
Chapter 4 Removal and Replacement
This chapter discusses removal and replacement procedures for the HP Workstation xw4200. This
chapter includes the following sections:
“Service Considerations” on page 68
“Pre-Disassembly Procedures” on page 73
“Removal and Replacement of Components” on page 73
Chapter 4
67

Service Considerations
The following sections discuss service considerations that should be reviewed and practiced before
removing and replacing any system components.
WARNING! When lifting or moving the workstation, do not use the front bezel as a handle or lifting point.
Lifting the workstation from the front bezel or lifting it incorrectly could cause the unit to fall and harm the
user and damage the workstation. To properly and safely lift the workstation, lift it from the bottom of the
unit.
Read Cautions, Warnings, and Safety Precautions
For your safety, you must review the “Important Safety Warnings” on page vii before accessing the
components of the workstation. Also, review the
workstation for more information.
Electrostatic Discharge Information
A sudden discharge of static electricity from your finger or other conductor can destroy static-sensitive
devices or microcircuitry. Often the spark is neither felt nor heard, but damage occurs. An electronic
device exposed to electrostatic discharge (ESD) might not appear to be affected at all and can work
perfectly throughout a normal cycle. The device might function normally for a while, but it has been
degraded in the internal layers, reducing its life expectancy.
Safety and Regulatory Guide
that came with your
Networks built into many integrated circuits provide some protection, but in many cases, the discharge
contains enough power to alter device parameters or melt silicon junctions.
Generating Static
The following table shows that:
Different activities generate different amounts of static electricity.
Static electricity increases as humidity decreases.
Table 4-1 Generating Static Electricity
Relative Humidity
Event 55% 40% 10%
Walking across carpet
Walking across vinyl floor
Motions of bench worker
Removing bubble pack from PCB
Packing PCBs in foam-lined box
NOTE: 700 volts can degrade a product.
7,500 V
3,000 V
400 V
7,000 V
5,000 V
15,000 V
5,000 V
800 V
20,000 V
11,000 V
35,000 V
12,000 V
6,000 V
26,500 V
21,000 V
68 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT

Preventing Electrostatic Damage to Equipment
Many electronic components are sensitive to ESD. Circuitry design and structure determine the degree
of sensitivity. The following packaging and grounding precautions are necessary to prevent damage to
electric components and accessories.
Transport products in static-safe containers, such as tubes, bags, or boxes to avoid hand contact.
Protect all electrostatic parts and assemblies with conductive or approved containers or packaging.
Keep electrostatic sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free stations.
Place items on a grounded surface before removing them from their container.
When handling or touching a sensitive component or assembly, ground yourself by touching the
chassis.
Avoid contact with pins, leads, or circuitry.
Place reusable electrostatic-sensitive parts from assemblies in protective packaging or conductive
foam.
Personal Grounding Methods and Equipment
To prevent static electricity damage to equipment, use the following equipment:
Wrist straps are flexible straps with a maximum of one-megohm ± 10% resistance in the ground
cords. To provide proper ground, wear the strap against bare skin. The ground cord must be
connected and fit snugly into the banana plug connector on the grounding mat or workstation.
Heel straps, toe straps, and boot straps can be used at standing workstations and are compatible
with most types of shoes or boots. On conductive floors or dissipative floor mats, use them on both
feet with a maximum of one-megohm ± 10% resistance between the operator and ground.
The following table shows static shielding protection levels.
Chapter 4
Table 4-2
Method Voltage
Antistatic plastic
Carbon-loaded plastic
Metallized laminate
Static Shielding Protection Levels
1,500
7,500
15,000
Grounding the Work Area
To prevent static damage at the work area:
Cover the work surface with approved static-dissipative material. Provide a wrist strap connected to
the work surface and properly grounded tools and equipment.
Use static-dissipative mats, foot straps, or air ionizers to give added protection.
Handle electrostatic sensitive components, parts, and assemblies by the case or PCB laminate.
Handle them only at static-free work areas.
Turn off power and input signals before inserting and removing connectors or test equipment.
Use fixtures made of static-safe materials when fixtures must directly contact dissipative surfaces.
SERVICE CONSIDERATIONS 69

