Page 1

Administrator's Guide
HP Session Allocation Manager (HP SAM) v.3.2
Page 2

© Copyright 2007–2010 Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P. The information
contained herein is subject to change
without notice.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and other
countries.
The only warranties for HP products and
services are set forth in the express warranty
statements accompanying such products and
services. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional
warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical
or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein.
This document contains proprietary
information that is protected by copyright.
No part of this document may be
photocopied, reproduced, or translated to
another language without the prior written
consent of Hewlett-Packard Company.
The MIT License
http://sourceforge.net/projects/expat/
http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mitlicense.php
Permission is hereby granted, free of
charge, to any person obtaining a copy of
this software and associated documentation
files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software
without restriction, including without
limitation the rights to use, copy, modify,
merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/
or sell copies of the Software, and to permit
persons to whom the Software is furnished to
do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this
permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the
Software. THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED
"AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY
KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT
HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM,
DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER
IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR
OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR
IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE
OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
Copyright © 2006 by the Open Source
Initiative
Technical questions about the website go to
Steve M.: webmaster at opensource.org /
Policy questions about open source go to the
Board of Directors.
The contents of this website are licensed
under the Open Software License 2.1 or
Academic Free License 2.1. OSI is a
registered non-profit with 501(c)(3) status.
Donating to OSI is one way to show your
support.
Part of the software embedded in this
product is gSOAP software.
Portions created by gSOAP are Copyright
(C) 2001-2004 Robert A. van Engelen,
Genivia inc. All Rights Reserved.
THE SOFTWARE IN THIS PRODUCT WAS
IN PART PROVIDED BY GENIVIA INC AND
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE
LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS
OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR
OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT
OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
Copyright (c) 1998-2007 The OpenSSL
Project. All rights reserved.
Copyright (C) 1995-1998 Eric Young
(eay@cryptsoft.com). All rights reserved.
Administrator's Guide
HP Session Allocation Manager (HP
SAM) v.3.2
Seventh Edition (November 2010)
Sixth Edition (April 2010)
Fifth Edition (August 2009)
Fourth Edition (November 2008)
Third Edition (December 2007)
Second Edition (August 2007)
First Edition (June 2007)
Document Part Number: 453252–007
Page 3

About This Book
WARNING! Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily
harm or loss of life.
CAUTION: Text set off in this manner indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage
to equipment or loss of information.
NOTE: Text set off in this manner provides important supplemental information.
iii
Page 4

iv About This Book
Page 5

Table of contents
1 Introduction ...................................................................................................................... 1
What's New in This Release ...................................................................................................... 1
Key Features ............................................................................................................................ 2
Overview ................................................................................................................................ 3
How HP SAM Works ................................................................................................. 4
HP SAM Software Components ................................................................................... 6
Remote Graphics Software (RGS) ................................................................................ 6
Common Tasks ........................................................................................................................ 7
Setting up HP SAM .................................................................................................... 7
Setting up a User with a Dynamic Resource .................................................................. 7
Setting up a User with Static (Dedicated) Resources ....................................................... 9
Configuring a Monitor Layout for a User .................................................................... 10
2 Requirements ................................................................................................................. 12
HP SAM Hardware and Software Requirements ......................................................................... 12
Architectural Considerations and Best Practices for Setting up an HP SAM Environment .. . 12
Domain Environment Requirements for HP SAM .......................................................... 15
HP SAM Web and SQL Server Requirements .............................................................. 15
HP SAM Registration Service Requirements ............................................................................... 20
Access Device Requirements .................................................................................................... 21
Thin Client .............................................................................................................. 21
Mobile Thin Client ................................................................................................... 22
Desktop or Notebook PC ......................................................................................... 22
Blade Workstation Clients ........................................................................................ 22
Personal Workstation Clients .................................................................................... 22
Other requirements ................................................................................................................. 23
Create a Service Account ......................................................................................... 23
Obtain Administrative Rights .................................................................................... 23
Change the Firewall ................................................................................................ 23
Active Directory ...................................................................................................... 23
3 Installation ..................................................................................................................... 25
Order of Installation ............................................................................................................... 25
New Installation ...................................................................................................... 25
Upgrade ................................................................................................................ 25
Install the HP SAM Web Server and SQL Software ..................................................................... 26
v
Page 6

Grant Users HP SAM Administrator Access ................................................................ 28
Configure HP SAM System Settings ........................................................................... 28
Configure Secure Socket Layer (SSL) .......................................................................... 29
Install and Validate the HP SAM Registration Service Software .................................................... 29
Install the HP SAM Registration Service ...................................................................... 29
Create the HP SAM Registration Service Configuration File .......................................... 30
Start/Restart the HP SAM Registration Service ............................................................ 32
Test the HP SAM Registration Service ......................................................................... 33
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software ........................................................................ 33
Internet Explorer-Based Client ................................................................................... 34
Windows-based Client ............................................................................................. 35
Linux-Based Client ................................................................................................... 36
Configuration Settings ............................................................................................. 38
Global and Local Client Configuration Files ................................................................ 47
Legal Banner .......................................................................................................... 48
Deploy the HP SAM Registration Service to All HP SAM Computing Resources .............................. 49
Deploy HP SAM Client Software to All HP SAM Access Devices .................................................. 50
4 Administration ................................................................................................................ 51
Log In ................................................................................................................................... 51
General Navigation and User Interface Design .......................................................................... 51
Display More (or Fewer) Items Per Page ..................................................................... 51
Move Columns ........................................................................................................ 51
Sort Result List ......................................................................................................... 51
Select More Than One Item ...................................................................................... 51
Managing the HP SAM Administrator Access List ....................................................................... 52
Add Individual Users to the HP SAM Administrator Group ............................................ 52
Add Security Groups or Organizational Units to the HP SAM Administrator Group ......... 53
Remove Users or Groups From the HP SAM Administrator Group .................................. 53
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs ....................................................................................... 54
Home Tab .............................................................................................................. 54
Users and Roles Tab ................................................................................................ 54
Resources tab ......................................................................................................... 62
Manage Data Centers ............................................................................................. 66
Policies Tab ............................................................................................................ 68
System Settings Tab ................................................................................................. 70
Reports Tab ............................................................................................................ 75
Log Tab ................................................................................................................. 78
Setting Up Smart Card Logon on the Access Device ................................................................... 79
Configuring Session Time Limits for Remote Sessions .................................................................. 80
Session Timers for Linux .......................................................................................................... 82
vi
Page 7

Resource Reservations (AKA Access Restrictions) ........................................................................ 82
Authenticate Before Allocation ................................................................................................. 83
Appendix A Firewall Rules ................................................................................................. 85
Web Server ........................................................................................................................... 85
Clients .................................................................................................................................. 85
Resources .............................................................................................................................. 85
SQL Server ............................................................................................................................ 86
Appendix B Frequently Asked Questions ........................................................................... 87
Appendix C Registration Service Error Codes ...................................................................... 93
Appendix D Glossary ......................................................................................................... 96
Index ................................................................................................................................. 98
vii
Page 8

viii
Page 9

1 Introduction
HP Remote Client Solutions are designed to support a variety of users’ needs, from the most basic
computing tasks to more demanding professional and technical applications, while giving IT greater
control over technology resources, simplifying desktop management, increasing agility and, in many
cases, reducing total cost of ownership.
Underlying HP Remote Client Solutions is a unified infrastructure that enables client deployment, session
allocation, balancing of computing resources, and supports the business needs of a diverse set of users
though the use of a common set of tools.
The HP Session Allocation Manager (HP SAM) system is the control point in managing an HP Remote
Client Solutions deployment. HP SAM manages the assignment of connections from an end-user's client
access device to desktop sessions running on computing resources in a centralized location (typically, a
data center). HP SAM makes these desktop sessions available to users as they are needed.
For more information about HP Remote Client Solutions, visit
What's New in This Release
Option to Prefer Allocation of Recently Used Resources:
●
With previous versions of HP SAM, and with this option disabled (which is the default), SAM
◦
allocates resources within a role to a user with a preference toward providing a resource that
has not recently been used. This helps provide more even utilization of resources.
When this new option (found in the General tab under System Settings on the HP SAM
◦
administrative console) is enabled, SAM will allocate resources within a role to a user with a
preference toward providing the resource that was most recently used by this user.
It is important to note that SAM cannot guarantee that a user will be returned to their most
◦
recently used resource because another user may already be using it. If you want to ensure
that each user will always get the same resource, you should use Dedicated Resources
instead of roles.
Also note that this feature does not affect allocation when the user has In-use or Disconnected
◦
sessions. SAM will always try to allocate resources reserved for the user, regardless of this
setting. It also has no affect on Dedicated Resources or their backup resources or backup
roles.
http://www.hp.com/go/rcs.
Additional Support:
●
Linux RHEL6 on access devices and resources
◦
VMware Virtual Machine Linux resources
◦
HP T5740e (WES7) Thin Clients
◦
Microsoft SQL 2008 R2
◦
What's New in This Release
1
Page 10

Control of Linux Resources from the HP SAM administrative console:
●
SAM 3.2 adds support for remotely performing the following operations on Linux-based
◦
resources from the Resources page of the HP SAM administrative console:
—Shutdown
—Restart
—Logoff
These operations were previously only functional for Windows-based resources.
◦
The “Send Message” operation is still not supported on Linux resources.
◦
The SAM 3.2 versions of the SAM Linux Blade Service and the SAM Server are required for
◦
this feature to work.
A certificate from the domain certificate authority must be installed on the HP SAM website to
◦
enable this feature.
New SAM Policies for RGS Experience Properties:
●
RGS 5.4.5 introduces new RGS settings to help provide a better experience in a WAN
◦
environment which has reduced bandwidth. Those setting include choosing between fixed or
self-adjusting image quality, as well as setting the minimum image quality and update rate
when using the self-adjusting option. SAM 3.2 gives the SAM administrator the ability to
force these settings to end users via SAM server policy. Consult the RGS User Guide for
details regarding usage of these new RGS settings.
Key Features
Allocation system to assign users to computing resources (such as blade PCs, workstation blades,
●
or virtual machines)
Self-registration of computing resources
●
Central management of access device remote connection settings
●
Follow-me roaming and persistence support to enable reconnection to an open session from a
●
different access device
Customizable administration levels
●
Usage and Capacity Planning reports
●
Dedicated user/display to computing resource mapping
●
2 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 11
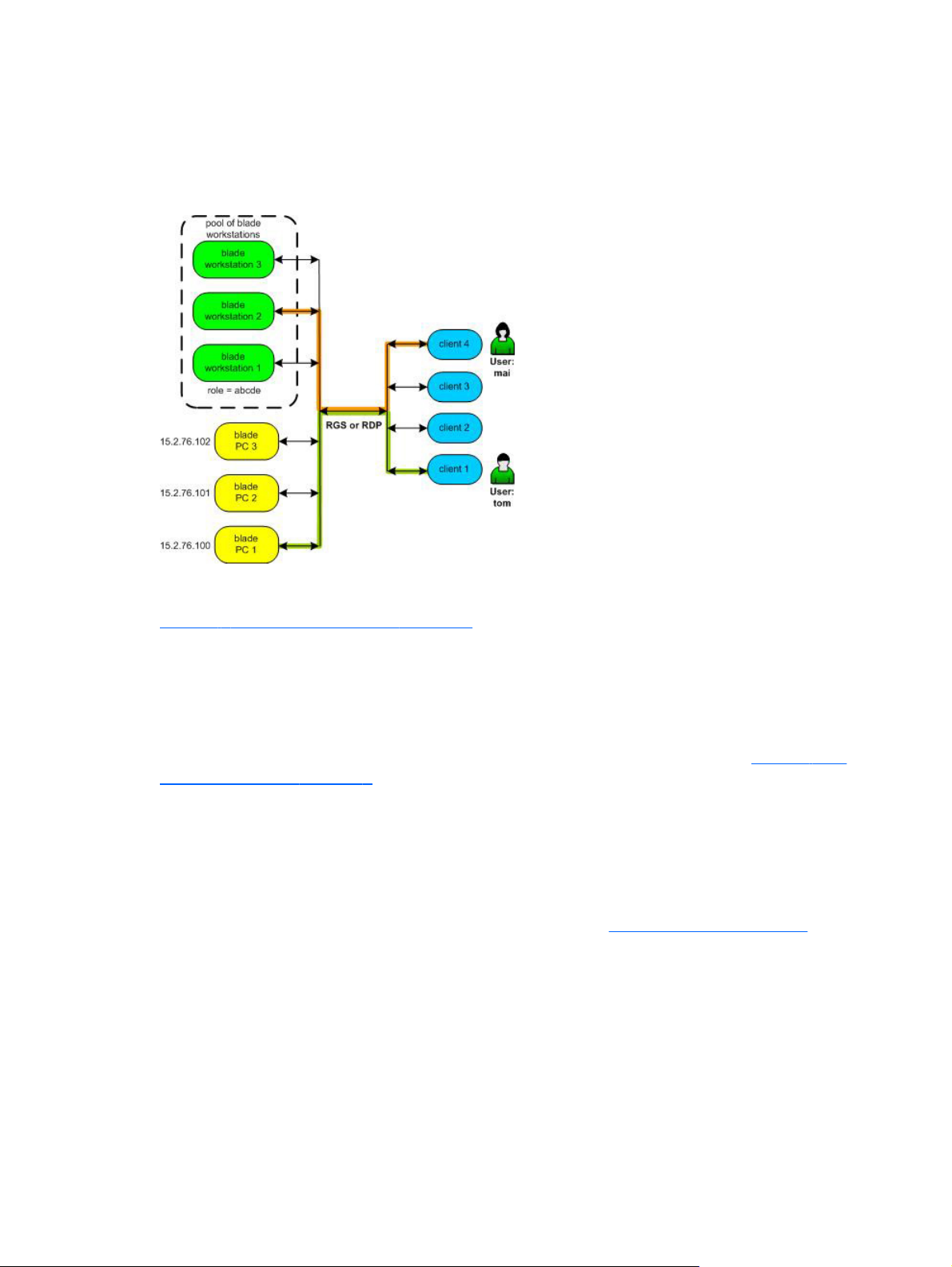
Overview
HP SAM enables automatic provisioning of remote computing resources to users.
Figure 1-1 HP SAM Configuration
HP SAM can be configured to enable a user to connect to the desktop session of a particular remote
computing resource (identified by its IP address or hostname)—this is known as a static connection. In
Figure 1-1 HP SAM Configuration on page 3, HP SAM has been configured to statically connect user
Tom to blade PC 1 with an IP address of 15.2.76.100. Regardless of which access device Tom uses,
he is automatically connected to blade PC 1 at address 15.2.76.100.
HP SAM can also be configured to enable a user to connect to any of a pool of computing resources—
this is known as a dynamic connection. HP SAM allows the administrator to define one or more roles
for each computing resource. A computing resource with a role of “abcde”, for example, might be
configured with applications to conduct stock transactions or accounting functions. In
SAM Configuration on page 3, HP SAM has been configured to allow user Mai to dynamically connect
to one of the three blade workstations supporting the role of “abcde.”
HP SAM uses HP Remote Graphics Software (RGS) or Microsoft® Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to
connect between access devices and computing resources.
RGS has features which make it particularly suitable for remote computing. RGS provides extremely fast
capture, compression, and transmission of the desktop image (the actual frame buffer pixels) using
standard TCP/IP networking. For more information on RGS, visit
http://www.hp.com/go/rgs.
Figure 1-1 HP
Overview
3
Page 12

How HP SAM Works
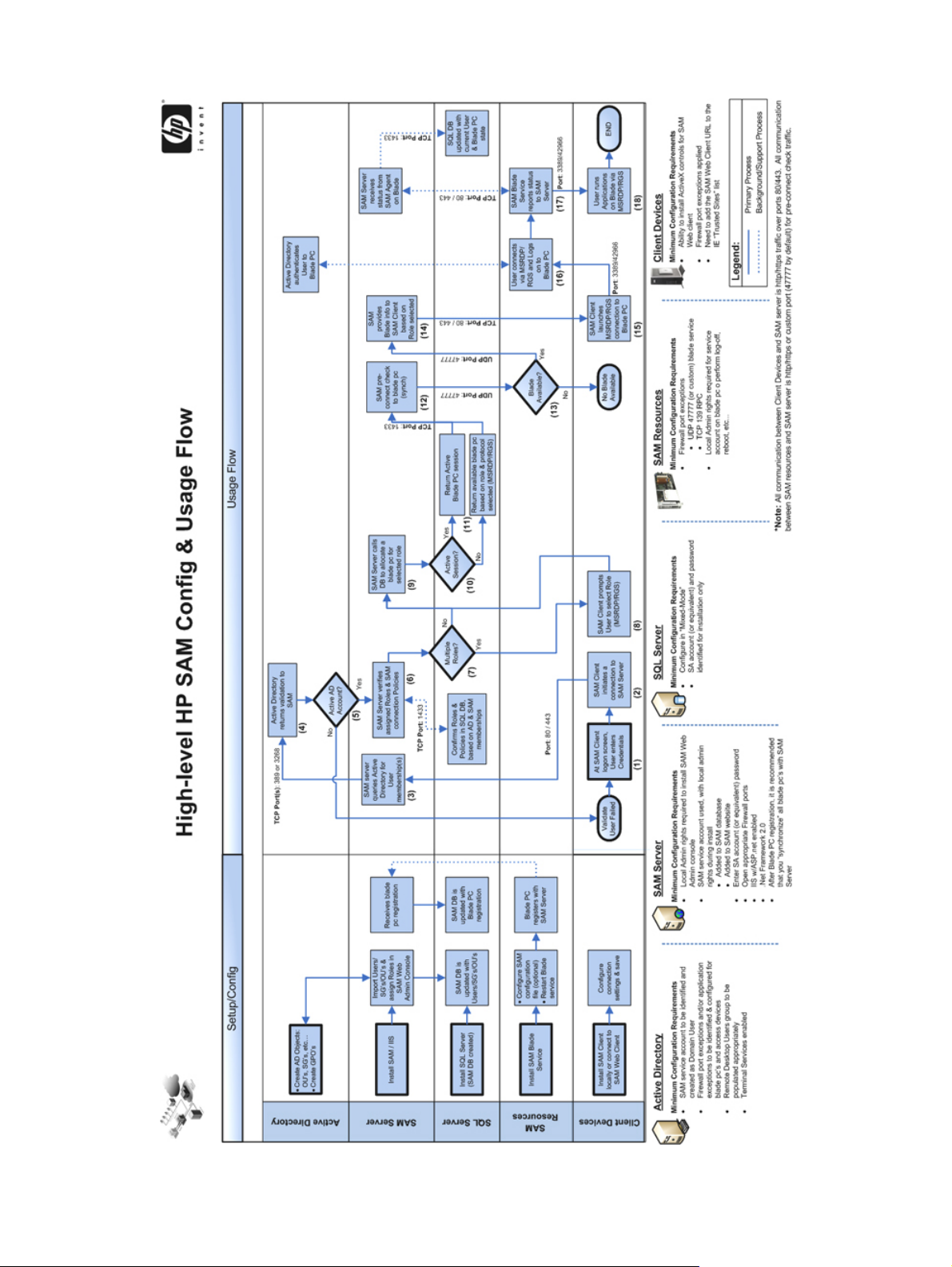
1. When a user on an access device (desktop, notebook, thin client) requests a desktop session, the
HP SAM client sends a request to the HP SAM Web server.
a. If configured, HP SAM supports server failover. If the HP SAM Web server does not respond,
the HP SAM client goes down the list to the next HP SAM Web server.
b. The HP SAM client sends the user name and domain information to the HP SAM server.
2. The HP SAM Web server receives the user name and domain name from the HP SAM client. The
web server validates this information with the Microsoft Active Directory server. The account must
be valid and enabled in Active Directory to continue. Normally, the password is not authenticated
at this point, but is authenticated when logging into the operating system on the resource. With HP
SAM 3.0 or later, the Authenticate Before Allocation feature can be enabled which will
cause the password authentication to occur during this step instead.
3. The HP SAM Web server returns the appropriate desktop session information to the HP SAM
client.
a. The HP SAM Web server determines whether or not the user still has a desktop session
running and, if so, reconnects the user to that same session (i.e., follow-me roaming). If the
user has no existing desktop session, the HP SAM Web server checks its internal database to
see what resources are available and connects the user to an appropriate resource.
b. If the user has more than one role or resource assignment, they will be prompted to choose.
c. The data returned to the HP SAM client contains the IP address(es) (or Host name(s),
depending on how it is configured on the HP SAM Web server) of the appropriate resources.
d. If no computing resource is available, the HP SAM client informs the user.
4. The HP SAM client connects to the appropriate desktop session.
NOTE: HP SAM uses HP Remote Graphics Software (RGS) or Microsoft® Remote Desktop
Protocol (RDP) to connect between access devices, computing resources, and OUs.
5. The user is then prompted at the logon screen for the password. The user name and domain is
prepopulated by the HP SAM client. This step is omitted if the user has already entered the
password on the HP SAM client and either RDP is used or RGS in Single Sign-on mode is enabled.
NOTE: With RDP, RGS 5.1 or later, or Authenticate Before Allocation (see Authenticate Before
Allocation on page 83), HP SAM allows users with expired passwords to log on. They are then
required to update their passwords immediately.
6. Once the user logs in, the HP SAM registration service on the computing resource reports back to
the HP SAM Web server.
7. Once the user disconnects or logs out, the HP SAM registration service updates the HP SAM Web
server with the new information.
4 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 13
Overview
5
Page 14
HP SAM Software Components
The following are the primary components of HP SAM.
HP SAM Client—The HP SAM Client runs on the access device and displays the graphical
●
interface employed by the user to request a connection from a client computer to a computing
resource. When the user requests a connection, the HP SAM client communicates this request to
the HP SAM Web Server for execution.
HP SAM Web Server—The HP SAM Web Server (web server) runs on Windows Server 2003
●
or 2008 and manages the operation of HP SAM. A request is made to the web server when a
user on an access device requests a connection to a computing resource. The web server validates
the request, and then communicates back to the access device to orchestrate the connection. In
addition, the web server supports a browser interface to allow the HP SAM administrator to set up,
configure, and administer HP SAM. The web server also creates and accesses a database in
Microsoft SQL Server.
HP SAM Registration Service—The HP SAM Registration Service (registration service or
●
blade service) runs on the computing resource and communicates the status of the computing
resource and its connections to the HP SAM Web Server.
NOTE: Refer to the documentation that shipped with your computing resource and your access device
to determine which of the above components are factory-installed on your hardware and which
components you’ll need to install. For example, the HP SAM Client and the RGS Receiver are both
factory-installed on some clients. Other RGS software is optional and must be acquired separately. For
more information on RGS, visit
http://www.hp.com/go/rgs.
Remote Graphics Software (RGS)
RGS is a communication protocol similar to Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). HP SAM allows
you to use either RGS or RDP.
RGS has a couple of advantages over RDP:
RGS has advanced graphics capabilities that provide a better experience with multimedia and 3D
●
graphics applications over a standard computer network.
RGS supports multiple monitors configured with an offset layout.
●
Thin clients are set to use RGS when possible. If both RGS and RDP are installed on the access device,
RGS is the default. If RGS is installed on both access device and computing resource, RGS is used. If
one or both do not have RGS, then RDP is used.
HP RGS is optional and must be acquired separately. For information on HP RGS, visit
http://www.hp.com/go/rgs. To view the HP Remote Graphics Software User Guide, visit
http://www.hp.com/support/rgs_manuals and scroll down to the User guide heading.
6 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 15
Common Tasks
Setting up HP SAM
1. Install HP SAM. See Installation on page 25.
2. Add users.
a. Add new users. See
b. Create administrative groups, assign users, and customize permissions. See
Administrative Permissions on page 56.
3. Create a policy. See
4. Create a role. See
5. Assign computing resources or roles to the users. See
Add New Users on page 61.
Create or Update a Policy on page 69.
Manage Resource Roles on page 54.
Manage Users on page 57.
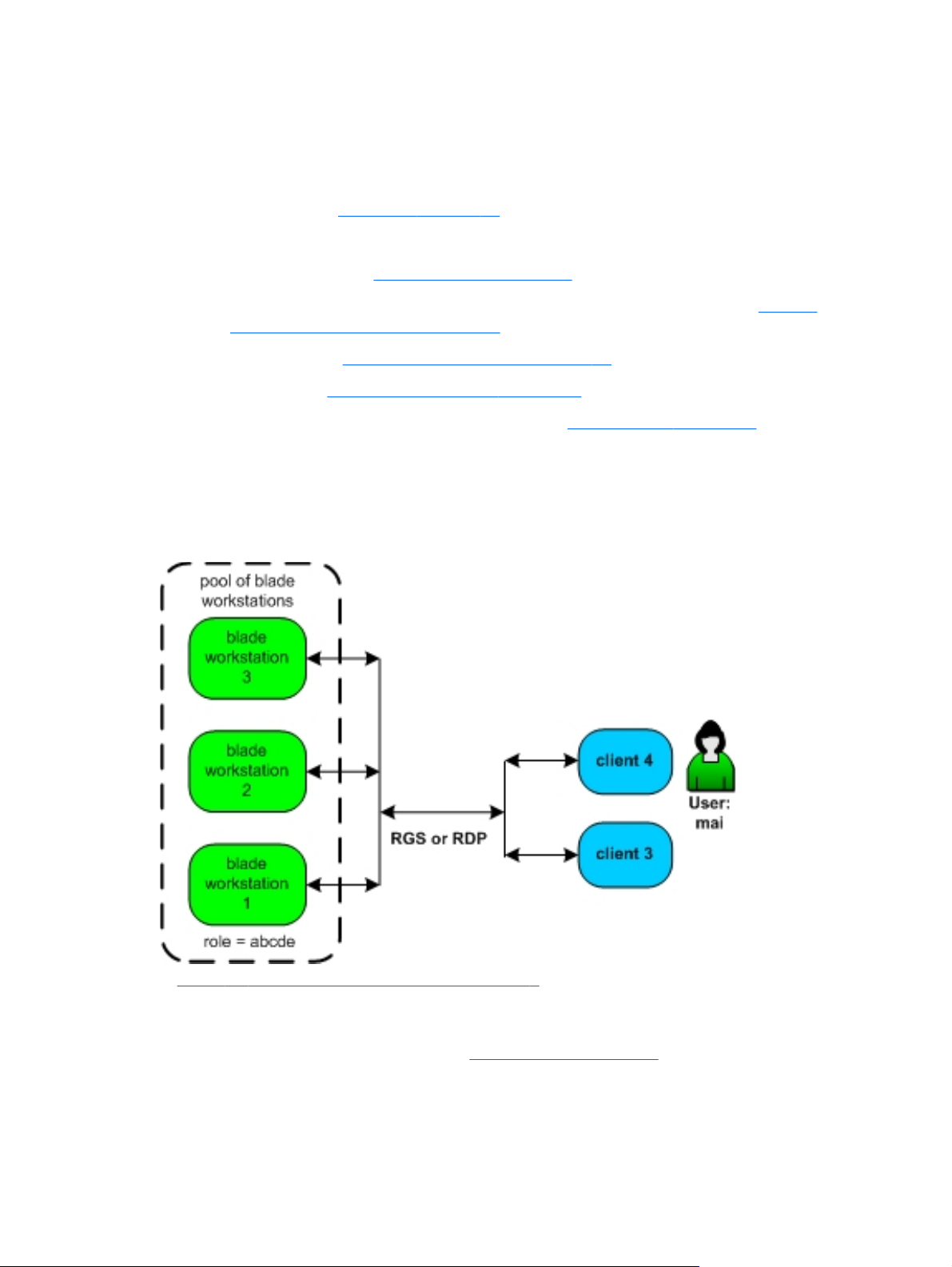
Setting up a User with a Dynamic Resource
HP SAM enables computing resources to be dynamically shared among users.
Figure 1-2 Dynamic Connection Example
Manage
In Figure 1-2 Dynamic Connection Example on page 7, we need to grant user Mai access to computing
resources. A pool of three blade workstations has been assembled, each configured to support the role
of “abcde”.
We assign Mai a role of “abcde.” See
▲
This means Mai is now authorized to access any computing resource which supports a role of “abcde.”
Therefore, when Mai requests connection to an “abcde” computing resource, HP SAM automatically
Manage Users on page 57.
Common Tasks
7
Page 16

