Page 1

HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager 2.5.0 Software for VMware® vSphere™ Client User Guide
Abstract
This guide is intended for VMware® and database administrators responsible for backing up databases and provides information
how to install, configure, and use HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager 2.5.0 Software for VMware®
vSphere™.
HP Part Number: QL226-96913
Published: June 2014
Page 2

© Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Acknowledgments
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows® XP, and Windows NT® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Java and Oracle are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement
WARNING: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority
to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is subjected to the following two conditions (1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Canadian Compliance Statement
This ClassA digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matérial brouilleur du Canada.
Page 3

Contents
1 Overview..................................................................................................6
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere.......................6
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter.......................................................................7
Virtual Volume Details..........................................................................................................7
LUN Provisioning for Recovery Manager for VMware................................................................8
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere...........................................................8
TpdVmWebService..............................................................................................................8
RMWebAccess Library.........................................................................................................8
RMVMware Admin Tool........................................................................................................8
RMVMwareCLI....................................................................................................................9
RMVMware InServRegister command.................................................................................9
RMVMware vCenterRegister command............................................................................10
RMVMware Create command.........................................................................................11
RMVMware Createrc command......................................................................................14
User authentication.................................................................................................................15
VMware vCenter Server Login for HP 3PAR Virtual Volume and Virtual Copy management..........16
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System login..............................................................................16
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage certificate..................................................................................16
Network ports used by HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware
vSphere............................................................................................................................17
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere interface........17
HP 3PAR Views in the vSphere Client........................................................................................18
Datastore view...................................................................................................................18
Virtual Machine view..........................................................................................................20
ESXi host view...................................................................................................................22
Cluster view......................................................................................................................22
Datacenter view.................................................................................................................23
Virtual Copy management.......................................................................................................24
Virtual Copy data consistency.............................................................................................24
Virtual Copy policy............................................................................................................24
Datastore Virtual Copies.....................................................................................................25
Virtual Machine Virtual Copies............................................................................................25
Remote Virtual Copies........................................................................................................26
The Virtual Copy browser....................................................................................................26
VMFS snapshots................................................................................................................27
Scheduling tool..................................................................................................................28
VASA support........................................................................................................................28
2 Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager
Software for VMware vSphere.......................................................................29
Supported platforms................................................................................................................29
Installation dependencies.........................................................................................................29
Support for VMware vCenter Server Linked mode.......................................................................29
Viewing and installing HP 3PAR Management plug-in certificate...................................................30
Registering an SMS Certificate for the VASA Provider..................................................................30
Extracting the SMS Certificate.............................................................................................31
Installing the SMS certificate................................................................................................32
Installing the SMS certificate through the VASA Web Service..............................................32
Installing SMS certificate on Windows 2008....................................................................32
Installing SMS certificate on Windows 2012/2012 R2.......................................................32
Extracting and saving certificates....................................................................................33
Contents 3
Page 4

Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware
vSphere.................................................................................................................................33
Upgrading from a previous version...........................................................................................33
Using secure service connections.........................................................................................34
3 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool...................36
Overview..............................................................................................................................36
HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool.......................................................................................................36
vCenter Plug-in tab..................................................................................................................36
vCenter Plug-in configuration...............................................................................................37
Plug-in registration..............................................................................................................39
Remote Copy pairs............................................................................................................40
The VASA tab........................................................................................................................41
The VASA configuration......................................................................................................41
StoreServ Credential tab..........................................................................................................43
4 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes..............................................47
Logging on to the vSphere Client..............................................................................................47
Viewing Virtual Volume mapping..............................................................................................50
Viewing Volume information................................................................................................51
The Upper pane............................................................................................................51
The Lower pane............................................................................................................53
Refreshing Virtual Volume information........................................................................................53
Creating Virtual Volumes and Datastores...................................................................................54
Creating a Virtual Volume from an existing HP 3PAR StoreServ template...................................54
Creating a Virtual Volume from existing Datastores.................................................................58
Adding an ESXi host to the vCenter Server.................................................................................58
5 Working with Virtual Copies......................................................................60
Viewing Virtual Copy information.............................................................................................60
Viewing Virtual Disk Details for Virtual Copies.......................................................................61
Viewing Virtual Copy event logs..........................................................................................62
Creating New Virtual Copies...................................................................................................62
Mounting Virtual Copies..........................................................................................................64
Unmounting Virtual Copies......................................................................................................64
Restoring Datastores by promoting a Virtual Copy.......................................................................65
Deleting Virtual Copies............................................................................................................66
Modifying Virtual Copy policies...............................................................................................66
Scheduling Virtual Copies........................................................................................................68
Restoring Virtual Disks, Guest OS Files, and Directories................................................................72
Restoring a Virtual Disk.......................................................................................................72
Restoring a Guest OS File or Directory from a Virtual Copy.....................................................73
6 Working with VASA Provider......................................................................75
7 Working with Remote Copy.......................................................................78
Registering Remote Copy Pairs.................................................................................................79
Updating Registered Remote Copy Pairs information....................................................................81
Viewing host information summary............................................................................................81
Viewing existing and newly added Remote Copy information.......................................................82
Creating Remote Virtual Copies................................................................................................84
Setting Policy for Remote Virtual Copies.....................................................................................85
Scheduling Remote Copy Virtual Copies....................................................................................86
Mounting Remote Virtual Copies...............................................................................................89
Mounting from Virtual Copy table........................................................................................89
Mounting from Virtual Volume mapping table........................................................................90
Unmounting Remote Virtual Copies...........................................................................................91
4 Contents
Page 5

Unmounting from Virtual Copy table.....................................................................................91
Unmounting from Virtual Volume Mapping table....................................................................91
Deleting Remote Virtual Copies................................................................................................91
Deleting Local Virtual Copies...................................................................................................92
Importing a Virtual Machine and reverting to a specific point-in-time Virtual Copy...........................93
8 Using HP 3PAR Peer Motion Manager Software with Recovery Manager.........94
9 Support and Other Resources.....................................................................95
Contacting HP........................................................................................................................95
HP 3PAR documentation..........................................................................................................95
Typographic conventions.........................................................................................................98
HP 3PAR branding information.................................................................................................98
10 Documentation feedback.........................................................................99
A Troubleshooting VASA Provider................................................................100
VASA Provider registration issue.............................................................................................100
Inspecting VASA Provider and vCenter Server communication.....................................................100
Alarm Type Message........................................................................................................100
Event Type Message.........................................................................................................109
B Troubleshooting for HP 3PAR Management plug-in......................................115
Resolving HP 3PAR multi-tab issue...........................................................................................115
Index.......................................................................................................116
Contents 5
Page 6

1 Overview
HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server (Insight Control for vCenter) is a single integrated
application that you use to manage ProLiant servers and/or HP Storage Systems. The application
consists of four modules. The core module is required along with at least one of the three optional
components.
• Server Module for vCenter—Adds HP Proliant and HP BladeSystem hardware monitoring into
the vCenter Server console. Provides server hardware management capabilities, including
comprehensive monitoring, firmware update, vSphere 5.x/ESXi 5.x image deployment, remote
control, end-to-end monitoring for Virtual Connect, and power optimization for HP servers in
the VMware environment.
• Storage Module for vCenter—Provides storage configuration and status information for mapping
VMs, datastores, and hosts to LUNs on HP storage arrays.
Supports provisioning on HP 3PAR StoreServ, HP StoreVirtual, HP MSA P2000 G3, and HP
EVA Storage Systems. Supported provisioning tasks include creating, expanding, or deleting
a datastore, and creating or cloning a VM. Displays view-only information for the HP StoreOnce
Backup systems.
NOTE: If you require VASA Provider, then you must select this option.
• Recovery Manager for HP 3PAR StoreServ—The following two installation options are provided:
RMV with Plug-in integration—Installs the vSphere Client and the Web Client to perform
◦
the RMV Plug-in functionality.
◦ RMV service only—Installs the RMV target server to handle Remote Copy operations.
NOTE: Core Module provides the framework required by Server Module for vCenter and
Storage Module for vCenter. This module is mandatory and is installed by default. Therefore,
no GUI option is provided to select this Module.
Insight Control for vCenter is integrated with the vCenter management server (also known as vCenter
Server) and the vSphere Client software from VMware. VMware vCenter is used as the single point
of management for VMware virtual environments, which can consist of many standalone or clustered
vSphere configurations. The virtual environment administrator accesses the vCenter management
capabilities using the vSphere Client software.
The Insight Control for vCenter software is installed on a server or a VM and is then configured to
connect and register with a vCenter server. After Insight Control for vCenter is registered with a
vCenter Server, all vSphere Clients connected to the vCenter Server can access the Insight Control
for vCenter software.
For more information on Insight Control for vCenter, see HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter
Server User Guide.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere Management Suite has three components, VMware vCenter Server, vSphere
Client, and Web Client. vCenter Server is a web service installed on a Windows server. vSphere
Client is a Windows desktop application, and is typically downloaded from the vCenter Server.
vSphere Web Client is a web based application that can be installed using VMware vSphere. You
can perform the various functionalities using either the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
The plug-in also contains a software component that acts as a vSphere Storage API for Storage
Awareness (VASA) provider in the vSphere environment. HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and
6 Overview
Page 7
Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere provides its own web servers. For more
information on Web Client, see the HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software
for VMware vSphere Web Client User Guide.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere is a suite of
services designed to work with the vCenter Server. The plug-in contains a web application and
deploys as a Web client and a vSphere Client plug-in (a vSphere Client plug-in is an external Web
application configured with the vCenter Server for vSphere Clients to display their pages). The
plug-in also contains a software component that acts as a vSphere Storage API for Storage
Awareness (VASA) provider in the vSphere environment. HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and
Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere provides its own web servers.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere includes the
following major components:
• HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter - Displays virtual volume mapping for easy
identification of HP 3PAR volumes used by Virtual Machines and Datastores. Also allows user
to provision LUNs to be used as Datastore or raw device.
• HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere - Provides Virtual Copy management of HP
3PAR Virtual Copies and recovery of Virtual Machines and Datastores.
• HP 3PAR VASA Provider for VMware vSphere - Enables the vCenter Server to connect to
obtain information about available storage topologies, capabilities, and state.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter is a free vSphere Client plug-in. The plug-in
enables easy identification of HP 3PAR virtual volumes used by Virtual Machines and Datastores
and displays commonly used volume properties and attributes. The plug-in also supports LUN
Provisioning that enables the creation of a virtual volume and/or Datastore based on an existing
configuration or template.
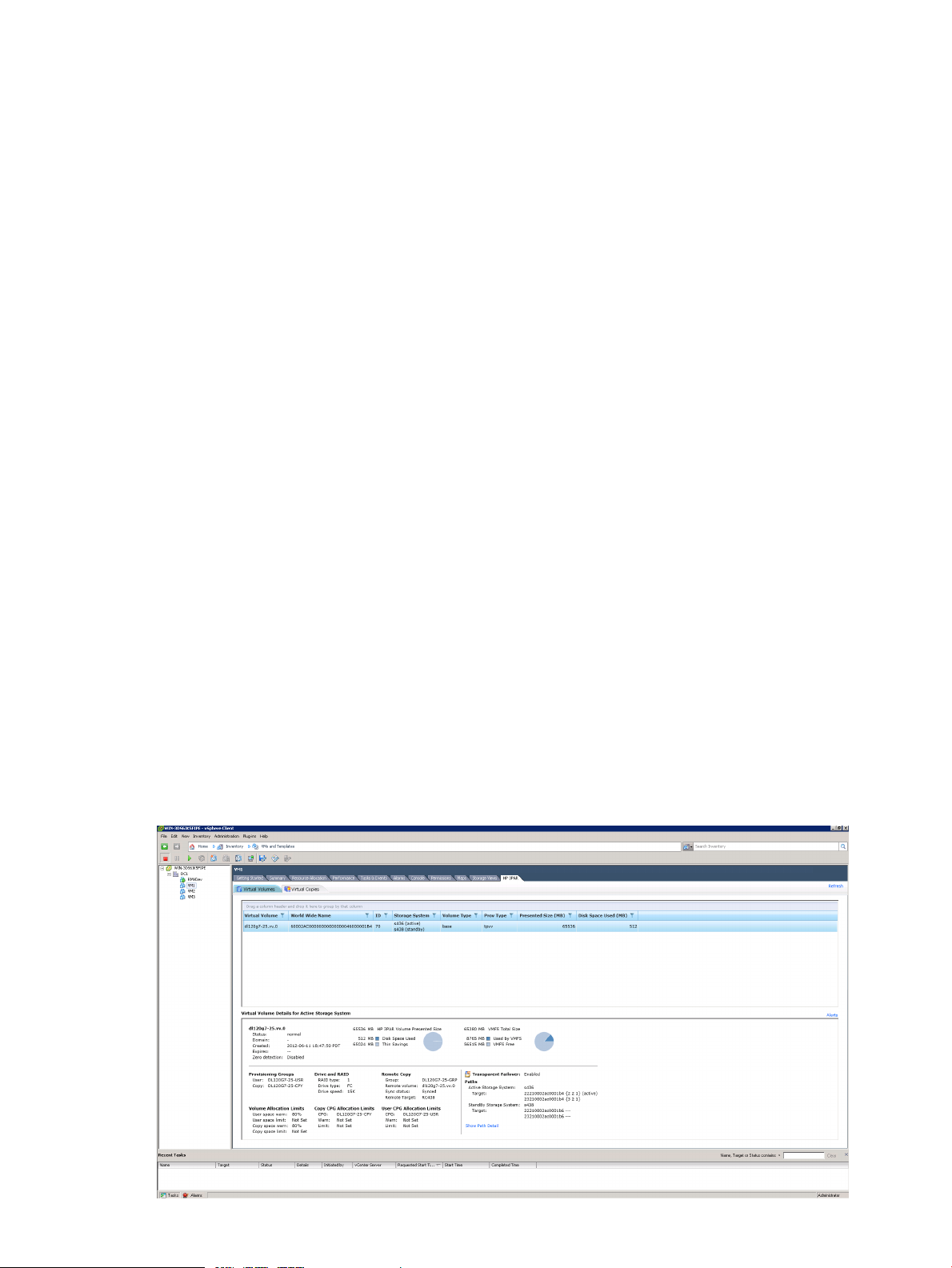
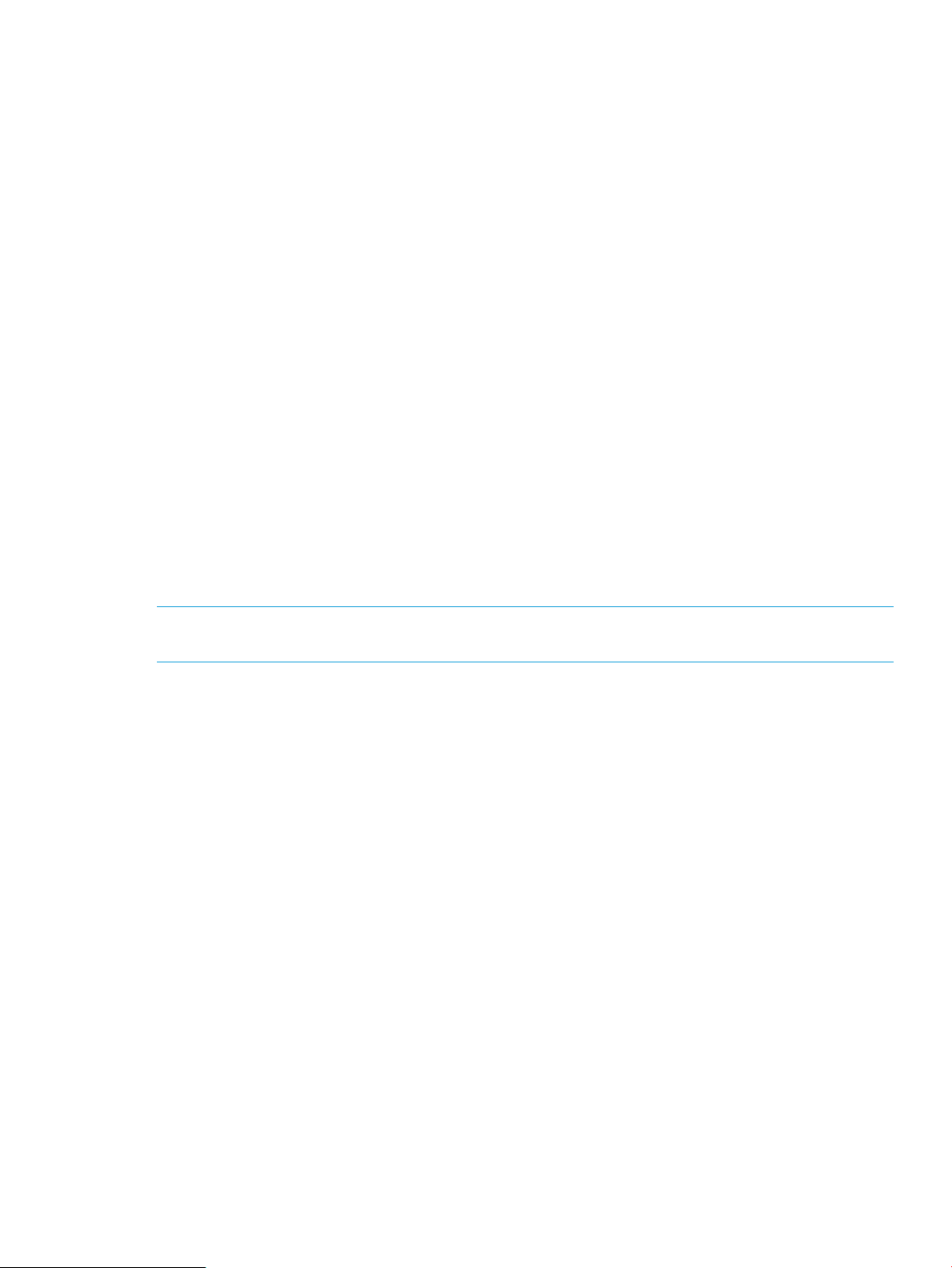
Virtual Volume Details
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter displays virtual volume information for each
volume used by a Virtual Machine (VM) or Datastore and Transparent Failover configuration details
via the HP 3PAR tab in the vSphere Client. The Transparent Failover configuration status only
displays when it is enabled via HP 3PAR Operating System Software.
Figure 1 Viewing Datastore Virtual Volumes
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter 7
Page 8

See “Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes” (page 47) for additional information about
viewing virtual volume details.
LUN Provisioning for Recovery Manager for VMware
This feature enables you to create virtual volumes based upon a storage system template or an
existing Datastore and export the virtual volumes to the vCenter managed ESXi hosts.
For more details about creating and managing virtual volumes and Datastores, see “Creating a
Virtual Volume from an existing HP 3PAR StoreServ template” (page 54)
NOTE: Only TPVV and CPVV provisioning are supported for this release.
NOTE: LUN provisioning does not require an RMV license.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere allows you to manage Virtual Copies
of VMs and Datastores. It is comprised of the following four components:
• TpdVmWebService
• RMWebAccess Library
• RMVMware Admin Tool
• RMVMwareCLI
See “Virtual Copy management” (page 24) for additional information.
TpdVmWebService
TpdVmWebService is a RESTful Web service, which is deployed as a Windows Service. The major
functions of Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere are implemented with this module. These
functions are:
• Provides a custom Web server to deliver plug-in application Web pages. The vCenter Servers
are configured with the address of this Web server during plug-in registration.
• Maps Virtual Machines and Datastores to underlying HP 3PAR virtual volumes.
• Creates, browses, deletes, and mounts Virtual Copies created on Virtual Machines and
Datastores.
RMWebAccess Library
NOTE: RMWebAccess Library is deployed as a Windows component dll file and is installed
as part of Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere.
Similar to the HP 3PAR Command Line Interface (CLI) and HP 3PAR Management Console (IMC),
the RMWebAccess Library is used for interacting with the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System
array. The RMWebAccess Library does not use HP 3PAR OS CLI but instead interacts with the
InServ Tpd TCL Service directly using secure network connections.
RMVMware Admin Tool
The RMVMware Admin Tool provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for administering Recovery
Manager for VMware vSphere registration with the vCenter server. This tool also includes HP 3PAR
StoreServ Storage System credential management, HP 3PAR VASA Provider configuration, and
Remote Copy paring configuration.
NOTE: Host Explorer is not associated with RMV from version 2.5 onwards. If required, you can
install Host Explorer as a separate package.
8 Overview
Page 9