Keep work area free of nonconductive materials such as ordinary plastic assembly aids and
Styrofoam.
Use field service tools, such as cutters, screwdrivers, and vacuums, that are conductive.
Recommended Materials and Equipment
Materials and equipment that are recommended for use in preventing static electricity include:
Antistatic tape
Antistatic smocks, aprons, or sleeve protectors
Conductive bins and other assembly or soldering aids
Conductive foam
Conductive tabletop workstations with ground cord of one-megohm ± 10% resistance
Static-dissipative table or floor mats with hard tie to ground
Field service kits
Static awareness labels
Wrist straps and footwear straps providing one-megohm ± 10% resistance
Material handling packages
Conductive plastic bags
Conductive plastic tubes
Conductive tote boxes
Opaque shielding bags
Transparent metallized shielding bags
Transparent shielding tubes
Tools and Software Requirements
To service the workstation, you might need the following equipment:
Torx T-15 screwdriver or Flat-bladed screwdriver (can be used in place of the Torx screwdriver)
Phillips screwdriver (to remove the rear fan, if necessary)
Diagnostics software
Tamper-resistant T-15 wrench (FailSafe key) or tamper-resistant bits (required if you get locked out
by the solenoid hood lock)
Screws
The screws used in the workstation are not interchangeable. The screws might have standard or metric
threads and might be of different lengths. If an incorrect screw is used during the reassembly process, it
can damage the unit. HP recommends that all screws removed during disassembly be kept with the part
that was removed, then returned to their proper locations.
70 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT

NOTE Metric screws have a black finish. American National (unified) screws have a silver finish.
NOTE As each subassembly is removed from the workstation, place the subassembly away from the
work area to prevent damage.
If necessary, additional drive guide screws are provided on the system chassis. There are eight Metric
screws located on the chassis near the 5.25-inch optical drive bays. These screws can be used to
mount additional optical drives or an optional diskette drive. There are four American National screws
located on the chassis near the hard drive. These screws can be used to mount additional hard drives in
the 3.5” hard drive cage. For more information about this procedure, see “Installing Hard Drives in the
5.5” slot (Optional)” on page 112.
NOTE The Metric (black) and American National (silver) screws are not interchangeable.
Chapter 4
1
2
1 Metric screws (8)
2 American National screws (4)
Special Handling of Components
The following components require special handling when servicing the workstation.
WARNING! Do not use the front bezel as a handle or lifting point when lifting or moving the workstation.
Lifting the workstation from the front bezel or lifting it incorrectly could cause the unit to fall and cause
harm to the user and damage to the workstation. To properly and safely lift the workstation, lift it from the
bottom of the unit from either the desktop or minitower configuration.
SERVICE CONSIDERATIONS 71

Cables and Connectors
Cables must be handled with care to avoid damage. Apply only the tension required to seat or unseat the
cables during insertion or removal from the connector. Handle cables by the connector whenever
possible. In all cases, avoid bending or twisting the cables, and ensure that the cables are routed in such
a way that they cannot be caught or snagged by parts being removed or replaced.
CAUTION When servicing this workstation, ensure that cables are placed in their proper location during
the reassembly process. Improper cable placement can damage the workstation.
Hard Drives
Handle hard drives as delicate, precision components, avoiding all physical shock and vibration. This
applies to failed drives as well as replacement spares.
If a drive must be mailed, place the drive in a bubble-pack mailer or other suitable protective
packaging and label the package “Fragile: Handle With Care.”
Do not remove hard drives from the shipping package for storage. Keep hard drives in their protective
packaging until they are actually mounted in the workstation.
Avoid dropping drives from any height onto any surface.
If you are inserting or removing a hard drive, turn off the workstation. Do not remove a hard drive
while the workstation is on or in standby mode.
Before handling a drive, ensure that you are discharged of static electricity. While handling a drive,
avoid touching the connector. For more information about preventing electrostatic damage, see
“Electrostatic Discharge Information” on page 68.
Do not use excessive force when inserting a drive.
Avoid exposing a hard drive to liquids, temperature extremes, or products that have magnetic fields,
such as monitors or speakers.
Lithium Coin Cell Battery
The battery that comes with the workstation provides power to the real-time clock and has a minimum
lifetime of about three years.
For instructions on battery removal and replacement procedures, see “Battery” on page 100.
WARNING! This workstation contains a lithium battery. There is a risk of fire and chemical burn if the
battery is handled improperly. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, dispose in
water or fire, or expose it to temperatures higher than 140º F (60º C).
CAUTION Do not dispose of batteries, battery packs, and accumulators together with the general
household waste.
Batterij niet
weggooien,
maar inleveren
als KCA.
72 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT

