Page 1

Getting Started
Démarrage rapide
Aan de slag
Page 2

Page 3

Getting Started
Page 4

The only warranties for Hewlett-Packard products and services are set forth in the
express statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable
for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
HP assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment
that is not furnished by HP.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. No
part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another
language without the prior written consent of HP.
Hewlett-Packard Company
P.O. Box 4010
Cupertino, CA 95015-4010
USA
© Copyright 2000–2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by U.S.
patents and other intellectual property rights. Use of this copyright protection
technology must be authorized by Macrovision, and is intended for home and other
limited viewing uses only unless otherwise authorized by Macrovision. Reverse
engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
Microsoft and Windows 7 are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
The Windows logo and Windows 7 are trademarks or registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries/regions.
Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 802.11n based on Draft 2.0
Draft 2.0 refers to the version of the not-yet-ratified IEEE 802.11n standard used in
Wi-Fi Alliance testing as of June 2007.
The specifications of the 802.11n WLAN (wireless local area network) are draft
specifications and not final. If the final specifications differ from the draft
specifications, it may affect the ability of this device to communicate with other
802.11n WLAN devices.
HP supports lawful use of technology and does not endorse or encourage the use of
our products for purposes other than those permitted by copyright law.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Setting Up Your Computer........................................................................... 1
Checking the Computer Installation .............................................................................. 1
Connecting Speakers or Microphones .......................................................................... 4
Connecting to a Network............................................................................................ 6
Connecting a Modem ................................................................................................ 7
Connecting the Television Signal and Video Cables....................................................... 7
Preparing to Use Your Computer............................................................... 13
Turning Off the Computer ......................................................................................... 14
Restarting the Computer............................................................................................ 14
Connecting to the Internet ......................................................................................... 14
Adjusting the Speaker Volume................................................................................... 16
Selecting the Microphone ......................................................................................... 16
Protecting Your Computer ......................................................................................... 17
Configuring the Computer for Automatic Microsoft Software Updates............................. 18
Setting Up User Accounts.......................................................................................... 19
Guidelines for Installing Software and Hardware Devices ............................................. 19
Transferring Files and Settings from an Old Computer to Your New Computer ................ 20
Special Features of Your Computer............................................................ 21
Using the Memory Card Reader ................................................................................ 21
Using a Vertical CD/DVD Drive................................................................................. 23
Using LightScribe Technology.................................................................................... 23
Using the Remote Control.......................................................................................... 24
Getting More Information .........................................................................25
Using the Help and Support Center............................................................................ 25
Accessing Support on the Web ................................................................................. 25
Finding Guides on the Web...................................................................................... 25
Finding Onscreen Guides ......................................................................................... 26
Using the PC Help & Tools Folder .............................................................................. 26
Using HP Advisor Software ....................................................................................... 26
Using the Computer with Safety and Comfort .............................................................. 27
Troubleshooting and Maintenance.............................................................29
Troubleshooting Computer Problems........................................................................... 29
Software Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 45
Maintenance........................................................................................................... 48
Keeping the Computer Free of Dust, Dirt, and Heat...................................................... 49
System Recovery...................................................................................................... 50
Performing the Post-Recovery Procedure...................................................................... 54
Additional Troubleshooting ....................................................................................... 54
Index........................................................................................................ 55
Table of Cont e n t s iii
Page 6

iv Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 7

Setting Up Your Computer
WARNING: The power supply is preset for the country/region in which
you purchased your computer. If you move, please check the voltage
requirements for your new location before plugging the computer into an
AC power outlet.
WARNING: Please read “Safety Notices” in the Regulatory and Safety
Information document before installing and connecting the computer to
the electrical power system.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious injury, read the Safety & Comfort
Guide. It describes proper workstation setup, posture, and health and
work habits for computer users. It also provides important electrical and
mechanical safety information.
Follow the steps on the setup poster to set up the computer:
1 Connect a keyboard and a mouse to the computer.
2 Connect a display (monitor) to the computer.
3 Connect power to the computer.
4 Turn on the computer. See “Preparing to Use Your Computer” on page 13.
NOTE: Do not connect or add other devices to the computer until after you turn on the
computer for the first time and complete the initial setup. See “Preparing to Use Your
Computer” on page 13.
Checking the Computer Installation
Place the computer in an appropriate location so that:
All ventilation openings are unobstructed.
All cabling is out of the way. Do not place any cable in a walkway or where it can
be stepped on or damaged from placing furniture on it.
WARNING: Place the computer in a location away from water, dust,
moisture, and soot. These can increase the inside temperature, causing
fire, trouble, and electrification.
Setting Up Your Computer 1
Page 8
Protect the monitor, computer, and connected accessories by connecting all power cords
to a power surge protection device. Use a power strip specifically labeled as having
surge protection, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), or a similar device.
If the computer has a television tuner, or a modem or telephone connection, protect the
computer by using surge protection with these signal inputs as well. Connect the
television cable or the telephone line cord to the inputs and outputs of the surge
protection device and then to the computer.
Look in the computer box for additional printed details or updates regarding your
computer.
Connecting other devices to the computer
Some peripheral devices can plug into connectors on the back of the computer or on the front
of the computer.
NOTE: The location, availability, and number of connectors on the computer may vary.
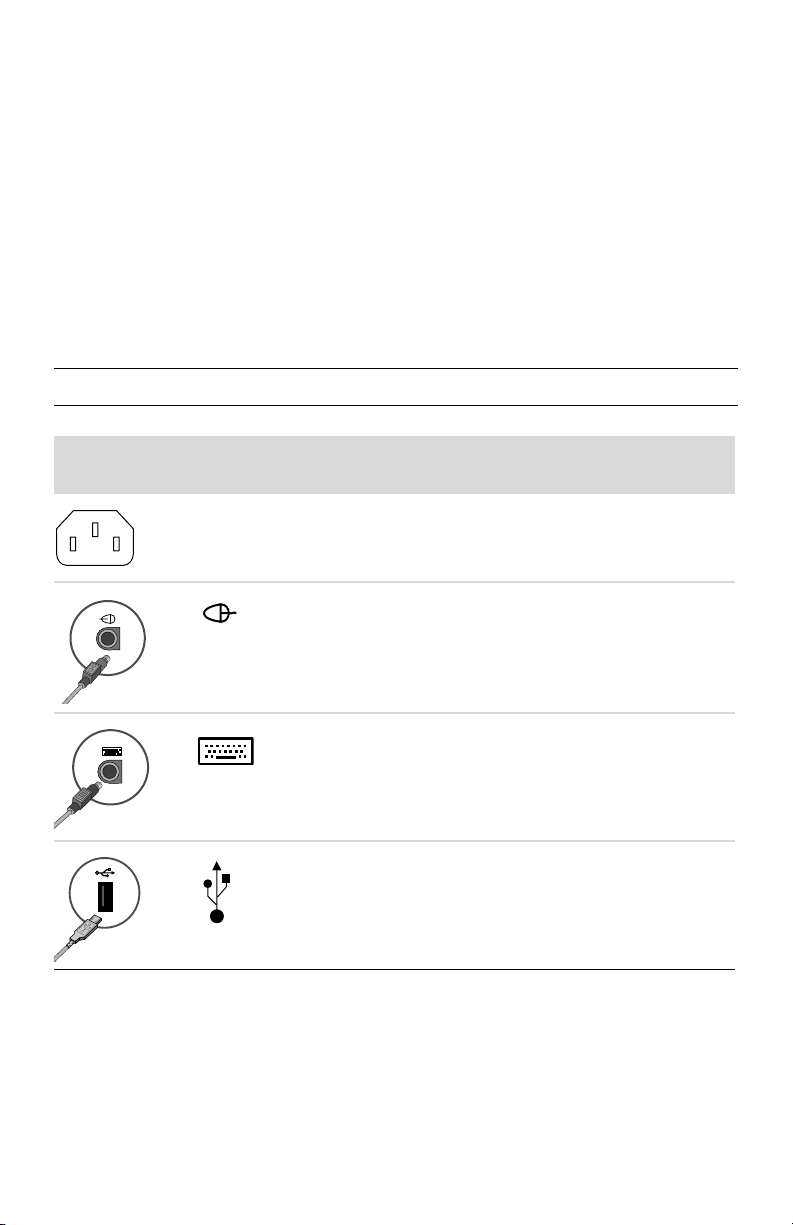
Power cord
and devices
Icon/label Description and function
Power connector.
Mouse (PS/2 connector).
Keyboard (PS/2 connector).
Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 for mouse, keyboard,
digital cameras, or other devices with USB
connectors.
2 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 9
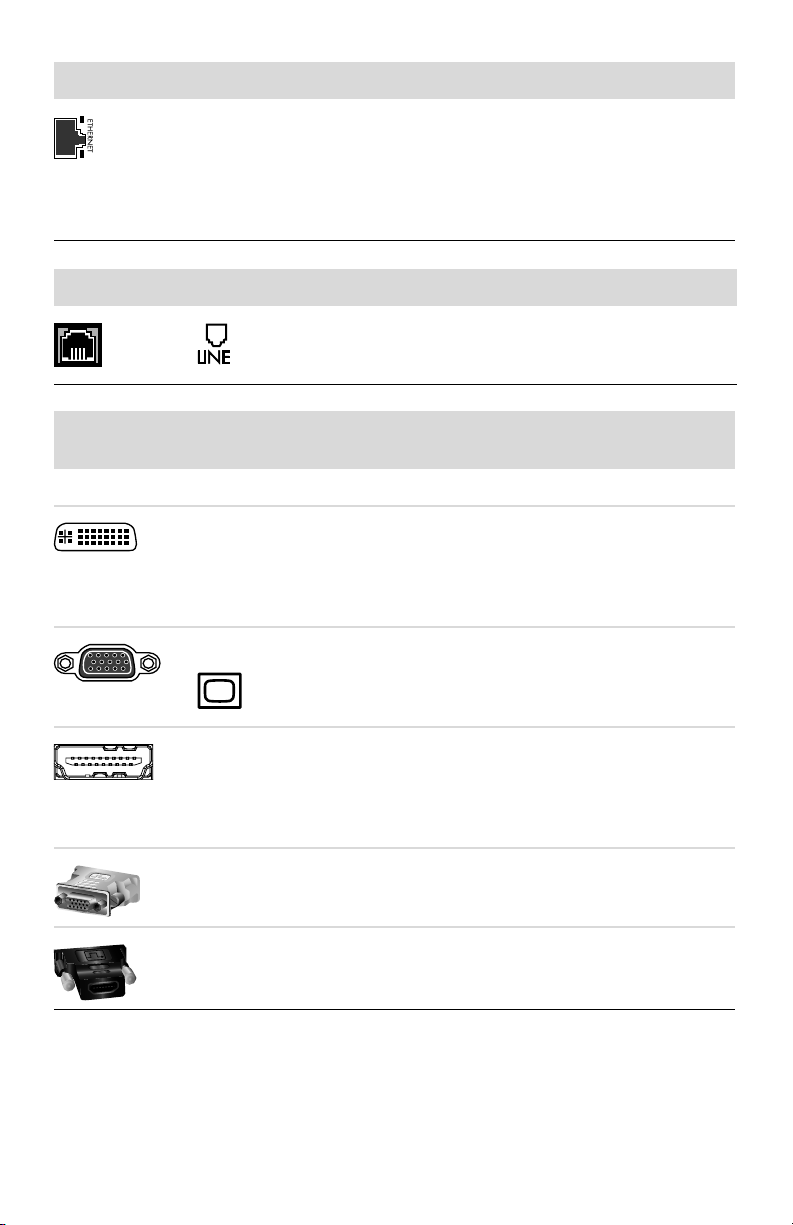
Network Icon/label Description and function
ETHERNET Ethernet LAN connector to connect to an Ethernet
(RJ-45) local area network (LAN) hub or any
broadband connection. This wired LAN connector is
a network interface adapter (also called a network
interface card, or NIC). The green LED indicates a
valid connection.
Modem Icon/label Description and function
Modem (Line In RJ-11) (select models only) to
connect the computer modem to a telephone wall
jack for dial-up connections to the Internet.
Display video
output
Icon/label Description and function
NOTE: For specific information, see the documentation that came with the display device.
DVI Recommended for connecting to a monitor. Digital
video output connector (select models only), to
connect to a TV or monitor. You may need to use a
VGA-to-DVI or an HDMI-to-DVI adapter to connect
the display to the computer.
VGA/Monitor VGA/Monitor (blue) display output connector, to
connect to a VGA monitor. You may need to use a
VGA-to-DVI adapter to connect a display with only a
DVI connector to the computer.
HDMI Recommended for connecting to a TV. HDMI display
output connector, to connect to an HDMI monitor or
TV display. You may need to use an HDMI-to-DVI
adapter to connect a display with only a DVI
connector to the computer.
VGA-DVI VGA-to-DVI adapter, to adapt a TV or a monitor
video cable so it can connect to the computer.
HDMI-DVI HDMI-to-DVI adapter, to adapt a TV or a monitor
video cable so it can connect to the computer.
Setting Up Your Computer 3
Page 10
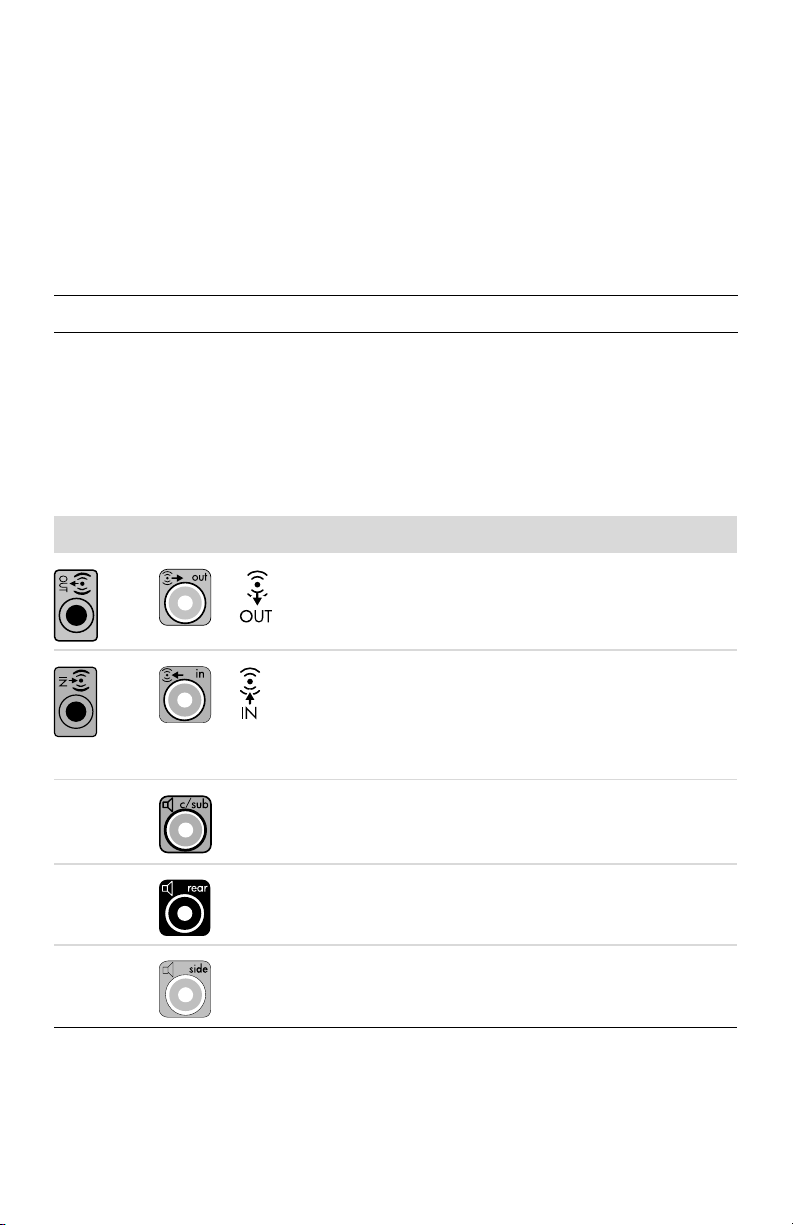
Connecting Speakers or Microphones
Speakers are available separately, or may be included with the monitor (select models only).
Headphones and microphones are available separately.
Your computer model may include audio connectors on the back of the computer. Some
computers also have connectors on the front of the computer. Audio connectors are stereo
mini-jacks that connect from the computer to active (powered) speakers or speaker systems, to
headphones, or to an input device such as a microphone, webcam, or audio player.
Some, but not all, audio connectors that may be on the computer appear in the
following table.
NOTE: The location, availability, and number of connectors on the computer may vary.
Connecting speakers
Speakers are available separately, or included with the monitor.
Your computer supports only active (powered) speaker systems; the speaker system must have
its own power source, such as batteries or a separate power cord.
For detailed instructions about how to connect and configure other multichannel speakers, go
to the Web support page for your model; see “Accessing Support on the Web” on page 25.
Audio connectors Icon/label Description and function
Audio Line Out (lime green) to connect front left
and front right analog speakers.
Audio Line In (blue) connector to connect input to
the computer from an analog audio device, such
as a CD player.
May function as rear Line Out in a multichannel
audio configuration.
Center Line C/Sub (gold) connector to connect
Center/Subwoofer speakers in a multichannel
audio configuration.
Rear Line Rear (black) connector to connect rear
speakers in a multichannel audio configuration.
Side Line Side (gray) connector to connect side
speakers in an eight-speaker system (7.1).
4 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 11
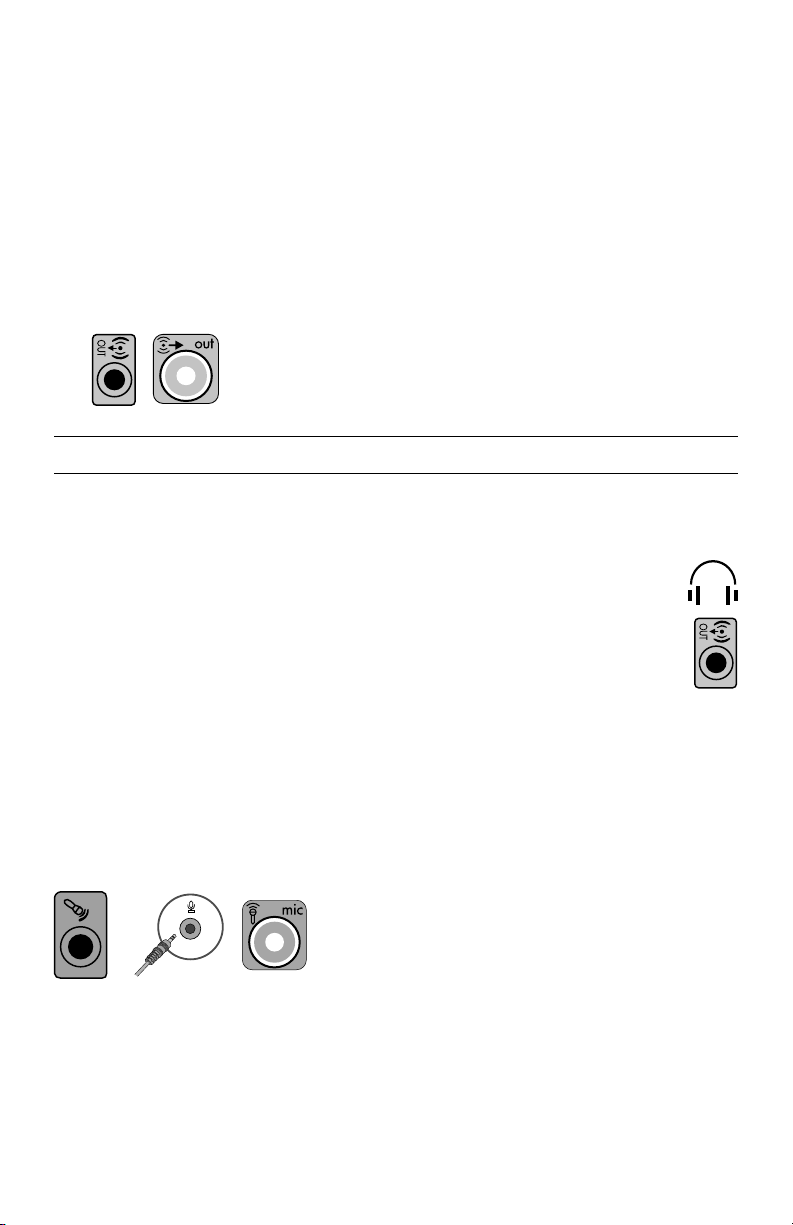
Connecting a stereo speaker system
To connect active speakers, such as left/right stereo speakers or a 2.1 system of two speakers
and a subwoofer, to the computer:
1 Ensure that the computer is turned off, and that the speaker system is turned off and
unplugged.
2 Connect the speaker system cable to the lime green Audio Line Out connector that
matches the back of your computer.
Or
For 2.1 speakers or other multichannel speakers that were shipped with your computer
(select models only), connect the subwoofer to the Audio Line Out connector on the
computer, and connect the left and right speakers to the subwoofer.
NOTE: Always turn on the computer before you turn on the speaker system.
Connecting headphones
Headphones are available separately.
Your computer comes with a headphones connector (lime green) on the front of the
computer. The headphones connector is labeled with a headphones icon.
You can also connect headphones to the Audio Line Out connector (lime green) on
the back of your computer.
When headphones are plugged in, the sound to the speakers (and the subwoofer) is
usually muted.
Connecting a microphone
Microphones are available separately.
Your computer comes with a microphone connector (pink) on the back of the computer. Some
models have a second microphone connector on the front of the computer (select
models only).
Connect the microphone to the microphone connector on the computer.
To adjust the recording volume or select the microphone, see “Selecting the Microphone” on
page 16.
Setting Up Your Computer 5
Page 12
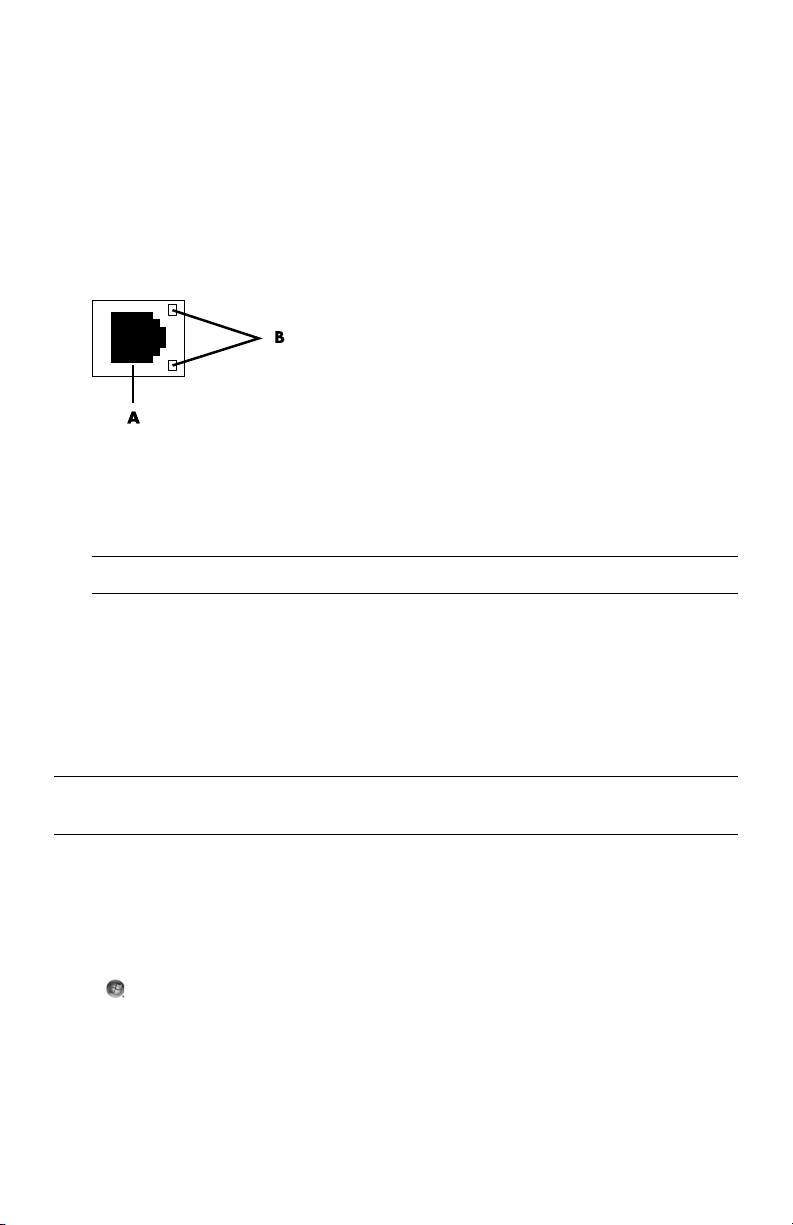
Connecting to a Network
This section describes connecting to a network through a wired or wireless connection.
Setting up a wired Ethernet network connection
The Ethernet (RJ-45) connector on the back of the computer provides a high-speed or
broadband connection to a network. After you connect this interface to a network, such as a
Local Area Network (LAN), you can connect to the Internet through the network.
1 Connect an Ethernet cable to the Ethernet (RJ-45) connector (A) on the back of the
computer, and to the network router or LAN device.
2 With the computer turned on, check the indicator lights (B) next to the Ethernet connector
for the status:
ACTIVITY — Lit yellow during network data transfer activity
LINK — Lit green when there is a valid network connection
NOTE: Your Ethernet connector may have only one indicator light.
Setting up a wireless network connection
(Select models only)
You can connect the computer to a wireless network supporting IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, or
802.11n by using the antenna that is included with the computer. If provided, connect the
external antenna to the wireless antenna connector on the network card to increase the range
and sensitivity of the wireless radio signal.
NOTE: For the best wireless performance, place the antenna on the top of the computer or in
an elevated and open area.
You need an existing wireless LAN with an Internet connection. Consult your Internet Service
Provider (ISP) for further information.
To verify that the integrated WLAN device is installed on the computer correctly, see “Internet
access” on page 37.
For more information about setting up a wireless network: Click the Windows Start
button , click Help and Support, and then type setting up a wireless network into the
Search Help box and press Enter.
6 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 13