RMVMwareCLI
The RMVMware CLI module is the command line interface for Recovery Manager for VMware
vSphere.
NOTE: The recommended method for creating Virtual Copies is through the Graphical User
Interface (see “Working with Virtual Copies” (page 60) for more details).
Four commands are provided through the CLI:
• RMVMware InServRegister
• RMVMware vCenterRegister
• RMVMware Create
• RMVMware Createrc
RMVMware InServRegister command
The RMVMware InServRegister command registers HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system
credentials. The syntax for the RMVMware InServRegister command is as follows:
RMVMware InServRegister
<-inserv "InServName"> <-inservuid "InServUserID"> <-inservpwd
"InServPassword">
RMVMware InServRegister
<-remove> <-inserv "InServName"> <-inservuid "InServUserID">
RMVMware InServRegister <-display>
NOTE: User’s who do not have the administrative privileges required to access the RMVMware
Admin Tool can use the RMVMware InServRegister command to create the appropriate
registration.
The options and arguments used for this command are described as follows:
• -inserv <InServName>
Specifies the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system login name to the vCenter Server. This option
is required.
• -inservuid <InServUserID>
Specifies the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system login user name. This option is required.
• -inservpwd <InServPassword>
Specifies the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system login password. This option is required when
registering an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
NOTE: This option will not be supported in a future release.
• -remove
Removes a registered HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system configuration.
• -display
Displays all registered HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system credentials.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere 9
Page 10
Example:
The following command will add a new entry for the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System s124:
C:\> RMVMware InServRegister -inserv s124 -inservuid root -inservpwd pass2word
RMVMware vCenterRegister command
The RMVMware vCenterRegister command manages the vCenter credentials. The syntax for
the RMVMware vCenterRegister command is as follows:
RMVMware vCenterRegister
<-vcserver "VCServerName"> <-vcuid "VCUserID"> <-vcpwd "VCPassword">
<-vcfile "CredentialFilePath">
RMVMware vCenterRegister <-remove> <-vcserver "VCServerName">
<-vcuid "VCUserID"> <-vcfile "CredentialFilePath">
RMVMware vCenterRegister <-display> <-vcfile "CredentialFilePath">
The options and arguments used for this command are described as follows:
• -vcserver <VCServerName>
Specifies the vCenter name.
• -vcuid <VCUserID>
Specifies the vCenter user name.
• -vcpwd <VCPassword>
Specifies the vCenter password.
• -vcfile <CredentialFilePath>
Specifies the path to the credential file.
• -display
Displays the content of the credential file.
• -remove
Removes the registered credential.
Example:
The following command will add a new entry for user Administrator on vCenter Server MyVC:
C:\> RMVMware vCenterRegister -vcserver MyVC -vcuid Administrator
-vcpwd myPassword -vcfile "c:\myCred.xml"
10 Overview
Page 11

RMVMware Create command
The RMVMware create command creates a Virtual Copy on a Datastore or a Virtual Machine.
The syntax for the RMVMware create command is as follows:
RMVMware Create
<[-ds "Datastore" [-consistency <yes/no> [-vmlist "VirtualMachine1, VirtualMachine2,
..."]]]|[-vm "VirtualMachine" [-consistency <yes/no>]
]>
[-setname "VirtualCopySetName"]
<[-vcserver "vCenterServerName" [-vcuid
"vCenterServerUserID"] [-vcpwd "vCenterServerPassword"] | [-vcfile
"VMwareCredentialStoreFileLocation"] ]>
<[-inserv "InServName"] [-inservuid "InServUserID"]>
[-inservpwd "InServPassword"]
[-expiry "VirtualCopyExpiryInHour"]
[-retention "VirtualCopyRetentionInHour"]
The options and arguments used for this command are described as follows:
• -ds <Datastore>|-vm <VirtualMachine>
Creates a Virtual Copy on the specified <Datastore> or <VirtualMachine>. By default,
a VM consistent Virtual Copy is created. The VM name must be unique within vCenter Server.
The vCenter Server can manage multiple ESXi hosts. The VM name should be unique across
ESXi hosts.
The UUID of the Datastore or Virtual Machine may also be used to create a Virtual Copy with
uuid-<myUUIDofDatastore> or uuid-<myUUIDofVirtualMachine> in place of the
Datastore or Virtual Machine name.
• -consistency <yes/no>
(Optional) Specifies whether or not (yes/no) the Virtual Copy is to maintain Virtual Machine
application consistency with supported data formats. If this option is not set, the default policy
is applied.
• -setname <VirtualCopySetName>
(Optional) Specifies that in addition to the Virtual Copy time stamp, the Virtual Copy set name
can be used to personalize the identity of the Virtual Copy set. By default, the name is set to
reflect the current time.
• -vcserver <vCenterServerName>
The VMware vCenter Server name or IP address. This option is required.
• -vcuid <vCenterServerUserID>
The VMware vCenter server login user name. This option is required.
• -vcpwd <vCenterServerPassword>
The VMware vCenter Server login password. This option is required unless -vcfile is used
to specify the credential store file.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere 11
Page 12

• -vcfile <VMwareCredentialStoreFileLocation>
The VMware credential stores file location. The –vcfile option is optional when –vcpwd is
specified. For example, C:\Users\[User Name]\AppData\Roaming\VMware\
credstore\myCred.xml.
NOTE: For VMware credential store file creation, refer to the vCenterRegister option.
NOTE: To run the RMVMware CLI command with the vCenter Credential Store File, you
must be added as a user to have permission to access the credential file.
• -inserv <InServName>
The name or IP address of the HP 3PAR storage system on which the VM or Datastore resides.
This option is required.
• -inservuid <InServUserID>
The HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system user login name.
• -inservpwd <InServPassword>
The HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system login password. This option is not required if the
Storage System name, user ID, and password have been registered.
NOTE: This option will not be supported in a future release.
• -vmlist
Optional to provide Virtual Machine names for application consistency snapshot. If not set,
all Virtual Machines under the Datastore is applied. This option can only be applied if
-consistency yes is specified.
• -expiry <VirtualCopyExpiryInHour>
(Optional) Sets the amount of time (in hours) before a Virtual Copy is deleted from the system
regardless of the maximum count. If an expiration time period is not specified with this option,
the Virtual Copy is deleted after it reaches the oldest position in the queue beyond the maximum
count specified through the policy settings. See “Working with Virtual Copies” (page 60) for
more details. If this option is not set, the default policy is applied.
• -retention <VirtualCopyRetentionInHour>
(Optional) Sets the amount of time (in hours) that Virtual Copies are retained, during which
period the Virtual Copy cannot be altered. The Virtual Copy is not deleted after the retention
period but is then available for modification and deletion. See “Working with Virtual Copies”
(page 60) for more details. If this option is not set, the default policy is applied.
Examples:
The following command will create an HP 3PAR Virtual Copy for the Datastore "My Datastore":
C:\> RMVMware create -ds "My Datastore" -vcserver vc365 -vcuid admin
-vcpwd pass2word -inserv s124 -inservuid rmvuser -inservpwd pass3word
12 Overview
Page 13
As an alternative to entering in all the command line options when creating a Virtual Copy of a
Virtual Machine or a Datastore, you can reference the server password or credentials from a given
file using the following command:
C:\ RMVMware create -ds "My Datastore" -vcserver vc365 -vcuid admin
-vcfile c:\myCred.xml -inserv s124 -inservuid rmvuser
For information about creating a credential file in xml format, see “RMVMware vCenterRegister
command” (page 10).
NOTE: If duplicate Datastore or Virtual Machine names exist under the same vCenter server, use
the following uuid-<myUUIDofDatastore> or uuid-<myUUIDofVirtualMachine>
commands in place of Datastore or virtual name such as
uuid-4220f0f6-3aec-258b-dc41-949f596c6ba8.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere 13
Page 14
RMVMware Createrc command
The RMVMware createrc command creates a remote Virtual Copy.
NOTE: When using the RMVMware createrc command, you must use the identical name of
the storage system registered in the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system credential database.
The syntax for the RMVMware createrc command:
RMVMware Createrc <-rcgroup "RemoteCopyGroup"> [-consistency <yes|no>] <[-vcserver
"vCenterServerName" [-vcuid "vCenterServerUserID"] [-vcpwd "v
CenterServerPassword"] | [-vcfile "VMwareCredentialStoreFileLocation"] ]> <-remotehost
"RemoteHostName"> <[-inserv "InServName"] [-inservuid "InServUs
erID"]> [-inservpwd "InServPassword"] <[-remoteinserv "InServName"] [-remoteinservuid
"InServUserID"]> [-remoteinservpwd "InServPassword"] [-expiry "V
irtualCopyExpiryInHour"] [-retention "VirtualCopyRetentionInHour"]
DESCRIPTION:
Create HP 3PAR Virtual Copies based on Remote Copy groups.
OPTIONS:
-rcgroup: Remote Copy group name for which the HP 3PAR remote Virtual Copy will
be created (this parameter is case sensitive)
-vcserver: VMware vCenter Server name or IP address
-vcuid: VMware vCenter Server log in user name
-vcpwd: VMware vCenter Server user password, optional when -vcfile is specified
-vcfile: Optional VMware credential store file location
-remotehost: remote host where Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere is installed
to take remote snapshot on.
-inserv: local HP 3PAR Storage System name
-inservuid: local HP 3PAR Storage System user name, required when registered
-inservpwd: local HP 3PAR Storage System password, optional if -inserv is
registered
-remoteinserv: remote HP 3PAR Storage System name
-remoteinservuid: remote HP 3PAR Storage System user name, required when
registered
-remoteinservpwd: remote HP 3PAR Storage System password, optional if
-remoteinserv is registered
-consistency: Optional to set Virtual Machine application consistency to yes or
no.
-expiry: Optional to set HP 3PAR Virtual Copy expiration in hours (1-43800).
-retention: Optional to set HP 3PAR Virtual Copy retention in hours (1-43800).
EXAMPLE:
The following command will create HP 3PAR Virtual Copy for the Remote Copy group
RMV_RCGROUP_ASYNC:
C:\> RMVMware createrc -rcgroup RMV_RCGROUP_ASYNC -vcserver caracal -vcuid
administrator -vcpwd ssmssm -remotehost 10.112.61.225 -inserv s25
6 -inservuid root -remoteinserv s336 -remoteinservuid root -consistency yes
The following options and arguments used for this command:
• -rcgroup
• -vcserver
• -vcuid
14 Overview
Remote Copy group name for which the HP 3PAR remote Virtual Copy will be created (this
parameter is case sensitive).
VMware vCenter Server name or IP address.
VMware vCenter Server log in user name.
Page 15

• -vcpwd
VMware vCenter Server user password, optional when -vcfile is specified.
• -vcfile
Optional VMware credential store file location.
• -remotehost
Remote host where Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere is installed to take remote snapshot
on.
• -inserv
Local HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system name.
• -inservuid
Local HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system user name, required when registered.
• -inservpwd
Local HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system password, optional if -inserv is registered.
NOTE: This option will not be supported in a future release.
• -remoteinserv
Remote HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system name.
• -remoteinservuid
Remote HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system user name, required when registered.
• -remoteinservpwd
Remote HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system password, optional if -remoteinserv is
registered.
NOTE: This option will not be supported in a future release.
• -consistency
Optional to set Virtual Machine application consistency to yes or no.
• -expiry
Optional to set HP 3PAR Virtual Copy expiration in hours (1-43800).
• -retention
Optional to set HP 3PAR Virtual Copy retention in hours (1-43800).
User authentication
As stated earlier, HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware
vSphere is deployed as a vSphere Client plug-in. You must first log into the vCenter Server before
accessing HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere’s
features. HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
does not ask for a user name or password. Instead, it uses a user login credentials to access
VMware inventory. This credential sharing is the VMware recommended way for transparent plug-in
authentication.
User authentication 15
Page 16

