Page 1

Hardware Reference Guide
HP Compaq Business Desktops
dx6120 Microtower Models
Document Part Number: 374967-001
September 2004
This guide provides basic information for upgrading this computer
model.
Page 2

© Copyright 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable
for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright.
No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to
another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard
Company.
WARNING: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow
Å
directions could result in bodily harm or loss of life.
CAUTION: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow
Ä
directions could result in damage to equipment or loss of information.
Hardware Reference Guide
HP Compaq Business Desktops
dx6120 Microtower Models
First Edition (September 2004)
Document Part Number: 374967-001
Page 3

Contents
1 Product Features
Standard Configuration Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Front Panel Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Rear Panel Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Windows Logo Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–5
Special Mouse Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–5
Serial Number Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–6
2 Hardware Upgrades
Serviceability Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Warnings and Cautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Removing the Computer Access Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Removing the Front Bezel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Installing Additional Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
DIMMs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
DDR2-SDRAM DIMMs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
Populating DIMM Sockets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
Installing DIMMs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Replacing or Upgrading a Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
Locating Drive Positions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–9
Removing a Drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
Replacing a Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–13
Removing or Installing an Expansion Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Reassembling the Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–25
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com iii
Page 4

Contents
A Specifications
B Battery Replacement
C Security Lock Provisions
Installing a Security Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C–1
Cable Lock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C–1
Padlock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C–2
D Electrostatic Discharge
Preventing Electrostatic Damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D–1
Grounding Methods. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D–1
E Routine Computer Care and Shipping Preparation
Routine Computer Care. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E–1
Optical Drive Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E–2
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E–2
Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E–2
Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E–2
Shipping Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . E–3
Index
iv www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 5