Connecting a Modem
(Select models only)
The modem connects the computer to the telephone line. Use it to connect to an ISP that
provides a telephone dial-up connection to the Internet. If you use a network connection, you
may not need a modem connection.
NOTE: Your computer may not come with a modem. The modem may be a connector on the
back of the computer or it may be an external device that plugs into a computer USB
connector.
Before you can use telephone dial-up to connect to the Internet and send or receive e-mail
and faxes, you must connect your telephone service line to the modem connector (A).
1 Plug a modem/telephone cable into the computer modem connector (A). Note that the
modem connector on the computer may be green.
2 Plug the other end of the modem/telephone cable into the telephone service line wall
jack connector.
Connecting the Television Signal and Video Cables
(Select models only)
This section describes how to connect the computer to a television and which cables to use.
Use cables to connect:
TV signal source coaxial cable for video/audio into the computer.
Or
TV signal source S-video or composite video into the computer.
TV signal source audio into the computer.
Or
Video out from the computer.
You may need to purchase cables, a coaxial cable signal splitter, or other accessories
separately. Your computer may not include all the cables you need for the television/video
setup.
Setting Up Your Computer 7
Page 14
Video and
audio input
Icon/label Description and function
S-Video S-video In connector to connect video input from a
TV set-top box output connector.
Composite
Video
Composite Video In connector (yellow) to connect
video input from a TV set-top box.
S-Video 2 Secondary S-video In connector to connect video
input from a VCR, video camera, or other analog
video source.
Composite
Video 2
Secondary Composite Video In connector (yellow)
to connect video input from a VCR, video camera,
or other analog source.
A/V In
Audio 1 L
Primary left Audio In connector to connect audio
input from a TV set-top box connector (white).
NOTE: You can record audio by using this Audio In
connector, which is connected to the motherboard.
Some computers include this primary left audio input
connector on the front of the computer.
A/V In
Audio 1 R
Primary right Audio In connector to connect audio
input from a TV set-top box connector (red).
NOTE: You can record audio by using this Audio In
connector, which is connected to the motherboard.
Some computers include this primary right audio
input connector on the front of the computer.
A/V In
Audio 2 L
Secondary left Audio In input connector (white).
NOTE: This Audio In connector is connected to the
TV tuner. To record or listen to audio only, you must
use the primary Audio In connector, which is
connected to the motherboard and located on the
back of the computer.
A/V In
Audio 2 R
Secondary right Audio In input connector (red).
NOTE: This Audio In connector is connected to the
TV tuner. To record or listen to audio only, you must
use the primary Audio In connector, which is
connected to the motherboard and located on the
back of the computer.
8 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 15
Television
output
Television
input
Icon/label Description and function
Analog Video Analog Video Out connector to connect S-video or
composite video connector to a TV.
Icon/label Description and function
TV/Cable Ant TV In connector to connect TV antenna or cable
input from wall outlet with no set-top box.
ATSC TV In connector for TV cable or antenna, to receive
ATSC (Advanced Television System Committee)
channels, which are over-the-air digital transmission
channels.
CATV TV In connector for TV cable or antenna, to receive
CATV (Community Antenna Television) channels or
cable TV channels.
NTSC TV In connector for TV cable or antenna, to receive
NTSC (National Television System Committee)
channels, which are over-the-air analog transmission
channels.
Setting Up Your Computer 9
Page 16
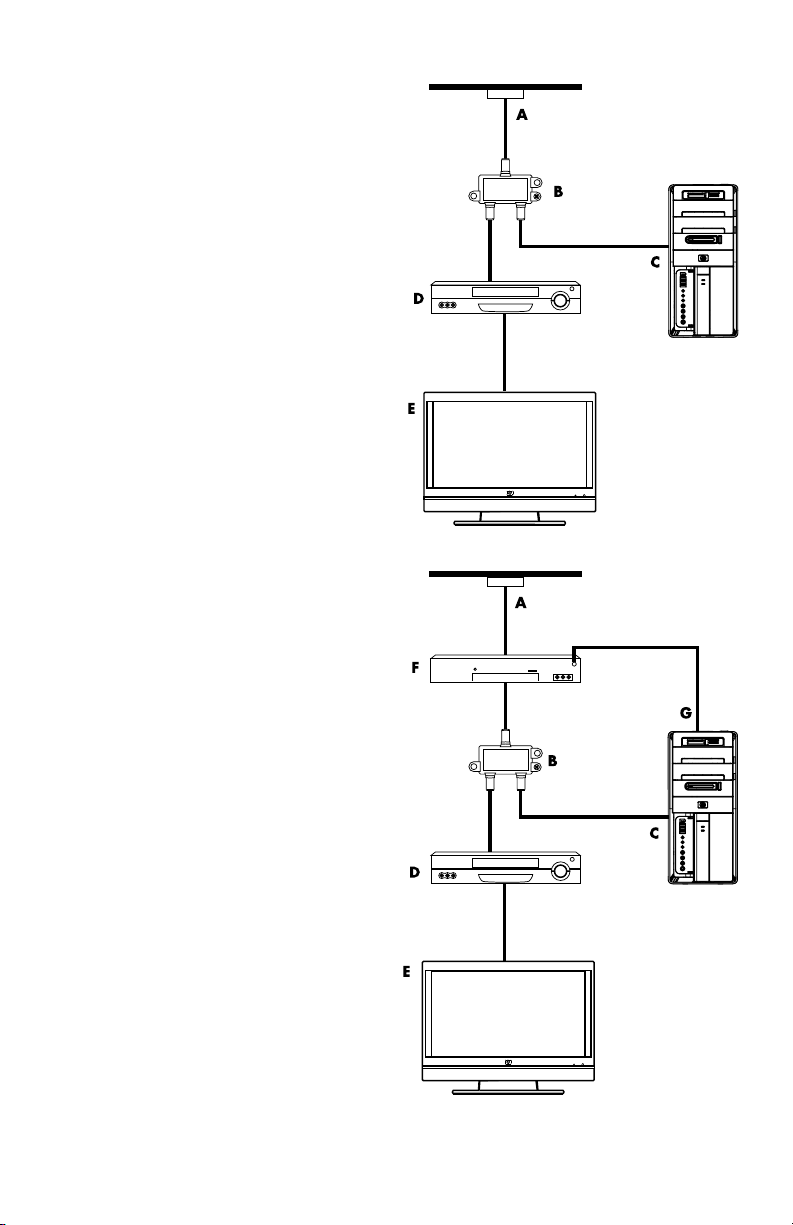
Connecting the TV signal source without a set-top box
To connect the computer into an existing setup
for the TV signal source without a set-top box,
insert (add) a splitter (B) to route the coaxial TV
signal cable from the wall outlet (A) to the
computer connector (C).
Callouts
A TV signal cable (coaxial) wall outlet (from
antenna or cable)
B Splitter
C Computer coaxial TV In connector
D Video recorder
E TV
Connecting the TV signal source with a set-top box
To connect the computer into an existing setup
for the TV signal source with a set-top box
(cable or satellite), insert (add) a splitter (B) to
route the coaxial TV signal cable from the
set-top box (F) to the computer connector (C).
Connect the remote control cable/IR blaster
(select models only) (G) to the IR OUT
connector on the computer, and then position
the blaster on the set-top box. This enables the
computer to change the channel on the set-top
box. See “Using an infrared receiver (IR)
blaster” on page 12 for IR blaster placement
details.
Callouts
A TV signal cable (coaxial) wall outlet
(from antenna or cable)
B Splitter
C Computer coaxial TV In connector
D Video recorder
E TV
F Set-top box/satellite box
G Remote control IR blaster cable (select
models only)
10 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 17
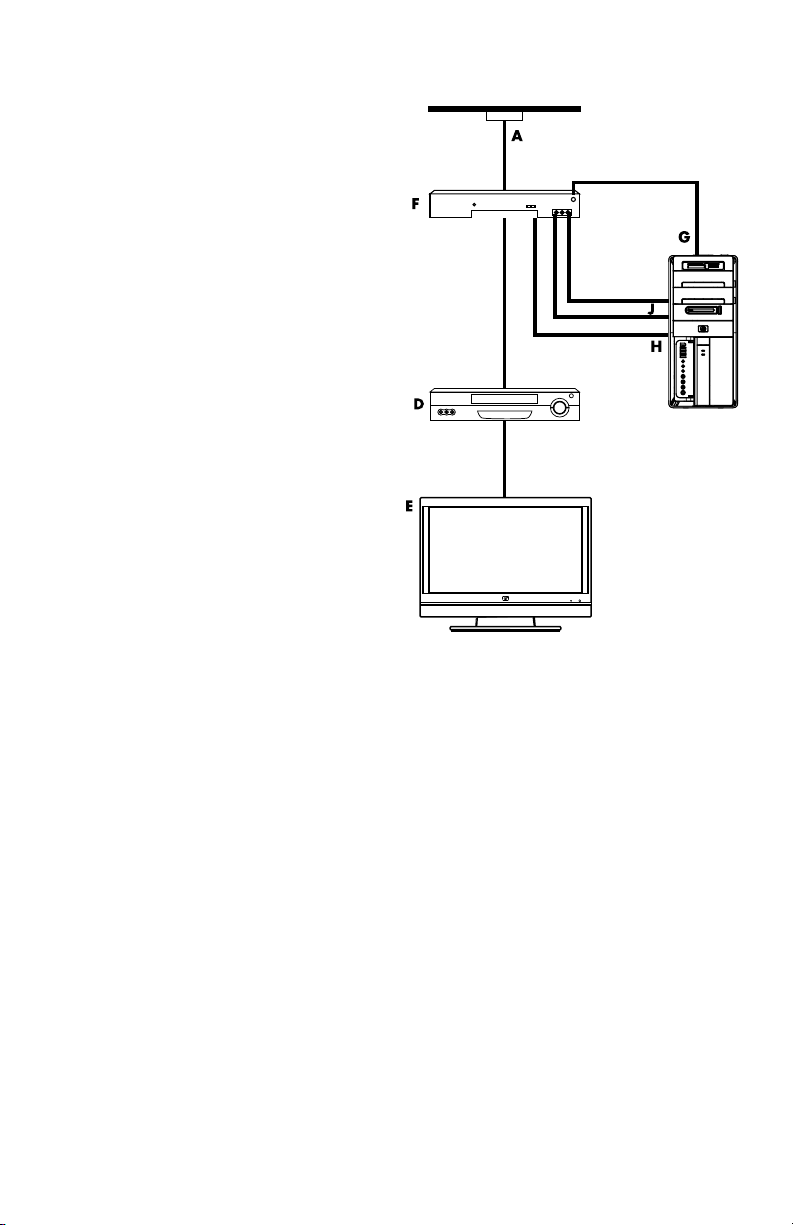
Connecting the TV signal source with a set-top box and using S-video or
composite video cable
To use video output from the set-top box (F),
add the cables to route video and audio to the
computer:
Do not detach any cables from the
existing setup.
Connect an S-video cable (or you can
use an S-video-to-composite cable
adapter) to the S-Video In connector (H)
on the computer.
Connect audio cables to the Audio In
right (red) and left (white) connectors (J)
on the computer.
Connect the remote control cable/IR
blaster (select models only) (G) to the
IR OUT connector on the computer, and
then position the blaster on the set-top
box. This enables the computer to
change the channel on the box. See
“Using an infrared receiver (IR) blaster”
on page 12 for blaster placement
details.
Callouts
A TV signal cable (coaxial) wall outlet (from
antenna or cable)
B Splitter
C Computer coaxial TV In connector
D Video recorder
E TV
F Set-top box/satellite box
G Remote control IR blaster cable (select models only)
H Computer S-video In connector
J Computer right and left Audio In (analog) connectors
Setting Up Your Computer 11
Page 18
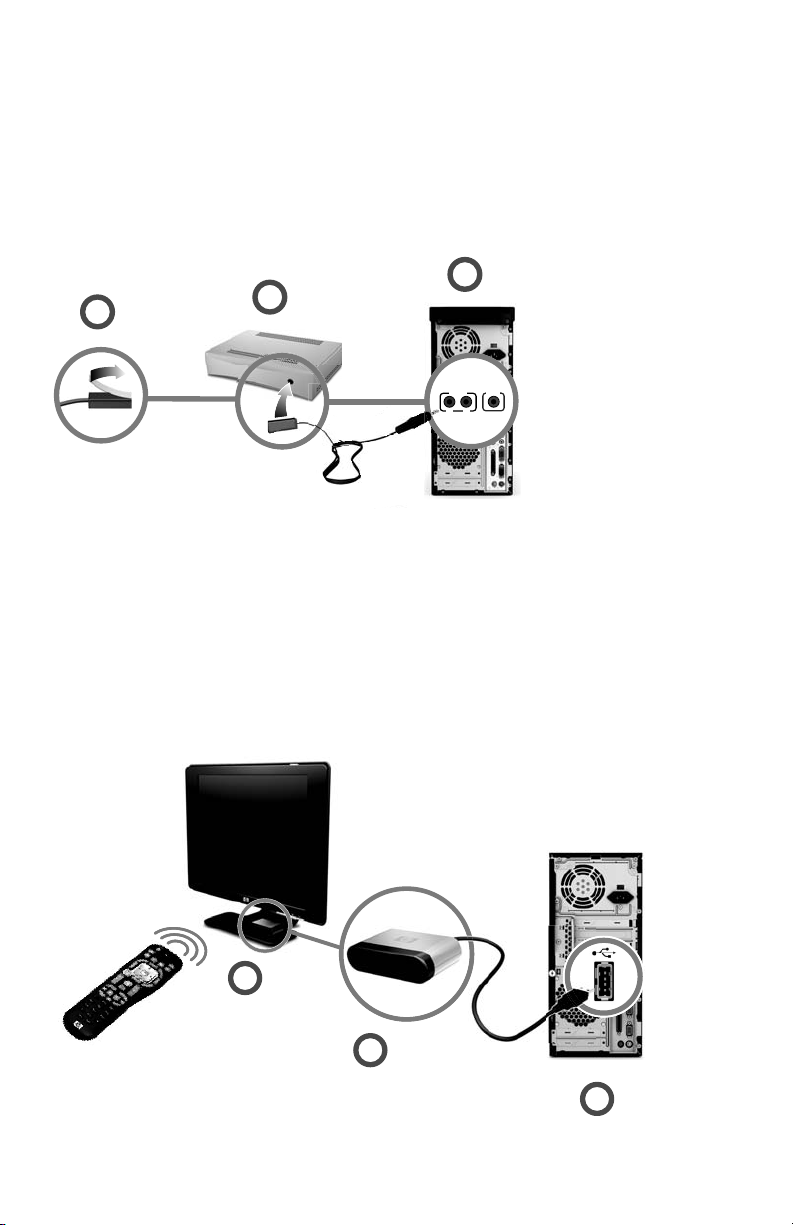
Using an infrared receiver (IR) blaster
(Select models only)
If you have a cable TV or satellite TV set-top box, you can control the set-top box from the
computer by using the remote control sensor cable/IR blaster (select models only) and the
connector on the computer (not available on all models). Remove the tape (1) on the end of
the blaster, adhere it to the IR receiver on the set-top box (2), and connect it to the IR OUT
connector (3) on the back of the computer. Point the remote control at the remote control
sensor on the front top of the computer.
3
1
2
IR IN
IR OUT
12
Using an external IR receiver
(Select models only)
If you do not have a direct line of sight to the remote sensor on the front of the computer, you
can use an external IR receiver and place the IR receiver in a location that can receive a
signal from the remote control.
Connect the external receiver to the red IR IN connector on the back of the computer (1).
Place the IR receiver (2) in a location with a direct line of sight to the remote control. Point the
remote control (3) at the external IR receiver.
3
2
12 Getting Started (features vary by model)
1
Page 19

Preparing to Use Your Computer
After you have completed the steps on the setup poster, you are ready to turn on the
computer.
NOTE: Do not connect or add other devices to the computer until after you turn on the
computer for the first time and complete the initial setup.
To turn on the computer:
1 Turn on the monitor.
2 Turn on the computer.
3 Turn on the external speakers, if they are present.
®
4 Set up the computer and Microsoft
instructions:
If prompted, select the country/region in which you are physically located, and
wait while the computer makes preparations. (When you select an alternate
language, it may take up to 30 minutes for this one-time language setup on the
computer.)
Follow the onscreen instructions to register, sign up for updates, and get online.
5 When you see the
For help with getting started using your computer, see the remaining topics in this section.
Windows 7 desktop, the initial setup is complete.
Windows®7 by following the onscreen
NOTE: If you skip some steps during the initial setup procedure or decline some options, you
will be reminded to complete the setup at a later time.
Preparing to Use Your Computer 13
Page 20