VMware vCenter Server Login for HP 3PAR Virtual Volume and Virtual Copy management
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere creates a
new vCenter Server role named HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Administrator upon plug-in registration.
The following restrictions apply for the HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Administrator role:
• All non-administrator users must be in this role.
• If an administrator logs in as Administrator or DOMAIN\Administrator, the permission check
is skipped.
NOTE: For VM access, the HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Administrator role must be provided
with access to all the domains. For Datastore access, the HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Administrator
role must be assigned at the datacenter level.
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System login
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere has to
connect to an HP 3PAR storage array in order to obtain volume details for mapping and Virtual
Copy management. You can log on to a system on an on-demand basis and HP 3PAR Management
Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere does not save any storage system
user names or passwords locally on the desktop, or centrally on the server. When HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere needs to access an
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System and no connection already exists, it will display an error and
provide instructions for entering the storage system name, user name, and password.
As a convenient option, you can use the auto login feature by selecting the “Remember me” check
box when logging onto a given system. In this case, the login details are stored in the Credential
database and you do not have to enter them every time you access the system. To replace the
currently saved credential, you must log out from the storage system and login again with “Remember
me” checked for the new credential. To remove the currently saved credential, logout from the
storage system and login again with the same credential with “Remember me” unchecked. You
can also remove the currently saved credential through the Admin Tool→StoreServ Credential tab.
NOTE: When the VMware Sphere client initially loads the HP 3PAR plug-in page during an a
vCenter session, HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere searches and identifies the
associating storage system. If the associating storage system is configured with the auto-login
option, the storage system information is also collected simultaneously. As a result, you may
experience an increase in time for the page to load and display the volume information. When
the auto-login is fully executed, all HP 3PAR pages should load according to the performance level
of the system.
NOTE: You must have a minimum of Edit level or 3PAR_RM level privileges for accessing the
Virtual Copies tab, and Browse level privileges for accessing the Virtual Volumes tab.
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage certificate
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage enables management of SSL certificate, and enforces certificate
validation by the host and client applications to establish a secure connection.
HP 3PAR CLI and HP 3PAR OS versions 2.3.1 MU5 P35, 3.1.1 MU3 P27, 3.1.2 MU3 P16, or
later, supports a self-signed 2048-bit RSA SSL certificate for HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage. You must
upgrade to one of these versions to enforce certificate validation. To use the SSL certificate, you
must upgrade to one of the HP 3PAR CLI and HP 3PAR OS versions that supports SSL certificate.
When the RMV web service receives a request, such as, a login request to connect to an HP 3PAR
StoreServ, it establishes a connection with the HP 3PAR StoreServ on behalf of the client. Before
establishing the connection, the RMV web service checks if a server certificate is available in the
RMV database for the HP 3PAR StoreServ. If a certificate is available, then the RMV web service
16 Overview
Page 17
retrieves the saved certificate, and sends a connection request to HP 3PAR StoreServ with the
certificate details. If the HP 3PAR StoreServ certificate is the same as the one specified in the request,
and if there are no other connection issues, then a connection is successfully established.
However, if there are no saved certificates in the RMV database, then the RMV web service sends
a connect request to HP 3PAR StoreServ without the server certificate. If HP 3PAR StoreServ has a
CA (Certificate Authority) signed certificate installed on the server, then a connection is successfully
established. However, if the connection fails due to SSL certificate issue, then the RMV web service
passes the server certificate to RMV. This certificate is also displayed in the GUI. You must verify
the certificate and respond to the server by accepting or rejecting the certificate. If you reject the
certificate, then the connection process stops with an invalid server certificate error message. Else,
the RMV web service re-sends a connect request using the certificate accepted by you. If there are
no other connection issues, then the connection is successfully established. You can also save this
accepted certificate in the RMV server database. If the server certificate is not changed and is not
expired, then the connection is directly established, without any verification, when you login the
next time.
Network ports used by HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere uses the
following network port:
The network ports used by the HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for
VMware vSphere are selected during installation of HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server.
To ensure that the same port number is used for RMV operation, you need to edit the required port
numbers during installation. For more information on the port numbers, see the HP Insight Control
for VMware vCenter Server Installation Guide.
NOTE: The TCP port numbers change based on the modules that you have selected during
installation.
Firewalls, if any, must be configured to allow traffic to these ports with the outbound connections
rule set to allow (default) for HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager for VMware
vSphere to function properly.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere interface
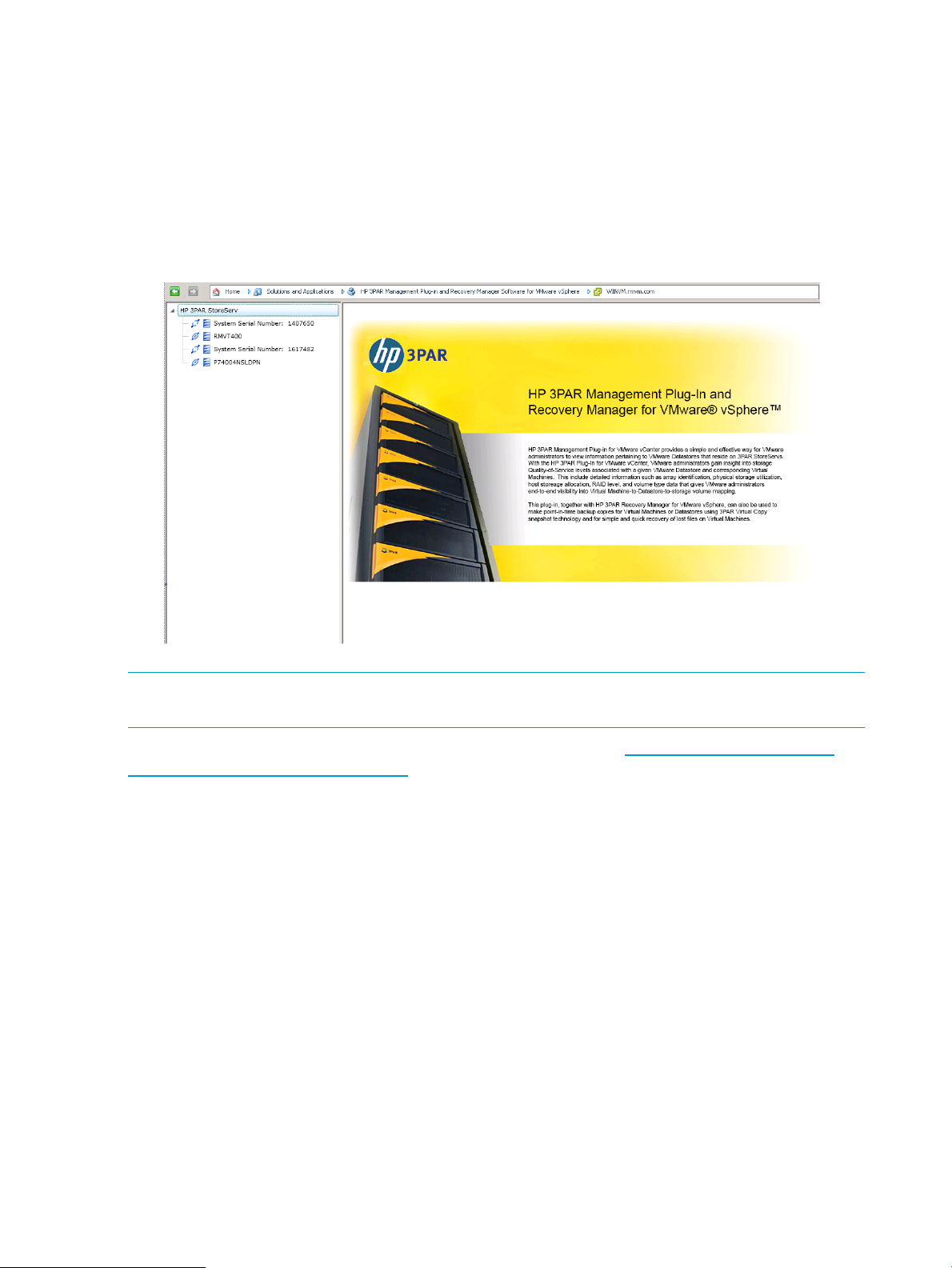
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere appears as
a tab in the vSphere Client. When the HP 3PAR tab is selected, the HP 3PAR Management Plug-in
and Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere interface appears as shown in Figure 2 (page 18).
The interface is divided into the following:
• Main menu navigation
• Navigation tree
• Tabs and detail pane
• Tasks and alerts pane
The interface elements are referenced later in this guide.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere interface 17
Page 18
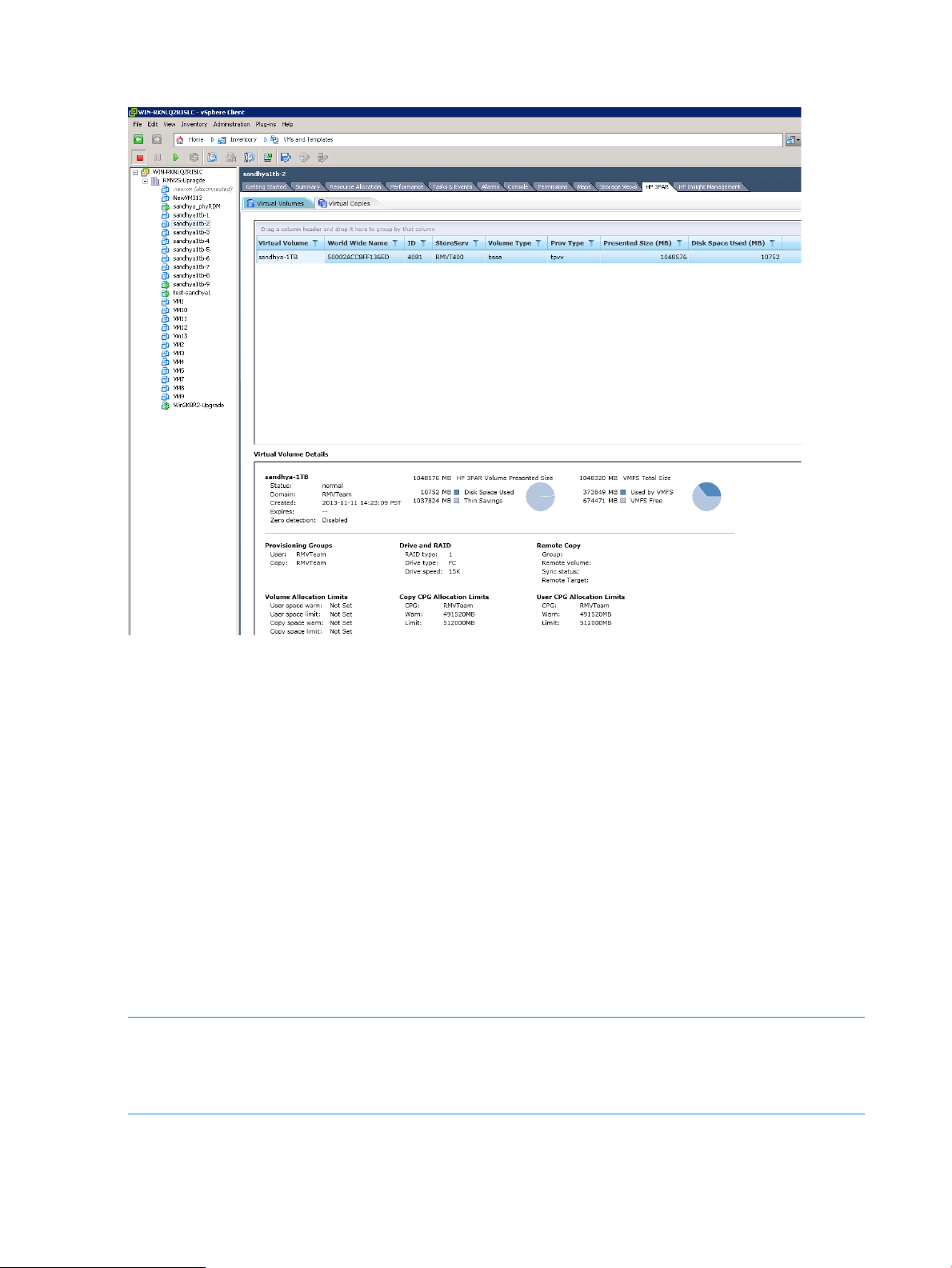
Figure 2 HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
interface
HP 3PAR Views in the vSphere Client
The HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and the Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere adds
its own plug-in views in the vSphere Client. Each plug-in view is associated with a VMware entity
such as a VM or Datastore (Virtual Volume). The details of plug-in views are defined in an XML
file URL, which is registered with the vCenter Server during plug-in registration.
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere adds the
following views to the vSphere Client:
• Datastore View - Displays all virtual volumes associated with a Datastore.
• Virtual Machine View - Displays all virtual volumes associated with a VM. Volumes that use
Raw Device Mapped (RDM) virtual disks are also displayed.
• ESXi Host View - Displays all virtual volumes that are assigned to the ESXi host.
• Cluster View - Displays all virtual volumes associated with every ESXi host in the cluster.
• Datacenter View - The VMware datacenter has several ESXi hosts and Clusters. This view
displays all virtual volumes associated with every ESXi host in the datacenter.
NOTE: HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
does not support a single ESXi host mapped to multiple HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system host
names. All WWNs for each Fiber Channel host adaptor on the same ESXi server should be used
to create a single host name on the storage system.
Datastore view
To access the Datastore view:
18 Overview
Page 19
1. Under Inventory from the vSphere Client home page, click Datastores.
Figure 3 Selecting Datastores
HP 3PAR Views in the vSphere Client 19
Page 20
All Datastores residing in the data center are displayed in the navigation tree.
Figure 4 Viewing Datastores in the navigation tree
2. Select a Datastore and then click the HP 3PAR tab.
Information about the virtual volumes associated with the Datastore are displayed.
Virtual Machine view
To access the Virtual Machine (VM) view:
20 Overview
Page 21
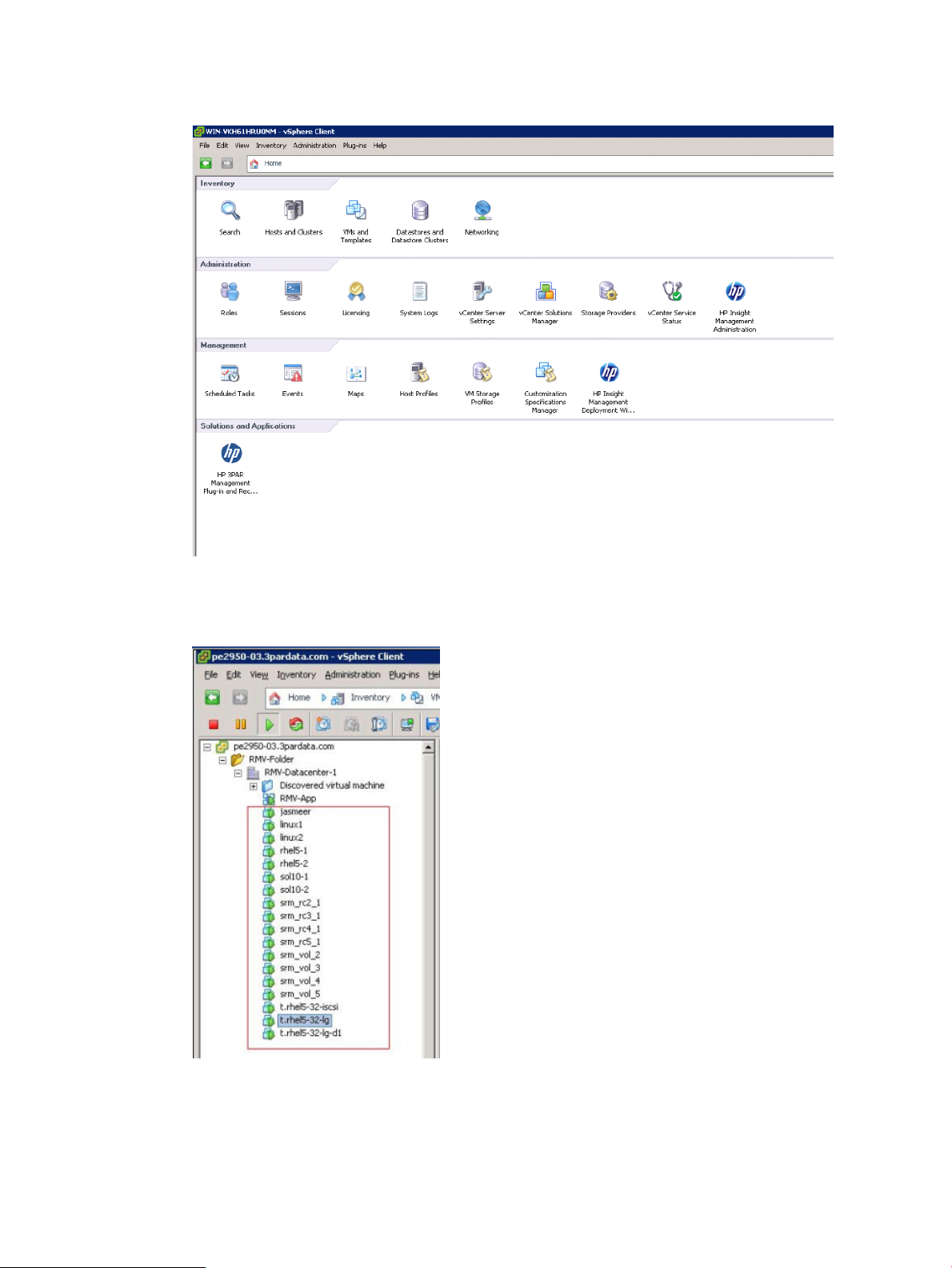
1. Under Inventory from the vSphere Client home page, click VMs and Templates.
Figure 5 Selecting VMs and Templates
All VMs in the data center are displayed in the navigation tree.
Figure 6 Viewing VMs in the navigation tree
2. Select a VM and then click the HP 3PAR tab.
Information about the virtual volumes associated with the VM is displayed.
HP 3PAR Views in the vSphere Client 21
Page 22
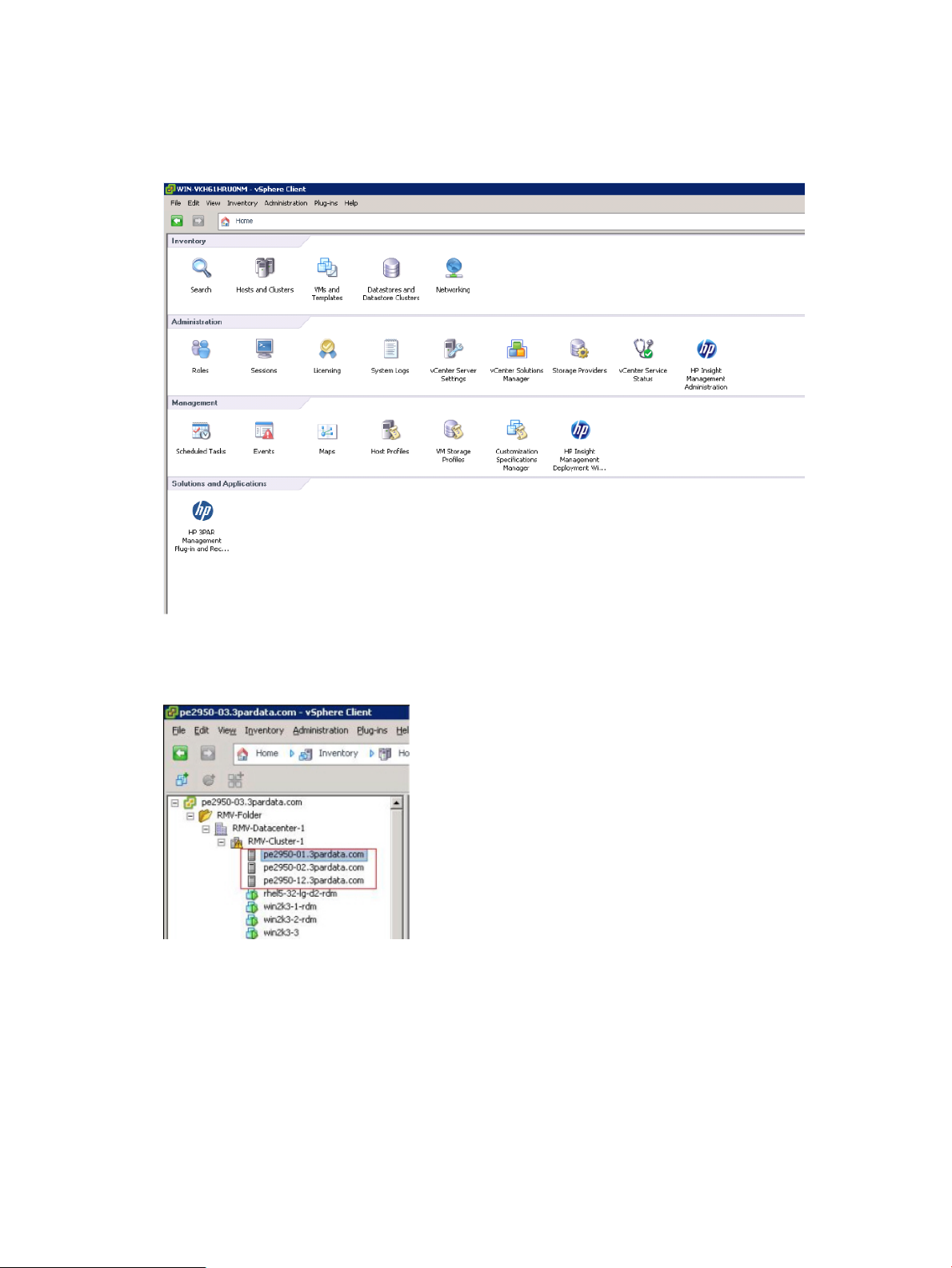
ESXi host view
To access the ESXi host view:
1. Under Inventory from the vSphere Client home page, click Hosts and Clusters.
Figure 7 Selecting Hosts and Clusters
2. Select a host and then click the HP 3PAR tab.
Cluster view
To access the cluster view:
All hosts in the data center are displayed in the navigation tree.
Figure 8 Viewing Hosts in the navigation tree
Information about the virtual volumes associated with the host is displayed.
22 Overview
Page 23
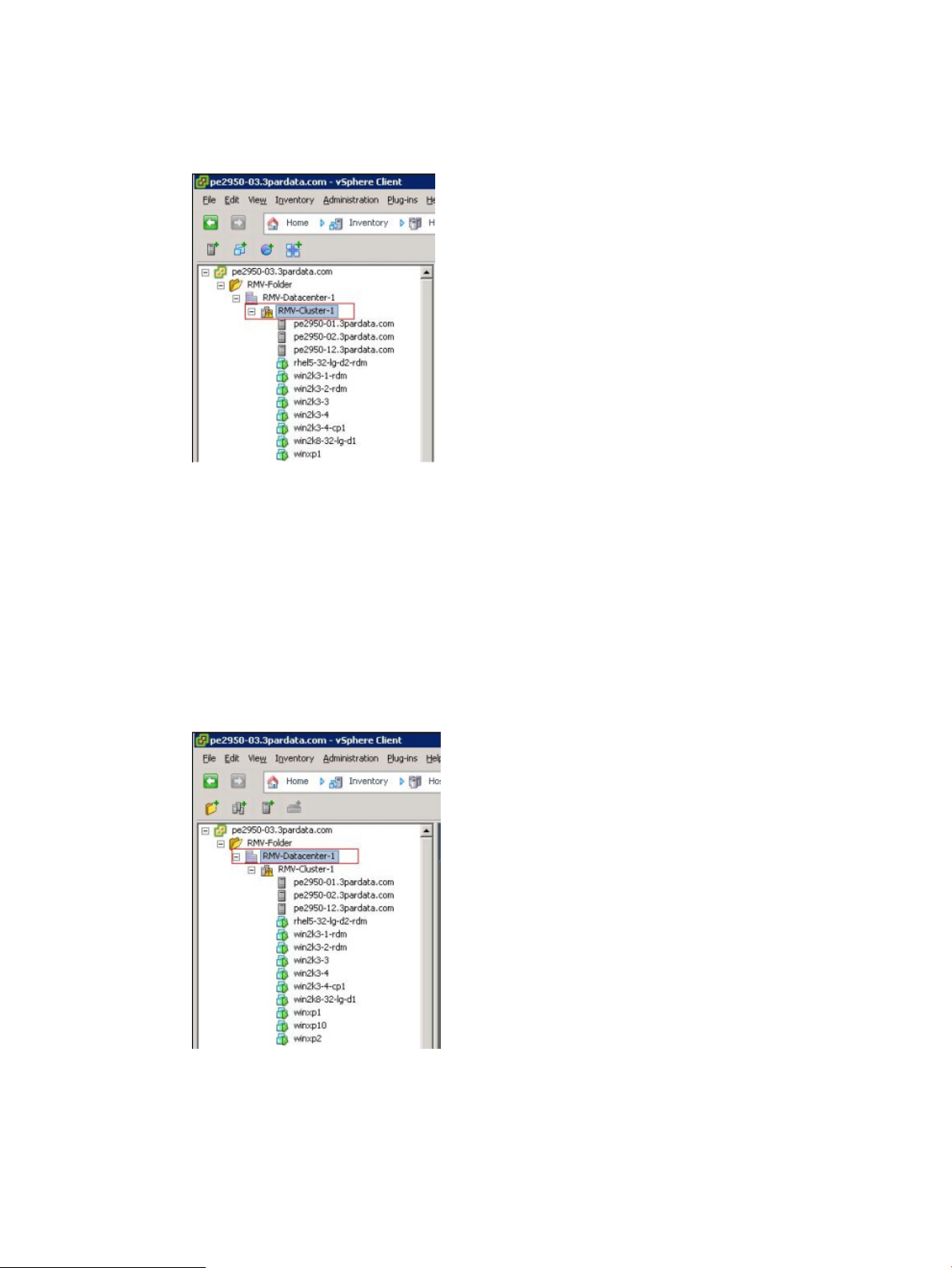
1. Under Inventory from the vSphere Client home page, click Hosts and Clusters (see Figure 7
(page 22)).
All clusters in the data center are displayed in the navigation tree.
Figure 9 Viewing clusters in the navigation tree
2. Select a cluster and then click the HP 3PAR tab.
Information about the virtual volumes associated with the cluster is displayed.
Datacenter view
To access the datacenter view:
1. Under Inventory from the vSphere Client home page, click Datastores, VMs and Templates,
or Hosts and Clusters (see Figure 3 (page 19), Figure 5 (page 21), or Figure 7 (page 22)).
All Datacenters are displayed in the navigation tree.
Figure 10 Viewing Datacenters in the navigation tree
2. Select a datacenter and then click the HP 3PAR tab.
Information about the virtual volumes associated with that datacenter is displayed.
HP 3PAR Views in the vSphere Client 23
Page 24

Virtual Copy management
NOTE: HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere is not functional without the HP 3PAR
Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere license. Additionally, the HP 3PAR Virtual Copy license
is required for Virtual Copy operation and the HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license is required for using
the volume retention policy. RMV will check for an existing HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license on the
storage system when a Virtual Copy is created with retention is specified.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere allows you to take LUN-level Virtual Copies of
Virtual Machines (VMs), Datastores and Remote Copy groups. A Datastore is created on one HP
3PAR volume, and a VM is created on one or more Datastores. During VM Virtual Copy creation,
Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere will identify all the underlying HP 3PAR volumes and take
Virtual Copies simultaneously for all volumes to ensure consistency. Recovery Manager for VMware
vSphere manages this set of Virtual Copies as a single entity. Remote Copy Virtual Copies are
based at the Remote Copy group level (storage system), versus the Virtual Machine or Datastore
level (VMware perspective).
NOTE: VMware Tools must be installed on the Guest OS in order for HP 3PAR Recovery Manager
for VMware vSphere to create successful VM/Application consistent Virtual Copies. Refer to
VMware documentation for more information about VMware Tools setup instructions.
Virtual Copy data consistency
Several types of data consistency are possible for VM Virtual Copies and backup.
NOTE: The current version of HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere supports system
crash, VM and application consistent Virtual Copies.
• Crash Consistent—A simple virtual volume Virtual Copy without quiescing the memory blocks
inside the guest OS results in a crash consistent Virtual Copy of the VM. Data not flushed will
be lost, but all data written to the file system will be available. Sanity checking of file system
(fsck) is needed after recovery.
• VM Consistent—All file system blocks are flushed from the memory of a VM before a Virtual
Copy is taken. This ensures that no file system data is lost if the VM crashes. Checking of file
system (fsck) is not required after recovery. No application data is flushed from memory before
the Virtual Copy is taken
• Application Consistent—Application consistency is provided for HP 3PAR snapshots of Virtual
Machines for data compatibility with supported applications.
NOTE: A VM consistent Virtual Copy is always attempted if VMware Tools is installed on the
Guest OS. VMware must first successfully create a VMFS snapshot. For information on the best
practices and limitations of VMware snapshots, see the VMware knowledge base http://
kb.vmware.com/.
Virtual Copy policy
Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere allows the creation of Virtual Copy policies for VMs
and/or Datastores. Only one policy is permitted for every VM and/or Datastore. Datastore and
VM policies exist independently; meaning a VM policy is independent of the policy of the
Datastore(s) of virtual disks it is using.
24 Overview
Page 25

In Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere, the Virtual Copy policy contains the following attributes:
• Maximum Number of Virtual Copy Sets - You can choose how many Virtual Copies to be
retained. When the number of Virtual Copies is at the maximum limit, the oldest Virtual Copy
is deleted when a new Virtual Copy is created.
• Enable expirable Virtual Copies - Allows you to specify that created Virtual Copies are removed
according to a specified schedule and are not affected by the maximum count.
• Retain Virtual Copy Set - The supported number of hours and days that a Virtual Copy set is
retained.
NOTE: The Retain Virtual Copy Set option requires the HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license. RMV
will check for an existing HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license on the storage system when a Virtual
Copy is created with retention is specified. Contact your local service provider for additional
information.
• Ensure Application Consistency - This option is used to create Virtual Copies that adhere to
data format standards used by Microsoft VSS for guest operating systems. This option is
available for Virtual Machine and Datastore with Virtual Machines.
Datastore Virtual Copies
A Datastore is created on a Fibre Channel or iSCSI LUN. During Virtual Copy creation, Recovery
Manager for VMware vSphere identifies the HP 3PAR volume used and takes a Virtual Copy of
the volume. Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere stores the details of all virtual disks and VMs
present in the Datastore.
This feature has the following restrictions:
• The Datastore must be on exactly one HP 3PAR volume. A Datastore that spans across more
than one LUN is not supported.
• RDM LUNs defined in the Datastore are not included in the Virtual Copy. It is possible that a
HP 3PAR LUN is used as RDM in a guest OS, which is defined in a Datastore created on
another HP 3PAR LUN.
NOTE: A Virtual Copy of a Datastore does not include any RDM 3PAR LUNs.
• All Datastore Virtual Copies can be VM or crash consistent. File system and/or application
integrity checks must be performed in the guest OS for the crash consistent Virtual Copies after
restoration.
• Network File System (NFS) Datastores are not supported.
• VMFS file systems spanning multiple hard disk partitions to create a single logical volume are
not supported.
• The Datastore must not be on an ESXi SAN boot disk. Virtual Copy operations are not supported
on Datastores residing in ESXi SAN boot disks.
For information about creating Virtual Copies, see “Creating New Virtual Copies” (page 62).
Virtual Machine Virtual Copies
A Virtual Machine (VM) configuration files are created in a Datastore. VMDK virtual disks used
by VMs are created on one or more Datastores. In addition, a VM can use HP 3PAR volumes
directly as RDM virtual disks. Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere identifies all of the HP 3PAR
volumes used by a VM and creates Virtual Copies of all of them simultaneously. A list of virtual
disk names and their type (RDM or VMDK) and configuration file name are also recorded in the
repository during Virtual Copy creation.
Virtual Copy management 25
Page 26

NOTE: A VM with a Physical RDM mapped to it is not supported for taking Application Consistent
Virtual Copy. Instead, you can take Crash Consistent Virtual Copy. However, the Virtual Copy is
not taken for the Physical RDM.
A VM Virtual Copy has the following restrictions:
• Virtual disks used by a VM must be from the HP 3PAR Datastore, and the latter must satisfy
the conditions mentioned in “Datastore Virtual Copies” (page 25).
• If the VM uses more than one HP 3PAR volume, all of them must be from the same HP 3PAR
storage array.
• VMs that use a mix of HP 3PAR LUNs and third party LUNs are not supported.
• All VM Virtual Copies can be VM or crash consistent. File system and/or application integrity
checks must be performed in the guest OS after restoration for the crash consistent Virtual
Copies.
• VMs using NFS Datastores are not permitted.
• VMFS file systems spanning multiple hard disk partitions to create a single logical volume are
not supported.
For information about creating VM Virtual Copies, see “Creating New Virtual Copies” (page 62).
Remote Virtual Copies
Remote Virtual Copies are based on the Remote Copy Group. If a VM or Datastore uses virtual
volumes outside of the Remote Copy group, HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere
cannot take a remote Virtual Copy of the group. Remote Virtual Copies require a remote host with
TCP/IP connectivity to the target Storage System.
• VMs or Datastores must be contained within the Remote Copy group
• Restore processes are currently performed manually
The Virtual Copy browser
NOTE: You must have an HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere license in order to
use the Virtual Copy browser.
In Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere, every Virtual Copy, VM, or Datastore has its own
metadata, which is used in instances where a restoration is necessary. Metadata is kept in a local
file system of the server.
You can view Virtual Copy metadata at any time after it was created using the Virtual Copy browser
of the VM and Datastore views of the plug-in.
26 Overview
Page 27
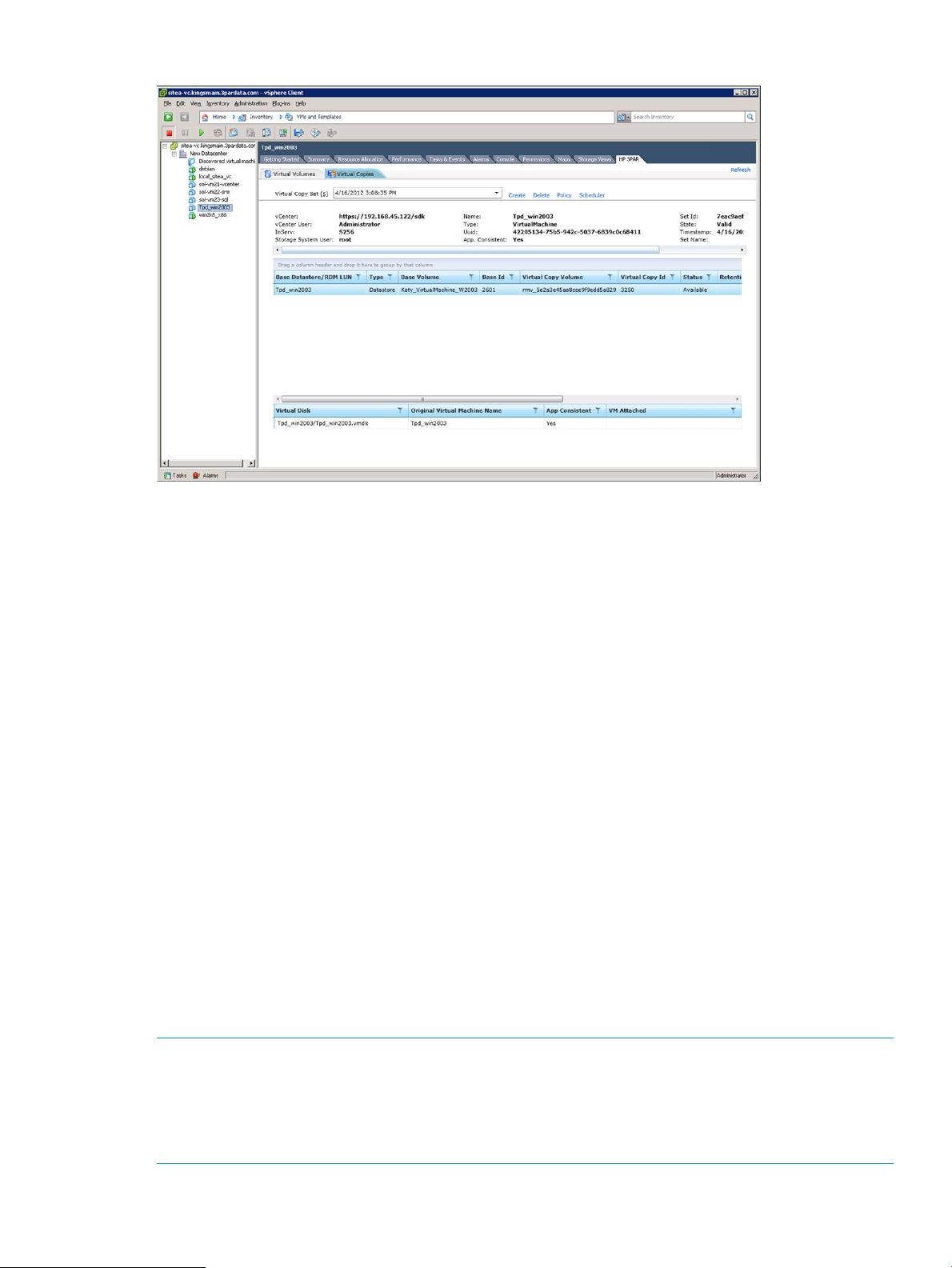
Figure 11 Virtual Copy browser
A Virtual Copy of a VM or Datastore has the following properties:
• The Virtual Copy creation time.
• The HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system where Virtual Copy volumes exist.
• The Virtual Copy set name (optional).
• The number of Virtual Copy volumes in the Virtual Copy.
• A list of pairs (source volume, Virtual Copy volume). Each pair can have a list of virtual disks
and/or VM names.
All Virtual Copies are organized in the browser based on their creation times. The browser displays
all relevant metadata so that you can make restore decisions faster and without actually mounting
Virtual Copy volumes.
The data shown in the Virtual Copy browser comes from the metadata repository and may not
reflect the current state of HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. It is possible that volumes shown in
the browser may not exist in the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system; for example, if a volume is
deleted.
For information about viewing the Virtual Copy browser, see Figure 33 (page 53).
VMFS snapshots
In order to maintain a VM consistent Virtual Copy, a VMFS snapshot will be created before creating
an HP 3PAR Virtual Copy and the VMFS copy will be deleted when the HP 3PAR Virtual Copy is
created. HP 3PAR Virtual Copies and VMFS snapshots cannot coexist. HP 3PAR Virtual Copy
creation in VM, Datastore, or Remote Copy will fail if there are preexisting VMFS snapshots for
the VM.
NOTE: When creating a VMFS snapshot, VMware can fail the operation with the message:
“Cannot create a quiesced snapshot because the create snapshot operation exceeded the time
limit for holding off I/O in the frozen Virtual Machine.”
If this message is displayed, the VMware Tools process should be restarted, or reinstalled to resolve
the issue.
Virtual Copy management 27
Page 28

Scheduling tool
You can automatically have Virtual Copies created according to a specified schedule by using the
scheduling tool (see “Scheduling Virtual Copies” (page 68) for details). You have the option of
scheduling when (hourly, daily, weekly, monthly) the Virtual Copy is to be created and then
specifying how often the task is to be performed. You can also schedule a Virtual Copy creation
task to occur on a one-time basis.
VASA support
Support is included for vSphere Storage APIs for Storage Awareness (VASA) that allows a VMware
administrators to view information about the physical storage array as well as the virtual Datastore.
For more information on VASA, see "Storage Providers" in vCenter Server.
NOTE: The VASA support is available, only if you have selected the Storage Module during the
HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server installation.
28 Overview
Page 29

2 Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management Plug-in
and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
This chapter describes how to install, register, remove, and upgrade HP 3PAR Management Plug-in
and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere.
Supported platforms
For information about supported platforms, refer to the HP 3PAR OS Configuration Matrix. For
information about supported hardware and software platforms, refer to http://www.hp.com/go/
3par/
Installation dependencies
Ensure that the following requirements are met, before you install HP 3PAR Management Plug-in
and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere:
• The HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere license and the HP 3PAR Virtual Copy
license is required for Virtual Copy operation. It is mandatory that you have these license
components on the StoreServ.
• The HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license is required for setting retention policies in Virtual Copy
creation. RMV will check for an existing HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license on the Storage System
when a Virtual Copy is created with retention. However, it is not mandatory to have a Virtual
Lock licence.
• The HP 3PAR Remote Copy license is required for remote Virtual Copy operation. However,
it is not mandatory to have a HP 3PAR Remote Copy licence.
• You must have the following minimum privileges:
Edit level privilege with access to all domains (or the 3PAR_RM role)—For Virtual Copy
◦
Set operations.
◦ Browse level privilege—For Virtual Volume operations.
◦ Administrator privilege—For vCenter Server plug-in registration.
• The Virtual Machines must have VMware Tools installed to perform the Virtual Copy Set
operations with application consistency. For more information on instructions about VMware
Tools setup, see the VMware documentation.
NOTE: The current release of Recovery Manager server is not internationalized, however it
supports installation on Windows server with English, Chinese, and Japanese locale. However
operations are supported only in English.
VASA is silently installed as part of HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server installer. vSphere
Client must be installed using VMware vSphere. For more information on installation, registration,
removal, and upgradation, see the HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server Installation
Guide.
Support for VMware vCenter Server Linked mode
The HP 3PAR Management Plug-in supports the Linked Mode feature of VMware that allows you
to create and manage a Linked Mode group during or after the vCenter Server installation.
To install Recovery Manager for VMware in a Linked Mode environment, do the following:
1. Verify that the RMV server is associated with the same Active Directory domain as the vCenters.
Supported platforms 29
Page 30
2. Ensure that the RMV plug-in is registered with all vCenters associated with the Linked Mode
configuration.
3. Log on to vSphere client using Active Domain user name.
4. Log on to an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
a. Navigate to the home page, and click HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery
Manager Software for VMware vSphere. The StoreServ home page for the vCenter
appears.
b. Use a valid user name and password to log on to the required StoreServ.
5. Select a vCenter from the drop-down list and repeat step 4 for the remaining vCenter servers.
NOTE: You may need to log on to the same storage system more than once if that particular
storage system is connected to more than one vCenter.
For more information about VMware vCenter Linked Mode, go to https://www.vmware.com/
products/vcenter-server/features.html.
To resolve HP 3PAR multi-tab issues, see “Resolving HP 3PAR multi-tab issue” (page 115).
Viewing and installing HP 3PAR Management plug-in certificate
HP 3PAR Management plug-in uses a self-signed certificate. If a Security Alert dialog box appears
and displays a message that the certificate is not trusted, do the following to install the certificate:
1. Click View Certificate. The Certificate dialog box appears.
2. Click Install Certificate.
3. Continue to follow the Wizard instructions. Select Place All certificates in the following store
on Certificate Store page, and click Browse.
4. Select Trusted Root Certification Authorities on the Select Certificate Store dialog box, and
click OK.
5. Complete the Wizard instructions.
6. Click OK to exit the Certificate dialog box.
Registering an SMS Certificate for the VASA Provider
Both the vCenter Server and VASA Provider use SSL certificates. The VASA Provider support included
with Recovery Manager for VMware uses the same certificate used by the Plug-in web service.
However, before you can use the vCenter Server to register the VASA provider, you must manually
30 Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
Page 31

install the SMS certificate extracted from the vCenter server onto the VASA installed host. This
process is required for every vCenter Server you intend to register with the VASA provider. The
same process is also required if the SMS certificate has a new certificate. The SMS extraction and
installation process is provided in the following section.
Extracting the SMS Certificate
Create the temp folder in the C:\ drive, before you perform the following procedure:
For vCenter installed on Windows system:
1. On vCenter Server installed host, navigate to the following location C:\Program Files\
VMware\Infrastructure\jre\bin.
2. Enter the following command specifying the location and name for the certificate file:
For Windows 2003
keytool -exportcert -v -keystore "C:\Documents and Settings\All
Users\Application Data\VMware\VMware VirtualCenter\SSL\sms.keystore"
-file c:\temp\sms_new.cer -alias sms
Copy the certificate and paste it in the RMV installed server/host.
For Windows 2008
keytool -exportcert -v -keystore "c:\Programdata\VMware\VMware
VirtualCenter\SSL\sms.keystore" -file c:\temp\sms_new.cer -alias
sms
Copy the certificate and paste it in the RMV installed server/host.
For Windows 2012/2012 R2
keytool -exportcert -v -keystore "c:\Programdata\VMware\VMware
VirtualCenter\SSL\sms.keystore" -file c:\temp\sms_new.cer -alias
Sms
Copy the certificate and paste it in the RMV installed server/host.
3. If the export is successful, the following message is displayed:
Certificate stored in file <file name>
For Virtual vCenter Appliances
1. SSH to the vCenter Server Appliance, and navigate to the follow directory:
/etc/vmware-vpx/ssl
2. Enter the following command specifying the location and name for the certificate file of your
choosing:
keytool -exportcert -v -keystore sms.keystore -file
sms_new.cer -alias sms
3. Click Enter when prompted to enter the keystore password.
If the export is successful, the following message is displayed:
Certificate stored in file <file name>
4. Download the newly created certificate file to the system where RMV is installed.
Registering an SMS Certificate for the VASA Provider 31
Page 32

Installing the SMS certificate
You need to install the SMS certificate on the VASA Provider host's Local Computer/Trusted Root
Certification Authorities store.
There are two methods to install SMS certificate:
• Using the VASA Provider web service (only applicable when the VASA web service is running).
• Manually registering the certificate through the certification store.
Installing the SMS certificate through the VASA Web Service
Perform the following steps to install the SMS certificate through the VASA web service:
1. Open the browser and enter the path for the VASA certificate registration service as follows:
<vasa web service url>/Config/Register
Here is an example:
https://myvasaserver:9997/config/Register
2. If the Choose a digital certificate screen appears, click OK to continue.
The HP 3PAR VASA Provider Certificate Registration screen should appear.
NOTE: If a certificate error occurs, click the Continue to this website (not recommended) link.
3. Click Browse to locate the extracted certificate, then click Submit to send it to VASA Provider.
Upon submission, a message is returned indicating whether the registration was successful.
If the registration was unsuccessful, try locating the required file again or try to install the SMS
Certificate manually as described in “Installing SMS certificate on Windows 2008” (page
32).
Installing SMS certificate on Windows 2008
To manually install the SMS certificate:
1. Copy the certificate to the VASA installed host.
2. Right click the certificate and select Install Certificate.
3. Supply the appropriate responses and information requested by the Certificate Import Wizard.
4. On Certificate Store page, select the Place all certificates in the following store radio button
and click Browse.
5. For the Select Certificate Store dialog, check the Show physical stores check box.
6. Expand the Trusted Root Certificate Authorities tree and select Local Computer.
7. Click OK.
8. From the Certificate Store dialog, the certificate store path should appear as follows:
Trusted Root Certificate Authorities\Local Computer
9. Click Next and then Finish to complete the import process.
Installing SMS certificate on Windows 2012/2012 R2
Before you install the SMS certificate on Windows 2012, you must create the following registry
key for Windows 2012 Server to send the list of Certificate Authorities that the client can choose
to pick the certificate from, and complete the client certificate request:
1. Right-click Start→Run, enter regedit, and then click OK. The Registry Editor appears.
32 Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
Page 33

