Page 1

HP ProLiant Servers
J
Troubleshooting Guide
une 2006 (Fifth Edition)
Part Number 375445-005
Page 2

© Copyright 2004-2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Windows Server 2003 is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Intel and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
June 2006 (Fifth Edition)
Part Number 375445-005
Audience assumptions
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems.
HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards
in products with hazardous energy levels.
Page 3

Contents
Introduction................................................................................................................................ 10
What's new............................................................................................................................................ 10
Revision history ....................................................................................................................................... 10
375445-xx4 (May 2006)...............................................................................................................10
375445-xx3 (September 2005) ...................................................................................................... 10
Getting started............................................................................................................................ 11
Pre-diagnostic steps ................................................................................................................................. 12
Important safety information............................................................................................................ 12
Symptom information ..................................................................................................................... 14
Prepare the server for diagnosis ......................................................................................................14
Common problem resolution ........................................................................................................ 15
Loose connections ...................................................................................................................................15
Service notifications.................................................................................................................................15
Updating firmware .................................................................................................................................. 15
Hard drive guidelines ..............................................................................................................................16
SAS and SATA hard drive guidelines ............................................................................................... 16
SCSI hard drive guidelines ............................................................................................................. 16
Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations ................................................................................................ 16
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations ..............................................................................................17
Diagnostic flowcharts .................................................................................................................. 19
Troubleshooting flowcharts .......................................................................................................................19
Start diagnosis flowchart ................................................................................................................ 20
General diagnosis flowchart ...........................................................................................................20
Power-on problems flowchart .......................................................................................................... 22
POST problems flowchart ...............................................................................................................26
Operating system boot problems flowchart .......................................................................................28
Server fault indications flowchart .....................................................................................................29
Hardware problems .................................................................................................................... 32
Procedures for all ProLiant servers.............................................................................................................. 32
Power problems ...................................................................................................................................... 32
Power source problems ..................................................................................................................32
Power supply problems ..................................................................................................................32
UPS problems ...............................................................................................................................33
General hardware problems.....................................................................................................................33
Problems with new hardware .......................................................................................................... 33
Unknown problem .........................................................................................................................34
Third-party device problems............................................................................................................ 35
Internal system problems ..........................................................................................................................35
CD-ROM and DVD drive problems...................................................................................................35
Diskette drive problems .................................................................................................................. 36
Tape drive problems ...................................................................................................................... 37
Hard drive problems...................................................................................................................... 39
Fan problems................................................................................................................................ 40
Memory problems ......................................................................................................................... 41
PPM problems............................................................................................................................... 42
Processor problems........................................................................................................................42
System open circuits and short circuits........................................................................................................ 43
External device problems.......................................................................................................................... 43
Contents 3
Page 4

Video problems.............................................................................................................................43
Mouse and keyboard problems....................................................................................................... 44
Audio problems............................................................................................................................. 45
Printer problems ............................................................................................................................ 45
Local I/O cable problems...............................................................................................................45
Modem problems ..........................................................................................................................45
Network controller problems ........................................................................................................... 47
Software problems...................................................................................................................... 49
Operating system problems and resolutions ................................................................................................ 49
Operating system problems ............................................................................................................ 49
Operating system updates .............................................................................................................. 50
Restoring to a backed-up version ..................................................................................................... 51
When to Reconfigure or Reload Software .........................................................................................51
Linux operating systems.................................................................................................................. 52
Application software problems.................................................................................................................. 52
Software locks up.......................................................................................................................... 52
Errors occur after a software setting is changed.................................................................................52
Errors occur after the system software is changed ..............................................................................52
Errors occur after an application is installed...................................................................................... 52
Remote ROM flash problems.....................................................................................................................52
General remote ROM flash problems are occurring ........................................................................... 52
Command-line syntax error ............................................................................................................. 53
Access denied on target computer ................................................................................................... 53
Invalid or incorrect command-line parameters....................................................................................53
Network connection fails on remote communication ........................................................................... 53
Failure occurs during ROM flash...................................................................................................... 53
Target system is not supported......................................................................................................... 53
Software tools and solutions......................................................................................................... 54
Configuration tools.................................................................................................................................. 54
Array Configuration Utility.............................................................................................................. 54
SmartStart software........................................................................................................................ 54
SmartStart Scripting Toolkit ............................................................................................................. 55
HP ROM-Based Setup Utility............................................................................................................ 55
Option ROM Configuration for Arrays .............................................................................................57
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack................................................................................... 57
Re-entering the server serial number and product ID........................................................................... 57
Management CD...........................................................................................................................58
Management tools................................................................................................................................... 58
Automatic Server Recovery .............................................................................................................58
ROMPaq utility..............................................................................................................................58
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition II................................................................................................... 58
Integrated Lights-Out technology...................................................................................................... 58
Erase Utility ..................................................................................................................................59
StorageWorks library and tape tools................................................................................................ 59
HP Systems Insight Manager........................................................................................................... 59
Management Agents......................................................................................................................59
HP ProLiant Essentials Virtualization Management Software ................................................................59
HP ProLiant Essentials Server Migration Pack - Physical to ProLiant Edition............................................. 60
HP BladeSystem Essentials Insight Control Data Center Edition ............................................................60
HP Control Tower .......................................................................................................................... 60
System Management homepage......................................................................................................61
USB support.................................................................................................................................. 61
Contents 4
Page 5

Clustering software........................................................................................................................ 61
Diagnostic tools ......................................................................................................................................61
HP Insight Diagnostics....................................................................................................................61
Survey Utility................................................................................................................................. 62
Integrated Management Log ...........................................................................................................62
Array Diagnostic Utility ..................................................................................................................63
Remote support and analysis tools............................................................................................................. 63
HP Instant Support Enterprise Edition................................................................................................63
Web-Based Enterprise Service......................................................................................................... 63
Open Services Event Manager........................................................................................................ 63
Keeping the system current ....................................................................................................................... 63
Drivers .........................................................................................................................................63
Version control.............................................................................................................................. 64
Resource Paqs............................................................................................................................... 64
ProLiant Support Packs ................................................................................................................... 64
Operating system version support.................................................................................................... 64
SoftPaqs....................................................................................................................................... 64
Change control and proactive notification ........................................................................................ 64
Care Pack ....................................................................................................................................65
Firmware maintenance.............................................................................................................................65
Types of ROM............................................................................................................................... 65
Methods for updating firmware ....................................................................................................... 66
Current firmware versions............................................................................................................... 67
Updating firmware ........................................................................................................................67
HP resources for troubleshooting................................................................................................... 69
Online resources..................................................................................................................................... 69
HP website ...................................................................................................................................69
Server documentation .................................................................................................................... 69
Service notifications....................................................................................................................... 69
Subscriber's choice........................................................................................................................69
Natural language search assistant ................................................................................................... 69
Care Pack ....................................................................................................................................69
White papers................................................................................................................................ 70
General server resources..........................................................................................................................70
Additional product information........................................................................................................70
Device driver information................................................................................................................ 70
External cabling information ........................................................................................................... 70
Fault tolerance, security, care and maintenance, configuration and setup .............................................70
Installation and configuration information for the server management system......................................... 70
Installation and configuration information for the server setup software................................................. 70
iLO information .............................................................................................................................70
Key features, option part numbers.................................................................................................... 70
Management of the server .............................................................................................................. 71
Operating system installation and configuration information (for factory-installed operating systems) ........71
Operating system version support.................................................................................................... 71
Overview of server features and installation instructions...................................................................... 71
Power capacity ............................................................................................................................. 71
Registering the server..................................................................................................................... 71
Server configuration information......................................................................................................71
Software installation and configuration of the server .......................................................................... 71
Switch settings, LED functions, drive, memory, expansion board and processor installation instructions, and
board layouts................................................................................................................................ 71
Server and option specifications, symbols, installation warnings, and notices ........................................ 72
Contents 5
Page 6

Teardown procedures, part numbers, specifications ........................................................................... 72
Technical topics............................................................................................................................. 72
Error messages........................................................................................................................... 73
ADU error messages................................................................................................................................73
Introduction to ADU error messages ................................................................................................. 73
Accelerator Board not Detected....................................................................................................... 73
Accelerator Error Log ..................................................................................................................... 73
Accelerator Parity Read Errors: X..................................................................................................... 73
Accelerator Parity Write Errors: X ....................................................................................................74
Accelerator Status: Cache was Automatically Configured During Last Controller Reset............................ 74
Accelerator Status: Data in the Cache was Lost... ..............................................................................74
Accelerator Status: Dirty Data Detected has Reached Limit... ...............................................................74
Accelerator Status: Dirty Data Detected... ......................................................................................... 74
Accelerator Status: Excessive ECC Errors Detected in at Least One Cache Line... ...................................74
Accelerator Status: Excessive ECC Errors Detected in Multiple Cache Lines... ........................................74
Accelerator Status: Obsolete Data Detected ......................................................................................75
Accelerator Status: Obsolete Data was Discarded ............................................................................. 75
Accelerator Status: Obsolete Data was Flushed (Written) to Drives.......................................................75
Accelerator Status: Permanently Disabled .........................................................................................75
Accelerator Status: Possible Data Loss in Cache.................................................................................75
Accelerator Status: Temporarily Disabled.......................................................................................... 75
Accelerator Status: Unrecognized Status...........................................................................................75
Accelerator Status: Valid Data Found at Reset ...................................................................................76
Accelerator Status: Warranty Alert................................................................................................... 76
Adapter/NVRAM ID Mismatch........................................................................................................ 76
Array Accelerator Battery Pack X not Fully Charged........................................................................... 76
Array Accelerator Battery Pack X Below Reference Voltage (Recharging) .............................................. 76
Board in Use by Expand Operation ................................................................................................. 76
Board not Attached........................................................................................................................ 76
Cache Has Been Disabled Because ADG Enabler Dongle is Broken or Missing .....................................76
Cache Has Been Disabled; Likely Caused By a Loose Pin on One of the RAM Chips .............................. 77
Configuration Signature is Zero.......................................................................................................77
Configuration Signature Mismatch................................................................................................... 77
Controller Communication Failure Occurred...................................................................................... 77
Controller Detected. NVRAM Configuration not Present ...................................................................... 77
Controller Firmware Needs Upgrading.............................................................................................77
Controller is Located in Special "Video" Slot ..................................................................................... 77
Controller Is Not Configured........................................................................................................... 77
Controller Reported POST Error. Error Code: X..................................................................................78
Controller Restarted with a Signature of Zero .................................................................................... 78
Disable Command Issued ...............................................................................................................78
Drive (Bay) X Firmware Needs Upgrading ........................................................................................78
Drive (Bay) X has Insufficient Capacity for its Configuration................................................................. 78
Drive (Bay) X has Invalid M&P Stamp...............................................................................................78
Drive (Bay) X Has Loose Cable........................................................................................................78
Drive (Bay) X is a Replacement Drive................................................................................................ 79
Drive (Bay) X is a Replacement Drive Marked OK.............................................................................. 79
Drive (Bay) X is Failed.................................................................................................................... 79
Drive (Bay) X is Undergoing Drive Recovery......................................................................................79
Drive (Bay) X Upload Code Not Readable........................................................................................ 79
Drive (Bay) X Was Inadvertently Replaced ........................................................................................79
Drive Monitoring Features Are Unobtainable..................................................................................... 80
Drive Monitoring is NOT Enabled for SCSI Port X Drive ID Y............................................................... 80
Contents 6
Page 7

Drive Time-Out Occurred on Physical Drive Bay X..............................................................................80
Drive X Indicates Position Y.............................................................................................................80
Duplicate Write Memory Error ........................................................................................................80
Error Occurred Reading RIS Copy from SCSI Port X Drive ID............................................................... 80
FYI: Drive (Bay) X is Third-Party Supplied .......................................................................................... 80
Identify Logical Drive Data did not Match with NVRAM......................................................................81
Insufficient adapter resources .......................................................................................................... 81
Inter-Controller Link Connection Could Not Be Established ..................................................................81
Less Than 75% Batteries at Sufficient Voltage ....................................................................................81
Less Than 75% of Batteries at Sufficient Voltage Battery Pack X Below Reference Voltage........................ 81
Logical Drive X Failed Due to Cache Error ........................................................................................81
Logical Drive X Status = Failed ........................................................................................................81
Logical Drive X Status = Interim Recovery (Volume Functional, but not Fault Tolerant).............................. 82
Logical Drive X Status = Loose Cable Detected... ...............................................................................82
Logical Drive X Status = Overheated ................................................................................................ 82
Logical Drive X Status = Overheating ............................................................................................... 82
Logical Drive X Status = Recovering (rebuilding data on a replaced drive) ............................................ 82
Logical Drive X Status = Wrong Drive Replaced ................................................................................ 83
Loose Cable Detected - Logical Drives May Be Marked FAILED Until Corrected...................................... 83
Mirror Data Miscompare................................................................................................................ 83
No Configuration for Array Accelerator Board.................................................................................. 83
One or More Drives is Unable to Support Redundant Controller Operation ........................................... 83
Other Controller Indicates Different Hardware Model.........................................................................83
Other Controller Indicates Different Firmware Version......................................................................... 84
Other Controller Indicates Different Cache Size.................................................................................84
Processor Reduced Power Mode Enabled in RBSU ............................................................................. 84
Processor Not Started (Processor Stalled).......................................................................................... 84
Processor Not Started (Stepping Does Not Match) ............................................................................. 84
Processor Not Started (Unsupported Processor Stepping) .................................................................... 84
Processor Not Supported (Unsupported Core Speed) .........................................................................84
RIS Copies Between Drives Do Not Match ........................................................................................ 84
SCSI Port X Drive ID Y Failed - REPLACE (failure message) .................................................................. 85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y Firmware Needs Upgrading ..........................................................................85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y Has Exceeded the Following Threshold(s)......................................................... 85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y is not Stamped for Monitoring........................................................................ 85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y May Have a Loose Connection....................................................................... 85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y RIS Copies Within This Drive Do Not Match..................................................... 85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y...S.M.A.R.T. Predictive Failure Errors Have Been Detected in the Factory Monitor and
Performance Data.......................................................................................................................... 85
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y...S.M.A.R.T. Predictive Failure Errors Have Been Detected in the Power Monitor and
Performance Data.......................................................................................................................... 86
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y Was Replaced On a Good Volume: (failure message)....................................... 86
Set Configuration Command Issued .................................................................................................86
Soft firmware upgrade required....................................................................................................... 86
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X has a Cabling Error (Bus Disabled)... ................................................86
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated a Door Alert.....................................................................86
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated a Power Supply Failure...................................................... 86
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated an Overheated Condition... ...............................................87
Storage enclosure on SCSI Bus X is unsupported with its current firmware version... ............................... 87
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated that the Fan Failed... ......................................................... 87
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated that the Fan is Degraded... ................................................87
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated that the Fan Module is Unplugged... ...................................87
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X - Wide SCSI Transfer Failed............................................................. 87
Swapped cables or configuration error detected. A configured array of drives...................................... 88
Contents 7
Page 8

Swapped Cables or Configuration Error Detected. A Drive Rearrangement........................................... 88
Swapped Cables or Configuration Error Detected. An Unsupported Drive Arrangement Was Attempted... 88
Swapped cables or configuration error detected. The cables appear to be interchanged... .....................88
Swapped cables or configuration error detected. The configuration information on the attached drives... .89
Swapped Cables or Configuration Error Detected. The Maximum Logical Volume Count X...................... 89
System Board is Unable to Identify which Slots the Controllers are in.................................................... 89
The Redundant Controllers Installed are not the Same Model...............................................................89
This Controller Can See the Drives but the Other Controller Can't ........................................................90
This Controller Can't See the Drives but the Other Controller Can ........................................................90
Unable to Communicate with Drive on SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y ............................................................ 90
Unable to Retrieve Identify Controller Data. Controller May be Disabled or Failed ................................. 90
Unknown Disable Code.................................................................................................................. 90
Unrecoverable Read Error ..............................................................................................................90
Unsupported Processor Configuration (Processor Required in Slot #1) .................................................. 91
Warning Bit Detected..................................................................................................................... 91
WARNING - Drive Write Cache is Enabled on X............................................................................... 91
WARNING - Mixed Feature Processors Were Detected...................................................................... 91
WARNING - Resetting Corrupted CMOS ......................................................................................... 91
WARNING - Resetting Corrupted NVRAM........................................................................................ 91
WARNING - Resetting Corrupted System Environment........................................................................ 91
WARNING - Restoring Default Configurations as Requested ...............................................................91
WARNING: Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated it is Operating in Single Ended Mode... ............92
Write Memory Error....................................................................................................................... 92
Wrong Accelerator........................................................................................................................92
POST error messages and beep codes....................................................................................................... 92
Introduction to POST error messages................................................................................................ 92
Non-numeric messages or beeps only ..............................................................................................93
100 Series ................................................................................................................................. 101
200 Series ................................................................................................................................. 103
300 Series ................................................................................................................................. 106
400 Series ................................................................................................................................. 107
600 Series ................................................................................................................................. 108
1100 Series ............................................................................................................................... 109
1600 Series ............................................................................................................................... 109
1700 Series ............................................................................................................................... 112
Event list error messages ........................................................................................................................124
Introduction to event list error messages..........................................................................................124
A CPU Power Module (System Board, Socket X)... ........................................................................... 124
ASR Lockup Detected: Cause ........................................................................................................124
Automatic operating system shutdown initiated due to fan failure.......................................................125
Automatic Operating System Shutdown Initiated Due to Overheat Condition....................................... 125
Blue Screen Trap: Cause [NT]... .................................................................................................... 125
Corrected Memory Error Threshold Passed (Slot X, Memory Module Y)...............................................125
EISA Expansion Bus Master Timeout (Slot X).................................................................................... 125
PCI Bus Error (Slot X, Bus Y, Device Z, Function X) ...........................................................................125
Processor Correctable Error Threshold Passed (Slot X, Socket Y)......................................................... 125
Processor Uncorrectable Internal Error (Slot X, Socket Y)................................................................... 125
Real-Time Clock Battery Failing...................................................................................................... 126
System AC Power Overload (Power Supply X).................................................................................126
System AC Power Problem (Power Supply X)...................................................................................126
System Fan Failure (Fan X, Location) ..............................................................................................126
System Fans Not Redundant.......................................................................................................... 126
System Overheating (Zone X, Location) ..........................................................................................126
System Power Supplies Not Redundant........................................................................................... 126
Contents 8
Page 9

System Power Supply Failure (Power Supply X)................................................................................ 126
Unrecoverable Host Bus Data Parity Error... .................................................................................... 126
Uncorrectable Memory Error (Slot X, Memory Module Y).................................................................. 127
HP BladeSystem infrastructure error codes ................................................................................................ 127
Server blade management module error codes................................................................................127
Power management module error codes......................................................................................... 130
Port 85 codes and iLO messages ............................................................................................................131
Troubleshooting the system using port 85 codes ..............................................................................131
Processor-related port 85 codes..................................................................................................... 131
Memory-related port 85 codes ...................................................................................................... 132
Expansion board-related port 85 codes.......................................................................................... 133
Miscellaneous port 85 codes ........................................................................................................ 133
Windows® Event Log processor error codes............................................................................................. 134
Message ID: 4137 ......................................................................................................................134
Message ID: 4140 ......................................................................................................................134
Message ID: 4141 ......................................................................................................................134
Message ID: 4169 ......................................................................................................................134
Message ID: 4190 ......................................................................................................................134
Insight Diagnostics processor error codes .................................................................................................135
MSG_CPU_RR_1......................................................................................................................... 135
MSG_CPU_RR_2......................................................................................................................... 135
MSG_CPU_RR_3......................................................................................................................... 135
MSG_CPU_RR_5......................................................................................................................... 135
MSG_CPU_RR_6......................................................................................................................... 135
MSG_CPU_RR_7......................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_8......................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_9......................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_10....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_11....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_12....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_13....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_14....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_15....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_16....................................................................................................................... 136
MSG_CPU_RR_17....................................................................................................................... 137
Contacting HP.......................................................................................................................... 138
Contacting HP technical support or an authorized reseller ..........................................................................138
Customer self repair............................................................................................................................... 138
Server information you need................................................................................................................... 139
Operating system information you need ................................................................................................... 139
Microsoft operating systems.......................................................................................................... 139
Linux operating systems................................................................................................................ 140
Novell NetWare operating systems ............................................................................................... 141
SCO operating systems ................................................................................................................ 141
IBM OS/2 operating systems........................................................................................................ 142
Sun Solaris operating systems .......................................................................................................142
Acronyms and abbreviations...................................................................................................... 144
Index....................................................................................................................................... 148
Contents 9
Page 10

Introduction
In this section
What's new........................................................................................................................................... 10
Revision history ...................................................................................................................................... 10
What's new
The fifth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx5, includes the
following additions:
• c-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart (on page 25)
• c-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 28)
• c-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 31)
• Windows® Event Log processor error codes (on page 134)
• Insight Diagnostics processor error codes (on page 135)
Revision history
375445-xx4 (May 2006)
The fourth edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx4, included
the following additions:
• Hot-plug SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations (on page 17)
• Operating system issues with Intel® dual-core processors (Hyper-Threading enabled) (on page 50)
• Tape drive problems (on page 37)
• New error messages in ADU error messages (on page 73) and POST error messages and beep
codes (on page 92)
375445-xx3 (September 2005)
The third edition of the HP ProLiant Servers Troubleshooting Guide, part number 375445-xx3, included
the following changes:
• Updated SCSI hard drive guidelines
• Added hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations (on page 16)
• Updated diagnostic flowcharts (on page 19)
• Added operating system problems (on page 49)
• Added Port 85 codes and iLO messages (on page 131)
• Added new error messages to ADU error messages and POST error messages and beep codes
Introduction 10
Page 11