Turning Off the Computer
For best results when using Windows 7, do not shut down the computer except when you must
turn off the power for safety reasons: to make repairs, to install new hardware or cards in the
computer, or to change a battery.
As an alternative to shutting down the computer, you can lock it or put it into either Sleep or
Hibernate mode, if it is available. You can set the power management timers to put the
computer automatically into Sleep or Hibernate mode.
The computer has these reduced power states:
Sleep mode saves your work to memory, so you can resume quickly. It saves
memory to the hard disk drive, and then goes into a reduced-power state.
During Sleep mode, the computer hardware light remains on, and the computer
is ready to wake quickly and resume your work where you left off. If it is present, simply
press the Sleep button on the keyboard to enter sleep mode.
Hibernate mode (available as an advanced power setting) saves the system memory
to a temporary file on the hard disk and then turns off the hardware. When you turn on
the computer again, the programs, folders, and documents that you had open are
restored to the screen.
Restarting the Computer
When you restart the computer, the computer clears some settings and starts over using the
operating system and software in its memory. Restarting is the easiest and most effective way
to solve many software issues for the computer.
Also, you may want to install additional software programs or hardware devices onto the
computer, and doing so may require that you restart the computer after installation.
To restart the computer:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Click the Arrow button next to Shut Down.
3 Click Restart.
Or
Quickly press the On button on the front of the computer.
Connecting to the Internet
Connecting to the Internet requires that you:
1 Purchase high-speed Internet service from an Internet service provider (ISP).
2 Purchase a broadband modem (DSL or cable). This may be provided by the ISP.
3 Purchase and install a wireless router (sold separately), if one is required.
The computer can connect to the Internet through a local area network (LAN) or digital
subscriber line (DSL). Check with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for specific information
on the connection.
14 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 21

1 Refer to “Setting Up Your Computer” on page 1 to make the hardware connections.
You need:
For a network connection, see “Connecting to a Network” on page 6. To check a
wireless LAN device installation, see “Internet access” on page 37.
For a modem, see “Connecting a Modem” on page 7.
2 To connect to the Internet:
Sign up with an ISP. If you already have an account with an ISP, skip this step and
follow the instructions provided by the ISP.
If you did not set up the computer for Internet service during the initial setup, do so
now by using Online Services:
a Click the Start button.
b Click All Programs.
c Click Online Services, and then click Get Online.
d Follow the onscreen instructions to select an ISP and set up Internet service.
NOTE: Online Services provides a list of ISPs; however, you may choose another
ISP or transfer an existing account to this computer. To transfer existing accounts,
follow the instructions provided by the ISP.
3 Connect to the Internet. You must connect through your ISP.
For dial-up only, double-click the ISP-provided icon on the desktop, and then log in.
4 Open your Web browser and browse the Internet.
You can use any Web browser; most computers have Microsoft Internet Explorer
®
. To
open Internet Explorer:
a Click the Start button.
b Click All Programs, and then click Internet Explorer.
NOTE: If you have issues connecting to the Internet, see “Internet access” on page 37.
Using wireless security features
When you set up a home WLAN or access an existing public WLAN, always enable security
features to protect the network from unauthorized access. The most common security levels
are Wi-Fi Protected Access Personal (WPA-Personal) and Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).
When setting up a network, use one or more of the following security measures:
Enable WPA-Personal or WEP security encryption on the router.
Change the default network name (SSID) and password.
Set up a firewall.
Set security on your Web browser.
Preparing to Use Your Computer 15
Page 22

Adjusting the Speaker Volume
There are several ways to adjust volume. Use the Volume icon on the Windows 7 taskbar to
set speaker volume. Then, you can adjust the volume by using:
The Volume knob or buttons on the keyboard (select models only).
The Volume knob on the speakers (select models only).
To set speaker volume, use the Volume icon on the taskbar:
1 Right-click the Volume icon on the taskbar, and then click Open Volume
Mixer.
The Volume Mixer settings window opens.
2 Adjust the volume by clicking the slider bar and moving it.
3 When you are satisfied with the sound level, close the window by clicking the X in the
upper-right corner.
For help with audio, check the troubleshooting items in “Audio and speakers” on page 36.
For more information, open the Help and Support Center or refer to the Support Web site;
see “Getting More Information” on page 25.
Selecting the Microphone
The microphone connector on your computer is ready to use. If you have more than one
microphone connected, select the microphone that you would like to use in Windows 7.
NOTE: When you have a webcam or an audio player connected to the computer, because
of the audio input from the device, Windows 7 may recognize each as a microphone input.
To select the microphone that you would like to use in Windows 7:
1 Right-click the Volume icon on the taskbar, and then click Recording
Devices. The Sound window opens.
2 Select the Microphone that you want to use, click Set Default, and then click
Apply.
3 Click OK.
Adjusting microphone recording level in Windows 7
To adjust the recording level of the microphone:
1 Right-click the Volume icon on the taskbar, and then click Recording
Devices. The Sound window opens.
2 Double-click the microphone connector that you want to use.
3 Click the Levels tab.
4 Adjust the recording level for the microphone by clicking the slider bar and moving it.
5 Click OK, and then click OK again.
16 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 23

Protecting Your Computer
Protect your computer, personal settings, and data from a variety of risks by using:
Passwords.
Antivirus software.
Firewall software.
Critical security updates.
NOTE: Security solutions are designed to act as deterrents, but they may not be able to
prevent software attacks or to prevent the computer from being mishandled or stolen.
Computer risk Computer feature
Unauthorized use of the computer or user
account
Computer viruses Antivirus program
Unauthorized access to data Firewall program
Unauthorized access to Setup Utility,
BIOS settings, and other system
identification information
Ongoing or future threats to the computer Windows 7 critical security updates from
User password
Windows 7 updates
Administrator password
Microsoft
Using passwords
A password is a group of characters that you choose to secure the computer information.
Several types of passwords can be set, depending on how you want to control access to your
information. Passwords can be set in the Windows 7 operating system on the computer.
CAUTION: To avoid being locked out of the computer, record each
password you set. Because passwords are not displayed as they are set,
changed, or deleted, it is essential to record each password immediately
and store it in a secure place. Do not store passwords in a file on the
computer.
You can use the same password for more than one Windows 7 security feature. A password
set in Windows 7 must be entered at a Windows 7 prompt.
For information on Windows 7 passwords: Click the Start button, click Help and
Support, and then type passwords into the Search Help box and press Enter. See “Using the
Help and Support Center” on page 25.
Preparing to Use Your Computer 17
Page 24

Using antivirus software
When you use the computer for e-mail, network, or Internet access, you expose it to computer
viruses. Computer viruses can disable or damage the operating system, software programs,
or computer utilities.
Antivirus software can detect most viruses, remove them, and, in most cases, repair any
damage that they have caused. To provide ongoing protection against newly discovered
viruses, you must keep the antivirus software up to date.
The antivirus program, which is preinstalled on the computer, includes antivirus and firewall
components. The software includes a free trial subscription of protection updates. To protect
the computer against new viruses beyond the trial period, purchase an extended update
service. Instructions for using and updating the antivirus software, and for purchasing
extended update service, are provided within the program.
For more information about computer viruses: Click the Start button, click Help and
Support, and then type viruses into the Search Help box and press Enter. See “Using the
Help and Support Center” on page 25.
Using firewall software
When you use the computer for e-mail, network, or Internet access, unauthorized persons
may be able to gain access to information about you, your computer, and your data. To
protect your privacy, use firewall software:
Windows 7 includes firewall software preinstalled on the computer.
The antivirus program, which is preinstalled on the computer, includes a firewall
program.
Firewall features include logging, reporting, and automatic alarms to monitor all incoming
and outgoing communications.
Under some circumstances, a firewall can block access to Internet games, interfere with
printer or file sharing on a network, or block authorized e-mail attachments. To solve the
problem temporarily, disable the firewall, perform the task that you want to perform, and then
enable the firewall again. To resolve the problem permanently, reconfigure the firewall.
Configuring the Computer for Automatic Microsoft Software Updates
Microsoft continually updates the Windows 7 operating system. Run Windows 7 Update
monthly to install these updates, or keep the operating system up to date by using the
Automatic Updates feature.
When you are connected to the Internet, Windows 7 Update automatically notifies you
(through a pop-up message or icon in the notification area) when critical updates are
available. When you see the Windows 7 Update message, allow the updates to download to
your system. If you update the system weekly, or even monthly, the time required for
download is minimal.
18 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 25

Installing critical security updates
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of information damage or loss from security
breaches and computer viruses, install all critical updates from Microsoft
as soon as you receive an alert.
Additional updates to the operating system and other software may have become available
after the computer was shipped. Download all available updates and install them onto the
computer.
Setting Up User Accounts
When you share a computer with several people, you can set up a user account for each
computer user. Windows 7 uses the information in the user account to determine what files
and folders the computer user can access, when they can make changes to the computer, and
their personal preferences. Each person can access only their own files and settings.
For more information, click the Start button, click Help and Support, and then type User
Accounts into the Search Help box and press Enter. See “Using the Help and Support Center”
on page 25.
Guidelines for Installing Software and Hardware Devices
After you set up the computer and complete the initial setup, you may want to install
additional software programs or hardware devices. Keep in mind the following important
guidelines:
Before installation, make a restore point by using the Microsoft System Restore program.
The restore point is a snapshot of the computer settings. By using System Restore, you
ensure that you have a stable set of settings to use.
Choose software that is compatible with the computer; check the operating system,
memory, and other requirements listed for the new software.
Install the new software according to the directions provided by the software
manufacturer. If you need help, check the manufacturer documentation or customer
service information.
For antivirus software, uninstall the existing software program before reinstalling it or
installing a new antivirus program.
NOTE: Use only licensed original software. Installing copied software may be illegal, or may
result in an unstable installation, or it may infect the computer with a virus.
Preparing to Use Your Computer 19
Page 26

Transferring Files and Settings from an Old Computer to Your New Computer
You can copy files from the old computer to your new computer by using CDs or DVDs,
memory sticks, or personal media drives, or by using the Windows Easy Transfer cable. To
transfer files and copy certain settings, such as Web browser Favorites and address books,
use Windows Easy Transfer software, which is included with Windows 7.
Windows Easy Transfer software guides you to copy files and settings to a storage device or,
using an Easy Transfer Cable, to the new computer. The Easy Transfer Cable is a USB cable
designed specifically to connect two computers and to work with the Windows Easy Transfer
software. (The cable is sold separately.) A standard USB cable does not work.
To transfer your files and settings:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Type Windows Easy Transfer into the Start Search box, and then click Windows Easy
Transfer.
3 Follow the onscreen instructions in the Windows Easy Transfer Wizard to transfer your
files from an old computer to your new one.
For more information, click the Start button, click Help and Support, and then type
moving files into the Search Help box and press Enter. See “Using the Help and Support
Center” on page 25.
20 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 27
Special Features of Your Computer
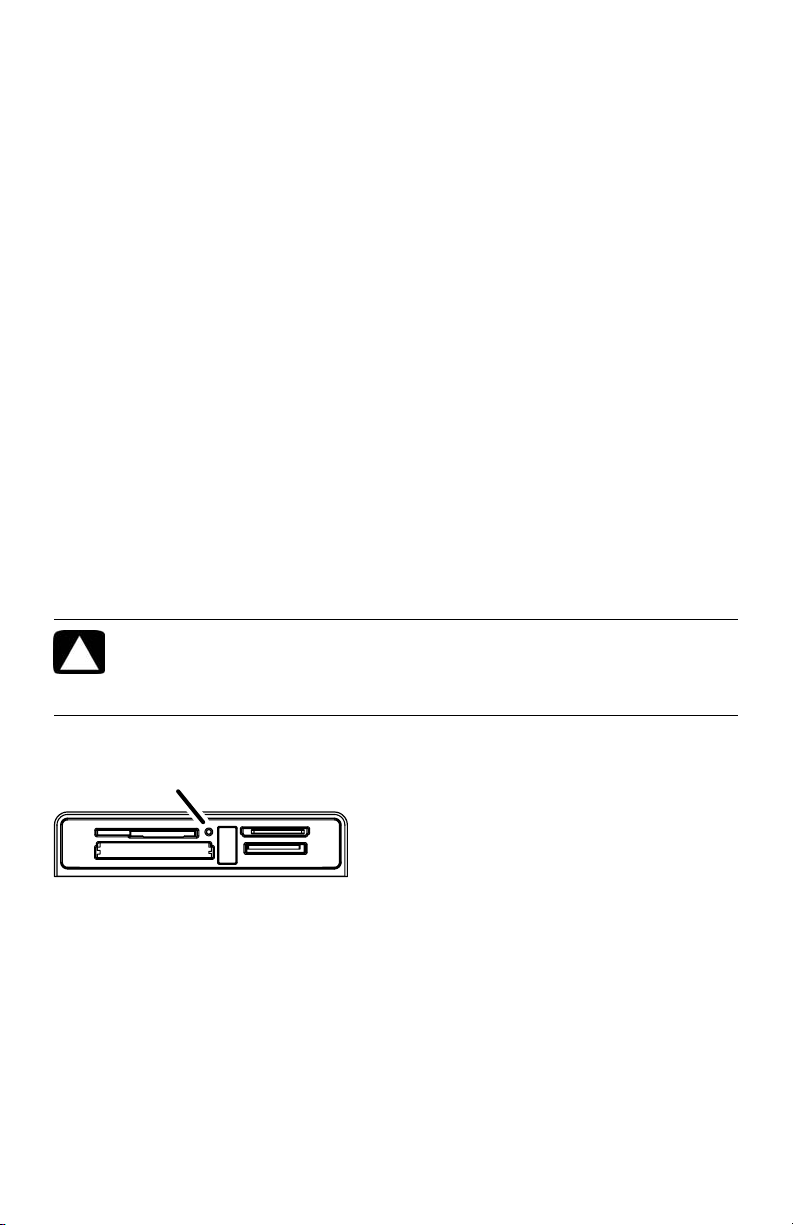
Using the Memory Card Reader
(Select models only)
Your computer may come with a multi-format memory card reader (optional, select models
only). Digital cameras and other digital imaging devices use memory cards, or media, to
store digital picture files. The memory card reader can read from and write to a variety of
types of memory cards and the IBM Microdrive disk drive.
The card reader is accessible directly on the front of the computer. It has two or four
horizontal card slots which accept the media.
You can place media in one or more of the card slots and use each media
independently. Place only one piece of media in a slot at one time.
Each card slot has its own drive letter and icon. When you insert media, the display
label may change to the title of the media, if a title is available.
When you insert media, the Safely Remove Hardware window may appear. If it opens,
or if you open the Safely Remove Hardware window by mistake, click Close.
CAUTION: Do not click Stop in the Safely Remove Hardware window with
the USB Mass Storage Device selected. Doing so removes the operating
system recognition of the memory card reader from your computer, and
you must restart the computer to see the memory card reader again.
Memory card reader
A
The activity light (A) blinks to indicate that the computer is accessing the memory card to read
or write.
Special Features of Your Computer 21
Page 28

To use the memory card reader:
1 Insert the media into the card slot until it stops.
The activity light (A) on the memory card reader lights, and the computer automatically
detects the media.
NOTE: You must insert media correctly. Note the direction of the notched corner on the
media. For more information, open the Help and Support Center or refer to the Support
Web site; see “Getting More Information” on page 25.
Also:
CompactFlash and Microdrive media are keyed and cannot be inserted incorrectly.
Insert the receptacle edge (holes) of this media into the slot.
Some memory cards, such as CF Ultra/III, are not compatible with the memory
card reader that came with your computer.
Do not use SM and xD media in the memory card reader at the same time. The
reader recognizes only the first one that is inserted.
2 Select a program to access your files. You can copy files from or to the media.
Or
If the AutoPlay window does not open, click the Start button, click Computer, and
then double-click the Memory Card icon to display the files on the media. You can
copy files from or to the media.
3 When you are finished, right-click the drive icon, click Eject, check that the memory
card reader activity light is on or off, but not blinking, and then remove the media.
CAUTION: Do not try to remove media when the activity light is blinking.
Doing so may cause loss of data.
22 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 29
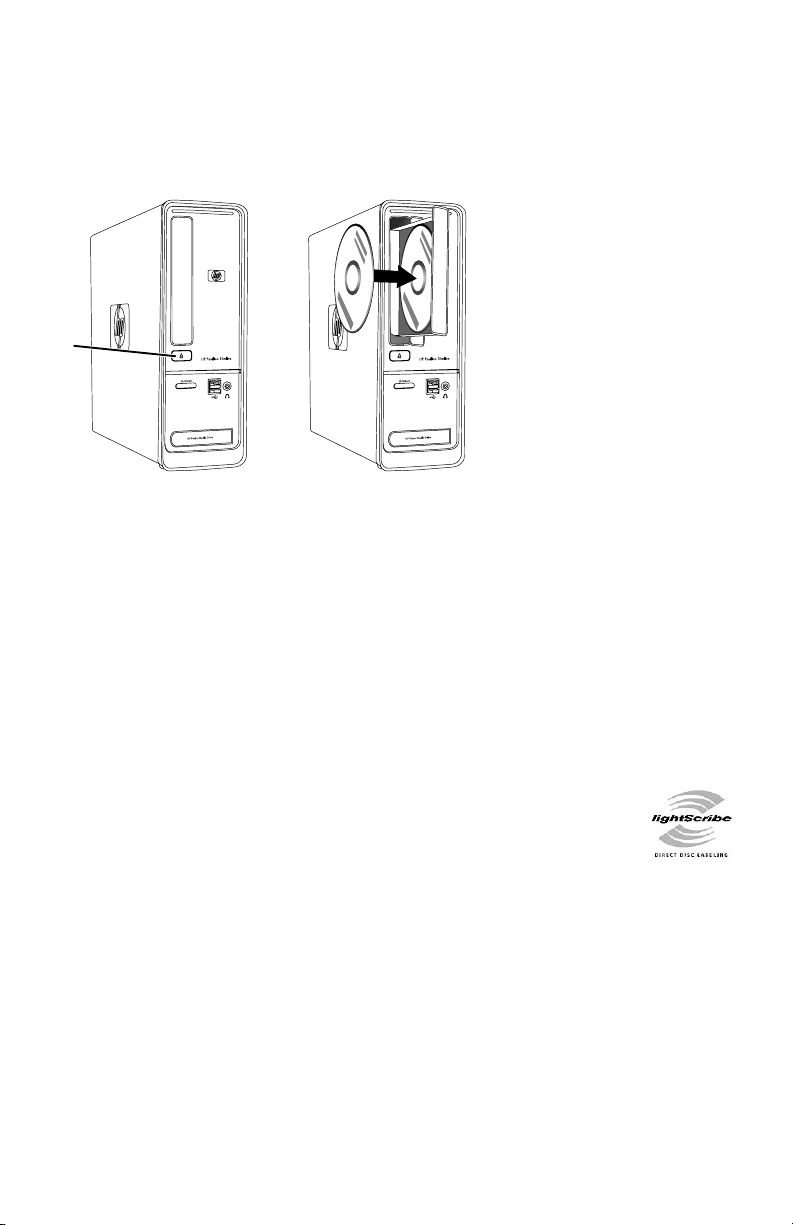
Using a Vertical CD/DVD Drive
A
(Select models only)
Your computer may have an optical disc drive that is installed in a vertical position. Press the
Eject button on or near the drive door (A) to eject the CD/DVD tray. Place a standard-sized
disc in the tray with the label facing out, and then press the front of the tray to close it.
Using LightScribe Technology
(Select models only)
What is LightScribe?
LightScribe is an innovative technology that uses a special disc drive, special media
(LightScribe-writable CDs or DVDs), and label-making software to burn labels directly onto the
disc. A LightScribe-enabled CD or DVD drive uses the optical laser in the drive to burn a label
onto a thin dye coating on the label side of the disc. There is no ink to smear or paper to curl,
and there are no adhesives to loosen.
LightScribe requirements
Burning a label with LightScribe requires three things:
A LightScribe-enabled optical disc drive (select models only), identified by
the LightScribe logo
Labeling software that supports LightScribe
A writable LightScribe disc (sold separately)
Making a LightScribe label by using CyberLink LabelPrint
You may burn data, music, and videos to the disc before or after labeling it.
For more information about making a LightScribe label:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Help and Support.
2 Type Lightscribe in the Search Help box, and then press Enter.
Special Features of Your Computer 23
Page 30

Using the Remote Control
O
(Select models only)
NOTE: Only use alkaline batteries in the remote control.
With your remote control, you can open Windows Media Center to view television
broadcasts, to record and play TV programs, and to play music, movies, or video.
To open Windows Media Center, point the remote control at the remote control sensor on the
top front of the computer, and press the Windows Media Center Start button on the remote
control.
r
To use the remote control, point it in a direct line of sight at the remote sensor. The remote
control and the sensor can be no farther than 8 meters apart. The remote control can be no
more than 22.5 degrees (45 degrees total) from the center of the remote sensor.
NOTE: Bright, direct light aimed toward the sensor might interfere with the remote control
operation.
24 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 31

Getting More Information
Using the Help and Support Center
(Select models only)
Information about your computer is in the Help and Support Center. Here, you can find links
to driver updates, access to technical support options, and information about commonly
asked questions.
To open the Help and Support Center:
Press the Help button (select models only) on your keyboard.
Or
Click the Start button, and then click Help and Support.
Accessing Support on the Web
You can find information for your computer by using the Internet to access the Support Web
site address listed in the Limited Warranty and Support Guide, or use the following steps:
1 Go to http://www.hp.com/support in your Web browser.
2 Select your country/region and language.
3 Click Support and Drivers.
4 Enter the model number of your computer, and then click Search . Click an item to
view it.
Finding Guides on the Web
You can find guides for your computer by using the Internet to access the Support Web site:
1 Go to the Support Web site and search for your model number using the previous
procedure.
2 Click Manuals.
3 Locate the manual you want, and then do one of the following:
Click the title to display the file in Adobe
download from the Manuals page if it is not currently installed on your computer).
Or
Right-click the title, click Save Target As, specify a location on the computer
where you want to save the file, rename the file (retaining the .pdf extension), and
then click Save.
®
Acrobat® Reader (which you can
Getting More Information 25
Page 32

