To and From Storage Logical Partitions ..................................................... 30
Deleting Storage Management Logical Partitions .................................................................... 31
Cache Logical Partition Operations ............................................................................................. 31
Creating a Cache Logical Partition ....................................................................................... 32
Migrating Resources To and From Cache Logical Partitions ...................................................... 33
Deleting Cache Logical Partitions .......................................................................................... 34
6 Troubleshooting ............................................................................... 35
General Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................ 35
Displaying an Error Message ..................................................................................................... 35
Troubleshooting Disk/Cache Partition .......................................................................................... 35
Calling HP Technical Support ..................................................................................................... 36
7 Support and Other Resources ............................................................ 37
Related Documentation .............................................................................................................. 37
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 3
Page 4

Conventions for Storage Capacity Values ..................................................................................... 37
HP Technical Support ................................................................................................................ 38
Subscription Service .................................................................................................................. 38
HP Websites ............................................................................................................................ 38
Documentation Feedback ........................................................................................................... 38
A Acronyms and Abbreviations ............................................................. 39
Index ................................................................................................. 41
4
Page 5

Figures
Storage Logical Partition (SLPR) ................................................................................. 101
Cache Logical Partition (CLPR) .................................................................................. 112
Storage Administrator and Storage Partition Administrator Privileges .............................. 153
Manual Migration between SLPRs ............................................................................. 164
Logical Partition Window (Storage System Selected) .................................................... 185
Storage Management Logical Partition Window (SLPR Selected) .................................... 196
Cache Logical Partition Window (CLPR Selected) ........................................................ 217
Select CU Dialog Box .............................................................................................. 248
License Key Partition Definition Window ..................................................................... 259
Product Name List ................................................................................................... 2510
Capacity List .......................................................................................................... 2611
Partition Status List ................................................................................................... 2712
Setting Box (Licensed Capacity Unlimited or Not Relevant) ........................................... 2713
Setting Box (License Capacity Limited) ....................................................................... 2814
Selecting the License Capacity .................................................................................. 3015
Selecting Enable (License Capacity Unlimited) ............................................................ 3016
Selecting the CU ..................................................................................................... 3417
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 5
Page 6

Tables
CLPR Data Capacity and the Recommended Cache Capacity ....................................... 111
Logical Partition Window Details (Storage System Selected) .......................................... 182
Storage Management Logical Partition Window (SLPR Selected) .................................... 193
Cache Logical Partition Window Details (CLPR Selected) .............................................. 214
Select CU Dialog Box Details ................................................................................... 245
Product Name List Details ......................................................................................... 256
Capacity List Details ................................................................................................ 267
Partition Status List Details ........................................................................................ 278
Setting Box Details (Licensed Capacity Unlimited or Not Relevant) ................................. 279
Setting Box Details (License Capacity Limited) ............................................................. 2810
Selecting the CU ..................................................................................................... 3411
General Troubleshooting for XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations .................................. 3512
Acronyms and Abbreviations .................................................................................... 3913
6
Page 7

1 Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Disk/Cache Partition Software
This chapter provides an introduction to XP Disk/Cache Partition Software.
• Introduction to Disk/Cache Partition, page 7
• Benefits of Disk/Cache Partition, page 8
• Feature Highlights, page 8
Unless otherwise specified, the term storage system in this guide refers to the following disk arrays:
• HP StorageWorks XP24000 Disk Array
• HP StorageWorks XP20000 Disk Array
The GUI illustrations in this guide were created using a Windows computer with the Internet Explorer
browser. Actual windows may differ depending on the operating system and browser used. GUI
contents also vary with licensed program products, storage system models, and firmware versions.
Introduction to Disk/Cache Partition
XP Disk/Cache Partition provides logical partitioning of ports, cache, and disk capacity, including
external storage to create independently managed and secure private virtual storage machines that
help maintain quality of service (QoS).
Large data centers typically support a high volume of users, systems, and applications—each with
constantly changing requirements for storage capacity, throughput, priority, security and access, as
well as management and control. Traditionally, isolated storage systems could be dedicated to specific
applications, but only at the cost of flexibility and ease of management. With decentralized access
and control, however, departments can manage their storage systems individually.
HP storage—specifically the XP24000 Disk Array and XP20000 Disk Array (herein after referred to
as storage system) – addresses these issues by enabling consolidation, aggregation, and management
of large sets of diverse, highly dynamic stored data. By virtualizing storage resources into a single
pool, the storage system facilitates flexibility and manageability for IT administrators.
XP Disk/Cache Partition is designed to complement the storage system by allowing IT departments
to isolate, segment, and control storage for specific applications, servers, or users. This tool enables
data center administrators to perform logical partitioning of ports, cache, and disk capacity, including
external storage, on the storage system to create independently managed private virtual storage
machines. These logical partitions act as dedicated storage resources that are independently managed
and reserved for specific applications.
XP Disk/Cache Partition enables administrators to treat logical partitions as if they were separate
storage machines, helping them maintain data security and integrity. The software also allows
administrators to grant decentralized access and control of specific partitions to departmental IT
managers—a feature that can enhance manageability and free data center administrators to focus
on corporate-level projects. By dedicating resources to each partition as needed, administrators also
can maintain high QoS for all users. Resources can be allocated based on business requirements and
dynamically reconfigured in real time to meet changing needs. Customers can use XP Disk/Cache
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 7
Page 8

Partition to create up to 32 private virtual storage machines on the storage system. With the ability
to manage each partition as its own storage system, IT managers can operate storage in an utility
like fashion, negotiating and providing different QoS by application and charging back business
units for storage usage.
Benefits of Disk/Cache Partition
Improves Security
XP Disk/Cache Partition restricts access to data and resources from users and storage administrators
without authorization to that partition. It also restricts access from users and administrators to data
and resources outside their authorized partition.
Assures Quality of Service
XP Disk/Cache Partition dedicates resources (for example, cache, disk) for exclusive use by specific
applications to maintain priority and QoS for business-critical applications. You can secure and/or
restrict access to storage resources to ensure confidentiality for specific applications. You can also
use XP Disk/Cache Partition to adjust data storage resources dynamically to satisfy changing business
requirements.
Enables Departmental View of Storage
A Departmental view of storage delivers accountability and chargeback, facilitates departmental
management and control within partitions, and permits centralized control over departments.
Feature Highlights
XP Disk/Cache Partition logically partitions a virtualized storage pool on the storage system, consisting
of internal and externally attached storage resources (regardless of physical location), into multiple
independently managed storage machines. It allows you to allocate storage resources to specific
applications. You can partition and isolate storage from access by users, applications, and
administrators of other partitions.
XP Disk/Cache Partition reconfigures partitions dynamically, in real time, without disruption of service.
It allows allocation of platform software licenses for use by partition administrators.
Overview of HP StorageWorks XP Disk/Cache Partition Software8
Page 9