•
Updated contacting HP:
• Contacting HP technical support or an authorized reseller
• Server information you need
Getting started
NOTE: For common troubleshooting procedures, the term "server" is used to mean servers and server
blades.
This guide provides common procedures and solutions for the many levels of troubleshooting a ProLiant
server—from the most basic connector issues to complex software configuration problems.
To understand the sections of this guide and to identify the best starting point for a problem, use the
following descriptions:
• Common problem resolution (on page 15)
Many server problems are caused by loose connections (on page 15), outdated firmware
("Updating firmware" on page 15), and other issues. Use this section to perform basic
troubleshooting for common problems.
• Problem diagnosis
When a server exhibits symptoms that do not immediately pinpoint the problem, use this section to
begin troubleshooting. The section contains a series of flowcharts that provide a common
troubleshooting process for troubleshooting ProLiant servers. The flowcharts identify a diagnostic tool
or a process to solve the problem.
• Hardware problems (on page 32)
When the symptoms point to a specific component, use this section to find solutions for problems
with power, general components, system boards, system open circuits and short circuits, and
external devices.
• Software problems (on page 49)
When you have a known, specific software problem, use this section to identify a solution to the
problem.
• Software tools and solutions (on page 54)
Use this section as a reference for software tools and utilities.
• HP resources for troubleshooting (on page 69)
When additional information becomes necessary, use this section to identify websites and
supplemental documents that contain troubleshooting information.
• Error messages
Use this section to locate a complete list of ADU error messages (on page 73), POST error messages
and beep codes (on page 92), event list error messages (on page 124), HP BladeSystem
infrastructure error codes (on page 127), and Port 85 codes and iLO messages (on page 131).
Getting started 11
Page 12
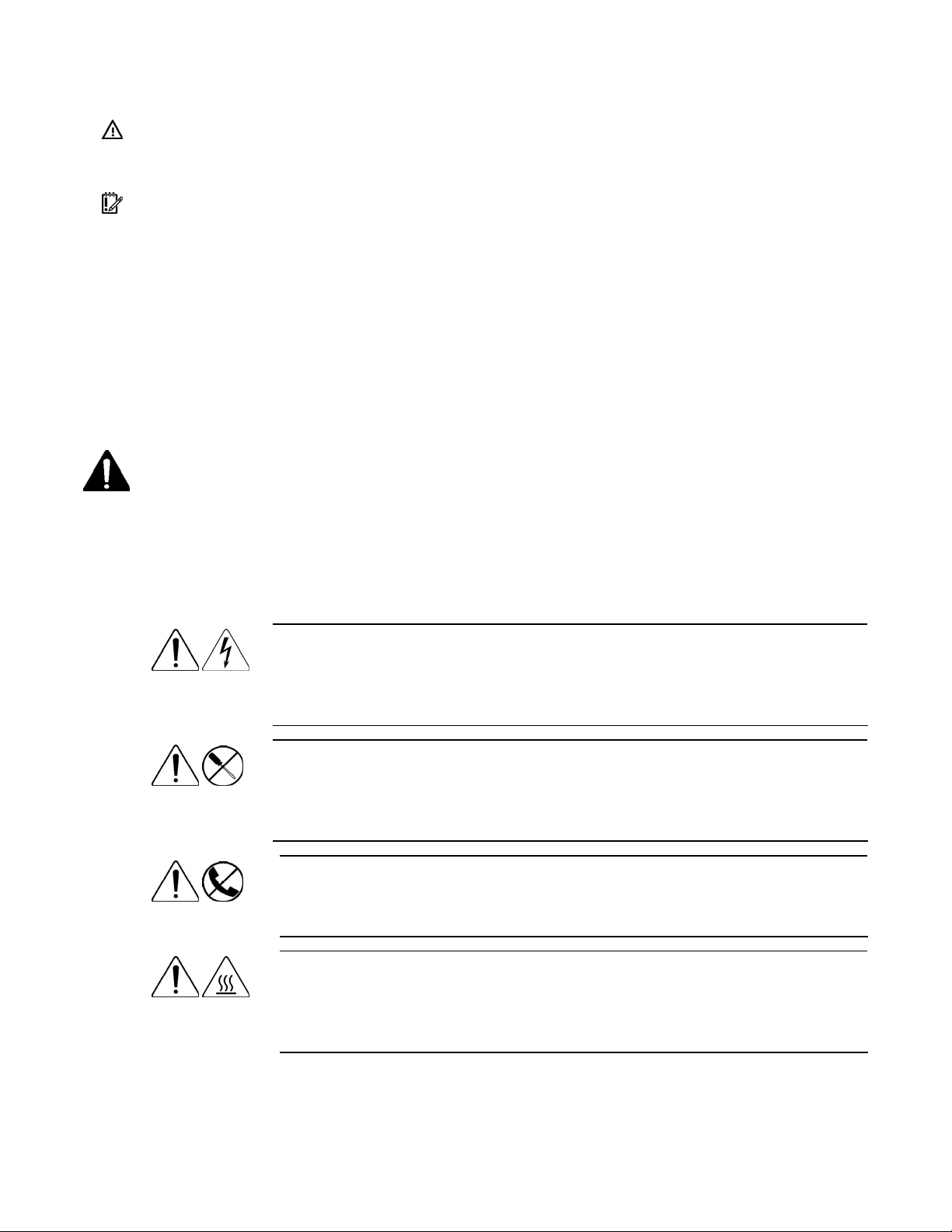
Pre-diagnostic steps
WARNING: To avoid potential problems, ALWAYS read the warnings and cautionary
information in the server documentation before removing, replacing, reseating, or
modifying system components.
IMPORTANT: This guide provides information for multiple servers. Some information may not apply to the
server you are troubleshooting. Refer to the server documentation for information on procedures, hardware
options, software tools, and operating systems supported by the server.
1. Review the important safety information (on page 12).
2. Gather symptom information (on page 14).
3. Prepare the server for diagnosis.
Important safety information
4. Use the Start diagnosis flowchart (on page 20) to begin the diagnostic process.
Familiarize yourself with the safety information in the following sections before troubleshooting the server.
Important safety information
Before servicing this product, read the Important Safety Information document provided with the server.
Symbols on equipment
The following symbols may be placed on equipment to indicate the presence of potentially hazardous
conditions.
This symbol indicates the presence of hazardous energy circuits or electric shock
hazards. Refer all servicing to qualified personnel.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from electric shock hazards, do not open
this enclosure. Refer all maintenance, upgrades, and servicing to qualified personnel.
This symbol indicates the presence of electric shock hazards. The area contains no
user or field serviceable parts. Do not open for any reason.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from electric shock hazards, do not open
this enclosure.
This symbol on an RJ-45 receptacle indicates a network interface connection.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electric shock, fire, or damage to the equipment,
do not plug telephone or telecommunications connectors into this receptacle.
This symbol indicates the presence of a hot surface or hot component. If this surface is
contacted, the potential for injury exists.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from a hot component, allow the surface to
cool before touching.
Getting started 12
Page 13
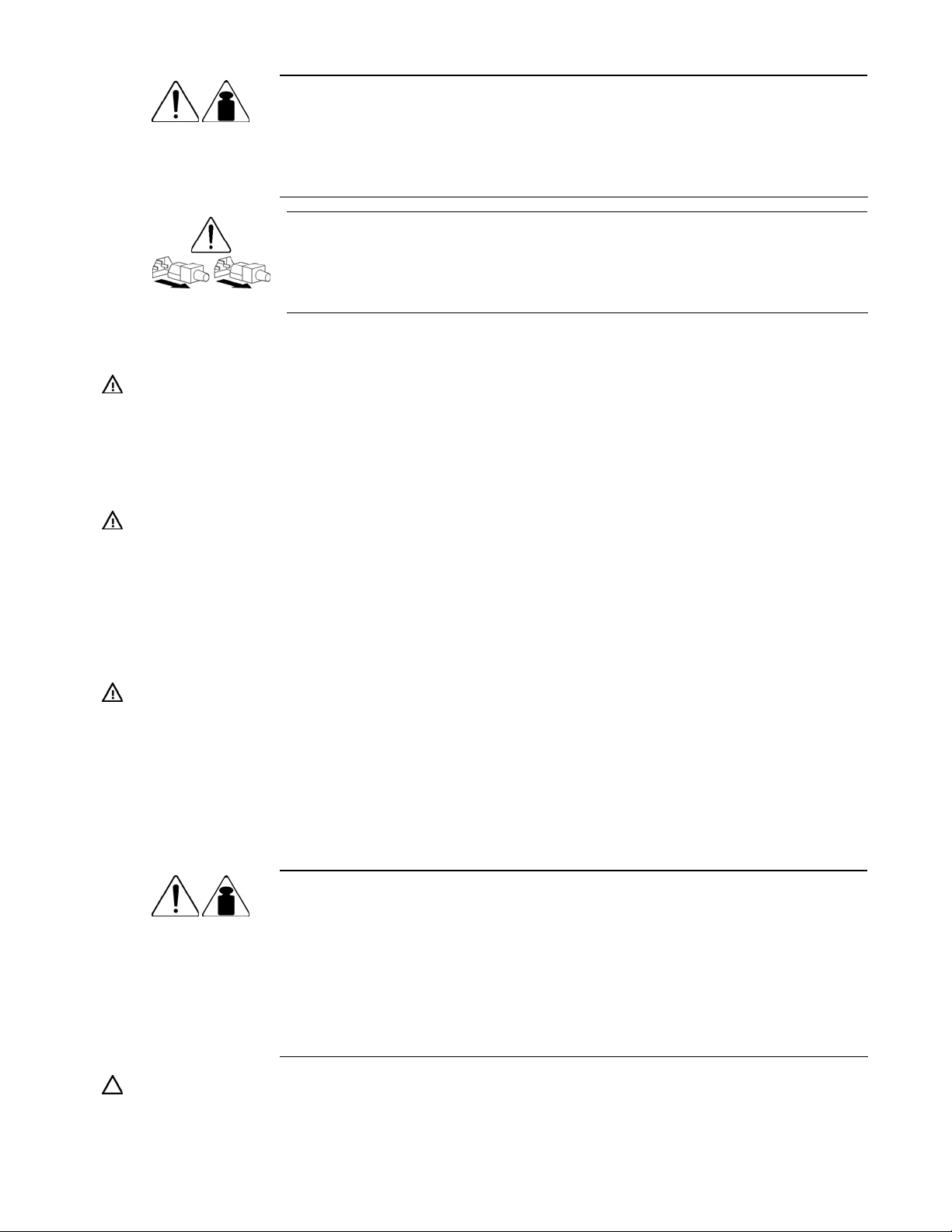
This symbol indicates that the component exceeds the recommended weight for one
weight in kg
weight in lb
individual to handle safely.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment,
observe local occupational health and safety requirements and guidelines for manual
material handling.
These symbols, on power supplies or systems, indicate that the equipment is supplied
by multiple sources of power.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of injury from electric shock, remove all power
cords to completely disconnect power from the system.
Warnings and cautions
WARNING: Only authorized technicians trained by HP should attempt to repair this
equipment. All troubleshooting and repair procedures are detailed to allow only
subassembly/module-level repair. Because of the complexity of the individual boards
and subassemblies, no one should attempt to make repairs at the component level or to
make modifications to any printed wiring board. Improper repairs can create a safety
hazard.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment, be sure
that:
• The leveling feet are extended to the floor.
• The full weight of the rack rests on the leveling feet.
• The stabilizing feet are attached to the rack if it is a single-rack installation.
• The racks are coupled together in multiple-rack installations.
• Only one component is extended at a time. A rack may become unstable if more than
one component is extended for any reason.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to the equipment:
• Do not disable the power cord grounding plug. The grounding plug is an important
safety feature.
• Plug the power cord into a grounded (earthed) electrical outlet that is easily
accessible at all times.
• Unplug the power cord from the power supply to disconnect power to the equipment.
• Do not route the power cord where it can be walked on or pinched by items placed
against it. Pay particular attention to the plug, electrical outlet, and the point where
the cord extends from the server.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury or damage to the equipment:
weight in kg
weight in lb
• Observe local occupation health and safety requirements and guidelines for
manual handling.
• Obtain adequate assistance to lift and stabilize the chassis during installation or
removal.
• The server is unstable when not fastened to the rails.
• When mounting the server in a rack, remove the power supplies and any other
removable module to reduce the overall weight of the product.
CAUTION: To properly ventilate the system, you must provide at least 7.6 cm (3.0 in) of clearance at the
front and back of the server.
Getting started 13
Page 14

CAUTION: The server is designed to be electrically grounded (earthed). To ensure proper operation, plug
the AC power cord into a properly grounded AC outlet only.
Symptom information
Before troubleshooting a server problem, collect the following information:
• What events preceded the failure? After which steps does the problem occur?
• What has been changed since the time the server was working?
• Did you recently add or remove hardware or software? If so, did you remember to change the
appropriate settings in the server setup utility, if necessary?
• How long has the server exhibited problem symptoms?
• If the problem occurs randomly, what is the duration or frequency?
To answer these questions, the following information may be useful:
• Run HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 61) and use the survey page to view the current configuration
or to compare it to previous configurations.
• Refer to your hardware and software records for information.
• Refer to server LEDs and their statuses.
Prepare the server for diagnosis
1. Be sure the server is in the proper operating environment with adequate power, air conditioning,
and humidity control. Refer to the server documentation for required environmental conditions.
2. Record any error messages displayed by the system.
3. Remove all diskettes and CDs from the media drives.
4. Power down the server and peripheral devices if you will be diagnosing the server offline. Always
perform an orderly shutdown, if possible. This means you must:
a. Exit any applications.
b. Exit the operating system.
c. Power down the server.
5. Disconnect any peripheral devices not required for testing (any devices not necessary to power up
the server). Do not disconnect the printer if you want to use it to print error messages.
6. Collect all tools and utilities, such as a Torx screwdriver, loopback adapters, ESD wrist strap, and
software utilities, necessary to troubleshoot the problem.
• You must have the appropriate Health Drivers and Management Agents installed on the server.
NOTE: To verify the server configuration, connect to the System Management homepage (on page 61) and
select Version Control Agent. The VCA gives you a list of names and versions of all installed HP drivers,
Management Agents, and utilities, and whether they are up to date.
• HP recommends you have access to the server documentation for server-specific information.
• HP recommends you have access to the SmartStart CD for value-added software and drivers
required during the troubleshooting process.
NOTE: Download the current version of SmartStart from the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
).
Getting started 14
Page 15

Common problem resolution
In this section
Loose connections .................................................................................................................................. 15
Service notifications................................................................................................................................ 15
Updating firmware ................................................................................................................................. 15
Hard drive guidelines ............................................................................................................................. 16
Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations............................................................................................... 16
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations............................................................................................. 17
Loose connections
Action:
• Be sure all power cords are securely connected.
• Be sure all cables are properly aligned and securely connected for all external and internal
components.
• Remove and check all data and power cables for damage. Be sure no cables have bent pins or
damaged connectors.
• If a fixed cable tray is available for the server, be sure the cords and cables connected to the server
are correctly routed through the tray.
• Be sure each device is properly seated.
• If a device has latches, be sure they are completely closed and locked.
• Check any interlock or interconnect LEDs that may indicate a component is not connected properly.
• If problems continue to occur, remove and reinstall each device, checking the connectors and sockets
for bent pins or other damage.
Service notifications
To view the latest service notifications, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport).
Select the appropriate server model, and then click the Troubleshoot a Problem link on the product
page.
Updating firmware
To update the system ROM or option firmware, use HP Smart Components. These components are
available on the Firmware Maintenance CD and the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
recent version of a particular server or option firmware is available on the following:
• HP Support website (http://www.hp.com/support)
• HP ROM-BIOS/Firmware Updates website
(http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/romflash.html
). The most
)
Common problem resolution 15
Page 16
Components for option firmware updates are also available from the HP Storage Products Software and
Drivers website (http://www.hp.com/support/proliantstorage
1. Find the most recent version of the component that you require. Components for controller firmware
updates are available in offline and online formats.
2. Follow the instructions for installing the component on the server. These instructions are included with
the CD and on the component website.
3. Follow the additional instructions that describe how to use the component to flash the ROM. These
instructions are provided with each component.
View additional documentation on updating firmware, such as the Regular Firmware Updates Essential for
Optimal Performance and Functionality of HP ProLiant Servers white paper, on the HP ROMBIOS/Firmware Updates website (http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/romflash.html
Hard drive guidelines
SAS and SATA hard drive guidelines
When adding hard drives to the server, observe the following general guidelines:
• The system automatically sets all drive numbers.
• If only one hard drive is used, install it in the bay with the lowest drive number.
• Drives must be the same capacity to provide the greatest storage space efficiency when drives are
grouped together into the same drive array.
).
).
NOTE: ACU does not support mixing SAS and SATA drives in the same logical volume.
SCSI hard drive guidelines
• Each SCSI drive must have a unique ID.
• The system automatically sets all SCSI IDs.
• If only one SCSI hard drive is used, install it in the bay with the lowest number.
• Drives must be the same capacity to provide the greatest storage space efficiency when drives are
grouped together into the same drive array.
Hot-plug SCSI hard drive LED combinations
Activity
LED (1)
On, off, or
flashing
On, off, or
flashing
On or
flashing
Online LED
(2)
On or off Flashing A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive.
On Off The drive is online and is configured as part of an array.
Flashing Off
Fault LED
(3)
Interpretation
Replace the drive as soon as possible.
If the array is configured for fault tolerance and all other drives in the
array are online, and a predictive failure alert is received or a drive
capacity upgrade is in progress, you may replace the drive online.
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may
terminate the current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is rebuilding or undergoing capacity expansion.
Common problem resolution 16
Page 17
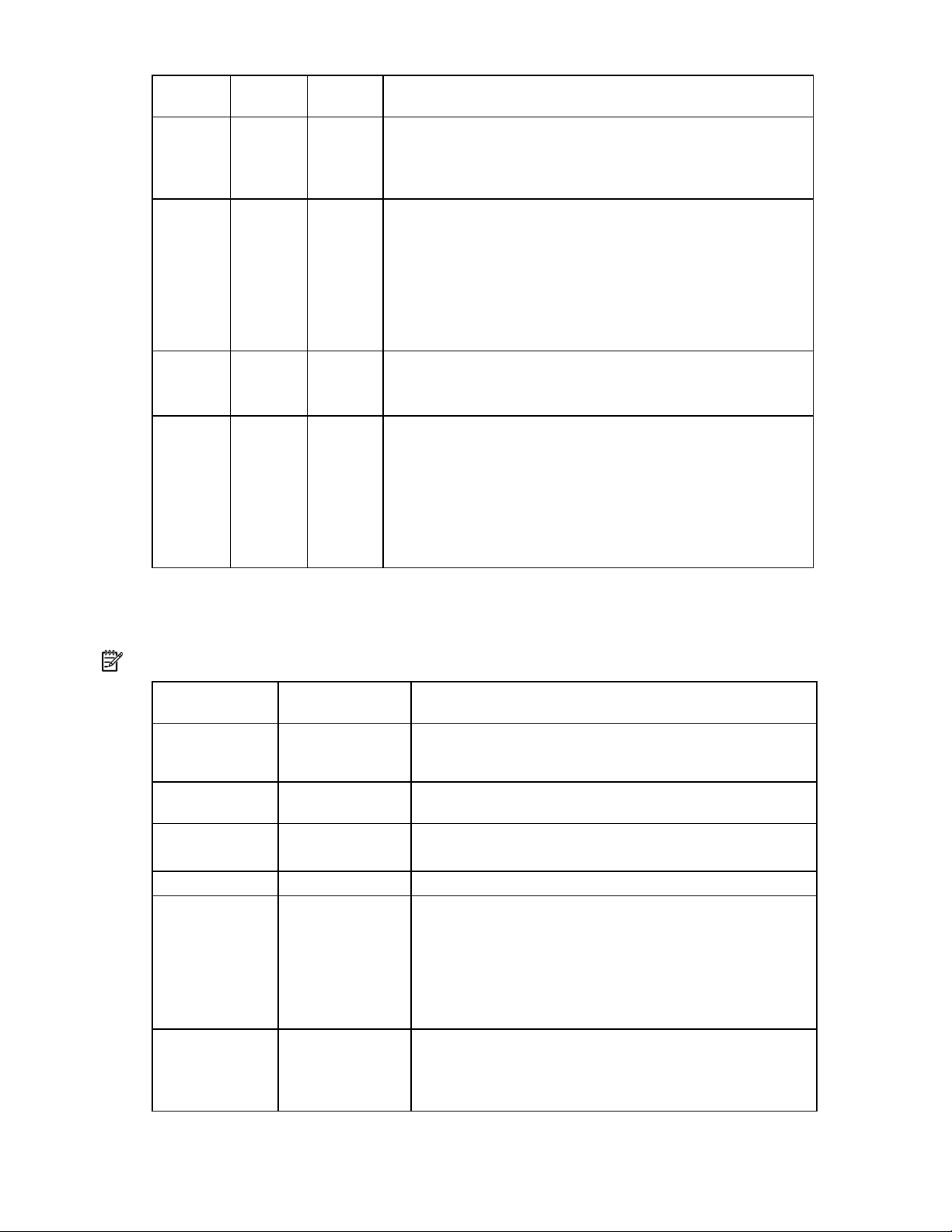
Activity
LED (1)
Online LED
(2)
Fault LED
(3)
Interpretation
On Off Off Do not remove the drive.
The drive is being accessed, but (1) it is not configured as part of an
array; (2) it is a replacement drive and rebuild has not yet started; or
(3) it is spinning up during the POST sequence.
Flashing Flashing Flashing
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may cause
data loss in non-fault-tolerant configurations.
One or more of the following conditions may exist:
• The drive is part of an array being selected by an array
configuration utility
• Drive Identification has been selected in HP SIM
• The drive firmware is being updated
Off Off On
The drive has been placed offline due to hard disk drive failure or
subsystem communication failure.
You may need to replace the drive.
Off Off Off One or more of the following conditions may exist:
• The drive is not configured as part of an array
• The drive is configured as part of an array, but it is a
replacement drive that is not being accessed or being rebuilt yet
• The drive is configured as an online spare
If the drive is connected to an array controller, you may replace the
drive online.
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations
NOTE: Predictive failure alerts can occur only when the server is connected to a Smart Array controller.
Online/activity LED
(green)
On, off, or flashing
On, off, or flashing Steadily blue
On
On Off The drive is online, but it is not active currently.
Flashing regularly
(1 Hz)
Flashing regularly
(1 Hz)
Fault/UID LED
(amber/blue)
Alternating amber
and blue
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off
Interpretation
The drive has failed, or a predictive failure alert has been
received for this drive; it also has been selected by a
management application.
The drive is operating normally, and it has been selected by a
management application.
A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive.
Replace the drive as soon as possible.
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may
terminate the current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is part of an array that is undergoing capacity
expansion or stripe migration, but a predictive failure alert has
been received for this drive. To minimize the risk of data loss, do
not replace the drive until the expansion or migration is
complete.
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may
terminate the current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is rebuilding, or it is part of an array that is undergoing
capacity expansion or stripe migration.
Common problem resolution 17
Page 18
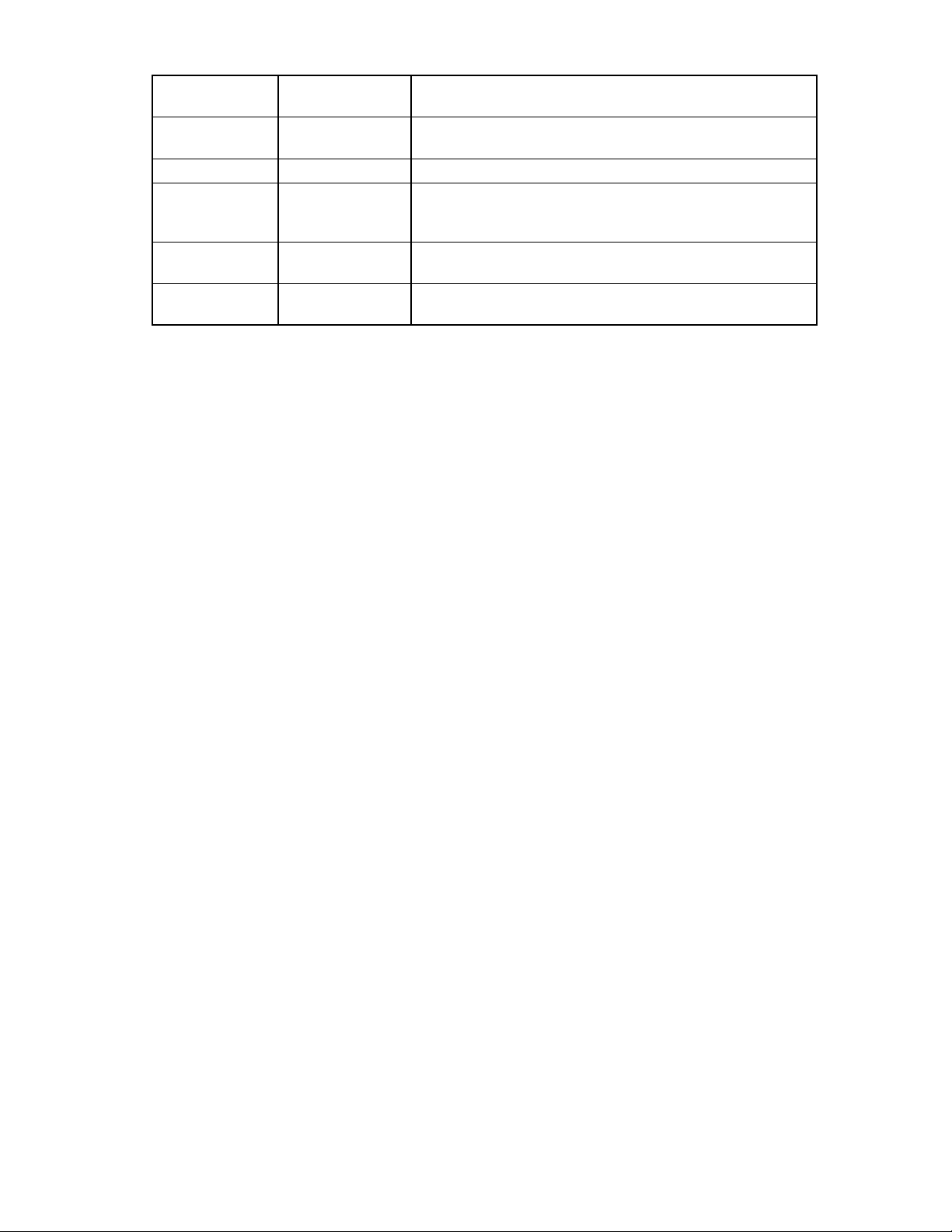
Online/activity LED
(green)
Flashing irregularly
Fault/UID LED
(amber/blue)
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Interpretation
The drive is active, but a predictive failure alert has been
received for this drive. Replace the drive as soon as possible.
Flashing irregularly Off The drive is active, and it is operating normally.
Off Steadily amber
A critical fault condition has been identified for this drive, and
the controller has placed it offline. Replace the drive as soon as
possible.
Off
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off Off
A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive.
Replace the drive as soon as possible.
The drive is offline, a spare, or not configured as part of an
array.
Common problem resolution 18
Page 19