Finding Onscreen Guides
(Select models only)
You can find onscreen guides for your computer in the User Guides folder.
1 Click the Start button.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click User Guides.
Click an item to view or use it.
NOTE: If there are no guide titles listed in the folder, your computer has no onscreen guides.
Using the PC Help & Tools Folder
The PC Help & Tools folder contains special utilities for computer owners, such as support
information and programs.
To see the items in the PC Help & Tools folder:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Click All Programs.
3 Click PC Help & Tools.
Using HP Advisor Software
(Select models only)
HP Advisor is a desktop tool you use to monitor and access system health information about
key areas of your computer. HP Advisor has four major areas:
PC Dock — Access HP and Partner software directly on your desktop and customize
your dock by dragging and dropping items.
PC Dashboard — Check your computer status at a glance with the PC Dashboard.
Access all the items you need to run your computer from HP and Partners.
PC Discovery — Explore HP and Partner software and online services that are
installed on your computer, and find offers for exciting new software and services.
To open the HP Advisor Dock, click the HP logo on the taskbar.
26 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 33

Using the Computer with Safety and Comfort
WARNING: To reduce the risk of serious injury, read the Safety & Comfort
Guide. It describes proper workstation setup, posture, and health and
work habits for computer users. It also provides important electrical and
mechanical safety information.
Before you begin using the computer, arrange the computer and your work area to maintain
your comfort and productivity. Refer to the Safety & Comfort Guide for important ergonomic
information:
Click the Start button, click All Programs, click User Guides, and then click
Safety & Comfort Guide.
Or
Type
http://www.hp.com/ergo
into the Web browser address box, and then press Enter on the keyboard.
Getting More Information 27
Page 34

28 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 35

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
This section contains:
Troubleshooting tables in “Troubleshooting Computer Problems” below.
Software repair information in “Software Troubleshooting” on page 45.
Maintenance information and guidelines in “Maintenance” on page 48.
For more information, refer to the Help and Support Center or access the Support Web site;
see “Getting More Information” on page 25.
Refer to the documentation provided by the product manufacturer for information about
peripheral-specific problems, such as issues with a monitor or a printer.
Troubleshooting Computer Problems
The following tables present some symptoms of issues you may encounter while installing,
starting up, or using your computer. The tables also provide possible solutions you can try.
The troubleshooting tables appear in the following order:
“Computer does not start” on page 30
“Power” on page 31
“Display (monitor)” on page 31
“Keyboard and mouse (with cable)” on page 32
“Wireless keyboard and mouse” on page 33
“Audio and speakers” on page 36
“Internet access” on page 37
“CD and DVD drives” on page 38
“Video” on page 40
“Hardware installation” on page 41
“Performance” on page 42
“Wireless devices” on page 43
“Remote control” on page 44
“Memory card reader” on page 44
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 29
Page 36

Computer does not start
Symptom Possible solution
Computer will not turn
on or start.
Computer seems to be
locked up and is not
responding.
Ensure that the cables connecting the computer to the external
power source are plugged in properly.
When the cables connecting the computer to the external
power source are plugged in properly, and the wall outlet is
functioning, the green power supply light on the back of the
computer should be on; if it is not, refer to the Limited Warranty
and Support Guide to contact Support.
If the display (monitor) is blank, the monitor may not be
properly connected. Connect the monitor to the computer, plug
it in, and turn it on. See “Display (monitor)” on page 31.
Set the line voltage selection switch to the correct setting for
your country/region, or refer to the Limited Warranty and
Support Guide to contact Support.
Test the wall outlet by connecting a different electrical
device to it.
Use the Windows Task Manager to close any programs not
responding, or restart the computer:
1 Press the Ctrl, Alt, and Delete keys on the keyboard
simultaneously.
2 Click Start Task Manager.
3 Select the program that is not responding, and then click
End Task.
If closing programs does not work, restart the computer:
1 Press the Ctrl, Alt, and Delete keys on the keyboard
simultaneously.
2 Click the Arrow button next to the red Shut Down button,
and then click Restart.
Or
1 Press and hold the On button for 5 or more seconds to turn
off the computer.
2 Press the On button to start the computer.
Error message: Hard
disk drive error.
30 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Refer to the Limited Warranty and Support Guide to contact
Support.
Page 37

Power
Symptom Possible solution
Error message: Invalid
system disk or
Non-System disk or
Disk error.
Computer does not turn
off when the On button
is pressed.
Computer shuts down
automatically.
When drive activity stops, remove the disk and press the
spacebar on the keyboard. The computer should start up.
Press and hold the On button until the computer turns off.
Check Power Settings.
The computer may be in an exceedingly hot environment. Let it
cool down.
Ensure computer air vents are not blocked and internal fan is
running. Note that your computer may not have an internal fan.
See “Cleaning the computer vents” on page 50.
Display (monitor)
Possible solution (In addition to the information listed here,
Symptom
Screen is blank, and
monitor power light is
not lit.
Screen is blank. Press the space bar on the keyboard or move the mouse to
also refer to the documentation that came with your monitor.)
Reconnect the power plug to the back of the monitor and to the
wall outlet.
Press the On button on the front of the monitor.
make the screen display visible again.
Images on the screen
are too large or too
small, or the images are
fuzzy.
Press the Sleep button (select models only), or the Esc key on the
keyboard, to resume from Sleep mode.
Press the On button to turn on the computer.
Inspect the monitor video connector for bent pins:
If any of the pins are bent, replace the monitor connector
cable.
If no pins are bent, reconnect the monitor connector cable
to the computer.
Adjust the monitor resolution setting in Windows 7:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
2 Under Appearance and Personalization, click Adjust
Screen Resolution.
3 Adjust resolution as necessary, and then click Apply.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 31
Page 38

Keyboard and mouse (with cable)
Symptom Possible solution
Keyboard commands
and typing are not
recognized by the
computer.
Mouse (with cable)
does not work or is not
detected.
Cursor does not
respond to mouse
movement.
Turn off the computer by using the mouse, unplug and
reconnect the keyboard to the back of your computer, and then
turn on your computer.
Unplug and reconnect the mouse cable to your computer.
If the mouse is still not detected, turn off the computer, unplug
and reconnect the mouse cable, and then restart the computer.
Restart your computer by using the keyboard:
1 Press the Alt and Tab keys on the keyboard simultaneously
to navigate to an open program.
2 Press the Ctrl and S keys on the keyboard
simultaneously to save your changes in the selected
program (Ctrl+S is the keyboard shortcut for Save on
most—not all—programs).
3 Repeat step 1 and step 2 to save changes in all open
programs.
4 After saving changes in all open programs, press the Ctrl
and Esc keys on the keyboard simultaneously to display
the Windows Start Menu.
5 Use the arrow keys to select the Arrow button next to
Shut Down. Select Shut Down, and then press the Enter
key on the keyboard.
6 After the shutdown is complete, unplug and reconnect the
mouse connector to the back of your computer, and then
turn on your computer.
32 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 39

Keyboard and mouse (with cable) (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
Cursor responds slowly,
moves only vertically or
horizontally, or does not
track smoothly.
I cannot move the
cursor using the arrow
keys on the number
key pad.
For a mouse with a roller ball:
Clean the roller ball: Remove the roller ball cover from
bottom of mouse (rotate it counterclockwise), remove the
ball, and clean it with a damp, lint-free cloth (not paper).
Also clean the rollers on which the ball moves.
Use a mouse pad or other rough surface under the mouse.
For an optical mouse:
Clean the optical mouse: Gently wipe the light sensor lens
on the bottom of the mouse with a lint-free cloth
(not paper).
Use a mouse pad, white sheet of paper, or other less
reflective surface under the mouse.
For detailed cleaning instructions, go to:
http://www.hp.com/support
Select your country/region and language, search on your
computer model number, and then search on the keyword
cleaning.
Press the Num Lock key on the keyboard to turn off the Num
Lock light. The Num Lock light should not be on if you want to
use the arrow keys on the number key pad.
Wireless keyboard and mouse
Symptom Possible solution
Wireless keyboard or
mouse does not work or
is not detected.
Check for these problems:
Ensure you are using the wireless keyboard or wireless
mouse within range of the receiver, approximately
10 meters for normal use, and within 30 cm during initial
setup or for resynchronization.
Replace the batteries in the keyboard and mouse: Turn the
devices over, turn the mouse off, take off the battery cover,
remove the old batteries, insert new alkaline batteries,
replace the battery cover, and then turn on the mouse.
NOTE: Do not use rechargeable batteries.
Ensure the mouse is not in Suspend mode, which occurs
after 20 minutes of inactivity. Click the left mouse button to
reactivate it.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 33
Page 40

Wireless keyboard and mouse (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
Wireless keyboard or
mouse does not work or
is not detected.
(continued)
Resynchronize the keyboard and mouse to the
receiver:
The receiver, wireless keyboard, and wireless mouse shown in
the illustrations are examples; your models may vary.
IMPORTANT: During these steps, place the wireless keyboard
and wireless mouse on the same level as the receiver, within
30 cm of the receiver, and away from interference from other
devices.
1 Unplug the receiver from a USB connector on the
computer, and then reconnect it. Your computer model
may have a connector dedicated to the receiver. If you
have a choice, use a USB connector on the front of the
computer.
2 The receiver may have an LED light or a Connect button,
which is also an LED light. Skip this step if your receiver
has no Connect button (A).
A
Push the Connect
button (A) on the
receiver (which is also the
LED light), and hold it for
5 to 10 seconds until the
light starts to flash.
34 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 41

Wireless keyboard and mouse (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
Wireless keyboard or
mouse does not work or
is not detected.
(continued)
3 Check that the mouse is on (B), and push and hold the
Connect button (C) on the underside of the mouse for
5to10seconds until the LED (A) on the receiver lights or
stops flashing.
NOTE: The receiver
connection session
times out after
C
60 seconds. To ensure
the connection was
B
Off
Connect
On
established, and that
the receiver did not
time out instead, move
the mouse and check
for response on the
screen.
4 After the mouse connection is established, continue with
the steps that follow to repeat the procedure for the
keyboard.
5 Skip this step if your receiver model has no Connect
button (A).
Push the Connect button on the receiver (A), and hold it
for 5 to 10 seconds until the light starts to flash.
6 Push and hold the Connect button (D) on the underside of
the keyboard for 5 to 10 seconds until the LED (A) on the
receiver lights or stops flashing.
D
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 35
Page 42

Audio and speakers
Symptom Possible solution
No sound is produced. If you use an HDMI connector on the graphics card (select
models only) to connect your display (monitor) to the computer,
you should also connect analog speakers to the computer
Audio Line Out connector if you want to hear sound during the
initial setup of the computer.
Refer to the setup poster to connect analog speakers.
Press the Mute button on the keyboard to see whether the Mute
feature is enabled.
Or
1 Right-click the Volume icon on the taskbar, and
then click Open Volume Mixer.
The Volume Mixer settings window opens.
2 If programs are muted, click the Mute button to unmute.
If you are using built-in monitor speakers, use the monitor front
panel Volume button to adjust volume. Use the front panel
buttons to enter the onscreen display (OSD) and ensure audio is
enabled and volume is set appropriately.
To increase the volume, click the Volume icon on the task bar,
or use the keyboard controls. Check the volume setting in your
software program.
Ensure that you connected powered (active) speakers and that
they are turned on.
Turn off your computer, and then unplug and reconnect the
speakers. Ensure the speakers are connected to an audio
connector, not a Line In or headphone connector.
To resume from Sleep mode, press the Sleep button (select
models only), or press the Esc key on the keyboard.
Unplug headphones if they are connected to your computer (or
speaker system).
Volume is very low or
unsatisfactory.
36 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Ensure that you connected the speakers to the Audio Out (lime
green) connector on the back of the computer. (Additional
audio connectors are used for multiple-channel speakers.)
Detached non-powered speakers (speakers without a separate
power source, such as batteries or a power cord) do not
produce satisfactory sound. Replace the non-powered speakers
with powered speakers.
Page 43

Internet access
Symptom Possible solution
I cannot connect to the
Internet.
Contact your ISP for assistance.
Verify that you are using the proper cables for your Internet
connection type. Your computer may have a dial-up modem
and an Ethernet network adapter (also called a network
interface card, or NIC). A modem uses a standard telephone
cable while the network adapter uses a network cable to
connect to a local area network (LAN). Do not connect a
telephone cable to the network adapter, and do not plug a
network cable into a telephone service line; doing so may
damage the network adapter.
For more information about connecting to the Internet, open the
Help and Support Center; see “Using the Help and Support
Center” on page 25.
Run the wireless setup wizard:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
2 Click Network and Internet, and then click
Network and Sharing Center.
3 In the Network and Sharing Center window, click Set up
a connection or network to open the wizard.
4 Follow the onscreen instructions.
Use Device Manager to verify that the integrated WLAN device
is installed on the computer correctly:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Type Device Manager into the Start Search box, and then
click Device Manager.
3 Click Network adapters. Your WLAN device should
be listed here. The WLAN device may include the term
wireless, wireless LAN, or 802.11.
4 Click the Start button.
5 Type Network and Sharing Center into the Start Search
box, and then click Network and Sharing Center to
open the Network and Sharing Center window.
6 Click Connect to a network, and then follow the
onscreen instructions.
If your system has an external antenna, try to move the antenna
to a better position. If the antenna is internal, try to move the
computer.
Try to connect again later, or contact your ISP for assistance.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 37
Page 44

Internet access (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
Internet programs do
not start automatically.
Log in to your ISP, and start the desired program.
CD and DVD drives
Symptom Possible solution
The CD or DVD drive
cannot read a disc, or it
takes too long to start.
I cannot remove a CD
or DVD.
Ensure the disc is inserted with the label facing out and
centered in the tray.
Wait at least 30 seconds for the drive to determine the type of
media.
Clean the disc with a disc cleaning kit, available from most
computer stores.
The driver may be corrupted or outdated. For detailed
information about restoring and updating drivers, see
“Updating drivers” on page 45.
Turn on your computer, and press the Eject button nearest the
drive to open the tray.
If you suspect a problem with the Eject button itself:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Computer.
2 Right-click the CD or DVD drive you want to open.
3 Select Eject from the menu.
My minidisc CD is
falling down inside the
computer.
38 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Vertical and slot-loading disc players cannot play non-standard
discs.
For a CD/DVD drive with a tray that is installed in a vertical
position, standard-sized discs fit into the drive tray vertically,
with the label facing out. To use a minidisc with a vertical drive
tray, you must first place the computer on its right side (select
models only) before you insert the minidisc:
1 Face the front of the computer and lay the computer down
on its right side.
2 Press the Eject button to open the CD/DVD tray.
3 Place the minidisc into the recess inside the tray, and then
press the front of the tray to close it.
Page 45

CD and DVD drives (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
I cannot create (record)
adisc.
Ensure the disc is inserted with the label facing out and
centered in the tray.
Verify that you are using the correct disc type (media) for the
drive. Try a different brand of disc.
Ensure the disc is clean and undamaged. If recording stopped
during a recording session, the disc may be damaged; use a
different disc.
Use the correct type of disc for the type of files you are
recording.
When using a CD-R disc, ensure it is blank if recording music,
and that it is blank or appendable (with space to add more
data files) if recording data.
Verify that you are using the correct disc type when you make a
copy of a disc. Some recording programs can record only to
the same disc type as the source. For example, you can record
a DVD only to a DVD+R/-R or a DVD+RW/-RW disc, and you
can record a CD only to a CD-R or a CD-RW disc.
Ensure that the disc is in the correct drive, and that you specify
the same drive in the CD or DVD recording software.
Select a slower write speed for the recording drive, if a slower
speed is available.
The recording software may not let you add a track if it exceeds
the available space on your disc. You can make space
available by removing one or more tracks from the list before
recording the files to the disc.
Close all software programs and windows before recording.
Ensure you have enough available space on your hard disk
drive to store a temporary copy of the content.
Click the Start button, and then click Computer. Right-click
the hard disk drive, and then click Properties to view the
available space.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 39
Page 46

CD and DVD drives (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
I cannot create (record)
adisc.
(continued)
I cannot play a DVD
movie on a DVD player.
If you are on a network, copy the files from a network drive to
your hard disk drive first, and then record them to disc.
Close all programs and windows, and then restart your
computer.
Your DVD player cannot play video files that were recorded
onto the DVD as data files. To play a movie properly, use a
video recording program. Some video files may be viewed on
a computer, but not on a home DVD video player.
Video
Symptom Possible solution
Some video files do
not play.
Codec error messages
appear when I try to
play certain video files.
Your file may be corrupt or in an unsupported format. Open the
video file in a video editor, and then resave the file in a
supported format.
Open the file in Windows Media Player. Ensure Windows
Media Player is configured to automatically download codecs.
If the correct codec is available, the file will play. Note
that you must be connected to the Internet to download the
codec file.
If the correct codec is not available, check to see whether
there is an update available for Windows Media Player.
For more information, open Windows Media Player Help and
search for codec.
Error message: Files
Needed To Display
Video Are Missing or
Corrupt.
40 Getting Started (features vary by model)
1 Click the Start button.
2 Type Device Manager into the Start Search box, and then
click Device Manager to open the Device Manager
window.
3 Click the plus sign (+) next to Sound, video and game
controllers.
4 Right-click TV tuner (select models only), and then click
Update Driver Software.
5 Select Search automatically for updated driver
software.
6 Follow the instructions to update the driver.
7 If you are prompted, restart the computer.
Page 47

Hardware installation
Symptom Possible solution
A new device is not
recognized as part of
the system.
A new device does
not work.
Install the device driver from the CD provided with the device,
or download and install the driver from the device manufacturer
Web site.
You may need an updated driver for Windows 7. Contact the
device vendor directly for an update.
For Hewlett-Packard peripheral devices, visit the HP Web site at
http://www.hp.com/support
Ensure that all cables are properly and securely connected and
that the pins in the cable or connector are not bent.
Turn off the computer, turn on the external device, and then turn
on the computer to integrate the device with the computer.
Restart the computer, and follow the instructions for accepting
the changes.
Disable the automatic settings in the operating system for the
new device, and choose a basic configuration that does not
cause a resource conflict.
You can also reconfigure or disable devices to resolve the
resource conflict.
To install or uninstall a device driver, you must be logged in
with administrative privileges. If you need to switch users, click
the Start button, click the Arrow button next to Shut Down,
and then click Switch User. Choose a user with administrative
privileges.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 41
Page 48

Hardware installation (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
A device does not work
after installing a new
device.
To resolve a device conflict, you may need to disable one of the
devices or uninstall an old device driver:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Type Device Manager into the Start Search box, and then
click Device Manager to open the Device Manager
window.
3 Click the plus sign (+) next to the problem device and
check for an exclamation point in a yellow circle near the
device icon. The exclamation point means there is a
device conflict or problem with the device. Exclamation
points do not always appear when a device is not
working properly.
4 If you have removed a hardware device, but the device
driver is still listed in the Device Manager, this may be
causing the device conflict. To uninstall the old driver so
that the new device driver works properly, right-click the
device, click Uninstall, and then click OK.
5 Right-click the name of the device, and then select
Properties.
6 Click the General tab to see whether your device is
enabled and working properly. If it is available, click the
Troubleshoot button, and follow the onscreen
instructions in the device troubleshooter wizard.
7 Restart the computer. Click the Start button, click the
Arrow button next to Shut Down, and then click Restart.
Performance
Symptom Possible solution
Computer displays a
processor speed that is
lower than expected.
Software programs and
files take longer than
expected to open or
respond.
42 Getting Started (features vary by model)
This happens when the processor is automatically running in a
lower power state, because the applications running do not
require the maximum processing power.
If you created multiple user accounts on your computer, ensure
other users are not logged in. If there are multiple users logged
in simultaneously, system resources must be shared among
them.
Page 49

Wireless devices
Symptom Possible solution
Bluetooth device is not
working.
Ensure the device and your computer are the correct distance
apart—not too far and not too near. For the correct distance,
refer to the device instructions.
Remove and then reinstall the device:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
2 Click Hardware and Sound, and then click
Bluetooth Devices.
3 Select the device that is not working, and then click
Remove.
4 Click Add, press the Reset button on the device, place a
check mark in the My device is set up and ready to
be found check box, and then click Next.
5 Follow the onscreen wizard instructions.
The device may have too many connections. Either wait until
the device is less busy, or set the other devices so they are not
discoverable. For information on how to turn off discoverability,
refer to the device instructions.
Ensure other devices that use radio frequencies (for example,
microwave ovens, cordless phones, and 802.11 wireless
networks) are not creating interference. Try moving the device
that is not working farther away from other devices.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 43
Page 50

Remote control
Symptom Possible solution
Remote sensor is not
receiving a signal from
the remote control.
Be sure to point the remote control at the sensor.
Be sure the remote control has fresh batteries.
For an external sensor with a USB connector, try enabling
the IR connection by following these steps:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Type Device Manager into the Start Search box, and then
click Device Manager to open the Device Manager
window.
3 Click the plus sign (+) next to Universal Serial Bus
controllers.
4 If eHome Infrared Receiver is listed under Universal Serial
Bus Controllers, Windows 7 is properly detecting the
IR receiver. If it is not listed, go to the next step.
5 Unplug the end of the USB cable on the remote sensor
from the computer, and then plug it back into the same
USB connector.
6 Disconnect all other USB devices, leaving the remote
sensor connected, and then restart the computer. Connect
other USB devices after the remote sensor appears in the
Device Manager window.
Memory card reader
Symptom Possible solution
Memory card reader
cannot read the
memory card.
44 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Do not insert or remove memory cards when the in-use (activity)
light is flashing. Doing so may cause data loss or permanent
damage to the card reader.
Some memory cards have a Read/Write or a Security switch.
Ensure the switch is set to Write Enabled before you attempt to
write data to the card.
Ensure the amount of stored data does not exceed the storage
limit of the memory card.
Page 51