2 About Disk/Cache Partition
This chapter provides a detailed description of Storage Logical Partition (SLPR) and Cache Logical
Partition (CLPR).
• Storage Logical Partition (SLPR), page 9
• Cache Logical Partition (CLPR), page 10
The storage systems can connect multiple hosts, and can be shared by multiple users, such as different
departments or even different companies. This can cause conflicts among the various users. For
example, if a particular host issues a lot of I/O requests, the I/O performance of other hosts may
decrease. If the various administrators have different storage policies and procedures, or issue
conflicting commands, that can cause management conflicts.
XP Disk/Cache Partition has two main functions: storage logical partition (SLPR), and Cache Logical
Partition (CLPR). Storage Logical Partition allows you to divide the available storage among various
users, to lessen conflicts over usage. Cache Logical Partition allows you to divide the cache into
multiple virtual cache memories, to reduce cache contention.
Initially, SLPR 0 is the pool of all ports and CLPRs in the storage system. SLPR 0 contains CLPR 0, the
initial pool of all cache and parity groups in the storage system. When another SLPR is created, the
required resources are reassigned from SLPR 0 to the new SLPR. The only users who have access to
SLPR 0 and CLPR 0 are storage administrators.
Storage Logical Partition (SLPR)
A storage system can be shared among several groups that may have different storage administrators.
This can cause problems if those administrators have differing or conflicting storage procedures, or
if two or more administrators attempt to perform operations on the same logical volume, such as LUN
Expansion (LUSE) or Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL). The storage logical partition function can allocate the
storage system resources into two or more virtual storage systems, each of which can be accessed
only by the storage administrator, the storage partition administrator for that storage logical partition,
and the users for that partition. You can create up to 32 storage logical partitions in one storage
system, including the default SLPR 0. There is no maximum or minimum size for an SLPR. See
“Creating a Storage Logical Partition” on page 29 for instructions on creating storage logical partitions.
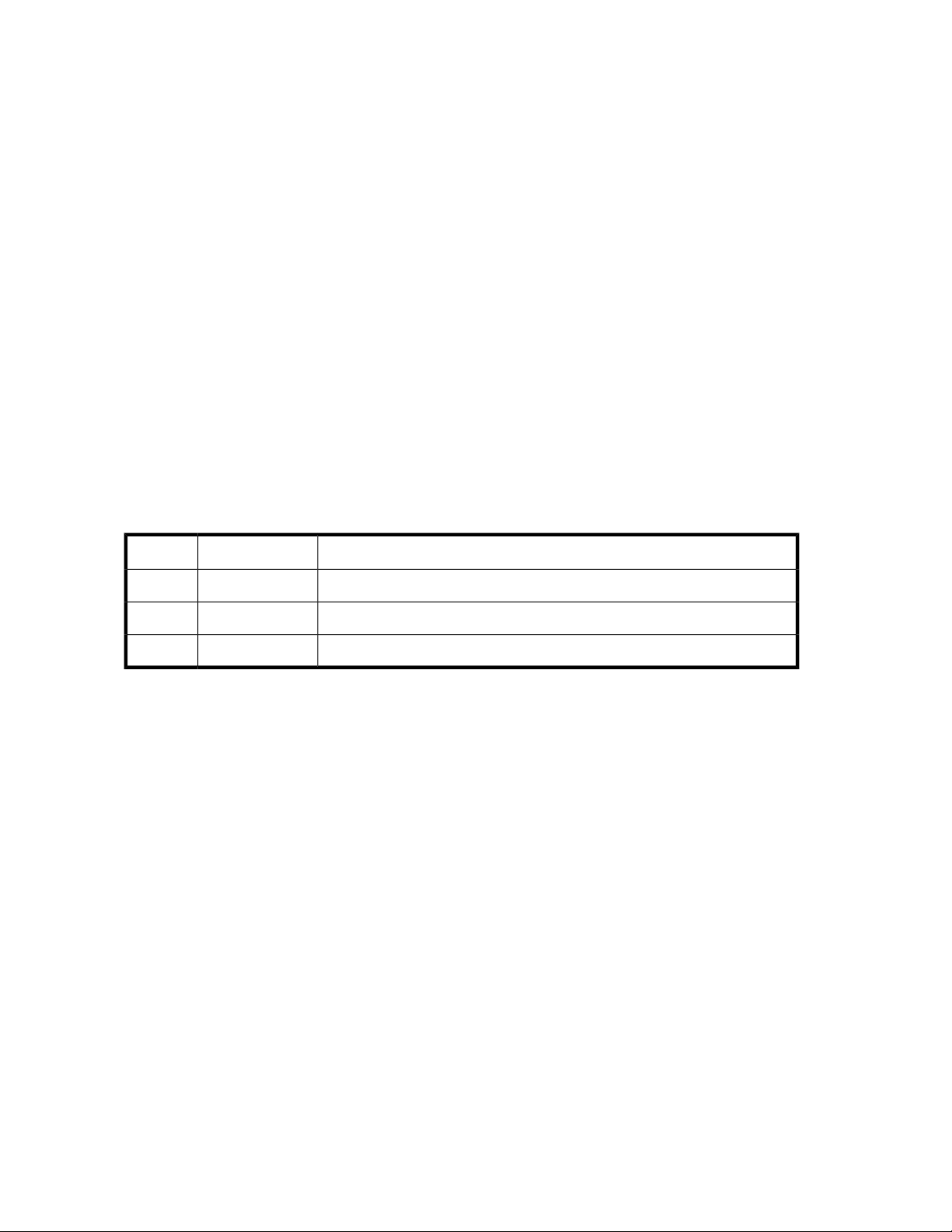
Figure 1 illustrates a storage system that is divided into two virtual partitions, so that the storage
administrator of each storage logical partition can only access that partition.
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 9
Page 10
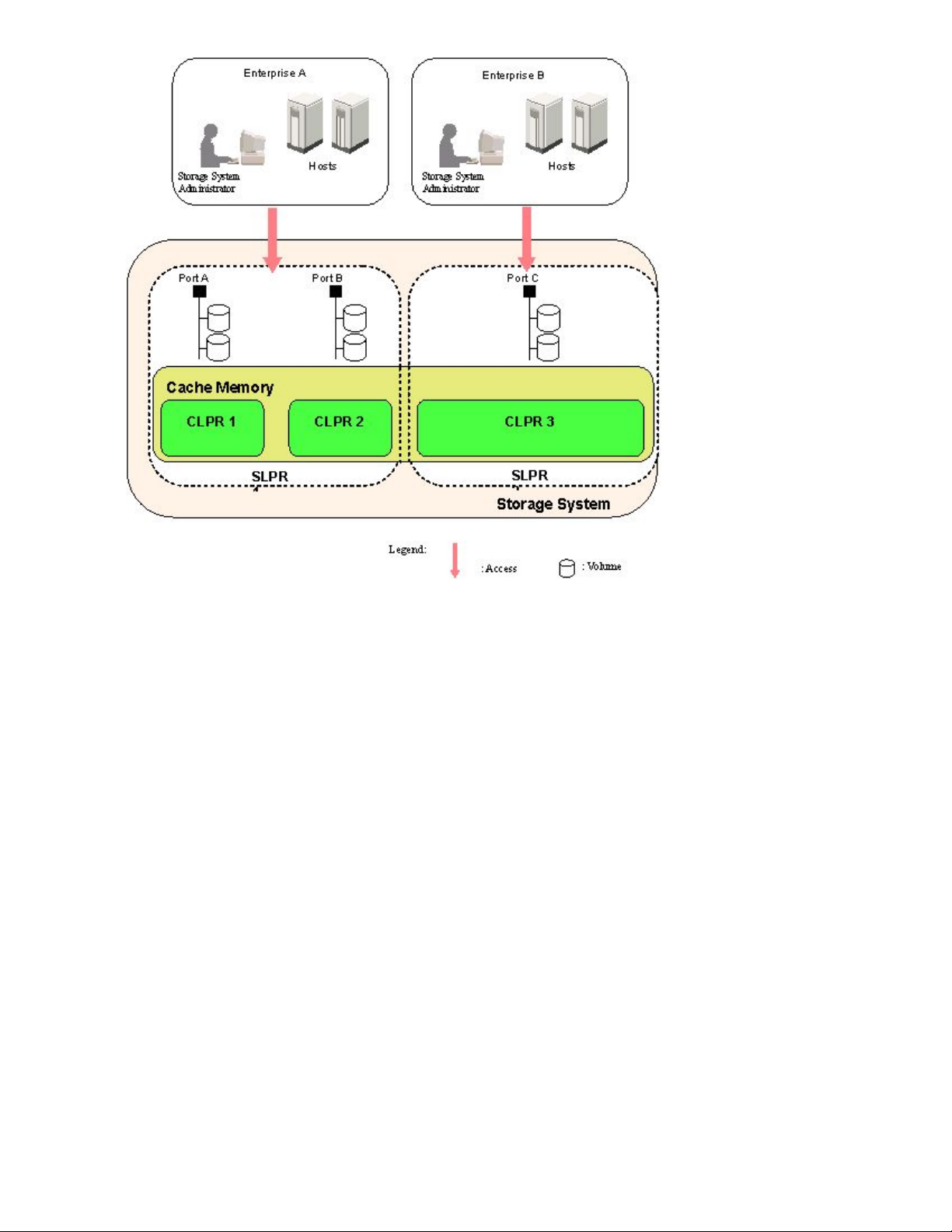
Figure 1 Storage Logical Partition (SLPR)
.
Cache Logical Partition (CLPR)
If one storage system is shared with multiple hosts, and one host reads or writes a large amount of
data, read and write data can require enough of the cache memory to affect other users. The cache
logical partition function creates two or more virtual cache memories, with each allocated to a different
host. This prevents contention for cache memory. Parity groups containing LDEVs that belong to the
optional LDKC can be allocated to a CLPR.
To add cache memory to the storage system, use the Standard Cache Access Model mode or the
High Performance Cache Access Model mode. If your storage system has any additional printed
circuit boards (PCBs), you must install the cache memory with the High Performance Cache Access
Model mode. If you want to use Cache Residency Manager, you can set up the required cache area
in one or more CLPRs. For more information on Cache Residency Manager, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Cache Residency Manager User's Guide. For more information about additional
cache memories, call HP technical support (see “Creating a Cache Logical Partition” on page 32).
Figure 2 illustrates the use of cache memory within a corporation. In this example, the cache memory
is partitioned into three segments of 40 GB each, which are each allocated to a branch office. The
host of branch A has a heavy I/O load. Because the cache memory is partitioned, that heavy I/O
load does not impact the cache memory for the other two branches.
About Disk/Cache Partition10
Page 11
You can create up to 32 cache logical partitions in one storage system, including the default CLPR
0. See “Creating a Cache Logical Partition” on page 32 for instructions on creating cache logical
partitions.
Figure 2 illustrates a cache logical partition.
Figure 2 Cache Logical Partition (CLPR)
.
Table 1 lists the recommended cache capacity, which is determined by the CLPR data capacity.
Table 1 CLPR Data Capacity and the Recommended Cache Capacity
Recommended Cache CapacityCLPR Data Capacity
4 GB or moreLess than 720 GB
8 GB or more720 GB or more
12 GB or more2,900 GB or more
16 GB or more8,650 GB or more
20 GB or more14,400 GB or more
24 GB or more20,160 GB or more
28 GB or more128,000 GB or more
32 GB or more146,000 GB or more
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 11
Page 12