connects her access device to one of the three blade workstations (presuming one is available)
supporting that role.
8 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 17
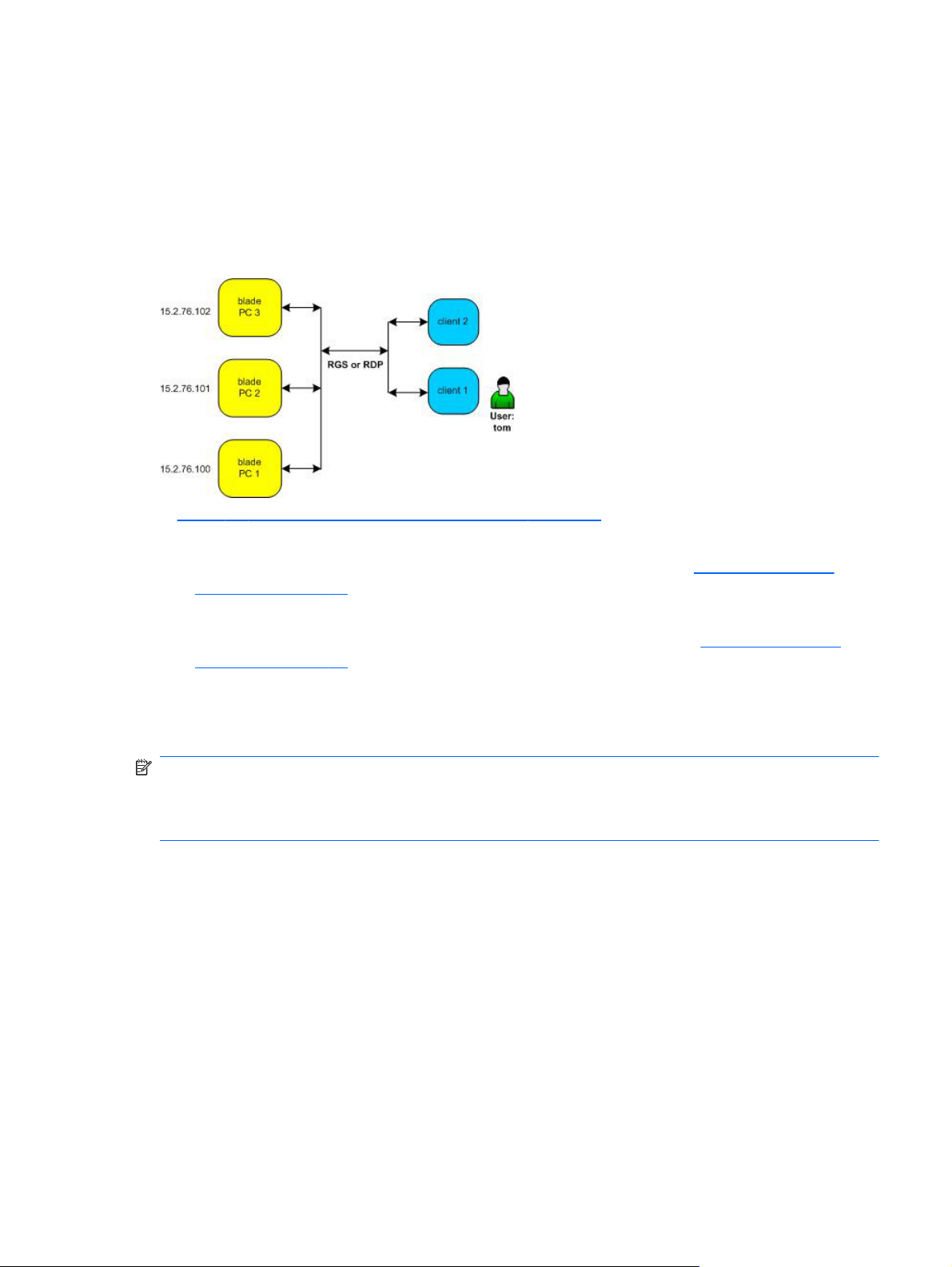
Setting up a User with Static (Dedicated) Resources
Dedicated (static) resource assignment allows one or more specific computing resources to be assigned
to a user and it allows one or more computing resources to be assigned as backup.
Support for Static roaming allows users to work from other locations. The differing display
configurations can be stacked on the client desktop to provide full access with fewer monitors.
Figure 1-3 Static (Dedicated) Connection Example
In Figure 1-3 Static (Dedicated) Connection Example on page 9, we need to grant user Tom access to a
specific computing resource. A blade PC has been configured to support Tom.
1. We assign blade PC 1 with an IP address of 15.2.76.100 to Tom. See
Manually on page 58.
2. To make sure Tom has a computing resource even if blade PC 1 is down, we assign blade PC 3
with an IP address of 15.2.76.102 to act as backup to blade PC 1. See
Manually on page 58.
Now, regardless of what client computer Tom uses, he is automatically connected to blade PC 1 at
address 15.2.76.100. If blade PC 1 fails, Tom clicks Connect and is automatically connected to
blade PC 3.
NOTE: If a blade is in a dynamic role and is reassigned as a dedicated resource to a user, that
blade is no longer available for allocation in the dynamic role to any other user, even if the current
status is Available. It is highly recommended that dedicated resources not be assigned to a dynamic
resource role, which will then help you accurately track the list of Available and In Use resources.
To Assign Resources
To Assign Resources
Common Tasks
9
Page 18
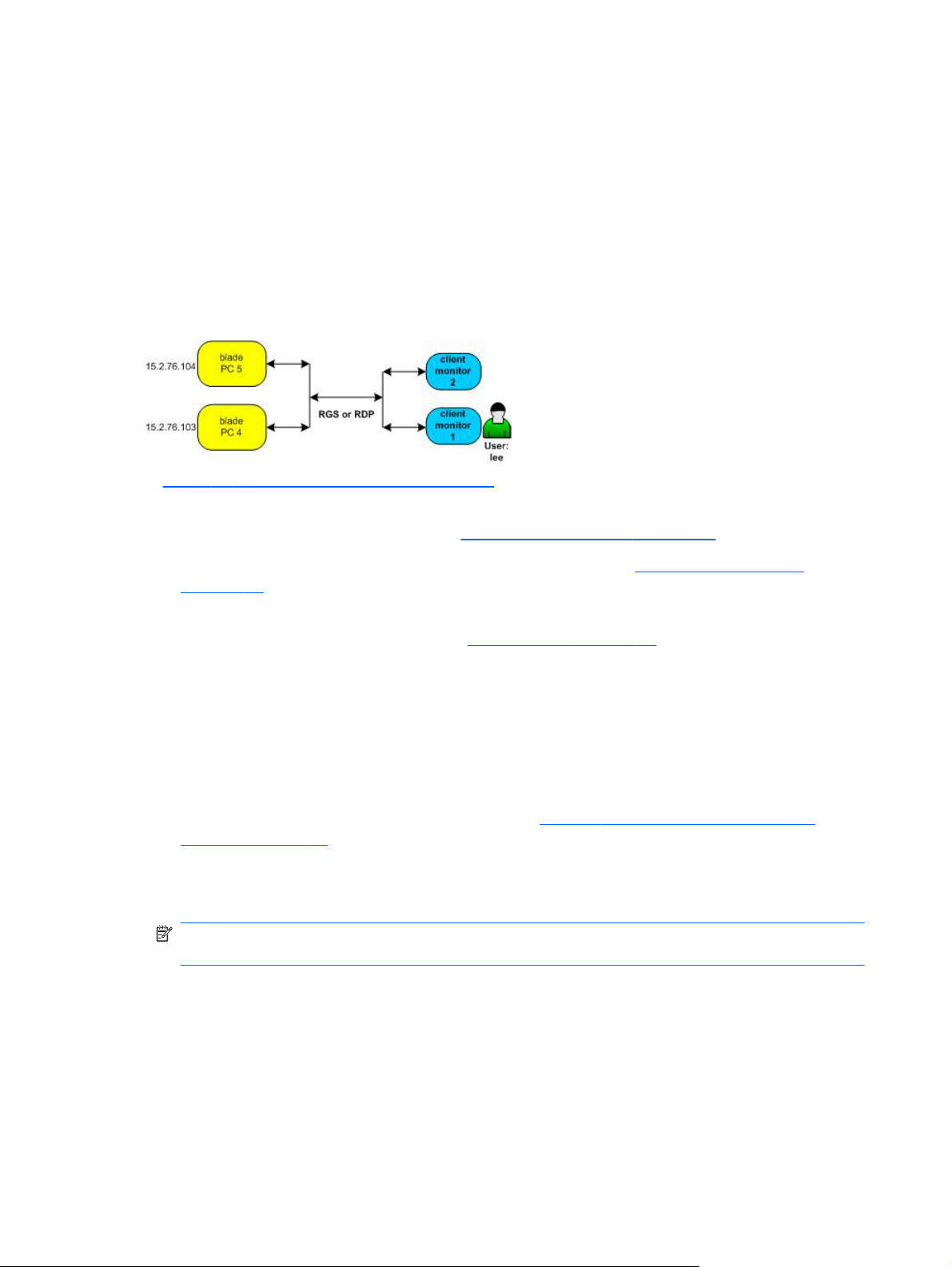
Configuring a Monitor Layout for a User
HP SAM allows a user to connect to multiple computing resources, thereby creating simultaneous
remote sessions. Resources can be made available either by static assignment to the user or by
assignment to roles allocated to the user.
Mapping a static user/display ID to computing resource(s) allows a specific combination of user ID and
client ID to be mapped to a specific computing resource or a specific group of computing resources.
When that user logs onto that client using RGS, the preconfigured computing resources are displayed
at a specific location and resolution on the client monitor or monitors.
Figure 1-4 Monitor Layout Example
In Figure 1-4 Monitor Layout Example on page 10, user Lee has static access to two blade PCs. HP
SAM needs to be configured to display the information from these blade PCs on Lee's two monitors.
1. We create a monitor layout ID first. See
2. We assign the new monitor layout ID to Lee's access device. See
on page 65.
3. We assign the Monitor Layout ID to Lee and select the two blade PCs already assigned to him as
resources for that Monitor Layout ID. See
Both monitors have the same resolution width and height, so we enter 1280 and 1024,
respectively, next to each blade PC selected.
HP SAM treats the set of monitors as a single unit. To display output from each blade PC on a
different monitor, we have to specify the horizontal and vertical offset, the distance from upper left,
at which the output should appear.
We want output from blade PC 4 to be displayed on Lee's left monitor and output from blade PC
5 to be displayed on his right monitor, as shown in
Example on page 11. To display output from blade PC 4 on the left monitor, the upper left
position, we set both the horizontal and vertical offsets to 0. To display output from blade PC 5 on
the right monitor, we must set the horizontal offset one monitor resolution over, so we set that
horizontal offset to 1280. The display is not lowered, however, so the vertical offset is still 0.
NOTE: Offsets are only honored when using the RGS protocol. Sessions using the RDP protocol
will typically appear stacked on the default display.
Support for roaming allows users to work from other locations. If Lee logs in from another client, the
differing display configurations can be stacked on the client desktop to provide full access with fewer
monitors.
Manage Monitor Layout on page 65.
Manage Access Devices
Manage Users on page 57.
Figure 1-5 Monitor Offset Configuration
10 Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 19
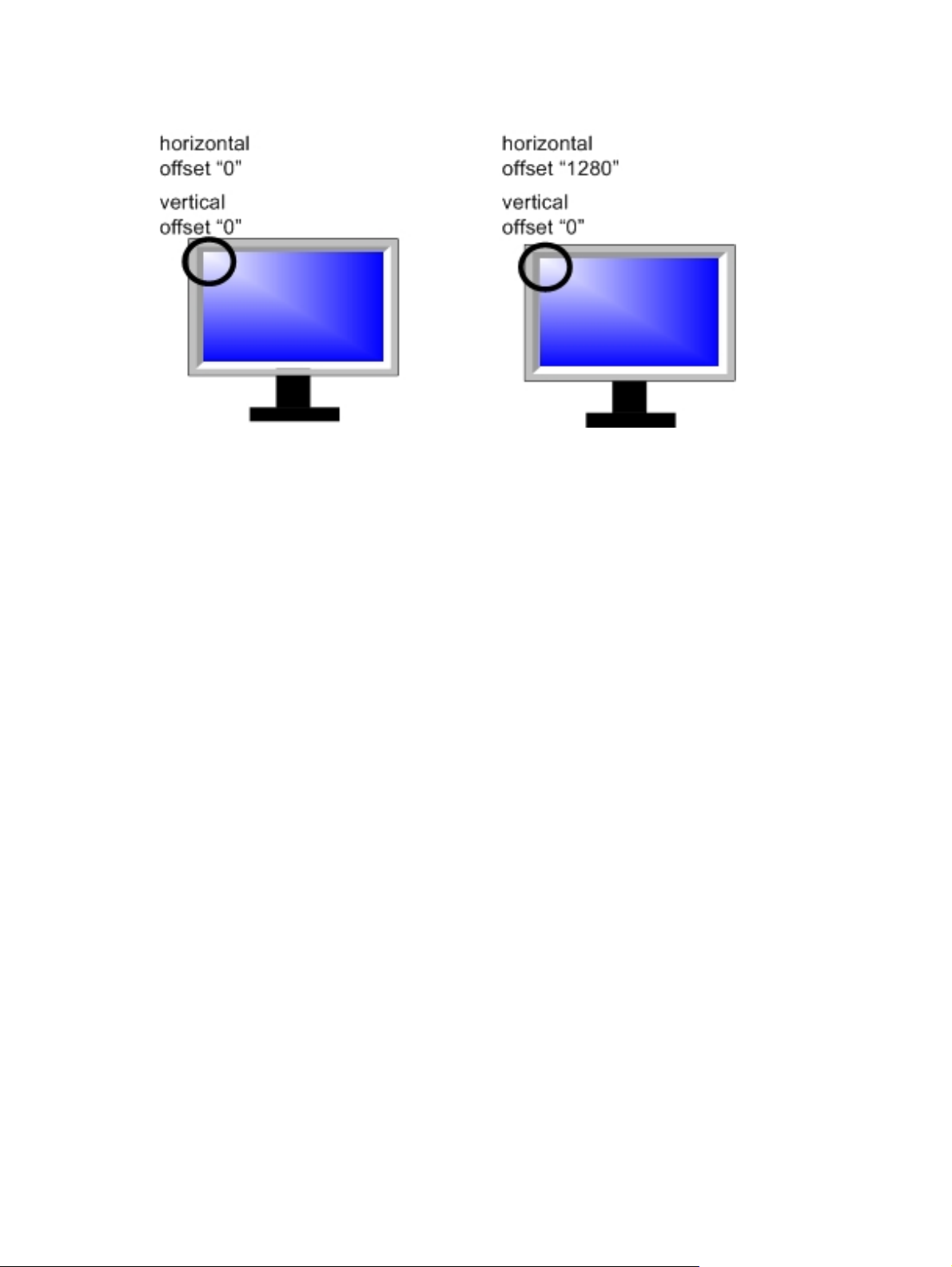
Figure 1-5 Monitor Offset Configuration Example
Common Tasks
11
Page 20

2Requirements
HP SAM Hardware and Software Requirements
Architectural Considerations and Best Practices for Setting up an HP SAM Environment
Server Sizing
In general, the HP SAM Server can handle a theoretical maximum user and resource population of
40,000.
This is based on the assumption that no more than 1% of users will attempt to connect within the
●
same 30-second window.
HP SAM Server, at minimum specification, has been shown to handle up to at least 500 blade
requests within the same 3-second time slot without giving a denial. The results may vary based on
the speed of the servers and infrastructure used.
Increase Memory as user population grows:
Performing HP SAM searches can tax memory because the HP SAM Server pulls a copy of the
●
database across the network to memory in order to complete this task.
One GB of RAM per 2,000 users or resources (whichever is greater) is a good rule of thumb.
●
Increase processor speed and cores as user population grows.
Memory is the primary gate on performance of the HP SAM Server. When handling large user
●
populations, the HP SAM Server has to search through the large database to get profiles and
resource assignments. Once the memory hurdle is cleared, the next gate in performance is the
processor.
2,000 Users/CPU Core is a reasonable rule of thumb.
●
Network I/O performance is not typically a bottleneck.
Extra NIC cards to handle higher load of users are not typically needed.
●
SQL Database Considerations
The HP SAM SQL database can be installed on the same server as the HP SAM Web Server to keep
from buying another hardware platform and another Server OS license, however HP recommends
separating them onto two different servers for the following reasons:
Recovery times from hardware failures will be faster.
●
As deployments grow in size and number of locations, there will likely be multiple HP SAM Web
●
Servers but only one centralized HP SAM SQL database.
12 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 21

Most Administrators already know how to size a SQL database based upon amount of data captured,
however, simultaneous HP SAM logons and logoffs can impact performance because these events have
to be written to the database. Therefore, the platform sizing for the SQL should take this into account as
user populations grow.
HP SAM is a multi-tier application and the actual user never logs into the database directly at any time.
HP SAM only needs one logon, which is the HP SAM service account. You may want have more than
one logon if you want manual access to the HP SAM database without using the HP SAM service
account.
HP SAM needs many concurrent connections. HP SAM does not have control over the number of
connections. Instead, the .NET Framework database engine decides whether it is more efficient to wait
for a connection, re-use an existing connection, or create a new connection. Normally, the busier the
database, the more connections are created. They are automatically destroyed once the operations are
complete.
You should not need to limit the concurrent connections. If you must set a limit, we recommend that you
set it for at least 200–300.
The HP SAM database consists of two files:
SAM_data.mdf: Location of the HP SAM tables
●
SAM_log.ldf: Location of transaction log information. SQL server uses this file to keep track of
●
SQL transactions.
The default size is 100MB for each file, but the actual data inside each file is about 10MB. This leaves
about 90MB free for each to grow before SQL has to expand the file.
The SAM_data.mdf file holds several HP SAM tables, including History and AuditLog tables. These two
tables store the HP SAM history data and events, and over time these two tables will grow larger. If you
disable history and audit logs, you will not outgrow the 100MB default with 100 users. If you do not
disable them, SAM_data.mdf will grow by at least 100MB a day.
The busier the database, the more transactions will be added to the SAM_log.ldf file. When a
transaction is complete, it is removed from the file. The maximum size of the file, therefore, is when the
concurrent transactions peak. For 100 users, the average size of this file should be less than 2 GB.
To optimize the HP SAM database performance, a database administrator should do two things:
Develop a SQL maintenance plan. This includes backing up HP SAM database and truncating
●
orphaned transaction logs in the LDF file. When backing up, the orphaned transactions are
truncated, but the size of the LDF file is not reduced. The database administrator can shrink the LDF
file as far as the 100MB default, if desired.
If the history and audit logs are not disabled, the database administrator will need to truncate
●
these two tables periodically. It is recommended that this be done on a weekly basis to keep
SAM_data.mdf under 1 GB.
Number of HP SAM Servers
It is recommended that, as user populations grow, the number of HP SAM Servers (gateways) be
increased to handle loading and provide backup gateways when another server is inaccessible for
whatever reason.
HP SAM Hardware and Software Requirements
13
Page 22

