Page 1

HP ProCurve 1700 Switches
Management and Configuration Guide
July 2009
Page 2

Page 3

HP ProCurve 1700 Switches
Management and Configuration Guide
Page 4

© Copyright 2007, 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in
the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Windows NT®, Windows®, and MS Windows® are US registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Publication Number
5991-6222
July 2009
Applicable Products
ProCurve Switch 1700-8 (J9079A)
ProCurve Switch 1700-24 (J9080A)
Disclaimer
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL, INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished by
Hewlett-Packard.
Warranty
See the Customer Support/Warranty booklet included with the product. A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your Hewlett
Packard products and replacement parts can be obtained from your HP Sales and Service Office or authorized dealer.
Page 5

Contents
1 Getting Started
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Related Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Getting Documentation From the Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Sources for More Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
To Set Up and Install the Switch in Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
2 Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Navigating the Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Home Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Panel Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Web Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Displaying System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Displaying the System Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Setting the Switch’s IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Configuring the Logon Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Rate Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Showing Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Trunk Membership . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
Aggregation Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Defining the Members of a Trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Deleting the Members of a Trunk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Trunk Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Modifying Trunk Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
iii
Page 6

LACP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Enabling LACP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
Disabling LACP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
LACP Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
VLAN Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Introduction to VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Creating a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Modifying a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Deleting a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
VLAN Port Config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
LLDP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
LLDP Neighbor Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-32
SNMP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
Ping Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
Restore to Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
Reboot Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
Upload/Download Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
Download Text Readable Configuration/Status File . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-37
Update Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-38
Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-39
3 Troubleshooting
Basic Troubleshooting Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Forgotten the IP Address or Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Testing the Switch by Resetting It . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
ProCurve Networking Customer Support Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Before Calling Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Index
iv
Page 7

Getting Started
Getting Started
Introduction
This Management and Configuration Guide is intended to support the
following switches:
■ ProCurve Switch 1700-8
■ ProCurve Switch 1700-24
This guide describes how to use the Web browser interface to configure,
manage, and monitor switch operation. A troubleshooting chapter is also
included.
Related Publications
1
Installation and Getting Started Guide. Use the Installation and Get-
ting Started Guide shipped with your switch to prepare for and perform the
physical installation. This guide also steps you through connecting the switch
to your network and assigning IP addressing, as well as describing the LED
indications for correct operation and trouble analysis.
You can download a copy of this guide from the ProCurve Networking Web
site,
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve. (See “Getting Documentation From the
Web” on page 1-2.)
Release Notes. Release notes are posted on the ProCurve Networking Web
site and provide information on new software updates:
■ New features and how to configure and use them
■ Software management, including downloading software to the switch
■ Software fixes addressed in current and previous releases
To view and download a copy of the latest release notes for your switch, see
“Getting Documentation From the Web” on page 1-2.
1-1
Page 8
Getting Started
Getting Started
2
Getting Documentation From the Web
Getting Documentation From the Web
1. Go to the ProCurve Networking Web site at
2. Click on the product for which you want to view or download a manual.
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve/manuals
1-2
Page 9

Sources for More Information
Getting Started
Getting Started
Sources for More Information
To Set Up and Install the Switch in Your Network
Use the Installation and Getting Started Guide shipped with your switch for
the following:
■ Instructions for physically installing the switch in your network.
■ Quickly assigning an IP address, subnet mask, and gateway, set a
Manager password, and (optionally) configure other basic features.
■ Interpreting LED behavior.
■ Notes, cautions, and warnings related to installing and using the
switch.
For the latest version of the Installation and Getting Started Guide and other
documentation for your switch, visit the ProCurve Networking Web site.
(Refer to “Getting Documentation From the Web” on page 1-2.)
1-3
Page 10

Page 11

Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Overview
This switch provides an embedded HTTP Web agent. Using a Web browser
you can configure the switch and view statistics to monitor network activity.
The Web agent can be accessed by any computer on the network using a
standard Web browser (Internet Explorer 5.5 or above).
Prior to accessing the switch from a Web browser, be sure you have first
performed the following tasks:
1. Configure the switch with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway. (Defaults: IP address 192.168.2.10; Subnet mask 255.255.255.0;
Gateway 0.0.0.0)
2. Set a new password using the Web interface (the default is no password).
Access to the Web interface is controlled by the password.
2
Note If you cannot remember the switch’s IP address, you can restore the original
settings by following the procedure described in the “Troubleshooting”
section.
Note If the Web Browser Interface is inactive for more than 300 seconds, the Web
Browser logs out the administrator and returns to the Login page.
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
Home Page
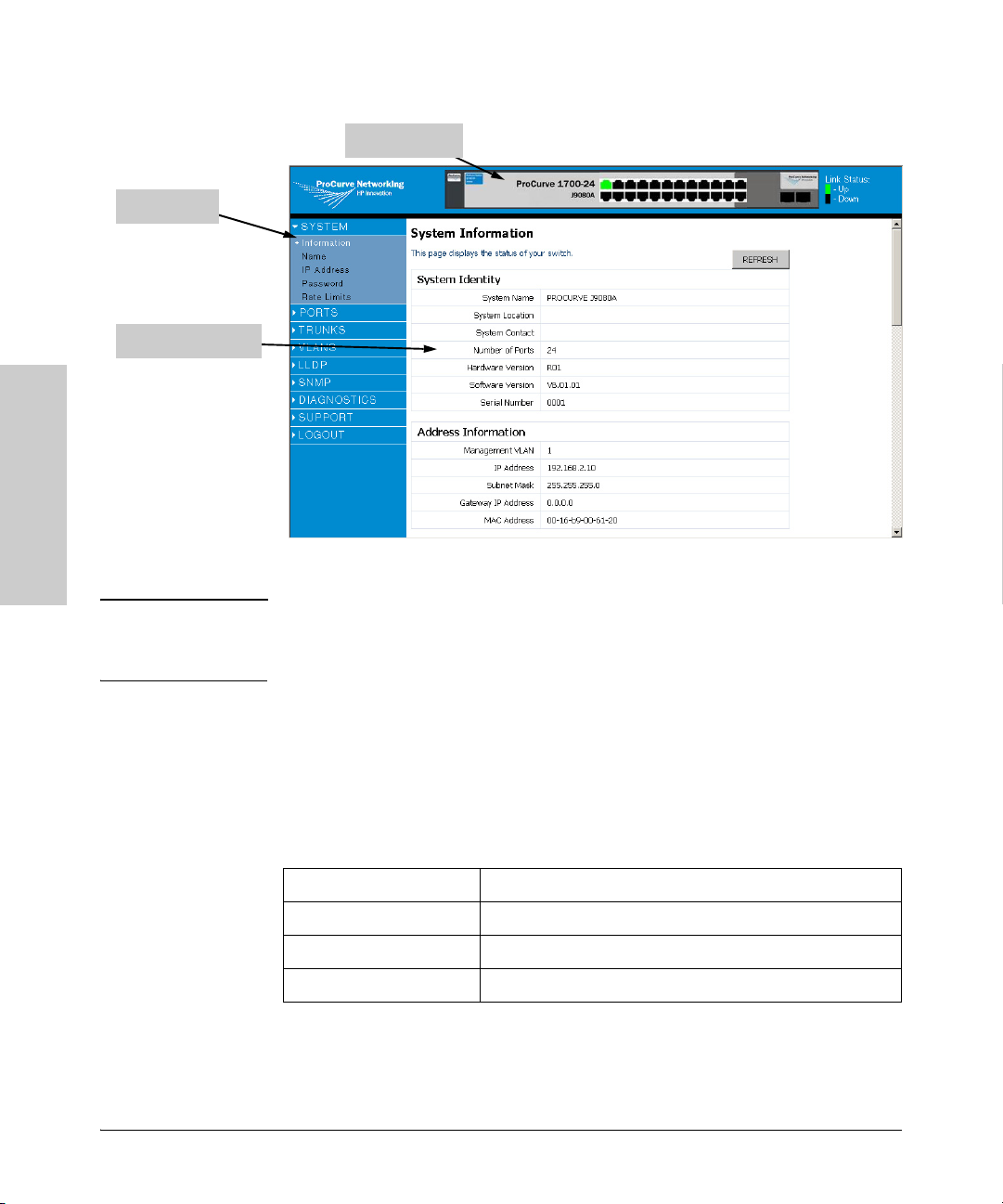
When your Web browser connects with the switch’s Web agent, the home page
is displayed as shown below. The home page displays the Main Menu on the
left side of the screen, System Information on the right side, and Device Image
on the top bar. The Main Menu links are used to navigate to other menus, and
display configuration parameters and statistics.
2-1
Page 12
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Main Menu
Information Screen
Device Image
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
Note The examples in this chapter are based on the 24-port switch. Other than the
2-2
number of fixed ports, there are no major differences between the 8-port and
24-port switch.
Configuration Options
Configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once a
configuration change has been made on a page, be sure to click on the Apply
button to confirm the new setting. The following table summarizes the Web
page configuration buttons.
Button Action
Apply Sets specified values to the system.
Cancel Discards all changes and restores current values.
Help Links directly to Web help
Page 13