Recommended Cache CapacityCLPR Data Capacity
40 GB or more182,000 GB or more
48 GB or more218,000 GB or more
56 GB or more254,000 GB or more
64 GB or more290,000 GB or more
72 GB or more326,000 GB or more
To calculate the data capacity:
The number of 3D+1P parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 3
+ the number of 6D+2P parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 6
+ the number of 7D+1P parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 7
+ the number of 2D+2D parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 2
To calculate the cache capacity for a CLPR:
Cache capacity (GB)
=Recommended cache capacity (GB)+
(Cache Residency capacity(MB)/2,048) x 2 GB
About Disk/Cache Partition12
Page 13

3 Preparing for XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations
This chapter discusses the preparation needed for XP Disk/Cache Partition operations.
• Storage Administrator and Storage Partition Administrator Privileges, page 13
• Possible Interacting and Conflicting Functions, page 15
Storage Administrator and Storage Partition Administrator Privileges
Once the XP Disk/Cache Partition license key has been installed for the HP StorageWorks XP Remote
Web Console Java API, a storage administrator with write permission for XP Disk/Cache Partition
can then log on to the storage system and allocate license capacities to various storage logical
partitions as needed, using the License Key Partition Definition panel. See “License Key Partition
Definition Window” on page 24 for a description of the window, and
“Partitioning and Allocating Licensed Capacity to Storage Logical Partitions” on page 30 for instructions
on allocating license key capacity to the SLPRs.
You will need to either purchase an unlimited license for an option, or allocate the license capacity
for that option among the various SLPRs. You will also need to enable or disable each option for each
of the storage logical partitions. You cannot use an option in SLPRs until the license capacity has been
allocated.
NOTE:
A storage partition administrator has authority only within the assigned storage logical partition.
Only storage administrators can make settings for SLPR 0. The storage administrator can also assign
write permission for one or more of the following functions:
• Open Volume Management
• Volume Shredder
• Data Retention Utility
• LUN Manager
• Cache Residency Manager
• XP Performance Monitor
• XP Remote Web Console
• API
Administrator access for the storage system is divided into two types:
• Storage Administrators manage the entire storage system and all of its resources, can create and
manage storage logical partitions and cache logical partitions, and assign access permission for
storage partition administrators. Storage administrators have sole access to the following functions:
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 13
Page 14

• Accessing Storage Logical Partition 0 (SLPR 0) and Cache Logical Partition 0 (CLPR 0)
• Managing mainframe volumes
• Storage Partition Administrators can view and manage only those resources that have been as-
signed to a specific storage logical partition. Storage partition administrators have access only to
the functions listed below. If a storage partition administrator is not granted write access to a
particular function, view access is available.
• System Information
• Information (Read Only)
• LUN Manager
• Port
• Authentication
• Volume Manager
• LUN Expansion
• Customized Volume
• Cache Residency
• XP Auto LUN / Perf Ctl / Perf Mon
• XP Performance Monitor
• XP Auto LUN
• Data Retention Utility
• Security
• Account
For detailed information on each function, see the manual for each program product. For instructions
on creating storage partition administrators and granting write access to one or more products, see
the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User's Guide. For information about
the functions that are not available for storage partition administrators, also see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User's Guide.
Preparing for XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations14
Page 15

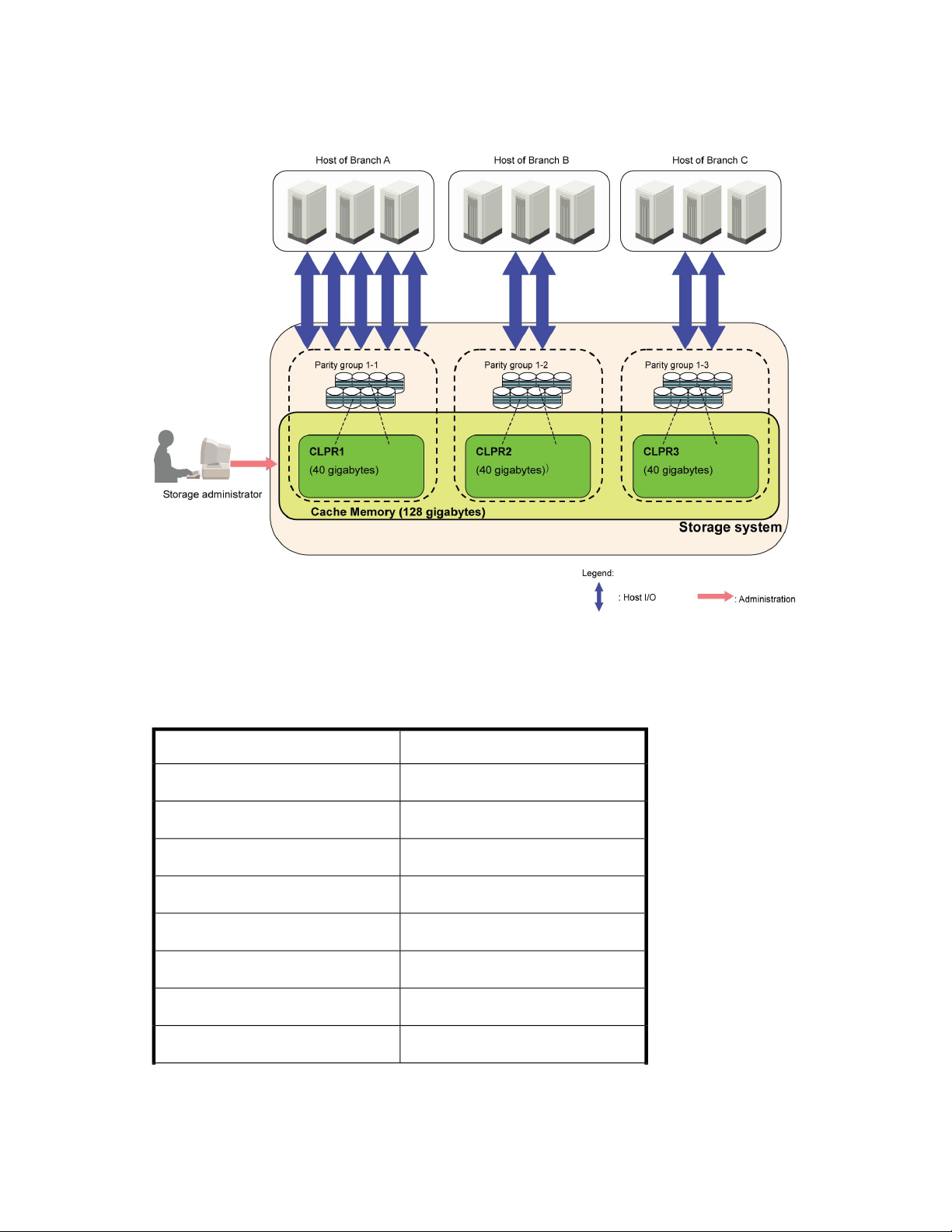
Figure 3 Storage Administrator and Storage Partition Administrator Privileges
.
Possible Interacting and Conflicting Functions
It is possible for actions taken by a storage administrator to interact and conflict with actions taken
by a partition storage administrator.
WARNING:
If you are using HP StorageWorks XP RAID Manager, you must use command device
security for the affected logical volumes, to prevent RAID Manager commands from having effects
across SLPR boundaries. For more information on RAID Manager, see the HP StorageWorks XP RAID
Manager User's Guide. For more information on securing command devices, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 LUN Manager User's Guide.
Before a storage administrator or storage partition administrator can create a customized volume
(CV) using the Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) function, the storage administrator must allocate the CU numbers
to the SLPR. This is necessary so that the storage partition administrator can allocate LDEVs to those
CU numbers when creating a customized volume. For more information on the VLL function, see the
HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User's Guide.
WARNING:
Making settings across SLPR boundaries is strongly discouraged, because you could
cause unintended and serious consequences, including having a storage partition administrator be
unable to perform one or more functions. If you attempt to make settings across more than one SLPR,
a warning message is displayed. If you do make settings across SLPR boundaries, be extremely careful
to avoid conflicts in LDKC, CU, and volume numbers across the various storage logical partitions.
For example, if a storage administrator performs any of the following types of actions across SLPR
boundaries, this could cause serious problems for the storage partition administrators:
• Manual migration with volume migration. For more information, contact HP technical support. See
“Calling HP Technical Support” on page 36.
• XP Business Copy Quick Restore (see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Business Copy
Software User's Guide and the Hitachi ShadowImage™ for Mainframe User's Guide: HP XP24000
Disk Array, HP XP20000 Disk Array)
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 15
Page 16