If you want to avoid continuing to increase memory and processor cores on the HP SAM Server, create
multiple gateway servers and split user populations to limit the number of users using a particular
gateway as their primary target. You may also split resources between HP SAM servers to distribute the
load between servers.
Regionalization of Data Centers
When placing users in one region and blades in another:
As population size increases, the HP SAM Server should be local to the blades/resources as
●
opposed to local to the users for the following reasons:
Because the database of users has to be pulled across the network to HP SAM Server
◦
memory, the WAN could impact performance if this database becomes too large.
If the two servers (SQL and HP SAM) are in the same data center, their communication can
◦
occur over the high speed backbone with little to no performance impact from the network.
With relatively small population sizes (fewer than 3,000), you may place the HP SAM Server local
●
to the users as opposed to local to the blades/resources for the following reasons:
The database of users being pulled across the network to HP SAM Server is small and
◦
impacted very little by the WAN.
The local HP SAM Server limits the number of users hitting that server, so the server can be
◦
smaller.
Disaster Recovery designs
Multiple HP SAM servers can be configured so that users and resources will failover to another HP
●
SAM server if a server becomes unreachable. It is recommended that the HP SAM servers be
installed in different locations for a greater likelihood that at least one server will remain
accessible.
Multiple SQL Databases
Typically, one SQL database should be shared between all HP SAM servers. Only in some situations
does it make sense to use more than one distinct SQL database:
When customers can keep user and resource populations in entirely separate support arenas and
●
users do not need to migrate between them.
When user populations go beyond 40,000.
●
When large user populations log on and off extremely frequently, because this will impact
●
performance for everyone on that SQL database.
Otherwise, you should only have a single SQL database
14 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 23

Domain Environment Requirements for HP SAM
HP SAM is supported in domains whose domain controllers are running Windows 2003 Server or
●
later.
HP SAM is supported in domains with Domain Functional Level of Windows 2003, Windows
●
2008, or Windows 2008 R2 Server.
NOTE: If the domain is using Windows 2008 domain functional level, you must install Service
Pack 1 for Microsoft .NET Framework on the HP SAM server.
HP SAM only supports domains in a single forest.
●
HP SAM requires UPN names on all user accounts to enable certain HP SAM functions, such as
●
logging in to the HP SAM administrative console and follow-me-roaming.
NOTE: The built in Domain Administrator group and the built-in Administrator user on the domain
controller (Windows 2003 or earlier) cannot be added into HP SAM.
HP SAM Web and SQL Server Requirements
You can install HP SAM on one or more failover HP SAM Web servers with one central HP SAM SQL
database. You can also install HP SAM on one server hosting both the HP SAM Web server and SQL
database.
HP SAM Web Server Hardware Requirements
Minimum:
x86-compatible server, such as an HP Proliant server with:
Processor: Pentium 4, 1.0 GHz
●
Hard drive: 10 GB (requires more if hosting both web server and SQL database)
●
System memory: 1 GB per 2,000 resources
●
HP SAM Hardware and Software Requirements
15
Page 24

HP SAM Web Server Software Requirements
NOTE: The HP SAM Web server software is not supported on a server running Windows 2008 R2
Server. This operating system is not available as a 32-bit edition and the HP SAM Web server software
cannot run on a 64-bit OS.
Minimum:
One of the following operating systems must be installed:
Windows Server 2003 R2, Standard Edition, with Service Pack 2
●
Windows Server 2003 R2, Enterprise Edition, with Service Pack 2
●
Windows Server 2003 R2, Web Edition, with Service Pack 2
●
Windows Server 2008, Standard Edition
●
Windows Server 2008, Enterprise Edition
●
Windows Server 2008, Web Edition
●
NOTE: A 64-bit operating system is not supported on the HP SAM Server.
You must install Microsoft .NET Framework Version 2.0 for the HP SAM Web Server to function. It is
recommended that Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0 is installed after IIS, for appropriate asp.net
registration.
If your domain controller is running Windows Server 2008 and its Domain Functional Level is set to
Windows 2008 mode, you must install the .NET Service Pack 1 patch for the HP SAM web
administrator to work properly.
HP SAM SQL Database Server Hardware Requirements
If you have an existing SQL database server, you can install the HP SAM database on the same server.
However, a separate dedicated HP SAM SQL database server for HP SAM is highly recommended to
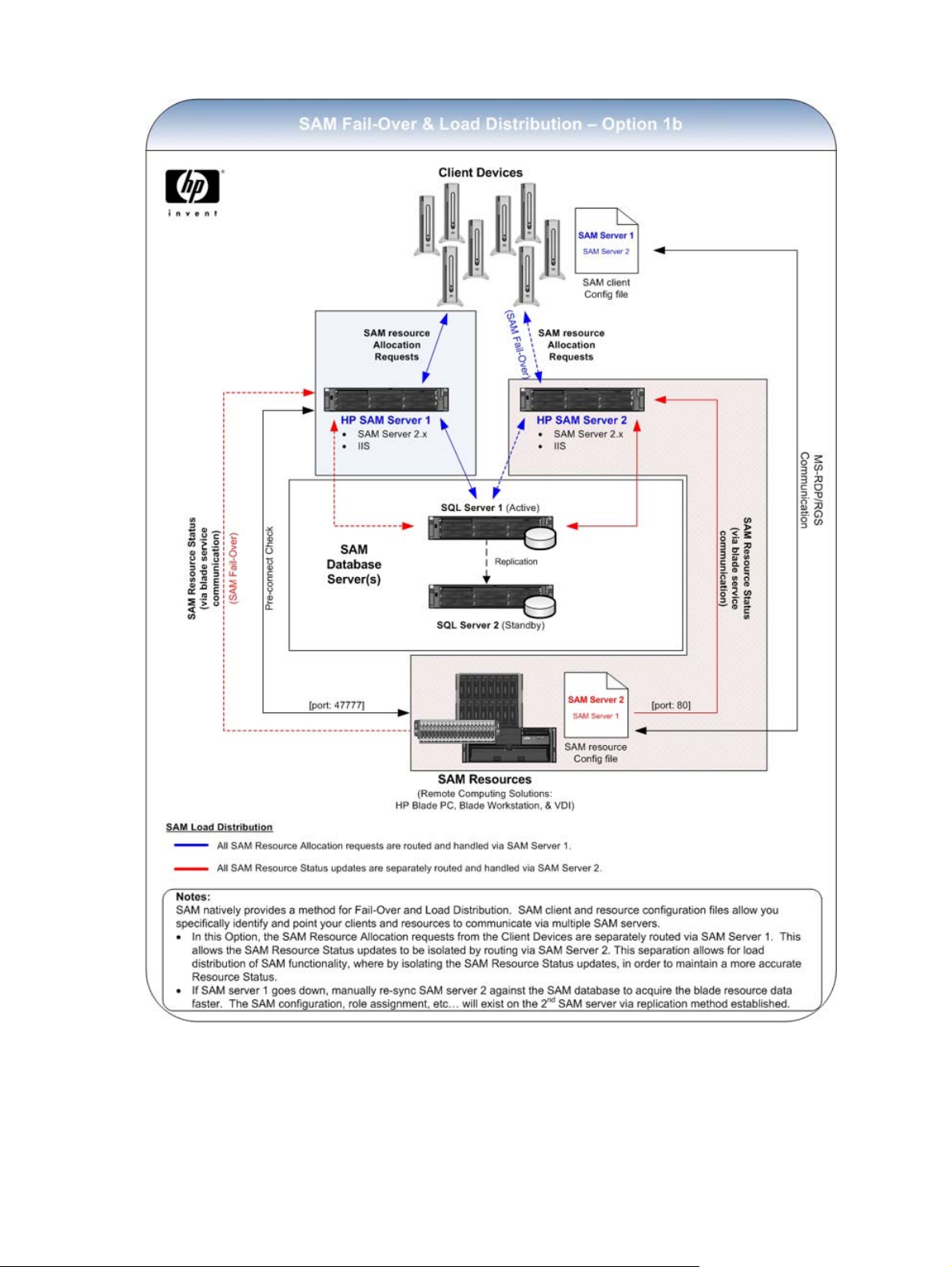
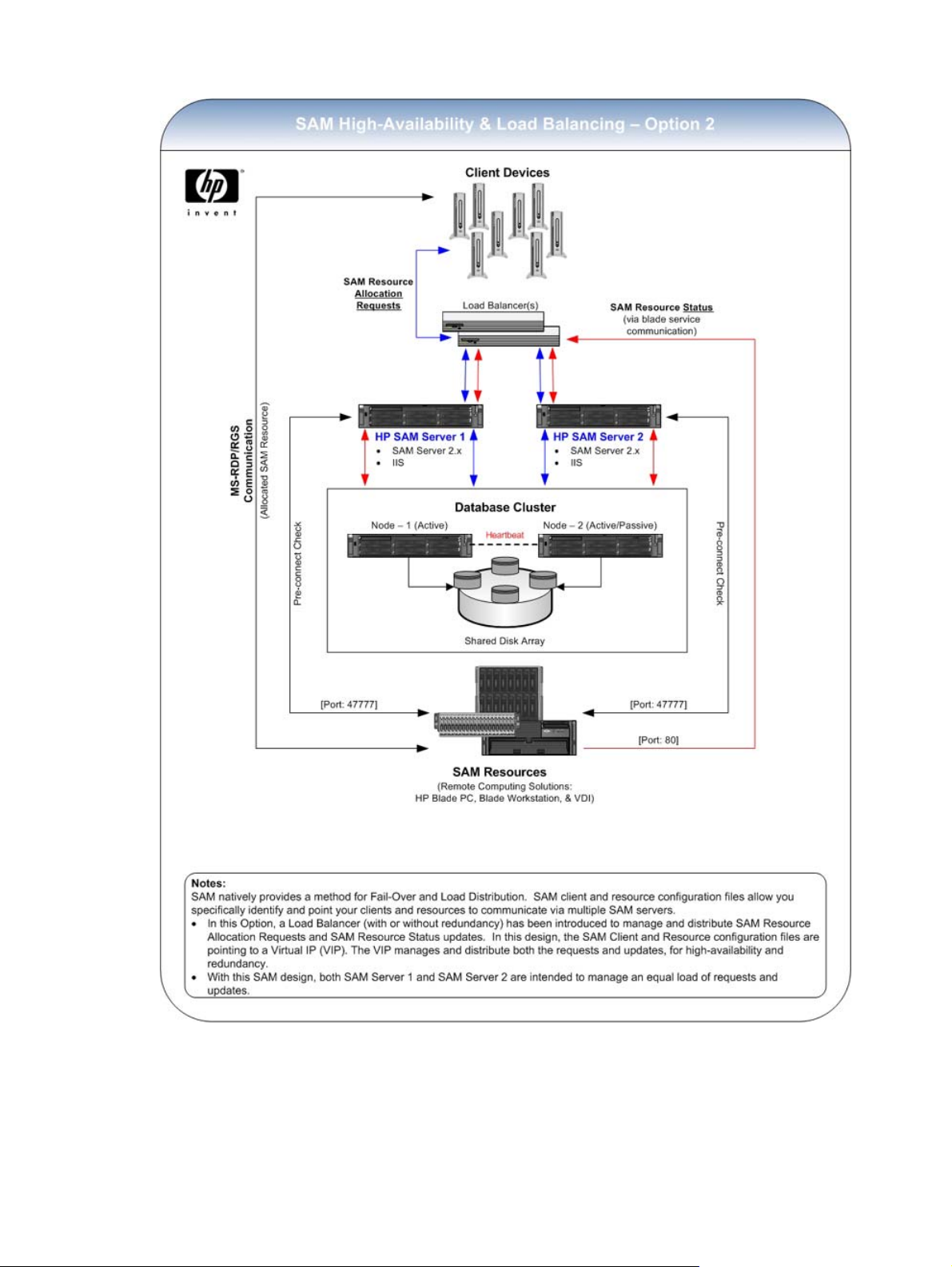
support future scaling of environment. See illustrations of possible setups allowing for load distribution
following this procedure.
Minimum:
x86-compatible server, such as an HP Proliant server with:
Processor: Pentium 4, 1.0 GHz
●
Hard drive: 10 GB (requires more if running both web server and SQL)
●
System memory: 1 GB or more
●
16 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 25
HP SAM Hardware and Software Requirements
17
Page 26
18 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 27
HP SAM Hardware and Software Requirements
19
Page 28
HP SAM SQL Database Server Software Requirements
Minimum:
One of the following must be installed:
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Enterprise, Standard, or Express Edition, with Service Pack 1 or
●
Service Pack 2
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Standard or Enterprise Edition
●
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Standard or Enterprise Edition
●
HP recommends using Microsoft SQL Server 2005 or 2008 Standard or Enterprise Edition. However, if
you use SQL Server 2005 or 2008 Express Edition, which has a 4GB database size limit, you should
either:
Disable history data and/or log collection.
●
or
Limit the number of days the system retains history data and set up the Log Maintenance Scheduler
●
to frequently and regularly remove logs from the database.
HP SAM Registration Service Requirements
Hardware Requirements
HP blade PC
●
NOTE: Linux is not supported on HP blade PCs.
HP blade workstation series
●
HP Personal Workstation
●
Virtual Machine on VMware vSphere 4.X
●
NOTE: If you are running VMware virtual sessions using VMware, refer to the VMware
documentation for hardware requirements.
Software Requirements
Install and enable one of the following operating systems:
Windows XP Professional 32-bit or 64-bit with Service Pack 2 or higher
●
Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 or later, 32-bit or 64-bit, as follows:
●
Business
◦
Enterprise
◦
Windows 7, 32-bit or 64-bit, as follows:
●
Professional
◦
Enterprise
◦
Linux RHEL4 64-bit (update 5 or later)
●
20 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 29

NOTE: HP SAM 2.2 and earlier clients are not able to connect to Linux resources.
Linux RHEL5 64 bit (update 2 or later)
●
Linux RHEL6 64-bit
●
Install and enable one or both of the following:
RGS Sender 5.1.3 or higher with Single Sign-on enabled
●
Terminal service enabled—RDP
●
Access Device Requirements
The following sections provide information about the requirements for access devices.
Thin Client
Hardware Requirements
HP Compaq t5720 thin client (with Windows XP Embedded operating system)
●
HP Compaq t5730 thin client (with Windows XP Embedded operating system)
●
HP Compaq t5730w (with Windows Embedded Standard (WES) operating system)
●
HP t5630 thin client (with Windows XP Embedded operating system)
●
HP t5630w (with Windows Embedded Standard (WES) operating system)
●
HP t5740 thin client (with Windows Embedded Standard (WES) operating system)
●
HP t5740e (with Windows Embedded Standard 7 (WES 7) operating system)
●
HP t5135 thin client (with HP ThinConnect embedded operating system)
●
HP t5145 thin client (with HP ThinConnect embedded operating system)
●
HP t5545 thin client (with HP ThinPro operating system)
●
HP t5745 thin client (with HP ThinPro operating system)
●
HP gt7725 thin client with (with HP ThinPro GT operating system)
●
HP gt7720 (with Windows XP Embedded operating system)
●
HP gt7720w (with Windows Embedded Standard operating system)
●
If the HP SAM client is preinstalled, you need only to configure the HP SAM client to connect to the
appropriate HP SAM Web server.
Software Requirements
Install and enable one or both of the following:
RGS Receiver 5.1.3 or later
●
RDP
●
Access Device Requirements
21
Page 30

Mobile Thin Client
Hardware Requirements
HP Compaq 6720t Mobile Thin Client (with Windows XP Embedded operating system)
●
HP Compaq 2533t Mobile Thin Client (with Windows XP Embedded operating system)
●
HP Compaq 4410t Mobile Thin Client (with Windows Embedded Standard (WES) operating
●
system)
Desktop or Notebook PC
Software Requirements
Install and enable one of the following operating systems:
Windows XP Professional, 32-bit or 64-bit, with Service Pack 2 or 3
●
NOTE: The HP SAM Client is unable to connect from access devices running Windows XP 64-bit
using the preinstalled version of RDP. This is due to the location (\windows\system32) of the
preinstalled RDP protocol files. In order to connect via RDP from an access device running
Windows XP 64-bit, you need to install RDP into a folder other than \windows.
Windows Vista, Business or Enterprise, 32-bit or 64-bit, with Service Pack 1 or later
●
Windows 7, Professional or Enterprise, 32-bit or 64-bit
●
Linux RHEL4, 32-bit or 64-bit (update 5 or later)
●
Linux RHEL5, 32-bit or 64-bit (update 2 or later)
●
Linux RHEL6, 32-bit or 64-bit
●
Install and enable one or both of the following:
RGS Receiver 5.1.3 or later
●
RDP
●
Blade Workstation Clients
Hardware Requirements
HP Compaq Blade Workstation Client
●
HP dc72 Blade Workstation Client
●
HP dc73 Blade Workstation Client
●
Software Requirements
Blade Workstation Client series with RGS Receiver and HP SAM client in the image
●
Personal Workstation Clients
Hardware Requirements
HP Personal Workstation
●
22 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 31

Software Requirements
Windows XP Professional, 32-bit or 64-bit, with Service Pack 2 or 3
●
Windows Vista, Business and Enterprise, 32-bit or 64-bit with Service Pack 1 or later
●
Windows 7, Professional or Enterprise, 32-bit or 64-bit
●
Linux RHEL4, 32-bit or 64 bit (update 5 or later)
●
Linux RHEL5, 32-bit or 64 bit (update 2 or later)
●
Linux RHEL6, 32-bit or 64-bit
●
Other requirements
Create a Service Account
The HP SAM Web server must run under a domain user account in which it can execute the HP SAM
services on the local server.
Create the account prior to installation of the HP SAM server application.
●
Change this account name and password as infrequently as possible to minimize interruptions to
●
HP SAM.
Add the account to the local server administrator group on all HP SAM Web servers.
●
Add the account to the administrator group on all resources (to enable logoff and restart
●
operations).
The account must be trusted in a multi-domain environment.
●
Use the HP SAM Configuration Utility found on the Start Menu on the HP SAM server to change
●
the service account password for HP SAM if the password of the service account has been
updated.
Obtain Administrative Rights
To fully install HP SAM, you must have the following administrative rights:
Administrative rights on all computing resources (such as blade PCs)
●
SQL administrative level account and password—only needed during setup
●
Administrative rights on the HP SAM Web server
●
Change the Firewall
If the network environment uses a hardware and/or software firewall, make appropriate changes to the
firewall for HP SAM to work. Refer to
Firewall Rules on page 85 for more details.
Active Directory
While Active Directory is not part of HP SAM, HP SAM requires Active Directory to perform user
account management.
Other requirements
23
Page 32

NOTE: Active Directory running on Windows Server 2000 Domain controllers is not supported.
Domain functionality levels supported
Windows 2003
●
Windows 2008
●
Windows 2008 R2
●
24 Chapter 2 Requirements
Page 33

3 Installation
Order of Installation
New Installation
For new setup, the recommended order of installation is:
Install the HP SAM Web Server and SQL Software on page 26
1.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Registration Service Software on page 29
2.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software on page 33
3.
Deploy the HP SAM Registration Service to All HP SAM Computing Resources on page 49
4.
Deploy HP SAM Client Software to All HP SAM Access Devices on page 50
5.
Upgrade
To upgrade an existing setup, the recommended order of installation is:
1. Backup the database.
2. Shrink the database. (See steps below.)
3. Stop Internet Information Services (IIS) or just the SAM website on all HP SAM servers. This
temporarily suspends all HP SAM activities.
4. Upgrade HP SAM servers (choose to install the HP SAM database as well as the HP SAM web
administrator). You must install both so that the database structure will be updated to work with the
latest version of HP SAM.
5. Upgrade HP SAM Registration Service on all computing resources, then restart the service (or the
entire system).
6. Upgrade HP SAM clients.
To shrink the database:
1. Truncate the Auditlog and History tables:
a. Open SQL Server Management Studio and expand the Databases folder.
b. Right-click on SAM database and select New Query.
c. In the query tab on the right type:
Truncate Table Auditlog
Truncate Table History
d. Click Execute.
Order of Installation
25
Page 34

You should see Command(s) completed successfully In the messages section.
2. Shrink the database:
a. Open SQL Server Management Studio and expand the Databases folder.
b. Right-click on SAM database, and select Tasks > Shrink > Files.
c. In the File type list, select Data.
d. In the Shrink action section, select Reorganize pages before releasing unused
space.
e. Set the Shrink file size to the default 100MB.
f. Click OK.
3. Verify that you have a 100MB SAM_data.mdf file.
NOTE: The default file location is C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1\MSSQL
\Data.
Install the HP SAM Web Server and SQL Software
The installation package installs the HP SAM server application and/or HP SAM database (HP SAM-xx
##.EXE where xx is the language code, and ## is the version of the software you want to install.
Language codes include: EN for English, JP for Japanese, FR for French, DE for German, KO for
Korean, ZH-CN for Simplified Chinese). You must install both the web server and the SQL components
during the installation. The language selected is meant for the installation wizard only. Once the
application is installed, the web application detects the browser language, and the user interface is
shown in that same language, if the application supports that language. If it does not, the user interface
is in English.
NOTE: HP SAM can have one or more HP SAM Web servers pointing to a single database. All HP
SAM Web servers contain the same feature set. You can set up HP SAM such that the servers loadbalance each other and act as failover servers. Additionally, each server can independently run an
automated task, such as synchronizing the computing resources or deleting HP SAM system log data
from the HP SAM database. See
events.
If you attempt to install the HP SAM Web Administration Package on a MS SQL Server that has
collation of the SQL Server set to case-sensitive, the installation will fail.
The HP SAM Web Administration package can be installed on a Domain Controller for demonstration
or pilot situations, but this is strongly discouraged in production installations.
To install HP SAM Web server and SQL software:
1. Log onto the server using an account with administrative rights.
2. Run the HP SAM-xx ##.EXE install file (where ## is the software version number). Replace xx
with EN for English, JP for Japanese, FR for French, DE for German, ZH-CN for Simplified
Chinese, KO for Korean.
3. Click Next on the welcome screen.
Administration on page 51 for more details on these scheduled
26 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 35

4. For HP SAM Web server installation, the installer asks for a user account. The user account is the
owner (known as the HP SAM service account) of the HP SAM website and the HP SAM server
service. The permissions required for this account are:
Administrative rights on all computing resources (such as blade PCs)
●
Administrative rights on the HP SAM web server
●
Domain user—not a local administrator
●
NOTE: HP highly recommends that you type a name and password from a service account, not
from a personal account. You should change this account name and password as infrequently as
possible to minimize interruptions to HP SAM.
In order to install the HP SAM web administrator component, the Service Account name used must
match the name listed in Active Directory, including the localized characters in that name, such as
ö, ä or é.
Use the HP SAM Configuration Utility found in the Start Menu on the HP SAM Server to change
the service account password for HP SAM if the password of the service account has been
updated.
5. You have the choice to install the HP SAM web application only, the HP SAM SQL database only,
or both. Both are required for HP SAM to operate. The default is both. Click on the pull-down
arrow next to HP SAM Web Site or HP SAM Database to see the list of options.
CAUTION: Do not clear HP SAM Web Site from this list when you perform an upgrade if you
want to keep the HP SAM Web site and the SQL database installed on the same server. Clearing
the HP SAM Web Site will remove the HP SAM Web Site from the server.
6. Leave the default installation folder as is or click the Browse button to change it. Click Next to
continue.
7. Type the SQL server name and either the NT authentication or the SQL authentication User
Name, and Password. The SQL user account needs the ability to create a database on the SQL
server for proper installation of the application. If the HP SAM database does not exist, the
installation creates one. If the database already exists, then the installation links the web server to
the HP SAM database server.
8. Click Next on the Web Resources Configuration screen.
9. Select New Web Site for new web installation, or select Existing to install on an existing
website or to upgrade HP SAM.
10. Click the IP Address list and map the website to the appropriate IP address.
11. Click Next to run all tests. We recommend that you run all of them to ensure proper installation.
Diagnostic tests are now run during the HP SAM web server installation. These tests check for
common configuration or environment problems that can lead to unsuccessful HP SAM
installations. HP SAM Service Account permissions; operating system, SQL Server, and .NET
Framework version support; domain environment support; and Windows Firewalls settings are
checked.
12. Click Next to start the installation, or click Cancel to exit.
13. Click Finish when the installation is complete.
Install the HP SAM Web Server and SQL Software
27
Page 36