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
Note To ensure proper screen refresh, be sure that Internet Explorer is configured
as follows: Under the menu “Tools / Internet Options / General / Temporary
Internet Files / Settings,” the setting for item “Check for newer versions of
stored pages” should be “Every visit to the page.”
Panel Display
The Web agent displays an image of the switch’s ports. The port will turn green
when the corresponding front-panel port is in connection with another device.
To show the port number, place mouse pointer onto the intended port.
Main Menu
Using the onboard Web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and
control the switch, and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The
following table briefly describes the selections available from the Webbrowser interface.
Menu Description Page
SYSTEM 2-5
Information Provides basic system description, including system
name, IP address, port, trunk, LACP, and VLAN
information.
Name Sets the name of the switch. 2-8
IP Address Sets the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway IP
address.
Password Changes the password. 2-10
Rate Limits Sets the storm control parameters. 2-11
PORTS 2-12
Configuration Configure the speed and duplex mode of ports. 2-12
Port Mirroring Sets up the port mirroring features of the switch to
enable traffic monitoring.
Statistics Shows statistics for each port on the switch. 2-15
2-5
2-8
2-13
2-3
Page 14
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
Menu Description Page
TRUNKS 2-16
Membership Selects ports to group into static trunks. 2-16
Configuration Configures static trunk connection settings. 2-19
LACP Setup Configures Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on
the switch.
LACP Status Displays aggregation information and LACP port status. 2-23
VLANS 2-25
VLAN Setup Create up to 64 VLANs. 2-25
VLAN Port Config Configures VLAN behavior for individual ports and
trunks.
LLDP 2-30
Configuration Configures Transmitted TLVs settings and LLDP state. 2-30
Neighbor Monitors LLDP neighbor information. 2-32
SNMP 2-33
Configuration Configures the Simple Network Management Protocol. 2-33
DIAGNOSTICS 2-33
Ping Test Sends a ping to other devices from the switch. 2-33
Factory Defaults Force the switch to perform a power reset and restore
the original factory settings.
Reboot Switch Reboots the switch. 2-36
SUPPORT 2-36
2-20
2-27
2-35
Configuration File Upload or download the switch configuration file. 2-36
Update Software Updates the switch system software using a file
provided by ProCurve Networking.
ProCurve Web Site Link to ProCurve Networking Web site. 2-39
LOGOUT Quits to the Login page.
2-38
Note The ProCurve Switch 1700 supports pass through (flooding) of spanning tree
BPDUs so that upstream devices on the network which support Spanning Tree
Protocol can detect loops that exist on the ProCurve Switch 1700 interface.
2-4
Page 15

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Web Configuration
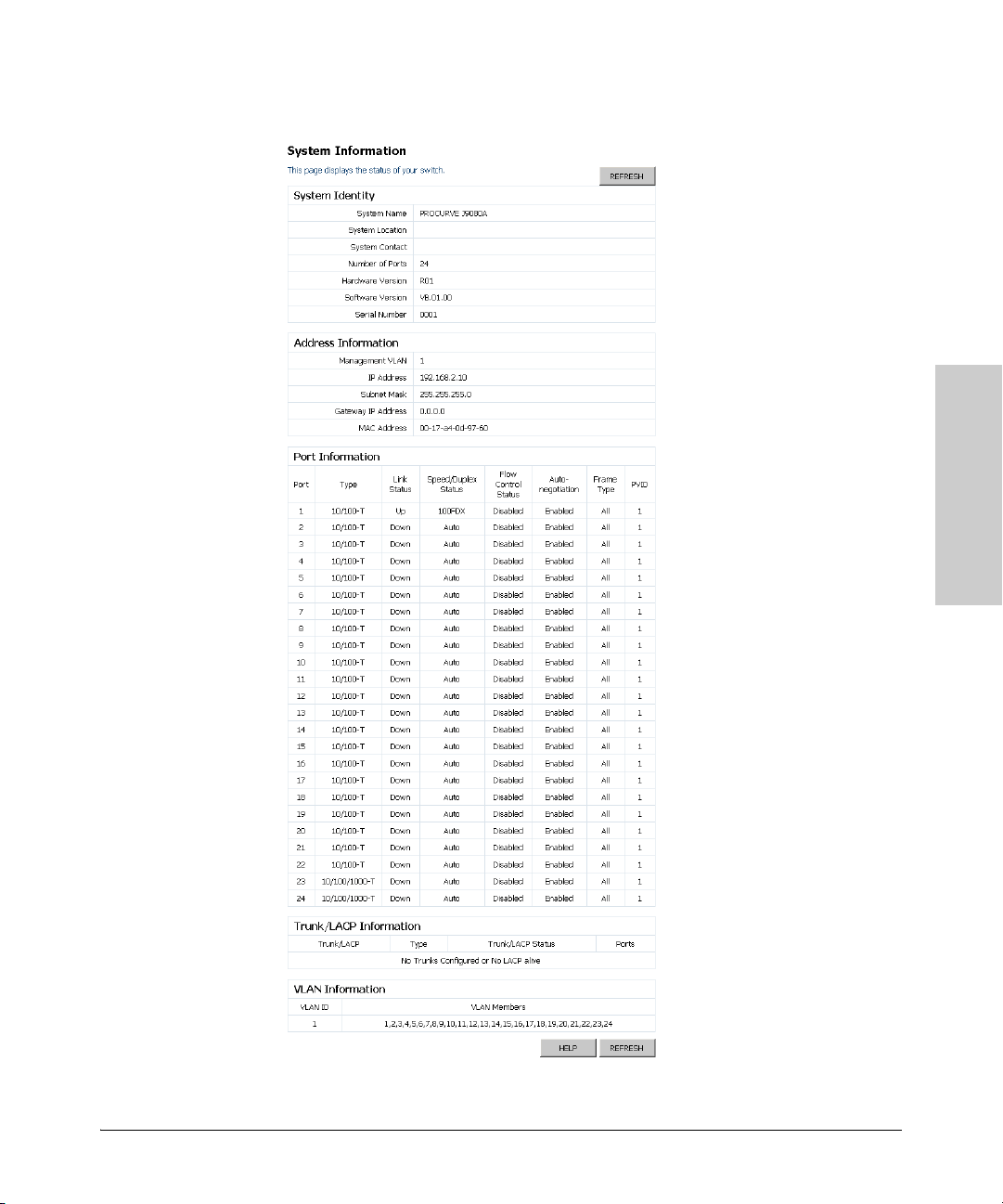
Displaying System Information
You can display a complete summary of identity, IP Address, port, Trunk/LACP,
and VLAN information for the switch.
Field Attributes
System Identity
• System Name – Name assigned to the switch system.
• System Location – Description of the switch location.
• System Contact – Contact information assigned to the switch.
• Number of Ports – Number of built-in ports.
• Hardware Version – Hardware version of the main board.
• Software Version – Version number of the code.
• Serial Number – The serial number of the switch.
Address Information
• Management VLAN – ID of a configured VLAN. By default, all ports
on the switch are members of VLAN 1. However, the management
station can be attached to a port belonging to any VLAN, as long as
that VLAN has been assigned an IP address.
• IP Address – Address of the VLAN to which the management station
is attached. (Note that the management station must always be in the
Management VLAN.)
• Subnet Mask – This mask identifies the host address bits used for
routing to specific subnets. (Default: 255.255.255.0)
• Gateway IP Address – IP address of the gateway router between the
switch and management stations that exist on other network
segments. (Default: 0.0.0.0)
• MAC Address – The physical layer address of the switch.
Port Information
•Port – Indicates the port number.
• Ty pe – Indicates the port type (10/100-T, 10/100/1000-T, or M).
• Link Status – Indicates if the link is Up or Down.
2-5
Page 16