Product Features
Standard Configuration Features
The HP Compaq Microtower features may vary depending on the
model. For a complete listing of the hardware and software installed
in the computer, run the Diagnostics for Windows utility. Instructions
for using this utility are provided in the Troubleshooting Guide on the
Documentation CD.
1
Microtower Configuration
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 1–1
Page 6
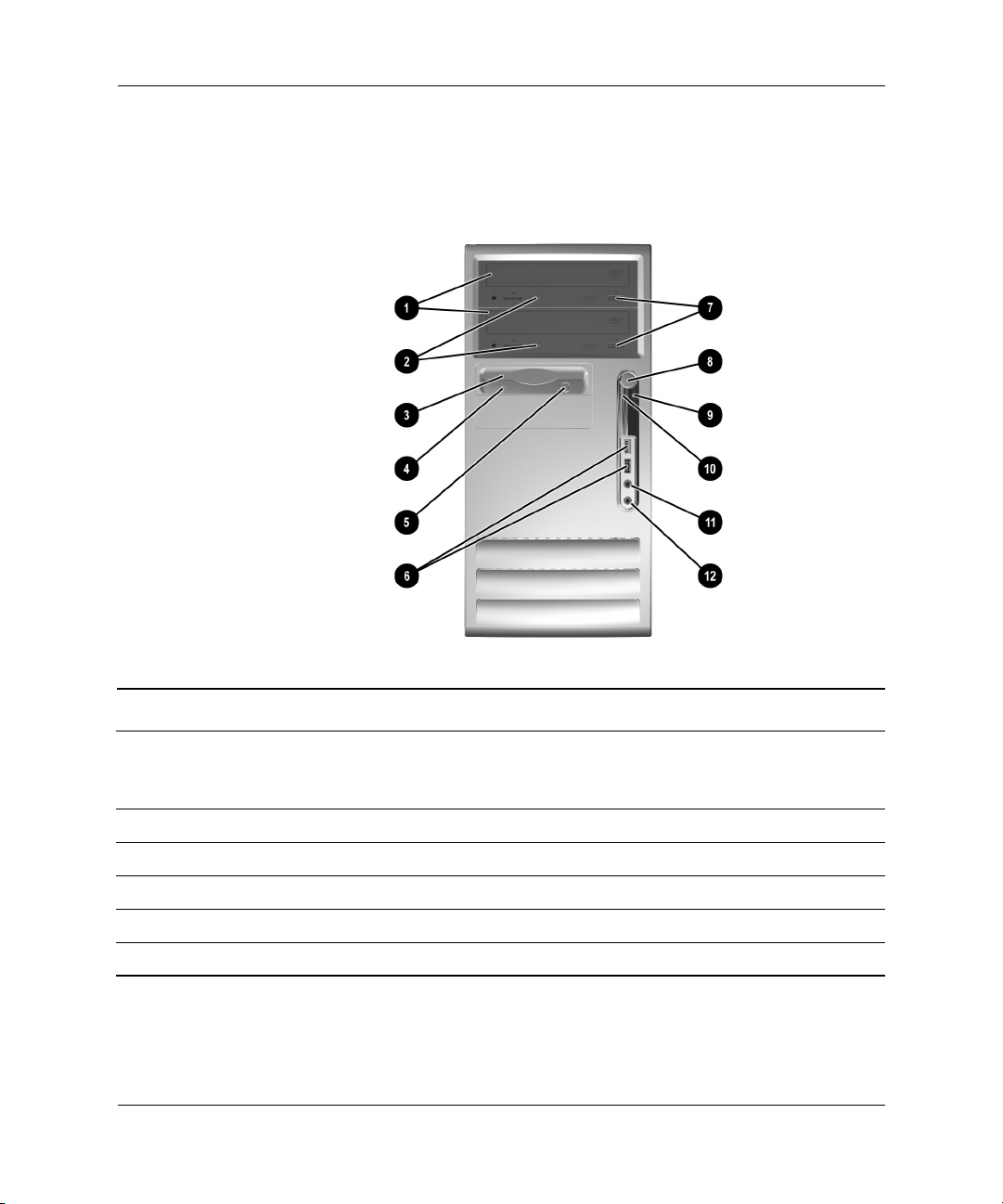
Product Features
Front Panel Components
Drive configuration may vary by model.
Front Panel Components
1 Optical Drives (CD-ROM, CD-R/RW,
DVD-ROM, DVD+R/RW, or
CD-RW/DVD Combo Drive)
2 Optical Drive Activity Lights 8 Power Button
3 Diskette Drive (optional) 9 Power On Light
4 Diskette Drive Activity Light (optional) - Hard Drive Activity Light
5 Diskette Eject Button (optional) q Headphone Jack
6 USB (Universal Serial Bus) Ports w Microphone Connector
1–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
7 Optical Drive Eject Buttons
Page 7
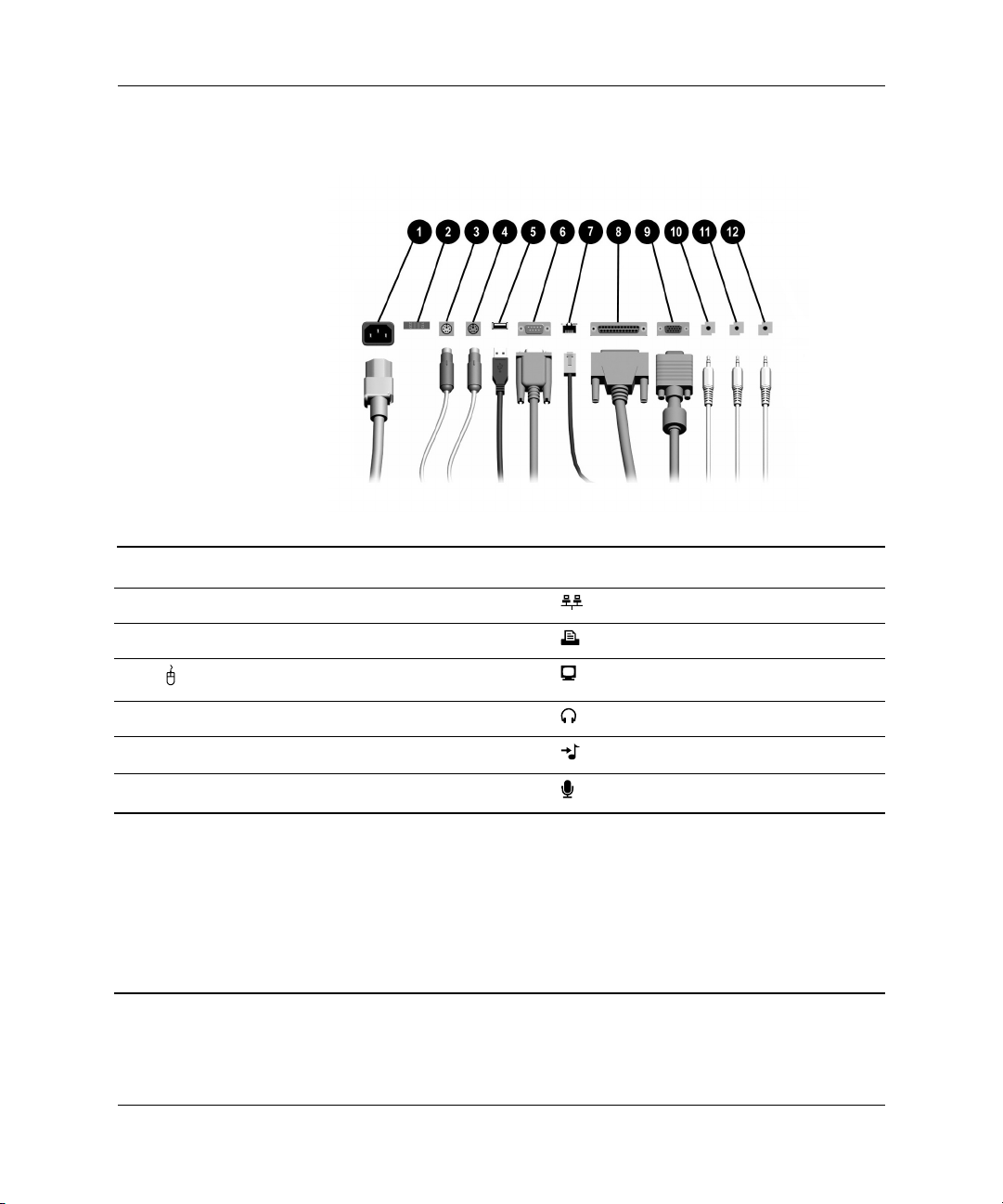
Rear Panel Components
Rear Panel Components
1 Power Cord Connector 7 RJ-45 Network Connector
Product Features
2 Voltage Select Switch 8
3
4
5
6
✎
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 1–3
PS/2 Mouse Connector 9 Monitor Connector
PS/2 Keyboard Connector - Headphone/Line-Out Connector
a
Universal Serial Bus (USB) q Line-In Audio Connector
o
m
Serial Connector w Microphone Connector
Arrangement and number of connectors may vary by model.
The monitor connector on the system board is inactive when a PCI Express graphics card is