2. Navigate to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL.
3. Click Edit→New→DWORD (32-bit) Value.
4. Enter SendTrustedIssuerList in Value name, and enter 1 (numeric value one) in Value
data. Close the Registry Editor.
To manually install the SMS certificate on Windows 2012/2012 R2:
1. Copy the certificate to the VASA installed host.
2. Right click the certificate and select Install Certificate.
3. Follow the instructions on the Certificate Import Wizard.
4. Select Local Machine under Store Location and click Next.
5. Select Place All the Certificate in the following store in the Certificate Store page and click
Browse.
6. Select Show physical stores in the Select Certificate Store dialog.
7. Expand the Trusted Root Certification Authorities tree and select Registry.
8. Click OK.
9. The certificate store path appears as follows:
Trusted Root Certification Authorities\Registry
10. Click Next and then click Finish to complete the certificate installation.
NOTE: In highly scalable set ups, after registering VASA there might be a delay to get and
display all the events.
Extracting and saving certificates
To extract and save certificates on Windows 2003, 2008, 2012/2012 R2:
1. Click Start→Run and enter the mmc command.
The Console1 dialog appears.
TIP: You can also run the mmc command from PowerShell.
2. Click File→Add/Remove Snap-in.
The Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog appears.
3. Select Certificates from Available Snap-ins and click Add.
The Certificate Snap-in dialog appears.
4. Select Computer account and click Finish.
5. Save console setting as console1.
Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
The vSphere Web Client is installed using VMware vSphere.
Upgrading from a previous version
When upgrading from a previous version, the installer detects whether a previous version is installed
and then either performs a new install or an upgrade. Before upgrading from a previous version,
consider the details provided in the following sections.
Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere 33
Page 34
You can upgrade to version 2.5 only from the versions 2.4.0 and 2.4.0 Patch 01. To upgrade,
follow the instructions of the Installer. For more information on installation, see the HP Insight Control
for VMware vCenter Server Installation Guide.
CAUTION: Auto login credentials created in RMV 2.4 for vSphere Client should be removed
manually using Admin Tool before you do an upgrade operation.
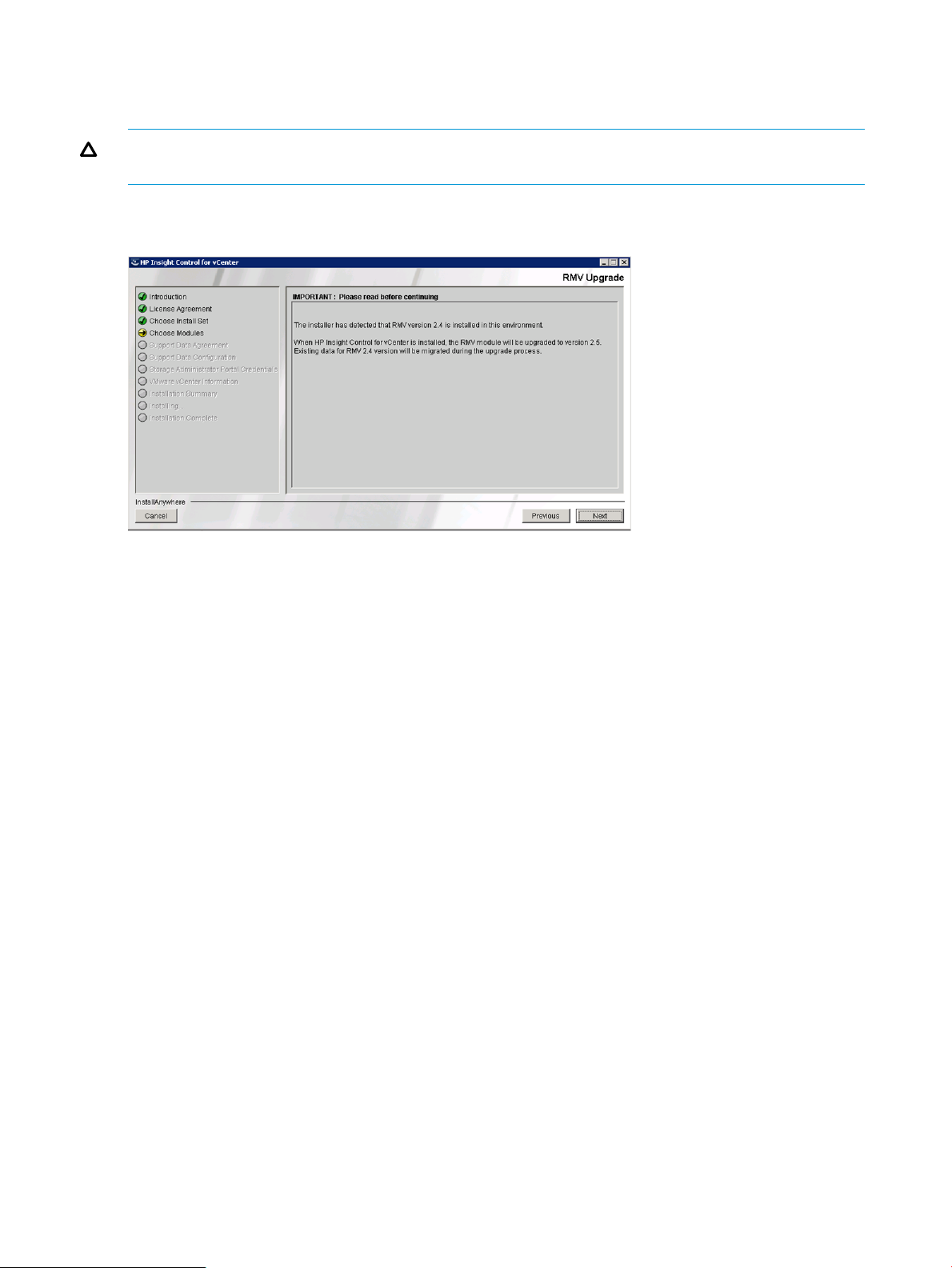
When upgrading from a previous version, you are prompted with the message The installer
has detected that RMV 2.x is installed in this environment.
Click Next to proceed further, and upgrade to RMV 2.5. When HP Insight Control for vCenter is
installed, the RMV module is upgraded to version 2.5. The existing data for the previous version
is migrated during the upgrade.
Using secure service connections
RMV uses secure connections for web service and StoreServ communications.
The Certificate column in the StoreServ Credential tab of Admin Tool displays the SSL certificate
status for HP 3PAR StoreServ. If the displayed status is No, then you must reregister the HP 3PAR
StoreServ, using the Validate option in Admin Tool.
34 Installing and removing HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
Page 35

CAUTION: RMV 2.5 has an additional security enhancement that requires StoreServ certificate
to be accepted to establish a successful connection. You are required to validate the StoreServ
credentials registered through Admin Tool to accept the certificate; otherwise connections to the
StoreServ will fail.
NOTE: The Port number used by RMV will change as part of the upgrade and integration with
HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server installation. To ensure that the same port number is
used for RMV operation, you need to edit the required port numbers during installation.
You can get the port numbers from the Configuration tab of vCenter Plug-in in Admin Tool.
Upgrading from a previous version 35
Page 36

3 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV
Admin Tool
This chapter describes the default HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software
for VMware vSphere configuration, as well as how to edit configuration settings using the HP 3PAR
RMV Admin Tool.
Overview
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere is provided
with default configuration settings that are compatible with most environments. However, it is
recommended that you verify the default parameters and make appropriate changes as necessary.
HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool, a GUI, is provided for making the configuration changes.
HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
The HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool is used to configure HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery
Manager Software for VMware vSphere, configure VASA, and set the storage system credentials.
NOTE: To use the HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool, you must have Administrator privileges. If you are
using Windows 2008, and have User Account Control activated, then you need to right click the
HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool and launch it using the Run as Administrator option.
To access the HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool, click Start→All Programs→HP Insight Control for
vCentre→HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool.
The configuration options are accessed through the following tabs, which are discussed in the
proceeding sections:
• vCenter Plug-in—Configures the RMV plug-in for the vCenter Server.
• VASA—Configures VASA functionality and HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system mapping.
• StoreServ Credential—Configures the credential information to access HP 3PAR StoreServ
storage systems.
vCenter Plug-in tab
The vCenter Plug-in tab allows you to edit HP 3PAR Management Plug-in parameters for optimal
use in your environment. You can also edit the log levels using the Admin Tool.
36 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
Page 37

Figure 12 vCenter Plug-in tab
Details concerning the fields of the vCenter Plug-in tab are provided in the following sections.
vCenter Plug-in configuration
The vCenter Plug-in configuration is used to view the host name and VM service port. You can
configure the debug settings here.
To modify the Debug setting on the Configuration option:
vCenter Plug-in tab 37
Page 38

1. Click Edit.
The Edit Configuration dialog box appears.
Figure 13 vCenter Plug-in configuration
NOTE: You can change the Debug level. However, to change the Recovery Manager server
name or the Recovery Manager service TCP port, you must run the HP Insight Control for
VMware vCenter Server installation again, to modify the settings.
The Configuration tab fields are shown in Table 1 (page 38).
Table 1 Configuration tab fields
DescriptionFieldGroup
Recovery Manager server nameConfiguration
Recovery Manager Server TCP port
The network host of the server where HP
3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery
Manager Software for VMware vSphere is
installed. The vCenter Server and all
desktops running the vSphere client using
the HP 3PAR plug-in must be able to reach
this server. The name is used while
registering the HP 3PAR plug-in with the
vCenter Server.
The fully qualified name of the DNS name
of the running server is the default name.
The name can be changed to any name or
IP address during the installation.
The network port number that the
TpdVmWebService Web service uses. for
secure connections. This can be changed
to any unused port.
The TCP port numbers change based on
the modules that you have selected during
installation of Insight Control for vCenter.
Secure service
38 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and
Recovery Manager Software for VMware
vSphere uses a secure Web service (using
SSL certificates) securing all interactions
between the VMware components (vCenter
Server and vSphere clients) and HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery
Manager Software for VMware vSphere.
Page 39

Table 1 Configuration tab fields (continued)
DescriptionFieldGroup
The SSL certificate for HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery
Manager Software for VMware vSphere
(provided by HP) must be installed.
2. Modify the fields as necessary.
3. Click Save, to save the changes.
NOTE: Changing the Debug settings requires restart of the RMV service for the changed Debug
settings to become effective.
Plug-in registration
The Plug-in Registration is used to view the current registration of the HP 3PAR plug-in with the
vCenter Server.
Figure 14 Plug-in registration
Binded to thumbprint
Debug levelDebug
Log folder
Displays the current thumbprint binded to
the TCP port.
Specifies the level of verbosity of the log
file. The default value is Low.
The trace file name. The default file name
is <system drive>:\Program Files\
<IC4VC Installed folder>\RMV\
Log.
vCenter Plug-in tab 39
Page 40

The fields available from the Plug-in Registration tab are shown in Table 2 (page 40).
Table 2 Plug-in registration fields
NOTE: Use Insight Control for vCenter Server Administrator Portal for vCenter to register or
unregister the Plug-in.
Remote Copy pairs
The Remote Copy Pairs option is used to manage the registration of Remote Copy pairs between
a local and remote system.
Figure 15 Remote Copy pairs
DescriptionField
The name of the vCenter Server.vCenter Server
The name of the Recovery Manager server.Recovery Manager Server Name
The TCP port number.Service TCP Port
vSphere Client or VMware Web ClientType
The Remote Copy Pairs list shows currently registered storage system Remote Copy pairs. The
following fields are displayed:
• Local StoreServ/User—Name of the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system and the associated
user.
• Local StoreServ Credential Windows User—Windows user credentials for the accessing the
local system.
40 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
Page 41

• Remote StoreServ User—Name of the remote HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system and associated
user.
• Remote StoreServ Credential Windows User—Windows user credentials for the accessing the
remote system.
• Remote Recovery Manager Server—Remote Recovery Manager Server host identifier.
To add a new Remote Copy pair registration, click Register New. The Register Remote Copy
StoreServ Pair screen appears
Figure 16 Register Remote Copy StoreServ pair
NOTE:
• See the information displayed for verifying the TCP Port while Remote Copy StoreServ Pair.
• HP recommends to use two RMV servers (local and remote) for regular Remote Copy groups,
and one RMV server (local) if the Remote Copy group is configured in Peer Persistence setup.
The VASA tab
A VASA Provider is a software component that acts as a server in the vSphere environment. A
vCenter Server connects to the VASA Provider to obtain information about available storage
topology, capabilities, and state. The vCenter Server can then provide the appropriate information
to vSphere clients.
The VASA configuration
The VASA configuration option is used to examine and configure VASA capabilities for your
installation.
The VASA tab 41
Page 42

Figure 17 VASA configuration
The options available in the VASA Configuration screen are described in Table 3 (page 42).
Table 3 VASA configuration options
DescriptionField
Displays the port to which the VASA web service is binding.VASA service TCP port
Displays if a secure service is selected.Secure service
Displays the URL address required to connect to VASA web service.Web service URL
Displays the installed RMV version.Version
Shows the folder where log files are stored.Log folder
Specifies the level of verbosity for the log file.Debug level
The default value is Medium.
To modify the VASA configuration options:
42 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
Page 43

• Click the Edit button.
The Edit Configuration dialog box appears.
Table 4 VASA Configuration Edit options
DescriptionField
VASA service TCP port
Secure services
Debug level
Displays the port number used by the VASA service. You can change the Port
number only through the installation process.
Indicates that secure communications are implemented. For security purposes, this
option is fixed and cannot be modified.
Displays the current thumbprint binded to the TCP port.Binded to thumbprint
Specifies the debug level. There are three debug levels to choose from (low, medium,
high). Setting the level to high will log everything including communication request
and responses between SMS and VASA.
The location of the log folder is fixed.Log folder
Saves the current configuration.Save (button)
Closes the Edit dialog.Close (button)
If the debug level is modified, changes are updated to the VASA web service immediately.
Figure 18 VASA Edit configuration
NOTE: The VASA Provider service uses the StoreServ credentials entered in Storage Administrator
Portal for vCenter for connecting to the Storage array. For more information on entering credentials
in Storage Administrator Portal for vCenter, see the HP Insight Control for VMware vCenter Server
User Guide.
StoreServ Credential tab
The StoreServ Credential tab allows you to add, remove, and validate HP 3PAR StoreServ credentials
associated with a specific Windows login account.
StoreServ Credential tab 43
Page 44

Figure 19 StoreServ credential tab
44 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
Page 45

You have the option of viewing all existing Windows users that have registered credentials, or you
can select a specific user from the list shown in the pull down menu.
A listing of registered credentials is shown for the selected users with fields defined as follows:
• StoreServ Name—Name of the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• StoreServ ID—System ID for the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• StoreServ User—User name for accessing the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• Windows User—Windows user that created the credentials.
• Reserved By—If available, displays the component for which the credentials are reserved. If
the credential are cashed via the Plug-in auto login feature, then credentials are valid only for
the Plug-in and are not valid for accessing any other components. To create credential for
auto login purpose, the “Remember Me” check box must be checked when logging onto a
given Storage System.
• Certificate—If the certificate is available, then Yes is displayed, else, No.
To specify a new Storage System credential:
1. Click Add.
The HP 3PAR StoreServ Credential Management dialog appears.
Figure 20 HP 3PAR StoreServ credential management
2. Enter the appropriate credential information for the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system and
user including the valid password, then click OK.
NOTE: When you add an HP 3PAR StoreServ with IP address, the IP address is translated
to the StoreServ Name and is displayed in the StoreServ List.
You can also remove or validate an entry. However, you can remove only one credential at
a time.
StoreServ Credential tab 45
Page 46
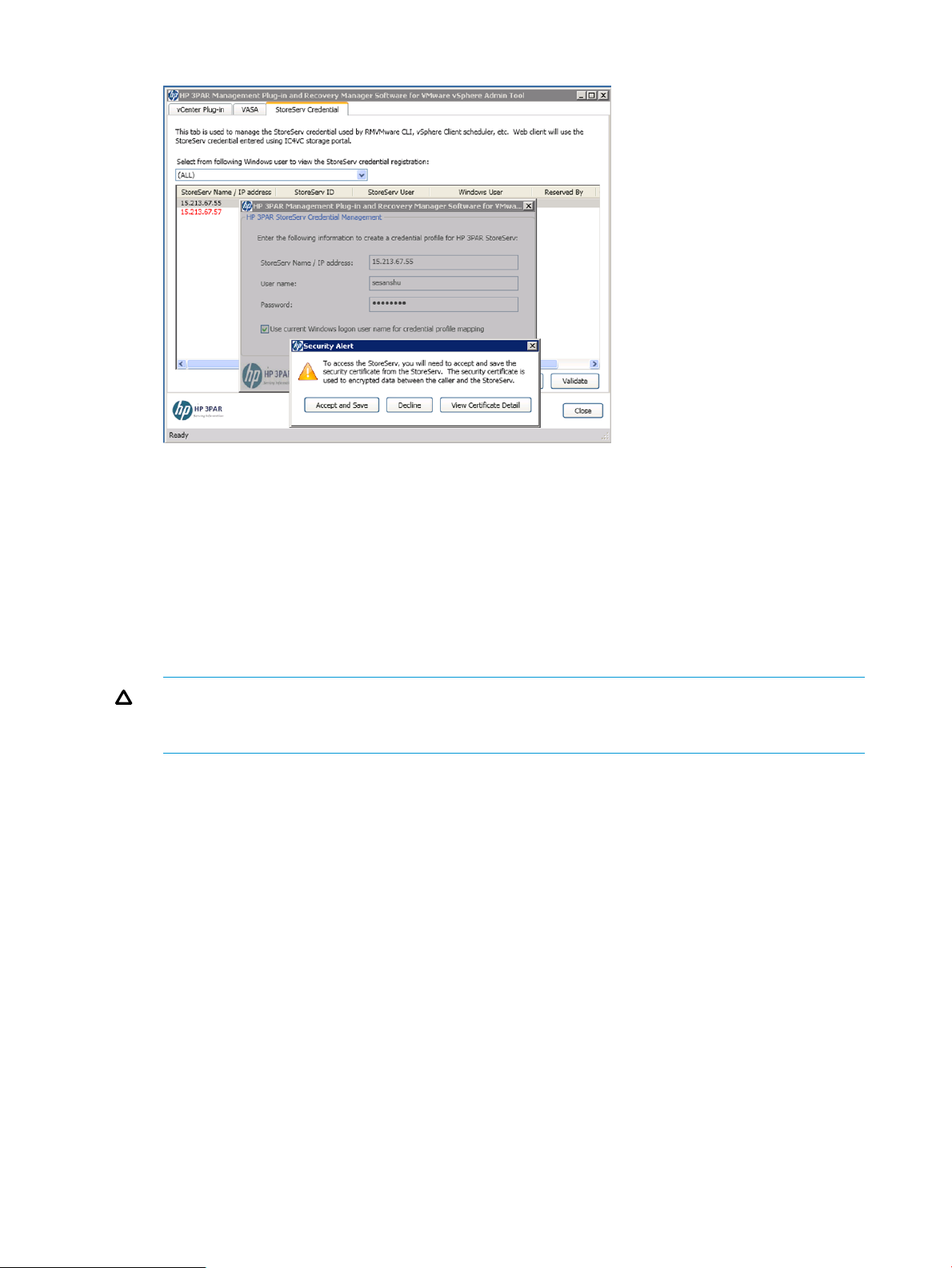
Figure 21 Accepting certificate
You must accept the certificate to perform any tasks on the HP 3PAR StoreServ. However, if
you do not accept the certificate, access to the HP 3PAR StoreServ is denied.
3. Click Close, to close the close the dialog box.
When you add a new credential, it is associated with the current Windows user login account
by default. The validation process returns the appropriate user privileges on successful
connection and validation with the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. When performing
operations like Remote Copying from a remote system, you can deselect the Using current
Windows logon user name option, and provide a specific Windows user name
(domain\username) associated with the user of the remote system.
CAUTION: Removing a HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system credential that is currently used
by the RMVMware CLI, VASA provider, Remote Copy Pairing, or the scheduler will prevent
these components from operating normally.
46 Modifying configuration settings using HP 3PAR RMV Admin Tool
Page 47

4 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
The HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter is used for viewing virtual volume mapping.
You can also create and expose virtual volumes to an ESXi host based on a template where you
fill in the details or based on the provisioning configuration of an existing Datastore. This chapter
explains how to log on to vSphere Client, view information about virtual volume mapping and
Transparent Failover setup, and create new virtual volumes.
NOTE: HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere
supports Microsoft Internet Explorer as the Windows default browser.
NOTE: When configured with secure access to the vCenter Server, the Security Information "This
page contains both secure and non-secure items” will be displayed.
To enable the display of secure and non secure content:
1. Click Start→Settings→Control Panel→Internet Options.
2. On the Security tab, click Custom level→Miscellaneous.
3. Enable the Display Mixed content option.
4. Click OK.
Logging on to the vSphere Client
To start the HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter:
1. Start the VMware vSphere Client on your desktop.
The VMware vSphere Client login screen appears (Figure 22 (page 47)).
Figure 22 Logging On to the vSphere Client
Logging on to the vSphere Client 47
Page 48