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
• Speed/Duplex Status – Shows the current speed and duplex mode.
– 10HDX
–10FDX
– 100HDX
– 100FDX
– 1000FDX
• Flow Control Status – Indicates whether flow control is enabled or
disabled.
• Auto-negotiation – Shows if auto-negotiation is enabled or disabled.
• Frame Type – Either “Tagged” or “All”. “Tagged” means that the port
will only receive VLAN-tagged frames. When set to “All,” the port will
also receive untagged frames.
• PVID – The VLAN ID assigned to untagged frames received on the
interface. Outgoing frames are tagged unless the frame’s VLAN ID is
the same as the PVID. When the PVID is set to “None,” all outgoing
frames are tagged. (Default: 1)
Trunk/LACP Information
• Trunk/LACP – The trunk label. “T1” through “T12” on the 24-port
switch and “T1” through “T4” on the 8-port switch are used as trunk
labels.
• Ty pe – Displays the trunk type as “Static” or “Dynamic.”
• Trunk/LACP Status – Indicates the speed and duplex setting of the
trunk.
– 10HDX
–10FDX
– 100HDX
– 100FDX
– 1000FDX
• Ports – The ports that are members of the trunk.
VLAN Information
• VLAN ID – A number in the range 1 - 4094 which identifies the VLAN.
• VLAN Member – A list of the ports that are members of the VLAN.
By default, all ports are members of VLAN 1.
2-6
Page 17
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web - Click System, Information.
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Web Configuration
2-7
Page 18
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
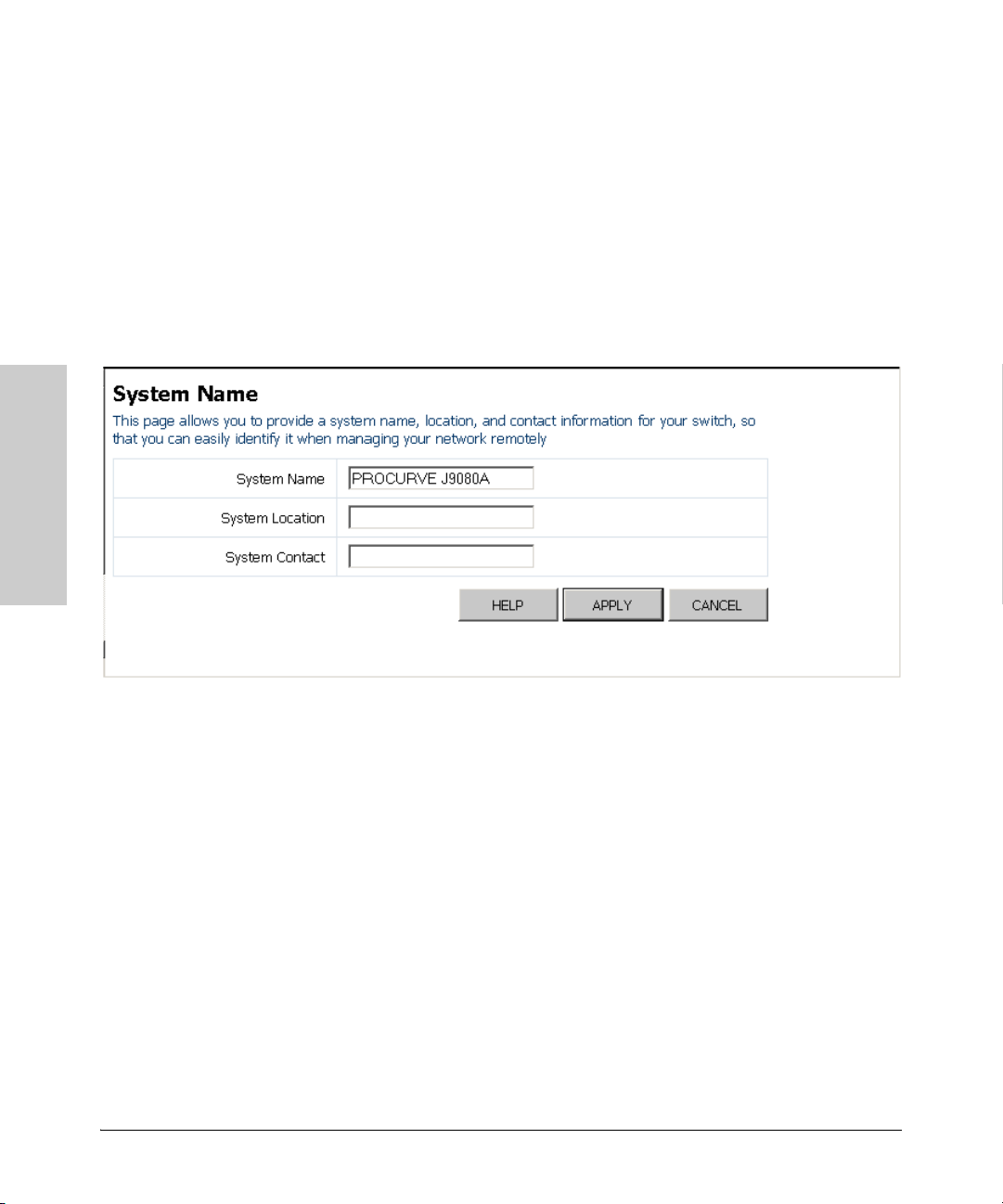
Displaying the System Name
You can identify the system by displaying the device name, location, and
contact information.
Field Attributes
• System Name – A name assigned to the switch system.
• System Location – Description of the switch location.
• System Contact – The contact name for the switch.
Web – Click System, Name.
Setting the Switch’s IP Address
This section describes how to configure an IP interface for management
access over the network. The IP address for this switch is 192.168.2.10 by
default. To manually configure an address, make sure the DHCP Enabled box
is unchecked, then change the switch’s default settings (IP address
192.168.2.10 and netmask 255.255.255.0) to values that are compatible with
your network. You may also need to establish a default gateway between the
switch and management stations that exist on another network segment.
Field Attributes
• DHCP Enabled – Enable or disable DHCP. If enabled, the IP address
will be acquired from a DHCP server. If disabled, the IP address must
be manually set by the user. (Default: Disabled)
• Switch IP Address – Address of the IP interface that is allowed
management access. Valid IP addresses consist of four numbers, 0 to
255, separated by periods. (Default: 192.168.2.10)
2-8
Page 19

