Page 1

HP Extended Cluster for RAC
Continuous availability with the flexibility of virtualization
Executive summary............................................................................................................................... 2
Business dilemma ................................................................................................................................3
The solution......................................................................................................................................... 3
Context for the solution ..................................................................................................................... 3
Solution overview............................................................................................................................. 4
Solution components......................................................................................................................... 4
HP Extended Cluster for RAC............................................................................................................. 7
The tests ............................................................................................................................................. 8
Testing methodology ........................................................................................................................ 8
Test architecture............................................................................................................................... 9
Supported hardware configuration ................................................................................................. 9
Supported software configuration................................................................................................. 10
Test descriptions............................................................................................................................. 10
IPC test description ..................................................................................................................... 10
I/O test description .................................................................................................................... 10
OLTP test description................................................................................................................... 10
Failover test description............................................................................................................... 11
Test results and tuning..................................................................................................................... 11
The next steps.................................................................................................................................... 12
Solution flexibility .............................................................................................................................. 12
Conclusions ...................................................................................................................................... 13
References ........................................................................................................................................ 13
For more information.......................................................................................................................... 14
Page 2

Executive summary
The concept of optimized resource utilization has moved to the forefront of every IT organization’s
agenda. The maturation of the clustering market has forced hardware vendors to differentiate their
products to gain a competitive edge. Consequently, these vendors have begun to offer some variant
of virtualization as the latest trend in high-availability capabilities.
Traditionally, every IT manager was confronted with the dilemma of having to balance risk and cost.
Reducing risk in an IT environment necessarily came at high costs; conversely, lowering one’s costs
engendered substantial risks. The prevailing model for risk reduction focuses on the duplication of
critical computing components, the elimination of single points of failure, and the potential use of a
secondary facility to continue operations in the event of a catastrophic loss of a primary data center.
Although this approach demonstrates diligence toward risk management, it also comes at the expense
1
of duplicative and underutilized resources. HP Extended Cluster for RAC (Real Application Clusters)
now addresses part of this utilization shortfall by taking advantage of the advancement in
virtualization technologies. HP is regarded as the industry leader for virtualization and is continually
raising the bar on optimized resource utilization.
The HP product line encompasses both high-availability and disaster-tolerant solutions. Coupled with
its powerful virtualization capabilities, HP is the only vendor offering products that seamlessly
integrate the three concepts of high availability, disaster tolerance, and virtualization. To illustrate this
compelling value proposition, this white paper will examine the HP solution for Oracle® RAC.
HP Extended Cluster for RAC combines the high-availability product, HP Serviceguard Extension for
RAC (SGeRAC) and the disaster-tolerant solution, HP Extended Campus Cluster. Moreover, when
integrated with BEA WebLogic Server and virtualization tools, the net result is a compelling solution
that specifically addresses risk reduction and capitalizes on IT investment in any environment that uses
an Oracle9i RAC database.
HP Extended Cluster for RAC enables a single Oracle database to be shared across two data centers,
up to a distance of 100 km. Because the two sites are functioning as a single virtual entity, all
resources can be utilized at all times. The ability to meld distributed IT components into a
homogeneous resource pool is made possible by the HP Virtual Server Environment (VSE) portfolio of
solutions.
Virtualization enables full resource utilization within an enterprise while still maintaining previous
levels of availability and data protection. Because data is replicated and synchronized between data
centers, the entire computing environment is said to function as a single virtual entity. A distance of
100 km between the data centers, for instance, will not preclude an administrator from managing the
application and data as if it were a traditional RAC application located in a single data center. Thus,
whether an IT environment is located in one data center or across two or more, HP solutions are
designed to protect mission-critical applications against hardware and software failures, planned or
unplanned.
With the VSE, HP has created a unique solution that provides unrivaled levels of risk management
and return on IT investment, and it has simultaneously enhanced an enterprise’s ability to rapidly
accommodate and capitalize on volatile business conditions.