• LU path settings and High Speed settings (see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 LUN
Manager User's Guide)
• LUSE settings (see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 LUN Expansion User's Guide)
If you are using HP StorageWorks XP Continuous Access Journal Software, XP Continuous Access
Journal data volumes and journal volumes can belong to the different CLPRs. All journal volumes in
the same journal group must belong to the same CLPR. For more information on XP Continuous Access
Journal, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Continuous Access Journal Software User's
Guide.
Figure 4 shows an example involving manual volume migration. In this example, volume
LDKC00:CU01:LDEV05 is manually migrated from SLPR1 to SLPR2, and volume LDKC00:CU02:LDEV10
is manually migrated from SLPR2 to SLPR1. CU01 is allocated to SLPR1. Because volume
LDKC00:CU01:LDEV05 belonged to CU01 before the manual migration, there is no conflict. However,
volume LDKC00:CU02:LDEV10 will be allocated to CU01 after manual migration, and that CU number
conflicts with the volume number.
If the CU number does not correspond with the volume number in the SLPR, an error does not occur,
but this can make storage system administration more difficult, particularly when you need to perform
a forced manual migration between the different SLPRs. For further information on the customized
volume, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 LUN Manager User's Guide. For more
information, contact the HP technical support. See “Calling HP Technical Support” on page 36.
Figure 4 Manual Migration between SLPRs
.
Preparing for XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations16
Page 17

4 Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI
This chapter describes the windows that comprise the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI.
• Logical Partition Window, page 17
• Storage Management Logical Partition Window, page 19
• Cache Logical Partition Window, page 21
• Select CU Dialog Box, page 23
• License Key Partition Definition Window, page 24
Logical Partition Window
To open the Partition Definition window, from the XP Remote Web Console main window click Go,
then Environmental Settings. Select Partition Definition , and then select a storage system in the Logical
Partition tree. If you are logged on as a storage partition administrator, this window shows only the
resources in that storage partition.
The Logical Partition window has the following features.
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 17
Page 18

Figure 5 Logical Partition Window (Storage System Selected)
.
Table 2 Logical Partition Window Details (Storage System Selected)
DescriptionItem
Partition definition tree
Storage system
resource list
The storage system and all of its logical partitions. The name and number of the
storage logical partition are displayed to the right of each SLPR icon.
The list provides the following information:
• No.: The storage system resource list number
• Item: The resource type (Storage Partition)
• Name: The storage logical partition numbers and names
• Cache (Num. of CLPRs): The cache capacity and number of cache logical partitions
• Num of PGs: Number of parity groups. For SLPR 0, the amount is calculated by
subtracting the number of parity groups of all other SLPRs from those of SLPR 0.
• Num of Ports: Number of ports. For SLPR 0, the amount is calculated by subtracting
the number of ports of all other SLPRs from those of SLPR 0.
Implements the settings that were made in this windowApply
Cancels any settings that were made in this windowCancel
Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI18
Page 19

Storage Management Logical Partition Window
The Storage Management Logical Partition window displays if you select an SLPR in the Partition
Definition tree of the Partition Definition tab. If you are logged on as a storage partition administrator,
this window shows only the resources in that storage partition.
The Storage Management Logical Partition window has the following features.
Figure 6 Storage Management Logical Partition Window (SLPR Selected)
.
Table 3 Storage Management Logical Partition Window (SLPR Selected)
DescriptionItem
Partition
definition
tree
The storage system and all of its logical partitions. The name and number of the storage logical
partition are displayed to the right of each SLPR icon. The cache logical partition number and
name are displayed to the right of each CLPR icon.
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 19
Page 20

Storage
logical
partition
resource list
Detail for
SLPR
DescriptionItem
When a storage logical partition is selected the Partition Definition tree, the Storage Logical
Partition resource list shows resource information, including logical partitions and ports, for the
selected storage logical partitions cache.
If SLPR 0 is selected in the Storage Logical Partition tree, this list shows all resources not
specifically assigned to another SLPR.
The list provides the following information:
• No.: The line number
• Resource Type: The resource type, including Cache Partition or Port (type)
• Name: The resource name
• If the resource type is Cache Partition, the CLPR number and name are displayed.
• If the resource type is Port, the port name displays.
• Properties: The capacity and number of parity groups allocated to the selected cache logical
partition
• Information: If the resource is a port, this is the channel adapter name.
The settings of the selected storage logical partition. See “Creating a Storage Logical
Partition” on page 29 for more information on storage logical partition operations.
If the storage partition administrator wants to use the Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) function, the CU
numbers and SSIDs must have previously been specified for each storage logical partition, so
that newly allocated CU numbers and SSIDs will not overlap those in another storage logical
partition. For more information on Virtual LVI/LUN, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User's Guide.
• SLPR Name: The name of the storage logical partition, up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
This field allows you to set or change the name of the storage logical partition, provided
that it is within the selected CU.
• CU (*: SSID assigned): The LDKC and CU number of the specified SLPR (00 to FE). An asterisk
(*) indicates that the SSIDs are assigned to the CU. To delete a CU from the specified SLPR,
select that CU from this list and click Delete to return the CU to the Available CU list.
• Available CU (* SSID assigned):
• LDKC:CU: the LDKC and CU numbers. An asterisk (*) indicates that the SSIDs are assigned
to the CU.
• SLPR: Displays the SLPR for that CU
• SSID (SLPR): If the SSID is assigned to the CU, it displays here. The SLPR for that SSID
displays to the right.
• SSID (* CU assigned): This is the SSIDs in the selected storage logical partition (0004 to
FFFE). An asterisk (*) indicates that the SSID is assigned to a CU. You can select up to 510
CUs that do not have SSIDs assigned and/or CUs that have SSIDs assigned.
If a customized volume (CV) is set by using Virtual LVI/LUN, and the CU No. and SSID are
registered to different storage logical partition, a dash (-) displays to the right of the SSID
number. For more information on the VLL function, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User's Guide.
• From The starting number of the SSID that is added (0004 to FFFE). This number must be
smaller than the number that is entered into the To field.
• To The ending number of the SSID that is added (0004 to FFFE). You may enter up to 2040
SSIDs from SLPR 0.
To add one or more SSIDs to the SLPR, enter the starting number into the From: field, and
the last number into the To then click Add. To delete an SSID from the SSID box, select that
SSID and click Delete.
Implements the settings that were made in this windowApply
Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI20
Page 21