2. Log on to the vSphere Client.
a. Enter the IP address or name vCenter Server.
b. Enter your user name and password.
c. Click Login.
The vCenter Server home page appears (Figure 23 (page 48)).
Figure 23 Virtual Center Home Page
3. Under Solutions and Applications, click HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager
for VMware vSphere.
A list of storage systems associated with the ESXi host displays on the left side.
Figure 24 HP 3PAR Management plug-in
To update the entire Storage System list, right-click the HP 3PAR StoreServ root-entry and select
the Refresh in the popup menu option.
To manually add a storage system entry that is not on the list, right-click the HP 3PAR StoreServ
and select connect. The HP 3PAR StoreServ connection screen appears requesting the login
details.
48 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
Page 49

Figure 25 HP 3PAR StoreServ connection screen
4. To connect to a specific storage system on the list, expand the list tree and click the desired
system to connect or right-click the desired entry to show the popup menu and select Login.
5. Enter the appropriate information In the connect dialog box:
a. Enter the HP 3PAR StoreServ system name or IP address.
b. Enter the StoreServ user name and password.
c. Select the Remember Me check box to prevent having to log on each time you access
this system.
6. Click Login.
The Summary tab shows detailed information about the selected system including the following:
Figure 26 StoreServ summary
Logging on to the vSphere Client 49
Page 50

Table 5 StoreServ Information Summary
NOTE: You can login to a different StoreServ credential by right-clicking the specific StoreServ,
and select Logout. Logging out does not remove the cached credential for auto login. Refer
“User authentication” (page 15) for more information.
Viewing Virtual Volume mapping
When logged in, you can view virtual volumes on the vCenter Server Virtual Machines (VMs) or
Datastores.
ValueGeneral
Name of storage systemSystem name
Model of storage systemSystem model
Storage system serial numberSerial number
Storage system ID numberSystem ID
World Wide Name of storage systemSystem WWN
Number of nodes available in storage systemNumber of nodes
Nodes appearing onlineNodes online
Login userLogged on as
NOTE: You can also view virtual volumes at the datacenter, cluster, and ESXi host level. See “HP
3PAR Views in the vSphere Client” (page 18) for details.
1. In the main menu navigation, click Home.
2. Under Inventory, click VMs and Templates or Datastores.
3. From the navigation tree, click the specific VM or Datastore volume to view.
50 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
Page 51

4. Click the HP 3PAR tab.
The information for all virtual volumes on the selected VM or Datastore is displayed.
Figure 27 Virtual Volume mapping
Viewing Volume information
After selecting a VM or Datastore, by default, all volumes on that VM or Datastore are displayed
in the Virtual Volumes tab (as shown in Figure 28 (page 51)).
The virtual volume information is divided into an upper and lower pane in the detail pane of the
interface.
• The upper pane displays general volume information.
• The lower pane provides the following details of Virtual Volumes (default view), Paths, and
Alerts.
The Upper pane
The upper pane of the Virtual Volumes tab is displayed as shown in Figure 28 (page 51). RMV
detects whether or not there are multiple paths with different storage system serial numbers. The
plug-in displays the VM, Datastore, or Remote Copy groups using a Peer Persistence setup as active
or standby under the StoreServ column.
Figure 28 Viewing the upper pane of the Virtual Volumes tab
Viewing Virtual Volume mapping 51
Page 52

The following filtering and sorting capabilities are provided:
• To filter, click the upper right corner of the column header. The virtual volume details in the
lower pane of the filtered virtual volumes are displayed. Click Clear Filter to clear the selected
filter.
Figure 29 Filtering Virtual Volumes
NOTE: The filter operation details panel may display incorrect volume details. To update the
details, select a volume from the grid to remove incorrect details.
You must provide both values for the filtering range.
Filters are applied to the set of volumes currently displayed in the grid. If you do multiple filtering
operations make sure that you clear the unwanted filter(s) before a new filter is applied. Otherwise
new filter will be applied to the previously filtered result set.
• To sort, drag a column header to group by that column. Click the selected upper right corner
of the column header to resume the default view.
Figure 30 Sorting Virtual Volumes
52 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
Page 53

The Lower pane
The lower pane of the Virtual Volumes tab displays information about the selected volume in the
upper pane. The lower pane provides three buttons, Details, Paths, and Alerts.
• Details (default when viewing the Virtual Volumes tab) displays details about the selected
volume in the upper pane (Figure 31 (page 53)). In addition, all the storage systems and their
paths are also displayed. When Peer Persistence is enabled, the Virtual Volumes Details pane
label changes to Virtual Volume Details for Active StoreServ. Depending on the system
configuration, the pane provides a status of Peer Persistence setup between an active and
standby storage system. In the event of an active system failing, the host traffic directing to
the failed or active storage system is redirected to the standby storage system without any
disruption to the hosts using SCSI path management configurations.
Figure 31 Viewing Virtual Volume details
• Paths displays path information about the selected volume (Figure 32 (page 53)).
Figure 32 Viewing Volume Paths
• Alerts displays any alerts associated with the selected volume (Figure 33 (page 53)).
Figure 33 Viewing alerts
Refreshing Virtual Volume information
A Refresh button is provided to update virtual volume information displayed in the HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere interface. The Refresh
button provides two options, Reload Current Page and Update Recovery Manager Cache.
• Select Reload Current Page if you have logged into an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system
and the pages do not show volume details.
• Select Update Recovery Manager Cache if you have logged into an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage
system and the vCenter Server inventory has changed; such as newly added Virtual Machines
or Datastores, changed HBA path policies, or added ESXi hosts.
Refreshing Virtual Volume information 53
Page 54

Creating Virtual Volumes and Datastores
You have the option of creating a new virtual volume on the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system
and have it exported to the vCenter managed ESXi host where it can be accessed.
Creating a Virtual Volume from an existing HP 3PAR StoreServ template
Follow these steps to create a new virtual volume:
1. In the main menu navigation, click Home→Inventory→Host and Clusters.
2. Go to the HP 3PAR→Virtual Volumes.
3. Click Provision New. The Provision Storage welcome screen appears with information
concerning the provisioning process.
NOTE: To prevent the welcome screen from displaying in the future, select the “Skip this
page in the future when provisioning storage” check box.
4. Click Next to select a storage system template to be used for provisioning.
Figure 34 Provision Storage template selection
NOTE: Only templates configured with at least TPVV or CPVV type, size, user CPG, and
copy CPG from Storage Systems associated with the selected ESXi host are displayed.
5. Select an appropriate template from the list based on the summary of details, and then click
Next.
54 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
Page 55

Figure 35 Virtual Volume provisioning parameters
6. Provide the virtual volume parameters for the virtual volume being provisioned. An option is
available to attach to a Virtual Machine when you want to create a raw disk only. Fill in the
following parameters and click Next when done.
• Number of virtual volumes: - Number of virtual volumes to create (1 – 99). The default
is 1.
• Virtual Volume name - Name for the virtual volume (1 – 31 characters for single volume
creations or 1– 26 characters for multiple volume creations). If the number of virtual
volumes to be created is set to 1, the specified name is sufficient for creating the virtual
volume. When creating multiple virtual volumes, a decimal number is automatically
appended to the name prefix for each virtual volume that is created up to the maximum
limit (.0 - .9999).
NOTE: When choosing a name for creating virtual volumes, you must consider the
following:
◦ If the number of virtual volume count = 1, the virtual volume name is set to 31 and
the Datastore name is set to 42.
◦ If number of the virtual volume count > 1, the virtual volume name prefix is set to 26
and the Datastore name prefix is set to 31.
• Create Datastore - Name for the Datastore (1– 42 characters for single Datastore creations
or 1– 31 characters for multiple Datastore creations). If the number of virtual volumes to
be created is set to 1, the specified name is sufficient for creating the Datastore. When
creating multiple Datastores, a decimal number is automatically appended to the name
prefix for each Datastore that is created up to the maximum limit (.0 - .9999999).
NOTE: If the specified Datastore name already exists regardless of its name case, the
operation will not be successful. The behavior is similar to vCenter Datastore creation.
Creating Virtual Volumes and Datastores 55
Page 56

Figure 36 Datastore parameters review
• VMFS-5/VMFS-3 option and Block Size - Specifies whether to use VMFS or VMFS-3. You
can optionally specify the block size. VMFS-5 is only valid for ESXi 5.0 or above hosts.
• Size (512 MB – 16 TB) - Size for the virtual volume. For VMFS-3, the VV size range is 512
MB to 2 TB, For VMFS-5, the VV size range is from 512 MB to 16 TB.
When specifying the size for a virtual volume, 256 MB is reserved for each node.
Depending on the cluster type, the minimum virtual volume size is calculated as 256 MB
times the number of nodes.
In a two node system, 512 MB is reserved when a TPVV is created. If an 80% user limit
is set for a 512 MB TPVV, only 410 MB of space can be allocated. However 512 MB
is the least amount required so the creation of the virtual volume fails. In other words, If
the allocation limit is set, the space after the % needs to be at least 512 MB in a 2 node
cluster.
VV growth increment is 256 MB (i.e., If 520 MB is selected for a virtual volume, a VV
size of 768 MB is automatically created.
• Create raw disk only—Creates a raw disk when checked. By default, this option is not
checked and a Datastore is automatically created. You can attach the disk to a Virtual
Machine and choose either Physical or Virtual compatibility mode.
• Enable zero detection—Select to create a zero-detect enabled VV. You can enable
zero-detect when provisioning new TPVV type of virtual volumes. By default, the check
box is cleared, and is visible only if you have selected a template of TPVV type in the
previous screen. This feature enables HP 3PAR StoreServ to scan for zeros in the incoming
write data.
NOTE: The zero detection status is either Enable or Disable, depending on whether
the Virtual Volume was created with or without zero-detect enabled, respectively. This
status is displayed in the Virtual Volume page.
56 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
Page 57

Click Next.
7. Review the parameters, then click Create. Click OK for confirmation. A confirmation is displayed
indicating that the Datastore is created.
NOTE: If you choose “ESXi Cluster”, the storage is assigned to the ESXi Cluster hosts. Otherwise,
the storage is only created on the selected host.
NOTE: If the selected ESXi host is connected to a storage system and currently does not have
LUNs exposed to the host, you need to log in to the summary page and create an entry for the
storage system. For more information, refer to “HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage System login” (page
16).
Creating Virtual Volumes and Datastores 57
Page 58

Creating a Virtual Volume from existing Datastores
Follow these steps to create a virtual volume from an existing Datastore:
1. In the main menu navigation, click Home→Inventory→Datastores and Datastore Clusters.
2. Go to HP 3PAR→Virtual Volumes.
3. Click Provision Similar. The Welcome page appears.
NOTE: To prevent the welcome page from displaying in the future, select the “Skip this page
in the future when provisioning storage” check box.
4. Click Next to enter the virtual volume parameters.
5. Enter the appropriate parameters, then click Next.
• Number of Virtual Volumes - Number of virtual volumes to be provisioned. You can specify
from 1 to 99 where 1 is the default.
• Virtual Volume name - Name for the virtual volume.
NOTE: When choosing a name for creating virtual volumes, you must consider the
following:
◦ If the number of virtual volume count equals 1, the virtual volume name is set to 31
and the Datastore name is set to 42.
◦ If number of the virtual volume count is greater than 1, the virtual volume name prefix
is set to 26 and the Datastore name prefix is set to 31.
• Create Datastore - Create a Datastore.
• Create raw disk only - Create a raw disk only. This parameter also allow you to attach
the Virtual Volume to a Virtual Machine and choose either Physical or Virtual compatibility
mode.
• Enable zero detection—Check to create zero-detect enabled Virtual Volumes. This check
box is displayed only if the Datastore selected for Provision Similar uses the TPVV
type of Virtual Volume.
NOTE: The zero detection status is either Enable or Disable, depending on whether
the Virtual Volume was created with or without zero-detect enabled, respectively. This
status is displayed in the Virtual Volume page.
After you click Next, a summary of the Datastore to be created is shown:
6. Review the parameters, then click Create. Click OK for each confirmation. A confirmation is
shown to indicate the Datastores are created successfully.
NOTE: When creating virtual volumes from an existing Datastore, the volume allocation
limit of the original virtual volume is also be applied to the newly created volume. Current
operation only supports TPVV or CPVV type.
Adding an ESXi host to the vCenter Server
If an ESXi host with connection to HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system is added to the vCenter Server
after vSphere client is launched and the storage system does not appear on the existing HP 3PAR
StoreServ Storage system list, you can manually add the StoreServ.
To add a new StoreServ to the RMV cache:
1. Log on to vSphere client.
2. Go to Home→Solutions and Applications→HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery
Manager Software for VMware vSphere.
58 Logging on and working with Virtual Volumes
Page 59

3. Select the storage system on the node tree pane view and right-click. Select Connect from the
option menu.
4. Enter the information of the storage system and click Login.
5. Verify the new storage system is added to the node tree pane.
6. Go to Home→Inventory→Hosts and Clusters→HP 3PAR.
7. Click Refresh, select Update Recovery Manager Cache option and click Refresh. All associated
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system virtual volume information should display.
NOTE: Another way to refresh the internal inventory cache, close and reopen the vSphere
client.
Adding an ESXi host to the vCenter Server 59
Page 60

5 Working with Virtual Copies
This chapter explains how to use HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere to
manage Virtual Copies.
NOTE: In the following sections, the type of Virtual Copy being created, mounted, or modified
is dependent on whether a VM or Datastore is selected from the navigation tree. For example, if
you have selected a Datastore from the navigation tree, subsequent create, mount, or modify
actions performed will affect the selected Datastore until a different Datastore or VM is selected.
NOTE: The ability to manage Virtual Copies provided by HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software
for VMware vSphere requires the HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere and
Virtual Copy licenses.
Viewing Virtual Copy information
In addition to viewing virtual volumes on the vCenter Server’s Virtual Machines (VMs) and Datastores
when logged in, you can also view Virtual Copies.
To view a VM or Datastore Virtual Copies:
1. Start the HP 3PAR Management Plug-in for VMware vCenter as described in “Logging on to
the vSphere Client” (page 47).
2. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Volume mapping” (page 50).
60 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 61

3. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
Information about the selected VM or Datastore Virtual Copies is displayed.
• Base Datastore/RDM LUN
• Type
• Base Volume
• Base ID
• Virtual Copy Volume
• Virtual Copy ID
• Status–Can be Available, Mounted, Missing or Mismatched.
NOTE: When a Virtual Copy set is displayed as Missing, the Virtual Copy has been
deleted from the storage system. The delete operation is only allowed to remove the
Virtual Copy.
When a Virtual Copy set is displayed as Mismatched, the Virtual Copy is created on a
different storage system instead of its current connected system. The mismatch may be
caused by an HP 3PAR Peer Motion operation. The delete operation is only allowed to
remove the record. Manually remove the actual Virtual Copy from the originating storage
system.
• Retention
• Expiry
• Exported Host
• LUN ID
• ESXi Host
• Virtual Copy Datastore
NOTE: The Virtual Copy timestamp displayed on the Virtual Copies tab is converted to the
local time zone of the vSphere Client. The Expiry and Retention values on the same display
are set to the time zone of the RMV server.
NOTE: If the VV(s) used are in a Peer Persistence configuration, local Virtual Copies will be
disabled. Remote Virtual Copies may be created in the Remote Copy tab. Remote Virtual
Copies will create local and remote virtual copies so when failover occurs, a remote virtual
copy (either local or remote) will exist for recovery purposes.
Viewing Virtual Disk Details for Virtual Copies
You can view details on the virtual disk associated with a Virtual Copy.
• Virtual Disk – Shows the virtual disk name.
• Original Virtual Machine Name – Provides additional information on the Virtual Machine
name associated with the VMDK. Snapshots created prior to version 2.3 will have this field
as N/A.
• Application Consistent – Provides information on whether this VMDK is application consistent.
• VM Attached – Shows whether the VM is attached.
Viewing Virtual Copy information 61
Page 62

Viewing Virtual Copy event logs
Virtual Copy operation event logs can be found at the vCenter Server level in the navigation tree,
the Tasks & Events tab, and the Events tab. Use the keyword HP 3PAR to select all events performed
by HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere.
Figure 37 Viewing the Virtual Copy event logs
Creating New Virtual Copies
Prior to creating a Virtual Copies, the following restrictions should be noted:
• Creating a Virtual Copy at the VM level requires available space on the Datastore where the
VMDK file resides.
• Datastore creation from NFS drives is not supported from Virtual Copy operations.
• Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere requires VMFS snapshots. However, taking a VMFS
snapshot of a VM participating in disk sharing, such as Microsoft MSCS, is not supported.
This is a VMFS limitation.
• The following steps only applies to Virtual Volumes that are not Peer Persistence enabled. If
Transparent Failover is enabled, use the Remote Copy page to create new Virtual Copies. See
“Creating Remote Virtual Copies” (page 84).
NOTE: Virtual Copy space must be available on the HP 3PAR Virtual Volume. In order to create
a Virtual Copy on an HP 3PAR base volume, the volume must have the Virtual Copy space allocated
during its creation.
To create a new Virtual Copy on the VM or Datastore, perform the following:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60).
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Click Create. You are then asked to supply the name for the Virtual Copy set.
NOTE: If you do not wish to name the Virtual Copy set, click OK. The created Virtual Copy
is identified by a date and time stamp.
62 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 63

4. (Optional) You can either accept the default name based on the time when the Virtual Copy
is created, or you can enter a name of your choosing. The Virtual Copy name cannot exceed
32 characters.
5. When creating the Virtual Copy, you have the choice of changing the Ensure Application
Consistency option (set by default) to specify whether or not the newly created Virtual Copy
should adhere to the data standards used by supported application. Selecting this option
ensures the data can be accessed with VM tools supporting these formats but may increase
the amount of data space and time required to create and access the Virtual Copy.
Figure 38 Ensure Application Consistency option
NOTE: Application consistency is not supported on Databases that are configured using
Physical Compatibility RDM LUNs. Application consistency is supported for Datastore Virtual
Copy creation and you have the option to select a VM to reside on the Datastore.
6. Click OK. The Virtual Copy creation task is submitted and started.
Information regarding the Virtual Copy creation process is shown under Recent Tasks in lower
portion of the screen. Once the Virtual Copy has been created, an entry is reflected in the
Virtual Copy Set list.
NOTE: When working with Virtual Copies, you may need to refresh the display in order to
view the most accurate volume details. See “Refreshing Virtual Volume information” (page 53).
NOTE: If the Virtual Copy operation fails, refer to the event log to review details. See “Viewing
Virtual Copy event logs” (page 62).
NOTE: The system allows snapshots to be taken for more than eight VMs for application consistent
Local or Remote Copy snapshots. However, if you select more than 8 VMs, a warning message is
displayed and the Recovery Set creation for application consistency might fail due to the time
required to quiesce the VMs.
Creating New Virtual Copies 63
Page 64

Mounting Virtual Copies
To mount a Virtual Copy:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60).
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Select the Virtual Copy to mount from the Virtual Copy Set list.
4. Right-click the Virtual Copy in the Virtual Copy table.
A menu appears providing two mount choices:
• Mount on ESX host as Datastore on—Select from the list of ESX/ESXi hosts managed by
the vCenter Server that share access to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
• Mount on Proxy Host—Select from a list of hosts not managed by the vCenter Server, but
which have access to the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system.
Figure 39 Mount Virtual Copies
5. Click the mount type and then select an ESX/ESXi host or Proxy Host from the menu that
appears.
The Confirm dialog box appears.
6. Click OK.
The Virtual Copy mount task is submitted and a message indicates that the request is being
processed.
You can check the status column to see that the Virtual Copy has been mounted.
Unmounting Virtual Copies
NOTE: Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere does not check if the volume being unmounted
is in use. Ensure that the volume is inactive prior to unmounting.
To unmount a previously mounted Virtual Copy:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60).
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Select the Virtual Copy you wish to unmount from the Virtual Copy Set list.
4. Right-click the mounted Virtual Copy in the Virtual Copy table.
5. Click Unmount and then select the host.
64 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 65