Memory card reader (continued)
Symptom Possible solution
Memory card reader
cannot read the
memory card.
(continued)
Ensure the memory card is one of the supported types:
CompactFlash (I, II, and Microdrive), Memory Stick, Memory
Stick Pro, MultiMedia, Secure Digital, SmartMedia, or xD.
Some models may support additional types, such as SDHC
(Secure Digital High-Capacity) memory cards.
Ensure the memory card is fully inserted into the correct slot.
Inspect the ends of the memory cards for dirt or material that
closes a hole or spoils a metal contact. Clean the contacts with
a lint-free cloth and a small amount of isopropyl alcohol.
Replace the memory card if necessary.
Software Troubleshooting
Your computer uses the operating system and installed software programs during normal
operation. If your computer works improperly or stops because of the software, you may be
able to repair it.
Some software repairs are as simple as restarting your computer, and others require
performing a system recovery from files on your hard disk drive.
Software repair overview
The most efficient way to repair software problems is simply to restart the computer or turn the
computer off completely and then power it back up again. If this does not work, then explore
the following methods for fixing your computer if you are experiencing software problems:
Updating drivers (see the following section, “Updating drivers”).
Microsoft System Restore (see “Microsoft System Restore” on page 46) — Restores your
computer configuration to a configuration that was in use before the current software
problem existed.
Software program and hardware driver reinstallation (See “Software program and
hardware driver reinstallation” on page 47) — Allows reinstallation of the
factory-installed software or hardware driver by using the Recovery Manager program.
System recovery (see “System Recovery” on page 50) — Erases and reformats the hard
disk drive, deleting all data files you have created, and then reinstalls the operating
system, programs, and drivers.
Updating drivers
A driver is a software program that enables your computer to communicate with an attached
device, such as a printer, hard disk drive, mouse, or keyboard.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 45
Page 52

Complete the following procedure to update a driver, or to revert to an earlier version of the
driver if the new one does not solve your problem:
1 Click the Start button.
2 Type Device Manager into the Start Search box, and then click Device Manager to
open the Device Manager window.
3 Click the plus sign (+) to expand the type of device you want to update or rollback.
(For example, DVD/CD-ROM drives).
4 Double-click the specific item (for example, HP DVD Writer 640b).
5 Click the Driver tab.
6 To update a driver, click Update Driver, and then follow the onscreen instructions.
Or
To revert to an earlier version of a driver, click Rollback Driver, and then follow the
onscreen instructions.
Microsoft System Restore
Microsoft Windows 7 includes a feature that enables you to restore your computer
configuration to a configuration that was in use before the current software problem existed.
The feature does this by creating a restore point where it records the computer settings at that
time and date.
When a new program is installed, the operating system automatically creates a restore point
before it adds the new software. You can also set restore points manually.
If you experience a problem that you think may be due to software on your computer, use
System Restore to return the computer to a previous restore point.
NOTE: Always use this System Restore procedure before you use the system recovery
program.
To start a System Restore:
1 Close all open programs.
2 Click the Start button, right-click Computer, and then click Properties.
3 Choose System protection, System Restore, and then click Next.
4 Follow the onscreen instructions.
To manually add restore points:
1 Close all open programs.
2 Click the Start button, right-click Computer, and then click Properties.
3 Click System protection.
4 Under Protection Settings, select the disk for which you want to create a restore point.
5 Click Create.
6 Follow the onscreen instructions.
46 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 53

For more information about software restore points:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Help and Support.
2 Type system restore in the Search Help box, and then press Enter.
Software program and hardware driver reinstallation
If an individual factory-installed software program or hardware driver is damaged, you can
reinstall it by using the Recovery Manager program (select models only).
NOTE: Do not use the Recovery Manager program to reinstall software programs that came
on CDs or DVDs included in the computer box. Reinstall these programs directly from the CDs
or DVDs.
Before you uninstall a program, be sure you have a way to reinstall it. Check that it is still
available from where you initially installed it (for example, discs or the Internet). Or check that
the program is in the list of programs you can reinstall from the Recovery Manager.
To check the list of installable programs in the Recovery Manager:
1 Click the Start button, All Programs, Recovery Manager, and then click
Recovery Manager. If prompted, click Yes to allow the program to continue.
2 Under I need help immediately, click Software Program Reinstallation.
3 Click Next at the Welcome screen.
A list of programs opens. Check whether your program is there.
To uninstall a program:
1 Close all software programs and folders.
2 Uninstall the damaged program:
a Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
b Under Programs, click Uninstall a program.
c Select the program you want to remove, and then click Uninstall.
d Click Yes if you want to continue with the uninstall process.
To reinstall a program using the Recovery Manager:
1 Click the Start button, click All Programs, click Recovery Manager, and then
click Recovery Manager.
2 Click Software Program Reinstallation.
3 Click Next at the Welcome screen.
4 Choose the program you want to install, click Next, and follow the onscreen
instructions.
5 When you have finished reinstalling, restart the computer.
NOTE: Do not skip this last step. You must restart the computer after recovering software
programs or hardware drivers.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 47
Page 54

Maintenance
This section includes information about tasks you can perform to help ensure trouble-free
operation of your computer, and to ease the recovery of important information on your
computer if problems arise in the future.
Maintenance tasks
It is important that you perform simple maintenance of your computer to ensure that it works
at peak performance.
Weekly
Software Cleanup Using Disk Cleanup or safe third-party cleaning tools removes
junk files and temporary files that accumulate and slow down
your system. Also, check for programs you no longer need and
uninstall them.
Defragmentation Running Disk Defragmenter keeps your hard disk in good
condition, as well as improves system performance. Frequently
performing this task does not harm your system.
Virus Scan Performing a full virus scan every week can catch anything that
may have slipped through unnoticed. Most antivirus products
have a scheduling feature to keep track of this automatically.
Monthly
Hardware Cleanup Thoroughly clean the inside and outside of your computer.
Software Updates Using Windows Updates can fix operating system bugs and
improve performance. Also, be sure to check for driver updates
for your hardware and new versions of your favorite programs.
Hard Disk Diagnostic Sometimes a failing hard disk can be caught beforehand,
saving you a lot of surprises in the future.
Yearl y
System Recovery In time, your system may still get bogged down, depending on
the usage of the computer. Use System Recovery to wipe your
Windows operating system installation clean, restoring it to the
original configuration when you first powered up your system.
Remember to make a backup first! Before proceeding with a
recovery, see “System Recovery” on page 50 for further details.
48 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 55

Creating data backup discs
Use CD or DVD recording (or burning) software that is installed on your computer to create
backup discs of important information, including personal files, e-mail messages, and Web
site bookmarks. You can also move data to an external hard disk drive.
When writing data to a backup disc, use software that includes write verification
functionality. This feature compares the data on your hard disk drive with the data copied to
the disc to ensure it is an exact copy. Depending on your disc recording software, you may
need to manually enable this feature (refer to the software documentation).
If you encounter recording issues, try alternate media (different types or brands). Also, use the
Windows Explorer tool to view your files and verify content was copied over. To open
Windows Explorer, right-click the Start button, and then click Explore.
Creating system recovery discs
This is a one-time procedure that you should perform while your computer is working
properly. If you encounter problems with your computer later, you can restore it to its original
factory settings by using the system recovery discs that you created. Refer to “Creating
recovery discs” on page 51 for details.
Keeping the Computer Free of Dust, Dirt, and Heat
Keeping your computer system free of dust, dirt, and heat will prolong its life. Dust, pet hair,
and other particles can build up, creating a blanket effect; as a result, components can
overheat, or, in the case of the keyboard and mouse, not work smoothly and effectively.
Check your system once a month for visible signs of dust and debris, and clean it about once
every three months.
Cleaning the computer and monitor
1 Unplug the computer from its power source.
2 Unplug the monitor from its power source.
3 Use a clean, dry cloth to dust the computer case and the monitor.
4 Use a clean cloth dampened with warm water to wipe the computer case and the
monitor case clean.
Do not use water on the monitor screen.
NOTE: If there is sticker residue or a spill on the computer or monitor case, use
isopropyl or rubbing alcohol and a lint-free cloth to remove it.
5 Use a clean cloth to dry the computer and monitor case.
6 Use a clean, dry cloth to clean the monitor screen, or, for more thorough cleaning use
an antistatic screen cleaner and a clean cloth.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 49
Page 56

Cleaning the computer vents
Air vents keep the computer and monitor cool. To maintain efficient air flow, keep these vents
clean by using a small battery-powered vacuum cleaner. (A battery-powered vacuum cleaner
eliminates the risk of electric shock.)
1 Run the vacuum over the vents in the computer case and the monitor case.
2 Remove any debris that has accumulated in and around the computer connectors (for
example, the Ethernet and USB connectors).
Cleaning the keyboard and mouse
When cleaning the keyboard keys, use a low setting on the battery-powered vacuum cleaner,
to avoid removing key caps and springs.
1 Vacuum between the keys of the keyboard and along the grooves.
2 Use a clean, dry cloth and isopropyl alcohol to clean buildup on the keyboard keys and
along its edges.
3 Wipe the body of the mouse and the mouse cord with cleaning wipes or a cloth and
cleanser.
If you have a roller ball mouse, clean the ball and rollers inside:
1 Turn the mouse upside down.
2 Rotate the ball-cover ring counterclockwise to remove the ring and release the roller ball.
3 Rinse the roller ball with soap and warm water.
4 Clean the rollers inside the mouse with a cotton swab dampened with isopropyl alcohol.
5 After the roller ball and rollers are completely dry, replace the ball and ball-cover ring.
System Recovery
System recovery completely erases and reformats the hard disk drive, deleting all data files
you have created. System recovery reinstalls the operating system, programs, and drivers.
However, you must reinstall any software that was not installed on the computer at the
factory. This includes software that came on CDs included in the computer accessory box,
and software programs you installed after purchase.
You must choose one of the following methods to perform a system recovery:
Recovery Image — Run the system recovery from a recovery image stored on your hard
disk drive. The recovery image is a file that contains a copy of the original
factory-shipped software. To perform a system recovery from a recovery image, see
“System recovery from the Windows 7 Start Menu” on page 52.
NOTE: The recovery image uses a portion of the hard disk drive that cannot be used for
data storage.
Recovery Discs — Run the system recovery from a set of recovery discs that you create
from files stored on your hard disk drive. To create recovery discs, see the next section.
50 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 57

Creating recovery discs
Complete the procedure described in this section to create a set of recovery discs from the
recovery image stored on your hard disk drive. This image contains the operating system and
software program files that were originally installed on your computer at the factory.
You can create only one set of recovery discs for your computer. Furthermore, the recovery
discs you create can be used only with your computer.
Choosing recovery discs
To create recovery discs, your computer must have a DVD writer.
Use DVD+R or DVD-R blank media to create your system recovery discs.
You cannot use CDs or DVD+RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW DL, DVD-RW DL, DVD+R DL, or
DVD-R DL discs to create recovery discs.
Use high-quality discs to create your set of recovery discs. The verification standard for the
recovery disc creation process is very high. You may see error messages such as Recording
failure when writing disc or Error detected during disc verification.
Your discs may be rejected if they are not defect-free. You will be prompted to insert a new
blank disc to try again. It is normal that some of your discs may be rejected.
The number of discs in the recovery disc set depends on your computer model (typically
1–3 DVD discs). The Recovery Disc Creator program tells you the specific number of blank
discs needed to make the set.
The process takes some time to verify that the information written on the disc is correct. You
can quit the process at any time. The next time you run the program, it resumes where it
left off.
To create recovery discs:
1 Close all open programs.
2 Click the Start button, click All Programs, click Recovery Manager, and then
click Recovery Disc Creation. If prompted, click Yes to allow the program to
continue.
3 Follow the onscreen instructions. Label each disc as you make it (for example,
Recovery 1, Recovery 2).
4 Store the recovery discs in a safe place.
System recovery options
You should attempt a system recovery in the following order:
1 Through the hard disk drive, from the Windows 7 Start menu.
2 Through the hard disk drive, by pressing the F11 key on the keyboard during system
startup.
3 Through recovery discs that you create.
4 Through recovery discs purchased from HP Support. To purchase recovery discs, go to
http://www.hp.com/support and visit the Software & Driver downloads page for
your computer model.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 51
Page 58

System recovery from the Windows 7 Start Menu
If the computer is working, and Windows 7 is responding, use these steps to perform a
system recovery.
NOTE: System recovery deletes all data and programs you created or installed after
purchase. Therefore, ensure you have backed up, to a removable disc, any data you want
to keep.
1 Turn off the computer.
2 Disconnect all peripheral devices from the computer, except the monitor, keyboard, and
mouse.
3 Turn on the computer.
4 Click the Start button, click All Programs, click Recovery Manager, and then
click Recovery Manager. If prompted, click Yes to allow the program to continue.
5 Under I need help immediately, click System Recovery.
6 Select Yes, and then click Next.
Your computer restarts.
NOTE: If your system does not detect a recovery partition, it will prompt you to insert a
recovery disc. Insert the disc and proceed to Step 7 in the section “Starting system
recovery from user-created recovery discs” on page 53.
7 Under I need help immediately, click System Recovery.
8 If you are prompted to back up your files, and you have not done so, select Back up
your files first (recommended), and then click Next. Otherwise, select Recover
without backing up your files, and then click Next.
System recovery begins. After system recovery is complete, click Finish to restart the
computer.
9 Complete the registration process, and wait until you see the desktop.
10 Turn off the computer, reconnect all peripheral devices, and turn the computer back on.
11 Perform the procedure “Performing the Post-Recovery Procedure” on page 54.
System recovery at system startup
If Windows 7 is not responding, but the computer is working, use these steps to perform a
system recovery:
NOTE: System recovery deletes all data and programs you created or installed after
purchase. Therefore, ensure you back up, to a removable disc, any data you want to keep.
1 Turn off the computer. If necessary, press and hold the On button until the computer
turns off.
2 Disconnect all peripheral devices from the computer, except the monitor, keyboard, and
mouse.
3 Press the On button to turn on the computer.
52 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 59

4 As soon as you see the initial company logo screen appear, repeatedly press the
F11 key on your keyboard until the Windows is Loading Files… message appears on
the screen.
5 Under I need help immediately, click System Recovery.
6 If you are prompted to back up your files, and you have not done so, select Back up
your files first (recommended), and then click Next. Otherwise, select Recover
without backing up your files, and then click Next.
System recovery begins. After system recovery is complete, click Finish to restart the
computer.
7 Complete the registration process, and wait until you see the desktop.
8 Turn off the computer, reconnect all peripheral devices, and turn the computer back on.
9 Perform the procedure “Performing the Post-Recovery Procedure” on page 54.
Starting system recovery from user-created recovery discs
This section contains the procedure for performing a system recovery from the recovery discs
you created as described in “Creating recovery discs” on page 51.
NOTE: System recovery deletes all data and programs you created or installed after
purchase. Therefore, ensure you back up, onto a removable disc, any data you want to keep.
To perform a system recovery using recovery discs:
1 If the computer is working, create a backup DVD containing all the data files you want
to save. When you are done, remove the backup disc from the drive tray.
CAUTION: All data on the hard disk drive will be deleted. You will lose
data if it is not backed up.
2 Insert recovery disc #1 into the DVD drive tray, and close the tray.
3 If the computer works, click the Start button, click the Arrow button next to Shut Down,
and then click Shut Down.
Or
If the computer is not responding, press and hold the On button for approximately
5 seconds, or until the computer turns off.
4 Disconnect all peripheral devices from the computer, except the monitor, keyboard, and
mouse.
5 Press the On button to turn on the computer.
If you are prompted to choose between running System Recovery from disc or from hard
drive, select Run program from disc, and then click Next.
6 Under I need help immediately, click Factory Reset.
7 If you are prompted to back up your files, and you have not done so, select Back up
your files first (recommended), and then click Next. Otherwise, select Recover
without backing up your files, and then click Next.
8 If you are prompted to insert the next recovery disc, do so.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance 53
Page 60

9 When the Recovery Manager is finished, remove all recovery discs from the system.
10 Click Finish to restart the computer.
11 After restarting the computer, see “Preparing to Use Your Computer” on page 13.
Performing the Post-Recovery Procedure
1 At the Welcome to Microsoft Windows screen, follow the onscreen setup instructions.
2 Follow the instructions in “Preparing to Use Your Computer” on page 13.
Additional Troubleshooting
For additional troubleshooting solutions, refer to the following:
HP Support Assistant
HP Support Assistant helps you maintain your PC performance and resolve problems faster
with automated updates, onboard diagnostics, and guided assistance.
To open HP Support Assistant, click the Start button, All Programs, HP, and then click
HP Support Assistant.
Windows 7 Troubleshooting Tools
Windows 7 provides troubleshooting tools that can automatically troubleshoot and fix
common computer problems. To access the Windows 7 Troubleshooting Tools:
1 Click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
2 Click System and Security.
3 Under Action Center, click Find and fix problems (troubleshooting).
54 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 61

Index
A
adapters
HDMI-to-DVI 3
VGA-to-DVI 3
antivirus software 18
audio
A/V In 8
connecting
Audio Line In 4
Audio Line Out 4
speakers 5
left and right connectors 8
troubleshooting 36
B
backup 49
buttons
eject
CD/DVD drive 23
Off, See turning off computer 14
C
card reader, memory 21
CD/DVD drive
troubleshooting 38–40
using vertical 23
cleaning 49
Composite video connector 8
computer
cleaning 49
Help & Tools 26
setting up 1
transferring files 20
turning on the computer 13
connecting
Ethernet 6
modem 7
monitor 3
peripherals 2
speakers 4–5
TV 7–11
wired network 6
wireless LAN 6
connectors
Analog Video Out 9
Audio Line In 4
Audio Line Out 4
Composite Video In 8
DVI 3
Ethernet 6
Ethernet LAN 3
HDMI 3
IR IN 12
IR OUT 12
keyboard (wired) 2
modem 3
monitor 3
mouse (wired) 2
network 3, 6
S-video In 8
TV/Cable Ant 9
VGA 3
creating a LightScribe disc label 23
CyberLink LabelPrint
using to create a LightScribe label 23
D
digital picture 21
display
see monitor
documentation, onscreen 26
drivers, update 46
Index 55
Page 62

E
Ethernet LAN connector 3
F
firewall 18
H
hardware
troubleshooting installation 41–42
HDMI-to-DVI 3
headphones
connecting 5
Help and Support 25
Hibernate mode 14
HP Advisor 26
I
Internet
connection 6–7
security 18
troubleshooting 37–38
IR
blaster 12
connection, enable 44
receiver 12
K
keyboard
wired
connecting 2
troubleshooting 32
wireless
troubleshooting 33–35
L
LAN (local area network)
antenna 6
connecting 3
connecting wireless LAN device 6
setting up 6
LightScribe 23
locking the computer 14
M
maintenance tasks 48
memory card reader
troubleshooting 44
memory card reader, using 21
microphone
adjusting recording levels 16
connecting 5
selecting in Windows 16
modem
connection 3, 7
monitor
connector 3
troubleshooting 31
mouse
wired
connecting 2
troubleshooting 32
wireless
troubleshooting 33–35
N
network interface adapter 3
P
passwords 17
performance
troubleshooting 42
power
troubleshooting 31
power connector 2
R
recording level, adjusting 16
Recovery Manager 47
reinstall a software program 47
remote control 24
troubleshooting 44
repairing software 45
repetitive strain injury (RSI), see Safety &
Comfort Guide
restarting the computer 14
restoring your computer configuration 46
S
Safety & Comfort Guide 27
safety warnings 1, 27
setting up computer 1
shutting down the computer 14
Sleep mode 14
software
repairing 45
software programs
reinstalling 47
sound
see audio
speakers
adjust volume 16
connecting 5
troubleshooting 36
56 Getting Started (features vary by model)
Page 63

startup
troubleshooting 30
Support Web site 25
surge protector 2
S-video In connector 8
System 46
System performance
troubleshooting 42
System recovery 50
System Restore, Microsoft 46
system recovery discs, making 49, 50
U
updating
drivers 46
system 18
Windows 7 18
V
VGA-to-DVI 3
video
troubleshooting 40
volume, adjusting audio 16
T
television
see TV
transferring information to your new
computer 20
troubleshooting
audio 36
CD/DVD drive 38–40
hardware installation 41–42
Internet connection 37–38
keyboard (wired) 32
keyboard (wireless) 33–35
memory card reader 44
monitor 31
mouse (wired) 32
mouse (wireless) 33–35
power 31
remote control 44
speakers 36
startup 30
system performance 42
video 40
wireless devices 43
turning off computer 14
TV
connecting to computer 7–11
W
Windows Update 18
wired network 6
wireless devices
troubleshooting 43
wireless LAN
checking installation 37
connection 6
network device 37
security 15
working in comfort 27
Index 57
Page 64