14. If your network environment uses a hardware and/or software firewall, then you need to make the
following changes to the firewall for the HP SAM web server and/or SQL server:
Web server
●
Incoming:
◦
- From access devices (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
- From blades (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
- From admin_workstation (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/443—HTTPS)
- From blades (UDP/47777) to web server (UDP/47777—Custom)
Outgoing:
◦
- From web server (TCP/ANY) to SQL_Server (TCP/1433—MSSQL)), if not running on
the same machine as the web server
- From web server (TCP/ANY) to blades (TCP/139—RPC)
- From web server (UDP/47777) to blades (UDP/47777—Custom)
SQL Server (only if not running on the same machine as the web server)
●
Incoming: From web server (TCP/ANY) to SQL_Server (TCP/1433)
◦
Outgoing: None
◦
15. On an HP SAM server, ASP.NET 2.0 is required. If other versions are installed as well, check the
Properties of the HP SAM website. Click the ASP.NET tab, and then select ASP.NET version
2.0.
Grant Users HP SAM Administrator Access
The Domain Administrator, Domain Users in the Administrators Group on the Domain Controller, and
Domain Users in the HP SAM server local Administrators Group are automatically members of the HP
SAM Administrator Group. HP highly recommends that you update the system by adding security
groups or individual names to the HP SAM Administrator access list, instead of using the Administrator
account to log on. This helps track who did what and when.
To add other users as HP SAM administrators, go to the HP SAM administrative console and add these
users to the Administrator group. See
Users and Roles Tab on page 54 for detailed instructions.
Configure HP SAM System Settings
Log onto the HP SAM administrative console, go to the System Settings tab, and make appropriate
changes. See
System Settings Tab on page 70 for detailed instructions.
28 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 37

Configure Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
SSL:
You may configure SSL on the HP SAM web server (which includes installing a certificate) to encrypt
your password and browser session when you log onto the HP SAM administrative console.
Manage: Access to the HP SAM administrative console
●
Webclient: Communication line between web client and HP SAM server
●
Only certain virtual directories under the main HP SAM website can be set to Require secure
channel (SSL). You should not set the main HP SAM website to Require secure channel (SSL).
Install and Validate the HP SAM Registration Service Software
Manually installing this software consists of these steps:
Install the HP SAM Registration Service on page 29
1.
Create the HP SAM Registration Service Configuration File on page 30
2.
Start/Restart the HP SAM Registration Service on page 32
3.
Test the HP SAM Registration Service on page 33
4.
Install the HP SAM Registration Service
Log onto the blade PC using an account with local administrative rights, and then run the
●
bladeservice_xx##.MSI file (## is the software version). Replace xx with
EN = English
◦
JA = Japanese
◦
FR = French
◦
DE = German
◦
KO = Korean
◦
ZH-CN = Simplified Chinese
◦
For Red Hat Linux, extract the HP SAM Linux Registration Service tar.gz package onto the system
●
by executing this command: tar xzvf <name of file.tar.gz>.
Next, run ./install.sh to install the package.
If necessary, stop the service by going to Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services,
●
and look for HP SAM Registration Service. If it is running, stop it. For Linux, enter the following
command in the terminal: /etc/init.d/daesvc stop.
Customize the service .CFG file. Edit the hpevent.cfg-sample file. For details about how to
●
customize this file, see
Create the HP SAM Registration Service Configuration File on page 30.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Registration Service Software
29
Page 38

After you customize the configuration file (required—see
●
Configuration File on page 30), rename (or Save As) the sample file to hpevent.cfg.
Start the HP SAM registration service by going to Control Panel > Administrative Tools >
●
Services, and start the service under the name HP SAM Registration Service. For Linux, enter the
following command in the terminal: /etc/init.d/daesvc start.
If the computing resource has a firewall, enable the ports below.
●
Incoming:
◦
- From web server (UDP/47777) to blade (UDP/47777)
- From web server (TCP/ANY) to blade (TCP/139)
- From access devices (TCP/ANY) to blade (TCP/3389)—RDP
- From access devices (TCP/ANY) to blade (TCP/42966)—RGS
NOTE: The default RGS port is TCP/42966; however, RGS 5.3 and later allows this to be
changed. Please see the RGS documentation for details. Non-default RGS ports are
supported in HP SAM 3.0 and later.
Outgoing:
◦
- From blade (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
- From blade (UDP/47777) to web server (UDP/47777)
Create the HP SAM Registration Service
NOTE: Another way to enable the port is to enable the software service itself. Follow the firewall
instructions to enable the HP SAM Registration Service software.
Create the HP SAM Registration Service Configuration File
The HP SAM registration service configuration file is a simple text file named hpevent.cfg. The HP SAM
registration service tries to locate the configuration file in the order of locations listed below.
In the same directory in which the service resides (usually C:\Program Files\Hewlett-
●
Packard\HP SAM Registration Service)
In %SystemRoot% (usually c:\windows\)
●
In %SystemDrive% (usually c:\)
●
Linux—In /opt/hpsamd/
●
Once the service locates the file, the service stops the search and extracts the contents.
Refer to the following sample template. You must update the [WebServerList] section. The [RolesList]
section is optional. If the [RolesList] section is not populated, it is shown in the HP SAM administrative
console with no role. Roles can be assigned using the HP SAM administrative console.
[hpEventCfg]
Gateway=WebServerList
Role=RolesList
AssetGroup=AssetGroupList
;ServicePort=47777
30 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 39

;DnsDomain=ExampleDomain.com
[WebServerList]
server1.yourdomain
server2.yourdomain
[RolesList]
sample-role-1
sample-role-2
[AssetGroupList]
sample-asset-group-1
sample-asset-group-2
[WebServerList]
The [WebServerList] section lists one or more HP SAM web servers. Each HP SAM web server (primary
and failover) is listed, one per line. The service uses this list in the order provided. The first HP SAM
web server in the list is the one tried first; if it fails, the service proceeds to try the remaining HP SAM
web servers in order. If a successful connection is established, the remaining HP SAM web servers are
not used.
To modify the server line, change just the server1.yourdomain string to the appropriate server name (use
web server DNS name or static IP address). For example:
●
●
[RolesList]
NOTE: Assigning roles in the .CFG file is optional. The usual method of assigning roles is via the
configuration file because this method self-registers the role. If no roles are specified in the .CFG file,
roles may be configured using the HP SAM administrative console. For more information, see
the HP SAM Registration Service to All HP SAM Computing Resources on page 49.
The [RolesList] section lists zero or more roles to which the computing resource can belong. A role is a
functional collection of computing resources (such as blade PCs). The first role in the list is the
computing resource’s primary role. All other roles, if any, are considered non-primary.
When a user requests a resource in a certain role, computing resources are allocated to the user in the
priority order below:
●
●
●
HP SAMservername
10.1.2.3
Deploy
Available computing resource assigned to this role only
Available computing resource assigned to multiple roles, with this role being the primary role
Available computing resource assigned to multiple roles, with this role being the non-primary role
NOTE: If at any time the configuration file is changed on the computing resource, you must restart the
service for the changes to take effect.
This may be overridden by roles assigned via the HP SAM administrative Console
Install and Validate the HP SAM Registration Service Software
31
Page 40

[AssetGroupList]
The [AssetGroupList] section lists zero or more asset groups to which the computing resource can
belong. The HP SAM administrator or domain administrator has full rights to all Asset Groups in the HP
SAM server. Asset Groups allow full HP SAM Administrators to limit or hide objects (resources, users,
etc.) that other administrators are allowed to see and manage. For more information, see
Asset Groups on page 55.
ServicePort
Use the setting to specify a non-default UDP port for HP SAM to use for communication between the HP
SAM Server and the resources. There are other settings you must also change when doing this. Please
see the
Frequently Asked Questions on page 87 for details.
DnsDomain
With this setting, you can specify a domain name string to override the DNS detection. For example, if
the resource Blade1 incorrectly detects the domain as americas.hpinternal.net but you want the domain
to be hp.com, you can specify DnsDomain=hp.com and the resulting FQDN name returned to HP SAM
will be Blade1.hp.com.
Start/Restart the HP SAM Registration Service
Manage
You can start or stop the service from the services applet (Control Panel > Administrative Tools >
Services) or from the command line.
Under the services applet, the service displays as HP SAM Registration Service.
●
Additionally, you can start or stop the service from the command line using the syntax:
●
C:> net start daesvc
and
C:> net stop daesvc
You can also start or stop the service using tools such as HP Rapid Deployment Pack. See the HP Rapid
Deployment Pack documentation for instructions.
You can start and stop the Linux blade service using the syntax:
/etc/init.d/daesvc start
and
/etc/init.d/daesvc stop
32 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 41

Test the HP SAM Registration Service
Log onto the HP SAM administrative console, click on the Resources tab, and search for the
computing resource within the role it was assigned.
If the computing resource was not found, check the firewall settings and make sure that the service
●
was started on that computing resource.
If the computing resource is found, select the Resources tab and select Synchronize from the
●
Operation list and click Go.
NOTE: If the computing resource is marked offline after the synchronize operation, this typically
means the HP SAM web server is unable to communicate to the computing resource. Check the firewall
setting on the computing resource to make sure it allows incoming on port 47777 or the HP SAM
registration service. You can find out if the firewall is blocking the necessary traffic by disabling the
firewall temporarily and then enabling it again later.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
HP SAM includes the following clients:
Internet Explorer-based client
●
Windows-based client
●
Blade Workstation Client series
●
Linux-based Client
●
The HP SAM client requires that RGS (on the Windows-based client, Blade Workstation Client series, or
Linux Client) and/or Remote Desktop Connection or rdesktop for Linux (all clients except the Blade
Workstation Client series) be functional on the access device.
NOTE: The Linux-based Client does not support versions of rdesktop previous to version 1.3.1.
There are differences in features between the various HP SAM clients.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
33
Page 42

Table 3-1 HP SAM Client Comparison
Features Internet
Explorer-Based
Operating System
support
Communication
protocol
Automatic failover
support
Windows XP
Windows XP 64-
Windows Vista,
32-bit and 64-bit
Windows 7, 32-bit
Windows XP
Standard (WES)
Windows XP
Embedded-
Based
Windows XP
Windows XP 64-
bit
and 64-bit
Embedded
Windows
Embedded
WES 7
RDP only RGS and RDP RGS RGS and rdesktop
XXX
bit
Windows Vista,
32-bit and 64-bit
Windows 7, 32-bit
and 64-bit
Windows XP
Embedded
Windows
Embedded
Standard (WES)
WES 7
Blade
Workstation
Client
Embedded OS-
Based
Blade Workstation
Client Embedded
OS
Linux-Based
HP ThinConnect
HP ThinPro
HP ThinPro GT
RHEL4 32-bit and
64-bit
RHEL5 32-bit and
64-bit
RHEL6 32-bit and
64-bit
Requires Internet
Explorer browser
Requires ActiveX
controls to be
downloaded in
order to run
Languages English, Japanese,
X
X
English, Japanese,
French, German,
Korean, Simplified
Chinese
French, German,
Korean, Simplified
Internet Explorer-Based Client
An access device can access HP SAM using Internet Explorer. To use the HP SAM Internet Explorerbased client, type the server name (http://HP SAMservername) in the Internet Explorer address bar.
If the access device is accessing the HP SAM server for the first time, the access device needs to install
two ActiveX controls (HP SAM Web Client Utility Class and Microsoft RDP Client Control). The installed
location for these controls are in the %SystemRoot%\Downloaded Program Files\ folder.
There are other HP SAM Internet Explorer-based client configuration settings that you can control from
the HP SAM server. Refer to
System Settings Tab on page 70 for more information.
English English
Chinese
34 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 43

NOTE: HP recommends that you add the HP SAM web server to the Trusted Sites list. On the access
device, open Internet Explorer and go to Tools > Internet Options > Security tab.
If a firewall is installed, you need to make appropriate changes to allow the HP SAM server client
through. For example, if HP Sygate Security Agent is installed, add a rule to allow port 3389 for
application IEXPLORE.EXE.
To use the Web Client on an access device running Windows XP, 64-bit, you must use Internet
Explorer, 32-bit.
HP SAM ActiveX Controls
The HP SAM ActiveX controls are stored as source for distribution on the HP SAM web server during
the web server installation process.
If the HP SAM ActiveX controls are replaced on the HP SAM web server during an upgrade, the HP
SAM client is automatically upgraded to the newer version the next time the access device connects to
the HP SAM web server.
The HP SAM ActiveX controls support RDP 5.0 only, even if RDP 6.0 or later or RGS is installed.
For the HP thin client running Windows XP Embedded or Windows Embedded Standard, the
installation of the HP SAM ActiveX components may be repeated every time the access device is
rebooted, if it is not saved as part of the thin client image. Use the Web Client Controls installer found
in the HP SAM SoftPaq so that you do not need to download and install any controls automatically via
the browser.
Windows-based Client
To install the HP SAM client on a Windows-based thin client or on a desktop/notebook PC running
Windows XP, Windows Vista, or Windows 7:
1. If you are installing the HP SAM client on a Windows-based thin client, unlock the write filter.
If you do not unlock the write filter before installing or saving configuration information to the XPe
client, the installation or configuration information will be lost when the client is turned off.
2. Log onto the access device under an account with local administrative rights and run the scw32-
xx##.MSI file (## is the software version) to install the Windows XP-based client. Replace xx with:
EN = English
●
JA = Japanese
●
FR = French
●
DE = German
●
KO = Korean
●
ZH-CN = Simplified Chinese
●
3. Follow the installation wizard.
4. After the software is installed, verify the program is placed on the start menu (Start > All
Programs > Hewlett-Packard > HP Session Allocation Client).
5. If you unlocked the write filter in step 1, re-enable it now.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
35
Page 44

Customization Steps
(Recommended)
1. Start up the HP SAM client.
2. Type the HP SAM web server name.
3. Click the Options button.
4. Change appropriate connection settings.
5. Click the Save Settings button.
6. Save the config file (hprdc.sam) to the default location, if possible (this may be locked down on
some thin clients).
When you launch the HP SAM client, your saved settings will take effect.
Additional settings can be set by manually editing the .SAM files (configuration files).
1. The HP SAM connection client searches first for the user-specific .SAM file, hprdc.sam.
2. It then checks the access device file, hprdc_accessdevice.sam, in the folder in which you installed
HP SAM. Parameters found in the access device file replace or are added to the merged file.
3. Then, the connection client checks the global file, hprdc_admin.sam, in the same folder.
Parameters found in the global file replace or are added to the merged file.
Refer to
client.
Configuration Settings on page 38 for a list of the options available for the Windows-based
Linux-Based Client
Different procedures are used to install the Linux Client onto the following platforms:
HP Blade Workstation Client Series on page 36
●
HP ThinPro GT Client for the HP gt7725 Thin Client on page 37
●
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Client on page 38
●
HP Blade Workstation Client Series
The HP SAM client is delivered preinstalled on the HP Blade Workstation Client series. To upgrade to a
newer HP SAM client, go to
appropriate client, select Workstation Blade Client Embedded OS, and reimage the client.
Customization Steps
(Recommended)
1. Start up the HP SAM client.
www.hp.com, click software & driver downloads, select the
2. Type the HP SAM web server name.
3. Type the username and domain. (This step is optional.)
4. Click the Options button.
36 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 45

5. Change appropriate connection settings.
6. Click the Save Settings button. Click OK in the message confirming that the settings were
saved.
7. Select \etc.
8. Click Save.
9. Click the Connect button to connect
10. If the HP SAM client is closed, it should start automatically. If it does not start, right-click and select
Remote Graphics.
Additional settings can be set by manually editing the .SAM files (configuration files).
1. The HP SAM connection client searches first for the user-specific .SAM file, hprdc.sam.
2. It then checks the access device file, /root/writable/opt/hpsam/hprdc_accessdevice.sam.
Parameters found in the access device file replace or are added to the merged file.
3. Then, the connection client checks the file, /root/writable/opt/hpsam/hprdc_admin.sam.
Parameters found in the global file replace or are added to the merged file.
Refer to
Configuration Settings on page 38 for a list of the options available for the Linux Client.
HP ThinPro GT Client for the HP gt7725 Thin Client
For the HP gt7725 thin client running HP ThinPro GT, use the following procedure to install or update
the HP SAM Client:
1.
Edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list and verify the following line exists (if it does not, add it): deb ftp://
ftp.hp.com/pub/tcdebian gt7725 main non-free.
2.
Save the file, then update the list with the following command: apt-get update.
3.
Set your http_proxy environment variable, if necessary. Run the following command: export
http_proxy='http://web-proxy.yourcompany.com:8080' substituting your proxy information. If you are
using Synaptic, set the proxy information under Preferences > Network.
4.
To install the HP SAM Client, run the following command: apt-get install hptc-sam-client or use the
Synaptic application to obtain the software.
Additional settings can be set by manually editing the .SAM files (configuration files).
1. The HP SAM connection client searches first for the user-specific .SAM file, hprdc.sam.
2. It then checks the access device file, /opt/hpsam/hprdc_accessdevice.sam. Parameters found in
the access device file replace or are added to the merged file.
3. Then, the connection client checks the file, /opt/hpsam/hprdc_admin.sam. Parameters found in
the global file replace or are added to the merged file.
Refer to
Client.
Configuration Settings on page 38 for a list of the options available for the HP ThinPro GT
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
37
Page 46

Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Client
To install the HP SAM Linux Client on a system running RHEL version 4 or 5:
1. Log onto the access device using an account with root permissions.
2. Extract the Linux Client tar.gz package onto the system by executing the following terminal
command: tar xzvf <name of file.tar.gz>.
3.
Run the install script by executing: ./install.sh.
4.
After the software is installed, verify the program has been installed into /opt/hpsam.
Customization Steps
(Recommended)
1. Start up the HP SAM client.
When you launch the HP SAM client (by executing /opt/hpsam/hprdclx.sh) your saved settings will
take effect.
2. Type the HP SAM web server name.
3. Click Options.
4. Change the appropriate connection settings.
5. Click Save.
Additional settings can be set by manually editing the .SAM files (configuration files).
1. The HP SAM connection client searches first for the user-specific .SAM file, hprdc.sam.
2. It then checks the access device file, /opt/hpsam/hprdc_accessdevice.sam. Parameters found in
the access device file replace or are added to the merged file.
3. Then, the connection client checks the file, /opt/hpsam/hprdc_admin.sam. Parameters found in
the global file replace or are added to the merged file.
Refer to
Configuration Settings on page 38 for a list of the options available for the RHEL Client.
Configuration Settings
Options
There are additional options to configure the settings. You can set these options by manually editing
the .SAM file. The following list provides supported keys and values within the [HPRDC] section.
Gateways—string value. Points to the section that lists HP SAM Servers.
●
DefaultDomain—string value. This is a default value to be loaded in the Domain edit box on
●
the client user interface. If this value is not specified, the program attempts to determine the
domain from the user’s logon information, which may or may not be accurate.
Policies—string value. Points to the section that lists settings that are loaded in the client’s Load
●
Predefined Settings list on the Other tab of the Options section. This allows the
administrator to pre-define a number of settings associated with various connection types. Refer to
Policy Entries on page 44.
38 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 47

DefaultPolicy—string value. This is the policy that should be selected by default in the client’s
●
Load Predefined Settings list on the Other tab of the Options section. It is not related to HP SAM
policies set in the HP SAM administrative console.
Autodial—integer value, 0 or 1. If value is set to 1, the program automatically tries to connect
●
on startup, without waiting for the user to type logon information. Default value is 0.
DefaultUsername—string value. If value is not specified, the program attempts to determine the
●
user name from the user’s logon information, which may or may not be accurate.
DefaultInsecurePassword—string value. You can use this field to pre-populate the password
●
box. This field was intended for automated load testing in an environment where security is not of
importance.
CAUTION: The DefaultInsecurePassword field is in plain text format and should not be
used in a production environment.
Debug—integer value, 0 or 1. If value is set to 1, debug logs for troubleshooting purposes are
●
captured to /tmp/hprdc.log. This option is valid only on the Linux Client. Default value is 0.
Failover—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, enables the failover capability of the access
●
device. If multiple web servers are defined, the access device fails over to the next available HP
SAM web server when a connection fails. Turning this feature on limits the user’s ability to type in
a new HP SAM server; the user still has the ability to choose between web servers defined in the
configuration file. Default value is 0 (off).
EnablePublicRoles—integer value, 0 or 1. If set to 1, the HP SAM client will show any
●
available public roles for the user to connect to. If set to 0, the HP SAM client will hide public
roles. Default is 1 (show).
ResetAfterSession—integer value, 0 or 1. If set to 1, access device settings, including
●
username, are reset back to defaults after each session. This is useful in kiosk mode to clear
previous user settings. The default is 0.
DefaultMonitorLayoutID—string value. The string value designates the Monitor Layout ID to
●
be used by default when logging in from the access device. This setting only takes effect when
new access devices are registered upon connection. To have this setting apply to existing access
devices, delete them from HP SAM so they will re-register.
AssetGroup=AssetGroupList—AssetGroupList refers to another section in the file with a
●
matching name [AssetGroupList] which has one or more Asset Groups listed in it.
ConnectionBar.Enable—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, the HP SAM connection bar is
●
enabled. Set this value to 1 to allow the user to manage multiple connections using the HP SAM
connection bar. This also prevents the user from opening multiple instances of the client. The
default value is 1 for Blade Workstation Client series and Linux Client and 0 for all others.
ConnectionBar.FollowMouse—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, the connection bar is
●
open on the monitor where the cursor is. The default value is 1.
ConnectionBar.Location—integer value. Sets the location of connection bar (if 0, top; if 1,
●
bottom; if 2, left; if 3, right). The default value is 0 (top).
ConnectionBar.EnableAddNew—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, enables the Add
●
New button on the connection bar. The default value is 1.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
39
Page 48

ConnectionBar.EnableCloseAll—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, enables the
●
Disconnect All button on the connection bar. The default value is 1.
ConnectionBar.EnableReconnectAll—integer value, 0 or 1. Default is 1 (enabled). Set to 0
●
to hide (disable) the Reconnect All button on the connection bar.
ConnectionBar.EnableDisconnectInstance—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, enables
●
the Disconnect button on the connection bar for each session. The default value is 1.
ConnectionBar.EnableContextMenu—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, a context menu
●
appears when right-clicking on a session's status icon on the connection bar. This menu allows the
user to switch to the selected session, move the selected session, minimize the selected session, or
minimize all currently connected sessions. When set to 0, this menu does not appear. Default is 1.
ConnectionBar.EnableSave—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, enables the Save button
●
on the connection bar that allows an Administrator to save the current session configuration to the
server as a Monitor Layout ID. Disconnected sessions are not saved back to the database. The
default value is 0.
ConnectionBar.ShowDelay—integer value. Specifies delay in milliseconds for connection bar
●
to appear after cursor has been moved to screen edge. The default value is 500 milliseconds.
ConnectionBar.ShowOnDisconnect—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, enables
●
connection bar to appear automatically when a session closes. The default value is 1.
ConnectionBar.AutoHideTimeout—integer value. Sets time in seconds for connection bar to
●
stay open when cursor is moved off connection bar. 0 = always stays open. The default value is 3.
ConnectionBar.ShowTimingFactor—integer value. Controls the speed of the animation when
●
the connection bar is appearing on the screen. A smaller number means faster animation. This can
be useful on slow client systems where the connection bar animation is too slow. The default value
is 5.
ConnectionBar.HideTimingFactor—integer value. Controls the speed of the animation when
●
the connection bar is disappearing from the screen. A smaller number means faster animation.
This can be useful on slow client systems where the connection bar animation is too slow. The
default value is 5.
ConnectionBar.SessionWindow.EnableIdentify—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an
●
RGS session chosen on the HP SAM Connection Bar will be highlighted and can be moved by the
user. This features requires RGS 5.1.3 or later. Default value is 1.
DisclaimerDisplay.Timeout—Time in seconds for the HP SAM client to be idle before the
●
Legal Disclaimer window reappears. Default value is 30.
Resolutions—string value. Specifies another section in the .SAM file that contains a list of
●
resolutions to show on the client UI. Open the default .SAM file to see the required format.
ConnectionBar.ShowLogoff—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an option to log off the
●
resource is shown when disconnecting. Default value is 0.
ConnectionBar.ShowReboot—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an option to restart the
●
resource is shown when disconnecting. Default value is 0.
40 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 49