installed in the computer.
If a standard PCI graphics card is installed, the connectors on the card and the system board
may be used at the same time. Some settings may need to be changed in Computer Setup to
use both connectors. For information about Boot Order, refer to the Computer Setup (F10)
Utility Guide on the Documentation CD.
Parallel Connector
Page 8
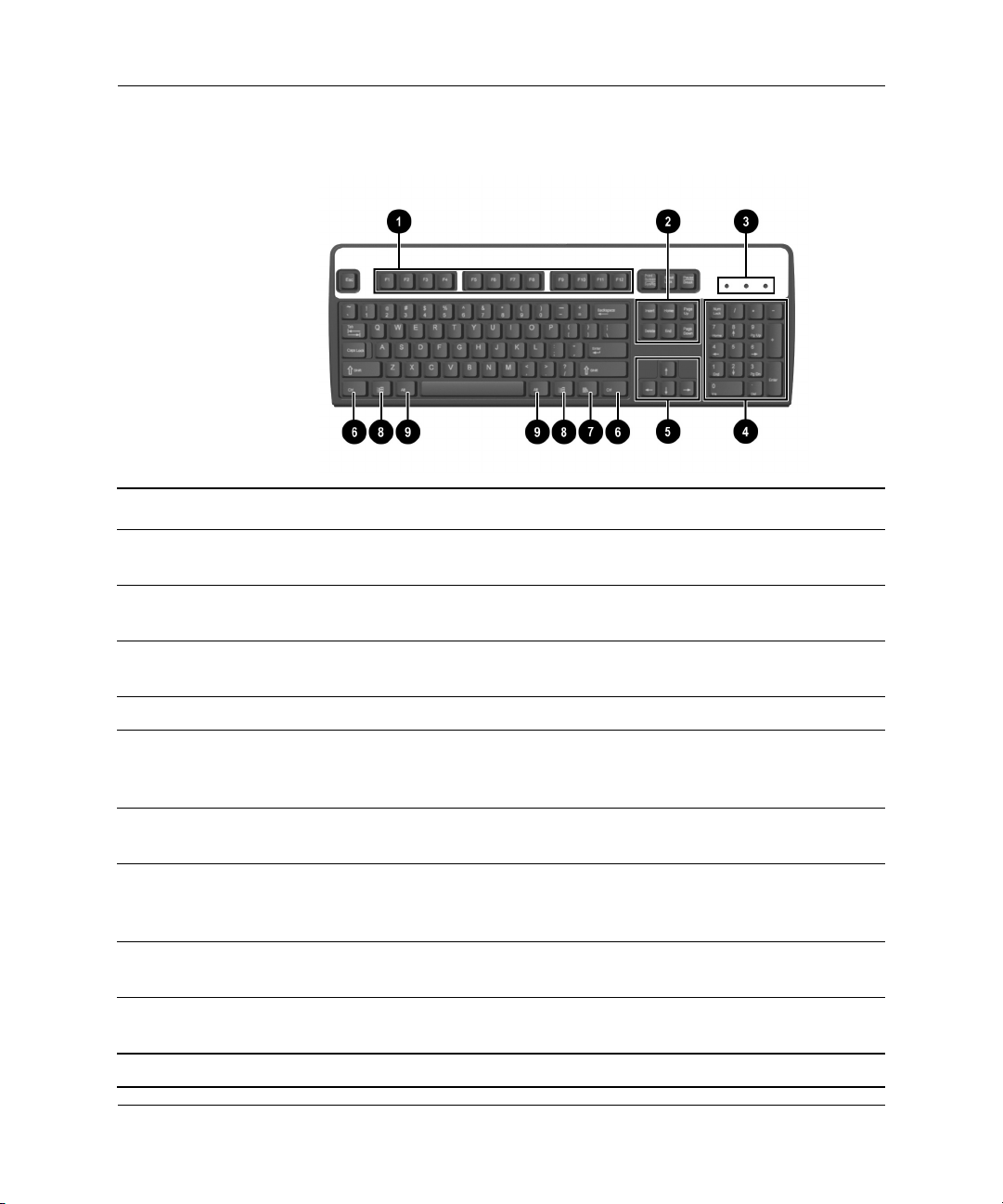
Product Features
Keyboard
Keyboard Components
1 Function Keys Perform special functions depending on the software application
being used.
2 Editing Keys Includes the following: Insert, Home, Page Up, Delete, End, and
Page Down.
3 Status Lights Indicate the status of the computer and keyboard settings
(Num Lock, Caps Lock, and Scroll Lock).
4 Numeric Keys Work like a calculator keypad.
5 Arrow Keys Used to navigate through a document or Web site. These keys
allow you to move left, right, up, and down, using the keyboard
instead of the mouse.
6 Ctrl Keys Used in combination with another key; its effect depends on the
application software you are using.
7 Application Key* Used (like the right mouse button) to open pop-up menus in a
Microsoft Office application. May perform other functions in other
software applications.
8 Windows Logo
Keys*
9 Alt Keys Used in combination with another key; its effect depends on the
*Keys available in select geographic regions.
1–4 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Used to open the Start menu in Microsoft Windows. Used in
combination with other keys to perform other functions.
application software you are using.
Page 9