Figure 40 Unmounting Virtual Copies
The Confirm dialog box appears.
6. Click OK. A message indicates that the request is being processed and the mounted copy is
unmounted.
Restoring Datastores by promoting a Virtual Copy
Normal restore scenarios involve restoring virtual disk images. In a VMFS Datastore, there can be
many virtual disks. Typically, you can identify the virtual disk to be restored and copy it over the
old one. However, in some cases the virtual machine file system may be corrupted and all virtual
disks need to be replaced. In such scenarios, promote one of the Virtual Copies to a base volume.
The HP 3PAR Operating System Software supports a non-disruptive Virtual Volume conversion from
a fully to thinly-provisioned or thinly to fully-provisioned Virtual Volume. Recovery Manager for
VMware limits the promotion of a Virtual Copy taken before a Virtual Volume conversion. A popup
message box with error message displays if the action occurs. Performing any RMV Virtual Copy
operations such as creating or deleting must only occur after a Virtual Volume conversion is
completed.
NOTE: After a Virtual Volume conversion is complete, also update the Recovery Manager Cache
to see changes if you are already logged on to the session. The RMV server does not notify the
RMV plug-in for backend data changes.
NOTE: If the underlying HP 3PAR volume used by the Datastore belongs to an HP 3PAR Remote
Copy volume group, stop the Remote Copy volume group prior to running the Datastore promote
operation.
To restore a Datastore by promoting a Virtual Copy:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60). Make sure that you
are in the Datastores view as you can only promote Datastores.
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Select the Virtual Copy that you wish to promote from the Virtual Copy Set list.
4. Click Promote.
The Confirm dialog box appears.
5. Click OK.
The Virtual Copy promote task is submitted and a message is displayed indicating that request
is being processed.
Restoring Datastores by promoting a Virtual Copy 65
Page 66

Deleting Virtual Copies
To delete a Virtual Copy:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60).
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Select the Virtual Copy you wish to delete from the Virtual Copy Set list.
4. Click Delete.
The Confirm dialog box appears.
5. Click OK.
The Virtual Copy deletion task is submitted and started and you are asked to confirm your
intent to delete the Virtual Copy.
The Virtual Copy is then removed from the Virtual Copy Set list.
Modifying Virtual Copy policies
The Virtual Copy policies can be defined for a given Virtual Machine or Datastore.
NOTE: This version of RMV supports virtual copy policies for remote copy groups. The primary
policy is enforced on both storage systems for the primary and secondary sites.
To modify the policy of a Virtual Copy:
NOTE: This version supports maximum Virtual Copy creation VMs on a Datastore. However, if
you create more than the maximum Virtual Copy Creation for Application-Consistency, then the
following warning message appears:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60).
2. Select the Virtual Machine or Datastore to apply a set of policies.
3. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
4. Click Policy.
The policy dialog appears.
a. Select the maximum number of Virtual Copy sets. Based on the order in which they are
created, non-expirable Virtual Copies are deleted when they reach a position in the queue
that exceeds this count.
66 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 67

b. (Optional) Select whether to enable expirable Virtual Copies. Expirable copies are
removed according to a specified schedule and are not affected by the maximum count.
When enabling the expirable Virtual Copies option, you must specify the length of time
(Hours or Days) from the current time that the Virtual Copies are to expire. You can set
the expiry period up to 1825 days.
NOTE: Expirable Virtual Copies are not included in the maximum count.
When enabling expirable Virtual Copies, you also have the choice of specifying how
existing non-expirable copies are handled.
• Delete the oldest when count reaches maximum. This is the recommended setting.
Select this option if you plan to create both expirable and non-expirable Virtual
Copies. All non-expirable copies (new and existing) will be counted against the
maximum count with the oldest being deleted as it exceeds the maximum count. The
RMVMware CLI and Scheduler have the option of overwriting the default policy.
However, Virtual Copies created using the GUI interface are bound by the default
policy.
• Phase out non-expirable Virtual Copies (Advanced).
Select this option if you plan to mostly create expirable Virtual Copies and want to
eventually phase out older non-expirable Virtual Copies. In this case, whenever a
newer expirable Virtual Copy is created, the oldest non-expirable copy will be
deleted. You can still create non-expirable Virtual Copies, as long as the aggregate
count is below the policy maximum.
NOTE: If all non-expirable Virtual Copies are in valid retention and have already
reached the maximum count, choosing the Enable expirable Virtual Copies option with
the Phase out non-expirable Virtual Copies setting will fail. If this happens, choose the
Delete the oldest when count reaches maximum option instead.
c. (Optional) Select a period of time to retain Virtual Copy sets.
A dialog box prompts you for the number of days to retain the Virtual Copy set.
i. Select the Retention Period.
ii. Select Hours or Days.
NOTE: Setting the retention policy requires the HP 3PAR Virtual Lock license on
the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system. RMV will check for an existing HP 3PAR
Virtual Lock license on the storage system when a Virtual Copy is created with
retention is specified.
NOTE: The Virtual Copy set can be retained for up to 43,800 hours or 1,825
days.
NOTE: When using both the expiry and retention options, the expiry value must
be equal to or greater than the retention value.
Modifying Virtual Copy policies 67
Page 68

d. Select whether to ensure application consistency. This option is used to create snapshots
of Virtual Copy sets that adhere to data format standards used by the VMware Tools.
NOTE: If new VMs are added to a Datastore, you also need to update the policy in
order to make the VM application consistent.
NOTE: When installing or upgrading VMware tools, you must be sure to reboot VMware
on the system where it running otherwise application consistent snapshots may not be
valid even though they are reported as completed successfully. This situation can also
occur when the VMware tools have not been upgraded on the VM system following an
upgrade of the ESXi server.
5. Click Save.
The Virtual Copy policy modification task is submitted and started. An alert appears indicating
that the new policy has been saved.
6. Click OK.
Scheduling Virtual Copies
You can automatically create Virtual Copies according to a specified schedule.
To view or create a scheduled Virtual Copy task:
1. Follow the instructions in “Viewing Virtual Copy information” (page 60).
2. Click the Virtual Copies tab.
3. Click Scheduler. The Schedule List dialog Figure 41 (page 68) appears.
Figure 41 Schedule List dialog
From the Scheduled List dialog, you can add a scheduled Virtual Copy creation task or modify
an existing one using the Schedule Task Wizard.
To add a new scheduled Virtual Copy task, follow these steps:
68 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 69

1. Click Add.
The Select Schedule Type dialog appears.
Figure 42 Select Schedule Type dialog
2. Select the time when the scheduled copy creation task is to be performed. You have the option
of scheduling when (hourly, daily, weekly, monthly) the Virtual Copy is to be created. You
can also schedule a Virtual Copy creation task to occur on a one-time basis.
3. Click Next. The wizard will request the appropriate information based on the option time
frame you have chosen. As an example that shows the types of information you need to supply,
if you choose Weekly, the Weekly Schedule Task dialog appears.
Figure 43 Weekly Schedule Task
4. Enter the start time of the day when the task is to be run and then indicate how often the task
is performed in weeks. You also need to select the day(s) of the week when the task is to be
run.
NOTE: If the vCenter server and RMV server are in different time zones, the default date
and time are based on the RMV server and vCenter server respectively. You need to synchronize
the time differences when creating the schedule.
Scheduling Virtual Copies 69
Page 70

5. Click Next.
The Schedule Credential dialog appears.
Figure 44 Schedule Credential
6. Enter a name for the scheduled task and the associated user name and password. The task
name must be unique.
7. Click Next.
The Snapshot Configuration dialog appears.
Figure 45 Virtual Copy Configuration dialog
8. Enter the appropriate vCenter server user name and location of the credential store file.
9. Specify whether or not to use application consistency for the scheduled task.
If application consistency is specified when creating the Virtual Copy for a Datastore, you
have the option of applying the application consistency to all Virtual Machines by selecting
the Apply to all Virtual Machines button or specify specific machines by choosing Apply to
the following Virtual Machines and enter the name of the Virtual Machines.
70 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 71

NOTE: Use commas to separate the Virtual Machine names.
10. Enter the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system user name.
11. Specify any default policy overrides.
a. Specify the amount of time (in hours or days) before the Virtual Copy expires.
b. Specify the amount of time (in hours or days) to retain the Virtual Copy set.
12. Click Next. The Schedule Task Summary dialog appears.
Figure 46 Schedule Task Summary Dialog
If application consistency was specified when the Virtual Copy was created, the summary
includes this information as shown.
NOTE: To schedule a task for a given user, an associated vCenter Credential Store File must
first be created using the RMVMware CLI with vCenterRegister option. To be used with
the Scheduler, the credential file must have “System” account level privileges. In addition, to
schedule tasks for user’s other than yourself, you must be added as a user to have permission
to access their credential files.
If the credential file is created as a domain user, specify the domain user when setting up the
schedule. If a local user is to be used for the scheduler, add the local user permission to the
credential file.
NOTE: Tasks scheduled for a given HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system must have an
associated Storage System Credential registration completed using the RMVMware Admin
Tool. In addition, since the Storage System credential registration is only accessible by the
creation owner and a member of administrators, the user account must have access to the
Storage System registration data.
Scheduling Virtual Copies 71
Page 72

13. Click Finish to complete the scheduling of the Virtual Copy task.
A message indicates whether the task has been created successfully. A listing for the scheduled
task is now shown in the Schedule List.
Figure 47 Schedule list with task
NOTE: If a VM or Datastore is removed, the associated scheduled tasks continues to run but
is no longer manageable from the HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager
Software for VMware vSphere scheduling interface. In this case, the task needs to be manually
removed from the Windows Scheduler.
NOTE: If the username associated with the user that created a scheduled task changes, the
defined task is no longer operational.
NOTE: To be used in the scheduler, users must have the proper credentials created through
the vCenter Credential Store File using RMVMware CLI with the vCenterRegister option
and have a valid Storage System Credential registration established through the Admin Tool.
NOTE: Since Storage System credential registration is only accessible by the creation owner
and members of Administrator, user accounts used in the scheduler have to have access to
the registration data.
NOTE: Any user account that is used in the scheduler requires access permission to the
specified vCenter Store file.
Restoring Virtual Disks, Guest OS Files, and Directories
The basic restore functionality provided in HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for VMware
vSphere is the ability to mount all, or some, Virtual Copy volumes on one or more ESXi hosts. You
can perform an actual restore by copying virtual disk images, or by mounting virtual disks on VMs
for guest OS level restore, by using already available VMware tools, most of which are integrated
with the vSphere Client. However, Recovery Manager for VMware vSphere also provides two
commands to simplify some of the commonly used restore user cases.
Restoring a Virtual Disk
After a Datastore Virtual Copy has been mounted on an ESXi host (see “Mounting Virtual Copies”
(page 64), the virtual disks grid displays the context menu.
NOTE: When copying or cloning a Virtual Machine (VM) to a different Datastore, the source
VM’s Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) is retained in the target VM. When using HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere to show the Virtual
Copies on the target VM, the Virtual Copies from the source VM will be displayed. To resolve this
problem, the target VM’s UUID should be changed. Refer to VMware documentation on how to
edit the VM’s UUID.
72 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 73

1. Right-click the virtual disk you wish to copy to a Datastore and click Copy to Datastore.
NOTE: When using the Copy to Datastore option to copy a virtual disk to a Datastore, it is
recommended that the copy and paste functions of the Datastore browser be used in order to
preserve the VMware Thin Provisioning disk feature.
2. Select a Datastore on the ESXi host where the Virtual Copy is mounted.
3. Specify the target location and click OK.
Figure 48 Specifying the target location
The copying operation is initiated.
Figure 49 Initiating the Copy Operation
Restoring a Guest OS File or Directory from a Virtual Copy
The second context menu command available in virtual disks grid allows you to attach a virtual
disk available on the selected Virtual Copy to any of the VMs currently running on the ESXi host
where the Virtual Copy is mounted.
1. Right-click the virtual disk you wish to attach and click Mount on Virtual Machine.
2. Select a VM on the ESXi host where the Virtual Copy is mounted.
3. When prompted for confirmation, click OK.
4. Once the task is completed, verify that the selected VM appears under the VM Attached
column.
The remainder of the restore operation must be performed on the VM. This involves re-scanning
for new disks and mounting the file system, and then manually copying the files.
Once the restore is complete, the virtual disk can be unmounted from the VM.
5. Right-click the virtual disk to be unmounted and click Unmount from Virtual Machine <VM
name>.
Restoring Virtual Disks, Guest OS Files, and Directories 73
Page 74

6. When prompted for confirmation, click OK.
The unmount commences.
Virtual disks created using HP 3PAR Virtual Copy can be mounted on any VM. However, if
you try to mount the Virtual Copy virtual disk on the same VM, the vSphere Client displays a
prompted question message.
In this case, you can choose whether to continue or not.
74 Working with Virtual Copies
Page 75

6 Working with VASA Provider
The communication between HP 3PAR VASA Provider and vCenter server is a secure connection
based on SSL certificate and Windows credential. License is not required for using VASA Provider.
Before VASA Provider can be registered by the vCenter server, VASA Provider requires that you
extract the SMS certificate from vCenter server and install it to the HP 3PAR Recovery Manager
for VMware installed host to allow client certificate negotiation in the Transport Layer. For information
on extracting and importing the certificate, see “Registering an SMS Certificate for the VASA
Provider” (page 30). After the SMS certificate is installed, you can register the Provider from the
vCenter server by clicking on the Storage Providers icon as shown below.
Figure 50 Registering the Provider
From the Storage Providers view, click the Add link to bring up the Add Vendor Provider dialog.
Figure 51 Adding Vendor Providers
75
Page 76

Table 6 Add Vendor Provider information fields
ValueField Name
Any name to identify the VASA provider.Name
URL
Login
VASA Service Web URL. For example
(https://<IPAddrOrHostName>:<VasaPort>/).
Windows user name to Recovery Manager for VMware
installed host.
Windows Password.Password
Once registration is successful, the provider status is available online.
NOTE: To register VASA Provider, the user must have the StorageViews Configure privilege.
VASA provider for HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system supports the Storage Capabilities profile
as defined by the VASA Specification.
• Provision type
• Virtual Volume type
• Drive type
• RAID type
• Whether or not the volume is in a Remote Copy group
The name and description of all HP 3PAR storage capabilities can be viewed from the Manage
Storage Capabilities pop-up from vCenter. To access the Manage Storage Capabilities window,
start from Home and then click VM storage Profiles from the Management tab. Click Manage
Storage Capabilities.
Figure 52 Manage Storage capabilities screen
The name of an HP 3PAR storage capability has five parts and each identifies the value of one of
the volume attributes. The following table shows the volume attributes and possible values. (Please
refer to HP 3PAR documentation for details of these attributes)
76 Working with VASA Provider
Page 77

Table 7 VASA Storage Capability Volume attributes
Storage Capability Name SegmentValueVolume Attribute
FullFully ProvisionedProvisioning Type
ThinThin Provisioned
BaseBase VolumeVolume Type
VCpyVirtual Copy Volume
FCFibre Channel DriveDrive Type
NLNear Line Drive
SSDSolid State Drive
MxMixed Drive
R0RAID 0RAID Type
R1RAID 1
R5RAID 5
R6RAID 6
Remote Copy
Remotecopy
RCRemote Copy Volume is in
NoRCVolume is not in Remotecopy
NOTE: Consult the appropriate VMware documentation for more details.
77
Page 78

7 Working with Remote Copy
A Remote Copy feature is now available for you to create and manage both Synchronous or
Periodic Virtual Copies at the RC Group level. In addition, the Remote Copy feature provides a
GUI interface and basic CLI command functionality to register, create, schedule, update and remove
Remote Copy pairings.
NOTE: The system allows snapshots to be taken for more than eight VMs for application consistent
Local or Remote Copy snapshots. However, if you select more than 8 VMs, a warning message is
displayed and the Recovery Set creation for application consistency might fail due to the time
required to quiesce the VMs.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager for VMware software supports Peer Persistence between multiple
servers through synchronized Remote Copy. The existing Remote Copy disaster recovery functionality
in synchronous mode compliments a Peer Persistence setup by including an automatic volume
creation on the secondary array when a primary volume is added to a group. Both the primary
and secondary clusters provide a path to an ESXi host virtual volume with the same world-wide-name.
The primary Remote Copy group provides the active path while the secondary Remote Copy group
provides a passive path to targeted virtual volume.
When Virtual Volumes are using Peer Persistence, RMV blocks the local Virtual Volume creation
for Virtual Machines and Datastores while allowing the creation of remote Virtual Copies on Remote
Copy Groups. As a result, when an active path failovers to a different storage system, the virtual
copies become available on either storage systems for restoration.
For more information about establishing Peer Persistence setup, refer to the HP 3PAR Remote Copy
User Guide.
Use the Admin tool to register and configure Remote Copy Pairs before launching the vCenter
plug-in feature to create a snapshot of your system.
Ensure the following requirements are satisfied before registering a Remote Copy pair:
• Remote Copy configuration already exists on the storage systems. Use the HP 3PAR OS CLI
or IMC GUI to create the Remote Copy configuration if they do not exists.
• Recovery Manager Software for VMware is already installed on the remote host situated in
a remote site.
• Establish IP access to the remote host.
• You can configure the Remote Copy volume group for synchronization in one of the following
modes:
◦ synchronous mode
◦ asynchronous periodic mode with replication period value set to zero
CAUTION: If you set the replication period value to zero, then the Remote Copy
replication is dependent on the RMV scheduler. So you must ensure that the RMV service
is available all the time.
78 Working with Remote Copy
Page 79

Registering Remote Copy Pairs
1. Launch Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere Admin Tool and click the HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere Admin
Tool→vCenter Plug-in.
NOTE: If you have a single RMV server, HP recommends that you register the remote copy
pairs in both directions. If you are using two RMV servers, register each direction just once
on each RMV server.
2. Under the vCenter Plug-in tab, click Remote Copy Pairs tab.
Figure 53 Registering Remote Copy pairs
3. Click Register New.
4. Enter the required information into the following fields for both Local and Remote systems.
Click Register.
Figure 54 Specifying Remote Copy pair details
Registering Remote Copy Pairs 79
Page 80

Table 8 Register Remote Copy Storage System Pair fields
ValueLocal
Name of local storage systemStoreServ:
Name of user for local storage systemStoreServ username:
Name of user for Microsoft WindowsWindows user name:
ValueRemote
Name of remote storage systemStoreServ:
Name of user for remote storage systemStoreServ username:
Name of user for Microsoft WindowsWindows user name:
Name of remote Recovery Manager server on remote siteRecovery Manager server name:
TCP port number of remote Recovery Manager serviceRecovery Manager service TCP port:
When the registration is successful, the Plug-in displays HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system pairing
in the Remote Copy Pairs tab.
NOTE: To verify the Recover Manager Service TCP port number, navigate to the Configuration
tab of the vCenter Plug-in, in the Admin tool.
When you upgrade the existing HP 3PAR CLI/HP 3PAR OS to a version that supports SSL certificate,
then the Admin Tool fails to retrieve the information of the HP 3PAR StoreServs that are already
registered.
For the Admin Tool to display the HP 3PAR StoreServ details, navigate to the StoreServ Credential
tab, and click Add to add the HP 3PAR StoreServ again. Also, you must add the HP 3PAR StoreServ
again if the HP 3PAR StoreServ SSL certificate is changed or upgraded.
80 Working with Remote Copy
Page 81

Updating Registered Remote Copy Pairs information
1. Launch Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere Admin Tool and click the HP 3PAR
Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager Software for VMware vSphere.
2. Click Remote Copy Pairs tab.
3. Select a Remote Copy pair from the list and click Update.
4. Select the new system information from the Local and Remote drop-down menus. If applicable,
enter another RMV host name.
5. Click Update.
Viewing host information summary
From the vSphere Plug-in StoreServ tree pane, select a storage system, and click the Summary in
the detail pane to view the information of the storage system.
NOTE: If Peer Persistence is enabled, the local Virtual Copies are disabled because VC snapshots
are taken both locally and remotely using Virtual Copy creation.
Table 9 Storage System summary information
ValueGeneral
Name of storage systemSystem name:
Model of storage systemSystem model:
Storage system serial numberSerial number:
Storage system ID numberSystem ID:
World Wide Name of storage systemSystem WWN:
Number of nodes available in storage systemNumber of nodes:
Nodes appearing onlineNodes online:
Login userLogged on as:
Updating Registered Remote Copy Pairs information 81
Page 82