Pre-Disassembly Procedures
Before servicing the workstation:
1 Remove/disengage any security devices that prohibit opening the workstation.
2 Close any open software applications.
3 Remove any diskette or compact disc from the workstation.
4 Exit the operating system.
5 Turn off the workstation and any peripheral devices that are connected to it.
6 Remove/disengage any security devices that prohibit opening the workstation.
CAUTION Turn off the workstation before disconnecting any cables.
CAUTION The cooling fan is off only when the workstation is turned off or the power cable has been
disconnected. The cooling fan is always on when the workstation is in the “On,” “Standby,” or “Suspend”
modes. You must disconnect the power cord from the power source before opening the workstation to
prevent system board or component damage.
7 Disconnect the power cord from the electrical outlet and then from the workstation.
8 Disconnect all peripheral device cables from the workstation. For more information, see “Electrostatic
Discharge Information” on page 68.
Chapter 4
Removal and Replacement of Components
This section discusses the procedures necessary to remove and install various hardware components
on your workstation. Review the safety and precautions and the “Service Considerations” on page 68, as
well as the
1 Read all safety information and precautions.
2 Locate and clear a suitable work area.
3 Shut down the system and remove power from the unit.
4 Gather your tools.
5 Service your unit.
6 Restore power to your unit.
Safety and Regulatory Guide,
before servicing or upgrading your system.
PRE-DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES 73
Disassembly Order
Use the following table to determine the order in which to remove the major components.
Pre-Disassembly (page 73)
Locks (page 75)
Access (Hood) Panel (page 77)
Access Panel (Hood) Sensor (page 78)
Front Bezel (page 80)
Front Panel I/O Assembly (page 83)
Power Button (page 84)
System Speaker (page 87)
Optical Drive (page 102)
Diskette Drive (page 106)
Bezel Blanks (page 80)
Power Supply (page 85)
System Fan (page 86)
Memory (page 93)
Battery (page 100)
Hard Drive (page 107)
Processor Heatsink (page 88)
Processor (page 91)
System Speaker (page 87)
PCI or PCI Express Cards (page 98)
System Board (page 114)
74 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT

Security Padlock (Optional)
If a security padlock is installed, remove it before servicing the unit. To remove the padlock, unlock it and
slide it out of the padlock loop as shown in the following illustration.
Cable Lock (Optional)
Chapter 4
If a cable lock is installed, remove it before servicing the unit. To remove the cable lock, unlock it and pull
it out of the cable lock slot as shown in the following illustration.
REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENTS 75

Universal Chassis Clamp Lock (Optional)
If a universal chassis clamp lock is installed, remove it before servicing the unit. To remove the noble
lock:
1 Unlock the screw cover from the universal clamp as shown in the following illustration.
2 Unscrew the universal clamp from the unit as shown in the following illustration.
76 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT

Access Panel
Before accessing the internal components of the HP Workstation xw4200, the access panel must be
removed.
To remove the panel:
WARNING! Ensure that the workstation is turned off and that the power cord is disconnected from the
electrical outlet before removing the workstation access panel.
1 Disconnect power from the system (page 73) and, if necessary, unlock the security lock and cable
lock (page 75), and disconnect the universal clamp lock (page 76).
2 Lay the unit in the desktop position as shown in the following illustration.
3 Pull up and out on the cover latch 1 and at the same time slide the cover 2 away from the bezel and
then lift up.
2
1
Chapter 4
To replace the access panel, lay it flat on the unit about one inch from the bezel. The hooks should fall
into the recesses. Then slide the cover towards the bezel until it snaps into place.
REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENTS 77