Product Features
Windows Logo Key
Use the Windows Logo key in combination with other keys to
perform certain functions available in the Windows operating system.
Refer to the “Keyboard” section to identify the Windows Logo key.
Windows Logo Key Functions
Windows Logo Key Displays or hides the Start menu.
Windows Logo Key + d Displays the Desktop.
Windows Logo Key + m Minimizes all open applications.
Shift + Windows Logo Key + m Undoes Minimize All.
Windows Logo Key + e Launches My Computer.
Windows Logo Key + f Launches Find Document.
Windows Logo Key + Ctrl + f Launches Find Computer.
Windows Logo Key + F1 Launches Windows Help.
Windows Logo Key + l Locks the computer if you are connected to a
network domain, or allows you to switch users if you
are not connected to a network domain.
Windows Logo Key + r Launches the Run dialog box.
Windows Logo Key + u Launches the Utility Manager.
Windows Logo Key + Tab Activates the next Taskbar button.
Special Mouse Functions
Most software applications support the use of a mouse. The functions
assigned to each mouse button depend on the software applications
you are using.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 1–5
Page 10

Product Features
Serial Number Location
Each computer has a unique serial number and a product ID number
that are located on the top cover of the computer. Keep these numbers
available for use when contacting customer service for assistance.
Serial Number and Product ID Location
1–6 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 11

Serviceability Features
The Microtower computer includes features that make it easy to
upgrade and service. No tools are needed for most of the installation
procedures described in this chapter.
Warnings and Cautions
Before performing upgrades be sure to carefully read all of the
applicable instructions, cautions, and warnings in this guide.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from electrical shock
Å
and/or hot surfaces, be sure to disconnect the power cord from the wall
outlet and allow the internal system components to cool before touching.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electrical shock, fire, or damage to the
Å
equipment, do not plug telecommunications/telephone connectors into
the network interface controller (NIC) receptacles.
2
Hardware Upgrades
CAUTION: Static electricity can damage the electrical components of the
Ä
computer or optional equipment. Before beginning these procedures,
ensure that you are discharged of static electricity by briefly touching a
grounded metal object. See Appendix D, “Electrostatic Discharge” for
more information.
CAUTION: Before removing the computer cover, ensure that the
Ä
computer is turned off and that the power cord is disconnected from the
electrical outlet.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–1
Page 12

Hardware Upgrades
Removing the Computer Access Panel
To remove the computer access panel:
1. Turn off the computer properly through the operating system and
turn off any external devices.
2. Disconnect the power cord from the power outlet and the
computer, and disconnect any external devices.
CAUTION: Before removing the computer access panel, ensure that the
Ä
computer is turned off and that the power cord is disconnected from the
electrical outlet.
3. Loosen the captive thumbscrew 1 that secures the access panel to
the computer chassis.
4. Slide the access panel back 2 about 2.5 cm (1 inch), then lift it
off the unit.
You may want to lay the computer on its side to install internal parts.
✎
Be sure the side with the access panel and pull grip is facing up.
Removing the Computer Access Panel
2–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 13

Removing the Front Bezel
To remove the front bezel:
1. Turn off the computer properly through the operating system and
turn off any external devices.
2. Disconnect the power cord from the power outlet and the
computer, and disconnect any external devices.
3. Remove the computer access panel.
4. To remove the front bezel, press down on all three tabs on the
left side of the bezel 1 then rotate the bezel off the chassis 2,
beginning with the left side then the right side.
Hardware Upgrades
Removing the Front Bezel
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–3
Page 14

Hardware Upgrades
Installing Additional Memory
The computer comes with double data rate 2 synchronous dynamic
random access memory (DDR2-SDRAM) dual inline memory
modules (DIMMs).
DIMMs
The memory sockets on the system board can be populated with up to
four industry-standard DIMMs. These memory sockets are populated
with at least one preinstalled DIMM. To achieve the maximum
memory support, you can populate the system board with up to 4GB
of memory configured in a high-performing dual channel mode.
DDR2-SDRAM DIMMs
For proper system operation, if the computer supports
DDR2-SDRAM DIMMs, the DIMMs must be:
■ industry-standard 240-pin
■ unbuffered PC3200 400 MHz-compliant or PC4300
533 MHz-compliant
■ 1.8 volt DDR2-SDRAM DIMMs
The DDR2-SDRAM DIMMs must also:
■ support CAS latency 2.5 or 3 (CL = 2.5 or CL = 3)
■ contain the mandatory JEDEC SPD information
In addition, the computer supports:
■ 256Mbit, 512Mbit, and 1Gbit non-ECC memory technologies
■ single-sided and double-sided DIMMS
■ DIMMs constructed with x8 and x16 DDR devices; DIMMs
constructed with x4 SDRAM are not supported
2–4 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 15

Populating DIMM Sockets
The system will automatically operate in single channel mode, dual
channel Asymmetric mode, or a higher-performing dual channel
Interleaved mode, depending on how the DIMMs are installed.
■ The system will operate in single channel mode if the DIMM
sockets are populated in one channel only.
■ The system will operate in dual channel Asymmetric mode if the
total memory capacity of the DIMMs in Channel A is not equal to
the total memory capacity of the DIMMs in Channel B.
■ The system will operate in a higher-performing dual channel
Interleaved mode if the total memory capacity of the DIMMs in
Channel A is equal to the total memory capacity of the DIMMs in
Channel B. However, the technology and device width can vary
between the channels. For example, if Channel A is populated
with two 256MB DIMMS and Channel B is populated with one
512MB DIMM, the system will operate in Interleaved mode.
■ In any mode, the maximum operational speed is determined by
the slowest DIMM in the system. For example, if the system is
populated with a DIMM that is 333 MHz and a second DIMM
that is 400 MHz, the system will run at the slower of the two
speeds.
Hardware Upgrades
There are four DIMM sockets on the system board, with two sockets
per channel. The sockets are labeled XMM1, XMM2, XMM3, and
XMM4. Sockets XMM1 and XMM2 operate in memory channel A.
Sockets XMM3 and XMM4 operate in memory channel B.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–5
Page 16

Hardware Upgrades
DIMM Socket Locations
Item Description Socket Color
1 DIMM socket XMM1, Channel A White
2 DIMM socket XMM2, Channel A Black
3 DIMM socket XMM3, Channel B White
4 DIMM socket XMM4, Channel B Black
2–6 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 17