DescriptionItem
Cancels any settings that were made in this windowCancel
Cache Logical Partition Window
The Cache Management Logical Partition window (see Figure 7) displays if you select a CLPR in the
Partition Definition tree of the Partition Definition tab. If you are logged on as a storage partition
administrator, this window shows only the resources in that storage partition.
The Cache Logical Partition window has the following features.
Figure 7 Cache Logical Partition Window (CLPR Selected)
.
WARNING:
Before changing the cache size or the cache residency size, verify that CLPR 0 has at
least 4 GB remaining after subtracting the cache residency size from the cache size.
Table 4 Cache Logical Partition Window Details (CLPR Selected)
DescriptionItem
CU
Selected CU
Indicates either All CUs or the selected CU number.
Open the Select CU dialog box, see Figure 17 on page 34.
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 21
Page 22

Partition
Definition
tree
Cache Logical Partition
Resource List
DescriptionItem
All of the storage logical partitions and cache logical partitions in the storage system. The
storage logical partition number and name are displayed to the right of the each SLPR icon
( ). The cache logical partition number and name are displayed to the right of the CLPR icon
( ).
When a CLPR is selected in the Partition Definition tree, the Cache Logical Partition resource
list show the resource information for the selected CU and CLPR.
If CLPR 0 is selected in the Cache Logical Partition tree, this list shows all resources not already
assigned to other partitions.
The list provides the following information:
• No. The row number
• Resource Type Type of resources of CLPR.Parity Group is displayed in this column
• Address
An address beginning with the letter E (for example, E1-1) indicates that the parity group
contains external volumes.
An address beginning with M (for example, M1–1) indicates that the parity group contains
migration volumes.
An address beginning with the letter V (for example, V1-1) indicates that the parity group
contains HP StorageWorks XP Snapshot virtual volumes.
An address beginning with the letter X (for example, X1-1) indicates that the parity group
contains HP StorageWorks XP Thin Provisioning Software virtual volumes.
• Properties
If a parity group contains internal volumes, the parity group and RAID configuration are
displayed.
If a parity group contains external volumes, the volume capacity is displayed, but the RAID
configuration is not displayed.
If a parity group contains virtual volumes (for example, XP Snapshot or XP Thin Provisioning),
the volume capacity is displayed, but the RAID configuration is not displayed.
• Emulation Emulation type of the parity group
Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI22
Page 23

Detail for
CLPR in System
DescriptionItem
Allows you to set or change the settings of the specified cache logical partition. See “Cache
Logical Partition Operations” on page 31 for more information on cache logical partition
operations.
You cannot directly change the capacity value of CLPR 0. Any changes in the capacity of the
other CLPRs will be reflected in the capacity of CLPR 0.
The maximum available cache capacity (mounted cache less the cache in use by other cache
logical partitions) displays for the upper limit of Cache Size, Cache Residency Size, Num. of
Cache Residency Areas. For more information on Cache Residency, see HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Cache Residency Manager User's Guide.
• CLPR Name allows you to set or change the name of the cache logical partition, provided
that it is within the selected CU. You can use up to 16 alphanumeric characters.
• Cache Size setting, as illustrated in Figure 7 on page 21, allows you to set or change the
cache capacity of each cache logical partition. You may select 4 GB or more up to a
maximum size of 508 GB, which is 4 GB smaller than the cache size of the whole storage
system. From a default value of 4 GB, you may increase the size in 2 GB increments. Cache
Residency Size setting, also illustrated in Figure 7 on page 21, allows you to set or change
the capacity of the Cache Residency cache. You may select nothing (0 GB) to a maximum
size of 504 GB, which is the Cache Residency size of the entire storage system. The default
value is 0 GB, to which you may add capacity in 0.5 GB increments.
• Cache Residency Size allows you to set or change the capacity of the Cache Residency
cache. The value of Cache Residency size must be selected or input from 0 to 248 GB in
0.5 GB increments. The default value is 0 GB.
Note:
If you have previously defined cache residency size for this cache logical partition
using Cache Residency Manager, the Cache Residency size selected for this cache logical
partition must be greater than that which was previously defined. Use Cache Residency
Manager to verify the size before you set the value for this field.
• Num. of Cache Residency Areas allows you to set or change the number of Cache Residency
areas, from 0 to 16,384. The default value is 0.
NOTE:
If you have previously defined Cache Residency areas for this cache logical
partition using Cache Residency Manager, the number of Cache Residency areas
selected for this cache logical partition must be more than that which was
previously defined. Use Cache Residency Manager to verify the number of areas
before
you set the value for this field.
Apply
Cancel
Implements settings made in this window
Cancels any settings made in this window
Select CU Dialog Box
To open the Select CU Dialog box, click Select CU on the Cache Logical Partition window (see Figure
8).
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 23
Page 24

Figure 8 Select CU Dialog Box
.
Table 5 Select CU Dialog Box Details
DescriptionItem
All CUs
Specific CU
Unallocated
When selected, information about all CUs can be displayed on the CLPR resource
list.
When selected, information about only the specified CU can be displayed on the
CLPR resource list.
• Use the LDKC list to specify LDKC
• Use the CU list to specify CU
When selected, only the information about CUs unallocated to CLPR is displayed
on the CLPR resource list.
Implements settings made in this windowSet
Cancels any settings made in this windowCancel
License Key Partition Definition Window
The License Key Partition Definition window (see Figure 9) lists options that are available to storage
logical partitions. From here, a storage administrator with the storage administrator role enabled can
allocate license key capacity among various storage logical partitions. Each option must first be
installed from the License Key window before its license capacity can be partitioned. For more
information on installing options, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console
User's Guide.
To open the License Key Partition Definition window, from the XP Remote Web Console main window
click Go, and then click Environmental Settings. Select the License Key Partition Definition tab.
Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI24
Page 25

Figure 9 License Key Partition Definition Window
.
The Product Name list is on the upper part of the window (see Figure 10), and lists the program
products for which the licensed capacity can be allocated to SLPRs.
Figure 10 Product Name List
.
Table 6 Product Name List Details
DescriptionItem
Name of the product, including:
• Option name
Product
Name
• Installed/Not Installed icon:
indicates Installed
indicates Not Installed
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 25
Page 26

Key Type
Permitted
Volumes
Term (days)
Status
DescriptionItem
The license type: Permanent, Temporary or Emergency. Not Installed is displayed, when the
option is not installed. Since all the SLPRs will be available when the key type of the program
product is Temporary or Emergency, you do not need to separate each SLPR. Therefore, no
partition status information for the program product whose key type is Temporary or Emergency
will be displayed in the License Key Partition Definition window, so that you cannot partition
the SLPR for that program product.
Unlimited is displayed if the size is unlimited.
Capacity Information:
• Available capacity (licensed capacity). Licensed capacities are calculated assuming that
1 KB = 1,024 bytes, 1 MB = 1,024 KB, 1 GB = 1,024 MB, and 1 TB = 1,024 GB.
• Capacity that is already being used. For example, if this column shows 10.0 TB (2.50 TB),
the licensed capacity is 10.0 TB and the capacity already being used is 2.50 TB.
• Unlimited is displayed if the size is unlimited.
The number of days that remain before temporary or emergency key expiration. After the
temporary key has expired, this column shows the number of days that remain before you can
re-install the temporary key.
The option's current status:
• Installed indicates that the option is available. The Product Name column displays the In-
stalled icon ( ).
• Not Installed indicates that the option is not available. The Product Name column displays
the Not Installed icon ( ).
• Not Enough indicates that the volume capacity is insufficient. The Product Name column
displays the Not Installed icon ( ).
• Capacity Insufficient indicates that the licensed capacity is insufficient because disk drives
have been added. The Product Name column displays the Installed icon ( ), but you
must purchase additional licensed capacity before the license key expires.
• Expired indicates that the license key of an option that had been in the Capacity Insufficient
status has expired. The Product Name column displays the Not Installed icon ( ).
• Time Out indicates that the term has already expired for the temporary key. The Product
Name column displays the Not Installed icon ( ).
When you select an option, the capacity list, which is directly under the Product Name list, is updated
(see Figure 11).
Figure 11 Capacity List
.
Table 7 Capacity List Details
DescriptionItem
Total licensed capacity for the selected option.Total Capacity
Remaining Capacity
Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI26
The remaining licensed capacity (in GB) that is not yet allocated to any
SLPR among the entire licensed capacity for the selected option.
Page 27