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
• Subnet Mask – This mask identifies the host address bits used for
routing to specific subnets. (Default: 255.255.255.0)
• Gateway IP Address – IP address of the gateway router between
this device and management stations that exist on other network
segments. (Default: 0.0.0.0)
• Management VLAN – ID of the configured VLAN (1-4093, no leading
zeroes). By default, all ports on the switch are members of VLAN 1.
However, the management station can be attached to a port belonging
to any VLAN, as long as that VLAN has been assigned an IP address.
Note Be sure to keep a record of the switch’s IP address. If you cannot remember
the switch’s IP address, you can restore the original settings by following the
procedure described in the “Troubleshooting” section.
If you change the switch IP address, you must close the Web interface and
start a new session using the new IP address.
Web – Click System, IP Address. Enter the IP address, subnet mask, gateway,
and select the Management VLAN, then click APPLY.
2-9
Page 20

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Configuring the Logon Password
The administrator has write access for all parameters governing the embedded
Web agent. You should therefore assign a new administrator password as soon
as possible, and store it in a safe place.
Field Attributes
Change Password
• Current Password – Input the current password. (Default is no
password)
• New Password – Specifies the new user password.
(Range: 1-16 characters plain text, case sensitive)
• Confirm New Password – Re-enter in the new password for
confirmation.
Note Be sure to keep a record of the switch’s password. If you cannot remember
the password, you can restore the original settings by following the procedure
described in the “Troubleshooting” section.
Web – Click System, Password. To change the password for the administrator,
enter the current password, the new password, confirm it by entering it again,
then click APPLY.
2-10
Page 21

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Rate Limits
Broadcast storms may occur when a device on your network is
malfunctioning, or if application programs are not well designed or properly
configured. If there is too much broadcast traffic on your network,
performance can be severely degraded, or everything can come to a complete
halt.
You can protect your network from broadcast storms by setting a threshold
for broadcast traffic for each port. Any broadcast packets exceeding the
specified threshold will then be dropped.
Note Rate limiting is not supported on the ProCurve Switch 1700-8 due to a
hardware limitation.
Field Attributes
• Enable Rate Limits – Click to select the box to enable rate limits.
(Default: Disabled)
• Limit (number of frames per second) – Threshold of port
bandwidth measured in number of frames per second. From the drop
down menu you can choose the desired limit. The value specifies the
size of the available input bandwidth that can be made available for
broadcast and multicast traffic. The same limit size is applied to every
port on the switch. When the limit size is exceeded, packets are
dropped, irrespective of the flow control settings.
Web – Click System, Rate Limits. This page enables you to set the broadcast
storm control parameters for the switch.
2-11
Page 22

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Port Configuration
You can use the Port Configuration page to manually set the speed, duplex
mode, and flow control. You can enable jumbo frames to support data packets
9216 bytes in size.
Field Attributes
• Enable Jumbo Frames – Click box to enable jumbo frames.
•Port – The port number.
• Speed/Duplex – Allows you to manually set the port speed and
duplex mode.
• Flow Control – Allows flow control to be enabled or disabled. When
the box is checked, flow control is enabled.
• Trunk – Indicates if a port is a member of a trunk.
Web – Click Ports, Configuration.
Note Ports within a trunk cannot be configured individually. However, you can use
the Trunk Configuration page to manually set the same speed, duplex mode,
and flow control for every port in a trunk.
2-12
Page 23

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Port Mirroring
You can mirror (copy) incoming and outgoing packets on multiple source
ports to a single target port for real-time analysis. You can then attach a
network analyzer or RMON probe to the target port and study the traffic
crossing the source ports in a completely unobtrusive manner.
Field Attributes
Port to Mirror to
• Port to Mirror to – The port that will be use to “mirror” another
port’s incoming and outgoing packets. Data packets will be dropped
when data coming in is greater than the port can handle.
Note If the total ingress bandwidth exceeds the mirror port’s egress bandwidth,
packets will eventually be dropped on ingress to the switch, which means they
will not reach the mirror port or their intended destination port. Input ratelimiting in conjunction with port flow-control should be used to ensure that
the total ingress bandwidth never exceeds the egress bandwidth.
Ports to Mirror
• Mirroring Enabled – A port whose traffic will be monitored. If
enabled, the incoming and outgoing packets on this port will be
mirrored. (Default: Disabled)
2-13
Page 24

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Web – Click Ports, Port Mirroring.
2-14
Page 25

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Showing Port Statistics
You can display statistics on network traffic from the ports. These statistics
can be used to identify potential problems with the switch (such as a faulty
port or unusually heavy loading). All values displayed for a port have been
accumulated since the last system reboot, but can be reset to zero by clicking
the CLEAR button. Clicking the CLEAR button will only reset the statistics of
the current port. The statistics on this page will auto-refresh. If you wish to
pause the auto-refresh operation, click the PAUSE button. To resume the autorefresh operation, click the CONTINUE button.
Parameter Description
Port Statistics
Port Number From the drop down menu, choose the port you would like
to view.
Port Speed/Duplex Displays the port speed and duplex mode.
Received Octets The total number of octets received on the port, including
Received Packets The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a
Received Broadcast/
Multicast Packets
Received Errors The number of inbound packets that contained errors
Transmitted Octets The total number of octets transmitted out of the port,
Transmitted Packets The total number of packets that higher-level protocols
Transmitted Broadcast/
Multicast Packets
Transmitted Errors The number of outbound packets that could not be
framing characters.
higher-layer protocol.
The number of packets, delivered by this sub-layer to a
higher (sub-)layer, which were addressed to a broadcast/
multicast address at this sub-layer.
preventing them from being deliverable to a higher-layer
protocol.
including framing characters.
requested be transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address,
including those that were discarded or not sent.
The total number of packets that higher-level protocols
requested be transmitted, and which were addressed to a
broadcast/multicast address at this sub-layer, including
those that were discarded or not sent.
transmitted because of errors.
2-15
Page 26