Installing DIMMs
CAUTION: The memory module sockets have gold metal contacts. When
Ä
upgrading the memory, it is important to use memory modules with gold
metal contacts to prevent corrosion and/or oxidation resulting from having
incompatible metals in contact with each other.
CAUTION: Static electricity can damage the electronic components of
Ä
the computer or optional cards. Before beginning these procedures,
ensure that you are discharged of static electricity by briefly touching a
grounded metal object. For more informations, refer to Appendix D,
“Electrostatic Discharge.”
CAUTION: When handling a memory module, be careful not to touch
Ä
any of the contacts. Doing so may damage the module.
1. Turn off the computer properly through the operating system and
2. Disconnect the power cord from the power outlet and disconnect
Hardware Upgrades
turn off any external devices.
any external devices.
3. Remove the computer access panel.
4. Locate the memory module sockets on the system board.
WARNING: To reduce risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow
Å
the internal system components to cool before touching.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–7
Page 18

Hardware Upgrades
5. Open both latches of the memory module socket 1, and insert the
memory module into the socket 2.
Installing a DIMM
A memory module can be installed in only one way. Match the notch
✎
on the module with the tab on the memory socket.
For maximum performance, poplulate the sockets so that the memory
✎
capacity of Channel A is equal to the memory capacity of Channel B.
Fo example, if you have one preinstalled DIMM in socket XMM1 and
are adding a second DIMM, it is recommended that you install a
DIMM of equal memory capacity into the XMM3 or XMM4 socket.
6. Push the module down into the socket, ensuring that the module
is fully inserted and properly seated. Make sure the latches are in
the closed position 3.
7. Repeat steps 5 and 6 to install any additional modules.
8. Replace the access panel.
The computer should automatically recognize the additional memory
the next time you turn on the computer.
2–8 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 19

Replacing or Upgrading a Drive
The computer supports up to six drives that may be installed in
various configurations.
This section describes the procedure for replacing or upgrading the
storage drives. A Torx screwdriver is needed to replace the guide
screws on a drive.
CAUTION: Make sure you back up your personal files on the hard drive
Ä
to an external storage device, such as a CD, before removing the hard
drive. Failure to do so will result in data loss. After replacing the primary
hard drive, you will need to run the Restore Plus! CD to load the HP
factory-installed files.
Locating Drive Positions
Hardware Upgrades
Drive Positions
1 Two 5.25-inch, half-height bays for optional drives
2 Two standard 3.5-inch, one-third height bays (1.44-MB
diskette drive shown)
3 Two internal 3.5-inch, one-third height bays for hard drives
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–9
Page 20

Hardware Upgrades
Removing a Drive
1. Turn off the computer properly through the operating system and
2. Remove the access panel and front bezel.
3. Disconnect the power and data cables from the back of the drive,
turn off any external devices. Disconnect the power cord from the
power outlet and disconnect any external devices.
as indicated in the following illustrations.
Disconnecting the Optical Drive Cables
2–10 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 21

Disconnecting the Diskette Drive Cables
Hardware Upgrades
Disconnecting the Hard Drive Cables
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–11
Page 22

Hardware Upgrades
4. A latch drive bracket with release tabs secures the drives in the
drive bay. Lift the release tab on the latch drive bracket 1 for
the drive you want to remove, then slide the drive from its drive
bay 2.
Removing the Drives
5. Remove the four guide screws (two on each side) from the old
drive. You will need these screws to install a new drive.
2–12 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 23

Replacing a Drive
CAUTION: To prevent loss of work and damage to the computer or drive:
Ä
■ If you are inserting or removing a hard drive, shut down the operating
■ Before handling a drive, ensure that you are discharged of static
■ Handle a drive carefully; do not drop it.
■ Do not use excessive force when inserting a drive.
■ Avoid exposing a hard drive to liquids, temperature extremes, or
le:
Make sure to back up the data on the old hard drive before removing
✎
it so that you can install the data onto the new hard drive.
1. Install the four guide screws (two on each side) that were
Hardware Upgrades
system properly, then turn off the computer. Do not remove a hard
drive while the computer is on or in standby mode.
electricity. While handling a drive, avoid touching the connector. For
more information about preventing electrostatic damage, refer to
Appendix D, “Electrostatic Discharge.”
products that have magnetic fields such as monitors or speakers.
removed from the old drive into the new drive. The screws help
guide the drive into its proper position in the bay. Extra guide
screws are provided on the front of the chassis under the front
bezel.
There are a total of eight extra guide screws on the front of the chassis
✎
under the bezel. Four have 6-32 standard threads and four have M3
metric threads. Standard screws are used for hard drives and have a
silver finish. Metric screws are used for all other drives and have a
black finish. Make sure to install the appropriate guide screws into the
drive.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–13
Page 24

Hardware Upgrades
2. Slide the drive into the drive bay, making sure to align the guide
screws with the guide slots, until the drive snaps into place.
Sliding the Drives into the Drive Cage
2–14 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 25

Hardware Upgrades
3. Reconnect the power and data cables to the drive as indicated in
the following illustrations.
Reconnecting the Optical Drive Cables
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–15
Page 26

Hardware Upgrades
Reconnecting the Diskette Drive Cables
Reconnecting the Hard Drive Cables
2–16 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 27

Hardware Upgrades
4. If installing a new hard drive, connect the data cable to the system
board.
The replacement hard drive kit includes several data cables. Make
✎
sure to use the cable that is exactly the same as the factory-installed
cable.
If your system has only one SATA hard drive, you must connect the
✎
hard drive data cable to the connector labeled P60 SATA 0 to avoid
any hard drive performance problems. If you are adding a second hard
drive, connect the hard drive data cable to the connector labeled P61
SATA 1.
5. Complete the procedure described in the “Reassembling the
Computer” section of this chapter.
6. Turn on the computer.
If you replaced the primary hard drive, insert the Restore Plus! CD to
✎
restore the operating system, software drivers, and/or any software
applications that were preinstalled on the computer from HP. Follow
the instructions in the guide included with the restore CD. When the
restore process has completed, reinstall any personal files that you
backed up before replacing the hard drive.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–17
Page 28