NOTE: The options to log off or reboot from the connection bar are disabled by default in the Global
policy. The following requirements must be met for Logoff and Restart:
—A certificate from the domain certificate authority must be installed on the HP SAM website to allow
usernames and passwords to be transmitted to the server.
—The HP SAM service account must have local administrator privileges on the resource to be granted
permissions to reboot or log off a user from the blade.
ConnectionBar.ShowHardReboot—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an option to cycle
●
power on the resource is shown when disconnecting. Default value is 0.
NOTE: The option to perform a power cycle from the connection bar is disabled by default in the
Global Policy. The following requirements must be met for Power Cycle:
—A certificate from the domain certificate authority must be installed on the HP SAM website to allow
usernames and passwords to be transmitted to the server.
—Version 4.20 or later Integrated Administrator (IA) software must be used on the HP BladeSystem PC
Blade Enclosure(s). By default, the IA software has a disabled SAM account. You must enable this
SAM account and create a password for the powercyle option to work.
—The IA password for the built-in SAM account must be saved in HP SAM on the Manage Data
Centers page.
—One of the following HP BladeSystem Blade PCs is required:
◦ HP BladeSystem bc2000 Blade PC
◦ HP BladeSystem bc2200 Blade PC
◦ HP BladeSystem bc2500 Blade PC
◦ HP BladeSystem bc2800 Blade PC
Smart Card Settings
NOTE: Smart card settings are not valid for Blade Workstation Client series or Linux Client.
SmartCardAlways—integer value, 0 or 1. Allows user to use smart card to enter credentials
●
and log on. If UiMode = 0 or 1, user has option of using smart card to log on. If UiMode = 2,
user must log on with smart card. See “UiMode” in
on page 42. Default is 1 (allow).
SmartCardRequiresClick—integer value, 0 or 1. Set to 1 to require that the user click
●
Connect after a smart card is detected. Changing this to 0 automatically initiates a connection
when the user inserts a recognized smart card. Default is 1.
SmartCardCSP—string value. The CSP to use for accessing the smart card. This must match
●
exactly the name of the CSP installed on the machine. Default is “ActivCard Gold Cryptographic
Service Provider.” For example: for ActivClient 6.x, use “ActivClient Cryptographic Service
Provider”.
User Interface Customization Settings
SmartCardUidType—integer value, 1 or 8. The Type field in the smart card certificate
●
properties enumeration, to use for determining the user UPN name. Value of 8 is
CERT_NAME_UPN_TYPE. If set to 8, you must specify SmartCardUidOid. Default is 1
(CERT_NAME_EMAIL_TYPE).
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
41
Page 50

SmartCardUidOid—string value. The OID associated with the entered SmartCardUidType. Not
●
all Types require an OID. An entry is required is SmartCardUidType=8. Default is blank.
SmartCardAutoDisconnect—integer value, 0 or 1. If set to 1, automatically disconnect the
●
session when the smart card is removed. Note that Active Directory policy settings may affect the
actual behavior of this property. Active Directory options include leave as is, password lock, and
log off. Active Directory does not include a disconnect option, so you must use
SmartCardAutoDisconnect for that functionality. Default is 1.
User Interface Customization Settings
UiMode—integer value, 0, 1 or 2. Select the type of user interface to display.
●
0 (default)—HP SAM Server, User name, and Domain fields visible in the user
◦
interface.
1—show the UPN mode, where the Domain field is not shown. The user must use the format
◦
username@domain.
2—show smart card mode, where both the User Name and Domain fields are hidden,
◦
and a message displays asking that the user insert the smart card. The Connect button is
disabled when no smart card is inserted. For the Blade Workstation Client Embedded OS
and Linux Client, this value (2) is treated as a 1.
Banner—string value, Allows a specified file to load as the banner image on the access device
●
main dialog. The image must be in Windows Bitmap (BMP) format. A fully qualified path is
required. The banner area is 385 x 60 pixels and 24-bit color. If you provide a file of different
resolution, it is resized to fit in the banner area.
TitlebarText—string value. Allows overriding the default text in the titlebar with a specified
●
string. By default, language-appropriate text displays.
ShowVersion—integer value, 0 or 1. If set to 1, displays the HP SAM client version text on the
●
main window. Default is 1.
EnableOptionsButton—integer value, 0 or 1. If set to 1, the Options button on the main
●
application dialog is visible. If set to 0, the button is not displayed. Default is 1.
EnablePassword—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, shows the Password box on the
●
access device user interface. When set to 0, the password box is not available. Default is 1.
UILanguage—language identifier. Supported identifiers include:
●
EN = English
◦
FR = French
◦
DE = German
◦
JA = Japanese
◦
KO = Korean
◦
ZH-CN = Simplified Chinese
◦
If the identifier is not supported or the property is not present in the file, the application default is
US English. A language support DLL must be present to support the language. Not valid for the
Blade Workstation Client series or Linux Client.
42 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 51

NOTE: The UILanguage specified must either be the same language as the HP SAM client
application that you have installed or English. If you installed the English HP SAM client
application, do not change the value to any other language. To minimize disk space, the English
HP SAM client application does not contain any other HP SAM client language DLL.
EnableServer—integer value, 0 or 1. If set to 1, the HP SAM Server box on the main
●
application dialog is visible. If set to 0, the field is not displayed. If the field is turned off, the value
is still required and must be defined in the configuration file. Default is 1.
EnableDomain—integer value, 0, 1, or 2. When set to 1, the Domain box on the main
●
application dialog is visible. If set to 0, the field is not displayed. If the field is turned off, the
domain specified using the DefaultDomain setting is applied (unless the username is entered in
UPN or domain\username format with a different domain). If set to 2, the field is visible but
cannot be edited. The domain set via DefaultDomain is always in effect and cannot be overridden
using UPN or domain\username format. Default is 1.
KioskMode—integer value. Not valid for Blade Workstation Client series. When set to non-zero,
●
the user interface is altered for use in a kiosk-mode environment. Valid values include:
Bit 1 – Enable/disable the Cancel button (if 1, disable)
◦
Bit 2 – Enable/disable the Minimize toolbar button (if 1, disable)
◦
Bit 3 – Enable/disable the Close toolbar button (if 1, disable)
◦
Default value is 0 (all features are enabled). For example, to turn off the Cancel and Minimize
buttons and leave the Close button on, set the value to 3.
DisplayShutdown—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an action button is added to the
●
client user interface to enable the user to shut down the access device. This is the same button
created by the DisplayShutdown, DisplayRestart, and DisplayLogoff options. If the button
already displays from another option setting, the Shutdown option is added to the button dropdown. Not valid for Blade Workstation Client series or Linux Client. The default value is 0 (do not
show).
DisplayRestart—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an action button is added to the client
●
user interface to enable the user to restart the access device. This is the same action button created
by the DisplayShutdown, DisplayRestart, and DisplayLogoff options. If the button
already displays from another option setting, the Restart option is added to the button drop-
down. Not valid for Blade Workstation Client series or Linux Client. The default value is 0 (do not
show).
DisplayLogoff—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an action button is added to the client
●
user interface to enable the user to log off the access device. This is the same action button
created by the DisplayShutdown,
already displays from another option setting, the Logoff option is added to the button drop-down.
Not valid for Blade Workstation Client series or Linux Client. The default value is 0 (do not show).
DefaultSessionAction—integer value, 0, 1, or 2. When set to 0, the default session action
●
(pressing the button without dropping down the list) for the button is Shutdown. If set to 1, the
default action is Restart. If set to 2, the default action is Logoff. If only one action is enabled, that
option is the default action, and this setting is ignored. If this value corresponds to an action that is
not enabled, no default action is available. Not valid for Blade Workstation Client series or Linux
Client. The default value is 0.
DisplayRestart, and DisplayLogoff options. If the button
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
43
Page 52

Policy Entries
You can set policy entries by manually editing the .SAM file. These settings must be located in a policy
section of the .SAM file, for example, [Local Area Network] or [saved settings]. These values only
specify the default settings in the UI. Values changed by the User in the UI will take effect.
Protocol—integer value, 0, 1, or 3. Specify which protocol to use for connection. RDP is 1, RGS
●
is 3. A value of 0 (automatic) uses autodetected settings, with a preference of RGS over RDP.
Default is 0.
Mute—0 or 1. If 0, audio is enabled for this connection. If 1, audio is disabled. Default is 0.
●
SoundQuality—integer value, 1, 2, or 3. Set to 1 for lowest 3 for highest sound quality. This
●
value is only supported for RGS connections. Default is 2.
SoundStereo—0 or 1. If 1, stereo sound is supported. If 0, mono sound is played. This value is
●
only supported for RGS connections. Default is 1.
BordersEnabled—integer value, 0 or 1. If 1, enables normal Windows borders. 0 = no
●
borders. This value is only supported for RGS connections. Default is 1.
WindowSnapEnabled—integer value, 0 or 1. If 1, allows the session window to “snap” to
●
edge of screen when moved. This value is only supported for RGS connections. Default is 1.
AudioFollowsFocus—integer value, 0 or 1. If 0, sound from all sessions is audible. If 1, only
●
audible sound is from session that has focus. This value is only supported for RGS connections.
Default is 0.
MicrophoneEnabled—integer value, 0 or 1. If 1, analog microphone input from the access
●
device is sent to RGS sessions. This value is only supported for RGS connections. Ignored by RDP
sessions. This feature requires RGS 5.1.3 or later. Default is 0.
KeyRepeatEnabled—integer value, 0 or 1. If 1, disables key repeat suppression normally
●
required by RGS to keep keys in hot key sequences from repeating when held down. This value is
only supported for RGS connections. Default is 0.
MapUSB—integer value, 0 or 1. If 1, allows USB redirection. This value is only supported for
●
RGS connections. With RGS 5.1.3 or later, you may remap USB devices to a selected session
from the HP SAM Connection Bar. Default is 0.
ImageQuality—integer value, 0–100. Sets image quality; 0 = lowest quality, lowest network
●
bandwidth usage. 100 = highest quality, highest network bandwidth usage. This value is only
supported for RGS connections. Default is 65.
Compression—0 or 1. If 1, RDP compression is enabled. This value is only supported for RDP
●
connections. Default is 1.
Wallpaper—0 or 1. If 1, the remote desktop wallpaper is displayed. This value is only
●
supported for RDP connections. Default is 1.
Connbar—0 or 1. If 1, a small bar is displayed at the top of the window. This window allows
●
the user to minimize during a full screen session. This value is only supported for RDP connections.
Default is 1.
FullDrag
●
only supported for RDP connections. Default is 1.
44 Chapter 3 Installation
—0 or 1. If 1, window contents are shown while a window is dragged. This value is
Page 53

Themes—0 or 1. If 1, Windows XP themes are shown in the session. This value is only supported
●
for RDP connections. Default is 1.
Animation—0 or 1. If 1, menu animation is shown in the session. This value is only supported
●
for RDP connections. Default is 1.
Caching—0 or 1. If 1, RDP bitmap caching is enabled. This value is only supported for RDP
●
connections. Default is 0.
AutoReconnect—0 or 1. If 1, RDP reconnection is enabled. Not recommended for an HP SAM
●
solution. This value is only supported for RDP connections. Default is 0.
MapDrives—0 or 1. If 1, local drives are made available to the remote session. This value is
●
only supported for RDP connections. Default is 0.
MapPorts—0 or 1. If 1, local serial ports are made available to the remote session. This value is
●
only supported for RDP connections. Default is 0.
MapPrinters—0 or 1. If 1, local printers are made available to the remote session. This value is
●
only supported for RDP connections. Default is 1 for Windows and is not supported with the Linux
Client and Blade Workstation Client series.
MapSmartcards—0 or 1. If 1, local smart cards are made available to the remote session. This
●
value is only supported for RDP connections. Default is 1 for Windows and 0 for Linux Client and
Blade Workstation Client series.
ColorDepth—integer value, 8, 16, 24, or 32. The color depth for the RDP session. This value is
●
only supported for RDP connections. Default is 24-bit but, for Linux, it may be lower depending on
the capabilities of the graphics on the access device. 32-bit color applies only to Windows.
FullScreen—0 or 1. If 1, a full screen session is created. Default is 1.
●
Keys—integer value, 0, 1, or 2. Indicates how to handle special key combinations (such as Alt +
●
tab) within an RDP session. If 0, the keys are handled on the local machine. If 1, the keys are
handled on the remote machine. If 2, the keys are handled on the remote machine while the
session is full screen. This value is only supported for RDP connections. Default is 2.
Height—integer value. Together with Width, indicates size of the window. Default is 600.
●
Width—integer value. Together with Height, indicates size of the window. Default is 800.
●
RgsWarningTimeout—integer value. The timeout in milliseconds used to detect and notify the
●
user of a network disruption. For more information, see rgreceiver.network.timeout.warning in the
RGS documentation. The default value is the user interface value of 2000 milliseconds - two
seconds. The user interface displays this value in seconds. This value is only supported for RGS
connections.
RgsErrorTimeout—integer value. The timeout in milliseconds used to detect and disconnect an
●
inactive connection. For more information, see rgreceiver.network.timeout.error in the RGS
documentation. The default value is the user interface value of 30000 milliseconds - 30 seconds.
The user interface displays this value in seconds. This value is only supported for RGS connections.
RgsDialogTimeout—integer value. The timeout in milliseconds used to display and wait on
●
responses from input dialogs such as the authorization dialog and PAM authentication dialog. For
more information, see rgreceiver.network.timeout.dialog in the RGS documentation. The default
value is the user interface value of 15000 milliseconds - 15 seconds. The user interface displays
this value in seconds. This value is only supported for RGS connections.
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
45
Page 54

ClearType—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, support for Font Smoothing is enabled in an
●
RDP6 session. This option is ignored for RDP5, RGS, and rdesktop. Set to 0 to disable. Default
value is 0.
ComposedUI—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, support for Vista Aero interface is enabled
●
(Desktop Composition). This requires RDP6 and is ignored for RDP5 and RGS. Additionally,
various hardware and operating system requirements must be met before the Vista Aero interface
can be shown. Set to 0 to disable. Default is 1.
Autosize—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, an RDP session is automatically resized to fit
●
when its containing window is resized. When set to 0, the window maximum size is that of the
remote session, and when sized down, scroll bars appear. This value is ignored for RGS and
rdesktop and is only valid in a windowed session. Default value is 0.
MapClipboard—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, the clipboard will be made available to
●
remote sessions, and allows limited cut-and-paste functionality from the local machine to the
remote session or vice versa. This option is ignored for with RGS versions prior to 5.2 and with
RDP5. When set to 0, this feature is disabled. Default is 1.
NOTE: Enabling or disabling the clipboard in the HP SAM Client UI affects all sessions
connected using that client.
The clipboard setting can be forced using HP SAM policy. If the policy is assigned to roles, it is
possible for a user to have several sessions open simultaneously, where some sessions allow copy
and paste and others do not.
NetworkAuthentication—integer value, 0, 1, or 2. When set to 1, the RDP client warns when
●
connecting to a resource that cannot be authenticated. When set to 2, the RDP client refuses to
connect to an unauthenticated resource. When set to 0, the connection succeeds regardless of the
authentication state. This setting requires RDP6 and is ignored for RDP5 or RGS. Default value is 0.
MapDrivesList—string value, RDP6 or later only. This field is valid only if MapDrives is set to
●
1. This allows control over which logical drives are made available to the remote session. The list
corresponds to the RDP configuration file format, and it looks as follows:
MapDrivesList=c:;d:;e:;DrivesDynamic
In this example, the drives c:, d:, and e: are made available, along with the drives connected after
the session is established (DrivesDynamic).
Span—integer value, 0 or 1. When set to 1, specify that the session should span over all
●
available monitors (to the limits of the protocol being used). This setting requires RDP6 or RGS and
is ignored for RDP5. The default value for this option is 0 (session shown on single monitor).
Additionally, the following restrictions apply for RDP6:
Combined monitor resolution can be no greater than 4096x2048 pixels.
◦
All monitors must be at same resolution.
◦
All monitors must be aligned side-by-side.
◦
MatchClientDisplays—integer value, 0 or 1. Setting this parameter to 1 allows RGS to map the
●
sender displays to the client display devices. RGS sessions must line up with the physical display
boundaries on the client desktop in order to set valid display resolutions on the sender. Use this
feature for multi-display clients on senders that have multiple physical displays. Senders that are
configured to use a single logical display will cause RGS to revert to setting a single display
instead of multiple displays. RGS 5.1.3 or later is required. Default is 0.
46 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 55

Global and Local Client Configuration Files
This feature allows administrators to 'lock down' certain options, while allowing other options to be
altered by users.
There are three levels of files:
Global: hprdc_admin.sam
●
Local: hprdc_accessdevice.sam
●
Personal: hprdc.sam
●
The order of precedence is:
Personal file is read first.
●
XPe: Anywhere on file system (double-click hprdc.sam)
◦
XPe search locations used in this order—when one is found, it stops looking:
◦
%AppData%; Default for XP: C:\Document and Settings\<username>\Application Data
\hprdc.sam. Default for Vista or Windows 7: C:\users\<username>\AppData\Roaming
\hprdc.sam
Install directory; Default: C:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Session Allocation Client
\hprdc.sam
$SystemRoot%; Default: C:\windows
Workstation Client OS file location:
◦
/root/user/hprdc.sam
Linux Client:
◦
/root/hprdc.sam for the root user
/home/<username>/hprdc.sam for other users
Parameters in the local file override the personal parameters
●
XP file location is the install directory. Default: C:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Session
◦
Allocation Client\hprdc_accessdevice.sam
Workstation Client OS file location: /opt/hpsam/hprdc_accessdevice.sam (/root/writable/
◦
opt/hpsam/hprdc_accessdevice.sam)
Linux Client:
◦
/opt/hpsam/hprdc_accessdevice.sam
Parameters in the global file override the personal and local parameters
●
XP file location is the install directory. Default: C:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Session
◦
Allocation Client\hprdc_admin.sam
Workstation Client OS file location: /opt/hpsam/hprdc_admin.sam (/root/writable/opt/
◦
hpsam/hprdc_admin.sam)
Linux Client:
◦
Install and Validate the HP SAM Client Software
47
Page 56

Legal Banner
This allows a legal disclaimer to be displayed before logon. Name the file disclaimer.<file type> and
copy the file into the appropriate directory (create the folder, if necessary). The following are the
default paths:
Access Device Client: Installing the legal banner on an access device causes the banner to be
●
displayed on that access device only. Name the file disclaimer.<file type> and copy the file into the
following directory (create the folder, if necessary) on the access device:
◦
◦
◦
Web Client: Installing the legal banner on an HP SAM web server causes the banner to be
●
displayed to all users connecting via Web Client. Name the file disclaimer.<file type> and copy the
file into the following directory (create the folder, if necessary) on the HP SAM server:
◦
/opt/hpsam/hprdc_admin.sam
Windows: C:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Session Allocation Client\$LANG
\disclaimer.<file type>
Workstation Client OS: /root/writable/opt/hpsam/site/$LANG/disclaimer.<file type>
Linux: /opt/hpsam/site/$LANG/disclaimer.<file type>
Web Client: C:\program files\hewlett-packard\SAM\webclient\images\$LANG
\disclaimer.<file type>
NOTE: Windows:Replace $LANG with the appropriate folder name for the language desired: EN
for English, JP for Japanese, FR for French, DE for German, KO for Korean, or CN for Simplified
Chinese.
Linux Client and Workstation Client OS:: Replace $LANG with a folder name that directly
correlates with the keyboard/locale that has been chosen (during setup or later). For the US English,
en_US.UTF-8 is the correct locale. For other keyboards/locales, refer to the table below for the folder
names needed. For the Workstation Client Series, it's driven off /etc/kbd_lang.table, and it shows up
in the "About Box" you can get from the right-click menu on the desktop.
fr_BE.UTF-8 Belgian-French -- Français (Belgique)
en_CA.UTF-8 Canadian -- Français Canadien
zh_CN.UTF-8 Chinese, Simplified
zh_TW.UTF-8 Chinese, Traditional
da_DK.UTF-8 Danish -- Dansk
nl_NL.UTF-8 Dutch -- Nederlands
en_US.UTF-8 English, International
en_GB.UTF-8 English, UK
en_GB.UTF-8 English, UK Extended
en_US.UTF-8 English, US
fi_FI.UTF-8 Finnish -- Suomi
fr_FR.UTF-8 French -- Français
48 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 57

de_DE.UTF-8 German -- Deutsch
it_IT.UTF-8 Italian -- Italiano
ja_JP.UTF-8 Japanese
ko_KR.UTF-8 Korean
nb_NO.UTF-8 Norwegian -- Norsk
pt_PT.UTF-8 Portuguese -- Português
pt_BR.UTF-8 Portuguese-Brazil -- Português do Brasil
es_ES.UTF-8 Spanish -- Español
es_MX.UTF-8 Spanish, Latin America -- América Latina
sv_SE.UTF-8 Swedish -- Svenska
de_CH.UTF-8 Swiss-German -- Deutsch (Schweiz)
tr_TR.UTF-8 Türkçe
The following file types are supported:
JPG
●
GIF
●
BMP
●
NOTE: This feature is enabled by default if the disclaimer file is found in the correct location.
Deploy the HP SAM Registration Service to All HP SAM Computing Resources
For high volume deployment, HP highly recommends that you use a software tool such as HP Rapid
Deployment Pack.
1. Install the service on all computing resources.
2. Create the HP SAM registration service configuration file (hpevent.cfg) on a single blade and save
this file as a template to use later.
3. Start or restart service on a single computing resource and verify that the computing resource self-
registered into the HP SAM web server.
4. Deploy the HP SAM registration service configuration file (hpevent.cfg) to all appropriate
computing resources and start the service on those units.
Deploy the HP SAM Registration Service to All HP SAM Computing Resources
49
Page 58
Deploy HP SAM Client Software to All HP SAM Access Devices
To deploy the HP SAM Internet Explorer-based client, instruct your users to go to the HP SAM server
website(s) that you have set up.
If the access device is accessing the HP SAM server for the first time, the access device needs to install
two ActiveX controls (HP SAM Web Client Utility Class and Microsoft RDP Client Control). The installed
location for these controls are in the %SystemRoot%\Downloaded Program Files\ folder.
NOTE: Use the Web Client Controls installer found in the HP SAM SoftPaq so that you do not need to
download and install any controls automatically via the browser. This is useful when the access device
is locked down to the point where the user is not allowed to install ActiveX controls automatically from
the browser.
Various methods can be used to deploy the Windows-based HP SAM client to the access devices.
Following are two examples.
Use software deployment tools such as HP Rapid Deployment Pack.
●
a. Install the HP SAM client on the access devices.
b. Update the client hprdc.sam file to connect to the HP SAM server and specify desired settings
(see the customization steps for the specific HP SAM client type).
Post the HP SAM Windows-based client installation file on a website or fileshare. If you created an
●
hprdc.sam file for your environment, you should post this file also. Then instruct the users to:
a. Download and install the client software.
b. Place the config file (hprdc.sam) on the desktop.
c. Double-click the HP SAM file to launch.
NOTE: If a firewall is installed, make appropriate changes to allow the HP SAM client through.
Do this at the application level instead of the port.
50 Chapter 3 Installation
Page 59