Page 65

Démarrage rapide
Page 66

Les garanties des produits et services Hewlett-Packard sont exclusivement
présentées dans les déclarations expresses accompagnant lesdits produits et
services. Aucun élément du présent document ne saurait être considéré comme une
garantie supplémentaire. La société HP ne saurait être tenue responsable des
erreurs ou omissions de nature technique ou rédactionnelle qui pourraient subsister
dans le présent document.
La société HP n’assume aucune responsabilité quant à l’utilisation ou à la fiabilité
de ses logiciels sur un matériel qui n’est pas fourni par HP.
Le présent document contient des informations exclusives protégées par copyright.
Aucune partie du présent document ne saurait être photocopiée, reproduite ou
traduite dans une autre langue sans l’autorisation écrite préalable de HP.
Hewlett-Packard Company
P.O. Box 4010-Cupertino,
CA 95015-4010
USA
© Copyright 2000–2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Ce produit intègre une technologie de protection des droits d’auteur qui est
protégée par des brevets américains et par d’autres droits à la propriété
intellectuelle. L’utilisation de cette technologie de protection des droits d’auteur doit
être autorisée par Macrovision et est destinée à l'usage des particuliers ou d'autres
utilisations de visualisation limitée dans l'absence d'autre autorisation de
Macrovision. La rétroingénierie ou le désassemblage du produit sont interdits.
Microsoft, le logo Windows, et Windows sont des marques de commerce ou des
marques déposées du groupe Microsoft aux États-Unis et/ou dans d'autres pays/
régions.
802.11n CERTIFIÉ Wi-Fi basé sur le projet 2.0
Le projet 2.0 se rapporte à la version de la norme 802.11n de l’IEEE non encore
ratifiée utilisée dans les tests de l’alliance Wi-Fi de juin 2007.
Les caractéristiques du réseau sans fil (WLAN) 802.11n sont provisoires et non
définitives. Si les caractéristiques définitives diffèrent des caractéristiques
provisoires, la capacité de ce périphérique à communiquer avec d’autres
périphériques WLAN 802.11n peut être affectée.
En faveur d’une utilisation licite des technologies, HP ne saurait appuyer ni
encourager l’utilisation de produits à d’autres fins que celles autorisées par la loi
sur les droits d’auteur.
Les informations contenues dans le présent document peuvent faire l’objet de
modifications sans préavis.
Page 67

Sommaire
Configuration de votre ordinateur............................................................... 1
Vérification de l’installation de l’ordinateur ................................................................... 1
Branchement de haut-parleurs ou de microphones.......................................................... 4
Connexion à un réseau .............................................................................................. 6
Branchement d’un modem .......................................................................................... 7
Connexion des câbles de signal TV et vidéo ................................................................. 7
Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur........................................... 13
Mise hors tension de l’ordinateur............................................................................... 14
Redémarrage de l'ordinateur..................................................................................... 14
Connexion à Internet................................................................................................ 14
Réglage du volume des haut-parleurs ......................................................................... 16
Choix du microphone............................................................................................... 16
Protection de votre ordinateur.................................................................................... 17
Configuration de l’ordinateur pour les mises à jour automatiques des
logiciels Microsoft.................................................................................................... 18
Configuration de comptes d’utilisateur........................................................................ 19
Directives pour l’installation des logiciels et des périphériques....................................... 19
Transfert de fichiers et paramètres d’un ancien ordinateur vers un nouvel ordinateur........ 20
Fonctionnalités spéciales de votre ordinateur ............................................21
Utilisation du lecteur de carte mémoire....................................................................... 21
Utilisation d’un lecteur CD/DVD vertical ..................................................................... 23
Utilisation de la technologie LightScribe...................................................................... 23
Utilisation de la télécommande.................................................................................. 24
Obtenir des informations supplémentaires................................................ 25
Utilisation du Centre d'aide et de support ................................................................... 25
Accès à l’assistance sur le Web................................................................................. 25
Manuels sur le Web................................................................................................. 25
Manuels en ligne..................................................................................................... 26
Utilisation du dossier Outils et Aide............................................................................ 26
Utilisation du logiciel HP Advisor (Conseiller HP) ......................................................... 26
Utilisation de l’ordinateur avec sécurité et ergonomie................................................... 27
Dépannage et maintenance ...................................................................... 29
Dépannage des problèmes ....................................................................................... 29
Dépannage logiciel.................................................................................................. 45
Maintenance........................................................................................................... 48
Garder l’ordinateur propre, sans poussière ni saletés et à l’abri de la chaleur................. 49
Récupération système............................................................................................... 50
Exécution de la procédure suivant la récupération ....................................................... 54
Dépannage supplémentaire ...................................................................................... 54
Index........................................................................................................55
Sommaire iii
Page 68

iv Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 69

Configuration de votre ordinateur
AVERTISSEMENT : le bloc d'alimentation électrique est préréglé pour le
pays ou la région où vous avez acheté votre ordinateur. Si vous
déménagez, vérifiez bien la tension requise dans ce nouvel
environnement avant de relier votre ordinateur à une prise de courant.
AVERTISSEMENT : avant d'installer votre système et de le relier à une
alimentation secteur, veuillez lire la section Avertissements concernant la
sécurité du document Informations sur la réglementation et la sécurité.
AVERTISSEMENT : pour réduire les risques de blessures graves, lisez le
Guide de sécurité et ergonomie du poste de travail. Vous y découvrirez
comment installer correctement votre poste de travail, quelle posture
prendre, quelques conseils de santé importants, et des habitudes de
travail devant être adoptées par les utilisateurs d’un ordinateur. Vous
pourrez également consulter les consignes de sécurité importantes
concernant la mécanique et l’alimentation électrique de votre système.
Suivez la procédure décrite sur l’affiche d’installation pour installer l’ordinateur :
1 Connectez un clavier et une souris à l’ordinateur.
2 Connectez un moniteur à l’ordinateur.
3 Branchez la prise de votre ordinateur.
4 Mettez l'ordinateur sous tension. Consultez Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur
page 13.
REMARQUE : attendez d’avoir démarré l’ordinateur une première fois et terminé la
configuration initiale avant de connecter ou d'ajouter d'autres périphériques à l'ordinateur.
Consultez Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur page 13.
Vérification de l’installation de l’ordinateur
■ Disposez votre ordinateur dans un endroit adéquat, afin que :
■ Aucune ouverture de ventilation ne soit obstruée.
■ Aucun câble ne soit trop éloigné. Ne placez pas les câbles sur le passage, à un
endroit où quelqu’un risque de marcher dessus ou à un emplacement où ils
pourraient être écrasés par un meuble.
AVERTISSEMENT : placez l’ordinateur dans un endroit éloigné la
poussière, de l’humidité et de la suie. Ces éléments peuvent augmenter la
température interne, provoquer un incendie, une panne ou une
électrocution.
Configuration de votre ordinateur 1
Page 70

■ Protégez votre moniteur, votre ordinateur et les accessoires connectés en reliant tous les
câbles d’alimentation à un appareil de protection contre les sautes de puissance.
Utilisez une barre multiprise disposant d’une protection contre les sautes de puissance,
une alimentation sans coupure (UPS) ou tout autre appareil similaire.
Si l'ordinateur dispose d’un dispositif d’accord de télévision, d’un modem ou d’une
connexion téléphonique, protégez aussi votre ordinateur en utilisant la protection contre
les sautes de puissance à l’aide de ces entrées des signaux. Connectez le câble de votre
téléviseur ou le cordon de téléphone aux entrées et sorties de l’appareil de protection
contre les sautes de puissance, puis à l’ordinateur.
■ Vérifiez si le carton d'emballage de l'ordinateur contient des informations détaillées
supplémentaires sous forme imprimée ou des mises à jour se rapportant au modèle de
votre ordinateur.
Branchement d’autres périphériques à l’ordinateur
D’autres périphériques peuvent être branchés aux connecteurs situés à l’arrière ou à l’avant
de l’ordinateur.
REMARQUE
peuvent varier.
Câbles d’alimentation
et périphériques
: l’emplacement, la disponibilité et le nombre de connecteurs de l’ordinateur
Icône/
Légende
Description et fonction
Connecteur d'alimentation.
Souris (connecteur PS/2).
Clavier (connecteur PS/2).
Port USB 2.0 (Universal Serial Bus) pour
la souris, le clavier, les appareils photo
numériques ou autres périphériques avec
connecteurs USB.
2 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 71

Réseau
Icône/
Légende
Description et fonction
ETHERNET Connecteur réseau local Ethernet à connecter à un
Icône/
Modem
Sortie
affichage
vidéo
REMARQUE : pour des informations plus spécifiques, reportez-vous à la documentation
livrée avec l'écran.
Légende
Icône/
Légende
DVI Recommandé pour connecter un moniteur.
concentrateur de réseau local Ethernet (RJ-45) ou
toute autre connexion à large bande. Ce connecteur
réseau local câblé est un adaptateur d’interface
réseau (également appelé carte interface réseau, ou
NIC). Un voyant vert indique une connexion valide.
Description et fonction
Modem (Entrée ligne RJ-11) (certains modèles
uniquement) à connecter au modem de l’ordinateur
via une prise téléphonique murale pour les
connexions à distance à Internet.
Description et fonction
Connecteur de sortie vidéo numérique (certains
modèles uniquement) pour connecter un téléviseur
ou un moniteur. Il se peut que vous ayez besoin d'un
adaptateur VGA-DVI ou d'un adaptateur HDMI-DVI
pour connecter l'écran à l'ordinateur.
VGA/Moniteur Le connecteur de sortie Monitor/VGA (bleu), à
HDMI Recommandé pour connecter un écran de télévision.
VGA-DVI Adaptateur VGA-DVI, à adapter à un écran de
HDMI-DVI Adaptateur HDMI-DVI, à adapter à un écran de
connecter avec un moniteur VGA. Il se peut que
vous ayez besoin d'un adaptateur VGA-DVI pour
connecter l'écran à l'ordinateur à l’aide d’un seul
connecteur DVI.
Le connecteur de sortie HDMI, à brancher avec un
moniteur HDMI ou à un écran de télévision. Il se
peut que vous ayez besoin d'un adaptateur
HDMI-DVI pour connecter l'écran à l'ordinateur à
l’aide d’un seul connecteur DVI.
télévision ou à un câble de moniteur vidéo pour le
connecter à l’ordinateur.
télévision ou à un câble de moniteur vidéo pour le
connecter à l’ordinateur.
Configuration de votre ordinateur 3
Page 72

Branchement de haut-parleurs ou de microphones
Les haut-parleurs peuvent être intégrés au moniteur (certains modèles uniquement) ou vendus
séparément. Les écouteurs et les microphones sont vendus séparément.
Votre modèle d’ordinateur est peut-être équipé de connecteurs pour microphone situés à
l'arrière. Certains modèles d'ordinateur possèdent aussi des connecteurs à l'avant. Les
connecteurs audio sont des mini-prises stéréo à connecter entre l’ordinateur et des hautparleurs actifs (alimentés) ou des systèmes de haut-parleurs, des écouteurs ou un périphérique
d’entrée comme un microphone, une webcam ou un lecteur audio.
Certains connecteurs audio (pas tous) dont dispose éventuellement votre ordinateur
apparaissent dans le tableau ci-dessous.
REMARQUE
: l’emplacement, la disponibilité et le nombre de connecteurs de l’ordinateur
peuvent varier.
Branchement des haut-parleurs
Les haut-parleurs sont vendus séparément, ou peuvent être inclus avec l’écran.
Votre ordinateur n’est compatible qu’avec des systèmes de haut-parleurs actifs (avec
alimentation électrique) ; le système de haut-parleurs doit comprendre son propre cordon
d'alimentation ou ses propres batteries.
Pour obtenir des instructions détaillées sur la façon de connecter et de configurer d’autres
haut-parleurs à plusieurs canaux, rendez-vous sur la page d’assistance en ligne de votre
modèle. Consultez Accès à l’assistance sur le Web page 25.
Icône/
Connecteurs audio
Légende
Haut-parleur
central
Description et fonction
Le connecteur de sortie audio (vert clair) se
branche aux haut-parleurs avant gauche et droit
analogiques.
Le connecteur d’entrée audio (bleu) permet de
brancher une source audio analogique telle
qu’un lecteur de CD à l’ordinateur.
Peut fonctionner en tant que sortie arrière dans
une configuration audio à plusieurs canaux.
Le connecteur Line C/Sub (jaune) se branche au
haut-parleur central ou au caisson de basse dans
une configuration audio multivoie.
Haut-parleur
arrière
Le connecteur Line Rear (noir) se branche aux
haut-parleurs arrière dans une configuration
audio multivoie.
Haut-parleur
latéral
Le connecteur Line Side (gris) se branche aux
haut-parleurs latéraux dans une configuration à
huit haut-parleurs (7.1).
4 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 73

Connexion d’un système de haut-parleurs stéréo
Pour connecter des haut-parleurs actifs, comme les haut-parleurs stéréo gauche et droit ou un
système 2.1 de deux haut-parleurs et un caisson de basses à l’ordinateur :
1 Assurez-vous que l’ordinateur est éteint et que le système de haut-parleurs est éteint et
débranché.
2 Connectez le câble du haut-parleur au connecteur de sortie audio vert clair à l’arrière
de l’ordinateur.
Ou
Pour les haut-parleurs 2.1 ou tout autre haut-parleur à plusieurs canaux livré avec votre
ordinateur (certains modèles uniquement), connectez le caisson de basses au
connecteur de sortie audio de l’ordinateur, et connectez les haut-parleurs gauche et droit
au caisson de basses.
REMARQUE
en marche.
: pensez toujours à allumer votre ordinateur avant de mettre les haut-parleurs
Branchement des écouteurs
Les écouteurs sont vendus séparément.
Votre ordinateur possède un connecteur de casque d’écoute (vert clair) à l’avant.
Ce connecteur est indiqué par une icône de casque d’écoute.
Vous pouvez également connecter le casque au connecteur de sortie audio (vert clair)
à l’arrière de l’ordinateur.
Généralement, lorsque le casque est branché, le son des haut-parleurs et du caisson
de basses est désactivé.
Branchement d’un microphone
Les micros sont vendus séparément.
Votre ordinateur est équipé d'un connecteur pour microphone (rose) situé à l'arrière. Certains
modèles d’ordinateurs disposent d’un second connecteur de microphone à l’avant (certains
modèles uniquement).
Branchez le microphone avec le connecteur du microphone sur l'ordinateur.
Pour régler le volume d’enregistrement ou sélectionner le microphone, reportez-vous à la
section Choix du microphone page 16.
Configuration de votre ordinateur 5
Page 74

Connexion à un réseau
Cette section décrit la façon de vous connecter à un réseau à l’aide d’une connexion avec ou
sans fil.
Configuration d'une connexion câblée (Ethernet)
Le connecteur Ethernet (RJ-45) situé à l’arrière de l’ordinateur fournit une connexion à haut
débit ou à large bande à un réseau. Une fois cette interface connectée à un réseau, par
exemple un réseau local (LAN), vous pouvez accéder à Internet par le réseau.
1 Branchez un câble Ethernet au connecteur Ethernet (RJ-45) (A) à l’arrière de l’ordinateur
et au routeur du réseau ou périphérique LAN.
2 Votre ordinateur étant allumé, vérifiez les voyants lumineux (B) à côté du connecteur
Ethernet pou connaître son état :
■ ACTIVITY — allumé et jaune durant l'activité de transfert de données réseau
■ LINK — allumé et vert lorsque la connexion au réseau est valide
REMARQUE
lumineux.
: il est possible que votre connecteur Ethernet n’ait qu’un seul voyant
Configuration d'une connexion à un réseau sans fil
(certains modèles uniquement)
Vous avez la possibilité de connecter votre ordinateur à un réseau sans fil adapté aux normes
IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, ou 802.11n en utilisant une antenne incluse avec l’ordinateur.
Si elle est fournie, connectez l’antenne externe au connecteur d’antenne sans fil de la carte
réseau pour améliorer la portée et la sensibilité du signal radio sans fil.
REMARQUE
le haut de l’ordinateur ou en hauteur, dans un lieu dégagé.
Vous devez disposer d’un réseau local sans fil avec une connexion Internet. Consultez votre
fournisseur d’accès à Internet (FAI) pour obtenir de plus amples informations.
Pour vérifier si un périphérique WLAN intégré est installé correctement sur votre ordinateur,
reportez-vous à la section Accès à Internet page 37.
Pour plus d’informations sur la mise en place d’un réseau sans fil : Cliquez sur le bouton
Démarrer , puis sur Aide et support, et saisissez configurer un réseau sans fil dans la
zone de recherche avant d’appuyer sur la touche Entrée.
6 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
: pour obtenir la meilleure performance du réseau sans fil, placez l’antenne sur
Page 75

Branchement d’un modem
(certains modèles uniquement)
Le modem connecte l’ordinateur à la ligne téléphonique. Utilisez-le pour vous connecter à un
FAI qui fournit l'accès à Internet par connexion à distance. Si vous utilisez une connexion
Internet, vous n’aurez peut-être pas besoin d’une connexion modem.
REMARQUE
un connecteur situé à l’arrière de l’ordinateur ou un périphérique externe à brancher sur un
connecteur USB de l’ordinateur.
Avant de pouvoir vous connecter à Internet à l’aide de votre ligne téléphonique pour recevoir
ou envoyer des courriers électroniques et des télécopies, vous devez connecter votre ligne de
téléphone au connecteur modem (A).
1 Branchez un câble modem ou téléphone sur le connecteur modem de l’ordinateur (A).
Remarque : le connecteur modem de l’ordinateur peut être vert.
2 Branchez l'autre extrémité du câble modem ou téléphone dans la prise
téléphonique murale.
: votre ordinateur n'est peut-être pas équipé d'un modem. Le modem peut être
Connexion des câbles de signal TV et vidéo
(certains modèles uniquement)
Cette section décrit comment brancher l’ordinateur à la télévision et identifie les câbles
à utiliser.
Utilisez ces câbles pour connecter :
■ Le câble coaxial du signal source audio/vidéo TV à l'ordinateur.
Ou
■ Le câble S-vidéo du signal source TV ou vidéo composite à l’ordinateur.
■ Le signal source audio TV à l'ordinateur.
Ou
■ La sortie vidéo depuis l’ordinateur.
Il est possible que vous deviez acheter des câbles, un séparateur de signal de câble coaxial
ou d’autres accessoires séparément. Votre ordinateur peut ne pas inclure tous les câbles dont
vous aurez besoin pour effectuer la configuration télévision/vidéo.
Configuration de votre ordinateur 7
Page 76

Entrée audio
et vidéo
Icône/
Légende
Description et fonction
S-vidéo Connecteur S-vidéo pour connecter une entrée vidéo
depuis une sortie de boîtier décodeur TV.
Vidéo
composite
Connecteur d’entrée vidéo composite (jaune) pour
brancher une entrée vidéo à un boîtier décodeur
de téléviseur.
S-vidéo 2 Connecteur d’entrée S-vidéo secondaire pour
connecter une entrée vidéo provenant d’un
magnétoscope, un caméscope ou d’une autre
source analogique.
Vidéo
composite 2
Connecteur d’entrée vidéo composite secondaire
(jaune) pour connecter une entrée vidéo provenant
d’un magnétoscope, un caméscope ou d’une autre
source analogique.
A/V In
Audio 1 L
Connecteur d’entrée audio gauche principale pour
connecter l’entrée audio provenant d’un téléviseur
au connecteur d’un boîtier décodeur (blanc).
REMARQUE
: vous pouvez enregistrer de l'audio
en utilisant ce connecteur Audio In, lequel se
branche à la carte mère. Certains modèles incluent
ce connecteur d'entrée audio gauche principale à
A/V In
Audio 1 R
l'avant de l'ordinateur
Connecteur d’entrée audio droite principale pour
connecter l’entrée audio provenant d’un téléviseur
au connecteur d’un boîtier décodeur (rouge).
REMARQUE
: vous pouvez enregistrer de l'audio
.
en utilisant ce connecteur Audio In, lequel se
branche à la carte mère. Certains modèles incluent
ce connecteur d'entrée audio droit principal à
l'avant de l'ordinateur
.
A/V In
Audio 2 L
Connecteur d’entrée audio gauche secondaire (blanc).
REMARQUE :
ce connecteur d'entrée audio se
branche sur la carte TV. Pour enregistrer ou écouter de
l'audio uniquement, vous devez utiliser le connecteur
Audio In principal, qui se branche à la carte mère et
se trouve à l'arrière de l'ordinateur.
A/V In
Audio 2 R
Connecteur d’entrée audio droit secondaire (rouge).
REMARQUE
: ce connecteur d'entrée audio se
branche sur la carte TV. Pour enregistrer ou écouter
de l'audio uniquement, vous devez utiliser le
connecteur Audio In principal, qui se branche à la
carte mère et se trouve à l'arrière de l'ordinateur.
8 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 77

Sortie
téléviseur
Icône/
Légende
Description et fonction
Entrée
téléviseur
Vidéo
analogique
Icône/
Légende
Câble/antenne TVConnecteur entrée TV pour brancher une antenne TV
ATSC Connecteur TV In pour le câble ou l'antenne TV, qui
CATV Connecteur TV In pour le câble ou l'antenne TV, qui
NTSC Connecteur TV In pour le câble ou l'antenne TV, qui
Connecteur sortie vidéo analogique pour brancher
un connecteur S-vidéo ou vidéo composite sur un
téléviseur.
Description et fonction
ou une entrée câble à partir d'une prise murale sans
boîtier décodeur.
reçoit les canaux ATSC (Advanced Television System
Committee) qui sont diffusés via les ondes de
transmission hertziennes numériques.
reçoit les canaux CATV (télévision communautaire)
ou chaînes câblées.
reçoit les canaux NTSC (National Television System
Committee) qui sont diffusés via les ondes de
transmission hertziennes analogiques.
Configuration de votre ordinateur 9
Page 78