Diagnostic flowcharts
In this section
Troubleshooting flowcharts ...................................................................................................................... 19
Troubleshooting flowcharts
To effectively troubleshoot a problem, HP recommends that you start with the first flowchart in this section,
"Start diagnosis flowchart (on page 20)," and follow the appropriate diagnostic path. If the other
flowcharts do not provide a troubleshooting solution, follow the diagnostic steps in "General diagnosis
flowchart (on page 20)." The General diagnosis flowchart is a generic troubleshooting process to be used
when the problem is not server-specific or is not easily categorized into the other flowcharts.
The available flowcharts include:
• Start diagnosis flowchart (on page 20)
• General diagnosis flowchart (on page 20)
• Power-on problems
• Server power-on problems flowchart (on page 22)
• p-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart (on page 23)
• c-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart (on page 25)
• POST problems flowchart (on page 26)
• Server and p-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 27)
• c-Class server blade POST problems flowchart (on page 28)
• Operating system boot problems flowchart (on page 28)
• Server fault indications flowchart (on page 29)
• Server and p-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 30)
• c-Class server blade fault indications flowchart (on page 31)
Diagnostic flowcharts 19
Page 20
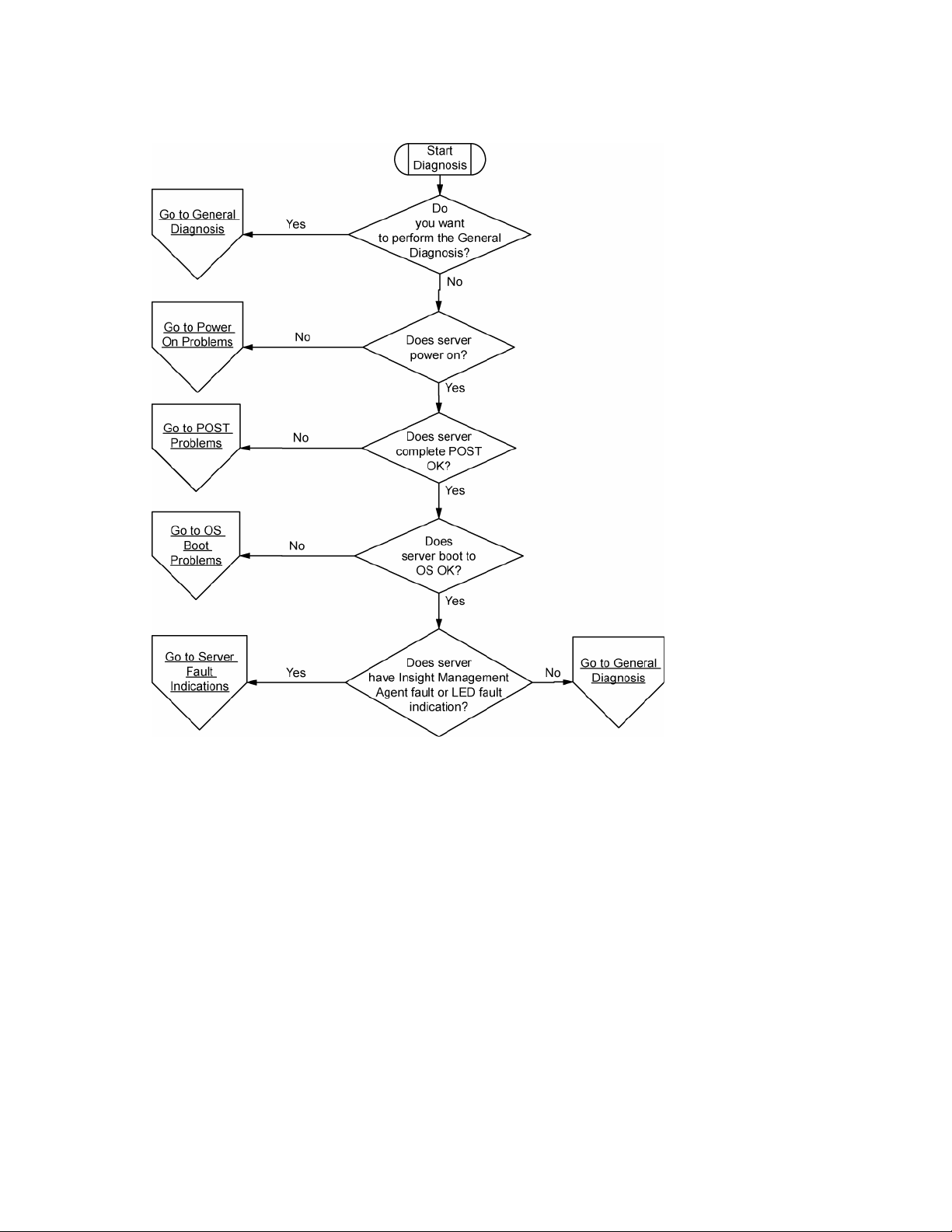
Start diagnosis flowchart
Use the following flowchart to start the diagnostic process.
General diagnosis flowchart
Diagnostic flowcharts 20
Page 21
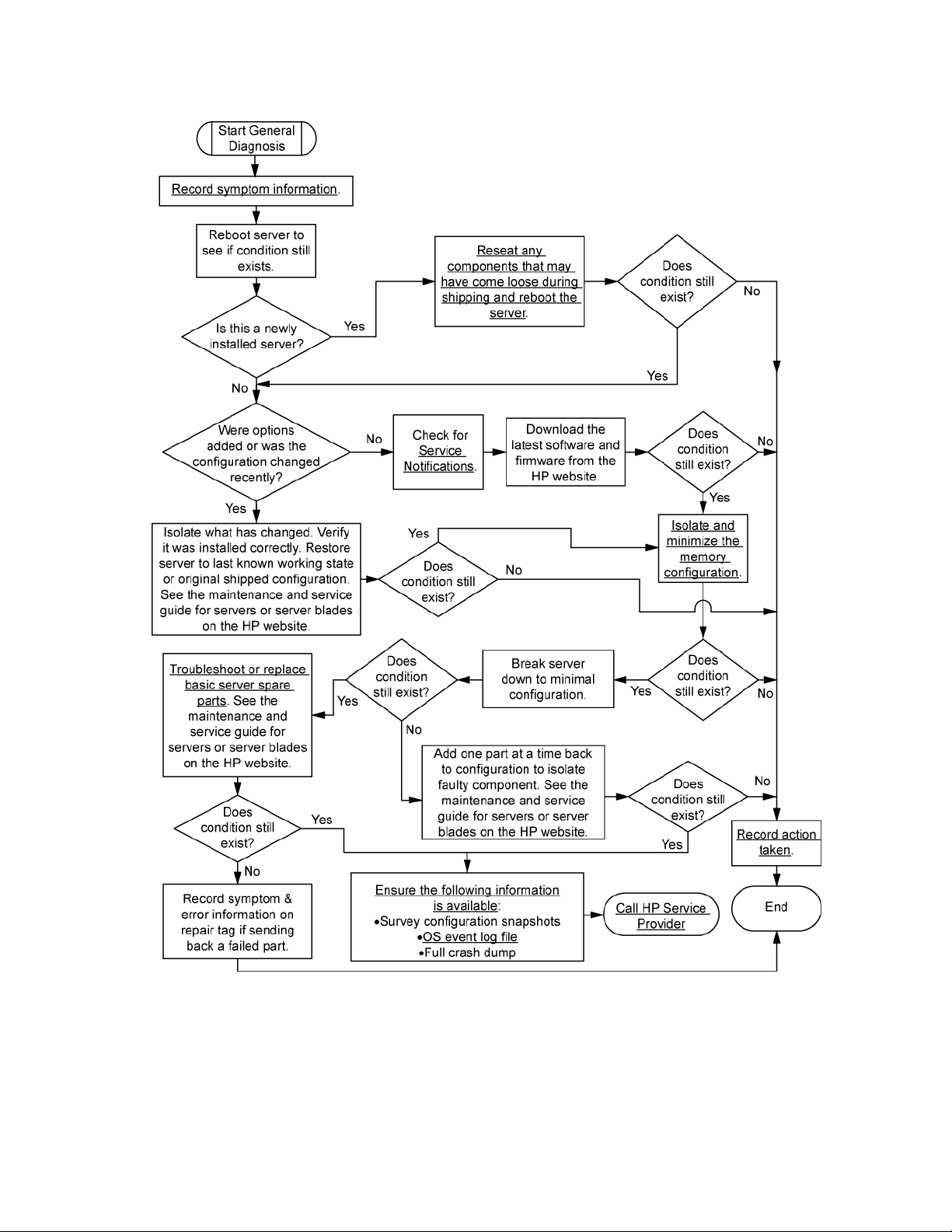
The General diagnosis flowchart provides a generic approach to troubleshooting. If you are unsure of the
problem, or if the other flowcharts do not fix the problem, use the following flowchart.
Diagnostic flowcharts 21
Page 22

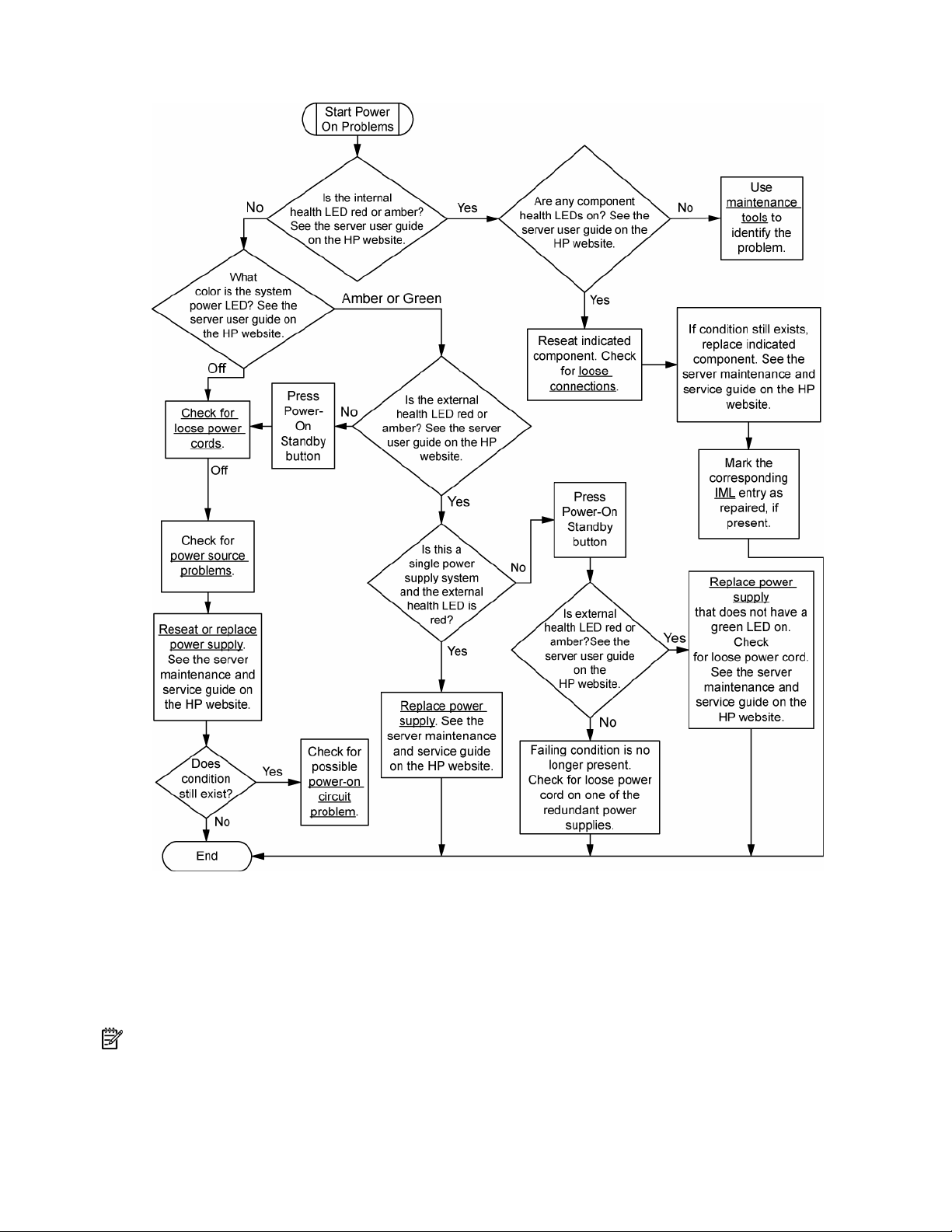
Power-on problems flowchart
Server power-on problems flowchart
Symptoms:
• The server does not power on.
• The system power LED is off or amber.
• The external health LED is red or amber.
• The internal health LED is red or amber.
NOTE: For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses, refer to the server documentation.
Possible causes:
• Improperly seated or faulty power supply
• Loose or faulty power cord
• Power source problem
• Power-on circuit problem
• Improperly seated component or interlock problem
• Faulty internal component
Diagnostic flowcharts 22
Page 23
p-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart
Symptoms:
• The server does not power on.
• The system power LED is off or amber.
• The health LED is red or amber.
NOTE: For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses, refer to the server documentation.
Possible causes:
• Improperly seated or faulty power supply
Diagnostic flowcharts 23
Page 24
•
Loose or faulty power cord
• Power source problem
• Power-on circuit problem
• Improperly seated component or interlock problem
• Faulty internal component
Diagnostic flowcharts 24
Page 25
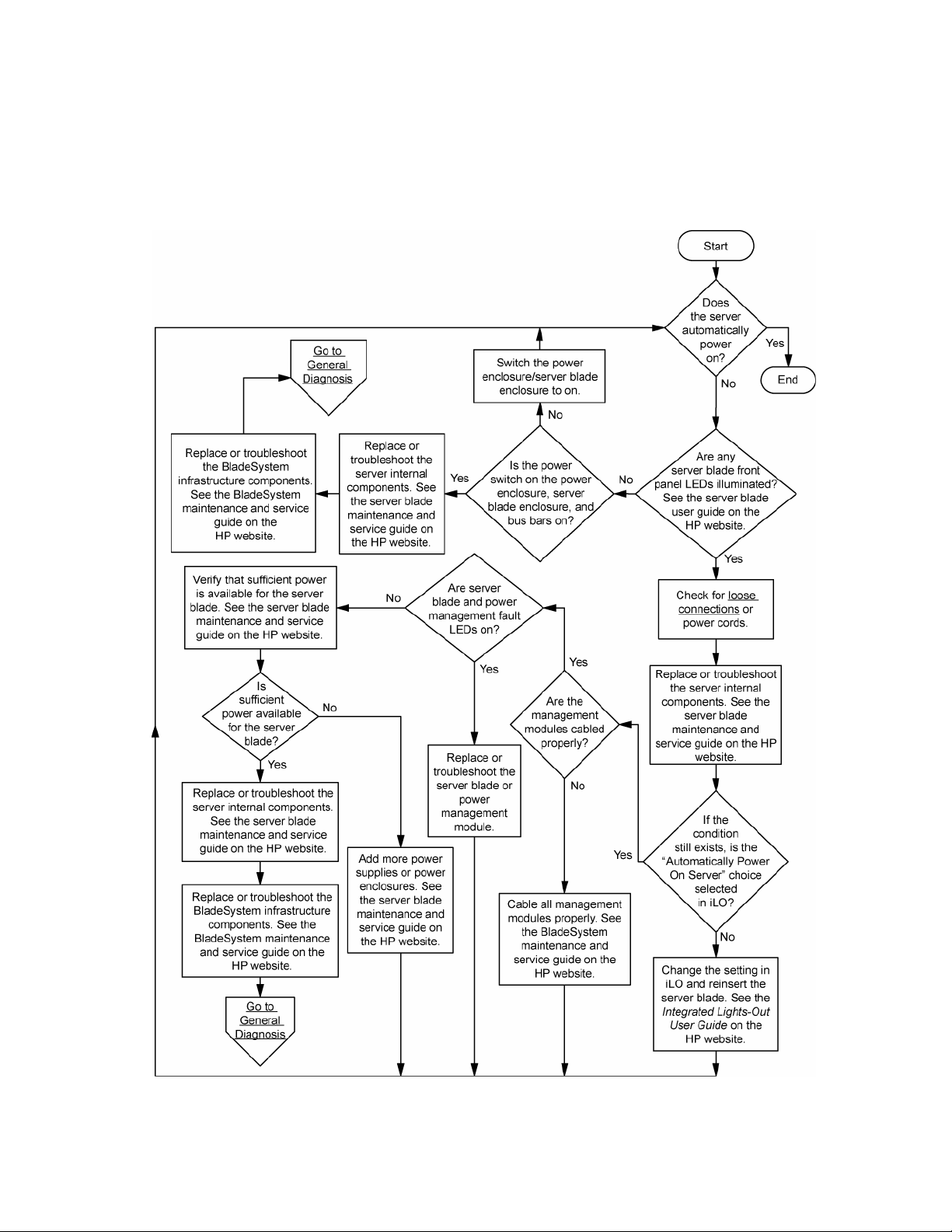
c-Class server blade power-on problems flowchart
Symptoms:
• The server does not power on.
• The system power LED is off or amber.
• The health LED is red or amber.
NOTE: For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses, refer to the server documentation.
Possible causes:
• Improperly seated or faulty power supply
• Loose or faulty power cord
• Power source problem
• Power on circuit problem
• Improperly seated component or interlock problem
• Faulty internal component
Diagnostic flowcharts 25
Page 26

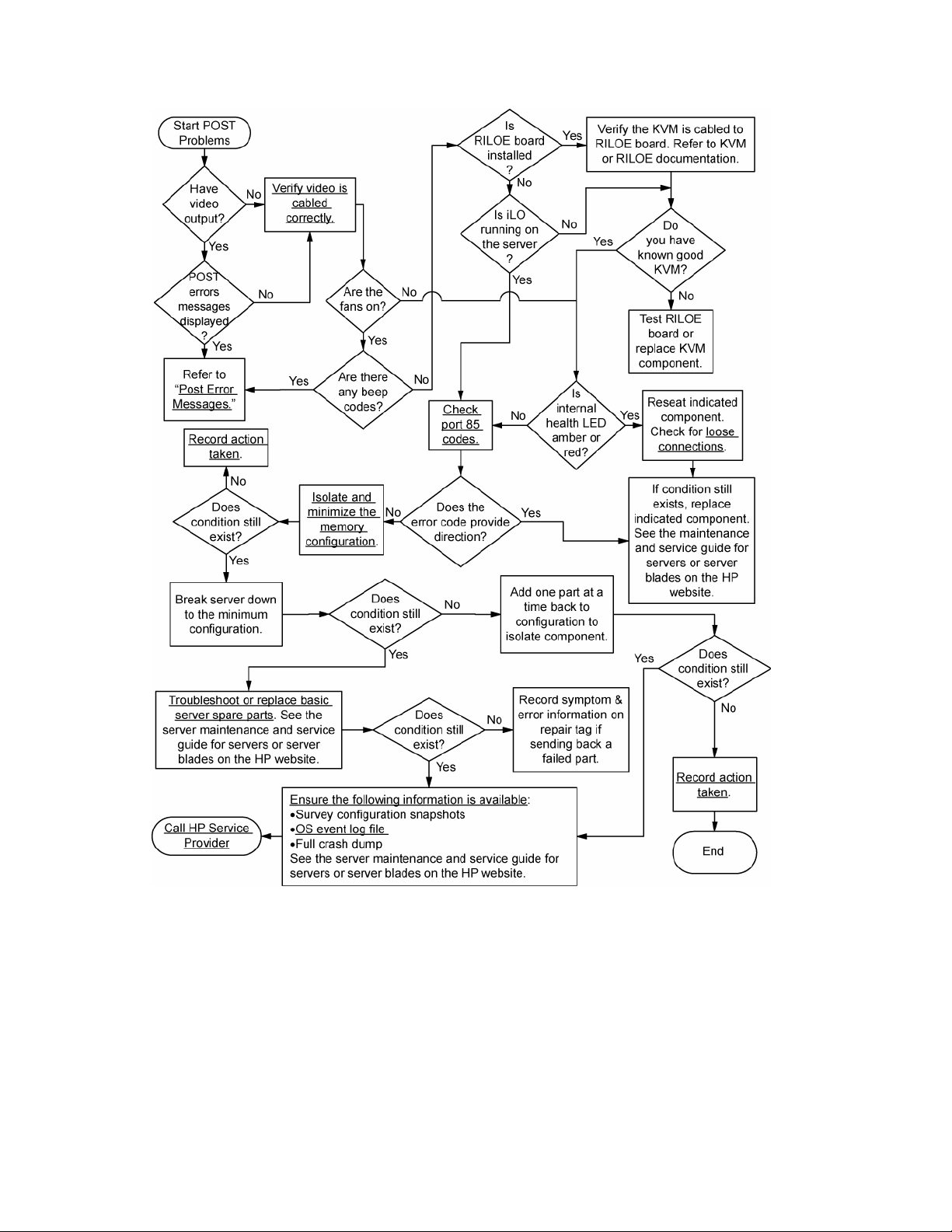
POST problems flowchart
Symptoms:
• Server does not complete POST
NOTE: The server has completed POST when the system attempts to access the boot device.
• Server completes POST with errors
Possible problems:
• Improperly seated or faulty internal component
• Faulty KVM device
• Faulty video device
Diagnostic flowcharts 26
Page 27
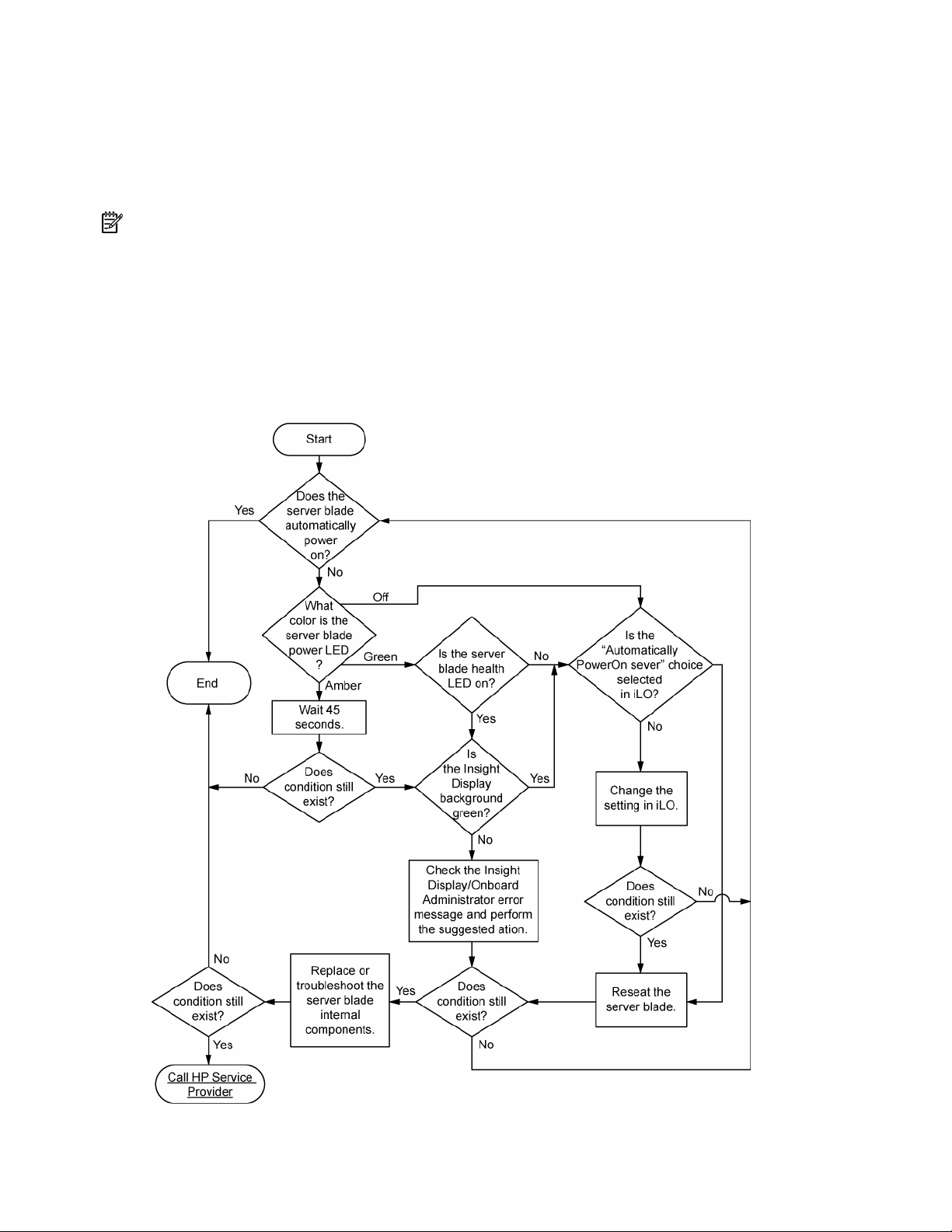
Server and p-Class server blade POST problems flowchart
Diagnostic flowcharts 27
Page 28
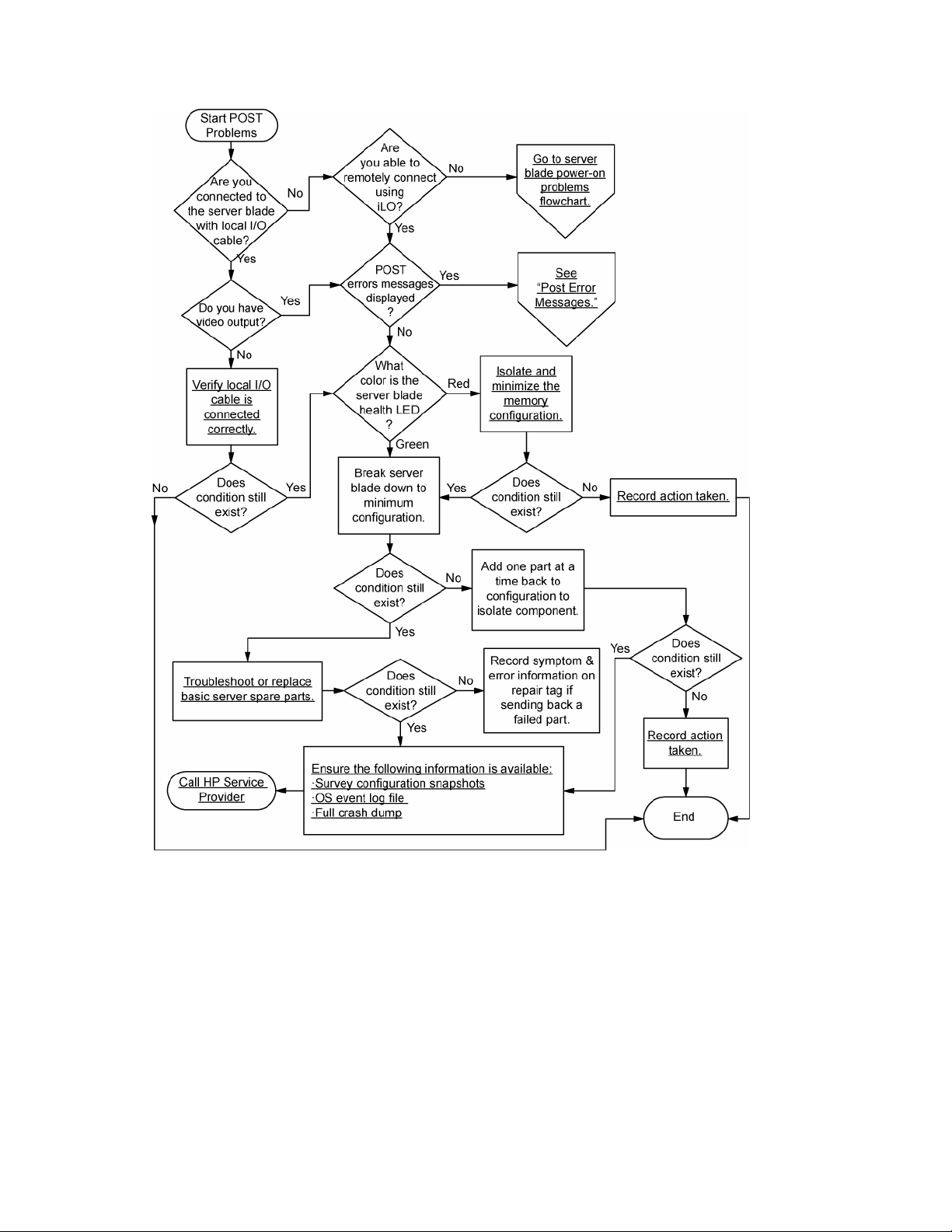
c-Class server blade POST problems flowchart
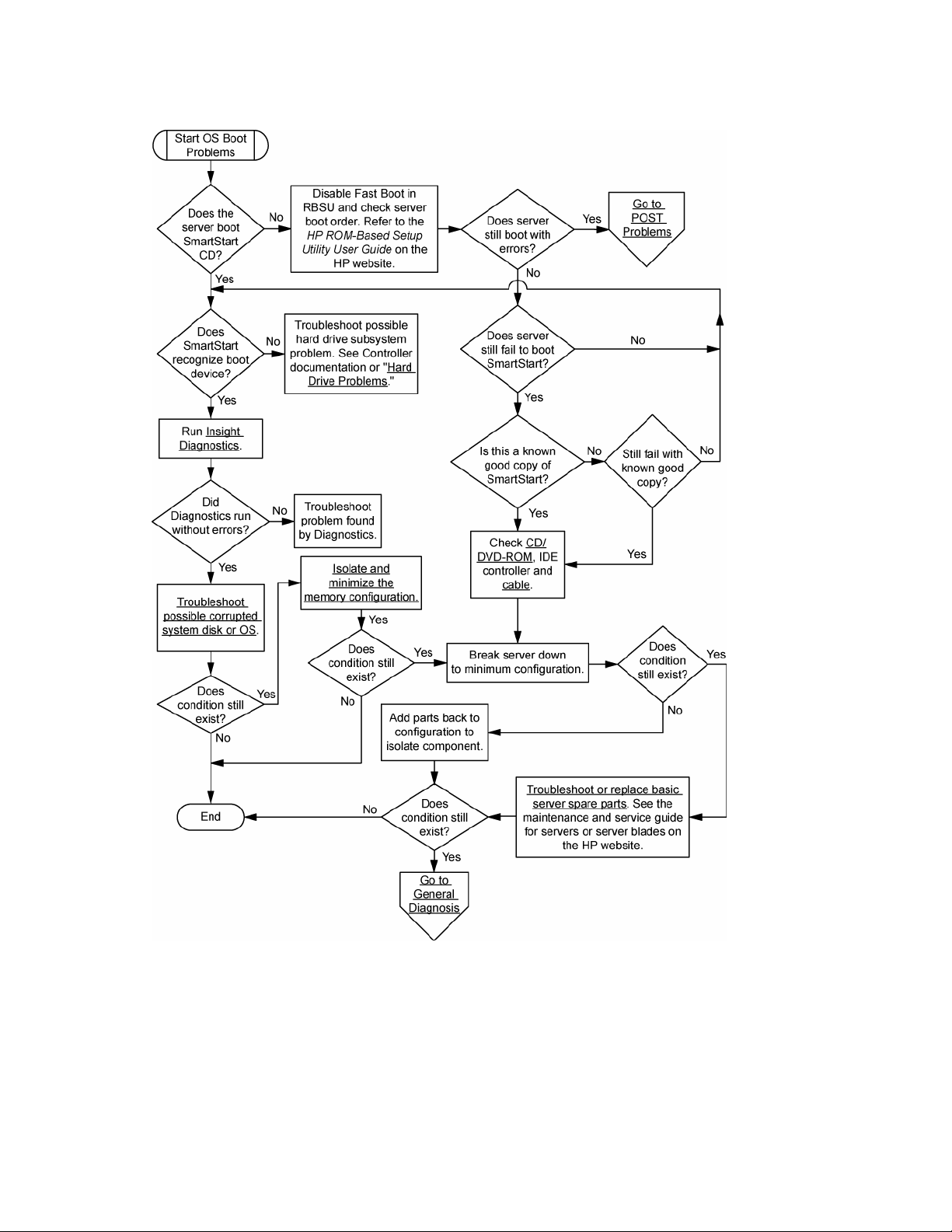
Operating system boot problems flowchart
Symptoms:
• Server does not boot a previously installed OS
• Server does not boot SmartStart
Possible causes:
• Corrupted OS
• Hard drive subsystem problem
• Incorrect boot order setting in RBSU
There are two ways to use SmartStart when diagnosing OS boot problems on a server blade:
Diagnostic flowcharts 28
Page 29
•
Use iLO to remotely attach virtual devices to mount the SmartStart CD onto the server blade.
• Use a local I/O cable and drive to connect to the server blade, and then restart the server blade.
Server fault indications flowchart
Symptoms:
• Server boots, but a fault event is reported by Insight Management Agents (on page 59)
• Server boots, but the internal health LED, external health LED, or component health LED is red or
amber
Diagnostic flowcharts 29
Page 30
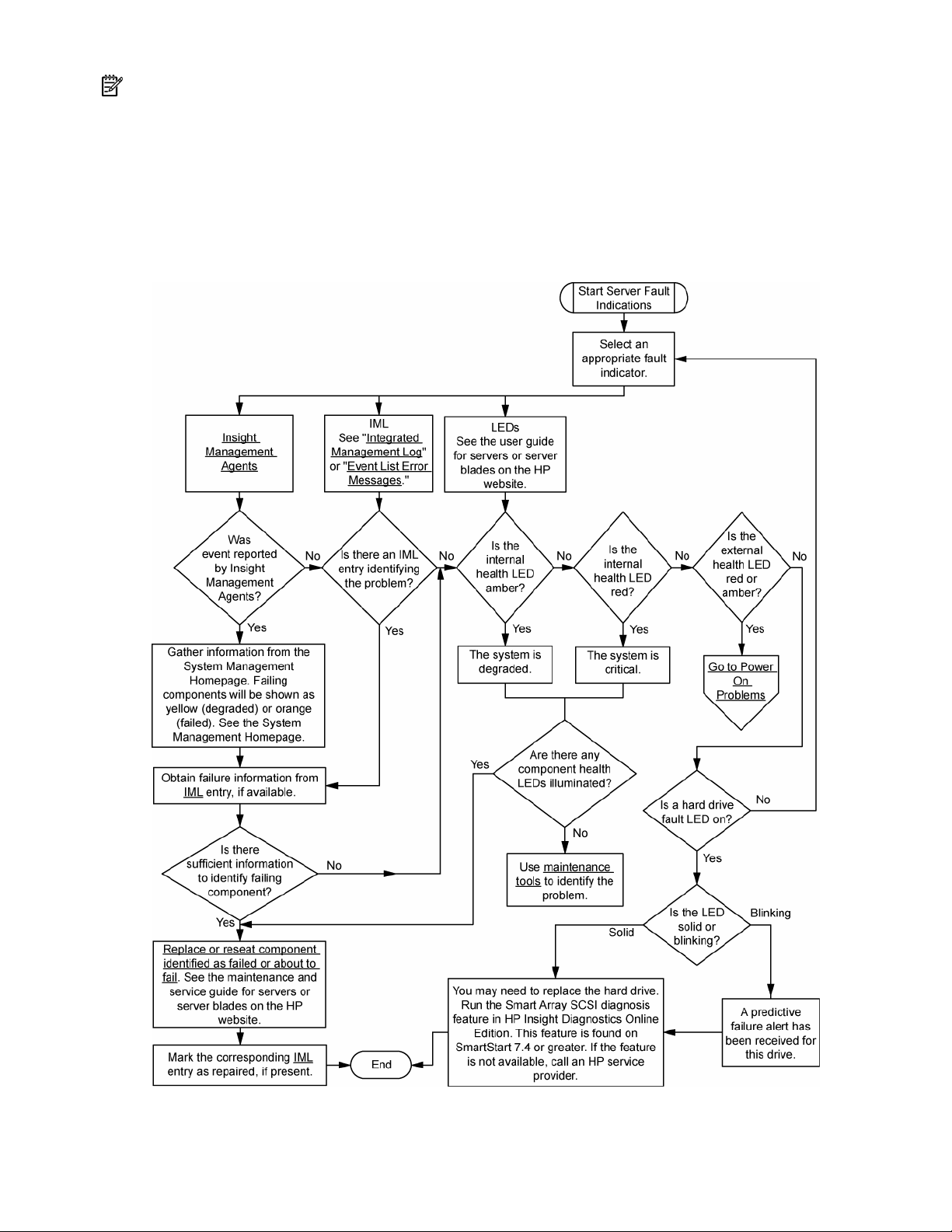
NOTE: For the location of server LEDs and information on their statuses, refer to the server documentation.
Possible causes:
• Improperly seated or faulty internal or external component
• Unsupported component installed
• Redundancy failure
• System overtemperature condition
Server and p-Class server blade fault indications flowchart
Diagnostic flowcharts 30
Page 31