By extending a RAC solution over distance with more efficient use of resources, HP has demonstrated
that global virtualization has arrived.
1
Oracle RAC technology allows multiple instances of an application to access a single logical database across multiple servers, with all nodes
able to concurrently execute transactions against the same database.
2
Page 3

Business dilemma
If a group of CIOs was asked to identify their primary cause of stress, the majority would answer
“controlling IT risks and costs.” Indeed, many would say that this is the most important challenge
within a CIO’s charter.
In striving to balance risk management and fiscal responsibilities, every IT manager is faced with a
difficult choice. On one hand, risk can be reduced by investing in duplication and redundancy, but
on the other hand, costs can be driven down by exposing the organization to increased levels of risk.
Therefore, simultaneously lowering both risk and cost ostensibly is mutually incompatible.
A previously acceptable and widely adopted approach to risk management was for an IT
organization to purchase excess equipment to create a pool of surplus CPU, storage, and connectivity
resources. This method was effective for dealing with various adverse situations. However, in today’s
cutthroat and fiscally cautious business climate, it represents a highly visible example of poor
utilization of IT assets.
To allow for changes in business conditions, IT systems are typically configured to handle maximum
anticipated loads and designed to be scalable, with additional hardware. This approach provides a
fair degree of flexibility, but it does so at the expense of asset utilization. HP studies have shown that,
on average, system use ranges from 20% to 40% of available resources, yet it is not unusual to see
many applications bottlenecked by resource constraints.
For many years, HP has been providing solutions that maximize clients’ return on IT investment. By
combining innovative technologies with proven industry-standard solutions, HP now ushers in the next
generation of solutions that increases utilization, manages risk, and makes the most of IT
expenditures.
The solution
Context for the solution
The Adaptive Enterprise is the HP vision for helping customers synchronize business and IT to
capitalize on change. Virtualization enables you to balance two seemingly contradictory concepts—
cost and agility—by pooling and sharing servers, storage, networking, and other infrastructure
devices and allocating them across applications and processes as your business demands them. The
new Adaptive Enterprise has management capabilities to sense changes in business demand and
trigger the dynamic supply of virtualized resources.
HP defines virtualization as managing an IT environment as a single entity by pooling and sharing
resources such that supply automatically meets demand in real time. This holistic approach allows the
entire IT resource pool to be viewed as a single virtual entity that can be allocated—through business
priorities and policies—to dynamically serve the requirements of the enterprise.
In isolation, virtualization over extended distances has the potential to actually increase the burden
placed on IT organizations. However, by combining virtualization with powerful real-time automation
tools, HP has been able to create a compelling suite of solutions that exploit previously underutilized
assets without causing additional IT overhead.
HP has included the core of its intelligent virtualization concept in the VSE portfolio of solutions. Each
of the VSE offerings is fundamentally designed to achieve a common set of objectives:
• Improve return on IT investment
• Provide enhanced functionality to accommodate and exploit business volatility
• Enable elevated levels of IT service to the enterprise
• Present unrivaled choices for the management and mitigation of risk
3
Page 4

Solution overview
At the center of the “risk versus cost” challenge is the question “How can I increase application
availability and resiliency while also aggressively managing costs?” The concept of using multiple
data centers, with replicated system configurations, to provide fallback capabilities through
redundancy has emerged as the preferred solution. This approach minimizes the impact of the total
loss of one data center, but it achieves this through the gross underutilization of IT assets.
HP has addressed this issue with a unique and compelling blend of optimally utilized high-availability
and disaster-tolerant solutions. HP has retained all the advantages of split data centers and is now
offering solutions that virtually eliminate redundant, underdeployed resources. This includes support
for Oracle RAC, which allows one of the world’s most popular databases to be deployed for high
availability and scalability.
Oracle9i RAC allows multiple instances to access a single logical database across multiple servers,
with all nodes able to concurrently execute transactions against the same database. However, for the
systems to be housed in separate data centers, several other key solution components must be present.