Access Panel (Hood) Sensor (Optional)
To remove the hood sensor:
1 Disconnect power from the system (page 73) and remove the access panel (page 77).
2 Disconnect the hood sensor 1 from the system board.
3 Slide the hood sensor 2 forward as shown in the following illustration.
CAUTION The hood sensor bracket and the chassis contain sharp edges that present a safety hazard.
Be careful when sliding the hood sensor forward.
4 Pull the hood sensor 3 down and remove it from the chassis.
2
3
To replace the hood sensor, reverse the previous steps.
1
78 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT
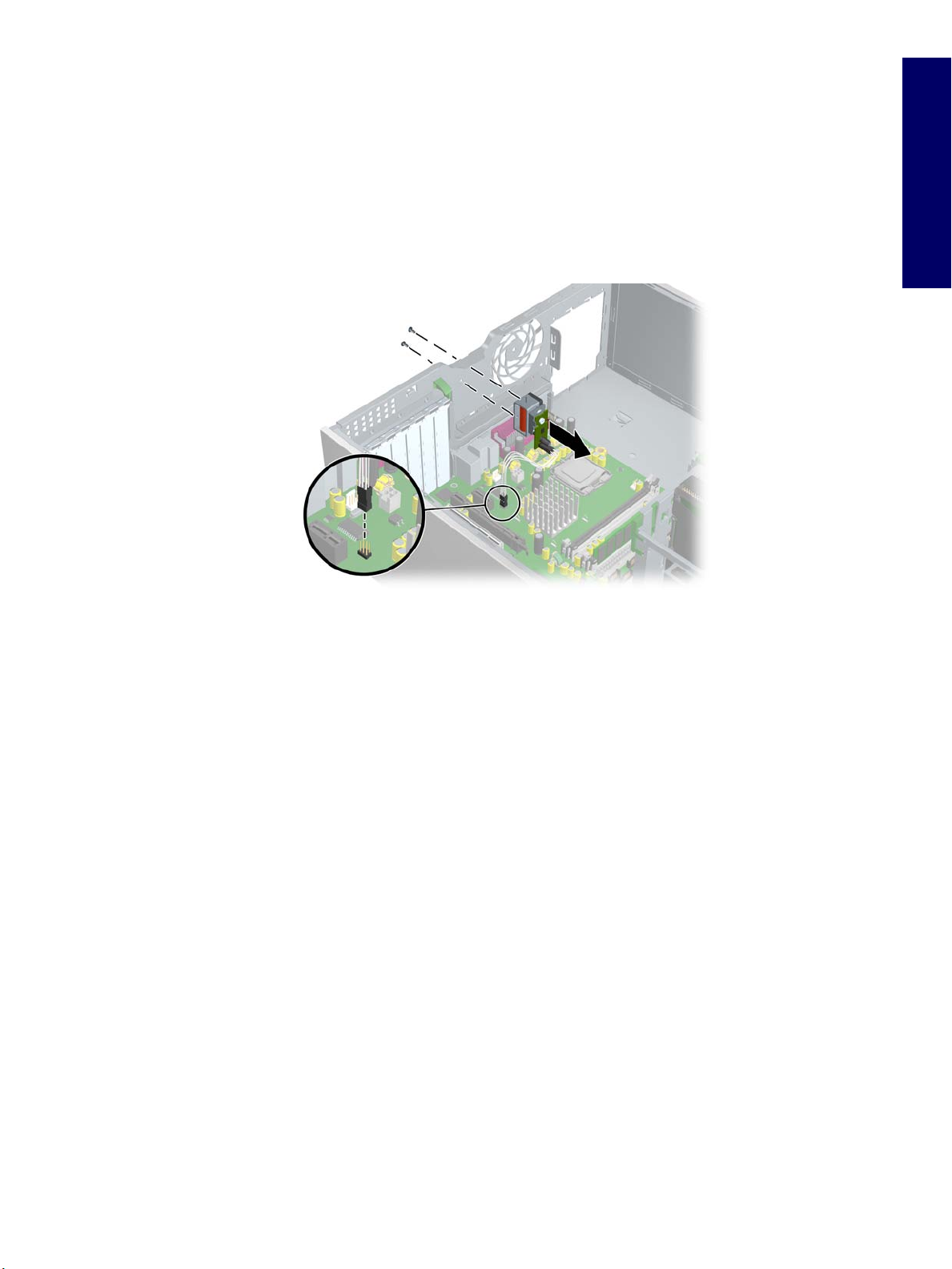
Solenoid Hood (Smart Cover) Lock (Optional)
To remove the solenoid lock:
1 Disconnect power from the system (page 73) and remove the access panel (page 77).
2 Disconnect the access panel lock cable 1 from the system board.
3 Using the FailSafe key, unscrew the two screws 2 from the back of the chassis as shown in the
following diagram.
4 Slide the access panel lock assembly 3 away from the chassis and out of the unit.
2
3
1
To replace the access panel lock assembly, reverse the previous steps.
Chapter 4
REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENTS 79
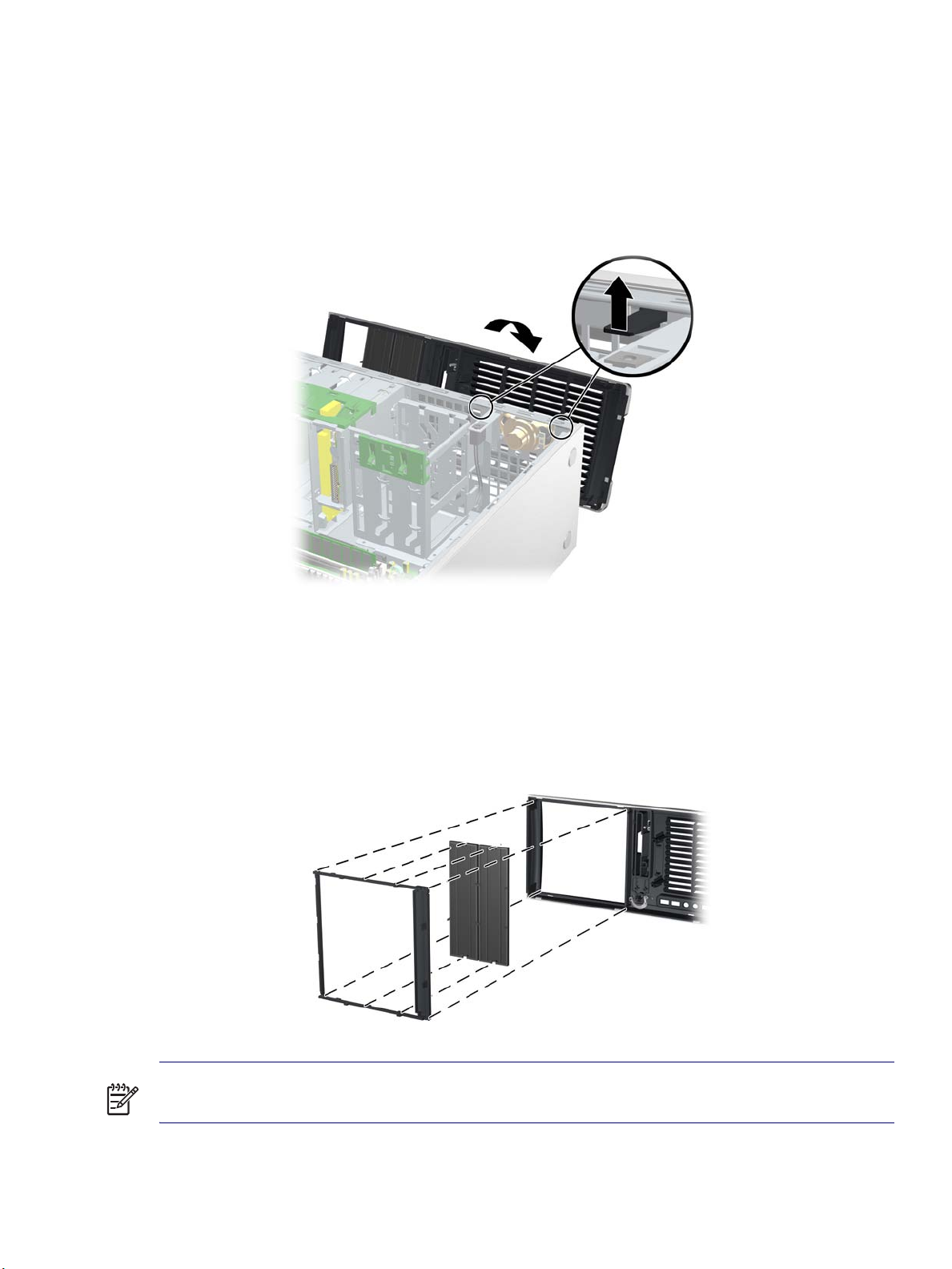
Front Bezel
To remove the bezel:
1 Disconnect power from the system (page 73) and remove the access panel (page 77).
2 Lift up on the two tabs 1 located on the front bezel.
3 Rotate the front bezel 2 away from the chassis as shown in the following illustration and remove the
bezel.
1
2
Bezel Blanks
To remove the bezel blanks:
1 Disconnect power from the system (page 73), and remove the access panel (page 80) and front
bezel. After removing the front bezel, gently pull the subpanel 1, with the bezel blanks secured in it,
away from the front bezel.
2 Remove the desired bezel blank 2 by pulling the blank away from the subpanel.
1
NOTE The bezel blanks are keyed to assist you in replacing the blanks. Also, the subpanel can be
rotated 90 degrees to install the optical drives in desktop orientation, if desired.
2
80 REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT

Chassis Feet
The HP Workstation xw4200 ships in a minitower configuration and chassis feet are installed on the base
of the workstation. The unit ships with additional feet should you convert the unit to a desktop.
To install the chassis feet on a desktop-oriented workstation:
1 Situate the unit into the appropriate position as shown in the following illustration.
2 Place the feet into the embossed areas of the unit.
Chapter 4
REMOVAL AND REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENTS 81
 Loading...
Loading...