c-Class server blade fault indications flowchart
Diagnostic flowcharts 31
Page 32

Hardware problems
In this section
Procedures for all ProLiant servers ............................................................................................................ 32
Power problems ..................................................................................................................................... 32
General hardware problems.................................................................................................................... 33
Internal system problems ......................................................................................................................... 35
System open circuits and short circuits ...................................................................................................... 43
External device problems ........................................................................................................................ 43
Procedures for all ProLiant servers
The procedures in this section are comprehensive and include steps about or references to hardware
features that may not be supported by the server you are troubleshooting.
Power problems
Power source problems
Action:
1. Press the Power On/Standby button to be sure it is on. If the server has a Power On/Standby button
that returns to its original position after being pressed, be sure you press the switch firmly.
2. Plug another device into the grounded power outlet to be sure the outlet works. Also, be sure the
power source meets applicable standards.
3. Replace the power cord with a known functional power cord to be sure it is not faulty.
4. Replace the power strip with a known functional power strip to be sure it is not faulty.
5. Have a qualified electrician check the line voltage to be sure it meets the required specifications.
Power supply problems
6. Be sure the proper circuit breaker is in the On position.
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
2. If the power supplies have LEDs, be sure they indicate that each power supply is working properly.
Refer to the server documentation. If LEDs indicate a problem with a power supply, replace the
power supply.
3. Be sure the system has enough power, particularly if you recently added hardware, such as hard
drives. Additional power supplies may be required. Check the system information from the IML and
use the server documentation for product-specific information.
Hardware problems 32
Page 33

UPS problems
UPS is not working properly
Action:
1. Be sure the UPS batteries are charged to the proper level for operation. See the UPS documentation
for details.
2. Be sure the UPS power switch is in the On position. See the UPS documentation for the location of
the switch.
3. Be sure the UPS software is updated to the latest version. Use the Power Management software
located on the Power Management CD.
4. Be sure the power cord is the correct type for the UPS and the country in which the server is located.
See the UPS reference guide for specifications.
5. Be sure the line cord is connected.
6. Be sure each circuit breaker is in the On position, or replace the fuse if needed. If this occurs
repeatedly, contact an authorized service provider.
7. Check the UPS LEDs to be sure a battery or site wiring problem has not occurred. See the UPS
documentation.
8. If the UPS sleep mode is initiated, disable sleep mode for proper operation. The UPS sleep mode can
be turned off through the configuration mode on the front panel.
9. Change the battery to be sure damage was not caused by excessive heat, particularly if a recent air
conditioning outage has occurred.
NOTE: The optimal operating temperature for UPS batteries is 25°C (77°F). For approximately every 8°C to
10°C (16°F to 18°F) average increase in ambient temperature above the optimal temperature, battery life is
reduced by 50 percent.
Low battery warning is displayed
Action:
1. Plug the UPS into an AC grounded outlet for at least 24 hours to charge the batteries, and then test
the batteries. Replace the batteries if necessary.
2. Be sure the alarm is set appropriately by changing the amount of time given before a low battery
warning. Refer to the UPS documentation for instructions.
One or more LEDs on the UPS is red
Action: Refer to the UPS documentation for instructions regarding the specific LED to determine the cause
of the error.
General hardware problems
Problems with new hardware
Action:
1. Refer to the server documentation to be sure the hardware being installed is a supported option on
the server. Remove unsupported hardware.
Hardware problems 33
Page 34

2.
Refer to the release notes included with the hardware to be sure the problem is not caused by a
change to the hardware release. If no documentation is available, refer to the HP support website
(http://www.hp.com/support
3. Be sure the new hardware is installed properly. Refer to the device, server, and OS documentation
).
to be sure all requirements are met.
Common problems include:
• Incomplete population of a memory bank
• Installation of a processor without a corresponding PPM
• Installation of a SCSI device without termination or without proper ID settings
• Setting of an IDE device to Primary/Secondary when the other device is set to CS
• Connection of the data cable, but not the power cable, of a new device
4. Be sure no memory, I/O, or interrupt conflicts exist.
5. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
6. Be sure all cables are connected to the correct locations and are the correct lengths. For more
information, refer to the server documentation.
7. Be sure other components were not unseated accidentally during the installation of the new
hardware component.
8. Be sure all necessary software updates, such as device drivers, ROM updates, and patches, are
installed, current, and the correct version for the hardware installed. For example, if you are using a
Smart Array controller, you need the latest Smart Array Controller device driver. Uninstall any
incorrect drivers before installing the correct drivers.
9. Run RBSU after boards or other options are installed or replaced to be sure all system components
recognize the changes. If you do not run the utility, you may receive a POST error message
indicating a configuration error. After you check the settings in RBSU, save and exit the utility, and
then restart the server. For more information on RBSU, refer to the HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User
Guide on the Documentation CD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
10. Be sure all switch settings are set correctly. For additional information about required switch settings,
).
refer to the labels located on the inside of the server access panel or the server documentation.
11. Be sure all boards are properly installed in the server.
12. Run HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 61) to see if it recognizes and tests the device.
13. Uninstall the new hardware.
Unknown problem
Action:
1. Disconnect power to the server.
2. Following the guidelines and cautionary information in the server documentation, strip the server to
its most basic configuration by removing every card or device that is not necessary to start the
server. Keep the monitor connected to view the server startup process.
3. Reconnect power, and then power the system on.
• If the video does not work, refer to "Video problems (on page 43)."
CAUTION: Only authorized technicians trained by HP should attempt to remove the system board. If you
believe the system board requires replacement, contact HP Technical Support before proceeding.
• If the system fails in this minimum configuration, one of the primary components has failed. If you
have already verified that the processor, PPM, power supply, and memory are working before
getting to this point, replace the system board. If not, be sure each of those components is
working.
Hardware problems 34
Page 35

•
If the system boots and video is working, add each component back to the server one at a time,
restarting the server after each component is added to determine if that component is the cause
of the problem. When adding each component back to the server, be sure to disconnect power
to the server and follow the guidelines and cautionary information in the server documentation.
Third-party device problems
Action:
1. Refer to the server and operating system documentation to be sure the server and operating system
support the device.
2. Be sure the latest device drivers are installed.
3. Refer to the device documentation to be sure the device is properly installed. For example, a third-
party PCI or PCI-X board may be required to be installed on the primary PCI or PCI-X bus,
Testing the device
respectively.
Action:
1. Uninstall the device.
If the server works with the device removed and uninstalled, a problem exists with the device, the
server does not support the device, or a conflict exists with another device.
2. If the device is the only device on a bus, be sure the bus works by installing a different device on the
bus.
3. Restarting the server each time to determine if the device is working, move the device:
a. To a different slot on the same bus (not applicable for PCI Express)
b. To a PCI, PCI-X, or PCI Express slot on a different bus
c. To the same slot in another working server of the same or similar design
If the board works in any of these slots, either the original slot is bad or the board was not properly
seated. Reinsert the board into the original slot to verify.
4. If you are testing a board (or a device that connects to a board):
a. Test the board with all other boards removed.
b. Test the server with only that board removed.
CAUTION: Clearing NVRAM deletes the configuration information. Refer to the server documentation for
complete instructions before performing this operation or data loss could occur.
5. Clearing NVRAM can resolve various problems. Clear the NVRAM, but do not use the backup .SCI
file if prompted. Have available any .CFG, .OVL, or .PCF files that are required.
Internal system problems
CD-ROM and DVD drive problems
System does not boot from the drive
Action:
1. Be sure the drive boot order in RBSU is set so that the server boots from the CD-ROM drive first.
2. If the CD-ROM drive jumpers are set to CS (the factory default), be sure the CD-ROM drive is
installed as device 0 on the cable so that it is in position for the server to boot from the drive.
Hardware problems 35
Page 36

3.
Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
4. Be sure the media from which you are attempting to boot is not damaged and is a bootable CD.
5. If attempting to boot from a USB CD-ROM drive:
• Refer to the operating system and server documentation to be sure both support booting from a
USB CD-ROM drive.
• Be sure legacy support for a USB CD-ROM drive is enabled in RBSU.
Data read from the drive is inconsistent, or drive cannot read data
Action:
1. Clean the drive and media.
2. If a paper or plastic label has been applied to the surface of the CD or DVD in use, remove the label
and any adhesive residue.
3. Be sure the inserted CD or DVD format is valid for the drive. For example, be sure you are not
inserting a DVD into a drive that only supports CDs.
Drive is not detected
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
2. Refer to the drive documentation to be sure cables are connected as required.
3. Be sure the cables are working properly. Replace with known functional cables to test whether the
original cables were faulty.
4. Be sure the correct, current driver is installed.
Diskette drive problems
Diskette drive light stays on
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
2. Be sure the diskette is not damaged. Run the diskette utility on the diskette (CHKDSK on some
systems).
3. Be sure the diskette is properly inserted. Remove the diskette and reinsert correctly into the drive.
A problem has occurred with a diskette transaction
Diskette drive cannot read a diskette
4. Be sure the diskette drive is cabled properly. Refer to the server documentation.
Action: Be sure the directory structure on the diskette is not bad. Run the diskette utility to check for
fragmentation (CHKDSK on some systems).
Action:
1. If the diskette is not formatted, format the diskette.
2. Check the type of drive you are using and be sure you are using the correct diskette type.
Hardware problems 36
Page 37

Drive is not found
Action: Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist with the drive.
Non-system disk message is displayed
Action:
1. Remove the non-system diskette from the drive.
2. Check for and disconnect any non-bootable USB devices.
Diskette drive cannot write to a diskette
Action:
1. If the diskette is not formatted, format the diskette.
2. Be sure the diskette is not write protected. If it is, use another diskette or remove the write protection.
3. Be sure you are attempting to write to the proper drive by checking the drive letter in the path
statement.
4. Be sure enough space is available on the diskette.
Tape drive problems
The following sections include the most common tape drive issues. Actions are listed in the order that they
should be tried. If the issue is resolved, it is not necessary to complete the remaining actions.
All actions may not apply to all tape drives.
For detailed tape drive troubleshooting information, see the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support/proliantstorage
).
To download HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools, see the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support/tapetools
).
Stuck tape issue
Action:
1. Manually press the Eject button. Allow up to 10 minutes for the tape to rewind and eject.
2. Perform a forced eject:
a. Press and hold the Eject button for at least 10 seconds.
b. Allow up to 10 minutes for the tape to rewind and eject. The green Ready LED should flash.
3. Power cycle the drive. Allow up to 10 minutes for the drive to become ready again.
4. Press the Emergency Reset button.
5. Check for conflicts in backup software services.
6. Check the SCSI/HBA/Driver configuration of the drive.
7. Inspect media and cables, and discard any that are faulty or damaged.
8. Run the Acceptance Test in HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools.
CAUTION: Running the Acceptance Test overwrites the tape. To avoid overwriting the tape, run the shorter
Device Analysis Test instead.
9. Contact HP support.
Hardware problems 37
Page 38

Read/write issue
Action:
1. Run the Acceptance Test in HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools.
CAUTION: Running the Acceptance Test overwrites the tape. To avoid overwriting the tape, run the shorter
Device Analysis Test instead.
2. Run the Media Validation Test in HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools.
Backup issue
Action:
1. Run the Acceptance Test in HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools.
CAUTION: Running the Acceptance Test overwrites the tape. To avoid overwriting the tape, run the shorter
Device Analysis Test instead.
2. Run the Media Validation Test in HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools.
3. Check back-up logs.
4. Verify a supported configuration is being used.
5. Check for media damage:
• Incorrect label placement
• Broken, missing, or loose leader pin
• Damaged cartridge seam
• Usage in incorrect environment
6. Check for software issues:
a. Check the back-up software.
b. Check that virus scanning software is not scheduled to run at the same time as the back-up.
7. Verify that a tape can be formatted.
Media issue
Action:
1. Verify that the correct media part number is being used.
2. Run the Media Validation Test in HP StorageWorks Library and Tape Tools.
3. Check for media damage:
4. Check if the Tape Error LED is flashing:
5. Discard any media that has been used at temperatures greater than 45°C (113ºF) or less than 5ºC
• Incorrect label placement
• Broken, missing, or loose leader pin
• Damaged cartridge seam
• Usage in incorrect environment
a. Reload the suspect tape. If the Tape Error LED stops flashing, the problem has cleared.
b. Load a new or known good tape. If the Tape Error LED stops flashing, the problem has cleared.
c. Reload the suspect tape. If the Tape Error LED flashes, discard the suspect media as faulty.
(41ºF).
Hardware problems 38
Page 39

Hard drive problems
System completes POST but hard drive fails
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
2. Be sure no device conflict exists.
3. Be sure the hard drive is properly cabled and terminated if necessary.
4. Be sure the hard drive data cable is working by replacing it with a known functional cable.
5. Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
No hard drives are recognized
indicated.
Action:
1. Be sure no power problems (on page 32) exist.
2. Check for loose connections (on page 15).
3. Be sure that the controller supports the hard drives being installed.
4. Be sure the controller has the most recent firmware.
Hard drive is not recognized by the server
Action:
1. Check the LEDs on the hard drive to be sure they indicate normal function. Refer to the server
documentation or the HP website (http://www.hp.com
2. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
3. Remove the hard drive and be sure the configuration jumpers are set properly.
4. If using an array controller, be sure the hard drive is configured in an array. Run the array
configuration utility.
5. Be sure the drive is properly configured. Refer to the drive documentation to determine the proper
configuration.
6. If it is a non-hot-plug drive, be sure a conflict does not exist with another hard drive. Check for SCSI
ID conflicts.
7. Be sure the correct drive controller drivers are installed.
A new hard drive is not recognized
Action:
1. Be sure the drive bay is not defective by installing the hard drive in another bay.
2. If the drive has just been added, be sure the drive is supported. Refer to the server documentation or
the HP website to determine drive support.
3. Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
4. If the drive is a replacement drive on an array controller, make sure that the drive is the same type
and of the same or larger capacity than the original drive.
) for information on hard drive LEDs.
You are unable to access data
Action:
Hardware problems 39
Page 40

1.
Be sure the files are not corrupt. Run the repair utility for the operating system.
2. Be sure no viruses exist on the server. Run a current version of a virus scan utility.
Server response time is slower than usual
Action: Be sure the hard drive is not full, and increase the amount of free space on the hard drive, if
needed. It is recommended that hard drives should have a minimum of 15 percent free space.
Fan problems
General fan problems are occurring
Action:
1. Be sure the fans are properly seated and working.
a. Follow the procedures and warnings in the server documentation for removing the access panels
and accessing and replacing fans.
b. Unseat, and then reseat, each fan according to the proper procedures.
c. Replace the access panels, and then attempt to restart the server.
2. Be sure the fan configuration meets the functional requirements of the server. Refer to the server
documentation.
3. Be sure no ventilation problems exist. If you have been operating the server for an extended period
of time with the access panel removed, airflow may have been impeded, causing thermal damage to
components. Refer to the server documentation for further requirements.
4. Be sure no POST error messages ("POST error messages and beep codes" on page 92) are
displayed while booting the server that indicate temperature violation or fan failure information.
Refer to the server documentation for the temperature requirements for the server.
5. Access the IML to see if any event list error messages (on page 124) relating to fans are listed.
6. Replace any required non-functioning fans and restart the server. Refer to the server documentation
for specifications on fan requirements.
7. Be sure all fan slots have fans or blanks installed. Refer to the server documentation for requirements.
8. Verify the fan airflow path is not blocked by cables or other material.
Hot-plug fan problems are occurring
Action:
1. Check the LEDs to be sure the hot-plug fans are working. Refer to the server documentation for LED
information.
NOTE: For servers with redundant fans, backup fans may spin up periodically to test functionality. This is
part of normal redundant fan operation.
2. Be sure no POST error messages ("POST error messages and beep codes" on page 92) are
displayed.
3. Be sure hot-plug fan requirements are being met. Refer to the server documentation.
Hardware problems 40
Page 41