These components include data center connectivity, workload balancing, and a variety of service
managers—for cluster arbitration, business policy enforcement, volume management, partitioning,
mirroring and synchronization, and so on—as well as supporting hardware.
To illustrate the real-world feasibility of hosting a single logical database across multiple discrete data
centers up to 100 km, HP enhanced its SGeRAC solution.
Solution components
The highly pervasive RAC configuration features comprehensive high-availability and scalability
functionality. SGeRAC delivers the ability to perform identical operations across two remotely-located
data centers and gives the configuration increased stability through additional high availability and
disaster tolerance. In addition, it produces efficiency gains through the utilization of all dynamicallyallocated resources.
4
Page 5
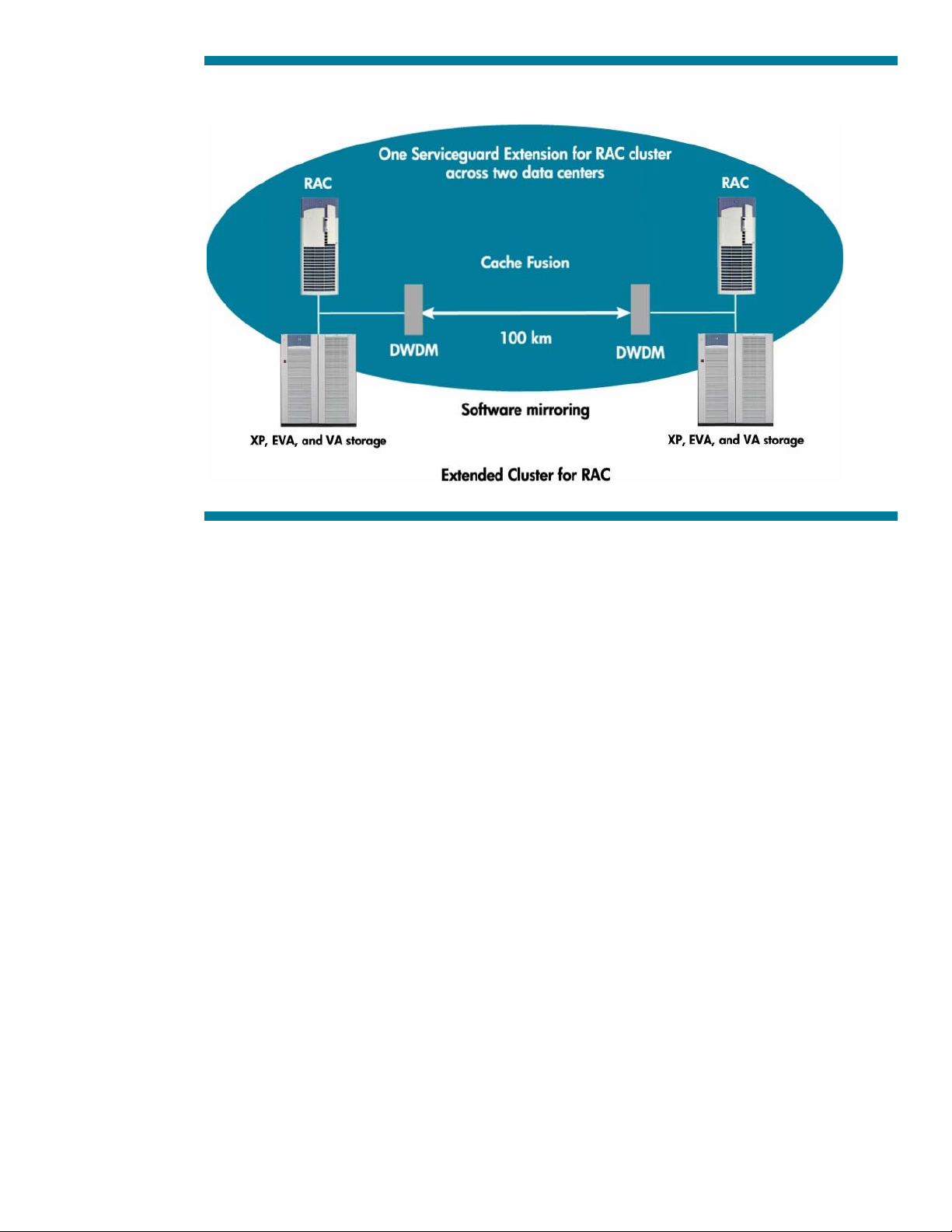
Figure 1. HP Extended Cluster for RAC—100 km
Cache Fusion is a key component of RAC that uses cluster interconnect technologies to facilitate virtual
buffer sharing through the use of direct memory accessing. The Cache Fusion architecture creates a
single virtual cache across all the nodes of the cluster. The resulting single view of all buffer caches
minimizes disk I/O by allowing any database request to be served by any node in the cluster. In
other words, Cache Fusion enables shared access to all the data on disk by all the nodes in the
cluster.