Connexion du signal source TV sans boîtier décodeur
Pour connecter votre ordinateur à une
configuration existante pour le signal source du
téléviseur sans boîtier décodeur, insérez
(ajoutez) un séparateur (B) pour diriger le câble
coaxial de signal télévisé de la prise murale (A)
au connecteur de votre ordinateur (C).
Légendes
A Prise murale (depuis une antenne ou un
câble) pour câble de signal TV (coaxial)
B Séparateur
C Connecteur coaxial d’entrée TV de
l’ordinateur
D Enregistreur vidéo
E TV
Connexion du signal source TV avec boîtier décodeur
Pour connecter votre ordinateur à une
configuration existante pour le signal source
du téléviseur avec boîtier décodeur (câble ou
satellite), insérez (ajoutez) un répartiteur (B)
pour diriger le câble coaxial de signal
télévisé du boîtier décodeur (F) au connecteur
de votre ordinateur (C).
Connectez le câble de la télécommande ou
l'émetteur à infrarouge (certains modèles
uniquement) (G) au connecteur de sortie
infrarouge IR OUT de l’ordinateur, et
positionnez l’émetteur sur le boîtier décodeur.
Vous pouvez ainsi changer de chaîne sur le
boîtier décodeur par le biais de l’ordinateur.
Voi r Utilisation d’un émetteur à infrarouge (IR)
page 12 pour obtenir des détails sur le
placement de l'émetteur à infrarouge.
Légendes
A Prise murale (depuis une antenne ou un
câble) pour câble de signal TV (coaxial)
B Répartiteur
C Connecteur coaxial d’entrée TV de
l’ordinateur
D Enregistreur vidéo
E TV
F Boîtier décodeur/satellite
G Câble de l’émetteur infrarouge de la télécommande (certains modèles uniquement)
10 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 79

Connexion de la source de signal TV à un boîtier décodeur et à l’aide
d’un câble S-vidéo ou vidéo composite
Pour utiliser une sortie vidéo du boîtier
décodeur (
F
), ajoutez les câbles pour
acheminer la vidéo et l'audio vers l'ordinateur :
■ Ne débranchez aucun câble de
l’installation en place.
■ Connectez un câble S-vidéo (ou un câble
adaptateur S-vidéo/composite) au
connecteur d'entrée S-Vidéo (H) à
l'ordinateur.
■ Raccordez les câbles audio aux
connecteurs audio droit (rouge) et
gauche (blanc) (J) sur l'ordinateur.
■ Connectez le câble de la télécommande
ou l'émetteur à infrarouge (certains
modèles uniquement) (G) au connecteur
de sortie infrarouge IR OUT de
l’ordinateur, puis positionnez l’émetteur
sur le boîtier décodeur. Vous pouvez
ainsi changer de chaîne sur le boîtier par
le biais de l’ordinateur. Voir Utilisation
d’un émetteur à infrarouge (IR) page 12
pour obtenir des détails sur le placement
de l'émetteur à infrarouge.
Légendes
A Prise murale (depuis une antenne ou un câble) pour câble de signal TV (coaxial)
B Répartiteur
C Connecteur coaxial d’entrée TV de l’ordinateur
D Enregistreur vidéo
E TV
F Boîtier décodeur/satellite
G Câble de l’émetteur infrarouge de la télécommande (certains modèles uniquement)
H Connecteur d’entrée S-vidéo de l’ordinateur
J Connecteurs audio (analogiques) gauche et droit de l’ordinateur
Configuration de votre ordinateur 11
Page 80

Utilisation d’un émetteur à infrarouge (IR)
(certains modèles uniquement)
Si vous disposez d’un boîtier décodeur pour téléviseur par câble ou par satellite, vous avez la
possibilité de contrôler le boîtier décodeur depuis votre ordinateur en utilisant le câble/
l’émetteur infrarouge (certains modèles uniquement) de la télécommande et le connecteur de
l’ordinateur (certains modèles uniquement). Retirez le ruban adhésif (1) au bout de l’émetteur,
collez-le au récepteur infrarouge du boîtier décodeur (2), puis connectez-le au connecteur de
sortie infrarouge (IR OUT) (3) à l’arrière de l’ordinateur. Il suffit ensuite de pointer la
télécommande en direction du télécapteur situé à l’avant de l’ordinateur.
3
1
2
IR IN
IR OUT
12
Utilisation d’un récepteur infrarouge externe
(certains modèles uniquement)
Si vous ne disposez pas d’une ligne de mire directe vers le télécapteur situé à l’avant de votre
ordinateur, vous avez la possibilité d’utiliser un récepteur infrarouge externe et de le placer à
un endroit où il pourra recevoir les signaux de la télécommande.
Connectez le récepteur externe au port d’entrée rouge IR IN à l’arrière de l’ordinateur (1).
Placez le récepteur infrarouge (2) dans un endroit disposant d’une ligne de mire directe avec
la télécommande. Pointez la télécommande (3) vers le récepteur infrarouge externe.
3
2
1
12 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 81

Préparation à l’utilisation
de votre ordinateur
Une fois les étapes de l'affiche d'installation effectuées, vous êtes prêt à allumer l’ordinateur.
REMARQUE
configuration initiale avant de connecter ou d'ajouter d'autres périphériques à l'ordinateur.
Pour allumer l’ordinateur
1 Allumez le moniteur.
2 Mettez l'ordinateur sous tension.
3 Allumez les haut-parleurs externes, le cas échéant.
4 Configurez l’ordinateur et Microsoft
l'écran :
■ Si vous y êtes invité, sélectionnez le pays ou la région où vous êtes domicilié et
■ Suivez les instructions affichées pour vous enregistrer, vous abonner aux mises à
5 Lorsque vous voyez le bureau
Si vous avez besoin d’aide pour commencer à utiliser votre ordinateur, consultez les autres
rubriques de cette section.
REMARQUE
ou si vous refusez certaines options, vous recevrez des rappels pour terminer la configuration
ultérieurement.
: attendez d’avoir démarré l’ordinateur une première fois et terminé la
:
®
Windows®7 en suivant les instructions affichées à
patientez pendant que l’ordinateur effectue les préparations nécessaires. (Lorsque
vous sélectionnez une autre langue, la configuration initiale de la langue sur
l'ordinateur peut prendre jusqu’à 30 minutes.)
jour et vous connecter à Internet.
Windows 7, la configuration initiale est terminée.
: si vous sautez certaines étapes lors de la procédure de configuration initiale
Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur 13
Page 82

Mise hors tension de l’ordinateur
Pour de meilleurs résultats sous Windows 7, n’éteignez pas l’ordinateur, sauf pour des raisons
de sécurité liées à l’alimentation : pour effectuer des réparations, installer un nouveau
matériel ou des cartes supplémentaires, ou encore pour changer la batterie.
Au lieu d'éteindre l'ordinateur, vous pouvez le verrouiller ou le mettre en mode veille ou veille
prolongée, si ces options sont disponibles. Vous pouvez régler les minuteries de gestion de
l’alimentation pour que l'ordinateur se mette automatiquement en mode veille ou veille
prolongée.
L’ordinateur prend en charge les modes d’économie d’énergie suivants :
■ Le mode veille enregistre votre travail en mémoire, vous permettant de
reprendre rapidement. Il enregistre la mémoire sur le disque dur, puis entre
dans un état d’alimentation réduite. En mode veille, le voyant de l’ordinateur
reste allumé, et l’ordinateur est prêt à se remettre en route rapidement et reprendre votre
travail où vous l’aviez laissé. Si c’est le cas maintenant, appuyez simplement sur le
bouton Veille sur le clavier pour passer en mode veille.
■ Le mode veille prolongée (disponible en tant que paramètre d’alimentation avancé)
enregistre la mémoire du système sur un fichier temporaire du disque dur, puis éteint le
disque dur. Lorsque vous rallumez l’ordinateur, vous retrouvez tout ce qui était à l'écran
(programmes, dossiers et documents).
Redémarrage de l'ordinateur
Lorsque vous redémarrez l’ordinateur, celui-ci supprime certains paramètres et se réamorce
en utilisant le système d'exploitation et les logiciels figurant dans sa mémoire. Le
redémarrage est la manière la plus facile et la plus efficace de résoudre de nombreux
problèmes logiciels de l’ordinateur.
De plus, si vous décidez d'installer des logiciels ou périphériques supplémentaires sur
l’ordinateur, il est possible que vous deviez redémarrer l'ordinateur après l'installation.
Pour redémarrer l’ordinateur :
1 Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer.
2 Cliquez sur le bouton flèche à côté de Arrêter.
3 Cliquez sur Redémarrer.
Ou
Appuyez brièvement sur le bouton d'alimentation à l'avant de l’ordinateur.
Connexion à Internet
Pour être connecté à Internet, effectuez les actions suivantes :
1 Souscrivez à un service d’accès Internet haut débit auprès d’un fournisseur d’accès
Internet (FAI).
2 Procurez-vous un modem à large bande (DSL ou câble). Celui-ci est généralement fourni
par le FAI.
3 Achetez et installez un routeur sans fil (vendu séparément), le cas échéant.
L’ordinateur peut se connecter à Internet via un réseau local (LAN) ou une ligne d’abonné
numérique (DSL). Pour obtenir des informations spécifiques quant à la connexion, consultez
votre fournisseur de services Internet.
14 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 83

1 Reportez-vous à Configuration de votre ordinateur page 1 pour effectuer les connexions
matérielles. Vous avez besoin de :
■ Pour une connexion réseau, reportez-vous à la section Connexion à un réseau
page 6. Pour vérifier l’installation d’un périphérique de réseau sans fil, reportezvous à la section Accès à Internet page 37.
■ Pour un modem, reportez-vous à la section Branchement d’un modem page 7.
2 Pour vous connecter à Internet :
■ Abonnez-vous auprès d’un fournisseur d’accès Internet (FAI). Si vous disposez déjà
d’un compte d’accès, passez cette étape et suivez les instructions données par le
fournisseur.
■ Si vous n’avez pas configuré votre ordinateur pour pouvoir bénéficier du service
Internet lors de la configuration initiale, faites-le maintenant en utilisant les Services
en ligne :
a Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer.
b Cliquez sur Tous les programmes.
c Cliquez sur Services en ligne, puis cliquez sur Se connecter à Internet.
d Suivez les instructions données à l’écran pour sélectionner un fournisseur
d’accès Internet et configurer le service.
REMARQUE
: les Services en ligne fournissent une liste des fournisseurs d’accès à
Internet. Cependant, vous pouvez choisir un autre fournisseur ou transférer un
compte existant sur cet ordinateur. Pour transférer un compte existant, suivez les
instructions du fournisseur d'accès.
3 Connectez-vous à Internet. Vous devez vous connecter via votre fournisseur d’accès.
■ Pour les connexions par réseau commuté uniquement, double-cliquez sur l'icône du
fournisseur d’accès Internet située sur le bureau, et ouvrez une session.
4 Ouvrez votre navigateur Internet et surfez sur le Web.
Vous pouvez utiliser le navigateur de votre choix. Microsoft Internet Explorer
®
est installé
sur la plupart des ordinateurs. Pour ouvrir Internet Explorer :
a Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer.
b Cliquez sur Tous les programmes, puis sur Internet Explorer.
REMARQUE
: si vous avez des problèmes pour vous connecter à Internet, consultez Accès à
Internet page 37.
Utilisation des fonctions de sécurité du réseau sans fil
Lorsque vous créez un réseau WLAN domestique ou accédez à un réseau WLAN public
existant, veillez à toujours activer les fonctions de sécurité pour protéger le réseau des accès
non autorisés. Les niveaux de sécurité les plus courants sont Wi-Fi Protected Access Personal
(WPA-Personal) et Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).
Lorsque vous configurez un réseau, utilisez l'une des mesures de sécurité suivantes :
■ Activez le cryptage WPA-Personal ou WEP sur le routeur.
■ Changez le nom du réseau par défaut (SSID) et son mot de passe.
■ Configurez un pare-feu.
■ Définissez la sécurité sur votre navigateur Web.
Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur 15
Page 84

Réglage du volume des haut-parleurs
Il existe plusieurs façons de régler le volume. Utilisez l'icône Volume sur la barre de tâches
Windows 7 pour régler le volume des haut-parleurs. Vous pouvez ensuite régler le volume en
utilisant :
■ La molette du volume ou les boutons du clavier (certains modèles uniquement).
■ Le bouton de volume sur les haut-parleurs (certains modèles uniquement).
Utilisez l'icône Volume de la barre de tâches pour régler le volume des haut-parleurs :
1 Faites un clic droit sur l'icône de Volume de la barre des tâches, puis cliquez
sur Ouvrir le mixeur audio.
La fenêtre des paramètres du mixeur de volume apparaît.
2 Ajustez le volume en cliquant sur la barre du curseur et en la faisant glisser.
3 Une fois satisfait du niveau sonore, cliquez sur le X (dans le coin supérieur droit) pour
fermer la fenêtre.
Pour obtenir de l’aide sur le système audio, consultez les conseils de dépannage dans Audio
et haut-parleurs page 36. Pour plus d’informations, ouvrez le Centre d'aide et de support ou
consultez le site Web d’assistance technique. Voir Obtenir des informations supplémentaires
page 25.
Choix du microphone
Le connecteur du microphone de votre ordinateur est prêt à être utilisé. Si plus d’un
microphone est connecté, sélectionnez le microphone que vous voulez utiliser sous
Windows 7.
REMARQUE : lorsqu’une webcam ou un lecteur audio est connecté à l’ordinateur,
Windows 7 peut reconnaître chacun d’entre eux comme une entrée de microphone à cause
de l’entrée audio du périphérique.
Pour sélectionner le microphone que vous souhaitez utiliser sous Windows 7 :
1 Faites un clic droit sur l'icône du Volume dans la barre des tâches, puis
cliquez sur Périphériques d’enregistrement. La fenêtre Son s'ouvre.
2 Sélectionnez le microphone que vous voulez utiliser, cliquez sur Définir par
défaut, puis sur Appliquer.
3 Cliquez sur OK.
Réglage du niveau d’enregistrement du microphone
sous Windows 7
Pour régler le niveau d’enregistrement du microphone :
Faites un clic droit sur l'icône du
1
Périphériques d’enregistrement
2
Double-cliquez sur le connecteur de microphone que vous souhaitez utiliser.
3
Cliquez sur l’onglet
4
Ajustez le niveau d’enregistrement en cliquant sur la barre du curseur et en la faisant glisser.
5
Cliquez sur OK, puis cliquez de nouveau sur OK.
16 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Niveaux
Volume
.
dans la barre des tâches, puis cliquez sur
. La fenêtre Son s'ouvre.
Page 85

Protection de votre ordinateur
Vous pouvez protéger votre ordinateur, paramètres personnels et données de nombreux
risques en utilisant :
■ Des mots de passe.
■ Un logiciel antivirus.
■ Un pare-feu.
■ Les mises à jour de sécurité critiques.
REMARQUE : les solutions de sécurité sont conçues comme des mesures de dissuasion, mais
elles n'évitent pas forcément les attaques logicielles ni le vol ou la mauvaise manipulation de
l'ordinateur.
Risque de l’ordinateur Caractéristique de l’ordinateur
Utilisation non autorisée de l’ordinateur
ou d’un compte utilisateur
Virus informatiques Logiciel antivirus
Accès non autorisé aux données Logiciel pare-feu
Accès non autorisé à l’utilitaire
d’installation, aux paramètres du BIOS et
à d’autres informations d’identification du
système
Menaces actuelles ou futures pour
l’ordinateur
Mot de passe utilisateur
Mises à jour Windows 7
Mot de passe administrateur
Mises à jour de sécurité essentielles de
Microsoft pour Windows 7
Utilisation de mots de passe
Un mo
t de passe est une série de caractères que vous choisissez pour protéger les
informations contenues dans l’ordinateur. Plusieurs types de mots de passe peuvent être définis
selon la manière dont vous souhaitez contrôler l’accès à vos informations. Les mots de passe
peuvent être définis dans le système d’exploitation Windows 7 exécuté sur l’ordinateur.
ATTENTION : pour éviter de ne pas pouvoir accéder à l’ordinateur, veillez
à consigner tous les mots de passe que vous définissez. Les mots de
passe ne sont pas affichés tels qu’ils sont définis, modifiés ou supprimés.
Il est donc essentiel que vous consigniez chaque mot de passe
immédiatement et que vous les conserviez en lieu sûr. Ne conservez pas
vos mots de passe dans un fichier sur l'ordinateur.
Vous pouvez utiliser le même mot de passe pour plus d'une fonction de sécurité de Windows 7.
Un mot de passe défini dans Windows 7 doit être saisi lorsque Windows 7 le demande.
Pour des informations sur les mots de passe sous Windows 7 : cliquez sur le bouton
Démarrer, puis sur Aide et support, et saisissez mots de passe dans la zone de
recherche avant d’appuyer sur la touche Entrée. Consultez Utilisation du Centre d'aide et de
support page 25.
Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur 17
Page 86

Utilisation d'un logiciel antivirus
Lorsque vous utilisez l’ordinateur pour accéder à votre messagerie électronique, au réseau ou
à Internet, vous vous exposez à des virus informatiques. Les virus informatiques peuvent
désactiver ou endommager le système d’exploitation, les logiciels ou les utilitaires de
l’ordinateur.
Un logiciel antivirus peut détecter la plupart des virus, les supprimer et dans la majorité des
cas, réparer tout dommage qu’ils pourraient avoir causé. Pour assurer une protection
continue contre les nouveaux virus, vous devez régulièrement mettre à jour le logiciel
antivirus.
Le logiciel antivirus préinstallé sur l’ordinateur comprend des composants antivirus et parefeu. Le logiciel comprend une version d’essai gratuite de mises à jour des protections. Pour
protéger votre ordinateur contre les nouveaux virus au-delà de cette période d’essai, achetez
un service de mise à jour étendu. Des instructions pour utiliser et mettre à jour le logiciel
antivirus et pour vous abonner au service de prolongation des mises à jour sont fournies dans
le programme.
Pour plus d’informations sur les virus informatiques : cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis
sur Aide et support, et saisissez virus dans la zone de recherche avant d’appuyer sur la
touche Entrée. Consultez Utilisation du Centre d'aide et de support page 25.
Utilisation du pare-feu
Lorsque vous utilisez l’ordinateur pour accéder à votre messagerie électronique, au réseau ou
à Internet, des personnes non autorisées risquent d’accéder à des informations vous
concernant, votre ordinateur et vos données. Pour protéger votre confidentialité, utilisez un
pare-feu :
■ Windows 7 comprend un pare-feu préinstallé sur votre ordinateur.
■ Le logiciel antivirus préinstallé sur l’ordinateur comprend un pare-feu.
Les fonctions du pare-feu comprennent la journalisation, la création automatique de rapports
et l’émission automatique d’alertes afin de contrôler toutes les communications entrantes et
sortantes.
Dans certains cas, un pare-feu peut empêcher l’accès à des jeux en ligne, affecter le partage
d’imprimantes ou de fichiers sur un réseau, ou bloquer des pièces jointes autorisées de
courriers électroniques. Pour résoudre temporairement ce problème, désactivez le pare-feu,
effectuez l’opération en question, puis réactivez le pare-feu. Pour résoudre définitivement le
problème, reconfigurez le pare-feu.
Configuration de l’ordinateur pour les mises à jour automatiques des logiciels Microsoft
Microsoft améliore en permanence le système d’exploitation Windows 7. Exécutez
Windows Update chaque mois pour installer ces mises à jour, ou gardez votre système
d’exploitation à jour en utilisant la fonctionnalité des Mises à jour automatiques.
Lorsque vous êtes connecté à Internet, cette fonction vous informe automatiquement, par un
message ou une icône apparaissant dans la zone de notification, de la disponibilité de mises
à jour critiques de Windows 7. Lorsque vous voyez ce message, autorisez le téléchargement
des mises à jour sur l’ordinateur. Si vous mettez à jour l’ordinateur chaque semaine, ou au
moins une fois par mois, la durée du téléchargement est minime.
18 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 87

Installation de mises à jour de sécurité critiques
ATTENTION : pour réduire le risque d’endommagement ou de perte des
informations en raison de brèches de sécurité et de virus informatiques,
installez toutes les mises à jour critiques de Microsoft dès que vous en
recevez l’alerte.
Des mises à jour récentes du système d’exploitation et d’autres logiciels peuvent être parues
après la livraison de l’ordinateur. Téléchargez toutes les mises à jour disponibles et installezles sur l’ordinateur.
Configuration de comptes d’utilisateur
Lorsque vous partagez un ordinateur avec plusieurs personnes, vous pouvez configurer un
compte utilisateur pour chaque utilisateur. Windows 7 utilise les informations d’un compte
utilisateur pour déterminer quels fichiers et quels dossiers sont accessibles à l’utilisateur,
quand ils peuvent apporter des modifications à l’ordinateur, ainsi que leurs préférences
personnelles. Chaque personne ne peut accéder qu’à ses propres fichiers et paramètres.
Pour plus d’informations, cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis sur Aide et support, et
saisissez comptes d’utilisateurs dans la zone de recherche avant d’appuyer sur la touche
Entrée. Consultez Utilisation du Centre d'aide et de support page 25.
Directives pour l’installation des logiciels et des périphériques
Après la configuration initiale de l’ordinateur, vous pouvez si vous le souhaitez y installer des
logiciels ou périphériques. Prenez en considération les directives importantes ci-dessous :
■ Avant l’installation, créez un point de restauration à l’aide du programme Restauration
du système de Microsoft. Le point de restauration est une capture de la configuration de
l’ordinateur. Utiliser la restauration du système vous permet de vous assurer que vous
avez une série de paramètres stables.
■ Choisissez un logiciel compatible avec l’ordinateur ; vérifiez la configuration requise
(système d’exploitation, mémoire, etc.) par le nouveau logiciel.
■ Installez le nouveau logiciel en respectant les consignes fournies par l’éditeur. Si vous
avez besoin d’aide, consultez la documentation fournie par l’éditeur ou le service
clientèle.
■ Dans le cas d’un logiciel antivirus, désinstallez d’abord le logiciel existant avant de le
réinstaller ou d’en installer un nouveau.
REMARQUE : n'utilisez que des logiciels originaux sous licence. L’installation de logiciels
copiés peut être illégale, s’avérer instable ou présenter des risques d’infection par un virus
informatique.
Préparation à l’utilisation de votre ordinateur 19
Page 88