4 Administration
Log In
In the Internet Explorer address bar, enter in the HP SAM web server name with “/manage” added to
the URL (for example, http://HP SAMservername/manage). Use “https:” if the HP SAM administrative
console has been set to require SSL.
If SSL is configured and a certificate-related security pop-up message is displayed, click Yes.
Once you get to the logon page, enter username, password, and click the Sign In button. You have
two ways to enter in your username. It can be entered as domain\username or your User Principal
Name (UPN) (yourname@yourcompany.com).
General Navigation and User Interface Design
The HP SAM administrative console is designed with tabs and hyperlinks for navigation. Depending on
the tab, there could also be a filter option section. The main work space or result list is at the bottom of
the page.
Display More (or Fewer) Items Per Page
The system defaults to show only a certain number of items per page. Select a new value (10, 25, 50,
100, 250, or 500) in the Show field to change this number. The page will immediately be updated to
reflect this new setting.
Move Columns
The system displays the result data grid in a certain way. You can move the columns by dragging and
dropping the column header to the appropriate place within the grid.
Sort Result List
Whenever there is a result grid, you can sort by any of the column shown. Click on the appropriate
column header to sort by that column. Click on the same column header to toggle between descending
and ascending.
Select More Than One Item
The top left side of the result grid includes a check box.
To select all items on all pages, not just the page shown, select this check box.
●
To clear all boxes on all pages, not just the page shown, clear this check box.
●
Log In
51
Page 60

Managing the HP SAM Administrator Access List
The Domain Administrator, Domain Users in the Administrators group on the domain controller, and
Domain Users in the HP SAM server Local Administrator Group are automatically members of the HP
SAM Administrator Group. To add another user to the HP SAM Administrator group, see
Attributes on page 57.
Add Individual Users to the HP SAM Administrator Group
If you are adding only a few users, add the names directly to the HP SAM Administrator group.
1. Go to the Add New Users page.
2. Set Search By to Users.
3. If you want to filter to a specific domain, in the Domain name list select the domain, or select
Global Catalog for all domains in the same Active Directory forest the HP SAM server is in.
4. Type one or more of the parameters, as shown in the following examples:
a. Last Name: Search is performed by last name when entering characters.
b. First name: Characters entered after a comma is typed initiate a search by first name. You
can also search by first name and last name by entering a space. Characters before the
space initiate a search by first name. Characters after the space initiate a search by last
name.
To Assign
c. UPN Name: Entering a name including an at sign (@) initiates a search by UPN Name
(i.e., jane.doe@)
NOTE: Results are shown as you type.
5. Click Add to add highlighted users to the list.
6. Select the users in the list that you want to add into HP SAM.
7. Click Save.
NOTE: After you have clicked Save, you can set user attributes, including Administrator Groups.
You also have the option of assigning dedicated resources automatically. If a user is already in HP
SAM, his attributes are changed to match what is set here.
52 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 61

Add Security Groups or Organizational Units to the HP SAM Administrator Group
To add many users:
1. Leverage Active Directory services by adding the names in Active Directory under a security group
or organizational unit.
2. Go to the Add New Users page.
3. Add the security group or organizational unit directly to the HP SAM Administrator group.
a. In Search By, select Organizations (OU) or Security Groups.
b. If you want to filter to a specific domain, in the Domain name list select the domain, or
select Global Catalog for all domains in the same Active Directory forest the HP SAM
server is in.
c. Search for groups by entering characters in the search field. Results are shown as you type.
You can highlight one group and use the View button to see the users who are direct
members of the group.
d. Click Add to add highlighted groups into the list.
e. Select the groups in the list that you want to add into HP SAM.
f. Click Save.
NOTE: After you have clicked Save, you can set SG or OU attributes, including Administrator
Group. If an SG or OU is already in HP SAM, the attributes are changed to match what is set
here.
NOTE: To make future changes, go to Active Directory and add or remove users from those groups.
You will not need to re-add the groups into HP SAM.
Remove Users or Groups From the HP SAM Administrator Group
To remove users from the HP SAM Administrators list, navigate to Users and Roles > Manage
users.
1. In the Filter Options section, from the Role list select [Administrator]. Administrator group
names are encased in square brackets, for example [Administrator Group].
2. Click Search.
3. Select the check box next to the appropriate names.
4. If you want to permanently delete the user(s) or group(s) from the system, select Delete in the
Operation list and click Go.
5. If you want to remove the user(s) or group(s) from the HP SAM Administrator Group without
deleting them from the system, perform the following steps:
a. In the Operation list, select Assign Attributes, and then click the Go button.
b. Next to the Administrator Group, select <blank> (or clear).
c. Click Save to save your changes.
Managing the HP SAM Administrator Access List
53
Page 62

HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
Home Tab
When you log onto HP SAM, the Home tab page is the default. HP SAM shows a snapshot of current
resource status grouped by roles, as a convenience to the administrator.
Users and Roles Tab
The Users and Roles tab facilitates the management of roles and user access list.
Manage Resource Roles
All roles, as created by computing resources when they self-registered or created with the Create
button, are shown.
Role column: A list of all roles.
●
NOTE: Role names are limited to 128 characters. If you type more than 128 characters for a
role name in a resource configuration file, the role name will work correctly, but it will be
truncated to 128 characters.
Asset Group column: Shows asset groups that belong to each role.
●
Description column: You can change the description for each role if the name by itself does not
●
clearly explain what it is or to further differentiate it from the other roles. The role name and
description are displayed to the user on the access device during connect phase, if the user has
access privilege to use more than one role.
Policy column: By default, the HP SAM client settings are assigned to the Global Policy. All
●
Global Policy connection forced settings, if any, within that policy are applied to all users.
NOTE: To override the Global Policy with another policy, create the policy first on the Policies
tab, and then reassign the role to use the appropriate policy here.
Enabled column:
●
If selected, the role is available for allocation.
◦
If there is no check mark, then all blades are unavailable for user connection through HP
◦
SAM within the scope of that role.
To change the setting, click the link for the role, select or clear the check box in the dialog
◦
box, and then click Save.
If the Enabled check box was cleared:
◦
- New user connection requests to this role are denied by the HP SAM web server.
- Current active connections are left as is.
- Disconnected users are not permitted to reconnect back to their disconnected sessions.
54 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 63

Public column:
●
If selected, the role is available for all users in Active Directory.
◦
If not selected, then the role is only available to user(s) in that particular role access list.
◦
To change the setting, click the link for the role, select or clear the check box in the dialog
◦
box, and then click Save.
Access Restriction column: Shows a summary of the resource reservations that have been
●
added to the role.
Create button: Click to create a new role that you can assign to resources.
●
Delete button: Click to delete selected roles.
●
Manage Asset Groups
The HP SAM administrator or domain administrator has full rights to all Asset Groups in the HP SAM
server. Asset Groups allow full HP SAM Administrators to limit or hide objects (resources, users, etc.)
that other administrators are allowed to see and manage:
Clients
●
Resources
●
Users, OUs, SGs
●
Roles
●
Monitor Layout IDs
●
Policies
●
Logs
●
Reports
●
The HP SAM administrator or domain administrator also creates the administrative groups.
Administrator groups can be assigned to control one or more asset group.
●
Users within each administrator group can control all assets in the Asset Groups identified.
●
Administrators will only be able to see assets associated with Asset Groups they control.
●
NOTE: The HP SAM administrator or domain administrator has full rights to all Asset Groups in the
HP SAM server.
Asset Group column: A list of all asset groups.
●
Description column: You can change the description for each asset group if the name by itself
●
does not clearly explain what it is or to further differentiate it from the other asset groups.
Create button: Click to create a new asset group.
●
You may also remove an asset group by selecting it and clicking Delete.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
55
Page 64

Manage Administrative Permissions
NOTE: You must have full HP SAM Administrator permissions to:
—Create, modify, or delete an Administrator group.
—Assign users to an Administrator group.
The following have this permission:
—HP SAM Server administrators
—Domain administrators
—Domain users assigned to “Administrator” Administrator group in HP SAM
Use this window to customize permissions for differing levels of administrator access. After you create
administrative levels, to grant user access you must add the users to the Administrator groups you
created.
NOTE: If you assign a user to multiple Administrator Groups which have different sets of access
privileges, the user will have all the privileges from the assigned Administrator Groups.
To create a new administrative permission group:
1. Click Create.
2. In the Group Name box, type a name for the administrator group.
3. In the Description box, type a description for the group.
4. In the Asset Group Assignment fields, select the asset group(s) to associate with the new
Administrator group.
5. In the Category list, select the category for which to specify specific permission levels.
6. In the Permissions area, select the permissions to allow for this category for this specific
administrative group.
7. Repeat steps 5 and 6 for each category.
8. Click Save.
To modify an Administrator group:
1. Select the group to modify by clicking the group name hyperlink.
2. Make changes as necessary.
3. To change values for the different categories, select a category from the Category list, and in the
Permissions area, change the permissions as necessary. Repeat this process for each category
you want to modify.
4. Click Save.
To delete an Administrator group:
1. Select the group or groups to delete. You can delete more than one group using this procedure.
2. Click Delete and click OK to confirm.
56 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 65

Manage Users
By default, the search shows all users, security groups, and OUs.
Search For: Organizations (OU), Security Groups, Users—Select in which group or
●
groups you want to perform the search
Filter Options: You can narrow the list of users shown by using the filter options. The filter
●
option is based on “AND” combinations, so the more boxes you enter, the narrower the list of
users shown.
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Operation
Name—Type the name to search for.
Role—Select the role to search within. Names with square brackets ([ ]) around them are
Administrator groups, for example, [Administrator]. Names without brackets are resource
roles.
Asset Group—Show users or groups that belong to a specific asset group.
First Name—Type a first name by which to search.
Last Name—Type a last name by which to search.
Domain Name—Type a domain in which to search.
To perform any of the operations listed below:
1. Select the appropriate user(s).
2. Select the task to perform from the Operation list.
3. Click the Go button.
To Assign Attributes
On this page, you can modify the roles and asset groups assigned to a user, assign a policy, and
assign an Administrator group to a user.
To assign attributes to a user:
1. Set the appropriate filter options (for example, filter the role from the list).
2. Click Search.
3. Select the check box next to the appropriate name(s).
4. From the Operation list, select Assign Attributes, and then click Go to open the Assign User
to Policy/Role window.
5. If you want to assign a policy to a user, select the policy from the Policy list.
6. If you want to assign the user to an Administrator group, select the group from the
Administrator Group list.
NOTE: Administrator groups are available only for Security Groups and user accounts.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
57
Page 66

7. Double-click asset groups or use the arrows between the Available and Selected boxes to move
the asset groups. Place all asset groups you want to assign to the selected user in the Selected
box.
8. Double-click roles or use the arrows between the Available and Selected boxes to move the
roles. Place all roles you want to assign to the selected user in the Selected box.
9. Click Save to save your changes.
To Assign Resources
This option allows you to assign a specific resource (such as a blade PC) to a user. You can also assign
a backup to a dedicated resource, as well as assign a user-friendly name to the resource. You have
three ways to assign resources:
Select a single user and assign resources manually.
●
Select one or more users and have their attributes and resources automatically assigned based on
●
a single template user.
Select one or more users and a role and have blades automatically assigned to each user from the
●
role.
NOTE: The Template User must have a statically assigned blade in a role and there must be enough
available resources in that role to satisfy the users during automatic assignment of static resources.
If a blade is in a dynamic role and is reassigned as a dedicated resource to a user, that blade is no
longer available for allocation in the dynamic role to any other user, even if the current status is
Available. With the exception of the template user, it is highly recommended that dedicated resources
not be assigned to a dynamic resource role, which will then help you accurately track Available and
In Use resources.
To Assign Resources Manually
1. Click Manage users.
2. Search for the user from the HP SAM database.
3. Select the check box next to the appropriate name.
NOTE: To assign resources manually, select only one name.
4. Select Assign Resources in the Operations field, and then click the Go button to open the
Assign Resource to User(s) window.
5. Select Manually Assign Resources, and click Continue.
6. If you want to assign a dedicated resource to the user:
a. Click Add.
b. Type the IP address or host name of the resource.
c. Click Search to search for resource to assign.
d. Select the resource from the list.
58 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 67

e. Click Save to change the resource assignment.
f. Repeat a–e for each additional resource to be assigned to the user.
7. If you want to change the friendly name for the resource, click the link in the Friendly Name
column, and then type a new friendly name for the resource in the Update Friendly Name
window.
The default friendly name is the resource host name.
8. If you want to assign a backup for the dedicated resource, in the Backup column, click either
Role or Resource for the user.
To select a role:
Select a role to assign as a backup for the user, and then click Save.
▲
To select a resource:
a. Type the IP address or host name of the backup resource, and then click Search.
b. Select the resource to act as the backup, and then click Save.
9. To remove everything on this row: dedicated resources, backup roles, and backup resources, click
Remove in the Operation column.
10. To remove the backup resource or role only:
a. Click the backup role or resource in the Backup column.
b. If removing a role, click the Role button, and then clear the check box of the role you want
to remove.
c. Click Save.
d. If removing a resource, click the Resource button, click Search, and then clear the check
box of the resource you want to remove.
e. Click Save.
11. Click Close.
To Assign Resources Automatically from Template User
1. Click Manage users.
2. Search for user(s).
3. Select the check box next to the appropriate name(s).
NOTE: Multiple users may be selected.
4. Select Assign Resources from the Operation list and click Go.
5. Select Assign Resources from Template User.
6. Select the template user from the list.
7. Click Continue.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
59
Page 68

NOTE: A message will be displayed if you attempt to assign resources to a user who already has
resources or if the primary roles do not have enough resources available.
The template user must have at least one dedicated resource that exists in a role. Only primary roles
are considered when assigning dedicated resources to multiple users. The selected users will be
assigned dedicated resources from free resources in this role. The selected users will also be assigned
the same Roles, Asset Groups, and Policies as the template user. The selected users will not be assigned
an Administrator group based on the template user.
To Assign Resources Automatically from Role
1. Click Manage users.
2. Search for user(s).
3. Select the check box next to the appropriate name(s).
NOTE: Multiple users may be selected.
4. Select Assign Resources from the Operation list and click Go.
5. Select Assign Resources from Role.
6. Select the role from the list.
7. Click Continue.
NOTE: A message will be displayed if the role does not have enough resources.
Only primary roles are considered when assigning dedicated resources to multiple users.
To Assign and Configure a Monitor Layout for the User
NOTE: You should create the monitor layout before assigning it to the user. See Manage Monitor
Layout on page 65.
1. Select the check box next to the appropriate name.
2. From the Operation list, select Assign Monitor Layouts, and then click the Go button to
open the Monitor Layouts for <username> window, which shows the monitor layouts, if
any, assigned to the selected user.
3. Click Add.
4. Select the monitor layout to be added from the Monitor Layout ID list.
5. Select the check box next to the computing resource(s) and role(s) you want to assign to the
monitor layout.
6. Type the new resolution width and height and the horizontal and vertical offset.
NOTE: If you do not specify the resolution and offset configuration, the system default
parameters are used.
7. Select the Common Policy, which specifies which session’s policy to use when all sessions are
connected.
60 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 69

8. Select the USB Default, which is the session you want RGS to use by default with USB devices
connected to the access device.
9. Click Save.
To Change the Monitor Layout Configuration for the User
1. Select the check box next to the appropriate name.
2. From the Operation list, select Assign Monitor Layouts, and then click the Go button to
open the Monitor Layouts for <username> window, which shows the monitor layouts, if
any, assigned to the selected user.
3. Click the link in the Monitor Layout ID column.
4. Type the new resolution width and height, the horizontal and vertical offset, common policy, and
USB default.
5. Click Save.
To Delete a Monitor Layout ID for the User
1. Select the check box next to the appropriate name.
2. From the Operation list, select Assign Monitor Layouts, and then click the Go button to
open the Monitor Layouts for <username> window, which shows the monitor layouts, if
any, assigned to the selected user.
3. Click Remove in the Operation column.
To Delete a User
Deletes a user from the system.
To delete a user:
1. Select the check box next to the appropriate name(s).
2. From the Operation list, select Delete, and then click the Go button.
Add New Users
For any role that is not public, users must be in the HP SAM access list to request a computing resource
(such as a blade PC) from that role. You can add the user as an individual, in a security group, or in an
organizational unit. When the system searches for the accounts added, it uses the HP SAM web server
domain and/or other Active Directory servers that are in the same forest as configured in the System
Settings > Active directory tab.
To Grant Access to Individual Users
1. Go to the Add New Users page.
2. Set Search By to Users.
3. If you want to filter to a specific domain, in the Domain name list select the domain, or select
Global Catalog for all domains in the same Active Directory forest the HP SAM server is in.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
61
Page 70

NOTE: Searching by Global Catalog displays all users from external domains. Users from other
domains can be added to HP SAM using Global Catalog, but they may not be able to log on if
the External setting has not been selected on the Active Directory page of the System
Settings tab.
4. Type one or more of the parameters, as shown in the following examples:
a. Last Name: Search is performed by last name when entering characters.
b. First name: Characters entered after a comma is typed initiate a search by first name. You
can also search by first name and last name by entering a space. Characters before the
space initiate a search by first name. Characters after the space initiate a search by last
name.
c. UPN Name: Entering a name including an at sign (@) initiates a search by UPN Name
(i.e., jane.doe@)
NOTE: Results are shown as you type.
5. Click Add to add highlighted users to the list.
6. Select the users in the list that you want to add into HP SAM.
7. Click Save.
To Grant Access to Security Groups or Organization Units
To add many users, leverage Active Directory services by adding the user names in Active Directory
under a security group or organization unit. Then add the security group or organization unit directly to
the HP SAM role access list. To change to the access list, go to Active Directory and add/remove users
there instead of the HP SAM administrative console.
1. Go to the Add New Users page.
2. Set Search By to Organizations (OU) or Security Groups.
3. If you want to filter to a specific domain, in the Domain name list select the domain, or select
Global Catalog for all domains in the same Active Directory forest the HP SAM server is in.
4. Type the name of the Organization (OU) or Security Group.
NOTE: Search for groups by entering characters in the search field. Results are shown as you
type.
5. Click Add to add highlighted groups to the list.
6. Select the groups in the list that you want to add into HP SAM.
7. Click Save.
Resources tab
The following sections explain what is available under the Resources tab.
62 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 71

Manage Resources
By default, the search shows all computing resources (such as blade PCs). You can narrow the list of
resources shown by using the filter options. The filter option is based on “AND” combinations, so the
more boxes you enter, the narrower the list of resources shown. The following are your filter options:
IP Address/Host Name—Show the list of resources where the IP address or host name
●
matches what you entered (or range or set of computing resources matching what you entered).
Dedicated Resource—Select to narrow the search to resources assigned as dedicated
●
resources.
Enabled—Show resources that are manually enabled or disabled only.
●
Role—Show resources that belong to a specific role.
●
Asset Group—Show resources that belong to a specific asset group.
●
Available—Show resources that are available for allocation (no users connected).
●
Disconnected—Show resources that have users in a disconnected state.
●
In-Use—Show resources that have users actively connected.
●
Offline—Show resources that are not available for allocation because the registration service is
●
not responding (service is not working properly, the hardware was powered off, etc.).
Auto Refresh Feature
After performing a search and displaying a list of resources, the following features are available.
Auto Refresh (seconds)—This feature allows the Resource tab web page to automatically refresh.
Doing so, the list of computing resources shown is pulled from the database with the latest information.
NOTE: If this option is turned on, then HP SAM administrative console does not time-out and log you
off the HP SAM administrative console. This could be a security issue, especially if the session is on a
public terminal and the user forgets to shut down the browser or log out.
To use, set the value to 5, 15, 30, or 60 seconds, turn off, set the value to Off, and then click Apply.
The setting takes effect immediately.
View Details
To view detail information regarding a resource, click on the magnifying glass under the Details
column.
NOTE: For a quick view to see who is currently connected to or disconnected from a computing
resource, move the mouse slowly to hover over the icon under the State column. This displays the user
account associated with that blade.
Operations
NOTE: Some of the operations below, such as Logoff, Restart, and Shutdown, require the HP
SAM Service Account to have administrative privileges on the computing resource (such as a blade
PC).
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
63
Page 72

To perform any of the operations listed below:
1. Select the appropriate resource(s).
2. Select the task to perform in the Operation list.
3. Click the Go button.
Operations
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Delete—Delete the resource from the system. Do this to clean up the database. You can delete
the computing resource only if its current status is Offline.
Disable—Prevent the resource from further allocation. If In-use, the current user session is
unaffected. If Disconnected, the user is not able to log back into the computing resource.
Enable—Allow the resource to be allocated.
Logoff User—Force logging off the current user on the resource.
Restart—Reboot the resource.
Send Message—Send a text message to the user on the resource (a pop-up message).
Not supported with Linux resources.
Shutdown—Power down the resource.
NOTE: Starting with SAM 3.2, the Logoff, Restart, and Shutdown operations are now supported
with Linux resources. To enable this, a certificate from the domain certificate authority must be
installed on the HP SAM website in IIS.
Synchronize—Send a request directly to the resource for it to send back its current status. In
●
normal situations, this is not needed, since the registration service sends back its status whenever
there is a change in status (power on, power off, user logon, user disconnect, and user logoff).
This is useful in situations where the network was temporarily interrupted between the resource
and HP SAM server in order to get the current status of the resource.
Assign Roles—Assign new roles to the resource. This setting overrides the configuration file for
●
the resource.
If you select this option, the Resource Role Assignment window opens. Use this window to select
primary and alternate roles for the resource.
You can also create new roles from this window.
NOTE: Once assigned to roles using the HP SAM administrative console, any changes to roles
in the configuration file will be ignored. To revert back to using the configuration file, delete the
resource from the database, and then restart the computing resource.
Assign Asset Groups—Assign new asset group(s) to the resource.
●
Customize View
Use this window to customize the columns that appear for the resources displayed on the Manage
Resource window. You can use the arrows, or you can double-click the items in the Available and
Selected boxes to move them back and forth. The single arrow moves only the selected item, while the
64 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 73

double arrows move all items in the list. You can display a minimum of three and a maximum of six
columns.
Manage Access Devices
To Add an Access Device Manually
NOTE: The Windows-based client, Blade Workstation Client, and Linux Client register access devices
automatically upon connection to the HP SAM server. The XP Embedded OS image on some thin client
access devices lack support needed for this to occur. For these systems, follow the instructions in the
CIMWIN32 folder found in the AddOns folder in the HP SAM SoftPaq.
1. Click Create.
2. Type the serial number and friendly name.
3. You may select the Asset Groups to which this access device will have access, if you want.
4. You may select a Monitor Layout, if you want.
5. Click Save.
To Change an Access Device
1. Type one or more parameters and click Search, or click Search to find all registered access
devices.
2. If you want to change the settings for the access device:
a. Click the Serial Number link, and then change desired settings for the access device in the
dialog box.
b. Click Save.
To Delete an Access Device
NOTE: You cannot delete an access device while it is in use.
1. Type one or more parameters and click Search, or click Search to find all registered access
devices.
2. Select the check box next to the appropriate access device or devices.
3. Click Delete and OK.
Manage Monitor Layout
This allows you to create a new layout or to modify or delete an existing layout.
To Create a Monitor Layout
1. Click Create.
2. Type the monitor layout ID.
3. Type a description of the layout.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
65
Page 74