The introduction of a second data center creates many advantages for risk management and
mitigation. However, until virtualization with SGeRAC was available, it also had the potential to
introduce significant levels of asset underutilization and operational complexity.
5
Page 6

The HP Extended Cluster for RAC architecture relies on the same components as the collocated system
configuration, but it introduces several additional key technologies. System-to-system communication is
now facilitated by the addition of a pair of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) devices
connected by dark fiber. Database replication is achieved through host-based software mirroring, and
RAC synchronizes the cache using Cache Fusion in the normal manner.
Figure 2. DWDM: Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
DWDM employs optoelectronic technology to simultaneously transmit multiple separate optical signals
through a single optical fiber by changing the wavelength of the incoming optical signals to permit
2
coexistence on a common fiber
.
The transmitting DWDM device can multiplex multiple converted optical inputs over the same fiber
optic cable. The destination DWDM reverses the process; it demultiplexes the signals and converts
them back to their original wavelength. This process allows network, disk, and application
communications to share the same DWDM link and provides the capability to extend the Fibre
Channel link distances. Examples shown in Figure 2 include the multiplexing and demultiplexing of
Fibre Channel, 100Base-FX, and ESCON (Enterprise System Connection—a large-system I/O channel
architecture) transmissions.
The DWDMs and fiber optic media together provide the low latency interconnect that is essential to
RAC performance and scalability.
Dark fiber is existing fiber optic cable that has not yet been lit. This excess fiber capacity is readily
available, and using it to connect DWDM devices is rapidly gaining popularity as a cost-effective
mechanism to increase bandwidth. Because the conduit is typically dedicated to this solution, it is
always available to offer full capacity and security to the associated transmissions.
2
An in-depth description of the evolution, testing, and deployment of DWDM can be found in the document titled, DWDM: A White Paper, by
Joseph Algieri and Xavier Dahan.
6
Page 7

The complex tasks of managing and linking business priorities to the appropriate resource allocations
are handled by the highly integrated components of the VSE portfolio of solutions:
• HP Serviceguard and SGeRAC
• HP Partitioning Continuum
• HP-UX Workload Manager (WLM) and HP Global Workload Manager (gWLM)
• HP Instant Capacity and Temporary Instant Capacity
HP SGeRAC brings data protection, application availability, and ease of management to servers and
server partitions to create an enterprise cluster that delivers highly available application services to
LAN-attached clients. HP Serviceguard monitors the health of each node and responds to failures in a
way that minimizes or eliminates application downtime. When used in conjunction with SGeRAC, it
allows for rapid and transparent recovery from LAN and application failures, while still maintaining
scalability, data integrity, and configuration flexibility.
HP Partitioning Continuum components are the industry’s broadest range of hard and virtual
partitions, and they offer partitioning tools that provide resource flexibility, improved system
utilization, and lower costs in consolidated environments while maintaining the appropriate level of
isolation. The flexibility of HP Partitioning Continuum is automated with WLM and gWLM, which can
reallocate resources between partitions based on business policies and real-time requirements.