Hardware Upgrades
Removing or Installing an Expansion Card
The computer has two PCI expansion slots that can accommodate an
expansion card up to 17.46 cm (6.875 inches) in length. The computer
also has one PCI Express x1 expansion slot and one PCI Express x16
expansion slot.
Expansion Slot Locations
Item Description
1 PCI expansion slot
2 PCI expansion slot
3 PCI Express x1 expansion slot
4 PCI Express x16 expansion slot
You can install a PCI Express x1, x4, x8, or x16 expansion card in the
✎
PCI Express x16 expansion slot.
2–18 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 29

Hardware Upgrades
To remove, replace, or add an expansion card.
1. Turn off the computer properly through the operating system and
turn off any external devices. Disconnect the power cord from the
power outlet and disconnect any external devices.
2. Remove the access panel and lay the computer on its side with the
opening to internal parts where the access panel was located
facing up.
3. On the rear of the computer, a sliding slot cover lock secures the
expansion card brackets and expansion slot covers in place.
Remove the screw that holds the slot cover lock in place 1 and
slide the slot cover lock away from the brackets 2 so that they are
no longer secured by the lock.
Releasing the Slot Cover Lock
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–19
Page 30

Hardware Upgrades
4. Before installing an expansion card, remove the expansion slot
cover or the existing expansion card.
a. If you are installing an expansion card in a vacant socket,
remove the appropriate expansion slot cover on the back of
the chassis. Pull the slot cover straight up from the socket
then away from the inside of the chassis.
Removing an Expansion Slot Cover
2–20 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 31

Hardware Upgrades
b. If removing a standard PCI expansion card, hold the card at
each end, and carefully rock it back and forth until the
connectors pull free from the socket. Pull the expansion card
straight up from the socket 1 then away from the inside of
the chassis 2 to release it from the chassis frame. Be sure not
to scrape the card against the other components.
Removing an Expansion Card
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–21
Page 32

Hardware Upgrades
c. If removing a PCI Express card, pull the retention arm on the
back of the expansion socket away from the card and
carefully rock the card back and forth until the connectors
pull free from the socket. Pull the expansion card straight up
from the socket then away from the inside of the chassis to
release it from the chassis frame. Be sure not to scrape the
card against the other components.
Before removing an installed expansion card, disconnect any cables
✎
that may be attached to the expansion card.
Removing a PCI Express Expansion Card
5. If not replacing the old expansion card with a new expansion
card, install an expansion slot cover to close the open slot. Insert
the metal slot cover in the opened slot and slide the slot cover
lock down to secure the slot cover in place.
CAUTION: After removing an expansion card, you must replace it with a
Ä
new card or expansion slot cover for proper cooling of internal
components during operation.
2–22 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 33

Hardware Upgrades
6. If replacing or adding a new expansion card, hold the card just
above the expansion slot on the system board then move the card
toward the rear of the chassis 1 so that the bracket on the card is
aligned with the open slot on the rear of the chassis. Gently press
the card straight down into the expansion slot on the system
board 2.
Replacing or Adding an Expansion Card
When installing an expansion card, press firmly on the card so that
✎
the whole connector seats properly in the expansion card slot.
7. If you are replacing an expansion card, store the old card in the
anti-static packaging that contained the new card.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–23
Page 34

Hardware Upgrades
8. While holding the expansion card bracket against the chassis,
slide the slot cover lock down toward the expansion card brackets
and slot covers 1 to secure them in place and replace the screw 2
that secures the slot cover lock.
Securing the Expansion Cards and Slot Covers
9. Complete the procedure described in the “Reassembling the
Computer” section of this chapter.
2–24 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 35

Reassembling the Computer
1. Position the chassis in the upright position. Insert the three hooks
on the right side of the bezel 1 into the rectangular holes on the
chassis then rotate the bezel into place 2 so that the three tabs on
the left side of the bezel snap into the slots on the chassis.
Hardware Upgrades
Replacing the Front Bezel
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com 2–25
Page 36

Hardware Upgrades
2. Place the side access panel in the proper position on the
chassis and slide it into place 1. Ensure that the hole for the
thumbscrew is aligned with the hole in the chassis and tighten
the thumbscrew 2.
Replacing the Side Access Panel
3. Reconnect the power cable to the computer and plug the cable
into an electrical outlet.
4. Reconnect all peripheral devices to the computer.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electrical shock, fire, or damage to the
Å
equipment, do not plug telecommunications or telephone connectors into
the network interface controller (NIC) ports.
5. Turn on the computer by pressing the power button.
2–26 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 37

A
Specifications
HP Compaq Microtower
Microtower Dimensions
Height
Width
Depth (depth will increase if the computer is
equipped with a port security bracket)
Approximate Weight 23.8 lb 10.82 kg
Temperature Range
Operating
Nonoperating
Relative Humidity (noncondensing)
Operating
Nonoperating
14.5 in
6.88 in
16.5 in
50° to 95°F
-22° to 140°F
10-90%
5-95%
36.8 cm
17.5 cm
42.0 cm
10° to 35°C
-30° to 60°C
10-90%
5-95%
Maximum Altitude (unpressurized)
Operating
Nonoperating
Operating temperature is derated 1.0° C per 300 m (1000 ft) to 3000 m (10,000 ft) above
✎
sea level, no direct sustained sunlight. Maximum rate of change is 10° C/Hr. The upper limit
may be limited by the type and number of options installed.
Heat Dissipation
Maximum
Typical (idle)
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com A–1
10,000 ft
30,000 ft
1575 BTU/hr
340 BTU/hr
3048 m
9144 m
397 kg-cal/hr
86 kg-cal/hr
Page 38