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Web – Click Ports, Statistics.
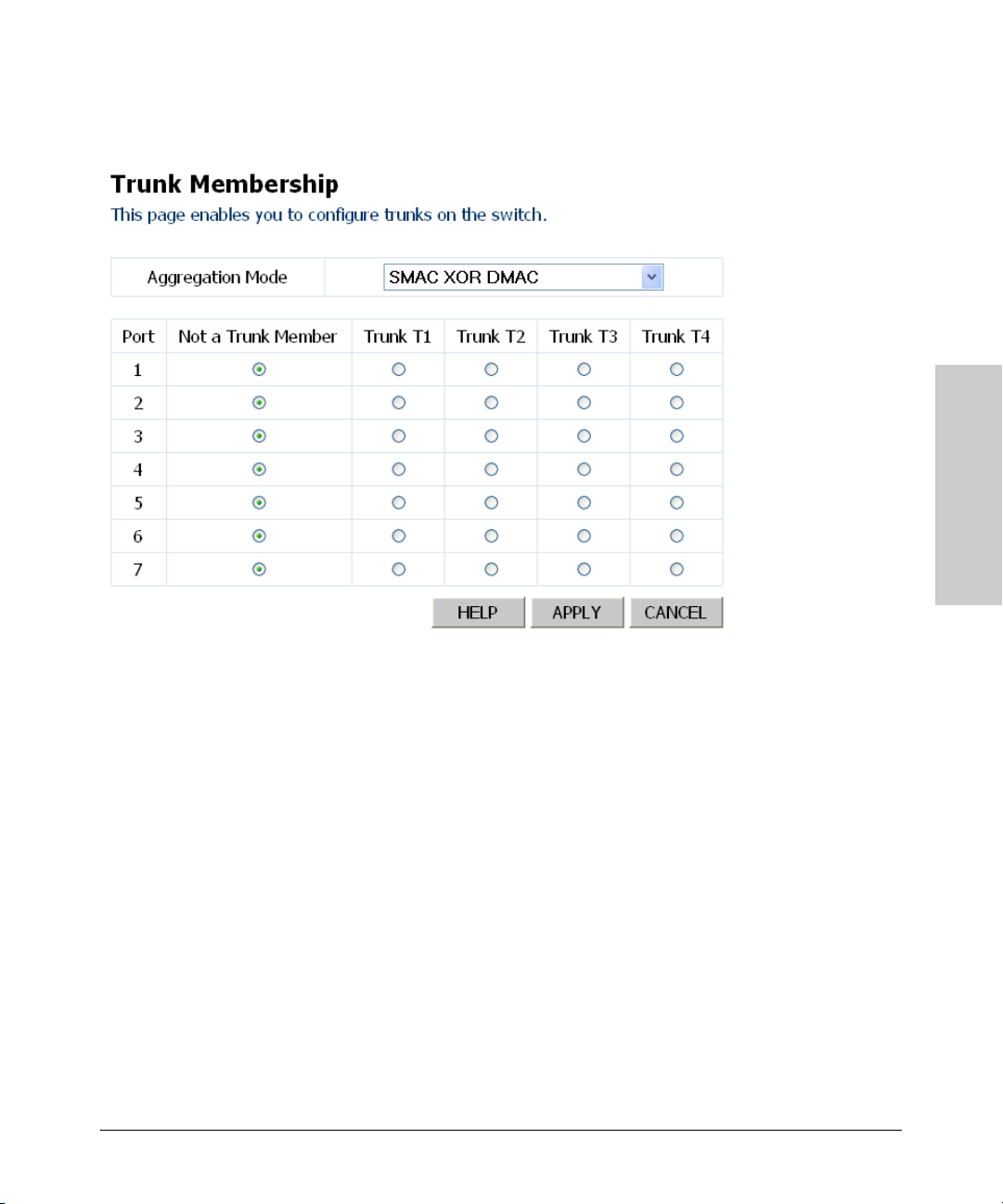
Trunk Membership
This page allows you to create static trunks. Trunking allows you to assign
physical links to one logical link (trunk) that functions as a single, higherspeed link providing dramatically increased bandwidth. This capability
applies to connections between backbone devices as well as to connections
in other network areas where traffic bottlenecks exist.
Port Trunking Support ProCurve 1700-8 ProCurve 1700-24
Ports per trunk (maximum) 7 8
Trunks per switch (maximum) 4 12
The Membership Table has one row for each port and a column for each trunk,
plus an additional column for ports that are not members of a trunk. Each row
contains radio buttons that are used to indicate which trunk (if any) the port
belongs to.
2-16
Page 27

Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Aggregation Mode
When incoming data frames are fowarded by the switch over a trunk, the
switch must determine which port link in the trunk to use for each outgoing
frame. To maintain the frame sequence for traffic flows between devices in
the network, the switch also needs to ensure that frames in each
“conversation” are mapped to the same trunk link. In order to meet this
requirement and to distribute a balanced load across all links in a trunk, the
switch uses an algorithm based on the frame source or destination addresses
to calculate an output link member in the trunk. However, depending on the
device to which a trunk is connected and the traffic flows in the network, this
load-balance algorithm may result in traffic being distributed mostly to one
port in a trunk.
To ensure that the switch traffic load is distributed evenly across all links in
a trunk, the source or destination addresses used in the load-balance
calculation can be selected to provide the best result for trunk connections.
The switch provides six load-balancing modes that apply for both static and
dynamic trunks:
■ SMAC: All traffic with the same source MAC address is output on the same
link in a trunk. This mode works best for switch-to-switch trunk links
where traffic through the switch is received from many different hosts.
■ DMAC: All traffic with the same destination MAC address is output on the
same link in a trunk. This mode works best for switch-to-switch trunk
links where traffic through the switch is destined for many different hosts.
Do not use this mode for switch-to-router trunk links where the destination MAC address is the same for all traffic.
■ SMAC XOR DMAC: The four least significant bits of the source and
destination MAC addresses in a frame are used to determine the output
link in the trunk. This mode works best for switch-to-switch trunk links
where traffic through the switch is received from and destined for many
different hosts. (This mode is the default setting.)
■ SMAC XOR DMAC XOR IP-Info: The source and destination MAC
addresses and IP information in a frame are used to determine the output
link in the trunk. This mode works best for switch-to-switch trunk links
where traffic through the switch is received from and destined for many
different hosts.
■ Pseudo-randomized: The output link in the trunk is randomly selected.
This mode is useful for networks where frame ordering within conversations can be neglected and where a high utilization of aggregated links is
important.
2-17
Page 28

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
■ IP-Info: The source and destination IP addresses and TCP/UDP ports in a
frame are used to determine the output link in the trunk. This mode works
best for switch-to-router trunk links where traffic through the switch is
received from and destined for many different hosts.
Defining the Members of a Trunk
1. On the Trunks Membership page, click on the radio button in any one of
these columns of the corresponding trunk.
For example, if you want ports 2, 3, 4, and 5 to become members of Trunk
2, click the radio buttons for 2, 3, 4, and 5 under the column labeled “Trunk
T2.”
2. Click APPLY.
Deleting the Members of a Trunk
1. On the Trunks Membership page, click on the radio button under the
column labeled “Not a Trunk Member” for any port you want to remove
from a trunk. To delete a trunk, remove all port members from that trunk.
For example, if you want to remove ports 2, 3, 4, and 5 from Trunk 2, click
the radio buttons for 2, 3, 4, and 5 under the column labeled “Not a Trunk
Member.”
2. Click APPLY.
Note For the 8 port switch, you can only create up to a maximum of 4 trunks of up
to 7 ports each.
Field Attributes
• Port – The port number.
• Not a Trunk Member – If the radio button in this column is selected,
the port is not a member of any trunks. This is the default state.
• Trunk T1-T12 – These columns correspond to the trunks that are
supported by the switch. To assign a port to a trunk, click on the radio
button in any one of these columns of the corresponding trunk and
then click APPLY.
2-18
Page 29
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web – Click Trunks, Membership. To assign a port to a trunk, click the required
trunk number, then click APPLY.
Web Configuration
Trunk Configuration
You can use the Trunk Configuration page to manually set the speed, duplex
mode, and flow control.
Modifying Trunk Settings
1. On the Trunks Configuration page, modify any of the following settings:
• Speed Duplex – Allows auto-negotiation to be enabled or disabled.
When auto-negotiation is disabled, you can force the settings for
speed, duplex mode, and flow control.
• Flow Control – Allows automatic or manual selection of flow control.
2. Click APPLY.
2-19
Page 30