WLM provides automatic resource allocation and application performance management through the
use of prioritized service level objectives on a single system. It is the key to enabling applications to
be stacked. Goal-based resource management provides highly predictable response times for all
mission-critical applications, regardless of their location. The tight integration of HP Serviceguard and
WLM allows CPU and memory resources to be assigned to specific HP Serviceguard packages after a
failover. gWLM builds on WLM and provides similar resource management functionality. gWLM has
been designed for a centralized IT environment and employs a central management station to
facilitate resource management implementation across multiple systems.
Both WLM and gWLM guarantee computing resources to mission-critical applications but allow lowerpriority applications to utilize those resources when they are otherwise unneeded by the missioncritical applications. In a SGeRAC implementation, one or more SGeRAC instances can be stacked
on the same infrastructure with the appropriate level of isolation while low-priority applications can
use the rest of the available computing cycles. For example, if a data center fails and the load
significantly increases on the remaining data center, it automatically transfers resources from the
lower-priority workloads to the Extended Cluster for RAC instances.
HP Instant Capacity is an innovative mechanism to rapidly respond to unpredictable business volatility
through the deployment of preconfigured systems that provide additional computing capacity. Clients
are charged when the additional resources are utilized. Instant Capacity provides a permanent
capacity increase while Temporary Instant Capacity allows additional capacity to be activated and
deactivated as required. Temporary Instant Capacity is integrated with WLM and gWLM 2.0+ to
automatically activate and deactivate capacity as needed. When used with SGeRAC, if one data
center goes offline and another data center picks up the load, additional CPU resources can
automatically be brought online to help maintain service levels.
HP Extended Cluster for RAC
The solution components bring together the best aspects of HP VSE, the HP suite of clustering
products, and Oracle RAC: comprehensive resource utilization, high availability, data integrity,
scalability, and reduced administration costs. Compelling on their own, these characteristics are
further complemented by the ability to share databases across multiple data centers, providing full
disaster tolerance and unprecedented levels of risk mitigation and cost effectiveness.
7
Page 8

Utilizing its intelligent policy engine, the WLM component of the VSE allows the real-time allocation of
assets throughout the virtual resource pool—yielding enhanced server utilization, increasing return on
IT investment, and dramatically improving the enterprise’s ability to accommodate business volatility.
If an entire data center is lost, the remaining data center continues to function during the rerouting of
users to the functioning environment. This capability provides continuous availability across the two
data centers. When the failed data center comes back online, all resynchronization takes place
automatically and is transparent to users.
The administration of the overall environment is greatly simplified because the application is resident
on a single data repository. The concept of unnecessarily replicated databases, with the associated
burden of replicated management chores, has been all but eliminated. Even when spread across a
distance of a hundred kilometers, the Oracle9i database is still a single database instance,
possessing inherent economies of system administration over multi-instance solutions.
The move to a 100-km separation thus represents a dramatic increase in overall application
resiliency. The ability to place such a large distance between two data centers ensures that only the
most widespread disaster will impact more than one of the installations.
The tests
Testing methodology
The depth of experience HP has had with extended clusters and SGeRAC was leveraged in
developing the test plans for the extended distance testing. Together with partners Oracle, AT&T, and
Nortel, the tests focused on demonstrating the ability to achieve a robust solution capable of
maximizing resource utilization between remote data centers, specifically, up to 100 km. In doing so,
particular attention was paid to high availability, disaster tolerance, and performance results across
this extended distance.
The underlying premise for the testing was the validation of the remotely distributed cluster’s ability to
sustain full functionality while being subjected to failovers. Testing was done at distances of 25, 50,
and 100 km to validate availability, performance, and network latency.
After the link between the data centers was established, a series of loading and failure scenarios was
executed to validate the expected disaster-tolerant characteristics of the configuration. The scenarios
simulated failure-inducing events on a loaded configuration that traditionally would prove catastrophic
in a non-SGeRAC environment. Each test was designed to yield significant transaction-based traffic,
triggering a set of failure-inducing events and the subsequent validation of data integrity during and
following the failure.