4. Select the Asset Groups associated with this monitor layout.
5. Click Save to add the new ID.
To Modify a Monitor Layout
1. If you want to change the name, description, or asset group of the monitor layout, click the link in
the Monitor Layout ID column and then change the desired settings.
2. Click Save to change the monitor layout ID.
To Delete a Monitor Layout
1. Select the check box next to the appropriate monitor layout.
2. Click Delete and then click OK.
Manage Data Centers
Data Centers in HP SAM are groupings of enclosures. Data centers serve only to save enclosure
passwords in order to enable the feature which allows users to power cycle blades from the HP SAM
Connection Bar.
NOTE: Version 4.20 or later Integrated Administrator (IA) software must be used on the HP
BladeSystem PC Blade Enclosure(s). By default, the IA software has a disabled SAM account. You must
enable the SAM account and create a password for the powercyle option to work.
The IA password for the built-in SAM account must be saved in HP SAM on the Manage Data Centers
page.
Blade power management in C-class enclosures (Blade Workstations) is not supported.
To Create a Data Center
1. Click Create.
2. Type the data center name and enclosure password.
3. Click Save.
To Change a Data Center
1. Click on a link in the Data Center column.
2. Change the Data Center name and/or password.
3. Click Save.
To Add Enclosures into a Data Center
1. Select the check box for the appropriate data center.
2. Choose View Enclosures from the Operation list and click Go.
3. Click Add.
4. Enter search terms (optional) then click Search.
66 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 75

5. Select the check boxes for the enclosures to add, and then click Save.
6. Click Close.
To Delete Enclosures from a Data Center
1. Select the check box for the appropriate data center.
2. Choose View Enclosures from the Operation list and click Go.
3. Select the check boxes for the enclosures to delete.
4. Click Delete.
5. Click Close.
To Delete a Data Center
1. Select the check box for the appropriate data center or data centers.
2. Choose Delete from the Operation list and click Go.
3. Click OK.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
67
Page 76

Policies Tab
Policy management allows administrator to override the user’s HP SAM client settings. In general, the
user is allowed the flexibility to customize the connection settings on the client side. If there are specific
settings that the user must always connect with, then the administrator may use the Policies tab to
define the forced settings.
The HP SAM hierarchical policy has 5 levels:
Global
●
Role
●
OU (organizational unit)
●
Security Group
●
User
●
Policy settings assigned to User override policy settings assigned to a Security Group, and so forth up
the list.
Steps:
1. Create or update the policy in the Policies tab. To update an existing policy, click the policy
name hyperlink.
2. Assign the policy:
to a role (User and Roles > Manage resource roles)
●
to a user, OU, or Security Group (User and Roles > Manage users)
●
HP SAM always creates the Global Policy. This policy applies to all user connections, unless overridden
by other policies. The default sets the Auto Reconnect box to Off. This ensures multiple users do not
attempt to log onto the same blade at the same time. When a network failure or something similar
occurs, the user may unknowingly have been logged off that resource, depending on the network and
AD group policy settings. HP SAM may allocate that computing resource to another user. If the autoreconnect feature is turned on, the original user reconnects to this computing resource, which could
potentially have been allocated to another person. If this is not a concern, then change Auto Reconnect
to an appropriate value.
Table 4-1 Effective Hierarchical Policy Example
Parameter Global Role OU SG1 SG2 User Effective
P1 ON Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned ON
1
P2
P3 ON OFF ON OFF Not Assigned Not Assigned OFF
2
P4
ON OFF Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned OFF
ON/No
Overrides
Allowed
OFF Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned ON
P5 ON/No
Overrides
Allowed
68 Chapter 4 Administration
OFF/No
Overrides
Allowed
Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned Not Assigned ON
Page 77

Table 4-1 Effective Hierarchical Policy Example (continued)
Parameter Global Role OU SG1 SG2 User Effective
3
P6
1
The order of policy assignment is User (highest) > Security Group > OU > Role > Global Policy (lowest).
Individual parameters assigned at the User level override parameters set at the Group level, and so forth. Note that Parameter
P2 is set at ON at the Global level, but is overridden by the OFF setting at the higher Role level, leaving an effective setting of
OFF.
2
No Overrides Allowed can be set at any level to prevent override by parameters set at higher levels. Note that the No
Overrides Allowed setting ON for Parameter P4 at the lowest Global level overrides the OFF setting at the higher Role level.
This option does not affect whether or not the effective setting is forced upon the user. The effective setting is always forced.
3
At the Security Group level, HP SAM checks all Security Groups in alphanumeric order and uses the policy, if any, in the first
Security Group encountered. Note that Security Group 1 is the first Security Group encountered, so the OFF setting for
Security Group 1 leaves Parameter P6 with an effective setting of OFF, and the ON setting for Security Group 2 is ignored.
ON OFF ON OFF ON Not Assigned OFF
The No Overrides Allowed option is set for a specific setting to prevent inheritance of other policies
that would override the setting.
Create or Update a Policy
To create a new policy, click the Create button and type a new policy name. To update or edit an
existing policy, click the policy name hyperlink. When the Update Policy window displays, set the value
that you want or leave the value blank to allow it to inherit a value.
When you update or create policies, you can view all available properties, or you can specify valid
properties for either RGS or RDP. In the Show Properties list, select either ALL, RDP5, RDP6, or
RGS to determine which values are active on-screen.
NOTE: For more information about RGS, refer to your Remote Graphics Software documentation.
View Effective Policy
Use this feature to view the effective policy for a given user. See Table 4-1 Effective Hierarchical Policy
Example on page 68.
1. Click View Effective Policy.
2. Type the UPN name of the user.
3. Click Go.
The hierarchical merge of policies applied to the user is displayed.
NOTE: You may also select a Role for the user to view the effective policy based on that Role, since
the effective policy can be different with each Role to which that user belongs.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
69
Page 78

System Settings Tab
This tab allows the administrator to set how the HP SAM server behaves.
General
This page allows the administrator to define the settings for the entire system. Make the appropriate
change(s) and click Save to apply.
New Role Settings—When a new role is created (computing resource self-registers with a role
●
that is brand new to the system), the flags are set accordingly based on the value assigned.
Enabled—If selected, when a new role is created, the role's enable flag is set to checked,
◦
which means the role is available immediately for allocation.
Public—If selected, when a new role is created, the public flag is set to checked, which
◦
means the role does not require any user access restriction.
New Resource Setting—When a new computing resource self-registers, the system
●
immediately sets it enabled or disabled for allocation.
Time Zone Synchronization—If selected, the time zone setting on the computing resource is
●
set to the same time zone as the user’s access device.
Log—If selected, the system collects audit log data. You can view log data from the Log tab.
●
NOTE: Log data can quickly and significantly increase the size of the HP SAM database. If
enabled, it is highly recommended that you set up a log maintenance schedule. See
Clean Up Scheduler on page 73.
History—If selected, the system records and retains historical data for reports for the number of
●
days selected in the Keep raw data for list. Use this option to limit the history database size.
Microsoft 2005 or 2008 Express Edition includes a database size limit of 4 GB. Data older than
the value in the Keep raw data for list is summarized into one entry per day. You can view
history data from the Reports tab.
Authenticate Before Allocation—If selected, HP SAM will authenticate user's passwords with
●
AD before allocating a resource to the user. This may be desirable in security-conscious
environments. If the Allow Expired Passwords option is enabled, HP SAM will allow users
who have expired passwords to be allocated to resources so they can update the password using
the operating system on the resource.
Synchronization Request Retries—The number of retries the system performs before marking
●
the resources as offline.
Synchronization Time Between Retries—The number of seconds the system waits between
●
the retries for the synchronization operation.
User Sign-in Time Out—The number of seconds allowed for the user to complete the log on
●
process. The resource will not be allocated to other users during this period. If time expires without
completing a logon, the computing resource is returned to the available list.
Audit Log
Access Restriction Warning Time Out—The time, in seconds, before the access restriction
●
feature forces a logoff that the user will see a warning dialog regarding the impending logoff.
70 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 79

Multi-Session Autoconnection—When enabled, allows the system to autoconnect users to all
●
resources of the chosen type which are assigned to the user when user is on an access device
without a monitor layout ID assigned. Select one or more:
Dedicated Resources
◦
Roles with Public Enabled
◦
Roles with Public Disabled
◦
Client-Resource Network—When the access device connects to the computing resource, you
●
can specify which method it uses.
Host Name—If this is chosen, the system passes the resource Computer Name to the
◦
access device in order to connect and relies on the DNS server to resolve the name to the
appropriate IP address.
IP Address—If this is chosen, the system passes the IP address of the computing resource to
◦
the user access device to connect. If the computing resource has more than one network
card, you must specify an option.
- Reported Subnet—The subnet to which the computing resource used to register/
communicate with HP SAM.
- Specified Subnet—If both the HP SAM server and the computing resource each have two
NICs communicating through two independent subnets, then it is necessary to specify which
subnet the access device needs to use to make a connection request.
NOTE: HP SAM allows you to enter in only one subnet range. If the network environment is complex,
then you must use Host Name instead of IP address.
Web Client
This page allows the administrator to define the settings for the web client. Make the appropriate
changes and click Save to apply.
●
●
●
●
●
●
Enable Access—Select this option to allow users to request a desktop session through the
Internet Explorer-based client.
Cookies—Select User choice so the user has the option to save the user name, domain, and
client settings information on the access device browser cookies. If you have a security concern
(i.e., public terminal access), then select Do not allow so the information is not saved, and the
user must always type in the user name and domain.
Show domain field—Select Enabled to show the domain input field and allow users to
specify a domain. If this option is not selected, users must type a UPN-formatted name.
Show password field—Select Enabled to show the Password field on the web client
screen.
Show configuration options—Select Enabled to show the configuration link on the web
client screen.
Show resolution selection—Select Enabled to show the resolution selection on the web
client screen.
Default domain—Type the default domain for web client log on.
●
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
71
Page 80

Banner text—Select the language and type the appropriate message in the box to change the
●
customizable message that is displayed to the user on the HP SAM web client page.
Smart Card
●
Smart card login—Select the value for the type of logon you want.
◦
- Disallowed—Select to disable logging in using a smart card. Only the traditional logon
information fields are displayed.
- Optional—Select to make optional the use of a smart card to logon. All logon fields are
displayed.
- Required—Select to require use of a smart card to logon. Only the smart card logon
information is displayed.
User name field—Select the appropriate value for the field on the certificate that contains
◦
the user’s logon name.
- Email—Select to have HP SAM look in the e-mail field on the certificate to find the logon
name. The data found in this field must match the user's UPN name.
- UPN—Select to have HP SAM look in the UPN field on the certificate to find the logon
name.
Auto-connect—Select Enabled so the client automatically connects when the user inserts
◦
the smart card.
Cryptographic service providers (CSP)—Type the name of the CSP that supports the
◦
smart card solution you select when configuring smart card logon. This value represents the
identifier of the cryptographic service provider (CSP) to use. Use the Create, Edit, or
Delete buttons to take the appropriate action for this value.
Active Directory
This page sets the system link to Active Directory services to retrieve user account information.
External—Select this option to search all domains.
●
NOTE: Clearing this box will not prevent users in other domains from appearing when
searching on the Add New Users page of the HP SAM administrative console. It will, however,
prevent HP SAM from allocating resources to those users when logging in via the HP SAM client.
Server Query Time Limit—Type the time-out value for HP SAM to wait while Active Directory
●
server extracts account information. The HP SAM web server retrieves user account information as
it is returned from Active Directory server within this time limit. Increase the value only if you have
been instructed to do so on the HP SAM administrative console on the Add New User page.
72 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 81

Auto Schedules
NOTE: These schedules can now be found on the Auto-Schedules page instead of the top menu.
Resource Synchronization Scheduler
To schedule when to run the synchronize operation task to capture any resources that are offline, set the
timer as instructed below and click Create or Update. In general, you do not need to do this if the
resources are running under normal operation. If you feel more comfortable knowing on a regular basis
that there is a heartbeat from the resource, then schedule the synchronize operation to run at the
appropriate interval (for example, once a day at midnight.)
Auto-Schedule Event—To turn it on, check the Enabled box.
●
Scheduled Start Date—Select the date when event is to start.
●
Scheduled Time—Select the time when the synchronization operation is to run. Check as many
●
times as needed.
Scheduled Day—Select one of the following options:
●
Daily—Enter the number of days after which the event is to recur.
◦
Weekly—Enter the number of weeks after which the event is to recur and on which day(s)
◦
of the week it is to recur.
To run the synchronization operation task manually, click the Resources tab, locate and display a list
of resources, and select the resources to synchronize. Then select the Synchronize option from the
Operation list.
Audit Log Clean Up Scheduler
To schedule when the system needs to run a database cleanup operation, set the timer as instructed
below and click Create or Update. This should be done to help keep the database to a manageable
size and minimize HP SAM performance impact.
Auto-Schedule Event—To turn it on, check the Enabled box.
●
Scheduled Start Date—Select the date when the event is to start.
●
Scheduled Time—Select the time when the synchronize operation is to run. Check as many as
●
appropriate.
Scheduled Day—Pick one of the options below.
●
Daily—Type the number of days after which the event is to recur.
◦
Weekly—Type the number of weeks after which the event is to recur and on which day(s) of
◦
the week it is to recur.
Clear Options
●
Delete entries older than—Type the number days to keep entries and delete if older.
◦
Delete types—Check Information, Warning, and/or Error to delete.
◦
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
73
Page 82

Delete without saving—Select this if it is okay for the data to be permanently deleted.
◦
Save as CSV file and then Delete—Select this to save to an external text file before
◦
deleting the data permanently.
—Type the file path where you want to store the CSV file.
Log Off User from Resource Scheduler
To schedule when the system will forcibly log off users from their resources, set the timer as instructed
below and click Create or Update.
NOTE: A certificate from the domain certificate authority must be installed on the HP SAM website in
IIS for this feature to work.
Auto-Schedule Event—To turn it on, check the Enabled box.
●
Scheduled Start Date—Select the date when the event is to start.
●
Scheduled Time—Select the time when the logoff operation is to run. Check as many as
●
appropriate.
NOTE: The time set here is the time of the HP SAM server. If the resources are in a different time
zone from the HP SAM server, you need to adjust this time appropriately.
Scheduled Day—Pick one of the options below:
●
●
Licensing
By default (i.e., no license key entered), you are allowed to run up to 30 resources (such as blade PCs).
This is meant for evaluation purposes only. For production environments, even for fewer than 30
resources, you must purchase licenses for all resources. There is no expiration date for this evaluation
software.
HP SAM licensing is done per resource, not per user. For example, in an environment with 300 users
sharing 100 resources, only 100 licensed seats are necessary. If the number of resources exceeds the
number of licensed seats, an orange warning banner is shown in the HP SAM administrative console.
No functionality is lost in this situation. HP SAM licenses are floating licenses that are not tied to a
particular resource.
License keys for HP SAM are encoded with a specific number of seats (resources), a version number,
and a Software Assurance (SA) expiration date, if applicable. This information can be seen on the
Licensing page described in this section. The version number determines which major HP SAM revision
the license is intended to cover. For example, a license key with a version of 2 means it was created for
use with HP SAM version 2.X. This license can be used to license resources in any 2.X version of HP
SAM. The license will never expire as long as a 2.X version is being used.
Daily—Type the number of days after which the event is to recur.
◦
Weekly—Type the number of weeks after which the event is to recur and on which day(s) of
◦
the week it is to recur.
Roles—Transfer roles from the box on the left to the box on the right to have users on the
resources in those roles logged off automatically at the specified time(s.)
Continuing the example above, if HP SAM is upgraded to a 3.X version, the version 2 license will
continue to work with any SAM version with an Effective Date (shown at the top of the HP SAM
74 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 83

administrative console) that is before the SA expiration date. If you install a version of SAM which has
an Effective Date that is after the SA expiration date, those licenses will no longer count. This may
cause an orange warning banner to be shown saying you have more resources than licenses. Even in
this situation, no functionality will be lost. The customer must then purchase version 3 licenses or revert
to an older version of HP SAM.
Click the Enter New Key button to add a new key to HP SAM. Once entered, the system displays the
information encoded on the key. To delete the key from the system, check the appropriate key(s), and
then click Delete.
NOTE: In order to successfully enter the license key for HP SAM, the HP SAM service account must be
a member of the server's Local Administrators group.
If a license message displays on the HP SAM administrative console at any time, go to this area to view
the details of the license message.
Reports Tab
NOTE: You must enable history recording in System Settings > General to populate reports.
Administrators are only able to see reports associated with the Asset Groups they control.
HP SAM provides three reports:
Resource Capacity Consumption Report—See the peak resource usage levels in terms of
●
percentages and highlight if any percentage value exceeds a specified threshold value.
Resource Capacity Consumption Trend Report—See the charting of peak resource usage
●
levels over a time period.
Resource Utilization Report—See the current status of resource usage activities. This report is
●
also posted on the main Home tab.
Resource Capacity Consumption Report
Select the filter options and display options, and click the Generate Report button.
Filters
Time Frame (From/To)—Narrow the data to show the time period you are interested in
●
Role Enabled—Narrow the data to all roles that are enabled only (Yes), disabled only (No), or
●
ignore this flag by selecting Both.
Role Public—Narrow the data to all roles that have no user access list restriction (Yes),
●
restricted access role (No), or ignore this flag by selecting Both.
Roles—See data for the selected roles only. If you choose this option, the system narrows the
●
selection based on your previous selections above.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
75
Page 84

Display Options
Threshold Percentages—On the report you can highlight the data if it exceeds the number
●
entered here.
◦
◦
Open in New Window—If selected, the result data are shown in a new browser window.
●
Output Report
Role Name—Name of role.
●
Minimum Available %—For the time period chosen, the peak value of minimum available is
●
shown. This value indicates the percentage of computing resources that are still available for
allocation dropped to this lowest value.
Minimum Available—This value complements the percentage number above to show
●
specifically how many resources within that role are still available.
Maximum Consumed %—This value indicates the highest percentage of resources that were
●
consumed during the time period chosen.
Maximum Consumed—This value complements the percentage number above to show
●
specifically how many resources within that role were consumed.
Minimum Available—If data is below the value entered, the report highlights it.
Maximum Consumed—If data is above the value entered, the report highlights it.
Out of Resource—For the time period chosen, this value indicates how many times the system
●
encountered the situation where there is no available computing resource to fulfill the connection
request.
NOTE: In general, the maximum consumed should be opposite of the minimum available. The
exception is when the computing resource is in multiple roles. Then the resource is counted multiple
times, one per role that it is in. If the computing resource is disabled, it is not counted in the overall
number.
Resource Capacity Consumption Trend Report
Select the filter options and display options, and click the Generate Report button.
Filters
Time Frame (From/To)—Narrow the data shown to the time period you are interested in
●
Role Enabled—Narrow the data to all roles that are enabled only (Yes), disabled only (No), or
●
ignore this flag by selecting both.
Role Public—Narrow the data to all roles that have no user access list restriction (Yes),
●
restricted access role (No), or ignore this flag by selecting both.
Roles—See data for the selected roles only. If you choose this option, the system narrows the
●
selection based on your previous selections above.
76 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 85

Display Options
Threshold Percentages—On the report you can highlight the data if it exceeds the number
●
entered here.
◦
◦
Time Interval—Chart the data where the scale is based on hour, day, week, or month.
●
Include raw data—If the raw data is also wanted in the report, check the Include raw data
●
box.
Open in New Window—If selected, the result data are shown in a new browser window.
●
Output Report
Minimum and Maximum Capacity graphs—The graphs show the minimum number of
●
blades available and the maximum number of blades used for the specified time period. In
general, these values should add up to 100%. However, if a blade supports multiple roles, then
the numbers will not add up because consuming a blade (which is in two or more roles) in one
role will also decrease the minimum available in the other role.
Time Interval—The time interval for which the report was run. This value is based on the
●
selection in Display Options: Time Interval.
Minimum Available—If data is below the value entered, the report highlights it.
Maximum Consumed—If data is above the value entered, the report highlights it.
Date—The date of the report.
●
Role Name—Name of role.
●
Minimum Available %—For the time period chosen, the peak value of minimum available is
●
shown. This value indicates the percentage of computing resources that are still available for
allocation dropped to this lowest value.
Minimum Available—This value complements the percentage number above to show
●
specifically how many resources within that role are still available.
Maximum Consumed %—This value indicates the highest percentage of resources that were
●
consumed during the time period chosen.
Maximum Consumed—This value complements the percentage number above to show
●
specifically how many resources within that role were consumed.
Out of Resource—For the time period chosen, this value indicates how many times the system
●
encountered the situation where there are not enough computing resources to fulfill the connection
requests.
Resource Utilization Report
Select the filter options and display options, and click the Generate Report button.
HP SAM Administrative Console Tabs
77
Page 86

Filters
Total Resources—Physical count is based on unique physical resource (i.e., primary role only).
●
Logical count produces higher numbers because a computing resource is counted multiple times if
it was assigned to multiple roles.
Role Enabled—Narrow the data to all roles that are enabled only (Yes), disabled only (No), or
●
ignore this flag by selecting both.
Role Public—Narrow the data to all roles that have no user access list restriction (Yes),
●
restricted access role (No), or ignore this flag by selecting both.
Roles—See data for the selected roles only. If you choose this option, the system narrows the
●
selection based on your previous selections above.
Display Options
Open in New Window—If selected, the result data are shown in a new browser window.
●
Output Report
Role Name—Name of role.
●
Offline—Number of offline computing resources
●
Disabled—Number of manually disabled computing resources
●
●
●
●
●
Log Tab
NOTE: Administrators are only able to see log entries associated with the Asset Groups they control.
To view system historical activities, set the filter options to narrow the content to display, and then click
Search.
Filters
●
●
Available—Number of available computing resources
Disconnected—Number of computing resources with users disconnected from the session
In-Use—Number of computing resources with users actively using
Total—Number of computing resources that are offline, available, disconnected, and in-use
Category—Default is all or you can narrow to one of the categories below.
Security—Narrow the data show security related incidents.
◦
Usage Activities—Narrow the data to show user connect/disconnect/logoff type data.
◦
Administration Activities—Narrow the data to show administration type activities.
◦
Type—Narrow the data to the level of the incident. Choices are Information, Warning, and
Error.
Description—Search for incidents with the Description box containing the text entered.
●
Time Frame—Narrow data to the dates entered.
●
Asset Groups—Narrow data to asset groups selected.
●
78 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 87

You have four operations you can perform:
Save selected
●
Save entire log
●
Delete selected
●
Delete entire log
●
Setting Up Smart Card Logon on the Access Device
NOTE: RGS 5.1.3 or later is required when logging in using RGS with smart cards. Smart Card
logon does not work if RGS Single Sign-on is enabled. You must enable Easy Login on the RGS Sender
and set the USB on the RGS Receiver to Remote and Local or Remote. Drivers for the smart card
reader hardware are needed on the resource as well as on the access device.
Before you attempt the following procedure for the HP SAM client, refer to this white paper to configure
the smart card on the computing resource: Implementing ActivIdentity Smart Cards for Use with HP
Compaq t5720 Thin Clients and HP Blade PCs at
SupportManual/c01153197/c01153197.pdf?jumpid=reg_R1002_USEN.
You must successfully configure the smart card on the computing resource before attempting to
configure it on the access device.
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/
Use the following steps to enable the HP SAM client to log on using a smart card.
1. Attach the smart card reader to the access device.
2. Install the smart card reader driver onto the access device.
3. Install the smart card cryptographic service provider (CSP) software onto the access device that
supports your smart card solution. This software is required to read the contents of the smart card.
4. Install the HP SAM client software onto the access device.
5. If using the Internet Explorer-based client, configure the client on the HP SAM administrative
console at System Settings > Web Client > Smartcard cryptographic service
providers (CSP). For more information, see
NOTE: If you set the client to read the UPN or e-mail field from the user's certificate, whatever it
reads from either of those fields must match the UPN name of the user.
6. If using the XPe Client, specify the CSP string in the .SAM file. Refer to Smart Card Settings
on page 41.
Web Client on page 71.
Setting Up Smart Card Logon on the Access Device
79
Page 88