Viewing existing and newly added Remote Copy information
Use the vSphere Client to navigate and view registered storage system Remote Copy pairs and
Remote Copy groups for local and remote systems.
Launch vSphere Client, select Home at the top of navigation bar and click HP 3PAR Management
Plug-in... From the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system tree pane, select a storage system and click
the Remote Copy tab.
NOTE: HP recommends setting your screen resolution height to at least 1024 pixels to view all
the information. If some information cannot be seen, you can move the vertical split bar to the left
or hide the Recent Task panel at the bottom.
To view details of the Remote Copy Groups associated with specific storage systems, click the
following tabs:
• Summary: The tab provides details of the Source and Target Remote Copy group name, role,
Transparent Failover status, mode and operating status, and link type.
Figure 55 Remote Copy Pair summary
• Virtual Volumes/Machines: The tab lists the source Virtual Volumes and the corresponding
target Virtual Volumes name along with Peer Persistence and Sync status in the Remote Copy
Group.
A Peer Persistence column lists the Peer Persistence setup status of all Virtual Volumes associated
with the Remote Copy Groups for Source and Target storage systems.
82 Working with Remote Copy
Page 83

Figure 56 Virtual Volumes/Machines
• Virtual Copies On: The tab displays remote Virtual Copies creation and expiration dates,
retention, mode, and application consistent status. The Remote Virtual Copies Mapping displays
if you select a Remote Virtual Copy.
Figure 57 Remote Virtual Copies On
• Virtual Copies On: The tab displays the details of the Remote Copy group(s) associated with
Source storage system and Remote Copy Group; Target Storage System and Remote Copy
Group; creation and expiration dates; and retention and application consistent status. The
Virtual Volume Mapping for Virtual Copy Timestamp displays the Status, Exported Host, LUN
ID, and Virtual Copy Datastore information if you select a Local Virtual Copy.
You can also click the available hyperlink within the Virtual Copy table to Mount, Unmount,
or Delete existing Virtual Copies of Virtual Volumes.
Viewing existing and newly added Remote Copy information 83
Page 84

Figure 58 Local Virtual Copies On
Creating Remote Virtual Copies
You can create either synchronous and periodic Remote Virtual Copy for Remote Copy groups
associated with a specific ESXi server. Other VMs from other ESXi hosts are not shown. When
creating synchronous Remote Virtual Copies, Recovery Manager creates a copy on both the local
and remote array. For periodic Remote Virtual Copies, a Remote Virtual Copy is only created on
the remote array.
1. Select the desired storage system in the left pane.
2. Select the Remote Copy tab.
a. From the upper right window, select the Remote Copy pair.
b. From the bottom right window, select the Remote Copy group.
c. Click Create Remote Virtual Copy.
3. Select the desired options for the Remote Virtual Copy.
• Enable expirable Virtual Copies
• Retain Virtual Copies
• Create remote Virtual Copy with application consistency
NOTE: If the Remote Virtual Copy for the Remote Copy group is set, the user will see the
maximum number of Virtual Copies in Policy in the dialog box.
84 Working with Remote Copy
Page 85

Figure 59 Create Remote Copy Virtual Copy
4. Click Create.
5. Click Yes to confirm.
6. Review the creation of the Virtual Copy in the Recent Tasks box at the bottom of the vSphere
client. Click OK to complete.
Setting Policy for Remote Virtual Copies
To manage remote VCs, you can set specific expirable and retention policies for each Virtual Copy
sets. Any policies set on a local storage system are also be applied to the virtual copy on remote
storage system during creation time.
NOTE: When the number of Virtual Copies is at the maximum limit, the oldest Virtual Copy is
deleted when a new Virtual Copy is created.
To set a policy for a Remote Virtual Copy:
1. From the Remote Copy tab, click Remote Virtual Copy Creation Policy.
2. Choose the maximum number of Virtual Copy sets. Use the arrows to adjust the number of
sets.
Setting Policy for Remote Virtual Copies 85
Page 86

3. Check the applicable policy options:
• Enable expirable Virtual Copies
Specify the expiration period. Click the appropriate option button relating to the handling
of existing non-expirable Virtual Copies.
• Retain Virtual Copy Set
Specify the expiration period.
Figure 60 Policy dialog
4. Ensure application consistency.
5. Click Save.
NOTE: After clicking Save, the process may take up to 15 minutes to complete depending
on the number Virtual Copy Sets specified.
Scheduling Remote Copy Virtual Copies
You can schedule a Remote Copy creation task or the selected Remote Copy group systems.
1. From the Remote Copy Summary tab, click Scheduler.
2. Click Add.
Figure 61 Adding Create Remote Copy Virtual Copy
86 Working with Remote Copy
Page 87

3. Choose the scheduling options for performing Virtual Copy creation tasks. Set the parameters
of the selected schedule option.
• Hourly Start time, Hour
• Daily Start time, Day
• Weekly Start time, Week, Day of the Week
• Monthly Start time, Day of Every Month
• One time only Start Date, Start Time
Figure 62 Setting scheduled type for performing Virtual Copy creation task
4. Click Next to continue.
5. Enter the credentials to complete the scheduled tasks.
• Schedule task name
• User name
• Password
Figure 63 Entering Schedule credential
6. Click Next to continue.
Scheduling Remote Copy Virtual Copies 87
Page 88

7. Select the schedule task settings.
• vCenter server user
• vCenter credential store file
• Enable expirable Virtual Copies
• Retain Virtual Copies
• Create Remote Copy Virtual Copy with application consistency
Figure 64 Setting RC Virtual Copy configuration
8. Click Next to continue.
9. Review the Scheduled Task Summary before continuing.
Figure 65 Reviewing Scheduled Task summary
88 Working with Remote Copy
Page 89
10. Click Finish to exit.
Mounting Remote Virtual Copies
Mounting from Virtual Copy table
To mount a Remote Virtual Copy:
1. Click the Remote Copy tab.
2. Choose the appropriate Remote Copy Group system.
3. Click the Virtual Copies On tab to display the list of Remote Virtual Copies.
4. Select the appropriate remote VC from the Remote VC Groups table.
NOTE: If the selected Remote VC has any unmounted VVs, the Mount above the VC table
is enabled.
NOTE: Only remote Virtual Copies existing on the current array selected can be mounted.
To mount a remote Virtual Copy onto another array, select the specific array located in the
left pane.
5. Click the Mount.
6. Choose a mounting option:
• Mount on ESX host as Datastore
• Mount on Proxy host
Choose a specific Proxy host.
Figure 66 Remote VC Mounting options
7. Click Mount.
8. Click Yes to confirm. Click No to cancel action.
Mounting Remote Virtual Copies 89
Page 90

9. Click Ok to complete action.
Figure 67 Mount Local Virtual Copy complete
Mounting from Virtual Volume mapping table
1. Click the Remote Copy tab.
2. Choose the appropriate Remote Copy Group system.
3. Click the Virtual Copies On tab to display the list of Remote Virtual Copy.
4. Select the appropriate remote VC from the Virtual Volume Mapping table.
NOTE: If one or more selected Remote VC has any unmounted VVs, the Mount above the
VV table is enabled.
5. Click the Mount.
6. Choose a mounting option:
• Mount on ESX host as Datastore
• Mount on Proxy host
Choose a specific Proxy host.
90 Working with Remote Copy
Page 91

Figure 68 Remote VC Mounting options
7. Click Mount.
8. Click Yes to confirm. Click No to cancel action.
9. Click OK to complete action.
Unmounting Remote Virtual Copies
Unmounting from Virtual Copy table
To unmount a Remote Virtual Copy:
1. Click the Remote Copy tab.
2. Choose the appropriate Remote Copy Group system.
3. Click the Virtual Copies On tab to display the list of Remote Virtual Copy.
4. Select the appropriate mounted remote VC from the Remote VC Groups table.
NOTE: If the selected Remote VC has any mounted VVs, the Unmount above the VC table
is enabled. You may select multiple VCs to unmount.
5. Click Unmount.
Unmounting from Virtual Volume Mapping table
1. Click the Remote Copy tab.
2. Choose the appropriate Remote Copy Group system.
3. Click the Virtual Copies On tab to display the list of Remote Virtual Copy.
4. Select the appropriate mounted remote VC from the Virtual Volume Mapping table.
NOTE: If the selected Remote VC has any mounted VVs, the Unmount above the VV table
is enabled. You may select multiple VCs to unmount.
5. Click the Unmount.
Deleting Remote Virtual Copies
When a remote RC Group Virtual Copy under the Remote Virtual Copies tab is no longer required,
the tabs can be removed.
Unmounting Remote Virtual Copies 91
Page 92

1. Click Remote Virtual Copies tab.
2. Select the specific remote Virtual Copy. To select multiple Remote Virtual Copies, press Ctrl
and click.
3. Click Delete.
Deleting Local Virtual Copies
When a local RC Group Virtual Copy under the Local Virtual Copies tab is no longer required, the
tabs can be removed.
1. Click Local Virtual Copies tab.
2. Select the specific local Virtual Copy. To select multiple Local Virtual Copies, press Ctrl and
click.
3. Click Delete.
NOTE: Only unmounted Virtual Copies can be deleted.
92 Working with Remote Copy
Page 93

Importing a Virtual Machine and reverting to a specific point-in-time Virtual Copy
1. Issue setcopygroup failover to Failover the desired Remote Copy group from the
secondary site. Verify the Remote Copy group displays Primary-Rev.
2. (Optional) Select a desired Virtual Machine Virtual Copy and issue promotesv to the
appropriate Virtual Volume(s) to revert.
NOTE: Issuing promotesv promotes the entire data of the virtual volume to a specific
point-in-time Virtual Copy. HP recommends creating a Virtual Copy as a recovery point from
the base volume before proceeding with the optional step.
3. Issue createvlun to expose the virtual volume to the ESXi host.
4. Connect to the vCenter Server and issue Rescan for Datastores... command to scan
for LUN exposed to the ESXi host.
5. Select the ESXi host from vCenter and click Configuration tab.
6. From Hardware located in left pane, click Storage to retrieve Datastores view.
7. From the Datastore browser, add the Virtual Machine to the vCenter Inventory.
a. Right-click the VMX file and select Add to Inventory.
b. Continue to follow the wizard.
8. Right-click the newly imported Virtual Machine and select Snapshot\Snapshot Manager.
NOTE: If Step 2 is not performed and the Virtual Copy is not application consistent, continue
on to Step 10.
9. From the Snapshot dialog, select the base Virtual Copy. Click Go to revert to the time the
Virtual Copy is created.
a. (Optional) When revert of snapshot is complete, click Delete All to remove all Virtual
Copies.
b. Click Close.
10. Update the network setting for the Virtual Machine.
11. Turn Virtual Machine power on. If you see a question mark, right-click the Virtual Machine
and select Guest\Answer Questions. Complete the questions to begin using the Virtual Machine.
12. Answer the following promoted questions to begin using the VM.
Importing a Virtual Machine and reverting to a specific point-in-time Virtual Copy 93
Page 94

8 Using HP 3PAR Peer Motion Manager Software with
Recovery Manager
HP 3PAR Peer Motion Manager is a feature of the HP 3PAR Operating System Software and
manages the migration of data in between existing storage systems or third party storage arrays.
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager now supports HP 3PAR Peer Motion Manager data migration activities
without any impact on host operations while monitoring the primary storage system.
If the virtual volume is already in use by an ESXi host before initiating migration, the following
conditions applies:
• You must remove any Virtual Copies created and managed by Recover Manager for VMware.
The Virtual Copies created by a potential migrating virtual volume cannot migrate with its
virtual volume during an active Peer Motion migration operation.
• You must remove all Virtual Copy scheduler tasks associated with the Datastore or Virtual
Machines using the potential migrating virtual volume before migrating data. If the tasks are
not removed and occurs during migration, the following error message may display during
or after the migration operation, "Could not create HP 3PAR snapshot. Object Id:
vm:uuid-4208b1f5-e2ca-1061-c44c-19cf67bee619. Please login into Storage System 014D
Method: CliCreateNewSnapshot."
• Previously created Virtual Copies will display Mismatched status. You cannot use Virtual Copies
with Mismatched status for mounting or restoring operations.
• You must remove the mismatched Virtual Copies records from the interface. Note, this does
not remove the physical Virtual Copies from the original storage system. You must perform a
manual cleanup of the files.
For more information about performing Peer Motion data migration, refer to the HP 3PAR Peer
Motion User Guide. Go to http://www.hp.com/go/3par/, navigate to your product page, click
Support, and then click Manuals.
94 Using HP 3PAR Peer Motion Manager Software with Recovery Manager
Page 95
9 Support and Other Resources
Contacting HP
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Specify the type of support you are requesting:
systems
Support requestHP 3PAR storage system
StoreServ 7000 StorageHP 3PAR StoreServ 7200, 7400, and 7450 Storage
HP 3PAR T-Class storage systems
HP 3PAR F-Class storage systems
HP 3PAR documentation
Supported hardware and software platforms
and administer HP 3PAR storage systems
Using the HP 3PAR CLI to configure and administer storage
systems
3PAR or 3PAR StorageHP 3PAR StoreServ 10000 Storage systems
See:For information about:
The Single Point of Connectivity Knowledge for HP
Storage Products (SPOCK) website:
http://www.hp.com/storage/spock
The HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage site:Locating HP 3PAR documents
http://www.hp.com/go/3par
To access HP 3PAR documents, click the Support link for
your product.
HP 3PAR storage system software
HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage Concepts GuideStorage concepts and terminology
HP 3PAR Management Console User's GuideUsing the HP 3PAR Management Console (GUI) to configure
HP 3PAR Command Line Interface Administrator’s
Manual
to manage host configuration and connectivity information
Model (CIM) to manage HP 3PAR storage systems
HP 3PAR Command Line Interface ReferenceCLI commands
HP 3PAR System Reporter Software User's GuideAnalyzing system performance
HP 3PAR Host Explorer User’s GuideInstalling and maintaining the Host Explorer agent in order
HP 3PAR CIM API Programming ReferenceCreating applications compliant with the Common Information
Contacting HP 95
Page 96

See:For information about:
HP 3PAR-to-3PAR Storage Peer Motion GuideMigrating data from one HP 3PAR storage system to another
Configuring the Secure Service Custodian server in order to
monitor and control HP 3PAR storage systems
Copy
Identifying storage system components, troubleshooting
information, and detailed alert information
Server
HP 3PAR Secure Service Custodian Configuration Utility
Reference
HP 3PAR Remote Copy Software User’s GuideUsing the CLI to configure and manage HP 3PAR Remote
HP 3PAR Upgrade Pre-Planning GuideUpdating HP 3PAR operating systems
HP 3PAR F-Class, T-Class, and StoreServ 10000 Storage
Troubleshooting Guide
HP 3PAR Policy Server Installation and Setup GuideInstalling, configuring, and maintaining the HP 3PAR Policy
HP 3PAR Policy Server Administration Guide
96 Support and Other Resources
Page 97

See:For information about:
Planning for HP 3PAR storage system setup
Hardware specifications, installation considerations, power requirements, networking options, and cabling information
for HP 3PAR storage systems
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Site Planning ManualHP 3PAR 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Site Planning Manual
HP 3PAR 10000 storage systems
Installing and maintaining HP 3PAR 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems
initializing the Service Processor
7450 storage systems
HP 3PAR host application solutions
Backing up Oracle databases and using backups for disaster
recovery
HP 3PAR StoreServ 10000 Storage Physical Planning
Manual
HP 3PAR StoreServ 10000 Storage Third-Party Rack
Physical Planning Manual
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Installation GuideInstalling 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems and
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Installation Guide
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage SmartStart Software
User’s Guide
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Service GuideMaintaining, servicing, and upgrading 7200, 7400, and
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Service Guide
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7000 Storage Troubleshooting GuideTroubleshooting 7200, 7400, and 7450 storage systems
HP 3PAR StoreServ 7450 Storage Troubleshooting Guide
HP 3PAR Service Processor Software User GuideMaintaining the Service Processor
HP 3PAR Service Processor Onsite Customer Care
(SPOCC) User's Guide
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Oracle User's
Guide
Backing up Exchange databases and using backups for
disaster recovery
Backing up SQL databases and using backups for disaster
recovery
Backing up VMware databases and using backups for
disaster recovery
Installing and using the HP 3PAR VSS (Volume Shadow Copy
Service) Provider software for Microsoft Windows
Best practices for setting up the Storage Replication Adapter
for VMware vCenter
Troubleshooting the Storage Replication Adapter for VMware
vCenter Site Recovery Manager
Installing and using vSphere Storage APIs for Array
Integration (VAAI) plug-in software for VMware vSphere
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft
Exchange 2007 and 2010 User's Guide
HP 3PAR Recovery Manager Software for Microsoft SQL
Server User’s Guide
HP 3PAR Management Plug-in and Recovery Manager
Software for VMware vSphere User's Guide
HP 3PAR VSS Provider Software for Microsoft Windows
User's Guide
HP 3PAR Storage Replication Adapter for VMware
vCenter Site Recovery Manager Implementation Guide
HP 3PAR Storage Replication Adapter for VMware
vCenter Site Recovery Manager Troubleshooting Guide
HP 3PAR VAAI Plug-in Software for VMware vSphere
User's Guide
HP 3PAR documentation 97
Page 98

Typographic conventions
Table 10 Document conventions
ElementConvention
Bold text
Monospace text
<Monospace text in angle brackets>
Bold monospace text
• Keys that you press
• Text you typed into a GUI element, such as a text box
• GUI elements that you click or select, such as menu items, buttons,
and so on
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument values
• Code variables
• Command variables
• Commands you enter into a command line interface
• System output emphasized for scannability
WARNING! Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death, or in
irreversible damage to data or to the operating system.
CAUTION: Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
NOTE: Provides additional information.
Required
Indicates that a procedure must be followed as directed in order to achieve a functional and
supported implementation based on testing at HP.
HP 3PAR branding information
• The server previously referred to as the "InServ" is now referred to as the "HP 3PAR StoreServ
Storage system."
• The operating system previously referred to as the "InForm OS" is now referred to as the "HP
3PAR OS."
• The user interface previously referred to as the "InForm Management Console (IMC)" is now
referred to as the "HP 3PAR Management Console."
• All products previously referred to as “3PAR” products are now referred to as "HP 3PAR"
products.
98 Support and Other Resources
Page 99

10 Documentation feedback
HP is committed to providing documentation that meets your needs. To help us improve the
documentation, send any errors, suggestions, or comments to Documentation Feedback
(docsfeedback@hp.com). Include the document title and part number, version number, or the URL
when submitting your feedback.
99
Page 100

A Troubleshooting VASA Provider
For information about system alerts, go to http://www.hp.com/support/hpgt/3par and select
your server platform.
NOTE: If you are using HP 3PAR OS Software version 3.1.1 or lower, refer to HP 3PAR InForm
OS 3.1.1 Messages and Operators Guide for information about system alerts.
VASA Provider registration issue
If an error occurs during the VASA Provider registration process on the vCenter server, it might be
caused by one of the following issues:
• The port used by Recovery Manager for the VMware installed host is being blocked by firewall
or antivirus software. The current port number can be obtained through the Admin Tool
interface.
• A proper SMS certificate has not been properly installed on the Recovery Manager for VMware
host prior to the VASA provider registration. Refer to “Registering an SMS Certificate for the
VASA Provider” (page 30)for more details.
Inspecting VASA Provider and vCenter Server communication
VASA provider and vCenter server communications can be inspected by setting the log level to
"High" from the Configuration option from the VASA tab available from the Admin Tools. When
the log level is set to "High", the received soap requests and replied responses will be written to
the log file. Following are descriptions of the alarm and event messages that might be generated
and suggested actions for each.
Alarm Type Message
MESSAGE
(ID:300de) -{Info}
SUGGESTED ACTION
Refer to Alert Code 0x300de in HP 3PAR InForm OS Message and Operator's Guide.
MESSAGE
(ID:300fa) -{Info}
SUGGESTED ACTION
Refer to Alert Code 0x300fa in HP 3PAR InForm OS Message and Operator's Guide.
MESSAGE
(ID:400fa) -{Info}
SUGGESTED ACTION
Refer to Alert Code 0x400fa in HP 3PAR InForm OS Message and Operator's Guide.
MESSAGE
(ID:e0001) -{Info}
SUGGESTED ACTION
Refer to Alert Code 0xe0001 in HP 3PAR InForm OS Message and Operator's Guide.
100 Troubleshooting VASA Provider
 Loading...
Loading...