After selecting an option, Partition Status List and Setting Box is displayed under the information about
the licensed capacity (see Figure 12, Figure 13, and Figure 14). This allows you to select and display
information regarding a storage logical partition.
Figure 12 Partition Status List
.
The Partition Status list provides the following information for the selected option.
Table 8 Partition Status List Details
DescriptionItem
SLPR Name
Used Volume
Storage logical partition name.
Amount of licensed capacity currently being used.
Volume status, which is determined by comparing allocated licensed capacity (Permitted
Volumes) and used licensed capacity (Used Volumes):
• Installed: License capacity for this option has been allocated to the SLPR. If the license
capacity is limited, this indicates that the partitioned licensed capacity is allocated to
the SLPR and the allocated licensed capacity is more than the capacity of Used Volumes.
Status
A storage partition administrator can use the option in the allocated SLPR.
• Not Installed: No license and licensed capacity for the selected option are allocated
to the SLPR.
• Capacity Insufficient: Licensed capacity that is allocated to the SLPR (Permitted Volumes)
is less than the currently used licensed capacity (Used Volumes). When the trial period
still remains, the number of remaining days display in parentheses.
Permitted
Volumes
Allocated licensed capacity to SLPR in GB when the option without unlimited licensed
capacity is selected. Blank when the option with unlimited licensed capacity is selected.
After selecting an option and an SLPR, if you select an option with an unlimited license capacity, or
where the licensed capacity is not relevant, the Setting box looks like Figure 13.
Figure 13 Setting Box (Licensed Capacity Unlimited or Not Relevant)
.
Table 9 Setting Box Details (Licensed Capacity Unlimited or Not Relevant)
DescriptionItem
Enables the license key for selected option.Enable
Disables the license key for the selected option.Disable
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 27
Page 28

If you select an option with a limited license capacity, the Setting box looks like Figure 14. You may
enter the licensed capacity to be allocated to the SLPR.
However, you cannot set the licensed capacity of SLPR0. If you select SLPR0, Set will be inactive.
Figure 14 Setting Box (License Capacity Limited)
.
Table 10 Setting Box Details (License Capacity Limited)
DescriptionItem
Selects the setting. The selected row of the option list and the Partition Status list change
to blue bold italics, and the displayed capacity in the Remaining Capacity field changes
Set
to the new capacity.
IMPORTANT:
The setting is not implemented until you click Apply (below).
Apply
Cancel
Implements the setting in the storage system.
Cancels the setting.
Using the XP Disk/Cache Partition GUI28
Page 29

5 XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations
This chapter provides detailed instructions for XP Disk/Cache Partition operations.
• Storage Logical Partition Operations, page 29
• Cache Logical Partition Operations, page 31
Storage Logical Partition Operations
Storage logical partition operations have the following requirements:
• You must have storage administrator access for all storage logical partition actions described in
this section.
• If you have not yet created any storage logical partitions, all resources will belong to SLPR 0.
• Mainframe volumes must be allocated to SLPR 0, and cannot be migrated. Mainframe operations
must be performed by storage administrators.
• If you want to allocate a port to an SLPR other than SLPR 0, it must be a Target port.
• Before you create a customized volume (CV) in a storage logical partition using the Virtual LVI/LUN
(VLL) function, you must allocate the CU numbers to that SLPR. This is necessary so that the storage
partition administrator can allocate LDEVs to those CU numbers when creating a customized
volume. For more information on the VLL function, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000
Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User's Guide.
• For instructions on creating storage partition administrators and granting write access to one or
more products, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User's Guide.
Creating a Storage Logical Partition
To create storage logical partition:
1. From the Partition Definition window, right-click a storage system in the Partition Definition tree,
then select Create SLPR. This adds a storage logical partition to the Partition Definition tree. In
addition to the default SLPR 0, you can create up to 31 storage logical partitions, either at this
point in the process or at a later time.
2. Select the SLPR that you want to define from the Partition Definition tree. This opens the Storage
Management Logical Partition window.
3. In the SLPR Name field, enter the name of the selected SLPR. You can use up to 32 alphanumeric
characters.
4. In the CU field, enter the CU numbers for the selected SLPR (00-FE). An asterisk (*) indicates that
the SSID is assigned to the CU:
• To add a CU to the SLPR, select the CU from the Available CU list, then click Add to move
that CU to the CU list. You can select up to 64 CUs, whether or not those CUs are defined
as LDEVs.
• To delete CU from the specified SLPR, select the CU from the CU list and click Delete to return
that CU to the Available CU list.
5. Available SSIDs are in SLPR 0. In the SSID field, select an available SSID as follows:
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 29
Page 30

• In the From field, enter the starting number of the SSID (0004 to FFFE).
• In the To field, enter the ending number of the SSID.
6. Click Apply to apply the settings, or click Cancel to cancel the settings.
Note:
At this point in the process, the newly created storage logical partition has no resources (for
example, cache logical partitions and ports). See
“Migrating Resources To and From Storage Logical Partitions” on page 30 for instructions on migrating
resources. See “Partitioning and Allocating Licensed Capacity to Storage Logical Partitions” on page
30 for instructions on adding and deleting resources.
Partitioning and Allocating Licensed Capacity to Storage Logical Partitions
You must already have created at least one SLPR in order to perform the operations in this section.
1. Log on as a storage administrator with write authority for XP Disk/Cache Partition and open the
XP Remote Web Console main window. Change to Modify mode.
2. On the menu bar, click Go, Environmental Settings, and then License Key Partition Definition to
open the License Key Partition window (see Figure 9 on page 25).
3. Select an option in the Product Name list. The Partition Status and Setting boxes are displayed
at the bottom of the window. In the Partition Status box, select a storage logical partition.
4. If license capacity for that option is limited, enter in the desired license capacity for this option
(see Figure 15).
However, you cannot set the licensed capacity of SLPR0.
5. If the licensed capacity for that option is unlimited, click Enable in the Setting box (see Figure
16).
6. Select Set. The new setting is displayed in the Remaining Capacity and Partition Status boxes.
7. Make additional settings, if desired, using above instructions.
8. Click Apply to implement setting, or click Cancel.
Figure 15 Selecting the License Capacity
.
Figure 16 Selecting Enable (License Capacity Unlimited)
.
Migrating Resources To and From Storage Logical Partitions
The resources of a storage logical partition include cache logical partitions and ports, which can be
migrated to another storage logical partition as needed. This process has the following restrictions:
• You can only migrate resources within the same LDKC.
• The only ports that can be migrated are Target ports. Initiator ports, RCU Target ports and External
ports cannot be migrated, and must remain in SLPR 0.
• Mainframe parity groups cannot be migrated out of SLPR 0.
To migrate one or more resources:
1. Open the Partition Definition window, and select an SLPR in the Partition Definition tree to open
the Storage Management Logical Partition window.
XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations30
Page 31

2. From the Storage Logical Partition Resource List, select one or more cache logical partitions
and/or target ports to be migrated. Right-click to display the pop-up menu, then click Cut. SLPRs
from other CUs are grayed out and unavailable.
3. On the Partition Definition tree, select the SLPR to which you want to migrate resources. SLPRs
from other CUs are grayed out and unavailable.
4. Right-click to display the pop-up menu, then click Paste CLPRs, Ports. You can select up to 31
CLPRs (not including CLPR 0) and 256 ports. A colored icon ( ) and black characters indicate
available destination SLPRs.
5. Cache logical partitions will be added to both the Partition Definition tree and the Storage
Management Logical Partition resource list. Ports will be added only to the SLPR resource list.
6. Click Apply to apply the settings.
Deleting Storage Management Logical Partitions
If you delete a storage logical partition, any resources in that storage logical partition will be
automatically returned to SLPR 0. SLPR 0 cannot be deleted
Note:
Before deleting a storage logical partition, you must do the following:
• Delete all user accounts for that SLPR. For more information, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User's Guide.
• Either set the license capacity for that SLPR to 0 GB, or disable the license for all program products
that are assigned to the SLPR. For more information, see
“Partitioning and Allocating Licensed Capacity to Storage Logical Partitions” on page 30.
1. Access the Partition Definition window, and select an SLPR in the Partition Definition tree on the
left side of the window to display the Storage Management Logical Partition window.
2. In the Logical Partition tree on the upper left portion of the window, right-click the storage logical
partition that you want to delete and click Delete SLPR from the pop-up menu.
3. Click Apply to apply the settings, or click Cancel to cancel the settings.
Cache Logical Partition Operations
The following items apply to CLPRs.
WARNINGS:
• Before you start a partition reconfiguration make sure that you have enough cache memory assigned
to a partition to support the disk storage assigned to that same partition. See
“Cache Logical Partition (CLPR)” on page 10 for more information on the required amount of
cache to support disk storage.
• As a general rule, you should perform cache logical partition operations either during the initial
installation and setup or during a maintenance window, because cache logical partition operations
can significantly degrade host performance. If you must perform such operations on a production
machine, you should use XP Performance Monitor to verify that the write pending rate, including
spikes, is well below 30%.
Note:
Changes to CLPR/SLPR configurations may take hours to implement and cannot be aborted or
modified until all changes have completed. For more information on XP Performance Monitor, see the
HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Performance Monitor User's Guide. For assistance or for more
information, contact your HP service representative.
cache logical partition operations have the following restrictions:
• You must have storage administrator access for all cache logical partition actions.
• If you have not yet created any cache logical partitions, all cache will belong to CLPR 0.
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 31
Page 32