7. If you want the system to automatically launch the HP SAM client when a users inserts a smart
card, see steps a and b. (NOTE: Step a is the default setting.)
a. For the Windows-based client (default setting), edit the ‘scwatch.cfg’ file with the following:
[scwatch]
Action=c:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Session
Allocation Client\hprdcw32.exe
ActionDir=c:\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP Session
Allocation Client\
— or —
b. For the Internet Explorer-based client, edit the ‘scwatch.cfg’ file with the following:
Action=c:\Program Files\internet explorer\iexplore.exe http://HP SAMServername
8. Start the service by:
a. Clicking Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services.
b. Right-clicking HP Smart Card Monitor Service.
c. Selecting Start.
For more information about HP SAM smart card settings, see
You can configure smart card-related settings on the web client after you complete this procedure. From
the HP SAM administrative console, go to System Settings > Web Client.
NOTE: The CAC is a high-security type of smart card used by the military. Its behavior in HP SAM
matches that of typical smart cards. HP SAM does not access extended data in the CAC card beyond
the certificate needed to determine the user's credentials.
Smart Card Settings on page 41.
Configuring Session Time Limits for Remote Sessions
HP CCI Session Timers allow administrators to control automatic disconnection or logoff of remote
sessions after specified periods of time. The integrated session timers have the ability to control RGS
sessions as well as RDP sessions. You can configure time periods for Active Sessions, Active But
Idle Sessions, and Disconnected Sessions and you can further configure CPU monitoring for
Active But Idle and Disconnected Sessions. This will prevent the disconnect or logoff action if the
CPU usage remains above a configurable threshold. This is useful for ensuring that connections are not
logged off while important calculations, for example, are occurring.
The session timers consist of two main pieces:
A utility (HPCCIST.EXE and its support files) that is installed onto the resource along with the HP
●
SAM Registration Service. HPCCIST.EXE is set to start when Windows starts but will only continue
running when a policy is set that requires it to run.
An Active Directory group policy administrative template allowing you to enable the HP CCI
●
Session Timers. The administrative template (HPCCIST.ADM) can be found in the c:\windows\inf
folder (assuming you installed Windows into the c:\windows folder.)
80 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 89

To import the session timers into the Group Policy Management utility on the domain controller:
1. Copy the HPCCIST.ADM file to the domain controller.
2. Create a Group Policy Object (GPO) on the domain controller in Group Policy Management.
Right-click on Group Policy Objects and select New.
▲
3. Right-click on the GPO, select Edit, and then edit the GPO.
4. Right-click Administrative Templates.
5. Click Add and browse to HPCCIST.ADM.
6. Click and drag your new GPO to your OU (which contains your resources) to create a link in the
OU.
7. Right-click on GPO, select Edit, and then edit the GPO to set HP Session Timer parameters.
On a Windows 2003 Server, the HP Session Timer policies can be found under Computer
Configuration > Administrative Templates > HP Client Consolidated Infrastructure.
On a Windows 2008 Server, the HP Session Timer policies can be found under Computer
Configuration > Policies/Administrative Templates > Classic Administrative
Templates > HP Client Consolidated Infrastructure.
NOTE: You can also set this policy for users under User Configuration. If conflicting policies
are set to both Computers and Users, the policy assigned to Computers will apply.
Once this administrative template has been imported into the Group Policy Management utility on the
domain controller, three new policies will be available:
Emulate Terminal Services Session Time Limits—This policy controls whether or not to
●
have the HP session timer utilities emulate the Microsoft session timer group policies. This is useful
for resources running Windows XP Pro with Service Pack 2 or earlier. The Microsoft session timers
(for Active, Active But Idle, and Disconnected sessions) did not work with these versions of XP.
Enabling this emulation allows those policies to work. If XP Pro with Service Pack 3, Vista, or
Windows 7 is installed on the resource, this emulation is unnecessary.
Set CPU utilization time limit for active but idle remote sessions—This policy allows
●
the administrator to set a time of no user input (keyboard or mouse) after which the system is
considered idle. At this point, another time period (set by the administrator) defines how long the
CPU usage on the system must fall below a configurable threshold before the user is disconnected
or logged off (as chosen by the administrator.) The administrator can also fine tune this by setting
the percentage of the time period that the CPU usage must remain below the threshold for the
disconnection of logoff to occur. This is useful to allow for a limited amount of CPU spiking but still
cause the system to disconnect or log off.
Set CPU utilization time limit for disconnected remote sessions—Similar to the above,
●
this policy allows the administrator to set a time period which starts when the session is
disconnected. If the CPU remains below the chosen threshold for this period of time, the user will
be logged off of the resource, freeing it to be used by other users.
For more detailed information on these settings, open the policy in the Group Policy Management
utility and click the Explain tab.
If the HP SAM administrator has no access to the domain controller, the policy can be applied on each
resource instead.
Configuring Session Time Limits for Remote Sessions
81
Page 90

Session Timers for Linux
HP SAM Session Timers for Linux have been added to provide functionality to administrators on Linux
resources similar to what previously existed only for Windows resources. It features the ability to
disconnect or log off users after a set amount of time when logged in, logged in but inactive, or in a
disconnected state. It can also be set to factor in CPU usage with configurable thresholds.
The Session Timers for Linux are included in the SAM download package as a file in the RPM format.
After copying the RPM file to the Linux-based resource, it can be installed with the following command:
rpm -ivh <hpst file>.rpm (for example, rpm -ivh hpst-1.0.0-1.x86_64.rpm).
The various session timer types (described below) and their options are set within the configuration file
(/etc/hpstd.conf) on each resource. Use the command /opt/hpst/sbin/hpstd –reload after changing
settings in the configuration file for those settings to take effect. The Active and Active But Idle timers
will disconnect the user when the timer is triggered. The Disconnect Session timers will log the user off
of the resource when triggered. All timers operate only when connected via the HP RGS protocol and
are not designed for use with resources which are intended to be logged into locally.
The following timer types are available:
Active Sessions – Allows the administrator to force a disconnection after the user has been
●
connected for the specified period of time.
Active But Idle Sessions – Allows the administrator to force a disconnection when the user is
●
connected and has been idle (i.e., no mouse or keyboard activity) for the specified period of time.
Disconnected Sessions – Allows the administrator to force a logoff the specified amount of time
●
after the user disconnects (either manually or via timers or network interruption.)
Disconnected Sessions CPU Low – Works like the Disconnected Sessions timer above, but will not
●
log the user off if the CPU activity is above the specified threshold. This timer helps to avoid
logging off a disconnect user who has CPU-intensive tasks still running.
Disconnected Sessions CPU High – Works like the timer above except that it will force a logoff if
●
the CPU activity is above the specified threshold. This is intended to free up resources which may
be stuck in an infinite loop.
Please refer to the help page (man hpstd) for more detailed info and additional options.
Resource Reservations (AKA Access Restrictions)
This feature allows the administrator to restrict when and from where users may access resources. It also
provides the ability to free up resources as needed for when other users require those resources.
Role settings now enable the administrator to specify the source IP Address range time of day, and
day(s) of the week. Users in that role will then only receive a resource from that role when using an
access device in the IP Address range and only on the specified day during the specified period of
time. In this case, the user will be sent directly to a resource in this role even if he has many other roles
—he will not see a role selection dialog. If outside of the IP range and time/day, the user will be
denied access to that role. Multiple such reservations can be designated on each role.
By default, at the end of the reservation period, the user is logged off of the resource. The Allow time
extension option can be set to allow a user to remain logged in beyond the current resource
reservation end time. They can remain logged in until another resource reservation time period for the
82 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 91

same role begins (or at 12:00 midnight, if no other reservations are set.) A dialog warns the user
before the logoff occurs. The lead time of this warning can be configured in System Settings on the
General page of the HP SAM administrative console.
For example, a school may use resource reservations to ensure students get a resource from the correct
role for each class and make sure resources are freed in time for a later class needing resources in the
same role. The administrator can set a reservation on the Math Class role specifying the IP address
range of a certain classroom and a certain time/day when the math class occurs. The student who logs
in using a computer in this classroom during the right day and time will get a resource in the Math
Class role without having to choose which role. He can then use the resource until the class is over.
Another reservation on the Math Class role may specify another math class in a different room at a
later time for the same resource(s). The automatic logoff feature ensures that those resources will be
available for students in the later class.
When the HP SAM Server and the access devices are in different time zones, note that the times set in
Resource Reservations are the times of the access device, not the time of the server. For example,
suppose the HP SAM server is in the Central Standard time zone and the time in the reservation is
specified as 4PM. This will correspond to 4PM on the access device in the Pacific Standard time zone
(even though the time on the HP SAM server operating system will show 6PM.) Therefore, be sure that
times and time zones are set correctly for all systems involved.
The automatic logoff time is given to the resource during user logon and is not updated if the
reservations are subsequently updated on the server. For example, if a user is logged in during a
reservation set for 2-3PM which has Allow time extensions enabled and there is another
reservation already set for 5-6PM, the resource will log the user off at 5PM. If, after the user logs in for
the first reservation, the HP SAM administrator adds a new reservation starting at 4PM, the user will still
not be logged off until 5PM. The Logoff Scheduler (
features can be used to set a logoff time slightly before 4PM to ensure the resources are free in time for
the newly added reservation. A manual or scheduled synchronize operation has no effect on resource
reservations.
Log Off User from Resource Scheduler on page 74)
NOTE: This feature is only supported on resources running a Windows operating system.
Refrain from using resources assigned to multiple roles while using this feature. This can cause the
automatic logoff to not occur when the resource is needed for a reservation set on one of the resource’s
other roles.
There are two other features in HP SAM that can bypass the role selection dialog for users with multiple
roles: Monitor Layouts and Multi-session Auto-connection. If a conflict occurs, Monitor
Layouts will prevail over Resource Reservations which will prevail over Multi-session Autoconnection.
Authenticate Before Allocation
When enabled, this feature enhances security by requiring the user to enter his username and
password on the HP SAM client, which will then be authenticated by Active Directory before sending a
user to a resource or displaying a list of roles and resources. The feature also eliminates the possibility
of Active Directory locking out a user because he mistyped his password during a single connection
attempt when trying to connect to multiple resources at once. This feature is disabled by default.
With this feature disabled, the behavior is the same as with previous versions of HP SAM where
password authentication is first done when logging into the operating system on the resource.
Authenticate Before Allocation
83
Page 92

To enable this feature, all of the following must be configured:
Enable Authentication before Allocation on the General page of System Settings on the HP
●
SAM administrative console.
Ensure that a certificate from the domain certificate authority is installed on the HP SAM website in
●
IIS on the HP SAM server.
The following option must be enabled via the HP SAM client configuration file on all access
●
devices: AuthenticateBeforeAllocation=1.
There is no setup needed for the web client, but the user must type in the URL using https instead of
●
http (e.g., https://samserver).
Ensure that communication between the access device and the HP SAM Server via SSL (typically
●
port 443) is not blocked by a firewall.
The Allow Expired Password setting in System Settings gives the HP SAM administrator the option
to allow users with expired passwords to continue on so that they can change the password using the
operating system on the resource.
NOTE: Versions of the HP SAM client prior to HP SAM 2.3 cannot be used when this feature is
enabled.
This feature is not compatible with Smart Card single sign-on and must be disabled before using Smart
Cards.
84 Chapter 4 Administration
Page 93

A Firewall Rules
This appendix lists the rules needed for communication between the various components. The values in
parenthesis represent ports, with ANY meaning any ports on that component.
Web Server
Incoming:
●
From clients (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
◦
From clients (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/443—HTTPS)
◦
From blades (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
◦
From admin_workstation (TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/443—HTTPS)
◦
From resources (UDP/47777) to web server (UDP/47777—Custom)
◦
Outgoing:
●
From web server (TCP/ANY) to SQL_Server (TCP/1433—MSSQL))
◦
From web server (TCP/ANY) to resources (TCP/139—RPC)
◦
◦
Clients
Incoming:
●
◦
Outgoing:
●
◦
◦
◦
◦
Resources
Incoming:
●
◦
From web server (UDP/47777) to resources (UDP/47777—Custom)
None
From clients (ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
From clients (ANY) to resources (TCP/3389—RDP)
From clients (ANY) to resources (TCP/42966—RGS)
NOTE: The default RGS port is TCP/42966; however, RGS 5.3 and later allows this to be
changed. Please see the RGS documentation for details.
From clients (ANY) to web server (TCP/443—HTTPS)
From web server (UDP/47777) to resources (UDP/47777—custom)
From web server (TCP/ANY) to resources (TCP/139—RPC)
◦
Web Server 85
Page 94

From clients (TCP/ANY) to resources (TCP/3389—RDP)
◦
From clients (TCP/ANY) to resources (TCP/42966)—RGS)
◦
NOTE: The default RGS port is TCP/42966; however, RGS 5.3 and later allows this to be
changed. Please see the RGS documentation for details.
Outgoing:
●
From resources TCP/ANY) to web server (TCP/80—HTTP)
◦
From resources (UDP/47777) to web server (UDP/47777)
◦
SQL Server
(only if not running on the same machine as the web server)
Incoming:
●
From web server (TCP/ANY) to SQL_Server (TCP/1433)
◦
Outgoing:
●
None
◦
86 Appendix A Firewall Rules
Page 95

B Frequently Asked Questions
Question Answer
Why do some users on the HP SAM client have to select a
role or resource to connect and others do not.
Can the user connect to multiple computing resources from the
same client access device?
Why is my blade being marked offline even though I am able
to connect to it using Remote Desktop Connection?
My user is unable to connect to a computing resource on the
browser-based web client. What’s going on?
Why is my client not switching to the failover server in my list? Make sure the FAILOVER=1 is defined in your .SAM file
Why are my users being asked to reconnect using the HP
SAM client every time there is a network glitch?
Users who are in more than one role must select the role to
connect. Those users who are in only one role do not see this
screen. A user assigned a single dedicated resource does not
have to select a role. Also, when Monitor Layout IDs or MultiSession Autoconnections or Resource Reservations are used,
the user is not prompted for a role or resource.
Yes. If multiple resources have been assigned to the user, the
user may connect to those resources. Additionally, if the user
is in multiple roles, the user can connect to a blade from each
role.
Check your firewall settings on the computing resource to
make sure the HP SAM port (47777) is allowed for incoming
connection.
Verify that the server is up and running and your firewall is
enabled to allow port 3389 for IEXPLORE.EXE
The Auto-Reconnect setting is set to OFF. If your network is set
to log your users off when they are disconnected or timed out,
any network glitch that disconnects a user or times the user out
will also log the user off. Another user could then connect. If
the Auto-Reconnect setting is set to On, the original user might
then automatically reconnect and bump off the new user. HP
recommends that you set Auto-Reconnect to OFF.
Why are my settings not working as I set them on the client
side?
Why does my user have to type the password twice every
time to log onto a computing resource?
I got an error during registration service upgrade installation. Check to see if the event log is open. If so, you must close the
The settings on the client side may have been overridden by
forced settings on the HP SAM server in the Policy tab. Also,
settings not valid on the protocol used are ignored.
This should not happen. The Active Directory policy is
requiring the user to log onto the blade interactively. Either
disable this policy or remove the Password box from the HP
SAM client by setting PasswordEnable=0 in the .SAM file.
This could also be caused by using RGS in Easy Login or
Default mode.
log so the tool can remove the old executable and upgrade to
the new one.
87
Page 96

Question Answer
How do I enable HP Sygate Security Agent on the Windows
XP Embedded-based thin client for the HP SAM client(s)?
I am unable to view the Japanese characters on the web
client.
Can I administer the HP SAM server using another browser
such as Opera and Firefox?
Go to HP Sygate Security Agent advance rules and create a
new rule for HP SAM. Add IEXPLORE.EXE and/or
hprdcw32.exe to the Application tab. On the Ports and
Protocol tab, set protocol to TCP and type 80,443,3389,42966
on the remote port line if you want both clients to work.
Otherwise, make sure port 3389 is set for IEXPLORE. You
can set port 80, 443, 3389, or 42966 for the Windowsbased client or leave it alone (all). For advanced methods
such as an Altiris script, you can create the script similarly
here or use the HP Sygate Security Agent Policy Editor tool
(download as a SoftPaq from the HP website).
Check to make sure the Japanese fonts are installed on the
access device.
No, these browsers are not supported.
88 Appendix B Frequently Asked Questions
Page 97

Question Answer
How can I change both the HP SAM web server http and https
ports to some other value beside the default 80 and 443?
After changing the desired value (TCP and/or SSL ports) in
Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager, modify the
CONNECTION.CONFIG file located on the HP SAM web
server in root of the HP SAM installation directory (usually c:
\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP SAM). Use Notepad to
edit the file. Modify the three lines below:
<!-- add key="ClientServiceURL" value="http://samservername:
80" / -->
<!--add key="ResourceServiceURL" value="http://samservername:
80" / -->
<!--add key="AdministrativeConsoleURL" value="http://
samservername:80" /-->
To:
<add key="ClientServiceURL" value="http://
sam_server_name:port_number" / >
<add key="ResourceServiceURL" value="http://
sam_server_name:port_number" / >
<add key="AdministrativeConsoleURL" value="http://
sam_server_name:port_number"/ >
Where sam_server_name is the name of the HP SAM server
and the http port is the port_number value as set in IIS
Manager (not the SSL Port value).
If you change only the SSL Port value in IIS Manager, you still
need to modify the CONNECTION.CONFIG file as
described. Do not use HTTPS in either of the previous lines.
If you change the TCP Port, you need to update the
configuration file on the HP SAM registration service
hpevent.cfg file on all computing resources to use the new
web server http port (for example, YourHP SAMservername:
8080). You also need to update all of the access devices to
use the same http port.
NOTE: Be sure to update your firewall exceptions
accordingly.
89
Page 98

Question Answer
How do I change the HP SAM datagram communication port
to another value beside the default 47777?
Can I use double-byte numbers in the user name? No. HP SAM only supports single-byte numbers.
I get warning messages when I am operating in a double-byte
character set (DBCS) Asian language on the HP SAM
administrative console and I input numeric values in System
Settings tab.
Why I do see line graphs in Resource Capacity Consumption
Report in the HP SAM administrative console in some
instances and not in other instances?
Modify the connection.config file located on the HP SAM
web server in the HP SAM installation directory (usually c:
\Program Files\Hewlett-Packard\HP SAM). Use Notepad to
edit the file. Add this line in the appSettings section:
<add key="ProtocolChannel" Value="port number"/>
Where port number is the new HP SAM datagram
communication port you want to use.
You must stop and restart the HP Session Allocation
Management Service on the HP SAM web server. You must
also update the HP SAM registration service hpevent.cfg file
on all computing resources to use the same HP SAM
datagram communication port, then restart the HP SAM
registration service on all computing resources. Also update
the appropriate firewall rules on the HP SAM web server and
the computing resources.
HP SAM administrative console accepts only single-byte
numbers as a value.
Make sure the browser language you are viewing the report is
the same as the HP SAM web server operating system
language. For example, if you are viewing the HP SAM
administrative console in Japanese, the HP SAM web server
operating system language must be Japanese.
The Internet Explorer AutoComplete window covers up the HP
SAM Add New Users search window. How can I see my
search results?
I've added a user as an HP SAM administrator, but she
cannot log onto the HP SAM administrative console.
I see a generic error message of the HP SAM administrative
console—how can I get more detailed information about the
error?
Disable the Internet Explorer AutoComplete feature for form
fields:
1. In Internet Explorer, click Tools on the menu bar.
2. On the Content tab, click AutoComplete.
3. Clear the Forms check box.
Be sure that AD Group Policy is set to enable Allow Logon
Locally. This situation applies to users that are not members of
the local server administrator group, but are members of the
HP SAM Administrator Group.
Computer Configuration\Local Policies\Users Rights
Assignment\Allow logon locally.
For security reasons, details of some types of errors cannot be
viewed remotely. If you reproduce the error on the HP SAM
server itself, you can see the details and a stack trace, which
can give you clues to the root cause of the failure. This
information may also be critical in helping support personal
diagnose the problem.
90 Appendix B Frequently Asked Questions
Page 99

Question Answer
Users are getting the message All resources are currently
in use. Please try again later but there appear to be free
resources according to the HP SAM administrative console.
What are the potential causes for this?
First, refresh the Resources list in the HP SAM administrative
console and check to see if any resources are available in the
role (or dedicated resource) the user is attempting to access. If
no resources are shown as Available, try performing a
Synchronize operation on all of the resources to ensure that
their status is current. If there are still no resources shown as
Available, the message is accurate and more resources can
be added to the pool or the HP SAM session timers can be
used to free up idle resources.
If there are resources shown as Available and users are still
getting this message, consider the other potential causes
below:
Some resources are marked as disabled in HP SAM.
●
Some resources are assigned to a user as a dedicated
●
resource. Check the Manage Users page to see if these
resources show up as dedicated to any users.
NOTE: If a resource is in a role and is also dedicated
to a user, it will never be allocated to user who requests
a resource using that role. In other words, it really is
dedicated to that one user only.
Some resources may be temporarily reserved. When HP
●
SAM allocates a resource to a user, it reserves the
resource for that user for a certain amount of time (3
minutes, by default) to allow that user time to log on.
During this time, the resource shows as Available in HP
SAM with no user logged in, but cannot be allocated to
any other user.
NOTE: This scenario may occur more frequently if this
time period is increased. This is set under System Settings
| General via the User Sign-In Time Out option.
Verify that the HP Session Allocation Management
●
Service is running on the HP SAM server. Typically, if
this service is not running, it causes resources to go
offline when users attempt to log on.
Verify that the HP SAM communication port (UDP
●
47777, by default) is not blocked by a firewall. This is
the port over which the HP SAM Registration Service and
the HP SAM Server communicate blade status. Typically,
when this port is blocked, resources go offline when
users attempt to log on.
Verify that the resources show the desired protocol in the
●
HP SAM administrative console. For example, if the HP
SAM clients are set to ONLY connect via RGS, then
resources which show as Available but do not show
the RGS protocol are not allocated to the users.
Verify that all users have valid UPN names in Active
●
Directory. Users without UPN names may be allocated to
a resource by HP SAM, but after disconnecting, they
may be sent to a different resource and not sent back to
their resource. UPN names are required for proper HP
SAM to operate properly.
91
Page 100

Question Answer
Why does a user, whose Security Group has been added to
HP SAM from a child domain, receive the error “Your account
cannot be assigned to any existing roles?”
I restored my HP SAM database from tape backup after the
HP SAM SQL server was recovered from an unexpected
failure. Is a synchronize operation enough to get all the latest
status for all computing resources?
The user may see this error when logging into HP SAM using
his username in UPN (user@domain.dom) format. When UPN
is used, HP SAM checks the global catalog for group
memberships in Active Directory. Local and Global Security
Groups are not visible this way. The administrator has two
options—either change the Security Group to be a Universal
Security Group, or, instruct the user not to use UPN format
when logging in.
It depends on when the database backup was performed.
New computing resources may be registered after the last
backup was performed. If so, those computing resources do
not exist in the backup data. The synchronize operation works
only on computing resources the system is aware of. If the
status of those computing resources was offline, disconnected,
or online when the SQL server went down, then you must find
those computing resources and add them back to the HP SAM
system. To do that, stop and restart the registration service on
those units. When in doubt, stop and restart the registration
service on all of the computing resources. This action has no
impact on current users active on the computing resources.
92 Appendix B Frequently Asked Questions
 Loading...
Loading...