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Note All the ports in the trunk will have the same speed, duplex mode, and flow
control as defined by the trunk. Once the trunk is deleted, the ports will no
longer be a member of that trunk but will retain the speed, duplex mode, and
flow control setting of that trunk.
Field Attributes
• Trunk – Indicates trunk identification.
• Speed/Duplex – Allows you to manually set the port speed and
duplex mode for all ports in the trunk.
• Flow Control – Allows flow control to be enabled or disabled. When
the box is checked, flow control is enabled.
• Member Ports – Indicates which ports belong to the trunk.
Web – Click Trunks, Configuration.
LACP Settings
The switch supports both static trunking and dynamic Link Aggregation
Control Protocol (LACP), which is specified in IEEE 802.3ad. Static trunks
have to be manually configured at both ends of the link, on the other hand,
LACP configured ports can automatically negotiate a trunked link with LACPconfigured ports on another device. You can configure any number of ports
on the switch as LACP, as long as they are not already configured as part of a
static trunk. If ports on another device are also configured as LACP, the switch
and the other device will negotiate a trunk link between them. If an LACP
trunk consists of more than eight ports, all other ports will be placed in a
standby mode. Should one link in the trunk fail, one of the standby ports will
automatically be activated to replace it.
You can use the LACP Setting page to configure LACP for each port.
2-20
Page 31
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Enabling LACP
1. On the LACP Setting page, click the box under the column labeled “LACP
Enabled on Port” for the ports you want to enable LACP.
2. Input a key value for the Link Aggregate Group.
3. Click APPLY.
Disabling LACP
1. On the LACP Setting page, click the box under the column labeled “LACP
Enabled on Port” to remove the check mark for the ports you want to
disable LACP.
2. Click APPLY.
Note Do not enable LACP or static trunks for ports 1 and 2 at the same time. Doing
so will result in the switch resetting to factory default configuration when
power cycled.
Field Attributes
• Port – The port number.
• LACP Enabled on Port – Allows LACP to be enabled or disabled.
When the box is checked, LACP is enabled.
• Key Value (0..255, 0 means autogenerated key) – Ports in an
aggregated link group must have the same LACP port Key. For a port
to be allowed to join an aggregated group, the port Key must be set
to the same value. When set to zero, the port Key is automatically set
by the switch.
2-21
Page 32

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Web – Click Trunks, LACP Setup.
2-22
Page 33

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
LACP Status
Displays the status of the LACP groups.
Field Attributes
Aggregation Information
• Aggregation Group – Displays the ID number of the LACP group.
• Partner MAC Address – Displays the MAC address of a device in
the LACP group that is attached to this switch.
• Local Port Aggregated – Displays port member list of the local
LACP group. The port members are port on this switch.
• Seconds Since Last Changed – Number of seconds since the last
LACP was received.
LACP Port Status
• Port – The port number.
• Protocol Active – Indicates if the port is a member of an active LACP
group.
• Partner Port Number – A list of port numbers assigned to the link
by the LACP partner.
• Operation Port Key – The current operational value of the key for
the LACP group.
2-23
Page 34

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Web – Click Trunks, LACP Status.
2-24
Page 35

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
VLAN Setup
This page allows you to create up to 64 VLANs based on the 802.1Q standard.
You can also delete or modify VLANs.
Introduction to VLANs
VLANs are logical partitions of the physical LAN. You can use VLANs to
increase network performance, improve internal network security, or create
separate broadcast domains.
If the network has adequate performance and security for your current needs,
it is recommended that you leave the VLAN settings in the default
configuration. The default configuration is as follows:
• All ports are members of VLAN 1
• The switch management interface is on VLAN 1
• All ports have a Port VLAN ID (PVID) of 1
• All ports can send and receive both VLAN-tagged and untagged
packets (that is, they are hybrid ports)
In the default configuration, any port is able to send traffic to any other port,
and a PC connected to any port will be able to access the management
interface. Broadcast traffic, for example, will be flooded to all ports on the
switch.
The four VLAN parameters you can configure for each port on the switch
include VLAN Aware Enabled, Ingress Filtering Enabled, Packet Type, and
PVID. Note that the ports within a trunk cannot be configured individually;
configure the trunk instead (trunks are labelled T1 to T12 for the 24-port
switch, and T1 to T4 for the 8-port switch).
Creating a VLAN
1. Use the VLAN Setup page to create VLANs on the Switch. In VLAN ID,
input a number from 1 to 4094.
2. Click ADD.
3. Select the ports to be a member of this VLAN.
4. Click APPLY.
2-25
Page 36

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Modifying a VLAN
1. Use the VLAN Setup page to modify a VLAN. Under the VLAN List section,
click on the radio button of the VLAN you would like to modify.
2. Click MODIFY.
3. Select the ports to be added to or removed from this VLAN.
4. Click APPLY.
Deleting a VLAN
1. Use the VLAN Setup page to delete a VLAN. Under the VLAN List section,
click on the radio button of the VLAN you would like to delete.
2. Click DELETE.
Note Before deleting a VLAN, make sure that all the ports in this VLAN are also a
member of another VLAN. Otherwise, the port will not be a member of any
VLAN.
Field Attributes
Add VLAN
• VLAN ID – Input a VLAN ID and click APPLY to create a new VLAN.
VLAN List
• VLAN List – The list of up to 64 VLANs. You can modify or delete
these VLANs.
2-26
Page 37

Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web – Click VLANS, VLAN Setup.
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Web Configuration
VLAN Port Config
You can configure VLAN behavior for specific interfaces, including the default
VLAN identifier (PVID) and accepted frame types. This page allows you to
change the VLAN membership and behavior of individual ports. Each row of
the table corresponds to one port or trunk; trunked ports cannot be configured
individually.
Field Attributes
VLAN Per Port Configuration
• Port/Trunk – The port number or the ID of a trunk.
2-27
Page 38