Memory problems
General memory problems are occurring
Action:
• Isolate and minimize the memory configuration.
• Be sure the memory meets the server requirements and is installed as required by the server.
Some servers may require that memory banks be fully populated or that all memory within a
memory bank must be the same size, type, and speed. Refer to the server documentation to
determine if the memory is installed properly.
• Check any server LEDs that correspond to memory slots.
• If you are unsure which DIMM has failed, test each bank of DIMMs by removing all other
DIMMs. Then, isolate the failed DIMM by switching each DIMM in a bank with a known working
DIMM.
• Remove any third-party memory.
Server is out of memory
• Run HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 61) to test the memory.
Action:
1. Be sure the memory is configured properly. Refer to the application documentation to determine the
memory configuration requirements.
2. Be sure no operating system errors are indicated.
3. Be sure a memory count error ("Memory count error exists" on page 41) did not occur. Refer to the
message displaying memory count during POST.
Memory count error exists
Possible Cause: The memory modules are not installed correctly.
Action:
1. Be sure the memory modules are supported by the server. Refer to the server documentation.
2. Be sure the memory modules have been installed correctly in the right configuration. Refer to the
server documentation.
3. Be sure the memory modules are properly seated.
4. Be sure no operating system errors are indicated.
5. Restart the server and check to see if the error message is still displayed.
6. Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
Server fails to recognize existing memory
Action:
1. Reseat the memory.
2. Be sure the memory is configured properly. Refer to the server documentation.
3. Be sure a memory count error ("Memory count error exists" on page 41) did not occur. Refer to the
message displaying memory count during POST.
Hardware problems 41
Page 42

Server fails to recognize new memory
Action:
1. Be sure the memory is the correct type for the server and is installed according to the server
requirements. Refer to the server documentation or HP website (http://www.hp.com
2. Be sure you have not exceeded the memory limits of the server or operating system. Refer to the
).
server documentation.
3. Be sure no Event List error messages (on page 124) are displayed in the IML.
4. Be sure the memory is properly seated.
5. Be sure no conflicts are occurring with existing memory. Run the server setup utility.
6. Test the memory by installing the memory into a known working server. Be sure the memory meets
the requirements of the new server on which you are testing the memory.
7. Replace the memory. Refer to the server documentation.
PPM problems
Action: If the PPMs are not integrated on the system board:
CAUTION: Do not operate the server for long periods with the access panel open or removed. Operating
the server in this manner results in improper airflow and improper cooling that can lead to thermal damage.
1. If applicable, check the PPM LEDs to identify if a PPM failure occurred. For information on LEDs, refer
to the server documentation.
2. Reseat each PPM, and then restart the server.
3. If reseating the PPMs is not effective, remove all but one PPM, restart the server to see if the PPM is
working, and then install each PPM individually, cycling power each time. Follow the warnings and
cautionary information in the server documentation.
Processor problems
Action:
1. If applicable, check the processor LEDs to identify if a PPM failure occurred. For information on LEDs,
refer to the server documentation.
2. Be sure each processor is supported by the server and is installed properly. Refer to the server
documentation for processor requirements.
3. Be sure the server ROM is up to date.
4. Be sure you are not mixing processor stepping, core speeds, or cache sizes if this is not supported
on the server. Refer to the server documentation for more information.
CAUTION: Removal of some processors and heatsinks require special considerations for replacement,
while other processors and heatsinks are integrated and cannot be reused once separated. For specific
instructions for the server you are troubleshooting, refer to processor information in the server user guide.
5. If the server has only one processor installed, replace it with a known functional processor. If the
problem is resolved after you restart the server, the original processor failed.
6. If the server has multiple processors installed, test each processor:
a. Remove all but one processor from the server. Replace each with a processor terminator board or
blank, if applicable to the server.
b. If the server includes PPMs that are not integrated on the system board, remove all PPMs from the
server except for the PPM associated with the remaining processor.
Hardware problems 42
Page 43

c.
Replace the remaining processor with a known functional processor. If the problem is resolved
after you restart the server, a fault exists with one or more of the original processors. Install each
processor and its associated PPM (if applicable) one by one, restarting each time, to find the
faulty processor or processors. Be sure the processor configurations at each step are compatible
with the server requirements.
System open circuits and short circuits
Action:
CAUTION: Do not operate the server for long periods with the access panel open or removed. Operating
the server in this manner results in improper airflow and improper cooling that can lead to thermal damage.
1. Check the server LEDs to see if any statuses indicate the source of the problem. For LED information,
refer to the server documentation.
2. Remove all power sources to the server.
3. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist in the area.
4. Be sure each component in the area is working. Refer to the section for each component in this
guide.
If you cannot determine the problem by checking the specific area, perform each of the following actions.
Restart the server after each action to see if the problem has been corrected.
• Reseat all I/O expansion boards.
• Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist in the rest of the server, particularly with the cables
that connect to the system board.
• Be sure no foreign material exists, such as screws, bits, or slot bracket blanks, that may be short
circuiting components.
External device problems
Video problems
Screen is blank for more than 60 seconds after you power up the server
Action:
1. Be sure the monitor power cord is plugged into a working grounded (earthed) AC outlet.
2. Power up the monitor and be sure the monitor light is on, indicating that the monitor is receiving
power.
3. Be sure the monitor is cabled to the intended server or KVM connection.
4. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
• For rack-mounted servers, check the cables to the KVM switch and be sure the switch is correctly
set for the server. You may need to connect the monitor directly to the server to be sure the KVM
switch has not failed.
• For tower model servers, check the cable connection from the monitor to the server, and then
from the server to the power outlet.
5. Press any key, or type the password, and wait a few moments for the screen to activate to be sure
the energy saver feature is not in effect.
6. Be sure the video driver is current. Refer to the third-party video adapter documentation for driver
requirements.
Hardware problems 43
Page 44

7.
Be sure a video expansion board, such as a RILOE board, has not been added to replace onboard
video, making it seem like the video is not working. Disconnect the video cable from the onboard
video, and then reconnect it to the video jack on the expansion board.
NOTE: All servers automatically bypass onboard video when a video expansion board is present.
8. Press any key, or type the password, and wait a few moments for the screen to activate to be sure
the power-on password feature is not in effect. You can also tell if the power-on password is enabled
if a key symbol is displayed on the screen when POST completes.
If you do not have access to the password, you must disable the power-on password by using the
Password Disable switch on the system board. Refer to the server documentation.
9. If the video expansion board is installed in a PCI hot-plug slot, be sure the slot has power by
checking the power LED on the slot, if applicable. Refer to the server documentation.
10. Be sure the server and the OS support the video expansion board.
Monitor does not function properly with energy saver features
Action: Be sure the monitor supports energy saver features, and if it does not, disable the features.
Video colors are wrong
Action:
• Be sure the 15-pin VGA cable is securely connected to the correct VGA port on the server and to the
monitor.
• Be sure the monitor and any KVM switch are compatible with the VGA output of the server.
Slow-moving horizontal lines are displayed
Action: Be sure magnetic field interference is not occurring. Move the monitor away from other monitors
or power transformers.
Mouse and keyboard problems
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist. If a KVM switching device is in use, be sure the
server is properly connected to the switch.
• For rack-mounted servers, check the cables to the switch box and be sure the switch is correctly
set for the server.
• For tower model servers, check the cable connection from the input device to the server.
2. If a KVM switching device is in use, be sure all cables and connectors are the proper length and are
supported by the switch. Refer to the switch documentation.
3. Be sure the current drivers for the operating system are installed.
4. Be sure the device driver is not corrupted by replacing the driver.
5. Restart the system and check whether the input device functions correctly after the server restarts.
6. Replace the device with a known working equivalent device (another similar mouse or keyboard).
• If the problem still occurs with the new mouse or keyboard, the connector port on the system I/O
board is defective. Replace the board.
• If the problem no longer occurs, the original input device is defective. Replace the device.
7. Be sure the keyboard or mouse is connected to the correct port. Determine whether the keyboard
lights flash at POST or the NumLock LED illuminates. If not, change port connections.
8. Be sure the keyboard or mouse is clean.
Hardware problems 44
Page 45

Audio problems
Action: Be sure the server speaker is connected. Refer to the server documentation.
Printer problems
Printer does not print
Action:
1. Be sure the printer is powered up and online.
2. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
3. Be sure the correct printer drivers are installed.
Printer output is garbled
Action: Be sure the correct printer drivers are installed.
Local I/O cable problems
NOTE: The local I/O cable is used only with HP ProLiant p-Class server blades.
Action: If the local I/O cable does not have hot-plug functionality, be sure you are not using a PS/2
keyboard or mouse. With a PS/2 keyboard or mouse, the local I/O cable cannot be connected as a hotplug device. Connect the local I/O cable before booting the server, or switch to USB devices (if
supported) to use the local I/O cable hot-plug functionality.
Modem problems
No dial tone exists
Action:
1. Be sure the cables are plugged in as specified in the modem documentation.
2. Connect a working telephone directly to the wall jack, and then test the line for a dial tone.
3. If no dial tone is detected, the phone line is not working. Contact the local telephone company and
No response occurs when you type AT commands
AT commands are not visible
arrange to correct the problem.
Action: Reconfigure the COM port address for the modem.
1. Be sure the communications software is set to the COM port to which the modem is connected.
2. Check IRQ settings in the software and on the modem to be sure no conflict exists.
3. Type AT&F at the command prompt to reset the modem to factory-default settings.
4. Be sure you are in terminal mode and not MS-DOS mode.
5. Refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com) for a complete list of AT commands.
Action: Set the echo command to On using the AT command ATE.
Hardware problems 45
Page 46

Data is displayed as garbled characters after the connection is established
Action:
1. Be sure both modems have the same settings, including speed, data, parity, and stop bits.
2. Be sure the software is set for the correct terminal emulation.
a. Reconfigure the software correctly.
b. Restart the server.
c. Run the communications software, checking settings and making corrections where needed.
d. Restart the server, and then reestablish the modem connection.
Modem does not answer an incoming call
Action:
1. Enable the auto-answer option in the communications software.
2. Be sure an answering machine is not answering the line before the modem is able to answer.
a. Turn off the answering machine.
or
Reconfigure the auto-answer option to respond in fewer rings than the answering machine.
b. Restart the server, and then reattempt the connection.
Modem does not connect to another modem
Action:
1. Be sure a dial tone exists.
2. Be sure the line is not in use at another extension before using it.
3. Be sure you are dialing the correct telephone number.
4. Be sure the modem on the other end is working.
Modem disconnects while online
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
2. Be sure no line interference exists. Retry the connection by dialing the number several times. If
conditions remain poor, contact the telephone company to have the line tested.
3. Be sure an incoming call is not breaking the connection due to call waiting. Disable call waiting,
and then reestablish the connection.
AT command initialization string is not working
Action: Use the most basic string possible to perform the task. The default initialization string is
AT&F&C1&D2&K3.
Connection errors are occurring
Action:
1. Check the maximum baud rate for the modem to which you are connecting, and then change the
baud rate to match.
2. If the line you are accessing requires error control to be turned off, do so using the AT command
AT&Q6%C0.
Hardware problems 46
Page 47

3.
Be sure no line interference exists. Retry the connection by dialing the number several times. If
conditions remain poor, contact the telephone company to have the line tested.
4. Be sure the modem is current and compliant with CCITT and Bell standards. Replace with a
supported modem if needed.
You are unable to connect to an online subscription service
Action:
1. If the line you are accessing requires error control to be turned off, do so using the AT command
AT&Q6%C0.
2. If the ISP you are accessing requires access at a decreased baud rate, reconfigure the
communications software to correct the connection baud rate to match the ISP.
3. If this does not work, force a slower baud rate (14400 baud) with the AT command
AT&Q6N0S37=11.
You are unable to connect at 56 Kbps
Action:
1. Find out the maximum baud rate at which the ISP connects, and change the settings to reflect this.
Reattempt to connect at a lower baud rate.
2. Be sure no line interference exists. Retry the connection by dialing the number several times. If
conditions remain poor, contact the telephone company to have the line tested.
Network controller problems
Network controller is installed but not working
Action:
1. Check the network controller LEDs to see if any statuses indicate the source of the problem. For LED
information, refer to the network controller documentation.
2. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
3. Be sure the network cable is working by replacing it with a known functional cable.
4. Be sure a software problem has not caused the failure. Refer to the operating system documentation
for guidelines on adding or replacing PCI Hot Plug devices, if applicable.
5. Be sure the server and operating system support the controller. Refer to the server and operating
system documentation.
6. Be sure the controller is enabled in RBSU.
7. Check the PCI Hot Plug power LED to be sure the PCI slot is receiving power, if applicable.
8. Be sure the server ROM is up to date.
9. Be sure the controller drivers are up to date.
10. Be sure a valid IP address is assigned to the controller and that the configuration settings are correct.
11. Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
Network controller has stopped working
Action:
1. Check the network controller LEDs to see if any statuses indicate the source of the problem. For LED
information, refer to the network controller documentation.
Hardware problems 47
Page 48

2.
Be sure the correct network driver is installed for the controller and that the driver file is not
corrupted. Reinstall the driver.
3. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
4. Be sure the network cable is working by replacing it with a known functional cable.
5. Check the PCI Hot Plug power LED to be sure the PCI slot is receiving power, if applicable.
6. Be sure the network controller is not damaged.
7. Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
Network controller stopped working when an expansion board was added
Action:
1. Be sure no loose connections (on page 15) exist.
2. Be sure the server and operating system support the controller. Refer to the server and operating
system documentation.
3. Be sure the new expansion board has not changed the server configuration, requiring reinstallation
of the network driver.
a. Uninstall the network controller driver for the malfunctioning controller in the operating system.
b. Restart the server and run RBSU. Be sure the server recognizes the controller and that resources
are available for the controller.
c. Restart the server, and then reinstall the network driver.
4. Refer to the operating system documentation to be sure the correct drivers are installed.
5. Refer to the operating system documentation to be sure that the driver parameters match the
configuration of the network controller.
Problems are occurring with the network interconnect blades
Action: Be sure the network interconnect blades are properly seated and connected.
Hardware problems 48
Page 49

Software problems
In this section
Operating system problems and resolutions............................................................................................... 49
Application software problems................................................................................................................. 52
Remote ROM flash problems.................................................................................................................... 52
The best sources of information for software problems are the operating system and application software
documentation, which may also point to fault detection tools that report errors and preserve the system
configuration.
Other useful resources include HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 61) and HP SIM ("HP Systems Insight
Manager" on page 59). Use either utility to gather critical system hardware and software information and
to help with problem diagnosis.
IMPORTANT: This guide provides information for multiple servers. Some information may not apply to the
server you are troubleshooting. Refer to the server documentation for information on procedures, hardware
options, software tools, and operating systems supported by the server.
Refer to "Software tools and solutions (on page 54)" for more information.
Operating system problems and resolutions
Operating system problems
Operating system locks up
General protection fault occurs
Action: Scan for viruses with an updated virus scan utility.
A general protection fault, or general protection error, occurs when the Microsoft operating system
terminates suddenly with an error, including but not limited to:
• Miscalculating the amount of RAM needed for an allocation
• Transferring execution to a segment that is not executable
• Writing to a read-only or a code segment
• Loading a bad value into a segment register
• Using a null pointer
A GPF is immediately identifiable by a blue screen with white text, and the text may contain information
that identifies the problem.
Action:
• Remove any newly installed software or hardware to verify that they are not the cause.
• Boot the server in Safe Mode or Last Known Good Configuration.
Software problems 49
Page 50

If neither of these actions resolve the problem, contact an authorized service provider. For more
information about debugging tools or specific GPF messages, refer to the Microsoft website
(http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/devtools/debugging/default.mspx
).
Errors are displayed in the error log
Action: Follow the information provided in the error log, and then refer to the operating system
documentation.
Problems occur after the installation of a service pack
Action: Follow the instructions for updating the operating system ("Operating system updates" on page
50).
NetWare attempts to load MEGA4 XX.HAM or 120PCI.HAM during installation, and a RILOE II board is installed
Action: No action is required. This occurrence does not impact the installation of NetWare.
During installation of Sun Solaris, the system locks up or a panic error occurs
Action: Disable ACPI support in Sun Solaris. Refer to the Sun website (http://www.sun.com) for
documentation on how to disable ACPI.
Operating system issues with Intel® dual-core processors (Hyper-Threading enabled)
Some versions of Microsoft® Windows® and distributions of Linux may hang during OS installation, fail
to complete OS installation, or fail to boot after installation on servers with either three or four Intel® dualcore processors installed.
Action:
Microsoft® Windows Server™ 2003-based media
• System may hang during installation or during boot. Windows Server™ 2003 SP1 Slipstream does
not exhibit this issue.
• If SP1 Slipstream media is not available, the base media installation can be performed using one of
the following methods:
• Install the OS with only one or two processor(s)
• Disable Hyper-Threading in RBSU, then apply SP1 before adding the additional processor(s) and
re-enabling Hyper-Threading
Linux distributions
• Additional information and the appropriate solutions for the Linux distributions (if any) can be found
at the HP website (http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/linux/processor-notes.html
).
Operating system updates
Use care when applying operating system updates (Service Packs, hotfixes, and patches). Before
updating the operating system, read the release notes for each update. If you do not require specific fixes
from the update, it is recommended that you do not apply the updates. Some updates overwrite files
specific to HP.
If you decide to apply an operating system update:
1. Perform a full system backup.
2. Apply the operating system update, using the instructions provided.
Software problems 50
Page 51

3.
Install the current drivers.
If you apply the update and have problems, refer to the Software and Drivers Download website
(http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/server
Restoring to a backed-up version
If you recently upgraded the operating system or software and cannot resolve the problem, you can try
restoring a previously saved version of the system. Before restoring the backup, make a backup of the
current system. If restoring the previous system does not correct the problem, you can restore the current
set to be sure you do not lose additional functionality.
) to find files to correct the problems.
Refer to the documentation provided with the backup software.
When to Reconfigure or Reload Software
If all other options have not resolved the problem, consider reconfiguring the system. Before you take this
step:
1. Weigh the projected downtime of a software reload against the time spent troubleshooting
intermittent problems. It may be advantageous to start over by removing and reinstalling the problem
software, or in some cases by using the System Erase Utility and reinstalling all system software.
CAUTION: Perform a backup before running the System Erase Utility. The utility sets the system to its
original factory state, deletes the current hardware configuration information, including array setup and disk
partitioning, and erases all connected hard drives completely. Refer to the instructions for using this utility.
2. Be sure the server has adequate resources (processor speed, hard drive space, and memory) for the
software.
3. Be sure the server ROM is current and the configuration is correct.
4. Be sure you have printed records of all troubleshooting information you have collected to this point.
5. Be sure you have two good backups before you start. Test the backups using a backup utility.
6. Check the operating system and application software resources to be sure you have the latest
information.
7. If the last-known functioning configuration does not work, try to recover the system with operating
system recovery software:
• Microsoft® operating systems:
Windows Server™ 2003—Automated System Recovery Diskette. If the operating system was
factory-installed, click Start>All Programs>Accessories>System Tools to access the
backup utility. Refer to the operating system documentation for more information.
Windows® 2000—Emergency Repair Diskette. If the operating system was factory-installed,
click Start>Programs>System Tools to access the Emergency Repair Disk Utility. Refer to
the operating system documentation for more information.
• Novell NetWare—Repair traditional volumes with VREPAIR. On NetWare 5.X systems, repair
NSS volumes with the NSS menu command, and on NetWare 6 systems, repair NSS volumes
using the NSS/PoolVerify command followed by the NSS/PoolRebuild command, if
necessary. Refer to the NetWare documentation for more information.
• Caldera UnixWare and SCO OpenServer from Caldera—Emergency boot diskette. Refer to the
Caldera UnixWare or SCO OpenServer from Caldera documentation for more information.
• Sun Solaris—Device Configuration Assistant boot diskette. Refer to the Solaris documentation for
more information.
• IBM OS/2—Power up the server from the startup diskettes. Refer to the OS/2 documentation for
more information.
Software problems 51
Page 52

•
Linux—Refer to the operating system documentation for information.
Linux operating systems
For troubleshooting information specific to Linux operating systems, refer to the Linux for ProLiant website
(http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/servers/linux
Application software problems
Software locks up
Action:
1. Check the application log and operating system log for entries indicating why the software failed.
2. Check for incompatibility with other software on the server.
3. Check the support website of the software vendor for known problems.
4. Review log files for changes made to the server which may have caused the problem.
5. Scan the server for viruses with an updated virus scan utility.
).
Errors occur after a software setting is changed
Action: Check the system logs to determine what changes were made, and then change settings to the
original configuration.
Errors occur after the system software is changed
Action: Change settings to the original configuration. If more than one setting was changed, change the
settings one at a time to isolate the cause of the problem.
Errors occur after an application is installed
Action:
• Check the application log and operating system log for entries indicating why the software failed.
• Check system settings to determine if they are the cause of the error. You may need to obtain the
settings from the server setup utility and manually set the software switches. Refer to the application
documentation, the vendor website, or both.
• Check for overwritten files. Refer to the application documentation to find out which files are added
by the application.
• Reinstall the application.
• Be sure you have the most current drivers.
Remote ROM flash problems
General remote ROM flash problems are occurring
Action: Be sure you follow these requirements for using the Remote ROM flash utility:
• A local administrative client system that is running the Microsoft® Windows NT® 4.0,
Windows® 2000, or Windows Server™ 2003 operating system
Software problems 52
Page 53

•
One or more remote servers with system ROMs requiring upgrade
• An administrative user account on each target system. The administrative account must have the
same username and password as the local administrative client system.
• All target systems are connected to the same network and use protocols that enable them to be seen
from the administrative client.
• Each target system has a system partition that is at least 32 MB in size.
• Verification that the ROM version to which you are upgrading can be used for all the servers or
array controllers that you are upgrading.
• Follow the instructions for the Remote ROM Flash procedure that accompany the software.
Command-line syntax error
If the correct command-line syntax is not used, an error message describing the incorrect syntax is
displayed and the program exits. Correct the syntax, and then restart the process.
Access denied on target computer
If you specify a networked target computer for which you do not have administrative privileges, an error
message is displayed describing the problem, and then the program exits. Obtain administrative
privileges for the target computer, and then restart the process. Be sure the remote registry service is
running on a Windows®-based system.
Invalid or incorrect command-line parameters
If incorrect parameters are passed into command-line options, an error message describing the invalid or
incorrect parameter is displayed and the program exits (Example: Invalid source path for system
configuration or ROMPaq files). Correct the invalid parameter, and then restart the process.
Network connection fails on remote communication
Because network connectivity cannot be guaranteed, it is possible for the administrative client to become
disconnected from the target server during the ROM flash preparation. If any remote connectivity
procedure fails during the ROM flash online preparation, the ROM flash does not occur for the target
system. An error message describing the broken connection displays and the program exits. Attempt to
ascertain and correct the cause of connection failure, and then restart the process.
Failure occurs during ROM flash
After the online flash preparation has been successfully completed, the system ROM is flashed offline. The
flash cannot be interrupted during this process, or the ROM image is corrupted and the server does not
start. The most likely reason for failure is a loss of power to the system during the flash process. Initiate
ROMPaq disaster recovery procedures.
Target system is not supported
If the target system is not listed in the supported servers list, an error message is displayed and the
program exits. Only supported systems can be upgraded using the Remote ROM Flash utility. To see if the
server is supported, refer to the Software and Drivers Download website
(http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/server
).
Software problems 53
Page 54

Software tools and solutions
In this section
Configuration tools................................................................................................................................. 54
Management tools.................................................................................................................................. 58
Diagnostic tools ..................................................................................................................................... 61
Remote support and analysis tools............................................................................................................ 63
Keeping the system current...................................................................................................................... 63
Firmware maintenance............................................................................................................................ 65
Configuration tools
Array Configuration Utility
ACU is a browser-based utility with the following features:
• Runs as a local application or remote service
• Supports online array capacity expansion, logical drive extension, assignment of online spares, and
RAID or stripe size migration
• Suggests the optimum configuration for an unconfigured system
• Provides different operating modes, enabling faster configuration or greater control over the
configuration options
• Remains available any time that the server is on
• Displays on-screen tips for individual steps of a configuration procedure
For optimum performance, the minimum display settings are 800 × 600 resolution and 256 colors.
Servers running Microsoft® operating systems require Internet Explorer 5.5 (with Service Pack 1) or later.
For Linux servers, refer to the README.TXT file for additional browser and support information.
For more information, refer to the HP Array Configuration Utility User Guide on the Documentation CD or
the HP website (http://www.hp.com
SmartStart software
SmartStart is a collection of software that optimizes single-server setup, providing a simple and consistent
way to deploy server configuration. SmartStart has been tested on many ProLiant server products,
resulting in proven, reliable configurations.
SmartStart assists the deployment process by performing a wide range of configuration activities,
including:
• Configuring hardware using embedded configuration utilities, such as RBSU and ORCA
• Preparing the system for installing "off-the-shelf" versions of leading operating system software
• Installing optimized server drivers, management agents, and utilities automatically with every
assisted installation
• Testing server hardware using the Insight Diagnostics Utility ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61)
).
Software tools and solutions 54
Page 55