8
Page 9

Figure 3. Two-data center Extended Cluster for RAC—up to 100 km currently-supported configuration
Test architecture
The test configuration for the 100-km evaluation followed the supported configuration for all
subsequent SGeRAC implementations.
Supported hardware configuration
• Two-node cluster (PA-RISC or HP Integrity servers, not mixed).
– A two-, four-, six- or eight-node cluster is supported up to 10 km with VERITAS Cluster Volume
Manager (CVM).
• Redundant heartbeat, plus one or two LANs for Cache Fusion traffic.
– Clusters with VERITAS CVM; only single-heartbeat subnet is supported (use primary/standby
LANs).
• Any Fibre Channel storage (using HP StorageWorks Virtual Array (VA), HP StorageWorks XP disk
array, HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array (EVA), or just a bunch of disks (JBOD)
technologies).
– Note: EVA disk arrays do not currently support VERITAS Volume Manager (VxVM)/CVM.
• Both TCP/IP networking and Fibre Channel data can go through the same DWDM box; redundant
DWDM boxes in each data center are not required if the box is designated as acceptably faulttolerant.
• At least two dark fiber links between data centers.
– During testing, AT&T-supplied dark fiber optic links were used between data centers (to further
enhance disaster tolerance capabilities, alternate physical routes can be added to remove single
points of failure).
– Note: TCP/IP networking and Fibre Channel data pass through the same DWDM box; in a non-
test environment, redundant DWDM boxes in each data center are not required if fault-tolerant
design specifications meet disaster tolerance requirements.
9
Page 10

• Cluster arbitration: dual cluster lock disks (Logical Volume Manager (LVM) volume groups) or
Quorum Server.
– Note: Three-site configuration is supported using Quorum Server to prevent split-brain, the
condition in which two equal-sized subgroups of cluster nodes re-form a cluster independent of
each other.
• Nortel OPTera DWDM switches were used for initial testing and certification.
Supported software configuration
• Operating system: HP-UX 11.11 or HP-UX 11i v2.0
• Shared Logical Volume Manager (with physical volume links and HP MirrorDisk/UX,
HP StorageWorks SecurePath with EVA storage)
• VERITAS VxVM/CVM 3.5 (with DMP and mirroring) for cluster volume management
• HP Serviceguard Quorum Server or dual cluster lock disks for cluster arbitration (The dual cluster
lock disks are required—one at each center—to facilitate recovery from an entire data center
failure.)
• HP Serviceguard and HP SGeRAC A.11.15 or later
• Oracle RAC 9.2 or later
• HP StorageWorks Extended Fabric on Fibre Channel switches (HP StorageWorks Extended Fabric
enables dynamically allocated long-distance configurations in a Fibre Channel switch.)
Test descriptions
The following categories of testing were performed:
• IPC (Inter-Process Communication) tests
• I/O tests
• Online transaction processing (OLTP)-like workload tests
• Failover tests
IPC test description
Raw IPC throughput was evaluated using CRTEST, a micro-level performance benchmark. The test first
updates a set of blocks in a hash cluster table on instance A, and then an increasing number of clients
running SELECT are started on instance B. These queries cause messages to be sent from instance B to
instance A; instance A returns a CR block. CR Fairness Down Converts were disabled for this test to
create a fundamental dialog of “send a message” and “receive a CR block” back.
The CRTEST (IPC) tests were performed initially using one Gigabit Ethernet network for cluster
interconnection, and then the tests were repeated using two interconnects.
I/O test description
The I/O tests were executed using the Diskbench (db) disk subsystem performance measurement tool.
The db tool measures the performance of a disk subsystem, host bus adapter, and driver in terms of
throughput (for sequential operation) and number of I/Os (for random operation). Diskbench can
evaluate the performance of kernel drivers and can be used on one-way or multiprocessor systems to
completely saturate the processors and effectively measure the efficiency of a disk subsystem and
associated drivers. The tests were performed using a mix of 60% reads and 40% writes to simulate
“real-world” traffic.