Specifications
HP Compaq Microtower (Continued)
Input Voltage
115 V 230 V
Power Supply
Operating Voltage Range*
Rated Voltage Range
Rated Line Frequency
Power Output 300 W 300 W
Rated Input Current (maximum)* 8A @ 100 VAC 4A @ 200 VAC
*This system utilizes a passive power factor corrected power supply. The power factor
correction is present in the 230V operating mode only. This allows the system to pass the CE
mark requirements for use in the countries of the European Union. This supply requires the use
of an input voltage range select switch.
90-132 VAC
100-127 VAC
50-60 Hz
180-264 VAC
200-240 VAC
50-60 Hz
A–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 39

Battery Replacement
The battery that comes with the computer provides power to the
real-time clock. When replacing the battery, use a battery equivalent
to the battery originally installed in the computer. The computer
comes with a 3-volt lithium coin cell battery.
The lifetime of the lithium battery can be extended by plugging the
✎
computer into a live AC wall socket. The lithium battery is only used
when the computer is NOT connected to AC power.
WARNING: The computer contains an internal lithium manganese dioxide
Å
battery. There is a risk of fire and burns if the battery is not handled properly. To
reduce the risk of personal injury:
■ Do not attempt to recharge the battery.
■ Do not expose to temperatures higher than 60°C (140ºF).
■ Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, or
dispose of in fire or water.
■ Replace the battery only with the HP spare designated for this product.
B
CAUTION: Before replacing the battery, it is important to back up the
Ä
computer CMOS settings. When the battery is removed or replaced, the
CMOS settings will be cleared. Refer to the Troubleshooting Guide on the
Documentation CD for information on backing up the CMOS settings.
Batteries, battery packs, and accumulators should not be disposed of
N
together with the general household waste. In order to forward them to
recycling or proper disposal, please use the public collection system or
return them to HP, their authorized partners, or their agents.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com B–1
Page 40

Battery Replacement
CAUTION: Static electricity can damage the electronic components of
Ä
the computer or optional equipment. Before beginning these procedures,
ensure that you are discharged of static electricity by briefly touching a
grounded metal object.
1. Turn off the computer properly through the operating system,
then turn off any external devices.
2. Disconnect the power cord from the power outlet and disconnect
any external devices. Then remove the computer access panel.
It may be necessary to remove an expansion card to gain access to
✎
the battery.
3. Locate the battery and battery holder on the system board.
4. Depending on the type of battery holder on the system board,
complete the following instructions to replace the battery.
Type 1
a. Lift the battery out of its holder.
Removing a Coin Cell Battery (Type 1)
b. Slide the replacement battery into position, positive side up.
The battery holder automatically secures the battery in the
proper position.
B–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 41

Battery Replacement
Type 2
a. To release the battery from its holder, squeeze the metal
clamp that extends above one edge of the battery. When the
battery pops up, lift it out 1.
b. To insert the new battery, slide one edge of the replacement
battery under the holder’s lip with the positive side up. Push
the other edge down until the clamp snaps over the other edge
of the battery 2.
Removing and Replacing a Coin Cell Battery (Type 2)
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com B–3
Page 42

Battery Replacement
Type 3
a. Pull back on the clip 1 that is holding the battery in place,
and remove the battery 2.
b. Insert the new battery and position the clip back into place.
Removing a Coin Cell Battery (Type 3)
After the battery has been replaced, use the following steps to
✎
complete this procedure.
5. Replace the computer access panel.
6. Plug in the computer and turn on power to the computer.
7. Reset the date and time, your passwords, and any special system
setups, using Computer Setup. Refer to the Computer Setup (F10)
Utility Guide on the Documentation CD.
B–4 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 43

Security Lock Provisions
Installing a Security Lock
The security locks displayed below and on the following page can be
used to secure the Microtower computer.
A port security bracket (not shown) is also available. Go to
✎
www.hp.com for more information.
Cable Lock
C
Installing a Cable Lock
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com C–1
Page 44

Security Lock Provisions
Padlock
I
Installing a Padlock
C–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 45

Electrostatic Discharge
A discharge of static electricity from a finger or other conductor may
damage system boards or other static-sensitive devices. This type of
damage may reduce the life expectancy of the device.
Preventing Electrostatic Damage
To prevent electrostatic damage, observe the following precautions:
■ Avoid hand contact by transporting and storing products in
static-safe containers.
■ Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they
arrive at static-free workstations.
■ Place parts on a grounded surface before removing them from
their containers.
■ Avoid touching pins, leads, or circuitry.
D
■ Always be properly grounded when touching a static-sensitive
component or assembly.
Grounding Methods
There are several methods for grounding. Use one or more of the
following methods when handling or installing electrostatic-sensitive
parts:
■ Use a wrist strap connected by a ground cord to a grounded
workstation or computer chassis. Wrist straps are flexible straps
with a minimum of 1 megohm +/- 10 percent resistance in the
ground cords. To provide proper ground, wear the strap snug
against the skin.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com D–1
Page 46

Electrostatic Discharge
■ Use heelstraps, toestraps, or bootstraps at standing workstations.
Wear the straps on both feet when standing on conductive floors
or dissipating floor mats.
■ Use conductive field service tools.
■ Use a portable field service kit with a folding static-dissipating
work mat.
If you do not have any of the suggested equipment for proper
grounding, contact an HP authorized dealer, reseller, or service
provider.
For more information on static electricity, contact an HP authorized
✎
dealer, reseller, or service provider.
D–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 47