•
Installing software drivers directly from the CD. With systems that have internet connection, the
SmartStart Autorun Menu provides access to a complete list of ProLiant system software.
• Enabling access to the Array Configuration Utility (on page 54), Array Diagnostic Utility (on page
63), and Erase Utility (on page 59)
SmartStart is included in the HP ProLiant Essentials Foundation Pack. For more information about
SmartStart software, refer to the HP ProLiant Essentials Foundation Pack or the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
SmartStart Scripting Toolkit
The SmartStart Scripting Toolkit is a server deployment product that delivers an unattended automated
installation for high-volume server deployments. The SmartStart Scripting Toolkit is designed to support
ProLiant BL, ML, and DL servers. The toolkit includes a modular set of utilities and important documentation
that describes how to apply these new tools to build an automated server deployment process.
Using SmartStart technology, the Scripting Toolkit provides a flexible way to create standard server
configuration scripts. These scripts are used to automate many of the manual steps in the server
configuration process. This automated server configuration process cuts time from each server deployed,
making it possible to scale server deployments to high volumes in a rapid manner.
For more information, and to download the SmartStart Scripting Toolkit, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/sstoolkit
).
).
HP ROM-Based Setup Utility
RBSU, an embedded configuration utility, performs a wide range of configuration activities that may
include:
• Configuring system devices and installed options
• Displaying system information
• Selecting the primary boot controller
• Configuring memory options
• Language selection
For more information on RBSU, refer to the HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User Guide on the Documentation
Using RBSU
CD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
The first time you power up the server, the system prompts you to enter RBSU and select a language.
Default configuration settings are made at this time and can be changed later. Most of the features in
RBSU are not required to set up the server.
To navigate RBSU, use the following keys:
• To access RBSU, press the F9 key during power up when prompted in the upper right corner of the
screen.
• To navigate the menu system, use the arrow keys.
• To make selections, press the Enter key.
).
IMPORTANT: RBSU automatically saves settings when you press the Enter key. The utility does not prompt
you for confirmation of settings before you exit the utility. To change a selected setting, you must select a
different setting and press the Enter key.
Software tools and solutions 55
Page 56

Auto-configuration process
The auto-configuration process automatically runs when you boot the server for the first time. During the
power-up sequence, the system ROM automatically configures the entire system without needing any
intervention. During this process, the ORCA utility, in most cases, automatically configures the array to a
default setting based on the number of drives connected to the server.
NOTE: The server may not support all the following examples.
NOTE: If the boot drive is not empty or has been written to in the past, ORCA does not automatically
configure the array. You must run ORCA to configure the array settings.
Drives installed Drives used RAID level
1 1 RAID 0
2 2 RAID 1
3, 4, 5, or 6 3, 4, 5, or 6 RAID 5
More than 6 0 None
To change any ORCA default settings and override the auto-configuration process, press the F8 key when
prompted.
By default, the auto-configuration process configures the system for the English language. To change any
default settings in the auto-configuration process (such as the settings for language, operating system, and
primary boot controller), execute RBSU by pressing the F9 key when prompted. After the settings are
selected, exit RBSU and allow the server to reboot automatically.
For more information, refer to the HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User Guide on the Documentation CD or
the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
Boot options
After the auto-configuration process completes, or after the server reboots upon exit from RBSU, the POST
sequence runs, and then the boot option screen is displayed. This screen is visible for several seconds
before the system attempts to boot from a diskette, CD, or hard drive. During this time, the menu on the
screen allows you to install an operating system or make changes to the server configuration in RBSU.
BIOS Serial Console
BIOS Serial Console allows you to configure the serial port to view POST error messages and run RBSU
remotely through a serial connection to the server COM port. The server that you are remotely configuring
does not require a keyboard and mouse.
For more information about BIOS Serial Console, refer to the BIOS Serial Console User Guide on the
Documentation CD or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
Configuring online spare memory
To configure online spare memory:
1. Install the required DIMMs.
2. Access RBSU by pressing the F9 key during power-up when the prompt is displayed in the upper
right corner of the screen.
3. Select System Options.
4. Select Advanced Memory Protection.
5. Select Online Spare with Advanced ECC Support.
6. Press the Enter key.
).
).
Software tools and solutions 56
Page 57

7.
Press the Esc key to exit the current menu, or press the F10 key to exit RBSU.
For more information on online spare memory, refer to the white paper on the HP website
(http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/servers/technology/memoryprotection.html
Option ROM Configuration for Arrays
Before installing an operating system, you can use the ORCA utility to create the first logical drive, assign
RAID levels, and establish online spare configurations.
The utility also provides support for the following functions:
• Reconfiguring one or more logical drives
• Viewing the current logical drive configuration
• Deleting a logical drive configuration
• Setting the controller to be the boot controller
If you do not use the utility, ORCA will default to the standard configuration.
For more information regarding array controller configuration, refer to the controller user guide.
For more information regarding the default configurations that ORCA uses, refer to the HP ROM-Based
Setup Utility User Guide on the Documentation CD.
).
HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack
The RDP software is the preferred method for rapid, high-volume server deployments. The RDP software
integrates two powerful products: Altiris Deployment Solution and the HP ProLiant Integration Module.
The intuitive graphical user interface of the Altiris Deployment Solution console provides simplified pointand-click and drag-and-drop operations that enable you to deploy target servers, including server blades,
remotely. It enables you to perform imaging or scripting functions and maintain software images.
For more information about the RDP, refer to the HP ProLiant Essentials Rapid Deployment Pack CD or
refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/rdp
).
Re-entering the server serial number and product ID
After you replace the system board, you must re-enter the server serial number and the product ID.
1. During the server startup sequence, press the F9 key to access RBSU.
2. Select the System Options menu.
3. Select Serial Number. The following warning is displayed:
WARNING! WARNING! WARNING! The serial number is loaded into the system
during the manufacturing process and should NOT be modified. This option
should only be used by qualified service personnel. This value should
always match the serial number sticker located on the chassis.
4. Press the Enter key to clear the warning.
5. Enter the serial number and press the Enter key.
6. Select Product ID.
7. Enter the product ID and press the Enter key.
8. Press the Esc key to close the menu.
9. Press the Esc key to exit RBSU.
10. Press the F10 key to confirm exiting RBSU. The server will automatically reboot.
Software tools and solutions 57
Page 58

Management CD
The Management CD contains the latest tools available for easily managing the server, such as HP SIM
("HP Systems Insight Manager" on page 59) and Management Agents (on page 59).
Run the Management CD shipped with the server. Refer to the Management CD user documentation as
well as the ProLiant Server Management website (http://www.hp.com/servers/manage
Management tools
Automatic Server Recovery
ASR is a feature that causes the system to restart when a catastrophic operating system error occurs, such
as a blue screen, ABEND, or panic. A system fail-safe timer, the ASR timer, starts when the System
Management driver, also known as the Health Driver, is loaded. When the operating system is
functioning properly, the system periodically resets the timer. However, when the operating system fails,
the timer expires and restarts the server.
ASR increases server availability by restarting the server within a specified time after a system hang or
shutdown. At the same time, the HP SIM console notifies you by sending a message to a designated
pager number that ASR has restarted the system. You can disable ASR from the HP SIM console or
through RBSU.
).
ROMPaq utility
Flash ROM enables you to upgrade the firmware (BIOS) with system or option ROMPaq utilities. To
upgrade the BIOS, insert a ROMPaq diskette into the diskette drive and boot the system.
The ROMPaq utility checks the system and provides a choice (if more than one exists) of available ROM
revisions. This procedure is the same for both system and option ROMPaq utilities.
For more information about the ROMPaq utility, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/manage
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition II
RILOE II enables browser access to servers through a hardware-based, OS-independent graphical remote
console. Some of the features include virtual diskette drive and power button, server management through
any standard browser, dedicated LAN connectivity, automatic network configuration, external power
backup, group administration, and functions available with the Remote Insight Board.
For more information about RILOE II features, refer to the Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition User Guide on
the Documentation CD or on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
Integrated Lights-Out technology
The iLO and iLO 2 subsystem is a standard component of selected ProLiant servers that provides server
health and remote server manageability. The iLO and iLO 2 subsystem includes an intelligent
microprocessor, secure memory, and a dedicated network interface. This design makes iLO and iLO 2
independent of the host server and its operating system. The iLO and iLO 2 subsystem provides remote
access to any authorized network client, sends alerts, and provides other server management functions.
).
).
Using iLO and iLO 2, you can:
• Remotely power up, power down, or reboot the host server.
• Send alerts from iLO and iLO 2 regardless of the state of the host server.
Software tools and solutions 58
Page 59

•
Access advanced troubleshooting features through the iLO and iLO 2 interface.
• Diagnose iLO and iLO 2 using HP SIM through a web browser and SNMP alerting.
For more information about iLO and iLO 2 features, refer to the iLO and iLO 2 documentation on the
Documentation CD or on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out).
Erase Utility
CAUTION: Perform a backup before running the System Erase Utility. The utility sets the system to its
original factory state, deletes the current hardware configuration information, including array setup and disk
partitioning, and erases all connected hard drives completely. Refer to the instructions for using this utility.
Run the Erase Utility if you must erase the system for the following reasons:
• You want to install a new operating system on a server with an existing operating system.
• You encounter an error when completing the steps of a factory-installed operating system installation.
The Erase Utility can be accessed from the Maintenance Utilities menu of the SmartStart CD
("SmartStart software" on page 54).
StorageWorks library and tape tools
HP StorageWorks L&TT provides functionality for firmware downloads, verification of device operation,
maintenance procedures, failure analysis, corrective service actions, and some utility functions. It also
provides seamless integration with HP hardware support by generating and emailing support tickets that
deliver a snapshot of the storage system.
For more information, and to download the utility, refer to the StorageWorks L&TT website
(http://h18006.www1.hp.com/products/storageworks/ltt
).
HP Systems Insight Manager
HP SIM is a web-based application that allows system administrators to accomplish normal administrative
tasks from any remote location, using a web browser. HP SIM provides device management capabilities
that consolidate and integrate management data from HP and third-party devices.
IMPORTANT: You must install and use HP SIM to benefit from the Pre-Failure Warranty for processors,
SAS and SCSI hard drives, and memory modules.
For additional information, refer to the Management CD in the HP ProLiant Essentials Foundation Pack or
the HP SIM website (http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim
).
Management Agents
Management Agents provide the information to enable fault, performance, and configuration
management. The agents allow easy manageability of the server through HP SIM software, and thirdparty SNMP management platforms. Management Agents are installed with every SmartStart assisted
installation or can be installed through the HP PSP. The Systems Management homepage provides status
and direct access to in-depth subsystem information by accessing data reported through the Management
Agents. For additional information, refer to the Management CD in the HP ProLiant Essentials Foundation
Pack or the HP website (http://www.hp.com/servers/manage
).
HP ProLiant Essentials Virtualization Management Software
The ProLiant Essentials Virtual Machine Management Pack and ProLiant Essentials Server Migration Pack
plug-ins extend HP Systems Insight Manager capabilities to manage virtual machines.
Software tools and solutions 59
Page 60

The Virtual Machine Management Pack provides the following functionality:
• Central management and control of VMware® and Microsoft® virtual machines with physical host to
virtual machine association
• Easy identification of VMs or host servers reaching high CPU, memory, or disk utilization levels
• Highly flexible move capabilities that enable live moves and moves to dissimilar host resources
• Back up, template, and alternate host capabilities that enable restoration of VMs on any available
host
The Server Migration Pack automates the manual processes required for migrating servers between
physical or virtual platforms (P2V, V2P, and V2V), enabling easy migration to appropriate physical or
virtual platforms that meet performance and capacity requirements.
For more information about virtualization management software, see the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/vmmanage
).
HP ProLiant Essentials Server Migration Pack - Physical to ProLiant Edition
The HP ProLiant Essentials Server Migration Pack – Physical to ProLiant Edition (SMP – P2P) software
enables administrators to upgrade or replace an existing server. SMP – P2P is an automated, accurate,
and affordable tool that migrates existing servers and their content to the latest server technologies.
SMP – P2P automates the migration of the operating system, applications, and data from one server to
another without errors, eliminating the need for manual redeployment of these elements on the new
server. During the migration process, the software automatically removes old drivers and loads new
drivers on the destination server. The wizard-based user interface simplifies migration and requires no
additional training.
For more information about the SMP – P2P, see the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/p2p
HP BladeSystem Essentials Insight Control Data Center Edition
HP BladeSystem Essentials Insight Control Data Center Edition is an integrated suite of software that
simplifies the management of HP BladeSystem infrastructures. Using a wizard-based installer, Insight
Control Data Center Edition installs and configures HP Systems Insight Manager (HP SIM) and HP ProLiant
Essentials management software rapidly and consistently, reducing manual procedures and enabling a
faster deployment of production HP server blades.
The software installed by Insight Control Data Center Edition delivers core management functionality for
HP BladeSystem lifecycles, including hardware resource deployment, health monitoring, performance
monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and patch management. Insight Control Data Center Edition is
delivered as a standard feature of HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosures and is available as a software
option for HP BladeSystem p-Class environments.
For more information about Insight Control Data Center Edition, see the HP website
(http://www.hp.com
).
HP Control Tower
HP Control Tower is an all-in-one software package that provides management and deployment for HP
BladeSystem and its ProLiant BL p-Class server blades.
Built on Linux, it delivers an easy-to-use interface tailored to blades and optimized for Linux users. HP
Control Tower enables operating system deployment using both standard installation and image-based
technologies.
).
For more information about HP Control Tower, see the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/controltower
).
Software tools and solutions 60
Page 61

System Management homepage
To access the System Management homepage of a server, go to https://localhost:2381
(https://localhost:2381
).
USB support
HP provides both standard USB support and legacy USB support. Standard support is provided by the
operating system through the appropriate USB device drivers. HP provides support for USB devices before
the operating system loads through legacy USB support, which is enabled by default in the system ROM.
HP hardware supports USB version 1.1.
Legacy USB support provides USB functionality in environments where USB support is normally not
available. Specifically, HP provides legacy USB functionality at:
• POST
• RBSU
• Diagnostics
• DOS
• Environments which do not support USB natively
For more information on ProLiant USB support, refer to the HP website
(http://www.compaq.com/products/servers/platforms/usb-support.html).
Clustering software
If the server uses cluster software, such as Microsoft® Cluster Server or Novell Cluster Services, refer to
the documentation provided with the application for cluster troubleshooting information. For software
troubleshooting information and frequently asked questions, refer to the Microsoft® or Novell websites.
To collect information on cluster configurations, run the Cluster Monitor integrated with HP SIM ("HP
Systems Insight Manager" on page 59).
For additional clustering documentation, refer to the High Availability website
(http://h18004.www1.hp.com/solutions/enterprise/highavailability
Diagnostic tools
HP Insight Diagnostics
HP Insight Diagnostics is a proactive server management tool, available in both offline and online
versions, that provides diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities to assist IT administrators who verify
server installations, troubleshoot problems, and perform repair validation.
HP Insight Diagnostics Offline Edition performs various in-depth system and component testing while the
OS is not running. To run this utility, launch the SmartStart CD.
HP Insight Diagnostics Online Edition is a web-based application that captures system configuration and
other related data needed for effective server management. Available in Microsoft® Windows® and
Linux versions, the utility helps to ensure proper system operation.
).
For more information or to download the utility, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/diags
).
Software tools and solutions 61
Page 62

Smart Array SCSI Diagnosis feature
NOTE: This feature is only available in HP Insight Diagnostics Online Edition.
The HP Insight Diagnostics Online Edition ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) provides the capability
to use non-intrusive system level checks to diagnose Smart Array SCSI hard drives. Diagnosis supports
SCSI, SATA, and SAS hard drives that are attached to a Smart Array controller and configured as part of
a logical volume. Diagnosis is not component testing, but is a combination of drive history and controller
error status.
Diagnosis assists in confirming hardware status and is faster than offline testing. Using the diagnosis
feature reduces downtime and provides information on one pass.
The diagnosis feature should be used:
• To troubleshoot why a hard drive is in a particular state.
• When HP SIM reports a hard drive pre-failure or that a hard drive has failed.
• When data corruption or storage problems occur, but no physical indications are evident.
• When conflicting errors exist.
• When repeated failures occur.
Survey Utility
Survey Utility, a feature within HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 61), gathers critical hardware and
software information on ProLiant servers.
This utility supports operating systems that may not be supported by the server. For operating systems
supported by the server, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/supportos
If a significant change occurs between data-gathering intervals, the Survey Utility marks the previous
information and overwrites the Survey text files to reflect the latest changes in the configuration.
Survey Utility is installed with every SmartStart-assisted installation or can be installed through the HP PSP
("ProLiant Support Packs" on page 64).
NOTE: SmartStart version 7.5 and later provides the memory spare part numbers for the server.
Integrated Management Log
The IML records hundreds of events and stores them in an easy-to-view form. The IML timestamps each
event with 1-minute granularity.
You can view recorded events in the IML in several ways, including the following:
• From within HP SIM ("HP Systems Insight Manager" on page 59)
• From within Survey Utility (on page 62)
• From within operating system-specific IML viewers
• For NetWare: IML Viewer
• For Windows®: IML Viewer
• For Linux: IML Viewer Application
• From within the iLO and iLO 2 user interface
• From within HP Insight Diagnostics (on page 61)
).
For more information, refer to the Management CD in the HP ProLiant Essentials Foundation Pack.
Software tools and solutions 62
Page 63

Array Diagnostic Utility
ADU is a tool that collects information about array controllers and generates a list of detected problems.
ADU can be accessed from the SmartStart CD ("SmartStart software" on page 54) or downloaded from
the HP website (http://www.hp.com
).
Remote support and analysis tools
HP Instant Support Enterprise Edition
ISEE is a proactive remote monitoring and diagnostic tool to help manage your systems and devices, a
feature of HP support. ISEE provides continuous hardware event monitoring and automated notification to
identify and prevent potential critical problems. Through remote diagnostic scripts and vital system
configuration information collected about your systems, ISEE enables fast restoration of your systems.
Install ISEE on your systems to help mitigate risk and prevent potential critical problems.
For more information on ISEE, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/hps/hardware/hw_enterprise.html
).
To download HP ISEE, visit the HP website (http://www.hp.com/hps/hardware/hw_downloads.html
For installation information, refer to the HP ISEE Client Installation and Upgrade Guide
(ftp://ftp.hp.com/pub/services/hardware/info/isee_client.pdf
Web-Based Enterprise Service
WEBES enables administrators to manage hardware events proactively, either locally or online. The
service provides real-time multiple event analysis, crash analysis, and notification, locally through SMTP
and remotely through ISEE for OpenVMS, Tru64, and Microsoft® Windows® operating system binary
error logs.
For more information, refer to the HP website (http://h18000.www1.hp.com/support/svctools/
Open Services Event Manager
OSEM is a standalone tool that performs real-time reactive and proactive service event filtering, analysis,
and notification. The tool gathers event data from SNMP traps or information provided over an HTTP
interface and notifies an administrator or HP through SMTP and ISEE.
For more information, refer to the HP website (http://h18000.www1.hp.com/support/svctools/
Keeping the system current
).
).
).
).
Drivers
The server includes new hardware that may not have driver support on all operating system installation
media.
If you are installing a SmartStart-supported operating system, use the SmartStart software (on page 54)
and its Assisted Path feature to install the operating system and latest driver support.
NOTE: If you are installing drivers from the SmartStart CD or the Software Maintenance CD, refer to the
SmartStart website (http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
of SmartStart. For more information, refer to the documentation provided with the SmartStart CD.
) to be sure that you are using the latest version
Software tools and solutions 63
Page 64

If you do not use the SmartStart CD to install an operating system, drivers for some of the new hardware
are required. These drivers, as well as other option drivers, ROM images, and value-add software can be
downloaded from the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
IMPORTANT: Always perform a backup before installing or updating device drivers.
).
Version control
The VCRM and VCA are Web-enabled Insight Management Agents tools that HP SIM uses to facilitate
software update tasks.
• VCRM manages the repository for Windows and Linux PSPs. Administrators can browse a graphical
view of the PSPs or configure VCRM to automatically update the repository with internet downloads
of the latest software from HP.
• VCA compares software versions and updates. Administrators can configure VCA to point to a
repository managed by VCRM.
For more information about version control tools, refer to the HP Systems Insight Manager Help Guide
and the Version Control User Guide on the HP Systems Insight Manager website
(http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim
).
Resource Paqs
Resource Paqs are operating system-specific packages of tools, utilities, and information for HP servers
running certain Microsoft® or Novell operating systems. The Resource Paqs include utilities to monitor
performance, software drivers, customer support information, and white papers on the latest server
integration information. Refer to the Enterprise Partnerships website
(http://h18000.www1.hp.com/partners
system, and follow the link to the appropriate Resource Paq.
ProLiant Support Packs
PSPs represent operating system-specific bundles of ProLiant optimized drivers, utilities, and management
agents. Refer to the PSP website
(http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/servers/management/psp.html
Operating system version support
Refer to the operating system support matrix (http://www.hp.com/go/supportos).
SoftPaqs
SoftPaqs are software utilities (such as diagnostics and configuration utilities), software upgrades,
ROMPaqs (firmware upgrades), and fixes that resolve software problems or provide workarounds. Refer
to the Software and Drivers Download website (http://h18007.www1.hp.com/support/files/server
), select Microsoft or Novell, depending on the operating
).
).
Change control and proactive notification
HP offers Change Control and Proactive Notification to notify customers 30 to 60 days in advance of
upcoming hardware and software changes on HP commercial products.
For more information, refer to the HP website
(http://h18023.www1.hp.com/solutions/pcsolutions/pcn.html
).
Software tools and solutions 64
Page 65

Care Pack
HP Care Pack Services offer upgraded service levels to extend and expand standard product warranty
with easy-to-buy, easy-to-use support packages that help you make the most of your server investments.
Refer to the Care Pack website (http://www.hp.com/hps/carepack/servers/cp_proliant.html
Firmware maintenance
HP has developed technologies that ensure that HP servers provide maximum uptime with minimal
maintenance. Many of these technologies also reduce server management efforts, enabling administrators
to work on issues and resolve problems without taking servers offline.
The process of updating system or option firmware is referred to as flashing the ROM. A ROM flash
removes the existing version of firmware from the ROM and replaces it with a more recent version.
Flash the ROM to:
• Support new features
• Correct problems in a previous ROM version
).
Without the correct firmware version, the server and hardware options may not function properly.
Types of ROM
Types of ROMs include:
• System ROM (on page 65)
System ROM
• Option ROMs (on page 66)
All ProLiant servers have a system ROM.
A system reboot is required for a ROM upgrade to take effect. For disaster recovery or ROM downgrade
purposes, backups of the most current ROM image are available in either redundant ROM or a ROM
backup.
Redundant ROM support
The server enables you to upgrade or configure the ROM safely with redundant ROM support. The server
has a 4-MB ROM that acts as two, separate 2-MB ROMs. In the standard implementation, one side of the
ROM contains the current ROM program version, while the other side of the ROM contains a backup
version.
NOTE: The server ships with the same version programmed on each side of the ROM.
When you flash the system ROM, ROMPaq writes over the backup ROM and saves the current ROM as a
backup, enabling you to switch easily to the alternate ROM version if the new ROM becomes corrupted
for any reason. This feature protects the existing ROM version, even if you experience a power failure
while flashing the ROM.
You can choose which ROM to use in RBSU ("HP ROM-Based Setup Utility" on page 55).
Automatic backup
A backup copy of the ROM image existing on the target server is made in the ROM image backup
subdirectory:
\CPQSYSTEM\FWBACKUP\SYSTEM
Software tools and solutions 65
Page 66

For additional information, refer to the HP Online ROM Flash User Guide on the HP website
(http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/romflash.html
Option ROMs
Smart Components for option ROMs provide for efficient administration of option ROM upgrades. Types
of option ROMs include:
• Array controller ROMs
• iLO ROMs
• RILOE II ROMs
• Hard drive ROMs
NOTE: Online ROM Flash components are not available for hard drive ROMs.
Methods for updating firmware
Methods for updating firmware include:
• Offline
• Online
).
Online ROM flash technology
The Online ROM Flash Component Utility enables system administrators to efficiently upgrade system or
controller ROM images across a wide range of servers and array controllers. This tool has the following
features:
• Works offline and online
• Supports Microsoft® Windows NT®, Windows® 2000, Windows Server™ 2003, Novell Netware,
and Linux operating systems
IMPORTANT: This utility supports operating systems that may not be supported by the server. For
operating systems supported by the server, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/supportos
• Integrates with other software maintenance, deployment, and operating system tools
• Automatically checks for hardware, firmware, and operating system dependencies, and installs only
the correct ROM upgrades required by each target server
To download the tool and for more information, refer to the HP website
(http://h18000.www1.hp.com/support/files/index.html
).
For OS-specific procedures, refer to the HP Online ROM Flash User Guide on the HP website
(http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/romflash.html
).
Offline ROM flash technology
ROMPaq utility
).
The ROMPaq diskette is bootable and contains all the necessary system and option ROM image files and
the configuration files required to upgrade the ROM firmware. ROMPaq diskettes include ROM images
for one or more servers that are a part of the same family.
To flash the ROM using ROMPaq:
1. Download the system ROMPaq utility diskette for each target server or option for which a ROM flash
is planned. ROMPaq downloads are available on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
Software tools and solutions 66
).
Page 67