OLTP test description
The industry-standard TPC-C test was utilized to simulate OLTP transactions over the cluster
interconnects and DWDM network. TPC-C can emulate multiple transaction types and complex
database structures. The benchmark involves a mix of five concurrent transactions of varying type and
10
Page 11

complexity that were executed online and queued for deferred execution. TPC-C is widely
acknowledged as providing one of the most realistic loading simulations within a comprehensive
computing environment.
Failover test description
Multiple tests were performed to simulate the wide variety of scenarios that could impact a data
center. Host failure, storage device failure, DWDM link failure, and catastrophic data center failure
were all emulated to stress the configuration in the most rigorous and realistic manner possible. Intradata center connections to storage, either through the Interswitch Linking (ISL) switch or directly to an
array, were removed one at a time to simulate localized failures. Characteristics of the configuration’s
response to each event were observed, including the reaction of the Oracle instance, and behavior
during resynchronization of data volumes as connections became reestablished was also noted. Data
integrity and user impact were also closely monitored throughout all phases of testing.
Test results and tuning
The most critical result of the testing is that the 100-km SGeRAC solution, running over DWDM, fully
exhibited the complete set of high-availability characteristics observed on a collocated HP
Serviceguard cluster, allowing the server and application cluster to continue to perform and be
accessible when failure occurred on one or more of the components. Data integrity was maintained
for the duration of all testing.
For host failure emulation, a server was shut down, making the Oracle database components resident
on that system inaccessible for two to three minutes. All traffic was able to move to the second data
center. When restarted, the failed system resumed operations.
A forced single storage device failure had no impact on the Oracle instance. Even though the test was
continued for several minutes, no visible user impact or loss of data integrity was observed.
DWDM link failure did not compromise the cluster, which continued to remain up for the duration of
the test cycle. No discernible adverse behavior in HP Serviceguard and SGeRAC performance or
functionality was noted.
The solution performed well against stringent proprietary and industry-standard benchmark tests,
providing the enterprise with unprecedented levels of disaster tolerance and resource utilization
across the 100-km divide. Even during recovery, the full functionality of the Oracle repository
remained available.
As expected, in the less than optimized configuration, IPC, I/O, and application operations did show
a degree of performance degradation related to separation distance. This result indicates that
assessment of the application and workload characteristics of the target environment are critical to
making the most of the implementation over extended distances. During the evaluation, informal
manipulation clearly demonstrated that tuning and hardware selection can have a significant impact
on overall system performance.
It was found that the assignment of buffer credits within the DWDM devices had a significant positive
impact on throughput performance of the RAC application. Configuring larger buffer credit values can
require more memory in the DWDM device. However, assigning larger buffer credit values helps
keep the pipeline full, thus improving throughput and making better use of the available bandwidth,
especially as the distance between the sites increases. For instance, doubling the buffer credits to 60
resulted in a throughput gain of over 100% at distances of 50 km and 100 km. It is expected that, in
practice, buffer credits much larger than 60 would be needed to take full advantage of the available
bandwidth.
The use of multiple DWDM channels allows each protocol to have its own unimpeded bandwidth,
subject to the total available aggregate bandwidth. Further increases in performance were observed
with the addition of extra interconnects from the servers to the DWDM device so that Cache Fusion
11
Page 12

traffic could be separated from other TCP/IP and Fibre Channel traffic. Moreover, adding Ethernet
and Fibre Channel I/O cards to the servers better distributed the I/O loads and resulted in increased
performance.
A thorough evaluation of the application transactions is recommended in conjunction with an analysis
of the following:
• Optimum buffer credit configuration
• Number of Ethernet cards in each server
• Number of Fibre Channel cards in each server
• Number of I/O slots and cards in the DWDM device
The next steps
A variety of performance enhancements at various levels within the Extended Cluster for RAC
architectural solution are available, such as network buffering, workload distribution, and database
partitioning. In many cases, these enhancements will be environment-specific. As these solutions are
deployed, a collection of best practices will be shared.