Routine Computer Care and
Routine Computer Care
Follow these suggestions to take care of the computer and monitor:
■ Operate the computer on a sturdy, level surface. Leave a 10.2-cm
(4-inch) clearance at the back of the system unit and above the
monitor to permit the required airflow.
■ Never operate the computer with the cover or side panel removed.
■ Never restrict the airflow into the computer by blocking the front
vents or air intake. Do not place the keyboard, with the keyboard
feet down, directly against the front of the desktop unit as this
also restricts airflow.
■ Keep the computer away from excessive moisture, direct sunlight,
and extremes of heat and cold. For information about the
recommended temperature and humidity ranges for the computer,
refer to Appendix A, “Specifications” in this guide.
E
Shipping Preparation
■ Keep liquids away from the computer and keyboard.
■ Never cover the ventilation slots on the monitor with any type of
material.
■ Turn off the computer before you do either of the following:
❏ Wipe the exterior of the computer with a soft, damp cloth as
needed. Using cleaning products may discolor or damage the
finish.
❏ Occasionally clean the air vents on the front and back of the
computer. Lint and other foreign matter can block the vents
and limit the airflow.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com E–1
Page 48

Routine Computer Care and Shipping Preparation
Optical Drive Precautions
Be sure to observe the following guidelines while operating or
cleaning the optical drive.
Operation
■ Do not move the drive during operation. This may cause it to
malfunction during reading.
■ Avoid exposing the drive to sudden changes in temperature, as
condensation may form inside the unit. If the temperature
suddenly changes while the drive is on, wait at least one hour
before you turn off the power. If you operate the unit
immediately, it may malfunction while reading.
■ Avoid placing the drive in a location that is subject to high
humidity, extreme temperatures, mechanical vibration, or direct
sunlight.
Cleaning
■ Clean the panel and controls with a soft, dry cloth or a soft cloth
lightly moistened with a mild detergent solution. Never spray
cleaning fluids directly on the unit.
■ Avoid using any type of solvent, such as alcohol or benzene,
which may damage the finish.
Safety
If any object or liquid falls into the drive, immediately unplug the
computer and have it checked by an authorized HP service provider.
E–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 49

Shipping Preparation
Follow these suggestions when preparing to ship the computer:
1. Back up the hard drive files on PD discs, tape cartridges, CDs,
or diskettes. Be sure that the backup media is not exposed to
electrical or magnetic impulses while stored or in transit.
The hard drive locks automatically when the system power is
✎
turned off.
2. Remove and store any program diskettes from the diskette drives.
3. Insert a blank diskette into the diskette drive to protect the drive
while in transit. Do not use a diskette on which you have stored or
plan to store data.
4. Turn off the computer and external devices.
5. Disconnect the power cord from the electrical outlet, then from
the computer.
6. Disconnect the system components and external devices from
their power sources, then from the computer.
Routine Computer Care and Shipping Preparation
Ensure that all boards are seated properly and secured in the board
✎
slots before shipping the computer.
7. Pack the system components and external devices in their original
packing boxes or similar packaging with sufficient packing
material to protect them.
For environmental nonoperating ranges, see Appendix A,
✎
“Specifications” in this guide.
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com E–3
Page 50

Routine Computer Care and Shipping Preparation
E–4 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
Page 51

Index
A
access panel
removing 2–2
replacing 2–26
application key 1–4
audio connector
1–3
B
backup files 2–9, 2–17
battery replacement
B–1
C
CD-R/RW drive
installing 2–9
locating 2–9
CD-ROM drive
installing 2–9
locating 2–9
components
front panel 1–2
keyboard 1–4
rear panel 1–3
computer
routine care E–1
security locks C–1
shipping preparation E–3
specifications A–1
D
diskette drive
activity light 1–2
eject button 1–2
installing 2–9
locating 2–9
drive positions 2–9
DVD+R/RW drive
installing 2–9
locating 2–9
DVD-ROM drive
installing 2–9
locating 2–9
E
electrostatic discharge, preventing damage
D–1
expansion card installation
2–18
F
front bezel
removing 2–3
replacing 2–25
front panel components 1–2
H
hard drive
activity light 1–2
installing SATA 2–9, 2–13
locating 2–9
restoring 2–17
headphone jack 1–2
headphone line-out connector
1–3
I
installing
drives 2–9, 2–13
Hardware Reference Guide www.hp.com Index–1
Page 52

Index
expansion card 2–18
memory 2–4
K
keyboard
components 1–4
connector 1–3
L
locks
cable lock C–1
padlock C–2
M
memory
Asymetric mode 2–5
capacity 2–4, 2–5, 2–8
identifying sockets 2–5
installing 2–4
Interleaved mode 2–5
populating sockets 2–5
single channel mode 2–5
specifications 2–4
microphone connector 1–2, 1–3
monitor, connecting
mouse
connector 1–3
special functions 1–5
1–3
O
optical drives
activity light 1–2
defined 1–2
eject button 1–2
installing 2–13
locating 2–9
removing 2–10
P
parallel connector 1–3
PCI card
See expansion card
power
button 1–2
cord connector 1–3
light 1–2
R
rear panel components 1–3
removing
computer access panel 2–2
drives 2–10
expansion card 2–18
expansion slot cover 2–20
front bezel 2–3
PCI Express card 2–22
restoring software 2–17
RJ-45 connector
1–3
S
SATA controllers 2–17
security locks
serial connector
serial number location
shipping preparation
specifications
memory 2–4
status lights 1–4
C–1
1–3
1–6
E–3
A–1
U
unlocking access panel C–1
USB ports
front panel 1–2
rear panel 1–3
W
Windows Logo key
functions 1–5
locations 1–4
Index–2 www.hp.com Hardware Reference Guide
 Loading...
Loading...