• Adding or changing CLPR definitions can require several hours or more.
• If you are using XP Continuous Access Journal, data and journal volumes can belong to the different
CLPRs, but the journal volumes in the same journal group must belong to the same CLPR. For more
information on XP Continuous Access Journal, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000
Continuous Access Journal Software User's Guide and the Hitachi Universal Replicator™ for
Mainframe User's Guide: HP XP24000/XP20000 Disk Array .
The following operations are not recommended with cache logical partitions:
• Creating LUSE volumes across multiple CLPRs.
NOTE:
If you forcibly perform this operation, the CLPR volumes included in the LUSE volumes cannot be
used for HP StorageWorks XP Continuous Access Software or the for Mainframe pair volumes.
• XP Business Copy Quick Restore operations that affect multiple CLPRs
• HP StorageWorks XP Auto LUN Software manual migration operations that affect multiple CLPRs
• Continuous Access Asynchronous or Asynchronous for Mainframe operations across CLPR
boundaries. If these are allocated to the same consistency group, you cannot create a Continuous
Access Asynchronous pair, and you cannot migrate a Continuous Access Asynchronous parity
group to another CLPR.
• A parity group that contains LDEVs assigned to Cache Residency cache extents cannot be migrated
to another CLPR
Creating a Cache Logical Partition
NOTE:
To create a CLPR, the remaining cache size which is calculated by subtracting Cache Residency size
from the cache size of CLPR 0 needs 8 GB or more.
To create a cache logical partition:
1. Access the Partition Definition window, and select an SLPR in the Partition Definition tree on the
left side of the window to display the Storage Logical Partition window.
2. Right-click an SLPR from the Partition Definition tree, on the upper left portion of the window, to
display the Create CLPR pop-up menu. Select Create CLPR. This will add a cache logical partition
to the Partition Definition tree.
3. Select the newly created CLPR to display the Cache Logical Partition window. In the Detail for
CLPR section, on the lower left portion of the window, do the following:
• In the CLPR Name field, enter the name of the cache logical partition, in up to 16 alphanumeric characters.
• In the Cache Size field, enter the cache capacity. You may select from 4 to 508 GB, in 2 GB
increments. The default value is 4 GB. The size of the cache will be allocated from CLPR 0,
but you must leave at least 8 GB remaining in CLPR 0.
• In the Cache Residency Area field, enter the desired capacity for the Cache Residency area.
You may enter the value within the range of 0 to 16384. The default value is 0.
4. Click Apply to apply the settings.
5. The change in cache capacity is reflected in this cache logical partition and in CLPR 0.
XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations32
Page 33

6. If you want to change the settings of an existing CLPR, repeat steps 3 through 5.
NOTE:
Note:
At this point, the cache logical partition has no parity groups. See
“Migrating Resources To and From Cache Logical Partitions” on page 33 for more information on
migrating resources to and from cache logical partitions.
Migrating Resources To and From Cache Logical Partitions
Notes:
• You can only migrate resources within the same CU.
• All concatenated parity groups must be in the same CLPR.
• LUSE volumes cannot be set across more than one CLPR.
• If a parity group contains one or more LDEVs that have defined Cache Residency extents, you
cannot migrate that parity group to another CLPR.
To migrate one or more parity groups to another cache logical partition:
1. Access the Storage Management Logical Partition window, then select a CLPR from the Partition
Definition tree, on the upper left portion of the window. This opens the Cache Logical Partition
window.
2. If you want to choose a CU, click the Select CU button on the upper right portion of the window
to display the Select CU dialog box (see Figure 17). Within that dialog box, do one of the following:
• Select the All CU radio button to display the information about all CUs on the CLPR resource
list.
• Select the Specific CU radio button, then specify the LDKC and the CU. This shows only CLPRs
from the selected CU.
• Select the Unallocated radio button to display only the information about CUs unallocated to
CLPR can be displayed on the CLPR resource list.
3. Click Set to close the dialog box.
4. From the Cache Logical Partition Resource List on the upper right portion of the window, select
one or more parity groups to be migrated. Right-click to display pop-up menu, then click Cut.
5. On the Partition Definition tree, on the upper left portion of the window, select the CLPR to which
you want to migrate resources, then right click and click Paste from the pop-up menu.
6. Click Apply to apply the settings.
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 33
Page 34

Figure 17 Selecting the CU
.
Table 11 Selecting the CU
DescriptionItem
Displays the information for all CUs in the CLPR resource list.All CUs
Displays the information for specified CU in the CLPR resource list.
Specific CU
• The LDKC drop-down list allows you to select the LDKC.
• The CU drop-down list allows you to select the CU.
Displays the information for the unallocated CUs in the CLPR list.Unallocated
Implements the setting in the storage system.Set
Cancels the setting.Cancel
Deleting Cache Logical Partitions
Before you delete a cache logical partition, be sure to migrate any resources (for example, parity
groups) to another CLPR. The CLPRs which are not necessary may be deleted, but CLPR 0 cannot be
deleted.
To delete a cache logical partition:
1. Select a CLPR in the Partition Definition tree to open the Cache Logical Partition window.
2. Right-click the CLPR that you want to delete and click Delete CLPR in the pop-up menu.
3. Click Apply to apply the settings.
XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations34
Page 35

6 Troubleshooting
This chapter describes some troubleshooting methods if you have problems with Disk/Cache Partition.
• General Troubleshooting, page 35
• Displaying an Error Message, page 35
• Troubleshooting Disk/Cache Partition, page 35
• Calling HP Technical Support, page 36
General Troubleshooting
• For troubleshooting information on the storage system, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000 Disk
Array Owner's Guide or the HP StorageWorks XP20000 Disk Array Owner's Guide.
• For troubleshooting information on the XP Remote Web Console software, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User's Guide.
• For information on the XP Remote Web Console software error codes, see the HP StorageWorks
XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console Error Codes.
Displaying an Error Message
To display an error message:
1. Right-click an SLPR on the Partition Definition tree, and then click Error Detail to open the message
box.
2. Click OK to close the message window.
Troubleshooting Disk/Cache Partition
Table 12 provides general troubleshooting instructions for XP Disk/Cache Partition operations.
Table 12 General Troubleshooting for XP Disk/Cache Partition Operations
All XP Disk/Cache Partition functions are
not available
The specified port cannot be migrated to
other storage logical partition.
A parity group cannot be migrated.
Only Storage administrators have access to XP Disk/Cache
Partition functions.
• Only Target ports on the same channel adapter can be
migrated to another storage logical partition. Initiator
ports, RCU Target ports and External ports cannot be migrated.
• Resources can only be migrated within the same CU.
• Only open-system parity groups can be migrated.
• Resources can only be migrated within the same CU.
Corrective ActionError
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 35
Page 36