2.
Shut down each server where the system or option ROM images are to be upgraded and reboot
using the correct ROMPaq diskette for that server.
3. Follow the interactive session in the ROMPaq utility, which enables you to select the devices to be
flashed.
4. After the ROMPaq utility flashes the ROM for the selected devices, cycle power manually to reboot
the system back into the operating system.
This procedure is most effective when flashing the ROM on a small number of servers located in close
proximity.
NOTE: Option ROMPaqs have been retired as an upgrade delivery method for storage options. Firmware
upgrades for storage options are now delivered using Smart Components and Smart Component
deployment utilities.
For additional information about the ROMPaq utility, refer to the server documentation or the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/support/files
).
ROM Update Utility
The ROM Update Utility is offline ROM flash technology.
To access the ROM Update Utility:
1. Boot the server from one of the following:
• HP SmartStart CD 6.x
• HP Firmware Maintenance CD 7.0 or later
2. Select the Maintenance tab.
Current firmware versions
Automatic firmware updates
• Subscriber's Choice (http://www.hp.com/go/subscriberschoice)
• VCRM ("Version control" on page 64)
Manual firmware updates
Download the latest firmware updates from the HP website
(http://h18023.www1.hp.com/support/files/server/us/romflash.html
Updating firmware
To verify the firmware version, use one of the following tools:
• Insight Diagnostics Online Edition ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61)
Access this tool from the System Management homepage (on page 61).
• VCA ("Version control" on page 64)
Access this tool from the System Management homepage (on page 61).
• HP SIM ("HP Systems Insight Manager" on page 59)
• VCRM ("Version control" on page 64)
To update the firmware:
1. Check the firmware version.
2. Determine the latest firmware version.
3. Update the firmware to the latest version supported for the hardware configuration.
).
Software tools and solutions 67
Page 68

4.
Verify the firmware update by checking the version of the current firmware.
Software tools and solutions 68
Page 69

HP resources for troubleshooting
In this section
Online resources .................................................................................................................................... 69
General server resources......................................................................................................................... 70
Online resources
HP website
Troubleshooting tools and information, as well as the latest drivers and flash ROM images, are available
on the HP website (http://www.hp.com
).
Server documentation
Server documentation is the set of documents that ships with a server. Most server documents are
available as a PDF or a link on the Documentation CD. Server documentation can also be accessed from
the HP Technical Support website (http://docs.hp.com
(http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport
Service notifications
To view the latest service notifications, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport).
Select the appropriate server model, and then click the Troubleshoot a Problem link on the product
page.
Subscriber's choice
HP's Subscriber's Choice is a customizable subscription sign-up service that customers use to receive
personalized email product tips, feature articles, driver and support alerts, or other notifications.
To create a profile and select notifications, refer to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/subscriberschoice
Natural language search assistant
The natural language search assistant (http://www.hp.com/support/natural_language_search) is a
search engine that finds information on HP products, including ProLiant servers. The search engine
responds to queries entered in question form.
) or the HP Business Support Center website
).
).
Care Pack
HP Care Pack Services offer upgraded service levels to extend and expand standard product warranty
with easy-to-buy, easy-to-use support packages that help you make the most of your server investments.
Refer to the Care Pack website (http://www.hp.com/hps/carepack/servers/cp_proliant.html
).
HP resources for troubleshooting 69
Page 70

White papers
White papers are electronic documentation on complex technical topics. Some white papers contain indepth details and procedures. Topics include HP products, HP technology, OS, networking products, and
performance. Refer to one of the following websites:
• HP Business Support Center (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
• HP Industry Standard Server Technology Papers
(http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/technology/whitepapers/index.html
General server resources
Additional product information
Refer to product information on the HP Servers website
Device driver information
(http://www.hp.com/country/us/eng/prodserv/servers.html
)
).
Refer to driver information on the HP Software and Drivers website (http://www.hp.com/support).
External cabling information
Refer to cabling information on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support).
Fault tolerance, security, care and maintenance, configuration and setup
Refer to the server documentation available in the following locations:
• Documentation CD that ships with the server
• HP Business Support Center website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
• HP Technical Documentation website (http://www.docs.hp.com)
Installation and configuration information for the server management system
Refer to the HP Systems Insight Manager Installation and User Guide on the Management CD or the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim
).
Installation and configuration information for the server setup software
Refer to the server user guide on the Documentation CD, the server installation poster shipped with the
server, and the SmartStart installation poster (if the server supports SmartStart) in the HP ProLiant Essentials
Foundation Pack.
iLO information
Refer to the HP Integrated Lights-Out User Guide on the Documentation CD or the Remote Management
website (http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
Key features, option part numbers
Refer to the QuickSpecs on the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
).
HP resources for troubleshooting 70
Page 71

Management of the server
Refer to the HP Systems Insight Manager Help Guide on the Management CD or the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/hpsim
).
Operating system installation and configuration information (for factory-installed operating systems)
Refer to the factory-installed operating system installation documentation that ships with the server.
Operating system version support
Refer to the operating system support matrix (http://www.hp.com/go/supportos).
Overview of server features and installation instructions
Refer to the server user guide on the Documentation CD or on the HP Business Support Center website
(http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport
).
Power capacity
Refer to the power calculator on the HP Enterprise Configurator website
(http://h30099.www3.hp.com/configurator/
).
Registering the server
To register the server, refer to the HP Registration website (http://register.hp.com).
Server configuration information
Refer to the server user guide on the Documentation CD, the server installation poster shipped with the
server, and the SmartStart installation poster (if the server supports SmartStart) in the HP ProLiant Essentials
Foundation Pack.
Software installation and configuration of the server
If the server supports SmartStart, refer to the SmartStart installation poster in the HP ProLiant Essentials
Foundation Pack.
Switch settings, LED functions, drive, memory, expansion board and processor installation instructions, and board layouts
Refer to the hood labels and the server user guide. The hood labels are inside the access panels of the
server, and the server user guide is available in the following locations:
• Documentation CD that ships with the server
• HP Business Support Center website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
• HP Technical Documentation website (http://www.docs.hp.com)
HP resources for troubleshooting 71
Page 72

Server and option specifications, symbols, installation warnings, and notices
Refer to the server documentation and printed notices. Printed notices are available in the Reference
Information pack. Server documentation is available in the following locations:
• Documentation CD that ships with the server
• HP Business Support Center website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
• HP Technical Documentation website (http://www.docs.hp.com)
Teardown procedures, part numbers, specifications
Refer to the server maintenance and service guide, available in the following locations:
• Documentation CD that ships with the server
• HP Business Support Center website (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
• HP Technical Documentation website (http://www.docs.hp.com)
Technical topics
Refer to white papers on one of the following:
• HP Business Support Center (http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport)
• HP Industry Standard Server Technology Papers
(http://h18004.www1.hp.com/products/servers/technology/whitepapers/index.html
)
HP resources for troubleshooting 72
Page 73

Error messages
In this section
ADU error messages............................................................................................................................... 73
POST error messages and beep codes...................................................................................................... 92
Event list error messages ....................................................................................................................... 124
HP BladeSystem infrastructure error codes............................................................................................... 127
Port 85 codes and iLO messages ........................................................................................................... 131
Windows® Event Log processor error codes ........................................................................................... 134
Insight Diagnostics processor error codes................................................................................................ 135
ADU error messages
Introduction to ADU error messages
This section contains a complete alphabetical list of all ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) error
messages.
IMPORTANT: This guide provides information for multiple servers. Some information may not apply to the
server you are troubleshooting. Refer to the server documentation for information on procedures, hardware
options, software tools, and operating systems supported by the server.
WARNING: To avoid potential problems, ALWAYS read the warnings and cautionary
information in the server documentation before removing, replacing, reseating, or
modifying system components.
Accelerator Board not Detected
Description: Array controller did not detect a configured array accelerator board.
Action: Install an array accelerator board on an array controller. If an array accelerator board is
installed, check for proper seating on the array controller board.
Accelerator Error Log
Description: List of the last 32 parity errors on transfers to or from the memory on the array accelerator
board. Displays starting memory address, transfer count, and operation (read and write).
Action: If many parity errors are listed, you may need to replace the array accelerator board.
Accelerator Parity Read Errors: X
Description: Number of times that read memory parity errors were detected during transfers from
memory on the array accelerator board.
Action: If many parity errors occurred, you may need to replace the array accelerator board.
Error messages 73
Page 74

Accelerator Parity Write Errors: X
Description: Number of times that write memory parity errors were detected during transfers to memory
on the array accelerator board.
Action: If many parity errors occurred, you may need to replace the array accelerator board.
Accelerator Status: Cache was Automatically Configured During Last Controller
Reset
Description: Cache board was replaced with one of a different size.
Action: No action is required.
Accelerator Status: Data in the Cache was Lost...
...due to some reason other than the battery being discharged.
Description: Data in cache was lost, but not because of the battery being discharged.
Action: Be sure the array accelerator is properly seated. If the error persists, you may need to replace
the array accelerator.
Accelerator Status: Dirty Data Detected has Reached Limit...
...Cache still enabled, but writes no longer being posted.
Description: Number of cache lines containing dirty data that cannot be flushed (written) to the drives
has reached a preset limit. The cache is still enabled, but writes are no longer being posted. This problem
usually occurs when a problem with the drive or drives occurs.
Action: Resolve the problem with the drive or drives. The controller can then write the dirty data to the
drives. Posted-writes operations are restored.
Accelerator Status: Dirty Data Detected...
...Unable to write dirty data to drives
Description: At least one cache line contains dirty data that the controller has been unable to flush
(write) to the drives. This problem usually occurs when a problem with the drive or drives occurs.
Action: Resolve the problem with the drive or drives. The controller can then write the dirty data to the
drives.
Accelerator Status: Excessive ECC Errors Detected in at Least One Cache Line...
...As a result, at least one cache line is no longer in use.
Description: At least one line in the cache is no longer in use due to excessive ECC errors detected
during use of the memory associated with that cache line.
Action: Consider replacing the cache. If cache replacement is not done, the remaining cache lines
generally continue to operate properly.
Accelerator Status: Excessive ECC Errors Detected in Multiple Cache Lines...
...As a result, the cache is no longer in use.
Error messages 74
Page 75

Description: The number of cache lines experiencing excessive ECC errors has reached a preset limit.
Therefore, the cache has been shut down.
Action:
1. Reseat the cache to the controller.
2. If the problem persists, replace the cache.
Accelerator Status: Obsolete Data Detected
Description: During reset initialization, obsolete data was found in the cache due to the drives being
moved and written to by another controller.
Action: No action is required. The controller either writes the data to the drives or discards the data
completely.
Accelerator Status: Obsolete Data was Discarded
Description: During reset initialization, obsolete data was found in the cache, and was discarded (not
written to the drives).
Action: No action is required.
Accelerator Status: Obsolete Data was Flushed (Written) to Drives
Description: During reset initialization, obsolete data was found in the cache. The obsolete data was
written to the drives, but newer data may have been overwritten.
Action: If newer data was overwritten, you may need to restore newer data; otherwise, normal operation
should continue.
Accelerator Status: Permanently Disabled
Description: Array accelerator board has been permanently disabled. It will remain disabled until it is
reinitialized using ACU.
Action: Check the Disable Code field. Run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54) to reinitialize
the array accelerator board.
Accelerator Status: Possible Data Loss in Cache
Description: Possible data loss was detected during power-up due to all batteries being below sufficient
voltage level and no presence of the identification signatures on the array accelerator board.
Action: No way exists to determine if dirty or bad data was in the cache and is now lost.
Accelerator Status: Temporarily Disabled
Description: Array accelerator board has been temporarily disabled.
Action: Check the Disable Code field.
Accelerator Status: Unrecognized Status
Description: A status was returned from the array accelerator board that ADU does not recognize.
Action: Obtain the latest version of ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63).
Error messages 75
Page 76

Accelerator Status: Valid Data Found at Reset
Description: Valid data was found in posted-write memory at reinitialization. Data will be flushed to
disk.
Action: No error or data loss condition exists. No action is required.
Accelerator Status: Warranty Alert
Description: Catastrophic problem exists with array accelerator board. Refer to other messages on
Diagnostics screen for exact meaning of this message.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board.
Adapter/NVRAM ID Mismatch
Description: EISA NVRAM has an ID for a different controller from the one physically present in the slot.
Action: Run the server setup utility.
Array Accelerator Battery Pack X not Fully Charged
Description: Battery is not fully charged.
Action: If 75% of the batteries present are fully charged, the array accelerator is fully operational. If
more than 75% of the batteries are not fully charged, allow 36 hours to recharge them.
Array Accelerator Battery Pack X Below Reference Voltage (Recharging)
Description: Battery pack on the array accelerator is below the required voltage levels.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board if the batteries do not recharge within 36 powered-on
hours.
Board in Use by Expand Operation
Description: Array accelerator memory is in use by an expand operation.
Action: Operate the system without the array accelerator board until the expand operation completes.
Board not Attached
Description: An array controller is configured for use with array accelerator board, but one is not
connected.
Action: Connect array accelerator board to array controller.
Cache Has Been Disabled Because ADG Enabler Dongle is Broken or Missing
Description: The cache has been disabled because RAID ADG volume is configured but the ADG
Enabler Dongle is broken or missing.
Action: Check the ADG Enabler Dongle. Replace if needed.
Error messages 76
Page 77

Cache Has Been Disabled; Likely Caused By a Loose Pin on One of the RAM Chips
Description: Cache has been disabled due to a large number of ECC errors detected while testing the
cache during POST. This is probably caused by a loose pin on one of the RAM chips.
Action: Try reseating the cache to the controller. If that does not work, replace the cache.
Configuration Signature is Zero
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) detected that NVRAM contains a
configuration signature of zero. Old versions of the server setup utility could cause this.
Action: Run the latest version of server setup utility to configure the controller and NVRAM.
Configuration Signature Mismatch
Description: The array accelerator board is configured for a different array controller board. The
configuration signature on the array accelerator board does not match the one stored on the array
controller board.
Action: To recognize the array accelerator board, run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54).
Controller Communication Failure Occurred
Description: Controller communication failure occurred. ADU was unable to successfully issue
commands to the controller in this slot.
Action:
1. Be sure all cables are properly connected and working.
2. Be sure the controller is working, and replace if needed.
Controller Detected. NVRAM Configuration not Present
Description: EISA NVRAM does not contain a configuration for this controller.
Action: Run the server setup utility to configure the NVRAM.
Controller Firmware Needs Upgrading
Description: Controller firmware is below the latest recommended version.
Action: Update the controller to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
Controller is Located in Special "Video" Slot
Description: Controller is installed in the slot for special video control signals. If the controller is used in
this slot, LED indicators on the front panel may not function properly.
Action: Install the controller into a different slot, and run the server setup utility to configure NVRAM.
Then, run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54) to configure the controller.
Controller Is Not Configured
Description: Controller is not configured. If the controller was previously configured and you change
drive locations, a problem might exist with the placement of the drives. ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on
Error messages 77
Page 78

page 63) examines each physical drive and looks for drives that have been moved to a different drive
bay.
Action: Look for messages indicating which drives have been moved. If no messages are displayed and
drive swapping did not occur, run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54) to configure the
controller and run the server setup utility to configure NVRAM. Do not run either utility if you believe
drive swapping has occurred.
Controller Reported POST Error. Error Code: X
Description: The controller returned an error from its internal POST.
Action: Replace the controller.
Controller Restarted with a Signature of Zero
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) did not find a valid configuration signature to
use to get the data. NVRAM may not be present (unconfigured) or the signature present in NVRAM may
not match the signature on the controller.
Action: Run the server setup utility to configure the controller and NVRAM.
Disable Command Issued
Description: The issuing of the Accelerator Disable command has disabled posted-writes. This occurred
because of an operating system device driver.
Action: Restart the system. Run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54) to reinitialize the array
accelerator board.
Drive (Bay) X Firmware Needs Upgrading
Description: Firmware on this physical drive is below the latest recommended version.
Action: Update the drive to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
Drive (Bay) X has Insufficient Capacity for its Configuration
Description: Drive has insufficient capacity to be used in this logical drive configuration.
Action: Replace this drive with a larger capacity drive.
Drive (Bay) X has Invalid M&P Stamp
Description: Physical drive has invalid monitor and performance data.
Action: Run the server setup utility to properly initialize this drive.
Drive (Bay) X Has Loose Cable
Description: The array controller could not communicate with this drive at power-up. This drive has not
previously failed.
Action:
1. Be sure all cables are properly connected and working.
2. Power down the system and attempt to reconnect data/power cable to the drive.
3. Power up the system.
Error messages 78
Page 79

4.
If the problem persists, power down the system and replace the cable.
5. If the problem persists, power down the system and replace the drive.
Drive (Bay) X is a Replacement Drive
Description: This drive has been replaced. This message is displayed if a drive is replaced in a faulttolerant logical volume.
Action: If the replacement was intentional, allow the drive to rebuild.
Drive (Bay) X is a Replacement Drive Marked OK
Description: The drive has been replaced and marked OK by the firmware, in one of three possible
scenarios: the drive was replaced in a non-fault-tolerant configuration; more drives were replaced than the
configured fault-tolerant-configuration mode could sustain; or the storage enclosure was powered down
before the server, preventing the drive from being rebuilt. The drive may contain incorrect data.
Action: Verify data on the drives. Always power down the server before powering down any external
drive enclosures.
Drive (Bay) X is Failed
Description: The indicated physical drive has failed.
Action:
1. Check for loose cable connections ("Loose connections" on page 15).
2. If cable connectors are secure, replace the drive.
Drive (Bay) X is Undergoing Drive Recovery
Description: This drive is being rebuilt from the corresponding mirror or parity data.
Action: No action is required.
Drive (Bay) X Upload Code Not Readable
Description: An error occurred while ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) was trying to read
the upload code information from this drive.
Action: If multiple errors occur, the drive may need to be replaced.
Drive (Bay) X Was Inadvertently Replaced
Description: The physical drive was incorrectly replaced after another drive failed.
Action:
CAUTION: Do not run the server setup utility and try to reconfigure, or data will be lost.
1. Power down the server.
2. Replace the drive that was incorrectly replaced.
3. Replace the original drive that failed.
Error messages 79
Page 80

Drive Monitoring Features Are Unobtainable
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) is unable to get monitor and performance
data due to a fatal command problem (such as drive time-out), or is unable to get data due to these
features not being supported on the controller.
Action: Check for other errors such as time-outs. If no other errors occur, upgrade the firmware to a
version that supports monitor and performance, if desired.
Drive Monitoring is NOT Enabled for SCSI Port X Drive ID Y
Description: The monitor and performance features have not been enabled on this drive.
Action: Run the server setup utility to initialize the monitor and performance features.
Drive Time-Out Occurred on Physical Drive Bay X
Description: ADU issued a command to a physical drive and the command was never acknowledged.
Action: The drive or cable may be bad. Check the other error messages on the Diagnostics screen to
determine resolution.
Drive X Indicates Position Y
Description: Message indicates a designated physical drive, which seems to be scrambled or in a drive
bay other than the one for which it was originally configured.
Action:
1. Examine the graphical drive representation on ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) to
determine proper drive locations.
2. Power down the server.
3. Remove drive X and place it in drive position Y.
4. Rearrange the drives according to the ADU instructions.
Duplicate Write Memory Error
Description: Data cannot be written to the array accelerator board in duplicate due to the detection of
parity errors. This is not a data-loss situation.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board.
Error Occurred Reading RIS Copy from SCSI Port X Drive ID
Description: An error occurred while ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) was trying to read
the RIS from this drive.
Action: HP stores the hard drive configuration information in the RIS. If multiple errors occur, the drive
may need to be replaced.
FYI: Drive (Bay) X is Third-Party Supplied
Description: Third-party supplied the installed drive.
Action: If problems exist with this drive, replace it with a supported drive.
Error messages 80
Page 81

Identify Logical Drive Data did not Match with NVRAM
Description: The identify unit data from the array controller does not match with the information stored
in NVRAM. This can occur if new, previously configured drives have been placed in a system that has
also been previously configured.
Action: Run the server setup utility to configure the controller and NVRAM.
Insufficient adapter resources
Description: The adapter does not have sufficient resources to perform posted-write operations to the
array accelerator board. Drive rebuild may be occurring.
Action: Operate the system without the array accelerator board until the drive rebuild completes.
Inter-Controller Link Connection Could Not Be Established
Description: Unable to communicate over the link connecting the redundant controllers.
Action: Be sure both controllers are using the same hardware and firmware revisions. If one controller
failed, replace it.
Less Than 75% Batteries at Sufficient Voltage
Description: The operation of the array accelerator board has been disabled due to less than 75% of
the battery packs being at the sufficient voltage level.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board if the batteries do not recharge within 36 powered-on
hours.
Less Than 75% of Batteries at Sufficient Voltage Battery Pack X Below Reference Voltage
Description: Battery pack on the array accelerator is below the required voltage levels.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board if the batteries do not recharge within 36 powered-on
hours.
Logical Drive X Failed Due to Cache Error
Description: This logical drive failed due to a catastrophic cache error.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board and reconfigure using ACU ("Array Configuration Utility"
on page 54).
Logical Drive X Status = Failed
Description: This status could be issued for several reasons:
• Logical drive is configured for No Fault Tolerance, and one or more drives failed.
• Mirroring is enabled, and any two mirrored drives failed.
• Data Guarding is enabled, and two or more drives failed.
• Another configured logical drive is in the WRONG DRIVE REPLACED or LOOSE CABLE DETECTED
state.
Error messages 81
Page 82

Action: Check for drive failures, wrong drive replaced, or loose cable messages. If a drive failure
occurred, replace the failed drive or drives, and then restore the data for this logical drive from the tape
backup. Otherwise, follow the procedures for correcting problems when an incorrect drive is replaced or
a loose cable is detected.
Logical Drive X Status = Interim Recovery (Volume Functional, but not Fault Tolerant)
Description: A physical drive in this logical drive has failed. The logical drive is operational, but the loss
of an additional drive may cause permanent data loss.
Action: Replace the failed drive as soon as possible.
Logical Drive X Status = Loose Cable Detected...
...SOLUTION: Turn the system off and attempt to reattach any loose connections. If this does not work, replace the
cable(s) and connection(s).
Description: At power up, the system does not detect a configured physical drive or an external storage
unit that was previously detected before the last system shutdown. This event can occur if the user removes
one or more drives after the system is powered down or if a loose cable or malfunction prevents the
drives from spinning up.
Action:
If a drive or enclosure has been removed or disconnected, do the following:
1. Power down the server.
2. Check cabling.
3. Power up the server and storage enclosure at the same time.
If drives are failed or purposely removed while the system is off:
1. Reboot the server.
2. When prompted during POST, press F2 to fail the missing drives.
Logical Drive X Status = Overheated
Description: The temperature of the Intelligent Array Expansion System drives is beyond safe operating
levels and has shut down to avoid damage.
Action: Check the fans and the operating environment.
Logical Drive X Status = Overheating
Description: The temperature of the Intelligent Array Expansion System drives is beyond safe operating
levels.
Action: Check the fans and the operating environment.
Logical Drive X Status = Recovering (rebuilding data on a replaced drive)
Description: A physical drive in this logical drive has failed and has now been replaced. The replaced
drive is rebuilding from the mirror drive or the parity data.
Action: No action is required. Normal operations can occur; however, performance will be less than
optimal until after the rebuild process completes.
Error messages 82
Page 83

Logical Drive X Status = Wrong Drive Replaced
Description: A physical drive in this logical drive has failed. The incorrect drive was replaced.
Action:
1. Power down the server.
2. Replace the drive that was incorrectly replaced.
3. Replace the original drive that failed with a new drive.
CAUTION: Do not run the server setup utility and try to reconfigure, or data will be lost.
Loose Cable Detected - Logical Drives May Be Marked FAILED Until Corrected
Description: At power up, the system does not detect a configured physical drive or an external storage
unit that was previously detected before the last system shutdown. This event can occur if the user removes
one or more drives after the system is powered down or if a loose cable or malfunction prevents the
drives from spinning up.
Action: If a drive or enclosure has been removed or disconnected, do the following:
1. Power down the server.
2. Check cabling.
3. Power up the server and storage enclosure at the same time.
If drives are failed or purposely removed while the system is off:
1. Reboot the server.
2. When prompted during POST, press F2 to fail the missing drives.
Mirror Data Miscompare
Description: Data was found at reset initialization in the posted-write memory; however, the mirror data
compare test failed resulting in that data being marked as invalid. Data loss is possible.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board.
No Configuration for Array Accelerator Board
Description: The array accelerator board has not been configured.
Action: If the array accelerator board is present, run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54) to
configure the board.
One or More Drives is Unable to Support Redundant Controller Operation
Description: At least one drive in use does not support redundant controller operation.
Action: Replace the drive that does not support redundant controller operation.
Other Controller Indicates Different Hardware Model
Description: The other controller in the redundant controller configuration is a different hardware model.
Action: Be sure both controllers are using the same hardware model. If they are, make sure the
controllers are fully seated in their slots.
Error messages 83
Page 84

Other Controller Indicates Different Firmware Version
Description: The other controller in the redundant controller configuration is using a different firmware
version.
Action: Be sure both controllers are using the same firmware revision.
Other Controller Indicates Different Cache Size
Description: The other controller in the redundant controller configuration has a different size array
accelerator.
Action: Be sure both controllers are using the same capacity array accelerator.
Processor Reduced Power Mode Enabled in RBSU
Description: Processors clocked down
Action: If you select the reduced power mode in RBSU, the processor are displayed as their reduced
speed during POST. This message indicates that the RBSU reduced power mode has been enabled and
also indicates the maximum speed for the installed processors.
Processor Not Started (Processor Stalled)
Description: If processor fails to launch or fails after being launched but before completing its
initialization, the processor is not started and this message is displayed. This is likely a defective
processor.
Processor Not Started (Stepping Does Not Match)
Description: If a processor has a stepping different than the bootstrap processor, the processor is not
started, and this message is displayed.
Processor Not Started (Unsupported Processor Stepping)
Description: If a processor has an unsupported stepping, it is not started, and this message is displayed.
Processor Not Supported (Unsupported Core Speed)
Description: If a processor has a core speed that is incompatible with the other installed processors, the
processor is not started, and this message is displayed.
RIS Copies Between Drives Do Not Match
Description: The drives on this controller contain copies of the RIS that do not match. The hard drives in
the array do not have matching configuration information.
Action:
1. Resolve all other errors encountered.
2. Obtain the latest version of ADU, and then rerun ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63).
3. If unconfigured drives were added, configure these drives using ACU ("Array Configuration Utility"
on page 54).
4. If drives or arrays were moved, be sure the movement follows the guidelines listed in the
documentation for the array controller.
Error messages 84
Page 85