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
• VLAN Aware Enabled – VLAN aware ports are able to use VLAN
tagged frames to determine the destination of the frame. Click to
enable or disable VLAN awareness mode for this port.
(Default: Enabled)
• Ingress Filtering Enabled – If enabled, incoming frames for VLANs
which do not include this ingress port in their member set will be
discarded. (Default: Disabled)
Note By default, Ingress Filtering is disabled on all ports. To prevent a port from
receipt of Ingress VLAN packets from a VLAN that is not configured for that
port, enable Ingress Filtering to drop those packets.
• Packet Type – Users can set the interface to accept all frame types,
or only tagged frames.
If the Packet Type is set to “All,” the port can accept incoming tagged
and untagged packets. Untagged packets will be associated with the
VLAN identified by the PVID. Tagged packets will be dropped unless
the port is a member of the VLAN identified by the VLAN tag in the
packet.
If the Packet Type is set to “Tagged Only,” the port will drop untagged
packets and will only receive tagged packets. Tagged packets will be
dropped unless the port is a member of the VLAN identified by the
VLAN tag in the packet. (Default: All)
• PVID – From a drop down menu, choose the VLAN ID that will be
assigned to untagged frames received on this port. It is not possible
to remove a port from VLAN 1 unless its PVID has been changed to
something other than 1. You can only choose “None” for the VLAN ID
when the packet type is set to “Tagged Only.” Outgoing packets are
tagged unless the packet’s VLAN ID is the same as the PVID. When
the PVID is set to “None,” all outgoing packets are tagged. (Default: 1)
Note When selecting “Tagged Only” mode for a port, it is recommended to set the
PVID to “None” as the standard configuration. Only set a PVID value for the
port in exceptional cases.
2-28
Page 39

Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web – Click VLANS, VLAN Port Config.
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Web Configuration
2-29
Page 40

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
LLDP Configuration
This page allows you to configure the Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
configuration. LLDP allows devices on the network to share information about
themselves for the reasons of simplified troubleshooting, enhanced network
management, and maintaining an accurate network topology. LLDP-capable
devices periodically transmit information in messages called Type Length
Value (TLV) fields to neighbor devices.
Field Attributes
LLDP State
• Port – The port number.
• State – You can choose to disable or enable LLDP for each port.
Enabling LLDP will allow the port to receive and transmit TLVs.
2-30
Page 41

Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web – Click LLDP, Configuration.
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Web Configuration
2-31
Page 42

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
LLDP Neighbor Table
This page displays the LLDP Neighbor Table. This table provides information
on neighboring devices. The table contains the following seven columns:
Field Attributes
• Local Port – The local port of the neighboring device.
• Chassis ID – The chassis information where the neighboring device
is located.
• Remote Port ID – The remote port ID on the neighboring device.
• System Name – The neighboring device’s full name.
• Port Description – The port description and information of the
neighboring device.
• System Capabilities – The system capabilities information of the
neighboring device.
• Management Address – Displays the management address of the
neighboring device.
Web – Click LLDP, Neighbor.
2-32
Page 43

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
SNMP Configuration
This page allows you to configure the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP). The SNMP agent permits READ ONLY access to the switch. Any
system in the network using management software can be used to discover
the switch. You can set the following options:
Field Attributes
• SNMP Enabled – Enables or disables SNMP. (Default: Enabled)
• Read Community – Community string for read access to the SNMP
protocol.
Web – Click SNMP, Configuration.
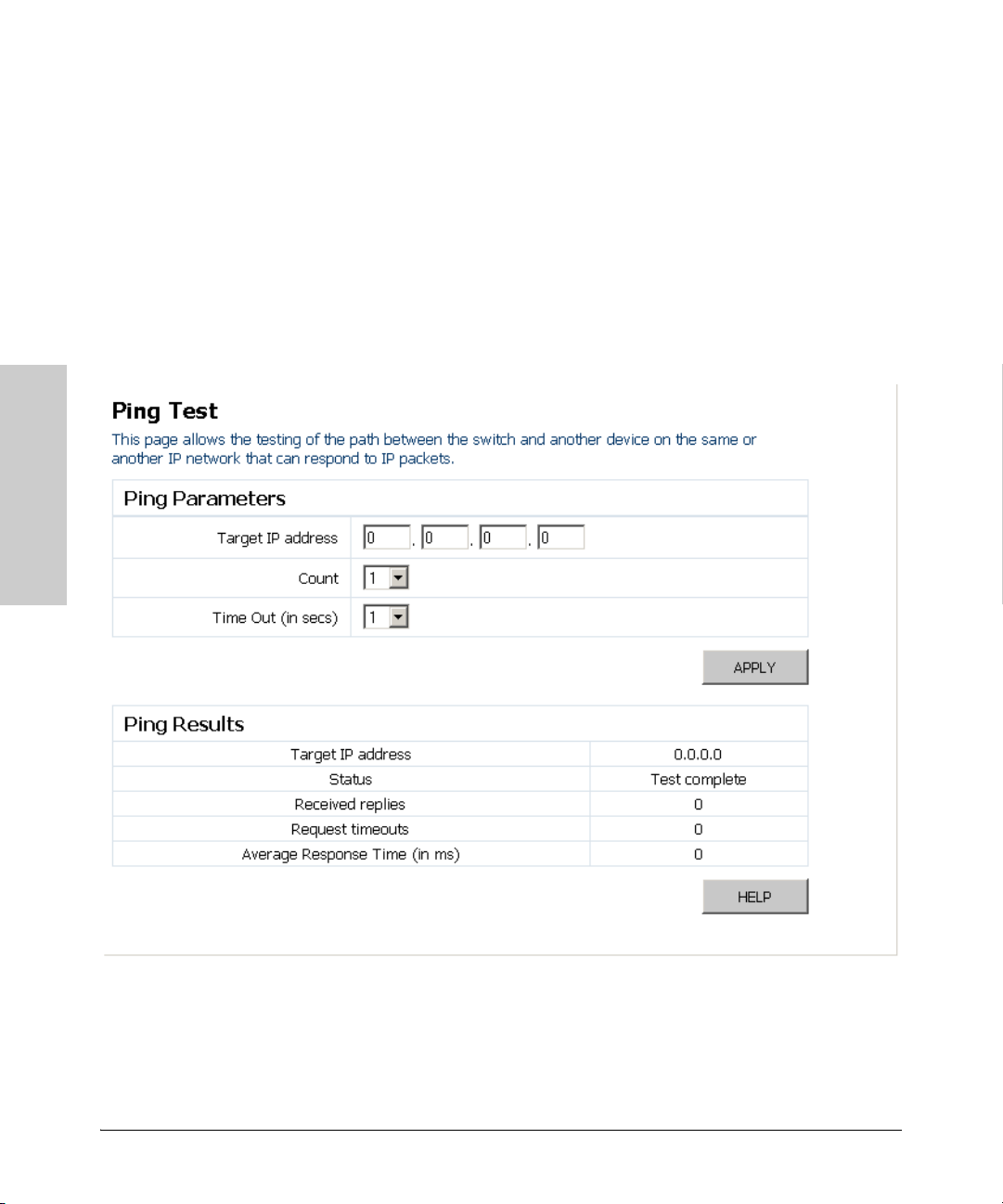
Ping Test
This operation allows you to test the network connections by sending an
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packet from the
switch to other devices on the network. The page will display the results of
the operation.
Field Attributes
Ping Parameters
• Target IP Address – The IP address of the device to ping on the
network.
• Count – Number of packets to send. (Default: 1)
• Time Out (in secs) – Number of seconds to wait for a response.
(Default: 1)
2-33
Page 44
Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Ping Results
• Target IP Address – The IP address of the device to ping on the
network.
• Status – Displays the current status of the ping operation.
• Received replies – Number of replies received.
• Request timeouts – Number of times the network device failed to
respond in the given time.
• Average Response Time (in ms) – Average response time of all the
packets.
Web – Click Diagnostics, Ping Test.
2-34
Page 45