When you attempt to migrate a parity
group to a CLPR in another SLPR, an LU
warning message is displayed.
When you attempt to migrate a CLPR to
another SLPR or deleted that CLPR, an LU
warning message is displayed.
Corrective ActionError
• LUs in parity groups must remain within the same SLPR.
• LUs in parity groups must remain within the same SLPR.
When you attempt to migrate a port to
another SLPR, an LU warning message is
displayed.
When you attempt to migrate a parity
group to another CLPR, an LU warning
message is displayed.
When the port in an SLPR migrates to
another SLPR, a warning message is
displayed.
The SLPR name cannot be changed.
The CLPR name cannot be changed.
The parity group in a CLPR cannot migrate
to another CLPR.
LUs that are associated with a port in a particular SLPR must
stay within that SLPR.
LUSE volumes cannot be set across more than one CLPR.
You are trying to allocate ports in a port block in High Speed
mode to more than one SLPR. Check the port settings and
make sure that all ports in the port block belong to the same
SLPR.
You cannot assign the same name to more than one SLPR.
The name you entered is already being used. Enter another
name.
You cannot assign the same name to more than one CLPR.
The name you entered is already being used or is reserved
by a system. Enter another name.
• Make sure that all concatenated parity groups belong to
the same CLPR.
• Make sure to click the Apply button when creating a new
CLPR.
Calling HP Technical Support
If you need to call HP technical support, make sure to provide as much information about the problem
as possible, including:
• The circumstances surrounding the error or failure
• The exact content of any error messages displayed on the host systems(s)
• The exact content of any error messages displayed by XP Remote Web Console
• The XP Remote Web Console configuration information (use the FD Dump Tool)
• The service information messages (SIMs), including reference codes and severity levels, displayed
by XP Remote Web Console
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Troubleshooting36
Page 37

7 Support and Other Resources
Related Documentation
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Cache Residency Manager User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP RAID Manager User’s Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Data Retention Utility User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 LUN Expansion User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 LUN Manager User’s Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Performance Monitor User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Auto LUN Software User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Performance Control User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Business Copy Software User's Guide
• Hitachi ShadowImage™ for Mainframe User's Guide: HP XP24000 Disk Array, HP XP20000 Disk
Array
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console Error Codes
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Remote Web Console User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Continuous Access Journal Software User's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Disk Array Owner's Guide
• HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000 Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User's Guide
You can find these documents on the HP Manuals website:
http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
In the Storage section, click Storage Software and then select a product.
Conventions for Storage Capacity Values
HP XP storage systems use the following values to calculate physical storage capacity values (hard
disk drives):
• 1 KB (kilobyte) = 1,000 bytes
•
1 MB (megabyte) = 1,0002bytes
•
1 GB (gigabyte) = 1,0003bytes
•
1 TB (terabyte) = 1,0004bytes
•
1 PB (petabyte) = 1,0005bytes
HP XP storage systems use the following values to calculate logical storage capacity values (logical
devices):
• 1 KB (kilobyte) = 1,024 bytes
•
1 MB (megabyte) = 1,0242bytes
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 37
Page 38

•
1 GB (gigabyte) = 1,0243bytes
•
1 TB (terabyte) = 1,0244bytes
•
1 PB (petabyte) = 1,0245bytes
• 1 block = 512 bytes
HP Technical Support
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Subscription Service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber’s Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
After registering, you will receive email notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
HP Websites
For additional information, see the following HP websites:
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
• http://www.hp.com/storage/spock
Documentation Feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, send a message to
storagedocsFeedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of HP.
Support and Other Resources38
Page 39

A Acronyms and Abbreviations
Table 13 Acronyms and Abbreviations
cache logical partitionCLPR
control unitCU
customized volumeCV
direct-access storage deviceDASD
host group
RAID
Used to segregate hosts by operating system platform. Also known as a host storage
domain.
local-area networkLAN
logical deviceLDEV
local control portLCP
logical unitLU, LUN
LUN ExpansionLUSE
logical volume imageLVI
megabytes per secondMB/s
network-attached storageNAS
nonvolatile storageNVS
printed circuit boardPCB
Redundant array of independent disks. RAID 1 and RAID 5 are specific RAID
architectures.
remote control unitRCU
storage-area networkSAN
service information messageSIM
storage logical partitionSLPR
storage system IDSSID
service processorSVP
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 39
Page 40

Virtual LVI/LUNVLL
virtual volumeV-VOL
world wide nameWWN
extended remote copyXRC
IBM z/OS operating systemz/OS
Acronyms and Abbreviations40
Page 41

Index
A
allocating license capacity
storage logical partitions (SLPRs), 30
allocating ports to SLPRs
restrictions on port type, 29
Auto LUN manual migration across multiple
CLPRs
restrictions, 32
B
Business Copy quick restore operations across
multiple CLPRs
restrictions, 32
C
cache logical partitions
overview, 10
cache memory for CLPR operations
restrictions, 31
CLPR
overview, 10
CLPR operations, 31
creating a CLPR, 32
deleting CLPRs, 34
migrating resources among CLPRs, 33
Continuous Access asynchronous operations
across multiple CLPR boundaries
restrictions, 32
conventions
storage capacity values, 37
creating a CLPR
instructions, 32
creating an SLPR
instructions, 29
creating LUSE volumes across multiple CLPRs
restrictions, 32
D
deleting CLPRs
instructions, 34
deleting SLPRs
instructions, 31
document
related documentation, 37
documentation
HP website, 37
providing feedback, 38
H
help
obtaining, 38
HP
technical support, 38
I
instructions
allocating license capacity among SLPRs, 30
creating a CLPR, 32
creating an SLPR, 29
deleting CLPRs, 34
deleting SLPRs, 31
migrating resources among CLPRs, 33
migrating resources among SLPRs, 30
L
license capacity
allocating among storage logical partitions
(SLPRs), 30
License Key Partition Definition tab
Setting box
license capacity limited, 28
license capacity not limited, 27
M
mainframe operations
restrictions, 29
migrating parity groups with LDEVs assigned to
Cache Residency extents
restrictions, 32
migrating resources among CLPRs
instructions, 33
migrating resources among SLPRs
instructions, 30
XP24000/XP20000 Disk/Cache Partition User's Guide 41
Page 42

O
operations
CLPR, 31
creating a CLPR, 32
creating an SLPR, 29
deleting CLPRs, 34
deleting SLPRs, 31
migrating resources among CLPRs, 33
migrating resources among SLPRs, 30
SLPR, 29
operations not recommended for CLPRs
restrictions, 32
overview
Cache Logical Partitions (CLPR), 10
storage logical partitions (SLPR), 9
P
production machines
restrictions on CLPR operations, 31
R
related documentation, 37
restrictions, 29
Auto LUN manual migration across multiple
CLPRs, 32
Business Copy quick restore operations across
multiple CLPRs, 32
cache memory for CLPR operations, 31
CLPR operations in general, 31
CLPR operations on production machines, 31
Continuous Access asynchronous operations
across multiple CLPR boundaries, 32
creating LUSE volumes across multiple CLPRs,
32
mainframe operations, 29
migrating parity groups with LDEVs assigned
to Cache Residency extents, 32
operations not recommended with CLPRs, 32
SLPR operations in general, 29
time required for CLPR operations, 32
types of ports allocated to SLPRs, 29
using Continuous Access Journal volumes for
CLPR operations, 32
S
Select CU Dialog Box, 23
settings across SLPR boundaries
avoiding conflicts, 15
SLPR
overview, 9
SLPR operations, 29
creating an SLPR, 29
deleting SLPRs, 31
migrating resources among SLPRs, 30
storage capacity values
conventions, 37
storage logical partitions
overview, 9
storage logical partitions (SLPRs)
allocating license capacity, 30
storage systems
supported models, 7
Subscriber's Choice, HP, 38
T
technical support, 38
HP, 36, 38
time required for CLPR operations
restrictions, 32
troubleshooting, 35
Disk/Cache Partition, 35
displaying an error message, 35
in general, 35
U
using Continuous Access Journal volumes for
CLPR operations, 32
W
warning
Auto LUN manual migration across multiple
CLPRs, 32
Business Copy quick restore operations across
multiple CLPRs, 32
cache memory for CLPR operations, 31
CLPR operations on production machines, 31
Continuous Access asynchronous operations
across multiple CLPR boundaries, 32
creating LUSE volumes across multiple CLPRs,
32
migrating parity groups with LDEVs assigned
to Cache Residency extents, 32
time required for CLPR operations, 32
using Continuous Access Journal volumes for
CLPR operations, 32
websites
HP, 38
HP Subscriber's Choice for Business, 38
product manuals, 37
42
 Loading...
Loading...