5.
If the error persists after completing steps 1 through 4, contact an HP authorized service provider.
SCSI Port X Drive ID Y Failed - REPLACE (failure message)
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) detected a drive failure.
Action: Correct the condition that caused the error, if possible, or replace the drive.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y Firmware Needs Upgrading
Description: Drive firmware may cause problems and should be upgraded.
Action: Update the drive to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y Has Exceeded the Following Threshold(s)
Description: The monitor and performance threshold for this drive has been violated.
Action: Check and resolve the threshold that has been violated.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y is not Stamped for Monitoring
Description: The drive has not been stamped with monitor and performance features.
Action: To stamp without destroying the current configuration:
1. Run ACU ("Array Configuration Utility" on page 54).
2. Change the array accelerator size and save the configuration.
3. Change the array accelerator back to the original size and save again.
This should cause ACU to stamp the drive with monitoring and performance features.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y May Have a Loose Connection...
...SOLUTION: Turn the system off and attempt to reattach any loose connections. If this does not work, replace the
cable(s) and connection(s).
Description: SMART is unable to communicate with the drive, because the cable is not securely
connected, or the drive cage connection has failed.
Action:
1. Power down the system.
2. Reconnect the cable securely.
3. Restart the system.
4. If the problem persists, replace the cables and connectors as needed.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y RIS Copies Within This Drive Do Not Match
Description: The copies of RIS on the drive do not match.
Action: Check for other errors. The drive may need to be replaced.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y...S.M.A.R.T. Predictive Failure Errors Have Been Detected in the Factory Monitor and Performance Data...
...SOLUTION: Please replace this drive when conditions permit.
Error messages 85
Page 86

Description: A predictive failure warning for this hard drive has been generated, indicating that a drive
failure is imminent.
Action: Replace this drive at the earliest opportunity. Refer to the server documentation for drive
replacement information before performing this operation.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y...S.M.A.R.T. Predictive Failure Errors Have Been Detected in the Power Monitor and Performance Data...
...SOLUTION: Please replace this drive when conditions permit.
Description: A predictive failure warning for this hard drive has been generated, indicating a drive
failure is imminent.
Action: Replace this drive at the earliest opportunity. Refer to the server documentation for drive
replacement information before performing this operation.
SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y Was Replaced On a Good Volume: (failure message)
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) found that this drive was replaced, even
though no problem occurred with the volume.
Action: No action is required.
Set Configuration Command Issued
Description: The configuration of the array controller has been updated. The array accelerator board
may remain disabled until it is reinitialized.
Action: Run the server setup utility to reinitialize the array accelerator board.
Soft firmware upgrade required
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) has determined that the controller is running
firmware that has been soft upgraded by the Upgrade Utility. However, the firmware running is not
present on all drives. This could be caused by the addition of new drives in the system.
Action: Update all drives to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X has a Cabling Error (Bus Disabled)...
...SOLUTION: The SCSI controller has an internal and external cable attached to the same bus. Please disconnect
the internal or external cable from the controller. If this controller supports multiple buses, the cable disconnected
can be reattached to an available bus.
Description: The current cabling configuration is not supported.
Action: Refer to the server documentation for cabling guidelines, and reconfigure as indicated.
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated a Door Alert...
...SOLUTION: Be sure that the storage enclosure door is closed or the side panel is properly installed.
Description: The side panel of the external storage unit is open.
Action: Be sure the side panel of the storage unit is securely closed.
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated a Power Supply Failure...
...SOLUTION: Replace the power supply.
Error messages 86
Page 87

Description: A power supply in the external storage unit has failed.
Action: Replace the power supply.
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated an Overheated Condition...
...SOLUTION: Make sure all cooling fans are operating properly. Also be sure the operating environment of storage
enclosure is within temperature specifications.
Description: The external storage unit is generating a temperature alert.
Action:
1. Be sure all fans are connected and operating properly.
2. Be sure the operating environment of the storage unit is within specifications.
3. For better airflow, remove any dust buildup from fans or other areas.
4. Check the server documentation for allowable temperature specifications and additional tips.
5. If the problem persists, replace the fan.
Storage enclosure on SCSI Bus X is unsupported with its current firmware version...
...SOLUTION: Upgrade the firmware version on the storage enclosure.
Description: The firmware version of the external storage unit is not supported.
Action: Update the storage device to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated that the Fan Failed...
...SOLUTION: Replace the fan.
Description: The cooling fan located in the external storage unit has failed.
Action: Replace the fan.
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated that the Fan is Degraded...
...SOLUTION: this condition usually occurs on enclosures with multiple fans and one of those fans has failed.
Replace any fans not operating properly.
Description: One or more fans in the external storage unit have failed.
Action: Replace the failed fans.
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated that the Fan Module is Unplugged...
...SOLUTION: Make sure the fan module is properly connected.
Description: A fan in the external storage unit is not connected properly.
Action: Check and reseat all fan connections securely.
Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X - Wide SCSI Transfer Failed...
...SOLUTION: This may indicate a bad SCSI cable on bus X. Try replacing the cable.
Description: A cable on bus X has failed.
Action:
1. Replace the failed cable.
2. If the problem persists, contact an authorized service provider.
Error messages 87
Page 88

Swapped cables or configuration error detected. A configured array of drives...
...was moved from another controller that supported more drives than this controller supports.
SOLUTION: Upgrade the firmware on this controller. If this doesn’t solve the problem, then power down system and
move the drives back to the original controller.
Description: You have exceeded the maximum number of drives supported for this controller, and the
connected controller was not part of the original array configuration.
Action:
1. Update the controller to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
2. If the problem persists:
Replace this controller with the original controller.
or
Replace this controller with a new controller that supports the number of drives in the array.
Swapped Cables or Configuration Error Detected. A Drive Rearrangement...
...was attempted while an expand operation was running. This is an unsupported operation.
SOLUTION: Power down system then move drives back to their original location. Power on system and wait for the
expand operation to complete before attempting a drive rearrangement.
Description: One or more drive locations were changed while an expand operation was in progress.
Action:
1. Power down the server.
2. Place the drives in their original locations.
3. Restart the server, and then complete the expand operation.
4. Move the drives to their new locations after the expand operation is completed.
Swapped Cables or Configuration Error Detected. An Unsupported Drive
Arrangement Was Attempted...
...SOLUTION: Power down system then move drives back to their original location.
Description: One or more physical drives were moved, causing a configuration that is not supported.
Action: Move all drives to their original locations, and then refer to the server documentation for
supported configurations.
Swapped cables or configuration error detected. The cables appear to be interchanged...
...SOLUTION: Power down system then move the drives or cables back to their original location.
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) has detected a change in the cable
configuration. One or more cables may be connected to the incorrect bus or one or more drives have
been moved to new locations.
Action:
1. Refer to the server documentation for supported configurations and cabling guidelines.
2. Restore to the original configuration.
Error messages 88
Page 89

Swapped cables or configuration error detected. The configuration information on the attached drives...
...is not backward compatible with this controller’s firmware.
SOLUTION: Upgrade the firmware on this controller. If this doesn’t solve the problem then power down system then
move drives back to the original controller.
Description: The current firmware version on the controller cannot interpret the configuration information
on the connected drives.
Action: Update the controller to the latest firmware version ("Firmware maintenance" on page 65).
or
If the problem persists, move the drives to the original controller.
Swapped Cables or Configuration Error Detected. The Maximum Logical Volume Count X...
...was exceeded during logical volume addition. All logical volumes beyond X have been lost and cannot be
recovered.
SOLUTION: Identify the drives that contain the lost logical volumes. Move those drives to another controller where
the logical volumes can be recreated. NOTE! If a drive contains a valid logical volume and a lost logical volume,
then do not move that drive to another controller.
Description: More logical drives were created than are supported on this controller, causing lost logical
drive volumes.
Action: Identify the drives containing lost volumes, and then move them to another controller so the lost
volumes can be recreated.
CAUTION: Removing a drive that contains valid volume data causes all valid data to be lost.
System Board is Unable to Identify which Slots the Controllers are in
Description: The slot indicator on the system board is not working correctly. Firmware recognizes both
controllers as being installed in the same slot.
Action:
1. Be sure both controllers are fully seated in their slots.
If the problem persists, this might indicate a controller problem or a system board problem.
CAUTION: Only authorized technicians trained by HP should attempt to remove the system board. If you
believe the system board requires replacement, contact HP Technical Support before proceeding.
2. Remove one of the controllers in the configuration and see if the remaining controller generates a
POST message.
3. Move the remaining controller to the other slot to see if it still generates a POST message.
4. Repeat these steps with the other controller.
If both controllers give POST messages in one slot but not the other, it is a system board problem. If one of
the controllers gives POST messages and the other controller does not, replace the controller that is giving
the POST messages. Contact an authorized service provider for any warranty replacements.
The Redundant Controllers Installed are not the Same Model...
...SOLUTION: Power down the system and verify that the redundant controllers are different models. If they are
different models, replace the other controller with the same model as this one.
Error messages 89
Page 90

Description: ADU detected two different controller models installed in a redundant controller
configuration. This is not supported and one or both controllers may not be operating properly.
Action: Use the same controller models for redundant controller configurations.
This Controller Can See the Drives but the Other Controller Can't
Description: The other controller in the redundant controller configuration cannot recognize the drives,
but this controller can.
Action: Resolve any other errors and then rerun ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63).
This Controller Can't See the Drives but the Other Controller Can
Description: The other controller in the redundant controller configuration can recognize the drives, but
this controller cannot.
Action: Resolve any other errors and then rerun ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63).
Unable to Communicate with Drive on SCSI Port X, Drive ID Y
Description: The array controller cannot communicate with the drive.
Action: If the hard drive amber LED is on, replace the drive.
Unable to Retrieve Identify Controller Data. Controller May be Disabled or Failed
...SOLUTION: Power down the system. Verify that the controller is fully seated. Then power the system on and look
for helpful error messages displayed by the controller. If this doesn’t help, contact your HP service provider.
Description: ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63) requested the identify controller data from the
controller, but was unable to obtain it. This usually indicates that the controller is not seated properly or
has failed.
Action:
1. Power down the server.
2. Be sure the controller is fully seated.
3. Restart the server.
4. Resolve any error messages displayed by the controller.
If this does not solve the problem, contact an HP authorized service provider.
Unknown Disable Code
Description: A code was returned from the array accelerator board that ADU does not recognize.
Action: Obtain the latest version of ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63).
Unrecoverable Read Error
Description: Read parity errors were detected when an attempt to read the same data from both sides
of the mirrored memory was made. Data loss will occur.
Action: Replace the array accelerator board.
Error messages 90
Page 91

Unsupported Processor Configuration (Processor Required in Slot #1)
Description: Processor required in slot 1.
Action: If you do not install a supported processor in slot 1, this message is displayed, and the system
halts.
Warning Bit Detected
Description: A monitor and performance threshold violation may have occurred. The status of a logical
drive may not be OK.
Action: Check the other error messages for an indication of the problem.
WARNING - Drive Write Cache is Enabled on X
Description: Drive has its internal write cache enabled. The drive may be a third-party drive, or the
operating parameters of the drive may have been altered. Condition can cause data corruption if power
to the drive is interrupted.
Action: Replace the drive with a supported drive or restore the operating parameter of the drive.
WARNING - Mixed Feature Processors Were Detected
Description: Mixed feature processors were detected. The server will boot using the lowest featured
processor.
If you install supported processors with different features in the same system, this informational message is
displayed.
WARNING - Resetting Corrupted CMOS
Description: This informational message displays when the ROM detects that CMOS is corrupted. The
default values are restored. This message does not display if a user has intentionally invalidated the
configuration through RBSU by erasing NVRAM.
WARNING - Resetting Corrupted NVRAM
Description: This informational message displays when the ROM detects that NVRAM is corrupted. The
default values are restored. This message does not display if a user has intentionally invalidated the
configuration through RBSU by erasing NVRAM.
WARNING - Resetting Corrupted System Environment
Description: This informational message is displayed when the System Environment Variables are
corrupted. The default values are restored. This message does not display if a user has intentionally
invalidated the configuration through RBSU by erasing NVRAM.
WARNING - Restoring Default Configurations as Requested
Description: If, on the subsequent power up, you select the option to erase NVRAM in RBSU, this
informational message is displayed.
Error messages 91
Page 92

WARNING: Storage Enclosure on SCSI Bus X Indicated it is Operating in Single Ended Mode...
...SOLUTION: This usually occurs when a single-ended drive type is inserted into an enclosure with other drive
types; and that makes the entire enclosure operate in single ended mode. To maximize performance replace the
single-ended drive with a type that matches the other drives.
Description: One or more single-ended mode SCSI drives are installed in an external storage unit that
operates in LVD mode.
Action: The array continues to operate, but installing all LVD drives maximizes performance.
Write Memory Error
Description: Data cannot be written to the cache memory. This typically means that a parity error was
detected while writing data to the cache. This can be caused by an incomplete connection between the
cache and the controller. This is not a data loss circumstance.
Action: Power down the system and be sure that the cache board is fully connected to the controller.
Wrong Accelerator
Description: This may mean that the board was replaced in the wrong slot or was placed in a system
previously configured with another board type. Included with this message is a message indicating (1) the
type of adapter sensed by ADU ("Array Diagnostic Utility" on page 63), and (2) the type of adapter last
configured in EISA NVRAM.
Action: Check the diagnosis screen for other error messages. Run the server setup utility to update the
system configuration.
POST error messages and beep codes
Introduction to POST error messages
The error messages and codes in this section include all messages generated by ProLiant servers. Some
messages are informational only and do not indicate any error. A server generates only the codes that
are applicable to its configuration and options.
HP ProLiant p-Class server blades do not have speakers and thus do not support audio output. Disregard
the audible beeps information if the server falls into this category.
IMPORTANT: This guide provides information for multiple servers. Some information may not apply to the
server you are troubleshooting. Refer to the server documentation for information on procedures, hardware
options, software tools, and operating systems supported by the server.
WARNING: To avoid potential problems, ALWAYS read the warnings and cautionary
information in the server documentation before removing, replacing, reseating, or
modifying system components.
Error messages 92
Page 93

Non-numeric messages or beeps only
Advanced Memory Protection mode: Advanced ECC
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: Advanced ECC support is enabled.
Action: None.
Advanced Memory Protection mode: Advanced ECC with hot-add support
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: Advanced ECC with Hot-Add support is enabled.
Action: None.
Advanced Memory Protection mode: Online spare with Advanced ECC
...Xxxx MB System memory and xxxx MB memory reserved for Online Spare.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: This message indicates Online Spare Memory is enabled and indicates the amount of
memory reserved for this feature.
Action: None.
Advanced Memory Protection mode: Multi-board mirrored memory with Advanced ECC
...Xxxx MB System memory and xxxx MB memory reserved for Mirroring.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: This message indicates Mirrored Memory is enabled and indicates the amount of
memory reserved for this feature.
Action: None.
Advanced Memory Protection mode: RAID memory with Advanced ECC
...Xxxx MB System memory and xxxx MB memory reserved for RAID.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: This message indicates RAID Memory is enabled and indicates the amount of memory
reserved for this feature.
Action: None.
An Unexpected Shutdown occurred prior to this power-up
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The server shut down because of an unexpected event on the previous boot.
Action: Check the System Management Log or OS Event Log for details on the failure.
Error messages 93
Page 94

Critical Error Occurred Prior to this Power-Up
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A catastrophic system error, which caused the server to crash, has been logged.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
Fan Solution Not Fully Redundant
Audible Beeps:
Possible Cause: The minimum number of required fans is installed, but some redundant fans are
missing or failed.
Action: Install fans or replace failed fans to complete redundancy.
Fan Solution Not Sufficient
Audible Beeps:
Possible Cause: The minimum number of required fans is missing or failed.
Action: Install fans or replace any failed fans.
Fatal DMA Error
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The DMA controller has experienced a critical error that has caused an NMI.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
Fatal Express Port Error
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A PCI Express port has experienced a fatal error that caused an NMI.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace the failed PCI Express
boards or reseat loose PCI Express boards.
Fatal Front Side Bus Error
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The processor front-side bus experienced a fatal error.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace any failed processors
or reseat any loose processors.
Fatal Global Protocol Error
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The system experienced a critical error that caused an NMI.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
Error messages 94
Page 95

Fatal Hub Link Error
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The hub link interface has experienced a critical failure that caused an NMI.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace failed components as
indicated.
FATAL ROM ERROR: The System ROM is not Properly Programmed.
Audible Beeps: 1 long, 1 short
Possible Cause: The System ROM is not properly programmed.
Action: Replace the physical ROM part.
Fibre Channel Mezzanine/Balcony Not Supported.
Audible Beeps: 2 short
Description: The Fibre Channel adapter is not supported on the server.
Action: Install the supported Fibre Channel adapter.
High Temperature Condition detected by Processor X
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: Ambient temperature exceeds recommended levels, fan solution is insufficient, or fans
have failed.
Action: Adjust the ambient temperature, install fans, or replace the failed fans.
Illegal Opcode - System Halted
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The server has entered the Illegal Operator Handler because of an unexpected event.
This error is often software-related and does not necessarily indicate a hardware issue.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace any failed
components as indicated. Be sure that all software is installed properly.
iLO Generated NMI
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The iLO controller generated an NMI.
Action: Check the iLO logs for details of the event.
Internal CPU Check - Processor
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A processor has experienced an internal error.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) and replace any failed
components as indicated, including processors and PPMs.
Error messages 95
Page 96

Invalid memory types were found on the same node. Please check DIMM compatibility. - Some DIMMs may not be used
Description: Invalid or mixed memory types were detected during POST.
Action: Use only supported DIMM pairs when populating memory sockets. Refer to the applicable server
user guide memory requirements.
Invalid Password - System Halted!
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: An invalid password was entered.
Action: Enter a valid password to access the system.
Invalid Password - System Restricted!
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A valid password that does not have permissions to access the system has been
entered.
Action: Enter a valid password with the correct permissions.
Memory found on unpopulated Node. — Processor is required to be installed for memory to be used.
Description: The system detects DIMMs, but is unable to use the DIMMs because a processor is not
installed in the corresponding socket.
Action: To use the installed DIMMs, install a processor in the corresponding socket.
Mixed processor speeds detected. Please make sure that all processors are the same speed. —
System Halted!
Audible Beeps: 1 long, 1 short
Description: Mixed processor speeds are not supported.
Action: Refer to the server documentation for supported processors. Be sure that all installed processors
are the same speed.
Network Server Mode Active and No Keyboard Attached
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A keyboard is not connected. An error has not occurred, but a message is displayed
to indicate the keyboard status.
Action: No action is required.
NMI - Button Pressed!
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The NMI button was pressed, initiating a memory dump for crash dump analysis.
Action: Reboot the server.
Error messages 96
Page 97

NMI - Undetermined Source
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: An NMI event has occurred.
Action: Reboot the server.
Node Interleaving disabled - Invalid memory configuration
Description: Each node must have the same memory configuration to enable interleaving.
Action: Populate each node with the same memory configuration and enable interleaving in RBSU.
No Floppy Drive Present
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: No diskette drive is installed or a diskette drive failure has occurred.
Action:
1. Power down the server.
2. Replace a failed diskette drive.
3. Be sure a diskette drive is cabled properly, if a diskette drive exists.
No Keyboard Present
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A keyboard is not connected to the server or a keyboard failure has occurred.
Action:
1. Power down the server, and then reconnect the keyboard.
2. Be sure no keys are depressed or stuck.
3. If the failure reoccurs, replace the keyboard.
Parity Check 2 - System DIMM Memory
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: An uncorrectable error memory event occurred in a memory DIMM.
Action: Run Insight Diagnostics ("HP Insight Diagnostics" on page 61) to identify failed DIMMs. Then,
use the DIMM LEDs to identify failed DIMMs and replace the DIMMs.
PCI Bus Parity Error, PCI Slot x
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A PCI device has generated a parity error on the PCI bus.
Action: For plug-in PCI cards, remove the card. For embedded PCI devices, run Insight Diagnostics and
replace any failed components as indicated.
Error messages 97
Page 98

Power Fault Detected in Hot-Plug PCI Slot x
Audible Beeps: 2 short
Possible Cause: PCI-X Hot Plug expansion slot was not powered up properly.
Action: Reboot the server.
Power Supply Solution Not Fully Redundant
Audible beeps: None
Possible cause: The minimum power supply requirement is installed, but a redundant power supply is
missing or failed.
Action: Do one of the following:
• Install a power supply.
• Replace failed power supplies to complete redundancy.
Redundant ROM Detected - This system contains a valid backup system ROM.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The system recognizes both the system ROM and redundant ROM as valid. This is not
an error.
Action: None
REDUNDANT ROM ERROR: Backup ROM Invalid. - ...
...run ROMPAQ to correct error condition.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The backup system ROM is corrupted. The primary ROM is valid.
Action: Run ROMPaq Utility ("SoftPaqs" on page 64) to flash the system so that the primary and backup
ROMs are valid.
REDUNDANT ROM ERROR: Bootblock Invalid. - ...
...contact HP Representative.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: ROM bootblock is corrupt.
Action: Contact an authorized service provider.
REDUNDANT ROM ERROR: Primary ROM invalid. Booting Backup ROM. -...
...run ROMPAQ to correct error condition
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The primary system ROM is corrupt. The system is booting from the redundant ROM.
Action: Run ROMPaq Utility ("SoftPaqs" on page 64) to restore the system ROM to the correct version.
Error messages 98
Page 99

Temperature violation detected - system Shutting Down in x seconds
Audible Beeps: 1 long, 1 short
Possible Cause: The system has reached a cautionary temperature level and is shutting down in X
seconds.
Action: Adjust the ambient temperature, install fans, or replace any failed fans.
There must be a first DIMM in pair if second DIMM in pair is populated. Second DIMM in pair ignored.
Description: The first DIMM socket in the pair is not populated. The second DIMM in the pair is not
recognized or used.
Action: Populate the DIMM socket.
This system only supports 667 MHz Front Side Bus Speed Processors. One or more 800 MHz Front Side Bus Speed Processors have been initialized at 667 MHz. System Halted!
Audible beeps: 1 long, 1 short
Possible cause: One or more 800-MHz front side bus speed processors have been initialized at 667-
MHz.
Action: Correct the processor configuration.
Unsupported DIMM(s) found in system. - DIMM(s) may not be used
Description: Unsupported memory types found in system.
Action: Refer to the applicable server user guide memory requirements and replace with supported
DIMMs.
Unsupported PCI Card Detected Remove PCI Card from Slot
Audible beeps: 2 short
Possible cause: The PCI card installed in the slot referenced in the message is strictly not supported on
this system.
Action: Remove the card from the slot reported in the message.
Unsupported Processor Detected System will ONLY boot ROMPAQ Utility. System Halted.
Audible Beeps: 1 long, 1 short
Possible Cause: Processor and/or processor stepping is not supported by the current system ROM.
Action: Refer to the server documentation for supported processors. If a ROM version exists that supports
the processor,
1. Power down the server.
2. Insert a Systems ROMPAQ diskette containing the latest ROM version.
3. Boot the system to flash the system to the latest ROM version. Allow 15 minutes for the process to
complete. Successful completion is indicated by a series of beeps of increasing pitch.
USB Tape-based One button Disaster Recovery (OBDR) drive detected.
<<Press F8 for configuration options>>
Select a configuration option:
Error messages 99
Page 100

1. Enable OBDR
2. Exit
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: A USB tape device that supports One Button Disaster Recovery (OBDR) is installed in
the system.
Action:
1. Press 1 or 2.
• Pressing 2 exits the configuration.
• Pressing 1 starts the configuration. The following message appears
2. Observe the configuration progress. The following error may appear:
Error - USB tape drive not in Disaster Recovery mode.
3. Follow the onscreen directions:
Remove power to USB drive and reboot.
The following message should appear:
OBDR is now enabled for the attached USB tape drive.
Attempting to enable OBDR for the attached USB tape drive...
WARNING: A Type 2 Header PCI Device Has Been Detected...
The BIOS will not configure this card.
It must be configured properly by the OS or driver.
Audible Beeps: 2 short
Possible Cause: Only Type 0 and Type 1 Header PCI Devices are configured by the system ROM. The
device will not work unless the OS or device driver properly configure the card. Typically this message
only occurs when PCI cards with a PCI to PCMCIA bridge are installed.
Action: Refer to the operating system documentation or the device driver information that ships with the
Type 2 PCI device.
WARNING - Mixed Stepping Processors were detected. System cannot proceed.
Audible beeps: 1 long, 1 short
Possible cause: One or more 800-MHz front side bus speed processors have been initialized at 667-
MHz.
Action: Correct the processor configuration.
WARNING: ProLiant Demand Based Power Management cannot be supported with the
following processor configuration. The system will run in Full Performance mode.
Audible Beeps: None
Possible Cause: The system is configured for HP Static Low mode and the current processor cannot
support this mode.
Action: For more information about the Power Regulator for ProLiant option, refer to the HP ROM-Based
Setup Utility User Guide on the Documentation CD or the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
).
Error messages 100
 Loading...
Loading...