To provide additional business value, HP is continually investing in the development of new solutions
and further enhancing existing portfolios. An example of this commitment is the future capability to
handle numbers of nodes even higher than the current specifications.
Solution flexibility
The Extended Cluster for RAC solution was tested using the components detailed earlier in the “Test
architecture” section. However, the configuration is quite accommodating in the choice of acceptable
hardware and software. This flexibility enables customers to leverage existing IT assets and rapidly
move toward an operational implementation without the unnecessary purchase of a completely new
infrastructure.
During the testing period, a wide range of storage devices was introduced into the configuration. The
majority of HP-UX enterprise server-compatible storage devices will perform suitably in the Extended
Cluster for RAC environment, from the high-end HP StorageWorks XP disk array models to the lowercost HP EVA storage solution.
In addition, HP Serviceguard Quorum Server can be introduced to provide cluster lock management
for tie-breaking and autonomous clustering, following any failure that impacts cluster integrity.
There are a variety of options for load balancing using access clients, including Resonate’s Central
Dispatch product and a selection of hardware-based choices from Cisco.
Given the transparency of the DWDM devices, it is possible to run a wide variety of protocols across
the fiber. During testing, Gigabit Ethernet was used for system-to-system connectivity. Network
switches can be 100Base-T (TX or FX), 1000Base-T (TX or FX), or Fiber Distributed Data Interface
(FDDI). The connections between the network switches and the DWDM boxes must currently remain
fiber optic.
As demonstrated by the Oracle9i RAC implementation, HP has introduced the VSE, enhanced for
specific application server and database environments. HP released the VSE Reference Architecture
for BEA WebLogic Server and Oracle databases on HP-UX, which provides the most effective way for
customers to quickly implement virtualization within their application server and database
environments to achieve the benefits of an Adaptive Enterprise.
12
Page 13

Conclusions
HP has successfully shown the viability of the Extended Cluster for RAC in a virtualized environment
over distance. In particular, HP demonstrated the feasibility of a SGeRAC configuration deployed
across two discrete data centers separated by 100 km. The 100-km distance significantly diminishes
the likelihood of a single disaster impacting more than one data center at any one time.
Traditionally, disaster tolerance in an IT environment had been accomplished through a configuration
of “active/standby”, that is, resources are not utilized until needed. The 100-km RAC solution destroys
this paradigm—there is now full utilization of all resources in all data centers at all times, that is, an
“active/active” environment. Data is replicated between the two data centers and is fully
synchronized, allowing location-independent access to the applications. The HP VSE permits both
data centers to see the data simultaneously and to leverage the aggregated resources from both
locations continuously. The HP VSE is the only solution available on the market today that tightly
integrates high availability, partitioning, and utility pricing.
HP is thus able to deliver a highly reliable solution incorporating SGeRAC, the VSE, BEA WebLogic
Server, and Oracle9i RAC. The refinement of VSE technologies makes possible the full utilization of IT
resources beyond 100 km as well.
full resource utilization will soon become mainstream, regardless of the distance separating data
centers.
HP has thus made extending a RAC solution a reality without sacrificing resource efficiency.
3
The leadership of HP in virtualization technologies ensures that
References
DWDM: A White Paper by Joseph Algieri and Xavier Dahan, available on request from HP
3
HP Continentalclusters for RAC is available for customers requiring a solution that extends beyond 100 km and incorporates the features of
extended RAC across two data centers located anywhere in the world.
13
Page 14

For more information
• http://www.hp.com/go/ha
http://www.hp.com/go/virtualization
•
© 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained
herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and
services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein.
Oracle is a registered U.S. trademark of Oracle Corporation, Redwood City,
California.
5982-3575EN, Rev. 2 August 2005
 Loading...
Loading...