Transfert de fichiers et paramètres d’un ancien ordinateur vers un nouvel ordinateur
Vous avez la possibilité de copier des fichiers depuis votre ancien ordinateur vers un nouvel
ordinateur en utilisant des CD ou des DVD, des cartes mémoire Memory Stick ou d’autres
périphériques de support personnels, ou en utilisant le câble Transfert de fichiers et
paramètres Windows. Vous pouvez également transférer des fichiers et copier certains
paramètres, comme vos favoris Internet et votre carnet d’adresses, à l’aide du logiciel
Transfert de fichiers et paramètres Windows, fourni avec Windows 7.
Le logiciel de Transfert de fichiers et paramètres Windows vous aide à copier des fichiers et
des paramètres sur un périphérique de stockage ou, via le câble de transfert de fichiers et
paramètres, vers le nouvel ordinateur. Le câble de transfert de fichiers et paramètres est un
câble USB conçu spécialement pour connecter deux ordinateurs et travailler avec le logiciel
Transfert de fichiers et paramètres Windows. (Le câble est vendu séparément.) Un câble USB
standard ne fonctionnera pas.
Pour transférer vos fichiers et paramètres :
1 Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer.
2 Tapez Transfert de fichiers et paramètres Windows dans la zone Rechercher, puis
cliquez sur Transfert de fichiers et paramètres Windows.
3 Suivez les instructions apparaissant à l’écran dans l’assistant Transfert de fichiers et
paramètres Windows afin de transférer vos fichiers d’un ancien ordinateur vers votre
nouveau.
Pour plus d’informations, cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis sur Aide et support, et
saisissez déplacement des fichiers dans la zone de recherche avant d’appuyer sur la touche
Entrée. Consultez Utilisation du Centre d'aide et de support page 25.
20 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 89

Fonctionnalités spéciales
de votre ordinateur
Utilisation du lecteur de carte mémoire
(certains modèles uniquement)
Votre ordinateur peut être livré avec un lecteur de carte mémoire multi-format (disponible sur
certains modèles uniquement). Les appareils photo numériques et autres appareils d’imagerie
numérique utilisent des cartes mémoire, ou supports, pour stocker des fichiers d'images
numériques. Le lecteur de carte mémoire permet de lire et d’enregistrer sur plusieurs types de
carte mémoire et sur le lecteur de disque IBM Microdrive.
■ Le lecteur de carte mémoire se trouve à l’avant de l’ordinateur. Il dispose de deux ou
quatre logements horizontaux qui acceptent les supports.
■ Vous pouvez placer un support de données dans un ou plusieurs logements et utiliser
chacun d'eux séparément. N’insérez qu’un seul support à la fois par logement.
■ Chaque logement de carte possède sa propre lettre de lecteur et sa propre icône.
Lorsque vous insérez un support, son éventuel titre peut devenir le libellé affiché.
■ Lorsque vous insérez le support, il est possible que la fenêtre Retirer le périphérique en
toute sécurité apparaisse. Si elle est déjà ouverte ou si vous avez ouvert la fenêtre
Retirer le périphérique en toute sécurité par erreur, cliquez sur Fermer.
ATTENTION : dans la fenêtre Retirer le périphérique en toute sécurité, ne
cliquez pas sur Arrêter quand Périphérique de stockage de masse USB
est sélectionné. Sinon, votre ordinateur ne détectera plus votre lecteur de
carte mémoire et vous devrez alors redémarrer l'ordinateur pour pouvoir
l’utiliser de nouveau.
Lecteur de carte mémoire
A
Le témoin d’activité (A) clignote pour indiquer que l’ordinateur est en train d’accéder à la
carte mémoire pour la lecture ou l’écriture.
Fonctionnalités spéciales de votre ordinateur 21
Page 90

Pour utiliser le lecteur de carte mémoire :
1 Enfoncez complètement le support dans le logement de carte.
Le témoin d’activité (A) du lecteur de carte s’allume, et l’ordinateur détecte
automatiquement le support.
REMARQUE
: vous devez insérer le support correctement. Notez la direction du coin
avec encoche sur le support. Pour plus d’informations, ouvrez le Centre d'aide et de
support ou consultez le site Web d’assistance technique. Voir Obtenir des informations
supplémentaires page 25.
Également :
■ Munis d’une clé, les supports CompactFlash et Microdrive doivent être insérés
correctement. Insérez le côté connecteur (orifices) du support dans le logement.
■ Certaines cartes mémoire, telles que les cartes CompactFlash Ultra/III, ne sont pas
compatibles avec le lecteur de carte mémoire de votre ordinateur.
■ N’utilisez pas de cartes SM et xD en même temps dans le lecteur de carte
mémoire. Le lecteur ne reconnaît que la première carte insérée.
2 Sélectionnez un programme pour accéder à vos fichiers. Vous pouvez copier des
fichiers depuis ou vers le support.
Ou
Si la fenêtre de lecture automatique ne s’ouvre pas, cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer,
sur Poste de travail, puis double-cliquez sur l’icône de carte mémoire pour
afficher les fichiers du support. Vous pouvez copier des fichiers depuis ou vers le
support.
3 Lorsque vous avez terminé, cliquez avec le bouton droit sur l’icône du lecteur,
sélectionnez Éjecter, vérifiez que le témoin d’activité du lecteur de carte mémoire est
allumé ou éteint sans clignoter, puis retirez le support.
ATTENTION : ne tentez pas de retirer un support alors que le témoin
d'utilisation est en train de clignoter. Cela pourrait entraîner la perte de
données.
22 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 91

Utilisation d’un lecteur CD/DVD vertical
A
(certains modèles uniquement)
Votre ordinateur peut disposer d’un lecteur de disque optique installé en position verticale.
Appuyez sur le bouton d’éjection sur ou à proximité du clapet du lecteur (A) pour éjecter le
plateau du CD/DVD. Insérez un disque de taille standard sur le plateau, étiquette tournée
vers l'extérieur, puis poussez le plateau pour le refermer.
Utilisation de la technologie LightScribe
(certains modèles uniquement)
Qu’est-ce que la technologie LightScribe ?
La technologie LightScribe utilise un lecteur de disque spécial, des médias spéciaux (CD ou
DVD inscriptibles avec LightScribe), et un logiciel de création d'étiquette qui grave les
étiquettes directement sur les CD et les DVD. Un graveur de CD ou de DVD LightScribe utilise
un laser optique interne pour graver une étiquette sur la fine couche de pigments du côté
étiquette d’un disque LightScribe. Fini l’encre qui coule et les étiquettes autocollantes qui se
décollent !
Configuration requise pour l’utilisation de LightScribe
La gravure d’une étiquette LightScribe nécessite trois éléments :
■ un graveur de disque optique LightScribe (certains modèles uniquement),
identifié par le logo LightScribe ;
■ un logiciel d'étiquetage prenant en charge LightScribe ;
■ un disque inscriptible LightScribe (vendu séparément).
Création d’une étiquette LightScribe à l’aide de CyberLink LabelPrint
Vous pouvez graver des données, de la musique et des vidéos sur le disque avant ou après
l'étiquetage du disque.
Pour plus d’informations sur la création d’une étiquette LightScribe :
1 Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis sur Aide et support.
2 Tapez Lightscribe dans la zone de recherche, puis appuyez sur Entrée.
Fonctionnalités spéciales de votre ordinateur 23
Page 92

Utilisation de la télécommande
O
(certains modèles uniquement)
REMARQUE
Avec votre télécommande, vous pouvez ouvrir Windows Media Center pour regarder la
télévision, enregistrer des émissions, écouter de la musique, regarder des films ou des vidéos.
Pour ouvrir Windows Media Center, il suffit de pointer la télécommande vers le télécapteur à
l’avant de l’ordinateur et d’appuyer sur le bouton Démarrer Windows Media Center de la
télécommande.
u
: la télécommande fonctionne uniquement avec des piles alcalines.
Pour utiliser la télécommande, pointez-la directement vers le télécapteur. La télécommande et
le télécapteur ne doivent pas être éloignés de plus de 8mètres. Par ailleurs, l’angle de la
télécommande à partir du centre du télécapteur ne doit pas dépasser 22,5 degrés
(soit 45 degrés au total).
REMARQUE
fonctionnement de la télécommande.
24 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
: une forte lumière dirigée directement sur le capteur peut interférer avec le
Page 93

Obtenir des informations
supplémentaires
Utilisation du Centre d'aide et de support
(certains modèles uniquement)
Les informations concernant votre ordinateur figurent dans le Centre d’aide et de support.
Il fournit des liens vers les mises à jour des pilotes, un accès aux options d’assistance
technique et des informations concernant les questions fréquemment posées.
Pour ouvrir le Centre d’aide et de support :
■ Appuyez sur le bouton Aide (certains modèles uniquement) de votre clavier.
Ou
■ Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis sur Aide et support.
Accès à l’assistance sur le Web
Vous trouverez des informations concernant votre ordinateur en utilisant Internet pour accéder
au site Web de l’assistance technique, dont l’adresse est reprise dans le Guide de garantie
limitée et de support, ou en suivant les étapes ci-dessous :
1 Accédez au site http://www.hp.com/support via votre navigateur Web.
2 Sélectionnez votre pays/région et la langue.
3 Cliquez sur Support et pilotes.
4 Entrez le numéro de modèle de votre ordinateur et cliquez sur Rechercher .
Cliquez sur un élément pour le visualiser.
Manuels sur le Web
Des manuels concernant votre ordinateur sont disponibles sur le site Web de l’assistance
technique :
1 Rendez-vous sur le site Web de l’assistance technique et recherchez votre numéro de
modèle en suivant la procédure précédente.
2 Cliquez sur Manuels.
3 Recherchez le manuel souhaité et effectuez l’une des opérations suivantes :
■ Cliquez sur le titre pour afficher le fichier dans Adobe
pouvez télécharger à partir de la page Manuels s’il n’est pas installé sur votre
ordinateur).
Ou
■ Cliquez avec le bouton droit de la souris sur le titre, cliquez sur Enregistrer la
cible sous, spécifiez le dossier de l’ordinateur où placer le fichier, renommez le
fichier (en conservant l’extension .pdf), puis cliquez sur Enregistrer.
Obtenir des informations supplémentaires 25
®
Acrobat® Reader (que vous
Page 94

Manuels en ligne
(certains modèles uniquement)
Vous trouverez des manuels en ligne pour votre ordinateur dans le dossier Manuels de
l’utilisateur.
1 Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer.
2 Cliquez sur Tous les programmes.
3 Cliquez sur Manuels de l’utilisateur.
Cliquez sur un élément pour le visualiser ou l'utiliser.
REMARQUE
l’ordinateur n'en possède pas.
: le fait que le dossier ne contienne aucun titre de manuel indique que
Utilisation du dossier Outils et Aide
Le dossier Outils et Aide contient des utilitaires s’adressant spécialement au propriétaire de
l’ordinateur, par exemple des programmes d’assistance et d’autres informations.
Pour accéder aux éléments du dossier Outils et Aide de l’ordinateur :
1 Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer.
2 Cliquez sur Tous les programmes.
3 Cliquez sur Aide et Outils.
Utilisation du logiciel HP Advisor (Conseiller HP)
(certains modèles uniquement)
HP Advisor (Conseiller HP) est un outil vous permettant de contrôler et d’accéder à des
informations sur l’état du système dans certaines zones importantes de l’ordinateur. HP
Advisor (Conseiller HP) se divise en quatre domaines principaux :
■ PC Dock (Dock PC) — Accédez directement au logiciel HP and Partner sur votre
bureau et personnalisez votre dock en effectuant un cliquer-glisser sur des éléments.
■ PC Dashboard (Tableau de bord PC) — Vérifiez d’un coup d’œil l’état de votre
ordinateur avec le tableau de bord PC Dashboard. Accéder à tous les éléments que
vous avez besoin d’exécuter sur votre ordinateur à partir de HP and Partners.
■ PC Discovery (Découverte PC) — Explorez le logiciel HP and Partner et les services
en ligne installés sur votre ordinateur, et découvrez des offres pour des nouveaux
logiciels et des services passionnants.
Pour ouvrir HP Advisor (Conseiller HP) Dock, cliquez sur le logo HP dans la barre des tâches.
26 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 95

Utilisation de l’ordinateur avec sécurité et ergonomie
AVERTISSEMENT : pour réduire les risques de blessures graves, lisez le
Guide de sécurité et ergonomie du poste de travail. Vous y découvrirez
comment installer correctement votre poste de travail, quelle posture
prendre, quelques conseils de santé importants, et des habitudes de
travail devant être adoptées par les utilisateurs d’un ordinateur. Vous
pourrez également consulter les consignes de sécurité importantes
concernant la mécanique et l’alimentation électrique de votre système.
Avant de commencer à utiliser l’ordinateur, organisez votre espace de travail et installez
l’ordinateur afin d’assurer confort et productivité. Lisez le Guide de sécurité et ergonomie du
poste de travail. Vous y trouverez des conseils importants :
■ Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis sur Tous les programmes, Manuels de
l’utilisateur et sur Guide de sécurité et ergonomie du poste de travail.
Ou
■ Entrez
http://www.hp.com/ergo
dans la barre d’adresse du navigateur, puis appuyez sur la touche Entrée du clavier.
Obtenir des informations supplémentaires 27
Page 96

28 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Page 97

Dépannage et maintenance
Cette section comprend :
■ Des tableaux de dépannage dans Dépannage des problèmes ci-dessous.
■ Des informations de réparation du logiciel dans Dépannage logiciel page 45.
■ Des informations et des directives de maintenance dans Maintenance page 48.
Pour plus d’informations, reportez-vous au Centre d'aide et de support ou consultez le site
Web d’assistance technique ; consultez la section Obtenir des informations supplémentaires
page 25.
Reportez-vous à la documentation fournie par le fabricant du produit pour obtenir de plus
amples informations sur les problèmes spécifiques aux périphériques, comme les problèmes
de moniteur ou d’imprimante.
Dépannage des problèmes
Les tableaux suivants présentent quelques problèmes que vous pourriez rencontrer lors de
l’installation, du démarrage, ou de l’utilisation de votre ordinateur. Ils proposent également
des solutions que vous pouvez essayer.
Les tableaux apparaissent dans l’ordre suivant :
■ L’ordinateur ne démarre pas page 30
■ Alimentation page 31
■ Affichage (moniteur) page 31
■ Clavier et souris (avec câble) page 32
■ Clavier et souris sans fil page 33
■ Audio et haut-parleurs page 36
■ Accès à Internet page 37
■ Lecteurs de CD et de DVD page 38
■ Vidéo page 40
■ Installation du matériel page 41
■ Performance page 42
■ Périphériques sans fil page 43
■ Télécommande page 44
■ Lecteur de carte mémoire page 44
Dépannage et maintenance 29
Page 98

L’ordinateur ne démarre pas
Symptôme Solution
L'ordinateur refuse de
démarrer ou de
s'allumer.
L’ordinateur semble
bloqué et ne
répond pas.
Assurez-vous que les câbles qui relient l’ordinateur à la source
d’alimentation externe sont correctement branchés.
Lorsque les câbles reliant l’ordinateur à une source
d’alimentation sont bien branchés et que la prise murale
fonctionne correctement, le témoin d’alimentation vert à
l’arrière de l’ordinateur doit s’allumer. Si ce n’est pas le cas,
reportez-vous au Guide de garantie limitée et de support pour
contacter l’assistance technique.
Si l’écran (moniteur) n’affiche rien, le moniteur est
probablement mal connecté. Connectez le moniteur à
l’ordinateur, puis branchez-le et allumez-le. Consultez Affichage
(moniteur) page 31.
Placez le sélecteur de tension sur la position appropriée pour
votre pays ou région, ou consultez le Guide de garantie limitée
et de support pour contacter le Centre d’assistance technique.
Testez la prise murale en y connectant un autre dispositif
électrique.
Utilisez le Gestionnaire des tâches de Windows pour fermer les
programmes qui ne répondent pas, ou pour redémarrer votre
ordinateur :
1 Appuyez sur les touches Ctrl, Alt et Suppr du clavier
simultanément.
2 Cliquez sur Ouvrir le gestionnaire de tâches.
3 Sélectionnez le programme qui ne répond pas, puis
cliquez sur Arrêter la tâche.
Si le problème persiste après avoir fermé le programme,
redémarrez l’ordinateur :
1 Appuyez sur les touches Ctrl, Alt et Suppr du clavier
simultanément.
2 Cliquez sur le bouton flèche situé à côté du bouton rouge
Arrêter, puis cliquez sur Redémarrer.
Ou
1 Appuyez sur le bouton de mise en marche pendant cinq
secondes ou plus pour éteindre l’ordinateur.
2 Appuyez sur le bouton de mise en marche pour démarrer
l'ordinateur.
Message d'erreur :
Erreur de disque dur.
30 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
Consultez le Guide de garantie limitée et de support pour
contacter le Centre d’assistance technique.
Page 99

Alimentation
Symptôme Solution
Message d'erreur :
le message Disque
système invalide ou
Disque non système ou
Erreur disque apparaît.
L’ordinateur ne s’éteint
pas lorsque l'on appuie
sur le bouton de mise
en marche (On).
L’ordinateur s’éteint
automatiquement.
Lorsque le voyant d'activité s'éteint, retirez le disque et
appuyez sur la barre d'espace du clavier. L’ordinateur doit
maintenant démarrer normalement.
Appuyez sur le bouton de mise en marche (On) et maintenez-le
enfoncé jusqu’à ce que l’ordinateur s’éteigne.
Vérifiez les paramètres d’alimentation.
La température ambiante est trop élevée. Laissez-le refroidir.
Vérifiez que les aérations de l’ordinateur ne sont pas obstruées
et que le ventilateur interne fonctionne. Il est possible que votre
ordinateur ne soit pas équipé d’un ventilateur interne.
Consultez Nettoyage des grilles d’aération de l’ordinateur
page 50.
Affichage (moniteur)
Solution possible
Symptôme
L’écran est occulté et le
voyant d’alimentation
est éteint.
L’écran n’affiche rien. Appuyez sur la barre d’espace du clavier ou déplacez la souris
Les images affichées à
l’écran sont trop
grandes, trop petites
ou floues.
reportez-vous à la documentation accompagnant votre moniteur.)
Rebranchez le câble d’alimentation au dos du moniteur et à la
prise murale.
Appuyez sur le bouton d'alimentation à l'avant du moniteur.
pour réactiver l’affichage.
Appuyez sur le bouton de Veille (certains modèles uniquement)
ou sur la touche Échap du clavier pour sortir du mode Veille.
Appuyez ensuite sur le bouton de mise sous tension pour
allumer l'ordinateur.
Assurez-vous qu’aucune broche du connecteur vidéo du
moniteur n’est endommagée :
■ Si l’une des broches est endommagée, remplacez le câble
de connexion du moniteur.
■ Si toutes les broches sont en bon état, rebranchez le câble
de connexion du moniteur à l’ordinateur.
églez le paramètre de résolution du moniteur dans Windows 7 :
R
1 Cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer, puis sur Panneau de
configuration.
2 Dans Apparence et personnalisation, cliquez sur Régler
la résolution de l’écran.
3 Réglez la résolution selon vos préférences, puis cliquez sur
Appliquer.
(Outre les informations fournies ci-dessous,
Dépannage et maintenance 31
Page 100

Clavier et souris (avec câble)
Symptôme Solution
Votre ordinateur ne
reconnaît pas les
commandes ou les
combinaisons de
touches du clavier.
La souris (avec câble)
ne fonctionne pas ou
n'est pas détectée après
l'installation.
Le curseur ne suit pas
les mouvements de
la souris.
Éteignez l’ordinateur en utilisant la souris, déconnectez et
reconnectez le clavier à l’arrière de l’ordinateur, puis allumez
votre ordinateur.
Débranchez et rebranchez le câble de la souris à l’ordinateur.
Si la souris n’est toujours pas détectée, éteignez l’ordinateur,
déconnectez et reconnectez le câble de la souris, puis rallumez
l’ordinateur.
Redémarrez votre ordinateur à l’aide du clavier :
1 Appuyez simultanément sur les touches Alt et Tabulation
pour accéder à un programme ouvert.
2 Appuyez simultanément sur les touches Ctrl et S pour
enregistrer les modifications dans le programme
sélectionné (Ctrl+S est le raccourci clavier de la
commande Enregistrer pour la plupart des programmes,
mais pas tous).
3 Répétez les étapes 1 et 2 pour enregistrer les
modifications dans tous les programmes ouverts.
4 Une fois les modifications enregistrées dans toutes les
applications ouvertes, appuyez simultanément sur les
touches Ctrl et Échap pour afficher le menu Démarrer de
Windows.
5 Utilisez les touches fléchées pour sélectionner le bouton
flèche à côté de Arrêter. Sélectionnez Arrêter puis
appuyez sur la touche Entrée sur le clavier.
6 Une fois la procédure d'arrêt terminée, débranchez et
rebranchez la prise de la souris à l'arrière de l'ordinateur
et allumez votre ordinateur.
32 Démarrage rapide (les caractéristiques peuvent varier selon le modèle)
 Loading...
Loading...