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Restore to Factory Defaults
This operation allows you to either restore the switch back to the original
factory default configuration, or to clear all configuration information except
the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway IP Address (see the SYSTEM > IP
Address page).
Field Attributes
• Restore Entire Factory Default Configuration – Restore the
switch to the original factory default configuration.
• Keep Current IP Address Only – Restore the switch to the original
factory default configuration, except for the IP Address, Subnet Mask
and Gateway IP Address.
Web – Click Diagnostics, Factory Defaults.
2-35
Page 46

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Reboot Switch
Reboots the switch if the switch stops responding or functioning. This
operation will not change any switch configuration settings. To reboot the
switch, click APPLY. The reboot will be complete when the user interface
displays the login page.
Web – Click Diagnostics, Reboot Switch.
Upload/Download Configuration
Upload or download the switch system configuration file. Click to select either
the “Upload” or “Download” box. If you click on “Upload,” then click on the
“Browse” button to select the configuration file. If you click on “Download,”
you will be prompted to save your file. Please enter a name for the
configuration file. Finally, press the APPLY button to upload or download the
configuration file.
Note After you have completely finished configuring the switch settings, it is
important to download the configuration file. You can use this saved
configuration file to restore the switch settings at a later point if the switch
settings have been changed or restored to the default settings.
Field Attributes
• Operation – To upload or download the configuration file.
• Configuration File – Click on the “Browse” button to select the
configuration file. (Only available for the upload operation.)
2-36
Page 47

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web – Click Support, Configuration File.
Web Configuration
Download Text Readable Configuration/Status File
This page allows you to download the switch system configuration and status
information in text file format. Select the type of information you would like
to download. After you click the APPLY button, you will be prompted to save
your file.
Field Attributes
• Options – Select either general information, VLAN and MAC
information, port statistics, or LACP and LLDP information.
Web – Click Support, Support File.
2-37
Page 48

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Update Software
Updates the switch software using a file provided by ProCurve Networking.
Click on the “Browse” button to select the software file. Press the APPLY
button to update the selected switch software file. You can download software
files for your switch from the support section of the ProCurve Networking
Web site at
Caution After new software has been downloaded, the switch automatically reboots.
Field Attributes
• Current Software Version – Displays the current software version
• Software File – Click on the “Browse” button to select the software
Web – Click Support, Update Software.
www.hp.com/go/procurve.
in the switch.
file.
2-38
Page 49

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
Support
This page directs you to the ProCurve Networking Web site for further
information.
Web – Click Support, ProCurve Web Site.
2-39
Page 50

Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
Using the ProCurve Web
Browser Interface
Web Configuration
2-40
Page 51

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
This section describes how to troubleshoot the switch. You can perform more
in-depth troubleshooting on the switch using the software tools available with
the switch, from the built-in Web browser interface.
This chapter describes the following:
■ basic troubleshooting tips (page 3-1)
■ forgotten the IP address or password (page 3-2)
■ testing the switch by resetting it (page 3-2)
■ ProCurve Networking Customer Support Services (page 3-2)
Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Common problems and their solution are listed in the following table.
3
For more information on possible network problems and their solutions, refer
to the technical note “Troubleshooting LAN Performance and Intermittent
Connectivity Problems”, which can be found on the ProCurve Networking
Web site,
Problem Resolution
Cannot connect using the
Web browser.
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve, in the Information Library section.
• Be sure you have configured the agent with a valid IP
address, subnet mask and default gateway.
• If you are trying to connect to the agent via the IP
address for a tagged VLAN group, your management
station must include the appropriate tag in its
transmitted frames.
• Check that you have a valid network connection to the
switch.
• Check network cabling between the management
station and the switch.
3-1
Page 52

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Forgotten the IP Address or Password
Forgotten the IP Address or Password
If you have forgotten the switch’s IP address or administration password you
can return the switch to its factory default state by doing the following:
1. Remove the power cord from the back of the switch.
2. Remove all cables from the front-panel ports.
3. Connect port 1 to port 2 on the front panel, using a standard network cable.
4. Reconnect the power cord to the rear of the switch.
5. Wait at least 40 seconds before disconnecting port 1 from port 2.
After completing this procedure, there will be no password, the IP address
will be returned to the default 192.168.2.10, and all configuration settings will
be returned to factory defaults.
Testing the Switch by Resetting It
If you believe the switch is not operating correctly, you can reset the switch
to test its circuitry and operating code. To reset a switch, unplug and plug in
the power cord (power cycling)
Power cycling the switch cause the switch to perform its power-on self test.
ProCurve Networking Customer Support Services
If you are still having trouble with your switch, ProCurve Networking offers
support 24 hours a day, seven days a week through the use of a number of
automated electronic services. See the Customer Support/Warranty booklet
that came with your switch for information on how to use these services to
get technical support. The ProCurve Networking Web site,
go/procurve
Additionally, your ProCurve Networking authorized network reseller can
provide you with assistance, both with services they offer and with services
offered by ProCurve Networking.
3-2
also provides up-to-date support information.
http://www.hp.com/
Page 53

ProCurve Networking Customer Support Services
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Before Calling Support
Before calling your networking dealer or ProCurve Networking Support, to
make the support process most efficient, you first should have retrieved the
following information:
Information Item Information Location
• product identification, including miniGBICs (mini-GBIC is for the 24 port
switch only)
• details about t he switch’s status incl uding the software (OS) version, a copy of
the switch configuration, and information about port statistics
• copy of your network topology map, including network addresses assigned to
the relevant devices
the front of the switch, and on labels on the
mini-GBICs (mini-GBIC is for the 24 port
switch only)
Web interface
your network records
3-3
Page 54

Page 55

Index
Index
A
administrator password … 2-10
B
basic troubleshooting tips … 3-1
blinking LEDs
error indications … 3-2
broadcast storm … 2-11
C
Configuration file
upload/download … 2-36
D
default settings … 2-35
DHCP … 2-8
H
hardware version, displaying … 2-5
I
ingress filtering … 2-28
IP address
DHCP … 2-8
setting … 2-8
L
LEDs
error indications … 3-2
LLDP
configuration … 2-30
neighbor table … 2-32
log in
Web interface … 2-1
mirror port, configuring … 2-13
P
Password … 2-10
passwords
administrator setting … 2-10
ports
broadcast storm, threshold … 2-11
configuring … 2-12
mirroring … 2-13
statistics … 2-15
R
rate limits, setting … 2-11
reboot switch … 2-36
S
SNMP
configuration … 2-33
software version, displaying … 2-5
software, update … 2-38
statistics
port … 2-15
statistics, switch … 2-5
System Information … 2-5
T
tips for troubleshooting … 3-1
troubleshooting … 3-1
basic tips … 3-1
common network problems … 3-1
trunk
configuration … 2-19
LACP Setting … 2-20
LACP status … 2-23
membership … 2-16
M
main menu … 2-3
U
updating software … 2-38
Index-1
Page 56

Index
user password … 2-10
V
VLANs
port configuration … 2-27
setup … 2-25
W
Web interface
configuration options … 2-2
home page … 2-1
main menu … 2-3
panel display … 2-3
Index-2
Page 57

ProCurve 5400zl Switches
Installation and Getting Startd Guide
*5991-6222*
Technology for better business outcomes
To learn more, visit www.hp.com/go/procurve/
© Copyright 2007, 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information
contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products
and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products
and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
HP will not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Printed in China
July 2009
Manual Part Number
5991-6222
 Loading...
Loading...